Page 1

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
1
Page 2

1
Evolution MK-425C/MK-449C/MK461C Advanced User Guide
Contents - MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced Guide
About The Advanced User Guide ............................................................... 2
Terminology ................................................................................................2
Programming & Editing The MK-425C/449C/461C
Introduction To Programming Options....................................................................4
Selecting A Controller For Editing...........................................................................5
Assigning MIDI CCís...............................................................................................6
Assigning An Individual MIDI Channel.................................................................... 6
Setting Toggle Values For the Buttons ...................................................................6
RPN/NRPN, SysEx And Other Advanced Messages .............................................7
Assigning MMC Control To A Button......................................................................7
Assigning RPN/NRPN To A Fader/Rotary Controller..............................................8
Assigning A Note To A Button ................................................................................9
About SysEx Messages & Device ID......................................................................9
Non-Volatile Memory ............................................................................................ 10
Memory Dump ...................................................................................................... 10
Assigning Device ID..............................................................................................10
Resetting To The Factory Default Setting............................................................. 10
MIDI Messages Explained
Program & Bank Changes Explained ...................................................................12
RPN/NRPNís Explained........................................................................................12
SysEx Explained...................................................................................................13
The Evolution Librarian
About The Librarian Software ................................................................... 16
Installing The Librarian Software .............................................................. 16
Setting Up The Librarian Software............................................................ 17
Librarian Overview ....................................................................................17
Organising Presets Received From A Device ..........................................17
Viewing The Contents Of A Memory ........................................................18
Saving A Setup ......................................................................................... 18
Loading A Setup .......................................................................................18
Future Development Of The Librarian ...................................................... 18
Appendix A-G & Factory Preset List
Appendix A - MIDI IMPLEMENTATION CHART...................................................20
Appendix B - Assignable MIDI CCís On MK-425C/449C/461C............................21
Appendix C - Hexadecimal Conversion Chart ......................................................23
Appendix D - Useful MIDI data ............................................................................. 24
Appendix E - Standard MIDI Controller numbers (MIDI CC's) ............................ 26
Appendix F - Roland GS and Yamaha XG NRPN Support to Roland JV/XP........27
Appendix G - General MIDI Reverb and Chorus Types........................................28
Page 3

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
About The Advanced Guide
In the MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced Guide we have made the assumption that you
have been through the Getting Started Guide which should have been supplied in
printed form with your keyboard. If you do not have this guide, please contact your
local distributor or download it from our website www.evolution.co.uk
The Getting Started Guide should insure that you are now familiar with the basic
operation of the keyboard so that we now can focus on more in-depth features.
First however, we need to explain some terminology we use throughout the guide.
Terminology
Edit Mode
Edit Mode describes the short period after a function button has been pressed during
which the parameters of that function can be altered. The numeric keypad can be
used to alter a parameter during this time. No data is sent out of the Evolution
MK-425C/449C/461C when it is in Edit mode except for program and bank changes.
LCD symbols shown in Edit mode will flash to show you that a particular parameter
can be edited. If a number is part entered, and a new controller turned, that number
will become the relevant parameter number for the new controller and the 3 second
editing period will re-trigger.
Default mode
Default Mode describes the state of the keyboard, when no function buttons have
been pressed within the last 3 seconds. In Default mode, the LCD will show the
controller symbol, and the 2 digit display will show the last selected controller. The 3
digits display the currently assigned MIDI CC number.
:
:
2
Page 4

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Programming
&
Editing The
MK-425C/449C/461C
3
Page 5
Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Introduction To Programming Options
Each of the MK-425C/449C/461C’s controllers can send MIDI cc, RPN/NRPN, GM 1&2
SysEx messages and even be assigned to individual MIDI channels.
MIDI cc (continuous controller) numbers are part of the standard MIDI specifications and
are typically used to control the real-time changing of parameters in musical equipment.
For a complete list of standard MIDI controller numbers from 0 to 131, please see
Appendix E on page 25.
Any of the real-time controllers on the keyboard can be assigned to a MIDI cc
number however the 10 assignable buttons have slightly different options from the 9
Faders (MK-449C/461C only) or rotary controllers.
The following 2 charts show all the transmit messages you can program for each
of the fader/controllers and assignable MIDI buttons respectively. We show you this already at this stage, so you can follow the principle of programming the controllers in the
following instructions and examples.
Please pay extra attention to the differences between how you program the faders or
controllers and how you program the buttons.
Faders & Controllers
ASSIGN Description Data Lsb
0-119 Standard MIDI CC’s - -
120-127 Channel Mode Messages - -
128 Pitch Bend Sensitivity - 129 Channel Fine Tune - 130 Channel Coarse Tune - 131 Channel Pressure - 132 RPN coarse RPN LSB RPN MSB
133 RPN fine RPN LSB RPN MSB
134 NRPN coarse NRPN LSB NRPN MSB
135 NRPN fine NRPN LSB NRPN MSB
136 Master Volume GM* Volume LSB Volume MSB
137 Master Pan* Pan LSB Pan MSB
138 Master Coarse Tune* Tuning LSB Tuning MSB
139 Master Fine Tune* Tuning LSB Tuning MSB
140 Chorus Mod rate** Mod rate 141 Chorus Mod Depth** Mod depth 142 Feedback** Feedback level 143 Send to Reverb** Reverb send level 144 Pitch Bend Pitch shift LSB Pitch shift MSB
255 Controller Off**** - -
* General MIDI SysEx messages - for details please see page 12 & 13.
** General MIDI 2 SysEx messages
*** MMC Sysex messages, for details please see page 7 & 13.
**** This value cannot be typed in using the numerical keypad. Type in
144 and then press the + button to set this value.
(Press Twice)
(Press Twice)
Data Msb
4
Page 6
Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Assignable MIDI Buttons
ASSIGN Description Program
0-119 Standard MIDI CC’s - Toggle Value 2 Toggle Value 1
120-127 Channel Mode Messages - Toggle Value 2 Toggle Value 1
128 Pitch Bend Sensitivity - Sensitivity value 129 Channel Fine Tune - Tuning amount 130 Channel Coarse Tune - Tuning amount 131 Channel P ressure - Pressure amount 132 RP N Coarse Value RPN LSB RPN MSB
133 RP N F i ne Value RP N LSB RPN MSB
134 NRP N Coars e V al ue NRPN LSB NRPN MSB
135 NRP N F i ne Value NRPN LSB NRPN MSB
136 Master Volum e * - Volume LSB Volume MSB
137 Master Pan* - Pan LSB Pan MSB
138 Master Coarse Tune* - Tuning LSB Tuning MSB
139 Mast er Fi ne Tune* - Tuning LSB Tuning MSB
140 Chorus Mod rat e** - Mod rate 141 Chorus Mod Dept h** - Mod depth 142 Feedbac k ** - Feedback level 143 S end to Reverb** - Reverb send level 144 Pitch Bend - Pitch shift LSB Pitch shift MSB
145 Program/Bank Preset Program Bank LSB Bank MSB
146 MIDI CC (on/off) MIDI CC B ut ton release value Button press value
147 Note (on/off) Note Velocity off Velocity on
148 Note (on/off toggle) Note Velocity off Velocity on
149
150
151
152
255
MMC Command*** - Command select. Reverb type ** - Type Reverb time ** - Time Chorus type ** - Type Controller Off****
(Press Twice)
- - -
Bank LSB (Press
Twice)
Data Msb (Press
Twice)
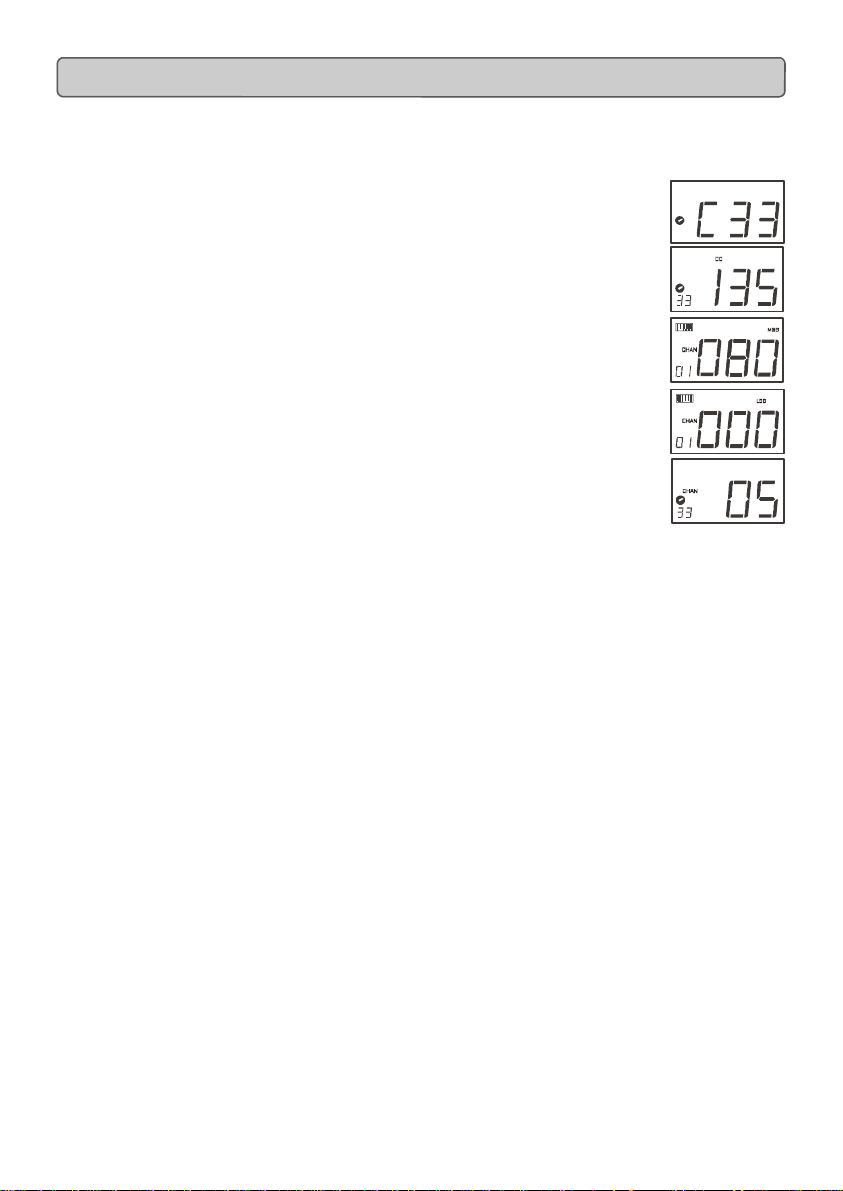
Selecting A Controller For Editing
Before you can assign a MIDI cc to one of the MK-425C/449C/461C’s controllers, you will
need to select it for editing. There are 2 methods for doing this:
1. Press CONTROL SELECT. The LCD will display the CONTROLLER symbol.
The symbol will be flashing to indicate the controller settings can be altered. The
3-digit display will show the number of the currently selected controller, proceeded
by a 'C', or an 'F' if the controller is a fader.
2. Type in the number of the controller using the numeric keypad, or the +/buttons.
or
Move a fader/rotary controller.
Simply moving a fader/rotary controller will make it the currently selected
controller, ready for editing.
It is not possible to select any of the 10 numerical buttons by pressing them, since during
edit mode, they are used to enter numerical values. To program these buttons, please use
the first method. We have given the buttons 0 to 9 the following numbers for the selection
process: MK-425C = 11-20, MK-449C = 20-29, MK-461C = 24-33 respectively.
5
Page 7
Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Assigning MIDI CC’s
Once the controller you want to edit has been selected, you can change the assigned
MIDI cc number in the following way:
1. Press “CONTROL ASSIGN”. The LCD will flash the CC symbol.
The 3 digit display will indicate the currently assigned MIDI cc number.
2. Type in a new MIDI cc value using the numeric keypad or '+' and '-' buttons.
The MIDI controller number you select will be assigned to the currently selected
controller, shown by the number on the small, 2-digit display.
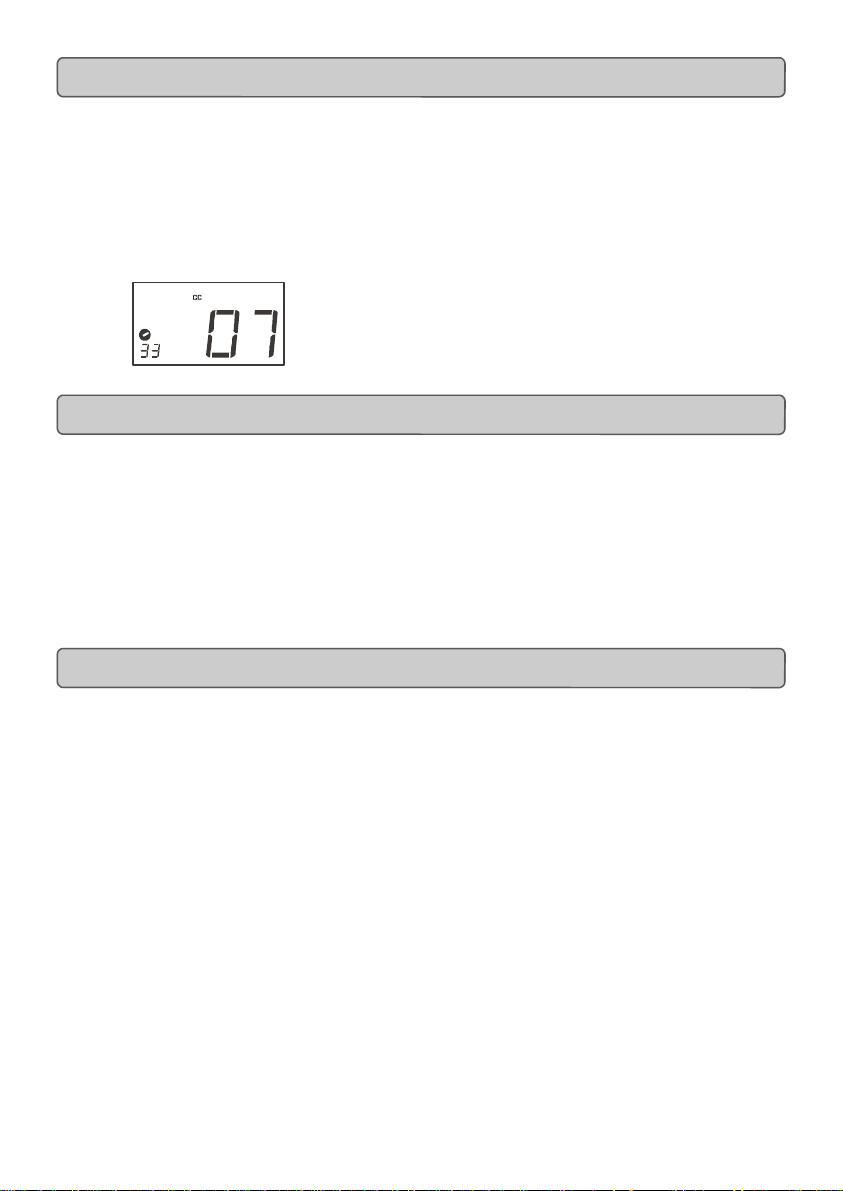
Example: After pressing ASSIGN, the display shows the
cc symbol and in this case displays that currently the MIDI cc 07 is
assigned to fader/rotary controller number 33.
Assigning An Individual MIDI Channel
1. Select the controller you want to edit as described earlier.
2. Press “CHANNEL ASSIGN”.
The LCD will display the CHAN symbol and the 3-digit display will show the
current channel assignment of the selected controller, preceded by a ’c’. The
small 2-digit display will show the currently selected controller for assignment.
3. Type the MIDI channel number (01-16) you want the controller to send to,
using the numeric keypad or the +/- keys.
If the controller is assigned to channel 00, it will transmit on the global channel.
Setting Toggle Values For The Buttons
The 10 assignable buttons can each be assigned to toggle between two values. You
may for instance want to send out value 15 when you first press the button followed by
value 74 when you press the button for a second time. This is how you do it:
1. Press the Function button labelled “DATA MSB” 2 times.
2. Type in 15 using the numerical keypad or the +/- keys.
3. Press the Function button labelled “DATA LSB” 2 times.
4. Type in 74 using the numerical keypad or the +/- keys.
If you want the button to send the same value every time you press it, simply type in the
same value both times.
6
Page 8
Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
RPN/NRPN, GM 1+2 SysEx & Other Messages
As already described, the standard MIDI controller numbers range from 0 to 131. We
have extended the list of MIDI cc’s that can be assigned to the controllers of the
keyboard to include RPN/NRPN, MMC and General MIDI 1&2 SysEx messages.
These advanced messages are as easy to program as a regular MIDI cc instruction by
entering values 132 to 152 when programming MIDI cc’s. The charts on page 8 and 9
(or Appendix B) show you what number correspond to each message
To program the values required for these advanced messages, the
MK-425C/449C/461C requires you to press the PROGRAM, DATA LSB and DATA
MSB buttons twice respectively. Pressing only once will send the program and bank
change instructions “on the fly” as described in the Getting Started guide.
Lets look at a couple of examples to see how this works. Please refer to the charts on
pages 4 & 5 so you get to grips with the principle:
Assigning MMC Control To A Button
1. Select the button you want to control the MMC message.
2. Press “CONTROL ASSIGN” on the MK-425C/449C/461C.
3. Type in “149” using the numerical keypad.
This is the number that correspond to the MMC instruction, as per the chart on
page 4 and 5.
4. Press “CHANNEL” once.
5. Type in “127”, using the numerical keypad.
This ensures that the message is set to all device ID numbers. For more
information about this, please read “About SysEx Messages & Device ID”
on page 9.
4. Press the “DATA LSB” button twice.
5. Enter a number from the chart on the next page to select the MMC
message you want:
Number MMC Command
01 STOP
02 PLAY
03 DEFERRED PLAY
04 FAST FORWARD
05 REWIND
06 RECORD STROBE
07 RECORD EXIT
08 RECORD PAUSE
09 PAUSE
10 EJECT
11 CHASE
12 COMMAND ERROR RESET
13 MMC RESET
7
Page 9
Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Assigning RPN/NRPN To A Fader/Rotary Controller
Note: For a detailed description of RPN/NRPN data see section RPN/NRPN’s
Explained on page 12.
1. Select the desired control as described earlier.
2. Press “CONTROL ASSIGN” twice and while the display is
flashing, enter controller 132 for RPN coarse, 133 for RPN
fine, 134 for NRPN coarse or 135 for NRPN fine.
3. Press “DATA MSB” twice to assign the number for
the RPN/NRPN MSB.
4. Press DATA LSB twice to assign the number for
RPN/NRPN LSB.
5. Press “CHANNEL ASSIGN” to assign the MIDI channel the
message should be sent on.
You will find most data sheets for synths that make use of NRPN’s will give the MSB
and LSB values that you should enter into DATA MSB and DATA LSB banks
Appendix F). However, some manuals may only give the hex values.
The MK-425C/449C/461C requires you to enter the decimal value. You can easily
convert hexadecimal values to decimal using the windows calculator. Simply select
Scientific mode, select hex and enter the hexadecimal value you need to convert.
Press the Dec button to convert it to a decimal value.
Alternatively, use the look up table in Appendix C.
(also see
8
Page 10

Assigning A Note T o A Button
The following shows how to set a button to transmit a note on when
pressed, and a note off when released.
1. Press “CONTROL SELECT” and press the “0” button.
2. Press “CONTROL ASSIGN” and enter '147' this is the
MIDI cc number that corresponds to Note on/off mode, as
shown in Appendix B.
3. Press “DATA MSB” twice and enter a value of '100'. This
means when you press the button, a Note on message will be
sent out with a velocity of 100.
4. Press “DATA LSB” twice, and enter a value of '000'. This
means when you release the button, a Note off message will
be sent out.
5. Press the “PROGRAM” button twice and enter '064'. This will
mean you are sending out MIDI note 64 or E4, each time you
press the button. The MIDI note numbers are given in
Appendix D.
This button mode has many uses. You can play a conventional sound on the
keyboard while triggering samples and effects on different MIDI channels from the
buttons. You could even trigger video clips or a lighting rig.
Note: When you press the button in note mode, the LCD display will briefly
show the note velocity.
Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
About SysEx Messages & Device ID
When transmitting SysEx messages, the individual control channel number does not
define a transmit channel, but a device ID. This is made clear since when you press
the CHANNEL button, the Channel symbol will not be shown and there is no ’c’ in the
3 digit display.
Device ID’s range between 00 – 127. In most cases, you should set the device ID as
127. 127 means the SysEx message will be received by all devices.
Please note that the device ID for a Sys Ex message assigned to a controller can not
be changed using the Device ID buttons. These buttons are used for varying the
global device ID of the MK-425C/449C/461C.
9
Page 11

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Non-Volatile Memory
The MK-425C/449C/461C uses non-volatile memory so that you can continue where
you left off even after powering down and restarting. The current controller and
channel assignments are stored whether you have stored your setup to a memory
locations or not. Also stored is Draw Bar mode (on/off), DATA LSB and DATA MSB
data, global channel setting and last used memory preset.
Memory Dump
The dual press “MEMORY DUMP” buttons will send out a number of Sys Ex data packets that represent the 10 memories you have set up in your MK-449C/461C (MK-225C:
Press “DATA LSB” and “RECALL” simultaneously to send out memory dump). This is
useful for storing or backing up the contents of your memory presets externally.
You can record the complete memory dump in to a standard sequencer. To recall the
memory dump back, play the MIDI track containing the recorded memory dump to the
keyboard, making sure that the MK-425C/449C/46 1C ’s driv e rs are selected as output
for that particular track.
The current controller assignments are not affected by a memory dump, or a memory
send to the keyboard. Once a memory dump has been sent to the keyboard, you will
need to recall a preset to access the new memory settings.
Assigning Device ID
The dual press “DEVICE ID” buttons will allow you to assign a Device ID to the
MK-449C/461C (MK-225C: Press “PROGRAM and DATA MSB”). The default Device ID
is 127, which means when a memory dump is performed, that dump can be received by
the same keyboard model, regardless of the Device ID setting.
If a device ID is assigned to any number other than 127, the memory dump performed
will be specific to MK-425C/449C/461C with the same device ID. If the device ID of a
MK-425C/449C/461C differs from the one recorded with the memory dump, the data will
be ignored.
The device ID is a handy way of differentiating between multiple keyboards.
Otherwise, we recommend you keep the device ID setting as 127.
When you press the Device ID buttons, you will see the small 2-digit display on LCD
display 'id'. The 3-digit display represents the assigned Device ID. You can enter a
new device ID using the numeric keypad, or the '+' and '-' buttons.
For more information on SysEx messages and device ID, please go to page 13.
Resetting To The Factory Default Setting
You can reset the MK-425C/449C/461C back to the factory defaults on power-up by
holding down the +/- buttons.
Note: Restoring the Factory presets will erase all setups stored to memory.
10
Page 12

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
MIDI Messages
Explained
11
Page 13

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Program & Bank Changes Explained
The original GM MIDI specification catered for only 128 voices, numbered from 0-127.
It is possible to access a different voice by sending a program change.
In order to expand on the GM set of voices, Bank changes were devised. Each bank
contains 128 patches, that can be accessed using a program change. There are
16,384 banks available, accessible by sending a 14-bit Bank change message. The
first 7 bits of this message are sent in a single byte known as the Bank LSB. The last
7 bits are specified by another byte known as the Bank MSB. The BANK LSB is the
most commonly used. This allows for 128 bank changes, and often there is no need to
send a Bank MSB.
You will find almost all MIDI devices respond to the program change, but some that do
not conform to the GM set of voices use the program change message for other
purposes. Many VST instruments have adopted this approach, allowing you to use a
program change to change the instrument patch. The FM7 by Native Instruments is a
good example of this.
Bank changes are more rarely used, although they do exist. Bank changes are useful
in manufacturer’s extensions to the MIDI specification, such as Roland’s GS
specification and Yamaha’s XG specification. Both of these require you to specify a
Bank change, in order to access the extra voices and effects that these specifications
provide.
Sending Program, Bank LSB and Bank MSB data is made simple using the
Mk-425C/449C/461C. Simply press the PROGRAM, DATA LSB or DATA MSB button
and enter the program or bank change you wish to send.
RPN/NRPN’s Explained
Non-registered parameter numbers (NRPN’s) are device specific messages that
enable the control of synths via MIDI. The MIDI specification defines parameter
numbers to allow scope for manufacturers to specify their own controllers. The more
common of these have been registered by the MIDI Manufacturer’s Association and
are part of the MIDI specification (hence the term Registered Parameter
Numbers – RPN's). (See Appendix F.)
MIDI controllers 98 and 99 represent the NRPN LSB and MSB respectively, while 100
and 101 represent the RPN LSB and MSB. This can be seen from the MIDI controllers
list in Appendix D. To transmit an NRPN/RPN, these two controller messages are sent
along with their user-specified values. A further controller message and value needs
to be sent to specify the (coarse or fine) value adjustment.
This is specified by controller number 6 (Data entry) for coarse adjustments or number
38 for fine adjustments.
12
Page 14

A list of NRPN’s will always be given in the User Manual of a device that receives NRPN
messages. It is always necessary that the NRPN MSB and LSB are sent together. Both will
be specified in the device’s manual. You may find the manufacturer’s have only specified
the numbers in Hexadecimal format. In this case, use Appendix C to translate the value to
Decimal.
Your Evolution keyboard makes the process of transmitting NRPN’s easy. All you need is
to enter the appropriate NRPN LSB by pressing the LSB/DATA button twice, enter the
NRPN MSB by pressing the MSB/DATA button twice, and as you move the controller, an
appropriate NRPN message will be sent out. Assign NRPN coarse to make big sweeps,
or NRPN fine to make slight adjustments.
Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
SysEx Explained
System Exclusive (SysEx) messages were defined in the MIDI specification to allow
individual devices to have individual control via MIDI. The format of SysEx messages
allows for virtually any function to be performed via MIDI – so long as the receiving device
is able to translate the message, and act accordingly. This allows devices to send audio
sample memory data, memory dumps, controller settings, and much more. It also allows
the controllers of one device to be controlled by another.
It is not possible to program your own specified SysEx message into the MK425C/449C/461C. However, there are some useful SysEx messages pre-programmed into
the keyboard, that can be accessed by assigning the appropriate MIDI CC to a controller
(see Appendix B)
It should be noted that a SysEx message is not transmitted on any specified channel. All
SysEx messages contain a device ID, that is used to single out devices to respond to the
SysEx message. All other devices are ignored. If you are using a SysEx message on the
MK-425C/449C/461C, the global channel is ignored. When you press CHANNEL, instead
of entering a channel for the controller, you will be enter a device ID instead. This is
indicated by the fact that the Chan symbol will not be showing.
Device ID’s run from 00 to 127. 127 is the default device number setting on the
MK-425C/449C/461C. This setting transmits the SysEx message to all devices.
Although it is not possible to program the controllers of the MK-425C/449C/461C with your
own SysEx messages, there are software applications that can receive a MIDI input signal
and transmit a different, user specified message. You can program your SysEx messages
into the translator software, then translate the incoming data from the keyboard to your
SysEx, depending on the controller you are using.
13
Page 15

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
14
Page 16

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
The Evolution
Librarian Software
15
Page 17

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
About The Evolution Librarian Software
The Evolution Librarian Software is a Windows PC librarian program developed for
Evolution products. The program not only works with the MK-425C/449C/461C keyboards but is also compatible with the Evolution UC-33e USB controller. That means
you can use one librarian package for both your keyboard and your controller, if you
own a UC-33e
And even better, you can swap patches between Evolution products that’s supported
by the Librarian so you never have to create the same patch twice.
The librarian itself, allows you to send and receive the 10 patches to and from the
MK-425C/449C/461C, load and save memory banks, view how individual patches
have been programmed and drag and drop patches in order to create new
combinations in the 10 memory locations.
Installing The Evolution Librarian Software
1. Insert the Evolution Installer CD-ROM in to your CD-ROM drive.
2. Click on “Librarian Installer”
3. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process
Once the installation has been completed, launch the program. The following is a
screenshot of what you should be seeing on your monitor.
2
1
16
Page 18

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Setting Up The Librarian Software
Before you start using the Librarian, check that the MK-425C/449C/461C has been
selected as input and output device.
1. Select MIDI Setup from the Options menu.
2. Ensure the USB driver for you MK-425C/449C/461C is selected in the
“Inputs” Column.
If you are using native drivers this may be named “USB Audio Device”.
1. In the “Outputs” column, select the USB driver for you MK-425C/449C/461C
If you are using native drivers this may be named “USB Audio Device”.
You should now be ready to use the Librarian software with you Evolution keyboard.
Librarian Overview
As you can see from the screenshot of the Librarian on page 16, you can save, load,
receive or send the complete content to and from either Bank column s.
To transmit the complete content of your MK-425C/449C/461C to the librarian,
simply press the “Receive” button on the Librarian software.
This process can only be completed successfully if the USB drivers for your keyboard
have been selected correctly, as described in the “Setting Up The Librarian Software”
section.
Once you have Received data from the keyboard, the memories are displayed in the
column.
Organising Presets Received From A Device
You can name the memories as you like. To re-name a memory, double-click on the
memory. You can then move memories around by dragging them to a new position, or
using the copy buttons between the two windows.
These buttons are defined below:
Will copy the selected memory in Bank 2 to Bank 1.
Will copy the selected memory in Bank 1 to Bank 2.
Will copy all memories in Bank 2 to Bank 1.
Will copy all the memories in Bank 1 to Bank 2.
Will undo the last copy you made. Only the last copy is remembered.
It’s a good idea to decide which column is your master column, to avoid confusion and
maybe loosing hours of work.
17
Page 19

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Viewing The Contents Of A Memory
Right-click on a memory to view the contents. Please note that it is not possible to edit
the contents of a memory. The Sys Ex librarian will simply allow you to rearrange the
order of memories, or copy memories between one dump and another. The screen shot
shown below shows the first memory of a memory dump from a 425C with the factory
defaults.
Saving A Setup
Once you have named all your presets, and organised them in the desired order, click
’save’ to save the content.
Alternatively you can click on the File menu and select save to save the file with the
previously assigned file name, or save as to assign the memory dump a new file name.
The shortcut key to save is CTRL+S.
Make sure you give the file a name which allows you to quickly identify your collection of
setups.
Loading A Setup
To load a memory setup file back in to the librarian, click on the ’Load’ button and select
the required file. The loaded preset setups will appear in the Edit Window. You can then
either send it directly to the Evolution device by clicking send, or edit it.
Alternatively, select Open from the File menu.
The shortcut key for loading is CTRL+O
Future Development Of The Librarian
We strongly recommend you register your ownership of the Evolution Librarian if you
would like to be kept informed about future development. As you can see from the version
number, the software is at an early version 1.0 stage and we will continue to work on
enhancements for the software.
To register your copy, please visit www.evolution.co.uk/register
18
Page 20

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Appendix A –G
19
Page 21

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Appendix A - MIDI IMPLEMENTATION CHART
Function Transmitted Received Remarks
Basic :Default
Channel:Changed
:Default
Mode :Messages
:Altered
Note
Number:True Voice
Velocity: Note ON
: Note OFF
After : Keys
Touch :Ch’s
Pitch Bend 0 X
1-16
1-16
--------X
*********
0-127
*********
0
0
0
0
X
X
X
X
X
Control 0-119
Change
120-127 0 X
Program
Change:True Number
System Exclusive GM, GM2, MMC
Song Position
Common:Song Select
System :Clock
Exclusive:Commands
Aux :Local ON/OFF
Messages :All Notes OFF
:Active Sense
:Reset
Notes: 0 = YES X=NO
0 X
0-127
*********
X
X
X
0
0
0
0
0
X
Memory
Dump
X
X
X
20
Page 22

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Appendix B - Assignable MIDI CC’s
on the MK-425C/449C/461C
B1 - The Faders and rotary Controllers:
MIDI CC Description Data Lsb (Press
Twice)
0-119 Standard MIDI CC’s - -
120-127 Channel Mode Messages - -
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
255
Pitch Bend Sensitivity - Channel Fine Tune - Channel Coarse Tune - Channel Pressure - RPN coarse RPN LSB RPN MSB
RPN fine RPN LSB RPN MSB
NRPN coarse NRPN LSB NRPN MSB
NRPN fine NRPN LSB NRPN MSB
Master Vo lume GM* Volume LSB Volume MSB
Master Pan GM* Pan LSB Pan MSB
Master Coarse Tune GM* Tuning LSB Tuning MSB
Master Fine Tune GM* Tuning LSB Tuning MSB
Chorus Mod rate GM2* Mod rate Chorus Mod Depth GM2* Mod depth Feedback GM2* Feedback level Send to Reverb GM2* Reverb send leve l Pitch Bend Pitch shift LSB Pitch shift MSB
Controller Off***
- -
Data Msb (Press
Twice)
* Sysex messages - for details please see pages 12 & 13.
** MMC Sysex messages, for details please see page 7.
*** This value cannot be typed in using the numerical keypad. Type in 144 and
then press the + button to set this value.
21
Page 23

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
B2-The Buttons:
MIDI CC Description Program
(Press Twice)
0-119 Standard MIDI CC’s - Toggle Value 2 Toggle Value 1
120-127 Channel Mode
Messages
128 Pitch Bend Range - Sensitivity value 129 Channel Fine Tune - Tuning amount 130 Channel Coarse Tune - Tuning amount 131 Channel Pressure - Pressure amount 132 RPN Coarse Value RPN LSB RPN MSB
133 RPN Fine Value RPN LSB RPN MSB
134 NRPN Coa r se Value NRPN LSB NRPN MSB
135 NRPN Fine Value NRPN LSB NRPN MSB
136 Master Vol ume GM* - Volume LSB Volume MSB
137 Master Pan GM* - Pan LSB Pan MSB
138 Master Coarse Tune
GM*
139 Master Fine Tune
GM*
140 Chorus Mod rate
GM2*
141 Chorus Mod Depth
GM2*
142 Feedback GM2* - Feedback level 143 Send to Reverb GM2* - Reverb send
144 Pitch Bend - Pitch shift LSB Pitch shift MSB
145 Program/Bank Preset Program Bank LSB Bank MSB
146 MIDI CC (on/off) MIDI CC Button press
147 Note (on/off) Note Velocity off Velocity on
148 Note (on/off toggle) Note Velocity off Velocity on
149
150
151
152
255
MMC Command** - Command select. Reverb type GM2 * - Type Reverb time GM2 * - Time Chorus type GM2* - Type Controller Off***
- Toggle Value 2 Toggle Value 1
- Tuning LSB Tuning MSB
- Tuning LSB Tuning MSB
- Mod rate -
- Mod depth -
- - -
Data Lsb
(Press Twice)
level
value
Data Msb
(Press Twice)
-
Button release
value
* Sysex messages - for details please see pages 12 & 13.
** MMC Sysex messages, for details please see page 7.
*** This value cannot be typed in using the numerical keypad. Type in 144 and
then press the + button to set this value.
22
Page 24

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Appendix C - Hexadecimal Conversion Chart
Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion Chart
Hexadeci-
mal value
0 0 2B 43 56 86
1 1 2C 44 57 87
2 2 2D 45 58 88
3 3 2E 46 59 89
4 4 2F 47 5A 90
5 5 30 48 5B 91
6 6 31 49 5C 92
7 7 32 50 5D 93
8 8 33 51 5E 94
9 9 34 52 5F 95
0A 10 35 53 60 96
0B 11 36 54 61 97
0C 12 37 55 62 98
0D 13 38 56 63 99
0E 14 39 57 64 100
0F 15 3A 58 65 101
10 16 3B 59 66 102
11 17 3C 60 67 103
12 18 3D 61 68 104
13 19 3E 62 69 105
14 20 3F 63 6A 106
15 21 40 64 6B 107
16 22 41 65 6C 108
17 23 42 66 6D 109
18 24 43 67 6E 110
19 25 44 68 6F 111
1A 26 45 69 70 112
1B 27 46 70 71 113
1C 28 47 71 72 114
1D 29 48 72 73 115
1E 30 49 73 74 116
1F 31 4A 74 75 117
20 32 4B 75 76 118
21 33 4C 76 77 119
22 34 4D 77 78 120
23 35 4E 78 79 121
24 36 4F 79 7A 122
25 37 50 80 7B 123
26 38 51 81 7C 124
27 39 52 82 7D 125
28 40 53 83 7E 126
29 41 54 84 7F 127
2A 42 55 85
Decimal
Value
Hexadeci-
mal value
Decimal
23
Value
Hexadeci-
mal value
Decimal
Value
Page 25

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Appendix D - Useful MIDI data
General MIDI Instruments
Piano Bass Reed Synth Effects
0 Acoustic Grand Piano
1 Bright Acoustic Piano
2 Electric grand Piano
3 Honky Tonk Piano
4 Electric Piano 1
5 Electric Piano 2
6 Harpsichord
7 Clavinet
Chromatic Percussion Strings/Orchestra Pipe Ethnic
8 Celesta
9 Glockenspiel
10 Music Box
11 Vibraphone
12 Marimba
13 Xylophone
14 Tubular bells
15 Dulcimer
Organ Ensemble Synth Lead Percussive
16 Drawbar Organ
17 Percussive Organ
18 Rock Organ
19 Church Organ
20 Reed Organ
21 Accordion
22 Harmonica
23 Tango Accordion
32 Acoustic Bass
33 Electric Fingered
Bass
34 Electric Picked Bass
35 Fretless Bass
36 Slap Bass 1
37 Slap Bass 2
38 Syn Bass 1
39 Syn Bass 2
40 Violin
41 Viola
42 Cello
43 Contrabass
44 Tremolo Strings
45 Pizzicato Strings
46 Orchestral Harp
47 Timpani
48 String Ensemble 1
49 String Ensemble 2
(Slow)
50 Syn Strings 1
51 Syn Strings 2
52 Choir Aahs
53 Voice Oohs
54 Syn Choir
55 Orchestral Hit
64 Soprano Sax
65 Alto Sax
66 Tenor Sax
67 Baritone Sax
68 Oboe
69 English Horn
70 Bassoon
71 Clarinet
72 Piccolo
73 Flute
74 Recorder
75 Pan Flute
76 Bottle Blow
77 Shakuhachi
78 Whistle
79 Ocarina
80 Syn Square Wave
81 Syn Sawtooth Wave
82 Syn Calliope
83 Syn Chiff
84 Syn Charang
85 Syn Voice
86 Syn Fifths Sawtooth
Wave
87 Syn Brass & Lead
96 SFX Rain
97 SFX Soundtrack
98 SFX Crystal
99 SFX Atmosphere
100 SFX Brightness
101 SFX Goblins
102 SFX Echoes
103 SFX Sci-Fi
104 Sitar
105 Banjo
106 Shamisen
107 Koto
108 Kalimba
109 Bag Pipe
110 Fiddle
111 Shanai
112 Tinkle Bell
113 Agogo
114 Steel Drums
115 Woodblock
116 Taiko Drum
117 Melodic Tom
118 Syn Drum
119 Reverse Cymbal
Guitar Brass Synth Pad Sound Effects
24 Nylon Acoustic
25 Steel Acoustic
26 Jazz Electric
27 Clean Electric
28 Muted Electric
29 Overdrive
30 Distorted
31 Harmonics
56 Trumpet
57 Trombone
58 Tuba
59 Muted Trumpet
60 French Horn
61 Brass Section
61 Syn Brass 1
62 Syn Brass 2
88 New Age Syn Pad
89 Warm Syn Pad
90 Polysynth Syn Pad
91 Choir Syn Pad
92 Bowed Syn Pad
93 Metal Syn Pad
94 Halo Syn Pad
95 Sweep Syn Pad
24
120 Guitar Fret Noise
121 Breath Noise
122 Seashore
123 Bird Tweet
124 Telephone Ring
125 Helicopter
126 Applause
127 Gun Shot
Page 26

MIDI Note Numbers
Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Octave
(n)
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Note Numbers
Cn C#n Dn D#n En Fn F#n Gn G#n An A#n Bn
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35
36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59
60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71
72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83
84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95
96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107
108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119
120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127
25
Page 27

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Appendix E -
Standard MIDI Controller numbers (MIDI CC’s)
00 Bank Select
01 Modulation
02 Breath Control
03 Controller 3
04 Foot Control
05 Porta Time
06 Data Entry
07 Channel Volume
08 Balance
09 Controller 9
10 Pan
11 Expression
12 Effects Controller 1
13 Effects Controller 2
14 Controller 14
15 Controller 15
16 Gen Purpose 1
17 Gen Purpose 2
18 Gen Purpose 3
19 Gen Purpose 4
20 Controller 20
21 Controller 21
22 Controller 22
23 Controller 23
24 Controller 24
25 Controller 25
26 Controller 26
27 Controller 27
28 Controller 28
29 Controller 29
30 Controller 30
31 Controller 31
32 Bank Select LSB
33 Modulation LSB
34 Breath Control LSB
35 Controller 35
36 Foot Control LSB
37 Porta Time LSB
38 Data Entry LSB
39 Channel Volume LSB
40 Balance LSB
41 Controller 41
42 Pan LSB
43 Expression LSB
44 Controller 44
45 Controller 45
46 Controller 46
47 Controller 47
48 Gen Purpose 1 LSB
49 Gen Purpose 2 LSB
50 Gen Purpose 3 LSB
51 Gen Purpose 4 LSB
52 Controller 52
53 Controller 53
54 Controller 54
55 Controller 55
56 Controller 56
57 Controller 57
58 Controller 58
59 Controller 59
60 Controller 60
61 Controller 61
62 Controller 62
63 Controller 63
64 Sustain Pedal
65 Portamento
66 Sostenuto
67 Soft Pedal
68 Legato Pedal
69 Hold 2
70 Sound Variation
71 Resonance
72 Release Time
73 Attack Time
74 Cut-off Frequency
75 Controller 75
76 Controller 76
77 Controller 77
78 Controller 78
79 Controller 79
80 Gen Purpose 5
81 Gen Purpose 6
82 Gen Purpose 7
83 Gen Purpose 8
84 Portamento Control
85 Controller 85
86 Controller 86
87 Controller 87
88 Controller 88
89 Controller 89
90 Controller 90
91 Reverb Depth
26
92 Tremelo Depth
93 Chorus Depth
94 Celeste (De-tune)
95 Phaser Depth
96 Data Increment
97 Data Decrement
98 Non-Reg Param LSB
99 Non-Reg Param MSB
100 Reg Param LSB
101 Reg Param MSB
102 Controller 102
103 Controller 103
104 Controller 104
105 Controller 105
106 Controller 106
107 Controller 107
108 Controller 108
109 Controller 109
110 Controller 110
111 Controller 111
112 Controller 112
113 Controller 113
114 Controller 114
115 Controller 115
116 Controller 116
117 Controller 117
118 Controller 118
119 Controller 119
Channel Mode Messages
120 All Sound off
121 Reset all Controllers
122 Local Control
123 All Notes Off
124 Omni Off
125 Omni On
126 Mono On (Poly Off)
127 Poly On (Mono Off)
Extra RPN Messages
128 Pitch Bend sensitivity
129 Fine Tune
130 Coarse Tune
131 Channel Pressure
Page 28

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
Appendix F - Roland GS and Yamaha XG NRPN Sup-
NRPN NRPN Data Data
MSB LSB MSB LSB
CC99 CC98 CC06 CC38
01 08 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Vibrato Rate (relative change)
01 09 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Vibrato Depth (relative change)
01 0A 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Vibrato Delay (relative change)
01 20 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Filter Cutoff Freq. (relative change)
01 21 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Filter Resonance (relative change)
01 63 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) EG (TVF&TVA) Attack Time (relative change)
01 64 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) EG (TVF&TVA) Decay Time (relative change)
01 66 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) EG (TVF&TVA) Release Time (relative change)
*14 00-7F 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Drum Filter Cutoff Freq. (relative change)
*15 00-7F 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Drum Filter Resonance (relative change)
*16 00-7F 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Drum EG Attack Rate (relative change)
*17 00-7F 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Drum EG Decay Rate (relative change)
18 00-7F 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Drum Instrument Pitch Coarse (relative change)
*19 00-7F 00-7F n/a (-64 - 0 - +63) Drum Instrument Pitch Fine (relative change)
1A 00-7F 00-7F n/a (0 to Max) Drum Instrument Level (absolute change)
1C 00-7F 00-7F n/a (Random, L>C>R) Drum Instrument Panpot (absolute change)
1D 00-7F 00-7F n/a (0 to Max) Drum Instrument Reverb Send Level (absolute change)
1E 00-7F 00-7F n/a (0 to Max) Drum Instrument Chorus Send Level (absolute change)
%1F 00-7F 00-7F n/a (0 to Max) Drum Instrument Variation Send Level (absolute change)
* = added by Yamaha XG; % changed from Delay to Variation by Yamaha XG
port to Roland JV/XP
Appendix G - General MIDI Reverb and Chorus
Types
Reverb Types
0: Small Room
1: Medium Room
2: Large Room
3: Medium Hall
4: Large Hall
8: Plate
Chorus Types
0: Chorus 1
1: Chorus 2
2: Chorus 3
3: Chorus 4
4: FB Chorus
5: Flanger
27
Page 29

Evolution MK-425C/449C/461C Advanced User Guide
28
 Loading...
Loading...