Page 1

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
TI
STANDARD WALL-MOUNTED INDOOR UNIT
INSTALLATION MANUAL
MA
• LMN078HVT 7 kBtu
• LSN090HSV4 9 kBtu
• LSN120HSV4 12 kBtu
• LMN158HVT 15 kBtu
• LSN180HSV4 18 kBtu
• LMN248HVT 24 kBtu
Page 2

PROPRIETARY DATA NOTICE
This document, as well as all reports, illustrations, data, information, and other
materials are the property of LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., and are
disclosed by LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., only in confidence.
Do not throw away, destroy, or lose this manual.
Please read carefully and store in a safe place for future reference.
Content familiarity required for proper installation.
The instructions included in this manual must be followed to prevent prod-
uct malfunction, property damage, injury, or death to the user or other
people. Incorrect operation due to ignoring any instructions will cause
harm or damage. A summary of safety precautions begins on page 4.
For more technical materials such as submittals, engineering
databooks, and catalogs, visit www.lghvac.com.
IM_MultiF_StdWallMount_11_15
For continual product development, LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., reserves the right to change specifications without notice.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc.
This document, as well as all reports, illustrations, data, information, and other materials are the property of LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc.
Page 3

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TI
MA
CONTENTS
Safety Instructions ..............................................................................................................4
Introduction .........................................................................................................................9
Unit Nomenclature ............................................................................................................11
General Data ....................................................................................................................12
Specications .............................................................................................................................13
Typical Multi F/Multi F Max Systems ..........................................................................................15
Refrigerant Piping Requirements ...............................................................................................17
General Installation Guidelines .........................................................................................18
Location Selection ...................................................................................................................... 18
Inspection ................................................................................................................................... 19
Install Wall-Mounted IDU Chassis ..............................................................................................20
Refrigerant Piping ....................................................................................................................... 22
Piping Materials and Handling .................................................................................................... 30
Piping Preparation ...................................................................................................................... 31
Installation Manual
Piping Connections ...........................................................................................................32
IDU to ODU ................................................................................................................................32
Piping Insulation ......................................................................................................................... 35
Drain Piping ................................................................................................................................ 37
Electrical Wiring ................................................................................................................38
Power Wiring Specications and Best Practices ........................................................................ 39
Controller Options .......................................................................................................................40
Indoor Unit Electrical Connections Guidelines ...........................................................................41
Indoor Unit Electrical Connections Procedure ............................................................................ 42
Self Diagnosis Functions ........................................................................................................... 44
LG SIMS - Self Diagnosis Functions ......................................................................................... 46
Optional Wall-Mounted Sensor and Controller ...........................................................................48
Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................49
Error Codes ............................................................................................................................... 49
Cautions for Refrigerant leaks ..........................................................................................50
Refrigerant Leaks ....................................................................................................................... 50
Installation Checklist .........................................................................................................51
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
3
Page 4
X
MUL
MUL
F
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
WARNING
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
DANGER
TI
F
TI
The instructions below must be followed to prevent product malfunction, property damage, injury or death to the user or other people. Incorrect operation due to ignoring any instructions will cause harm or damage. The level of seriousness is classified by the symbols below.
MA
TABLE OF SYMBOLS
This symbol indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
This symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
This symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury.
Note:
This symbol Indicates situations that may result in equipment or property damage accidents only.
This symbol indicates an action that should not be performed.
INSTALLATION
Don’t use or store ammable gas or combustibles near the unit.
There is risk of re, explosion, and physical injury or death.
Do not install, remove, or re-install the unit by yourself
(end-user). Ask the dealer or an LG trained technician to
install the unit.
Improper installation by the user may result in water leakage, re,
explosion, electric shock, physical injury or death.
For replacement of an installed unit, always contact an
LG trained service provider.
There is risk of re, electric shock, explosion, and physical injury or death.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
The outdoor unit is shipped with refrigerant and the service
valves closed. Do not open service valves on the unit until
all non-condensibles have been removed from the piping
system and authorization has been obtained from the commissioning agent.
There is a risk of physical injury or death.
Do not run the compressor with the service valves
closed.
There is risk of explosion, physical injury, or death.
Periodically check that the outdoor unit is not damaged.
There is risk of explosion, physical injury, or death.
Replace all control box and panel covers.
If cover panels are not installed securely, dust, water and animals may
enter the unit, causing re, electric shock, and physical injury or death.
Always check for system refrigerant leaks after the unit has
been installed or serviced.
Exposure to high concentration levels of refrigerant gas may lead to
illness or death.
4
Do not install the unit using defective hanging, attaching,
or mounting hardware.
There is risk of physical injury or death.
Wear protective gloves when handling equipment.
Sharp edges may cause personal injury.
Dispose of the packing materials safely.
• Packing materials, such as nails and other metal or wooden parts
may cause puncture wounds or other injuries.
• Tear apart and throw away plastic packaging bags so that children
may not play with them and risk suffocation and death.
Do not install the unit in any location exposed to open
ame or extreme heat. Do not touch the unit with wet hands.
There is risk of re, electric shock, explosion, and physical injury or death.
Install the unit considering the potential for earthquakes.
Improper installation may cause the unit to fall, resulting in physical
injury or death.
Do not change the settings of the protection devices.
If the pressure switch, thermal switch, or other protection device is
shorted and forced to operate improperly, or parts other than those
specied by LG are used, there is risk of re, electric shock, explosion,
and physical injury or death.
If the air conditioner is installed in a small space, take measures to prevent the refrigerant concentration from exceeding safety limits in the event of a refrigerant leak.
Consult the latest edition of ASHRAE (American Society of Heating,
Refrigerating, and Air Conditioning Engineers) Standard 15. If the refrigerant leaks and safety limits are exceeded, it could result in personal
injuries or death from oxygen depletion.
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 5

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
CAUTION
F
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
TI
MA
INSTALLATION – CONTINUED
Be very careful when transporting the product.
• Do not attempt to carry the product without assistance.
• Some products use polypropylene bands for packaging. Do not use polypropylene bands to lift the unit.
• Suspend the unit from the base at specified positions.
• Support the unit at a minimum of four points to avoid slippage from rigging apparatus.
• Failure to follow these directions may result in minor or moderate physical injury.
Note:
Properly insulate all cold surfaces to prevent “sweating.”
Cold surfaces such as uninsulated pipe can generate condensate that may
drip and cause a slippery oor condition and/or water damage to walls.
When installing the unit in a hospital, mechanical room, or
similar electromagnetic eld (EMF) sensitive environment,
provide sufcient protection against electrical noise.
Inverter equipment, power generators, high-frequency medical equipment, or radio communication equipment may cause the air conditioner to
operate improperly. The unit may also affect such equipment by creating
electrical noise that disturbs medical treatment or image broadcasting.
Do not use the product for special purposes such as preserving foods, works of art, wine coolers, or other precision
air conditioning applications. This equipment is designed to
provide comfort cooling and heating.
There is risk of property damage.
Do not make refrigerant substitutions. Use R410A only.
If a different refrigerant is used, or air mixes with original refrigerant, the
unit will malfunction and become damaged.
Do not install the unit in a noise sensitive area.
When connecting refrigerant tubing, remember to allow for
pipe expansion.
Improper piping may cause refrigerant leaks and system malfunction.
Take appropriate actions at the end of HVAC equipment life
to recover, recycle, reclaim or destroy R410A refrigerant according to applicable U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
(EPA) rules.
Periodically check that the outdoor unit is not damaged.
There is a risk of equipment damage.
Install the unit in a safe location where no one can step on or
fall onto it.
attaching, or mounting hardware.
There is risk of unit and property damage.
Install the drain hose to ensure adequate drainage.
There is a risk of water leakage and property damage.
Don’t store or use ammable gas / combustibles near the
unit.
There is risk of product failure.
Always check for system refrigerant leaks after the unit has
been installed or serviced.
Low refrigerant levels may cause product failure
The unit is shipped with refrigerant and the service valves
closed.
non-condensibles have been removed from the piping system and authorization to do so has been obtained from the
commissioning agent.
There is a risk of refrigerant contamination, refrigerant loss and equipment damage.
Do not install the unit with defective hanging,
Do not open service valves on the unit until all
Installation Manual
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
5
Page 6

X
MUL
MUL
F
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
DANGER
WARNING
TI
F
WIRING
High voltage electricity is required to operate this system.
Adhere to the National Electrical Codes and these
instructions when wiring.
Improper connections and inadequate grounding can cause accidental
injury or death.
Always ground the unit following local, state, and National
Electrical Codes.
The information contained in this manual is intended for use
by an experienced, trained electrician familiar with the U.S.
National Electric Code (NEC) who is equipped with the proper
tools and test instruments.
Failure to carefully read and follow all instructions in this manual can
result in equipment malfunction, property damage, personal injury or
death.
Ensure the unit is connected to a dedicated power source
that provides adequate power.
If the power source capacity is inadequate or the electric work is not per-
formed properly, it may result in re, electric shock, physical injury or death.
TI
Turn the power off at the nearest disconnect before servicing
the equipment.
Electric shock can cause physical injury or death.
Properly size all circuit breakers or fuses.
There is risk of re, electric shock, explosion, physical injury or death.
Refer to local, state, and federal codes, and use power wires
of sufcient current capacity and rating.
Wires that are too small may generate heat and cause a re.
Secure all eld wiring connections with appropriate wire
strain relief.
Improperly securing wires will create undue stress on equipment power
lugs. Inadequate connections may generate heat, cause a re and
physical injury or death.
Properly tighten all power connections.
Loose wiring may overheat at connection points, causing a re, physical
injury or death.
MA
Note:
Do not cut, lengthen or shorten the communications and
power cable between any dry contact unit and its connected
indoor unit. Do not install the unit in a location where the communications and power cable cannot be safely and easily connected between the two units. Do not allow strain on this cable.
Poor cable connections can cause equipment malfunction.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
6
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 7

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
F
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
TI
MA
OPERATION
Do not provide power to or operate the unit if it is ooded
or submerged.
There is risk of re, electric shock, physical injury or death.
Use a dedicated power source for this product.
There is risk of re, electric shock, physical injury or death.
Do not operate the disconnect switch with wet hands.
There is risk of re, electric shock, physical injury or death.
Do not allow water, dirt, or animals to enter the unit.
There is risk of unit failure, re, electric shock, physical injury or death.
Avoid excessive cooling and periodically perform ventilation
to the unit.
Inadequate ventilation is a health hazard.
Do not touch refrigerant piping during or after operation.
It can cause burns or frostbite.
Do not operate the unit with the panel(s) or protective
cover(s) removed; keep ngers and clothing away from
moving parts.
The rotating, hot, cold, and high-voltage parts of the unit can cause
physical injury or death.
Periodically check power cable and connection for damage.
Cable must be replaced by the manufacturer, its service agent, or similar
qualied persons in order to avoid physical injury and/or electric shock.
Securely attach the electrical cover to the unit.
Non-secured electrical covers can result in burns or electric shock due to
Periodically verify the hanging bolts and other hardware
securing the unit have not deteriorated.
If the unit falls from its installed location, it can cause property damage,
product failure, physical injury or death.
If refrigerant gas leaks out, ventilate the area before operating the unit.
If the unit is mounted in an enclosed, low-lying, or poorly ventilated area
and the system develops a refrigerant leak, it may cause re, electric
shock, explosion, physical injury or death.
dust or water in the service panel.
Do not open the inlet grille of the unit during operation.
Do not operate the unit with the panels or guards removed.
Do not insert hands or other objects through the inlet or
outlet when the unit is powered. Do not touch the electro-
static lter, if the unit includes one. The unit contains sharp,
rotating, hot, and high voltage parts that can cause personal
injury and/or electric shock.
Ensure no power is connected to the unit other than as
directed in this manual. Remove power from the unit before
removing or servicing the unit.
There is risk of unit failure, re, electric shock, physical injury or death.
Do not open the inlet grille of the unit during operation.
Do not operate the unit with the panels or guards removed.
Do not insert hands or other objects through the inlet or outlet with the unit is plugged in. Do not touch the electrostatic
lter, if the unit includes one.
The unit contains sharp, rotating, hot, and high voltage parts that can
cause personal injury and/or electric shock.
Installation Manual
To avoid physical injury, use caution when cleaning or
servicing the air conditioner.
Note:
Clean up the site after installation is nished, and check
that no metal scraps, screws, or bits of wiring have been left
inside or surrounding the unit.
purpose applications such as preserving foods, works of art,
wine coolers or refrigeration. This equipment is designed to
provide comfort cooling and heating.
Provide power to the compressor crankcase heaters at least
six (6) hours before operation begins.
Starting operation with a cold compressor sump(s) may result in severe
bearing damage to the compressor(s). Keep the power switch on during
the operational season.
Do not use this equipment in mission critical or special-
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Do not block the inlet or outlet.
Unit may malfunction.
Securely attach the electrical cover to the indoor unit. Non-
secured covers can result in re due to dust or water in the
service panel.
Periodically verify the equipment mounts have not deteriorated.
If the base collapses, the unit could fall and cause property damage or
product failure.
Do not allow water, dirt, or animals to enter the unit.
There is risk of unit failure.
7
Page 8

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
TI
MA
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
8
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 9

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
WARNING
F
INTRODUCTION
TI
MA
Multi F and Multi F MAX Standard
Wall-Mounted Units
This manual describes how to install the LG Multi F and Multi F MAX
(Multi Zone) Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Units (IDU) for Multi
F heat pump systems. Table 1 lists the available models. Refer to
LG’s Multi F Indoor Unit Engineering Manual for complete detailed
engineering data and selection procedures.
Safety
Safety of personnel is the primary concern during all
procedures. Read and understand the safety summary at the front of this manual. Read and understand
this installation procedure before beginning installation. Use the appropriate tools and accessories
during installation. Plan your work and do not work
alone, if possible. Know how to obtain emergency
medical and firefighting assistance.
Installation Personnel
This equipment is intended for installation by personnel trained
in the required construction, mechanical, electrical, and/or other
disciplines.
Applicable Codes
Personnel must be familiar with and follow the applicable national,
state, and/or local codes.
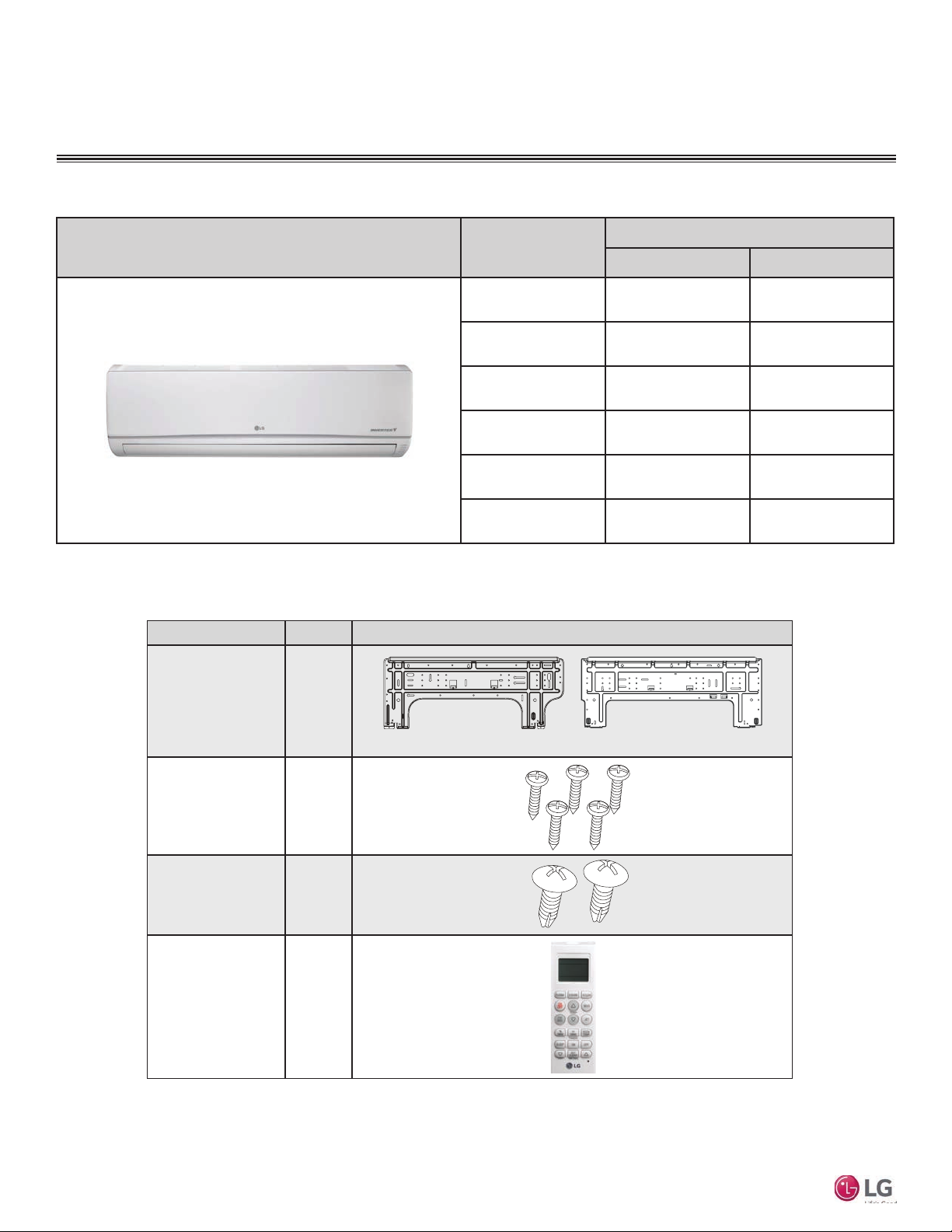
Figure 1: Typical Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
Installation Manual
Installation work must be performed by trained personnel and in
accordance with national wiring standards and all local or other
applicable codes. Improper installation can result in re, electric shock,
physical injury, or death.
Note:
Please read all instructions before installing this product. Become familiar
with the unit’s components and connections, and the order of installation.
Incorrect installation can degrade or prevent proper operation.
Required Tools (field provided)
Required Parts (field provided)
• Level
• Screwdriver
• Electrical lineman pliers
• Electric drill
• Hole saw
• Connecting cable (power and control)
• Pipes - vapor line and liquid line, with
insulation
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
• Drill
• Flaring tool set
• Tubing cutter
• Tube/pipe reamer
• Torque wrenches
• Insulated drain hose
• Additional drain hose
• Allen wrench
• Gas-leak detector
• Thermometer
9
Page 10
X
MUL
MUL
F
INTRODUCTION
TI
F
Table 1: Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Units
Typical Unit Model Number
LMN078HVT 7,000 8,100
LSN090HSV4 9,000 10,400
LSN120HSV4 12,000 13,800
LMN158HVT 14,300 16,500
LSN180HSV4 18,000 20,800
LMN248HVT 24,000 27,000
TI
Nominal Capacity
Cooling (Btu) Heating (Btu)
MA
Part Quantity Image
Installation Plate One (1)
Type “A” Screws Five (5)
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
Type “B” Screws
(M4 x 12L)
Wireless
Controller with Holder
HVT: AKB73635606
HSV: AKB73835312
Two (2)
One (1)
Table 2: Included Items
7,000 ~ 15,000 Btu/h Indoor Units
18,000 and 24,000 Btu/h Indoor Units
10
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 11
X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
UNIT NOMENCLATURE
TI
MA
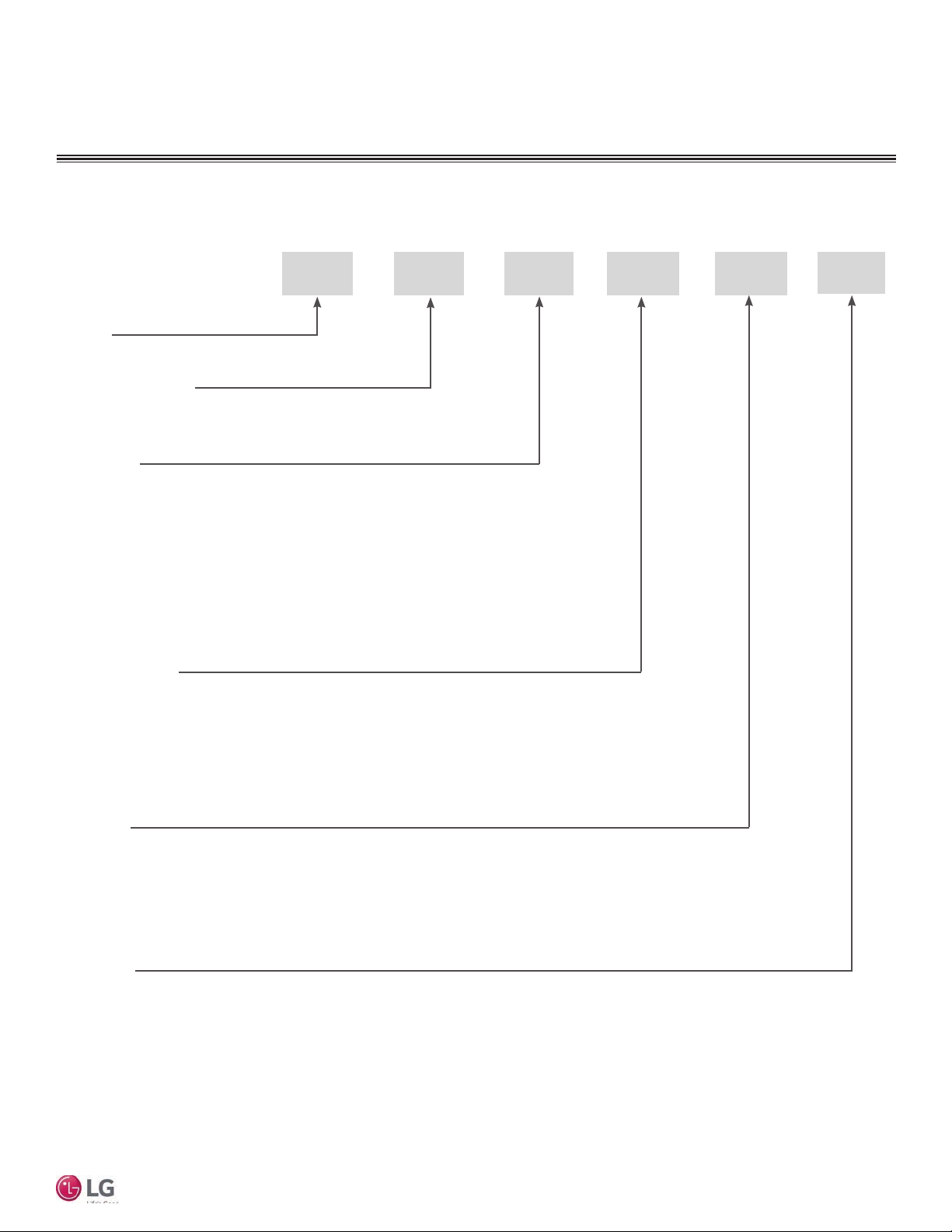
Multi F Multi-Zone Systems — Indoor Units
L
L = LG
Type: M = Multi-Zone
A/S = Single Zone (Gen 4 Single Zone units also compatible with Multi Zone)
Component:
AN: Art Cool™ Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
N: Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
CN: Four-Way Ceiling-Cassette Indoor Unit
DN: Ceiling-Concealed Duct (Low Static) Indoor Unit
HN: Ceiling-Concealed Duct (High Static) Indoor Unit
VN: Vertical-Horizontal Air Handling Indoor Unit
M
N 158 HVT
Installation Manual
Nominal Capacity
(Nominal cooling capacity in Btu/h):
078 = 7,000
090 = 9,000
120 = 12,000
Features:
H = Heat Pump
V = Inverter
T = High Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
P = Art Cool Gallery Indoor Unit
Generation
3 = Third (also Third Gen if no number in this position)
4 = Fourth
• Voltage for all equipment is 208-230V, 60 Hz, 1-phase.
• All indoor units are compatible with wired controllers
158 = 15,000
180 = 18,000
248 = 24,000
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
11
Page 12
X
MUL
MUL
F
GENERAL DATA
WARNING
TI
F
TI
MA
R410A Refrigerant
R410A refrigerant has a higher operating pressure in comparison to R22 refrigerant. All piping system materials installed must have
a higher resisting pressure than the materials traditionally used in R22 systems.
R410A refrigerant is an azeotrope of R32 and R125, mixed at 50:50. The ozone depletion potential (ODP) is 0.
• Do not place refrigerant cylinder in direct sunlight. Refrigerant cylinder may explode causing severe injury or death.
Note
• Because R410A is a combination of R32 and R125, the required additional refrigerant must be charged in its liquid state. If the
refrigerant is charged in its gaseous state, its composition changes and the system will not work properly.
• Do not heat piping more than necessary during installation. Piping may become soft and fail when pressurized.
• Do not use any piping that has not been approved for use in high-pressure refrigerant systems. Piping wall thickness must comply
with the applicable local, state, and federal codes for the 551 psi design pressure of R410A. Inadequate piping may fail when
pressurized.
Allowable Indoor Unit to Outdoor Unit Connections
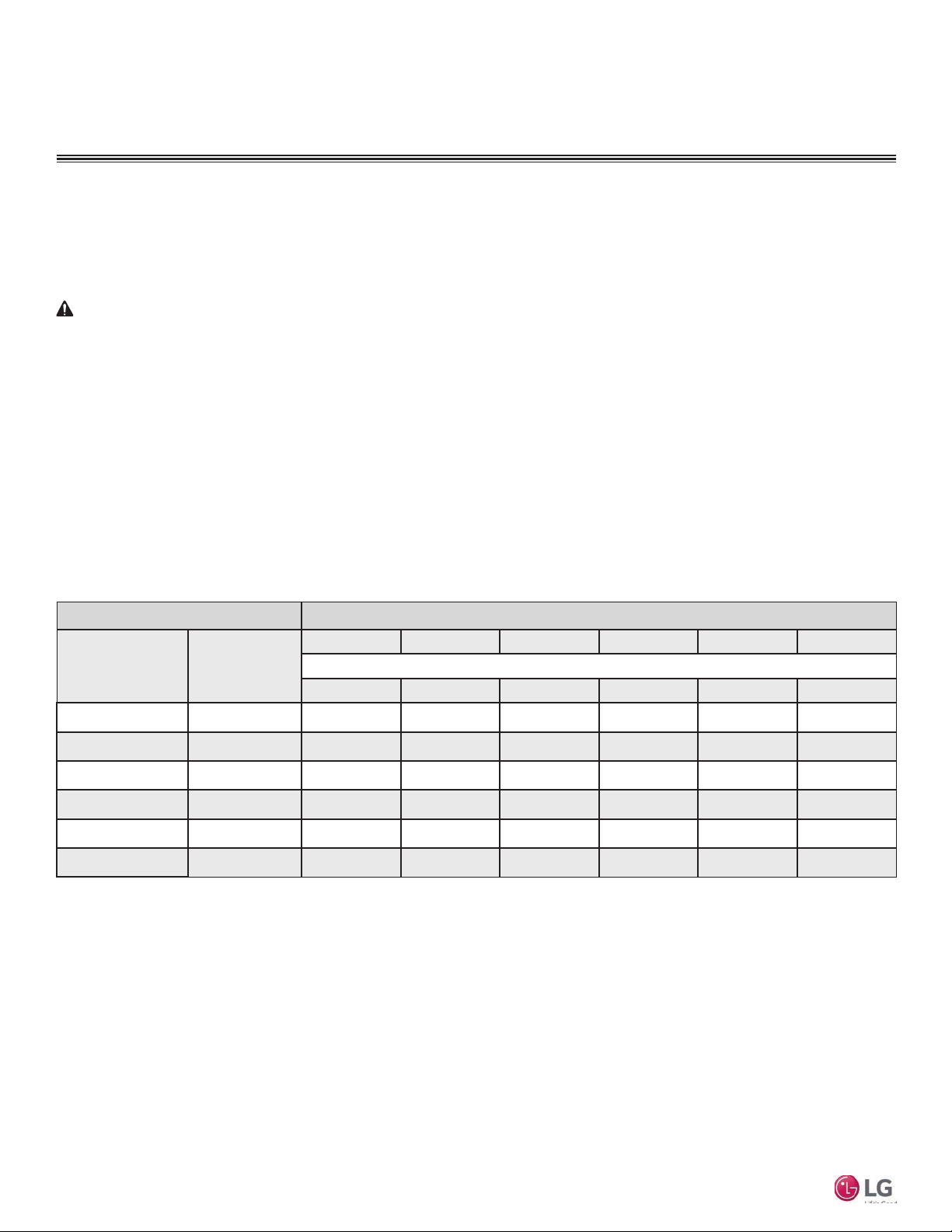
In Multi F/Multi Zone systems, the standard wall-mounted IDUs can be connected to the Multi F outdoor units (ODUs) listed in Table 3.
Table 3: Allowable Indoor Unit to Outdoor Unit Connections.
Indoor units Outdoor units
Model Number
LMN078HVT 7,000 O O O O O O
LSN090HSV4 9,000 O O O O O O
LSN120HSV4 12,000 O O O O O O
LMN158HVT 15,000 O O O O O O
Indoor Unit Nominal
Capacity (Btu/h)
LMU18CHV LMU24CHV LMU30CHV LMU36CHV LMU480HV LMU540HV
2 3 4 4 8 8
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
LSN180HSV4 18,000 – O O O O O
LMN248HVT 24,000 – O O O O O
connection allowed: O
connection not allowed: –
Device Connection Limitations
• The minimum number of connected and operating indoor units to Multi F / Multi F MAX systems is two.
• The maximum number of indoor units for each Multi F / Multi F MAX heat pump system is:
LMU18CHV = 2 LMU24CHV = 3 LMU30CHV = 4
LMU36CHV = 4 LMU480HV = 8 LMU540HV = 8
Maximum No. of Connectable Indoor Units
• The maximum allowable total indoor unit capacity (Btu/h) for each Multi F / Multi F MAX heat pump system is:
LMU18CHV = 24,000 LMU24CHV = 33,000 LMU30CHV = 40,000
LMU36CHV = 48,000 LMU480HV = 65,000 LMU540HV = 73,000
• Refer to the Multi F Engineering Manual to properly determine total indoor unit connected capacity.
12
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 13
X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
GENERAL DATA
TI
Nominal Cooling Capacity
(Btu/h)
Nominal Heating Capacity
(Btu/h)
Operating Range
Cooling (°F WB)
Heating (°F DB)
Fan
Type
Motor Output (W) x Qty.
Motor/Drive
Airflow Rate CFM (H/M/L)
Unit Data
Refrigerant Type
Refrigerant Control
Power Supply V, Ø, Hz3
Rated Amps (A)
Sound Pressure Level ±3 dB(A)
(H/M/L)4
Dimensions (W x H x D, in.)
Net Unit Weight (lbs.)
Shipping Weight (lbs.)
Power Wiring / Communications
Cable (No. x AWG)5
Heat Exchanger (Row x Column
x Fin / inch) x Number
Pipe Size
Liquid (in.)
Vapor (in.)
Connection Size
Liquid (in.)
Vapor (in.)
Drain O.D. / I.D. (in.)
1
Nominal capacity is rated 0 ft. above sea level with corresponding refrigerant piping
length in accordance with standard length of each outdoor unit and a 0 ft. level difference
between outdoor and indoor units. All capacities are net with a combination ratio between
95 – 105%.
Nominal cooling capacity rating obtained with air entering the indoor unit at 80ºF dry bulb
(DB) and 67ºF wet bulb (WB) and outdoor ambient conditions of 95ºF dry bulb (DB) and
75ºF wet bulb (WB).
Nominal heating capacity rating obtained with air entering the indoor unit at 70ºF dry bulb
(DB) and 60ºF wet bulb (WB) and outdoor ambient conditions of 47ºF dry bulb (DB) and
43ºF wet bulb (WB).
MA
Table 4: Multi F Multi Zone Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit Specications
Model Name LMN078HVT LSN090HSV4 LSN120HSV4 LMN158HVT LSN180HSV4 LMN248HVT
1
1
2
7,000 9,000 12,000 14,300 18,000 24,000
8,100 10,400 13,800 16,500 20,800 27,000
198 / 177 / 162 247 / 230 / 212 335 / 318 / 300 371 / 318 / 247 572 / 501 / 434 720 / 600 / 466
33 / 30 / 26 33 / 30 / 27 39 / 36 / 31 43 / 39 / 34 37 / 33 / 28 42 / 39 / 36
35-1/4 x 11-3/8
x 8-9/32
23 20 20 23 31
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
34-13/16 x 11-1/4
x 8-1/4
(2 x 16 x 23) x 1 (3 x 18 x 22) x 1
Specications
57-77
59-81
Cross Flow
14.4 x 1 76.0 x 1
Brushless Digitally Controlled / Direct
R410A
Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV)
208-230, 1, 60
0.2 0.3
34-13/16 x 11-1/4
x 8-1/4
26 36 37
3/8 1/2
1/4 3/8 1/4
3/8 5/8 1/2
2
This unit comes with a dry helium charge.
3
Acceptable operating voltage: 187V-253V.
4
Sound pressure levels are tested in an anechoic chamber under ISO Standard 3745 and
are the same in both cooling and heating mode. These values can increase due to ambient
conditions during operation.
5
All power wiring / communications cable to be minimum 18 AWG, 4-conductor, stranded,
shielded, and must comply with applicable local and national codes.
35-1/4 x 11-3/8
4 x 18
1/4
27/32, 5/8
x 8-9/32
40-9/16 x 12-13/16
x 9-13/16
40-9/16 x 12-13/16
x 9-13/16
Installation Manual
13
Page 14
X
MUL
MUL
F
GENERAL DATA
Gas pipe connection port
TI
F
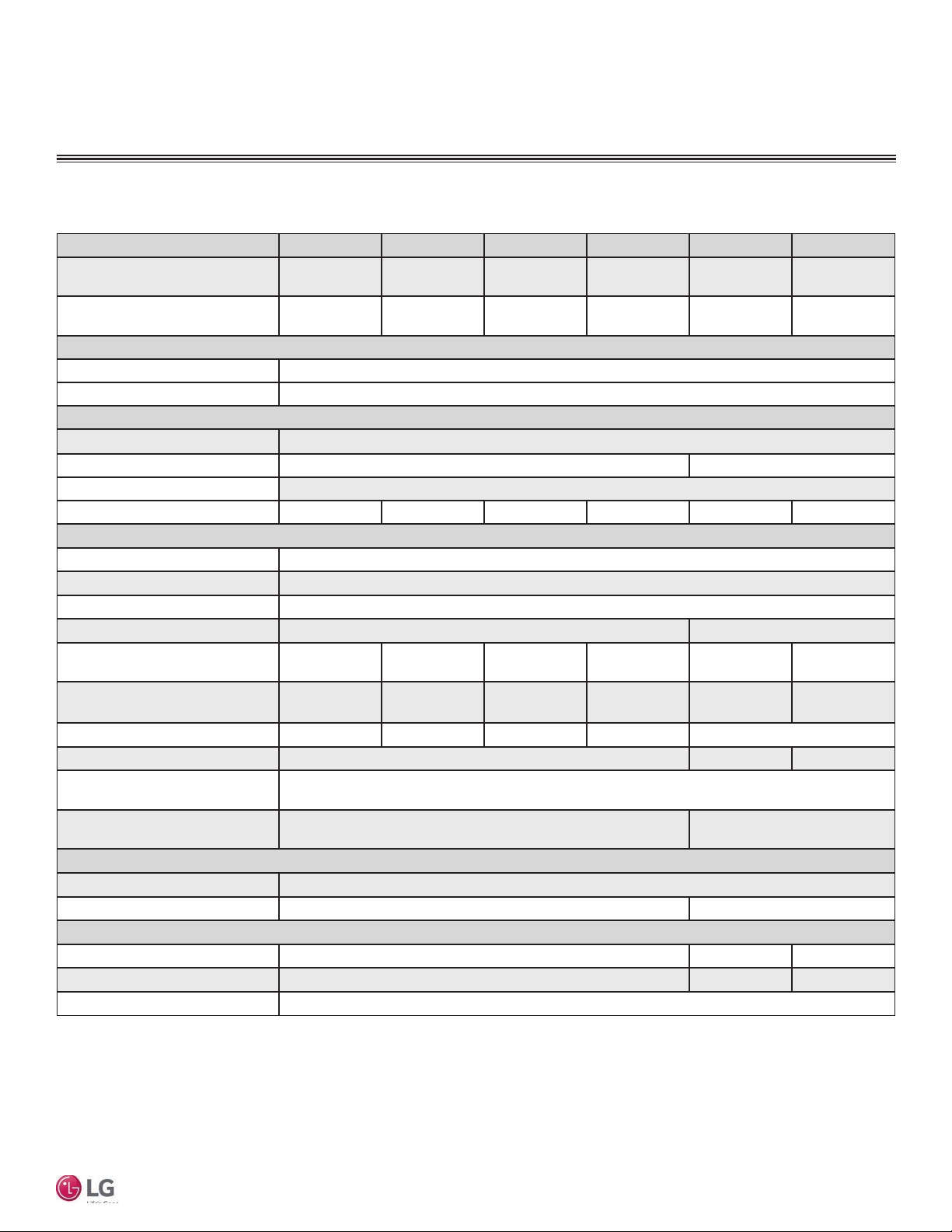
Refrigerant Piping
Cross Flow Fan
Heating
Cooling
Evaporator Inlet Temperature
Thermistor for
M
Heat Exchanger
Thermistor for Evaporator
Outlet Temperature
TI
(flare connection)
Indoor Air Temperature
Thermistor for
Liquid pipe connection port
(flare connection)
MA
Table 5: Multi F Multi Zone Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit Refrigerant Pipe Connection Port Diameters
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
14
Model No. Vapor (inch) Liquid (inch)
LMN078HVT
LSN090HSV4
LSN120HSV4
LMN158HVT
LSN180HSV4 Ø5/8 Ø3/8
LMN248HVT Ø1/2 Ø1/4
Table 6: Multi F Multi Zone Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit Refrigerant Pipe Sizes
Model No. Vapor (inch, OD) Liquid (inch, OD)
LMN078HVT
LSN090HSV4
LSN120HSV4
LMN158HVT
LSN180HSV4
LMN248HVT
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Ø3/8 Ø1/4
Ø3/8 Ø1/4
Ø1/2 Ø1/4
Page 15
X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
Max. 49.2 feet
Max. 24.6 feet
A
B
C
D
ODU
F
GENERAL DATA
TI
MA
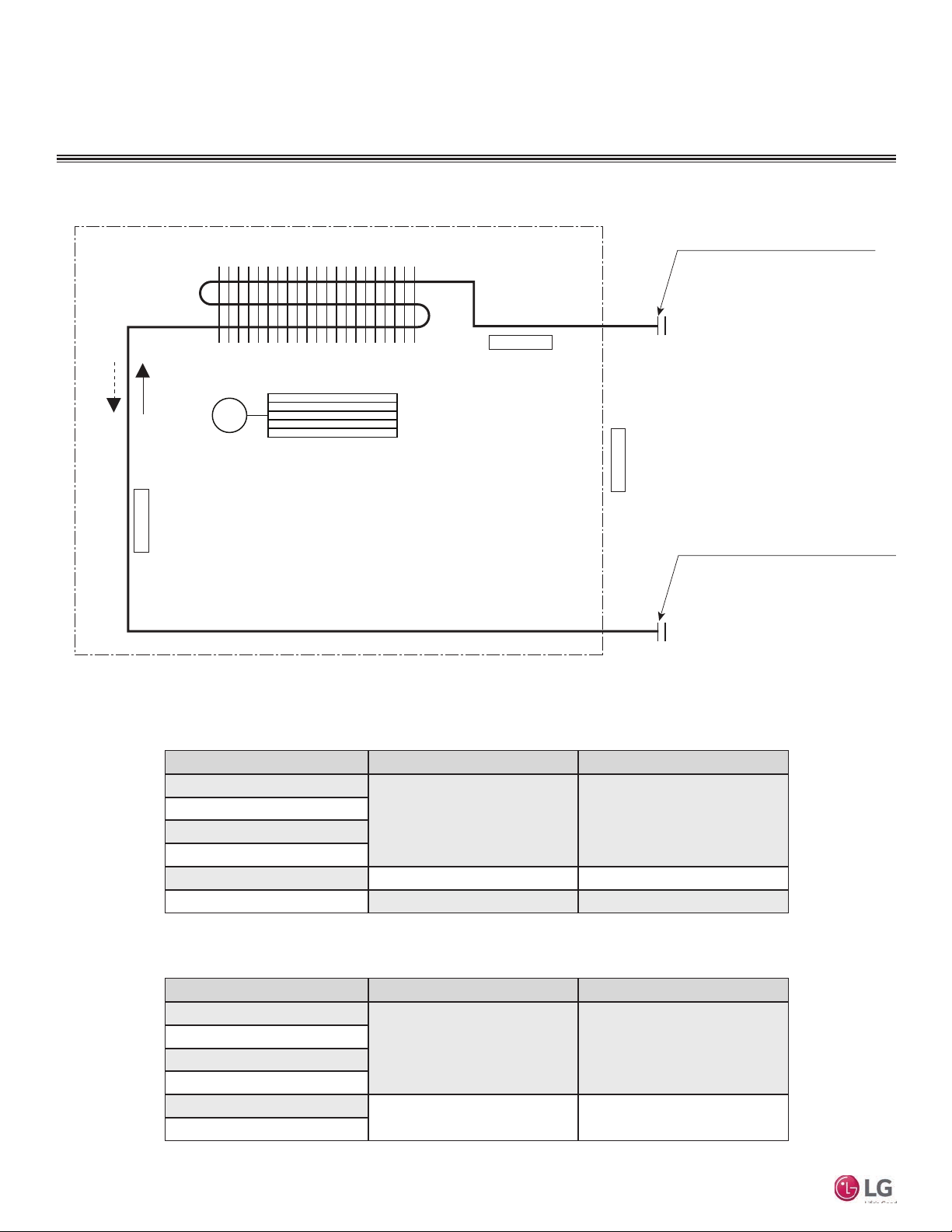
Typical Multi F/Multi F Max Systems
Major System Components
A typical Multi F system consists of an outdoor unit (ODU), refrigerant piping, and two to four indoor units (IDUs). The standard
wall-mounted units described in this manual are one of the types of IDUs that can be connected to a Multi F system.
A typical Multi F Max system consists of an ODU, refrigerant piping, one or two branch distribution units (BDU), and two to eight
IDUs. The standard wall-mounted units described in this manual are one of the types of IDUs that can be connected to a Multi F
Max system.
Typical Multi F System
Example: LMU36CHV outdoor unit with four (4)
indoor units connected.
ODU: Outdoor Unit.
IDU: Indoor Unit.
A, B, C, D: Piping from Outdoor Unit to Indoor Unit.
Installation Manual
Table 7: Multi F Outdoor Unit Refrigerant Piping System Limitations.
Outdoor
Unit
LMU18CHV 9.8 82 82 - - 164
LMU24CHV 9.8 82 82 82 - 246.1
LMU30CHV 9.8 82 82 82 82 246.1
LMU36CHV 9.8 82 82 82 82 246.1
Minimum Length for Each
Pipe Segment (ft.)
Maximum Equivalent Pipe Length
to Each Indoor Unit (ft.)
A B C D
Maximum Equivalent Pipe Length
for Each System (ft.)
Typical Multi F MAX System with One Branch Distribution Unit
Example: LMU540HV outdoor unit with four
(4) indoor units, and one (1) branch distribution unit connected.
ODU: Outdoor Unit.
IDU: Indoor Unit.
BDU: Branch Distribution Unit.
A: Main Piping.
B: Branch Piping (Branch Distribution Unit to
Indoor Unit[s]).
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
h1 ≤ 98.4 feet
A
BDU
h3 ≤ 32.8 feet
IDU
B
B
B
B
IDU
h2 ≤ 49.2 feet
IDU
IDU
15
Page 16
X
MUL
MUL
F
GENERAL DATA
ODU
TI
F
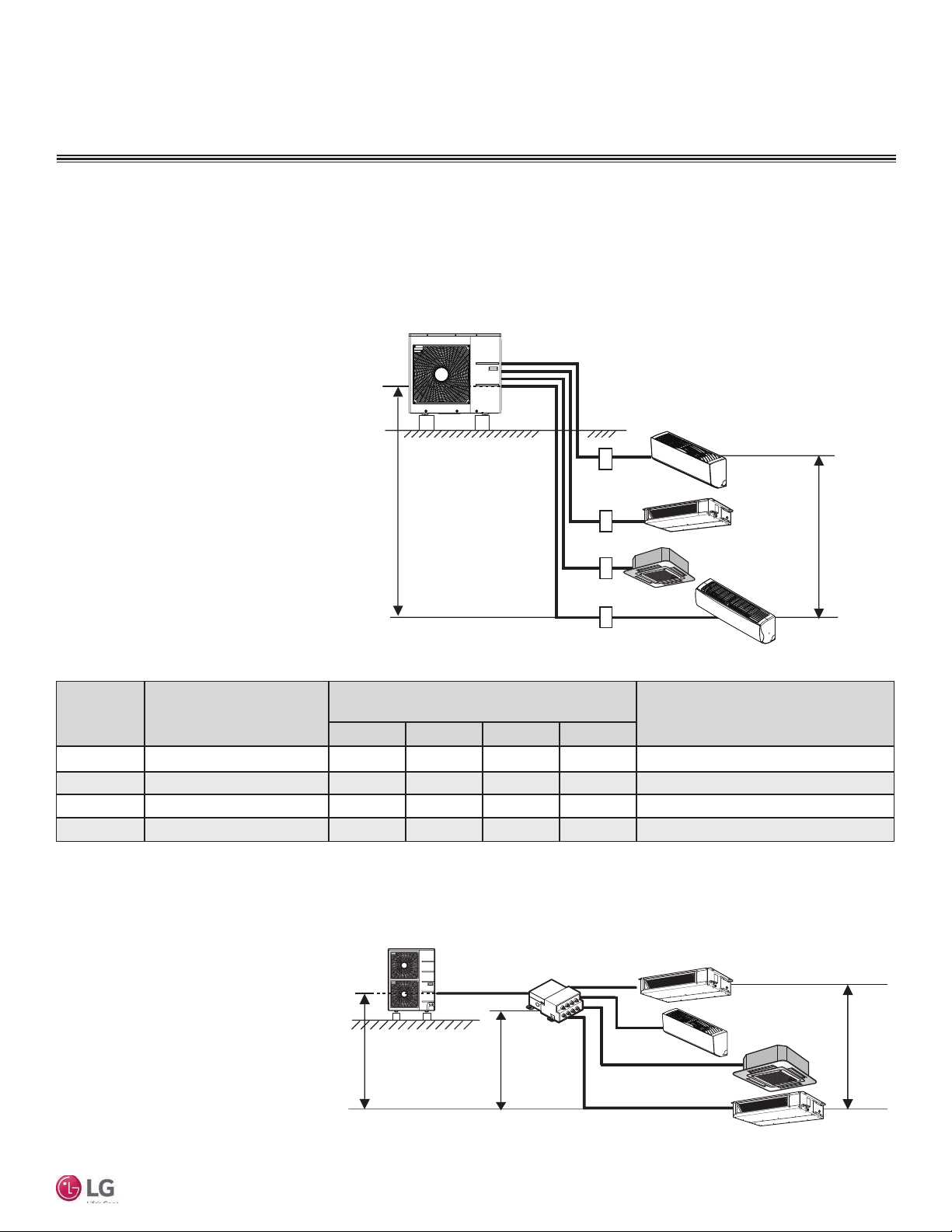
Typical Multi F/Multi F Max Systems
Typical Multi F MAX System with Two Branch Distribution Units
Example: LMU540HV outdoor unit with seven
(7) indoor units, and two (2) branch distribution units connected.
ODU: Outdoor Unit.
IDU: Indoor Unit.
BD: Branch Distribution Unit(s).
ΣA: Main Piping.
ΣB: Branch Piping (Branch Distribution Unit[s]
to Indoor Unit[s]).
h4 ≤ 49.2 feet
h1 ≤ 98.4 feet
A
BDU Y-Branch
A
A
BDU
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
IDU
IDU
IDU
IDU
TI
IDU
IDU
MA
h3 ≤ 32.8 feet
h2 ≤ 49.2 feet
Table 8: Multi F MAX Outdoor Unit Refrigerant Piping System Limitations.
Pipe Length
(ELF = Equivalent
Length of pipe
in Feet)
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
Elevation Differential
(All Elevation
Limitations are
Measured in
Actual Feet)
(Outdoor Unit to Branch
Distribution Units: ΣA)
(Branch Distribution Units
to Indoor Units: B)
If outdoor unit is above or below indoor unit (h1)
Between the farthest two indoor units (h2)
Between branch distribution unit and farthest
Between branch distribution units (h4)
Total piping length (ΣA + ΣB)
Main pipe
Total branch piping length (ΣB)
Branch pipe
connected indoor unit(s) (h3)
Minimum
Maximum
Minimum
Maximum
≤475.7 feet
9.8 feet
≤180.4 feet
≤295.3 feet
9.8 feet
≤49.2 feet
≤98.4 feet
≤42.9 feet
≤32.8 feet
≤42.9 feet
Table 9: Multi F MAX Piping Sizes.
Piping
Liquid Ø3/8
Main Pipe A
(inch)
Gas Ø3/4
Depends on the size
of the indoor unit piping
IDU
Branch Pipe B
16
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 17
X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
GENERAL DATA
TI
MA
Refrigerant Piping Requirements
Field Supplied Refrigerant Piping
Type ACR copper is the only approved refrigerant pipe material for use with LG Multi F air conditioning
products. ACR rated tubing is the only type that ships with yellow caps. Approved tubing for use with
Multi V products will be marked “R410 RATED” along the length of the tube. Tube wall thickness should
meet local code requirements and be approved for a maximum operating pressure of 551 psi.
Refer to the refrigerant piping section (starting on page 22) of the General Installation Guidelines for
more information on piping.
Using Refrigerant Components
Field-supplied elbows are allowed if they are long radius and designed for use with R410A refrigerant. Be
sure to account for the additional pressure losses in equivalent pipe length calculations for each elbow,
y-branch, and branch distribution unit. The equivalent pipe length of each elbow, Y-branch, and/or branch
distribution unit must be added to each pipe segment to ensure maximum lengths are not exceeded.
Table 10: Equivalent Piping Length for Elbows,
Y-branches, and Branch Distribution Units.
Component
Size (Inches)
1/4 3/8 1/2 5/8 3/4
Installation Manual
Elbow (ft.)
Y-Branch Kit (ft.)
(Multi F MAX systems only)
Branch Distribution Unit (ft.)
(Multi F MAX systems only)
1
Kit contains two Y-branches: one for liquid and one for vapor.
0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 1.2
1
1.6
8.2
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
17
Page 18

X
MUL
MUL
F
DANGER
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
>4 inches
Recommended height
>6-1/2 feet from floor
>4 inches
HVT; 9/12k HSV4 Units: ≥5 inches
LSN180HSV4 Units: ≥8 inches
TI
F
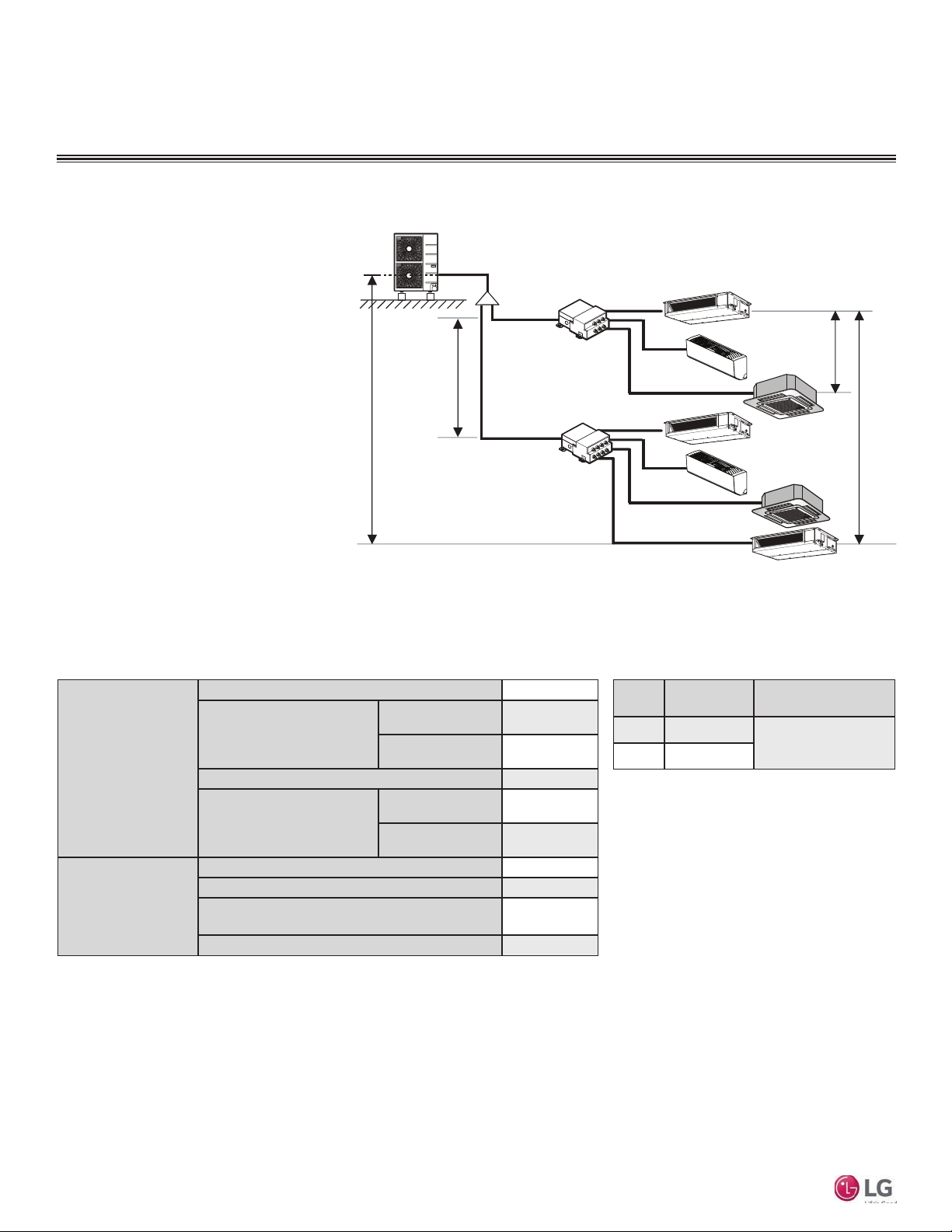
Location Selection
To avoid the possibility of re, do not install the unit in an area where combustible gas may generate, ow, stagnate, or leak. Failure to do so will
cause serious bodily injury or death. Before beginning installation, read the safety summary at the beginning of this manual.
Select a location for installing the wall-mounted indoor unit (IDU) that meets the following conditions:
• Where there is enough structural strength to bear the weight of the unit
• Where air circulation will not be blocked
• Where noise prevention is taken into consideration
• Ensure there is sufcient space from the ceiling and oor
• Locate the indoor unit in a location where it can be easily connected to the outdoor unit/branch distribution unit
• Include space for drainage to ensure condensate ows properly out of the unit when it is in cooling mode
• Use a level indicator to ensure the unit is installed on a level plane
Note:
The unit may be damaged, may malfunction, and/or will not operate as designed if installed in any of the following conditions:
Do not install the unit where it will be subjected to direct thermal radiation from other heat sources.
Do not install the unit in an area where combustible gas may generate, flow, stagnate, or leak.
TI
MA
Do not install the unit in a location where acidic solution and spray (sulfur) are often used.
Do not use the unit in environments where oil, steam, or sulfuric gas are present.
Do not install additional ventilation products on the chassis of the unit.
Do not install the unit near high-frequency generator sources.
Do not install the unit near a doorway.
Installing in an Area Exposed to Unconditioned Air
In some installation applications, areas (floors, walls) in some rooms may be exposed to unconditioned air (room may be above or next to an
unheated garage or storeroom). To countermeasure:
• Verify that carpet is or will be installed (carpet may increase the temperature by three degrees).
• Add insulation between the oor joists.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
• Install radiant heat or another type of heating system to the oor.
Required Clearances
Figure 6 shows required clearance distances around a typical installed wall-mounted unit.
Figure 2: Required Clearances Around Typical Installed Unit
18
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 19

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
CAUTION
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
MA
Unpack and Inspect for Freight Damage
Shipping and net weights of the wall-mounted units are listed in Table 4. To help avoid injury to personnel and
damage to the unit, use two people when carrying a unit by hand.
Note:
Do not unpack the unit and remove the protective materials until ready to install. Before unpacking,
carefully move the packaged unit to a work area near the installation location.
After opening, if the unit is damaged, repack the unit as it was shipped to you. RETAIN ALL PACKING
MATERIALS. In general, freight damage claims will be denied if the original packing materials are not
retained for the claims adjustor to inspect. Contact your supervisor on how to proceed with filing a freight
claim and to order a replacement unit.
Note:
Before opening the shipping container, check the container labeling to verify the unit received is the correct
unit. Verify the unit capacity, type, and voltage. Refer to the chart on “Dimensions of the Flare” on page 29.
1. Before opening the shipping container, verify you have the correct unit as described in the Note
above.
2. Place the box on a solid surface right side up.
3. Cut the reinforced nylon straps.
4. Open the top of the box and fold back all four flaps.
5. Remove the protective cardboard/Styrofoam® top sheet and place to the side.
6. The walls and top panels are not attached to the bottom of the box. Lift the cardboard carton by the
flaps and remove the box walls and top and place it to the side.
7. Remove the moisture barrier plastic bonnet.
8. Check the unit nameplate data and model number. Verify the unit voltage, and capacities are correct
before proceeding.
9. Locate and retain the piping/condensate accessory kit located in the bottom of the box under the
refrigerant pipe stubs.
10. Using two people, carefully lift the unit and inspect for freight damage. DO NOT lift by the refrigerant
piping or drain pipe stub. Lift by the hangar brackets or chassis frame only. If damage is found, repack
the unit as it was received in the original container.
11. If the unit is undamaged, remove and retain the installation manual. It is located under or on top of
the unit.
Inspection
Installation Manual
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
19
Page 20

X
MUL
MUL
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
Frame
Hooks
Ø2-3/4 inches
Place a level on raised tab
Right rear piping
Left rear piping
TI
F
Install Wall-Mounted IDU Chassis
WARNING
• Mounting hardware must be securely installed to prevent the chas-
sis falling from its installation location. There is risk of personnel
injury or property damage from falling equipment.
• When choosing a location for the wall mount plate, be sure to take
into consideration routing of wiring for power outlets within the wall.
Touching wiring can cause serious bodily injury, or death.
• Installation work must be performed by trained personnel and in
accordance with all local or other applicable codes. There is risk of
injury to personnel from incorrect installation.
Note:
• Ensure the unit is properly installed. Incorrectly installed units can
result in degraded performance or an inoperative unit/system.
• Use a level indicator to ensure the installation plate and chassis
are installed on a level plane.
• If the unit is installed near a body of water, certain components
are at risk of being corroded. Appropriate anti-corrosion methods
should be taken for the unit and all components.
Mounting the Installation Plate
The mounting wall should be strong and solid enough to protect the
unit from vibration. It should securely hold the installation plate and
the weight of the chassis.
TI
Figure 3: Installation Plate for LMN078HVT, LSN090HSV4,
LSN120HSV4, and LMN158HVT Units.
Unit Outline
Ø2-9/16
5-3/16 3-11/16
6-7/8
Figure 4: Installation Plate for LSN180HSV4 and LMN248HVT Units.
Unit Outline
18-1/8 inches 22-7/16 inches
Place a level on raised tab
17-3/8 17-3/8
5
MA
Ø2-9/16
8-1/2
1. Determine the installation location.
2. Refer to Figure 3 or Figure 4 for the appropriate mounting
diagram.
3. Mount the installation plate on the wall using the Type “A” screws.
If mounting the unit on concrete, consider using anchor bolts.
Use a level to ensure the plate is level.
4. Always mount the installation plate horizontally. Measure the wall
and mark the centerline using thread and a level.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
Installation Plate
Left rear
piping
2-23/32 inches
4-1/8 inches
Figure 5: Installation Plate Attaching Screw Placement.
Type "A" Screws
Installation Plate
Measuring Tape
Measuring Tape Hanger
A-Type
B-Type
Ø2-3/4 inches
Right rear
piping
2-7/32 inches
8-5/32 inches
20
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 21

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
(3/16"~5/16")
Installation plate
Tubing Clamp
Right
Tubing Clamp
Down
Left
Back
Frame Cover
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
MA
Drilling Piping Hole in the Wall
Use caution when drilling holes through walls. Drilling into power wiring in the wall can
cause serious bodily injury or death.
Follow the left or right piping clearance recommendations in Figure 3 or Figure 4.
1. Using a 2-5/8 (ø 65mm) inch hole core drill bit, drill a hole at either the right or
left side of the wall mounting (Figure 6). The hole should slant 3/16” to 5/16” from
level (upward on the indoor unit side and downward on the outdoor unit side).
2. Finish off the newly drilled hole as shown with bushing and sleeve covering.
Sleeve and bushing prevents damage to the tubing/bundling of the piping.
Hanging the Indoor Unit Chassis
1. Attach the three (3) hooks on the top of the indoor unit to the top edge of
the installation plate. Verify the hooks are properly attached to the installation plate by gently shaking the indoor unit from side to side.
2. Unlock the tubing clamp from the indoor unit frame. For easier access between the bottom of the indoor unit and the wall, prop the clamp between
the indoor unit frame and installation plate.
3. Remove the screw covers at the bottom of the indoor unit, unscrew the
two (2) screws, remove the frame cover, remove the piping connection
cover, and position the piping for installation (down, back, left, or right).
Install Wall-Mounted IDU Chassis
Figure 6: Drilling Piping Hole
WALL
Indoor
Core Drill
Bushing
Sleeve
Figure 7: Locking the Indoor Unit onto the Installation Plate.
Outdoor
Installation Manual
Figure 8: Accessing the Back of the Indoor Unit.
Figure 10: Exterior Back View of Indoor Unit. Figure 11: Piping Installed to the Left.
Figure 9: Removing the Frame Cover.
Tape
Connecting
pipe
Drain hose
Figure 12: Piping Installed to the Right.
Tape
Connecting
pipe
Drain hose
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
21
Page 22

X
MUL
MUL
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
3X
Minimum
TI
F
Refrigerant Piping
TI
MA
Preparing for Piping Installation to the Indoor Unit
Note:
Do not bend the piping / drain hose from side to side, it may damage the components.
Prepare the refrigerant piping and drain hose (indoor unit piping) for installation through the wall. Press on the top of the tubing clamp
and slowly guide the piping/hose down (depending on installation requirements, then to the left or right). Relock the tubing clamp after
the piping/hose are released.
No Pipe Size Substitutions
Use only the pipe size selected by the LATS Multi F pipe system design software or as conveyed in the product installation instructions.
Using a different size is prohibited and may result in a system malfunction or failure to work at all.
Pipe Slope
The horizontal pipe slope cannot exceed 10° up or down. Y-branches have additional restrictions described below.
In-line Refrigeration Components
Components such as oil traps, solenoid valves, filter-dryers, sight glasses, tee fittings, and other after-market accessories are not permitted on the refrigerant piping system between the outdoor units and the indoor / branch distribution units.
Multi F/Multi F Max systems have redundant systems that ensure oil is properly returned to the compressor. Sight-glasses and solenoid
valves may cause vapor to form in the liquid stream.
Note:
Over time, dryers may deteriorate and introduce debris into the system. The designer and installer should verify the refrigerant piping system is
free of traps, sagging pipes, sight glasses, lter dryers, etc.
Field-Provided Isolation Ball Valves
LG recommends installing field-supplied ball valves with Schrader ports at each indoor unit. Full-port isolation ball valves with Schrader
ports (positioned between valve and indoor unit) rated for use with R410A refrigerant should be used on both the liquid and vapor lines.
For Multi F MAX systems, position valves with a minimum distance of three (3) to six (6) inches of pipe on either side of the valve, and
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
between six (6) and twelve (12) inches from the first upstream Y-branch or branch distribution unit. If ball valves are installed away from
the first Y-branch and/or branch distribution unit and closer to the indoor unit, oil may accumulate where it cannot be returned to the
outdoor unit and may cause a shortage of oil in the compressor.
Valves should be easily accessible for service. If necessary, install drywall access doors or removable ceiling panels, and position the
valves to face the access door or ceiling panel opening. Mount valves with adequate space between them to allow for placement of
adequate pipe insulation around the valves.
Obstacles
When an obstacle, such as an I-beam or concrete T, is in the
path of the planned refrigerant pipe run, it is best practice to
route the pipe over the obstacle. If adequate space is not available to route the insulated pipe over the obstacle, then route
the pipe under the obstacle. In either case, it is imperative the
horizontal section of pipe above or below the obstacle be a
minimum of three (3) times greater than the longest vertical rise
(or fall) distance.
Figure 13: Installing Piping Above and Below an Obstacle.
Above an obstacle.
Below an obstacle.
22
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 23

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
Viewed from A in direction of arrow
Horizontal
plane
Within ±5
°
A
Vertical Up Configuration
Within ± 3°Within ± 3°
Vertical Down Configuration
Liquid and Gas
Pipe Joints
Y-Branch Kit Insulation
Insulation for
Field-Installed Piping
Field-Supplied Insulation Tape
A
B
X
Y
1
2
3
1
2
3
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
MA
Refrigerant Piping
Multi F MAX Y-Branch Kit PMBL5620
The LG supplied Y-Branch Kit PMBL5620 MUST be used when two branch distribution units are connected to one Multi F MAX system.
Field-supplied fittings are not permitted. Each Y-Branch kit comes with two (2) Y-branches (one for the liquid line and one for the vapor line)
and insulation covers.
Y-branches may be installed in horizontal or vertical configurations. When installed vertically, position the Y-branch so the straight-through
leg is ±3° of plumb. When installed horizontally, position the Y-branch so the take-off leg is level and shares the same horizontal plane as the
straight-through leg ±5° rotation.
Y-branches should always be installed with the single port facing the outdoor unit and the two-port end facing the branch distribution units.
Do not install Y-branches backwards as refrigerant flow cannot make U-turns. The Y-branch kit must be located at least three (3) feet from
the outdoor unit. Provide a minimum of 20 inches between a Y-branch and the branch distribution unit.
Figure 14: Y-Branch Port Identication and Dimensions.
Table 12: Multi F MAX Y-Branch Connection Diameters.
Model
PMBL5620
Y-Branch
Type
Liquid Ø3/8 Ø3/8 Ø3/8
Vapor Ø3/4 Ø3/4 Ø3/4
Y-Branch
Type
Liquid 13.80 3.24
Vapor 12.48 3.02
Port Identier (inch)
1 2 3
Dimensions (inch)
X Y
Installation Manual
A = To Outdoor Unit
B = To Branch Distribution Unit
Figure 15: Y-branch Horizontal Installation Alignment.
Y-Branch Kit Insulation
Each Y-branch kit comes with clam-shell type peel-andstick insulation jackets molded to fit the Y-branch fittings—
one for the liquid line, one for the vapor line.
Table 11: Insulation Jacket Properties.
Material
UL94 Flame Classication
Density
Thermal Conductivity
Thickness
Polyolefin Foam
1.84 lbs./ft.
.0208 Btu/h/ft. ºR
Figure 16: Y-branch Vertical Installation Alignment.
Figure 17: Y-Branch Insulation Jacket Diagram.
HF-1
1/2 inch
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
3
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
23
Page 24

X
MUL
MUL
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
F
Refrigerant Piping
TI
MA
Selecting Field-Supplied Copper Tubing
Copper is the only approved refrigerant pipe material for use with Duct Free System products, and LG recommends seamless phosphorous
deoxidized ACR type copper pipe, hard-drawn rigid type “K” or “L”, or annealed-tempered, copper pipe.
• Drawn temper (rigid) ACR copper tubing is available in sizes 3/8 through 2-1/8 inches (ASTM B 280, clean, dry, and capped).
• Annealed temper (soft) ACR copper tubing is available in sizes 1/4 through 2-1/8 inches (ASTM B 280, clean, dry, and capped).
Tube wall thickness should meet local code requirements and be approved for an operating pressure of 551 psi. If local code does not
specify wall thickness, LG suggests using tube thickness per table below. When bending tubing, try to keep the number of bends to a minimum, and
use the largest radii possible to reduce the equivalent length of installed pipe; also, bending radii greater than ten (10) pipe diameters can minimize
pressure drop. Be sure no traps or sags are present when rolling out soft copper tubing coils.
Table 13: ACR Copper Tubing Material
Type Seamless Phosphorous Deoxidized
Class UNS C12200 DHP
Straight Lengths H58 Temper
Coils O60 Temper
Table 14: Piping Tube Thicknesses
OD (in) 1/4 3/8 1/2 5/8 3/4 7/8 1-1/8 1-3/8 1-5/8
Material Rigid Type “K” or “L” and Soft ACR Acceptable Rigid Type “K” or “L” Only
Min. Bend
Radius (in)
Min. Wall
Thickness (in)
Nominal Pipe
Outside
Diameter (in)
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
1/4 0.250 -- -- -- 0.030 0.081 .00020
3/8 0.375 0.030 0.126 .00054 0.032 0.134 .00053
1/2 0.500 0.035 0.198 .00101 0.032 0.182 .00103
5/8 0.625 0.040 0.285 .00162 0.035 0.251 .00168
3/4 0.750 0.042 0.362 .00242 0.042 0.362 .00242
7/8 0.875 0.045 0.455 .00336 0.045 0.455 .00336
1-1/8 1.125 0.050 0.655 .00573 0.050 0.655 .00573
1
All dimensions provided are in accordance with ASTM B280 – Standard.
2
Design pressure = 551 psig.
3
ACR Tubing is available as hard drawn or annealed (soft) and are suitable for use with R410A refrigerant.
4
The Copper Tube Handbook, 2010, Copper Development Association Inc., 260 Madison Avenue, New York, NY 10016.
.563 .9375 1.5 2.25 3.0 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5
.03 .03 .035 .040 .042 .045 .050 .050 .050
1-4
Weight (lb/ft)
Actual Outside
Diameter (in)
Table 15: ACR Copper Tubing Dimensions and Physical Characteristics
Drawn Temper Annealed Temper
Nominal Wall
Thickness (in)
Weight (lb/ft)
Cubic ft per
Linear ft
Nominal Wall
Thickness (in)
Cubic ft per
Linear ft
• Commercially available piping often contains dust and other materials. Always blow it clean with a dry, inert gas.
• Prevent dust, water or other contaminants from entering the piping during installation. Contaminants can cause mechanical failure.
24
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 25

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
MA
Refrigerant Piping
No Pipe Size Substitutions
Note:
Use only the pipe size recommended by this installation manual. Using a different size is prohibited and may result in system malfunction or failure.
Copper Expansion and Contraction
Under normal operating conditions, the vapor pipe temperature of a
Duct Free System can vary as much as 280°F. With this large variance in pipe temperature, the designer must consider pipe
expansion and contraction to avoid pipe and fitting fatigue failures.
Refrigerant pipe along with the insulation jacket form a cohesive unit that
expands and contracts together. During system operation, thermal heat
transfer occurs between the pipe and the surrounding insulation.
If the pipe is mounted in free air space, no natural restriction to
movement is present if mounting clamps are properly spaced and
installed. When the refrigerant pipe is mounted underground in a
utility duct stacked among other pipes, natural restriction to linear
movement is present. In extreme cases, the restrictive force of
surface friction between insulating jackets could become so great
that natural expansion ceases and the pipe is “fixed” in place. In this
situation, opposing force caused by change in refrigerant fluid/vapor
temperature can lead to pipe/fitting stress failure.
The refrigerant pipe support system must be engineered to allow
free expansion to occur. When a segment of pipe is mounted
between two fixed points, provisions must be provided to allow pipe
expansion to naturally occur. The most common method is the
inclusion of expansion Loop or U-bends. Each segment of pipe has
a natural fixed point where no movement occurs. This fixed point is
located at the center point of the segment assuming the entire pipe
is insulated in a similar fashion. The natural fixed point of the pipe
segment is typically where the expansion Loop or U-bend should be.
Linear pipe expansion can be calculated using the following formula:
LE = C x L x (T
LE = Anticipated linear tubing expansion (in.)
C = Constant (For copper = 9.2 x 10
L = Length of pipe (ft.)
T
R
T
a
12 = Inches to feet conversion (12 in./ft.)
– Ta) x 12
r
= Refrigerant pipe temperature (°F)
= Ambient air temperature (°F)
-6
in./in.°F)
1. In Table 16 find the row corresponding with the actual length of
the straight pipe segment.
2. Estimate the minimum and maximum temperature of the pipe.
In the column showing the minimum pipe temperature, look up the
anticipated expansion distance. Do the same for the maximum
pipe temperature.
3. Calculate the difference in the two expansion distance values.
The result will be the anticipated change in pipe length.
Example:
A system is installed and the design shows that there is a 100 foot
straight segment of tubing between an indoor unit and the outdoor
unit. In heating, this pipe transports hot gas vapor to the indoor units
at 120°F. In cooling, the same tube is a suction line returning refrigerant vapor to the outdoor unit at 40°F. Look up the copper tubing
expansion at each temperature and calculate the difference.
Vapor Line
Transporting Hot Vapor: 100 ft. pipe at 120 °F = 1.40 in.
Transporting Suction Vapor: 100 ft. pipe at 40 °F = 0.40 in.
Anticipated Change in Length: 1.40 in. – 0.40 in. = 1.00 in.
Liquid Line
The liquid temperature remains relatively the same temperature; only
the direction of flow will reverse. No significant change in length of
the liquid line, therefore, is anticipated.
When creating an expansion joint, the joint height should be a
minimum of two times the joint width. Although different types of
expansion arrangements are available, the data for correctly sizing
an Expansion Loop is provided in Table 1010. Use soft copper with
long radius bends on longer runs or long radius elbows for shorter
pipe segments. Using the anticipated linear expansion (LE) distance
calculated, look up the Expansion Loop or U-bend minimum design
dimensions. If other types of expansion joints are chosen, design per
ASTM B-88 Standards.
Installation Manual
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
25
Page 26

X
MUL
MUL
F
Large Tubing U-bend (>3/4 in.) Loop Small Tubing U-bend (<3/4 in.)
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
F
Refrigerant Piping
See table below for precalculated anticipated expansion for various pipe sizes and lengths of refrigerant tubing.
To find the anticipated expansion value:
1. From the table below, find the row corresponding with the actual feet of the straight pipe segment.
2. Estimate the minimum and maximum temperature of the pipe.
3. In the column showing the minimum pipe temperature, look up the anticipated expansion distance corresponding to the segment length.
Do the same for the maximum pipe temperature.
4. Calculate the difference in the two expansion distance values. The result will be the change in pipe length.
Table 16: Linear Thermal Expansion of Copper Tubing in Inches
Pipe
1
Length
1
Pipe length baseline temperature = 0°F. "Expansion of Carbon, Copper and Stainless Steel Pipe," The Engineers' Toolbox, www.engineeringtoolbox.com.
35° 40° 45° 50° 55° 60° 65° 70° 75° 80° 85° 90° 95° 100° 105° 110° 115° 120° 125° 130°
10 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.08 0.09 0.09 0.10 0.10 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.15
20 0.08 0.08 0.10 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.17 0.18 0.19 0.20 0.21 0.22 0.22 0.23 0.26 0.28 0.29 0.30
30 0.12 0.12 0.15 0.18 0.20 0.21 0.23 0.24 0.26 0.27 0.29 0.30 0.32 0.33 0.32 0.35 0.39 0.42 0.44 0.45
40 0.16 0.16 0.20 0.24 0.26 0.28 0.30 0.32 0.34 0.36 0.38 0.40 0.42 0.44 0.43 0.46 0.52 0.56 0.58 0.60
50 0.20 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.33 0.35 0.38 0.40 0.43 0.45 0.48 0.50 0.53 0.55 0.54 0.58 0.65 0.70 0.73 0.75
60 0.24 0.24 0.30 0.36 0.39 0.42 0.45 0.48 0.51 0.54 0.57 0.60 0.63 0.66 0.65 0.69 0.78 0.84 0.87 0.90
Fluid Temperature °F
TI
MA
Figure 18: Coiled Expansion Loops and Offsets
L
R
Table 17: Radii of Coiled Expansion Loops and Developed Lengths of Expansion Offsets
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
Anticipated Linear
Expansion (LE) (inches)
1/2
1
1-1/2
2
2-1/2
3
3-1/2
4
L
1
R
2
L
1
R
2
L
1
R
2
L
1
R
2
L
1
R
2
L
1
R
2
L
1
R
2
L
1
R
2
L
6 7 8 9
38 44 50 59
9 10 11 13
54 63 70 83
11 12 14 16
66 77 86 101
12 14 16 19
77 89 99 117
14 16 18 21
86 99 111 131
15 17 19 23
94 109 122 143
16 19 21 25
102 117 131 155
17 20 22 26
109 126 140 166
1/4 3/8 1/2 3/4
R
Nominal Tube Size (OD) inches
L
26
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 27

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
Max. 12" Max. 12"
Max. 12"
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
MA
Inserts and Pipe Supports
Inserts
An insert can be installed into a floor or beam before the concrete sets so that fittings such as ducts,
pipes, or suspension bolts can be added at a later time. Decide where the inserts should be placed
before support installation.
Pipe Supports
Note:
The pipe system must be adequately supported to avoid pipe sagging. Sagging pipes become oil traps that
lead to equipment malfunction.
Pipe supports should never touch the pipe wall; supports should be installed outside
(around) the primary pipe insulation jacket. Insulate the pipe before installing the supports. Pipe supports are field-provided and must meet local code. If local codes do not
specify pipe support spacing, install pipe supports a maximum of 5 feet on center for
straight segments of pipe up to 3/4” outside diameter size.
Wherever the pipe changes direction, place a hanger within twelve (12) inches on one
side and within twelve to nineteen (12 to 19) inches of the bend on the other side. Support piping at indoor units as shown. Support Y-Branch fittings as shown.
Refrigerant Piping
Figure 19: Installing an Insert Into
a Concrete Beam.
Anti-vibration Material
Insert
Concrete Beam
Figure 20: Pipe Hanger Details.
Suspension Bolt
Nail
Installation Manual
Figure 21: Typical Pipe Support Location—Change
in Pipe Direction.
~ 12" – 19"
Figure 23: Pipe Support at Y-branch Fitting.
Max. 12"
Figure 22: Pipe Support at Indoor Unit.
A
A + B ~ 12" – 19"
B
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
27
Page 28

X
MUL
MUL
F
Bolt
PVC
PVC
Welding
Refrigerant Pipe
Insulated
Support Band
Insulated
Support Band
Down
Stop
Welding
Plate Nut
Hexagonal Nut
O-ring Band
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
F
Refrigerant Piping
Examples of Supports
Figure 24: U-Bolt Support with Insulation. Figure 25: O-Ring Support with Insulation.
Insulation
Bolt
1.5t
Plate
Figure 26: Saddle-Type Support.
Support at Intervals Between 5 and 6-3/4 Feet
TI
Note:
Do not compress the insulation with the saddle-type support. If the insulation is compressed, it may tear open and allow condensation to
generate during product operation.
Figure 27: U-Bolt Support with an Insulated Pipe. Figure 28: O-Ring Band Support with an Insulated Pipe.
MA
To prevent
insulation from
pressing and
lagging, use a cover.
Sheathing
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
Figure 29: One-Point Down-Stop Support (>441 lbs.).
O-Ring
Band
Lags
Sheathing
Figure 30: Two-Point Down-Stop Support.
28
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 29

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
40 in40 in
A
B
D
F
G
B
G
D
B
H
I
J
A
E
B
I
A
B
D
C
Inside wall (concealed)
Floor (fire-resistance)
Area between fire-resistant
insulation and boundary wall
Roof pipe shaft
Outside wall
Outside wall (exposed)
Sleeve
Insulation
Lagging
Caulk
Band
Water-resistant layer
Sleeve with edge
Lagging
Mortar or other fire-resistant caulk
Fire-resistant insulation
When filling an access hole with mortar, cover the
area with steel plate so that the insulation will not
fall through. For this area, use fire-resistant
materials for both the insulation and cover. (Vinyl
cover should not be used.)
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
MA
Pipe Sleeves at Penetrations
LG requires that all pipe penetrations through walls, floors, and
pipes buried underground be routed through a properly insulated
sleeve that is sufficiently sized to provide free movement of the pipe
and does not compress the insulation. Route underground refrigerant pipe inside a protective sleeve to prevent insulation deterioration. Follow federal, state, and local regulations and codes when
choosing a sleeve type.
Figure 31: Pipe Sleeve Options.
Refrigerant Piping
Note:
Pipe diameter plus insulation thickness determines wall
penetration diameter.
For example:
Diameter of Gas Piping: 1/2"
Diameter of Liquid Piping: 1/4"
Thickness of Gas Piping Insulation: 0.4" x 2
Thickness of Liquid Piping Insulation: 0.4" x 2
Surplus: 0.8"
Sleeve diameter (total): 3.1" minimum
Installation Manual
Underground Refrigerant Piping
Route refrigerant pipe installed underground inside a vapor tight protective sleeve to prevent insulation deterioration and water infiltration. Refrigerant pipe installed inside underground casing must be
continuous without any joints. Underground refrigerant pipe must be
located at a level below the frost line.
Liquid
Pipe
1/4 (1.0)
3/8 (1-1/8)
1
OD pipe diameter in inches; Values in parenthesis () indicate OD of pipe with insulation
jacket.
2
Diameter of pipe with insulation. Thickness of pipe insulation is typical. Actual required
thickness may vary based on surrounding ambient conditions and should be calculated
and specified by the design engineer.
3
Insulation thickness (value in parenthesis) = 3/8 inch.
4
Insulation thickness (value in parenthesis) = 1 inch.
5
Insulation thickness (value in parenthesis) = 3/4 inch.
1
3
3
Table 18: Utility Conduit Sizes.
Vapor Pipe
3/8 (1-1/8
2,3
) 1/2 (2.0
4 4 4 4
4 4 4 5
2,5
) 5/8 (2-1/8
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
1
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
2,5
) 3/4 (2-1/4
2,5
)
Figure 32: Typical Arrangement of Refrigerant Pipe
and Cable(s) in a Utility Conduit.
Figure 33: Underground Refrigerant Piping.
Vapor Line
Insulation Material
Liquid Line
Pipe Sleeve
Insulation
Material
Min. 18 Gauge
Power/Communication
Cable
29
Page 30

X
MUL
MUL
F
GENERAL INSTALLATION GUIDELINES
TI
F
Piping Materials and Handling
Piping Materials and Handling
Pipes used for the refrigerant piping system must include the specified thickness, and the
interior must be clean.
While handling and storing, do not bend or damage the pipes, and take care not to contaminate the interior with dust, moisture, etc. See Table 19 for care of piping.
Table 19: Three Principles of Refrigerant Piping
Dry Clean Airtight
Principles No moisture should be inside the piping. No dust should be inside the piping. No leaks should occur.
Problems
Caused
Solutions
Moisture
- Significant hydrolysis of refrigerant oil.
- Refrigerant oil degradation.
- Poor insulation of the compressor.
- System does not operate properly.
- EEVs, capillary tubes are clogged.
- Remove moisture from the piping.
- Piping ends should remain capped until
connections are complete.
- Do not install piping on a rainy day.
- Connect piping properly at the unit’s side.
- Remove caps only after the piping is
cut, the burrs are removed, and after
passing the piping through the walls.
- Evacuate system to a minimum of 500
microns and ensure the vacuum holds at
that level for 24 hours
- Refrigerant oil degradation.
- Poor insulation of the compressor.
- System does not operate properly.
- EEVs and capillary tubes become
clogged.
- Remove dust from the piping.
- Piping ends should remain capped until
connections are complete.
- Connect piping properly at the side of
the unit.
- Remove caps only after the piping is cut
and burrs are removed.
- Retain the cap on the piping when
passing it through walls, etc.
Dust
Figure 34: Keep Piping Capped While Storing
- Refrigerant gas leaks / shortages.
- Refrigerant oil degradation.
- Poor insulation of the compressor.
- System does not operate properly.
- Test system for air tightness.
- Perform brazing procedures that comply
with all applicable standards.
- Perform flaring procedures that comply
with all applicable standards.
- Perform flanging procedures that
comply with all applicable standards.
- Ensure that refrigerant lines are pressure
tested to 550 psig.
TI
Leaks
MA
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
30
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 31

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
PIPING CONNECTIONS
TI
MA
Piping Preparation
Piping Preparation
• Do not allow the refrigerant to leak during brazing; if refrigerant combusts, it generates a toxic gas which can cause physical injury or death.
• Do not braze in an enclosed location, and always test for gas leaks before/after brazing. Gas leaks can cause physical injury or death.
• After brazing, check for refrigerant gas leaks. Refrigerant gas leaks can cause physical injury or death.
• When selecting flare fittings, always use a 45° fitting rated for use with high pressure refrigerant R410A. Failure to do so may result in
refrigerant leaks which in turn could result in personal injuries or death from oxygen depletion. Selected fittings must also comply with local,
state, or federal standards.
Note:
1. If piping becomes kinked due to excessive bending, do not use the pipe.
2. Braze the pipes to the service valve pipe stub of the outdoor unit.
Creating a Flare Fitting
Note:
One of the main causes of refrigerant leaks is defective ared connections. Be sure to properly form the are connections.
1. Cut the pipe to length.
• Measure the distance between the indoor unit and the
outdoor unit.
• Cut the pipes a little longer than measured distance.
• Cut the cable 4.9 ft longer than the pipe length.
1.
Figure 35: Creating a Flare Fitting
Copper
tube
90°
Slanted Uneven Rough
Installation Manual
2A. Remove the burrs.
• Completely remove all burrs from pipe ends.
• When removing burrs, point the end of the copper pipe
down to avoid introducing foreign materials in the pipe.
2B. Slide the flare nut onto the copper tube.
3. Flaring the pipe end.
• Use the proper size aring tool to nish ared connections
as shown.
• Refer to the diagram in step 3 of Figure 35 and the dimen-
sions in Table 20 for positioning the pipe in the aring tool.
• ALWAYS create a 45° are when working with R410A. See
Warning on this page.
4. Carefully inspect the flared pipe end.
• Compare the are with the illustration in step 4 of Figure 35.
• If the are is defective, cut it off and re-do procedure.
• If are looks good, blow clean the pipe with dry nitrogen.
Table 20: Flare “A” Measurement
Pipe Outside
Diameter (inch)
1/4 0.04 – 0.5
3/8 0.06 – 0.7
1/2 0.06 – 0.7
5/8 0.06 – 0.7
3/4 0.07 – 0.8
“A” Measurement
(inch)
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
2A. 2B.
Point
down
3.
Bar
Smooth
4.
Even length
Pipe
Reamer
"A"
Copper pipe
Clamp handle
Copper
tube
Bar
Inside is shiny with no scratches
Slanted
Flare nut
Handle
Red arrow
Incorrect Flares
Damaged
surface
Yoke
Cone
Cracked Uneven
thickness
31
Page 32

X
MUL
MUL
F
Gas Piping Connections
Liquid
Piping
Connection
A
B
Flare
to
Indoor
Unit
Flare
to
Outdoor
Unit
Connection Socket
(Factory-supplied with
the indoor unit)
PIPING CONNECTIONS
TI
F
IDU to ODU
Multi F Outdoor Unit to Indoor Unit Piping Connections
Avoid Pipe Damage
• When routing eld-provided piping, avoid damaging the outdoor unit from excessive vibration.
• Correctly route the piping so it does not make contact with mounting bolts. Allow room for eld installation.
• Properly insulate the liquid and gas lines separately up to the point of connection at the unit frame.
• See table below for Multi F outdoor unit connection types.
Table 21: Outdoor Unit Piping Connections.
Outdoor Unit Piping Connections LMU18CHV LMU24CHV LMU30CHV LMU36CHV
Liquid Line Connection (in., OD) x Qty. 1/4 x 2 1/4 x 3 1/4 x 4 1/4 x 4
Vapor Line Connection (in., OD) x Qty. 3/8 x 2 3/8 x 3 3/8 x 4 3/8 x 4
Table 22: Wall Mounted Indoor Unit Pipe Sizes.
Indoor Unit Capacity
7,000 Btu/h
9,000 Btu/h
12,000 Btu/h
15,000 Btu/h
18,000 Btu/h
24,000 Btu/h
Vapor Line Size
(in., OD)
Ø3/8
Ø1/2
Liquid Line Size
(in., OD)
Ø1/4
Figure 36: Multi F Refrigerant Pipe Connections
(LMU36CHV shown as example).
s
TI
A-UNIT
B-UNIT
C-UNIT
D-UNIT
MA
Table 23: Wall Mounted Indoor Unit Piping Connections.
Indoor Unit Capacity
7,000 Btu/h
9,000 Btu/h
12,000 Btu/h
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
15,000 Btu/h
18,000 Btu/h Ø5/8 Ø3/8
24,000 Btu/h Ø1/2 Ø1/4
Connection sockets (included as a factory-supplied accessory with the indoor
units) may need to be used when piping the indoor units to the outdoor unit.
Table 24: Connection Socket Dimensions.
Indoor Unit
Capacity
18,000 Btu/h Ø3/8 → Ø1/2, Ø1/2 → Ø5/8 Ø1/4 → Ø3/8
24,000 Btu/h Ø3/8 → Ø1/2 N/A
Using the Connection Socket
1. Align the center of the piping sections and tighten the flare nut by
hand.
2. Tighten the flare nut with a torque wrench, using the arrows on
the wrench as a guide, until a click is heard.
32
Vapor Line
Connection (in., OD)
Ø3/8 Ø1/4
Vapor (in., OD) Liquid (in., OD)
A B A B
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Liquid Line
Connection (in., OD)
Main gas
valve
Main liquid
valve
Figure 37: Connection Socket Diagram.
Figure 38: Performing Connections.
Page 33

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
Flare nut
Piping
1. 3/8 in. to 3/8 in. Connection
2. 3/8 in. to 1/2 in.
Connection
Flare side to
branch distribution unit or ODU
Flare side to indoor unit
Ø3/8 in.
Flare side to indoor unit or
pipe to indoor unit
Ø1/2 in.
Connection socket
Flare nut
Piping
Ø3/8 in.
Ø3/8 in.
Spanner
Field Piping
Flare nut
Torque
wrench
3. 1/2 in. to 5/8 in.
Connection
Ø5/8 in.
Connection socket
Flare nut
Piping
Ø1/2 in.
4. 1/4 in. to 3/8
Connection
Flare side to indoor unit
Ø3/8 in.
Connection socket
Flare nut
Piping
Ø1/4 in.
Flare
side to
branch distribution unit or ODU
Flare side to indoor unit
Flare
side pipe
from branch distribution unit or ODU
Flare
side to
branch distribution unit or ODU
F
PIPING CONNECTIONS
TI
MA
IDU to ODU
Multi F System Piping Connections
Note:
Do not use polyolyester (POE) or any other type of mineral oil as a thread lubricant. These lubricants are not compatible with PVE oil used in this
system and create oil sludge leading to equipment damage and system malfunction.
1. When connecting the flare nuts, coat the flare (inside and outside) with polyvinyl ether (PVE)
refrigeration oil only.
2. Align the center of the piping sections and tighten the flare nut by hand.
3. Tighten the flare nut with a torque wrench and a backup wrench until a click is heard.
4. Wrap insulation around the connection.
5. If it is necessary to loosen the flare nuts, always use two wrenches to do so.
Table 25: Tightening Torque for Flare Nuts.
Pipe size (Inches O.D.) Tightening torque (ft-lbs) Width of the are (A [inches])
1/4Ø 13.9 - 18 1/8
3/8Ø 24.5 - 30.3 1/8
1/2Ø 39.7 - 47.7 1/8
5/8Ø 45.5 - 59.2 1/16
Figure 39: Possible Outdoor Unit or Branch Distribution Unit to Indoor Unit Connections.
Figure 40: Tightening the Flare Nuts.
Union
Installation Manual
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
33
Page 34

X
MUL
MUL
F
WARNING
PIPING CONNECTIONS
TI
F
IDU to ODU
TI
MA
Refrigerant Safety
Verify the maximum refrigerant concentration level in the space where the indoor unit will be mounted meets the concentration limit for the application.
There is risk of asphyxiation from oxygen deprivation.
ASHRAE Standards 15-2010 and 34-2010 offer guidelines that address refrigerant safety and the maximum allowable concentration of
refrigerant in an occupied space. Refrigerant will dissipate into the atmosphere, but a certain volume of air is required for this to occur safely.
For R410A refrigerant, the maximum allowable concentration of refrigerant is twenty-six (26) lbs. per 1,000 cubic feet of an occupied space.
Buildings with twenty-four (24) hour occupancy allow half of that concentration.
ASHRAE Standards 15 and 34 assume that if a system develops a leak, its entire refrigerant charge will dump into the area where the leak
occurs. To meet ASHRAE Standards 15 and 34, calculate the refrigerant concentration that may occur in the smallest room volume on the
system, and compare the results to the maximum allowable concentration number.1 Also consult state and local codes in regards to refrigerant safety.
1
Information about ASHRAE Standard 15-2010/34-2010 and addenda current as of the date of this publication.
1
Brazing
Note:
It is imperative to keep the piping system free of contaminants and debris such as copper burrs, slag, or carbon dust during installation.
1. All joints are brazed in the field. Multi V IV refrigeration system components contain very small capillary tubes, small orifices, electronic
expansion valves, oil separators, and heat exchangers that can easily become blocked. Proper system operation depends on the
installer using best practices and utmost care while assembling the piping system.
• Store pipe stock in a dry place and keep stored pipe capped and clean.
• Purge all pipe sections clean with dry nitrogen prior to assembly.
2. Proper system operation depends on the installer using best practices and the utmost care while assembling the piping system.
• Use adapters to assemble different sizes of pipe.
• Always use a non-oxidizing material for brazing. Do not use ux, soft solder, or anti-oxidant agents. If the proper material is not used,
oxidized lm may accumulate and clog or damage the compressors. Flux can harm the copper piping or refrigerant oil.
• Use a tubing cutter; do not use a saw to cut pipe. De-bur and clean all cuts before assembly.
3. Brazing joints:
• Use a dry nitrogen purge operating at a minimum pressure of three (3) psig and maintain a steady ow.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
• Use a 15% silver phosphorous copper brazing alloy to avoid overheating and produce good ow.
• Protect isolation valves, electronic expansion valves, and other heat-sensitive control components from excessive heat with a wet rag or
heat barrier spray.
Figure 41: Using Nitrogen Gas During Brazing
Refrigerant Pipe
Welding Point
Nitrogen gas
3.0 psi or less
Regulator
34
Do not block outlet side.
When pressure inside pipe
is above atmospheric pressure,
pinhole leaks can occur.
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Tape
(no air bubbles)
Auxiliary
Valve
Nitrogen
Gas
Tank
Page 35

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
Indoor unit piping
Flare nut Field-installed
piping
Spanner
Field-installed
piping
Flare nut
Torque
wrench
Narrow tape
Adhesive
Drain extension
Indoor unit
drain hose
F
PIPING CONNECTIONS
TI
MA
Piping Insulation
Connecting the Indoor Unit Piping to the Field-Installed Piping
1. Center align the indoor unit piping (refrigerant and drain) and the
field-installed piping, then hand tighten the flare nut.
2. Tighten the flare nut with a torque wrench.
3. Attach the drain tube piping to the
indoor unit drain hose as shown.
Figure 43: Extending the Drain Hose.
Note:
If the drain hose is routed inside a room,
add insulation to prevent condensation
from forming.
Figure 42: Indoor Unit to Field-Installed Piping Connection.
Refrigerant Piping System Insulation
All refrigerant piping including Y-branch connections, field-provided isolation ball valves, service valves, and elbows must be completely
insulated using closed cell pipe insulation (up to the indoor unit piping connections). To prevent heat loss/heat gain through the refrigerant
piping, all refrigerant piping including liquid lines and vapor lines must be insulated separately. Insulation must be a minimum 1/2″ thick, and
thickness may need to be increased based on ambient conditions and local codes. Table 26 lists recommended minimum wall thickness
requirements for Ethylene Propylene Diene Methylene (EPDM) insulation.
Installation Manual
Inside the outdoor unit, maximum pipe temperature is 248°F and minimum pipe temperature is -40°F. For field insulation of refrigerant piping
between outdoor units and indoor units, consider the following pipe temperature ranges for an operating heat pump system:
Note:
Follow locals codes when selecting EPDM insulation wall thickness. Thickness in Table 26 is based on heat conductivity of 0.61 Btu/in/h/ft2/°F.
1. Air-conditioned, Typical location
2. Air-conditioned, Special location
3. Non-air conditioned, Typical location
4. Non-air conditioned, Special location (when both conditions listed below are present)
• Heating mode refrigerant temperature ranges: Liquid 75-118°F; High Pressure Vapor 95-220°F
• Cooling mode refrigerant temperature ranges: Liquid 75-118°F; Low Pressure Vapor 40-90°F
Table 26: Insulation Guidelines for Typical and Special Circumstances.
Classication
ø1/4 inches
Liquid pipe
Vapor pipe
• When piping passes through an indoor area where the indoor unit operates, such as an apartment, classroom, ofce, mall, hospital, etc.
• When the location is air conditioned, but has severe temp/humidity difference due to high ceilings, such as a church, auditorium, theater, etc.
• When the location is air conditioned, but internal temperature/humidity are high, such as a bathroom, swimming pool, locker room, etc.
• When piping passes through an indoor area where the indoor unit does not operate, such as a hallway, dormitory, or school, etc.
• When piping passes through an indoor area that is not conditioned
• When the humidity is high and there is no air ow in the location where the piping is installed
ø3/8 inches
≥ø1/2 inches 1/2 inches 1/2 inches 1/2 inches 1/2 inches
ø3/8 inches
ø1/2 inches
ø5/8 inches
ø3/4 inches
1. Typical location 2. Special location 3. Typical location 4. Special location
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Air-conditioned location Non-air conditioned location
1/2 inches 1/2 inches 1/2 inches 1/2 inches
1/2 inches 3/4 inches 3/4 inches 1 inch
35
Page 36

X
MUL
MUL
F
PIPING CONNECTIONS
WARNING
No Clearance
Overlap Insulation Where the
Port and the Piping Meet
Insulation for Indoor Unit Port
(Field Supplied)
Insulation for Refrigerant
Piping (Field Supplied)
Insulation Clip (Field Supplied)
Bands
TI
F
IDU to ODU
Installing Refrigerant Piping Insulation
Ensure all refrigerant piping is insulated. Exposed refrigerant piping may cause burns if touched.
Wrap all refrigerant and condensate piping including field-provided isolation ball valves and flexible pipe connection kits
provided by LG. All pipes must be insulated and each pipe must be separately wrapped. Any exposed piping may generate condensate or will cause burns if touched. Sufficiently insulate all cold surfaces to prevent moisture forming.
Ensure insulation material fits snugly against the refrigeration pipe with no air space between the pipe surface and the
surrounding insulation.
Protect insulation inside hangers and supports with a second insulation layer. Ensure insulation on all pipe passing
through pipe hangers, inside conduit, and/or sleeves is not compressed.
Glue all insulation joints with no air gaps. Be sure insulation material fits snugly against the refrigeration pipe with no air
space between it and the pipe. All pipe insulation exposed to the sun and outdoor elements must be properly protected
with PVC, aluminum vapor barrier, or alternatively placed in a weather-resistant enclosure such as a pipe rack with a top
cover; and must meet local codes. Pay special attention to insulating the pipes installed in a ceiling plenum.
TI
MA
Figure 44: Typical Refrigerant Line Flare Fitting Insulation Detail
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
Figure 45: Insulating the Piping.
1.
Field-supplied
piping
Wide tape
2.
3.
Piping
Drain hose
Narrow tape
Insulation
Wrap with tape
Wrap with tape
Wide tape
Indoor unit
piping
Piping
36
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 37

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
Drain pan
Drain
hose
Drain hose
connection
Check for
leaks
Check for
leaks
Indoor unit
Gradient of at least 1/50~1/100
Clamp the Flexible Drain Hose Connection
Metal clamp
Drain pan
Insulation
Flexible drain hose
Insulation
F
PIPING CONNECTIONS
TI
MA
Drain Piping
Drain Piping
The standard wall-mounted indoor units have a factory-provided flexible pipe (27/32” O.D./ 5/8” I.D.) to drain condensate water. The
flexible pipe connects to field-provided drain pipe. Use materials that comply with local codes for drain pipe and insulation.
1. Install the flexible drain pipe as straight as possible; sharp angles may cause the pipe to deteriorate and may crack over time.
2. Connect the flexible drain pipe with a round clamp. If the flexible drain pipe is not
installed properly, water will leak from the connection.
3. Do not include a reverse slope in the drain connection.
Figure 49: Indoor Unit with Gravity Drain.
Figure 47: Flexible Drain Hose
Connection.
Installation Manual
Drain Slope
Drain hose should point down so water can flow away easily. The
gradient for drain piping should be at least 1/50 to 1/100. Ensure any
holes through ceilings, walls, etc., are large enough to accommodate
both the drain piping and any insulation.
Figure 48: Drain Piping Gradient Recommendation.
Drain Pipe Insulation
Drain piping must have insulation a minimum of 7/32 inches thick.
1. Overlap the insulation at the connection of the field-installed piping and the indoor unit piping. Tape together so that no gaps exist.
2. Secure insulation to the rear piping housing section with vinyl tape.
3. Bundle the piping and drain hose with tape where they meet at the back of the indoor unit frame. Position the drain hose at the bottom of
the bundle (positioning the drain hose at the top of the bundle may cause the drain pan to overflow inside the indoor unit).
Checking the Drainage System
1. Pour water on the indoor unit evaporator. Do not use any other
liquid to test the drain.
2. Ensure the water flows through and out of the hose and away
from the indoor unit without leaking.
Figure 46: Checking the Drainage System.
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
37
Page 38

X
MUL
MUL
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
F
• All power wiring and communication cable installation must be
performed by trained service providers working in accordance with
local, state, and National Electrical Code regulations related to
electrical equipment and wiring, and following the instructions in
this manual. Electric shock can cause physical injury or death.
• Undersized wiring may lead to unacceptable voltage at the unit and
may cause a fire hazard.
• Properly ground the Multi Zone outdoor and indoor units. Ground
wiring must always be installed by a trained technician Ground wiring
is required to prevent accidental electrical shock during current
leakage.
• Do not connect ground wire to refrigerant, gas, or water piping;
to lightning rods; to telephone ground wiring; or to the building
plumbing system. Failure to properly provide a National Electrical
Code-approved earth ground can result in electric shock, physical
injury or death.
• Verify that the branch switch and circuit breaker are set to OFF
before installing the wiring system. Electric shock can cause physical injury or death.
• Install appropriately sized breakers / fuses / overcurrent protection
switches and wiring in accordance with local, state, and National
Electrical Code regulations related to electrical equipment and wiring, and following the instructions in this manual. Using an oversized breaker or fuse may result in electric shock, physical injury or
death.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
TI
• Consider ambient conditions (temperature, direct sunlight, inclement weather, etc.) when selecting, installing, and connecting the
power wiring.
• Properly ground the Multi Zone outdoor and indoor unit. Improperly
grounded wire can cause communication problems from electrical
noise, and motor current leakage. Ground wiring must always be
installed by a trained technician.
• If the system operates in reversed phase, it may damage the compressors and other components.
• If there is a possibility of reversed phase, phase loss, momentary
blackout, or the power goes on and off while the system is
operating, install a field-supplied phase loss protection circuit.
• Do not connect ground wire to refrigerant, gas, or water piping;
to lightning rods; to telephone ground wiring; or to the building
plumbing system. Failure to properly provide a National Electrical
Code-approved earth ground can result in property damage and
equipment malfunction.
• Install appropriately sized breakers / fuses / overcurrent protection
switches and wiring in accordance with local, state, and National
Electrical Code regulations related to electrical equipment and
wiring, and following the instructions in this manual. Using an
oversized breaker or fuse may result in equipment malfunction and
property damage.
• Use only copper wiring that is stranded and shielded with the wires
separately insulated.
• Do not use a multi-conductor cable with more than five (5)
wires in one (1) core.
• Power wiring and communications cable sizes must comply with
applicable federal UL / ETL, state, and local codes.
• Do not operate the air conditioning system until the refrigerant
piping installation is complete. Operating the system before refrigerant piping is finalized may damage the compressor.
• Install a ground wire for the outdoor units, indoor units, and branch
distribution units.
• Install a main shutoff switch or circuit breaker that interrupts all
power sources simultaneously (circuit breaker should be resistant
to electromagnetic currents).
• Use ring terminals to attach the wiring. Verify that all power wiring
and communications cable terminals are securely attached. Ensure
enough slack is included in the wiring and cables to avoid damaging the connections.
• Use a conduit to protect the power wiring.
MA
38
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 39

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
Power Wiring
:Copper Wire
Terminate multiple power wires of
the same gauge to both sides.
Do not terminate two wires on
one side.
Do not terminate different gauge
wires to a terminal block.
GN/YL
13/16 inch
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
MA
Power Wiring Specications and Best Practices
Line Voltage Wiring and Communications Cable Installation
For both Multi F and Multi F MAX systems, line voltage is wired to the outdoor unit only. The outdoor unit will supply power to the
branch distribution units (Multi F MAX systems only) and the indoor units through the power wiring/communications cable.
Electrical Specifications
1. Multi F and Multi F MAX Outdoor Units: 1Ø, 208-230V, 60Hz
2. Indoor units/Branch Distribution Units (Multi F MAX systems only): 1Ø, 208-230V, 60Hz from ODU (Indoor units draw minimal power.)
3. Select power supply wire type and size based on NEC and local codes. Maximum voltage uctuation ±10% of the nameplate rated value.
4. Properly ground the outdoor unit per NEC and/or local code.
5. Use only copper wiring that is stranded and shielded with the wires separately insulated.
Power Wiring/Communications Cable Specications
• From Multi F Outdoor Units to Indoor Units = 4 x 18AWG
• From Multi F MAX Outdoor Units to Branch Distribution Units = 4 x 16AWG
• From Multi F MAX Branch Distribution Units to Indoor Units = 4 x 18AWG
• Maximum Allowable Temperature for Wiring: 194°F
• Indoor Unit(s) to Wired Controller: Three-core cable
• Multi F System Maximum Cable Length: 82 ft.
• Multi F MAX System Maximum Cable Length:
- Outdoor Unit to Branch Distribution Unit(s): 180.4 ft.
- Branch Distribution Unit(s) to Indoor Unit(s): 49.2 ft.
Figure 52: Power Wiring and Communica-
tions Cable from the Multi F ODU to the
IDUs, or from the Multi F MAX ODU to the
BDUs and from the BD Unit to the IDUs.
Installation Manual
Figure 50: Close up of a Typical Ring Terminal
Ring Terminal
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Figure 51: Proper and Improper Power Wiring Connections
39
Page 40

X
MUL
MUL
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
F
Power Wiring Specications and Best Practices/Controller Options
Power Supply/Power Wiring Specifications, continued
• If power wires are not properly terminated and firmly attached, there is risk of fire, electric shock, and physical injury or death.
TI
MA
Note:
• Never apply line voltage power to the communications cable terminal block. If contact is made, the PCBs may be damaged.
• Always include some allowance in the wiring length when terminating. Provide some slack to facilitate removing the electrical
panels while servicing.
• Never ground the shield of the communications cable to the indoor unit frame or other grounded entities of the building. Ground
the communications cable shield only at the outdoor unit. Improperly grounding this cable can cause communications errors.
General Power/Communication Cable Specifications
• Use a four (4) conductor, shielded, stranded cable between the
Multi Zone outdoor unit and the indoor units.
• Minimum 18 gauge shielded CVVS or CPEVS cable.
• Insulation material as required by local code.
• Rated for continuous exposure of temperatures up to 140°F.
Note:
• Always verify the communication cable is connected to a communications terminal on the Multi Zone unit. Never apply line voltage
power to the communication cable connection. If contact is made, the circuit boards may be damaged.
• The shield of the communications cable connecting the outdoor unit to the indoor unit should be grounded only to the outdoor unit frame.
• Tie the shield of each cable segment together using a wire nut at each indoor unit. Maintain polarity throughout the communication network.
• Position the 4-conductor ODU/IDU communications and power cable away from the input line voltage wiring.
• Maximum allowable cable length: 984 feet.
• Firmly attach the cable; provide slack but secure in a way to prevent external forces from being imparted on the terminal block.
• Wiring should be completed without splices.
• Terminate the cable shield to a grounded surface at the outdoor
unit only.
Communication Cables Between the Wall Indoor Unit and the Controller
• Simple Controllers: eld-provided, 18 gauge, stranded and shielded, four-conductor communication cable.
• All other Central Controllers: eld-provided, 18 gauge, stranded and shielded, two-conductor communication cable.
• Insulation material as recommended by local code.
• Connect all central control devices such as ACP, BACnet® and LonWorks® gateways, and energy recovery ventilators all on the same cable.
Order does not matter. Polarity does. Keep “A” terminals with “A” terminals, and “B” terminals with “B” terminals.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
• Starting at the outdoor unit, terminate the cable on terminals Internet A and Internet B. Route the cable as needed between each device.
Controller Options
Refer to Table 19 as to which remote controller model is used for each IDU. Once all wiring is connected to the indoor and outdoor units be
sure to test the accompanying remote controllers for performance. As always, follow all safety warnings and notes when operating the units
using the remote controller. Additionally, all of the Multi F/Multi F Max outdoor models can use the following controllers when accompanied
with the PI 485 VNet Accessory:
• AC Smart
• ACP
• BACnet®
• LonWorks®
• LGMV
Table 27: IDU Models and Associated Wireless Controller Model
Multi Zone IDU Model Wireless Controller Model
LSNXXXHSV4 AKB73835312
LMNXX8HVT AKB73635606
BACnet® is a registered trademark of ASHRAE. LonWorks® is a registered trademark of Echelon Corporation.
40
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 41

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
Terminal block
Power wiring /
communications cable
Wired Remote Controlle
r
Terminal (Optional)
Cable restraint
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
MA
Indoor Unit Electrical Connections Guidelines
Power Wiring / Communications Cable Guidelines
• These instructions are for the IDU only. For ODU wiring, refer to the ODU installation manual.
• Conrm power source specications.
• Conrm that the electrical capacity is sufcient.
• Starting current must be maintained ±10 percent of the rated current marked on the outdoor unit name plate.
• Conrm cable thickness specications.
• It is recommended that a circuit breaker is installed, especially if conditions could become wet or moist.
• Include a disconnect in the power wiring system. Add an air gap contact separation of at least 1/8 inch in each active (phase) conductor.
• A voltage drop may cause the following problems:
1. Magnetic switch vibration, fuse breaks, or disturbance to the
normal function of an overload protection device.
2. Compressor will not receive the proper starting current.
The general guidelines for connecting electrical and communication
cables are similar for all standard wall-mounted indoor units; however, the connections on the terminal block may differ. Depending
on your indoor unit, the location of the terminal block on the indoor
unit might vary from these typical images. Figure 53 shows typical
connections.
Figure 53: Typical IDU Power and Communications
Cable Connections
Installation Manual
The electrical connections procedure includes wiring diagrams for
each type of standard wall-mounted indoor unit.
IDU Electrical Connections Procedure
• Be sure that main power to the unit is completely off before
beginning this procedure. Electric shock can cause severe physical
injury or death.
• Follow all safety and warning information outlined at the beginning
and throughout this manual. Failure to do so may cause bodily injury
or death.
Note:
• Follow all safety and warning information outlined at the beginning
and throughout this manual. Failure to do so may cause unit failure.
• Some units might require you to remove the Control Cover from
the terminal block area. Most Control Covers are attached with a
phillips screw.
• Connect the electrical cable to the indoor unit by connecting the
wires to the terminals on the control board individually according to
the outdoor unit connection. Be sure that the color of the wires at
the outdoor unit and the terminal numbers are the same as those
for the indoor unit.
• Loose wiring may cause unit malfunction, or the terminal to overheat
and catch re. Terminal screws may become loose during transport.
Properly tighten the terminal connections during installation.
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
41
Page 42

X
MUL
MUL
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
F
Indoor Unit Electrical Connections Procedure
Be sure there is no power input to the system before proceeding with
these connections. There is risk of electrical shock resulting in serious
bodily injury or death.
1. At the bottom panel of the indoor unit, unsnap the latches cover-
ing the phillips head screws (Figure 54).
• Normally, there are three (3) screws on the panel, however, your
indoor unit model may be different.
2. Using a phillips head screwdriver, remove the screws from the
bottom panel of the indoor unit and set aside (Figure 55).
3. Remove the bottom panel (Figure 56).
• Removal is necessary to gain access to the terminal block
located at the bottom of most indoor units.
4. Route the electrical/communications wiring through the back/bottom of the indoor unit (through a knockout panel, Figure 57).
5. Using a screwdriver, connect the wires as shown in Figure 58 and
Figure 59. Also refer to the appropriate wiring diagram for the IDU
(Figure 60 through Figure 63).
• Each wire should be securely attached to the terminal block.
• Ensure the green/yellow ground cable is securely connected to
the correct screw terminal.
6. When done, reattach the bottom panel to the indoor unit, being
careful to align panel using the rear tabs.
• You might need to give the panel a gentle tap with the palm of your
hand to be sure it engages at the bottom.
7. Using a phillips screwdriver, reattach the screws to the bottom
panel and secure.
8. Once screws are in place, re-snap the latches over the screws.
9. If all other piping and electrical wiring to the outdoor unit has
been completed, you can turn the system on to test.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
• If you have not completed the piping connections, do not turn
power on at this time. Be sure to complete all other piping,
(including the drain hose) and wiring to the system.
TI
Figure 54: Latch over Screws on Bottom Panel, Indoor Unit
Figure 55: Remove Screws from Bottom Panel
Figure 57: Indoor Unit Knockout (Communication Wires)
MA
Figure 56: Removal (and Reattachment) of Bottom Panel
42
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 43

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
090HSV4,120HSV4,
180HSV4
GRN / YLW
GRN / YLW
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
Figure 58: Typical Indoor Unit Terminal Block with Grounding Cable
MA
Indoor Unit Electrical Connections
Figure 59: Typical Indoor Unit Terminal Block Connections
Terminal Block
Expanded View
Grounding
Cable
Terminal Block
Connecting Cables
Cable Restrainer
Installation Manual
Figure 60: Indoor Unit to Outdoor Unit / Branch Distribution Unit Terminal
Connections—LMN078HVT, LSN090HSV4, LSN120HSV4, and LMN158HVT.
Indoor Unit Terminal Block
GND
1(L1 )2(L2)
Figure 61: Indoor Unit to Outdoor Unit / Branch Distribution Unit Terminal
GND
Branch Distribution Unit Terminal Block or
Outdoor Unit Terminal Block
BDU:
3
BL
BR
Connections—LSN180HSV4 and LMN248HVT.
Indoor Unit Terminal Block
1(L1 )2(L2)
BR
BL
RD
3
RD
ODU:
Branch Distribution Unit Terminal Block or
Outdoor Unit Terminal Block
BDU:
ODU:
S N L
3 or S
GND
S N L
3 or S
GND
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
43
Page 44

X
MUL
MUL
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
F
Self Diagnosis Functions
TI
MA
LG Monitoring View (LGMV) Diagnostic Software
LGMV software (PRCTSL1 and PRCTFE1) allows the service technician or commissioning agent to connect a computer USB port to the
outdoor unit’s main printed circuit board (PCB) using an accessory cable. The monitoring screen for LGMV allows the user to view the
following real time data on one screen (Figure 62):
• Actual inverter compressor speed
• Target inverter compressor speed
• Actual outdoor fan speed
• Target outdoor unit fan speed
• Actual superheat
• Target superheat
• Actual subcooler circuit superheat
• Target subcooler circuit superheat
• Main EEV position
• Subcooling EEV position
• Inverter compressor current transducer
value
• Outdoor air temperature
• Actual high pressure/saturation
temperature
• Actual low pressure/saturation
temperature
• Suction temperature
• Inverter compressor discharge
temperature
• Front outdoor coil pipe temperature
• Back outdoor coil pipe temperature
• Liquid line pipe temperature
• Subcooler inlet temperature
• Subcooler outlet temperature
• Average indoor
unit (IDU) pipe
temperature
• Inverter compressor operation
indicator light
• Liquid injection
valves’ operation
indicator lights
• Hot gas bypass
valve operation
indicator light
• Four-way
reversing valve
operation
indicator light
• Pressure graph showing actual low
pressure and high pressure levels
• Error code display
• Operating mode indicator
• Target high pressure
• Target low pressure
• Printed circuit board (PCB) version
• Software version
• Installer name
• Model number of IDUs
Figure 62: MV Real-time Data Screen
• Site name
• Total number of connected IDUs
• Communication indicators
• IDU capacity
• IDU operating mode
• IDU fan speed
• IDU EEV position
• IDU room temperature
• IDU inlet pipe temperature
• IDU outlet pipe temperature
• IDU error code
Note:
Images on these pages are examples of LGMV screenshots. Actual images
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
may differ depending on the version of the software and the unit installed.
Additional screens can be accessed by tabs on the main screen.
Additional screens include the following:
1. Cycleview (Figure 63): Graphic of internal components including:
• Compressors showing actual speeds
• EEVs
• IDUs
• Temperature and pressure sensors
• Four-way reversing valve
2. Graph: Full screen graph of actual high and low pressures and high
and low pressure limits. A sliding bar enables user to go back in
time and view data.
3. Control FTN: Enables user to turn on IDUs in 1.8°F increments.
4. Useful Tab
• Unit Conversion: Converts metric values to imperial values.
44
Figure 63: MV Cycleview
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 45

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
LG Monitoring View (LGMV) Diagnostic Software and Cable - Continued
5. Data
• Data Saving Start: Recording of real time data to a separate le created to be
stored on the user’s computer.
• Data Loading Start: Recorded data from a saved “.CSV” le can be loaded to
create an LGMV session.
6. Monitoring
• Electrical: The lower half of main screen is changed to show Inverter
Compressor Amps, Volts, Power Hz, Inverter control board fan Hz.
MA
Note:
Images on these pages are examples of LGMV screenshots. Actual images
may differ depending on the version of the software and the unit installed.
Error Codes
LGMV software helps the service technician or commissioning agent
to troubleshoot system operation issues by displaying error codes
(Figure 65). These error codes can be seen on the main screen of
the LGMV software program. For an overview of unit error codes,
see Troubleshooting using Error Codes. For detailed information on
how to troubleshoot individual error codes, see the unit’s service
manual.
Self Diagnosis Functions
Figure 64: MV Control Indoor Units Screen
Installation Manual
Figure 65: Error Code Screen
The software is available in a high version with all of the listed
features The low version has all features as the high version without
Target High Pressure and Target Low Pressure values shown on
main screen.
Instead of connecting to the outdoor unit, there is the option to
connect to an IDU with a USB to RS-485 connector kit. When
connected through an IDU, data recording is not available.
This software can be used to both commission new systems and
troubleshoot existing systems. LGMV data can be recorded to a
“.CSV” file and emailed to an LG representative to assist with
diagnostic evaluations.
Recommended Minimum PC Configuration:
®
• CPU: Pentium
• Main Memory: 1G
• Operating System: Windows® XP/Vista/7 32 bit (recommended), 64 bit
• Hard Disk: 600 MB when operating
• MS Ofce 2003, 2007 (recommended) for select reporting functions
IV 1.6 GHz
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
45
Page 46

X
MUL
MUL
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
F
LG SIMS - Self Diagnosis Functions
The SIMs WLAN module and the smart phone app together provide monitoring and troubleshooting
capability for LG Duct Free Systems. SIMs functions only with LG Duct Free products (Figure 66).
SIMs can display and graph operational data for the air conditioner system including the indoor unit
and the outdoor unit. SIMs also displays error codes and a troubleshooting guide. A full copy of
the LG SIMs Smart Inverter Monitoring System User’s Manual is available on the www.lghvac.com
website.
To use SIMs you must be a trained HVAC service technician familiar with variable refrigerant
flow (VRF) systems in general and with LG’s Duct Free System products. You should understand the inverter air conditioning operation cycle, the meaning of the data displayed by SIMs,
and how to use the data to troubleshoot the system.
Figure 67 shows a typical Multi F configuration used with the SIMs module and app.
High voltages capable of causing death are used in
this equipment. Outdoor unit power remains connected
during this procedure. Take extreme caution not to
touch electrical components or connections. Failure to
observe this warning can result in death or severe injury.
Figure 67: SIMs WLAN Module to a Typical Multi F System
TI
Figure 66: LG SIMs App and WLAN Module
MA
Note:
• The Duct Free System air conditioning system must run for
at least 15–20 minutes before data collected by SIMs 2.0 is
valid for troubleshooting.
• You must have the free SIMs app correctly installed on your
smart phone before using SIMs.
• Some ODUs have an LGMV extension cable accessed by
removing the side handle cover. If the ODU does not have
this extension cable, access the LGMV connector by removing the top cover of the ODU.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
SIMs App Main Info Screen
The main screen (Figure 68) is the first screen displayed after wireless
connection is established. Tap the Main Info tab to display current readings regarding your indoor and outdoor unit(s). The Operational Info area
of the screen will show active functions or modes by illuminating the light
to the right of the function.
Additional Help information can be accessed by tapping the Help Menu
buttons at the bottom of this screen.
LG SIMs App
on Smart Phone
Operational
Information
AC Cycle
Information on
Main Info Tab
LG SIMs
WLAN Module
Figure 68: SIMs App Main Info Screen
46
Help Menu
(File is Factory Use Only)
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 47

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
MA
SIMs App Screens
Outdoor Info/
Component Screen
Displays the following
information:
• Frequency
• FAN1 RPM
• FAN2 RPM
• DC Link
• Current
• Voltage
• EEV Mode
• Restart Timer
• Comp Mode
• EEV
LG SIMS - Self Diagnosis Functions
Outdoor Info/
Temperature Screen
Displays the following
information:
• Inv TD
• Suction
• Discharge
• Cond Mid
• Cond Out
• Heatsink
• Air Temp
Installation Manual
Indoor Info Tab
Displays the following
information:
• Frequency
• Operation
• THM Mode
• REM Mode
• FAN
• EEV
• Air Temp
• Pipe-in
• Pipe-mid
• Pipe-out
Graph Info Tab
This tab has three sub
sections:
• IDU - Indoor Unit
Temperature graph.
Displays IDU
information in graph
format. Information
displayed is for the
IDU # selected on
the Main screen.
• ODU - Outdoor Unit
Temperature and
Frequency graph.
Displays ODU
information in graph
format.
• ODU Electric
- Outdoor Unit
Electric data graph
is displayed.
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
47
Page 48

X
MUL
MUL
F
ELECTRICAL WIRING
TI
F
Optional Wall-Mounted Sensor and Controller
TI
Wall-Mounted Sensor Installation
Proper indoor unit operation depends on the location of the room sensor. A good location will protect the zone controller from direct sunlight
and external local sources of water vapor, and heated or cooled air. If no mounting height was specified by the building designer, place the
handy box approximately five feet above the finished floor.
• It may be necessary to use a handy box that is sized in metric units, depending on the controller model. Check with your LG representative
to verify which size of handy box is needed for the zone controller in question.
• Use only LG-supplied communications cable. Using eld-supplied cable may result in communications problems between the zone controller and the indoor unit.
Do not route power wiring and communications cables in the same conduit.
Do not cut the quick-connect plugs off or adjust the length of the cable. Keep the communications cable away from high voltage wires
and electromagnetic field (EMF) producing equipment.
Wall-Mounted Controller Installation
Since the room temperature sensor is inside the remote controller, the remote controller should be installed in a place away from direct sunlight, high humidity and direct supply of hot or cold air to maintain proper space temperature. Install the remote controller about 5 ft above
the floor in an area with good air circulation and an average temperature.
Do not install the remote controller where it can be affected by the following:
• Drafts or dead spots behind doors and in corners
• Hot or cold air from ducts
• Radiant heat from sun or appliances
• Concealed pipes and chimneys
• Uncontrolled areas such as an outside wall behind the remote controller
This remote controller is equipped with a seven segment LED display. For proper
display of the remote controller LED’s, the remote controller should be installed
properly as shown below. The standard height is 4 - 5 ft from floor level.
1. Pull communications cable between the zone controller handy box (if used) and
the indoor unit. The wall-mounted zone controller comes with a thirty (33) foot
length of cable.
2. Store a minimal amount of cable in the handy box. Any additional cable should be
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
coiled and stored near the indoor unit control panel.
3. If additional cable length is needed, order a thirty (33) foot LG Wired Remote
Group Control Extension cable (Model No. PZCWRC1).
4. If the cable between the zone controller and the indoor unit is too long, do not cut the cable and shorten. Coil any spare communications
cable, tie-wrap it, and leave it next to the indoor unit location.
Figure 69: Wired Remote Controller Installation
yes
Remote Controller
5ft
TEMP
no
Rem
no
TEMP
Remote Controller
no
TEMP
ote Controller
MA
48
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 49

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
TROUBLESHOOTING
TI
MA
Troubleshooting Using Error Codes
Refer to Table 28 for information on error codes generated from the
indoor and outdoor units. These codes are the most common for
these units. Your particular model duct free system might generate
additional codes not listed here. Please contact LG Support if you
see these types of errors and a simple power down and boot up has
not corrected the issue. You should not attempt to repair the system
yourself.
Error Codes
• Figure 70 shows typical indoor unit LEDs used for error code
display.
• Indicate different types of unit failures, assists in self-diagnosis
and to track the frequency of occurrence.
• Error codes are shown on the LEDs of indoor units, wired remote controller, the unit control board, and LG Monitoring View
(LGMV) Diagnostic Software.
• If two or more errors occur simultaneously, the lower error code
number is displayed rst.
• After the error is resolved, the error code does not display.
Error Codes
Decoding the Error Display
The first and second number on the LED indicates error number.
Example: 21 = LED1 (Green light) 2x blink, LED2 (Red light) 1x blink
Error Code Nomenclature Definitions
• MICOM: Non-volatile memory chip where unit setup information
is stored.
• EPROM: Non-volatile memory chip where device identication,
size, and factory dened default component operating parameters are stored.
Installation Manual
Figure 70: Typical Indoor Unit LEDs for Error Code Display
Cooling
LED 1
Heating
LED 2
Preheating
Table 28: Multi Zone Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit Error Codes
Number of Times Indoor Unit
Error
Code
1 Indoor unit room temperature sensor error
2 Indoor unit inlet pipe sensor error - 2X
4 Float switch error (optional) - 4X
5 Communication error between indoor unit and outdoor units - 5X
6 Indoor unit outlet pipe sensor error - 6X
9 Indoor unit EPROM error - 9X
10 Indoor unit BLDC motor fan lock 1X 12 Indoor unit middle pipe sensor error 1X 2X
Description
LED 2
(Heating LED)
- 1X
LEDs Blink
LED 1
(Cooling LED)
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
49
Page 50

X
MUL
MUL
F
CAUTIONS FOR REFRIGERANT LEAKS
TI
F
Refrigerant Leaks
TI
MA
Cautions for Refrigerant Leaks
ASHRAE Standards 15-2010 and 34-2010 offer guidelines that address refrigerant safety and the maximum allowable concentration of refrigerant in an occupied space. Refrigerant will dissipate into the atmosphere, but a certain volume of air is required for this to occur safely. For
R410A refrigerant, the maximum allowable concentration is 0.026 lbs./ft3 per 1,000 ft3 of air in an occupied space. Buildings with twenty-four
(24) hour occupancy allow half of that concentration.
ASHRAE Standards 15 and 34 assume that if a system develops a leak, its entire refrigerant charge will dump into the area where the leak
occurs. To meet ASHRAE Standards 15 and 34, calculate the refrigerant concentration that may occur in the smallest room volume on
the system, and compare the results to the maximum allowable concentration number (see below for information on how to calculate the
refrigerant concentration).1 Also consult state and local codes in regards to refrigerant safety.
Verify the maximum refrigerant concentration level in the space where the indoor unit will be mounted meets the concentration limit for the
application. If the refrigerant leaks and safety limits are exceeded, it could result in personal injuries or death from oxygen depletion.
Take appropriate actions at the end of HVAC equipment life to recover, recycle, reclaim or destroy R410A refrigerant according to applicable
US EPA rules.
To calculate the potential refrigerant concentration level (RCL):
1. Measure the occupied space dimensions (in feet).
2. Calculate the cubic foot volume of air in the smallest occupied
space. (To obtain a detailed overview of the RCL, perform the
same calculations to the second smallest zone, the third smallest zone until the RCL is obtained for all zones. Also, pay special
attention to areas such as basements, etc., where refrigerant
cannot dissipate easily.)
1
Refrigerant Concentration Limit (RCL) Calculations
To calculate total refrigerant amount per system:
Amount of
Factory-Charged
Refrigerant per
Outdoor Unit
RCL (lbs./ft3) =
Amount of
+ =
Additional Refrigerant Trim
Charge
Total System Refrigerant Charge (lbs.)
Volume of Smallest Occupied Space (ft
Total System
Refrigerant
Charge
3
)
3. Divide the refrigerant charge of the system serving the area in
pounds by the results of step 1.
4. If the calculation indicates that the potential refrigerant concen-
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
tration level is higher than the allowed RCL, increase the cubic
volume of the smallest occupied space or modify the piping
system design.
5. The allowable RCL limit for most applications must be equal to
or less than 0.026 lbs./ft
such as hospitals and nursing homes where occupants may have
limited mobility, the allowable RCL limit is cut in half. See ASHRAE
Standard 34-2007 and local codes for detailed information.
1
American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (ASHRAE). Atlanta, GA. ASHRAE, Inc. Information about
ASHRAE Standard 15-2010 / 34-2010 and addenda current as of the
date of this publication.
50
3
. In special occupied spaces, however,
1
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 51

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
INSTALLATION CHECKLIST
TI
System ID No.: _________________________________________________ Indoor Unit ID.: ____________________________________
Checked by: __________________________________ Date:__________________ Signature: ___________________________________
MA
PAGE 1 of 2
Major Component Rough-In
Description Check
The unit was connected properly per local code and the product installation procedures.
All literature and bagged accessories have been removed from the fan discharge.
Indoor unit was installed, properly supported, and located indoors in a non-corrosive environment.
The unit’s gravity condensate drain line was connected and routed where it properly drains away or, if installed in a
mechanical room, was connected and properly routed to a drain terminal.
Piping and Insulation
Description Check
Copper
Over 5/8 inches—Rigid ACR only.
5/8 inches and under—Can use soft ACR.
15% silver brazing material only.
All refrigerant pipes and valves were insulated separately. Insulation butts up against the walls of the indoor units. No gaps or
cracks. Insulation was not compressed at clamps and hangers.
LG Y-branches were used per manufacturer’s recommendations.
(Optional) Full port ball valves for all indoor units. (Schrader between the valve body and the indoor units)
Condensate piping installed on indoor unit (1” ID, 1-1/4” OD). Pipe is insulated to prevent condensation. Pipe material is
acceptable under local code.
Installation Manual
Brazing Practices
Description Check
Medical grade (there are 4 available) dry nitrogen used for purging during brazing (constant 3 psi while brazing).
Installation
(For more information on any procedure, refer to the detail provided in the installation section.)
Refrigerant Piping
Description Check
Have in possession a copy of the “As-Designed” LATS Multi V piping tree diagram. BEFORE ANY FIELD PIPE SIZE OR LENGTH
CHANGES ARE MADE, PROPOSED CHANGES MUST BE FORWARDED TO THE DESIGN ENGINEER SO THAT THEY CAN
INPUT THE CHANGES INTO LATS and RE-ISSUE A NEW LATS PIPING TREE DIAGRAM. Installer must receive change authorization from the design engineer, because any change made requires the review of the entire tree diagram and verification that the
change did not impact the size of piping segments in other parts of the system.
All pipe materials were properly stored, capped, and clean. All burrs were removed after cutting and pipe ends were reamed
before brazing.
During refrigerant pipe installation, for each segment of pipe, a record was made of the pipe length (including expansion loops,
offsets, double-back sections), and sizes, as well as the quantity and type of elbows used.
All long runs of straight pipe were provided with expansion loops.
Ensure horizontal Y-branches are installed with no more than ±5° of rotation from horizontal plane.
Ensure vertical Y-branches are installed within ±3° of vertical.
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
51
Page 52

X
MUL
MUL
F
INSTALLATION CHECKLIST
TI
F
TI
PAGE 2 of 2
System ID No.: _________________________________________________ Indoor Unit ID.: ____________________________________
Checked by: __________________________________ Date:__________________ Signature: ___________________________________
MA
Refrigerant Piping – continued
A torque wrench and backup wrench were used to tighten all flare connections.
The back side of all flares were lubricated with a small drop of PVE refrigeration oil before tightening flare fittings.
Ensure all field made flares are 45°. Use LG-supplied flare nuts only.
Pipe segments were properly supported and all wall penetrations were sleeved.
Pipe insulation was not compressed at any point.
Y-branches were properly supported per details provided in the installation manual.
Ensure Y-branches are installed in the correct direction. Flow is always from the single end to the double end.
No oil traps, solenoid valves, sight glasses, filter driers, or any other unauthorized refrigerant specialties were present.
(Optional) High quality R410A rated full port ball valves with a Schrader port were used at all indoor units and at will in the
refrigerant piping network. (Recommended for serviceability.)
Best practice of installing a minimum of 20″ of straight pipe between each elbow was followed.
Condensate Pump / Drain Installation
Description Check
Indoor unit condensate drain pipes were installed correctly.
All condensate vertical risers are equal to or less than 27-1/2″ from the bottom of the indoor unit.
Indoor units with condensate pumps were level. Units with gravity drains were level or slightly canted toward the drain connection
and are supported properly.
Pumped condensate drain lines were properly connected (no traps, and connect to the top surface of the main drain line).
Power Wire and Communications Cables
Description Check
Power wiring was connected to a single phase 208-230V source.
Multi F Standard Wall-Mounted Indoor Unit
Ground wire was installed and properly terminated at the unit.
The power supplied was clean with voltage fluctuations within specifications. (±10% of nameplate).
Power wiring to the Multi F/Multi F MAX outdoor unit was installed per all local electrical code requirements.
Power wiring to the indoor unit and branch distribution unit (if used) was installed per all local electrical code requirements.
Power and communications cable between the Multi F/Multi F MAX outdoor unit and each indoor unit/branch distrubution unit
(Multi F MAX only) was connected . No “star” or multiple parallel circuits. No cable splices or wire caps were used to connect
communications cables.
LG-supplied cable was used between the indoor unit and its zone controller. No cables spliced and no wire caps used.
Communication type RS-485–BUS type.
IDU communications/power wiring was a minimum of 18-AWG, four (4) conductor, stranded, shielded or unshielded, with insula-
tion material per local code. If shielded, must be grounded to outdoor unit only. Cable segment shields were tied together.
Used appropriate crimping tool to attach ring or spade terminals at all power wiring and control cable terminations.
Verify all ring and spade terminals are copper bearing in all communications daisy chains. Galvanized or nickel plated steel connectors were not used.
ODU to IDU power and control wires (only) were run in the same conduit as provided in the product installation manual. 208-230V
ODU input power was not run in same conduit as power and control wires to IDU, and was separated per manufacturer’s guidelines.
All power and control wires were properly separated using the recommended distance provided in the product installation manual.
52
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
Page 53

X
MUL
TI
MUL
F
F
TI
MA
For further technical materials such as submittals, engineering
manuals, service manuals, and catalogs, visit www.lghvac.com.
Installation Manual
Who to call for assistance
Freight Damage and Unit Replacements Your LG Manufacturer Representative
Missing Parts Your LG Manufacturer Representative
Freight Damage and Unit Replacements Your LG Manufacturer Representative
Received Wrong Indoor Unit Model Your LG Manufacturer Representative
Installation, Startup, and Commissioning Technical Assistance 1-888-865-3026
For warranty information, visit www.lghvac.com.
Due to our policy of continuous product innovation, some specifications may change without notification.
©LG Electronics U.S.A., Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ. All rights reserved. “LG” is a registered trademark of LG Corp.
53
Page 54

LG Electronics
20001747 ISO 9001: 2008
LG ELECTRONICS INC.
Commercial Air Conditioning Division
11405 Old Roswell Road
Alpharetta, Georgia 30009
www.lghvac.com
LG Customer Information Center, Commercial Products
1-888-865-3026 USA
Follow the prompts for commercial A/C products and parts.
IM_MultiF_StdWallMount_11_15
Supercedes: IM-Multi-F_StdWallMount-03-15
 Loading...
Loading...