Lowrance electronic X86 DS, X86 TX User Manual

www.lowrance.com
Pub. 988-0151-411
X86 DS & X86 TX
Fish-finding & Depth Sounding Sonars
Installation and Operation
Instructions

Copyright © 2006 Lowrance Electronics, Inc.
All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be copied, reproduced, republished,
transmitted or distributed for any purpose, without prior written
consent of Lowrance Electronics. Any unauthorized commercial
distribution of this manual is strictly prohibited.
Lowrance® is a registered trademark of Lowrance Electronics, Inc.
Lowrance Electronics may find it necessary to change or end our
policies, regulations, and special offers at any time. We reserve the
right to do so without notice. All features and specifications subject to
change without notice. All screens in this manual are simulated. On the
cover: X86 DS shown.
For free owner's manuals and the most current information on
this product, its operation and accessories,
visit our web site:
www.lowrance.com
Lowrance Electronics Inc.
12000 E. Skelly Dr.
Tulsa, OK USA 74128-2486
Printed in USA.

Table of Contents
Section 1: Introduction....................................................................1
Specifications: X86 DS and X86 TX ....................................................1
How Sonar Works.................................................................................2
Preparations .........................................................................................3
Section 2: Installation & Accessories..........................................5
Recommended Tools and Supplies ..................................................5
Selecting a Transducer Location .....................................................5
How low should you go? ...................................................................6
Shoot-thru-hull vs. Transom Mounting ..........................................7
Transom Transducer Assembly and Mounting ..............................8
Trolling Motor Bracket Installation..............................................11
Transducer Orientation and Fish Arches.....................................12
Shoot-Thru-Hull Preparation ........................................................13
Shoot-thru-hull Installation ..........................................................15
Power and Cable Connections ....................................................... 16
Mounting The Sonar Unit: In-Dash or Bracket ...........................18
Portable Installation ......................................................................21
Portable Transducer Assembly .....................................................22
Section 3: Operation.......................................................................25
Keyboard Basics .................................................................................25
Memory ...............................................................................................26
Menus.................................................................................................. 26
Display ................................................................................................26
FasTrack ..........................................................................................27
Pages ...................................................................................................28
Full Chart ...........................................................................................28
Depth Range .......................................................................................29
Zoom ....................................................................................................30
Sensitivity...........................................................................................31
Grayline ..............................................................................................33
Chart Speed ........................................................................................ 34
Frequency ...........................................................................................34
Fish I.D. ...........................................................................................35
FishTrack™ ........................................................................................36
Alarms.................................................................................................37
Fish Alarm ..........................................................................................37
Depth Alarms .....................................................................................38
Shallow Alarm ....................................................................................38
Deep Alarm.........................................................................................39
Battery Alarm.....................................................................................39
Noise Rejection and ASP ................................................................40
i

Depth Display.....................................................................................41
Temperature Display .........................................................................41
Voltage ................................................................................................42
Units....................................................................................................42
Backlight.............................................................................................43
Contrast ..............................................................................................43
Simulator ............................................................................................44
Set Language ......................................................................................44
Software Information.........................................................................44
Reset Options......................................................................................44
Troubleshooting..............................................................................45
ii

Section 1: Introduction
Thank you for buying a Lowrance sonar! Your unit is a high-quality
sonar designed for both professional and novice fishermen. All
Lowrance sonars have an automatic mode that finds and displays the
bottom, fish, underwater structure and more – right out of the box. All
you have to do is press the on (
To get started with your Lowrance sonar, first read the installation section. It contains instructions for mounting the sonar unit, the transducer and any optional accessories, such as a speed sensor.
Following recommended installation practices will pay off in optimum
performance of your Lowrance sonar. Improper installation can cause
problems down the road, especially if the transducer is badly mounted.
After you've read the installation instructions, install the unit and accessories. Then, read the rest of the manual. The more you know about
your sonar, the better it will work for you.
Capabilities and Specifications: X86 DS and X86 TX
Case size:........................... 5.4" H x 6.9" W x 3.4" D (13.8 cm H x 17.6 cm
Display: ............................4.5" (11.4 cm) Film SuperTwist LCD display,
Resolution: ......................240V x 240H pixel resolution; 57,600 total
Backlighting: ..................Incandescent backlit screen and keypad for
Input power: ...................10 to 17 volts DC.
Current drain: ................110 ma lights off; 250 ma lights on.
Back-up memory:...........Built-in memory stores sonar settings when
Languages: ......................11 International languages.
PWR) key.
General
W x 8.6 cm D). Sealed and waterproof; suitable for saltwater use.
4-level gray scale definition with
GRAYLINE
pixels.
night use.
unit is turned off.
.
Sonar
Frequency: ......................83/200 kHz
Transducers:...................A compact Dual-Search Skimmer
ducer with built-in temperature sensor is
packed with the unit.
Watts:................................1,500 watts peak-to-peak; 188 watts RMS.
1
trans-

Depth capability: ...........To 1,000 feet (305 meters) with 83 kHz. Ac-
tual capability depends on transducer configuration and installation, bottom composition and water conditions. All sonar units
typically read deeper in fresh water than in
salt water.
Depth display: ................Continuous display.
Audible alarms:..............Deep/shallow/fish/battery.
Automatic ranging: .......Yes.
Auto bottom track: ........Yes.
Zoom bottom track:....... Yes.
Surface water temp: .....Yes.
NOTICE!
The storage temperature for your unit is from -4 degrees to +167
degrees Fahrenheit (-20 degrees to +75 degrees Celsius). Extended
storage in temperatures higher or lower than specified will damage
the liquid crystal display in your unit. This type of damage is not
covered by the warranty. For more information, contact the factory's Customer Service Department; phone numbers are inside the
manual's back cover.
How Sonar Works
Sonar has been around since the 1940s, so if you already know how it
works, skip ahead to the next segment on the typographical conventions
used in this manual. But, if you've never owned a sonar fish finder, this
segment will tell you the underwater basics.
Sonar is an abbreviation for SOund NA
ogy developed during World War II for tracking enemy submarines. A
sonar consists of a transmitter, transducer, receiver and display. In
simple terms, here's how it finds the bottom, or the fish:
The transmitter emits an electrical impulse, which the transducer converts into a sound wave and sends into the water. (The sound frequency
can't be heard by humans or fish.) The sound wave strikes an object
(fish, structure, bottom) and bounces back to the transducer, which
converts the sound back into an electrical signal.
The receiver amplifies this return signal, or echo, and sends it to the
display, where an image of the object appears on the scrolling sonar
chart. The sonar's microprocessor calculates the time lapse between the
transmitted signal and echo return to determine the distance to the
object. The whole process repeats itself several times each second.
vigation and Ranging, a technol-
2

Dual Search Transducer
Your unit is packed with a Dual Search Skimmer Transducer that can
transmit at 83 kHz and 200 kHz.
A new innovation, the 83 kHz frequency offers superior sonar performance at all depths from very shallow up to 1,000 ft and provides up to
120º of fish-finding coverage.
Preparations
You can install the sonar system in some other order if you prefer, but
we recommend this installation sequence:
Caution:
You should read over this entire installation section before drilling any holes in your vessel!
1. Determine the approximate location for the sonar unit, so you can
plan how and where to route the cables for the transducer and power.
This will help you make sure you have enough cable length for the desired configuration.
2. Determine the approximate location for the transducer and its cable
route.
3. Determine the location of your battery or other power connection,
along with the power cable route.
4. Install the transducer and route the transducer cable to the sonar
unit.
5. Install the power cable and route it to the sonar unit.
6. Mount the sonar unit.
3

Notes
4

Section 2:
Installation & Accessories
These instructions will help you install your Skimmer
transom, on a trolling motor or inside a hull. Please read all instructions before proceeding with any installation.
Your Skimmer transducer typically comes packaged with a one-piece
stainless steel bracket for mounting it to the transom of your boat. The
optional trolling motor mount uses a one-piece plastic bracket with an
adjustable strap. These are "kick-up" mounting brackets. They help prevent damage if the transducer strikes an object while the boat is moving.
If the transducer does "kick-up," the bracket can easily be pushed back
into place without tools.
Read these instructions carefully before attempting the installation.
Determine which of the installation methods is right for your boat.
Remember, the transducer installation is the most critical part
of a sonar installation.
Recommended Tools and Supplies
If you prefer the option of routing the cable through the transom, you
will need a 5/8" drill bit. The following installation types also call for
these recommended tools and required supplies (supplies are not included):
Transom installation
Tools include: two adjustable wrenches, drill, #29 (0.136") drill bit, flathead screwdriver. Supplies: high quality, marine grade above- or belowwaterline sealant compound.
Trolling motor installations
Tools: two adjustable wrenches, flat-head screwdriver. Supplies: plastic
cable ties.
Shoot-through hull installations
Tools: these will vary depending on your hull's composition. Consult
your boat dealer or manufacturer. Supplies: 100 grit sandpaper, good
quality epoxy adhesive.
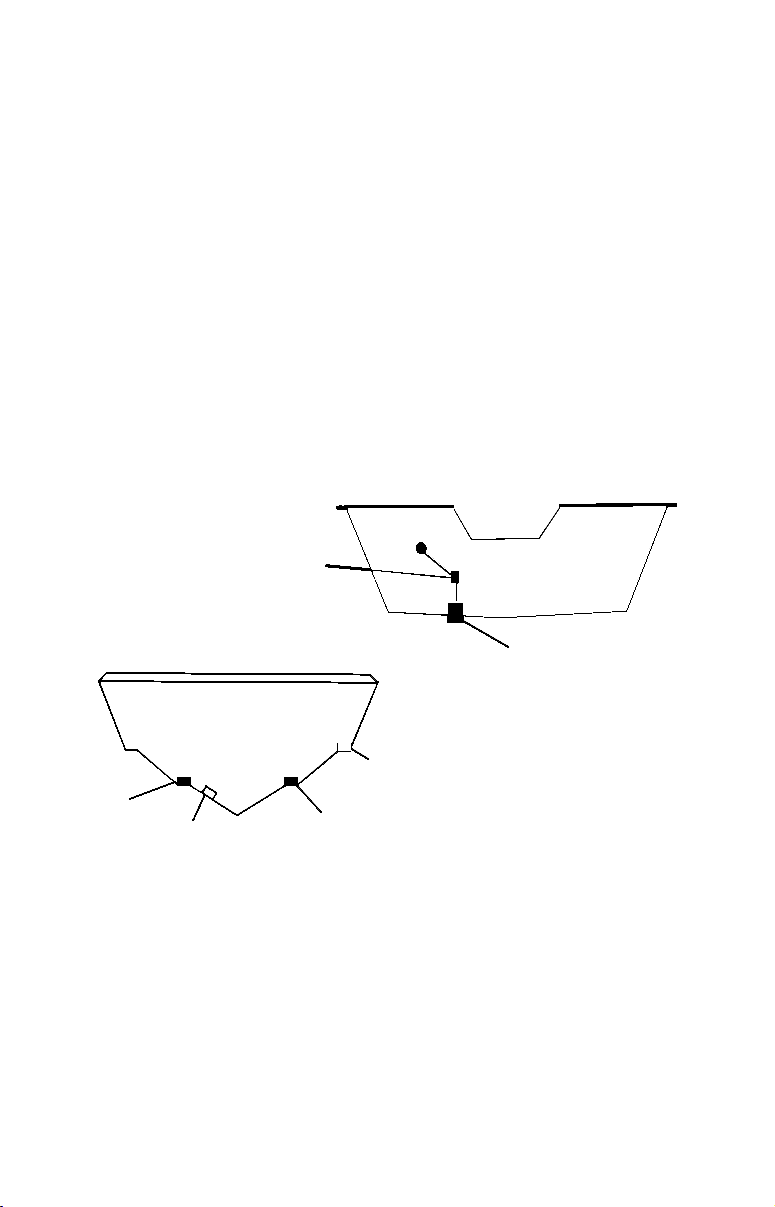
Selecting a Transducer Location
1. The transducer must be placed in a location that has a smooth flow
of water at all times. If the transducer is to be mounted inside the
hull, then the chosen location must be in the water at all times. If the
transducer is not placed in a smooth flow of water, interference
caused by bubbles and turbulence will show on the sonar's display in
the form of random lines or dots whenever the boat is moving.
5
transducer on a
NOTE:
p
Some aluminum boats with strakes or ribs on the outside of the
hull create large amounts of turbulence at high speed. These boats
typically have large outboard motors capable of propelling the boat
at speeds faster than 35 mph. Typically, a good location on aluminum boats is between the ribs closest to the engine.
2. The transducer should be installed with its face pointing straight
down, if possible.
3. If the transducer is mounted on the transom, make sure it doesn't
interfere with the trailer or hauling of the boat. Also, don't mount it
closer than approximately one foot from the engine's lower unit. This
will prevent cavitation (bubble) interference with propeller operation.
4. If possible, route the transducer cable away from other wiring on the
boat. Electrical noise from engine wiring, bilge pumps and aerators
can be displayed on the sonar's screen. Use caution when routing the
transducer cable around these wires.
CAUTION: Clamp the transducer cable to transom near
the transducer. This will help
revent the transducer from
entering the boat if it is
knocked off at high speed.
Good location
Poor location
Good
location
Poor angle
Good and poor transducer locations.
Good location
How low should you go?
For most situations, you should install your Skimmer transducer so
that its centerline is level with the bottom of the boat hull. This will
usually give you the best combination of smooth water flow and protection from bangs and bumps.
6
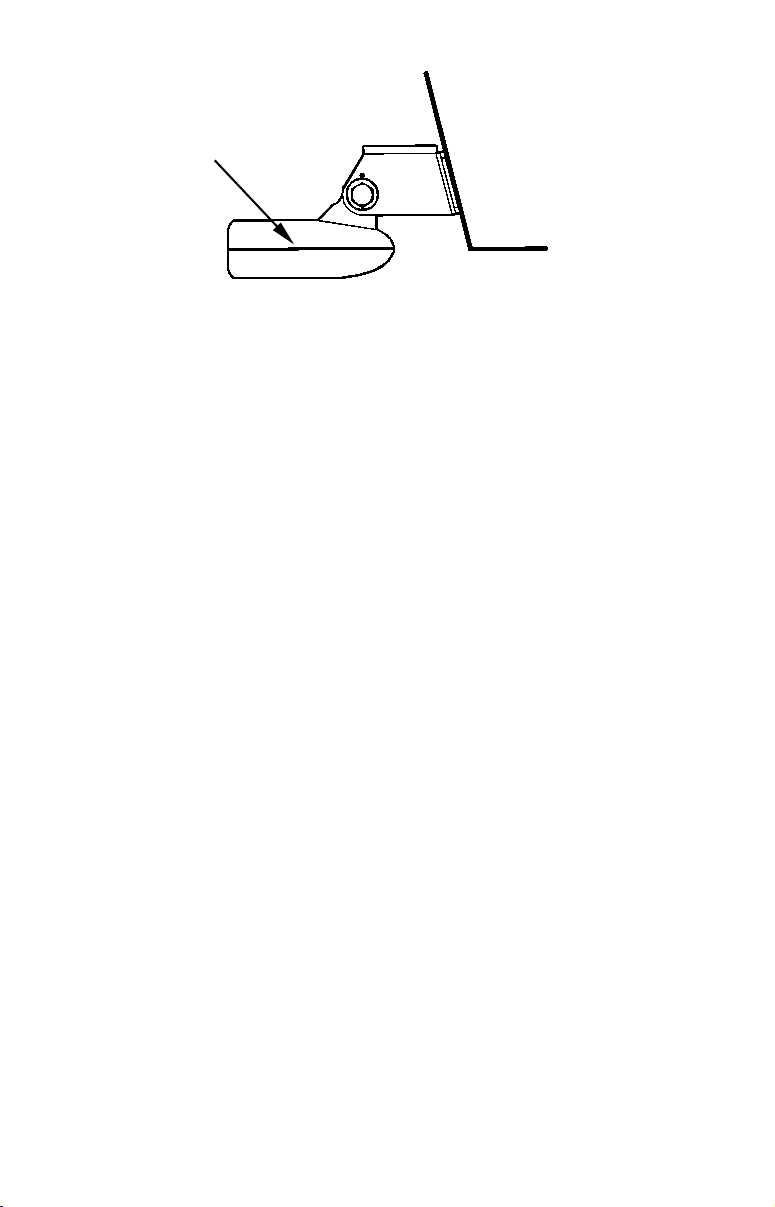
Transducer
centerline
Align transducer centerline with hull bottom.
Transom
Hull bottom
If you want to adjust the transducer slightly higher or lower, the slots
in the mounting brackets allow you to loosen the screws and slide the
transducer up or down. If you frequently lose bottom signal lock while
running at high speed, the transducer may be coming out of the water
as you cross waves or wakes. Move the transducer a little lower to help
prevent this.
If you cruise or fish around lots of structure and cover, your transducer
may be frequently kicking up from object strikes. If you want, you may
move the transducer a little higher for more protection.
There are two extremes you should avoid. Never let the edge of the
mounting bracket extend below the bottom of the hull. Never let the
bottom – the face – of the transducer rise above the bottom of the hull.
Shoot-thru-hull vs. Transom Mounting
In a shoot-thru-hull installation, the transducer is bonded to the inside
of the hull with epoxy. The sonar "ping" signal actually passes through
the hull and into the water. This differs from a bolt-thru-hull installation (often called "thru-hull"). In that case, a hole is cut in the hull and
a specially designed transducer is mounted through the hull with a
threaded shaft and nut. This puts the transducer in direct contact with
the water.
Typically, shoot-thru-hull installations give excellent high speed operation and good to excellent depth capability. There is no possibility of
transducer damage from floating objects, as there is with a transommounted transducer. A transducer mounted inside the hull can't be
knocked off when docking or loading on a trailer.
The shoot-thru-hull installation does have its drawbacks, though. First,
some loss of sensitivity does occur, even on the best hulls. This varies
from hull to hull, even from different installations on the same hull.
This is caused by differences in hull lay-up and construction.
Second, the transducer angle cannot be adjusted for the best fish
arches on your sonar display.
7
Lack of angle adjustment can be particularly troublesome on hulls that
sit with the bow high when at rest or at slow trolling speeds.
Third, a transducer CAN NOT shoot through wood and metal hulls.
Those hulls require either a transom mount or a thru-hull installation.
Fourth, if your Skimmer transducer has a built in temp sensor, it will
only show the temperature of the bilge, not the water surface temp.
Follow the testing procedures listed in the shoot-thru-hull installation
section at the end of this instruction booklet to determine if you can
satisfactorily shoot through the hull.
Transom Transducer Assembly and Mounting
The best way to install the transducer is to loosely assemble all of the
parts first, place the transducer's bracket against the transom and see if
you can move the transducer so that it's parallel with the ground.
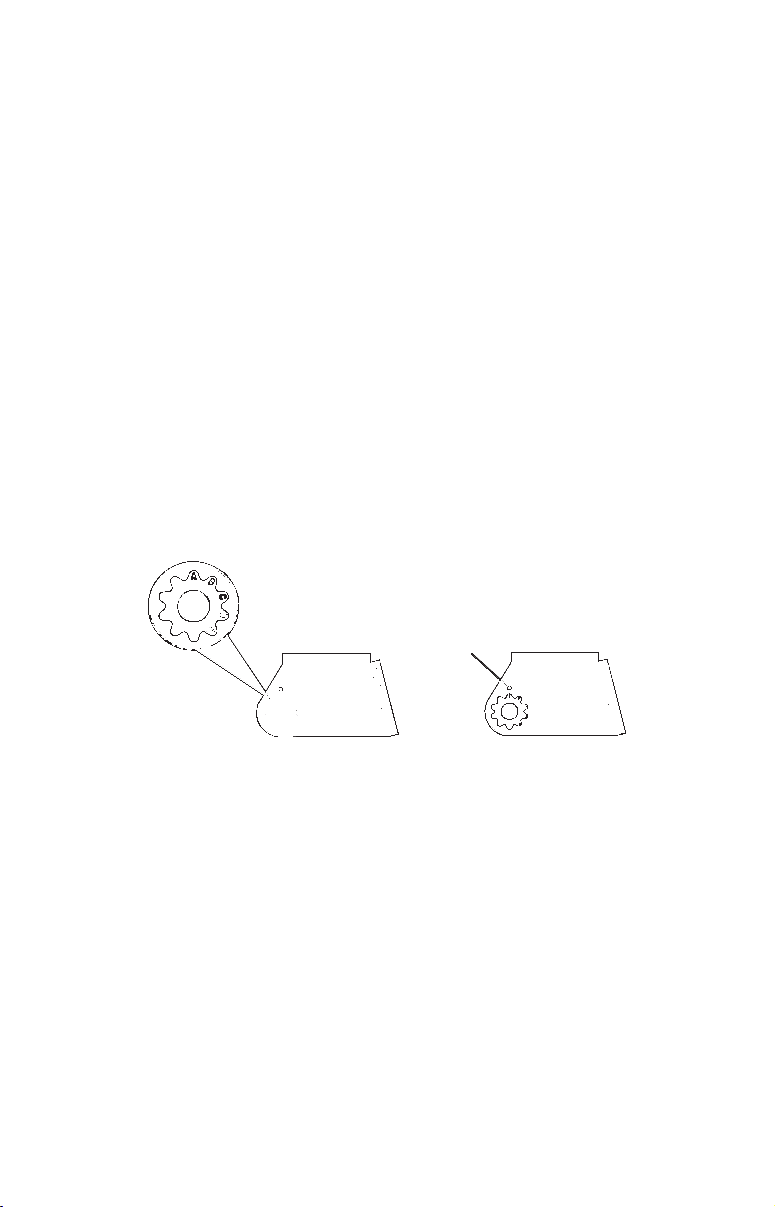
1. Assembling the bracket. Press the two small plastic ratchets into the
sides of the metal bracket as shown in the following illustration. Notice
there are letters molded into each ratchet. Place each ratchet into the
bracket with the letter "A" aligned with the dot stamped into the metal
bracket. This position sets the transducer's coarse angle adjustment for a
14° transom. Most outboard and stern-drive transoms have a 14° angle.
Dot
Align plastic ratchets in bracket.
2. Aligning the transducer on the transom. Slide the transducer
between the two ratchets. Temporarily slide the bolt though the
transducer assembly and hold it against the transom. Looking at the
transducer from the side, check to see if it will adjust so that its face
is parallel to the ground. If it does, then the "A" position is correct for
your hull.
If the transducer's face isn't parallel with the ground, remove the
transducer and ratchets from the bracket. Place the ratchets into the
holes in the bracket with the letter "B" aligned with the dot stamped
in the bracket.
Reassemble the transducer and bracket and place them against the
transom. Again, check to see if you can move the transducer so it's
parallel with the ground.
8
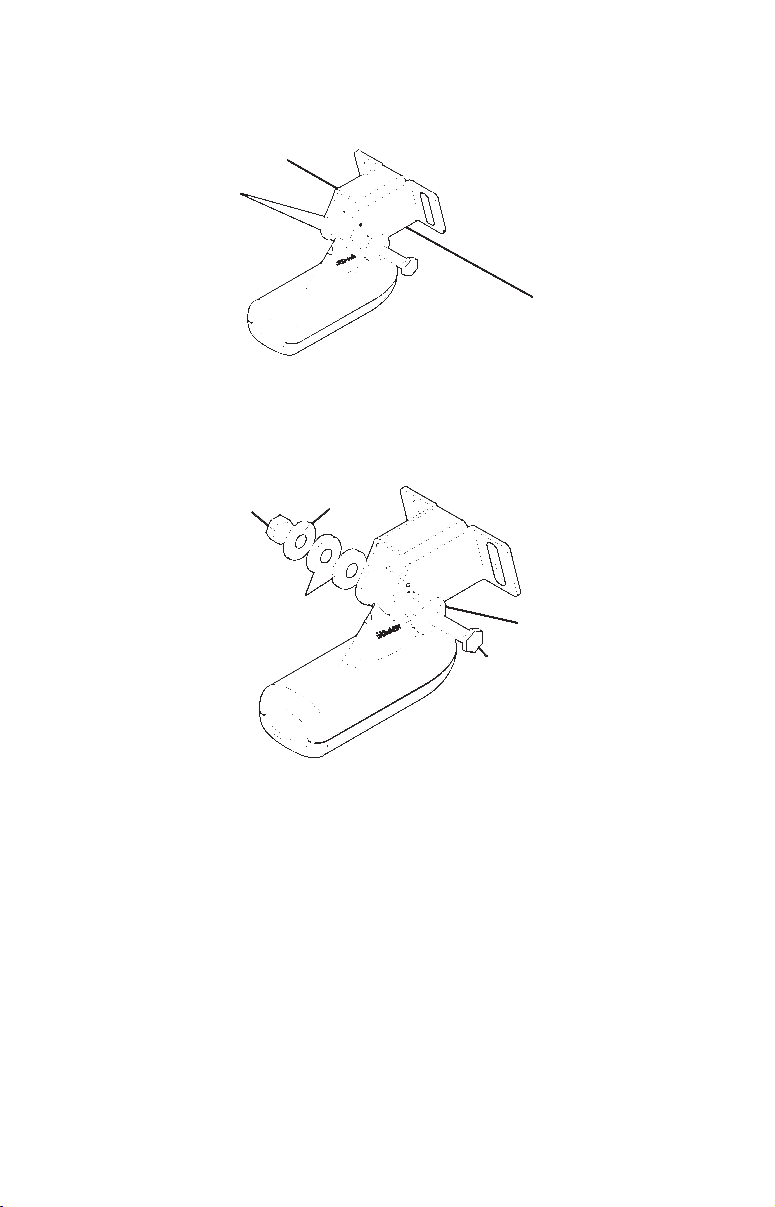
If you can, then go to step 3. If it doesn't, repeat step 2, but use a different alignment letter until you can place the transducer on the
transom correctly.
Ratchets
Insert bolt and check transducer position on transom.
3. Assembling the transducer. Once you determine the correct posi-
tion for the ratchets, assemble the transducer as shown in the following
figure. Don't tighten the lock nut at this time.
Metal
Nut
washer
Rubber
washers
Assemble transducer and bracket.
Metal washer
Bolt
4. Drilling mounting holes. Hold the transducer and bracket assembly
against the transom. The transducer should be roughly parallel to the
ground. The transducer's centerline should be in line with the bottom
of the hull. Don't let the bracket extend below the hull!
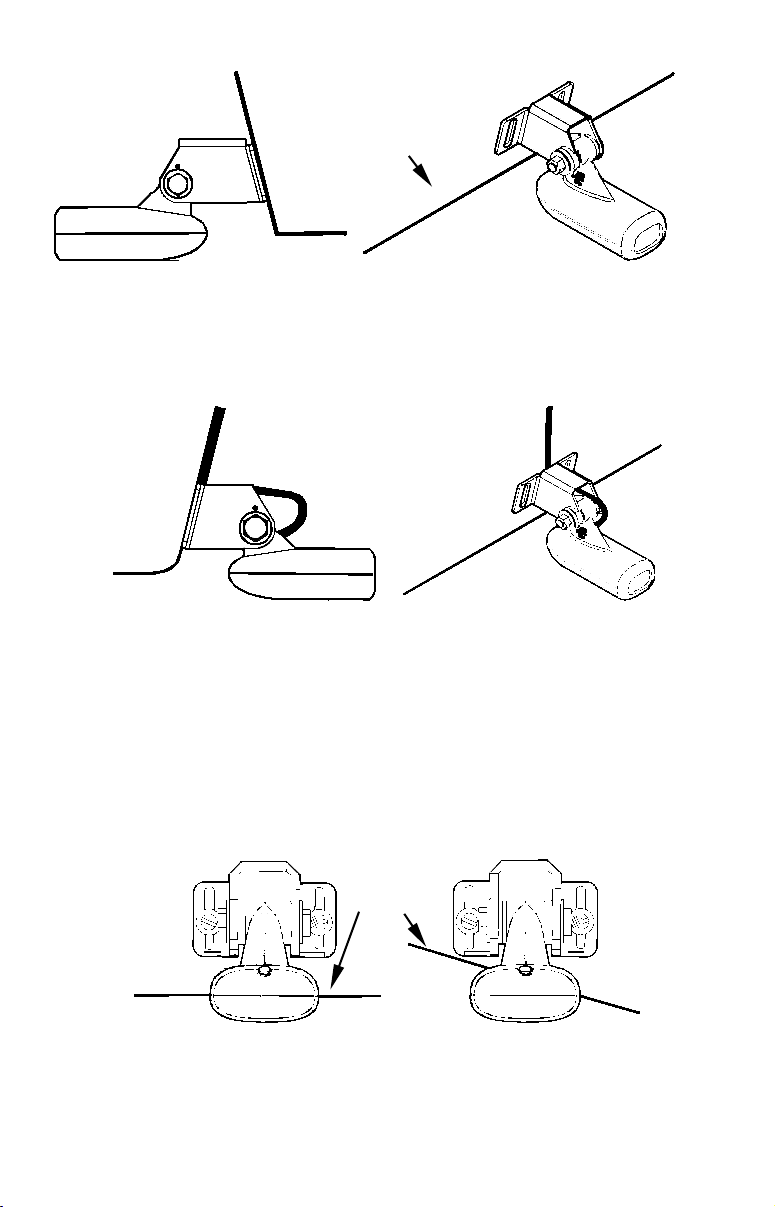
Mark the center of each slot for the mounting screw pilot holes. You
will drill one hole in the center of each slot.
Drill the holes using the #29 bit (for the #10 screws).
9
Transom
Transom
Position transducer mount on transom and mark mounting holes.
Side view (left) and shown from above (right).
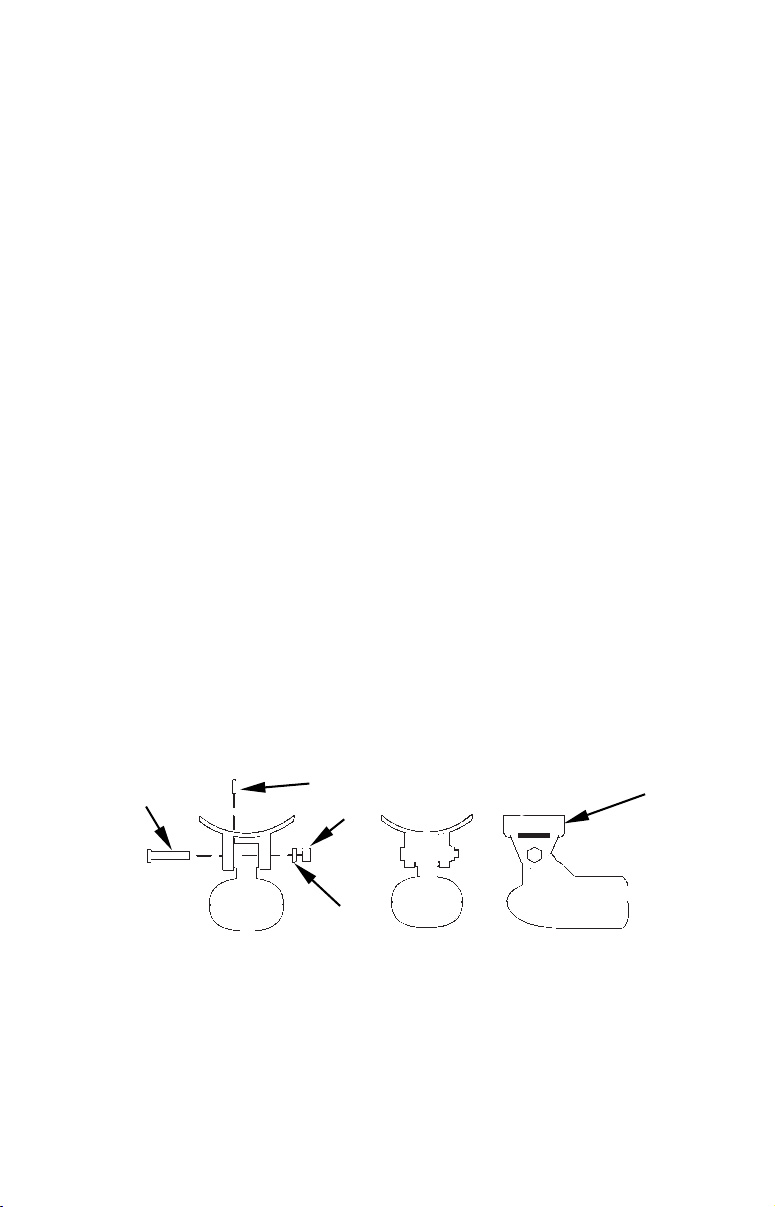
5. Attaching transducer to transom. Remove the transducer from
the bracket and re-assemble it with the cable passing through the
bracket over the bolt as shown in the following figures.
Route cable over bolt and through bracket. Side view (left) and shown
from above (right).
Attach the transducer to the transom. Slide the transducer up or
down until it's aligned properly with the bottom of the hull as shown
in the preceding and following figures. Tighten the bracket's mounting screws, sealing them with the sealant compound.
Adjust the transducer so that it's parallel to the ground and tighten
the nut until it touches the outer washer, then add 1/4 turn. Don't
over tighten the lock nut! If you do, the transducer won't "kick-up" if
it strikes an object in the water.
Bottom
of
hull
Flat-bottom hull Deep-"vee" hull
Align transducer centerline with hull bottom and attach to transom.
10
6. Route the transducer cable through or over the transom to
r
the sonar unit. Make sure to leave some slack in the cable at the
transducer. If possible, route the transducer cable away from other
wiring on the boat. Electrical noise from the engine's wiring, bilge
pumps, VHF radio wires and cables, and aerators can be picked up by
the sonar. Use caution when routing the transducer cable around these
wires.
WARNING:
Clamp the transducer cable to the transom close to the
transducer. This can prevent the transducer from entering the boat if it is knocked off at high speed.
If you need to drill a hole in the transom to pass the connector through,
the required hole size is 5/8".
Caution:
If you drill a hole in the transom for the cable, make sure it is
located above the waterline. After installation, be sure to seal the
hole with the same marine grade above- or below-waterline
sealant used for the mounting screws.
7. Make a test run to determine the results. If the bottom is lost at
high speed, or if noise appears on the display, try sliding the transducer bracket down. This puts the transducer deeper into the water,
hopefully below the turbulence causing the noise. Don't allow the
transducer bracket to go below the bottom of the hull.
Trolling Motor Bracket Installation
1. Attach the optional TMB-S bracket to the transducer as shown in the
following figure, using the hardware supplied with the transducer.
The internal tooth washer is supplied with the TMB-S.
Bolt
Internal tooth washer
Nut
TMB-S bracket
Flat washe
Attach motor mounting bracket to transducer.
2. Slide the adjustable strap supplied with the TMB-S through the slot
in the transducer bracket and wrap it around the trolling motor. Position the transducer to aim straight down when the motor is in the
water. Tighten the strap securely.
11
3. Route the transducer cable alongside the trolling motor shaft. Use
plastic ties (not included) to attach the transducer cable to the trolling motor shaft. Make sure there is enough slack in the cable for the
motor to turn freely. Route the cable to the sonar unit and the transducer is ready for use.
Transducer mounted on trolling motor, side view.
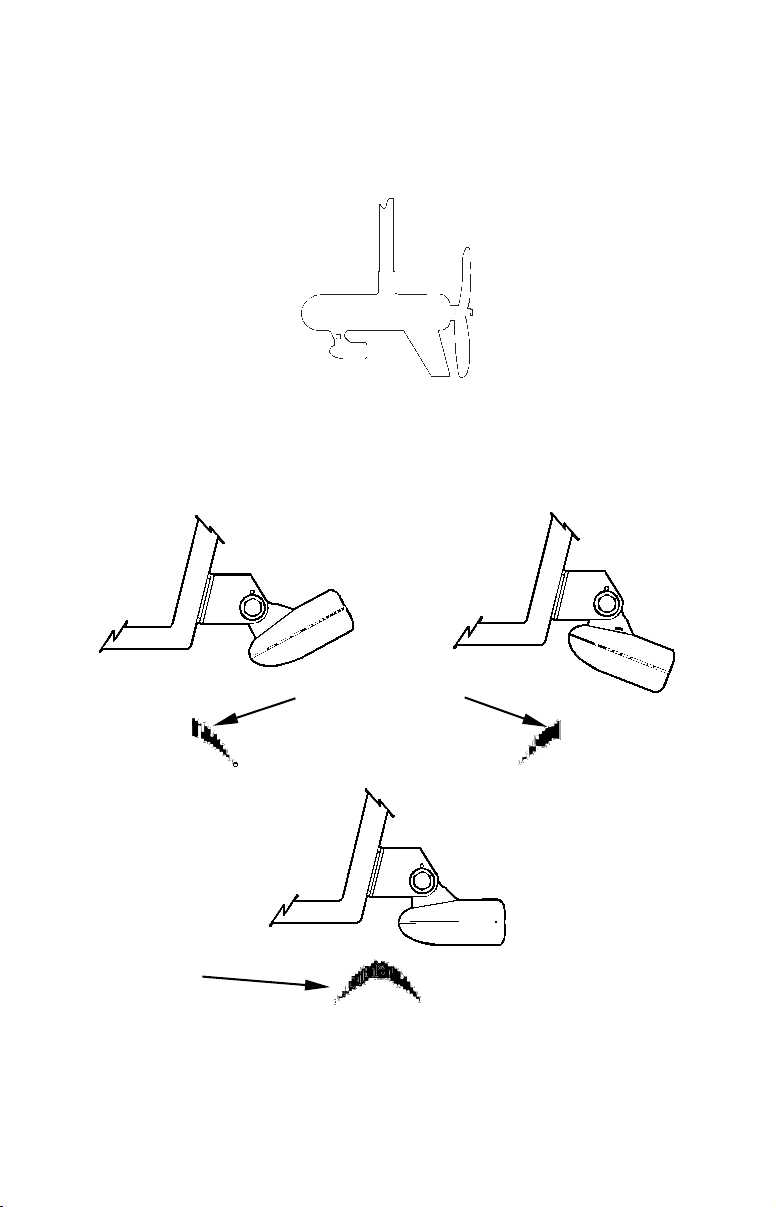
Transducer Orientation and Fish Arches
If you do not get good fish arches on your display, it could be because
the transducer is not parallel with the ground when the boat is at rest
in the water or at slow trolling speeds.
Partial fish arches
Transducer aimed
too far back
Full fish arch
Transducer angles and their effects on fish arches.
Proper transducer angle
Transducer aimed
too far forward
If the arch slopes up – but not back down – then the front of the transducer is too high and needs to be lowered.
12
If only the back half of the arch is printed, then the nose of the transducer is angled too far down and needs to be raised.
NOTE:
Periodically wash the transducer's face with soap and water to remove any oil film. Oil and dirt on the face will reduce the sensitivity or may even prevent operation.
Shoot-Thru-Hull Preparation
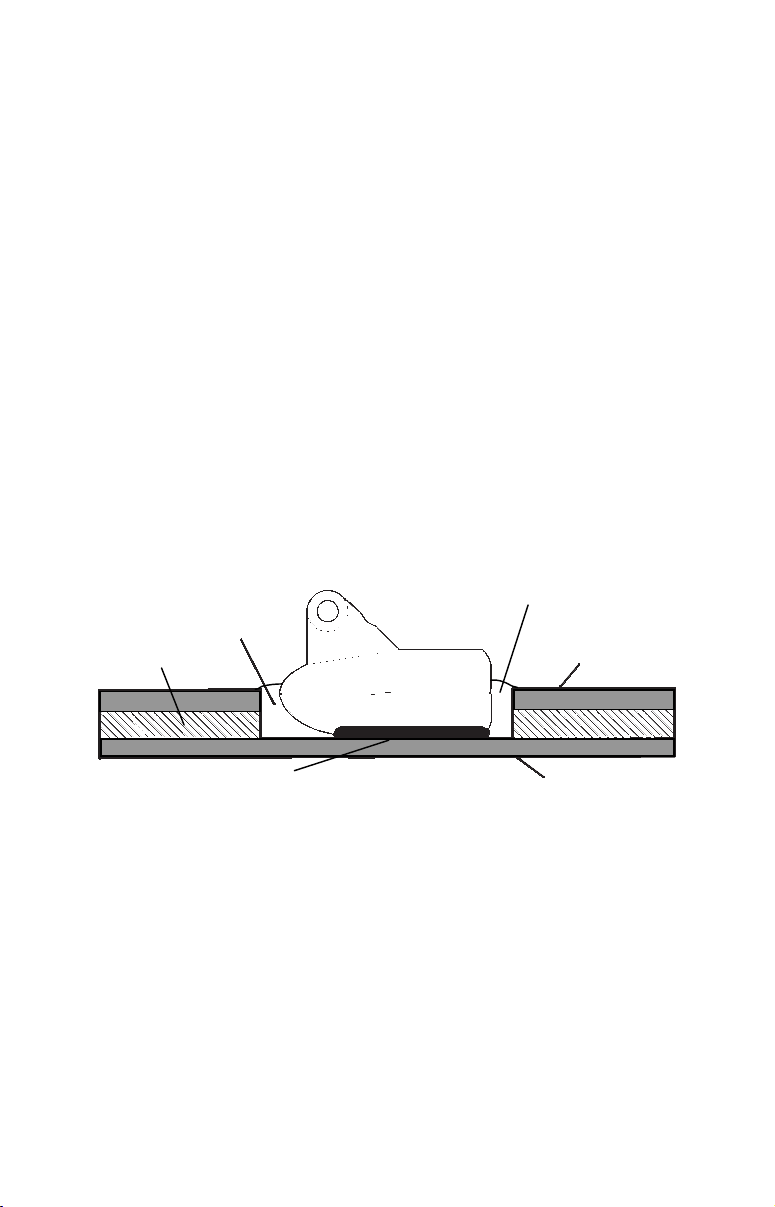
Hulls With Flotation Materials
The transducer installation inside a fiberglass hull must be in an area
that does not have air bubbles in the resin or separated fiberglass layers. The sonar signal must pass through solid fiberglass. A successful
transducer installation can be made on hulls with flotation materials
(such as plywood, balsa wood or foam) between layers of fiberglass if
the material is removed from the chosen area. See the figure below.
WARNING:
Do not remove any material from your inner hull unless
you know the hull's composition. Careless grinding or
cutting on your hull can result in damage that could
sink your boat. Contact your boat dealer or manufacturer to confirm your hull specifications.
Fill with
Fill with resin
Flotation material
Inner hull
Epoxy to hull first
Epoxy the transducer to a solid portion of the hull.
Outer hull
Some (but not all) manufacturers use a layer of fiberglass, then a core
of balsa wood, finishing with an outer layer of fiberglass. Removing the
inner layer of fiberglass and the balsa wood core exposes the outer
layer of fiberglass. The transducer can then be epoxied directly to the
outer layer of fiberglass. After the epoxy cures, the hull is watertight
and structurally sound. Remember, the sonar signal must pass through
solid fiberglass. Any air bubbles in the fiberglass or the epoxy will reduce or eliminate the sonar signals.
To choose the proper location for shoot-thru-hull mounting, follow these
testing procedures. You may need a helper to complete these steps.
13
 Loading...
Loading...