Mallory Ignition 674M User Manual
®
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
HYFIRE® VIIC CONTROL UNIT
PART NO. 674
FORM #1492 (REV. B) 9/00
RPM Switch:
NOTE: This feature is not available on the HYFIRE® 667C. The builtin RPM switch can either turn an electrical load off or on at a selected
RPM. See below for more detail.
NC This is the RPM switch (mode 7) relay contact that is normally
closed. In other words, as long as you havent reached the point
where the RPM switch is active, this contact remains connected to
the common or C terminal. You would use this connection if, for
example, you wanted to turn something OFF (such as a nitrous
system) when you reached the RPM switch point. See example 1.
C This is the common terminal for the RPM switch (mode 7) relay in
the main unit. It is connected to the RPM switch, where it will switch
the accessory connected to the NC terminal OFF, and the accessory connected to the NO terminal ON when the RPM switch
value is reached. The C terminal can be used to switch either to
power or ground.
NO This is the RPM switch (mode 7) relay contact that is normally
open. In other words, as long as you havent reached the point
where the RPM switch is active, this contact isnt connected to the
C contact. You would use this contact to turn something ON (such
as a shift light or an air shifter) at a specific RPM. See example 2
and example 3.
RPM Limiters:
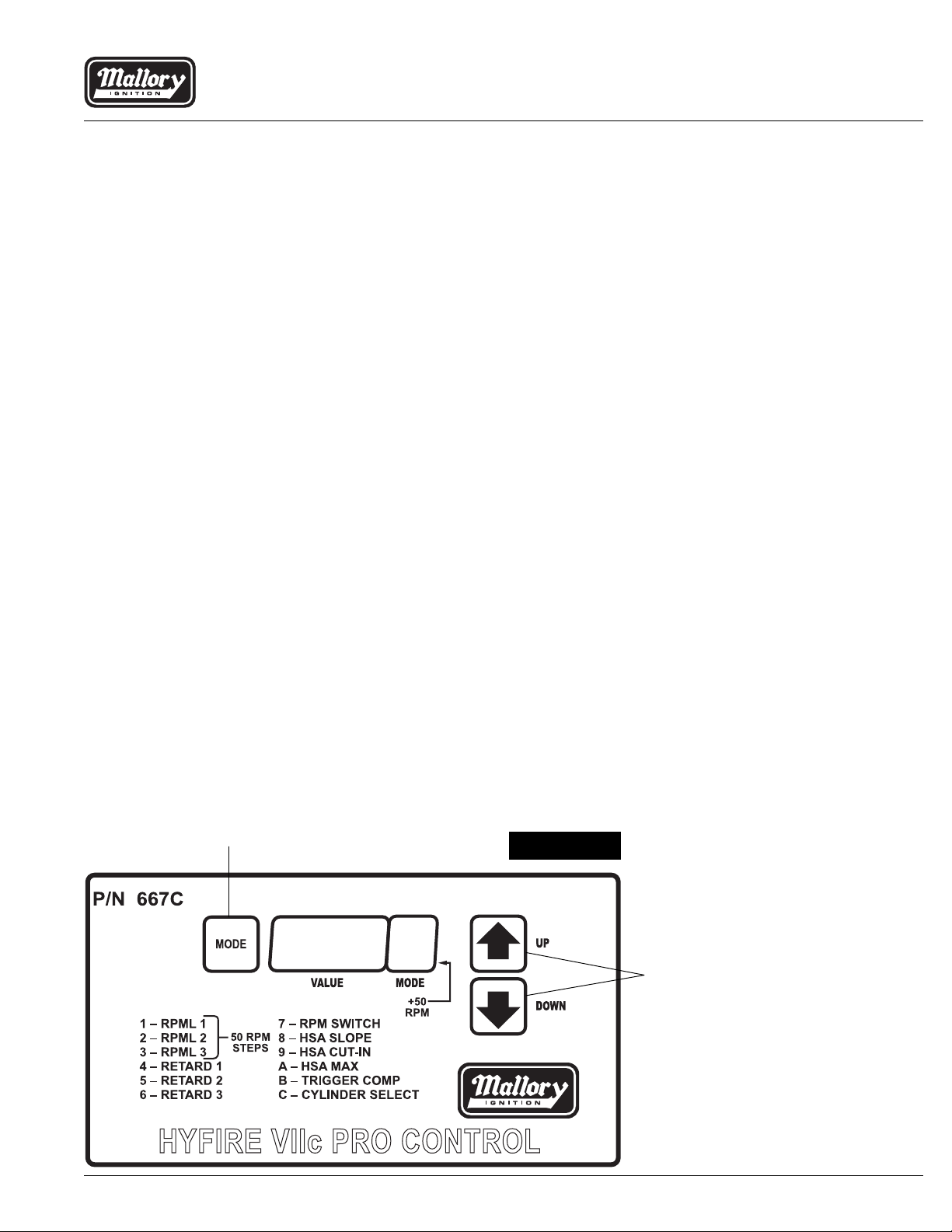
The HYFIRE® 667C has three built-in RPM limiters. Each one has a range of
1000 to 12,800 RPM in 50 RPM steps. On the main display, there is a decimal
point on the mode digit. When that decimal point is lit up, the RPM limit is
increased by 50 RPM.
RPM1 (Mode 1)This is the RPM limit that is always active if you havent
selected any other RPM limit.
RPM2 (Mode 2) This is an auxiliary RPM limiter that is activated when you
apply 12 volts to the RPM2 terminal on the top-side connector.
This could be a burnout limiter. When selected, it overrides RPM 1
(the main engine protection RPM limiter). See example 4.
RPM3 (Mode 3) This is the other auxiliary RPM limiter. It also is activated
by 12 volts on the RPM3 terminal on the top-side connector, and
overrides both RPM2 and RPM1. Use this limit as a staging (starting line) RPM limiter. See example 5.
High Speed Timing Retards:
RET1, RET2, RET3 (Modes 4, 5, 6) These are all high-speed timing retard
functions that are activated by 12 volts on the appropriate top-side connector
terminal. Each higher stage overrides the lower stages, which means that
you set each stage for exactly the amount of retard you want, rather than
adding up each stage to get the actual retard. See example 6.
Push this button to change the mode.
NOTE: When you apply 12 volts to RPM2, RPM3, RET1, RET2, or
RET3 the display will switch to show that function. If you have both
an auxiliary RPM limit AND a retard selected, the display will show
the retard value.
See the accompanying illustrations for some examples of how to use the RPM
limiters, the RPM switch, and the timing retard functions.
FIGURE 1
Push either of these buttons to change
the value of the mode.
NOTE: If any button is held down for more
®
than 1/2 second, the displayed value will
change automatically.
1

Additional Functions:
The HYFIRE® 667C has two more functions that can make the ignition installation and setup work better. One of these is the high speed advance function.
This lets you put small amounts of timing in the engine after the torque peak to
pick up a bit of horsepower. There are three things that need to be set up for
this: the cut-in RPM (Mode 9), the maximum advance (Mode A), and the
slope (Mode 8). The cut-in RPM is the RPM where you want the curve to start
working. The slope is how much the timing will advance every 1000 RPM
after the cut-in RPM. The maximum advance is the highest amount of advance you want the system to reach.
For example, say that your engine has the torque peak at 6500 RPM, and
you want to add some timing after this. You might want to start adding timing
after 7000 RPM, so this becomes your cut-in speed. If you then want 2
degrees additional timing at 8000 RPM, then the slope would be set for 2
degrees per 1000 RPM. However, lets say that you dont want more than 2
degrees of advance, so you would set the maximum advance at 2 degrees.
See example 7 for more detail.
The other additional function available is trigger compensation, which is set
when the mode indicator is b. This lets you compensate for the various
delays in ignition timing caused by both electronic and mechanical changes.
To set the trigger compensation, set mode 9 to 5000 RPM, and mode 8 to
zero. What this does is tell the system to start the high-speed advance at 5000
RPM, but with a slope of zero, there should be no advance. Once the system
is set up this way, watch the timing as the engine revs past 5000 RPM. If the
timing does not stay at a steady value (once the 5000 RPM point is reached)
then adjust the compensation value until it is as flat as possible. For example,
if the timing retards slightly as the RPM goes up, increase the compensation
value. If the timing advances slightly as the RPM goes up, decrease the compensation value.
NOTE: This function is only valid for RPM above the high-speed
advance cut-in RPM. If you have the high-speed advance cut-in set
above the normal operational range of the motor, the compensation
function does nothing.
Once the compensation is set, then the high speed advance settings will be
accurate. The factory setting should be correct for most types of flying magnet
type crank trigger systems, and should not normally need to be adjusted
unless you are using a different trigger type.
Number of cylinders selection
The final mode that can be set is mode C. This allows you to select 4 through
12 cylinder operation. This ensures that the RPML and the timing are proper
for the engine. Mode 6F is specialthis is for odd-fire V6 engines ONLY! The
cylinder firing spacing should be 45/75 (at the distributor) or 90/150 at the
crank.
NC
N
NO
To Ground
COIL
CONTACT
From Nitrous
Activation Switch
RPM2
RPM3
RET1
COIL
CONTACT
RET2
RET2
To +12 Volts
To Nitrous System
RELAYUse a relay if you are
switching more than 3-5 amps.
EXAMPLE 1: Using the RPM switch (Mode 7) to turn OFF a nitrous system at a particular RPM.
(Not available when used with the HYFIRE® 667S)
NC
To Ground
N
NO
RPM2
RPM3
RET1
RET2
To +12 Volts
RET2
EXAMPLE 1: Using the RPM switch (Mode 7) to turn ON a shift light.
(Not available when used with the HYFIRE® 667S)
2
 Loading...
Loading...