Page 1

USER GUIDE
Wireless-G
ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Model No: WAG310G (E2)
Page 2

About This Guide
Icon Descriptions
While reading through the User Guide you may see
various icons that call attention to specific items. Below is
a description of these icons:
NOTE: This check mark indicates that there is
a note of interest and is something that you
should pay special attention to while using the
product.
WARNING: This exclamation point indicates
that there is a caution or warning and it is
something that could damage your property or
product.
About This Guide
WEB: This globe icon indicates a noteworthy
website address or e-mail address.
Online Resources
Website addresses in this document are listed without
http:// in front of the address because most current web
browsers do not require it. If you use an older web browser,
you may have to add http:// in front of the web address.
Resource Website
Linksys www.linksys.com
Linksys International www.linksys.com/international
Glossary www.linksys.com/glossary
Network Security www.linksys.com/security
Copyright and Trademarks
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco
Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain
other countries. Copyright © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All
rights reserved. Other brands and product names are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
holders.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
i
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Product Overview 4
Front Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Top Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Back Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Chapter 2: Wireless Security Checklist 6
General Network Security Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Additional Security Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Chapter 3: Advanced Conguration 7
Setup > Basic Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Setup > DDNS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Setup > Advanced Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Wireless > Basic Wireless Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Wireless > Wireless Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Wireless > Wireless Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Wireless > Advanced Wireless Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Security > Firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Security > VPN Passthrough. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Access Restrictions > Internet Access Policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Applications and Gaming > Single Port Forwarding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Applications and Gaming > Port Range Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Applications & Gaming > Port Range Triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Applications and Gaming > DMZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Applications and Gaming > QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Administration > Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Administration > Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Administration > Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Administration > Backup & Restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Administration > Firmware Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Status > Gateway. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Status > Local Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Status > Wireless . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Status > DSL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 27
Appendix B: Specications 2
Appendix C: Warranty Information 2
Appendix D: Regulatory Information 3
FCC Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Safety Notices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Industry Canada Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Avis d’Industrie Canada. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
8
9
0
ii
Page 4

Declaration of Conformity with Regard to EU Directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive) . .31
CE Marking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
National Restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Product Usage Restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Technical Documents on www.linksys.com/international . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
User Information for Consumer Products Covered by EU Directive 2002/96/EC on Waste
Electric and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Table of Contents
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
iii
Page 5

Chapter 1
Product Overview
Chapter 1:
Product Overview
Thank you for choosing the Linksys Wireless-G ADSL2+
IAD Gateway. IAD stands for Integrated Access Device.
The Gateway lets you access the Internet via a wireless
connection or through one of its four switched ports. It also
connects to a traditional phone line, the Public Switched
Telephone Network (PSTN), so you can make calls using
the traditional service or Voice over IP (VoIP).
You can also use the Gateway to share resources such as
computers, printers and files. A variety of security features
help to protect your data and your privacy while online.
Security features include WPA2 security, a Stateful Packet
Inspection (SPI) firewall and NAT technology. Configuring
the Gateway is easy using the provided browser-based
utility.
Front Panel
Security (Green/Red) The Security LED lights
up when wireless security is enabled. It flashes
during the Wi-Fi Protected Setup process. The
LED becomes red when wireless security is
disabled.
USB Green. The USB LED lights up when the
Gateway is connected to a device through the
USB port. It flashes to indicate USB activity.
Phone 1-2 (Green) The Phone 1 or 2 LED
lights up when a phone is connected to the
corresponding port on the Gateway’s back
panel. It flashes when the phone is being used.
Line (Green) The Line LED lights up when the
Gateway is connected to the Public Switched
Telephone Network (PSTN) through the Line
port. It flashes when the phone line is in use.
DSL (Green) The DSL LED lights up when there
is a DSL connection. It flashes when the Gateway
is establishing the ADSL connection.
Internet (Green/Red) The Internet LED lights
up when the Gateway is connected to the
Internet. It flashes to indicate network activity
over the Internet port. The LED becomes red
when the Internet connection fails.
Power (Green/Red) The Power LED lights up
when the Gateway is powered on. It flashes
during the self-test. The LED becomes red
during a malfunction.
Ethernet 1-4 (Green) These numbered LEDs,
corresponding with the numbered Ethernet
ports on the Gateway’s back panel, serve two
purposes. If the LED is continuously lit, the
Gateway is connected to a device through that
port. It flashes to indicate network activity over
that port.
WAN/LAN 5 (Green) The WAN/LAN 5 LED
corresponds with the WAN/LAN5 port and
serves two purposes. If the LED is continuously
lit, the Gateway is successfully connected to a
device through that port. It flashes to indicate
network activity over that port.
Traffic (Green) The Traffic LED lights up when
the wireless feature is enabled. It flashes when
the Gateway is sending or receiving data over
the wireless network.
Top Panel
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
4
Page 6

Chapter 1
Product Overview
Wi-Fi Protected Setup If you have client
devices, such as a wireless adapter, that supports
Wi-Fi Protected Setup, then you can use Wi-Fi
Protected Setup to automatically configure
wireless security for your wireless network(s).
If your client device has a Wi-Fi Protected Setup
button, click or press that button. Then click the
Wi-Fi Protected Setup button on the Gateway’s
top panel.
If your client device asks for the Gateway’s PIN
number, enter this number: 88888888 on your
client device.
The Wi-Fi Protected Setup process is automatic.
Back Panel
Reset There are two ways to reset the Gateway’s
factory defaults. Either press and hold the Reset
button for approximately five seconds, or restore
the defaults from the Administration > Factory
Defaults screen of the Gateway’s web-based
utility.
NOTE: To safely wall mount this unit,
the side panel with antenna must face
upward.
NOTE: You can also use the Wi-Fi
Protected Setup feature through
the Wireless > Basic Wireless Settings
screen of the Gateway’s web-based
utility.
DSL The DSL port connects to the ADSL line.
Line The Line port connects to the Public
Switch Telephone Network (PSTN).
Phone 1-2 The Phone ports connect standard
analog telephones to the Gateway.
USB The USB port connects to a USB device.
Ethernet WAN/LAN5 The WAN/LAN5 port can
act as a WAN (Internet) or LAN (local network)
port. As a WAN port, it connects to a broadband
modem. As a LAN port, it connects to a wired
computer or other Ethernet network device.
Ethernet LAN 1-4 These Ethernet ports (1, 2,
3, 4) connect the Gateway to wired computers
and other Ethernet network devices.
Power Switch Use this switch to power on or
off the Gateway.
Power The Power port is where you will
connect the power adapter.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
5
Page 7

Chapter 2
Wireless Security Checklist
Chapter 2:
Wireless Security Checklist
Wireless networks are convenient and easy to install, so
homes with high-speed Internet access are adopting them
at a rapid pace. Because wireless networking operates by
sending information over radio waves, it can be more
vulnerable to intruders than a traditional wired network.
Like signals from your cellular or cordless phones, signals
from your wireless network can also be intercepted. Since
you cannot physically prevent someone from connecting
to your wireless network, you need to take some additional
steps to keep your network secure.
1. Change the default wireless
network name or SSID
Wireless devices have a default wireless network name
or Service Set Identifier (SSID) set by the factory. This
is the name of your wireless network, and can be up
to 32 characters in length. Linksys wireless products
use linksys as the default wireless network name. You
should change the wireless network name to something
unique to distinguish your wireless network from other
wireless networks that may exist around you, but do not
use personal information (such as your Social Security
number) because this information may be available for
anyone to see when browsing for wireless networks.
2. Change the default password
For wireless products such as access points, routers, and
gateways, you will be asked for a password when you
want to change their settings. These devices have a default
password set by the factory. The Linksys default password
is admin. Hackers know these defaults and may try to
use them to access your wireless device and change your
network settings. To thwart any unauthorized changes,
customize the device’s password so it will be hard to
guess.
4. Enable encryption
Encryption protects data transmitted over a wireless
network. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA/WPA2) and Wired
Equivalency Privacy (WEP) offer different levels of security
for wireless communication.
A network encrypted with WPA/WPA2 is more secure
than a network encrypted with WEP, because WPA/WPA2
uses dynamic key encryption. To protect the information
as it passes over the airwaves, you should enable the
highest level of encryption supported by your network
equipment.
WEP is an older encryption standard and may be the
only option available on some older devices that do not
support WPA.
General Network Security Guidelines
Wireless network security is useless if the underlying
network is not secure.
Password protect all computers on the network and
•
individually password protect sensitive files.
Change passwords on a regular basis.
•
Install anti-virus software and personal firewall
•
software.
Disable file sharing (peer-to-peer). Some applications
•
may open file sharing without your consent and/or
knowledge.
Additional Security Tips
Keep wireless routers, access points, or gateways away
•
from exterior walls and windows.
Turn wireless routers, access points, or gateways
•
off when they are not being used (at night, during
vacations).
Use strong passphrases that are at least eight characters
•
in length. Combine letters and numbers to avoid using
standard words that can be found in the dictionary.
3. Enable MAC address filtering
Linksys routers and gateways give you the ability to
enable Media Access Control (MAC) address filtering. The
MAC address is a unique series of numbers and letters
assigned to every networking device. With MAC address
filtering enabled, wireless network access is provided
solely for wireless devices with specific MAC addresses.
For example, you can specify the MAC address of each
computer in your home so that only those computers can
access your wireless network.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
WEB: For more information on wireless
security, visit www.linksys.com/security
6
Page 8
Chapter 3
Chapter 3:
Advanced Configuration
After setting up the Gateway with the Setup Wizard
(located on the CD-ROM), the Gateway will be ready
for use. However, if you’d like to change its advanced
settings, use the Gateway’s web-based utility. This chapter
describes each web page of the utility and each page’s key
functions. You can access the utility via a web browser on
a computer connected to the Gateway.
The web-based utility has these main tabs: Setup,
Wireless, Security, Access Restrictions, Applications &
Gaming, Administration, and Status. Additional tabs will
be available after you click one of the main tabs.
NOTE: When first installing the Gateway, you
should use the Setup Wizard on the Setup CDROM. If you want to configure advanced settings,
use this chapter.
Advanced Configuration
How to Access the Web-Based Utility
To access the web-based utility, launch the web browser
on your computer, and enter the Gateway’s default IP
address, 192.168.1.1, in the Address field. Then, press
Enter.
A login screen appears. The first time you open the webbased utility, use the default user name and password,
admin. (You can set a new user name and password from
the Administration tab’s Management screen.) Click OK to
continue.
Login Screen
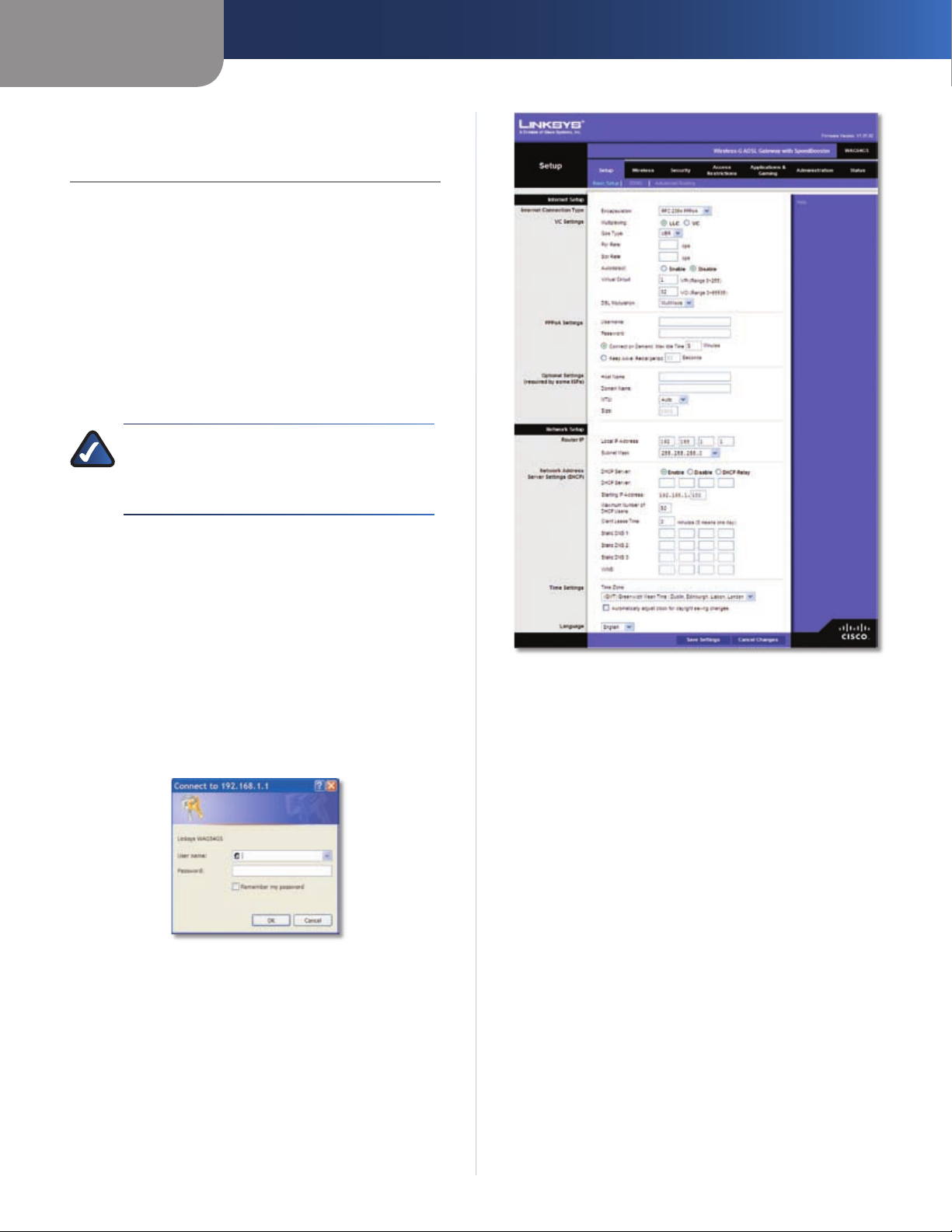
Setup > Basic Setup
Setup > Basic Setup
Internet Setup
The Internet Setup section configures the Gateway to
your Internet connection. Most of this information can be
obtained through your ISP.
Internet Connection Type
The Gateway supports six encapsulation methods. Select
the appropriate type of encapsulation from the dropdown menu. Each Basic Setup screen and available features
will differ depending on what type of encapsulation you
select. These are the available types:
RFC 2364 PPPoA
•
RFC 2516 PPPoE
•
RFC 1483 Routed
•
The first screen that appears is the Basic Setup screen. This
allows you to change the Gateway’s general settings.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
IPoA
•
RFC 1483 Bridged
•
Bridge Mode Only
•
VC Settings
Configure your Virtual Circuit (VC) settings in this section.
Multiplexing Select LLC or VC, depending on your ISP.
7
Page 9

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
QoS Type Select from the drop-down menu: CBR
(Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed bandwidth for voice
or data traffic; UBR (Unspecific Bit Rate) for application that
are not time-sensitive, such as e-mail; or VBR (Variable Bit
Rate) for bursty traffic and bandwidth-sharing with other
applications.
Pcr Rate For the Peak Cell Rate (PCR), divide the DSL line
rate by 424 to get the maximum rate the sender can send
cells. Enter the rate in the field (if required by your service
provider).
Scr Rate The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell
rate that can be transmitted. The SCR value is normally less
than the PCR value. Enter the rate in the field (if required
by your service provider).
Autodetect Select Enable to have the settings
automatically entered, or select Disable to enter the
values manually.
Virtual Circuit These fields consist of two items: VPI
(Virtual Path Identifier) and VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier).
Enter the settings provided by your ISP.
DSL Modulation Select the appropriate mode:
MultiMode, T1.413, G.dmt, G.lite, ADSL2, or ADSL2+.
Contact your ISP if you are not sure which mode to use.
inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Gateway to
automatically re-establish your connection as soon as you
attempt to access the Internet again. To use this option,
select Connect on Demand. In the Max Idle Time field,
enter the number of minutes you want to have elapsed
before your Internet connection terminates. The default
Max Idle Time is 5 minutes.
Keep Alive: Redial Period If you select this option,
the Gateway will periodically check your Internet
connection. If you are disconnected, then the Gateway
will automatically re-establish your connection. To use
this option, select Keep Alive. In the Redial Period field,
you specify how often you want the Gateway to check
the Internet connection. The default Redial Period is
30 seconds.
RFC 2516 PPPoE
Some DSL-based ISPs use PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol
over Ethernet) to establish Internet connections. If you are
connected to the Internet through a DSL line, check with
your ISP to see if they use PPPoE. If they do, you will have
to enable PPPoE.
Follow the instructions for your type of encapsulation.
RFC 2364 PPPoA
Some DSL-based ISPs use PPPoA (Point-to-Point Protocol
over ATM) to establish Internet connections. If you are
connected to the Internet through a DSL line, check with
your ISP to see if they use PPPoA. If they do, you will have
to enable PPPoA.
Internet Connection Type > RFC 2364 PPPoA
PPPoA Settings
Username and Password Enter the Username and
Password provided by your ISP.
Connect on Demand: Max Idle Time You can configure
the Gateway to cut the Internet connection after it has
been inactive for a specified period of time (Max Idle Time).
If your Internet connection has been terminated due to
Internet Connection Type > RFC 2516 PPPoE
PPPoE Settings
Username and Password Enter the Username and
Password provided by your ISP.
Connect on Demand: Max Idle Time You can configure
the Gateway to cut the Internet connection after it has
been inactive for a specified period of time (Max Idle Time).
If your Internet connection has been terminated due to
inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Gateway to
automatically re-establish your connection as soon as you
attempt to access the Internet again. To use this option,
select Connect on Demand. In the Max Idle Time field,
enter the number of minutes you want to have elapsed
before your Internet connection terminates. The default
Max Idle Time is 5 minutes.
Keep Alive: Redial Period If you select this option,
the Gateway will periodically check your Internet
connection. If you are disconnected, then the Gateway
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
8
Page 10

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
will automatically re-establish your connection. To use
this option, select Keep Alive. In the Redial Period field,
you specify how often you want the Gateway to check
the Internet connection. The default Redial Period is
30 seconds.
RFC 1483 Routed
If you are required to use RFC 1483 Routed, then select
RFC 1483 Routed.
Internet Connection Type > RFC 1483 Routed
IP Settings
Your ISP provides these settings.
Internet IP Address Enter the Gateway’s IP address, as
seen from the Internet.
Subnet Mask Enter the Gateway’s Subnet Mask, as seen
from the Internet (including your ISP).
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the ISP server.
Primary (Required) and Secondary (Optional)
DNS Enter the DNS (Domain Name System) server IP
address(es) provided by your ISP. At least one is required.
RFC 1483 Bridged
If you are required to use RFC 1483 Bridged, then select
RFC 1483 Bridged.
IP Settings
Your ISP provides these settings.
Internet IP Address Enter the Gateway’s IP address, as
seen from the Internet.
Subnet Mask Enter the Gateway’s Subnet Mask, as seen
from the Internet (including your ISP).
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the ISP server.
Primary (Required) and Secondary (Optional)
DNS Enter the DNS (Domain Name System) server IP
address(es) provided by your ISP. At least one is required.
IPoA
If you are required to use IPoA (IP over ATM), then select
IPoA.
Internet Connection Type > RFC 1483 Bridged
IP Settings
Select Obtain an IP Address Automatically if your ISP
says you are connecting through a dynamic IP address.
If you are required to use a permanent (static) IP address
to connect to the Internet, then select Use the following
IP Address. Your ISP provides the settings needed for the
following fields:
Internet IP Address Enter the Gateway’s IP address, as
seen from the Internet.
Subnet Mask Enter the Gateway’s Subnet Mask, as seen
from the Internet (including your ISP).
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the ISP server.
Primary (Required) and Secondary (Optional)
DNS Enter the DNS (Domain Name System) server IP
address(es) provided by your ISP. At least one is required.
Internet Connection Type > IPoA
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Bridge Mode Only
If you are using your Gateway as a bridge, which makes
the Gateway act like a stand-alone modem, select Bridge
9
Page 11
Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
Mode Only. All NAT and routing settings are disabled in
this mode.
Internet Connection Type > Bridge Mode Only
Optional Settings
Some of these settings may be required by your ISP. Verify
with your ISP before making any changes.
Optional Settings
Host Name and Domain Name These fields allow you
to supply a host and domain name for the Gateway.
Some ISPs, usually cable ISPs, require these names as
identification. You may have to check with your ISP to see
if your broadband Internet service has been configured
with a host and domain name. In most cases, leaving these
fields blank will work.
MTU MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It specifies
the largest packet size permitted for Internet transmission.
Select Manual if you want to manually enter the largest
packet size that is transmitted. To have the Gateway select
the best MTU for your Internet connection, keep the
default, Auto.
Size When Manual is selected in the MTU field, this option
is enabled. Leave this value in the 1200 to 1500 range. The
default, MTU is configured automatically.
Network Setup
The Network Setup section changes the settings on the
network connected to the Gateway’s Ethernet ports.
Wireless setup is performed through the Wireless tab.
Router IP
The values for the Gateway’s Local IP Address and Subnet
Mask are shown here. In most cases, keeping the default
values will work.
Local IP Address The default value is 192.168.1.1.
Subnet Mask The default value is 255.255.255.0.
Network Address Server Settings (DHCP)
The settings allow you to configure the Gateway’s Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server function. The
Gateway can be used as a DHCP server for your network.
A DHCP server automatically assigns an IP address to each
computer on your network. If you choose to enable the
Gateway’s DHCP server option, make sure there is no
other DHCP server on your network.
Network Address Server Settings (DHCP)
DHCP Server A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) server automatically assigns an IP address to each
computer on your network for you. Unless you already
have one, Linksys recommends that you keep the default,
Enable. You can also use the Gateway in DHCP Relay
mode. (This setting is not available for all encapsulation
types.)
DHCP Server If you enable the DHCP Relay mode for the
DHCP Server setting, enter the IP address for the DHCP
relay server in the fields provided. (This setting is not
available for all encapsulation types.)
Starting IP Address Enter a value for the DHCP server
to start with when issuing IP addresses. Because the
Gateway’s default IP address is 192.168.1.1, the Starting IP
Address must be 192.168.1.2 or greater, but smaller than
192.168.1.253. The default is 192.168.1.100.
Maximum Number of DHCP Users Enter the maximum
number of users (network devices) that can obtain an IP
address. The number will vary depending on the starting
IP address entered and cannot be greater than 253. The
default is 50.
Client Lease Time The Client Lease Time is the amount
of time a network device will be allowed connection to
the Gateway with its current dynamic IP address. Enter the
number of minutes that the device will be “leased” this
dynamic IP address. After the time is up, the device will
be automatically assigned a new dynamic IP address. The
default is 0 minutes, which means one day.
Router IP
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Static DNS 1-3 The Domain Name System (DNS) is how
the Internet translates domain or website names into
Internet addresses or URLs. At least one DNS server IP
address is provided by your ISP. You can enter up to three
10
Page 12
Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
DNS server IP addresses here. The Gateway will use these
for quicker access to functioning DNS servers.
WINS The Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS)
converts NetBIOS names to IP addresses. If you use a WINS
server, enter that server’s IP address here. Otherwise, leave
this field blank.
Time Settings
Time Zone Select the time zone in which your network
functions.
Automatically adjust clock for daylight saving
changes Select this option if you want the Gateway to
automatically adjust for daylight saving time.
Time Settings and Language
Language
Select the language you want the web-based utility to
use: English, French, or German.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
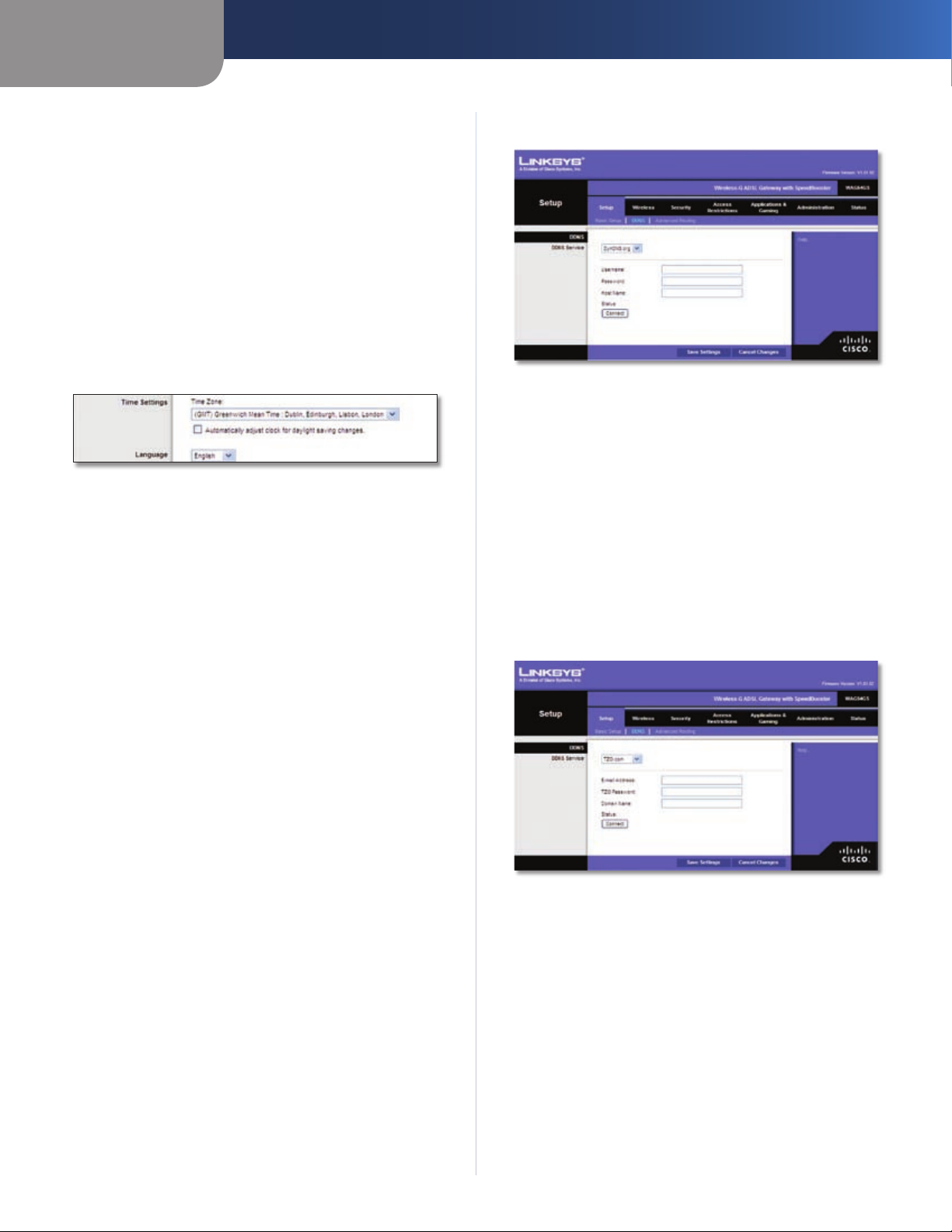
Setup > DDNS
DynDNS.org
Setup > DDNS > DynDNS
Username Enter the Username for your account.
Password Enter the Password for your account.
Host Name Enter the DDNS URL assigned by the service.
Status The status of the DDNS service connection is
displayed.
Connect To manually trigger an update, click this
button.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
TZO.com
The Gateway offers a Dynamic Domain Name System
(DDNS) feature. DDNS lets you assign a fixed host and
domain name to a dynamic Internet IP address. It is useful
when you are hosting your own website, FTP server, or
other server behind the Gateway.
Before you can use this feature, you need to sign
up for DDNS service with a DDNS service provider,
www.dyndns.org or www.TZO.com. If you do not want to
use this feature, keep the default, Disabled.
DDNS
DDNS Service
If your DDNS service is provided by DynDNS.org, then
select DynDNS.org from the drop-down menu. If your
DDNS service is provided by TZO, then select TZO.com.
The features available on the DDNS screen will vary,
depending on which DDNS service provider you use.
Setup > DDNS > TZO
E-mail Address Enter the E-mail Address for your
account.
TZO Password Enter the Password for your account.
Domain Name Enter the DDNS URL assigned by the
service.
Status The status of the DDNS service connection is
displayed here.
Connect To manually trigger an update, click this
button.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
11
Page 13

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
Setup > Advanced Routing
This screen is used to set up the Gateway’s advanced
functions. Operating Mode allows you to select the
type(s) of advanced functions you use. Dynamic Routing
automatically adjusts how packets travel on your network.
Static Routing sets up a fixed route to another network
destination.
Setup > Advanced Routing
Destination IP Address The Destination IP Address is
the IP address of the remote network or host to which you
want to assign a static route.
Subnet Mask The Subnet Mask determines which
portion of a Destination IP Address is the network portion,
and which portion is the host portion.
Gateway This is the IP address of the gateway device that
allows for contact between the Gateway and the remote
network or host.
Hop Count This is the number of hops to each node until
the destination is reached (16 hops maximum). Enter the
appropriate Hop Count.
Click Show Routing Table to view the static routes you
have already set up.
Advanced Routing
NAT
Enabled/Disabled If this Gateway is hosting your
network’s connection to the Internet, keep the default,
Enabled. If another gateway or router exists on your
network, select Disabled.
Dynamic Routing
RIP This feature enables the Gateway to automatically
adjust to physical changes in the network’s layout and
exchange routing tables with the other router(s). The
Gateway determines the network packets’ route based on
the fewest number of hops between the source and the
destination. Select Enabled to use the Dynamic Routing
feature. Otherwise, keep the default, Disabled.
RIP Version Select the appropriate protocol version,
RIP1 or RIP2.
Static Routing
A static route is a pre-determined pathway that network
information must travel to reach a specific host or network.
Enter the information described below to set up a new
static route.
Advanced Routing > Routing Table
Routing Table
For each route, the Destination LAN IP address, Subnet
Mask, Gateway, and Interface are displayed. Click
Refresh to update the information. Click Close to exit
this screen.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Select set number To set up a static route between the
Gateway and another network, select a number from the
drop-down list. Click Delete This Entry to delete a static
route.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
12
Page 14

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
Wireless > Basic Wireless Settings
The basic settings for wireless networking are set on this
screen.
Wireless > Basic Wireless Settings
There are two ways to configure the Gateway’s wireless
settings, manual and SecureEasySetup. For manual
configuration, use this screen to change the settings.
SecureEasySetup is a feature that makes it easy to set up
your wireless network. If you have devices that support
SecureEasySetup, run the Gateway’s Setup Wizard
CD-ROM and follow the on-screen instructions to use
SecureEasySetup.
by the Gateway. If you want to broadcast the Gateway’s
SSID, keep the default, Enable. Otherwise, select Disable.
Wireless SES Function If you want to allow use of the
SecureEasySetup (SES) feature, keep the default, Enable.
Otherwise, select Disable.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Wireless > Wireless Security
The Wireless Security screen configures the security
of your wireless network(s). There are four wireless
security mode options supported by the Gateway:
WPA2-Personal, WPA2-Mixed, WPA Personal, and WEP.
(WPA stands for Wi-Fi Protected Access, which is a
security standard stronger than WEP encryption, and
WEP stands for Wired Equivalent Privacy.) These four
are briefly discussed here. For detailed instructions on
configuring wireless security for the Gateway, refer to
“Chapter 2: Wireless Security”.
NOTE: If you used SecureEasySetup to configure
your wireless network(s), then wireless security
has already been set up. Do not make changes
to the Wireless Security screen.
NOTE: SecureEasySetup ONLY uses WPA-Personal
with TKIP security. If your current wireless devices
do not support WPA-Personal security OR you
want to use WPA2 security, then you cannot use
SecureEasySetup on your network. You need to
manually configure the security settings for your
wireless network.
Wireless Network
Wireless Network Mode Select the wireless standards
running on your network. If you have Wireless-G and
Wireless-B devices in your network, keep the default,
Mixed. If you have only Wireless-G devices, select G-Only.
If you have only Wireless-B devices, select B-Only. If you
do not have any wireless devices, select Disabled.
Wireless Network Name (SSID) The network name is
case-sensitive and must not exceed 32 characters (use any
of the characters on the keyboard). Linksys recommends
that you change the default, linksys, to a unique name of
your choice.
Wireless Channel Select the channel you want to use.
All devices in your wireless network must use the same
channel in order to communicate.
Wireless Security
Security Mode Select the security method for your
wireless network. Proceed to the appropriate instructions.
If you do not want to use wireless security, keep the
default, Disabled.
NOTE: If you are using wireless security,
remember that each device in your wireless
network MUST use the same security method
and settings, or else the wireless devices cannot
communicate.
WPA2-Personal
Wireless SSID Broadcast When wireless devices survey
the local area for wireless networks to associate with, they
will detect the wireless network name or SSID broadcast
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Security Mode > WPA2-Personal
Encryption AES is automatically selected.
13
Page 15

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
Passphrase Enter a Passphrase (also called a WPA shared
key) of 8-63 characters.
Key Renewal Enter a Key Renewal period, which instructs
the Gateway how often it should change the encryption
keys. The default is 3600 seconds.
WPA2-Mixed
Security Mode > WPA2-Mixed
Encryption TKIP + AES is automatically selected.
Passphrase Enter a Passphrase (also called a WPA shared
key) of 8-63 characters.
Key Renewal Enter a Key Renewal period, which instructs
the Gateway how often it should change the encryption
keys. The default is 3600 seconds.
WPA-Personal
WEP
Security Mode > WEP
Encryption Select a level of WEP encryption, 64-bit or
128-bit.
Passphrase Enter a Passphrase to automatically generate
WEP keys. Then click Generate.
NOTE: The WEP Passphrase is compatible with
Linksys wireless products only. If you are use nonLinksys products, manually enter the appropriate
WEP key on those devices.
WEP Key 1-4 If you did not enter a Passphrase, enter the
WEP key(s) manually.
TX Key Select which TX (Transmit) Key to use. The default
is 1.
Security Mode > WPA-Personal
Encryption WPA supports two encryption methods, TKIP
and AES, with dynamic encryption keys. Select the type
of algorithm, TKIP or AES. The default is AES, which is
stronger than TKIP.
Passphrase Enter a Passphrase (also called a WPA shared
key) of 8-63 characters.
Key Renewal Enter a Key Renewal period, which instructs
the Gateway how often it should change the encryption
keys. The default is 3600 seconds.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Wireless > Wireless Access
Wireless access can be filtered by using the MAC addresses of
the wireless devices transmitting within your network’s radius.
Wireless > Wireless Access
Wireless Network Access
Allow All/Restrict Access
address, either permitting or blocking access, select Restrict
To filter wireless users by MAC
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
14
Page 16

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
Access. If you do not wish to filter users by MAC address,
keep the default, Allow All
Prevent listed computers from accessing the wireless
network Select this to block wireless access by MAC
address. This setting is selected by default.
Permit only listed computers to access the wireless
network Select this to allow wireless access by MAC
address.
Update Filter List Click this to open the MAC Address
Filter List screen.
.
MAC Address Filter List
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Wireless > Advanced Wireless Settings
This Advanced Wireless Settings screen is used to set up the
Gateway’s advanced wireless functions. These settings
should only be adjusted by an expert administrator as
incorrect settings can reduce wireless performance.
Wireless > Advanced Wireless Settings
Advanced Wireless
MAC Address Filter List
MAC 01-20 Enter the MAC addresses of the devices
whose wireless access you want to block or allow.
Wireless Client MAC List Click this to open the
Wireless Client List screen.
Wireless Client List
Wireless Client List
This screen lists the MAC addresses of the wireless
devices. Select Enable MAC Filter for any device you
want to add to the MAC Address Filter List. Then click
Update Filter List.
To retrieve the most up-to-date information, click
Refresh. To exit this screen and return to the Wireless
MAC Filter List screen, click Close.
Authentication Type The default is Auto, which allows
either Open System or Shared Key authentication to be
used. With Open System authentication, the sender and
the recipient do NOT use a WEP key for authentication.
With Shared Key authentication, the sender and recipient
use a WEP key for authentication. Select Shared Key to
only use Shared Key authentication.
Control TX Rate The Control TX Rate should be set
depending on the speed of your wireless network. Select
from a range of transmission speeds, or keep the default,
Auto. When the Auto setting is selected, the Gateway
automatically uses the fastest possible data rate and
enables the Auto-Fallback feature, which negotiates the
best possible connection speed between the Gateway
and a wireless device.
Wireless Afterburner To improve wireless performance
when the Gateway is used with devices that support
SpeedBooster, keep the default, Enable. Otherwise, select
Disable.
Beacon Interval Enter a value between 1 and 65,535
milliseconds. The Beacon Interval value indicates the
frequency interval of the beacon. A beacon is a packet
broadcast by the Gateway to synchronize the wireless
network(s). The default value is 100.
DTIM Interval This value, between 1 and 255, indicates
the interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication Message
(DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing
clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and
multicast messages. When the Gateway has buffered
broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
15
Page 17

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. Its clients
hear the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast
and multicast messages. The default value is 1.
Fragmentation Threshold This value specifies the
maximum size for a packet before data is fragmented
into multiple packets. If you experience a high packet
error rate, you may slightly increase the Fragmentation
Threshold. Setting the Fragmentation Threshold too low
may result in poor network performance. Only minor
reduction of the default value is recommended. In most
cases, it should remain at its default value of 2346.
RTS Threshold Should you encounter inconsistent
data flow, only minor reduction of the default, 2346, is
recommended. If a network packet is smaller than the
preset RTS threshold size, the RTS/CTS mechanism will
not be enabled. The Gateway sends Request to Send (RTS)
frames to a particular receiving station and negotiates
the sending of a data frame. After receiving an RTS, the
wireless station responds with a Clear to Send (CTS) frame
to acknowledge the right to begin transmission. The RTS
Threshold value should remain at its default value of
2346.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Filter Java Applets Java is a programming language for
websites. If you deny Java, you run the risk of not having
access to Internet sites created using this programming
language. Select Filter Java Applets to enable Java
filtering. Deselect the feature to allow Java usage
Filter Cookies A cookie is data stored on your computer
and used by Internet sites when you interact with them.
Select Filter Cookies to filter cookies. Deselect the feature
to allow cookie usage
Filter ActiveX ActiveX is a programming language for
websites. If you deny ActiveX, you run the risk of not having
access to Internet sites created using this programming
language. Select Filter ActiveX to enable ActiveX filtering.
Deselect the feature to allow ActiveX usage
.
.
.
Block WAN Requests
Block Anonymous Internet Requests This feature
makes it more difficult for outside users to work their
way into your network. This feature is selected by default.
Deselect the feature to allow anonymous Internet
requests
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
.
Security > Firewall
The Firewall screen is used to configure a firewall that
can filter out various types of unwanted traffic on the
Gateway’s local network.
Security > Firewall
Firewall
SPI Firewall Protection To use firewall protection,
keep the default selection, Enable. To turn off firewall
protection, select Disable.
Additional Filters
Filter Proxy Use of WAN proxy servers may compromise
the Gateway’s security. Denying Proxy will disable access
to any WAN proxy servers. Select Filter Proxy to enable
proxy filtering. Deselect the feature to allow proxy access
Security > VPN Passthrough
The VPN Passthrough screen allows you to enable VPN
tunnels using IPSec, PPTP, or L2TP protocols to pass through
the Gateway’s firewall.
Security > VPN Passthrough
VPN Passthrough
IPSec Passthrough Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is
a suite of protocols used to implement secure exchange
of packets at the IP layer. To allow IPSec tunnels to pass
through the Gateway, keep the default, Enable.
PPTP Passthrough Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
(PPTP) allows the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to be
tunneled through an IP network. To allow PPTP tunnels to
pass through the Gateway, keep the default, Enable.
.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
16
Page 18

Chapter 3
L2TP Passthrough Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol is the
method used to enable Point-to-Point sessions via the
Internet on the Layer 2 level. To allow L2TP tunnels to pass
through the Gateway, keep the default, Enable.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Access Restrictions > Internet Access Policy
The Internet Access Policy screen allows you to block or
allow specific kinds of Internet usage and traffic, such as
Internet access, designated services, and websites during
specific days and times.
Advanced Configuration
Summary
Status Policies are disabled by default. To enable a policy,
select the policy number from the drop-down menu, and
select Enable.
Access Restrictions > Internet Access Policy
Internet Access Policy
Internet Access Policy Access can be managed by a
policy. Use the settings on this screen to establish an
access policy (after Save Settings is clicked). Selecting a
policy from the drop-down menu will display that policy’s
settings. To delete a policy, select that policy’s number
and click Delete. To view all the policies, click Summary.
To create a policy, follow steps 1-11. Repeat these steps to
create additional policies, one at a time.
Select a number from the Internet Access Policy drop-
1.
down menu.
To enable this policy, select Enable.
2.
Enter a Policy Name in the field provided.
3.
Click Edit List of PCs to select which computers will be
4.
affected by the policy. The Internet Access PC List screen
appears. You can select a computer by MAC address or
IP address. You can also enter a range of IP addresses
if you want this policy to affect a group of computers.
After making your changes, click Save Settings to
apply your changes, or click Cancel Changes to cancel
your changes. Then click Close.
Summary
The policies are listed with the following information: No.,
Policy Name, Days, and Time of Day. To delete a policy,
select Delete. To return to the Internet Access Policy screen,
click Close.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Internet Access PC List
17
Page 19

Chapter 3
Select the appropriate option, Deny or Allow,
5.
depending on whether you want to block or allow
Internet access for the computers you selected on the
Internet Access PC List screen.
Decide which days and what times you want this policy
6.
to be enforced. Select the individual days during which
the policy will be in effect, or select Everyday. Then
enter a range of hours and minutes during which the
policy will be in effect, or select 24 Hours.
You can block websites with specific URL addresses.
7.
Enter each URL in a separate Website Blocking by URL
Address field.
You can also block websites using specific keywords.
8.
Enter each keyword in a separate Website Blocking by
Keyword field.
You can filter access to various services accessed over
9.
the Internet, such as FTP or telnet.
From the Blocked Services list, select the service you
want to block. The port numbers and protocol for the
selected service are automatically displayed.
If the service you want is not listed, select User-
10.
Defined. Enter its port numbers in the fields provided.
Then select its protocol: ICMP, TCP, UDP, or TCP &
UDP from the drop-down menu.
Click Save Settings to save the policy’s settings. To
11.
cancel the policy’s settings, click Cancel Changes.
Applications and Gaming > Single Port
Forwarding
The Single Port Forwarding screen allows you to customize
port services for common applications on this screen.
When users send these types of requests to your network via
the Internet, the Gateway will forward those requests to the
appropriate servers (computers). Before using forwarding,
you should assign static IP addresses to the designated
servers.
Advanced Configuration
Applications and Gaming > Single Port Forwarding
Single Port Forwarding
To forward a port, enter the information on each line for
the criteria required.
Application Enter the name you wish to give the
application. Each name can be up to 12 characters.
External Port Enter the external port number used by
the server or Internet application. Check with the Internet
application documentation for more information.
Internal Port Enter the internal port number used by
the server or Internet application. Check with the Internet
application documentation for more information.
Protocol Select the protocol used for this application,
either TCP or UDP, or Both.
IP Address For each application, enter the IP address of
the computer that should receive the requests.
Enabled For each application, select Enabled to enable
port forwarding.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Applications and Gaming > Port Range
Forwarding
The Port Range Forwarding screen allows you to set up
public services on your network, such as web servers,
ftp servers, e-mail servers, or other specialized Internet
applications. (Specialized Internet applications are any
applications that use Internet access to perform functions
such as videoconferencing or online gaming. Some Internet
applications may not require any forwarding.)
18
Page 20

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
When users send these types of requests to your network via
the Internet, the Gateway will forward those requests to the
appropriate servers (computers). Before using forwarding,
you should assign static IP addresses to the designated
servers.
If you need to forward all ports to one computer, click the
DMZ tab.
Applications and Gaming > Port Range Forwarding
Applications & Gaming > Port Range
Triggering
The Port Range Triggering screen allows the Gateway to
watch outgoing data for specific port numbers. The IP
address of the computer that sends the matching data is
remembered by the Gateway, so that when the requested
data returns through the Gateway, the data is pulled back
to the proper computer by way of IP address and port
mapping rules.
Port Range Forwarding
To forward a port range, enter the information on each
line for the criteria required.
Application In this field, enter the name you wish to give
the application. Each name can be up to 12 characters.
Port Range Start and End Enter the number or range of
port(s) used by the server or Internet applications. Check
with the Internet application documentation for more
information.
Protocol Select the protocol used for this application,
either TCP or UDP, or Both.
IP Address For each application, enter the IP address of
the computer running the specific application.
Enable Select Enable to enable port forwarding for the
applications you have defined.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Applications and Gaming > Port Range Triggering
Port Range Triggering
To trigger a port range, enter the information on each line
for the criteria required.
Application Name Enter the application name of the
trigger.
Triggered Range Start Port and End Port For each
application, enter the starting and ending port numbers of
the triggered port number range. Check with the Internet
application documentation for the port number(s)
needed.
Forwarded Range Start Port and End Port For each
application, enter the starting and ending port numbers
of the forwarded port number range. Check with the
Internet application documentation for the port number(s)
needed.
Enabled Select Enabled to enable port triggering for the
applications you have defined.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Applications and Gaming > DMZ
The DMZ feature allows one network computer to be
exposed to the Internet for use of a special-purpose
service such as Internet gaming or videoconferencing.
DMZ hosting forwards all the ports at the same time to
one PC. The Port Range Forwarding feature is more secure
19
Page 21

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
because it only opens the ports you want to have opened,
while DMZ hosting opens all the ports of one computer,
exposing the computer to the Internet.
Applications and Gaming > DMZ
DMZ
Any computer whose port is being forwarded must have
its DHCP client function disabled and should have a new
static IP address assigned to it because its IP address may
change when using the DHCP function.
DMZ Hosting To disable DMZ hosting, keep the default,
Disable. To expose one PC, select Enable. Then configure
the following setting:
DMZ Host IP Address Enter the IP address of the
computer.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Applications and Gaming > QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) ensures better service to
high-priority types of network traffic, which may
involve demanding, real-time applications, such as
videoconferencing.
QoS (Quality of Service)
QoS To use QoS, select Enable. Otherwise, keep the
default, Disable.
Application-based QoS
Application-based QoS manages information as it is
transmitted and received. Depending on the settings of
the QoS screen, this feature will assign information a high,
medium, or low priority for the five preset applications
and three additional applications that you specify.
The five preset applications are the following:
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
•
A protocol used to transfer files over a TCP/IP network
(Internet, UNIX, etc.). For example, after HTML pages
are developed for a website on a local machine, they
are typically uploaded to the web server using FTP.
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol)
•
The communications protocol used to connect to
servers on the World Wide Web. Its primary function
is to establish a connection with a web server and
transmit HTML pages to the client web browser.
Telnet
•
A terminal emulation protocol commonly used on
Internet and TCP/IP-based networks. It allows a user at
a terminal or computer to log onto a remote device
and run a program.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
•
The standard e-mail protocol on the Internet. It is a
TCP/IP protocol that defines the message format and
the message transfer agent (MTA), which stores and
forwards the mail.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3)
•
A standard mail server commonly used on the Internet.
It provides a message store that holds incoming e-mail
until users log on and download it. POP3 is a simple
system with little selectivity. All pending messages
and attachments are downloaded at the same time.
POP3 uses the SMTP messaging protocol.
Specific Port# You can add three more applications by
entering their respective port numbers in these fields.
Applications and Gaming > QoS
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
High priority/Medium priority/Low priority For each
application, select High priority (traffic on this queue
shares 60% of the total bandwidth), Medium priority
(traffic on this queue shares 18% of the total bandwidth),
or Low priority (traffic on this queue shares 1% of the
total bandwidth).
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
20
Page 22

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
Administration > Management
The Administration > Management screen allows the
network’s administrator to manage specific Gateway
functions for access and security.
Administration > Management
Gateway Access
Local Gateway Access
To ensure the Gateway’s security, you will be asked for your
username and password when you access the Gateway’s
web-based utility. The default username and password
are admin.
NOTE: When you are in a remote location
and wish to manage the Gateway, enter
http://<Internet_IP_address>:port. Enter
the Gateway’s specific Internet IP address in
place of <Internet_IP_address>, and enter
the Management Port number in place of the
word port.
SNMP
SNMP is a popular network monitoring and management
protocol.
Device Name Enter the name of the Gateway.
SNMP To use SNMP, select Enable. Otherwise, select
Disable.
Get Community Enter the password that allows read-only
access to the Gateway’s SNMP information.
Set Community Enter the password that allows
read/write access to the Gateway’s SNMP information.
Trap Management: Trap to Enter the IP address of
the remote host computer that will receive the trap
messages.
UPnP
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) allows Windows XP
and Vista to automatically configure the Gateway for
various Internet applications, such as gaming and
videoconferencing.
UPnP If you want to use UPnP, keep the default, Enable.
Otherwise, select Disable.
Gateway Userlist Select the number of the user. The
default is user 1.
Gateway Username Enter the default Gateway
Username, admin.
Gateway Password Linksys recommends that you
change the default Gateway Password, admin, to one of
your choice.
Re-enter to Confirm Enter the Gateway Password again
to confirm.
For non-admin users, select a different user number, and
then configure the Gateway Username and Password
settings.
Remote Gateway Access
Remote Management To permit remote access of the
Gateway, from outside the local network, select Enable.
Otherwise, keep the default, Disable.
Management Port Enter the port number that will be
open to outside access.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
WLAN
If you are using the Gateway in a public domain where you
are giving wireless access to your guests, you can disable
wireless access to the Gateway’s web-based utility.
Management via WLAN This feature allows the Gateway
to be managed by a wireless computer on the local
network when it logs into the Gateway’s web-based
utility. You will only be able to access the utility via a wired
connection if you disable this feature. To allow wireless
access to the utility, keep the default, Enable. Otherwise,
select Disable.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
21
Page 23

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
Administration > Reporting
The Gateway can keep logs of traffic and events for your
Internet connection.
Administration > Log
Reporting
Log To disable the Log function, keep the default, Disable.
To monitor traffic between the network and the Internet,
select Enable. With logging enabled, you can choose to
view temporary logs.
Log
Type Select ALL, Access Log, or Firewall Log.
Click pageRefresh to update the log. Click Clear to
clear all the information that is displayed. Click Previous
Page to view the previous page of information. Click
Next Page to view the next page of information.
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Administration > Diagnostics
The ping test allows you to check the connections of your
network devices, including connection to the Internet.
E-Mail Alerts To enable E-Mail Alerts, select Enable.
Denial of Service Thresholds Enter the number of Denial
of Service attacks that will trigger an e-mail alert.
SMTP Mail Server Enter the IP address of the SMTP
server.
E-Mail Address for Alert Logs Enter the e-mail address
that will receive alert logs.
Return E-Mail address Enter the return address for the
e-mail alerts. (This can be a dummy address.)
View Log To view the logs, click View Log.
Administration > Diagnostics
Ping Test
Ping Test Parameters
The ping test checks the status of a connection.
Ping Target IP Enter the IP address that you want to
ping. This can be either a local (LAN) or Internet (WAN) IP
address.
Ping Size Enter the packet size you want to use. The
default is 60 bytes.
Number of Pings Enter how many times you want to
ping. The default is 1.
Ping Interval Enter the number of milliseconds between
pings. The default is 1000 milliseconds.
Ping Timeout Enter the number of milliseconds before the
ping test will time out. The default is 5000 milliseconds.
Start Test To run the test, click this button. The Ping Test
screen will show if the test was successful. Click Close to
return to the Diagnostics screen.
Log > View Log
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
22
Page 24

Chapter 3
Diagnostics > Ping
Ping Result The results of the ping test are displayed.
Advanced Configuration
Administration > Factory Defaults
The Administration > Factory Defaults screen allows you to
restore the Gateway’s configuration to its factory default
settings.
Administration > Factory Defaults
Click Save Settings to apply your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Administration > Backup & Restore
The Backup & Restore screen allows you to back up or restore
the Gateway’s settings using a configuration file.
Administration > Backup & Restore
Backup Configuration
Backup To save the Gateway’s settings in a configuration
file, click this button and follow the on-screen
instructions.
NOTE: Restoring factory defaults deletes custom
settings. Note your custom settings before
restoring the factory defaults.
Factory Defaults
Restore Factory Defaults To reset settings to the
default values, click this button and follow the on-screen
instructions. Any custom Gateway settings you have saved
will be lost when the default settings are restored.
Administration > Firmware Upgrade
The Firmware Upgrade screen allows you to upgrade the
Gateway’s firmware. Do not upgrade the firmware unless
you are experiencing problems with the Gateway or the
new firmware has a feature you want to use.
Restore Configuration
To use this option, you must have previously backed up its
configuration settings.
Please select a file to restore Click the Browse button
and select the Gateway’s configuration file.
Restore To restore the Gateway’s configuration settings,
click this button and follow the on-screen instructions.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Administration > Firmware Upgrade
23
Page 25

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
NOTE: The Gateway may lose the settings
you have customized. Before you upgrade its
firmware, write down all of your custom settings.
After you upgrade its firmware, you will have to
re-enter all of your configuration settings.
Firmware Upgrade
Before upgrading the firmware, download the Gateway’s
firmware upgrade file from the Linksys website,
www.linksys.com/international. Then extract the file.
Language Select the language you want the web-based
utility to use: English, French, or German.
Please Select a File to Upgrade Click Browse and select
the extracted firmware upgrade file.
Start to Upgrade After you have selected the
appropriate file, click this button, and f
instructions.
ollow the on-screen
Status > Gateway
The Gateway screen displays information about the
Gateway and its current settings.
Status > Local Network
The Local Network screen displays information about the
local, wired network.
Status > Local Network
Local Network
MAC Address The MAC address of the Gateway’s local,
wired interface is displayed.
IP Address The Gateway’s IP address, as it appears on
your local network, is displayed.
Status > Gateway
Gateway Information
Firmware Version The version number of the Gateway’s
current firmware is displayed.
MAC Address The Gateway’s MAC address, as seen by
your ISP, is displayed.
Current Time The time set on the Gateway is displayed.
Subnet Mask The Subnet Mask of the Gateway is
displayed.
DHCP Server
DHCP Server The status of the Gateway’s DHCP server
function is displayed.
Start IP Address For the range of IP addresses used by
devices on your local network, the starting IP address is
displayed.
End IP Address For the range of IP addresses used by
devices on your local network, the ending IP address is
displayed.
DHCP Client Table Click this button to view a list of
devices that are using the Gateway as a DHCP server.
Internet Connection
This section shows the current network information
stored in the Gateway. The information varies depending
on the Internet connection type selected on the Basic
Setup screen.
Click Refresh to update the on-screen information.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
DHCP Active IP Table
DHCP Active IP Table
The DHCP Active IP Table lists computers and other
devices that have been assigned IP addresses by
24
Page 26

Chapter 3
Advanced Configuration
the Gateway. The list displays Client Host Name, IP
Address, MAC Address, and Expires time (how much
time is left for the current IP address). To remove a
DHCP client, click Delete. To retrieve the most up-todate information, click Refresh. To exit this screen and
return to the Local Network screen, click Close.
ARP/RARP Table Click this button to view the current
IP and MAC addresses for the local network clients of the
Gateway.
ARP/RARP Table
ARP/RARP Table
An ARP request is a request sent by the Gateway
asking local network devices with IP addresses for
their MAC addresses, so the Gateway can map IP
addresses to MAC addresses. RARP is the reverse of
ARP. (This data is stored in temporary memory and
changes periodically.) To retrieve the most up-to-date
information, click Refresh. To exit this screen and
return to the Local Network screen, click Close.
Status > Wireless
Mode The wireless network mode of the Gateway is
displayed.
SSID The wireless network name, which is also called the
SSID, is displayed.
Channel The channel of the wireless network is
displayed.
Encryption Function The wireless security method is
displayed.
Wireless Clients Connected Click this button to view a
list of wireless clients connected to the Gateway.
Networked Computers
Networked Computers
The list of wireless devices displays Computer Name, IP
Address, and MAC Address. To retrieve the most up-todate information, click Refresh. To exit this screen and
return to the Wireless screen, click Close.
Status > DSL
The DSL screen displays information about your DSL
connection.
The Wireless screen displays information about your
wireless network.
Status > Wireless
Wireless
Firmware Version The version number of the firmware
is displayed.
MAC Address The wireless MAC address of the Gateway’s
local, wireless interface is displayed.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Status > DSL
DSL Connection
Status The status of the DSL connection is displayed.
Downstream Rate The download speed of traffic from
the Internet to the Gateway is displayed.
Upstream Rate The upload speed of traffic from the
Gateway to the Internet is displayed. For ADSL connection,
25
Page 27

Chapter 3
the Upstream Rate is typically 25% of the Downstream
Rate.
NOTE: The Downstream and Upstream Rates are
affected by distance from and configuration of
the DSL central office.
PVC Connection
Encapsulation The Encapsulation setting selected on
the Basic Setup screen is displayed.
DSL Modulation Mode The DSL Modulation Mode
selected on the Basic Setup screen is displayed.
Multiplexing The Multiplexing setting selected on the
Basic Setup screen is displayed.
Qos The QoS method selected on the Basic Setup screen
is displayed.
Pcr Rate The Pcr Rate value entered on the Basic Setup
screen is displayed.
Advanced Configuration
Scr Rate The Scr Rate value entered on the Basic Setup
screen is displayed.
Autodetect The Autodetect setting selected on the Basic
Setup screen is displayed.
VPI The VPI value entered on the Basic Setup screen is
displayed.
VCI The VCI value entered on the Basic Setup screen is
displayed.
Enable The number of Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVC)
is displayed.
PVC Status The status of the PVC is displayed.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
26
Page 28

Appendix A
Troubleshooting
Appendix A:
Troubleshooting
Your computer cannot connect to the Internet.
Follow the instructions until your computer can connect
to the Internet:
Make sure that the Gateway is powered on. The Power
•
LED should be green and not flashing.
If the Power LED is flashing, then power off all of
•
your network devices, including the Gateway and
computers. Then power on each device in the
following order:
Gateway
1.
Computer
2.
Check the LEDs on the front panel of the Gateway.
•
Make sure the Power, DSL, and at least one of the
numbered LEDs are lit. If they are not, then check
the cable connections. The computer should be
connected to one of the ports numbered 1-4 on the
Gateway, and the Line port of the Gateway must be
connected to the ADSL line.
You need to modify the advanced settings on the
Gateway.
Open the web browser (for example, Internet Explorer
or Firefox), and enter the Gateway’s IP address in the
address field (the default IP address is 192.168.1.1). When
prompted, complete the User name and Password fields
(the default user name and password is admin). Click the
appropriate tab to change the settings.
WEB: If your questions are not addressed
here, refer to the Linksys website,
www.linksys.com/international
When you double-click the web browser, you are
prompted for a username and password. If you want to
get rid of the prompt, follow these instructions.
Launch the web browser and perform the following steps
(these steps are specific to Internet Explorer but are similar
for other browsers):
Select Tools > Internet Options.
1.
Click the Connections tab.
2.
Select Never dial a connection.
3.
Click OK.
4.
The computer cannot connect wirelessly to the network.
Make sure the wireless network name or SSID is the
same on both the computer and the Gateway. If you
have enabled wireless security, then make sure the same
security method and key are used by both the computer
and the Gateway.
You need to modify the basic settings on the Gateway.
Run the Setup Wizard on the Setup CD-ROM.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
27
Page 29

Appendix B
Appendix B:
Specifications
Model WAG310G
Environmental
Dimensions xxx x xxx x xx mm)
Weight xxx g
Power External, xVDC, xA
Certification
Operating Temp. x to xx°C
Storage Temp. -xx to xx°C
Operating
Humidity xx to xx% Noncondensing
Storage Humidity x to xx% Noncondensing
Specifications
Wireless-G ADSL Gateway with SpeedBooster
28
Page 30

Appendix C
Warranty Information
Appendix C:
Warranty Information
Contact your service provider if the warranty support
issues are to be handled by them as per your service
agreements.
Linksys warrants to You that, for a period of one year
(the “Warranty Period”), your Linksys Product will be
substantially free of defects in materials and workmanship
under normal use. Your exclusive remedy and Linksys’
entire liability under this warranty will be for Linksys at
its option to repair or replace the Product or refund Your
purchase price less any rebates. This limited warranty
extends only to the original purchaser.
If the Product proves defective during the Warranty
Period call Linksys Technical Support in order to obtain
a Return Authorization Number, if applicable. BE SURE
TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE ON HAND WHEN
CALLING. If You are requested to return the Product, mark
the Return Authorization Number clearly on the outside
of the package and include a copy of your original proof
of purchase. RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED
WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. You are responsible
for shipping defective Products to Linksys. Linksys pays
for UPS Ground shipping from Linksys back to You only.
Customers located outside of the United States of America
and Canada are responsible for all shipping and handling
charges.
TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT
WILL LINKSYS BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST DATA, REVENUE
OR PROFIT, OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INCIDENTAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, REGARDLESS OF THE
THEORY OF LIABILITY (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), ARISING
OUT OF OR RELATED TO THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO
USE THE PRODUCT (INCLUDING ANY SOFTWARE), EVEN
IF LINKSYS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT WILL LINKSYS’ LIABILITY
EXCEED THE AMOUNT PAID BY YOU FOR THE PRODUCT.
The foregoing limitations will apply even if any warranty or
remedy provided under this Agreement fails of its essential
purpose. Some jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or
limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the
above limitation or exclusion may not apply to You.
This Warranty is valid and may be processed only in
the country of purchase.
Please direct all inquiries to: Linksys, P.O. Box 18558, Irvine,
CA 92623.
ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE ARE LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF THE
WARRANTY PERIOD. ALL OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF NONINFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED. Some jurisdictions do
not allow limitations on how long an implied warranty
lasts, so the above limitation may not apply to You. This
warranty gives You specific legal rights, and You may also
have other rights which vary by jurisdiction.
This warranty does not apply if the Product (a) has been
altered, except by Linksys, (b) has not been installed,
operated, repaired, or maintained in accordance with
instructions supplied by Linksys, or (c) has been subjected
to abnormal physical or electrical stress, misuse,
negligence, or accident. In addition, due to the continual
development of new techniques for intruding upon and
attacking networks, Linksys does not warrant that the
Product will be free of vulnerability to intrusion or attack.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
29
Page 31

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
Appendix D:
Regulatory Information
FCC Statement
This product has been tested and complies with the
specifications for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in
a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used according to the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which is found by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
•
Increase the separation between the equipment or
•
devices
Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the
•
receiver’s
Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician
•
for assistance
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure
limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This
equipment should be installed and operated with
minimum distance 20 cm between the radiator and your
body.
FCC Part 68 Statement
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC Rules. A
label is attached to the equipment that contains, among
other information, its FCC registration number and ringer
equivalence number. If requested, this information must
be provided to the telephone company.
The REN is useful to determine the quantity of devices
that may be connected to the telephone line and still have
all of those devices ring when your telephone number is
called. In most, but not all areas, the sum of RENs should
not exceed 5. To be certain of the number of devices that
may be connected to the line, as determined by the total
RENs, contact the telephone company to determine the
maximum REN for the calling area.
If this equipment causes harm to the telephone network,
the telephone company may discontinue your service
temporarily. If advance notice is not practical, the
telephone company will notify the customer as soon as
possible. Also, you will be advised of your right to file a
complaint with the FCC if you believe it is necessary.
The telephone company may make changes in its
facilities, equipment, operations, or procedures that could
affect the operation of the equipment. If this happens, the
telephone company will provide advance notice in order
for you to make the necessary modifications in order to
maintain uninterrupted service.
In the event this equipment should fail to operate properly,
disconnect the unit from the telephone line. Try using
another FCC approved device in the same telephone
jack. If the trouble persists, call the telephone company
repair service bureau. If the trouble does not persist and
appears to be with this unit, disconnect the unit from the
telephone line and discontinue use of the unit until it is
repaired. Please note that the telephone company may ask
that you disconnect the equipment from the telephone
network until the problem has been corrected or until
you are sure that the equipment is not malfunctioning.
The user must use the accessories and cables supplied by
the manufacturer to get optimum performance from the
product.
No repairs may be done by the customer. If trouble is
experienced with this equipment, please contact your
authorized support provider for repair and warranty
information. If the trouble is causing harm to the
telephone network, the telephone company may request
you remove the equipment from the network until the
problem is resolved. This equipment cannot be used on
telephone company provided coin service. Connection to
Party Line Service is subject to state tariffs.
This equipment uses the following USOC Jack: RJ-11.
An FCC compliant telephone cord and modular plug
is provided with this equipment. This equipment is
designed to be connected to the telephone network or
premises wiring using a compatible modular jack, which
is FCC Part 68 compliant. Connection to the telephone
network should be made by using the standard modular
telephone jack.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Safety Notices
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire, use only No.26 AWG
•
or larger telecommunication line cord.
Do not use this product near water, for example, in a
•
wet basement or near a swimming pool.
Avoid using this product during an electrical storm.
•
There may be a remote risk of electric shock from
lightning.
30
Page 32

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
Industry Canada Statement
This device complies with Industry Canada ICES-003 and
RSS210 rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
This device may not cause interference and
1.
This device must accept any interference, including
2.
interference that may cause undesired operation
of the device.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users,
the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen
that the EIRP is not more than required for successful
communication.
Industry Canada Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits
set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment
should be installed and operated with minimum distance
20 cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in
conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Avis d’Industrie Canada
Declaration of Conformity with Regard to
EU Directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive)
Compliance Information for 2,4-GHz and 5-GHz Wireless
Products Relevant to the EU and Other Countries Following
the EU Directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE Directive)
Бъ л га р ск и
[Bulgarian]
Česky
[Czech]:
Dansk
[Danish]:
Deutsch
[German]:
Eesti
[Estonian]:
Това оборудване отговаря на съществените
изисквания и приложими клаузи на
Директива 1999/5/ЕС.
Toto zařízení je v souladu se základními
požadavky a ostatními odpovídajícími
ustanoveními Směrnice 1999/5/EC.
Dette udstyr er i overensstemmelse med
de væsentlige krav og andre relevante
bestemmelser i Direktiv 1999/5/EF.
Dieses Gerät entspricht den grundlegenden
Anforderungen und den weiteren
entsprechenden Vorgaben der Richtlinie
1999/5/EU.
See seade vastab direktiivi 1999/5/EÜ olulistele
nõuetele ja teistele asjakohastele sätetele.
Cet appareil est conforme aux normes NMB003 et RSS210
d’Industrie Canada.
L’utilisation de ce dispositif est autorisée seulement aux
conditions suivantes :
il ne doit pas produire de brouillage et
1.
il doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique reçu,
2.
même si ce brouillage est susceptible de compromettre le
fonctionnement du dispositif.
Afin de réduire le risque d’interférence aux autres
utilisateurs, le type d’antenne et son gain doivent
être choisis de façon à ce que la puissance isotrope
rayonnée équivalente (p.i.r.e.) ne soit pas supérieure
au niveau requis pour obtenir une communication
satisfaisante.
Avis d’Industrie Canada concernant l’exposition
aux radiofréquences
Ce matériel est conforme aux limites établies par IC
en matière d’exposition aux radiofréquences dans un
environnement non contrôlé. Ce matériel doit être installé
et utilisé à une distance d’au moins 20 cm entre l’antenne
et le corps de l’utilisateur.
L’émetteur ne doit pas être placé près d’une autre antenne
ou d’un autre émetteur, ou fonctionner avec une autre
antenne ou un autre émetteur.
English:
Español
[Spanish]:
Ελληνική
[Greek]:
Français
[French]:
Íslenska
[Icelandic]:
Italiano
[Italian]:
Latviski
[Latvian]:
Lietuvių
[Lithuanian]:
This equipment is in compliance with the
essential requirements and other relevant
provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC.
Este equipo cumple con los requisitos
esenciales asi como con otras disposiciones
de la Directiva 1999/5/CE.
Αυτός ο εξοπλισµός είναι σε συµµόρφωση µε
τις ουσιώδεις απαιτήσεις και άλλες σχετικές
διατάξεις της Οδηγίας 1999/5/EC.
Cet appareil est conforme aux exigences
essentielles et aux autres dispositions
pertinentes de la Directive 1999/5/EC.
Þetta tæki er samkvæmt grunnkröfum og
öðrum viðeigandi ákvæðum Tilskipunar
1999/5/EC.
Questo apparato é conforme ai requisiti
essenziali ed agli altri principi sanciti dalla
Direttiva 1999/5/CE.
Šī iekārta atbilst Direktīvas 1999/5/EK
būtiskajām prasībām un citiem ar to
saistītajiem noteikumiem.
Šis įrenginys tenkina 1999/5/EB Direktyvos
esminius reikalavimus ir kitas šios direktyvos
nuostatas.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
31
Page 33

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
Nederlands
[Dutch]:
Malti
[Maltese]:
Magyar
[Hungarian]:
Norsk
[Norwegian]:
Polski
[Polish]:
Português
[Portuguese]:
Română
[Romanian]
Dit apparaat voldoet aan de essentiele eisen
en andere van toepassing zijnde bepalingen
van de Richtlijn 1999/5/EC.
Dan l-apparat huwa konformi mal-ħtiġiet
essenzjali u l-provedimenti l-oħra rilevanti
tad-Direttiva 1999/5/EC.
Ez a készülék teljesíti az alapvető
követelményeket és más 1999/5/EK
irányelvben meghatározott vonatkozó
rendelkezéseket.
Dette utstyret er i samsvar med de
grunnleggende krav og andre relevante
bestemmelser i EU-direktiv 1999/5/EF.
Urządzenie jest zgodne z ogólnymi
wymaganiami oraz szczególnymi warunkami
określonymi Dyrektywą UE: 1999/5/EC.
Este equipamento está em conformidade com
os requisitos essenciais e outras provisões
relevantes da Directiva 1999/5/EC.
Acest echipament este in conformitate
cu cerintele esentiale si cu alte prevederi
relevante ale Directivei 1999/5/EC.
The following standards were applied during the
assessment of the product against the requirements of
the Directive 1999/5/EC:
Radio: EN 300 328
•
EMC: EN 301 489-1, EN 301 489-17
•
Safety: EN 60950 and either EN 50385 or EN 50371
•
CE Marking
For the Linksys Wireless-N, -G, -B, and/or -A products,
the following CE mark, notified body number (where
applicable), and class 2 identifier are added to the
equipment.
Slovensko
[Slovenian]:
Slovensky
[Slovak]:
Suomi
[Finnish]:
Svenska
[Swedish]:
Ta naprava je skladna z bistvenimi zahtevami
in ostalimi relevantnimi pogoji Direktive
1999/5/EC.
Toto zariadenie je v zhode so základnými
požiadavkami a inými príslušnými nariadeniami
direktív: 1999/5/EC.
Tämä laite täyttää direktiivin 1999/5/EY
olennaiset vaatimukset ja on siinä asetettujen
muiden laitetta koskevien määräysten
mukainen.
Denna utrustning är i överensstämmelse med
de väsentliga kraven och andra relevanta
bestämmelser i Direktiv 1999/5/EC.
For all products, the Declaration of Conformity (DofC) is
available through one or more of these options:
A pdf file is included on the product’s CD.
•
A print copy is included with the product.
•
A pdf file is available on the product’s webpage.
•
Visit www.linksys.com/international and select your
country or region. Then select your product.
If you need any other technical documentation, see the
“Technical Documents on www.linksys.com/international”
section, as shown later in this appendix.
or
or
or
Check the CE label on the product to find out which
notified body was involved during the assessment.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
32
Page 34

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
National Restrictions
This product may be used in all EU countries (and other
countries following the EU directive 1999/5/EC) without
any limitation except for the countries mentioned below:
Ce produit peut être utilisé dans tous les pays de l’UE (et dans
tous les pays ayant transposés la directive 1999/5/CE) sans
aucune limitation, excepté pour les pays mentionnés cidessous:
Questo prodotto è utilizzabile in tutte i paesi EU (ed in tutti
gli altri paesi che seguono le direttive EU 1999/5/EC) senza
nessuna limitazione, eccetto per i paesii menzionati di
seguito:
Das Produkt kann in allen EU Staaten ohne Einschränkungen
eingesetzt werden (sowie in anderen Staaten die der EU
Direktive 1999/5/CE folgen) mit Außnahme der folgenden
aufgeführten Staaten:
In the majority of the EU and other European countries,
the 2,4- and 5-GHz bands have been made available
for the use of wireless local area networks (LANs). The
table labeled “Overview of Regulatory Requirements for
Wireless LANs” provides an overview of the regulatory
requirements applicable for the 2,4- and 5-GHz bands.
Later in this document you will find an overview of
countries in which additional restrictions or requirements
or both are applicable.
The requirements for any country may evolve. Linksys
recommends that you check with the local authorities for
the latest status of their national regulations for both the
2,4- and 5-GHz wireless LANs.
Overview of Regulatory Requirements for Wireless LANs
Frequency
Band (MHz)
2400-2483.5 100 X
Max Power Level
(EIRP) (mW)
Indoor
ONLY
Indoor &
Outdoor
France
For 2,4 GHz, the product should not be used outdoors
in the band 2454 - 2483,5 MHz. There are no restrictions
when used in other parts of the 2,4 GHz band when used
indoors. Check http://www.arcep.fr/ for more details.
Pour la bande 2,4 GHz, l’ équipement ne doit pas être utilisé
en extérieur dans la bande 2454 - 2483,5 MHz. Il n’y a pas de
restrictions pour des utilisations en intérieur dans d’autres
parties de la bande 2,4GHz. Consultez http://www.arcep.fr/
pour de plus amples détails.
Applicable Power Levels in France
Location
Indoor
(No restrictions)
Outdoor
Frequency
Range (MHz)
2400-2483.5 100 mW (20 dBm)
2400-2454
2454-2483.5
Power (EIRP)
100 mW (20 dBm)
10 mW (10 dBm)
Italy
This product meets the National Radio Interface and
the requirements specified in the National Frequency
Allocation Table for Italy. Unless this 2,4-GHz wireless LAN
product is operating within the boundaries of the owner’s
property, its use requires a “general authorization”. Please
check http://www.comunicazioni.it/it/ for more details.
Questo prodotto è conforme alla specifiche di Interfaccia
Radio Nazionali e rispetta il Piano Nazionale di ripartizione
delle frequenze in Italia. Se non viene installato all’interno
del proprio fondo, l’utilizzo di prodotti Wireless LAN a
2,4 GHz richiede una “Autorizzazione Generale”. Consultare
http://www.comunicazioni.it/it/ per maggiori dettagli.
Latvia
The following countries have restrictions and/or
requirements in addition to those given in the table
labeled “Overview of Regulatory Requirements for
Wireless LANs”:
.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
The outdoor usage of the 2,4 GHz band requires an
authorization from the Electronic Communications Office.
Please check http://www.esd.lv for more details.
2,4 GHz frekveču joslas izmantošanai ārpus telpām
nepieciešama atļauja no Elektronisko sakaru direkcijas.
Vairāk informācijas: http://www.esd.lv.
Notes:
Although Norway, Switzerland and Liechtenstein are
1.
not EU member states, the EU Directive 1999/5/EC has
also been implemented in those countries.
The regulatory limits for maximum output power are
2.
specified in EIRP. The EIRP level of a device can be
calculated by adding the gain of the antenna used
(specified in dBi) to the output power available at the
connector (specified in dBm).
33
Page 35

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
Product Usage Restrictions
This product is designed for indoor usage only. Outdoor
usage is not recommended, unless otherwise noted.
2,4 GHz Restrictions
This product is designed for use with the standard, integral
or dedicated (external) antenna(s) that is/are shipped
together with the equipment. However, some applications
may require the antenna(s), if removable, to be separated
from the product and installed remotely from the device
by using extension cables. For these applications, Linksys
offers an R-SMA extension cable (AC9SMA) and an R-TNC
extension cable (AC9TNC). Both of these cables are 9
meters long and have a cable loss (attenuation) of 5 dB. To
compensate for the attenuation, Linksys also offers higher
gain antennas, the HGA7S (with R-SMA connector) and
HGA7T (with R-TNC connector). These antennas have a
gain of 7 dBi and may only be used with either the R-SMA
or R-TNC extension cable.
Combinations of extension cables and antennas resulting
in a radiated power level exceeding 100 mW EIRP are
illegal.
Third-Party Software or Firmware
The use of software or firmware not supported/provided
by Linksys may result that the equipment is no longer
compliant with the regulatory requirements.
Technical Documents on
www.linksys.com/international
Follow these steps to access technical documents:
User Information for Consumer Products
Covered by EU Directive 2002/96/EC on
Waste Electric and Electronic Equipment
(WEEE)
This document contains important information for users
with regards to the proper disposal and recycling of
Linksys products. Consumers are required to comply with
this notice for all electronic products bearing the following
symbol:
English - Environmental Information for Customers in
the European Union
European Directive 2002/96/EC requires that the equipment
bearing this symbol on the product and/or its packaging must
not be disposed of with unsorted municipal waste. The symbol
indicates that this product should be disposed of separately
from regular household waste streams. It is your responsibility to
dispose of this and other electric and electronic equipment via
designated collection facilities appointed by the government or
local authorities. Correct disposal and recycling will help prevent
potential negative consequences to the environment and
human health. For more detailed information about the disposal
of your old equipment, please contact your local authorities,
waste disposal service, or the shop where you purchased the
product.
Enter http://www.linksys.com/international in your
1.
web browser.
Select the country or region in which you live.
2.
Click the Products tab.
3.
Select the appropriate product category.
4.
Select the product sub-category, if necessary.
5.
Select the product.
6.
Select the type of documentation you want from the
7.
More Information section. The document will open
in PDF format if you have Adobe Acrobat installed on
your computer.
NOTE: If you have questions regarding
the compliance of this product or you
cannot find the information you need,
please contact your local sales office or visit
www.linksys.com/international
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
Български (Bulgarian) - Информация относно
опазването на околната среда за потребители в
Европейския съюз
Европейска директива 2002/96/EC изисква уредите, носещи
този символ върху изделието и/или опаковката му, да не
се изхвърля т с несортирани битови отпадъци. Символът
обозначава, че изделието трябва да се изхвърля отделно от
сметосъбирането на обикновените битови отпадъци. Ваша
е отговорността този и другите електрически и електронни
уреди да се изхвърлят в предварително определени от
държавните или общински органи специализирани пунктове
за събиране. Правилното изхвърляне и рециклиране
ще спомогнат да се предотвратят евентуални вредни за
околната среда и здравето на населението последствия. За
по-подробна информация относно изхвърлянето на вашите
стари уреди се обърнете към местните власти, службите за
сметосъбиране или магазина, от който сте закупили уреда.
34
Page 36

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
Ceština (Czech) - Informace o ochraně životního
prostředí pro zákazníky v zemích Evropské unie
Evropská směrnice 2002/96/ES zakazuje, aby zařízení označené
tímto symbolem na produktu anebo na obalu bylo likvidováno
s netříděným komunálním odpadem. Tento symbol udává,
že daný produkt musí být likvidován odděleně od běžného
komunálního odpadu. Odpovídáte za likvidaci tohoto produktu
a dalších elektrických a elektronických zařízení prostřednictvím
určených sběrných míst stanovených vládou nebo místními
úřady. Správná likvidace a recyklace pomáhá předcházet
potenciálním negativním dopadům na životní prostředí a lidské
zdraví. Podrobnější informace o likvidaci starého vybavení si
laskavě vyžádejte od místních úřadů, podniku zabývajícího se
likvidací komunálních odpadů nebo obchodu, kde jste produkt
zakoupili.
Dansk (Danish) - Miljøinformation for kunder i EU
EU-direktiv 2002/96/EF kræver, at udstyr der bærer dette symbol
på produktet og/eller emballagen ikke må bortskaffes som
usorteret kommunalt affald. Symbolet betyder, at dette produkt
skal bortskaffes adskilt fra det almindelige husholdningsaffald.
Det er dit ansvar at bortskaffe dette og andet elektrisk og
elektronisk udstyr via bestemte indsamlingssteder udpeget
af staten eller de lokale myndigheder. Korrekt bortskaffelse
og genvinding vil hjælpe med til at undgå mulige skader for
miljøet og menneskers sundhed. Kontakt venligst de lokale
myndigheder, renovationstjenesten eller den butik, hvor du
har købt produktet, angående mere detaljeret information om
bortskaffelse af dit gamle udstyr.
Deutsch (German) - Umweltinformation für Kunden
innerhalb der Europäischen Union
Die Europäische Richtlinie 2002/96/EC verlangt, dass technische
Ausrüstung, die direkt am Gerät und/oder an der Verpackung mit
diesem Symbol versehen ist , nicht zusammen mit unsortiertem
Gemeindeabfall entsorgt werden darf. Das Symbol weist darauf
hin, dass das Produkt von regulärem Haushaltmüll getrennt
entsorgt werden sollte. Es liegt in Ihrer Verantwortung, dieses
Gerät und andere elektrische und elektronische Geräte über
die dafür zuständigen und von der Regierung oder örtlichen
Behörden dazu bestimmten Sammelstellen zu entsorgen.
Ordnungsgemäßes Entsorgen und Recyceln trägt dazu bei,
potentielle negative Folgen für Umwelt und die menschliche
Gesundheit zu vermeiden. Wenn Sie weitere Informationen zur
Entsorgung Ihrer Altgeräte benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an
die örtlichen Behörden oder städtischen Entsorgungsdienste
oder an den Händler, bei dem Sie das Produkt erworben haben.
Eesti (Estonian) - Keskkonnaalane informatsioon
Euroopa Liidus asuvatele klientidele
Euroopa Liidu direktiivi 2002/96/EÜ nõuete kohaselt on
seadmeid, millel on tootel või pakendil käesolev sümbol ,
keelatud kõrvaldada koos sorteerimata olmejäätmetega. See
sümbol näitab, et toode tuleks kõrvaldada eraldi tavalistest
olmejäätmevoogudest. Olete kohustatud kõrvaldama käesoleva
ja ka muud elektri- ja elektroonikaseadmed riigi või kohalike
ametiasutuste poolt ette nähtud kogumispunktide kaudu.
Seadmete korrektne kõrvaldamine ja ringlussevõtt aitab vältida
võimalikke negatiivseid tagajärgi keskkonnale ning inimeste
tervisele. Vanade seadmete kõrvaldamise kohta täpsema
informatsiooni saamiseks võtke palun ühendust kohalike
ametiasutustega, jäätmekäitlusfirmaga või kauplusega, kust te
toote ostsite.
Español (Spanish) - Información medioambiental para
clientes de la Unión Europea
La Directiva 2002/96/CE de la UE exige que los equipos que
lleven este símbolo en el propio aparato y/o en su embalaje
no deben eliminarse junto con otros residuos urbanos no
seleccionados. El símbolo indica que el producto en cuestión
debe separarse de los residuos domésticos convencionales con
vistas a su eliminación. Es responsabilidad suya desechar este y
cualesquiera otros aparatos eléctricos y electrónicos a través de
los puntos de recogida que ponen a su disposición el gobierno y
las autoridades locales. Al desechar y reciclar correctamente estos
aparatos estará contribuyendo a evitar posibles consecuencias
negativas para el medio ambiente y la salud de las personas. Si
desea obtener información más detallada sobre la eliminación
segura de su aparato usado, consulte a las autoridades locales,
al servicio de recogida y eliminación de residuos de su zona o
pregunte en la tienda donde adquirió el producto.
ξλληνικά (Greek) - Στοιχεία περιβαλλοντικής
προστασίας για πελάτες εντός της Ευρωπαϊκής
Ένωσης
Η Κοινοτική Οδηγία 2002/96/EC απαιτεί ότι ο εξοπλισμός ο οποίος
φέρει αυτό το σύμβολο στο προϊόν και/ή στη συσκευασία
του δεν πρέπει να απορρίπτεται μαζί με τα μικτά κοινοτικά
απορρίμματα. Το σύμβολο υποδεικνύει ότι αυτό το προϊόν θα
πρέπει να απορρίπτεται ξεχωριστά από τα συνήθη οικιακά
απορρίμματα. Είστε υπεύθυνος για την απόρριψη του παρόντος
και άλλου ηλεκτρικού και ηλεκτρονικού εξοπλισμού μέσω των
καθορισμένων εγκαταστάσεων συγκέντρωσης απορριμμάτων οι
οποίες παρέχονται από το κράτος ή τις αρμόδιες τοπικές αρχές.
Η σωστή απόρριψη και ανακύκλωση συμβάλλει στην πρόληψη
πιθανών αρνητικών συνεπειών για το περιβάλλον και την υγεία.
Για περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με την απόρριψη του
παλιού σας εξοπλισμού, παρακαλώ επικοινωνήστε με τις τοπικές
αρχές, τις υπηρεσίες απόρριψης ή το κατάστημα από το οποίο
αγοράσατε το προϊόν.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
35
Page 37

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
Français (French) - Informations environnementales
pour les clients de l’Union européenne
La directive européenne 2002/96/CE exige que l’équipement
sur lequel est apposé ce symbole sur le produit et/ou son
emballage ne soit pas jeté avec les autres ordures ménagères. Ce
symbole indique que le produit doit être éliminé dans un circuit
distinct de celui pour les déchets des ménages. Il est de votre
responsabilité de jeter ce matériel ainsi que tout autre matériel
électrique ou électronique par les moyens de collecte indiqués
par le gouvernement et les pouvoirs publics des collectivités
territoriales. L’élimination et le recyclage en bonne et due forme
ont pour but de lutter contre l’impact néfaste potentiel de ce
type de produits sur l’environnement et la santé publique. Pour
plus d’informations sur le mode d’élimination de votre ancien
équipement, veuillez prendre contact avec les pouvoirs publics
locaux, le service de traitement des déchets, ou l’endroit où vous
avez acheté le produit.
Italiano (Italian) - Informazioni relative all’ambiente
per i clienti residenti nell’Unione Europea
La direttiva europea 2002/96/EC richiede che le apparecchiature
contrassegnate con questo simbolo sul prodotto e/o
sull’imballaggio non siano smaltite insieme ai rifiuti urbani
non differenziati. Il simbolo indica che questo prodotto non
deve essere smaltito insieme ai normali rifiuti domestici. È
responsabilità del proprietario smaltire sia questi prodotti sia
le altre apparecchiature elettriche ed elettroniche mediante
le specifiche strutture di raccolta indicate dal governo o dagli
enti pubblici locali. Il corretto smaltimento ed il riciclaggio
aiuteranno a prevenire conseguenze potenzialmente negative
per l’ambiente e per la salute dell’essere umano. Per ricevere
informazioni più dettagliate circa lo smaltimento delle vecchie
apparecchiature in Vostro possesso, Vi invitiamo a contattare gli
enti pubblici di competenza, il servizio di smaltimento rifiuti o il
negozio nel quale avete acquistato il prodotto.
Latviešu valoda (Latvian) - Ekoloģiska informācija
klientiem Eiropas Savienības jurisdikcijā
Direktīvā 2002/96/EK ir prasība, ka aprīkojumu, kam pievienota
zīme uz paša izstrādājuma vai uz tā iesaiņojuma, nedrīkst
izmest nešķirotā veidā kopā ar komunālajiem atkritumiem
(tiem, ko rada vietēji iedzīvotāji un uzņēmumi). Šī zīme nozīmē
to, ka šī ierīce ir jāizmet atkritumos tā, lai tā nenonāktu kopā ar
parastiem mājsaimniecības atkritumiem. Jūsu pienākums ir šo
un citas elektriskas un elektroniskas ierīces izmest atkritumos,
izmantojot īpašus atkritumu savākšanas veidus un līdzekļus, ko
nodrošina valsts un pašvaldību iestādes. Ja izmešana atkritumos
un pārstrāde tiek veikta pareizi, tad mazinās iespējamais
kaitējums dabai un cilvēku veselībai. Sīkākas ziņas par
novecojuša aprīkojuma izmešanu atkritumos jūs varat saņemt
vietējā pašvaldībā, atkritumu savākšanas dienestā, kā arī veikalā,
kur iegādājāties šo izstrādājumu.
Lietuvškai (Lithuanian) - Aplinkosaugos informacija,
skirta Europos Sąjungos vartotojams
Europos direktyva 2002/96/EC numato, kad įrangos, kuri ir
kurios pakuotė yra pažymėta šiuo simboliu (įveskite simbolį),
negalima šalinti kartu su nerūšiuotomis komunalinėmis
atliekomis. Šis simbolis rodo, kad gaminį reikia šalinti atskirai
nuo bendro buitinių atliekų srauto. Jūs privalote užtikrinti, kad
ši ir kita elektros ar elektroninė įranga būtų šalinama per tam
tikras nacionalinės ar vietinės valdžios nustatytas atliekų rinkimo
sistemas. Tinkamai šalinant ir perdirbant atliekas, bus išvengta
galimos žalos aplinkai ir žmonių sveikatai. Daugiau informacijos
apie jūsų senos įrangos šalinimą gali pateikti vietinės valdžios
institucijos, atliekų šalinimo tarnybos arba parduotuvės, kuriose
įsigijote tą gaminį.
Malti (Maltese) - Informazzjoni Ambjentali għal Klijenti
fl-Unjoni Ewropea
Id-Direttiva Ewropea 2002/96/KE titlob li t-tagħmir li jkun fih issimbolu fuq il-prodott u/jew fuq l-ippakkjar ma jistax jintrema
ma’ skart muniċipali li ma ġiex isseparat. Is-simbolu jindika
li dan il-prodott għandu jintrema separatament minn ma’ liskart domestiku regolari. Hija responsabbiltà tiegħek li tarmi
dan it-tagħmir u kull tagħmir ieħor ta’ l-elettriku u elettroniku
permezz ta’ faċilitajiet ta’ ġbir appuntati apposta mill-gvern jew
mill-awtoritajiet lokali. Ir-rimi b’mod korrett u r-riċiklaġġ jgħin
jipprevjeni konsegwenzi negattivi potenzjali għall-ambjent u
għas-saħħa tal-bniedem. Għal aktar informazzjoni dettaljata
dwar ir-rimi tat-tagħmir antik tiegħek, jekk jogħġbok ikkuntattja
lill-awtoritajiet lokali tiegħek, is-servizzi għar-rimi ta’ l-iskart, jew
il-ħanut minn fejn xtrajt il-prodott.
Magyar (Hungarian) - Környezetvédelmi információ az
európai uniós vásárlók számára
A 2002/96/EC számú európai uniós irányelv megkívánja, hogy
azokat a termékeket, amelyeken, és/vagy amelyek csomagolásán
az alábbi címke megjelenik, tilos a többi szelektálatlan lakossági
hulladékkal együtt kidobni. A címke azt jelöli, hogy az adott
termék kidobásakor a szokványos háztartási hulladékelszállítási
rendszerektõl elkülönített eljárást kell alkalmazni. Az Ön
felelõssége, hogy ezt, és más elektromos és elektronikus
berendezéseit a kormányzati vagy a helyi hatóságok által
kijelölt gyűjtõredszereken keresztül számolja fel. A megfelelõ
hulladékfeldolgozás segít a környezetre és az emberi egészségre
potenciálisan ártalmas negatív hatások megelõzésében. Ha
elavult berendezéseinek felszámolásához további részletes
információra van szüksége, kérjük, lépjen kapcsolatba a helyi
hatóságokkal, a hulladékfeldolgozási szolgálattal, vagy azzal
üzlettel, ahol a terméket vásárolta.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
36
Page 38

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
Nederlands (Dutch) - Milieu-informatie voor klanten
in de Europese Unie
De Europese Richtlijn 2002/96/EC schrijft voor dat apparatuur die
is voorzien van dit symbool op het product of de verpakking,
niet mag worden ingezameld met niet-gescheiden huishoudelijk
afval. Dit symbool geeft aan dat het product apart moet worden
ingezameld. U bent zelf verantwoordelijk voor de vernietiging
van deze en andere elektrische en elektronische apparatuur via de
daarvoor door de landelijke of plaatselijke overheid aangewezen
inzamelingskanalen. De juiste vernietiging en recycling van
deze apparatuur voorkomt mogelijke negatieve gevolgen voor
het milieu en de gezondheid. Voor meer informatie over het
vernietigen van uw oude apparatuur neemt u contact op met
de plaatselijke autoriteiten of afvalverwerkingsdienst, of met de
winkel waar u het product hebt aangeschaft.
Norsk (Norwegian) - Miljøinformasjon for kunder i EU
EU-direktiv 2002/96/EF krever at utstyr med følgende symbol
avbildet på produktet og/eller pakningen, ikke må kastes
sammen med usortert avfall. Symbolet indikerer at dette
produktet skal håndteres atskilt fra ordinær avfallsinnsamling
for husholdningsavfall. Det er ditt ansvar å kvitte deg med
dette produktet og annet elektrisk og elektronisk avfall via egne
innsamlingsordninger slik myndighetene eller kommunene
bestemmer. Korrekt avfallshåndtering og gjenvinning vil
være med på å forhindre mulige negative konsekvenser for
miljø og helse. For nærmere informasjon om håndtering av
det kasserte utstyret ditt, kan du ta kontakt med kommunen,
en innsamlingsstasjon for avfall eller butikken der du kjøpte
produktet.
Polski (Polish) - Informacja dla klientów w Unii
Europejskiej o przepisach dotyczących ochrony
środowiska
Dyrektywa Europejska 2002/96/EC wymaga, aby sprzęt
oznaczony symbolem znajdującym się na produkcie i/lub jego
opakowaniu nie był wyrzucany razem z innymi niesortowanymi
odpadami komunalnymi. Symbol ten wskazuje, że produkt
nie powinien być usuwany razem ze zwykłymi odpadami z
gospodarstw domowych. Na Państwu spoczywa obowiązek
wyrzucania tego i innych urządzeń elektrycznych oraz
elektronicznych w punktach odbioru wyznaczonych przez władze
krajowe lub lokalne. Pozbywanie się sprzętu we właściwy sposób
i jego recykling pomogą zapobiec potencjalnie negatywnym
konsekwencjom dla środowiska i zdrowia ludzkiego. W celu
uzyskania szczegółowych informacji o usuwaniu starego sprzętu,
prosimy zwrócić się do lokalnych władz, służb oczyszczania
miasta lub sklepu, w którym produkt został nabyty.
Português (Portuguese) - Informação ambiental para
clientes da União Europeia
A Directiva Europeia 2002/96/CE exige que o equipamento
que exibe este símbolo no produto e/ou na sua embalagem
não seja eliminado junto com os resíduos municipais não
separados. O símbolo indica que este produto deve ser
eliminado separadamente dos resíduos domésticos regulares.
É da sua responsabilidade eliminar este e qualquer outro
equipamento eléctrico e electrónico através das instalações
de recolha designadas pelas autoridades governamentais ou
locais. A eliminação e reciclagem correctas ajudarão a prevenir
as consequências negativas para o ambiente e para a saúde
humana. Para obter informações mais detalhadas sobre a
forma de eliminar o seu equipamento antigo, contacte as
autoridades locais, os serviços de eliminação de resíduos ou o
estabelecimento comercial onde adquiriu o produto.
Română (Romanian) - Informaţii de mediu pentru
clienţii din Uniunea Europeană
Directiva europeană 2002/96/CE impune ca echipamentele care
prezintă acest simbol pe produs şi/sau pe ambalajul acestuia să
nu fie casate împreună cu gunoiul menajer municipal. Simbolul
indică faptul că acest produs trebuie să fie casat separat de
gunoiul menajer obişnuit. Este responsabilitatea dvs. să casaţi
acest produs şi alte echipamente electrice şi electronice prin
intermediul unităţilor de colectare special desemnate de guvern
sau de autorităţile locale. Casarea şi reciclarea corecte vor ajuta
la prevenirea potenţialelor consecinţe negative asupra sănătăţii
mediului şi a oamenilor. Pentru mai multe informaţii detaliate
cu privire la casarea acestui echipament vechi, contactaţi
autorităţile locale, serviciul de salubrizare sau magazinul de la
care aţi achiziţionat produsul.
Slovenčina (Slovak) - Informácie o ochrane životného
prostredia pre zákazníkov v Európskej únii
Podľa európskej smernice 2002/96/ES zariadenie s týmto
symbolom na produkte a/alebo jeho balení nesmie byť
likvidované spolu s netriedeným komunálnym odpadom.
Symbol znamená, že produkt by sa mal likvidovať oddelene
od bežného odpadu z domácností. Je vašou povinnosťou
likvidovať toto i ostatné elektrické a elektronické zariadenia
prostredníctvom špecializovaných zberných zariadení určených
vládou alebo miestnymi orgánmi. Správna likvidácia a recyklácia
pomôže zabrániť prípadným negatívnym dopadom na životné
prostredie a zdravie ľudí. Ak máte záujem o podrobnejšie
informácie o likvidácii starého zariadenia, obráťte sa, prosím, na
miestne orgány, organizácie zaoberajúce sa likvidáciou odpadov
alebo obchod, v ktorom ste si produkt zakúpili.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
37
Page 39

Appendix D
The available channels supported by the wireless products
in various countries are different by firmware.
Regulatory Information
Slovenčina (Slovene) - Okoljske informacije za stranke
v Evropski uniji
Evropska direktiva 2002/96/EC prepoveduje odlaganje opreme,
označene s tem simbolom – na izdelku in/ali na embalaži – med
običajne, nerazvrščene odpadke. Ta simbol opozarja, da je treba
izdelek odvreči ločeno od preostalih gospodinjskih odpadkov.
Vaša odgovornost je, da to in preostalo električno in elektronsko
opremo odnesete na posebna zbirališča, ki jih določijo
državne ustanove ali lokalna uprava. S pravilnim odlaganjem
in recikliranjem boste preprečili morebitne škodljive vplive na
okolje in zdravje ljudi. Če želite izvedeti več o odlaganju stare
opreme, se obrnite na lokalno upravo, odpad ali trgovino, kjer
ste izdelek kupili.
Suomi (Finnish) - Ympäristöä koskevia tietoja EUalueen asiakkaille
EU-direktiivi 2002/96/EY edellyttää, että jos laitteistossa on tämä
symboli itse tuotteessa ja/tai sen pakkauksessa, laitteistoa
ei saa hävittää lajittelemattoman yhdyskuntajätteen mukana.
Symboli merkitsee sitä, että tämä tuote on hävitettävä erillään
tavallisesta kotitalousjätteestä. Sinun vastuullasi on hävittää
tämä elektroniikkatuote ja muut vastaavat elektroniikkatuotteet
viemällä tuote tai tuotteet viranomaisten määräämään
keräyspisteeseen. Laitteiston oikea hävittäminen estää
mahdolliset kielteiset vaikutukset ympäristöön ja ihmisten
terveyteen. Lisätietoja vanhan laitteiston oikeasta hävitystavasta
saa paikallisilta viranomaisilta, jätteenhävityspalvelusta tai siitä
myymälästä, josta ostit tuotteen.
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved
by the party responsible for compliance could void your authority to
operate the equipment.
Svenska (Swedish) - Miljöinformation för kunder i
Europeiska unionen
Det europeiska direktivet 2002/96/EC kräver att utrustning med
denna symbol på produkten och/eller förpackningen inte får
kastas med osorterat kommunalt avfall. Symbolen visar att denna
produkt bör kastas efter att den avskiljts från vanligt hushållsavfall.
Det faller på ditt ansvar att kasta denna och annan elektrisk och
elektronisk utrustning på fastställda insamlingsplatser utsedda
av regeringen eller lokala myndigheter. Korrekt kassering och
återvinning skyddar mot eventuella negativa konsekvenser
för miljön och personhälsa. För mer detaljerad information om
kassering av din gamla utrustning kontaktar du dina lokala
myndigheter, avfallshanteringen eller butiken där du köpte
produkten.
WEB: For additional information, please visit
www.linksys.com/international
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement:
1. This Transmitter must not be co-located or operating in
conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Wireless-G ADSL2+ IAD Gateway
7062610NC-JL
38
 Loading...
Loading...