Page 1

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem
Reference Manual
Doc. No. 102752B
April 6, 2006
Page 2

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Revision Record
Revision Date Comments
A 9/28/2005 Initial release.
B 4/6/2006 Rev. B release.
© 2005, 2006 Conexant Systems, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Information in this document is provided in connection with Conexant Systems, Inc. (“Conexant”) products. These materials are
provided by Conexant as a service to its customers and may be used for informational purposes only. Conexant assumes no
responsibility for errors or omissions in these materials. Conexant may make changes to this document at any time, without notice.
Conexant advises all customers to ensure that they have the latest version of this document and to verify, before placing orders, that
information being relied on is current and complete. Conexant makes no commitment to update the information and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to its specifications and product descriptions.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as
provided in Conexant’s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Conexant assumes no liability whatsoever.
THESE MATERIALS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF CONEXANT PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, MERCHANTABILITY, OR
INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. CONEXANT FURTHER
DOES NOT WARRANT THE ACCURACY OR COMPLETENESS OF THE INFORMATION, TEXT, GRAPHICS OR OTHER ITEMS
CONTAINED WITHIN THESE MATERIALS. CONEXANT SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST REVENUES OR LOST PROFITS, WHICH MAY
RESULT FROM THE USE OF THESE MATERIALS.
Conexant products are not intended for use in medical, lifesaving or life sustaining applications. Conexant customers using or selling
Conexant products for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Conexant for any damages
resulting from such improper use or sale.
The following are trademarks of Conexant Systems, Inc.: Conexant and the Conexant C symbol. Product names or services listed
in this publication are for identification purposes only, and may be trademarks of third parties. Third-party brands and names are the
property of their respective owners.
For additional disclaimer information, please consult Conexant’s Legal Information posted at www.conexant.com which is
incorporated by reference.
Reader Response: Conexant strives to produce quality documentation and welcomes your feedback. Please send comments and
suggestions to conexant.tech.pubs@conexant.com. For technical questions, contact your local Conexant sales office or field
applications engineer.
ii Conexant 102752B
Page 3

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Contents
Revision History............................................................................................................................................. x
1 Introduction..........................................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.1.1 Command Syntax ........................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.1.2 Command Descriptions .................................................................................................................................. 1-1
1.2 Reference Documentation .............................................................................................................................................. 1-1
2 Syntax and Procedures.........................................................................................................................2-1
2.1 Alphabet.......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 DTE Commands Lines .................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2.1 Command Line General Format...................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2.2 Command Line Editing ................................................................................................................................... 2-2
2.2.3 Command Line Echo ...................................................................................................................................... 2-2
2.2.4 Repeating a Command Line ........................................................................................................................... 2-2
2.2.5 Types of DTE Commands ............................................................................................................................... 2-2
2.3 Basic Syntax Commands ................................................................................................................................................ 2-3
2.3.1 Basic Syntax Command Format ..................................................................................................................... 2-3
2.3.2 S-Parameters.................................................................................................................................................. 2-3
2.4 Extended Syntax Commands .......................................................................................................................................... 2-4
2.4.1 Command Naming Rules................................................................................................................................ 2-4
2.4.2 Values............................................................................................................................................................. 2-4
Numeric Constants ................................................................................................................................. 2-4
String Constants..................................................................................................................................... 2-5
Compound Values .................................................................................................................................. 2-5
2.4.3 Action Commands .......................................................................................................................................... 2-5
Action Execution Command Syntax........................................................................................................ 2-5
Action Test Command Syntax ................................................................................................................ 2-6
2.4.4 Parameter Commands.................................................................................................................................... 2-6
Parameter Types..................................................................................................................................... 2-6
Parameter Set Command Syntax............................................................................................................ 2-7
Parameter Read Command Syntax......................................................................................................... 2-7
Parameter Test Command Syntax .......................................................................................................... 2-7
2.4.5 Additional Syntax Rules.................................................................................................................................. 2-7
Concatenating Commands after Extended Syntax Commands............................................................... 2-7
Concatenating Commands after Basic Format Commands .................................................................... 2-8
2.5 Issuing Commands......................................................................................................................................................... 2-8
102752B Conexant iii
Page 4

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
2.6
Executing Commands..................................................................................................................................................... 2-8
2.6.1 Aborting Commands ...................................................................................................................................... 2-8
2.6.2 Handling of Invalid Numbers and S-Parameter Values .................................................................................. 2-9
2.7 Modem Responses......................................................................................................................................................... 2-9
2.7.1 Responses...................................................................................................................................................... 2-9
2.7.2 Extended Syntax Result Codes ..................................................................................................................... 2-10
2.7.3 +<name>: <compound_value>Information Text Formats for Test Commands............................................ 2-11
Range of Values.................................................................................................................................... 2-11
Compound Range of Values ................................................................................................................. 2-11
3 Data Command Set...............................................................................................................................3-1
3.1 Command Guidelines...................................................................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 Escape Code Sequence................................................................................................................................... 3-1
3.2 Data Commands ............................................................................................................................................................. 3-1
3.2.1 Generic Modem Control ................................................................................................................................. 3-2
Z - Soft Reset and Restore Profile.......................................................................................................... 3-2
+FCLASS - Select Active Service Class................................................................................................... 3-2
+VCID - Caller ID (CID)........................................................................................................................... 3-3
-SCID - Snooping CID (Type II).............................................................................................................. 3-4
+VRID - Report Retrieved Caller ID (CID)............................................................................................... 3-5
\N - Operating Mode ............................................................................................................................... 3-6
I - Identification ...................................................................................................................................... 3-7
+GMI - Request Manufacturer Identification .......................................................................................... 3-7
+GMI9 - Request Conexant Identification............................................................................................... 3-8
+GMM - Request Model Identification.................................................................................................... 3-8
+GMR - Request Revision Identification ................................................................................................ 3-8
+GCI - Country of Installation................................................................................................................. 3-9
&F - Restore Factory Configuration (Profile) ........................................................................................ 3-10
&T - Local Analog Loopback Test ........................................................................................................ 3-10
&Y - Designate a Default Reset Profile................................................................................................. 3-11
&W - Store Current Configuration ........................................................................................................ 3-11
&Zn=x - Store Telephone Number........................................................................................................ 3-12
%7 - Plug and Play Serial Number .......................................................................................................3-12
%8 - Plug and Play Vendor ID and Product Number ........................................................................... 3-13
**- Download Firmware Code .............................................................................................................. 3-13
3.2.2 DTE-Modem Interface commands................................................................................................................ 3-15
E - Command Echo............................................................................................................................... 3-15
Q - Quiet Results Codes Control........................................................................................................... 3-15
V - Result Code Form ........................................................................................................................... 3-16
W - Connect Message Control.............................................................................................................. 3-16
X - Extended Result Codes ................................................................................................................... 3-17
&C - RLSD (DCD) Option ..................................................................................................................... 3-22
&D - DTR Option .................................................................................................................................. 3-22
&K - Flow Control ................................................................................................................................. 3-23
&M - Asynchronous/Synchronous Mode Selection ............................................................................. 3-24
&Q - Sync/Async Mode ........................................................................................................................ 3-25
&R - RTS/CTS Option ........................................................................................................................... 3-26
iv Conexant 102752B
Page 5

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&S - DSR Override ...............................................................................................................................
+IPR - Fixed DTE Rate .......................................................................................................................... 3-27
+IFC - DTE-Modem Local Flow Control ................................................................................................ 3-28
+IBC – In Band Commands .................................................................................................................. 3-29
3.2.3 Call Control................................................................................................................................................... 3-33
D - Dial.................................................................................................................................................. 3-33
T - Set Tone Dial Default....................................................................................................................... 3-35
P - Set Pulse Dial Default...................................................................................................................... 3-35
A - Answer............................................................................................................................................ 3-35
H - Disconnect (Hang-Up) .................................................................................................................... 3-36
O - Return to On-Line Data Mode......................................................................................................... 3-37
L - Speaker Volume .............................................................................................................................. 3-38
M - Speaker Control ............................................................................................................................. 3-38
&G - Select Guard Tone........................................................................................................................ 3-39
&P - Select Pulse Dial Make/Break Ratio.............................................................................................. 3-39
&V - Display Current Configuration and Stored Profiles ...................................................................... 3-40
&V1 - Display Last Connection Statistics ............................................................................................. 3-41
\V - Single Line Connect Message Enabl .............................................................................................. 3-42
%L - Report Line Signal Level.............................................................................................................. 3-43
%Q - Report Line Signal Quality........................................................................................................... 3-43
*B - Display Blacklisted Numbers ........................................................................................................ 3-43
*D - Display Delayed Numbers............................................................................................................. 3-44
–SLP= - Set Low Power Mode ............................................................................................................. 3-45
–STE= - Set Telephony Extension......................................................................................................... 3-46
-TRV – Tip & Ring Voltage ................................................................................................................... 3-51
-TTE - Threshold Adjustments for Telephony Extension ...................................................................... 3-52
3.2.4 Modulation Control Commands ................................................................................................................... 3-53
+MS - Modulation Selection ................................................................................................................. 3-53
+MR - Modulation Reporting Control................................................................................................... 3-55
%E - Enable/Disable Line Quality Monitor and Auto-Retrain or Fallback/Fall Forward ......................... 3-57
B - CCITT or Bell ................................................................................................................................... 3-58
3.2.5 Error Control Commands ............................................................................................................................. 3-59
+ES - Error Control and Synchronous Mode Selection ........................................................................ 3-59
+EB - Break Handling in Error Control Operation ................................................................................. 3-61
+ESR - Selective Repeat ....................................................................................................................... 3-61
+EFCS - 32-bit Frame Check Sequence ................................................................................................ 3-62
+ER - Error Control Reporting .............................................................................................................. 3-63
+ETBM - Call Termination Buffer Management .................................................................................... 3-65
\B - Transmit Break to Remote ............................................................................................................. 3-66
\K - Break Control ................................................................................................................................. 3-67
3.2.6 Data Compression Commands..................................................................................................................... 3-69
+DS - Data Compression...................................................................................................................... 3-69
+DS44 - V.44 Compression Select ....................................................................................................... 3-70
+DR - Data Compression Reporting..................................................................................................... 3-71
%C - Enable/Disable Data Compression............................................................................................... 3-73
3-26
102752B Conexant v
Page 6

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3.2.7
Synchronous Access Mode Commands....................................................................................................... 3-74
+ESA - Configure Synchronous Access Submode ............................................................................... 3-74
+ITF - Transmit Flow Control Thresholds ............................................................................................. 3-76
3.2.8 Diagnostic Commands ................................................................................................................................. 3-78
%TT - PTT Test Command ................................................................................................................... 3-78
DTMF Tones ......................................................................................................................................... 3-78
FSK, V.22 and V.22 bis Spectrum ........................................................................................................ 3-78
V.32 and V.32bis Spectrum.................................................................................................................. 3-80
Tone Generation ................................................................................................................................... 3-81
V.34 Spectrum...................................................................................................................................... 3-82
Japan-Specific Sequences.................................................................................................................... 3-83
3.2.9 Fast Connect Commands.............................................................................................................................. 3-85
$F – Fast Connect Control .................................................................................................................... 3-85
3.2.10 V.92 +P and –Q Commands ......................................................................................................................... 3-86
+PCW - Call Waiting Enable.................................................................................................................. 3-86
+PMH - Modem-on-Hold Enable .......................................................................................................... 3-87
+PMHT – Modem-on-Hold Timer......................................................................................................... 3-88
+PMHR - Initiate Modem-on-Hold........................................................................................................ 3-89
+PIG - PCM Upstream Ignore............................................................................................................... 3-90
+PMHF - V.92 Modem-on-Hold Hook Flash ......................................................................................... 3-90
+PQC - V.92 Phase 1 and Phase 2 Control........................................................................................... 3-91
+PSS - Use Short Sequence ................................................................................................................. 3-92
-QCPC - Force Full Startup Procedure Next Connection....................................................................... 3-93
-QCPS - Enable Quick Connect Profile Save......................................................................................... 3-93
3.3 S-Parameters................................................................................................................................................................ 3-94
S - Read/Write S-Parameter ................................................................................................................. 3-94
3.3.1 Factory Defaults............................................................................................................................................ 3-94
3.3.2 S-Parameter Definitions ............................................................................................................................... 3-96
S0 - Number of Rings to Auto-Answer................................................................................................. 3-96
S1 - Ring Counter................................................................................................................................. 3-96
S2 - Escape Character .......................................................................................................................... 3-96
S3 - Carriage Return Character ............................................................................................................ 3-96
S4 - Line Feed Character ...................................................................................................................... 3-96
S5 - Backspace Character..................................................................................................................... 3-97
S6 - Wait Time before Blind Dialing or for Dial Tone............................................................................ 3-97
S7 - Wait Time for Carrier, Silence, or Dial Tone.................................................................................. 3-97
S8 - Pause Time For Dial Delay ............................................................................................................ 3-98
S9 - Carrier Detect Response Time ...................................................................................................... 3-98
S10 - Lost Carrier To Hang Up Delay ................................................................................................... 3-98
S11 - DTMF Tone Duration................................................................................................................... 3-98
S12 - Escape Prompt Delay (EPD) ....................................................................................................... 3-99
S14 - General Bit Mapped Options Status ............................................................................................ 3-99
S16 - Test Mode Bit Mapped Options Status ....................................................................................... 3-99
S17 - Point Of Sale Options Selection ................................................................................................ 3-100
S19 - Reserved................................................................................................................................... 3-101
S20 - Reserved................................................................................................................................... 3-101
vi Conexant 102752B
Page 7

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
S21 - V.24/General Bit Mapped Options Status..................................................................................
S22 - Speaker/Results Bit Mapped Options Status ............................................................................3-103
S23 - General Bit Mapped Options Status .......................................................................................... 3-104
S24 - Sleep Inactivity Timer ............................................................................................................... 3-104
S25 - Delay To DTR Off ...................................................................................................................... 3-104
S26 - RTS to CTS Delay...................................................................................................................... 3-104
S27 - Bit Mapped Options Status ....................................................................................................... 3-105
S28 - Bit Mapped Options Status ....................................................................................................... 3-105
S29 - Flash Dial Modifier Time ........................................................................................................... 3-106
S30 - Disconnect Inactivity Timer ...................................................................................................... 3-106
S31 - Bit Mapped Options Status ....................................................................................................... 3-106
S36 - LAPM Failure Control................................................................................................................ 3-107
S38 - Delay Before Forced Hang Up ................................................................................................... 3-107
S39 - Flow Control Bit Mapped Options Status .................................................................................. 3-108
S40 - General Bit Mapped Options Status .......................................................................................... 3-108
S41 - General Bit Mapped Options Status .......................................................................................... 3-109
S46 - Data Compression Control........................................................................................................ 3-109
S48 - V.42 Negotiation Control .......................................................................................................... 3-109
S86 - Call Failure Reason Code .......................................................................................................... 3-110
S91 - PSTN Transmit Attenuation Level............................................................................................. 3-111
S95 - Extended Result Codes Control ................................................................................................ 3-111
S210 – V.34 Symbol Rates................................................................................................................. 3-112
3.4 Result Codes............................................................................................................................................................... 3-113
3-102
4 Fax Class 1 and Fax Class 1.0 Commands............................................................................................4-1
4.1 Fax I/O Processing.......................................................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1.1 DTE-to-Modem Transmit Data Stream ........................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1.2 Modem-to-DTE Receive Data Stream............................................................................................................. 4-1
4.1.3 Fax Mode Selection ........................................................................................................................................ 4-1
4.1.4 Fax Origination ............................................................................................................................................... 4-3
4.1.5 Fax Answering ................................................................................................................................................ 4-3
4.1.6 Fax Control Transmission............................................................................................................................... 4-3
4.1.7 Fax Control Reception .................................................................................................................................... 4-3
4.1.8 Fax Data Transmission ................................................................................................................................... 4-4
4.1.9 Fax Data Reception......................................................................................................................................... 4-5
4.2 Commands and Parameters ........................................................................................................................................... 4-6
4.2.1 Mode Entry Commands.................................................................................................................................. 4-6
+FCLASS=1 - Select Facsimile Class 1 Mode ......................................................................................... 4-6
+FCLASS=1.0 - Select Facsimile Class 1.0 Mode................................................................................... 4-6
4.2.2 Mode Commands ........................................................................................................................................... 4-6
+FAA - Auto Answer Enable.................................................................................................................... 4-6
+FAE - Auto Answer Enable .................................................................................................................... 4-7
+FTS - Transmit Silence ......................................................................................................................... 4-7
+FRS - Receive Silence........................................................................................................................... 4-8
+FTM - Transmit Facsimile ..................................................................................................................... 4-9
+FRM - Receive Facsimile .................................................................................................................... 4-10
+FTH - Transmit Data with HDLC Framing ........................................................................................... 4-11
102752B Conexant vii
Page 8

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+FRH - Receive Data with HDLC Framing.............................................................................................
4.2.3 Service Class 1 Parameters.......................................................................................................................... 4-13
+FAR - Adaptive Reception Control ...................................................................................................... 4-13
+FCL - Carrier Loss Timeout ................................................................................................................ 4-14
+FDD - Double Escape Character Replacement.................................................................................... 4-15
+FIT - DTE Inactivity Timeout ............................................................................................................... 4-16
+FPR - Fixed DTE Rate ......................................................................................................................... 4-17
+FMI? - Request Manufacturer Identification....................................................................................... 4-18
+FMM? - Request Model Identification ................................................................................................ 4-18
+FMR? - Request Revision Identification ............................................................................................. 4-18
+FLO - Flow Control.............................................................................................................................. 4-19
4.3 Examples ...................................................................................................................................................................... 4-19
4-12
5 Voice Commands .................................................................................................................................5-1
5.1 Voice Commands Overview ............................................................................................................................................ 5-1
5.1.1 <DLE> Shielded Event Codes Sent to the DTE ............................................................................................... 5-2
5.1.2 <DLE> Shielded Codes Sent to the Modem (DCE) ......................................................................................... 5-3
5.2 Voice Commands............................................................................................................................................................ 5-4
5.2.1 Configuration Commands............................................................................................................................... 5-4
+FCLASS=8 - Select Voice Mode............................................................................................................ 5-4
+VNH - Automatic Hang-up Control ....................................................................................................... 5-4
5.2.2 Voice Commands ........................................................................................................................................... 5-5
+VIP - Voice Initialize All Parameters ..................................................................................................... 5-5
+VRX - Start Modem Receive (Record).................................................................................................. 5-5
+VTR - Start Voice Transmission and Reception (Voice Duplex)........................................................... 5-6
+VTS - Send Voice Tone(s) .................................................................................................................... 5-7
+VTX - Start Modem Transmit (Playback).............................................................................................. 5-9
+VGR - Voice Gain Receive (Record Gain) ............................................................................................. 5-9
+VGT - Voice Gain Transmit (Playback Volume) .................................................................................. 5-10
+VIT - Voice Inactivity Timer (DTE/Modem)......................................................................................... 5-11
+VLS - Analog Source/Destination Selection ....................................................................................... 5-11
+VRA - Ringback Goes Away Timer ..................................................................................................... 5-15
+VRN - Ringback Never Appeared Timer ............................................................................................. 5-16
+VSD - Silence Detection (Quiet and Silence) ...................................................................................... 5-17
+VSM - Compression Method Selection .............................................................................................. 5-18
+VTD - Beep Tone Duration Timer........................................................................................................ 5-19
+VDR - Distinctive Ring........................................................................................................................ 5-20
+VDT - Control Tone Cadence Reporting ............................................................................................. 5-21
+VPR - Select DTE/Modem Interface Rate (Turn Off Autobaud) .......................................................... 5-22
5.2.3 Speakerphone Commands ........................................................................................................................... 5-23
+VSP - Speakerphone ON/OFF ............................................................................................................. 5-23
+VDX - Speakerphone Duplex Mode .................................................................................................... 5-24
+VGM - Microphone Gain..................................................................................................................... 5-25
+VGS - Speaker Gain ............................................................................................................................ 5-26
viii Conexant 102752B
Page 9

Tables
Table 3-1. Result Codes.................................................................................................................................................... 3-19
Table 3-2. Supported V.80 Commands............................................................................................................................. 3-31
Table 3-3. +MS Command Supported Rates .................................................................................................................... 3-53
Table 3-4. S-Parameter Summary .................................................................................................................................... 3-95
Table 3-5. Result Code Definitions ................................................................................................................................. 3-114
Table 4-1. Fax Class 1 and Fax Class 1.0 Commands......................................................................................................... 4-2
Table 4-2. Fax Class 1 and Fax Class 1.0 Modulation Modes and Rates ............................................................................ 4-9
Table 4-3. Inactivity Timer Start and Stop Events............................................................................................................. 4-16
Table 4-4. Fax Class 1 Calling Sequence (Transmitting a Single Page)............................................................................ 4-20
Table 4-5. Fax Class 1 Answering Sequence (Receiving a Single Page)........................................................................... 4-21
Table 5-1. Voice Commands............................................................................................................................................... 5-1
Table 5-2. Supported <DLE> Shielded Codes Sent to the DTE ........................................................................................... 5-2
Table 5-3. Supported <DLE> Shielded Codes Sent to the Modem (DCE) ........................................................................... 5-3
Table 5-4. +VNH Command Behavior ................................................................................................................................. 5-4
Table 5-5. +VLS Command Options ................................................................................................................................. 5-13
Table 5-6. Events Detectable in the Voice Mode per V.253 .............................................................................................. 5-14
AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
102752B Conexant ix
Page 10

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Revision History
Incorporated in Doc. No. 102752A
Initial release.
Incorporated in Doc. No. 102752B
Section 3.2.8: General revision.
x Conexant 102752B
Page 11
AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
This manual describes the host command and responses for the Conexant CX930xx
modem.
1.1.1 Command Syntax
The fundamental DTE interface command syntax is described in Section 2.
1.1.2 Command Descriptions
Commands are grouped into the following categories:
Syntax and procedures Section 2
Data commands Section 3
Voice Pass-Through commands Section 4
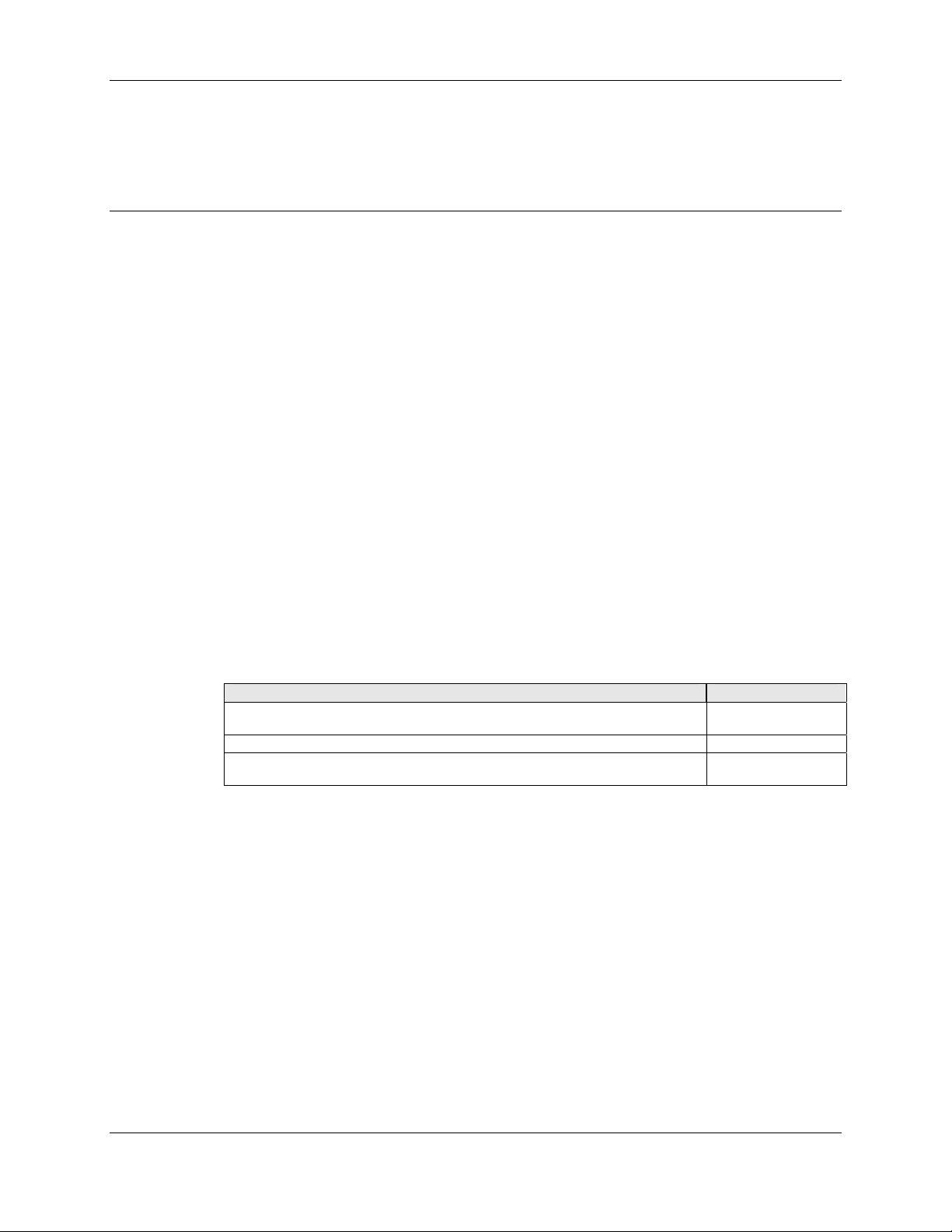
1.2 Reference Documentation
Document Title Document No.
CX93010 UCMxx USB V.92/V.32bis Controllered Modem with CX20548 SmartDAA
Data Sheet
CX93011 CSMxx V.92/V.34/V.32bis Controllered Serial Modem Data Sheet 102635
CX93021 CSM92-SP V.92 Controllered Serial Modem with Speakerphone Data
Sheet
102627
102613
102752B Conexant 1-1
Page 12

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
This page is intentionally blank.
1-2 Conexant 102752B
Page 13

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
2 Syntax and Procedures
The command and response syntax and procedures generally conform to referenced
recommendations and standards. Since these recommendations and standards describe
characteristics universal to a large installed base of modems to a maximum degree, there
may be syntax and procedural differences due to extensions and behavioral differences in
implemented commands, parameters, and responses beyond those described in these
recommendations and standards.
The syntax and procedures described in this section are based on V.250 and V.253 with
additional information included for implemented extensions, behavioral differences
beyond V.250, and legacy commands.
2.1 Alphabet
The T.50 International Alphabet 5 (IA5) is used in this document. Only the low-order
seven bits of each character are significant to the modem; any eighth or higher-order
bit(s), if present, are ignored for the purpose of identifying com mands and parameters.
Lower-case characters are considered identical to their upper-case equivalents when
received by the modem from the DTE. Result codes from the modem are in upper case.
2.2 DTE Commands Lines
Words enclosed in <angle brackets> are references to syntactical elements. The brackets
are not used when the words appear in a command line. Words enclosed in [square
brackets] represent optional items which may be omitted from the command line at the
specified point. The square brackets are not used when the words appe ar in the command
line. Other characters that appear in syntax descriptions must be included as shown.
Any modem responses are mentioned in terms of their alphabetic format; the actual
response issued will depend on the setting of parameters that affect response formats,
e.g., Q and V commands (see
2.2.1 Command Line General Format
A command line is made up of three elements: the prefix, the body, and the termination
character.
The command line prefix consists of the characters "AT" or "at" or, to repeat the
execution of the previous command line, the characters "A/" or "a/".
The body is made up of individual commands described in this document. Space
characters (IA5 2/0) are ignored and may be used freely for formatting purposes, unless
they are embedded in numeric or string constants. The termination character may not
appear in the body. The modem can accept at least 50 characters in the body.
The termination character may be selected by a user option (parameter S3), the default
being CR.
2.7).
102752B Conexant 2-1
Page 14

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
2.2.2 Command Line Editing
The character defined by parameter S5 (default, BS) is interpreted as a request from the
DTE to the modem to delete the previous character. Any control characters (IA5 0/0
through 1/15, inclusive) that remain in the command line after receipt of the termination
character are ignored by the modem.
The modem checks characters from the DTE first to see if they match the termination
character (S3), then the editing character (S5), before checking for other characters. This
ensures that these characters will be properly recognized even if they are set to values
that the modem uses for other purposes. If S3 and S5 are set to the same value, a
matching character will be treated as matching S3 (S3 is checked before S5).
2.2.3 Command Line Echo
The modem may echo characters received from the DTE during command state and
online command state back to the DTE, depending on the setting of the E command. If
enabled, characters received from the DTE are echoed in the same format as received.
Invalid characters in the command line or incomplete or improperly-formed command
line prefixes may not be echoed.
2.2.4 Repeating a Command Line
If the prefix "A/" or "a/" is received, the modem immediately executes once again the
body of the preceding command line. No editing is possible, and no termination character
is necessary. A command line may be repeated multiple times in this manner. Responses
to the repeated command line are issued using format of the original command line. If
"A/" is received before any command line has been executed, the preceding command
line is assumed to have been empty (that results in an OK result code).
2.2.5 Types of DTE Commands
There are two types of commands: action commands and parameter commands.
Commands of either type may be included in command lines, in any order.
Action commands may be "executed" (to invoke a particular function of the equipment,
which generally involves more than the simple storage of a value for later use), or
"tested" (to determine whether or not the equipment implements the action command,
and, if subparameters are associated with the action, the ranges of subparameter values
that are supported).
Parameters may be "set" (to store a value or values for later use), "read" (to determine the
current value or values stored), or "tested" (to determ i ne whethe r or n ot the equi pment
implements the parameter, and the ranges of values supported).
2-2 Conexant 102752B
Page 15

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
2.3 Basic Syntax Commands
2.3.1 Basic Syntax Command Format
The format of Basic Syntax commands, except for the D and S commands, is as follows:
<command>[<number>]
where <command> is either a single character, or the "&" character followed by a single
character per V.250. In addition, <command> can be the "%" character followed by a
single character, the "*" character followed by a single character, or the "^" character
followed by a single character.
<number> may be a string of one or more characters from "0" through "9" representing a
decimal integer value. Commands that expect a <number> are noted in the description of
the command. If a command expects <number> and it is missing (<command> is
immediately followed in the command line by another <command> or the termination
character), the value "0" is assumed. If a command does not expect a <number> and a
number is present, an ERROR is generated. All leading "0"s in <number> are ignored by
the modem.
Additional commands may follow a command (and associated parameter, if any) on the
same command line without any character required for separation. The actions of some
commands cause the remainder of the command line to be ignored (e.g., A).
See the D command for details on the format of the information that follows it.
2.3.2 S-Parameters
Commands that begin with the letter "S" are known as "S-parameters". The number
following the "S" indicates the "parameter number" being referenced. If the number is not
recognized as a valid parameter number, an ERROR result code is issued.
Immediately following this number, either a "?" or "=" character must appear. "?" is used
to read the current value of the indicated S-parameter; "=" is used to set the S-parameter
to a new value.
S<parameter_number>?
S<parameter_number>=[<value>]
If the "=" is used, the new value to be stored in the S-parameter is specified in decimal
following the "=". If no value is given (i.e., the end of the command line occurs or the
next command follows immediately), the S-parameter specified may be set to 0, or an
ERROR result code issued and the stored value left unchanged. The ranges of acceptable
values are given in the description of each S-parameter.
If the "?" is used, the modem transmits a single line of information text to the DTE. The
text portion of this information text consists of exactly three characters, giving the value
of the S-parameter in decimal, with leading zeroes included.
102752B Conexant 2-3
Page 16

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
2.4 Extended Syntax Commands
2.4.1 Command Naming Rules
Both actions and parameters have names, which are used in the related commands.
Names always begin with the character “+” or “–”. Following the “+” or “–”, from one to
16 additional characters appear in the command name. These characters will be selected
from the following set:
A through Z (IA5 4/1 through 5/10)
0 through 9 (IA5 3/0 through 3/9)
! (IA5 2/1)
% (IA5 2/5)
- (IA5 2/13)
. (IA5 2/14)
/ (IA5 2/15)
: (IA5 3/10)
_ (IA5 5/15)
The first character following the “+” or “–” is an alphabetic character in the range of "A"
through "Z". This first character generally implies the application in which a command is
used (e.g., V for voice).
2.4.2 Values
The modem considers lower-case characters to be the same as their upper-case
equivalents.
When subparameters are associated with the execution of an action, or when setting a
parameter, the command may include specification of values. This is indicated by the
appearance of <value> in the descriptions below.
<value> consists of either a numeric constant or a string constant.
Numeric Constants
Numeric constants are expressed in decimal, hexadecimal, or binary.
Decimal numeric constants consist of a sequence of one or more of the characters "0"
through "9", inclusive.
Hexadecimal numeric constants consist of a sequence of one or more of the characters
"0" through "9", inclusive, and "A" through "F" inclusive. The characters "A" through
"F" represent the equivalent decimal values 10 through 15.
Binary numeric constants consist of a sequence of one or more of the characters "0" and
"1".
In all numeric constants, the most significant digit is specified first. Leading "0"
characters are ignored by the modem. No spaces, hyphens, periods, commas, parentheses,
or other generally-accepted numeric formatting characters are permitted in numeric
constants; note in particular that no "H" suffix is appended to the end of hexadecimal
constants.
2-4 Conexant 102752B
Page 17

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
String Constants
String constants consist of a sequence of displayable IA5 characters, each in the range
from 2/0 to 7/15, inclusive, except for the characters ‘"’ (IA5 2/2) and "\" (IA5 5/12).
String constants are bounded at the beginning and end by the double-quote character (‘"’,
IA5 2/2).
Any character value may be included in the string by representing it as a backslash ("\")
character followed by two hexadecimal digits. For example, "\0D" is a string consisting
of the single character <CR> (IA5 0/13). If the "\" character itself is to be represented in a
string, it is encoded as "\5C". The double-quote character, used as the beginning and
ending string delimiter, is represented within a string constant as "\22".
A "null" string constant, or a string constant of zero length, is represented by two
adjacent delimiters ("").
Compound Values
Actions may have more than one subparameter associated with them, and parameters
may have more than one value. These are known as "compound values" , and their
treatment is the same in both actions and parameters.
A compound value consists of any combination of numeric and string values (as defined
in the description of the action or parameter). The comma character must be included as a
separator, before the second and all subsequent values in the compound value. If a value
is not specified (i.e., defaults assumed), the required comma separator must be specified;
however, trailing comma characters may be omitted if all associated values are also
omitted.
2.4.3 Action Commands
Action Execution Command Syntax
There are two general types of action commands: those that have associated subparameter
values that affect only that invocation of the command, and those that have no
subparameters.
If subparameters are associated with a command, the definition of the action command
indicates, for each subparameter, whether the specification of a value for that
subparameter is mandatory or optional. For optional subparameters, the definition
indicates the assumed (default) value for the subparameter if no value is specified for that
subparameter; the assumed value may be either a previous value (i.e., the value of an
omitted subparameter remains the same as the previous invocation of the same command,
or is determined by a separate parameter or other mechanism), or a fixed value (e.g., the
value of an omitted subparameter is assumed to be zero). Generally, the default value for
numeric subparameters is 0, and the default value for string subparameters is "" (empty
string).
The following syntax is used for actions that have no subparameters:
+<name> or –<name>
102752B Conexant 2-5
Page 18

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
The following syntax is used for actions that have one sub p a rameter:
+<name>[=<value>] or –<name>[=<value>]
The following syntax is used for actions that have two or more subparameters:
+<name>[=<compound_value>] or –<name>[=<compound_value>]
For actions that accept subparameters, if all subparameters are defined as being optional,
and the default values for all subparameters are satisfactory, the data terminal equipment
(DTE) may use the first syntax above (i.e., omit the "=" from the action execution
command as well as all of the subparameter value string).
If all other relevant criteria are met (e.g., the modem is in the proper state), the command
is executed with any indicated subparameters. If <name> is not recognized, the modem
issues the ERROR result code and terminates processing of the command line. An
ERROR is also generated if a subparameter is specified for an action that does not accept
subparameters, if too many subparameters are specified, if a mandatory subparameter is
not specified, if a value is specified of the wrong type, or if a value is specified that is not
within the supported range.
Action Test Command Syntax
The DTE may test if an action command is implemented in the modem by using the
syntax:
+<name>=?
If the modem does not recognize the indicated name, it returns an ERROR result code
and terminates processing of the command line. If the modem does recognize the action
name, it returns an OK result code. If the named action accepts one or more
subparameters, the modem sends an information text response to the DTE, prior to the
OK result code, specifying the values supported by the modem for each such
subparameter, and possibly additional information. The format of this information text is
defined for each action command.
2.4.4 Parameter Commands
Parameter Types
Parameters may be defined as "read-only" or "read-write". "Read-only" parameters are
used to provide status or identifying information to the DTE, but cannot be set by the
DTE; attempting to set their value is an error. In some cases (specified in the description
of the individual parameter), the modem may ignore attempts to set the value of such
parameters rather than respond with an ERROR result code, if the continued correct
operation of the interface between the modem and DTE will not be affected by such
action. Read-only parameters may be read and tested.
"Read-write" parameters may be set by the DTE, to store a value or values for later use.
Read-write parameters may be set, read, and tested.
Parameters may take either a single value, or multiple (compound) values. Each value
may be either numeric or string; the definition of the parameter will specify the type of
value for each subparameter. Attempting to store a string value in a numeric parameter,
or a numeric value in a string parameter, is an error.
2-6 Conexant 102752B
Page 19

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Parameter Set Command Syntax
The definition of the parameter indicates, for each value, whether the specification of that
value is mandatory or optional. For optional values, the definition indicates the assumed
(default) value if none is specified; the assumed value may be either a previous value
(i.e., the value of an omitted subparameter retains its previous value), or a fixed value
(e.g., the value of an omitted subparameter is assumed to be zero). Generally, the default
value for numeric parameters is 0, and the default value for string parameters is "" (empty
string).
The following syntax is used for parameters that accept a single value:
+<name>=[<value>] or –<name>=[<value>]
The following syntax is used for parameters that accept more than one value:
+<name>=[<compound_value>] or –<name>=[<compound_value>]
For each implemented parameter, if all mandatory values are specified, and all values are
valid according to the definition of the parameter, the specified values are stored. If
<name> is not recognized, one or more mandatory values are omitted, or one or more
values are of the wrong type or outside the permitted range, the modem issues the
ERROR result code and terminates processing of the command line. An ERROR is also
generated if too many values are specified. In case of an error, all previous values of the
parameter are unaffected.
Parameter Read Command Syntax
The DTE may determine the current value or values stored in a parameter by using the
following syntax:
+<name>? or –<name>?
The modem responds by sending the current values stored for the parameter to the DTE
in an information text response. The format of this response is described in the definition
of the parameter. Generally, the values are sent in the same form in which they would be
issued by the DTE in a parameter setting command; if multiple values are supported, they
will generally be separated by commas, as in a parameter setting command.
Parameter Test Command Syntax
The DTE may test if a parameter is implemented in the modem, and determine the
supported values, by using the syntax:
+<name>=? or –<name>=?
If the modem does not recognize the indicated name, it returns an ERROR result code
and terminates processing of the command line. If the modem does recognize the
parameter name, it returns an information text response to the DTE, followed by an OK
result code. The information text response indicates the values supported by the modem
for each such subparameter, and possibly additional information. The format of this
information text is defined for each parameter.
2.4.5 Additional Syntax Rules
Concatenating Commands after Extended Syntax Commands
Additional commands may follow an extended-syntax command on the same command
line if a semicolon (";") is inserted after the preceding extended command as a separator.
102752B Conexant 2-7
Page 20

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
The semicolon is not necessary when the extended syntax command is the last command
on the command line.
Concatenating Commands after Basic Format Commands
Extended syntax co mmands may appear on the same command line after a basic syntax
command without a separator, in the same manner as concatenation of basic syntax
commands.
2.5 Issuing Commands
All characters in a command line must be issued at the same data rate, and with the
same parity and format.
The modem will ignore any command line that is not properly terminated. The modem
may consider 30 seconds of mark idle time between any two characters as an improperly
terminated command line. In this case the modem may or may not generate an ERROR
message. The modem will ignore any characters received from the DTE that are not part
of a properly-formatted command line.
If the maximum number of characters that the modem can accept in the body is exceeded,
an ERROR result code is generated after the command line is terminated.
The DTE will not begin issuing a subsequent command line until at least one-tenth of a
second has elapsed after receipt of the entire result code issued by the modem in response
to the preceding command line.
2.6 Executing Commands
Upon receipt of the termination character, the modem commences execution of the
commands in the command line in the order received from the DTE. Should execution of
a command result in an error, or a character be not recognized as a valid command,
execution is terminated, the remainder of the command line is ignored, and the ERROR
result code is issued. Otherwise, if all commands execute correctly, only the result code
associated with the last command is issued; result codes for preceding commands are
suppressed. If no commands appear in the command line, the OK result code is issued.
2.6.1 Aborting Commands
Some action commands that require time to execute may be aborted while in progress;
these are explicitly noted in the description of the command. Aborting of commands is
accomplished by the transmission from the DTE to the modem of any character. A single
character is sufficient to abort the command in progress; however, characters transmitted
during the first 125 milliseconds after transmission of the termination character are
ignored (to allow for the DTE to append additional control characters such as line feed
after the command line termination character). To ensure that the aborting character is
recognized by the modem, it should be sent at the same rate as the preceding
command line; the modem may ignore characters sent at other rates. When such an
aborting event is recognized by the modem, the modem terminates the command in
progress and returns an appropriate result code to the DTE, as specified for the particular
command.
2-8 Conexant 102752B
Page 21

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
2.6.2 Handling of Invalid Numbers and S-Parameter Values
The modem reacts to undefined numbers and S-parameter values in one of three ways:
1. Issue the ERROR result code, and leave the previous value of the parameter
unchanged;
2. Issue the OK result code, and leave the previous value of the parameter unchanged;
or,
3. Issue the OK result code, and set the parameter value to the valid value nearest to
that specified in the command line.
The description of each command specifies which of these three techniques is used to
handle invalid parameter values for that command or parameter.
2.7 Modem Responses
While in command state and online command state, the modem will issue responses
using the same rate, word length, and parity as the most recently received DTE command
line. In the event that no DTE command has yet been received, rate, word length, and
parity used will depend on the capabilities of the modem.
When the modem transitions from the command state or online command state to the
online data state, the result code CONNECT should be issued at the bit rate and parity
used during the command state. When the modem transitions from the online data state to
the command state or online command state, the result codes should be issued at the bit
rate used during the online data state. Thereafter, any unsolicited result codes should use
the bit rate and parity of the last command line issued by the DTE to the modem.
The characters of a response will be contiguous, with no more than 100 milliseconds of
mark idle issued between characters in addition to stop elements.
2.7.1 Responses
There are two types of responses that may be issued by the modem: information text and
result codes.
Information Text. Information text responses consist of three parts: a header,
information text, and a trailer:
1. The characters transmitted for the header are determined by the V command.
2. The trailer consists of two characters, being the character having the ordinal value of
3. Information text usually consists of a single line; information text returned in
Result Code Parts. Result codes consist of three parts: a header, the result text, and a
trailer.
1. The characters transmitted for the header and trailer are determined by the V
2. The result text may be transmitted as a number or as a string, also depending on a the
parameter S3 followed by the character having the o rdinal value of parameter S4.
response to some commands may contain multiple lines, and the text may therefore
include CR, LF, and other formatting characters to improve readability.
command setting.
V command setting.
102752B Conexant 2-9
Page 22

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Result Code Types. There are three types of result codes: final, intermediate, and
unsolicited. Result codes are described in Section
1. A final result code indicates the completion of a full modem action and a ability to
accept new commands from the DTE.
2. An intermediate result code is a report of the progress of an modem action. The
CONNECT result code is an intermediate result code. In the case of a dialing or
answering command, the modem switches from command state to online data state,
and issues a CONNECT result code. This is an intermediate result code for the
modem because it cannot accept commands from the DTE while in online data state.
When the modem switches back to the command state it then issues a final result
code (such as OK or NO CARRIER).
3. Unsolicited result codes (such as RING) indicate the occurrence of an event not
directly associated with the issuance of a command from the DTE.
2.7.2 Extended Syntax Result Codes
Extended syntax result codes may be issued in response to either basic or extended
commands, or both. The appropriate responses are specified in the definitions of the
commands, the responses, or both.
The general format of extended syntax result codes is the same as result codes defined in
TIA-602 with regard to headers and trailers. The characters specified in S-parameters S3
and S4 are used in headers and trailers of exten ded syntax result codes as they are in
basic format result codes. The setting of the V command affects the headers and trailers
associated with extended syntax result codes in the same manner as basic format result
codes; however, unlike basic format result codes, extended syntax result codes have no
numeric equivalent, and are always issued in alphabetic form.
3.4.
Extended syntax result codes are subject to suppression by the Q1 command, as with
basic format result codes. The issuance of extended syntax result codes are not be
affected by the setting of the X command.
Extended syntax result codes may be either final, intermediate, or unsolicited; the type
being indicated in the definition of the result code.
Extended syntax result codes are prefixed by the "+" character to avoid duplication of
basic format result codes specified in TIA-602. Following the "+" character, the name of
the result code appears; result code names follow the same rules as command names.
Extended syntax result codes may include the reporting of values. The definition of the
result code specifies whether or not values are appended to the result code, and, if so,
how many, their types, and their assumed default values if omitted.
Data/Voice Pass-Through Modes. When no values are to be reported, the result code
appears in the simplest form:
+<name>
If a single value is to be reported, the form of the result code is:
+<name>: <value>
A single space character separates the colon character from the <value>; no space
appears between the result code name and the colon. If multiple values are to be reported
with the result code, the form is:
+<name>: <compound_value>
2-10 Conexant 102752B
Page 23

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
2.7.3 +<name>: <compound_value>Information Text Formats for Test Commands
In general, the format of information text returned by extended syntax commands is
described in the definition of the command.
The modem may insert intermediate <CR> characters in very long information text
responses in order to avoid overrunning DTE receive buffers. If intermediate <CR>
characters are included, the modem does not include the character sequences "0 <CR>"or
"OK<CR>", so that DTE can avoid false detection of the end of these information text
responses.
Range of Values
When the action accepts a single numeric subparameter, or the parameter accepts only
one numeric value, the set of supported values may be presented in the information text
as an ordered list of values. The list is preceded by a left parenthesis (() , and is followed
by a right parenthesis ()). If only a single value is supported, it appears between the
parentheses. If more than one value is supported, then the values may be listed
individually, separated by comma characters, or, when a continuous range of values is
supported, by the first value in the range, followed by a hyphen character (-), followed by
the last value in the range. The specification of single values and ranges of values may be
intermixed within a single information text. In all cases, the supported values are
indicated in ascending order.
For example, the following are some examples of value range indications:
(0) Only the value 0 is supported.
(1,2,3) The values 1, 2, and 3 are supported.
(1-3) The values 1 through 3 are supported.
(0,4,5,6,9,11,12) The several listed values are supported.
(0,4-6,9,11-12) An alternative expression of the above list.
Compound Range of Values
When the action accepts more than one subparameter, or the parameter accepts more than
one value, the set of supported values is presented as a list of the parenthetically-enclosed
value range strings described above, separated by commas. For example, the information
text in response to testing an action that accepts three subparameters, and supports
various ranges for each of them, could appear as follows:
(0),(1-3),(0,4-6,9,11-12)
This indicates that the first subparameter accepts only the value 0, the second accepts any
value from 1 through 3 inclusive, and the third subparameter accepts any of the values 0,
4, 5, 6, 9, 11, or 12.
102752B Conexant 2-11
Page 24

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
This page is intentionally blank.
2-12 Conexant 102752B
Page 25

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3 Data Command Set
3.1 Command Guidelines
The commands used to control and report modem operation in data modem mode are
defined in this section.
The Data Modem Mode commands and responses described in this section are applicable
when command +FCLASS=0. (See Section
command.)
The default values are typical of a fully configured modem supporting all data rates and
options. The actual default value is dependent upon installed modem firmware and
country specific parameters.
Commands are accepted by the modem once the previous command has been fully
executed, which is normally indicated by the return of an appropriate result code.
Execution of commands D and A, either as a result of a direct command or a re-execute
command, will be aborted if another character is entered before completion of the
handshake.
3.2.1 for the definition of the FCLASS
3.1.1 Escape Code Sequence
When the modem has established a connection and has entered on-line data mode, it is
possible to break into the data transmission in order to issue further commands to the
modem in an on-line command mode. This is achieved by the DTE sending to the modem
a sequence of three ASCII characters specified by register S2. The default character is '+'.
The maximum time allowed between receipt of the last character of the three escape
character sequence from the DTE and sending of the OK result code to the DTE is
controlled by the S12 register.
3.2 Data Commands
The modem will respond to the commands detailed below. Parameters applicable to each
command are listed with the command description. The defaults shown for each
configuration command are those used in the Conexant factory profile 0.
102752B Conexant 3-1
Page 26

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3.2.1 Generic Modem Control
Z - Soft Reset and Restore Profile
This command causes the modem to perform a soft reset and restore (recall) the
configuration profile. If no <value> is specified, zero is assumed.
Syntax
Z<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected profile.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
0 Soft reset and restore stored profile 0.
1 Soft reset and restore stored profile 1.
+FCLASS - Select Active Service Class
This command selects the active service class (mode).
Syntax
+FCLASS=<mode>
Defined Values
<mode> Decimal number which corresponds to the selected service
class.
0 Select Data Mode (Section
1 Select Facsimile Class 1 Mode. (Section
1.0 Select Facsimile Class 1.0 Mode. (Section
8 Select Voice Mode. (Section
Result Codes
OK For <mode> = 0, 1, 1.0, and 8
ERROR Otherwise.
1). (Default.)
5).
4).
4).
3-2 Conexant 102752B
Page 27

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +FCLASS?
Response: <mode>
Example: 0 For the default setting.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +FCLASS=?
Response: (<mode> range)
Example: 0, 1, 1.0, 8
+VCID - Caller ID (CID)
This command controls the reporting and presentation of data associated with the Caller
ID services in the Incoming Call Line ID (ICLID) data format for the next call.
Syntax
+VCID=<mode>
Defined Values
<mode> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Disable Caller ID reporting. (Default.)
1 Enables Caller ID with formatted presentation to
the DTE. The modem presents the data items in a
<Tag><Value> pair format. The expected pairs
are date, time, name, and caller code (telephone
number),
2 Enables Caller ID with unformatted presentation
to the DTE.
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +VCID?
Response: <mode>
Example: 0 For the default setting.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +VCID=?
Response: (<mode> range)
Example: (0-2)
102752B Conexant 3-3
Page 28
AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
-SCID - Snooping CID (Type II)
This command allows the modem to snoop a telephone line for Type II CID and relay
this information in order to report to DTE while on-hook. It is similar in functionality
with the standard Type II CID, which fetches CID information while off-hook. The main
difference is that the -SCID command requires equipment with Type II CID capability
connected in parallel with the modem, and hence the name Snooping CID. It will not
work without the CID equipment.
Syntax
-SCID=<pmode>
Defined Values
<pmode> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Disables snooping mechanism only. It does not
disable Type I CID nor Line In Use features.
(Default)
1 Enables snooping mechanism, Type I CID with
formatted presentation to the DTE, and Line In
Use features. The expected pairs are date, time,
name, and caller code (telephone number.)
Forces +VCID=1 and sets the Line In Use bit in
–STE command.
2 Enables the snooping mechanism, Type I CID
with unformatted presentation to the DTE, and
Line In Use features.
Forces +VCID=2 and sets the Line In Use bit in
–STE command.
Example:
The following command sequence demonstrates how the –SCID affects both Line In Use
and Type I CID features:
AT Comm and Snooping CID Type I CID Line In Use Comment
ATZ -SCID: 0 +VCID: 0 -STE: 0 All three features are disabled
AT-SCID=1 -SCID: 1 +VCID: 1 -STE: 1 Enables all three features
AT-SCID=0 -SCID: 0 +VCID: 1 -STE: 1 Disables SCID only
AT-STE=21 -SCID: 0 +VCID: 1 -STE: 2 Enables extension pick-up while
AT-SCID=2 -SCID: 2 +VCID: 2 -STE: 3 Enables all three features with
1. Line In Use is bit 0 and extension pick-up is bit 1. See -STE command.
2. The –SCID command only toggled the Line In Use bit and left the extension pick-up bit as is.
disabling Line In Use
unformatted CID info. Toggles Line In
2
.
Use bit
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: -SCID?
Response: <pmode>
Example: 0 For the default setting.
3-4 Conexant 102752B
Page 29

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+VRID - Report Retrieved Caller ID (CID)
This command reports the data associated with the Caller ID services in the Incoming
Call Line ID (ICLID) data format for the last received call.
Syntax
+VRID=<mode>
Defined Values
<mode> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Reports Caller ID with formatted presentation to
the DTE. The modem presents the data items in a
<Tag><Value> pair format. The expected pairs
are date, time, name, and caller code (telephone
number),
1 Reports Caller ID with unformatted presentation
to the DTE.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +VRID=?
Response: (<mode> range)
Example: (0,1)
102752B Conexant 3-5
Page 30

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
\N - Operating Mode
This command controls the preferred error correcting mode to be negotiated in a
subsequent data connection. This command is affected by the OEM firmware
configuration.
Syntax
\N<mode>
Defined Values
<mode> Decimal number which corresponds to the selected mode.
0 Selects normal speed buffered mode (disables
error-correction mode). (Forces &Q6.)
1 Selects direct mode and is equivalent to &M0,
&Q0 mode of operation. (Forces &Q0.)
2 Selects reliable (error-correction) mode. The
modem will first attempt a LAPM connection
and then an MNP connection. Failure to make a
reliable connection results in the modem hanging
up. (Forces &Q5, S36=4, and S48=7.)
3 Selects auto reliable mode. This operates the
same as \N2 except failure to make a reliable
connection results in the modem falling back to
the speed buffered normal mode. (Forces &Q5,
S36=7, and S48=7.)
4 Selects LAPM error-correction mode. Failure to
make an LAPM error-correction connection
results in the modem hanging up. (Forces &Q5
and S48=0.) Note: The -K1 command can
override the \N4 command.
5 Selects MNP error-correction mode. Failure to
make an MNP error-correction connection
results in the modem hanging up. (Forces &Q5,
S36=4, and S48=128.)
Result Codes
OK <mode> = 0 to 5.
ERROR Otherwise.
3-6 Conexant 102752B
Page 31

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
I - Identification
This command causes the modem to reports the requested result according to the
command parameter.
Syntax
I<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected information.
0 Reports product code, e.g., “56000”.
1 Reports “OK”.
2 Reports “OK”.
3 Reports masked firmware identification code.
Example:
CX93000-V92
4 Reports “OK”
5 Reports Country Code parameter (see +GCI).
6 Reports “OK”.
7 Reports “OK”.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 - 7.
ERROR Otherwise.
+GMI - Request Manufacturer Identification
This command causes the modem to report the modem product manufacturer.
Syntax
+GMI
Typical Response
+GMI: CONEXANT
OK
102752B Conexant 3-7
Page 32

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+GMI9 - Request Conexant Identification
This command causes the modem to report CONEXANT ACF identification.
Syntax
+GMI9
Response
+GMI9: CONEXANT ACF
OK
+GMM - Request Model Identification
This command causes the modem to report the modem product.
Syntax
+GMM
Typical Response
+GMM: V90
+GMR - Request Revision Identification
This command causes the modem to report the modem version, revision level or date.
This is the same as the I3 command.
Syntax
+GMR
Typical Response
+GMR: CX93000-V92
OK
3-8 Conexant 102752B
Page 33

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+GCI - Country of Installation
This extended syntax command selects and indicates the country of installation for the
modem. This parameter selects the settings for any operational parameters that need to be
adjusted for national regulations or telephone networks.
Syntax
+GCI=<country_code>
Defined Values
<country_code> 8-bit country code from Annex A of T.35. The value is the
hexadecimal equivalent of the T.35 code, with bit 8 treated as
the most significant bit and bit 1 treated as the least significant
bit.
The supported countries are listed in the CX930xx modem
data sheet.
Default
If the modem is specified for use in only one country, that country code is the default.
Otherwise, the default is defined by the OEM. Factory default is B5 (United States).
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +GCI?
Response: +GCI: <current country_code>
Example: +GCI: 3D The modem is set for France.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +GCI=?
Response: +GCI: (<country_code>[,<country_code>[,<country_code].......]]
Example: +GCI: (00,B4,B5) The modem can be set for Japan, United
Kingdom, or the United States.
102752B Conexant 3-9
Page 34

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&F - Restore Factory Configuration (Profile)
The modem loads the factory default configuration (profile). The factory defaults are
identified for each command and in the S-Parameter descriptions. A configuration
(profile) consists of a subset of S-Parameters.
Syntax
&F[<value>]
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected configuration.
0 Restore factory configuration 0.
1 Restore factory configuration 1.
Result Codes
OK
ERROR If the modem is connected.
&T - Local Analog Loopback Test
The modem will perform the local analog loopback test if &T1 is selected. The test can
be run only when in an asynchronous operation in non-error-correction mode (normal),
e.g., AT&Q6. To terminate the test in progress, the escape sequence must be entered first
(see Section
3.1.1).
Syntax
&T[<value>]
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Terminates test in progress. Clears S16.
1 Initiates local analog loopback, V.54 Loop 3.
Sets S16 bit 0. If a connection exists when this
command is issued, the modem hangs up. The
CONNECT XXXX message is displayed upon
the start of the test.
3-10 Conexant 102752B
Page 35

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&Y - Designate a Default Reset Profile
This command selects which user profile will be used after a hard reset.
Syntax
&Y<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected profile.
0 The modem will use profile 0.
1 The modem will use profile 1.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 1.
ERROR If <value> > 1, or if NVRAM is not installed or is not
operational.
&W - Store Current Configuration
Saves the current (ac tive) configuration (profile), including S-Parameters, in one of the
two user profiles in NVRAM as denoted by the parameter value. This command will
yield an ERROR message if the NVRAM is not installed or is not operational as detected
by the NVRAM test.
The current configuration is comprised of a list of storable parameters illustrated in the
&V command. These settings are restored to the active configuration upon receiving a Zn
command or at power up (see &Yn command).
Syntax
&W<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected profile.
0 Store the current configuration as profile 0.
1 Store the current configuration as profile 1.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
102752B Conexant 3-11
Page 36

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&Zn=x - Store Telephone Number
The modem can store up to four telephone numbers and each telephone number dial
string can contain up to 31 digits. (Requires 256-byte NVRAM installed.)
Syntax
&Z<value>=<string>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number from 0 to 3 corresponding to the selected
telephone number.
<string> Dial string from 0 to 31 characters.
Result Codes
OK For <value> 3 and <string> 31 digits.
ERROR If <value> > 3 or <string> > 31 digits.
%7 - Plug and Play Serial Number
Sets and stores eight serial numbers in hex format used for serial Plug and Play and for
ISA Plug and Play which use the Conexant 11596 Plug and Play device. Applicable to
Desktop configuration only.
Syntax
%7<8 hex numbers><same 8 hex numbers>
Example
%70000000100000001
Result Codes
OK <8 hex numbers><same 8 hex numbers>
ERROR Otherwise
To display the stored serial number, issue AT"?.
3-12 Conexant 102752B
Page 37

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
%8 - Plug and Play Vendor ID and Product Number
Sets and stores Vendor ID and product number for serial Plug and Play and for ISA Plug
and Play which use the Conexant 11596 Plug and Play device. Applicable to Desktop
configuration only.
Syntax
%8<3 ASCII characters><4 hex numbers><same 3 ASCII characters><same 4 hex
numbers>
Example
%8CXT0324CXT0324
Result Codes
OK
ERROR Otherwise
**- Download Firmware Code
The AT** command allows users to customize modem firmware and add or override
country profiles by uploadin g NVRAM or SRAM patches.
Uploading NVRAM Patch
The NVRAM loader allows NVRAM connected to the modem serial EEPROM bus to be
upgraded with custom patch code. This process transfers the modem patch code from the
host computer to the modem, which transfers the data to the NVRAM device. Uploading
an NVRAM patch to the NVRAM device is a two-step process.
1. When the AT** command is issued, the modem firmware boot loader is invoked and
the user will first load the NVRAM loader into the modem's RAM. The data transfer
is done via an ASCII transfer. The NVRAM loader contains the programming
algorithm for the NVRAM device being programmed.
2. The user will then load the NVRAM patch which the NVRAM loader will then
program into the NVRAM device. This transfer is done via ASCII transfer.
Procedure
1. Put the NVRAM loader (e.g., NVM02-16.S37) and the NVRAM patch file (e.g.,
PatchB3-05-00_NVM.S37) in an appropriate directory on the computer's hard disk.
2. Configure the communications applicat ion program for a DTE rate of between 9600
bps and 115200 bps and RTS/CTS flow control.
3. Check the modem for response by typing AT.
4. Initiate the download process using the AT** command. The “Download initiated ..”
message appears upon issuing the AT** command.
5. Perform an ASCII transfer of the NVRAM loader file (e.g., NVM02-16.S37) from
the host computer to the modem RAM using an industry standard communications
software or an equivalent process (ensure that all ASCII translation or pacing is
turned off).
6. After the NVRAM loader has been loaded perform an AASCI transfer of the
NVRAM patch file (e.g., PatchB3-05-00_NVM.s37) from the host computer to the
102752B Conexant 3-13
Page 38

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
modem RAM using industry standard communications software or an equivalent
process.
Uploading SRAM patch
An internal SRAM patch does not require a loader. The AT** command can be used to
transfer the SRAM patch directly to the modem’s internal RAM. When the AT**
command is issued, the modem firmware boot loader is invoked and the user will transfer
the SRAM patch into the modem's RAM. The data transfer is done via an ASCII transfer.
Procedure
1. SRAM patch file (e.g., PatchB3-05-00_RAM.S37) in an appropriate directory on the
computer's hard disk.
2. Configure the communications applicat i on pr o gram for a DTE rate of between 9600
bps and 115200 bps and RTS/CTS flow control.
3. Check the modem for response by typing AT.
4. Initiate the download process using the AT** command. The “Download initiated ..”
message appears upon issuing the AT** command.
5. Perform an ASCII transfer of the SRAM patch file (e.g., PatchB3-05-00_RAM.s37)
from the host computer to the modem RAM using industry standard communications
software or an equivalent process.
3-14 Conexant 102752B
Page 39

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3.2.2 DTE-Modem Interface commands
The parameters defined in this section control the operation of the interface between the
DTE and modem.
E - Command Echo
The modem enables or disables the echo of characters to the DTE. The parameter value,
if valid, is written to S14 bit 1.
Syntax
E<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the option.
Result Codes
0 Disables command echo.
1 Enables command echo. (Default.)
OK <value> = 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
Q - Quiet Results Codes Control
The command enables or disables the sending of result codes to the DTE. The parameter
value, if valid, is written to S14 bit 2.
Syntax
Q<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the option.
0 Enables result codes to the DTE. (Default.)
1 Disables result codes to the DTE.
Result Codes
OK <value>= 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
102752B Conexant 3-15
Page 40

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
V - Result Code Form
This command selects the sending of short-form or long-form result codes to the DTE.
The parameter, if valid, is written to S14 bit 3.
Syntax
V<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Enables short-form (terse) result codes. Line feed
is not issued before a short-form result code.
1 Enables long-form (verbose) result codes.
(Default.)
Result Codes
OK <value>= 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
W - Connect Message Control
This command, in conjunction with S95 bits 0, 2, 3, and 5 (bits 2, 3, and 5 can be written
directly by the host or by the +MR, +ER, and +DR commands, respectively), control the
format of CONNECT messages (see Section
messages reported reflect the W command setting and the S95 bit settings. (Also see
+MR, +ER, and +DR commands.)
The W parameter value, if valid, is written to S31 bits 2 and 3.
Syntax
W<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Upon connection, the modem reports only the
1 Upon connection, the modem reports the
2 Upon connection, the modem reports the D CE
3.4 and Table 3-5). The actual result code
DTE speed (e.g., CONNECT 19200).
Subsequent responses are disabled. (Default.)
modulation, line speed, the error correction
protocol, and the DTE speed, respectively.
Subsequent responses are disabled.
speed (e.g., CONNECT 14400). Subsequent
responses are disabled.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0, 1, or 2.
ERROR Otherwise.
3-16 Conexant 102752B
Page 41

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
X - Extended Result Codes
This command selects the subset of the result code messages used by the modem to
inform the DTE of the results of commands.
Blind dialing is enabled or disabled by country parameters. If the user wishes to enforce
dial tone detection, a "W" can be placed in the dial string (see D command). The
information below is based upon the default implementation of the X results table.
Table 3-1 indicates the messages which are enabled for eac h X value.
If the modem is in facsimile mode (+FCLASS=1 or 1.0), the only message sent to
indicate a connection is CONNECT without a speed indication.
Syntax
X<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Disables reporting of busy tones unless forced
otherwise by country requirements; send only
OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER,
ERROR, and NO ANSWER result codes. Blind
dialing is enabled/disabled by country
parameters. If busy tone detection is enforced
and busy tone is detected, NO CARRIER will be
reported. If dial tone detection is enforced or
selected and dial tone is not detected, NO
CARRIER will be reported instead of NO DIAL
TONE. The value 000b is written to S22 bits 6,
5, and 4, respectively.
1 Disables reporting of busy tones unless forced
otherwise by country requirements; send only
OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER,
ERROR, NO ANSWER, and CONNECT
XXXX (XXXX = rate). Blind dialing
enabled/disabled by country paramet ers. If busy
tone detection is enforced and busy tone is
detected, NO CARRIER will be reported instead
of BUSY. If dial tone detection is enforced or
selected and dial tone is not detected, NO
CARRIER will be reported instead of NO DIAL
TONE. The value 100b is written to S22 bits 6,
5, and 4, respectively.
102752B Conexant 3-17
Page 42

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
2 Disables reporting of busy tones unless forced
otherwise by country requirements; send only
OK, CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER,
ERROR, NO DIAL TONE, NO ANSWER, and
CONNECT XXXX. If busy tone detection is
enforced and busy tone is detected, NO
CARRIER will be reported instead of BUSY. If
dial tone detection is enforced or selected and
dial tone is not detected, NO DIAL TONE will
be reported instead of NO CARRIER. The value
101b is written to S22 bits 6, 5, and 4,
respectively.
3 Enables reporting of busy tones; send only OK,
CONNECT, RING, NO CARRIER, ERROR,
NO ANSWER, and CONNECT XXXX. Blind
dialing is enabled/disabled by country
parameters. If dial tone detection is enforced and
dial tone is not detected, NO CARRIER will be
reported. The value 110b is written to S22 bits 6,
5, and 4, respectively.
4 Enables reporting of busy tones; send all
messages. The value 111b is written to S22 bits
6, 5, and 4, respectively. (Default.)
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 4.
ERROR Otherwise.
3-18 Conexant 102752B
Page 43

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Table 3-1. Result Codes
Short Form Long Form n Value in ATXn Command Notes
0 1 2 3 4
0 OK x x x x x
1 CONNECT x x x x x
2 RING x x x x x
3 NO CARRIER x x x x x
4 ERROR x x x x x
5 CONNECT 1200 1 x x x x
6 NO DIAL TONE 3 3 x x x
7 BUSY 3 3 3 x x
8 NO ANSWER x x x x x
9 CONNECT 600 1 x x x x
10 CONNECT 2400 1 x x x x
11 CONNECT 4800 1 x x x x
12 CONNECT 9600 1 x x x x
13 CONNECT 7200 1 x x x x
14 CONNECT 12000 1 x x x x
15 CONNECT 14400 1 x x x x
16 CONNECT 19200 1 x x x x
17 CONNECT 38400 1 x x x x
18 CONNECT 57600 1 x x x x
19 CONNECT 115200 1 x x x x
20 CONNECT 230400 x x x x x
22 CONNECT 75TX/1200RX 1 x x x x
23 CONNECT 1200TX/75RX 1 x x x x
24 DELAYED 4 4 4 4 x
25 MESSAGE-WAITING
32 BLACKLISTED 4 4 4 4 x
39 +MRR: 75 x x x x x
40 +MRR: 300 x x x x x
42 +MRR: 600 x x x x x
44 +MRR: 1200/75 x x x x x
45 +MRR: 75/1200 x x x x x
46 +MRR: 1200 x x x x x
47 +MRR: 2400 x x x x x
48 +MRR: 4800 x x x x x
49 +MRR: 7200 x x x x x
50 +MRR: 9600 x x x x x
51 +MRR: 12000 x x x x x
52 +MRR: 14400 x x x x x
53 +MRR: 16800 x x x x x Note 2
54 +MRR: 19200 x x x x x Note 2
55 +MRR: 21600 x x x x x Note 2
56 +MRR: 24000 x x x x x Note 2
57 +MRR: 26400 x x x x x Note 2
58 +MRR: 28800 x x x x x Note 2
59 CONNECT 16800 1 x x x x Note 2
61 CONNECT 21600 1 x x x x Note 2
62 CONNECT 24000 1 x x x x Note 2
63 CONNECT 26400 1 x x x x Note 2
64 CONNECT 28800 1 x x x x Note 2
66 +DR: ALT x x x x x
102752B Conexant 3-19
Page 44

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Short Form Long Form n Value in ATXn Command Notes
0 1 2 3 4
67 +DR: V42B x x x x x
68 +DR: V44 x x x x x
69 +DR: NONE x x x x x
70 +ER: NONE x x x x x
77 +ER: LAPM x x x x x
78 +MRR: 31200 x x x x x Note 2
79 +MRR: 33600 x x x x x Note 2
80 +ER: ALT x x x x x
83 LINE IN USE x x x x x
84 CONNECT 33600 1 x x x x Note 2
85 OFF-HOOK INTRUSION x x x x x
86 LINE REVERSAL DETECTED x x x x x
87 NO LINE x x x x x
91 CONNECT 31200 1 x x x x Note 2
134 +MCR: B103 x x x x x
135 +MCR: B212 x x x x x
136 +MCR: V21 x x x x x
137 +MCR: V22 x x x x x
138 +MCR: V22B x x x x x
139 +MCR: V23 x x x x x
139 +MCR: V23C x x x x x
140 +MCR: V32 x x x x x
141 +MCR: V32B x x x x x
142 +MCR: V34 x x x x x Note 3
145 +MCR: V90 x x x x x Note 3
146 +MCR: V92 x x x x x
147 +MCR: V29 x x x x x
150 +MRR: 32000 x x x x x Note 3
151 +MRR: 34000 x x x x x Note 3
152 +MRR: 36000 x x x x x Note 3
153 +MRR: 38000 x x x x x Note 3
154 +MRR: 40000 x x x x x Note 3
155 +MRR: 42000 x x x x x Note 3
156 +MRR: 44000 x x x x x Note 3
157 +MRR: 46000 x x x x x Note 3
158 +MRR: 48000 x x x x x Note 3
159 +MRR: 50000 x x x x x Note 3
160 +MRR: 52000 x x x x x Note 3
161 +MRR: 54000 x x x x x Note 3
162 +MRR: 56000 x x x x x Note 3
165 CONNECT 32000 x x x x x Note 3
166 CONNECT 34000 x x x x x Note 3
167 CONNECT 36000 x x x x x Note 3
168 CONNECT 38000 x x x x x Note 3
169 CONNECT 40000 x x x x x Note 3
170 CONNECT 42000 x x x x x Note 3
171 CONNECT 44000 x x x x x Note 3
172 CONNECT 46000 x x x x x Note 3
173 CONNECT 48000 x x x x x Note 3
174 CONNECT 50000 x x x x x Note 3
175 CONNECT 52000 x x x x x Note 3
176 CONNECT 54000 x x x x x Note 3
180 CONNECT 28000 x x x x x Note 3
3-20 Conexant 102752B
Page 45

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Short Form Long Form n Value in ATXn Command Notes
0 1 2 3 4
181 CONNECT 29333 x x x x x Note 3
182 CONNECT 30667 x x x x x Note 3
183 CONNECT 33333 x x x x x Note 3
184 CONNECT 34667 x x x x x Note 3
185 CONNECT 37333 x x x x x Note 3
186 CONNECT 38667 x x x x x Note 3
187 CONNECT 41333 x x x x x Note 3
188 CONNECT 42667 x x x x x Note 3
189 CONNECT 45333 x x x x x Note 3
190 CONNECT 46667 x x x x x Note 3
191 CONNECT 49333 x x x x x Note 3
192 CONNECT 50667 x x x x x Note 3
193 CONNECT 53333 x x x x x Note 3
194 CONNECT 54667 x x x x x Note 3
195 +MRR: 28000 x x x x x Note 3
196 +MRR: 29333 x x x x x Note 3
197 +MRR: 30667 x x x x x Note 3
198 +MRR: 33333 x x x x x Note 3
199 +MRR: 34667 x x x x x Note 3
200 +MRR: 37333 x x x x x Note 3
201 +MRR: 38667 x x x x x Note 3
202 +MRR: 41333 x x x x x Note 3
203 +MRR: 42667 x x x x x Note 3
204 +MRR: 45333 x x x x x Note 3
205 +MRR: 46667 x x x x x Note 3
206 +MRR: 49333 x x x x x Note 3
207 +MRR: 50667 x x x x x Note 3
208 +MRR: 53333 x x x x x Note 3
209 +MRR: 54667 x x x x x Note 3
210 +MRR: 25333 x x x x x
211 +MRR: 26667 x x x x x
212 +MRR: 25333 x x x x x
213 +MRR: 22666 x x x x x
214 DIGITAL LINE DETECTED x x x x x
Notes:
1. An 'x' in a column indicates that the message (either the long form if verbose, or the value only for short form) will be
generated when that particular value of 'n' (shown at the top of the column) has been selected by the use of ATXn. If the
column is blank, then no message will be generated for that x option. A numeral indicates which less explicit message
(verbose or short form) will be output for that X option. (Also, see Section 3.3).
2. V.34, V.90, and V.92 models only.
3. V.90 and V.92 models only.
102752B Conexant 3-21
Page 46

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&C - RLSD (DCD) Option
The modem controls the RLSD output in accordance with the parameter supplied. The
parameter value, if valid, is written to S21 bit 5.
Syntax
&C<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 RLSD remains ON at all times.
1 RLSD follows the state of the carrier. (Default.)
Result Codes
OK 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
&D - DTR Option
This command interprets the ON to OFF transition of the DTR signal from the DTE in
accordance with the parameter supplied. The parameter value, if valid, is written to S21
bits 3 and 4. Also, see S25.
Syntax
&D<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 DTR drop is interpreted according to the current
&Qn setting as follows:
&Q0, &Q5, &Q6: DTR is ignored (assumed
ON). Allows operation with DTEs which do not
provide DTR.
&Q1: DTR drop causes the modem to hang up.
Auto-answer is not affected.
&Q2 &Q3: DTR drop causes the modem to hang
up. Auto-answer is inhibited.
3-22 Conexant 102752B
Page 47

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
1 DTR drop is interpreted according to the current
&Qn setting as follows:
&Q0, &Q1, &Q5, &Q6: DTR drop is interpreted
by the modem as if the asynchronous escape
sequence had been entered. The modem returns
to asynchronous command state without
disconnecting.
&Q2 &Q3: DTR drop causes the modem to hang
up. Auto-answer is inhibited.
2 DTR drop is interpreted according to the current
&Qn setting as follows:
&Q0 through &Q6: DTR drop causes the
modem to hang up. Auto-answer is inhibited.
(Default.)
3 DTR drop is interpreted according to the current
&Qn setting as follows:
&Q0, &Q1, &Q5, &Q6: DTR drop causes the
modem to perform a soft reset as if the Z
command were received. The &Y setting
determines which profile is loaded.
&Q2 &Q3: DTR drop causes the modem to hang
up. Auto-answer is inhibited.
If &Q5 or &Q6, is in effect, the action taken is the same as for &Q0.
&K - Flow Control
This command defines the DTE/DCE (terminal/modem) flow control mechanism. The
parameter value, if valid, is written to S39 bits 0, 1, and 2.
Syntax
&K<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Disables flow control.
3 Enables RTS/CTS flow control. (Default for data
modem modes.)
4 Enables XON/XOFF flow control.
5 Enables transparent XON/XOFF flow control.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0, 3, 4, or 5.
ERROR Otherwise.
102752B Conexant 3-23
Page 48

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&M - Asynchronous/Synchronous Mode Selection
This command determines the DTR operating mode. The modem treats the &M
command as a subset of the &Q command.
Syntax
&M<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Selects direct asynchronous operation. The
command sequence &M0\N0 selects normal
buffered mode, but the command sequence
\N0&M0 selects direct mode. This is because the
\N0 command is analogous to the &Q6
command. The value 000b is written to S27 bits
3, 1, and 0, respectively. (See &Q).
1 Selects synchronous connect mode with async
off-line command mode. The value 001b is
written to S27 bits 3, 1, and 0, respectively.
(Serial interface operation only.)
2 Selects synchronous connect mode with async
off-line command mode. Same as &M1 except
that &M2 enables DTR dialing of directory slot
0. The modem will disconnect if DTR is OFF for
more than the period in S25 (in units of
hundredths of a second): the data connection will
be synchronous. The value 010b is written to
S27 bits 3, 1, and 0, respectively. (Serial
interface operation only.)
3 Selects synchronous connect mode. This mode
allows DTR to act as a talk/data switch. The call
is manually initiated while DTR is inactive.
When DTR becomes active, the handshake
proceeds in originate or answer mode according
to S14 bit 7. The value 011b is written to S27
bits 3, 1, and 0, respectively. (Serial interface
operation only.)
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 3
ERROR Otherwise.
3-24 Conexant 102752B
Page 49

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&Q - Sync/Async Mode
This command is an extension of the &M command and is used to control the connection
modes permitted. It is used in conjunction with S36 and S48. (Also, see \N.)
NOTE: When the &Q0 to &Q3 command is issued to select the mode, the subsequent
connect message will report the DCE speed regardless of the W command and S95
settings.
Syntax
&Q<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Selects direct asynchronous operation. The value
000b is written to S27 bits 3, 1, and 0,
respectively. See &M0.
1 Selects synchronous connect mode with async
off-line command mode. The value 001b is
written to S27 bits 3, 1, and 0, respectively. See
&M1. (Serial interface operation only.)
2 Selects synchronous connect mode with async
off-line command mode and enables DTR
dialing of directory 0. The value 010b is written
to S27 bits 3, 1, and 0, respectively. See &M2.
(Serial interface operation only.)
3 Selects synchronous connect mode with async
off-line command mode and enables DTR to act
as Talk/Data switch. The value 011b is written to
S27 bits 3, 1, and 0, respectively. See &M3.
(Serial interface operation only.)
5 The modem will try to negotiate an error-
corrected link. The modem can be configured
using S36 to determine whether a failure will
result in the modem returning on-hook or will
result in fallback to an asynchronous connection.
The value 101b is written to S27 bits 3, 1, and 0,
respectively. (Default.)
6 Selects asynchronous operation in normal mode
(speed buffering). The value 110b is written to
S27 bits 3, 1, and 0, respectively.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 3, 5, or 6
ERROR Otherwise.
102752B Conexant 3-25
Page 50

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&R - RTS/CTS Option
This selects how the modem controls CTS. CTS operation is modified if hardware flow
control is selected (see &K command). The parameter value, if valid, is written to S21 bit
2.
Syntax
&R<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 In sync mode, CTS tracks the state of RTS; the
RTS-to-CTS delay is defined by S26. In async
mode, CTS is normally ON and will turn OFF
only if required by flow control.
1 In sync mode, CTS is always ON (RTS
transitions are ignored). In async mode, CTS is
normally ON and will turn OFF only if required
by flow control.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
&S - DSR Override
This command selects how the modem will control DSR. The parameter value, if valid, is
written to S21 bit 6.
Syntax
&S<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 DSR will remain ON at all times. (Default.)
1 DSR will become active after answer tone has
been detected and inactive after the carrier has
been lost.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
3-26 Conexant 102752B
Page 51

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+IPR - Fixed DTE Rate
This numeric extended-format parameter specifies the data rate at which the modem will
accept commands during online operation. It may be used to select operation at rates at
which the modem is not capable of automatically detecting the data rate being used by
the DTE. Specifying a value of 0 disables the function and allows o perati o n onl y at rates
automatically detectable by the modem. The specified rate takes effect following the
issuance of any result code(s) associated with the current command line.
The <rate> specified does not apply in OnLine Data State if Normal Mode (Direct Mode)
of operation is selected.
Syntax
+IPR=<rate>
Defined Values
<rate> Specifies the DTE-modem interface operation rate in bits/s.
The available rates are: 0, 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600,
19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, or 230400
If unspecified or set to 0, automatic detection is selected and
the character format is also forced to autodetect, +ICF=0.
If the rate specified is not supported by the modem, an
ERROR result code will be returned
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +IPR?
Response: +IPR: <rate>
Example 1: +IPR: 0 For automatic rate detection.
Example 2: +IPR: 115200 For 115200 bps.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +IPR=?
Response: +IPR (<rate> range)
Example: +IPR: (0,300,1200,2400,4800,9600,19200,38400,57600,115200, 230400)
102752B Conexant 3-27
Page 52

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+IFC - DTE-Modem Local Flow Control
This extended-format compound parameter controls the operation of local flow control
between the DTE and the modem during the data state when V.42 error control is used, or
when fallback to non-error control mode is specified to include buffering and flow
control. It accepts two numeric subparameters.
Syntax
+IFC=[<modem_by_DTE>[,<DTE_by_modem>]]
Defined Values
<modem_by_DTE> Specifies the method to be used by the DTE to control the
flow of received data from the modem.
0 None.
1 XON/XOFF on transmitted data (XON/XOFF on
transmit data); do not pass XON/XOFF
characters to the remote modem.
2 Circuit 133 (Ready for Receiving). (Default.)
3 DC1/DC3 on circuit 103 (Transmitted Data) with
DC1/DC3 characters being passed through to the
remote DCE in addition to being acted upon for
local flow control
<DTE_by_modem> Specifies the method to be used by the modem to control the
flow of transmitted data from the DTE.
0 None.
1 XON/XOFF on received data.
2 CTS/RTS. (Default.)
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +IFC?
Response: +IFC: <modem_by_DTE>,<DTE_by_modem>
Example: +IFC: 2,2 For the defaults.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +IFC=?
Response: +IFC: (<modem_by_DTE> range),(<DTE_by_modem> range)
Example: +IFC: (0-3),(0-2)
3-28 Conexant 102752B
Page 53

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+IBC – In Band Commands
This command provides a mechanism by which an in-band secondary channel may be
implemented. This in-band secondary channel can be utilized to transparently exchange
commands and responses to/from the modem during a data connection. This is an
alternative approach to using the +++ escape sequence. The +IBC command also
provides a mechanism to exchange V.24 signaling via the secondary channel. The
primary reason the In Band Channel is implemented is to retrieve Caller ID type II
information.
The supported In Band Channel command is compatible with the ITU-T V.80 standard
but is not a full V.80 implementation. TheV.80 protocol supported is described below.
Portions of the V.80 protocol not desc ri bed are not supported. Please refer Section 7 of
the ITU-T V.80 standard for more details.
Syntax
+IBC=<IB>,<105>,<106>,<107>,<108>,<109>,<110>,<125>,<132>,<133>,<135>,
<142>,<hook>
Defined Values
<IB> Enables or disables in-band control sequence.
0 Disable in-band control sequences.
1 Enable 7-bit in-band control sequences. Ignore
eighth bit.
2 Enable 8-bit in-band control sequences.
<105> Enables or disables circuit number 105: RTS (Ready to Send).
0 Disable in-band reporting for this circuit.
1 Enable in-band reporting for this circuit.
<106> Enables or disables circuit number 106: CTS (Clear to Send).
0 Disable in-band reporting for this circuit.
1 Enable in-band reporting for this circuit.
<109> Enables or disables circuit number 109: DCD (Data Carrier
Detect).
0 Disable in-band reporting for this circuit.
1 Enable in-band reporting for this circuit.
<125> Enables or disables circuit number 125: RI (Ring Indicate).
0 Disable in-band reporting for this circuit.
1 Enable in-band reporting for this circuit.
<other> Not supported; leave ‘0’ for the unsupported circuit types.
<hook> Not supported; leave ‘0’.
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +IBC?
Response: +IBC=<value>,<value>,<value>,0,0,<value>,0,<value>,0,0,0,0,0
Example: +IBC=0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0
102752B Conexant 3-29
Page 54

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +IBC=?
Response: +IBC: (0-2),(0-1),(0-1),0,0,(0-1),0,(0-1),0,0,0,0,0
Entering and Exiting In Band Active State
In Band Command mode will be active only when a modem connection has been made
and DCD is on and the modem is not in command mode. Upon a data connection before
the connect message is sent, an In Band message will be sent to the DTE to notify that all
further data will be EM shielded and should be filtered. Any other time (i.e., command
mode or idle mode) the DTE should allow all user data to be in pass-through mode in
which the data is unfiltered.
The DTE will receive one of the following active messages:
EM<60h><26h><62h>+IBC:1 to indicate In Band is active and the server is V.92
EM<60h><26h><62h>+IBC:2 to indicate In Band is active and the server is non-V.92
Upon Hang up or escape to command mode, the In Band command mode will end and
the DTE should stop filtering EM data and return to pass-through mode.
The DTE will receive the following inactive In Band message:
EM<60h><26h><62h>+IBC:0 to indicate In Band is inactive
EM Shielding Data
When in-band control sequences are enabled, the DTE and the modem must shield and
filter data containing EM. In V.80, in-band data is shielded from normal data by an EM
character represented by a <19h> or <99h>. If the DTE’s data contains an EM, an
additional character is inserted.
For example, sending <19h> from the DTE to the modem requires inserting a
<singleEM> or <5Ch> into the data stream (e.g., <19h><5Ch>). The modem encodes
this as one <19h> in the user data. On the other hand, sending <19h> from the modem to
the DTE requires inserting a <singleEM> or <7Ch>. See
Table 3-2. Please refer to the
V.80 standard for more information.
3-30 Conexant 102752B
Page 55

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Table 3-2. Supported V.80 Commands
Command Hex Codes Description
Supported V.80 DTE-to-DCE Commands
<extend0> <length>
<control> <rest of command>
<105off>
<105on>
<singleEMp>
<doubleEMp>
<singleEM>
<doubleEM>
<poll> <5Eh> The DCE decodes this command and deliver a set of status commands,
<extend0> <length>
<status> <rest of command>
<106off>
<106on>
<109off>
<109on>
<125off>
<125on>
<singleEMp>
<doubleEMp>
<singleEM>
<doubleEM>
<40h>
<42h>
<42h>
<43h>
<58h>
<59h>
<5Ch>
<5Dh>
Supported V.80 DCE-to-DTE Commands
<60h>
<62h>
<62h>
<63h>
<66h>
<67h>
<6Ah>
<6Bh>
<76h>
<77h>
<7Ch>
<7Dh>
The DCE decodes this as a sequence of 3 + (<length>-1Fh).
Circuit 105 is OFF.
Circuit 105 is ON.
The DCE decodes this as one <99h> in user data.
The DCE decodes this as <99h><99h> in user data.
The DCE decodes this as on <19h> in user data.
The DCE decodes this as <19h><19h> in user data.
one for each circuit enabled.
The DCE decodes this as a sequence of 3 + (<length>-1Fh).
Circuit 106 is OFF.
Circuit 106 is ON.
Circuit 109 is OFF.
Circuit 109 is ON.
Circuit 125 is OFF.
Circuit 125 is ON.
The DCE encodes this as one <99h> in user data.
The DCE encodes this as <99h><99h> in user data.
The DCE encodes this as on <19h> in user data.
The DCE encodes this as <19h><19h> in user data.
102752B Conexant 3-31
Page 56

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
In band processing of AT commands
When in-band control sequences are enabled, the modem responds to EM shielded AT
commands via the extend-0 CONTROL sequence. This command may be used to
transmit any AT commands to the modem as follows:
EM <extend-0> <length> <CONTROL> <AT Command without AT and trailing
carriage return>
Upon receipt of an in-band command, the modem responds with the extend-0 STATUS
REPORT sequence. This sequence will contain the response to the AT command issued
via the CONTROL sequence with the trailing <cr> <lf> omitted:
EM <extend-0> <length> <STATUS> <AT Command response without trailing LF>
Example: Send +VRID=2 command to the modem and respond with terse caller ID:
EM <60h> <27h> <42h> +VRID=2
Note: <length> is 27h corresponding to 27h-1Fh=8. This is the length of the sequence
following the <length> octet.
The modem responds to this command by transmitting the caller ID information to the
DTE via the in-band sequence:
EM <60h> <length> <62h> <raw caller ID information>
EM<60h><22h><62h>OK
In this case, the <length> octet is the actual length of the raw caller ID + 1 + 1Fh.
In band signaling of CTS and Ring Indicate (Circuit 106 and Circuit 125)
Whenever the V.24 circuit selected via the +IBC command changes, the modem will
send an unsolicited EM shielded frame to the DTE to inform the DTE of the new state.
This is used for CTS and RI. For MOH applications, the DTE is specifically interested in
circuit 125 (Ring Indicate).
When RI is asserted, the sequence EM <125on> or 19h 6Bh is sent to the DTE.
When RI is de-asserted, the sequence EM <125off> or 19h 6Ah is sent to the DTE.
3-32 Conexant 102752B
Page 57

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3.2.3 Call Control
D - Dial
This command directs the modem to go on-line, dial according to the string entered and
attempt to establish a connection. If no dial string is supplied, the modem will go on-line
and attempt the handshake in originate mode.
NOTE: If the ATD command is issued before the S1 register has cleared, the modem
will respond with the NO CARRIER result code.
If +FCLASS=0 is selected, the modem will behave as a data modem and will attempt to
connect to another data modem. The modem will have up to the period of time specified
by register S6 or S7 to wait for carrier and complete the handshake. If this time expires
before the modem can complete the handshake, the modem will go on-hook with the NO
CARRIER response. This command will be aborted in progress upon receipt of any DTE
character before completion of the handshake.
Dial Modifiers
The valid dial string parameters are described belo w. Pu nc t uat i on cha ract ers may be used
for clarity, with parentheses, hyphen, and spaces being ignored.
Syntax
D<string>
Defined Values
<string> Character string corresponding to the selected option(s).
0-9 DTMF digits 0 to 9.
* The 'star' digit (tone dialing only).
# The 'gate' digit (tone dialing only).
A-D DTMF digits A, B, C, and D. Some countries
may prohibit sending of these digits during
dialing.
L Re-dial last number: the modem will re-dial the
last valid telephone number. The L must be
immediately after the D with all the following
characters ignored).
P Select pulse dialing: pulse dial the numbers that
follow until a "T" is encountered. Affects current
and subsequent dialing. Some countries prevent
changing dialing modes after the first digit is
dialed.
T Select tone dialing: tone dial the numbers that
follow until a "P" is encountered. Affects current
and subsequent dialing. Some countries prevent
changing dialing modes after the first digit is
dialed.
102752B Conexant 3-33
Page 58

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
R This command will be accepted, but not acted
on.
S=n Dial the number stored in the directory (n = 0 to
3). (See &Z.)
! Flash: the modem will go on-hook for a time
defined by the value of S29. Country
requirements may limit the time imposed.
W Wait for dial tone: the modem will wait for dial
tone before dialing the digits following "W". If
dial tone is not detected within the time specified
by S7 (US) or S6 (W-class), the modem will
abort the rest of the sequence, return on-hook,
and generate an error message.
@ Wait for silence: the modem will wait for at least
5 seconds of silence in the call progress
frequency band before continuing wit h the ne xt
dial string parameter. If the modem does not
detect these 5 seconds of silence before the
expiration of the call abort timer (S7), the
modem will terminate the call attempt with a NO
ANSWER message. If busy detection is enabled,
the modem may terminate the call with the
BUSY result code. If answer tone arrives during
execution of this parameter, the modem
handshakes.
& Wait for credit card dialing tone before
continuing with the dial string. If the tone is not
detected within the time specified by S7 (US
models) or S6 (W-class models), the modem will
abort the rest of the sequence, return on-hook,
and generate an error message.
, Dial pause: the modem will pause for a time
specified by S8 before dialing the digits
following ",".
; Return to command state. Added to the end of a
dial string, this causes the modem to return to the
command state after it processes the portion of
the dial string preceding the ";". This allows the
user to issue additional AT commands while
remaining off-hook. The additional AT
commands may be placed in the original
command line following the ";" and/or may be
entered on subsequent command lines. The
modem will enter call progress only after an
additional dial command is issued without the ";"
terminator. Use "H" to abort the dial in progress,
and go back on-hook.
^ Toggles calling tone enable/disable: applicable to
current dial attempt only.
( ) Ignored: may be used to format the dial string.
- Ignored: may be used to format the dial string.
3-34 Conexant 102752B
Page 59

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
<space> Ignored: may be used to format the dial string.
<i> Invalid character: will be ignored.
> If enabled by country specific parameter, the
modem will generate a grounding pulse on the
EARTH relay output.
T - Set Tone Dial Default
This command forces DTMF dialing until the next P dial modifier or P command is
received. The modem will set an S-Parameter bit to indicate that all subsequent dialing
should be conducted in tone mode. The DP command will override this command. Clears
S14 bit 5.
This command may not be permitted in some countries. (See P.)
Result Code
OK
P - Set Pulse Dial Default
This command forces pulse dialing until the next T dial modifier or T command is
received. Sets S14 bit 5.
As soon as a dial command is executed which explicitly specifies the dialing mode for
that particular call (e.g., ATDT...), this command is overridden so that all future dialing
will be tone dialed. (See T command.)
This command may not be permitted in some countries.
Result Code
OK
A - Answer
The modem will go off-hook and attempt to answer an incoming call if correct conditions
are met. Upon successful completion of answer handshake, the modem will go on-line in
answer mode. This command may be affected by the state of Line Current Sense, if
enabled. (Most countries do not require Line Current Sense.) Operation is also dependent
upon +FCLASS command and country-specific requirements.
If +FCLASS=0 is selected, the modem will enter the connect state after exchanging
carrier with the remote modem. If no carrier is detected within a period specified in
register S7, the modem hangs up. Any character entered during the connect sequence will
abort the connection attempt.
102752B Conexant 3-35
Page 60

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
H - Disconnect (Hang-Up)
This command initiates a hang up sequence.
This command may not be available for some countries due to PTT restrictions.
Syntax
H<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 The modem will release the line if the modem is
currently on-line, and will terminate any test
(AT&T) that is in progress. Country specific,
modulation specific, and error correction
protocol specific (S38) processing is handled
outside of the H0 command.
1 If on-hook, the modem will go off-hook and
enter command mode. For US models, the
modem will remain off-hook. For W-class
models, the modem will return on-hook after a
period of time determined by S7.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
3-36 Conexant 102752B
Page 61

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
O - Return to On-Line Data Mode
This command determines how the modem will enter the on-line data mode. If in the online command mode, the modem enters the on-line data mode with or without a retrain. If
in the off-line command mode (no connection), the modem reports ERROR.
Syntax
O<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Enters on-line data mode without a retrain.
Handling is determined by the Call
Establishment task. Generally, if a connection
exists, this command connects the DTE back to
the remote modem after an escape (+++).
1 Enters on-line data mode with a retrain before
returning to on-line data mode.
2 Fast retrain without speed change (used for
diagnostic purpose only).
3 Renegotiate rate without speed change (used for
diagnostic purpose only.
4 Renegotiate rate down one speed (used for
diagnostic purpose only).
5 Renegotiate rate up one speed (used for
diagnostic purpose only).
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 5 and a connection exists.
ERROR Otherwise or if not connected.
102752B Conexant 3-37
Page 62

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
L - Speaker Volume
This command sets the speaker volume control. The parameter value, if valid, is written
to S22 bits 0 and 1.
Syntax
L<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Low volume.
1 Low volume. (Default.)
2 Medium volume.
3 High volume.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 3.
ERROR Otherwise.
M - Speaker Control
This command selects when the speaker will be on or off. The parameter value, if valid,
is written to S22 bits 2 and 3.
Syntax
M<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Speaker is always off.
1 Speaker is on during call establishment, but off
when receiving carrier. (Default.)
2 Speaker is always on.
3 Speaker is off when receiving carrier and during
dialing, but on during answering.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 3.
ERROR Otherwise.
3-38 Conexant 102752B
Page 63

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&G - Select Guard Tone
This command causes the modem to generate the guard tone selected by this command
(DPSK modulation modes only). The parameter value, if valid, is written to S23 bits 6
and 7.
Syntax
&G<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Disables guard tone. (Default.)
1 Disables guard tone.
2 Selects 1800 Hz guard tone.
This command may not be permitted in some countries.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 2.
ERROR Otherwise.
&P - Select Pulse Dial Make/Break Ratio
This command determines the make/break ratio used during pulse dialing. The default is
country-dependent. The parameter value, if valid, is written to S28 bits 3 and 4.
Syntax
&P<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Selects 39%-61% make/break ratio at 10 pulses
per second. (Default.)
1 Selects 33%-67% make/break ratio at 10 pulses
per second.
2 Selects 39%-61% make/break ratio at 20 pulses
per second.
3 Selects 33%-67% make/break ratio at 20 pulses
per second.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 to 3.
ERROR Otherwise.
102752B Conexant 3-39
Page 64

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&V - Display Current Configuration and Stored Profiles
This command reports the current (active) configuration, the stored (user) profiles, and
the first four stored telephone numbers. The stored profiles and telephone numbers are
not displayed if the NVRAM is not installed or is not operational as detected by the
NVRAM test during reset processing.
Result Code
OK
Example:
AT&V
ACTIVE PROFILE:
B1 E1 L1 M1 N0 QO T V1 W0 X4 Y0 &C1 &D2 &G0 &J0 &K3 &Q5
&R1 &S0 &T5 &X0
S00:000 S01:000 S02:043 S03:013 S04:010 S05:008 S06:002
S07:050 S08:001 S09:006
S10:014 S11:085 S12:050 S18:000 S25:005 S26:001 S36:007
S38:020 S46:138
S48:007 S95:000
STORED PROFILE 0:
B1 E1 L1 M1 N0 QO T V1 W0 X4 Y0 &C1 &D2 &G0 &J0 &K3 &Q5
&R1 &S0 &T5 &X0
S00:000 S02:043 S06:002 S07:050 S08:001 S09:006 S10:014
S11:085 S12:050 S18:000
S36:007 S40:104 S41:195 S46:138 S95:000
STORED PROFILE 1:
B1 E1 L1 M1 N0 QO T V1 W0 X4 Y0 &C1 &D2 &G0 &J0 &K3 &Q5
&R1 &S0 &T5 &X0
S00:000 S02:043 S06:002 S07:050 S08:001 S09:006 S10:014
S11:085 S12:050 S18:000
S36:007 S40:168 S41:195 S46:138 S95:000
TELEPHONE NUMBERS:
0 = 1 =
2 = 3 =
OK
3-40 Conexant 102752B
Page 65

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
&V1 - Display Last Connection Statistics
Displays the last connection statistics in the following format (shown with typical
results):
TERMINATION REASON.......... NONE
LAST TX rate................ 26400 BPS
HIGHEST TX rate............. 26400 BPS
LAST RX rate................ 50667 BPS
HIGHEST RX rate............. 50667 BPS
PROTOCOL.................... LAPM
COMPRESSION................. V44
Line QUALITY................ 015
Rx LEVEL.................... 013
Highest Rx State............ 67
Highest TX State............ 67
EQM Sum..................... 008A
RBS Pattern................. 04
Rate Drop................... 00
Digital Loss................ 2000
Local Rtrn Count............ 00
Remote Rtrn Count........... 00
V90
TERMINATION REASON: Call termination reason.
LAST TX rate: Last transmit speed achieved.
HIGHEST TX rate: Highest transmit speed achieved.
LAST RX rate: Last receive speed achieved.
HIGHEST RX rate: Highest transmit rate achieved.
PROTOCOL: Error correction protocol.
COMPRESSION: Data compression pr ot ocol.
Line QUALITY: Quantitative measure of the line quality. A value of 0 indicates no
quality degradation.
Rx LEVEL: Indicates receive level in dBm.
Highest Rx State: Highest handshake receiver state (modulation dependant).
Highest TX State: Highest handshake transmitter state (modulation dependant).
EQM Sum: Eye Quality Monitor Sum. Used by the modem to determine the speed
selection.
RBS Pattern: Indicates the robbed bit pattern (least significant 6 bytes), e.g., 03
indicates 2 robbed bits in positions 0 and 1.
Rate Drop: Indicates speed rate drops from the attempted speed.
Digital Loss: Indicates loss in dB caused by digital pads.
Local Rtrn Count: Number of retrains initiated by the modem.
Remote Rtrn Count: Number of retrains initiated by the remote modem.
V90: Indicates connection mode.
102752B Conexant 3-41
Page 66

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
\V - Single Line Connect Message Enable
This command enables or disables the single line connect message format as follows:
Syntax
\V<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Connect messages are controlled by the
command settings X, W, and S95.
1 Connect messages are displayed in the single
line format described below subject to the
command settings V (Verbose) and Q (Quiet). In
Non-Verbose mode (V0), single line connect
messages are disabled and a single numeric
result code is generated for CONNECT DTE.
When single line connect messages are enabled, there are no CARRIER, PROTOCOL
(+ER:), or COMPRESSION (+DR:) messages apart from the fields described below.
The single line connect message format is:
CONNECT <DTE Speed>/<Modulation>/<Protocol>/<Compression>/
<Line Speed>
Where:
DTE Speed = DTE speed, e.g., 57600.
Modulation = “V92” for V.92 modulation.
“V90” for V.90 modulation.
“V34” for V.34 modulation.
“V32” for V.32 or V.32bis modulation.
Note: Modulation is omitted for all other modulations.
Protocol = “NONE” for no protocol.
“ALT” for Microcom Network Protocol.
“LAPM” for LAP-M protocol.
Compression = “V44” for V.44 compression.
“V42B” for V.42bis compression.
“ALT” for Microcom MNP5 compression.
Note: Compression is omitted if protocol is NONE.
Line Speed = Asymmetric rates are displayed as “/rate:TX/rate:RX”, e.g.,
/1200 TX/75 RX.
Symmetric rates are displayed as a single DCE rate, e.g.,
14400.
3-42 Conexant 102752B
Page 67

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
%L - Report Line Signal Level
Returns a value which indicates the received signal level. The value returned is a direct
indication (DAA dependent) of the receive level at the MDP, not at the telephone line
connector. For example, 009 = -9 dBm, 043 = -43 dBm, and so on.
Result Codes
OK If connected.
ERROR If not connected..
%Q - Report Line Signal Quality
Reports the line signal quality (DAA dependent). Returns the higher order byte of the
EQM value. Based on the EQM value, retrain or fallback/fall forward may be initiated if
enabled by %E1 or %E2.
Example:
AT%Q
015
Result Codes
OK If connected.
ERROR If not connected, or connected in 300 bps or V.23 mode.
*B - Display Blacklisted Numbers
This command requests the modem to return a list of blacklisted numbers to the DTE.
The format of the response is shown by the example below. Permanently forbidden
numbers as defined by country requirements will not appear on this list. If no numbers
are blacklisted, only the OK result code is issued.
Syntax
*B
Example
NO. - PHONE NUMBER -
------ ------------------------------
1; 4175537660
2; 8288924961
3; 3887278862
4; 3124839442
5; 6284664
OK
102752B Conexant 3-43
Page 68

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
*D - Display Delayed Numbers
This command causes the modem to send a list of the delayed numbers together with the
delay associated with each. The modem will return a list of delayed telephone numbers as
defined in the *B command. The format of the response is shown by the example below
(delay times are shown as hours:minutes:seconds ). If no nu mbers are delayed, only the
OK result code is issued.
Syntax
*D
Example
NO. - PHONE NUMBER -DELAY
------ -------------------------------------------
1; 8264734660 2:00:00
2; 7532634661 2:00:00
3; 2587334662 0:02:00
4; 7532651663 0:03:25
5; 7459931664 0:01:45
OK
3-44 Conexant 102752B
Page 69

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
–SLP= - Set Low Power Mode
This command sets the modem low power mode entered when no line connection exists
or when no host activity occurs for the period specified in the S24 register.
Syntax
-SLP=<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option:
0 = Idle mode. The CPU and LSD run at a low
frequency. The modem can detect and qualify
ring signals and process AT commands. The
modem returns to normal mode upon receiving
an AT command or receiving a qualified ring.
1 = Sleep mode. The CPU and LSD run at a lower
frequency than idle mode. The modem can detect
and qualify ring signals. The modem cannot
process AT commands. The modem can be
awakened by the host sending a single (any)
character (typically followed by an AT
command) or by the modem receiving a qualified
ring.
2 = Stop mode. The CPU runs at the same low
frequency as the sleep mode, however, the LSD
is turned off. The modem cannot process AT
commands and cannot detect and qualify ring
signals. The modem can be awakened by the host
sending a single (any) character (typically
followed by an AT command).
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0-2
ERROR Otherwise.
102752B Conexant 3-45
Page 70

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
–STE= - Set Telephony Extension
The –STE command enables/disables Line In Use, Exte nsion Pickup, and Remote
Hangup detection features.
Note: Additional hardware may be required to support these features.
Syntax
-STE=<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected bit-mapped
options. The bit fields are defined as follows:
Bit 0 Line In Use detection enable/disable.
Bit 1 Extension Pickup detection enable/disable.
Bit 2 Remote Hangup detection enable/disable.
<value>
(Dec.)
0 (default) Disabled Disabled Disabled
1 Disabled Disabled Enabled
2 Disabled Enabled Disabled
3 Disabled Enabled Enabled
4 Enabled Disabled Disabled
5 Enabled Disabled Enabled
6 Enabled Enabled Disabled
7 Enabled Enabled Enabled
Remote
Hangup
Extension
Pickup
Line In Use
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: -STE?
Response: -STE: <value>
Example: -STE: 4 Remote Hangup enabled, Extension
Pickup disabled, and Line In Use
disabled.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: -STE=? Show available options.
Response: -STE: 0-7
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0-7
ERROR Otherwise.
3-46 Conexant 102752B
Page 71

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Behavior in Data Mode (+FCLASS=0) and Fax Mode (+FCLASS=1, 1.0)
When on-hook, if the line is in use and an ATDT is issued, the modem will not go offhook and will return with the message LINE IN USE.
When off-hook and either an extension is picked up or a line reversal is detected, the
modem will drop the connection. The disconnect reason in register S86=25 (this is also
defined for #UD). The user must flash the hook in order to get a dial tone due because the
remote server will be retraining.
If the local handset is picked up while the modem is off-hook, the modem will do a linkdisconnect, flash the hook for 1.5 seconds, then connect the local handset to the line. At
this point, the user dial tone should be on the local handset. The disconnect reason in
S86=25.
Behavior in Voice Mode (+FCLASS=8)
When in voice mode and an extension is picked-up, a <DLE>P is sent to the DTE. When
the modem is off-hook , a line reversal may also be detected in which case a <DLE>l is
sent to the DTE.
In voice mode, there is no blocking of ATDT when the line is in use. Also, there is no
automatic hang-up in voice mode as in data mode. There is only the above stated <DLE>
shielding event reporting.
Operation in Data Mode
Line In Use (Enabled by AT-STE=1, AT-STE=3, AT-STE=5, or AT-STE=7)
Case 1: Telephone Line is in Use
If an ATDT, ATDP or ATDL is issued while Line In Use detection is enabled and the
telephone line is in use, the modem will immediately return the message LINE IN USE to
the DTE without going off-hook, and then return to command mode.
Case 2: Telephone Line is in Use But Disconnected
If an ATDT, ATDP or ATDL is issued while Line In Use detection is enabled and the
telephone line is NOT in use, the modem will go off-hook after a short pause, then
respond with CONNECT or NO CARRIER message.
Case 3: Telephone Line is Not Connected to Modem
If an ATDT, ATDP or ATDL is issued while Line In Use detection is enabled and the
telephone line is not connected, the modem will go off-hook momentarily, go back onhook, then respond with NO LINE message.
Extension Pick-up (Enabled by AT-STE=2, AT-STE=3, AT-STE=6, or AT-STE=7):
Case 1: Modem off-hook, Local Handset Goes Off-Hook
If the local handset goes off-hook while the modem is in a data connection, the local
handset will be muted. The modem will then send a GSTN Cleardown to the remote
modem and then go on-hook. The modem will then send an OFF HOOK INTRUSION
message to the DTE. A result code of 25 will be left in S86 register. After 2 seconds, the
local handset will be connected to the telephone line so the user hears the dial tone.
102752B Conexant 3-47
Page 72

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Case 2: Modem off-hook, Extension Pick-up
If the modem is connected and another extension goes off-hook, the modem will send a
GSTN Cleardown to the remote modem and then immediately hang-up. Due to the noise
possibly being added to the line when a telephone extension is picked-up, a GSTN
Cleardown may or may not successfully be received by the remote mode. If the GSTN
Cleardown is not received successfully by the remote modem, the remote modem may
attempt a retrain until the retrain fails and the remote modem drops the line. In any case,
the modem will send an OFF HOOK INTRUSION message to the DTE immediately
after sending the GSTN Cleardown. A result code of 25 will be left in the S86 register.
Because the extension is off-hook, the modem cannot flash the hook for the central office
to generate a dial tone. In this case, the user must flash the extension handset to obtain a
dial tone.
Remote Hang-up (enabled by AT-STE=4, AT-STE=5, AT-STE=6, or AT-STE=7):
Case 1: Modem off-hook, Remote Hang-up
If the modem is connected (off-hook) and the remote modem/server goes hangs up, the
central office may issue a line polarity reversal. If a line polarity reversal is detected, the
modem will drop the call and respond with NO LINE REVERSAL DETECTED. The
reason for hang-up can be determined by #UD or by S8 6=2 5. A line reversal can also be
simulated by simply pulling out the telephone line during a connection.
Operation in Voice Mode
Line In Use (enabled by AT-STE=1, AT-STE=3, AT-STE=5, or AT-STE=7):
This feature does not apply in voice mode.
Extension Pickup (Enabled by AT-STE=2, AT-STE=3, AT-STE=6, or AT-STE=7)
If the modem is off-hook and an extension goes off-hook, the modem issues a <DLE>P
to the DTE. The application software should then hang up the line (VLS=0).
Remote Hang-up (Enabled by AT-STE=4, AT-STE=5, AT-STE=6, or AT-STE=7)
If the modem is off-hook and the remote user goes on-hook, the mod e m issues a
<DLE>P to the DTE. The application software should then hang up the line (VLS=0).
Examples
User is talking on an extension and the modem tries to dial
AT-STE=7
ATDT555-1212
LINE IN USE
3-48 Conexant 102752B
Page 73

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
The line is not in use and the modem tries to dial
AT-STE=7
ATDT555-1212
Modem goes off-hook
CONNECT
An extension is off-hook but there is silence on the line and the modem tries to dial
AT-STE=3
ATDT555-1212
Modem goes off-hook
NO LINE
Modem is connected in data mode and an extension goes off-hook
AT-STE=2
ATDT555-1212
CONNECT
OFF HOOK INTRUSION Extension is picked up, GSTN
Cleardown sent
ATS86=?
025
Modem is connected in data mode and remote modem goes on-hook
AT-STE=4
ATDT555-1212
CONNECT
OFF HOOK INTRUSION Remote modem drops line
ATS86=?
025
102752B Conexant 3-49
Page 74

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Modem is connected in data mode and the LOCAL HANDSET goes off-hook
AT-STE=7
ATDT555-1212 5 sec delay
CONNECT
LINE REVERSAL DETECTED Local handset goes off-hook,
GSTN Cleardown sent, and remote
modem goes on-hook
ATS86=?
025
500 ms after no carrier a dial tone
is heard on the local handset
Modem is in answer machine mode and an extension goes off-hook
AT-STE=2
AT+FCLASS=8
OK
<DLE>h Local handset on-hook
<DLE>R Ring
AT+VLS=1
OK
AT+VSM=1,7200,0,0
AT+VTX Starts to play greeting message
<DLE>P User picks up extension
<DLE>! DTE send abort to end playback
AT+VLS=0 DTE hangs up
3-50 Conexant 102752B
Page 75

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Automated system that needs to periodically use the line while giving the voice user the highest priority
A common use for these features would be an automated system that needs to
periodically use the line while giving the voice user the highest priority.
The automated system would make a connection when the line is free. It would do this
without disturbing the line if the line is in use. The automated system would periodically
retry the connection until the line is free. Once the line is free it would dial and make its
connection. If a voice user wishes to use the line while the modem is connected. The
modem will drop the line and give the line to the user. The modem will then try to regain
control of the line by once again periodically retrying to establish a connection.
AT-STE=7
OK
ATDT5551212
CONNECT
Sometime later, the user picks up
phone
NO CARRIER
ATS86?
25
OK
Delay 30 seconds
ATDT5551212
LINE IN USE
Try again some time later user
hangs up the phone
CONNECT
-TRV – Tip & Ring Voltage
This command allows the host to read the voltage that the modem sees across Tip &
Ring.
Syntax
-TRV
Example
Command: AT-TRV
Response: 1.4
Note: The voltage measurement is read on the opposite of the diode bridge, so the
modem assumes and compensates for the voltage drop across 2 diodes. Therefore, if no
line is connected, the modem will report 1.4V.
102752B Conexant 3-51
Page 76

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
-TTE - Threshold Adjustments for Telephony Extension
This command allows the host to set/tune the telephone extension features for the modem
to determine Line In Use, Extension Pickup, Remote Hang-up, and Digital Line
Protection and Line Interruption Immunity conditions. An ATZ or AT&F will load
default values.
Syntax
-TTE=<Line In Use voltage drop threshold>, <Extension Pickup voltage drop
threshold>, <Remote Hang-up voltage drop threshold>, <Digital Line Protection
current threshold >, <Line Interruption Imm uni t y >,<RES ERVED>
1
Range: (0-9999)
Units: 1/10 volt (first three parameters), 1 mA (fourth parameter), 100 ms (fifth
parameter)
Defined Values
<Line In Use voltage drop threshold>
1000 = 10.00 V drop while modem is on-hook. (Default.)
<Extension Pickup voltage drop threshold>
150 = 1.50 V drop while modem is off-hook; this value must
<Remote Hang-up voltage drop threshold>
500 = 5.00 V drop while modem is off-hook; this value must
<Digital Line Protection current threshold>
160 = 160 mA while modem is off-hook (Default.) :
<Line Interruption Immunity>
0 = 200 ms (Default.)
1 = 200 ms
2 = 200 ms
n (where n > 2) = n*100 ms
<RESERVED> 0 (Default.)
, (0-9999) 1, (0-9999) 1, (0-9999), (0-255), (0-255)
1
1
be less than the Remote Hang-up voltage drop threshold.
(Default.)
1, 2
be greater than the Extension Pickup voltage drop threshold.
(Default.)
Reporting Current or Selected Value
Command: AT-TTE? Queries current setting
Notes:
1. Thresholds are difference thresholds. Example: The line would be considered “in
use” if the Tip & Ring voltage dropped by 10.00 V. Another Example: If the modem
is off-hook and the voltage drops by more than 2.50 V, then the modem would
consider the condition as an extension pickup.
2. The <Remote Hang-up voltage drop threshold> must always be less than the
<Extension Pickup voltage drop threshold). Otherwise, the extension pickup will not
function.
3-52 Conexant 102752B
Page 77

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3.2.4 Modulation Control Commands
+MS - Modulation Selection
This extended-format compound parameter controls the manner of operation of the
modulation capabilities in the modem. It accepts six subparameters.
Syntax
+MS=[<carrier>[,<automode>[,<min_tx_rate>[,<max_tx_rate>[,<min_rx_rate>
[,<max_rx_rate>]]]]]]
Where possible <carrier>, <min_tx_rate>, <max_tx_rate>, <min_rx_rate>, and
<max_rx_rate> values are listed in
Table 3-3. +MS Command Supported Rates
Modulation <carrier> Possible (<min_rx_rate>, <min_rx_rate>, (<min_tx_rate>),
Bell 103 B103 300
Bell 212 B212 1200 Rx/75 Tx or 75 Rx/1200 Tx
V.21 V21 300
V.22 V22 1200
V.22 bis V22B 2400 or 1200
V.23 V23C 1200
V.32 V32 9600 or 4800
V.32 bis V32B 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, or 4800
V.34 V34 33600, 31200, 28800, 26400, 24000, 21600, 19200, 16800,
V.90 V90 56000, 54667, 53333, 52000, 50667, 49333, 48000, 46667,
V.92 downstream V92 56000, 54667, 53333, 52000, 50667, 49333, 48000, 46667,
V.92 upstream V92 48000, 46667, 45333, 44000, 42667, 41333, 40000, 38667,
Table 3-3.
and <max_tx_rate>) Rates (bps)
14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, 4800, or 2400
45333, 44000, 42667, 41333, 40000, 38667, 37333, 36000,
34667, 33333, 32000, 30667, 29333, 28000
45333, 44000, 42667, 41333, 40000, 38667, 37333, 36000,
34667, 33333, 32000, 30667, 29333, 28000
37333, 36000, 34667, 33333, 32000, 30667, 29333, 28000,
26667, 25333, 24000
102752B Conexant 3-53
Page 78

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Defined Values
<carrier> A string which specifies the preferred modem carrier to use in
originating or answering a connection. <carrier> values are
strings of up to eight characters, consisting only of numeric
digits and upper case letters. <carrier> values for ITU standard
modulations take the form: <letter><1-4 digits><other letters
as needed>. Defined values are listed in
Table 3-3.
<automode> A numeric value which enables or disables automatic
modulation negotiation (e.g., ITU -T V.32bis Annex A or V.8).
0 = Automode disabled.
1 = Automode enabled. (Default.)
<min_rx_rate> and <max_rx_rate>
Numeric values which specify the lowest (<min_rx_rate>) and
highest (<max_rx_rate>) rate at which the modem may
establish a receive connection. May be used to condition
distinct limits for the receive direction as distinct from the
transmit direction. Values for this subparameter are decimal
encoded, in units of bit/s. The possible values for each
modulation are listed in
Table 3-3. Actual values will be
limited to possible values corresponding to the entered
<carrier> and fall-back <carrier> as determined during
operation. (Default = lowest (<min_rx_rate>) and highest
(<max_rx_rate>) rate supported by the selected carrier.)
<min_tx_rate> and <max_tx_rate>
Numeric values which specify the lowest (<min_tx_rate>) and
highest (<max_tx_rate>) rate at which the modem may
establish a transmit connection. Non-zero values for this
subparameter are decimal encoded, in units of bit/s. The
possible values for each modulation are listed in
Table 3-3.
Actual values will be limited to possible values corresponding
to the entered <carrier> and fall-back <carrier> as determined
during operation. (Default = lowest (<min_tx_rate>) and
highest (<max_tx_rate>) rate supported by the selected
carrier.)
3-54 Conexant 102752B
Page 79

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +MS?
Response: +MS:<carrier>,<automode>,<min_tx_rate>, <max_tx_rate>,
<min_rx_rate>,<max_rx_rate>
Note: The current active settings are reported under control of the +MR parameter.
Example: +MS: V92, 1,300,48000,300,56000
For default values. This example allows maximum system flexibility to
determine optimal receive and transmit rates during operation.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +MS=?
Response: +MS: (< carrier> range),(<automode> range),(<min_tx_rate> range),
(<max_tx_rate> range), (<min_rx_rate> range), (<max_rx_rate> range)
Example: +MS: (B103,B212,V21,V22,V22B,V23C,V32,V32B,V34,
V90,V92),(0,1),(300-33600),(300-48000),(300-56000),(300-56000)
Result Code
OK Valid subparameter string
ERROR Otherwise.
+MR - Modulation Reporting Control
This extended-format numeric parameter controls whether or not the extended-format
+MCR:<carrier> and +MRR:<rate> intermediate result codes are transmitted from the
modem to the DTE. If enabled, +MCR:<carrier> and +MRR:<rate> intermediate result
codes represent the current (negotiated or renegotiated) modulation <carrier> and <rate>
that are transmitted at the point during connect negotiation (handshaking) at which the
modem has determined which modulation and rate will be used, i.e., before any Error
Control or Data Compression reports are transmitted, and before any final result code
(e.g., CONNECT) is transmitted.
S95 bit 2 is reset to 0 for +MR=0 and is set to a 1 for +MR=1 or +MR=2. The more
recent setting of +MR or S95 bit 2, and the W command setting, determines modulation
result code reporting (see S95 Parameter and W Command).
Syntax
+MR=[<value>]
102752B Conexant 3-55
Page 80

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Defined Values
<value> A decimal number corresponding to the selected option:
0 Disables reporting of modulation connect ion
(+MCR: and +MRR: are not transmitted).
(Default.)
1 Enables reporting of modulation connection
(+MCR: and +MRR: are transmitted with tx rate,
rx rate).
2 Enables reporting of modulation connection
(+MCR: and +MRR: are transmitted with rx rate
only).
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +MR?
Response: +MR: <current value>
Example: +MR: 0 For default setting
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +MR=?
Response: +MR: (<value>range)
Example: +MR: (0-2)
+MCR: Report Syntax
Response: +MCR: <carrier>
<carrier> Alphanumeric code corresponding to the reported carrier.
Defined values are:
B103 For Bell 103
B212 For Bell 212
V21 For V.21
V22 For V.22
V22B For V.22bis
V23C For V.23
V32 For V.32
V32B For V.32bis
V34 For V.34
V90 For V.90
V92 For V.92
3-56 Conexant 102752B
Page 81

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+MRR: Report Syntax
Response: +MRR: <tx_rate>,<rx_rate>
<tx_rate> Decimal transmit rate in bits/s.
<rx_rate> Decimal receive rate in bits/s.
Example: +MRR: 28800, 48000
%E - Enable/Disable Line Quality Monitor and Auto-Retrain or Fallback/Fall Forward
Controls whether or not the modem will automatically monitor the line quality and
request a retrain (%E1) or fall back when line quality is insufficient or fall forward when
line quality is sufficient (%E2). The parameter value, if valid, is written to S41 bits 2 and
6.
If enabled, the modem attempts to retrain for a maximum of 30 seconds.
Syntax
%E<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Disable line quality monitor and auto-retrain.
1 Enable line quality monitor and auto-retrain.
2 Enable line quality monitor and fallback/fall
forward. (Default.)
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0, 1, or 2.
ERROR Otherwise.
Fallback/Fall Forward. When %E2 is active, the modem monitors the line quality
(EQM). When line quality is insufficient, the modem will initiate a rate renegotiation to a
lower speed within the V.34/V.32 bis/V.32 (RC336) modulation speeds. The modem will
keep falling back within the current modulation if necessary until the speed reaches 2400
bps (V.34) or 4800 bps (V.32). Below this rate, the modem will only do retrains if EQM
thresholds are exceeded. If the EQM is sufficient for at least one minute, the modem will
initiate a rate renegotiation to a higher speed within the current modulation speeds. The
rate renegotiations will be done without a retrain if a V.32 bis connection is established.
Speeds attempted during fallback/fall forward are those shown to be available in the rate
sequences exchanged during the initial connection. Fallback/fall forward is availab le in
error correction and normal modes, but not in direct mode or synchronous mode with
external clocks.
102752B Conexant 3-57
Page 82

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
B - CCITT or Bell
When the modem is configured to allow either option, the modem will select Bell or
CCITT modulation for a line speed connection of 300 or 1200 bps. Any other line speed
will use a CCITT modulation standard. The parameter value, if valid, is written to S27 bit
6.
Syntax
B<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Selects CCITT operation at 300 or 1200 bps
during Call Establishment and a subsequent
connection. (Default.)
1 Selects BELL operation at 300 or 1200 bps
during Call Establishment and a subsequent
connection.
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0 or 1.
ERROR Otherwise.
3-58 Conexant 102752B
Page 83

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3.2.5 Error Control Commands
+ES - Error Control and Synchronous Mode Selection
This extended-format command specifies the initial requested mode of operation when
the modem is operating as the originator, optionally specifies the acceptable fallback
mode of operation when the modem is operating as the originator, and optionally
specifies the acceptable fallback mode of operation when the modem is operating as the
answerer. It accepts three numeric subparameters:
Syntax
+ES=[<orig_rqst>[,<orig_fbk>[,<ans_fbk>]]]
Defined Values
<orig_rqst> Decimal number which specifies the initial requested mode of
<orig_fbk> Decimal number which specifies the acceptable fallback mode
operation when the modem is operating as the originator. The
options are:
0 Initiate call with Direct Mode.
1 Initiate call with Normal Mode (also referred to
as Buffered Mode) only.
2 Initiate V.42 without Detection Phase. If V.8 is
in use, disable V.42 Detection Phase.
3 Initiate V.42 with Detection Phase. (Default.)
4 Initiate MNP.
6 Initiate V.80 Synchronous Access Mode when
connection is completed, and Data State is
entered. (See +ESA and +ITF commands.)
7 Initiate Frame Tunneling Mode when connection
is complete, and Data Mode is entered.
of operation when the modem is operating as the originator.
0 LAPM, MNP, or Normal Mode error control
optional. (Default.)
1 LAPM, MNP, or Direct Mode error control
optional.
2 LAPM or MNP error control required;
disconnect if error control is not established.
3 LAPM error control required; disconnect if error
control is not established.
4 MNP error control required; disconnect if error
control is not established.
102752B Conexant 3-59
Page 84

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
<ans_fbk> Decimal number which specifies the acceptable fallback mode
of operation when the modem is operating as the answerer or
specifies V.80 Synchronous Access Mode.
0 Direct Mode.
1 Error control disabled, use Normal Mode.
2 LAPM, MNP, or Normal Mode error control
optional. (Default.)
3 LAPM, MNP, or Direct Mode error control
optional.
4 LAPM or MNP error control required;
disconnect if error control is not established.
5 LAPM error control required; disconnect if error
control is not established.
6 MNP error control required; disconnect if error
control is not established.
8 Initiate V.80 Synchronous Access Mode when
connection is completed, and Data State is
entered (see +ESA and +ITF commands).
9 Initiate Frame Tunneling Mode when connection
is complete, and Data Mode is entered.
Examples
+ES=6 Enable V.80 Synchronous Access Mode originator.
+ES=6 Enable V.80 Synchronous Access Mode originator.
+ES=,,8 Enable V.80 Synchronous Access Mode answerer.
+ES=6,,8 Enable V.80 Synchronous Access Mode originator and answerer.
+ES=3 Enable V.42 with Detection Phase originator. Disable V.80
Synchronous Access Mode originator.
+ES=,,2 Allow LAPM, MNP, or Normal Mode connection answerer. Disable
V.80 Synchronous Access Mode answerer.
+ES=3,,2 Enable V.42 with Detection Phase originator, allow LAPM, MNP, or
Normal Mode connection answer. Disable Synchronous Access Mode
originator and answerer.
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +ES?
Response: +ES: <orig_rqst>,<orig_fbk>,<ans_fbk>
Example: +ES: 3,0,2 For the default setting.
+ES: 6,0,8 For V.80 Synchronous Access Mode
originator and answerer.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +ES=?
Response: +ES: (<orig_rqst> range),( <orig_fbk> range), (<ans_fbk> range)
Example: +ES: (0-4,6,7),(0-4),(0-6,8,9)
3-60 Conexant 102752B
Page 85

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+EB - Break Handling in Error Control Operation
This extended-format compound parameter controls the break handling in V.42
operation. It accepts three numeric subparameters:
Syntax
+EB=[<break_selection>[,<timed>[,<default_length>]]]
Defined Values
<break_selection> Decimal number 0 specifying that break is to be ignored, i.e.,
not signaled to remote DCE.
<timed> Decimal number 0 specifying that any transmitted V.42 L-
SIGNAL will not indicate break signal length
<default_length> Decimal number 0 specifying that break is not delivered to the
DTE.
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +EB?
Response: +EB: <break_selection>,<timed>,<default_length><CR>
Example: +EB: 0,0,0 For default settings.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +EB=?
Response: +EB: (<break_selection> range),(<timed> range),
(default_length> range)
Example: +EB: (0),(0),(0)
+ESR - Selective Repeat
This extended-format numeric parameter controls the use of the selective repeat (SREJ)
option in V.42.
Syntax
+ESR=[<value>]
Decimal number 0 specifying that SREJ is not used.
Reporting Current or Selected Values:
Command: +ESR?
Response: +ESR: <value>
Example: +ESR: 0 For default setting
102752B Conexant 3-61
Page 86

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values:
Command: +ESR=?
Response: +ESR: (<value>)
Example: +ESR: (0)
+EFCS - 32-bit Frame Check Sequence
This extended-format numeric parameter controls the use of the 16-bit or 32-bit frame
check sequence (FCS) option in V.42.
Syntax
+EFCS=[<value>]
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number 0 specifying the use of the 16-bit FCS
specified in V.42.
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +EFCS?
Response: +EFCS: <value>
Example: +EFCS: 0 For default setting.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +EFCS=?
Response: +EFCS: (<value> range)
Example: +EFCS: (0)
3-62 Conexant 102752B
Page 87

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+ER - Error Control Reporting
This extended-format numeric parameter controls whether or not the extended-format
+ER: intermediate result code is transmitted from the modem to the DTE.
S95 bit 3 is reset to 0 for +ER=0 and is set to a 1 for +ER=1. The more recent setting of
+ER or S95 bit 3, and the W command setting, determines the actual error control result
code reporting (see S95 Parameter and W Command).
Syntax
+ER=[<value>]
Defined Values
<value> A decimal number corresponding to the selected error control
option:
0 = Error control reporting disabled (no +ER
intermediate result code transmitted). (Default.)
1 = Error control reporting enabled (+ER
intermediate result code transmitted).
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +ER?
Response: +ER: <current value>
Example: +ER: 0 for the default setting
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +ER=?
Response: +ER: (<value> range)
Example: +ER: (0,1)
102752B Conexant 3-63
Page 88

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+ER: <type>
The +ER: <type> reported represents the current (negotiated or renegotiated) modemmodem error control type. If enabled, the intermediate result code is transmitted at the
point during error control negotiation (handshaking) at which the modem has determined
which error control protocol will be used (if any), before the final result code (e.g.,
CONNECT) is transmitted. The format of this result code is:
The +ER intermediate result code, if enabled, is issued after the Modulation report
(+MCR and +MRR) and before the Data Compression Report (+DR).
Syntax
+ER: <type>
Defined Values
<type> An alphanumeric code corresponding to the selected protocol.
NONE Error control is not in use.
LAPM V.42 LAPM protocol is in use.
ALT MNP is in use.
Example
+ER: LAPM
3-64 Conexant 102752B
Page 89

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+ETBM - Call Termination Buffer Management
This extended-format compound parameter controls the handling of data remaining in
modem buffers upon call termination. It accepts three numeric subparameters:
Syntax
+ETBM=[<pending_TD>[,<pending_RD>[,<timer>]]]
Defined Values
<pending_TD> Decimal number 0 specifying that disconnect will occur
immediately and all buffered transmit data will be discarded
when the local DTE requests call disconnection.
<pending_RD> Decimal number 0 specifying that disconnect will occur
immediately and all buffered receive data will be discarded
when the local DTE requests call disconnection.
<timer> Decimal number 0 specifying that the modem will not attempt
to deliver the buffered data before abandoning the attempt a nd
discarding remaining data.
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +ETBM?
Response: +ETBM: <pending_TD>,<pending_RD>,<timer>
Example: +ETBM: 0,0,0
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +ETBM=?
Response: +ETBM: (<pending_T D> range),(<pending_RD> range),
(<timer> range)
Example: +ETBM: (0),(0),(0)
102752B Conexant 3-65
Page 90

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
\B - Transmit Break to Remote
In non-error correction mode, the modem will transmit a break signal to the remote
modem with a length in multiples of 100 ms according to parameter specified. If a
number in excess of 9 is entered, 9 is used. The command works in conjunction with the
\K command.
In error correction mode, the modem will signal a break through the active error
correction protocol, giving no indication of the length.
Syntax
\B<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
1-9 Break length in 100 ms units. (Default = 3.)
(Non-error corrected mode only.)
Result Codes
OK If connected in data modem mode.
NO CARRIER If not connected in data modem mode.
Note: When the modem receives a break from the remote modem, break is passed to the
DTE as follows: In non-error correction mode direct, the break length is passed; in nonerror correction mode normal and in error correction mode, a 300 ms break is passed.
3-66 Conexant 102752B
Page 91

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
\K - Break Control
Controls the response of the modem to a break received from the DTE or the remote
modem or the \B command. The parameter value, if valid, is written to S40 bits 3, 4, and
5.
Syntax
\K<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
The response is different in three separate states.
The first state is where the modem receives a break from the
DTE when the modem is operating in data transfer mode:
0 Enter on-line command mode, no break sent to
the remote modem.
1 Clear data buffers and send break to remote
modem.
2 Same as 0.
3 Send break to remote modem immediately.
4 Same as 0.
5 Send break to remote modem in sequence with
transmitted data. (Default.)
The second case is where the modem is in the on-line
command state (waiting for AT commands) during a data
connection, and the \B is received in order to send a break to
the remote modem:
0 Clear data buffers and send break to remote
modem.
1 Clear data buffers and send break to remote
modem. (Same as 0.)
2 Send break to remote modem immediately.
3 Send break to remote modem immediately.
(Same as 2.)
4 Send break to remote modem in sequence with
data.
5 Send break to remote modem in sequence with
data. (Same as 4.) (Default.)
102752B Conexant 3-67
Page 92

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
The third case is where a break is received from a remote
modem during a non-error corrected connection:
0 Clears data buffers and sends break to the DTE.
1 Clears data buffers and sends break to the DTE.
(Same as 0.)
2 Send a break immediately to DTE.
3 Send a break immediately to DTE. (Same as 2.)
4 Send a break in sequence with received data to
DTE.
5 Send a break in sequence with received data to
DTE. (Same as 4.) (Default.)
Result Codes
OK 0 to 5.
ERROR Otherwise.
3-68 Conexant 102752B
Page 93

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3.2.6 Data Compression Commands
This section contains parameters to condition modem use of standard ITU-T V.42bis
Data Compression Procedures.
+DS - Data Compression
This extended-format compound parameter controls the V.42bis data compression
function if provided in the modem. It accepts four numeric subparameters:
Syntax
+DS=[<direction>[,<compr_neg>[,<max_dict>[,<max_string>]]]]
Defined Values
<direction> Specifies the desired direction(s) of operatio n of the data
<compr_neg> Specifies whether or not the modem should continue to
<max_dict> Specifies the maximum number of dictionary entries (2048
<max_string> Specifies the maximum string length (32 bytes) to be
compression function; from the DTE point of view.
0 Negotiated; no compression (V.42bis P0=0).
3 both directions, accept any direction (V.42bis
P0=11). (Default.)
operate if the desired result is not obtained.
0 Do not disconnect if V.42bis is not negotiated by
the remote modem as specified in <direction>.
entries) which should be negotiated (may be used by the DTE
to limit the codeword size transmitted, based on its knowledge
of the nature of the data to be transmitted).
negotiated (V.42bis P2).
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +DS?
Response: +DS: <direction>,<compr_neg>,<max_dict>,<max_string>
Example: +DS: 3,0,2048,32 for the defaults and 2048 entry max
dictionary.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +DS=?
Response: +DS: (<direction> range),(< compr_neg > range),
(<max_dict> range),(<max_string> range)
Example: +DS: (0,3),(0),(2048),(32)
102752B Conexant 3-69
Page 94

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+DS44 - V.44 Compression Select
This extended-format compound parameter controls the V.44 data compression function.
Syntax
+DS44=[<direction>[,< compress_negotiation >[,<capability>[,<max_c odewords_tx>
[,<max_codewords_rx>[,<max_string_tx>[,<max_string_rx>[,<max_history_tx>
[,<max_history_rx>]]]]]]]]]
Defined Values
<direction> Decimal number that specifies the desired direction(s) of
operation of the data compression function; from the DTE
point of view.
0 Negotiated, no compression.
3 Both directions, accept any direction. (Default.)
<compress_negotiation> Decimal number that specifies whether or not the modem
should continue to operate if the desired result is not
obtained.
0 Do not disconnect if V.44 is not negotiated by
the remote DCE as specified in <direction>.
(Default.)
<capability> Decimal number that specifies the use of stream method,
packet method, multi-packet method.
0 Stream method. (Default.)
<max_codewords_tx> Decimal number that specifies the maximum number of
codewords which should be negotiated in the transmit
direction. (Default = 512.)
<max_codewords_rx> Decimal number that specifies the maximum number of
codewords which should be negotiated in the receive
direction. (Default = 512.)
<max_string_tx> Decimal number from 32 to 255 that specifies the
maximum string length to be negotiated in the transmit
direction. (Default = 32.)
<max_string_rx> Decimal number from 32 to 255 that specifies the
maximum string length to be negotiated in the receive
direction. (Default = 32.)
<max_history_tx> Decimal number that specifies the maximum size of the
history buffer to be negotiated in the transmit direction.
(Default = 1024.)
<max_history_rx> Decimal number that specifies the maximum size of the
history buffer to be negotiated in the receive direction.
(Default = 1024.)
3-70 Conexant 102752B
Page 95

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +DS44?
Response: +DS44: <direction>,<compression_negotiation>,<capability>,
<max_codewords_tx>,<max_codewords_rx>,<max_string_tx>,
<max_string_rx>,<max_history_tx>,<max_history_rx>
Example: +DS44: 3,0,0,512,512,32,32,1024,1024 For the default setting.
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +DS44=?
Response: +DS44: (list of supported <direction> values),(list of supported
<compression_negotiation> values),(list of supported <capability>
values),(list of supported <max_codewords_tx> values),(list of supported
<max_codewords_rx> values),(lis t of su p po rte d <m ax_st ring_tx>
values),(list of supported <max_string_rx> values),(list of supported
<max_history_tx> values),(list of supported <max_history_rx> values)
+DR - Data Compression Reporting
This extended-format numeric parameter controls whether or not the extended-format
+DR: intermediate result code is transmitted from the modem to the DTE.
S95 bit 5 is reset to 0 for +DR=0 and is set to a 1 for +DR=1. The more recent setting of
+DR or S95 bit 5, and the W command setting, determines the actual data compression
result code reporting (see S95 Parameter and W Command).
Syntax
+DR=[<value>]
Defined Values
<value> decimal number corresponding to the selected option:
0 Data compression reporting disabled (no +DR
result code transmitted). (Default.)
1 Data compression reporting enabled (+DR result
code transmitted).
Reporting Current or Selected Values
Command: +DR?
Response: +DR: <current value>
Example: +DR: 0 For the default setting.
102752B Conexant 3-71
Page 96

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
Reporting Supported Range of Parameter Values
Command: +DR=?
Response: +DR: (<value> range)
Example: +DR: (0,1)
+DR: <type> Intermediate Result Code
The +DR: <type> reported represents the current (negotiated or renegotiated) modemmodem data compression type. If enabled, the intermediate result code is transmitted at
the point after error control negotiation (handshaking) at which the modem has
determined which data compression technique will be used (if any) and the direction of
operation. The +DR intermediate result code, if enabled, is issued after the Error Control
Report (+ER) and before the final result code (e.g., CONNECT).
The format of this result code is:
Result Code Syntax
+DR: <type>
Defined Values
<type> An alphanumeric code corresponding to the selected option:
NONE Data compression is not in use.
V42B V.42bis is in use in both directions.
V42B RD V.42 bis is in use in receive direction only
V42B TD V.42 bis is in use in transmit direction only
V44 V.44 is in use in both directions
V44 RD V.44 is in use in receive direction only
V44 TD V.44 is in use in transmit direction only
ALT MNP 5 compression.
Example
+DR: V42B
3-72 Conexant 102752B
Page 97

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
%C - Enable/Disable Data Compression
Enables or disables data compression negotiation. The modem can only perform data
compression on an error corrected link. The parameter value, if valid, is written to S41
bits 0 and 1.
Syntax
%C<value>
Defined Values
<value> Decimal number corresponding to the selected option.
0 Disables data compression. Resets S46 bit 1.
1 Enables MNP 5 data compression negotiation.
Resets S46 bit 1.
2 Enables V.42 bis data compression. Sets S46
bit 1.
3 Enables both V.42 bis and MNP 5 data
compression. Sets S46 bit 1. (Default.)
Result Codes
OK <value> = 0, 1, 2, or 3.
ERROR Otherwise.
102752B Conexant 3-73
Page 98

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
3.2.7 Synchronous Access Mode Commands
Three commands support Synchronous Access Mode:
+ES Enables and disables Synchronous Access Mode in the client
or central site modem
+ESA Configures the operation of the Synchronous Access Submode
+ITF Selects Transmit Flow Control Thresholds
Enabling Synchronous Access Mode enables the use of the 8-bit command characters
defined in Table 9/V.80 of the Draft ITU-T Recommendation V.80 (DATA
COMMUNICATION OVER THE TELEPHONE NETWORK; In-Band DCE Control
and Synchronous Data Modes for Asynchronous DTE).
+ESA - Configure Synchronous Access Submode
The operation of the Synchronous Access sub-Mode is configured by the +ESA
parameter.
This extended-format compound parameter is used to control the manner of operation of
the Synchronous Access Mode in the modem. It accepts six numeric subparameters:
Syntax
+ESA=[<trans_idle>[,<framed_idle>[,<framed_un_ov>[,<hd_auto>[,<crc_type>[,<
nrzi_en>[,<syn1>[,<syn2>]]]]]]]]
Defined Values
<trans_idle> Specifies the bit sequence transmitted by the modem when a
transmit data buffer underrun condition occurs, while
operating in Transparent sub-Mode. The options are:
0 In Transparent sub-Mode, modem transmits 8-bit
SYN sequence on idle. Modem receiver does not
hunt for synchronization sequence (default and
fixed).
<framed_idle> Specifies the bit sequence transmitted by the modem when a
transmit data buffer underrun condition occurs immediately
after a flag, while operating in Framed sub-Mode. The options
are:
0 In Framed sub-Mode, modem transmits HDLC
flags on idle (default and fixed).
<framed_un_ov> Specifies the actions undertaken by the modem when a
transmit data buffer underrun or overrun condition occurs
immediately after a non-flag octet, while operating in Framed
sub-Mode.
0 In Framed sub-Mode, modem transmits abort on
underrun in middle of frame (default).
1 In Framed sub-Mode, DCE transmits a flag on
underrun in middle of frame, and notifies DTE of
underrun or overrun.
3-74 Conexant 102752B
Page 99

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
<hd_auto> Specifies whether or not, in V.34 half-duplex operation,
additional procedures besides those specified in § 12/V.34
shall be performed by the modem when switching from
primary channel to secondary channel operation, and vice
versa. This subparameter should not be commanded.
<crc_type> Specifies the CRC polynomial used while operating in Framed
sub-Mode. The options are:
0 CRC generation and checking disabled (default).
1 In Framed sub-Mode, the 16-bit CRC is
generated by the modem in the transmit
direction, and checked by the modem in the
receive direction.
<nrzi_en> Specifies if Non Return to Zero Inverted (NRZI) encoding is
to be used by the modem for transmit and receive data. The
options are:
0 NZRI encoding and decoding disabled (default
and fixed).
<syn1>, <syn2> Specifies the octet value(s) to be used while p e rforming
character-oriented framing. <syn1> is to be commanded to
255 (FFh); <syn2> is not to be commanded.
Reporting Selected Options
The modem reports the selected options in response to the following command:
+ESA?
The response is:
+ESA: <trans_idle>,<framed_idle>,<framed_un_ov>,<hd_auto>,
<crc_type>,<nrzi_en>,<syn1>,<syn2>
Example:
+ESA?
+ESA: 0,0,0, ,0,0,255, For the defaults.
Reporting Supported Options
The modem reports the supported options in response to the following command:
+ESA=?
The response is:
+ESA: (list of supported <trans_idle> values), (list of supported <framed_idle>
values),(list of supported <framed_un_ov> values) , (list of supported <hd_auto>
values),(list of supported <crc_type> values), (list of supported <nrzi_en> values),
(list of supported <syn1> values), (list of supported <syn2> values)
Example:
+ESA=?
+ESA: (0),(0),(0-1), ,(0-1),(0),(255 ),
102752B Conexant 3-75
Page 100

AT Commands for CX930xx Modem Reference Manual
+ITF - Transmit Flow Control Thresholds
The +ITF command determines the flow control thresholds used by the modem for
transmit data from the DTE.
This optional compound parameter allows the DTE to determine the input buffer size in
the modem for data on circuit 103 (transmit data) from the DTE, to control the thresholds
used for flow control of such data, and to control how often the modem reports to the
DTE the number of octets in this buffer. The DTE can adjust its own thresholds for flow
control of data on circuit 104 (received data) from the modem.
Syntax
+ITF=[<off>[,<on>[,<report_period>]]]
Defined Values
<off> Determines the threshold, in octets, above which the modem
will generate a flow off signal. Applicable in Synchronous
Access and Frame Tunneling modes. Default <off> value is
255.
For the <on> and <off> subparameters, the input buffer is
assumed to reside between the modem’s V.24 interface and
the Synchronous Access protocol layer; i.e., the buffer count
includes all octets, including EM codes, received from the
DTE, with the exception of DC1 and DC3 if these are used to
signal <modem-by-DTE> flow control.
The modem returns the ERROR result code if the DTE
specifies that the <off> subparameter be set to a value less
than or equal to the <on> subparameter; in this case, the
current parameter value settings are not modified.
<on> Determines the threshold, in octets, below which the modem
will generate a flow on signal. Applicable in Synchronous
Access and Frame Tunneling modes. Default <on> value is
64.
<report_period> Not supported. A fixed value of zero is used and reported.
Reporting Selected Options
The modem sends a string of information text to the DTE consisting of selected
options in response to the following command:
+ITF?
The response is:
+ITF: <off>,<on>,<report_period>
Example:
+ITF?
+ITF: 255,64,0 Default values
3-76 Conexant 102752B
 Loading...
Loading...