Page 1

E/OS SNMP Support Manual
P/N 620-000131-630
REV A
Page 2
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
ii
Record of Revisions and Updates
Copyright © 2005 McDATA Corporation. All rights reserved.
Printed June 2005
Ninth Edition
McDATA, the McDATA logo, McDATA Eclipse, Fabricenter, HotCAT, Intrepid, Multi-Capable Storage
Network Solutions, Networking the World's Business Data, nScale, nView, OPENready, SANavigator,
SANtegrity, SANvergence, SecureConnect and Sphereon are trademarks or registered trademarks of
McDATA Corporation. OEM and Reseller logos are the property of such parties and are reprinted with limited
use permission. All other trademarks are the property of their respective companies. All specifications subject
to change.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a
database or retrieval system, without the prior written consent of McDATA Corporation.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. McDATA Corporation
assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear.
All computer software programs, including but not limited to microcode, described in this document are
furnished under a license, and may be used or copied only in accordance with the terms of such license.
McDATA either owns or has the right to license the computer software programs described in this document.
McDATA Corporation retains all rights, title and interest in the computer software programs.
McDATA Corporation makes no warranties, expressed or implied, by operation of law or otherwise, relating
to this document, the products or the computer software programs described herein. McDATA
CORPORATION DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. In no event shall McDATA Corporation be liable for (a) incidental, indirect,
special, or consequential damages or (b) any damages whatsoever resulting from the loss of use, data or
profits, arising out of this document, even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
Revision Date Description
620-000131-000 6/2001 Initial release of Manual
620-000131-100 11/2001 Update to manual
620-000131-200 5/2002 Update to manual
620-000131-300 9/2002 Update to support EFCM 6.1and 6.2
620-000131-400 10/2002 Update to support EFCM 6.1, 6.2, & 6.3
620-000131-500 2/2003 Update to support E/OS 5.1 and EFCM 7.0
620-000131-600 8/2003 Update to support E/OS 5.2 and EFCM 7.2
620-000131-610 11/2003 Update to support E/OS 6.0
620-000131-620 2/2005 Update to support E/OS 7.0
620-000131-630 6/2005 Update to support E/OS 8.0
Page 3
Contents
iii
Preface............................................................................................................................ vii
Chapter 1 Introduction to SNMP
Network Management using SNMP..............................................1-1
SNMP Features ..........................................................................1-2
SNMP Commands.....................................................................1-2
Why Variables exist In a Managed Device ............................1-3
How SNMP Changes Variables in a Managed Device ........1-3
SNMPv3 ......................................................................................1-4
SNMP Community co-existence..............................................1-5
Security Features........................................................................1-5
E/OS SNMPv3 Configuration .................................................1-6
Standard MIBs............................................................................1-7
Private Enterprise MIBs............................................................1-8
Traps and Their Purpose ..........................................................1-9
Chapter 2 McDATA SNMP Support
Overview............................................................................................2-1
E/OS Trap Overview .......................................................................2-2
E/OS Trap summary table.......................................................2-3
MIB Definitions: MIB-II..................................................................2-20
System Group...........................................................................2-20
Interfaces Group .....................................................................2-22
Address Translation Group ..................................................2-29
IP Group...................................................................................2-30
IP Routing group ....................................................................2-36
ICMP Group ............................................................................2-42
TCP Group...............................................................................2-47
Contents
Page 4

E/OS SNMP Support Manual
iv
Contents
UDP Group..............................................................................2-52
SNMP Group...........................................................................2-53
Fabric Element Management MIB................................................2-60
Predefined types......................................................................2-60
Fibre Alliance MIB..........................................................................2-96
Type definitions.......................................................................2-96
Trap Types..............................................................................2-146
Appendix A Fibre Alliance MIB
FA MIB ..............................................................................................A-1
Textual conventions for this MIB...........................................A-4
Connectivity unit group ..........................................................A-6
Event group.............................................................................A-34
SNMP trap registration group..............................................A-65
Related traps............................................................................A-68
Conformance definitions.......................................................A-69
Conformance units .................................................................A-70
Appendix B FC Management MIB
FCMGMT-MIB Definitions ............................................................ B-1
Connectivity unit group ................................................................. B-4
Sensor table.............................................................................. B-19
Port Table........................................................................................ B-23
Event Group ................................................................................... B-35
Link Table ................................................................................ B-39
Port Statistics........................................................................... B-46
FC Simple Name Server Table.............................................. B-64
SNMP Trap Registration Group.................................................. B-69
Related Traps.................................................................................. B-73
Appendix C McDATA Private Enterprise MIB
FCEOS.MIB.......................................................................................C-1
Textual conventions for this MIB...........................................C-3
Enterprise Specific Object Identifiers.....................................C-5
Fibre Channel product lines....................................................C-5
Groups in FCEOS MIB.............................................................C-5
System Group............................................................................C-6
Fibre Channel FRU Group ....................................................C-10
Fibre Channel Port Group.....................................................C-13
NPIV Information...................................................................C-39
Fibre Channel Zoning Group ...............................................C-42
Page 5
v
Contents
Contents
Fibre Channel Threshold Alert Group................................ C-47
FCEOS Enterprise-specific Trap Definitions............................. C-51
Appendix D Fabric Element Management MIB
FCFE.MIB .........................................................................................D-1
Configuration group................................................................D-6
Operation group.....................................................................D-18
F_Port Fabric Login table...................................................... D-21
FxPort Fabric Login table......................................................D-25
Error group ............................................................................. D-30
Accounting Groups................................................................ D-35
Class 2 Accounting table.......................................................D-40
Class 3 Accounting Group....................................................D-43
Capability Group ................................................................... D-46
Appendix E MIB II
Groups in MIB II...............................................................................E-1
System group.............................................................................E-2
Interfaces group ........................................................................E-5
Address Translation group....................................................E-14
IP group....................................................................................E-16
ICMP group .............................................................................E-33
TCP group................................................................................E-40
SNMP group ............................................................................E-50
Appendix F SNMP Framework MIB
SNMP Framework MIB...................................................................F-1
Textual Conventions.................................................................F-2
The snmpEngine Group...........................................................F-7
Appendix G SNMPv3 MIB
SNMPv3 MIB ...................................................................................G-1
User based SM MIB ................................................................. G-1
SNMP View Based Acm MIB Definitions .......................... G-21
MIB views................................................................................ G-32
SNMP-COMMUNITY-MIB .................................................. G-40
Appendix H MIB Objects Listing
MIB Objects Listed by OID ...........................................................H-1
Page 6

E/OS SNMP Support Manual
vi
Contents
MIB Objects Listed Alphabetically ............................................ H-45
MIB Objects Listed Alphabetically ............................................ H-82
Index ................................................................................................................................i-1
Page 7
vii
Preface
This publication is part of the documentation suite that supports the
McDATA
®
Sphereon™ 3016 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 3032 Fabric
Switch, Sphereon 3216 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 3232 Fabric Switch,
Sphereon 4300 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 4400 Fabric Switch, Sphereon
4500 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 4700 Fabric Switch, ES-1000 Switch,
ED-5000 Director, Intrepid
®
6064 Director, and Intrepid 6140
Director.
Who Should Use This Manual
Use this publication if you are planning to use SNMP to manage any
of the McDATA switching products listed above.
The publications listed in Related Publications provide considerable
information about both concepts and McDATA products
.Organization of This Manual
This publication is organized as follows:
Chapter 1, Introduction to SNMP, provides an introduction and
overview of Simple Network Management (SNMP) and its
operation.
Chapter 2, McDATA SNMP Support, describes specific
information available through SNMP, especially the Management
Information Bases (MIBs) that are supported and the SNMP traps
generated by the McDATA directors and switches.
Appendix A, Fibre Alliance MIB lists the MIB definitions of Fibre
Alliance MIB.
Page 8

viii
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
Preface
Appendix B, FC Management MIB, lists the FC Management MIB
3.0.
Appendix C, McDATA Private Enterprise MIB, lists the McDATA
private enterprise MIBs.
Appendix D, Fabric Element Management MIB, lists the SNMP
Framework MIB.
Appendix E, MIB II lists the MIB-II, the RFC1213.mib renamed.
Appendix F, SNMP Framework MIB lists the definitions of
managed objects for the Fabric Element in Fibre Channel
Standard.
Appendix G, SNMPv3 MIB contains the listing of MIB objects by
OID and alphabetically.
Appendix H, MIB Objects Listing lists the definitions of managed
objects for SNMPv3.
An Index is also provided.
Manual Updates
Check the McDATA web site at www.mcdata.com for possible
updates or supplements to this manual.
Related Publications
Other publications that provide additional information about the
products mentioned in this manual are:
• E/OS Command Line Interface User Manual (620-000134-740)
• McDATA Enterprise Fabric Connectivity Manager User Manual
(620-005001)
• McDATA Products in a SAN Environment -Planning Manual
(620-000124)
•Intrepid 6140 and 6064 Directors Element Manager User Manual
(620-000172).
• McDATA Intrepid 6064 Director Installation and Service Manual
(620-000108)
• McDATA Intrepid 6140 Director Installation and Service Manual
(620-000157)
• McDATA Sphereon 3016 and 3216 Fabric Switch Element Manager
User Manual (620-000174)
Page 9
Preface
ix
Preface
• McDATA Sphereon 3032 and 3232 Fabric Switch Element Manager
User Manual (620-000173)
• McDATA Sphereon 3016 and 3216 Switch Installation and Service
Manual (620-000154)
• McDATA Sphereon 3032 and 3232 Switch Installation and Service
Manual (620-000155)
• McDATA Sphereon 4500 Switch Installation and Service Manual
(620-000159)
• McDATA Sphereon 4500 Fabric Switch Element Manager User
Manual (620-000175)
• McDATA Sphereon 4400 Fabric Switch Installation and Service
Manual (620-000238)
• McDATA Sphereon 4400 Switch Element Manager User Manual
(620-000241)
• EFCM Basic User Manual (620-000240)
• McDATA Sphereon 4700 Fabric Switch Installation and Service
Manual (620-000239)
• McDATA Sphereon 4700 Fabric Switch Element Manager User
Manual (620-000242)
• McDATA Sphereon 4300 Switch Installation and Service Manual
(620-000171)
• SANavigator User Guide (621-000013)
• SNMP Agent User Manual (621-000021)
Page 10

x
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
Preface
Manual Conventions The following notational conventions are used in this document.
Where to Get Help For technical support, McDATA® end-user customers should call the
phone number located on the service label attached to the front or
rear of the hardware product.
McDATA’s “Best in Class” Solution Center provides a single point of
contact for customers seeking help. The Solution Center will research,
explore, and resolve inquires or service requests regarding McDATA
products and services. The Solution Center is staffed 24 hours a day,
7 days a week, including holidays.
NOTE: To expedite warranty entitlement, please have your product serial
number available.
McDATA Corporation
380 Interlocken Crescent
Broomfield, CO 80021
Phone: (800) 752-4572 or (720) 558-3910
Fax: (720) 558-3851
E-mail: support@mcdata.com
Convention Meaning
Italic Outside book references, names of user interface
windows, panels, buttons, and dialog boxes
Bold Keyboard keys
Click. As in “click the icon on
the navigation control panel.”
Click with the left mouse button on the object to activate a
function.
Right-click. As in “right click
the product icon.”
Click with the right mouse button on the object to activate
a function.
Select. As in “select the log
entry.”
Click once on the object to highlight it.
Page 11
Preface
xi
Preface
NOTE: Customers who purchased the hardware product from a company
other than McDATA should contact that company’s service representative
for technical support.
Forwarding
Publication
Comments
We sincerely appreciate any comments about this publication. Did
you find this manual easy or difficult to use? Did it lack necessary
information? Were there any errors? Could its organization be
improved?
Please send your comments via e-mail, our home page, or FAX.
Identify the manual, and provide page numbers and details. Thank
you.
Ordering Publications To order a paper copy of this manual, submit a purchase order as
described in Ordering McDATA Documentation Instructions, which is
found on McDATA’s web site, http://www.mcdata.com. To obtain
documentation CD-ROMs, contact your sales representative.
Trademarks The following terms, indicated by a registered trademark symbol (®)
or trademark symbol (™) on first use in this publication, are
trademarks of McDATA Corporation in the United States, other
countries, or both:
Registered Trademarks
Trademarks
Fabricenter
®
E/OS™
HotCAT
®
Eclipse™
Intrepid
®
Fibre Channel Director™
McDATA
®
OPENconnectors™
OPENready
®
SANvergence™
SANavigator
®
Sphereon™
SANtegrity
®
All other trademarked terms, indicated by a registered trademark
symbol (®) or trademark symbol (™) on first use in this publication,
E-mail: pubsmgr@mcdata.com
Home Page: http://www.mcdata.com
FAX: Technical Communications Manager
(720) 558-8999
Page 12

xii
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
Preface
are trademarks of their respective owners in the United States, other
countries, or both.
Page 13

Introduction to SNMP
1-1
1
Introduction to SNMP
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a complete but
simple mechanism for network management. Network management
is a broad term, including workstation configuration, assignment of
IP addresses, network design, architecture, network security, and
topologies. All this can fall within the scope of a network manager.
Any protocol for managing networks must allow virtually all
network devices and systems to communicate statistics and status
information to network management stations (network managers).
This communication must be independent of the primary network
transmission medium and impose little effect on the efficiency of the
network. Network managers must be able to obtain status
information from managed devices, and make changes in the way the
managed devices handle network traffic. SNMP is one way of
meeting these requirements.
Network Management using SNMP
SNMP is designed on the manager-agent paradigm, with the agent
residing in the managed device. Information is exchanged between
agents (devices on the network being managed) and managers
(devices on the network through which management is done).
Administrators can use SNMP to manage the switch configuration,
faults, performance, accounting, and security from remote SNMP
management stations.
There are many possible transactions between agents and managers.
These transactions vary widely with the different types of devices
Page 14

1
1-2
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
Introduction to SNMP
that can be managed. In such a case, the list of commands a manager
must be able to issue is overwhelming, and every new manageable
device increases the list. SNMP was created to simplify the task of
managing and meeting the demands of any growing network.
SNMP operates on a simple fetch-store concept. With SNMP, the
available transactions between manager and agent are limited to a
handful. The manager can request information from the agent or
modify variables on the agent. The agent can respond to a request by
sending information, or if enabled to do so, voluntarily notify the
manager of a change of status on the agent (issue a trap).
SNMP Features
SNMP is the only network management protocol that is widely
available from many vendors of TCP/IP networks and
internetworks.
Features of SNMP:
• Simple set of commands for network management.
• Minimal intervention required to manage new devices added to a
network.
• Adequate for many basic network management needs.
• Generalized for application to networks other than TCP/IP, such
as IPX and OSI.
• Considerable versatility for managing many types of devices.
• Same method of management can be used for all networks.
• Addresses security threats through authentication, data
encryption and access control.
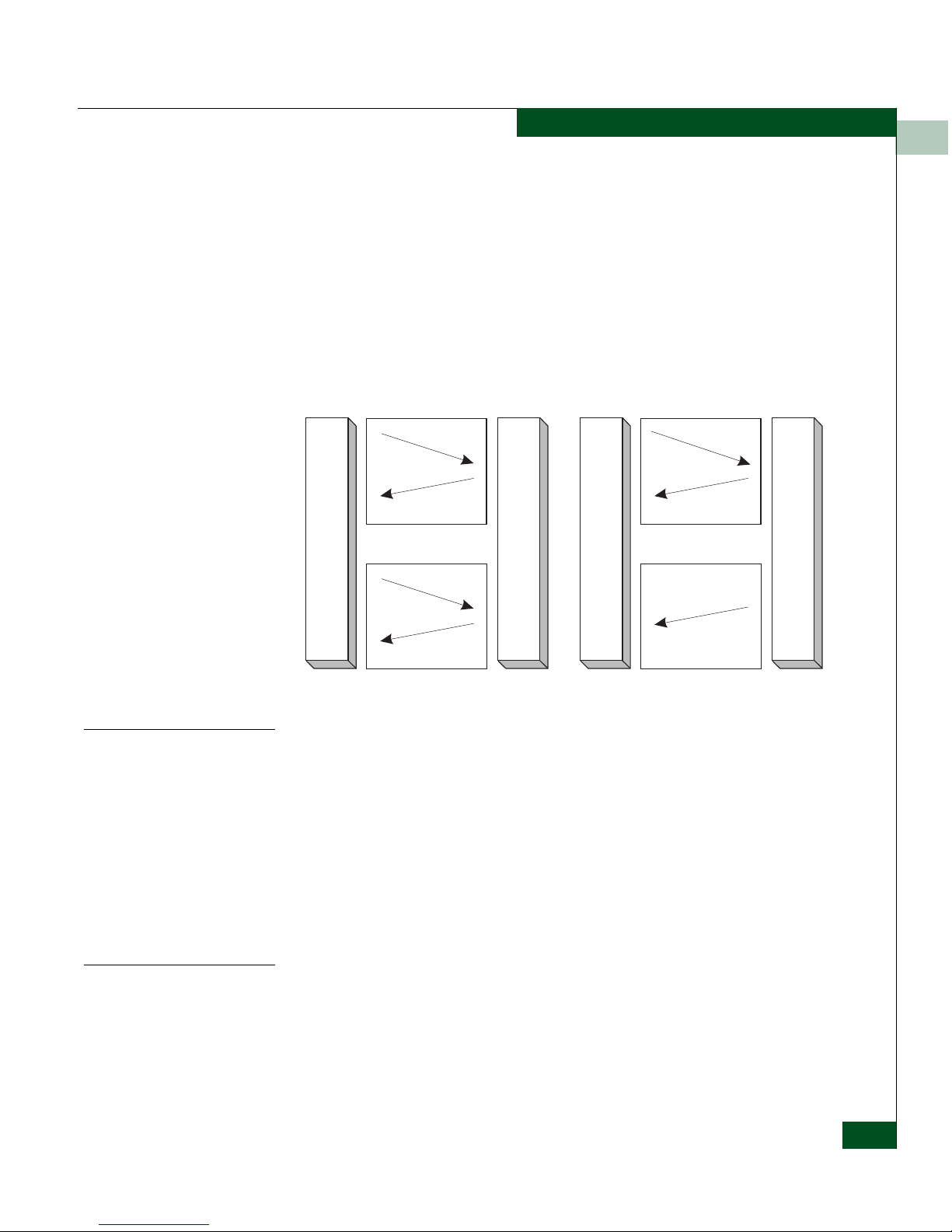
SNMP Commands
The main SNMP commands are Get, GetNext, GetResponse, GetBulk,
Inform, Trap and Set.
• Get – The manager uses this command to fetch the value of a
specified variable from the agent.
• GetNext –The manager uses this command to fetch the value of
the variable next to the one specified in the command. This
command is used to retrieve lists and tables of management data.
• GetResponse –An agent sends the requested information to the
manager using this PDU.
Page 15
1
Network Management using SNMP
1-3
Introduction to SNMP
• Set–A manager can change the variables in the agent by sending
this single command. This command is used to change the
management data.
• GetBulk–This command is used by the manager to retrieve
voluminous data from a large table in the agent.
• Trap–An Agent uses this command to inform the manager about
some unusual events. Refer to Traps and Their Purpose on page 1-9.
• Inform– This command is used by a manager to send alert to
another manager.
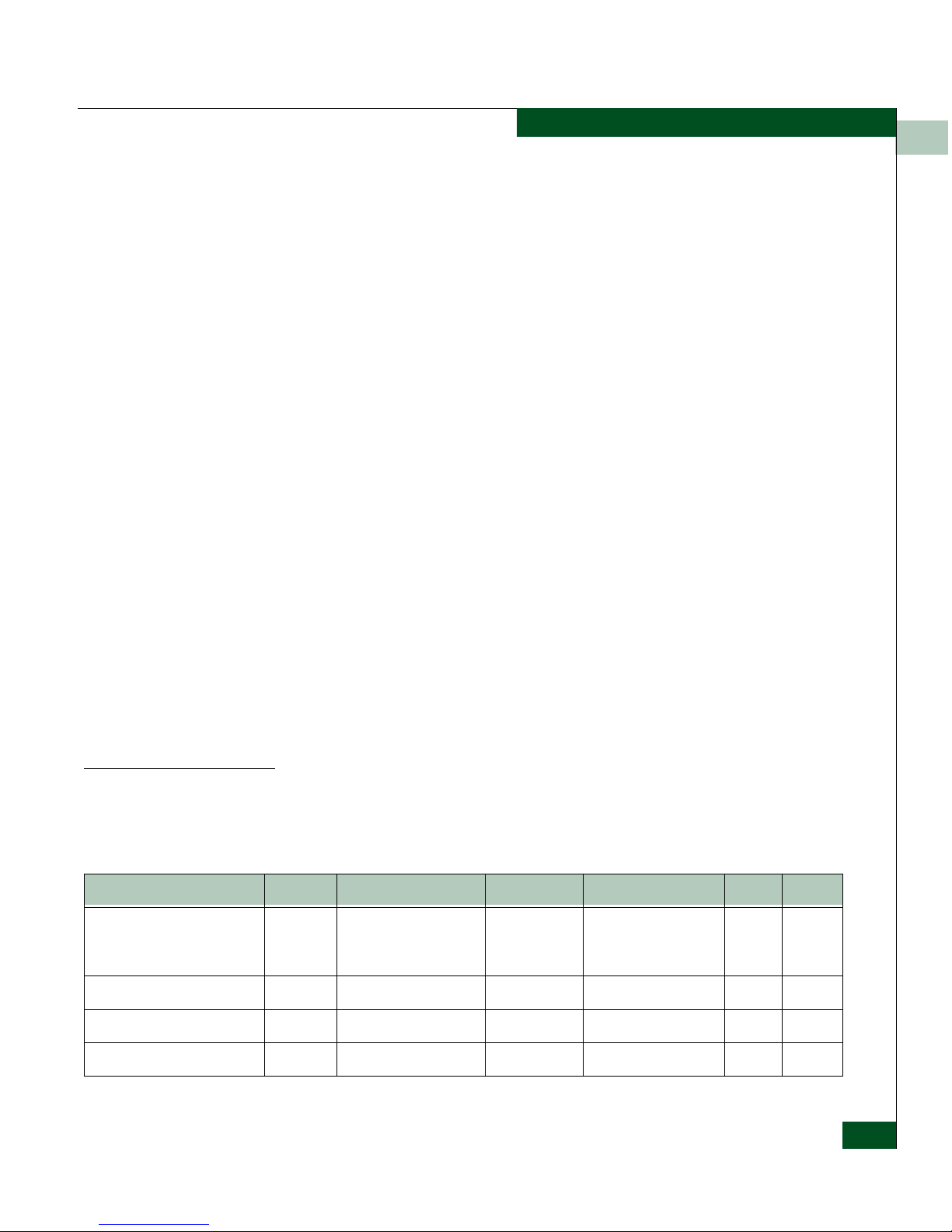
Figure 1-1 SNMP Commands and Responses
Why Variables exist
In a Managed
Device
Variables are the means by which devices like switches and directors
keep track of and control their performance apart from providing
access about their performance to network managers. A simple
example of a variable’s use is to set a port offline and turn the port
back on. Some variables just hold values that indicate status (for
example error counts). SNMP allows the network managers to have
access to some of the same variables for network management.
For purposes of the following explanation, an object is a data variable
that represents an attribute of a managed device.
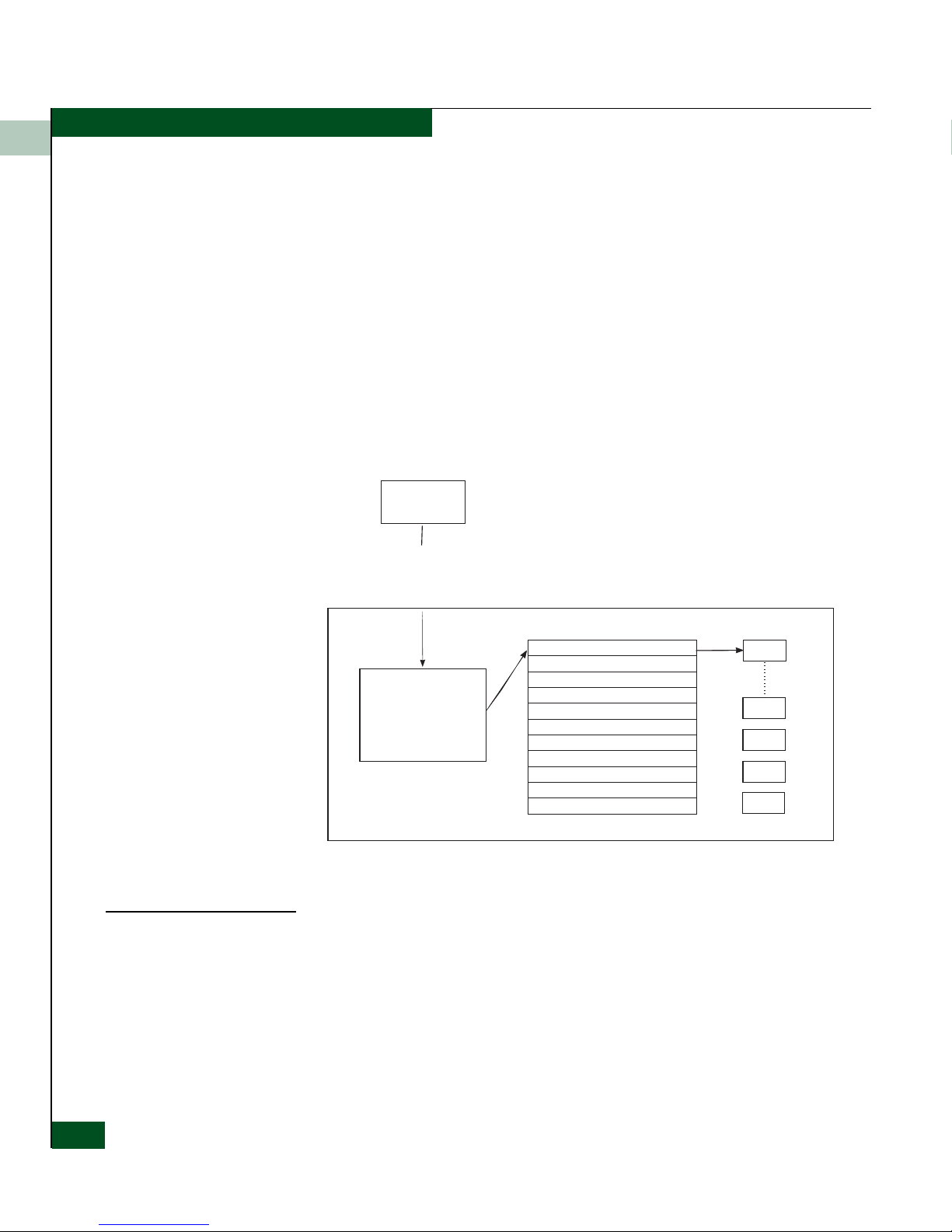
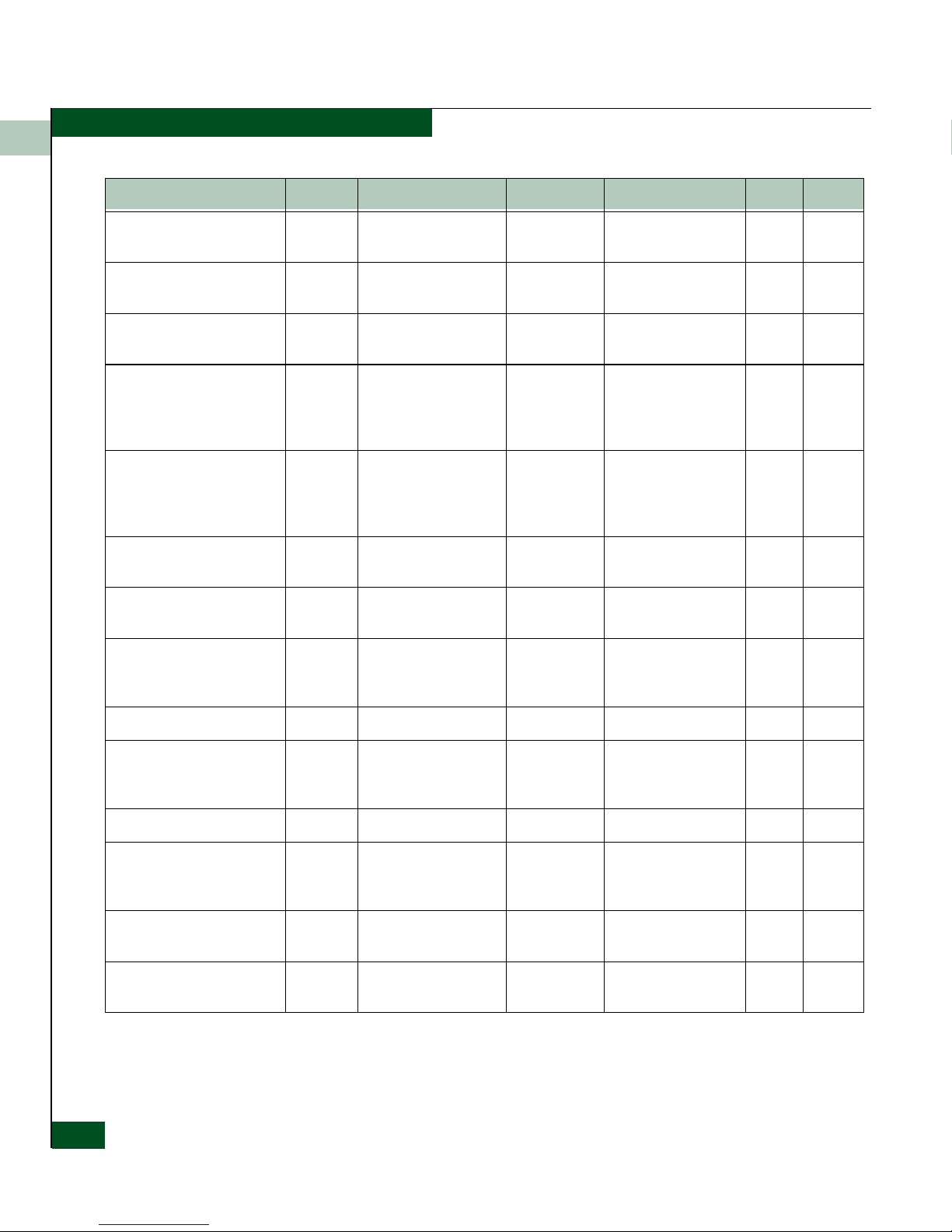
How SNMP Changes
Variables in a
Managed Device
An agent has an interface to the actual object being managed
(Figure 1-2 on page 1-4). The agent understands SNMP and translates
between the manager and the object. Each SNMP element manages
specific objects. Each object has an identifier, OID. Objects may be
Ge
tRes
pons
ePD
U
G
et
R
e
qu
e
st
P
D
U
Get Values
NMS Switch
Se
tRes
pons
ePD
U
S
et
R
e
qu
e
st
P
D
U
Set Values
GetR
espo
nse
PDU
GetNextR
equest PDU
Get Next Values
NMS Switch
Tr
ap P
DU
Send Trap
Page 16
1
1-4
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
Introduction to SNMP
retrieved and/or modified by the manager, and it is the agent’s job to
return the requested object’s value.
Within the agent is at least one, maybe several, collections of
definitions called Management Information Bases (MIBs). MIB
provides each OID with a readable label and other parameters. The
MIB acts as a dictionary that is used to assemble or interpret the
SNMP messages.
When an agent supports a standard MIB, it agrees to provide and
make available the variables listed in the MIB.
A MIB is an hierarchical tree of groups and variables. Operators at a
network management station enter a command with supported
groups and variables from the MIB.
Figure 1-2 Retrieving or Setting Values Using MIBs
SNMPv3
The E/OS provides additional level of security in the existing SNMP
framework by supporting the SNMPv3, which supplements the
SNMPv2c framework by providing security for messages and explicit
access control. The E/OS also supports SNMP versions 1 and 2,
Variable a
Variable b
Variable c
Variable d
Variable e
Variable f
Variable g
-
-
-
Agent
(Use MIB to
identify variable)
Managed
Device
Read status information
with GetRequest command
or
Set a variable to a value
with SetRequest command
NMS
MIB
Actual
Variable (object)
(x)y
(x)y
(x)y
(x)y
(x)y
Page 17

1
Network Management using SNMP
1-5
Introduction to SNMP
which authenticate the SNMP requests based on the “community”
string.
ATTENTION!Before enabling SNMPv3, ensure all desired communities are
configured for SNMPv3 access. If existing community strings are not
configured for SNMPv3, then existing SNMP access will be lost.
SNMP Community co-existence
When SNMPv3 is enabled, SNMP Community Coexistence table
provides a way to use the earlier versions such as SNMPv1 and
SNMPv2c. The SNMP Community Coexistence table maps the
community names for SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 to a Security Name.
After retrieving the user name (security name) for the community
string, message processing occurs in the same way as that for
SNMPv3 packets.
Security Features
SNMPv3 provides the User-based Security Model (USM) and View-based
Access Control Model (VACM) features to address authentication, data
encryption, and access control.
User-based Security Model (USM)
The main security threats to an SNMP message are modification of
information, masquerading, disclosure, and message stream
modification. The User-based Security Model (USM) protects
SNMPv3 packets from these threats by utilizing the concept of
multiple users where each user has to specify a key for authentication
and privacy. The USM deals with authenticating/encrypting/
decrypting SNMP packets. The authentication protocols supported
are HMAC-MD5-96 and HMAC-SHA-96. The privacy protocol
supported is CBC-DES.
The SNMP agent recognizes up to 32 user names that can have one of
the following security levels:
• No authentication and no privacy (none)
• Authentication only (auth only)
• Authentication and privacy (authpriv)
Page 18

1
1-6
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
Introduction to SNMP
Authentication can be used to restrict communication between two
authorized entities. Users cannot save messages and replay them
with altered content. Only authorized users can change
configurations of network devices.
View-based Access Control Model (VACM)
The View-based Access Control Model defines a set of services that
an application can use for checking access rights. It determines the
access rights of a group.
A group defines the access rights afforded to all the security names
(user names) which belong to that group. The combination of a
security model and a security name maps to at most one group
identified by a group name. The access rights that can be given to a
group are read-view, write-view and notify-view.
E/OS SNMPv3 Configuration
The security and access features for SNMPV3 provided by the
User-based Security Model (USM) and View-based Access Control
Model (VACM) require using multiple tables: User Table, Access
Table, Security-to-Group Table, and Target Table. The following
sections describe how SNMPv3 has been implemented in the E/OS.
USM Message Processing
The following steps describe how SNMPv3 messages are processed
in the User-based Security Model:
1. User table contains information such as user name, authentication
protocol, authentication key, privacy protocol, and encryption
key. Based on the user name field in the received packet, the
SNMP engine finds out the user entry from the table.
2. Flags are checked to see if authentication or security is needed.
3. If authentication is needed, the hash value is calculated using the
authentication protocol and authentication key, and matched
against the header.
Page 19

1
Network Management using SNMP
1-7
Introduction to SNMP
4. If privacy is needed, the message is decrypted using the private
key; it is encrypted again before sending back.
NOTE: The authentication/privacy key (password) configured for an
SNMPv3 user on a switch is not localized. Therefore, the
authentication/privacy key configured in the SNMP management
application must be configured as a non-localized authentication/privacy
key in ASCII format. For more information on localization, refer to
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3414.txt?number=3414.
VACM Message Access Control
The following steps describe how SNMPv3 messages are processed
in the View-based Access Control Model:
1. A security name and security model pair are mapped to a group
name string. On receiving the packet, the agent checks for the
user name and security model and extracts the group name from
the security-to-group name table.
2. The vacmContextTable is used to store all locally available contexts.
The contextName found in the scoped PDU is then searched in
this table. If the search is successful, it gives an index of the
context in the table. Otherwise a noSuchContext error is returned.
3. The vacmAccessTable is used get the view name of the MIB to be
referenced. This decision is based on the group name, context
name, security model and security level. The security model and
security level are derived from the received packet.
4. The derived view name is used to index into the
vacmFamilyTreeTable for access checking. The OID of a managed
object is then checked against this MIB view. If the OID is part of
the current MIB view, then access is granted; otherwise
errorIndication (notInView) is returned.
Currently, you can configure SNMPv3 only through the command
line interface (CLI) of the switch. Refer to the E/OS Command Line
Interface User Manual for detailed information about the commands
and their respective parameters.
Standard MIBs
Standard MIBs are those created and approved by the Internet
Engineering Task Force (IETF) and other Internet standards bodies
and are readily available for use with SNMP network management
stations. The standard MIBs provide a baseline of common
Page 20

1
1-8
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
Introduction to SNMP
operations across a wide variety of managed devices. Chapter 2
describes the standard MIBs used by the various McDATA products.
Standard MIBs supported by McDATA products are:
• MIB-II (Internet MIB) as described in RFC1213: supported by all
switches and directors.
• User-based Security Model (USM) as described in RFC2574
• View-based Access Control Model (VACM) as described in
RFC2575
• SNMP Community MIB as described in RFC2576
• Fibre Alliance (FCMGMT) MIB, version 3.0: supported by EFC
Server, Sphereon™ 3016 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 3032 Fabric
Switch, Sphereon 3216 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 3232 Fabric
Switch, Sphereon 4300 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 4400 Fabric
Switch, Sphereon 4500 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 4700 Fabric
Switch, Intrepid
®
6064 Director, and Intrepid 6140 Director.
• Fibre Alliance (FCMGMT) MIB, version 3.1: supported by EFC
Server, Sphereon 3016 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 3032 Fabric
Switch, Sphereon 3216 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 3232 Fabric
Switch, Sphereon 4300 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 4400 Fabric
Switch, Sphereon 4500 Fabric Switch, Sphereon 4700 Fabric
Switch, Intrepid 6064 Director, and Intrepid 6140 Director.
• Fibre Channel Fabric Element (FCFE), version 1.10: supported by
all switches and directors.
Private Enterprise
MIBs
Private MIBs are those provided by the manufacturer of the managed
devices to allow management of device-specific items. Chapter 2
describes the McDATA private MIBs in more detail.
The McDATA private enterprise MIBs are:
• es1000 MIB, used by the ES-1000 switch
• ed5000 MIB, used by the ED-5000 director
• fcEos MIB, used by the supported by Sphereon 4500 switch,
Sphereon 4300 switch, Sphereon 3016 switch, Sphereon 3216
switch, Sphereon 3232 switch, Sphereon 4400 switch, Sphereon
4700 switch, Intrepid 6064 Director, and Intrepid 6140 Director
(updated to support zoning, port binding, threshold alerts, and
open trunking).
Page 21

1
Network Management using SNMP
1-9
Introduction to SNMP
Traps and Their
Purpose
Traps are unsolicited status reports, or status change indicators a
managed object sends to a network manager. The destination address
and UDP port number for traps can be configured for each managed
agent. If no specific value is configured for UDP port number it takes
the default value. The default value for UDP port number is 162.
Page 22

1
1-10
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
Introduction to SNMP
Page 23

McDATA SNMP Support
2-1
2
McDATA SNMP
Support
Overview
SNMP is a protocol that uses the User Data Protocol (UDP) to
exchange messages between an SNMP agent (in a managed device)
and a management station residing on a network. Although SNMP
can be made available over other protocols, McDATA only supports
UDP.
To be monitored and managed remotely by a network management
station, each switch or director is equipped with an SNMP agent. This
agent is a software process within the switch that receives
management requests and generates corresponding responses by
accessing the data specified for the MIB-II, Fabric Element MIB, Fibre
Alliance MIB, and FCEOS enterprise specific MIB. In addition, the
agent gives each switch the ability to notify a management station
when an important event occurs by sending a trap to the
management station.
Seven MIBs are supported:
• A subset of the Standard MIB-II for TCP/IP –based Internet as
specified in RFC1213.
• Fabric Element MIB containing support for FL ports as specified
in Fibre Channel standards.
• Fibre Alliance MIB (also referred to as the FC Management MIB).
• Fibre Alliance MIB, version 3.0
Page 24

2
2-2
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
• FCEOS MIB, the McDATA enterprise specific MIB supporting the
McDATA switch and director firmware.
•SNMP Framework MIB.
•SNMPv3 MIB.
E/OS Trap Overview
NOTE: E/OS traps support SNMP V1/V2c/V3 format regardless of MIB
definition syntax.
SNMP traps are specific types of SNMP messages enclosed in UDP
packets as shown:
[ IP Packet [ UDP Packet [ SNMP Message ] ] ]
The SNMP message format is:
[ Version | Community | SNMP PDU ]
There are different formats for the SNMP PDUs, including trap
PDUs, for SNMPv1 and SNMPv2. These are summarized here:
SNMPv1 Trap PDU:
[ Enterprise | Agent address | Generic trap type | Specific trap code
| Time stamp | Object/Value 1 | Object/Value 2…. ]
The following descriptions summarize these fields:
Enterprise—Identifies the type of managed object generating the
trap.
Agent address—Provides the address of the managed object
generating the trap.
Generic trap type—Indicates one of a number of generic trap types.
Specific trap code—Indicates one of a number of specific trap codes.
Time stamp—Provides the amount of time that has elapsed between
the last network reinitialization and generation of the trap.
Variable bindings—The data field of the SNMPv1 Trap PDU. Each
variable binding associates a particular object instance with its
current value.
Page 25
2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-3
McDATA SNMP Support
The following descriptions summarize the fields illustrated below for
the SNMPv2 PDU format:
PDU type—Identifies the type of PDU transmitted (Get, GetNext,
Inform, Response, Set, or Trap).
Request ID—Associates SNMP requests with responses.
Error status—Indicates one of a number of errors and error types.
Only the response operation sets this field. Other operations set this
field to zero.
Error index—Associates an error with a particular object instance.
Only the response operation sets this field. Other operations set this
field to zero.
Variable bindings—Serves as the data field of the SNMPv2 PDU.
Each variable binding associates a particular object instance with its
current value (with the exception of Get and GetNext requests, for
which the value is ignored).
Get, GetNext, Inform, Response, Set, and Trap PDUs Contain the
Same Fields:
[PDU type | Request ID | Error status | Error index | Object/Value
1 | Object/Value 2]
For the SNMPv2 trap PDU, the first and second variable bindings
contain the uptime and the trap OID respectively. Following the
uptime and trap OID are all the variable bindings specified in the
MIB for that particular trap.
E/OS Trap summary
table
This table shows the different kinds of traps supported by the switch
E/OS firmware.
Trap Severity Sent because MIB Tr a p O I D E/OS EFCM
Generic Authentication
Failure
N/A SNMP request from
an invalid community
is received
RFC-1157 YES YES
Generic Link Up N/A RFC-1157 YES NO
Generic Warm Start N/A Software reset RFC-1157 YES NO
Generic Cold Start N/A Power up RFC-1157 YES NO
Page 26
2
2-4
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ES port change N/A A change in port
status
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.1 YES NO
ES FRU change N/A A change in FRU
status
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2 YES NO
ES invalid attachment N/A Invalid attachment to
a port.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.3 YES NO
ES threshold alert N/A Threshold specified in
threshold table has
been exceeded for a
port.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.4 YES NO
ES FRU removed* N/A A FRU has been
removed or
transitioned to
unknown status.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.5 YES NO
ES FRU active* N/A A FRU transitioned to
the active state.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.6 YES NO
ES FRU backup* N/A A FRU transitioned to
the backup state.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.7 YES NO
ES FRU update* N/A A FRU transitioned to
the update/busy
status.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.8 YES NO
ES FRU failed* N/A A FRU failed. FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.9 YES NO
ES link bit error event* N/A The bit error rate for a
link has exceeded an
allowed threshold.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.10 YES NO
ES link no signal event* N/A Loss of signal or sync. FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.11 YES NO
ES link NOS event* N/A A not operational
primitive sequence
timeout occurred.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.12 YES NO
ES link failure event* N/A A primitive sequence
timeout occurred.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.13 YES NO
ES link invalid event* N/A An invalid primitive
sequence is detected.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.14 YES NO
Trap Severity Sent because MIB Tr a p O I D E/OS EFCM
Page 27
2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-5
McDATA SNMP Support
* EOS 6.0 and later only.
The following sections describe each trap and the variables within the
traps. For each variable, the OID is expressed as a numeric value first
followed by a second line showing the symbolic object name.
Appended to the right of the OIDs are the index values for each
object. Most of the objects within traps are actually table values. (That
is, they refer to a MIB object which is part of a table defined in the
MIB). Each SNMP table value must have an index appended to
identify a specific table row.
For example, the enterprise specific port status change trap has the
variable binding for fcEosPortOpStatus, which is a table entry value.
So the OID for fcEosPortOpStatus (1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.3.1.1.3)
specifies a table column – to get a value for a specific port the table
index (port_number+1) must be appended to the OID. If the trap
occurred because of a change on port 5, then the actual variable OID
would be 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.3.1.1.3.
Enterprise-specific
Port Status Change
Trap
This trap is sent for each port which has a status change. There is 1
variable binding as follows:
ES link added event* N/A A new link has been
detected. NOTE: up to
10 seconds may
elapse after link is
added before trap is
sent.
FCEOS 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.15 YES NO
Switch SCN Alert Change in switch
status.
FC-MGMNT 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.1 YES YES
Switch Deletion Alert A switch is removed
from management
control.
FC-MGMNT 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.2 NO YES
Event SCN Info A new system event
was generated.
FC-MGMNT 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.3 YES YES
Sensor SCN Alert Change in status for
FAN/FAN2/POWER
FRUs.
FC-MGMNT 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.4 YES YES
Port SCN Alert A change in port
status.
FC-MGMNT 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.5 YES YES
Trap Severity Sent because MIB Tr a p O I D E/OS EFCM
Page 28
2
2-6
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
Enterprise-specific
FRU Status Change
Trap
This trap is sent for each FRU which has a status change. There is 1
variable binding as follows:
Enterprise-specific
Invalid Attachment
Trap
This trap is sent when an invalid attachment occurs (a device is
attached, with a WWN specifically disallowed by port binding).
There is 1 variable binding.
Binding OIB Value
1 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.3.1.1.3.port_number+1
fcEosPortOpStatus.port_number+1
New status value. See definition for
fcEosPortOpStatus
Binding OID Values
1 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.2.1.1.3.fru_code.fru_pos
fcEosFruStatus.fru_code.fru_pos
Where fru_code has one of the following values:
0x01, Backplane
0x02, Control Processor card
0x03, Serial Crossbar
0x04, Shasta 32 center fan module
0x05, Fan module
0x06, Power supply module
0x07, Reserved
0x08, Longwave, Single-Mode, LC connector, 1 Gig (Port card)
0x09, Shortwave, Multi-Mode, LC connector, 1 Gig (Port card)
0x0A, Mixed, LC connector, 1 Gig (Port card)
0x0B, SFO pluggable, 1 Gig
0x0C, SFO pluggable, 2 Gig
0x0D, Longwave, Single-Mode, MT-RJ connector, 1 Gig
0x0E , Shortwave, Multi-Mode, MT-RJ connector, 1 Gig
0x0F , Mixed, MT-RJ connector, 1 Gig
0x10 , F-Port, internal, 1 Gig
And where fru_pos is a number specific to each possible FRU
position, which varies from product to product. For example, on an
Intrepid 6140 director, there are three fans numbered 1 to 3.
New status value. See definition for
fcEosFruStatus
Page 29
2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-7
McDATA SNMP Support
Enterprise-specific
Threshold Alert Trap
This trap is sent when port traffic exceeds a specified threshold.
There are 2 variable bindings.
Enterprise-specific
FRU Traps
The enterprise specific FRU traps (FRU removed, FRU active, FRU
backup, FRU update, FRU failed: type codes 5-9) share the same
bindings. There are 4 variable bindings for these traps:
Binding OID Value
1 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.4.1.1.4.port_number+1
fcEosPortAttachedWWN.port_number+1
WWN of invalid attached device. See
definition for fcEosPortAttachedWWN.
Binding OID Value
1 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.3.1.1.1.port_number+1
fcEosPortIndex.port_number+1
Port number of port with threshold alert.
2 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.6.1.1.1.threshold_number
fcEosTAIndex.threshold_number
The index of the threshold which was
triggered.
Binding OID Value
1 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.2.1.1.1.fru_code.fru_position
fcEosFruCode.fru_code.fru_position
The FRU code for this FRU. See table
below.
2 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.2.1.1.2.fru_code.fru_position
fcEosFruPosition.fru_code.fru_position
The FRU position for this FRU. The first
position is 1.
3 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.1.15.0
fcEosSysSwitchName
The ASCII name of the switch
4 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.1.16.0
fcEosSysSwitchId
The Worldwide Name of the switch.
Page 30
2
2-8
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
Enterprise-specific
Link Traps
The enterprise specific link traps (link bit error, link no signal, link
NOS, link failure, link invalid, link added: type codes 10 – 15) share
the same bindings. There are 5 variable bindings for these traps:
FRU Code Description
1 Backplane
2 Control Processor card
3 Serial Crossbar
4 Shasta 32 center fan module
5Fan module
6 Power supply module
7 Reserved
8 Longwave, Single-Mode, LC connector, 1 Gig
9 Shortwave, Multi-Mode, LC connector, 1 Gig
10 Mixed, LC connector, 1 Gig
11 SFO pluggable, 1 Gig
12 SFO pluggable, 2 Gig
13 Longwave, Single-Mode, MT-RJ connector, 1 Gig
14 Shortwave, Multi-Mode, MT-RJ connector, 1 Gig
15 Mixed, MT-RJ connector, 1 Gig
16 F-Port, internal, 1 Gig
17 F-Port, internal, 1 Gig - XPM
18 F-Port, internal, 1 Gig - IPM
Page 31

2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-9
McDATA SNMP Support
FA MIB Switch Status
Change Trap
This trap is sent when the switch status changes. There are 2 variable
bindings.
FA MIB Event Trap This trap is sent when an internal software event is generated. There
are 4 variable bindings.
Binding OID Value
1 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.3.1.1.1.port_index
fcEosPortIndex.port_index
The fixed physical port number on the
switch. It ranges from 1 to the number of
physical ports that can be supported in
the switch.
2 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.3.1.1.152.port_index
fcEosPortName.port_index
A string describing the addressed port
3 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.3.1.1.153.port_index
fcEosPortWWN.port_index
The Port WWN.
4 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.1.15.0
fcEosSysSwitchName
The ASCII name of the switch
5 1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2.1.16.0
fcEosSysSwitchId
The Worldwide Name of the switch.
Binding OID Value
1 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.3.1.6.<unit-id>
fcConnUnitStatus.<unit-id>
Where unit-id is the WWN of the switch with 8 zeros appended for a
total length of 16. Example: 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
Unit status. See definition for
fcConnUnitStatus.
2 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.3.1.5.<unit-id>
fcConnUnitState.<unit-id>
Where unit-id is the WWN of the switch with 8 zeros appended for a
total length of 16. Example: 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
Unit state. See definition for
fcConnUnitState.
Page 32

2
2-10
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
FA MIB Se nsor Tra p This trap is generated whenever a status change occurs for a fan or
power supply FRU. There is 1 variable binding.
Binding OID Value
1 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.3.1.1.<unit-id>
fcConnUnitId.<unit-id>
Where unit-id is the WWN of the switch with 8 zeros appended for a
total length of 16. Example: 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
The value is the same as unit-id: the
WWN of the switch with 8 zeros
appended for a total length of 16.
Example: 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
2 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.7.1.5.<unit-id><event-index>
fcConnUnitEventType.<unit-id><event-index>
Where unit-id is the WWN of the switch with 8 zeros appended for a
total length of 16. Example: 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
And where event-index is an integer index of the event table, a unique
incrementing value assigned to each event. The event table always
contains the most recent 200 events which met the filter criteria in
place when the event occurred.
See definition for fcConnUnitEventType.
3 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.7.1.6.<unit-id><event-index>
fcConnUnitEventObject.<unit-id><event-index>
Where unit-id is the WWN of the switch with 8 zeros appended for a
total length of 16. Example: 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
And where event-index is an integer index of the event table, a unique
incrementing value assigned to each event. The event table always
contains the most recent 200 events which met the filter criteria in
place when the event occurred.
The value of this variable is the OID for
fcConnUnitId:
1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.3.1.1.<unit-id>
Where unit-id is the WWN of the switch
with 8 zeros appended for a total length of
16. Example:
1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
4 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.7.1.7.<unit-id><event-index>
fcConnUnitEventDescr.<unit-id><event-index>
Where unit-id is the WWN of the switch with 8 zeros appended for a
total length of 16. Example: 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
And where event-index is an integer index of the event table, a unique
incrementing value assigned to each event. The event table always
contains the most recent 200 events which met the filter criteria in
place when the event occurred.
Event description string with a maximum
length of 80 characters. This string will
contain a numeric event code and other
values describing the specific event. See
QMS-00019 for a description of events.
Page 33

2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-11
McDATA SNMP Support
FA MIB Por t Sta tus
Change Trap
This trap occurs whenever a port status change occurs. There are 2
variable bindings.
Enterprise-specific
Traps
fcEosPortScn
Type Number 1
Product Mapping Generated when Fibre Channel port operational state changes.
Trap Variables fcEosPortOpStatus
Description An fcEosPortScn(1) is generated whenever a Fc_Port changes its
operational state. For instance, the Fc_Port goes from online to
offline.
fcEosFruScn
Type Number 2
Binding OID Value
1 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.5.1.3.<unit-id>.<sensor-index>
fcConnUnitSensorStatus.<unit-id>.<sensor-index>
Where unit-id is the WWN of the switch with 8 zeros appended for a
total length of 16. Example: 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
And where sensor-index refers to the FRU in the sensor table which
has changed state. For example if sensor-index was 5, then you could
look at the 5
th
entry in the sensor table to determine which FRU was
affected.
See description for
fcConnUnitSensorStatus
Binding OID Value
1 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.6.1.6. <unit-id>.<port-index>
fcConnUnitPortStatus. <unit-id>.<port-index>
Where port-index is the port number normalized to the range 1-140.
See definition for fcConnUnitPortStatus.
2 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.1.1.6.1.5. <unit-id>.<port-index>
fcConnUnitPortState. <unit-id>.<port-index>
Where port-index is the port number normalized to the range 1-140.
See definition for fcConnUnitPortState.
Page 34

2
2-12
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
Product Mapping Generated when FRU operational state changes.
Trap Variables fcEosFruStatus
Description An fcEosFruScn(2) is generated whenever a FRU status changes to
operational state.
fcEosPortBindingViolation
Type Number 3
Product Mapping Generated when Port binding violation occurs.
Trap Variables fcEosPortAttachedWWN
Description An fcEosPortBindingViolation(3) is generated whenever the switch
detects that a port binding violation occurs.
fcEosThresholdAlert
Type Number 4
Product Mapping Generated when Threshold alert occurs.
Trap Variables fcEosPortIndex
fcEosTAIndex
Description An fcEosThresholdAlert(4) is generated whenever a threshold alert
occurs.
fcEosFruRemoved
Type Number 5
Product Mapping Generated when a FRU is removed or its status changes to unknown.
Trap Variables fcEosFruCode
fcEosFruPosition
fcEosSysSwitchName
fcEosSysSwitchId
Description An fcEosFruRemoved trap is generated when a FRU is removed or its
status changes to unknown
Page 35

2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-13
McDATA SNMP Support
fcEosFruActive
Type Number 6
Product Mapping Generated when a FRU status changes to an active status.
Trap Variables fcEosFruCode
fcEosFruPosition
fcEosSysSwitchName
fcEosSysSwitchId
Description An fcEosFruActive trap is generated when a FRU status changes to
an active status.
fcEosFruBackup
Type Number 7
Product Mapping Generated when a FRU status changes to a backup status.
Trap Variables fcEosFruCode
fcEosFruPosition
fcEosSysSwitchName
fcEosSysSwitchId
Description An fcEosFruBackup trap is generated when a FRU status changes to a
backup status.
fcEosFruUpdate
Type Number 8
Product Mapping Generated when a FRU status changes to update/busy.
Trap Variables fcEosFruCode
fcEosFruPosition
fcEosSysSwitchName
fcEosSysSwitchId
Description An fcEosFruFailed trap is generated when a FRU status changes to
update/busy.
Page 36

2
2-14
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
fcEosFruFailed
Type Number 9
Product Mapping Generated when a FRU status changes to a failed status.
Trap Variables fcEosFruCode
fcEosFruPosition
fcEosSysSwitchName
fcEosSysSwitchId
Description An fcEosFruFailed trap is generated when a FRU status changes to a
failed status.
fcEosLinkBit ErrorEvent
Type Number 10
Product Mapping Generated when the bit error rate for a link exceeds the threshold.
Trap Variables fcEosPort Index
fcEosPortName
fcEosPort WWN
fcEosSysSwitchName
Description An fcEosLinkBit trap is generated when the bit error rate for a link
exceeds an allowed threshold.
fcEosLinkNoSignalEvent
Type Number 11
Product Mapping Generated when there is a loss of signal or sync.
Trap Variables fcEosPortIndex
fcEosPortName
fcEosPortWWN
fcEosSysSwitchName
Description An fcEosLinkNoSignalEvent trap is generated when there is a loss of
signal or sync.
Page 37

2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-15
McDATA SNMP Support
fcEosLinkNOSEvent
Type Number 12
Product Mapping Generated when a not operational primitive sequence is received.
Trap Variables fcEosPortIndex
fcEosPortName
fcEosPortWWN
fcEosSysSwitchName
Description An fcEosLinkNOSEvent trap is generated when a not operational
primitive sequence is received.
fcEosLinkFailureEvent
Type Number 13
Product Mapping Generated when a primitive sequence timeout occurs.
Trap Variables fcEosPortIndex
fcEosPortName
fcEosPortWWN
fcEosSysSwitchName
Description An fcEosLinkFailureEvent trap is generated when a primitive
sequence timeout occurs.
fcEosLinikInvalidEvent
Type Number 14
Product Mapping Generated when an invalid primitive sequence is detected.
Trap Variables fcEosPortIndex
fcEosPortName
fcEosPortWWN
fcEosSysSwitchName
Description An fcEosLinikInvalidEvent trap is generated when an invalid
primitive sequence is detected.
Page 38

2
2-16
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
fcEosLinkAddedEvent
Type Number 15
Product Mapping Generated when the firmware detects that a new connection has been
established on a port.
Trap Variables fcEosPortIndex
fcEosPortName
fcEosPortWWN
fcEosSysSwitchName
Description An fcEosLinkAddedEvent trap is generated when the firmware
detects that a new connection has been established on a port.
EXAMPLE: Interpretation of trap information from HP OpenView
The output from HP OpenView for a series of traps is shown below:
- Minor Thu May 02 09:29:30 10.235.4.111 NO TRAPD.CONF
FMT FOR .1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.1 ARGS(2): [1]
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitStatus.3.2.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
(Integer): ok [2]
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitState.3.2.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
(Integer): online
- Minor Thu May 02 09:29:31 10.235.4.111 NO TRAPD.CONF
FMT FOR .1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.1 ARGS(2): [1]
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitStatus.7.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
(Integer): ok [2]
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitState.7.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
(Integer): online
- Minor Thu May 02 09:29:46 10.235.4.111 NO TRAPD.CONF
FMT FOR .1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.1 ARGS(2): [1]
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitStatus.3.2.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
(Integer): ok [2]
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitState.3.2.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
(Integer): online
Page 39

2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-17
McDATA SNMP Support
- Minor Thu May 02 09:29:47 10.235.4.111 NO TRAPD.CONF
FMT FOR .1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.1 ARGS(2): [1]
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitStatus.7.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
(Integer): ok [2]
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitState.7.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
(Integer): online
This output from HP OpenView contains information for 4 traps.
Blank lines have been added for clarity. The first step is to determine
which trap caused this output. Looking after the words “NO TRAPD.
CONF FMT FOR” you can see the numbers 1.3.6.1.2.1.8888.0.1 which
identifies this as a switch SCN trap (from table in section 2.3). After
the trap OID, the variable bindings are listed. HP OpenView calls
them “ARGS” and shows how many have been found in this
particular trap (in this case, 2).
The first arg is identified by it’s OID in symbolic form:
mgmt.mib-2.fcMgmtMIB.fcMgmtObjects.fcMgmtConfig.fcConnUnit
Table.fcConnUnitEntry.fcConnUnitStatus.
The numbers following fcConnUnitStatus are the unit-id which
identifies a particular switch in a fabric. (The unit-id is the first index
for all tables in the Fibre Alliance MIB). In this case, these traps are
most likely from the EFC Server, which uses a different numbering
scheme for the unit-id than the E/OS firmware (see below). In both
cases the unit-id is a string of 16 numbers. Following the unit-id is the
actual value of the first variable: ok. The value transmitted in the trap
is numeric (an integer) but HP OpenView has cross-referenced this
numeric value with the MIB definitions to provide the symbolic form
(ok). The second variable binding is fcConnUnitState and has the
same indexing scheme for unit-id.
Numbering scheme for unit-id (fcConnUnitId) for E/OS and EFCM:
E/OS: WWN(8 numbers).0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
EFCM: product-code.product-id.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
In both cases the total length is 16 numbers.
This identifier is used as the first index in all FA MIB tables.
Page 40

2
2-18
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
EXAMPLE: Interpretation of trap information from MG-SOFT MIB
Browser
5. 3: Specific trap #3 trap(v1) received from: 172.16.7.243 at
09/25/2002 3:06:45 PM
Time stamp: 0 days 00h:00m:12s.36th
Agent address: 172.16.7.243 Port: 161 Transport: IP/UDP
Protocol: SNMPv1 Trap
Manager address: 172.16.7.107 Port: 162 Transport: IP/UDP
Community: public
SNMPv1 agent address: 172.16.7.243
Enterprise: fcMgmtMIB
Specific Trap MIB Lookup Results
Name: fcEosPortBindingViolation, Module: FCEOS-MIB,
Enterprise: mcData
Bindings (4)
Binding #1:
fcConnUnitId.16.0.8.0.136.122.40.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0 *** (octets)
00.00.00.10.00.00.00.00.00.00.00.08.00.00.00.00 (hex)
Binding #2:
fcConnUnitEventType.16.0.8.0.136.122.40.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.295 ***
(int32) status(3)
Binding #3:
fcConnUnitEventObject.16.0.8.0.136.122.40.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.295 ***
(oid) fcConnUnitId.16.0.8.0.136.122.40.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
Binding #4:
fcConnUnitEventDescr.16.0.8.0.136.122.40.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.295 ***
(octets) Reason code
410<00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><
00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><
00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00><00 ...
6. 4: Specific trap #1 trap(v1) received from: 172.16.7.243 at
09/25/2002 3:06:45 PM
7. 5: Specific trap mcData::fcEosFruScn #2 trap(v1) received from:
172.16.7.243 at 09/25/2002 3:06:45 PM
Page 41

2
E/OS Trap Overview
2-19
McDATA SNMP Support
8. 6: Specific trap #3 trap(v1) received from: 172.16.7.243 at
09/25/2002 3:06:45 PM
9. 7: Specific trap #3 trap(v1) received from: 172.16.7.243 at
09/25/2002 3:06:45 PM
As displayed by the MG-SOFT browser, the output above is shown in
hierarchical tree form. Trap number 3 has been expanded to show the
details of the information contained in the trap. The agent address is
the IP address of the switch, and the management address is the
address of the PC which was running MG-SOFT. In this case the trap
can be identified by the Enterprise (fcMgmtMIB – also known as the
FA MIB) and the specific trap number (3), which identifies this as an
FA MIB event trap. Lines labeled 4-7 are each for different traps.
Referring to trap 3 again, the browser clearly displays the 4 variable
bindings contained within an FA MIB event trap. Each variable
binding is displayed in the format: OID data-type value.
Page 42

2
2-20
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
There are eleven groups of objects specified in MIB-II. The E/OS
SNMP agent supports eight groups:
• System Group . This group provides general information about the
managed system.
• Interfaces Group
• Address Translation Group
• This group is implemented, but the corresponding table may be
empty.
• IP Group
• ICMP Group
• TCP Group
• UDP Group
• SNMP Group This group keeps statistics on the SNMP agent
implementation itself.
System Group
sysDescr
Type DisplayString(0..255)
Access R
Description A textual description of the entity. This value should include the full
name and version identification of the system's hardware type,
software operating system, and networking software. It is mandatory
that this only contain printable ASCII characters.
sysObjectID
Type Object Identifier
Access R
Page 43

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-21
McDATA SNMP Support
Description The vendor’s authoritative identification of the network management
subsystem contained in the entity. This value is allocated within the
SMI enterprises subtree (1.3.6.1.4.1) and provides an easy and
unambiguous means for determining ‘what kind of box’ is being
managed. For example, if vendor ‘Flintstones, Inc.’ was assigned the
subtree 1.3.6.1.4.1.4242, it could assign the identifier
1.3.6.1.4.1.4242.1.1 to its ‘Fred Router’.
sysUpTime
Type TimeTicks
Access R
Description The time (in hundredths of a second) since the network management
portion of the system was last re-initialized.
sysContact
Type DisplayString (0..255)
Access R
Description The textual identification of the contact person for this managed
node, together with information on how to contact this person.
sysName
Type DisplayString (0..255)
Access RW
Description An administratively-assigned name for this managed node. By
convention, this is the node's fully-qualified domain name.
sysLocation
Type DisplayString (0..255)
Access RW
Description The physical location of this node (e.g., `telephone closet, 3rd floor').
Page 44

2
2-22
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
sysServices
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description A value which indicates the set of services that this entity primarily
offers. The value is a sum. This sum initially takes the value zero,
then, for each layer, L, in the range 1 through 7, that this node
performs transactions for, 2 raised to (L - 1) is added to the sum. For
example, a node which performs primarily routing functions would
have a value of 4 (2^(3-1)). In contrast, a node which is a host offering
application services would have a value of 72 (2^(4-1) + 2^(7-1)).
Note that in the context of the Internet suite of protocols, values
should be calculated accordingly:
layer functionality
1 physical (e.g., repeaters)
2 datalink/subnetwork (e.g., bridges)
3 internet (e.g., IP gateways)
4 end-to-end (e.g., IP hosts)
7 applications (e.g., mail relays)
For systems including OSI protocols, layers 5 and 6 may also be
counted.
Interfaces Group
ifNumber
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The number of network interfaces (regardless of their current state)
present on this system.
Page 45

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-23
McDATA SNMP Support
Interfaces Table The interfaces table contains information on the entity's interfaces.
Each interface is thought of as being attached to a “subnetwork”.
Note that this term should not be confused with “subnet” which
refers to an addressing partitioning scheme used in the Internet suite
of protocols.
ifIndex
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description A unique value for each interface. Its value ranges between 1 and the
value of ifNumber. The value for each interface must remain constant
at least from one re-initialization of the entity's network management
system to the next re-initialization.
ifDescr
Type DisplayString(0..255)
Access R
Description A textual string containing information about the interface. This
string should include the name of the manufacturer, the product
name and the version of the hardware interface.
ifType
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The type of interface, distinguished according to the physical/link
protocol(s) immediately below the network layer in the protocol
stack.
Values:
other(1), none of the following
regular1822(2),
hdh1822(3),
ddn-x25(4),
rfc877-x25(5),
Page 46

2
2-24
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ethernet-csmacd(6),
iso88023-csmacd(7),
iso88024-tokenBus(8),
iso88025-tokenRing(9),
iso88026-man(10),
starLan(11),
proteon-10Mbit(12),
proteon-80Mbit(13),
hyperchannel(14),
fddi(15),
lapb(16),
sdlc(17),
ds1(18), T-1
e1(19), european equivalent of T-1
basicISDN(20),
primaryISDN(21), proprietary serial
propPointToPointSerial(22),
ppp(23),
softwareLoopback(24),
eon(25) CLNP over IP [11]
ethernet-3Mbit(26),
nsip(27), --XNS over IP
slip(28), -- generic SLIP
ultra(29), --ULTRA technologies
ds3(30), --T-3
sip(31), -- SMDS
frame-relay(32)
Page 47

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-25
McDATA SNMP Support
ifMtu
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The size of the largest datagram which can be sent/received on the
interface, specified in octets. For interfaces that are used for
transmitting network datagrams, this is the size of the largest
network datagram that can be sent on the interface.
ifSpeed
Type Gauge
Access R
Description An estimate of the interface's current bandwidth in bits per second.
For interfaces which do not vary in bandwidth or for those where no
accurate estimation can be made, this object should contain the
nominal bandwidth.
ifPhysAddress
Type PhysAddress
Access R
Description The interface's address at the protocol layer immediately `below' the
network layer in the protocol stack. For interfaces which do not have
such an address (e.g., a serial line), this object should contain an octet
string of zero length.
ifAdminStatus
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The desired state of the interface. The testing(3) state indicates that no
operational packets can be passed.
Page 48

2
2-26
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ifOperStatus
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The current operational state of the interface. The testing(3) state
indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
ifLastChange
Type TimeTicks
Access R
Description The value of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current
operational state. If the current state was entered prior to the last
re-initialization of the local network management subsystem, then
this object contains a zero value.
ifInOctets
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of octets received on the interface, including
framing characters.
ifInUcastPkts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered to a
higher-layer protocol.
ifInNUcastPkts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of non-unicast (i.e., subnetwork-broadcast or
subnetwork-multicast) packets delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
Page 49

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-27
McDATA SNMP Support
ifInDiscards
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of inbound packets which were chosen to be discarded
even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being
deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for
discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space.
ifInErrors
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing
them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
ifInUnknownProtos
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of packets received via the interface which were
discarded because of an unknown or unsupported protocol
ifOutOctets
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including
framing characters.
ifOutUcastPkts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
transmitted to a subnetwork-unicast address, including those that
were discarded or not sent.
Page 50

2
2-28
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ifOutNUcastPkts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be
transmitted to a non-unicast (i.e., a subnetwork-broadcast or
subnetwork-multicast) address, including those that were discarded
or not sent.
ifOutDiscards
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of outbound packets which were chosen to be discarded
even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being
transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could
be to free up buffer space.
ifOutErrors
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted
because of errors.
ifOutQLen
Type Gauge
Access R
Description The length of the output packet queue (in packets).
ifSpecific
Type OBJECT IDENTIFIER
Access R
Description A reference to MIB definitions specific to the particular media being
used to realize the interface. For example, if the interface is realized
Page 51

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-29
McDATA SNMP Support
by an ethernet, then the value of this object refers to a document
defining objects specific to ethernet. If this information is not present,
its value should be set to the OBJECT IDENTIFIER { 0 0 }, which is a
syntactically valid object identifier, and any conforming
implementation of ASN.1 and BER must be able to generate and
recognize this value.
Address Translation Group
Implementation of the Address Translation group is mandatory for
all systems. Note however that this group is deprecated by MIB-II.
That is, it is being included solely for compatibility with MIB-I nodes,
and will most likely be excluded from MIB-III nodes. From MIB-II
and onwards, each network protocol group contains its own address
translation tables.
The Address Translation group contains one table which is the union
across all interfaces of the translation tables for converting a
NetworkAddress (e.g., an IP address) into a subnetwork-specific
address. For lack of a better term, this document refers to such a
subnetwork-specific address as a `physical' address. Examples of
such translation tables are: for broadcast media where ARP is in use,
the translation table is equivalent to the ARP cache; or, on an X.25
network where non-algorithmic translation to X.121 addresses is
required, the translation table contains the NetworkAddress to X.121
address equivalences.
atIfIndex
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The interface on which this entry's equivalence is effective. The
interface identified by a particular value of this index is the same
interface as identified by the same value of ifIndex.
atPhysAddress
Type PhysAddress
Access RW
Description The media-dependent `physical' address. Setting this object to a null
string (one of zero length) has the effect of invaliding the
Page 52

2
2-30
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
corresponding entry in the atTable object. That is, it effectively
disassociates the interface identified with said entry from the
mapping identified with said entry. It is an implementation-specific
matter as to whether the agent removes an invalidated entry from the
table. Accordingly, management stations must be prepared to receive
tabular information from agents that corresponds to entries not
currently in use. Proper interpretation of such entries requires
examination of the relevant atPhysAddress object.
atNetAddress
Type NetworkAddress
Access RW
Description The NetworkAddress (e.g., the IP address) corresponding to the
media-dependent `physical' address.
IP Group
ipForwarding
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The indication of whether this entity is acting as an IP gateway in
respect to the forwarding of datagrams received by, but not
addressed to, this entity. IP gateways forward datagrams. IP hosts do
not (except those source-routed via the host). Note that for some
managed nodes, this object may take on only a subset of the values
possible. Accordingly, it is appropriate for an agent to return a
`badValue' response if a management station attempts to change this
object to an inappropriate value.
ipDefaultTTL
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The default value inserted into the Time-To-Live field of the IP
header of datagrams originated at this entity, whenever a TTL value
is not supplied by the transport layer protocol.
Page 53

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-31
McDATA SNMP Support
ipInReceives
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of input datagrams received from interfaces,
including those received in error.
ipInHdrErrors
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of input datagrams discarded due to errors in their IP
headers, including bad checksums, version number mismatch, other
format errors, Time-To-Live exceeded, errors discovered in
processing their IP options, etc.
ipInAddrErrors
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of input datagrams discarded because the IP address in
their IP header's destination field was not a valid address to be
received at this entity. This count includes invalid addresses (e.g.,
0.0.0.0) and addresses of unsupported classes (e.g., Class E). For
entities which are not IP Gateways and therefore do not forward
datagrams, this counter includes datagrams discarded because the
destination address was not a local address.
ipForwDatagrams
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of input datagrams for which this entity was not their
final IP destination, as a result of which an attempt was made to find
a route to forward them to that final destination. In entities which do
not act as IP Gateways, this counter will include only those packets
which were Source-Routed via this entity, and the Source-Route
option processing was successful.
Page 54

2
2-32
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ipInUnknownProtos
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of locally-addressed datagrams received successfully
but discarded because of an unknown or unsupported protocol.
ipInDiscards
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of input IP datagrams for which no problems were
encountered to prevent their continued processing, but which were
discarded (e.g., for lack of buffer space). Note that this counter does
not include any datagrams discarded while awaiting re-assembly.
ipInDelivers
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of input datagrams successfully delivered to IP
user-protocols (including ICMP).
ipOutRequests
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of IP datagrams which local IP user-protocols
(including ICMP) supplied to IP in requests for transmission. Note
that this counter does not include any datagrams counted in
ipForwDatagrams.
ipOutDiscards
Type Counter
Access R
Page 55

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-33
McDATA SNMP Support
Description The number of output IP datagrams for which no problem was
encountered to prevent their transmission to their destination, but
which were discarded (e.g., for lack of buffer space). Note that this
counter would include datagrams counted in ipForwDatagrams if
any such packets met this (discretionary) discard criterion.
ipOutNoRoutes
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of IP datagrams discarded because no route could be
found to transmit them to their destination. Note that this counter
includes any packets counted in ipForwDatagrams which meet this
`no-route' criterion. Note that this includes any datagrams which a
host cannot route because all of its default gateways are down.
ipReasmTimeout
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The maximum number of seconds which received fragments are held
while they are awaiting reassembly at this entity.
ipReasmReqds
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of IP fragments received which needed to be
reassembled at this entity.
ipReasmOKs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of IP datagrams successfully.
Page 56

2
2-34
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ipReasmFails
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of failures detected by the IP re-assembly algorithm (for
whatever reason: timed out, errors, etc). Note that this is not
necessarily a count of discarded IP fragments since some algorithms
(notably the algorithm in RFC 815) can lose track of the number of
fragments by combining them as they are received.
ipFragOKs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of IP datagrams that have been successfully fragmented
at this entity.
ipFragFails
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of IP datagrams that have been discarded because they
needed to be fragmented at this entity but could not be, e.g., because
their Don't Fragment flag was set.
ipFragCreates
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of IP datagram fragments that have been generated as a
result of fragmentation at this entity.
Page 57

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-35
McDATA SNMP Support
IP Address Table The IP address table contains this entity's IP addressing information.
ipAdEntAddr
Type IpAddress
Access R
Description The IP address to which this entry's addressing information pertains.
ipAdEntIfIndex
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The index value which uniquely identifies the interface to which this
entry is applicable. The interface identified by a particular value of
this index is the same interface as identified by the same value of
ifIndex.
ipAdEntNetMask
Type IpAddress
Access R
Description The subnet mask associated with the IP address of this entry. The
value of the mask is an IP address with all the network bits set to 1
and all the hosts bits set to 0.
ipAdEntBcastAddr
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The value of the least-significant bit in the IP broadcast address used
for sending datagrams on the (logical) interface associated with the IP
address of this entry. For example, when the Internet standard
all-ones broadcast address is used, the value will be 1. This value
applies to both the subnet and network broadcasts addresses used by
the entity on this (logical) interface.
Page 58

2
2-36
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ipAdEntReasmMaxSize
Type INTEGER (0..65535)
Access R
Description The size of the largest IP datagram which this entity can re-assemble
from incoming IP fragmented datagrams received on this interface.
IP Routing group
The IP routing group contains an entry for each route presently
known to this entity.
ipRouteDest
Type IpAddress
Access RW
Description The destination IP address of this route. An entry with a value of
0.0.0.0 is considered a default route. Multiple routes to a single
destination can appear in the table, but access to such multiple entries
is dependent on the table-access mechanisms defined by the network
management protocol in use.
ipRouteIfIndex
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The index value which uniquely identifies the local interface through
which the next hop of this route should be reached. The interface
identified by a particular value of this index is the same interface as
identified by the same value of ifIndex.
ipRouteMetric1
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The primary routing metric for this route. The semantics of this
metric are determined by the routing-protocol specified in the route's
Page 59

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-37
McDATA SNMP Support
ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its value should be set
to -1.
ipRouteMetric2
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description An alternate routing metric for this route. The semantics of this
metric are determined by the routing-protocol specified in the route's
ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its value should be set
to -1.
ipRouteMetric3
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description An alternate routing metric for this route. The semantics of this
metric are determined by the routing-protocol specified in the route's
ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its value should be set
to -1.
ipRouteMetric4
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description An alternate routing metric for this route. The semantics of this
metric are determined by the routing-protocol specified in the route's
ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its value should be set
to -1.
ipRouteNextHop
Type IpAddress
Access RW
Description The IP address of the next hop of this route. (In the case of a route
bound to an interface which is realized via a broadcast media, the
value of this field is the agent's IP address on that interface.)
Page 60

2
2-38
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ipRouteType
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The type of route. Note that the values direct(3) and indirect(4) refer
to the notion of direct and indirect routing in the IP architecture.
Setting this object to the value invalid(2) has the effect of invalidating
the corresponding entry in the ipRouteTable object. That is, it
effectively disassociates the destination identified with said entry
from the route identified with said entry. It is an implementationspecific matter as to whether the agent removes an invalidated entry
from the table. Accordingly, management stations must be prepared
to receive tabular information that corresponds to entries not
currently in use. Proper interpretation of such entries requires
examination of the relevant ipRouteType object.
Values:
ipRouteProto
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The routing mechanism via which this route was learned. Inclusion
of values for gateway routing protocols is not intended to imply that
hosts should support those protocols.
The remaining values are all gateway routing protocols:
egp(5),
ggp(6),
other(1), none of the following
invalid(2), an invalidated route
direct(3), route to directly connected (sub-)network
indirect(4) route to a non-localhost/network/sub-network
other(1) none of the following
local(2) -protocol information, e.g., manually configured entries
netmgmt(3) set via a network management protocol
icmp(4) e.g., obtained via ICMP, Redirect
Page 61

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-39
McDATA SNMP Support
hello(7),
rip(8),
is-is(9),
es-is(10),
ciscoIgrp(11),
bbnSpfIgp(12),
ospf(13),
bgp(14)
ipRouteAge
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The number of seconds since this route was last updated or otherwise
determined to be correct. Note that no semantics of `too old' can be
implied except through knowledge of the routing protocol by which
the route was learned.
ipRouteMask
Type IpAddress
Access RW
Description Indicate the mask to be logical-ANDed with the destination address
before being compared to the value in the ipRouteDest field. For
those systems that do not support arbitrary subnet masks, an agent
constructs the value of the ipRouteMask by determining whether the
value of the correspondent ipRouteDest field belong to a class-A, B,
or C network, and then using one of:
If the value of the ipRouteDest is 0.0.0.0 (a default route), then the
mask value is also 0.0.0.0. It should be noted that all IP routing
subsystems implicitly use this mechanism.
mask network
255.0.0.0 class-A
255.255.0.0 class-B
255.255.255.0 class-C
Page 62

2
2-40
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
ipRouteMetric5
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description An alternate routing metric for this route. The semantics of this
metric are determined by the routing-protocol specified in the route's
ipRouteProto value. If this metric is not used, its value should be set
to -1.
ipRouteInfo
Type OBJECT IDENTIFIER
Access R
Description A reference to MIB definitions specific to the particular routing
protocol which is responsible for this route, as determined by the
value specified in the route's ipRouteProto value. If this information
is not present, its value should be set to the OBJECT IDENTIFIER { 0 0
}, which is a syntactically valid object identifier, and any conforming
implementation of ASN.1 and BER must be able to generate and
recognize this value.
IP Address Translation
Table
The IP address translation table contain the IpAddress to physical
address equivalences. Some interfaces do not use translation tables
for determining address equivalences (e.g., DDN-X.25 has an
algorithmic method); if all interfaces are of this type, then the
Address Translation table is empty, i.e., has zero entries.
ipNetToMediaIfIndex
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The interface on which this entry's equivalence is effective. The
interface identified by a particular value of this index is the same
interface as identified by the same value of ifIndex.
ipNetToMediaPhysAddress
Type PhysAddress
Access RW
Page 63

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-41
McDATA SNMP Support
Description The media-dependent `physical' address.
ipNetToMediaNetAddress
Type IpAddress
Access RW
Description The IpAddress corresponding to the media-dependent `physical'
address
ipNetToMediaType
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The type of mapping. Setting this object to the value invalid(2) has
the effect of invalidating the corresponding entry in the
ipNetToMediaTable. That is, it effectively disassociates the interface
identified with said entry from the mapping identified with said
entry. It is an implementation-specific matter as to whether the agent
removes an invalidated entry from the table. Accordingly,
management stations must be prepared to receive tabular
information that corresponds to entries not currently in use. Proper
interpretation of such entries requires examination of the relevant
ipNetToMediaType object.
Values:
other(1), none of the following
invalid(2), an invalidated mapping
dynamic(3),
static(4)
Additional IP objects
ipRoutingDiscards
Type Counter
Access R
Page 64

2
2-42
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
Description The number of routing entries which were chosen to be discarded
even though they are valid. One possible reason for discarding such
an entry could be to free up buffer space for other routing entries.
ICMP Group
icmpInMsgs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of ICMP messages which the entity received. Note
that this counter includes all those counted by icmpInErrors.
icmpInErrors
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP messages which the entity received but
determined as having ICMP-specific errors (bad ICMP checksums,
bad length, etc.).
icmpInDestUnreachs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages received.
icmpInTimeExcds
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages received.
icmpInParmProbs
Type Counter
Access R
Page 65

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-43
McDATA SNMP Support
Description The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages received.
icmpInSrcQuenchs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Source Quench messages received.
icmpInRedirects
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Redirect messages received.
icmpInEchos
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages received.
icmpInEchoReps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages received.
icmpInTimestamps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Timestamp (request) messages received.
icmpInTimestampReps
Type Counter
Access R
Page 66

2
2-44
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
Description The number of ICMP Timestamp Reply messages received.
icmpInAddrMasks
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Address Mask Request messages received.
icmpInAddrMaskReps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Address Mask Reply messages received
icmpOutMsgs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of ICMP messages which this entity attempted to
send. Note that this counter includes all those counted by
icmpOutErrors.
icmpOutErrors
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP messages which this entity did not send due to
problems discovered within ICMP such as a lack of buffers. This
value should not include errors discovered outside the ICMP layer
such as the inability of IP to route the resultant datagram. In some
implementations there may be no types of error which contribute to
this counter's value.
icmpOutDestUnreachs
Type Counter
Page 67

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-45
McDATA SNMP Support
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages sent.
icmpOutTimeExcds
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages sent.
icmpOutParmProbs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages sent.
icmpOutSrcQuenchs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Source Quench messages sent.
icmpOutRedirects
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Redirect messages sent. For a host, this object
will always be zero, since hosts do not send redirects.
icmpOutEchos
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages sent.
Page 68

2
2-46
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
icmpOutEchoReps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages sent.
icmpOutTimestamps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Timestamp (request) messages sent.
icmpOutTimestampReps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Timestamp Reply messages sent.
icmpOutAddrMasks
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Address Mask Request messages sent.
icmpOutAddrMaskReps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of ICMP Address Mask Reply messages sent.
Page 69

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-47
McDATA SNMP Support
TCP Group
Note that instances of object types that represent information about a
particular TCP connection are transient; they persist only as long as
the connection in question.
tcpRtoAlgorithm
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The algorithm used to determine the timeout value used for
retransmitting unacknowledged octets.
Values:
tcpRtoMin
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The minimum value permitted by a TCP implementation for the
retransmission timeout, measured in milliseconds. More refined
semantics for objects of this type depend upon the algorithm used to
determine the retransmission timeout. In particular, when the
timeout algorithm is rsre(3), an object of this type has the semantics of
the LBOUND quantity described in RFC 793.
tcpRtoMax
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The maximum value permitted by a TCP implementation for the
retransmission timeout, measured in milliseconds. More refined
semantics for objects of this type depend upon the algorithm used to
determine the retransmission timeout. In particular, when the
other(1), none of the following
constant(2) a constant rto
rsre(3) MIL-STD-1778, Appendix B
vanj(4) Van Jacobson's algorithm [10]
Page 70

2
2-48
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
timeout algorithm is rsre(3), an object of this type has the semantics of
the UBOUND quantity described in RFC 793.
tcpMaxConn
Type INTEGER
Access R
Description The limit on the total number of TCP connections the entity can
support. In entities where the maximum number of connections is
dynamic, this object should contain the value -1.
tcpActiveOpens
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition
to the SYN-SENT state from the CLOSED state.
tcpPassiveOpens
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition
to the SYN-RCVD state from the LISTEN state.
tcpAttemptFails
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition
to the CLOSED state from either the SYN-SENT state or the
SYN-RCVD state, plus the number of times TCP connections have
made a direct transition to the LISTEN state from the SYN-RCVD
state.
tcpEstabResets
Type Counter
Page 71

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-49
McDATA SNMP Support
Access R
Description The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition
to the CLOSED state from either the ESTABLISHED state or the
CLOSE-WAIT state.
tcpCurrEstab
Type Gauge
Access R
Description The number of TCP connections for which the current state is either
ESTABLISHED or CLOSE-WAIT.
tcpInSegs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of segments received, including those received in
error. This count includes segments received on currently established
connections.
tcpOutSegs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of segments sent, including those on current
connections but excluding those containing only retransmitted octets.
tcpRetransSegs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of segments retransmitted. That is, the number of
TCP segments transmitted containing one or more previously
transmitted octets.
Page 72

2
2-50
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
TCP Connection Table The TCP connection table contains information about this entity's
existing TCP connections.
tcpConnState
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description The state of this TCP connection. The only value which may be set by
a management station is deleteTCB(12). Accordingly, it is appropriate
for an agent to return a `badValue' response if a management station
attempts to set this object to any other value. If a management station
sets this object to the value deleteTCB(12), then this has the effect of
deleting the TCB (as defined in RFC 793) of the corresponding
connection on the managed node, resulting in immediate termination
of the connection. As an implementation-specific option, an RST
segment may be sent from the managed node to the other TCP
endpoint (note however that RST segments are not sent reliably).
Values:
closed(1),
listen(2),
synSent(3),
synReceived(4),
established(5),
finWait1(6),
finWait2(7),
closeWait(8),
lastAck(9),
closing(10),
timeWait(11),
deleteTCB(12)
tcpConnLocalAddress
Type IpAddress
Access R
Page 73

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-51
McDATA SNMP Support
Description The local IP address for this TCP connection. In the case of a
connection in the listen state which is willing to accept connections
for any IP interface associated with the node, the value 0.0.0.0 is used.
tcpConnLocalPort
Type INTEGER (0..65535
Access R
Description The local port number for this TCP connection.
tcpConnRemAddress
Type IpAddress
Access R
Description The remote IP address for this TCP connection.
tcpConnRemPort
Type INTEGER (0..65535)
Access R
Description The remote port number for this TCP connection.
Additional TCP
Objects
tcpInErrs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of segments received in error (e.g., bad TCP
checksums)
tcpOutRsts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of TCP segments sent containing the RST flag.
Page 74

2
2-52
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
UDP Group
udpInDatagrams
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of UDP datagrams delivered to UDP users.
udpNoPorts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of received UDP datagrams for which there was no
application at the destination port.
udpInErrors
Type Counter
Access R
Description The number of received UDP datagrams that could not be delivered
for reasons other than the lack of an application at the destination
port.
udpOutDatagrams
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of UDP datagrams sent from this entity.
Page 75

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-53
McDATA SNMP Support
UDP Listener Table The UDP listener table contains information about this entity's UDP
end-points on which a local application is currently accepting
datagrams.
udpLocalAddress
Type IpAddress
Access R
Description The local IP address for this UDP listener. In the case of a UDP
listener which is willing to accept datagrams for any IP interface
associated with the node, the value 0.0.0.0 is used.
udpLocalPort
Type INTEGER (0..65535)
Access R
Description The local port number for this UDP listener.
SNMP Group
Some of the objects defined below will be zero-valued in those SNMP
implementations that are optimized to support only those functions
specific to either a management agent or a management station. In
particular, it should be observed that the objects below refer to an
SNMP entity, and there may be several SNMP entities residing on a
managed node (e.g., if the node is hosting acting as a management
station).
snmpInPkts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of messages delivered to the SNMP entity from the
transport service.
Page 76

2
2-54
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
snmpOutPkts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP messages which were passed from the
SNMP protocol entity to the transport service.
snmpInBadVersions
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP messages which were delivered to the
SNMP protocol entity and were for an unsupported SNMP version.
snmpInBadCommunityNames
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP messages delivered to the SNMP protocol
entity which used a SNMP community name not known to said
entity.
snmpInBadCommunityUses
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP messages delivered to the SNMP protocol
entity which represented an SNMP operation which was not allowed
by the SNMP community named in the messages.
snmpInASNParseErrs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of ASN.1 or BER errors encountered by the SNMP
protocol entity when decoding received SNMP messages.
Page 77

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-55
McDATA SNMP Support
snmpInTooBigs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP PDUs which were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
`tooBig.'
snmpInNoSuchNames
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP PDUs which were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
`noSuchName.'
snmpInBadValues
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP PDUs which were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
`badValue.'
snmpInReadOnlys
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number valid SNMP PDUs which were delivered to the
SNMP protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field
is `readOnly.' It should be noted that it is a protocol error to generate
an SNMP PDU which contains the value `readOnly' in the
error-status field, as such this object is provided as a means of
detecting incorrect implementations of the SNMP.
Page 78

2
2-56
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
snmpInGenErrs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP PDUs which were delivered to the SNMP
protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field is
`genErr.'
snmpInTotalReqVars
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of MIB objects which have been retrieved
successfully by the SNMP protocol entity as the result of receiving
valid SNMP Get-Request and Get-Next PDUs.
snmpInTotalSetVars
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of MIB objects which have been altered successfully
by the SNMP protocol entity as the result of receiving valid SNMP
Set-Request PDUs.
snmpInGetRequests
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Get-Request PDUs which have been
accepted and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
snmpInGetNexts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Get-Next PDUs which have been
accepted and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
Page 79

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-57
McDATA SNMP Support
snmpInSetRequests
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Set-Request PDUs which have been
accepted and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
snmpInGetResponses
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Get-Response PDUs which have been
accepted and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
snmpInTraps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Trap PDUs which have been accepted
and processed by the SNMP protocol entity.
snmpOutTooBigs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP PDUs which were generated by the
SNMP protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field
is `tooBig.’
snmpOutNoSuchNames
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP PDUs which were generated by the
SNMP protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status is
`noSuchName.’
Page 80

2
2-58
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
snmpOutBadValues
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP PDUs which were generated by the
SNMP protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field
is `badValue.’
snmpOutGenErrs
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP PDUs which were generated by the
SNMP protocol entity and for which the value of the error-status field
is `genErr.’
snmpOutGetRequests
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Get-Request PDUs which have been
generated by the SNMP protocol entity.
snmpOutGetNexts
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Get-Next PDUs which have been
generated by the SNMP protocol entity.
snmpOutSetRequests
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Set-Request PDUs which have been
generated by the SNMP protocol entity.
Page 81

2
MIB Definitions: MIB-II
2-59
McDATA SNMP Support
snmpOutGetResponses
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Get-Response PDUs which have been
generated by the SNMP protocol entity.
snmpOutTraps
Type Counter
Access R
Description The total number of SNMP Trap PDUs which have been generated by
the SNMP protocol entity.
snmpEnableAuthenTraps
Type INTEGER
Access RW
Description Indicates whether the SNMP agent process is permitted to generate
authentication-failure traps. The value of this object overrides any
configuration information; as such, it provides a means whereby all
authentication-failure traps may be disabled. Note that it is strongly
recommended that this object be stored in non-volatile memory so
that it remains constant between re-initializations of the network
management system.
Values:
enabled(1),
disabled(2)
Page 82

2
2-60
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
Fabric Element Management MIB
There are five groups of objects defined in the Fabric Element
Management MIB.
Predefined types
DisplayString
Syntax OCTET STRING
MilliSeconds
Syntax INTEGER (0..2147383647)
2^31 – 1
MicroSeconds
Syntax INTEGER (0..2147383647)
FcNameId
Syntax OCTET STRING (SIZE(8))
Description World wide Name or Fibre Channel Name associated with an FC
entity. It is a Network_Destination_ID or Network_Source_ID
composed of a value up to 60 bits wide, occupying the remaining 8
bytes while the first nibble identifies the format of the
Name_Identifier with hex values: 0: ignored, 1: IEEE 48-bit address, 2:
IEEE extended, 3: Locally assigned, 4: 32-bit IP address.
FabricName
Syntax FcNameId
Description The Name Identifier of a Fabric. Each Fabric shall provide a unique
Fabric Name. Only the following formats are allowed: IEEE48, and
Local.
Page 83

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-61
McDATA SNMP Support
FcPortName
Syntax FcNameId
Description The Name Identifier associated with a port. Only the following
formats are allowed: IEEE48, IEEE extended, and Local.
FcAddressId
Syntax OCTET STRING (SIZE (3))
Description Fibre Channel Address Identifier. A 24-bit value unique within the
address space of a Fabric.
FcRxDataFieldSize
Syntax INTEGER (128..2112)
Description Receive Data_Field Size.
FcBbCredit
Syntax INTEGER (0..32767)
Description Buffer-to-buffer Credit.
FcphVersion
Syntax INTEGER (0..255)
Description
FcStackedConnMode
Syntax INTEGER
Description The values are defined as follow: none(1), transparent(2),
lockedDown(3).
FcCosCap
Syntax INTEGER (0..127)
Description bit 0 – Class F
bit 1 – Class 1
Page 84

2
2-62
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
bit 2 -- Class 2
bit 3 – Class 3
bit 4 – Class 4
bit 5 – Class 5
bit 6 – Class 6
bit 7 – reserved for future
Fc0BaudRate
Syntax INTEGER
Description The values are defined as follow:
Fc0BaudRateCap
Syntax INTEGER (0..127)
Description
other(1) none of below
oneEighth(2) 155 Mbaud (12.5MB/s)
quarter(4) 266 Mbaud (25.0MB/s)
half(8) 532 Mbaud (50.0MB/s)
full(16) 1 Gbaud (100MB/s)
double(32) 2 Gbaud (200MB/s)
quadruple(64) 4 Gbaud (400MB/s)
bit 0 other
bit 1 oneEighth
bit 2 quarter
bit 3 half
bit 4 full
bit 5 double
bit 6 quadruple
bit 7 reserved for future
Page 85

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-63
McDATA SNMP Support
Fc0MediaCap
Syntax INTEGER (0..65535)
Description
Fc0Medium
Syntax INTEGER
Description The values are defined as follows:
unknown(1)
sm(2)
m5(4)
m6(8)
tv(16)
mi(32)
stp(64)
tw(128)
lv(256)
Fc0TxType
Syntax INTEGER
Description The values are defined as follows:
bit 0 unknown
bit 1 single mode fibre (sm)
bit 2 multi-mode fibre 50 micron (m5)
bit 3 multi-mode fibre 62.5 micron (m6)
bit 4 video cable (tv)
bit 5 miniature cable (mi)
bit 6 shielded twisted pair (stp)
bit 7 twisted wire (tw)
bit 8 long video (lv)
bits 9-15 reserved for future use.
Page 86

2
2-64
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
unknown(1)
longWaveLaser(2) – (LL)
shortWaveLaser(3)—(SL)
longWaveLED(4) – (LE)
electrical(5) – (EL)
shortWaveLaser-noOFC(6) – (SN)
Fc0Distance
Syntax INTEGER
Description The values are defined as follow: unknown(1), long(2),
intermediate(3), short(4).
FcFeModuleCapacity
Syntax INTEGER (1..256)
Description Represents the maximum number of modules within a Fabric
Element.
FcFeFxPortCapacity
Syntax INTEGER (1..256)
Description Represents the maximum number of FxPorts within a module.
FcFeModuleIndex
Syntax INTEGER (1..256)
Description Represents the module index within a conceptual table.
FcFeFxPortIndex
Syntax INTEGER (1..256)
Description Represents the FxPort index within a conceptual table.
FcFeNxPortIndex
Syntax INTEGER (1..126)
Page 87

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-65
McDATA SNMP Support
Description Represents the NxPort index within a conceptual table
FcFxPortMode
Syntax INTEGER
Description The values are defined as follow: unknown(1), fPort(2), flPort(3).
FcBbCreditModel
Syntax INTEGER
Description The values are defined as follow: regular(1), alternate(2).
MIB objects defined in the Fabric Element MIB:
fcFabricName
Type FabricName
Access R
Description The Name_Identifier of the Fabric to which this Fabric Element
belongs.
FcElementName
Type FcNameId
Access R
Description The Name_Identifier of the Fabric Element.
FcFeModuleCapacity
Type FcFeModuleCapacity
Access R
Description The maximum number of modules in the Fabric Element, regardless
of their current state.
Module Table
A table that contains one entry for each module in the Fabric Element,
containing information about the modules
Fabric Element MIB Object Name
Page 88

2
2-66
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
fcFeModuleDescr
Type DisplayString (SIZE(256))
Provided By McK DEV_TBL
Access R
Description A textual description of the module. This value should include the
full name and version identification of the module. It should contain
printable ASCII characters.
This string should be derived from VPD information stored in the
FRU EEPROM.
FcFeModuleObjectID
Type OBJECT IDENTIFIER
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description This is a fixed object identifier assigned from the McDATA enterprise
subtree (1.3.6.1.4.1.289.2.1.1.2).
fcFeModuleOperStatus
Type INTEGER
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description This object indicates the operational status of the module: online(1) –
the module is functioning properly; offline(2) – the module is not
available; testing(3) – the module is under testing; and faulty(4) – the
module is defective in some way.
The status is evaluated from fcFPortPhysOperStatus as following
order.
Te s ti n g( 3 ) :
The module is under testing if all four ports on the current module
are testing.
faulty(4):
The module is defective if any of the ports on the current module is
faulty.
Page 89

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-67
McDATA SNMP Support
Online(1):
The module is functioning properly if any of the ports on the current
module is online or testing.
offline(2):
The module is not available if any of the ports on the current module
is offline.
FcFeModuleLastChange
Type TIMETICKS
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description This object contains the value of sysUpTime when the module
entered its current operational status. A value of zero indicates that
the operational status of the module has not changed since the agent
last restarted.
This is SS_TIM_RD_TICKS(MILLISEC) * 10.
fcFeModuleFxPortCapacity
Type FcFeFxPortCapacity
Provided By AS
Access R
Description The number of Fx_Port that can be contained within the module.
Within each module, the ports are uniquely numbered in the range
from 1 to fcFeModuleFx_PortCapacity inclusive. However, the
numbers are not required to be contiguous.
This is AS_glob.prod_cnfg_ptr->ports_per_module.
fcFeModuleName
Type FcNameId
Provided By PCP
Access R
Description The Name_Identifier of the module. This is the port module world
wide name.
Page 90

2
2-68
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
Fx_Port Configuration Table
A table that contains one entry for each Fx_Port in the Fabric
Element, containing configuration and service parameters of the
Fx_Ports.
fcFxConfFxPortIndex
Type FcFeFxPortIndex
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description This object identifies the Fx_Port within the module. This number
ranges from 1 to the value of fcFeModulePortCapacity for the
associated module. The value remains constant for the identified
Fx_Port until the module is re-initialized.
This number ranges from 1 to
AS_glob.prod_cnfg_ptr->ports_per_module.
FcFxPortName
Type FcPortName
Provided By PCP
Access R
Description The name identifier of this Fx_Port. Each Fx_Port has a unique port
name within the address space of the Fabric.
This is the WWN assigned to the port.
FcFxPortFcphVersionHigh
Type FcphVersion
Provided By FC2
Access R
Description The highest or most recent version of FC-PH that the Fx_Port is
configured to support. Since the switch is not capable of changing its
support for FC-PH version, the version reported is the one currently
in use for this port. If there is no device logged in, then the value is 0.
If a device is logged in, the values reported are:
Page 91

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-69
McDATA SNMP Support
6 = FC-PH 4.0
7 = FC-PH 4.1
8 = FC-PH 4.2
9 = FC-PH 4.3
0x10 = FC-PH2
0x20 = FC-PH3
FcFxPortFcphVersionLow
Type FcphVersion
Provided By FC2
Access R
Description The lowest or earliest version of FC-PH that the Fx_Port is configured
to support. Since the switch is not capable of changing its support for
FC-PH version, the version reported is the one currently in use for
this port. If there is no device logged in, then the value is 0. For values
see FcFxPortFcphVersionHigh on page 2-68.
FcFxPortBbCredit
Type FcBbCredit
Provided By PCP
Access R
Description The total number of receive buffers available for holding Class 1
connect-request, Class 2 or 3 frames from the attached Nx_Port. It is
for buffer-to-buffer flow control in the direction from the attached
Nx_Port (if applicable) to F_port.
FcFxPortRxBufSize
Type FcRxDataFieldSize
Provided By LOGIN SERVER
Access R
Description The largest Data_Field Size (in octets) for an FT_1 frame that can be
received by the Fx_Port.
Page 92

2
2-70
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
This is fixed at 2112.
FcFxPortRatov
Type MilliSeconds
Provided By PCP
Access R
Description The Resource_Allocation_Timeout Value configured for the Fx_Port.
This is used as the timeout value for determining when to reuse an
NxPort resource such as a Recovery_Qualifier. It represents
E_D_TOV (see next object) plus twice the maximum time that a frame
may be delayed within the Fabric and still be delivered.
FcFxPortEdtov
Type MilliSeconds
Provided By PCP
Access R
Description The E_D_TOV value configured for the Fx_Port. The
Error_Detect_Timeout Value is used as the timeout value for
detecting an error condition.
FcFxPortCosSupported
Type FcCosCap
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description A value indicating the set of Classes of Service supported by the
Fx_Port.
This is fixed at CLASS_2 | CLASS_3 (0x0C).
fcFxPortIntermixSupported
Type INTEGER
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Page 93

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-71
McDATA SNMP Support
Description A flag indicating whether or not the Fx_Port supports an Intermixed
Dedicated Connection. The values are defined as follow: yes(1) and
no(2).
This is fixed at no(2).
FcFxPortStackedConnMode
Type FcStackedConnMode
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description A value indicating the mode of Stacked Connect supported by the
Fx_Port.
This is fixed at none(1).
FcFxPortClass2SeqDeliv
Type INTEGER
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description A flag indicating whether or not Class 2 Sequential Delivery is
supported by the Fx_Port. The values are defined as follow: yes(1)
and no(2).
This is fixed at yes(1).
FcFxPortClass3SeqDeliv
Type INTEGER
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description A flag indicating whether or not Class 3 Sequential Delivery is
supported by the Fx_Port. The values are defined as follow: yes(1)
and no(2).
This is fixed at yes(1).
Page 94

2
2-72
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
FcFxPortHoldTime
Type MicroSeconds
Provided By PCP
Access R
Description The maximum time (in microseconds) that the Fx_Port shall hold a
frame before discarding the frame if it is unable to deliver the frame.
The value 0 means that the Fx_Port does not support this parameter.
This is equal to quarter of d the E_D_TOV which is obtained from
PCP.
FcFxPortBaudRate
Type Fc0BaudRate
Provided By FPM
Access R
Description The FC-0 baud rate of the Fx_Port.
One of these values, or no value will be returned.
0x10, 1 Gbaud (100 MB/s)
0x20, 2 Gbaud (200 MB/s)
0x40 4 Gbaud (400 MB/s)
FcFxPortMedium
Type Fc0Medium
Provided By FPM
Access R
Description The FC-0 medium of the Fx_Port.
The value is a bitwise OR of these values:
0x02 Single Mode fibre
0x04 Multi-mode fibre 50 micron
0x08 Multi-mode fibre 62.5 micron
Or it will be unknown (0x01) if no information is available.
Page 95

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-73
McDATA SNMP Support
FcFxPortTxType
Type Fc0TxType
Provided By FPM
Access R
Description The FC-0 transmitter type of the Fx_Port.
1 Unknown (long distance laser)
2 LongwaveLaser (LC version)
3 ShortwaveLaser
6 ShortwaveLaser-no OFC
FcFxPortDistance
Type Fc0Distance
Provided By FPM
Access R
Description The FC-0 distance range of the Fx_Port transmitter.
1 Unknown
2 Long
3 Intermediate
4 Short
Fx_Port Operation
Table
A table that contains one entry for each Fx_Port in the Fabric
Element, operational status and parameters of the Fx_Ports.
fcFxPortOperFxPortIndex
Type FcFeFxPortIndex
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description This object identifies the Fx_Port within the module. This number
ranges from 1 to the value of fcFeModulePortCapacity for the
associated module. The value remains constant for the identified
Fx_Port until the module is re-initialized.
Page 96

2
2-74
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
FcFxPortID
Type FcAddressId
Provided By Login Server
Access R
Description The address identifier by which this Fx_Port is identified within the
Fabric. The Fx_Port may assign its address identifier to its attached
NxPort(s) during Fabric Login.
Return a port id if the port is logged into the fabric, otherwise this
address is 000000 in FCEOS.
fcFPortAttachedPortName
Type FcPortName
Provided By Login Server
Access R
Description The port name of the attached N_Port, if applicable. If the value of
this object is ‘0000000000000000’H, this F_Port has no NxPort
attached to it. This variable has been deprecated and may be
implemented for backward compatibility. Not supported for
NL_ports.
FcFPortConnectedPort
Type FcAddressId
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description The address identifier of the destination Fx_Port with which this
Fx_Port is currently engaged in a either a Class 1 or loop connection.
If the value of this object is ‘000000’H, this Fx_Port is not engaged in a
class 1 connection. This variable has been deprecated and may be
implemented for backward compatibility.
This address is fixed at 0x000000.
FcFxPortBbCreditAvailable
Type Gauge
Page 97

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-75
McDATA SNMP Support
Provided By PSCC
Access R
Description The number of buffers currently available for receiving frames from
the attached port in the buffer-to-buffer flow control. The value
should be less than or equal to fcFxPortBbCredit.
FcFxPortOperMode
Type FcFxPortMode
Provided By AS
Access R
Description The current operational mode of the Fx_Port.
This value is F_Port(2) if the port_state_data is unavailable or the port
is an F_Port, or unknown(1) for the other port state.
FcFxPortAdminMode
Type FcFxPortMode
Provided By AS
Access R
Description The desired operational mode of the Fx_Port.
This value is F_Port(2) if the port_state_data is unavailable or the port
is an F_Port, or unknown(1) for the other port state.
Fx_Port Physical Level
Table
A table that contains one entry for each Fx_Port in the Fabric
Element, containing physical level status and parameters of the
Fx_Ports
fcFxPortPhysFxPortIndex
Type FcFeFxPortIndex
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description This object identifies the Fx_Port within the module. This number
ranges from 1 to the value of fcFeModulePortCapacity for the
Page 98

2
2-76
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
associated module. The value remains constant for the identified
Fx_Port until the module is re-initialized.
FcFxPortPhysAdminStatus
Type INTEGER
Provided By PCP, FPM
Access R/W
Description The desired state of the Fx_Port. A management station may place
the Fx_Port in a desired state by setting this object accordingly. The
testing(3) state indicates that no operational frames can be passed.
When a Fabric Element initializes, all Fx_Port start with
fcFxPortPhysAdminStatus in the offline(2) state.
As the result of either explicit management action or per
configuration information accessible by the Fabric Element,
fcFxPortPhysAdminStatus is then changed to either the online(1) or
testing(3) states, or remains in the offline state. The values are defined
as follow: online(1) – place port online, offline(2) – take port offline,
testing (3).
If the port cannot be set to testing because it is inactive or in a failed
state, the return value will be resource_unavailable(13).
FcFxPortPhysOperStatus
Type INTEGER
Provided By FPM, SNMP
Access R
Description The current operational status of the Fx_Port. The testing(3) status
indicates that no operational frames can be passed. If
fcFxPortPhysAdminStatus is offline(2) then fcFxPortPhysOperStatus
should be offline(2).
If fcFxPortPhysAdminStatus is changed to online(1) then
fcFxPortPhysOperStatus should change to online(1) if the Fx_Port is
ready to accept Fabric Login request from the attached NxPort; it
should proceed and remain in the link-failure(4) state if and only if
there is a fault that prevents it from going to the online(1) state.
Page 99

2
Fabric Element Management MIB
2-77
McDATA SNMP Support
The values are defined as online(1) – Login may proceed, offline(2) –
Login cannot proceed, testing(3) – port is under test, link-failure(4) –
failure after online/testing.
FcFxPortPhysLastChange
Type TimeTicks
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description The value of sysUpTime at the time the Fx_Port entered its current
operational status. A value of zero indicates that the Fx_Port’s
operational status has not changed since the agent last restarted.
This is SS_TIM_RD_TICKS(MILLISEC) * 10.
FcFxPortPhysRttov
Type MilliSeconds
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description The Receiver_Transmitter_Timeout value of the Fx_Port. This is used
by the receiver logic to detect Loss of Synchronization.
This value is fixed at 100ms.
Fx_Port Fabric Login
Table
An entry containing service parameters established from a successful
Fabric Login.
fcFxlogiFxPortIndex
Type FcFeFxPortIndex
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description This object identifies the Fx_Port within the module. This number
ranges from 1 to the value of fcFeModulePortCapacity for the
associated module. The value remains constant for the identified
Fx_Port until the module is re-initialized.
Page 100

2
2-78
E/OS SNMP Support Manual
McDATA SNMP Support
FcFxlogiNxPortIndex
Type FcFeNxPortIndex
Provided By SNMP
Access R
Description The object identifies the associated NxPort in the attachment for
which the entry contains information.
FcFxPortFcphVersionAgreed
Type FcphVersion
Provided By Login Server
Access R
Description The version of FC-PH that the Fx_Port has agreed to support from the
Fabric Login.
FcFxPortNxPortBbCredit
Type FcBbCredit
Provided By Login Server
Access R
Description The total number of buffers available for holding Class 1
connect-request, Class 2 or Class 3 frames to be transmitted to the
attached NxPort. It is for buffer- to-buffer flow control in the
direction from Fx_Port to Nx_Port. The buffer-to-buffer flow control
mechanism is indicated in the respective fcFxPortBbCreditModel.
FcFxPortNxPortRxDataFieldSize
Type FcRxDataFieldSize
Provided By Login Server
Access R
Description The Receive Data Field Size of the attached NxPort. This is a binary
value that specifies the largest Data Field Size for an FT_1 frame that
can be received by the NxPort. The value is in number of bytes and
ranges from 128 to 2112 inclusive.
 Loading...
Loading...