Page 1

Liebert iTRUST UPS System
User Manual
E1-20020516-C-1.0
Liebert Corporation
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction .....................................................................................................................1
1.1 Basics.................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Configuration ......................................................................................................................1
1.3 Operation Theory................................................................................................................2
1.4 Structure and Layout ..........................................................................................................3
1.5 Operation Modes................................................................................................................4
1.6 Basic Functions ..................................................................................................................8
1.7 Specifications .....................................................................................................................8
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation .......................................................................................................13
2.1 Environmental Conditions.................................................................................................13
2.2 Unpacking.........................................................................................................................13
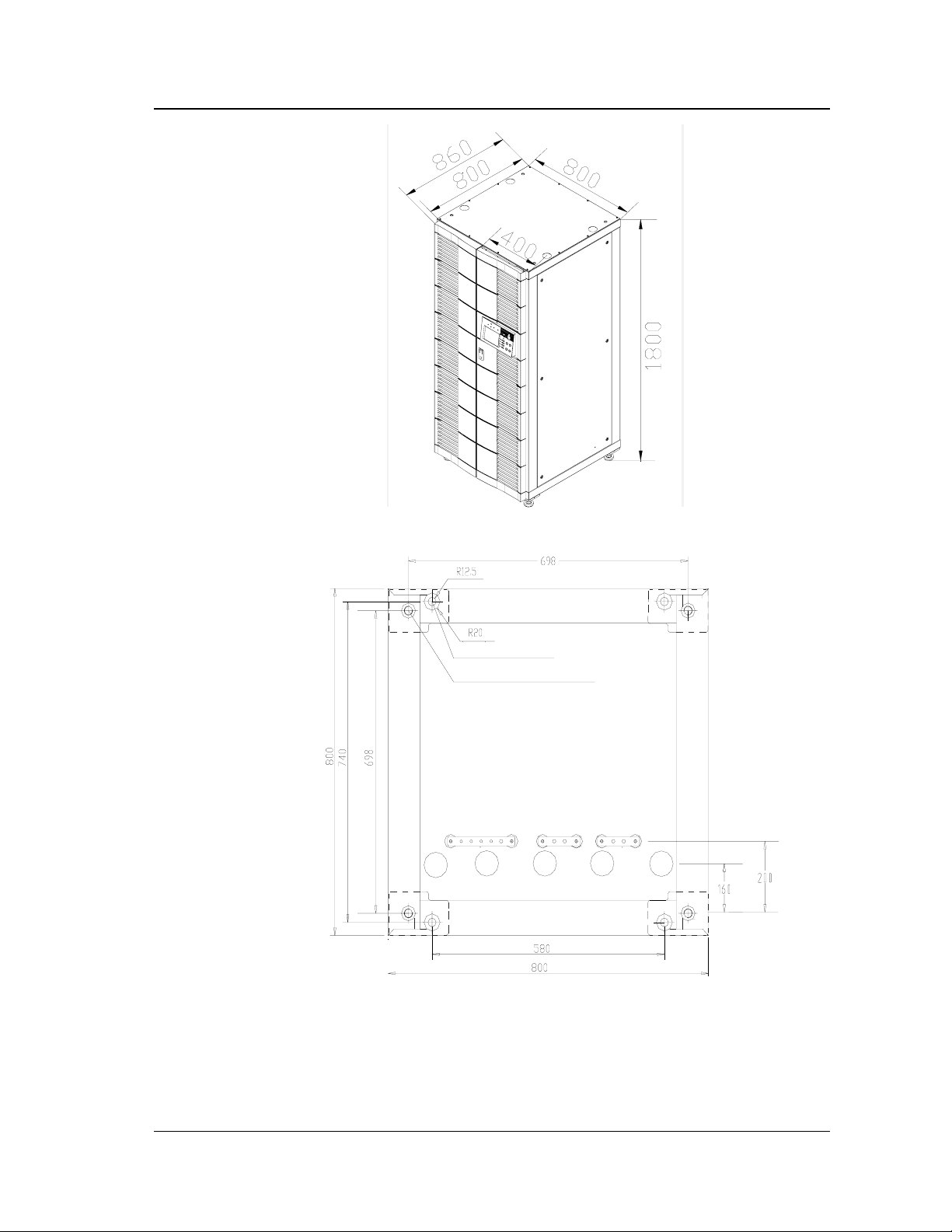
2.3 Dimensions.......................................................................................................................13
2.4 Transportation ..................................................................................................................16
2.5 Positioning of UPS............................................................................................................16
2.6 Cable Access....................................................................................................................18
2.7 Ventilation.........................................................................................................................19
2.8 Layout of Cabinet .............................................................................................................20
Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly.......................................................................................................23
3.1 Selection of cables ...........................................................................................................23
3.1.1 Current carrying capacity of cables ........................................................................23
3.1.2 Selection of power cables.......................................................................................23
3.1.3 Selection of signal cables.......................................................................................24
3.2 Cable connections............................................................................................................24
3.2.1 Power cables..........................................................................................................24
3.2.2 Signal cable............................................................................................................28
3.3 Connection of Single UPS System ...................................................................................35
Chapter 4 Commissioning of UPS.................................................................................................37
4.1 Startup Procedure ............................................................................................................37
4.1.1 Explanation of Circuit Breakers ..............................................................................37
4.1.2 Startup....................................................................................................................37
4.2 Setting the functions.........................................................................................................38
4.3 Functional checks.............................................................................................................40
4.3.1 Check the function of the display panel..................................................................41
4.3.2 Switching between operation mode........................................................................41
Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel ...........................................................................................43
5.1 Display panel....................................................................................................................43
5.1.1 Layout of Display Panel..........................................................................................43
5.1.2 LED Indication........................................................................................................44
5.1.3 Functional Keys......................................................................................................45
Page 4

5.1.4 Alarm Buzzer..........................................................................................................46
5.1.5 LCD and Menu Keys .............................................................................................. 46
5.2 The displayed information ................................................................................................ 48
5.2.1 Opening display ......................................................................................................48
5.2.2 Main Menu Display.................................................................................................48
5.2.3 UPS Basic Information...........................................................................................48
5.2.4 Menu Keys Display Window...................................................................................49
5.2.5 Information of main menu.......................................................................................50
5.3 Function Setup .................................................................................................................54
5.3.1 Language setup .....................................................................................................54
5.3.2 Address setup ........................................................................................................55
5.3.3 Time setup .............................................................................................................55
5.3.4 Manual battery self-test..........................................................................................58
5.3.5 Contrast adjustment ...............................................................................................59
5.3.6 History log ..............................................................................................................59
5.3.7 background communication setup.......................................................................... 60
5.3.8 Call-back number setup ..........................................................................................61
5.4 Prompt window.................................................................................................................63
5.5 Events and State Information: .......................................................................................... 66
Chapter 6 Maintenance ................................................................................................................. 69
6.1 Setup procedures.............................................................................................................69
6.1.1 Start up...................................................................................................................69
6.1.2 Shutdown ............................................................................................................... 70
6.1.3 Transferring between operation modes..................................................................71
6.1.4 Emergency shutdown and recovery.......................................................................71
6.1.5 Mute .......................................................................................................................72
6.1.6 Fault clear ..............................................................................................................72
6.1.7 Monitoring system..................................................................................................73
6.1.8 Input and output contacts........................................................................................75
6.1.9 Temperature measuring.........................................................................................76
6.2 Maintenance.....................................................................................................................76
6.2.1 Daily maintenance..................................................................................................76
6.2.2 Battery maintenance .............................................................................................. 78
6.2.3 Shutdown maintenance..........................................................................................80
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting............................................................................................................81
7.1 UPS system troubleshooting............................................................................................81
7.1.1 Basics.....................................................................................................................81
7.1.2 Procedures............................................................................................................. 81
7.2 LED indicator....................................................................................................................81
7.2.1 LED display............................................................................................................81
7.2.2 LED indicator of lightning protection device ...........................................................82
7.3 Buzzer alarm ....................................................................................................................82
7.4 LCD indication for fault information .................................................................................. 83
Page 5

Chapter 8 Parallel System.............................................................................................................87
8.1 System Introduction..........................................................................................................87
8.1.1 Basics.....................................................................................................................87
8.1.2 Theory of Operation...............................................................................................88
8.1.3 Operation modes....................................................................................................90
8.2 Installation ........................................................................................................................91
8.2.1 Cabinet installation .................................................................................................91
8.2.2 Electrical installation...............................................................................................92
8.3 External Power Distribution ..............................................................................................93
8.4 Start up of Parallel Operation System ..............................................................................93
8.5 Using the Parallel Operation System ................................................................................94
8.5.1 Switch on the Parallel System................................................................................94
8.5.2 Shutdown the Parallel Operation System...............................................................95
8.5.3 Transferring between Operation Modes .................................................................96
8.5.4 Repairing the failed UPS unit in parallel operation system .....................................97
8.5.5 Emergency shutdown.............................................................................................98
8.5.6 Fault and Fault Process Methods...........................................................................99
Chapter 9 Optional Parts .............................................................................................................101
9.1 Battery ............................................................................................................................101
9.1.1 Capacity selection ................................................................................................101
9.2 Battery cabinet................................................................................................................102
9.2.1 External Dimensions.............................................................................................102
9.2.2 Installation of battery cabinet................................................................................103
9.2.3 Wiring of the batteries...........................................................................................103
9.3 SNMP Card and the Software ........................................................................................106
9.3.1 Product structure and ports ..................................................................................106
9.3.2 Technical features ................................................................................................106
9.4 Network Software ...........................................................................................................107
9.5 MODEM..........................................................................................................................107
9.6 Temperature sensor TMP12Z.........................................................................................108
9.7 Level C Lightning Protection System SPD24Z...............................................................108
9.7.1 Introduction of SPD24Z ........................................................................................109
9.7.2 Installation procedures of SPD24Z.......................................................................109
9.7.3 Using and Maintenance.........................................................................................111
9.8 Bypass Isolation Transformer.........................................................................................111
Chapter 10 Service after Sales....................................................................................................112
10.1 Abnormal Fault Handling..............................................................................................112
10.2 Technical support ............................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
10.3 Warranty.......................................................................................................................115
Page 6

Page 7
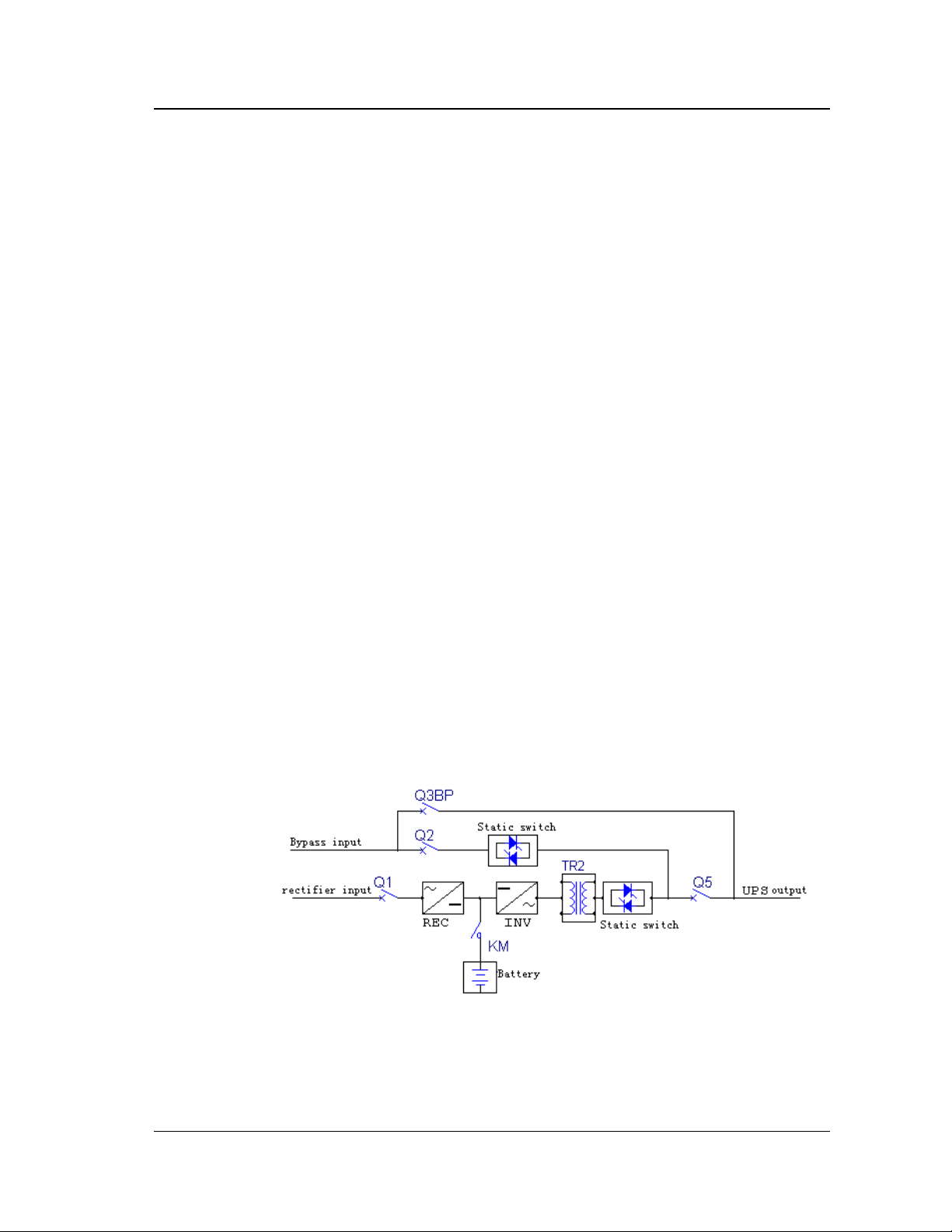
1.1 Basics
The Liebert iTrust UPS System is connected between the utility source and the
critical load to provide uninterruptible power to the load. The power from the UPS
being free of voltage and frequency variation and disturbances from utility. The UPS
has an output isolation transformer to provide galvanic isolation between the load
and utility. The UPS also uses the latest in high frequency double conversion
PWM technology and a fully digital control.
It also has advanced network management functions.
1.2 Configuration
The UPS consists of the following modules : rectifier, inverter, static bypass,
maintenance bypass, output isolation transformer, inverter static switch, battery and
input and output circuit breakers.
Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 1 Introduction
As shown in Figure 1-1, the AC utility source is input at Q1 and the rectifier
converts the AC Utility into DC source. The Inverter will convert the DC source or
the DC source from the batteries into AC source that is output from the isolation
transformer. The battery will power the load through the inverter in case of a power
failure. The utility source can also power the load through the static bypass.
Besides this, if maintenance or repair of the UPS is necessary, the UPS can
support the load through the maintenance bypass without interrupting the load.
Figure 1-1 Theory of UPS
1
Page 8
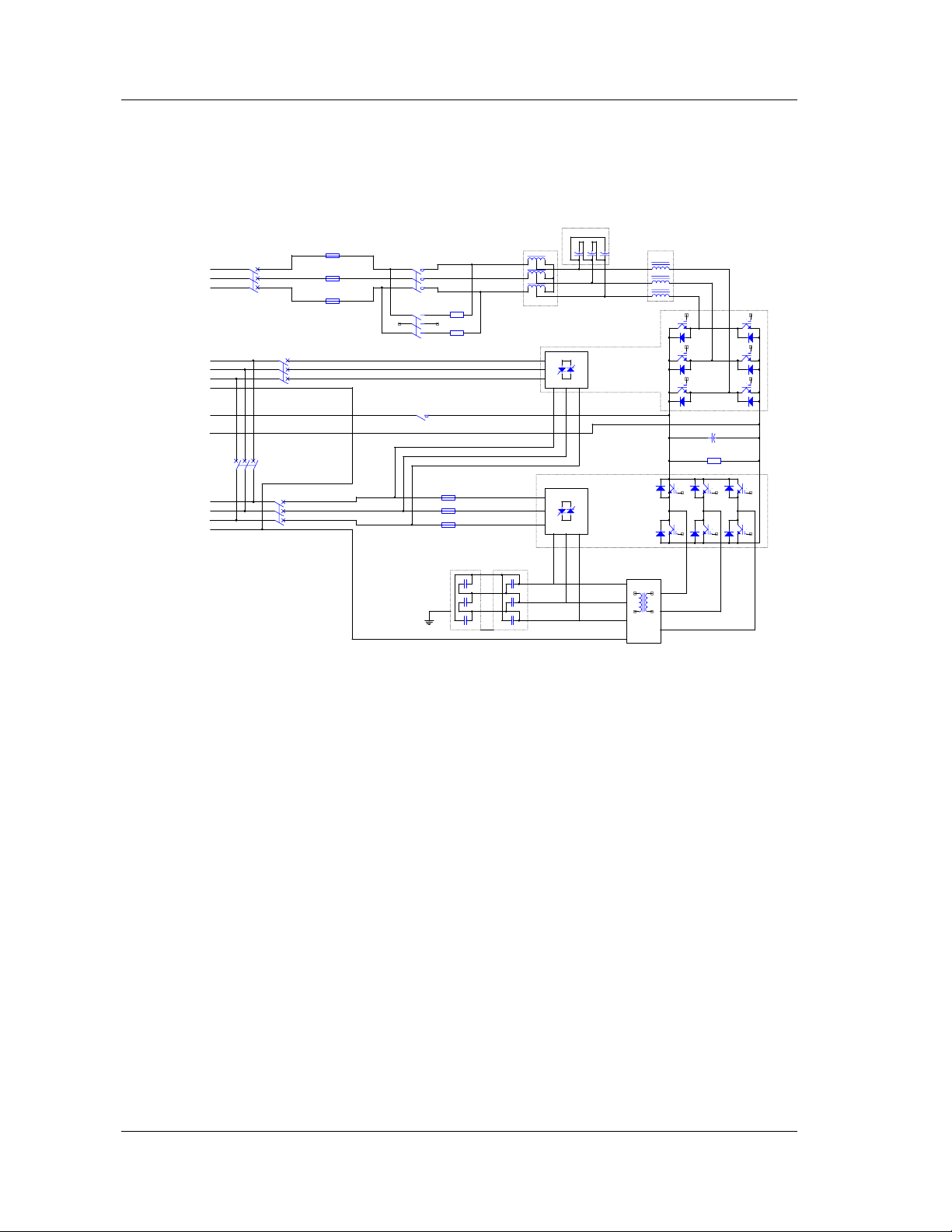
1.3 Operation Theory
The UPS circuit diagram is shown in Figure 1-2.
A1
B1
C1
A2
B1
C1
N2
BP
BN
U
V
W
N
Q1
Q2
Q3BP
Q5
FU1
FU2
FU3
Chapter 1 Introduction
KM1
KA1
Res1
Res2
KM2
FU4
FU5
FU6
AC2
TR1
L1
DC1
+
Res3
AC4
AC3
TR2
DZN6
Figure 1-2 Main circuit of UPS
The utility source is input at Q1 and flows through the fuse, the transformer,
inductor and into the high frequency rectifier which will convert the AC power into
DC power. The rectifier has PFC and charger function and make use of soft start
and DSP digital technology to improve the system immunity against surge, improve
the stability of the DC bus voltage, reduce the charging current ripple and prolongs
the battery life.
The battery is connected to the UPS through contactor. If the DC bus voltage drop
through certain threshold, then the contactor will activate to connect the battery to
the DC bus. The battery will supply the DC power to the inverter through a filtering
circuit.
The inverter uses digital vector control technology based on DSP to modulate six
IGBTs through SVPWM and invert DC power to AC three phase power.
The output is isolated from the load by Delta/Zig-Zag transformer, static switch,
fuse and circuit breakers.
The bypass source is input at Q2 and output through the bypass static switch.
2
Page 9
The double DSP and MCU form the full digital control system to realize the powerful
function of the UPS. The switching between the operation modes is realized by
controlling the bypass static switch and the inverter static switch. Advanced battery
management prolongs battery life.
Multi-communication ports and management software make it possible for the
customer to monitor the UPS performance locally or remotely. The Liebert UPS
uses full digital, discrete and on-line parallel operation technology. In parallel
operation, several UPS units input parallel logic signals and cross current detection
signals through parallel operation boards to enable a maximum of four UPS units to
operate in parallel. (N+X) redundancy parallel operation, capacity expansion and
hot-standby configuration can be realized. If an additional UPS is required to be
added to the system, no auxiliary equipment is required and power to the load
need not be interrupted.
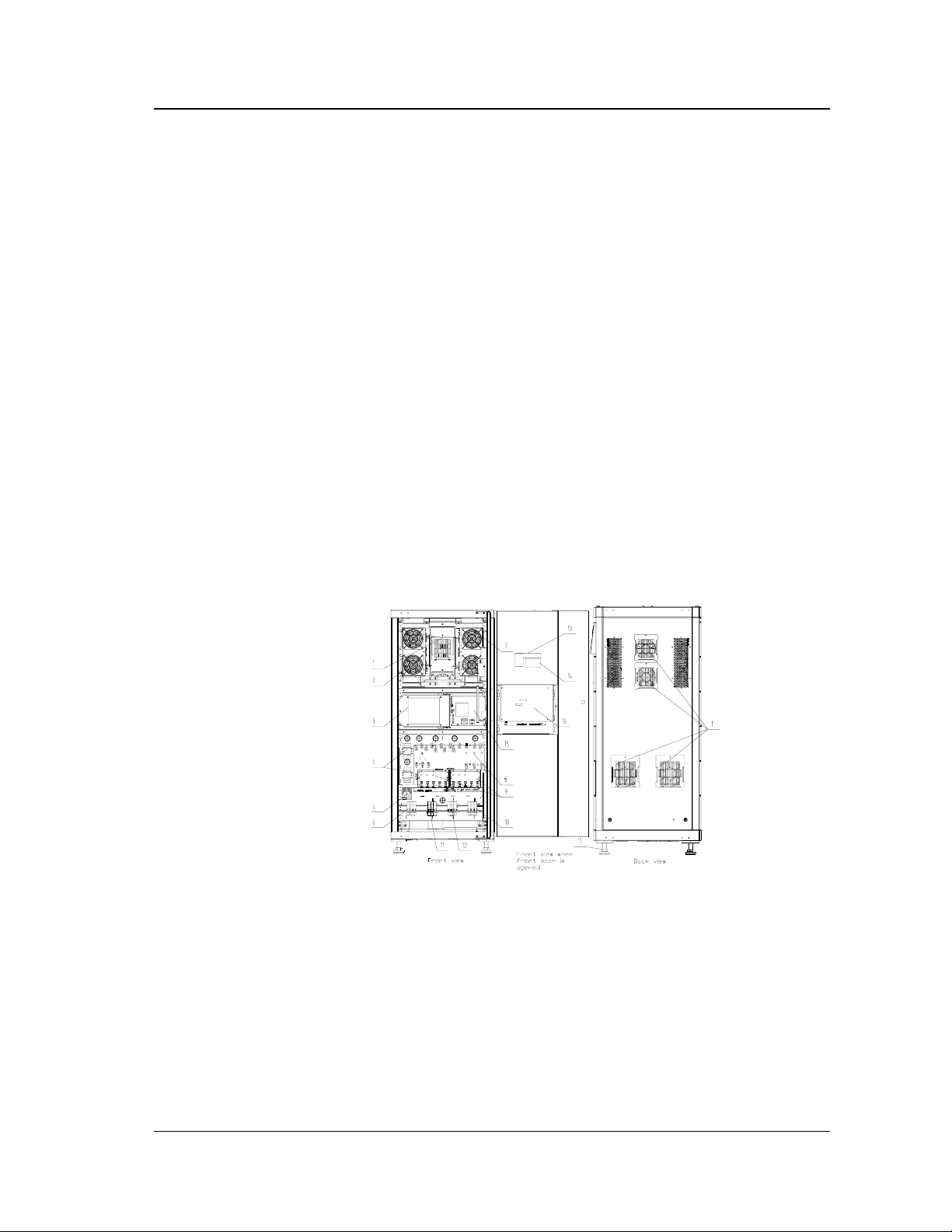
1.4 Structure and Layout
The structure and layout of the system is shown on Figures 1-3 and 1-4. The
system consists of the rectifier, inverter, auxiliary power supply, input and output
power distribution, monitoring system, parallel control system, lightning protection
unit, EMI filter, fan and input and output isolation filters.
Chapter 1 Introduction
1:Fan 2:rectifier 3:two auxiliary power supply boards ULW2L61M5
4:contactor 5:battery input terminals 6:circuit breaker Q3BP for maintenance
7:Inverter 8:Power distribution board ULK2L61R1
9:D level lightning protection device SPD12Z
10: Output circuit breaker Q5 11:rectifier input circuit breaker Q1
12:bypass input circuit breaker Q2 13:operation keypad board ULW2L61K1
14:LCD 15:parallel board ULW2L61M3
16:monitoring board ULW2L61U2 17:4 leveling feet (M20)
Figure 1-3 Components of 20/30kVA UPS
3
Page 10
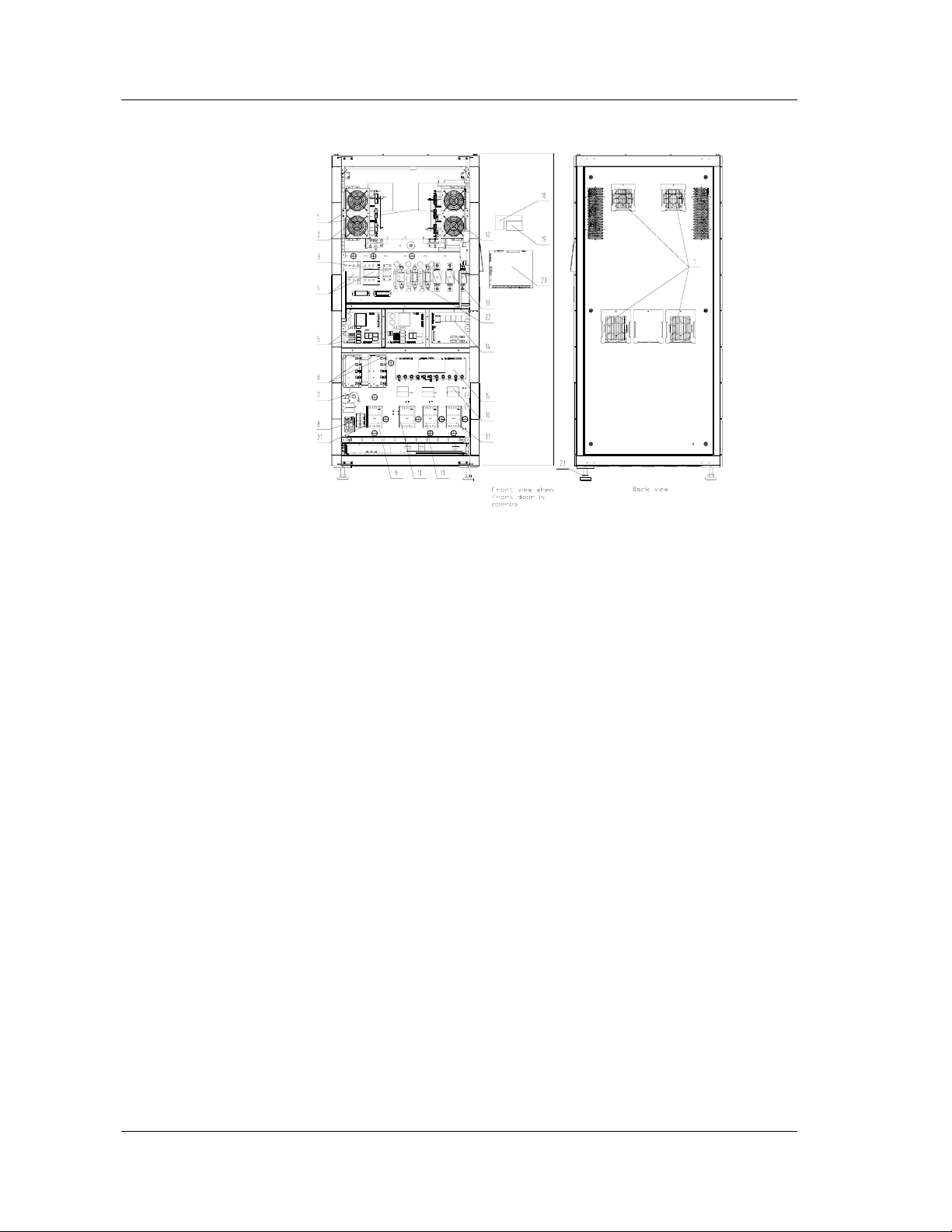
Chapter 1 Introduction
Front view
1:Fan 2:rectifier 3: softstart relays 4:contactor
5: two auxiliary power supply boards ULW2L61M5
6: D level lightning protection device SPD12Z 7: Hall current sensor
8:battery input terminals 9:circuit breaker Q3BP for maintenance
10:rectifier input circuit breaker Q1 11:bypass input circuit breaker Q2
12:Inverter 13: fast fuse
14: parallel board ULW2L61M3 15: EMI board ULW2L61M4
16: magnetic core 17: output circuit breaker
18:operation keypad board 19: LCD
20: monitoring board ULW2L61U2 21: Battery EMI board
22: Fuse NT100 23: 4 leveling feet (M20)
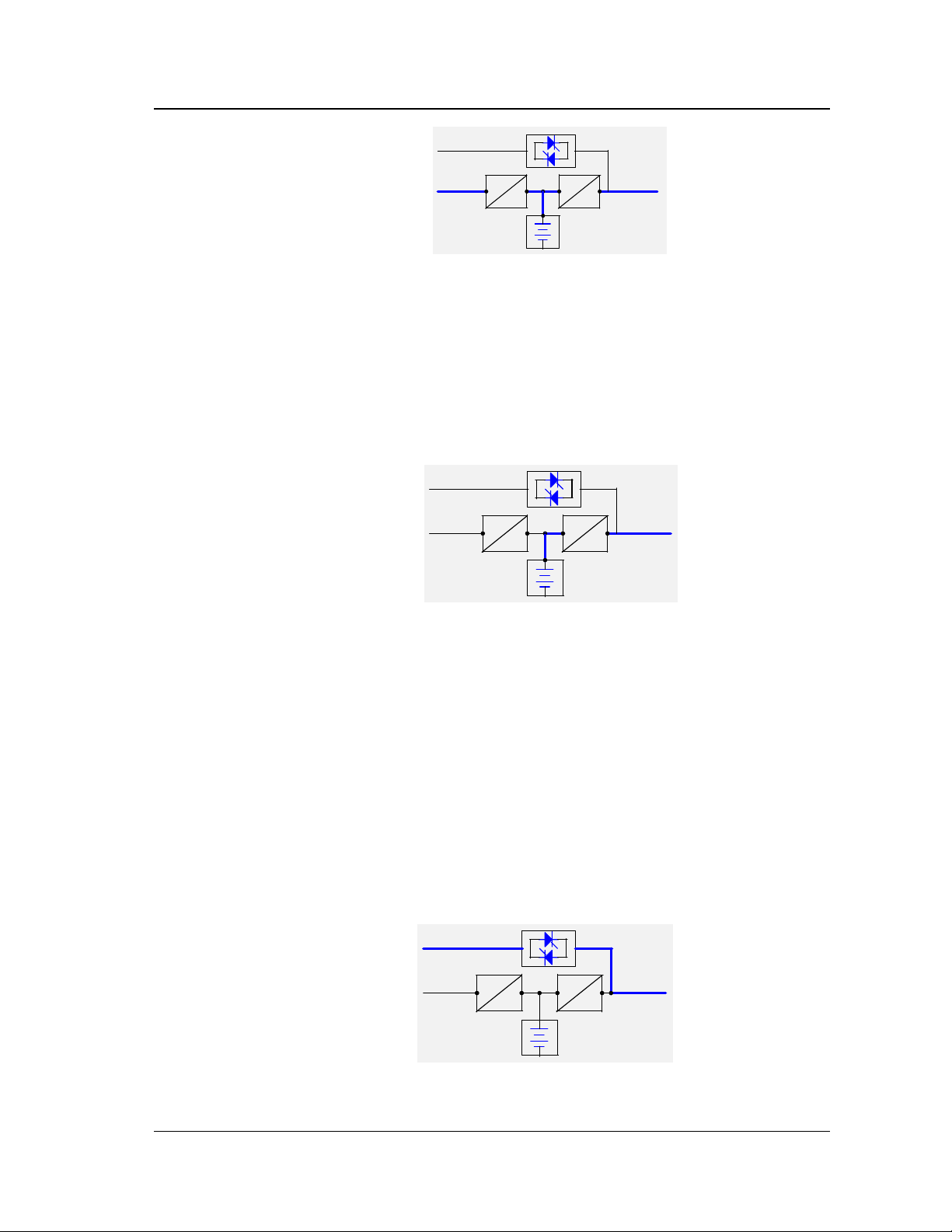
1.5 Operation Modes
1. Normal mode
When the utility is normal, the UPS powers the load through the rectifier and
inverter and charges the batteries at the same time, as shown in Figure 1-5. This is
called the Normal Mode.
Figure 1-4 Components of 40/60kVA UPS
4
Page 11
Chapter 1 Introduction
-
~
-
output
Bypass
Mains output
2. Battery Mode
When the utility fails, the UPS system will switch to battery mode without
interruption and the battery will power the load through the inverter.
The UPS can return to normal mode automatically when the utility returns to normal,
as shown in Figure 1-6.
Bypass
Mains
~
Figure 1-5 Normal mode
~
-~
Figure 1-6 battery mode
3. Bypass Mode
In the event of an inverter overload which last longer than the typical time, an
output short circuit or a fault on the inverter, the UPS will transfer the load to bypass.
There are two kinds of bypass modes. In the first kind, the UPS can be set to
return to normal mode automatically when the fault is cleared. In the second kind,
the UPS is set to return to normal mode only with a manual transfer.
When the main UPS circuit fails, the battery is depleted or a severe fault occurs,
the inverter will be shut down and the system will remain in the bypass mode. The
system can return to normal mode only with a manual reset after the fault is cleared,
as shown in Figure 1-7.
Bypass
Mains
~-
output
~-
Figure 1-7 bypass mode
5
Page 12
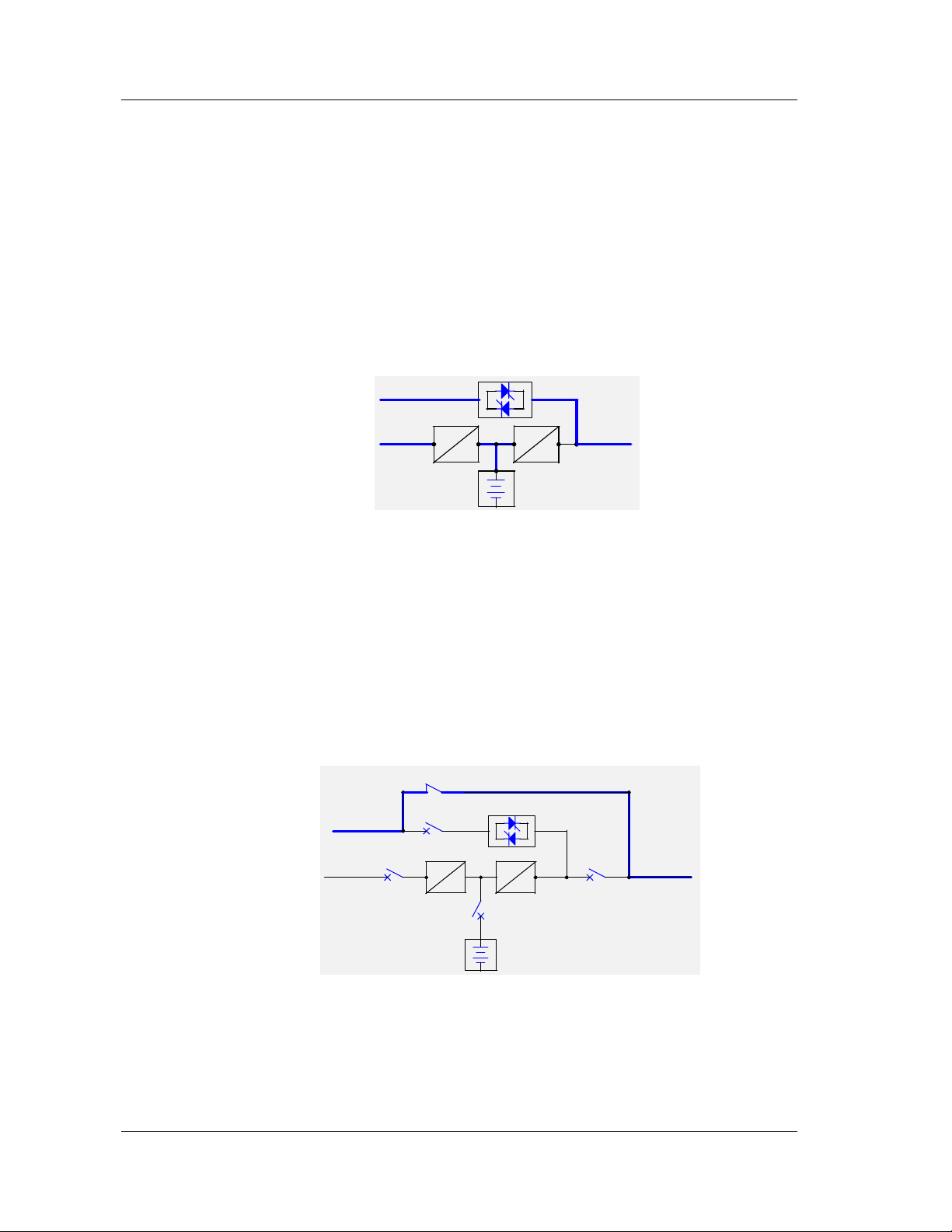
Chapter 1 Introduction
4. ECO Mode
If the load has no requirement for power quality but has a high requirement for
efficiency, then the UPS can be set in ECO mode. In this mode, the system will
power the load through the static bypass switch and the rectifier will charge the
batteries. When the bypass source fails or out of normal range, the UPS will revert
back to normal mode and powers the load through the batteries. The total transfer
time will be less than 15 msecs. When the bypass source recovers back to normal,
the system will return to ECO mode automatically and the system efficiency is
greatly improved, as shown in Figure 1-8. Note that the ECO mode function can
only be set by qualified personnel and applies to single UPS modules only.
-
-~
outputMains
~
Bypass
Figure 1-8 ECO mode
5. Maintenance Mode
When the UPS has to be repaired or has to undergo routine maintenance, the UPS
can be set to maintenance mode by switching on the maintenance bypass circuit
breaker. The load will be powered from the maintenance bypass supply without
interruption.
During maintenance, the circuit breakers Q1, Q2, QF1 and Q5 should be switched
off to ensure the safety of maintenance personnel. See Figure 1-9.
Q3BP
-
-~
QF1
~
Q5
OutputMains
Bypass
Q1
Q2
6
Figure 1-9
Page 13
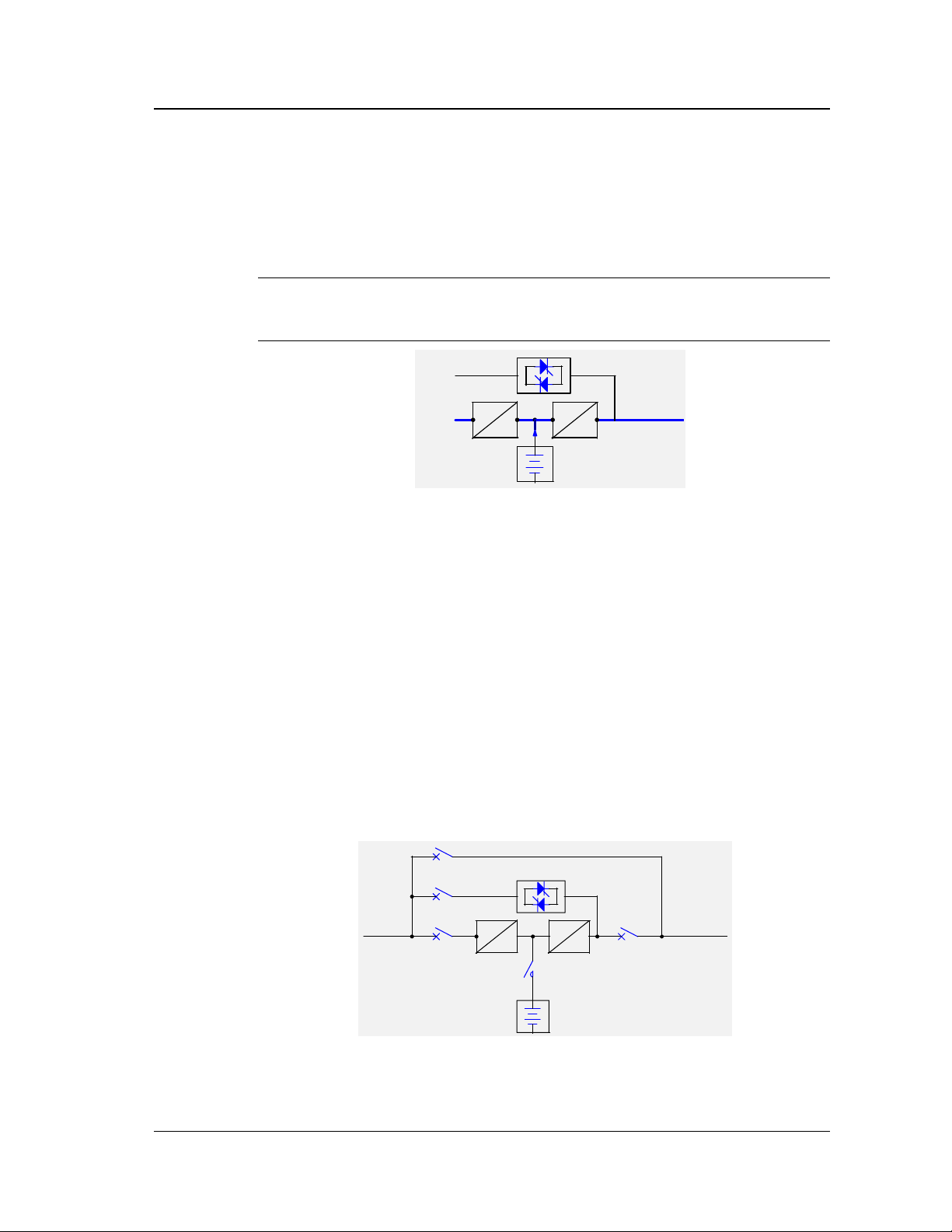
Chapter 1 Introduction
6. United Power Mode
When the utility is not available and the capacity of the generator set is inadequate
to support the load, the battery will power the load together with the generator
automatically. The operating time under this mode should not exceed the autonomy
time of the batteries, as shown in Figure 1-10
Note :
This mode can only be set by qualified personnel only.
-
-
outputMains
~
Bypass
~
Figure 1-10
7. Parallel Operation mode
When several UPS units (maximum four units) are in parallel operation mode, they
will share the load automatically amongst themselves. If one unit fails, this unit will
be shut down automatically and the remaining units will share the load equally. If
overload occurs, the UPS will transfer to bypass operation mode. Parallel operation
mode also has normal mode, battery mode, bypass mode, maintenance mode and
united power mode.
8. Dual Input Mode
The main circuit and the bypass can use the same or different sources. The input
methods are shown in Figure 1-11 and Figure 1-12.
7
-
Fig 1-11
~
Mains output
~
Page 14
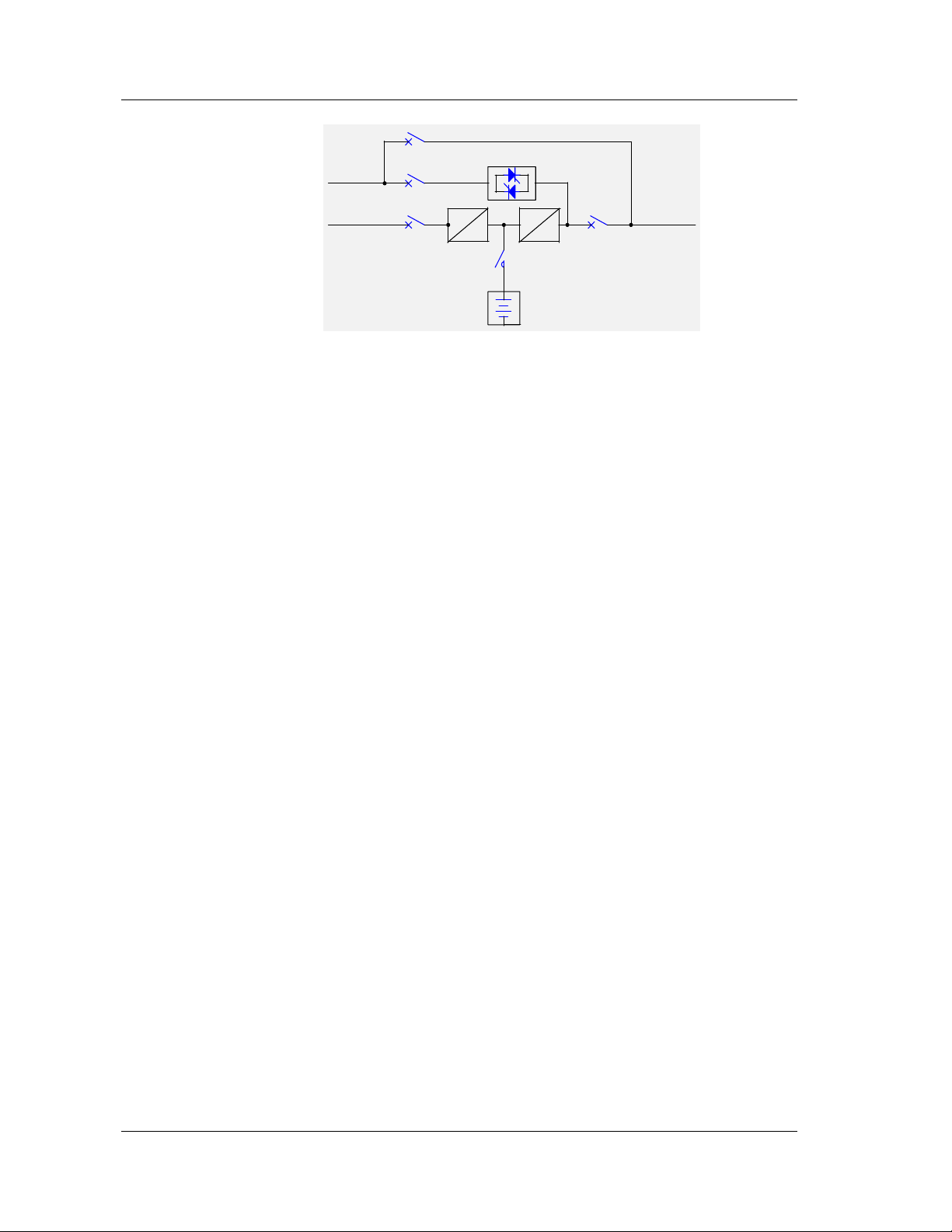
Bypass
Mains
Chapter 1 Introduction
~
-~
-
output
1.6 Basic Functions
Battery Management Function - The UPS has advanced battery management
functions including battery fault detection and backup time forecast.
Soft Start Function - Complete delay soft start function can reduce the surge to the
UPS unit and utility source.
Alarm and Protection Function - The UPS can generator audible and visual alarm
through LCD, input/output contacts and network transmission. It can help
maintenance personnel to locate and clear the faults that are sent out in time,
accurately and in detail.
Dark Start Function - When the utility is unavailable, the UPS can start from battery
that is connected to the DC Bus.
Automatic Re-start when Utility returns - This function only applies to the UPS that
has batteries. The UPS shuts down due to low battery, and restart automatically
when the utility returns. At this time , its operation mode is the one before the utility
fails.
Fig 1-12
Monitoring Functions - The UPS monitoring system has an advanced monitoring
function and parallel control functions. It supports flexible network monitoring to
satisfy different customer requirements.
1.7 Specifications
1. Functional Parameters
8
Page 15
Chapter 1 Introduction
Parameters of Liebert iTrust UPS are given in Table1-1
Capacity 20kVA 30kVA 40kVA 60kVA
Model UL33-0200L UL33-0300L UL33-0400L UL33-0600L
Input Voltage 380/400/415V(line-to-line voltage)
AC Power Input Three-phase three-wire
Power Factor >0.99
Harmonic Current <4%(Voltage distortion lower than 2% at rated load)
Rectifier
input
Bypass input
Voltage Range
Input current limiting
frequency range
Input Voltage 380/400/415V(line-to-line voltage)
Input Voltage Range
AC Power Input Three-phase four-wire
Frequency range
Voltage regulation
(balanced load)
Voltage transient response
Transient recovery time <60ms
Voltage distortion(linear load)
+15%~-20%
Lowest operating voltage: -45%
Input Current: <115%In for continuous operation; 115~140%In
for 5 minutes; 140~165%In for 1minute; Current limiting at
current over 165%In(In is the rated output current without
deration)
50Hz ±10%
10%
±
50Hz±10%
380/400/415V±1%
(±5% adjustable)
5%(0~100%linear load)
±
THD<2%(line-to-neutral voltage)(battery float charge state,
rated balance load)
Output
Voltage distortion(nonlinear
load)
Power Factor 0.8(lagged)
Frequency Syn. Range
Frequency regulation(Battery
mode)
Phase Displacement (ThreePhase)
Voltage unbalance rate at
100% unbalance load
Frequency slew rate <1Hz/s
THD<5%(line-to-neutral voltage)(battery float charge state,
rated balance load)
50Hz±2Hz
0.1%
±
120± 1°(balanced load or unbalanced load)
2%(battery float charge state)
±
9
Page 16
Chapter 1 Introduction
Capacity 20kVA 30kVA 40kVA 60kVA
Model UL33-0200L UL33-0300L UL33-0400L UL33-0600L
105% < load 125% , transfer to bypass mode after 10±0.1min;
Output
System
Overload capability(inverter)
125% < load 150% , transfer to bypass mode after 1 minute;
When load > 150%, transfer to bypass mode after 200ms
135% Rated Current continuously
135%~170% for 1 minute
Overload capability(bypass)
>170%, shutdown in 2s
1000% rated current for 20ms(a standard for selecting static
switch)
Ratio of output current peak
value to RMS value
Transfer time(normal mode)
3: 1
0(uninterrupted transfer),15ms(interrupted transfer)
Transfer time(ECO mode) 15ms
System efficiency(linear load) 87% 87% 88% 89%
Efficiency in battery
mode(linear load)
92% 93% 93% 94%
Display LCD+LED
Conduction EN50091-2
Radiation EN50091-2 CLASS-A
EMC/EMI
Harmonic IEC1000-3-4
EN 61000-4-2.3.4..6.8.9.11 Level III,
Immunity
EN 61000-4-5 Level Ⅳ
MTBF(inverter) 30,000 hours
MTBF(Single UPS) 150,000 hours
MTBF(1+1 parallel operation
system)
400,000 hours
Safety CCEE
Audible noise at 2m <60dB <65dB
Cross current without
load(1+1)
Cross current without
load(3+1)
<3A
<4A
current unbalance rate(1+1) <3%
current unbalance rate(3+1) <4%
10
Page 17
Chapter 1 Introduction
Capacity 20kVA 30kVA 40kVA 60kVA
Model UL33-0200L UL33-0300L UL33-0400L UL33-0600L
Insulation Resistance >2M(500VDC)
Dielectric Strength
Surge Immunity
System
Protection index IP20
Number of battery cells 30 battery cells(12V)
Installation Cable access mode top/bottom cable access modes optional
(input to earth, output to earth)2820Vdc, leakage current lower
than 3.5mA, 1min without arc
Satisfy the class IV requirements specified by IEC60664-1, the
ability to withstand 1.2/50us+8/20us not lower than 6kV/3kA
2. Electrical Parameters
For designing of utility power source, air-conditioner, input and output power
distribution and cable selection, please refer to Table 1-2
Table 1-2 electrical parameters
Model UL33-0200L UL33-0300L UL33-0400L UL33-0600L
UPS rated power 20kVA 30kVA 40kVA 60kVA
AC input
Rated loss 2.40kW 3.60kW 4.37kW 5.94kW
Air intake(m3/hour) 500 800 1400 2200
Rectifier: 380/400/415V+15%~(3¢3W), Bypass: 380/400/415V±10%(3¢4W)
Rectifier input
current
Bypass input current 37A 56A 74A 112A
UPS output current 37A 56A 74A 112A
Battery input current 56A 84A 112A 168A
44A 66A 88A 132A
11
Page 18

Page 19

Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
2.1 Environmental Conditions
Operating Temperature : 0~ 40°C
Storage Temperature: -40~ 70°C(with no battery)
-20~ 55°C(with battery)
Relative Humidity:5%
Cooling method : Fan cooling
Elevation:1500m
Maximum Tilt : 5 degrees
Pollution :Class II
The UPS should be installed in a cool place with good ventilation, low humidity and
free of dust. The recommended operating temperature is 20 – 25 degree C, and
the humidity should be controlled at 50% RH.
Note :
The UPS room should not be stored with flammable, corrosive or explosive
materials. It is not advisable to install the UPS in areas with conductive dust.
2.2 Unpacking
Unpack the UPS only at the installation site and check the equipment for
completeness and damage. Keep accessories for later use.
~95
%, no condensation
Unpacking method is illustrated on the carton. For reliable operation of the UPS,
the installation method should be based on the actual environment condition and
site design standard.
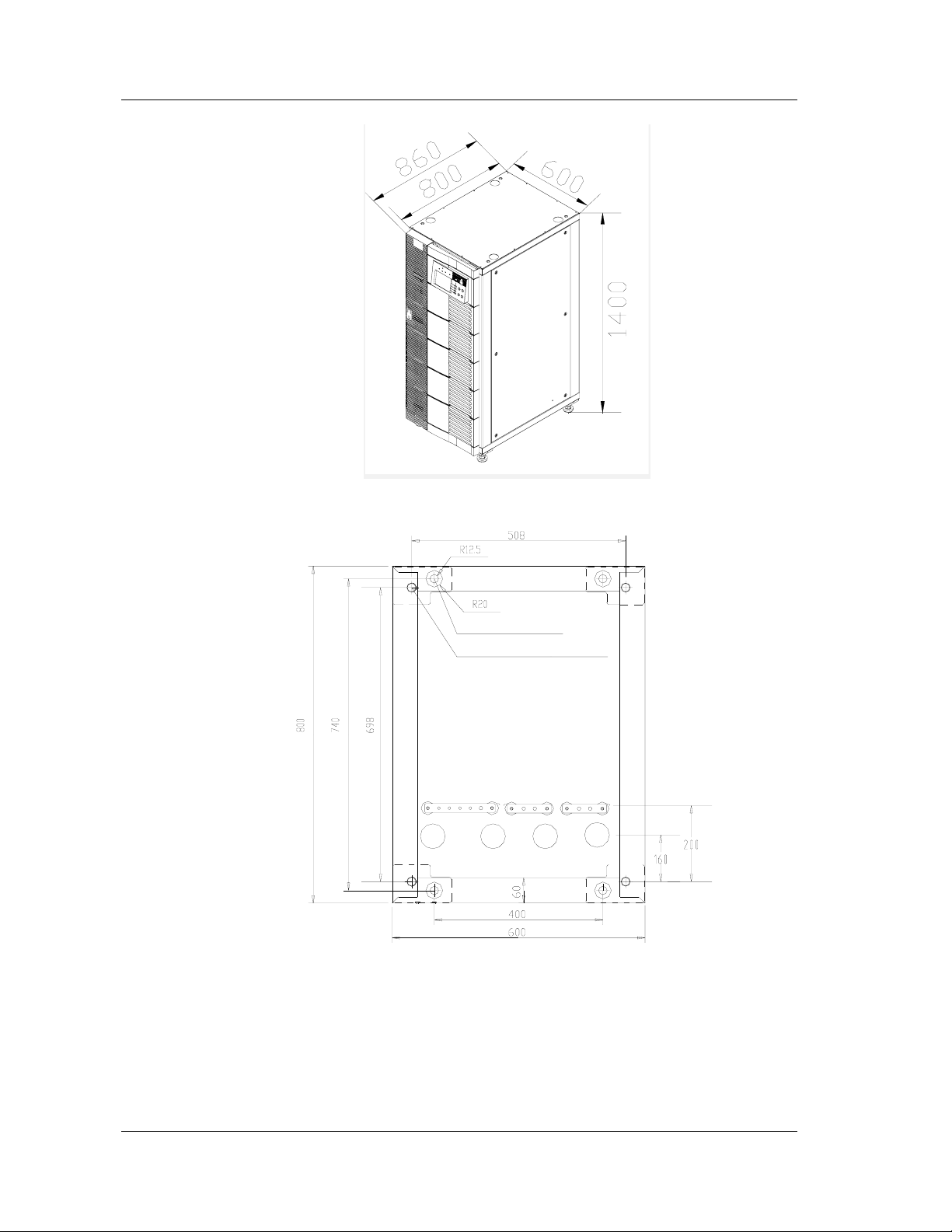
2.3 Dimensions
The dimensions of the UPS are listed in Table 2-1
13
Page 20
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
Figure 2-1
4 fixing holes
4 screws for levelling feet
Figure 2-2
External Dimensions of 40/60kVA UPS are shown in Fig. 2-3 and its installation
position is shown in Fig. 2-4.
14
Page 21
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
Figure 2-3 40/60kVA UPS Outline Dimension
4 fixing holes
4 screws for levelling feet
Figure 2-4 40/60kVA UPS Fixing Holes
15
Page 22

2.4 Transportation
1. Hoisting the UPS
Prepare four cables of length 1.5 m and the weight bearing capacity of each cable
of 1.5 tons. The UPS has four lifting rings and should be installed at the top of the
UPS
2. Transportatio with Forklift
The UPS can be raised by forklift in four directions – front, back, left and right. But
the transportation distance should not exceed 10 m.
2.5 Positioning of UPS
The UPS cabinet exerts its weight on the floor through four castors. If the load
bearing capacity of the floor is inadequate, add auxiliary equipment to distribute
the weight over a larger area, such as a big iron sheet or increasing the number of
supporting castor wheels.
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
Note
As the UPS is cooled from the bottom, at least 10 cm space should be left at the
bottom of the UPS for ventilation
There are three kinds of positioning methods:
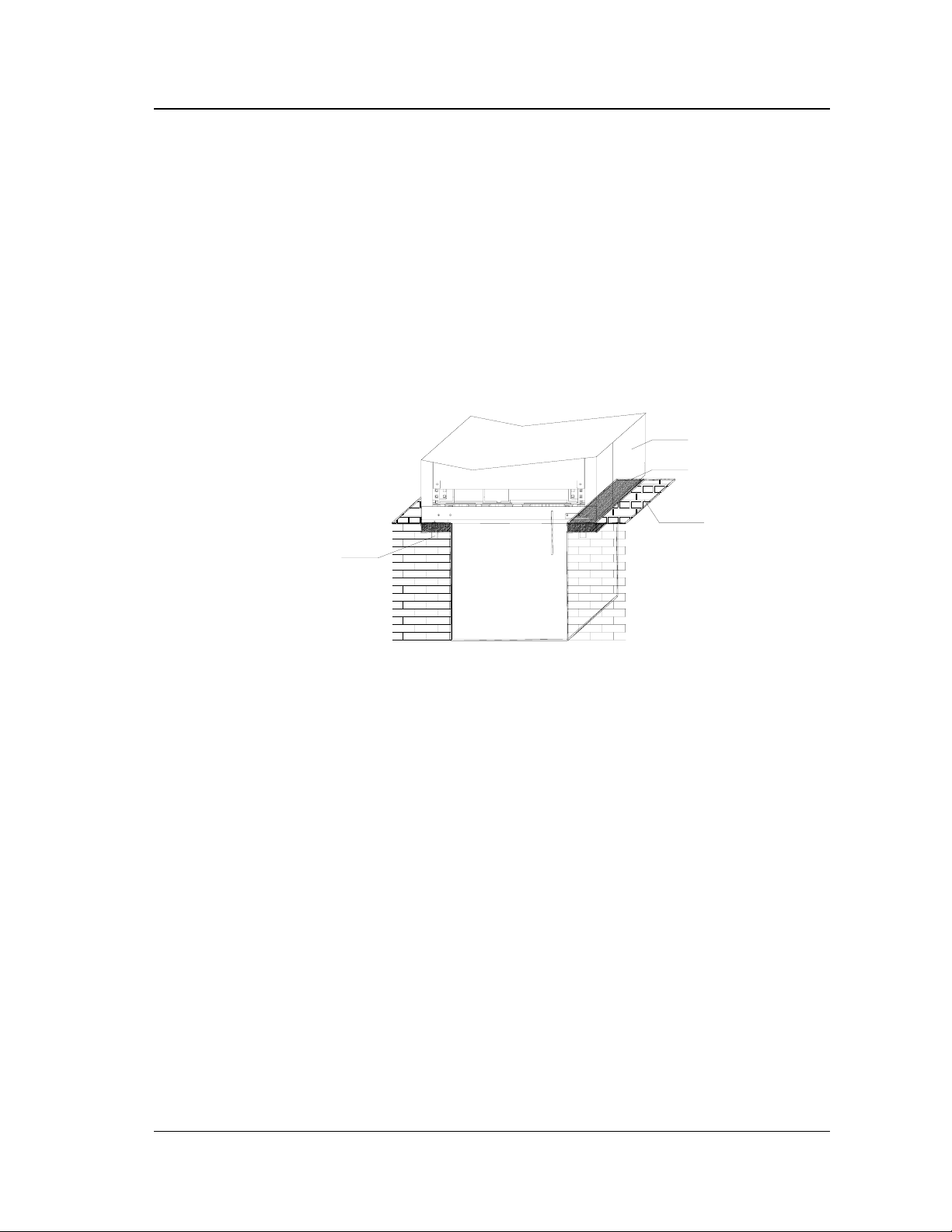
1. Non-Fixed position
Place the UPS directly on the flat ground . The ground should be made of Industrial
cement. Level the UPS by lowering and adjusting the leveling bolt at the base of
the UPS.
4 M20 screws for
levelling feet
16
Figure 2-5
Page 23
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
2. Fixed position without a base
In earthquake prone areas, place UPS on a conduit as shown in Figure 2-6.
1. At the edge of the conduit, drill holes for fixing expansion bolts
2. Hoist the cabinet at least 250 mm to remove the four leveling bolts. Take off
the plastic cover of the installation holes on the beam.
3. Position the cabinet at the right position and align the holes on the beam and
the holes on the expansion bolts.
4. Insert the expansion bolts into the installation holes. Adjust the tilt of the
cabinet and screw the expansion bolts to fix the cabinet.
Front door
Steel of conduit
floor of machine
room
Expansive
bolts
Cabinet
Cables
Cement
floor
Figure 2-6 Install UPS on a Conduit
Conduit
Cement
floor
3. Fixed cabinet position on a base
If the UPS is place in a ESD proof floor, a support rack should be designed to
support the cabinet. The design of the rack is illustrated in Figure 2-4 and Figure 27 considering the load carrying capacity of the floor. Level the cabinet according to
section 2.5 – 1
17
Page 24
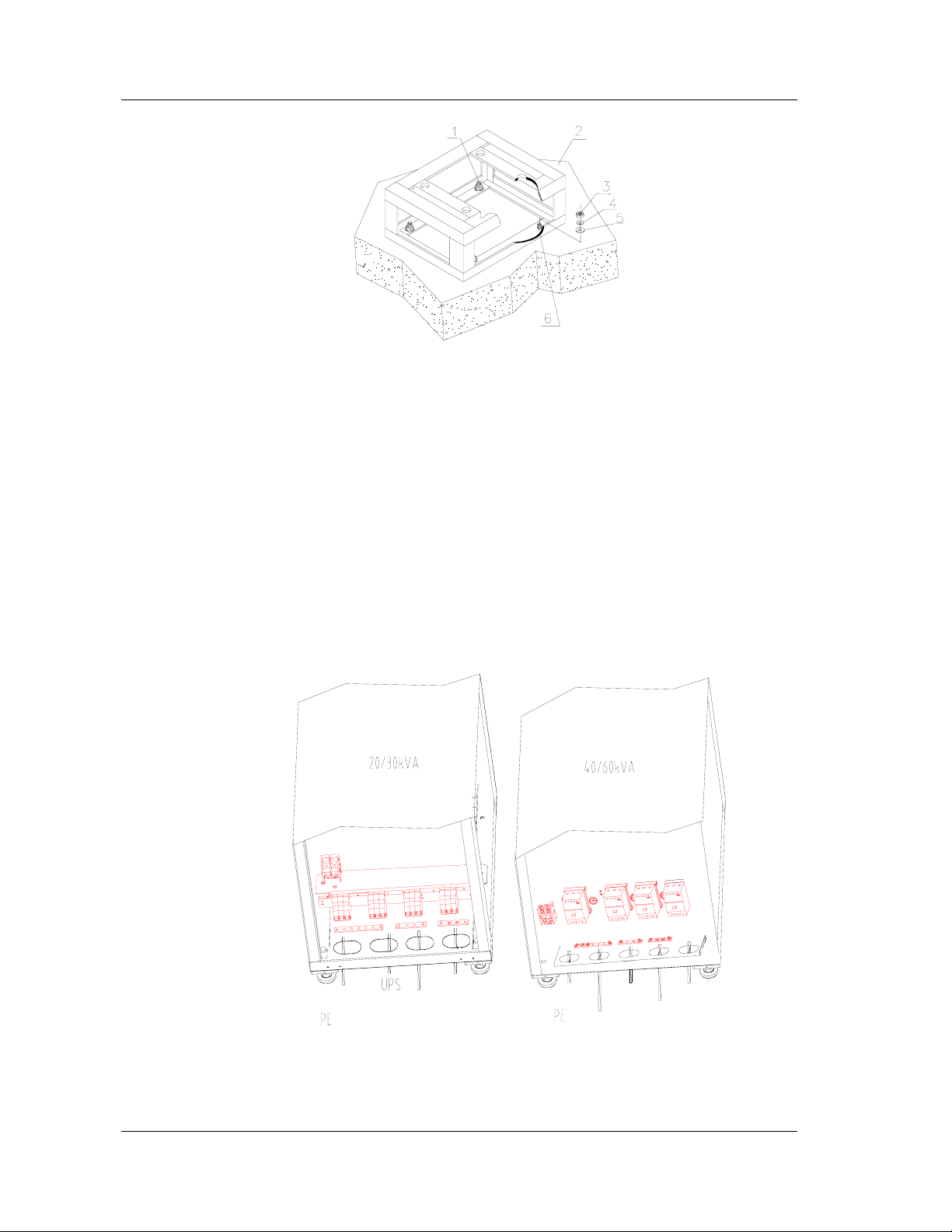
2.6 Cable Access
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
Figure 2-7 Install the UPS on a support rack
1. Finished state 2. Concrete floor
3. Nut 4. Spring washer
5. Flat washer 6. Supporting frame
The UPS has various methods of cable access. One is bottom access where the
cables are routed in conduit from the bottom of the UPS. This is shown in Figure 2-
8.
Another is top access where the cables are routed on cable trays from the top and
into the UPS as shown in Figures 2-9.
Battery
cables
input N
Cabinet
Signal cables
UPS output
output N
Battery
cables
Rectifier
input
Cabinet
Bypass input
input N
Signal cables
UPS output
output N
Fig. 2-8 UPS input/output cables
18
Page 25
2.7 Ventilation
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
Input cable
Battery cable
Output cable
Signal cable
Fig. 2-9 UPS top cable output
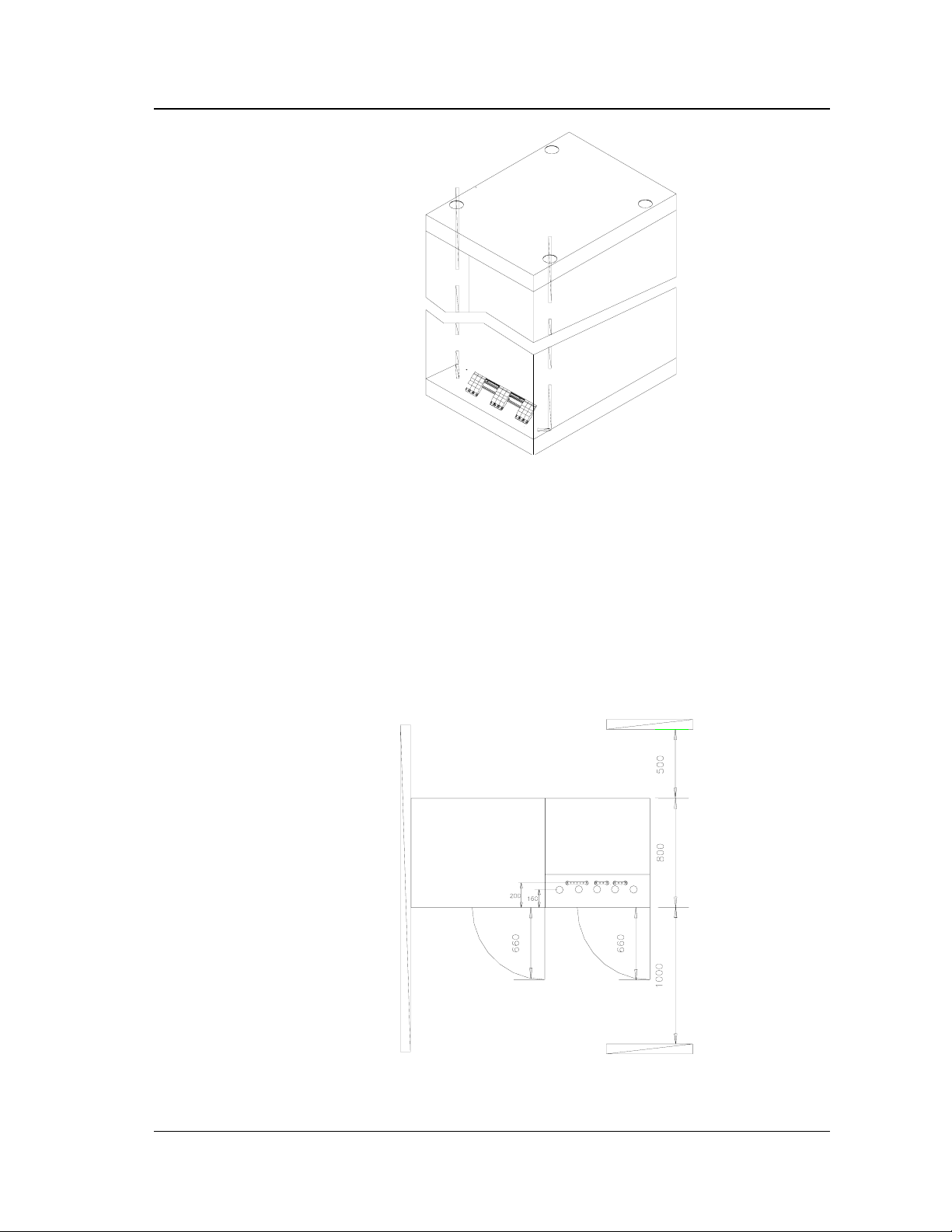
The cooling air comes into the UPS from the bottom and the fan circulates the cool
air inside the UPS. The air is expelled out of the UPS from the back.
Table 2-3 shows the relationship between the power consumed and air intake.
The rear clearance required by the UPS is 500 mm. The front clearance required is
1 m for the convenient of door opening and maintenance, shown in Figure 2-10.
Battery cabinet
UPS cabinet
bottom board
Fig. 2-10 Relative position of cabinet
19
Page 26
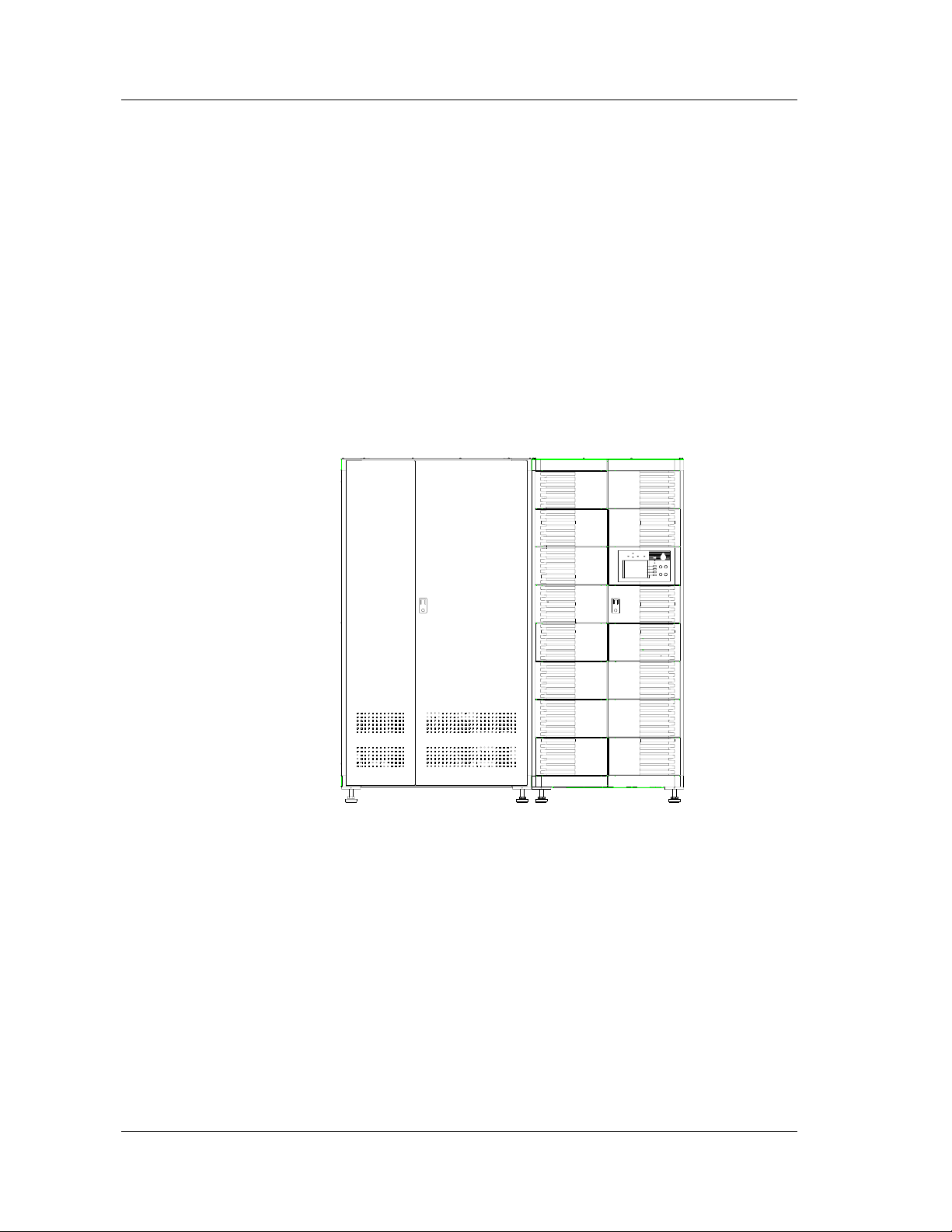
2.8 Layout of Cabinet
Besides the UPS cabinet, there are also battery cabinets, input/output distribution
cabinet and cabinet for bypass transformer. All these cabinets should be laid out
correctly. The layout of battery cabinet and UPS cabinet is shown below.
1. One UPS cabinet and one battery cabinet
If the required battery backup time is 15 – 16 minutes, one battery cabinet is
required to hold all the required batteries. There is no strict requirement for the
relative position of the UPS and the battery cabinet. Figure 2-11 shows this kind of
layout.
Capacity expansion must be considered into layout design.
Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
Battery cabinet
Fig. 2-11 Layout 1
UPS cabinet
2. One UPS cabinet and several battery cabinets
More than one UPS cabinet should be used if the required backup time is more
than 30 minutes. Please refer to Chapter 9 for the relationship between the battery
backup time and the battery capacity.
The battery cabinets should be placed side-by-side and the UPS cabinet can be
placed on the left or right side, in front of or behind the battery cabinets. Be sure to
leave space for maintenance.
20
Page 27

Chapter 2 Cabinet Installation
Battery cabinet 1
Battery cabinet 2
Fig. 2-12 Layout 2
UPS cabinet
21
Page 28

Page 29
Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly
Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly
This chapter introduces the connection methods of the power and signal cables.
3.1 Selection of cables
3.1.1 Current carrying capacity of cables
The current carrying capacity can be selected according to the voltage drop and
permissible temperature increase.
Table 3-1 Current carrying capacity of cables
Cross sectional area(mm
carrying
capacity (A)
1 1.5 2.5 4 6 10 16 25 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240
2
) Current
Rubber
25°C
Rubber
35°C
21 27 35 45 58 85 110 145 180 230 285 345 400 470 540 660
Plastic
19 24 32 42 55 75 105 138 170 215 265 325 / / / /
20 25 33 42 54 80 103 136 168 215 267 323 374 439 505 617
Plastic
18 22 30 39 51 70 96 129 159 201 248 304 / / / /
3.1.2 Selection of power cables
The power cables include input power cables of main circuit and that of the bypass,
the UPS output cables, battery input cables, protective earth cables and the
lightning protection cables.
1. Calculation of current of power cables
The first calculation method is done according to the following formula:
If the power factor is 0.80, the efficiency is 0.9, the minimum input voltage is 176
volts, output line to neutral voltage is 220V, minimum battery voltage is 324 V,
bypass overload capability is 135% and that of the inverter is 125%,
2. Selection of cable cross sectional areas
2
Power cables are selected according to two factors - 3 – 5 A/mm
current density
and the maximum voltage drop be less than 3 W.
The cross-sectional areas of bypass input neutral cable and UPS output neutral
cable should be 1.5 times of the phase cable. The cross sectional area of the
23
Page 30
Chapter 3 Electrical Assemble
protective earth cable and lightning protection earth cable, should be 0.5 times of
phase cable.
The relationship between the current and cross-sectional area is shown in Table 3-
2.
Table3-2 Recommended cross sectional area of cables
20kVA 30kVA 40kVA 60kVA
Name
Battery 56 25 84 25 112 35 168 50
Bypass 37 16 56 16 74 25 112 35
Output 37 16 56 16 74 25 112 35
Input 44 16 66 16 88 25 132 35
Neutral line 25
Earth cable 16
Current
(A)
Cable
(mm
3.1.3 Selection of signal cables
Signal cables should use shielded multi-conductor cables. But if cable with single
conductor is used, the different cables should be bonded together to increase the
mechanical strength. The number of the bonded cables should not exceed 30. The
cross-sectional area of the cable with single conductor should be at least 0.5 sqmm. Serial communication cables should use 3 or 5 shielded conductor cables.
3.2 Cable connections
2
)
Current
(A)
Cable
(mm2)
25
16
Current
(A)
Cable
(mm2)
35
25
Current
(A)
Cable
(mm2)
50
25
3.2.1 Power cables
1. Cabling layout
Cabling layout is shown in Figures 3-1 and 3-2. For single input UPS, the rectifier
input and bypass input are connected together.
24
Page 31

Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly
Battery
cables
UPS input
input N
UPS output
output N
Fig. 3-1 20/30kVA UPS bottom cable output
Battery cables
Rectifier input
Bypass input
Bypass N
UPS output
Output N
Fig. 3-2 40/60kVA UPS cable connection at bottom
2. Cable routing
1. Bottom entry configuration – the cables are input and output from the bottom of
the UPS
2. Top entry configuration – the cables are input and output from the top of the
UPS. To do this, punch out the cable entry cut-outs on the top of the UPS,
and feed the cables through the cutouts and guide them through the metal
conduit to the bottom of the UPS. From the front view, the battery cable, the
input power cables of rectifier and bypass input cables should be input from
the left. The output cable and signal cables should be input from the right.
The layout of the cables is shown in Figure 2-8.
25
Page 32

Chapter 3 Electrical Assemble
3. Cable connection
Note
All the switches should be switched off during cable connection.
1. Feed cables
Feed cables according to the cable entry mode, with reference to Figures 2-7, 2-8,
3-1, 3-2
2. Assembling cable lugs to cables
First strip the insulation layer 20 mm from the end. Then insert the conductor into
the cable lug. Then press the cable lug against the cable till tight.
The parameters of the cable lugs are given in Table 3-3
20kVA 30kVA 40kVA 60kVA
Name
terminal
Battery
Bypass H16/24
Output H16/24
Input H16/24
Neutral
line
Earth
cable
GTNR25-8
GTNR25-8
GTNR25-8
3. Connecting the rectifier input to utility
Connect the three phase cables of phase A1, B1 and C1 to the circuit breaker Q1
4.Connecting the bypass input to utility
Connect the three phase cables of phase A2, B2 and C2 to the circuit breaker Q2.
Note :
Cable
)
terminal
GTNR25-8
H16/24
H16/24
H16/24
GTNR25-8
GTNR25-8
2
(mm
25
16
16
16
25
16
Cable
terminal
2
)
(mm
25
16
16
16
25
16
GTNR50-8
H35/30
H35/30
H35/30
GTNR50-8
GTNR25-8
Cable
terminal
2
)
(mm
35
25
25
25
35
25
GTNR50-8
H35/30
H35/30
H35/30
GTNR50-8
GTNR25-8
Cable
2
)
(mm
50
35
35
35
50
25
In single input system, jumper the respective terminals on Q1 to Q2 with a 300mm
length cable. The utility will be connected to Q1 as described in 3.
26
Page 33

Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly
Wire terminal
Input power cable
Parallel power cable
Fig. 3-3 Power cable connection of One branch utility source
5. Connect the Load to the U, V, W terminals of UPS output breaker Q5.
6.Connection of battery cables
The positive and negative cables of batteries are connected to the Positive and
Negative terminals of JX3 respectively.
7. Connection of Neutral cable
The neutral cable of bypass source is connected to the JX5 copper bar, that is
marked with “N/INPUT”. The neutral cable of UPS output source is connected to
copper bar JX4, that is marked with “N/OUTPUT”.
Note
The phase rotation of circuit breakers Q1, Q2, Q5 cannot be wrong and the phase
rotation is shown in Figure 3-4.
ABC
TRS
UWV
L1 L2 L3
ABC
RTS
WUV
L1 L3L2
Q1
B
A
C
T
SR
U
W
V
L1
L2
L3
BC
A
TRS
UWV
L1 L2 L3
Q2
R
U
L1
A
R
L1
BUA
C
S
T
WWV
L3
L2
C
B
ST
V
L2
L3
Q5
Fig. 3-4 Phase rotation
27
Page 34

Chapter 3 Electrical Assemble
4. Earthing Method
The UPS rectifier source has no neutral cable. The bypass and output source have
neutral cables and the input and output neutral cables are short circuited.
The lightning protection earth PE and the protection earth of the cabinet are
connected as shown in Figure 3-5. The user can decide whether to use a
connection cable according to his earthing requirement.
PE for lightning protection
PE inside cabinet
Protective earth
Fig. 3-5 Wiring inside cabinet
Generally, the separated neutral mode is better for human safety. The united
connection mode is better for the UPS system. If there is C-level lightning
protection unit inside the UPS, the cabinet protection earth and the lightning
protection earth should be connected together.
In the bottom cable entry mode, the protection earth cable should be connected
with a copper terminal on the beam inside the cabinet or connected to the copper
busbar marked with PE. User board M8x12 to fix the cable.
The leakage current of the UPS should be less than 1 ampere.
The earthing resistance of the UPS cabinet should be less than 1 ohm.
3.2.2 Signal cable
The Signal cable includes serial communication cables, control cables of
input/output contacts, logic and load sharing cables.
1. Routing the signal cable
Note
The signal cables should be routed according to Figure 3-6
28
Page 35

Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly
Fig. 3-6 Layout of signal cables of 20/30/40/60kVA UPS
2. Connection method
1.Parallel connection method
Open the door of the UPS to see a circuit board ULW2L61M3. On the board, 15pin connectors P1 and P2 are used to connect the parallel logic cables. 9-pin
connectors P3 and P4 are used for connecting the load sharing cables. Each UPS
system has two pieces of 15 meters length cables.
Parallel logic cable
Parallel load sharing cable
Fig. 3-7 Parallel Board ULW2L61M3
29
Page 36

Chapter 3 Electrical Assemble
2.Connection of serial connection cables
The monitoring board ULW2L61U2 is shown in Figure 3-8, where the locations of
RS232, RS485 and input and output contacts are marked. The user can connect
the cables with reference to this board.
communication cable RS485-
communication cable RS485+
r
o
s
r
r
o
o
t
a
r
e
n
e
g
r
o
f
A
.
C
.
D
e
A
t
B
c
a
r
p
r
p
u
o
e
o
t
t
o
n
e
g
r
o
f
B
.
C
.
D
s
s
s
V
r
y
y
4
c
e
c
2
n
n
w
r
e
e
o
o
g
g
p
f
r
r
.
e
e
V
C
4
m
.
m
2
E
D
E
+
e
e
c
e
e
e
r
u
l
a
v
t
V
n
4
e
2
m
r
n
o
f
o
r
.
i
v
C
.
n
e
D
u
l
u
u
u
l
l
a
o
a
a
v
s
v
v
t
r
t
t
V
n
V
e
n
n
2
e
4
e
e
1
w
2
m
r
o
m
m
r
n
o
p
n
n
f
o
o
f
o
o
r
.
V
i
r
r
.
i
i
2
v
C
v
v
.
C
1
n
.
n
n
D
e
+
D
e
e
n
e
t
s
u
r
p
o
f
n
i
e
e
c
r
r
u
u
t
t
o
a
n
s
r
e
e
r
i
p
e
b
w
m
m
o
e
A
t
p
r
r
r
a
a
a
l
l
l
r
a
a
a
e
e
r
u
r
t
o
a
r
s
e
n
p
e
s
m
f
e
t
o
y
d
r
n
e
t
u
t
o
a
r
b
g
w
w
w
w
o
o
o
o
l
l
l
p
y
y
y
y
r
r
r
r
e
e
e
e
t
t
t
t
a
b
r
o
f
C
.
N
t
t
t
t
t
a
a
a
a
b
b
b
b
r
r
r
r
o
o
o
f
o
f
f
f
.
.
.
.
C
C
O
.
C
.
.
.
C
C
N
N
r
r
r
r
r
e
w
o
p
y
r
e
t
r
e
e
e
e
e
w
w
v
w
w
o
o
o
o
o
p
p
t
p
p
r
r
n
r
y
e
e
e
e
r
i
t
t
t
r
r
e
r
b
t
e
e
t
e
v
v
m
v
a
a
n
n
n
b
i
i
i
r
r
r
r
r
o
o
o
o
f
o
f
f
f
f
.
.
.
.
.
C
C
O
C
.
C
.
.
.
.
N
N
N
N
C
p
p
o
r
r
t
o
t
e
e
s
s
v
v
t
t
o
o
n
n
t
t
e
e
n
n
g
g
r
e
e
r
i
i
e
b
e
b
e
e
r
e
m
r
r
m
m
m
u
e
u
t
u
a
e
a
t
t
r
a
a
r
r
r
r
a
o
r
r
f
o
o
o
e
f
f
f
e
e
.
p
.
.
.
p
p
C
m
.
C
C
O
m
.
m
.
.
e
N
e
t
e
t
C
C
N
t
m
m
p
m
r
r
r
o
a
a
t
l
l
a
l
s
a
a
a
t
n
n
n
n
o
o
e
o
g
m
m
r
m
e
m
m
m
o
o
m
o
c
c
e
c
r
r
r
r
o
o
o
o
f
f
f
f
.
.
.
.
C
O
O
C
.
.
.
.
C
N
N
N
m
m
m
r
r
r
e
e
e
w
w
w
o
o
o
p
p
p
r
d
r
r
d
d
o
a
t
o
o
a
a
o
o
l
l
r
r
e
e
v
v
o
o
r
r
o
o
f
f
.
.
C
C
.
.
C
N
t
t
o
a
l
a
a
r
r
r
r
e
e
e
e
n
n
n
v
e
e
e
o
g
g
g
r
r
r
r
o
o
f
f
o
o
f
f
.
.
.
.
O
C
.
.
C
O
.
.
N
N
C
N
Fig. 3-8 Monitoring Board ULW2L61U2
The length of the serial communication cables is different according to actual
conditions. The cables are not supplied with the UPS.
The communication modes of RS232, RS485, modem and SNMP can be used
together, but only one mode can be used at any time.
1) RS232 Connection
The J20 is the RS232 communication port. One end of the communication cables
should be connected to J20 and the other end should be connected to background
monitoring equipment. The meaning of each pin is shown in Figure 3-9.
Pin 2:receiving Pin 3:Transmitting Pin 5:Ground Other pins:Void
Fig. 3-9 RS232 Serial Port
30
Page 37

Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly
2) Connection of modem
MODEM or SNMP
SNMP cables
Monitoring board
20/30kVA Front view when
Front door is opened
Monitoring board
SNMP cables
MODEM or SNMP
40/60kVA Front view when
right door is opened
Fig. 3-10 Installation of MODEM or SNMP
1. Figure 3-10 shows the location of Modem and SNMP card. Before installing the
modem, the user should remove the iron box use for SNMP card and installed the
modem there.
communication port
serial pore
communication port
Power source
Communication port
Fig. 3-11 MODEM Connection Method
2.Connecting the communication cables. The communication cables of modem are
connected to J20.
3. Connection of power source cables. Connect the power source cables of modem
directly to J8. The Pin 1 of J8 is ground. Pin 2 is 12V power.
4.Connection of Telephone line. Connect the telephone line after connecting the
power source and communication cables to realize remote communication.
31
Page 38

Chapter 3 Electrical Assemble
3)Connection of SNMP Card
Installation of SNMP card
Unpack the SNMP card and place it in the iron case shown in Figure 3-10
Connect the cables
On the monitoring board, there is a jack J22 with a cable to plug in directly to the
SNMP card, after the SNMP Card is installed. Please do not remove this cable
even if the SNMP card is not used.
4)Connection of RS485
Connector J23 on the monitoring board is the RS485 communication port. One
end of the communication cable is connected to J23 while the other end is
connected to the user’s equipment.
RS485+
RS485-
SHIELD
J23
1
2
3
4
Pin 1:Signal + Pin 2:Signal Pin 4:Shielded ground
Fig. 3-12 RS485 Port
3. Connection of input and output voltage free contacts
The input and output contacts can be connected to shielded cables, and single
cables. One end of the cables are connected to J9 to J18. The other end is for
connection by user.
Note:
The contact should satisfy the SELV safety requirements.
The J9-J14 connectors on the monitoring board are monitoring dry contacts of
relays. The relays have a normally open, normally closed and a common terminal.
The capacity of the contacts are 0.3A/125VAC, 0.3A/110VDC and 1A/24DC.
The transmission distance of the dry contact signals are dependent on the voltage
level and the cross sectional area of the cables. J15 – J18 are the input contacts
for external signals.
32
Page 39

Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly
Table 3-4 Definitions of input/output contacts
Connector Name of contacts Board name input/output
Normally closed contacts for
battery low alarm
BLV-C output
J9
J10
J11
Central contacts for battery low
alarm
Normally open contacts for
battery low alarm
Normally closed contacts for
battery mode
Central contacts for battery
mode
Normally open contacts for
battery mode
Normally closed contacts for
inverter mode
Central contacts for inverter
mode
Normally open contacts for
inverter mode
Normally closed contacts for
ambient over-temperature
Central contacts for ambient
over-temperature
BLV-S output
BLV-O output
BAT-C output
BAT-S output
BAT-O output
INV-C output
INV-S output
INV-O output
TMP-C output
TMP-S output
J12
J13
J14
Normally open contacts for
ambient over-temperature
Normally closed contacts for
emergency shutdown
Central contacts for emergency
shutdown
Normally open contacts for
emergency shutdown
Normally closed contacts for
common alarm
Central contacts for common
alarm
Normally open contacts for
common alarm
Normally closed contacts for
overload
33
TMP-O output
URG-C output
URG-S output
URG-O output
WRN-C output
WRN-S output
WRN-O output
OVR-C output
Page 40

Chapter 3 Electrical Assemble
Connector Name of contacts Board name input/output
Central contacts for overload OVR-S output
J12
J13
J14
J17
J16
Normally open contacts for
overload
Normally closed contacts for
generator mode
Central contacts for generator
mode
Normally open contacts for
generator mode
+24V power for environmental
signal
24V power for environmental
signal 1
24V power for environmental
signal 2
24V power for environmental
signal 3
+12V power for environmental
signal
12V environmental signal ENV
OVR-O output
GEN-C output
GEN-S output
GEN-O output
+24V power output
ENV1
ENV2
ENV3
+12V power output
connect to dry
contacts
connect to dry
contacts
connect to dry
contacts
connect to dry
contacts
J18
J15
NC NC
Ambient temperature input V-AD 0~5V signal input
Dry contacts H of generator GEN-H connect to dry contacts
Dry contacts L of generator GEN-L
Emergency shutdown H UCTRH
Emergency shutdown L UCTRL
NC NC
12V
Power Source of Sensor
Battery Temperature BAT-T 0~5V signal input
GND of Sensor GND power output
+
connect to dry
contacts
connect to dry
contacts
connect to dry
contacts
power output
Terminals J9~J14 are the dry contacts for monitoring that can be used by users.
The relays have central contacts.
34
Page 41

Chapter 3 Electrical Assembly
4. Battery Temperature detection cable
When the user select the temperature compensation technology, he should select
the TMP12Z sensor that is installed inside the battery cabinet or battery room. Use
a cable to send a temperature signal to J15 on the monitoring board. Shield cable
is recommended to be used because the transmission distance is long.
The location of the temperature sensor is shown o Figure 3-13.
Fig. 3-13 Dry Contact
1. Circuit Breaker QF1 2. Temperature Sensor TMP12Z
Fig. 3-13 Installation of TMP12Z
3.3 Connection of Single UPS System
The circuit breaker of bypass source is selected according to its disconnecting
capacity and short circuit current. The selected circuit breaker should be able to
protect the static switch according to its maximum permissible current.
35
Page 42

Page 43

Chapter 4 Commissioning of UPS
Chapter 4 Commissioning of UPS
4.1 Startup Procedure
4.1.1 Explanation of Circuit Breakers
From the layout of Figure 1-3 and Figure 1-4, the startup of UPS has connections
with the following circuit breakers
Q1 : Connects rectifier to Utility source
Q2 : Connects bypass to Utility source
Q5 : Connects UPS output to the Load
Q3BP : Connects bypass input source to the load switch
4.1.2 Startup
QF1 : Battery Circuit Breaker
All the circuit breakers of the UPS should be switched off and phase rotation correct.
The battery cables are connected correctly. Q1 and Q2 are connected to utility.
Note
Before startup, do not connect the load
The UPS should be started up according to the following procedures:
Step 1 : Switch on Q2 and Q5. The power source indicator on the panel turns on
and the LCD displays information during startup.
Step 2 : Switch on Q1 and QF1. The sound of the relay closing should be heard.
After 2 secs, the main contactor closes. The rectifier starts after the soft start relay
opens. The rectifier indicator flashes several times and the rectifier enters normal
operation states after about 10 secs.
Step 3 : The battery input contactor closes automatically after the DC bus reaches
the pre-set value. The battery indicator illuminates before the battery contactor
closes and it turns off after the contactor closes.
Step 4 : Press the button “inverter start” for two seconds. The inverter will start up
and enters normal operating state when the inverter indicator flash.
37
Page 44

Step 5 : After the UPS transfers from bypass to inverter, the bypass indicator turns
off, and the inverter and the load indicator turns on. The transfer may fail if the
phase rotation of bypass and inverter output are different.
During operation, if the AC power recovers after failure, the rectifier will restart
automatically after some time. If the UPS transfer to generator power, the
monitoring system will determine the quality of the generator supply. The time it
takes to determine this, ranges from 1 second to 255 seconds.
After startup, use the keypad to set the functions of the UPS.
Note
Power failure means the line to neutral voltage is lower than 120V or the Line to
Line voltage is lower than 208V over 10 msecs.
4.2 Setting the functions
The methods of setting the functions will be described in details in Chapter 5.
Chapter 4 Commissioning of UPS
This chapter only introduces the setting that relates to commissioning.
The user enters the menu of “set functions” shown in the figure below.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -08 12:50:30
English
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
Chinese
1
Fig. 4-1 Function Setup Menu
Language selection : select “Chinese” or “English” as shown in Figure 4-3
Address setup : set the address of this UPS in the monitoring system as shown in
Figure 4-3.
Date and Time setup : format is “YYYY-MM-DD” and “HH:MM:SS” as shown in
Figure 4-3
38
Page 45

Chapter 4 Commissioning of UPS
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11£ -08 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
English
Chinese
1
m
Fig. 4-2 Setup Language
Manual Battery Self Test : Select “start self test” or “stop self test”
Contrast Adjustment : Change the display contrast according to the 11 bars, as
shown in Figure 4-4.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Manual Batt Test
Start
Stop
Display contrast adjust
Record Query Range
0: all records
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
3 days
m
Fig. 4-4 Manual Battery Self-test
History Record : The set range is 1-30 days. If “0” is set, all records will be
available for viewing.
Background Communication Setup : select between modem and RS232, as shown
in Figure 4-5
Baud Rate setup : Select from available baud rates of 9600, 4800, 2400 or 1200,
as shown in Figure 4-5
Callback time setup : the available set range is from 1-5 times, as shown in Figure
4-5
39
Page 46

Chapter 4 Commissioning of UPS
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Comm. Mode Set
MODEM
RS232
Comm. Baudrate Set 9600
4800
9600
Callback Times Set 3
3
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
2400
RS232
1200
m
Fig. 4-5 Background Communication
Callback number 1 : the first callback number can be a mobile phone number, a
fixed line phone number, a beeping pager or an extension telephone. The length of
the telephone number is 15 digits. Input the number from the first digit and any
remaining blanks digits has to be entered with an asterisk “*”
Callback number 2 : same as for callback number 1
Callback number 3 : same as for callback number 1
4.3 Functional checks
Check the functions of switching between operation modes, visual and audible
alarms and the display functions.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Comm. Mode Set
MODEM
RS232
Comm. Baudrate Set 9600
4800
9600
Callback Times Set 3
3
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
Fig. 4-6 Fault Call-back
2400
RS232
1200
m
40
Page 47

Chapter 4 Commissioning of UPS
4.3.1 Check the function of the display panel
Press the button “inverter shutdown” for 2 seconds and check that the inverter
stops.
Rectifier
indicator
Bypass
indicator
Battery
indicator
Inverter
indicator
Load
indicator
Alarm
indicator
Emergency
shutdown
UL33-0400L
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Äæ±ä¿ªÆô ² ¢»ų́Êý 2/4
Out
Ö÷·ÊäÈë
Local
ÅÔ·ÊäÈë
System
½»Á÷Êä³ö
Battery
±¾»ú¸ºÔØ
Records
²¢»ú¸ºÔØ
Settings
µç³ØÊý¾Ý
Input Breaker Closed
ÊäÈë¿Õ¿ª±ÕºÏ
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
Êä³ö¿Õ¿ª±ÕºÏ
UPS in Battery Mode
Ö÷·Äæ±ä¹©µç
Battery low
µç³Ø¾ù³ä
2001-11-08
2001-11-08
Language
A(B)
Chinese
Ïàµçѹ V
Com. Adress Set
µç Á ÷ A
Ƶ  ÊHz
Date & Time Set
¹¦ÂÊÒòÊý
Ïßµçѹ V
221
11. 8
1
50.2
0.99
2001£ -11£ -08 12:50:30
381 380 382
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:15
11£ -08 12:50
11£ -08 12:12
B(C) C(A)
English
220 221
12.3
50.1
0.99
12:50:30
12:50:30
Chinese
1
50.1
Alarm
F1
F2
Inverter
stare
F3
m
F4
Fault
clearing
Inverter
stop
Mute
Fig. 4-7 Display Panel
Press the button “Emergency shutdown” and check that the UPS shuts down
Press the button “fault clear” to restart the UPS
Simulate a fault to check the visual and audible alarm functions.
Press “Mute” button to silence the alarm
4.3.2 Switching between operation mode
t
Fig. 4-8 UPS Circuit Breaker Operation
41
Page 48

Chapter 4 Commissioning of UPS
1. Switch from normal mode to battery mode. Switch off Q1 to enter battery mode
and after a few seconds, switch on Q1 again to return to normal mode
2. Press “inverter shutdown” button to switch to bypass mode. After a short while,
start inverter again to return to normal mode.
3. In bypass mode, switch on Q1 and press “inverter start” button after the rectifier
starts. The UPS should switch to normal mode.
4. Switch from normal mode to maintenance bypass mode. Press “inverter
shutdown” button, switch off Q1, switch on Q3BP, switch off Q2, Q5, QF1. At this
time the bypass source will power the load through Q3BP.
5. Check that the generator set and the UPS battery can work together.
6. A parallel system can also switch between different operation mode.
42
Page 49

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
5.1 Display panel
5.1.1 Layout of Display Panel
The display panel of the UPS is shown in Figure 5-1.
Start
Shutdown
Faullt clear
1:LCD 2:Rectifier indicator
3:Battery operation indicator 4:Bypass source indicator
5:Inverter operation indicator 6:UPS output indicator
7:Buzzer 8:Alarm indicator
9: cover used for preventing wrong operation of Emergency shutdown button
10:Emergency shutdown button (EPO) 11:Inverter start button
12:Inverter shutdown button 13:Fault clear button
14:Alarm mute button 15:F1 Functional key
16:F2 Functional key 17:F3 Functional key 18:F4 Functional key
Fig. 5-1 Display Panel
Mute
The display panel is divided into three sections:
1.LED section
2.Functional Keys
3.LCD
43
Page 50

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
Rectifier
indicator
UL33-0400L
Äæ±ä¿ªÆô ² ¢»ų́Êý 2/4
Ö÷·ÊäÈë
Local
ÅÔ·ÊäÈë
System
½»Á÷Êä³ö
Battery
±¾»ú¸ºÔØ
²¢»ú¸ºÔØ
µç³ØÊý¾Ý
Input Breaker Closed
ÊäÈë¿Õ¿ª±ÕºÏ
Byp. Breaker Closed
Êä³ö¿Õ¿ª±ÕºÏ
Ö÷·Äæ±ä¹©µç
Battery low
µç³Ø¾ù³ä
Bypass
indicator
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Ïàµçѹ V
Com. Adress Set
µç Á ÷ A
Records
Settings
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Ƶ  ÊHz
¹¦ÂÊÒòÊý
Ïßµçѹ V
2001-11-08
2001-11-08
Language
A(B)
Chinese
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11£ -08 12:50:30
English
221
11. 8
50.2
0.99
381 380 382
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:15
11£ -08 12:50
11£ -08 12:12
Battery
indicator
12:50:30
12:50:30
Inverter
indicator
Alarm
Chinese
B(C) C(A)
220 221
1
12.3
50.1
50.1
0.99
m
Fig. 5-2 Function Dividing
F1
F2
F3
F4
Load
indicator
Alarm
indicator
Emergency
Inverter
stare
Fault
clearing
shutdown
Inverter
stop
Mute
5.1.2 LED Indication
There are six LEDs to indicate the operation state and fault.
Yellow – Normal
Red – Fault condition
Bypass LED
Yellow – Load on Bypass power
Red – Bypass Voltage out of normal range
Off – Bypass Normal
Rectifier LED
Yellow – Load on Rectifier
Flashing Yellow – Utility Normal, but rectifier not operating
Red – Rectifier fault
Off – Utility abnormal
Battery LED
Green – Battery powers the load
44
Page 51

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
Flashing Green – End of battery discharge
Red – Battery Abnormal (overtemp, low battery, contactor fused)
Off – Battery Normal but not in operation
Inverter LED
Green – Inverter powers the load normally
Flashing Green - Inverter standby
Red – Inverter Fails
Off – Inverter Normal but not in operation
Load LED
Green – UPS output on
Red – UPS shuts down due to overload
Orange – UPS overload
Alarm LED: If the red LED turns on, that means the system itself has fault; If green
LED turns on, that means there is no alarm; If orange color(actually red and green
illuminate together) means there is a fault in the environment of the system, such
as rectifier input abnormal, bypass voltage abnormal and battery disconnected.
5.1.3 Functional Keys
There are five buttons.
Emergency shutdown – Use to totally shut down the UPS including the rectifier, the
inverter and the battery
Inverter Start-Use to start the inverter, but if the inverter is not ready, pressing this
key will have no use
Inverter Stop-use to shut down the Inverter during operation,
Fault clear – If the UPS shuts down due to a fault, press this key to restart the UPS
after the fault is cleared
Mute-Use to silence the alarm and re-pressing the button will sound the buzzer
again. Any new fault will sound the buzzer again.
Pressing any one of the above keys, a short click can be heard.
Note
To ensure any of the button is properly activated, press down the key for about 2
seconds
45
Page 52

5.1.4 Alarm Buzzer
If there is no alarm sound, it means that either the alarm is muted or the system is
not in a fault condition
There are three types of sound from the buzzer
1.Single click - The sound can be heard when any button is pressed
2. 1 sec click with a 2 secs interval - when system has common fault or alarm
3. Continuous alarm – when system has serious faults
Press Mute button to silence alarm.
5.1.5 LCD and Menu Keys
There are four menu keys
1. Menu key
Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
Each key has two functions, and the functions are defined in the following table
Key
Function 1
Function 1
F1
Shift Up
F2
F3
Down
C
Exit
Fig. 5-3 Icons of functional keys and the meanings
left
Right
F4
OK
r
e
t
n
E
m
Modify
2. LCD
The LCD can display alarm information in real time. 220 historical events can be
stored and retrieved.
46
Page 53

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
Menu Display
Window
Current event
window
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
2001-11-08
Vphase
Iphase A
Freq.Hz
P.F.
Vline V
12:30:20
B(C)
A(B)
221
11. 8
50.2
0.99
381 380 382
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
C(A)
220 221
12.3 12.5
50.1
50.1
0.99
0.99
Fig. 5-4 Sections of the LCD
The LCD are divided into five windows :
UPS information window (restricted for factory use)
Keypad window (restricted for factory use)
Menu display window
Current event window
Alarm window
UPS information
window
Measuring and
setup window
Kaypad Window
Pressing the F1 key can scroll through the windows that can be operated by user.
UPS information window-This window displays the UPS basic information and is
not necessary for the user to operate. The displayed information is given in the
following table.
Menu display window-This window displays the information of measuring and setup
sub-windows. There are 6 menus, but actually 8. The user can select the menu by
pressing F2 or F3. These 8 menus are: rectifier input, bypass input, AC output, load,
parallel load, battery data, history record and function setup
Keypad Window – The display window shows the picture of the keys and near the
pictures of the keys, the operations can be done by the user are displayed.
Measuring and Setup window – select the module which you want to query and the
parameters will be displayed in this window
Current event and alarm window – displays detailed current event and alarms of
UPS
47
Page 54

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
5.2 The displayed information
5.2.1 Opening display
At power up of the UPS, the opening display is shown in Figure 5-5.
5.2.2 Main Menu Display
Fig. 5-5 Opening Display
After the UPS is power up and self test is completed, the main menu will be
displayed, as shown in Figure 5-6. Use the arrow-up and arrow-down key to scroll
the menu and the history log.
5.2.3 UPS Basic Information
The current basic UPS information will be displayed by pressing the F1 and F4
keys together.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Bypass
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
2001-11-08
Power KW
Cap.
KVA
Load%
Crestor
Factor
B(C)
A(B)
220 221
221
12.3
11. 8
50.2
50.1
1.40
1.41
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
12:30:20
Fig. 5-6 Main Menu
C(A)
12.5
50.1
1.41
48
Page 55

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
5.2.4 Menu Keys Display Window
The window is displayed in Figure 5-6. Use the arrow-up and arrow-down keys to
select from the menu and the measured information will be displayed.
For example, if the user the first menu (main rectifier input) then the measuring
window will display the input line-line voltage and the current.
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
*------------------------------------------------------------------*
*----------------Emerson Network Power-----------------*
*------------------------------------------------------------------*
* UPS version£ º 1.00 *
* UPS model£ º itrust0400L - *
* UPS type£ º Single normal *
* UPS ID£ º NO.3 *
* Rectifier version£ º 1.00 *
* Inverter version£ º 1.00 *
* Monitor version £ º 1.00 *
* Record start time£ º 05-11-02 12: 23: 12 *
*----------------Press any key to continue----------------*
*------------------------------------------------------------------*
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Fig. 5-7 Display Menu
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
2001-11-08
Vphase
Iphase A
Freq.Hz
P.F.
B(C)
A(B)
220 221
221
12.3 12.5
11. 8
50.2
50.1
0.99
0.99
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
12:30:20
C(A)
50.1
0.99
Fig. 5-8 Press Up(F2) or Down (F3) to Move the Cursor
Scroll Up and down the window by pressing the F1 key.
If the selected menu is not a historical record, then pressing F1 will display current
events and alarms.
49
Page 56

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
If the window displays the current events or current alarms, pressing F2 and F3 can
display events and alarms of other modules.
5.2.5 Information of main menu
Eight main menu will be displayed on the LCD. They are
Rectifier input
Bypass input
AC output
Load of single module UPS system
Parallel load
Battery data
History Log
Function setup
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
2001-11-08
Vphase
Iphase A
Freq.Hz
P.F.
12:30:20
B(C)
A(B)
220 221
221
12.3
11. 8
50.2
50.1
0.99
0.99
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
Fig. 5-9 Shift key(F1) display
C(A)
12.5
50.1
0.99
Pressing F1 can switch from present window to measuring sub-window.
Rectifier Input – displays three phase line-line voltage, line current, frequency and
power factor of rectifier, as shown in Figure 5-8
Bypass Input - displays three phase line-line voltage, line current, frequency and
power factor of bypass source, as shown in Figure 5-10
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
2001-11-08
Vphase
Freq.Hz
Vline V
12:30:20
B(C)
A(B)
221
50.2
381
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
C(A)
220 221
50.1
50.1
382
380
Fig. 5-10 Bypass input display LCD
50
Page 57

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
AC Output - displays three phase line-neutral voltage, line current, frequency,
power factor and line-line voltage, as shown in Figure 5-11
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
2001-11-08
Vphase
Iphase A
Freq.Hz
P.F.
Vline V
12:30:20
B(C)
A(B)
220 221
221
12.3
50.1
0.99
12.5
11. 8
50.2
0.99
381 380 382
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
C(A)
50.1
0.99
Fig. 5-11 AC output display LCD
Parallel load - Displays the power and capacity of parallel load as shown in Figure
5-12
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
2001-11-08
kWout
kVAout
12:30:20
B(C)
A(B)
21.2
22.3
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
C(A)
20.3 20.8
21.7
22.2
Fig. 5-12 Parallel Load Display LCD
Battery Data - Displays battery information under different conditions, such as
Battery not connected, equalization charge, float charge, discharge and pre-alarm
upon discharge.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
Batt. Disconnnected
UPS in Normal Mode
2001-11-08
Battery Disconnected
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
12:30:20
Fig. 5-13 Displaying contents when the battery are not connected
51
Page 58

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:30:20
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Batt. Volt V 423
Batt. Curr. A 4.56
Batt. Temp. C 23.2
Batt. Boost Charging
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
Fig. 5-14 Displaying LCD at equalization charging state
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:30:20
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Batt. Volt V 423
Batt. Curr. A 4.56
Batt. Temp. C 23.2
Batt. Float Charging
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Float Charging
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
Fig. 5-15 Displaying LCD at float charging state
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:30:20
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Batt. Volt V 423
Batt. Curr. A 4.56
Batt. Temp. C 23.2
Backup Time Min 56
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:25
11£ -08 12:25
Fig. 5-16 Displaying LCD at discharging state
52
Page 59

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:30:20
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Batt. Volt V 423
Batt. Curr. A 4.56
Batt. Temp. C 23.2
Backup Time Sec 176
Battery
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery Low
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:25
11£ -08 12:25
11£ -08 12:50
Fig. 5-17 Pre-alarm when battery discharges to end of discharge voltage
History Log – According to the prompt information in keypad window, pressing F3
key(“Down” key) to display interface of “History Log” as shown in Figure 5-18.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Bypass
Output
Local
System
Battery
Records
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery Low
2001-11-08
Byp. Out of Syn.
2001£ -11£ -08 12:08:30
2001£ -11£ -08 12:08:58
UPS in Bypass Mode
2001£ -11£ -08 12:09:58
2001£ -11£ -08 12:20:30
UPS in Normal Mode
2001£ -11£ -08 12:20:30
2001£ -11£ -08 12:28:48
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:25
11£ -08 12:25
11£ -08 12:50
12:30:20
Fig. 5-18 History log
Function setup - Pressing F3 key(“Down” key) to display the last interface of
“Function setup” as shown in Figure 5-19
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
English
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11£ -08 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
Chinese
1
Fig. 5-19 Functional setup
53
Page 60

5.3 Function Setup
In the Menu Display Window select “Function Setup”, pressing F1 key to switch the
present window to Measuring and Setup Window and modify each settable items.
Pressing F3 key can scroll through all the settable items (total number of the
settable items is 12). Pressing F4 to modify and confirm the set parameters.
If need no setup, press F1 to exit the current window.
Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
5.3.1 Language setup
According to the information displayed on the Menu Display Window, pressing F4
to enter the Language setting menu, use F2 and F3 keys to select the language,
and then pressing F4 to confirm and exit the Language Setting Menu. If you do not
want to modify the language, pressing F1(ESC) to escape.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -08 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
Chinese
English
1
Fig. 5-20 Function setup
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11£ -08 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
Chinese
English
1
m
c
ok
Fig. 5-21 Setup the language
54
Page 61

5.3.2 Address setup
According to the information displayed on Fig.5-22, select the “Equipment Address
Setup” and pressing F3(UP) or F2(DOWN) to modify the address of the equipment,
and then pressing F4 to confirm and exit. If you do not want to modify the language,
pressing F1(ESC) to escape.
Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
5.3.3 Time setup
According to the information displayed on the Fig.5-23, select the “Time Setup” to
modify the system time. If you do not want to modify the language, pressing
F1(ESC) to escape.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
UL33-0400L
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set 1
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11£ -08 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
Fig. 5-22 Equipment address
2001-11-08
Chinese
English
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set 1
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11£ -08 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
Chinese
English
c
ok
c
ok
Fig. 5-23 Setup the date
Suppose the time is 2001-11-09 12:50:20, pressing F2 (move left) and F3 (move
right) keys to move the cursor to the location of date, as shown in Fig. 5-24.
55
Page 62

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -08 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
English
Chinese
1
c
m
Fig. 5-24 Setup the date 1
Pressing F4 to let the date to be able to be modified, as shown in Fig. 5-25.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set 1
Chinese
English
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -08 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
c
ok
Fig. 5-25 Setup the date 2
Pressing F2(up) to change the date to 09, then press F4(Enter) to confirm and exit,
as shown in Fig. 5-26. If you do not want to modify the date, pressing F1(ESC) to
escape.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
English
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -09 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
Chinese
1
c
ok
Fig. 5-26 Setup the date 3
56
Page 63

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
After escaping the modification state, the date displayed by the UPS basic
information window has become a new date. Then use F2 (move left) and F3
(move right) keys to move the cursor to the location of “second”, as shown in Fig. 5-
27.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -09 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
English
Chinese
1
c
ok
Fig. 5-27 Setup the date 4
Pressing F4 to let the “second” to be able to be modified, as shown in Fig. 5-28.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
English
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -09 12:50:30
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
Chinese
1
C
ok
Fig. 5-28 Setup the date 5
Pressing F3(down) to change the “second” to 20, press F4(Enter) to confirm and
exit, as shown in Fig. 5-29. If you do not want to modify the “second”, pressing
F1(ESC) to escape.
57
Page 64

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set 1
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -09 12:50:20
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
English
Chinese
c
ok
Fig. 5-29 Setup the date 6
After modification, pressing F1(ESC) to exit and the F1 key will become the
switching key. Pressing F1(switch) to switch the present alarm Window. Pressing
F3 may enter the function setting of next interface.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
Language
Chinese
Com. Adress Set
English
1
Date & Time Set
2001£ -11 £ -09 12:50:20
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
Chinese
1
m
5.3.4 Manual battery self-test
Setting of “manual battery self-test” is shown in Fig. 5-31. The Alarm Subwindow
will record the setting.
Pressing F4 to let “manual battery self-test” to be settable, then pressing F2(left)
and F3(right) to move the cursor to “Start Self-test”. If you do not want to start the
“manual battery self-test”, pressing F1(ESC) to escape. If pressing F4 to confirm
the setting(“Start Self-test”), the Current Events and Alarm Window will record the
event of “battery in self test”, after the testing is over, the Window will display
“Switching to Equalization Charging”. The whole testing process needs no manual
intervening. The testing time is dependent on the load capacity.
For example, If the load of 40 kVA UPS is 9kW, the test time is 35 minutes. If the
self-test conditions can’t be satisfied, “Battery Self-test is disabled” will be recorded.
Fig. 5-30 Setup the date 7
58
Page 65

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
5.3.5 Contrast adjustment
The contrast adjustment is shown in Fig. 5-32. Pressing F2(move left) and F3(move
right) to adjust the bars shown the figure below, thus the contrast is adjusted. Store
the adjusting results after confirmation and exit the contrast adjustment interface.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
UL33-0400L
Manual Batt Test
Start
Stop
Display contrast adjust
Record Query Range
3 days
0: all records
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
Fig. 5-31 Manual battery self test
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Manual Batt Test
Start
Stop
Display contrast adjust
Record Query Range
0: all records
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
3 days
m
c
ok
5.3.6 History log
Setting of the range of “history log” (the range is 0-30 days). That is, set up the
number of the days when the history log recorded can be viewed. “0” means all the
history records can be inquired. Pressing F2(up) and F3(left) to adjust the number
of days. Thus, the information of recorded in these days can be viewed and
scrolled through. After modifying the number of days, pressing F3(down) to select
the next item—Background communication mode selection.
Fig. 5-32 Contrast adjustment
59
Page 66

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
5.3.7 background communication setup
Background communication setup includes setting up the communication
mode(MODEM or RS232) , baud rate selection(9600, 4800, 2400 and 1200), callback times(1-5 times), as shown in Figure 5-34.
Pressing F4(modification key) to start setting the background communication mode,
pressing F2 (move left) and F3 (move right) to move the cursor to the expected
value, and pressing F4(Enter key) to confirm. If you do not want to modify the
parameters, pressing F1(ESC) to escape.
2001-11-08
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Manual Batt Test
Start
Display contrast adjust
Record Query Range
0: all records
Fig. 5-33 History log
Stop
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
3 days
c
ok
The setting method of baud rate is the same with above.
The call-back times setup means that when the UPS has a fault, the UPS can call
the number in preset times(if it is set to 5, then call 5 times) through MODEM
automatically. Pressing F4(modifying key) to enter the menu of setting call-back
times, pressing F2 (move left) and F3 (move right) to change the times. Pressing
F4 to store the changed parameter and exit.
After setting the above three parameters, pressing F3 (down) to select the last
three items to be set.
60
Page 67

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
5.3.8 Call-back number setup
Call-back numbers include call-back number 1, call-back number 2 and call-back
number 3, shown in Fig. 5-35. The length of telephone number is 15 digits, the
number can be that of fixed phone, mobile phone, BP phone or internal extension
phone. Input the number from the first digit and any remaining blanks digits has to
be entered with an asterisk “*”.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Comm. Mode Set
MODEM
Comm. Baudrate Set 9600
4800
9600
Callback Times Set 3
3
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
Fig. 5-34 Background communication
RS232
2400
RS232
1200
m
When the UPS has any fault, the UPS will call the number through a MODEM
automatically.
Example: Set the call-back number as 0755 8787001. First press F4(modification
key) to enter setting states, the cursor will stop at No.1 digit, waiting for
confirmation and modify this digit or select other digit, as shown in Fig. 5-36.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Phone Call No. 1
*******************
Phone Call No. 2
*******************
Phone Call No. 3
*******************
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
ok
Fig. 5-35 Fault call-back
61
Page 68

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:50:30
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Phone Call No. 1
*******************
Phone Call No. 2
*******************
Phone Call No. 3
*******************
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
c
m
Fig. 5-36 Setup fault call-back number 1
Pressing F4 key to confirm and save the changed parameter, and then the
functions of keys will be re-defined again, as shown in Fig. 5-37.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Phone Call No. 1
*******************
Phone Call No. 2
*******************
Phone Call No. 3
*******************
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
c
ok
Fig. 5-37 Setup fault call-back number 2
The range of each digit is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, *. “*” means the digit is void.
Pressing F3 (down key) to change the first digit to 0 and pressing F4 to confirm and
return to the higher level menu, as shown in Fig. 5-38.
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
2001-11-08
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Phone Call No. 1
0******************
Phone Call No. 2
*******************
Phone Call No. 3
*******************
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
c
m
Fig. 5-38 Setup fault call-back number 3
62
Page 69

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
Move the cursor to the corresponding bit to modify the number and confirm, then
the 0755 8787001 can be set, fill in the “*” character in other blank bits, as shown in
Fig.5-39. Pressing F1(ESC) to exit the setup of the fault call-back number 1. Other
fault call-back numbers will be set in the same way. At the moment, all the 12
setting items are finished.
5.4 Prompt window
The prompt window will be displayed during the operation of the system when the
system needs the user to confirm or to conduct some operations. This system has
about 5 “prompt windows” that will be introduced below.
From bypass to inverter mode with interruption:
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units 2/4 ID: 1
Out
Local
System
Battery
Records
Settings
Input Breaker Closed
Byp. Breaker Closed
Mains Volt. Abnormal
UPS in Battery Mode
Battery low
Figure 5-39 Call-back number setup
2001-11-08
ÊÖ¶¯µç³Ø×Ô¼ì
Phone Call No. 1
07558787001******
Phone Call No. 2
*******************
Phone Call No. 3
*******************
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:28
11£ -08 12:50
12:50:30
C
ok
If the bypass voltage or frequency exceeds the synchronized range and utility
voltage or frequency is normal, the inverter can’t be in synchronize with the bypass,
and the output can only transfer to bypass after an interruption of about 15ms when
the user press the “Start” key of inverter. Before transferring, the system should let
the user to confirm whether the interruption can be accepted, as shown in Fig.5-40.
Other operations can only be done after confirmation. If the bypass voltage restores
to normal before the user makes confirmation, the UPS will transfer to inverter
mode automatically. At the same time, the prompt window will disappear
automatically.
63
Page 70

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:30:20
Inv. On Units: ID 1
B(C)
Mains
Bypass
Out
Local
System
Battery
Power KW
Cap.
Load%
Crestor
Factor
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
A(B)
221
11. 8
Transfer with Interupt
KVA
, Confirm
50.2
1.41
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
C(A)
220 221
12.3
12.5
50.1
50.1
1.40
1.41
OK
Fig. 5-40 Bypass to inverter prompt
From inverter to bypass mode with interruption:
If the bypass voltage or frequency exceeds the synchronized range and the UPS is
in inverter mode, the system must let the user to confirm and accept the power
interruption danger before pressing the inverter stop key to shutdown the output of
the inverter. The user can also cancel the shutdown operation, as shown in Fig. 5-
41. If the bypass voltage restores to normal before the user makes the confirmation,
the UPS will transfer to bypass operation mode automatically, and at the same time
the prompt window will disappear soon.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:30:20
Inv. On Units: ID 1
B(C)
Mains
Bypass
Out
Local
System
Battery
Power KW
Cap.
Load%
Crestor
Factor
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
A(B)
221
This operation leads
11.8
KVA
to output shutdown,
50.2
Confirm or cancel
1.41
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
C(A)
220 221
12.3
12.5
50.1
50.1
1.40
1.41
C
OK
Fig. 5-41 Transfer to bypass prompt
Overload due to shutdown: The parallel operation system is in inverter mode, if the
load capacity exceeds the total capacity of the remained UPS units when shut
down one UPS unit. The UPS that is to be shut down will display a prompt window
to ask the user to confirm before shutting down, as shown in Fig.5-42. If the load is
reduced before the user makes confirmation, there will be no overload for the
remained UPS units, this UPS unit will shut down automatically, and the Prompt
window will disappear automatically, the functions of the keys in the Keypad display
window will restore to normal functions.
64
Page 71

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:30:20
Inv. On Units: ID 1
B(C)
Mains
Bypass
Out
Local
System
Battery
Power KW
Cap.
Load%
Crestor
Factor
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
A(B)
221
This operation leads
11. 8
KVA
to overload, Confirm
50.2
or cancel
1.41
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
C(A)
220 221
12.3 12.5
50.1
50.1
1.40
1.41
C
OK
Fig. 5-42 Capacity expansion
Start UPS capacity inadequate: When the UPS is in bypass mode, if the load
capacity is larger than that of one or more than one UPS unit, the UPS that has
already been start-up will not transfer to inverter mode and prompt a window to ask
the user to confirm.
When the load is reduced to be lower than the capacity of UPS, the Prompt window
will disappear.
UL33-0400L
2001-11-08
12:30:20
Inv. On Units: ID 1
B(C)
Mains
Bypass
Out
Local
System
Battery
Power KW
Cap.
Load%
Crestor
Factor
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
A(B)
221
System overload,
11. 8
KVA
Turn on More UPS
50.2
1.41
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
C(A)
220 221
12.3 12.5
50.1
50.1
1.40
1.41
Fig. 5-43 UPS capacity inadequate
Load capacity higher than that of single module UPS system: If the UPS is in
bypass operation mode, and the load capacity exceeds the total capacity of one or
more than one UPS units, the LCD of the UPS that start first will display a Prompt
window, as shown in Fig. 5-44. Under this condition, the user must decrease the
load until the load is lower than the UPS capacity, or switch on the remained UPS
until the total capacity exceeds the load capacity, thus the system can transfer to
inverter mode and the Prompt window disappears.
65
Page 72

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
UL33-0400L
Inv. On Units: ID 1
Mains
Bypass
Out
Local
System
Battery
Power KW
Cap.
Load%
Crestor
Factor
Input Breaker Close
Byp. Breaker Close
Output Breaker Open
UPS in Normal Mode
Batt. Boost Charging
Fig. 5-44 Load capacity exceed that of single module UPS system
5.5 Events and State Information:
Two kinds of UPS events and status information: Current events and historic events.
Current events are the current status information of UPS and the events that
happen only just now. The information will be displayed in the current event and
alarm display window in time sequence. If a certain status changes or a certain
event happens again, then the status or the event will disappear from the current
event and alarm display window and becomes the historic information.
2001-11-08
A(B)
221
The Load is Too
11.8
KVA
Heavy to Be
50.2
Transferred
1.41
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
11£ -08 12:09
12:30:20
B(C)
C(A)
220 221
12.3
12.5
50.1
50.1
1.40
1.41
Historic status information means the information that happens before and not exits
at the moment, or the information happens last time. These kinds of information will
be recorded in the history log in real time according to the time sequence. Each
history log has a start time and if the record is ended normally, there will be an end
time for the history log. If the end time is not recorded due to power failure, then the
historic log will have no end time.
66
Page 73

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
Table 5-3 UPS Events
No. Event Reason
Start through keypad The user presses down the inverter start key, the system will
1
Start through keypad failed The user presses down the inverter start key, the system
2
3 Shutdown through keypad The user presses down the inverter stop key
4 Emergency shutdown The user presses down the emergency shutdown key
5 Fault clear The user presses down the fault clear key
Manual mute When the system is in alarm state, the user presses down
6
Manual mute cancel When the system is in mute state, the user presses down
7
start inverter
can’t start inverter
the mute key
the mute key
Confirm the interrupted
8
transfer
Single UPS shutdown
9
confirmation
Parallel operation system
10
shutdown confirmation
Manual battery self-test In function setting menu, the user selects the “Manual
11
Stop battery self-test manually In function setting menu, the user selects the “Stop battery
12
Note: If the same event occurs once again, it will be displayed on the current event and alarm display
window according to the time sequence. The last event will become the history log and will disappear
from the current event and alarm display window, and this event can be found in history log. So, only the
event that occurs most recently can be displayed in the current event and alarm display window.
When the system displays the prompt window to require the
user to confirm, the user presses the “Enter” key
When the system displays the prompt window to require the
user to confirm, the user presses the “Enter” key
When the system displays the prompt window to require the
user to confirm, the user presses the “Enter” key
battery self-test”
self-test manually”
67
Page 74

Chapter 5 Operation of Display Panel
Table 5-4 UPS states
No. State Reason
1 Bypass mode UPS bypass powers the load
2 Normal mode
3 Battery mode The UPS powers the load through battery
4 United power mode
Bypass and inverter all
5
shutdown
6 Output power interruption The UPS has no output
7 Battery is under self-test UPS is in battery self test condition
8 Generator connection Connect the generator to UPS through dry contacts.
9 Generator exit Rectifier exits the intelligent generator mode
10 Generator run Rectifier enters the intelligent generator mode
11 Non-charging state Battery is not in charging state
12 Equalization charging state Battery in equalization charging state
13 Float charging state Battery in float charging state
14 Input circuit breaker closes Input circuit breaker closes
15 Input circuit breaker opens Input circuit breaker opens
The UPS powers the load through rectifier and
inverter
The UPS powers the load through rectifier and
battery together
Bypass and inverter are all shut down
16 Output circuit breaker closes Output circuit breaker closes
17 Output circuit breaker opens Output circuit breaker opens
18 Bypass circuit breaker closes Bypass circuit breaker closes
19 Bypass circuit breaker opens Bypass circuit breaker opens
Maintenance circuit breaker
20
closes
Maintenance circuit breaker
21
opens
Note: When the UPS is in the above states, current event and alarm display window will display
the states according to the time sequence; When the states are cleared, the information will also
be cleared from the current event and alarm display window and the start time and end time of
the state will be recorded in history log.
Maintenance circuit breaker closes
Maintenance circuit breaker opens
68
Page 75

Chapter 6 Maintenance
This chapter mainly introduces the daily using and maintenance of UPS and the
operation inside the UPS is not covered here. If maintenance should be done to the
UPS, Q1, Q2 and QF1 should be disconnected, and then wait for 8 minutes until
there is no high voltage inside the UPS. Don’t touch any components of the UPS
before reading this manual.
Anything not understood, please consult out technical support engineer.
6.1 Setup procedures
6.1.1 Start up
After the UPS is switched on and if the UPS input power meets specified input
requirements, the following operations can be done:
Chapter 6 Maintenance
1. Start from utility
1) Make preparations according to Section 4.1.1, introduce the input source to the
input terminals of UPS cabinet;
2)Turn on Q2 and Q5 and wait until the bypass indicator turns green;
3) Turn on Q1 and the QF1 according to Section 4.1.2. The UPS will transfer to
inverter mode without interruption after the inverter starts normally.
2. Start from utility
When the battery is normal and is connected to the DC bus all the time, the inverter
can start from battery. The start procedures are: press “start” button on the
operation panel for longer than 2s, close Q5 when the inverter operation indicator
turns green. Now the inverter powers the load. At this time the battery indicator and
load indicator all illuminate green.
Note:
The UPS can not start from the battery that is used for the first time.
69
Page 76

6.1.2 Shutdown
1. Shutdown in normal mode
When the UPS requires periodical checking or needs to stop operation, the
shutdown process in normal mode is given below:
1.Press the “inverter shutdown” button on the UPS panel for longer than two
seconds, shutdown the inverter and the system transfers to bypass mode.
2.Switch off the Q1 and QF1 one by one;
At this time the load is powered by bypass. If the load needs not to be powered,
then switch off Q2 and Q5 directly; If the load needs to be powered continuously,
the UPS should be shutdown for maintenance, follow the steps below:
3.Switch on the internal maintenance bypass switch Q3BP;
4.Switch off Q2 and Q5 one by one;
Now the load is powered by the maintenance bypass. Don’t conduct repairing and
maintenance work after waiting for 8 minutes until the voltage of DC bus capacitor
become zero due to discharging.
Chapter 6 Maintenance
5.External maintenance bypass KBP should be installed if the UPS needs to be
shutdown totally. Switch off Q2 and Q5, close the KBP, and then switch off the
internal maintenance bypass Q3B, the load will transfer to external maintenance
bypass power without interruption. After this, the UPS unit replacement or capacity
expansion can be done after switching off UPS input and output switches.
2. Shutdown in bypass mode
Follow from step 2 to step 5 of the above “shutdown in normal mode” to shut down
the UPS in bypass mode.
3. Shutdown in battery mode
Note: when the bypass power is abnormal, shut down the UPS in battery mode will
result in the power interruption to the load.
Because the utility is not available, in order to shut down the UPS that is in battery
mode, switch off all the switches to realize shutdown in bypass mode after finishing
the first step in “shutdown in normal mode” .
4. Shutdown in ECO mode
The procedures of shutdown in ECO mode are the same with those of shutdown in
bypass mode.
70
Page 77

Chapter 6 Maintenance
5. Shutdown in United powering mode
The procedures of shutdown in United powering mode is the same with those of
shutdown in normal mode.
6.1.3 Transferring between operation modes
The UPS can transfer among various operation modes after it is in normal mode.
The following operations can be done if the input power source of UPS meets the
requirements and the load capacity is lower than that of single module UPS system.
1. From normal mode to battery mode
Switch off Q1, the UPS can transfer from normal mode to battery mode
automatically.
2. From normal mode to bypass mode
Press “inverter shutdown” button to transfer from normal mode to bypass mode
without power interruption.
3.From bypass mode to normal mode
Q1 is closed, press the “inverter start” button on the display panel to transfer from
bypass mode to normal mode. If the bypass source exceeds the normal range,
there will be interruption in the transferring process.
4.From ECO mode to normal mode
Set the UPS in normal mode again and the UPS can transfer from ECO mode to
normal mode.
Note: The engineer should set through software.
5.From battery mode to normal mode
When the rectifier source is normal, switch on Q1, the UPS will transfer from
battery mode to normal mode automatically.
6.1.4 Emergency shutdown and recovery
Under any status, press the “emergency shutdown” button on the panel for 2
seconds if overload or the faults that may endanger the safety occur. The system
will then shut down the rectifier, inverter and stop outputting power(including the
inverter and bypass), at the same time, disconnect the battery contactor.
At this, if the user confirms that the fault is cleared, press the “fault clear” button to
let the system get out of the emergency shutdown state. When the UPS enters the
normal state, the rectifier starts again, the battery contactor closes and the bypass
71
Page 78

begins to power the load. Press the “inverter start” if the user wants the inverter to
operate.
6.1.5 Mute
The buzzer sounds when the UPS has faults. The user can press the “Mute” button
for two seconds to silence the sound. If the user press the key again, the sound can
be heard again. When the UPS is in fault clear state, new fault may cause the
buzzer to sound again.
6.1.6 Fault clear
1.Fault mode and fault handling
The UPS has self-diagnosing functions and the fault types can be inquired through
LCD or background computer. Clear the fault with reference to Chapter 7 or notify
the maintenance engineer to repair. The UPS faults can be classified into the
following types:
1) Alarm fault: The UPS or its parts have fault, but the system operation states
won’t be changed. For example: over load occurs in preset time (Usually overload
may change the system operation state)
Chapter 6 Maintenance
2) Recoverable fault: After the fault occurs, the system will shut down the rectifier or
inverter and can recover to normal operation automatically after the fault is cleared.
For example: transformer over-temperature fault.
3) Fault that can be recovered manually: The system is locked up when fault occurs.
It can’t recover normal operation without restarting.
2 Shutdown due to battery low
According to the user’s setting and the setting of host, when rectifier and bypass
power failure occurs, the system will operate from battery continuously until shut
down due to battery low. If the Utility power recovers after UPS shutdown, the
methods to restart the UPS are given below:
1) If the system is set as “select inverter mode manually”, the system will maintain
its locking state until the user starts the inverter.
2) If the system is set as “automatic bypass mode”, the system will transfer from
locking state to bypass mode after the Utility source or bypass restores to normal.
3) If the system is set as “automatic inverter mode”, the system will transfer from
locking state to inverter mode after the Utility source or bypass restores to normal.
72
Page 79

6.1.7 Monitoring system
1. Background communication
The monitoring system of this UPS system provides one RS232 port and one
RS485 port (the definition of the port is in Section 3.4.3), several input and output
dry contacts (refer to Section 3.4.4). The user can introduce the signal to the
nearest management office to conduct equipment management. All the data
displayed on the panel will be monitored by background monitoring software.
Besides, there are also MODEM and SNMP cards, which are used for MODEM and
SNMP communication.
1)RS232 mode
The transmission distance of RS232 mode is shorter than 15m. This RS232
mode is suitable for the short distance monitoring required by UPS operator or
user.
2)RS485 mode
Chapter 6 Maintenance
The J23 connector on the monitoring board is used for user’s RS485 port.
“485+” and “485-” are used as the user’s positive terminal and negative terminal
respectively. SHIELD terminal is used as the shielding terminal that connects the
shielding layer.
The transmission distance is shorter than 1000m. The user can use any
RS485/RS232 converter(such as the OCI-6 provided by us) to realize
networking of RS485+RS232 mode.
3)MODEM mode
The user can monitor the UPS remotely via a MODEM and the monitoring
software- POWERSTAR by dialing the preset telephone number. Refer to
“Directions of MODEM” and “Directions of POWERSTAR” for details.
4)SNMP mode
The parts of SNMP card UF-SNMP111 is compatible with 10/100M either net.
The SNMP card supports various kinds of protocols of SNMP, TFTP, HTTP and
TELNET and providing a solution for high speed network access method.
The user can connect the UPS to the LAN through the SNMP card and realize
the network management.
Refer to “Directions of SNMP” card for details.
73
Page 80

Chapter 6 Maintenance
2. Monitoring single UPS
UPS support the communication modes through RS232, RS485, MODEM and
SNMP card. These communication modes can’t be used by one same UPS. The
single UPS monitoring theory is shown in Fig.6-1.
Fig. 6-1 Monitoring of Single UPS
3. Monitoring parallel operation system
The communication of parallel operation system is realized through its internal
RS485 bus. Any UPS module can be nominated as a master UPS. The user can
use any communication mode to get the information of any UPS module through
this master UPS. The monitoring method of parallel system is shown in Fig.6-2.
Fig. 6-2 Monitoring of Parallel UPS System
74
Page 81

6.1.8 Input and output contacts
The functions of input and output contacts are introduced in Chapter 3.
1. Output dry contact
This UPS provides 8 kinds of dry contacts output and the definition is given below:
Battery low: This signal is active when the pre-alarm of UPS battery occurs;
Battery mode: This signal is active when the battery powers the load;
Inverter mode: This signal is active when the utility powers the inverter normally;
Ambient over-temperature: This signal is active when the ambient temperature is
too high;
Emergent shutdown: This signal is active when the UPS is shut down by user in
emergency;
Common alarm: This signal is active when the UPS has fault;
Chapter 6 Maintenance
Overload: This signal is active when the load is too heavy;
Generator mode: This signal is active when the generator powers the UPS;
2. Input contacts
The UPS can connect to 6 circuit-branches of contacts for environment parameters:
24V contacts for environment parameters (3 circuit branches): ENV1-3, suitable for
connecting the 24V sensor for environment parameters, such as the infrared sensor.
The contacts are relay dry contacts.
12V contacts for environment parameters (1 circuit branch): ENV, suitable for
connecting the 12V sensor for environment parameters, such as the water sensor.
The contacts are relay dry contacts.
Generator contacts: These are the dry contacts of intelligent generator and are
connected to the UPS input terminals. The contacts are used to notify the UPS that
the generator has been connected. If the user wants to use intelligent generator
mode, but the generator has no signal to transmit to these contacts, short connect
the “GEN-H” and “GEN-L” to notify the UPS that the generator is connected after
the generator starts.
Note:
If the user wants to use the generator mode, it is required that the UPS should be
set to “Generator mode enabled” through the background host first. Otherwise, the
generator signal is inactive.
75
Page 82

Emergent stop: If the user is in short distance, short connecting the “UCTRH” and
“UCTRL” can make the UPS shut down. Relay dry contacts should be used here.
Note:
The user should be careful when using this function. The power will be interrupted
completely once the emergency shutdown happens. When the user connects the
wires, the length of the wire should be no longer than 10m. Protection measures
should be done to the wire if the length of the wire is longer than 10m.
6.1.9 Temperature measuring
Two circuit branches of temperature can be measured.
J12 socket: Used to measure the battery temperature with the temperature sensor
TMP12Z made by Avansys. During installation, our service engineer has set the
function of “temperature compensation enabled”. Temperature compensation is
realized once the TMP12Z is connected.
J16 socket: The V-AD pin of this socket is used to measure the ambient
temperature of other points. Our service engineer can set the over temperature
alarm point through background host. The UPS will alarm when the temperature is
too high. Note: The 1.0~5.0V signal corresponds to 0~100°C.
Chapter 6 Maintenance
6.2 Maintenance
6.2.1 Daily maintenance
There are few moving parts inside the UPS with the exception of the fans, thus few
components need to be maintained. The user should check according to the
following methods:
1. Daily checking
1)Check the control panel: All the LEDs should illuminate normally. The LCD
should display all the parameters normally without alarm.
2)Check whether there is over-temperature phenomena of the air blown out by
fan;
3)Check whether there is any abnormal noise;
4)Check whether the ventilation holes are obstructed;
76
Page 83

Chapter 6 Maintenance
5)Check whether all the fans operate normally. The life of the fan in continuous
operating state is 20000—40000 hours and will be shortened if the fan operates in
high temperature environment.
2. Weekly checking
1)Measure and record the battery charging voltage;
2)Measure and record the battery charging current;
3)Measure and record the UPS three-phase output voltage;
4)Measure and record the output current of each output phase of UPS; If the
current differs greatly with previous values, record the load capacity, types and
location for later analysis.
Please contact us if the displayed value differs with the calculated value.
3. Annual checking
Note:
The annual checking must be done by qualified person because the person may be
required to test the high voltage components inside the UPS.
During annual checking, the load should be powered by maintenance bypass.
Each year, the UPS should be cleaned and the following items should be checked:
1)At first, check the weekly checking items;
2)Switch off the UPS and let the maintenance bypass to power the load;
3)Switch off the input switch and battery switch;
4)Make sure that the input terminals of the UPS(R1, S1 and T1), battery terminals,
output terminals(U4, V4 and W4) and bypass input terminals (R4, S4 and T4) are
not energized;
5)Open the UPS door and internal protection door
6)Check the UPS power components and auxiliary components, pay attention to
the following parts:
Capacitor: check whether there is any leakage and deform phenomenon;
Magnetic component: Check whether there is any over-temperature marks and
cracks, and the secure degree
77
Page 84

Chapter 6 Maintenance
Cable and connectors: Check whether the cable is aged, damaged or burnt; check
whether the connector of the PCB is secure;
PCB: Check the cleaness and completeness
7)Use vacuum pump to clear the dirt on the surface;
8)Switch on the UPS again and let the inverter powers the load according to the
start-up process of UPS;
9)If necessary, switch off the Q1, check the battery backup time, switch on Q1
when the battery voltage is higher than the end of discharge voltage by 5V(Note:
The end of discharge voltage is 300Vdc. When the battery voltage reaches 300Vdc,
the battery input contactor will disconnect and the load will transfer to bypass ), and
record the backup time.
4. Other checking
1)Check the insulation sleeve of input/output cables and the connectors: check
periodically and the UPS should be switched off when checking. The checking
interval should not be longer than 2 years;
2)Lightning protection checking: Check according to the methods of weekly
checking because you can only check the indicator of lightning protection device by
opening the door. Check each day in wet seasons or the seasons with lots of
thunders. Check the lightning device in time when lightning occurs nearby to find
problems in time.
6.2.2 Battery maintenance
The internal battery of iTrust series UPS is a sealed, lead-acid, maintenance-free
battery. The battery life depends on the ambient temperature, charge and discharge
times. High ambient temperature and deep discharge will shorten battery life.
1 battery storage
To ensure battery life, the battery should be maintained regularly:
1)Check the battery state periodically. Keep the battery room and battery cabinet
clean. Clear the oxidization objects at the terminal or connection bar periodically
and apply some butter. Tighten the loose screws and keep the battery well
connected to prevent big voltage drop during discharging.
2)Check the battery insulation every 2-3 months. Check the total battery voltage
once a week. Use the automatic battery management function to charge the battery
whose voltage is low. Clean the leakage solutions periodically.
78
Page 85

Chapter 6 Maintenance
3)Keep the ambient temperature between 15℃ and 25℃.
4 ) To prevent small current discharge, continuous battery discharge time
exceeding 24 hours is prohibited.
5)Please contact the distributor if the battery backup time is greatly shortened, or
the UPS LCD displays “battery needs to be replaced”. Confirm whether the battery
needs to be replaced. Please confirm whether the parameters of the replaced
battery and new battery are same.
6)Check whether the auto battery management function is normal because many
battery maintenance work is done automatically through the battery management
functions, for example, charging the battery periodically, temperature compensation,
EC/FC switchover, battery low alarm and battery life forecast.
2. Manual battery self-test
The conditions for self test:
1)Battery contactor closes
2)Battery is in float charging state;
3)Rectifier and inverter communicate normally;
4)Battery status is normal;
5)Rectifier operates normally;
6)Utility source voltage is normal;
7)Inverter operates normally
8)Load capacity is larger than the battery capacity set by battery curves;
9)UPS is not in united operation (generator + battery) mode
The battery self test will be conducted only all of the above conditions are satisfied.
During the self test, if any one of the above condition is not satisfied, the system will
exit the self test state and enter equalization charging state.
Pressing the “stop manual self test” can stop the self test process and the battery
transfers to equalization state.
Battery will transfer to equalization state after self test is over.
3. Auto battery self test
Auto self-test is start if the UPS operation states satisfies the manual self-test
condition and the last self-test interval satisfy the “battery discharging interval”. The
79
Page 86

system will not start battery self test if the last self-test interval satisfies the “battery
discharging interval”, but does not satisfy the manual self test condition, and the
system will wait until the conditions are satisfied.
6.2.3 Shutdown maintenance
For large capacity UPS, periodical checking is required to ensure the normal
operation and proper condition. Notify us if any fault is found. In order to maintain
the uninterrupted power supply to the load, please shut down the UPS according to
the following procedures:
1.Press the “inverter shutdown” button to shut down the inverter, the system
transfers to bypass mode;
2. Switch off Q1 and QF1 one by one;
3. Switch on the maintenance bypass switch Q3BP;
4. Switch off the Q2 and Q5 one by one.
5. Now, the load is powered by the maintenance bypass of UPS. Conduct
maintenance or checking to the UPS after waiting for 8 minutes and the DC bus
capacitor discharges to zero voltage.
Chapter 6 Maintenance
If the UPS is required to be shutdown totally, switch on the external maintenance
bypass switch KBP after switch off the Q2 and Q5; then switch off the Q3BP, thus
the load can be powered by the maintenance bypass with interruption, and the UPS
units replacement and capacity expansion can be done after switching off the input
and output power distribution switches.
80
Page 87

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
7.1 UPS system troubleshooting
The following information are only for service engineers who are trained in the
repair and troubleshooting of the UPS. The maintenance engineer must be familiar
with the UPS because the UPS is rather complicated.
7.1.1 Basics
Generally, the UPS faults happen suddenly and the UPS will be shutdown or
transfer to bypass mode. So making record is very important for maintenance.
Please observe the following contents:
The error of UPS output voltage should not exceed 2%;
The battery charging current should not exceed 6A.
Find out the reasons if the UPS displayed value differs greatly with the calculated
values. The user should be informed of the load condition before starting
troubleshooting.
7.1.2 Procedures
Status recording: Record the displayed information, the buzzer sound, states of
indicators and the states of various switches when fault occurs.
Fault types: After recording all the information, look up the fault information table
and the fault indicators, if the fault type can not be determined yet, please contact
supplier or technical support engineer.
Fault record: After identifying the fault type, please notify our service engineers for
repairing.
7.2 LED indicator
7.2.1 LED display
There are 6 LEDs used for indicate the operation status and fault. There is a fault if
the LED illuminates red.
Bypass indicator: If it turns red, that means the bypass input exceeds the normal
range;
81
Page 88

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
Rectifier indicator: If it turns red, that means the rectifier fails;
Battery indicator: If it turns red, that means the battery is abnormal;
Inverter indicator: If it turns red, that means the inverter fails;
Load indicator: If it turns red, that means overload occurs;
Alarm indicator: If it turns red, that means the system fails;
7.2.2 LED indicator of lightning protection device
LED indicators of lightning protection device of 40/60kVA UPS are shown in Fig.7-1.
From bottom to up the LEDs are: Lightning protection indicators of Phase A, B and
C; LED indicators of lightning protection device of 40/60kVA UPS are arranged from
left to right and are indicators of Phase A, B and C respectively. The device is
normal if the indicator illuminates green, and fails if the indicator turns off. The
checking of the indicators is described in Chapter 6.
7.3 Buzzer alarm
If the buzzer sounds 1 second “click” every 2 seconds, that means the system has
normal alarm or the system is abnormal;
If the buzzer sounds continuously, that means the system has serious fault.
Fig. 7-1 Lightning protection LED
82
Page 89

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
7.4 LCD indication for fault information
The LCD on the UPS displays the fault information of Table 7-1 and Table 7-2. The
user should locate and analyze the fault according to the tables and feedback the
fault information to our service engineers.
Table 7-1 Fault information
No.1 Fault description Reason Actions to be taken
Communication of
1
inverter fails
Communication of
2
rectifier fails
Ambient over-
3
temperature
Environment
4
parameter 1 abnormal
Environment
5
parameter 2 abnormal
Environment
6
parameter 3 abnormal
Environment
7
parameter abnormal
Rectifier input voltage
8
abnormal
Rectifier input under-
9
voltage
Communication between monitoring
unit and inverter fails
Communication between monitoring
unit and rectifier fails
over-temperature of UPS room Check the ventilation of UPS room
Environment parameter channel 1
has alarm
Environment parameter channel 2
has alarm
Environment parameter channel 3
has alarm
12V environment parameter channel
has alarm
Line-to-neutral voltage of rectifier
exceeds normal operation range
Line-to-neutral voltage of rectifier
lower than 305V, but higher than
208V
Notify the service engineer for repairing
Notify the service engineer for repairing
Check the devices relating to the channel
Check the devices relating to the channel
Check the devices relating to the channel
Check the devices relating to the channel
Check the line-to-neutral voltage
amplitude of rectifier
Check the line-to-neutral voltage
amplitude of rectifier
Rectifier’s input
voltage frequency is
10
abnormal
11 Input fuse blows Rectifier input fuse blows up Notify the service dept for repairing
Input transformer over
12
temperature
Input phase rotation
13
reverse
14 Input softstart fails Input softstart fails Notify the service dept for repairing
Rectifier frequency exceeds the
normal range
Temperature of input transformer is
too high
Rectifier’s input phase rotation is
reverse
83
Check the rectifier’s input voltage
frequency
Check the ambient temperature and
ventilation
Notify the UPS service engineer, check
the wiring of rectifier input cables
Page 90

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
No.1 Fault description Reason Actions to be taken
Bypass voltage or frequency is out
Bypass
15
unsynchronized
Bypass ratings exceed
16
the normal range
17 Bypass SCR fails Bypass SCR is damaged Notify the service dept for repairing
of normal range and inverter output
is not synchronized with the bypass
output.
Bypass voltage or frequency
exceeds the normal range and the
bypass will not power the load
anymore.
Check the bypass voltage and frequency
Check the bypass voltage and frequency
Bypass over current
18
timeout
Shutdown due to
19
bypass fault
Battery needs to be
20
replaced
No battery
21
Pre-alarm for end of
22
battery discharging
battery over
23
temperature
Battery contactor is
24
abnormal
If the over current time exceeds the
limit, the UPS may shut down the
bypass and the inverter.
When the overload delay time is due
in inverter mode, if at this time the
bypass has fault, then the inverter is
shutdown.
The battery life is reduced due to
aging, which may endanger the
normal operation of UPS. Warn the
user that the battery is abnormal and
needs to be replaced.
Batteries are not connected.
The battery discharges to pre-alarm
point (the battery capacity is
inadequate), the system may shut
down after a few minutes
battery temperature is too high
Battery contactor fails Notify the service dept for repairing
Check the load, if it is normal, then restart
the UPS
Repair the bypass and reduce the load,
and then restart the UPS. Note: Don’t let
the UPS in over load state for a long time.
Notify the service dept for replacing the
battery and set the battery model and
parameters through software.
Check the battery and the wiring of
batteries
Shut down the load in time
Check the battery temperature and
ventilation
battery self-test is
25
disabled
Battery is connected
26
reverse
Bypass phase rotation
27
is reverse
28 Rectifier fails
Rectifier heatsink over
29
temperature
The battery condition for self-test is
not satisfied
Battery is connected reverse
Bypass phase rotation is reverse
Rectifier is abnormal and has
serious fault
Rectifier heatsink temperature is too
high
84
Start the self test after the conditions can
meet the requirements
Notify the UPS service engineer to
connect the battery again
Notify the UPS service engineer to
change the bypass phase rotation
Notify the service dept for repairing
The UPS can recover automatically.
Check the environment and ventilation
Page 91

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
No.1 Fault description Reason Actions to be taken
30 Rectifier fan fails
Rectifier fan is abnormal Replace the fan in time and the UPS can
recover automatically
Rectifier contactor
31
abnormal
Auxiliary contactor
32
abnormal
Auxiliary power supply
33
1 fails
34 Rectifier over current
35 Inverter asynchronous
36 Inverter fails Inverter output fails and shuts down Notify the service dept for repairing
Inverter heatsink over
137
temperature
38 Inverter fan fails Inverter fan is abnormal
39 Inverter SCR fails
Auxiliary power supply
40
2 fails
Rectifier contactor can’t be closed or
opened normally
Auxiliary contactor abnormal can’t
be closed or opened normally
At least one auxiliary power supply
fails
The IGBT of rectifier has over
current resulting in the shut down of
rectifier.
Inverter is asynchronous with
bypass
Inverter heatsink temperature is too
high
Inverter SCR fails and has no
output. UPS shuts down
At least one auxiliary power supply
fails
Notify the service dept for repairing
Notify the service dept for repairing
Notify the service dept for repairing
Notify the service dept for repairing
Check if the bypass is normal. The fault
alarm stops automatically after the
bypass recovers normal
The UPS can recover automatically.
Check the environment and ventilation
Replace the fan in time and the UPS can
recover automatically
Notify the service dept for repairing
Notify the service dept for repairing
The IGBT of inverter has over
41 Inverter over current
Shutdown due to low
42
bus voltage
Output transformer
43
over temperature
44 overload
Overload exceeds
45
normal time
46 Output fuse blows up Output fuse blows Notify the service dept for repairing
AC output over
47
voltage
48 Output surge current
current resulting in the shut down of
inverter.
DC bus voltage is too low resulting
in the shutdown of inverter
Output transformer temperature is
too high
Load is too heavy Disconnect unnecessary load and ensure
Over load occurs in inverter mode,
transfers to bypass mode
Output over voltage Notify the service dept for repairing
Surge current occurs in bypass
mode, the system shutdown
85
Restart the inverter, if the fault can’t be
cleared, notify the service dept for
repairing.
Check whether there is fault in rectifier
side, if no, then check whether overload
occurs. Restart after clearing the fault.
Auto recovery, ambient and ventilation of
UPS should be checked.
the safety.
If the load decreases after 5 minutes, the
system will back to inverter mode
Avoid applying big load abruptly and short
circuit
Page 92

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
No.1 Fault description Reason Actions to be taken
The system transfers to bypass
Transfer to bypass
49
due to surge
mode due to surge current and back
to inverter mode after load is
decreased
Avoid applying load abruptly and the UPS
can recover automatically
User’s wrong
50
operation
The actual transfer
times exceed the
51
permissible transfer
times per hour
Wrong operation such as start the
UPS with the maintenance bypass
switched on
Transfer times exceed the times set
by background. The system will stay
in bypass mode until next hour.
Operate with reference to User’s Manual
Avoid frequent overload
Table 7-2 Fault of parallel operation system
No. Fault description Reasons Fault processing
Overload of parallel
1
operation system
Neighbouring UPS
module requires to
2
transfer to bypass
mode
3 Load sharing fault
Overload occurs and the
redundancy is not available
In parallel operation system,
some UPS module may
require to transfer to bypass
due to surge or overload,
other modules will transfer to
bypass after receiving the
signal sent by this UPS
module that requires to
transfer to bypass mode
The load current of each UPS
module is noticeably
unbalanced, thus the system
loading ability is affected.
Disconnect the load of low priority, maintain the
power supply to important load
If the parallel operation system transfers to
bypass mode, and the operation condition
enables, all the UPS modules can recover to
normal mode synchronously.
Notify the service dept for repairing
Parallel operation
4
board fails
The board is damaged. Notify the service dept for repairing
86
Page 93

Chapter 8 Parallel System
8.1 System Introduction
8.1.1 Basics
The Liebert UPS uses intelligent and reliable decentralized parallel operation
technology. A maximum of four single units of the same capacity can operate in
parallel.
The UPS system has two paralleling modes:
Paralleling for redundancy
Paralleling for capacity
1. Conditions for parallel operation
Chapter 8 Parallel System
Each UPS unit has the same capacity, same software and hardware version
Each UPS in the system must share the same bypass source
The UPS output are connected together. The rectifier input can be from a different
source, but the phase rotation of the rectifier input, bypass input and output must
be the same
The parallel logic cable and load sharing cable must be connected
2. Features of parallel systems
1)The hardware and firmware of each unit in the system must be compatible and
changing the operation mode can be done only with changing the software setting.
2)The parallel signal bus is simple, reliable and designed for redundancy, which
provides the user with maximum flexibility. Shutting down or starting up the UPS in
the parallel system can be done in any sequence. If an overload occurs, the
system can recover automatically from bypass mode after the overload is cleared.
3)The operation status can be queried from each UPS’s LCD display.
4)The UPS monitoring module (optional) can monitor the system parameters of
the whole system.
5)Any single module UPS system in the parallel system can be designated as the
host for communication with remote computer. The total load current, number of
87
Page 94

UPS in the system, and operation condition of each unit can be monitored through
the remote computer.
8.1.2 Theory of Operation
1. Parallel System consisting of two units
This is the most frequently used configuration and its operation theory is shown in
Figure 8-1
Chapter 8 Parallel System
Fig. 8-1 UPS parallel operation mode(two UPS modules)
2. Paralleling for Redundancy of more than two units
(N+X) system : N number of UPS is supporting the load and X number of UPS are
redundant. If the rating of each UPS unit is Po and the total load capacity is Pmax,
then (N-1) x Po < Pmax < N x Po, as shown in Figure 8-2
88
Page 95

Chapter 8 Parallel System
Fig. 8-2 Redundancy operation mode
This system can improve the system reliability noticeably. In normal condition, each
UPS does not work at full load, so even if the load is increased, the system will not
transfer to bypass.
When X number of UPS shuts down due to failure, the remaining N numbers of
UPS can still powers the load. At this time, the system will give out the alarm.
3. Paralleling for Capacity Expansion
In this system, X is zero then if the rating of each UPS unit is Po and the total load
capacity is Pmax, then (N-1) x Po < Pmax < N x Po, as shown in Figure 8-3. This
system cannot improve the reliability, but can improve the system capacity to
support an increased load.
Fig. 8-3 Capacity expansion
4. Series “Hot-Standby” parallel system
Two UPS units are connected in series, one is the Master and the other Slave.
The Slave output is the bypass source of the Master, as shown in Figure 8-4. In
normal condition, both UPS are in normal mode with the inverter supporting the
load. If one unit fails, the other will power the load. In order for the system to rotate
powering the load, the alternative operation time must be set. If two different UPS
are connected in series, the load capacity must be smaller than the UPS with the
smallest rating.
89
Page 96

Chapter 8 Parallel System
Note
The default value of alternative operation time is 168 hours and the range is 0-4320
hours
8.1.3 Operation modes
The parallel operation system also has operation modes such as normal mode,
battery mode, bypass mode and maintenance bypass mode. All the UPS units
inside the parallel operation system should operate in harmony. For example if one
UPS is in inverter mode, the bypass of other units should be shut down.
Normal mode: The load is powered by the inverters of all the UPS units inside the
system. If the bypass frequency is in the synchronous range, the inverter will be
synchronous with the bypass. Otherwise, the system will operate at nominal
frequency.
Battery mode: The batteries of the system powers the load through inverters of all
the UPS units. The system operates at nominal frequency.
Fig. 8-4 Series backup mode
Bypass mode: The condition to transfer to bypass mode is same with that of single
module UPS system. The bypasses of all the UPS units power the load.
90
Page 97

Maintenance mode: The condition to transfer to maintenance mode is same with
that of single module UPS system. The maintenance switches should be switched
on synchronously as possible. Thus the system can be repaired without interrupting
the power supply to load.
8.2 Installation
The installation method of parallel operation system is the same with that of single
module UPS system. The following contents only introduce the installation
procedures relating to parallel operation system.
8.2.1 Cabinet installation
1. Parallel operation system with two UPS units
The layout of 40/60 kVA UPS system is shown in Fig.8-5. Two UPS units are placed
in the middle side by side. Each battery cabinet is placed next to the UPS unit. The
battery cabinet should be placed in front of or behind the UPS cabinet if considering
capacity expansion.
Chapter 8 Parallel System
The layout of 20/30 kVA UPS system is the same with that of 40/60kVA UPS.
battery cabinet 1
UPS cabinet 1
Fig. 8-5 40/60KVA UPS Layout
UPS cabinet 2
battery cabinet 2
2. Parallel operation system with multi UPS units
Please place the battery cabinet in front of or behind the UPS cabinet for shorten
the battery cables and battery temperature sampling cables and for convenient
capacity expansion.
91
Page 98

8.2.2 Electrical installation
1. Power cables
Wiring of power cables is the same with that of single module UPS system.
Note:
The length and specifications of power source cables including the bypass input
and UPS output cables should be the same, thus the load can be shared evenly in
bypass mode.
2. Signal cables
Wiring of signal cables is the same with that of single module UPS system. Parallel
connection cables should be connected.
You can see the holes for parallel connection cables when opening the front door of
the UPS system. According to the routes, two parallel connection cables are
connected to the P1(P2) and P3(P4) sockets on the ULW2L61M3 parallel board, at
the same time tighten the screws between the connector and sockets. P1/P2 on the
ULW2L61M3 board are two 15-pin sockets with same functions and are used to
transmit parallel logic signal. P3/P4 are two parallel 9-pin sockets with same
functions and are used to transmit the load sharing detection signal. The wiring
method of parallel connection cables of three UPS units are shown in Fig.8-6.
Chapter 8 Parallel System
Logic cable
Load sharing detection
UPS 1 parallel
board
left post
left post
Logic cable
Load sharing detection
UPS 2 parallel
board
Logic cable
Fig.8-6 Connection of Parallel Operation Cables
92
Load sharing detection
UPS 3 parallel
board
left post
Page 99

Chapter 8 Parallel System
8.3 External Power Distribution
Parameters such as maximum permissible input current (In is the rated input
current) of each UPS, capacity of input circuit breaker(suitable for rectifier input and
bypass input) are given in Table 3-5. It is recommended that the input power source
of each UPS unit should be input to its own circuit breaker in the switchgear. The
battery group shouldn’t be shared among the UPS units. Each UPS unit should be
equipped with an output circuit breaker for the convenience of switching off the
UPS during maintenance. The capacity of the output switch of the power cabinet
should be selected according to the maximum capacity of the parallel operation
system considering the redundancy. The specifications of the switch are given in
Table 8-2.
Table 8-2 Output Power distribution parameters
Single module UPS system 63A 63A 100A 100A
1+1 63A 63A 100A 100A
UPS capacity Capacity of output circuit breaker
20kVA 30kVA 40kVA 60kVA
2+1 125A 125A 200A 200A
Parallel
operation
modes
3+1 200A 200A 300A 300A
4+1 250A 250A 400A 400A
5+1 300A 300A 500A 500A
6+1 400A 400A 600A 600A
7+1 450A 450A 700A 700A
8 UPS units 500A 500A 800A 800A
8.4 Start up of Parallel Operation System
Check the input and output wiring of each UPS unit. Ensure that the phase rotation
of the rectifier, bypass and output of each UPS unit is same. Ensure the parallel
connection cables are connected firmly.
1. Switch on the UPS units one by one and check their operation states:
(1)Commission each UPS unit referring to Chapter 4 for the methods.
(2)Set the parameters of each UPS unit through background host and adjust the
parameters of parallel operation system.
Configuration setup: Each UPS unit should be set as “parallel” mode. The UPS unit
that is connected to the background host should be set as “connect to background
host”;
93
Page 100

Chapter 8 Parallel System
Code setup: Each UPS unit has its own code, and set the codes of each UPS unit
as 1, 2, 3 .n(n8) one by one;
Set the number of UPS units N and number of redundancy UPS units X: If there is
M UPS units in the system, if the system is the paralleling system for capacity
expansion, then M=N, X=0; In redundancy system, M=N+X, Xƒ1. The settings of N
and X should take the actual load capacity into considerations.
(3)After the commissioning of each UPS unit is completed, press “inverter
shutdown” to shutdown the inverter, switch off Q2 and Q5;
2. Switch on Q5 of each UPS unit, press the “inverter start” button of each UPS unit
and check the output phase rotation. If the phase rotation is not correct, the LCD on
the UPS unit will display “inverter asynchronized” , the inverter indicator flashes
continuously and the unit cannot transfer to inverter mode. If some UPS unit has
abnormal alarm sound, the parallel connection cables must have problem.
3. Switch on the bypass switch Q2 of each UPS unit to input the bypass source;
4. Press the “inverter shutdown” button of each UPS unit one by one, transfer to
bypass source;
5. Switch on each UPS inverter one by one and apply the load after the last UPS
transfers to inverter mode. The load parameters can be inquired through the panel
of any UPS. When the load is heavy, check the load rate of each UPS unit and if
the rates are roughly the same, then the parallel operation system must operate
normally.
Note:
After commissioning, the UPS can only operate after the qualified engineers have
set the parameters.
8.5 Using the Parallel Operation System
The user can use the UPS that has start up. The using methods of parallel system
are the same with that of single module UPS system.
8.5.1 Switch on the Parallel System
1. Start from utility
The process of switching on the parallel system that has no load is same with the
start up process.
94
 Loading...
Loading...