Page 1

DVD /CD Rewri table D rive
S E RVICE MANUAL
MODEL: G WA - 4 1 6 4 B /
G WA - 4 1 6 6 B /
G S A - 4 1 6 6 B
P/NO : 3828HS1049D
J u l y, 2005
Printed in Korea
MODEL : GWA-4164B/GWA-4166B/GSA-4166B
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................................................................3
FEATURES................................................................................................................................................................................4
SPECIFICATIONS...............................................................................................................................................................5~14
LOCATION OF CUSTOMER CONTROLS .......................................................................................................................15~16
DISASSEMBLY.................................................................................................................................................................17~18
1. CABINET and CIRCUIT BOARD DISASSEMBLY..........................................................................................................17
2. MECHANISM ASSY DISASSEMBLY..............................................................................................................................17
EXPLODED VIEW.............................................................................................................................................................19~20
MECHANICAL REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST ................................................................................................................21~23
GLOSSARY.............................................................................................................................................................................24
THE DIFFERENCES OF CD-R/CD-RW DISCS AND GENERAL CD-ROM.....................................................................25~29
1. Recording Layer..............................................................................................................................................................25
2. Disc Specification............................................................................................................................................................25
3. Disc Materials..................................................................................................................................................................26
4. Reading Process of Optical Disc.....................................................................................................................................27
5. Writing Process of CD-R Disc .........................................................................................................................................28
6. Writing Process of CD-RW Disc......................................................................................................................................28
7. Organization of the PCA, PMA and Lead-in Area ...........................................................................................................29
8. Function of PCA and PMA area ......................................................................................................................................30
9. OPC and ROPC ..............................................................................................................................................................30
10. Writing Process of DISC................................................................................................................................................31
THE DIFFERENCES OF DVD-R/RW, DVD+R/RW DISCS AND DVD-ROM....................................................................32~40
1. Recording Layer..............................................................................................................................................................32
2. Disc Specification............................................................................................................................................................33
3. Disc Materials..................................................................................................................................................................33
4. Writing Pulse Waveform of DVD+R.................................................................................................................................36
5. Writing Pulse Waveform DVD+RW.................................................................................................................................38
6. Organization of Inner Drive Area, Outer Drive Area, Lead-in Zone and Lead-out Zone .................................................39
LightScribe MEDIA...........................................................................................................................................................41~44
1. LightScribe Media............................................................................................................................................................41
2. Hardware Block Diagram of LightScribe Label Printing...................................................................................................42
3. MD Assy For LightScribe.................................................................................................................................................43
4. Optical Encoder Assy......................................................................................................................................................44
DVD & CD DATA PROCESSING......................................................................................................................................45~48
1. Data Processing Flow......................................................................................................................................................45
2. Copy Protection and Regional Code Management Block ...............................................................................................46
3. About Prevention the DVD-ROm from to be copy...........................................................................................................47
4. About the DVD-ROM Regional Code..............................................................................................................................48
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE PICK-UP....................................................................................................................49~51
1. Block Diagram of the Pick-up..........................................................................................................................................49
2. Pick up Pin Assignment...................................................................................................................................................50
3. Signal detection of the P/U..............................................................................................................................................51
DESCRIPTION OF CIRCUIT.............................................................................................................................................52~56
1. ALPC Circuit....................................................................................................................................................................52
2. Focus/Tracking/Sled Servo Circuit..................................................................................................................................53
3. Spindle Circuit .................................................................................................................................................................55
MAJOR IC INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM AND PIN DESCRIPTION.............................................................................57~74
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE..........................................................................................................................................75~91
BLOCK DIAGRAM............................................................................................................................................................92~94
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM..........................................................................................................................................................95~97
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD DIAGRAM.........................................................................................................................98~101
ELECTRICAL REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST......................................................................................................................102
CAUTION - INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN AVOID EXPOSURE TO BEAM.
Page 3
3
INTRODUCTION
GSA-4164B series Design Specfications
This service manual provides a variety of service
information.
I
t contains the mechanical structure of the DVD/CD
Rewritable Drive and the electronic circuits in
schematic form. This DVD/CD Rewritable Drive was
manufactured and assembled under our strict quality
control standards and meets or exceeds industry
specifications and standards.
This DVD/CD Rewritable drive is an internal drive
unit designed for use with IBM PC, HP Vectra, or
compatible computer. It can write as much as 700
Mbytes of digital data into CD-R/RW disc, and can
read as much as 700 Mbytes of digital data stored
in a CD-ROM, CD-R and CD-RW disc.
It can write as much as 4.7Gbytes of digital data
into DVD+R/RW disc, and can read as much as
4.7Gbytes of digital data stored in a DVD-ROM,
DVD-R, DVD-RW, DVD+R and DVD+RW disc.
This DVD/CD Rewritable Drive can easily meet
the upcoming MPC level 3 specification, and its
Enhanced Intelligent Device Electronics (E-IDE)
and ATAPI interface allows Plug and play
integration in the majority of today’s PCs without
the need of an additional interface card.
Light Scribe
CD-R
CD-RW
DVD-R
DVD-RW
DVD-R DL
DVD+R
DVD+RW
DVD+R DL
DVD-RAM
GWA-4164B
X
40x w
32x w
16x w
6x w
4x w
16x w
8x w
6x w
X
GWA-4166B
O
40x w
32x w
16x w
6x w
4x w
16x w
8x w
6x w
X
GSA-4166B
O
48x w
32x w
16x w
8x w
4x w
16x w
8x w
6x w
5x w
CD-ROM
CD-R
CD-RW
DVD-ROM
DVD-R
DVD-RW
DVD-R DL
DVD+R
DVD+RW
DVD+R DL
DVD-RAM
GWA-4164B
40x
40x
32x
16x
10x
8x
8x
10x
8x
8x
X
GWA-4166B
40x
40x
32x
16x
10x
8x
8x
10x
8x
8x
X
GSA-4166B
48x
48x
32x
16x
16x
8x
8x
16x
8x
8x
5x
• Write
• Read
Page 4

4
FEATURES
1 General
1) Enhanced IDE (ATAPI) interface.
2) Internal Half-height Drive.
3) CD-R/RW, DVD-R/RW/+R/+R DL(Double Layer)/+RW read and write compatible CD Family and DVDROM read compatible.
4) Buffer Under-run prevention function embedded.
5) 2MB buffer memory.
6) Power loading and power eject of a disc. Bare media loading.
7) MTBF : 100,000 POH
8) Vertical and Horizontal installable.
9) Support LightScribe Direct Label Printing Technology
2. Supported disc formats
1) Reads data in each CD-ROM, CD-ROM XA, CD-I, Video CD, CD-Extra and CD-Text.
2) Reads data in Photo CD (Single and Multi session).
3) Reads standard CD-DA.
4) Reads and writes CD-R discs conforming to “Orange Book Part 2”.
5) Reads and writes CD-RW discs conforming to “Orange Book Parts 3”.
6) Reads data in each DVD-ROM, DVD-R(Ver.1.0, Ver.2.0 for Authoring).
7) Reads and writes in each DVD-R(Ver.2.0 for General), DVD-RW, DVD+R, DVD+R DL, DVD-R DL and
DVD+RW.
8) LightScribe DVD+R conforming to “LightScribe Media Specification”
9) LightScrive CD-R conforming to “LightScribe Media Specification”
3. Supported write method
1) CD-R/RW : Disc at once, Session at Once, Track at once and Packet Write.
2) DVD-R : Disc at Once and Incremental Recording.
3) DVD-RW : Disc at Once, Incremental Recording and Restricted Overwrite.
4) DVD+R : Sequential Recording
5) DVD+R DL(Double Layer)/DVD-R DL(Dual Layer) : Sequential Recording
6) DVD+RW : Random Write
7) LightScribe Label Printing Functions complying with “LightScribe System Specification”
4. Audio
1) 16 bit digital data output through ATA interface.
2) Software Volume Control
3) Equipped with audio line output for audio CD playback.
Page 5

5
SPECIFICATIONS
I. MODEL : GWA-4164B
1. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
-CPU: IBM Compatible Pentium4 1.6GHz (or faster)
(For High speed, 2GHz or faster recommended.)
-128MB Memory or greater
• SUPPORTING OPERATING SYSTEM
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 Applicable disc formats
DVD DVD-ROM: 4.7GB (Single Layer)
8.5GB (Dual Layer)
DVD-R: 3.95GB (Ver.1.0 : read only)
4.7GB (Ver.2.0 for Authoring : read only)
4.7GB (Ver.2.0 for General: read & write)
DVD-RW: 4.7GB (Ver.1.1)
DVD+R: 4.7GB
DVD+R DL: 8.5GB
DVD+RW: 4.7GB
CD CD-ROM Mode-1 data disc
CD-ROM Mode-2 data disc
CD-ROM XA, CD-I, Photo-CD Multi-Session, Video CD
CD-Audio Disc
Mixed mode CD-ROM disc (data and audio)
CD-Extra
CD-Text
CD-R (Conforming to “Orange Book Part2”: read & write)
CD-RW (Conforming to “Orange Book Part3”: read & write)
2.2 Disc diameter..............................................120mm
80mm (Horizontal only)
2.3 Data capacity
• User Data/Block DVD-ROM/R/RW/+R/+RW ...............2,048 bytes/block
CD (Yellow Book)..........................................2,048 bytes/block(Mode 1 & Mode 2 Form 1)
2,336 bytes/block (Mode 2)
2,328 bytes/block (Mode 2 Form 2)
2,352 bytes/block (CD-DA)
2.4 RPC (Regional Playback Control) Phase2, No Region
* Operating System
Window 98 Second Edition (Not supported in
LightScribe)
Windows Millennium Edition(Me) (Not supported in
LightScribe)
Window 2000 Professional
Window XP Home Edition, Professional
* Recording tool
(1) RecordNow (Sonic)
(2) DLA (sonic)
(3) Nero(Ahead)
(4) In CD(Ahead)
(5) Easy CD Creator (Roxio)
(6) Direct CD (Roxio)
Page 6

6
3. DRIVE PERFORMANCE
3.1 Host interface ........................................................X3T13 ATA/ATAPI5/1321D
INF-8090i Rev.5.3
3.2 Read/Write & Rotational speed
<Read> CD-R/ROM, data/CD-I.........................17x ~ 40x (CAV), Approx. 8,100r/min
CD-RW ................................................15x ~ 32x (CAV), Approx. 6,500 r/min
CD-DA (DAE).......................................17x ~ 40x (CAV), Approx. 8,100 r/min
CD-DA (Audio out)/VideoCD ............... 6x ~ 15x (CAV), Approx. 3,130 r/min
DVD-ROM ............Single layer...........6.7x ~ 16x (CAV), Approx. 9,420 r/min
Dual layer..............3.3x ~ 8x (CAV), Approx. 5,180 r/min
DVD-Video(CSS).................................3.3x-8x(CAV)
DVD-R...................3.95GB..................4.2x ~ 10x (CAV), Approx. 5,950 r/min
4.7GB ...................4.2x ~ 10x (CAV), Approx. 5,950 r/min
DVD-RW................4.7GB....................3.3x ~ 8x (CAV), Approx. 4,720 r/min
DVD+R..................4.7GB....................4.2x ~ 10x (CAV), Approx. 5,950 r/min
DVD+R DL.............8.5GB....................3.3x ~ 8x (CAV), Approx. 4,720r/min
DVD+RW...............4.7GB....................3.3x ~ 8x (CAV), Approx. 4,720 r/min
<Write> CD-R....................................................10x, 16x (CLV), 24x, 40x (CAV)
CD-RW ................................................4x (CLV), High speed Disc, 10x (CLV)
Ultra speed Disc 16x(CLV), 24x(ZCLV), 32x(ZCLV)
DVD-R .................................................2x, 4x (CLV), 8x (ZCLV)
DVD-RW..............................................2x, 4x (CLV)
DVD+R DL...........................................2.4x (CLV)
DVD+R ................................................2.4x, 4x (CLV), 8x (ZCLV)
DVD+RW.............................................2.4x, 4x (CLV)
DVD-R DL............................................4x(CLV)
* Rotational speed (CLV, ZCLV)
CD-ROM/R/RW ...................................1x: Approx. 500 (Inside) to 210 r/min (Outside)
DVD-R/RW/ROM/+R/RW....................1x: Approx. 1,390(Inside) ~ 580 r/min(Outside)
* LightScribe Label Printing
Pixel Resolution...................................600DPI
Track Resolution .................................500~1600TPI
Linear Velocity.....................................0.25~0.75m/sec
Laser Power.........................................30~60mW as Objective emission light
of 780nm wavelength
Color....................................................Monochrome
Page 7

3.3 Data transfer rate
3.3.1 Sustained transfer rate
<Read> CD-ROM/R.....................................................2,550 ~ 6,000 kbytes/s (40x) Max.
CD-RW...........................................................2,250 ~ 4,800 kbytes/s (32x) Max.
CD-DA(DAE)..................................................2,550 ~ 6,000 kbytes/s (40x) Max.
DVD-ROM ............Single layer......................9.28 ~ 22.16 Mbytes/s (16x) Max.
Dual layer........................4.58 ~ 11.08 Mbytes/s (8x) Max.
DVD-R............................................................5.73 ~ 13.85 Mbytes/s (10x) Max.
DVD-RW ........................................................4.58 ~ 11.08 Mbytes/s (8x) Max.
DVD+R...........................................................5.73 ~ 13.85 Mbytes/s (10x) Max.
DVD+R DL.....................................................4.58 ~ 11.08 Mbytes/s (8x) Max.
DVD+RW .......................................................4.58 ~ 11.08 Mbytes/s (8x) Max.
<Write> CD-R .....................10x,16x (CLV) .................1.5, 2.4 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
24x (ZCLV)......................1.8 ~ 3.6 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
40x(CAV).........................2.4 ~ 6.0 Mbytes/s(Mode-1)
CD-RW..................4x, 10x (CLV) ..................0.6, 1.5 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
16x (ZCLV)......................1.8 ~ 2.4 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
24x (ZCLV)......................1.8 ~ 3.6 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
32x(ZCLV).......................1.8 ~ 4.8 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
DVD-R...................2x, 4x(CLV), 8x(ZCLV)....2.77, 5.44, 5.44~11.08 Mbytes/s
DVD-RW................1x, 2x, 4x(CLV)................1.38, 2.77, 5.44 Mbytes/s
DVD+R..................2.4x, 4x(CLV) ..................3.32, 5.54 Mbytes/s
8x(ZCLV).........................5.44~11.08 Mbytes/s
DVD-R DL .............4x (CLV) .........................5.44 Mbytes/s
DVD+R DL.....................................................2.4x (CLV) 5.54Mbytes/s
DVD+RW...............2.4x, 4x (CLV) .................3.32, 5.54 Mbytes/s
3.3.2 Burst transfer rate
Ultra DMA Mode 2..........................................33.3 Mbytes/s Max.
Multiword DMA Mode 2..................................16.6 Mbytes/s Max.
PIO Mode 4....................................................16.6 Mbytes/s Max.
3.4 Access time (Random)
* Typical value
DVD-ROM(SL)...............................................140 ms Typ.
(Note 1)
DVD-ROM(DL)...............................................175 ms Typ.
(Note 1)
CD-ROM ........................................................120 ms Typ.
(Note 1)
Note :
1) Average random access time is the typcal value of more than 50 times including latency and error correction time.
Test Disc : DVD : ALMEDIO TDV-520 / TDR-820
CD : ALMEDIO TCDR-701 / HITACH HCD-1
*) Typical value defines a measured value in normal temperature (20 deg.C.) and horizontal position.
3.5 Data error rate (Measured with 5 retries maximum)
DVD-R/RW/ROM...<10
-12
DVD+R/RW...........<10
-12
CD-ROM/R/RW.....<10
-12
(Mode-1)
<10-9(Mode-2)
Condition : It is assumed that the worst case raw error rate of the disc is 10
-3
3.6 Data buffer capacity .......................................................2Mbytes
7
Page 8
8
3.7 LightScribe Label Printing
* Note (1) DRF Parameters for this spec : LV=250mm/sec, TrackShift=85, Laser Power=34mW
3.7.1 Printing Time
1070TPI * 12cm Entire Disc.......................................less than 36 minutes
800TPI * 12cm Entire Disc.........................................less than 28 minutes
530TPI * 12cm Entire DIsc ........................................less than 20 minutes
3.7.2 Image Contrast complying to the colorimetry standard CIE L*a*b, defined as Delta L(
∆L)
1070TPI * LS CD-R Media (973423 : 795973)...........higher than 28
800TPI * LS CD-R Media (973423 : 795973).............higher than 20
530TPI * LS CD-R Media (973423:795973)...............higher than 12
4. Quality and Reliability
4.1 MTBF..................................................125,000 Power On Hours(Consecutive/Cumulative POH)
Assumption : ..........................Used in a normall office environment at room temperature.
-POH per year.........................3,000
-ON/OFF cycles per year........600
-Operating duty cycle..............20% of power on time (Seek: 5% of operating time)
4.2 Tray cycle test...................................30,000 times
No degeneration in the mechanical part after test
4.3 Actuator mechanism........................1,000,000 full stroke seek
4.4 MTTR (Mean Time To Repair) ...........0.5 h
4.5 Component life .................................5 years or 2,000 h of Laser radiating time
Assumption : ..........................Used in a normall office environment.
5. POWER REQUIREMENTS
5.1 Source voltage
+5V +5% tolerance, less than 100 mVp-p Ripple voltage
+12V +10% tolerance, less than 100 mVp-p Ripple voltage
5.2 Current
Idle (Hold track state)..............+5V DC 0.6A Typ. < 1.0 A Max.
+12V DC 0.5A Typ. < 1.0 A Max.
Write (Active)..........................+5V DC 0.9A Typ. < 1.3 A Max.
+12V DC 0.5A Typ. < 1.2 A Max.
Read (Active)..........................+5V DC 0.6A Typ. < 1.2 A Max.
+12V DC 0.6A Typ. < 1.2 A Max.
Seek (Acess) ..........................+5V DC 0.7A Typ. < 1.2 A Max.
+12V DC 1.0A Typ. < 1.8 A Max.
Label Printing +5V DC 0.7A typ. < 1.0 A max.
+12V DC 0.3A typ. < 0.5 A max.
5.3 Standby
Sleep mode (No disc).............2.5 W Typ. 3.0 W Max.
6. AUDIO PERFORMANCE
Item Typical Test Signal Test Condition Note
Output Level 0.7 Vrms 1KHz 0 dB No Filter
Frequency response +/-3dB 20-20kHz 0dB at 47kΩ
THD 0.1% 1KHz 0 dB with IHF-A + 20KHz LPF
Headphone output level(Optional) - - - None
AUDIO OUT
Page 9

7. Acoustic noise
Less than 50dB, A scale, at 0.5 m away from the drive
Note : 1. Disc : Less than unbalance 0.3 x10-4Nm
2. Installation : Horizontal
3. Ambient temperature : Normal temperature
4. Except loading, unloading and seek
8. Dimensions
External dimensions (W x H xD) 146x41.3x184.7mm
Front bezel (WxHxD) 148x42x5 mm
9. Mass .................................................880g+/-10g(net)
* Please Contact the friendly staff of LG Service Care at: Website http: //www.LGEservice.com
9
Page 10

10
SPECIFICATIONS
II. MODEL : GWA-4166B
1. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
-CPU: IBM Compatible Pentium4 1.6GHz (or faster)
(For High speed, 2GHz or faster recommended.)
-128MB Memory or greater
• SUPPORTING OPERATING SYSTEM
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 Applicable disc formats
DVD DVD-ROM: 4.7GB (Single Layer)
8.5GB (Dual Layer)
DVD-R: 3.95GB (Ver.1.0 : read only)
4.7GB (Ver.2.0 for Authoring : read only)
4.7GB (Ver.2.0 for General: read & write)
DVD-RW: 4.7GB (Ver.1.1)
DVD+R: 4.7GB
DVD+R DL: 8.5GB
DVD+RW: 4.7GB
CD CD-ROM Mode-1 data disc
CD-ROM Mode-2 data disc
CD-ROM XA, CD-I, Photo-CD Multi-Session, Video CD
CD-Audio Disc
Mixed mode CD-ROM disc (data and audio)
CD-Extra
CD-Text
CD-R (Conforming to “Orange Book Part2”: read & write)
CD-RW (Conforming to “Orange Book Part3”: read & write)
2.2 Disc diameter 120mm
80mm (Horizontal only)
2.3 Data capacity
• User Data/Block DVD-ROM/R/RW/+R/+RW ...............2,048 bytes/block
CD (Yellow Book)..........................................2,048 bytes/block(Mode 1 & Mode 2 Form 1)
2,336 bytes/block (Mode 2)
2,328 bytes/block (Mode 2 Form 2)
2,352 bytes/block (CD-DA)
2.4 RPC (Regional Playback Control) Phase2, No Region
* Operating System
Window 98 Second Edition (Not supported in
LightScribe)
Windows Millennium Edition(Me) (Not supported in
LightScribe)
Window 2000 Professional
Window XP Home Edition, Professional
* Recording tool
(1) RecordNow (Sonic)
(2) DLA (sonic)
(3) Nero(Ahead)
(4) In CD(Ahead)
(5) Easy CD Creator (Roxio)
(6) Direct CD (Roxio)
Page 11

11
3. DRIVE PERFORMANCE
3.1 Host interface...........................................................X3T13 ATA/ATAPI5/1321D
INF-8090i Rev.5.3
3.2 Read/Write & Rotational speed
<Read> CD-R/ROM, data/CD-I............................17x ~ 40x (CAV), Approx. 8,100r/min
CD-RW...................................................15x ~ 32x (CAV), Approx. 6,500 r/min
CD-DA (DAE).........................................17x ~ 40x (CAV), Approx. 8,100 r/min
CD-DA (Audio out)/VideoCD.................. 6x ~ 15x (CAV), Approx. 3,130 r/min
DVD-ROM .............Single layer .............6.7x ~ 16x (CAV), Approx. 9,420 r/min
Dual layer................3.3x ~ 8x (CAV), Approx. 5,180 r/min
DVD-Video(CSS)....................................3.3x ~ 8x (CAV)
DVD-R ...................3.95GB....................4.2x ~ 10x (CAV), Approx. 5,950 r/min
4.7GB......................4.2x ~ 10x (CAV), Approx. 5,950 r/min
DVD-RW................4.7GB......................3.3x ~ 8x (CAV), Approx. 4,720 r/min
DVD+R...................4.7GB......................4.2x ~ 10x (CAV), Approx. 5,950 r/min
DVD+R DL.............8.5GB......................3.3x ~ 8x (CAV), Approx. 4,720r/min
DVD+RW...............4.7GB......................3.3x ~ 8x (CAV), Approx. 4,720 r/min
<Write> CD-R ......................................................10x, 16x (CLV), 24x, 40x (CAV)
CD-RW...................................................4x (CLV), High speed Disc, 10x (CLV)
Ultra speed Disc 16x(CLV), 24x(ZCLV), 32x(ZCLV)
DVD-R....................................................2x, 4x (CLV), 8x (ZCLV), 12x, 16x(CAV)
DVD-RW.................................................1x, 2x, 4x (CLV), 6x (ZCLV)
DVD+R DL..............................................2.4x (CLV), 6x, 8x
DVD+R...................................................2.4x, 4x (CLV), 8x (ZCLV), 12x, 16x (CAV)
DVD+RW................................................2.4x, 4x, 8x (CLV)
DVD-R DL ..............................................4x(CLV)
* Rotational speed (CLV, ZCLV)
CD-ROM/R/RW......................................1x: Approx. 500 (Inside) to 210 r/min (Outside)
DVD-R/RW/ROM/+R/RW.......................1x: Approx. 1,390(Inside) ~ 580 r/min(Outside)
* LightScribe Label Printing
Pixel Resolution......................................600DPI
Track Resolution ....................................500~1600TPI
Linear Velocity........................................0.25~0.75m/sec
Laser Power...........................................30~60mW as Objective emission light
of 780nm wavelength
Color ......................................................Monochrome
3.3 Data transfer rate
3.3.1 Sustained transfer rate
<Read> CD-ROM/R.............................................2,550 ~ 6,000 kbytes/s (40x) Max.
CD-RW...................................................2,250 ~ 4,800 kbytes/s (32x) Max.
CD-DA(DAE)..........................................2,550 ~ 6,000 kbytes/s (40x) Max.
DVD-ROM .............Single layer .............9.28 ~ 22.16 Mbytes/s (16x) Max.
Dual layer................4.58 ~ 11.08 Mbytes/s (8x) Max.
DVD-R....................................................5.73 ~ 13.85 Mbytes/s (10x) Max.
DVD-RW.................................................4.58 ~ 11.08 Mbytes/s (8x) Max.
DVD+R...................................................5.73 ~ 13.85 Mbytes/s (10x) Max.
DVD+R DL..............................................4.58 ~ 11.08 Mbytes/s (8x) Max.
DVD+RW................................................4.58 ~ 11.08 Mbytes/s (8x) Max.
Page 12

<Write> CD-R .....................10x,16x (CLV) .................1.5, 2.4 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
24x (ZCLV)......................1.8 ~ 3.6 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
40x(CAV).........................2.4 ~ 6.0 Mbytes/s(Mode-1)
CD-RW..................4x, 10x (CLV) ..................0.6, 1.5 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
16x (ZCLV)......................1.8 ~ 2.4 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
24x (ZCLV)......................1.8 ~ 3.6 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
32x (ZCLV)......................1.8 ~ 4.8 Mbytes/s (Mode-1)
DVD-R...................2x, 4x(CLV), 8x(ZCLV)....2.77, 5.44, 5.44~11.08 Mbytes/s
12x, 16x (CAV)................8.91~16.62 Mbytes/s
8.91~22.16 Mbytes/s
DVD-R dual...........4x(CLV)...........................5.44 Mbytes/s
DVD-RW................1x, 2x, 4x(CLV)................1.38, 2.77, 5.44 Mbytes/s
DVD+R..................2.4x, 4x(CLV) ..................3.32, 5.54 Mbytes/s
8x(ZCLV).........................5.44~11.08 Mbytes/s
12x, 16x (CAV)................8.91~16.62Mbytes/s
8.91~22.16Mbytes/s
DVD+R DL ............2.4x (CLV) ......................5.54 Mbytes/s
6x ....................................8.28 Mbytes/s
8x ....................................5.44~11.08 Mbytes/s
DVD+RW...............2.4x, 4x (CLV) .................3.32, 5.54 Mbytes/s
3.3.2 Burst transfer rate
Ultra DMA Mode 2..........................................33.3 Mbytes/s Max.
Multiword DMA Mode 2..................................16.6 Mbytes/s Max.
PIO Mode 4....................................................16.6 Mbytes/s Max.
3.4 Access time (Random)
* Typical value
DVD-ROM(SL)...............................................140 ms Typ.
(Note 1)
DVD-ROM(DL)...............................................175 ms Typ.
(Note 1)
CD-ROM ........................................................120 ms Typ.
(Note 1)
Note :
1) Average random access time is the typcal value of more than 50 times including latency and error correction time.
Test Disc : DVD : ALMEDIO TDV-520 / TDR-820
CD : ALMEDIO TCDR-701 / HITACH HCD-1
*) Typical value defines a measured value in normal temperature (20 deg.C.) and horizontal position.
3.5 Data error rate (Measured with 5 retries maximum)
DVD-R/RW/ROM...<10
-12
DVD+R/RW...........<10
-12
CD-ROM/R/RW.....<10
-12
(Mode-1)
<10-9(Mode-2)
Condition : It is assumed that the worst case raw error rate of the disc is 10
-3
3.6 Data buffer capacity .......................................................2Mbytes
12
Page 13
13
3.7 LightScribe Label Printing
* Note (1) DRF Parameters for this spec : LV=250mm/sec, TrackShift=85, Laser Power=34mW
3.7.1 Printing Time
1070TPI * 12cm Entire Disc.......................................less than 36 minutes
800TPI * 12cm Entire Disc.........................................less than 28 minutes
530TPI * 12cm Entire DIsc ........................................less than 20 minutes
3.7.2 Image Contrast complying to the colorimetry standard CIE L*a*b, defined as Delta L( ∆L)
1070TPI * LS CD-R Media (973423 : 795973)...........higher than 28
800TPI * LS CD-R Media (973423 : 795973).............higher than 20
530TPI * LS CD-R Media (973423:795973)...............higher than 12
4. Quality and Reliability
4.1 MTBF..................................................125,000 Power On Hours(Consecutive/Cumulative POH)
Assumption : ..........................Used in a normall office environment at room temperature.
-POH per year.........................3,000
-ON/OFF cycles per year........600
-Operating duty cycle..............20% of power on time (Seek: 5% of operating time)
4.2 Tray cycle test...................................30,000 times
No degeneration in the mechanical part after test
4.3 Actuator mechanism........................1,000,000 full stroke seek
4.4 MTTR (Mean Time To Repair) ...........0.5 h
4.5 Component life .................................5 years or 2,000 h of Laser radiating time
Assumption : ..........................Used in a normall office environment.
5. POWER REQUIREMENTS
5.1 Source voltage
+5V +5% tolerance, less than 100 mVp-p Ripple voltage
+12V +10% tolerance, less than 100 mVp-p Ripple voltage
5.2 Current
Idle (Hold track state)..............+5V DC 0.6A Typ. < 1.0 A Max.
+12V DC 0.5A Typ. < 1.0 A Max.
Write (Active)..........................+5V DC 0.9A Typ. < 1.3 A Max.
+12V DC 0.5A Typ. < 1.2 A Max.
Read (Active)..........................+5V DC 0.6A Typ. < 1.2 A Max.
+12V DC 0.6A Typ. < 1.2 A Max.
Seek (Acess) ..........................+5V DC 0.7A Typ. < 1.2 A Max.
+12V DC 1.0A Typ. < 1.8 A Max.
Label Printing..........................+5V DC 0.7A typ. < 1.0 A max.
+12V DC 0.3 A typ. < 0.5 A max.
5.3 Standby
Sleep mode (No disc).............2.5 W Typ. 3.0 W Max.
6. AUDIO PERFORMANCE
Item Typical Test Signal Test Condition Note
Output Level 0.7 Vrms 1KHz 0 dB No Filter
Frequency response +/-3dB 20-20kHz 0dB at 47kΩ
THD 0.1% 1KHz 0 dB with IHF-A + 20KHz LPF
Headphone output level(Optional) - - - None
AUDIO OUT
Page 14

14
7. Acoustic noise
Less than 50dB, A scale, at 0.5 m away from the drive
Note : 1. Disc : Less than unbalance 0.3 x10-4Nm
2. Installation : Horizontal
3. Ambient temperature : Normal temperature
4. Except loading, unloading and seek
8. Dimensions
External dimensions (W x H xD) 146x41.3x184.7mm
Front bezel (WxHxD) 148x42x5 mm
9. Mass .................................................880g+/-10g(net)
* Please Contact the friendly staff of LG Service Care at: Website http: //www.LGEservice.com
Page 15
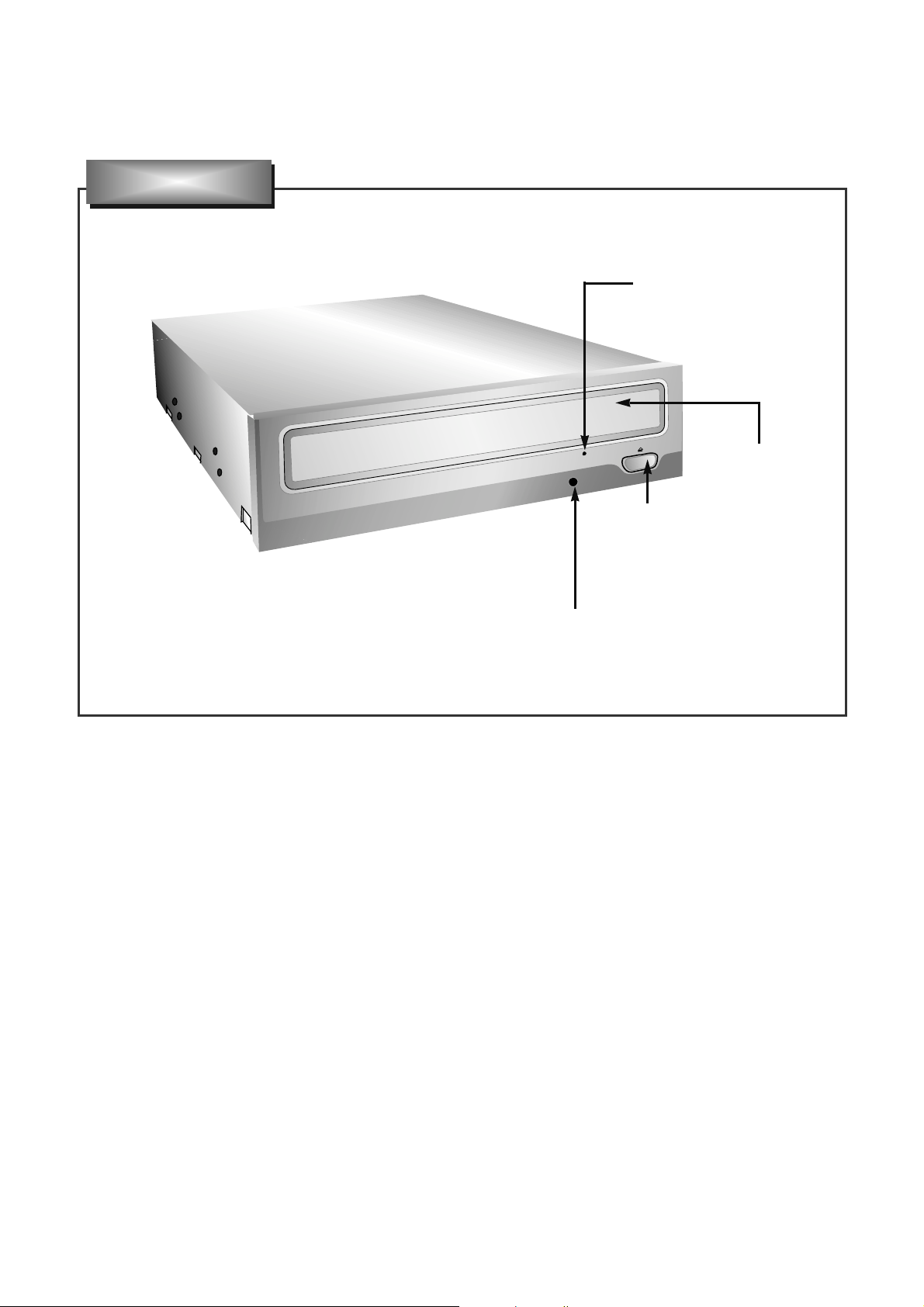
Drive Activity Indicators
Stop/Eject Button
Disc Tray
Emergency Eject Hole
LOCA TION OF CUSTOMER CONTROLS
15
1. Disc tray
This is the tray for the disc. Place the disc on the
ejected disc tray, then lightly push the tray (or
push the eject button) and the CD will be loaded.
NOTE: Don’t pull out or push in the disc tray
forcibly. This might cause damage to the loading
section of the drive.
2. Stop/Eject button
This button is pressed to open the CD tray.
This button works only when power is supplied to
the drive.
3. Emergency Eject Hole
Insert a paper clip here to eject the Disc tray
manually or when there is no power.
4. Drive activity indicator
Green colored LED is used to indicate the
operation of the Drive.
Front Panel
Page 16

16
1. Power Connector
Connects to the power supply (5-and 12-V DC) of
the host computer.
NOTE : Be careful to connect with the proper
polarity. Connecting the wrong way may damage
the system (and is not guaranteed). Usually this
connector can only be attached one-way.
2. IDE Interface Connector
Connect to the IDE (Integrated Device
Electronics) Interface using a 40-pin flat IDE
cable.
NOTE : Do not connect or disconnect the cable
when the power is on, as this could cause a short
circuit and damage the system. Always turn the
power OFF when connecting or disconnecting the
cable.
3. Jumper Connector
This jumper determines whether the drive is
configured as a master or slave. Changing the
master-slave configuration takes effect after
power-on reset.
4. Analog Audio Output Connector
Provides output to a sound card (analog signal).
Generally you need this to play a regular audio
CD.
5. Digital Audio Output Connector
This connector is not supported.
Digital Audio Output
Connector
Jumper Connector
Analog Audio Output Connector
IDE Interface Connector
Power Connector
Rear Panel
Page 17

1. CABINET and CIRCUIT BOARD
DISASSEMBL Y
1-1. Bottom Chassis
A. Release 4 screws (A) and remove the Bottom Chassis
in the direction of arrow (1). (See Fig.1-1)
1-2. Front Bezel Assy
A. Insert and press a rod in the Emergency Eject
Hole and then the CD Tray will open in the direction
of arrow (2).
B. Remove the Tray Door in the direction of arrow
(3) by pushing the stoppers forward.
C. Release 3 stoppers and remove the Front Bezel Assy.
1-3. Cabinet and Main Circuit Board
A. Remove the Cabinet in the direction of arrow (4).
(See Fig. 1-3)
B. When the CD tray has been opened completely, lift
2 points (a) and remove the CD tray while drawing
out simultaneously.
C. Remove the Soldering of the LD- and LD+ (b) for
the Loading Motor, and then remove the Main
Circuit Board.
D. At this time, be careful not to damage the 5
connectors of the Main Circuit Board.
2. MECHANISM ASSY DISASSEMBL Y
2-1. Pick-up Unit
A. Release screws (B).
B. Separate the Pick-up Unit in the direction of arrow (6).
Main
Circuit Board
Cabinet
(4)
(5)
(a)
(b)
Fig. 1-1
Fig. 1-2
DISASSEMBLY
17
Fig. 1-3
Mechanism Assy
Pick-up Unit
(6)
(B)
(B)
Fig. 2-1
(1)
(A)
Bottom Chassis
(A)
(A)
(A)
(3)
Stoppers
Emergency Eject Hole
(2)
Tray Door
Front Bezel Assy
CD Tray
Page 18

2-2. Pick-up
A. Release 1 screw (C) and remove the Pick-up.
Pick-up Unit
Pick-up
(C)
Fig. 2-2
18
Page 19
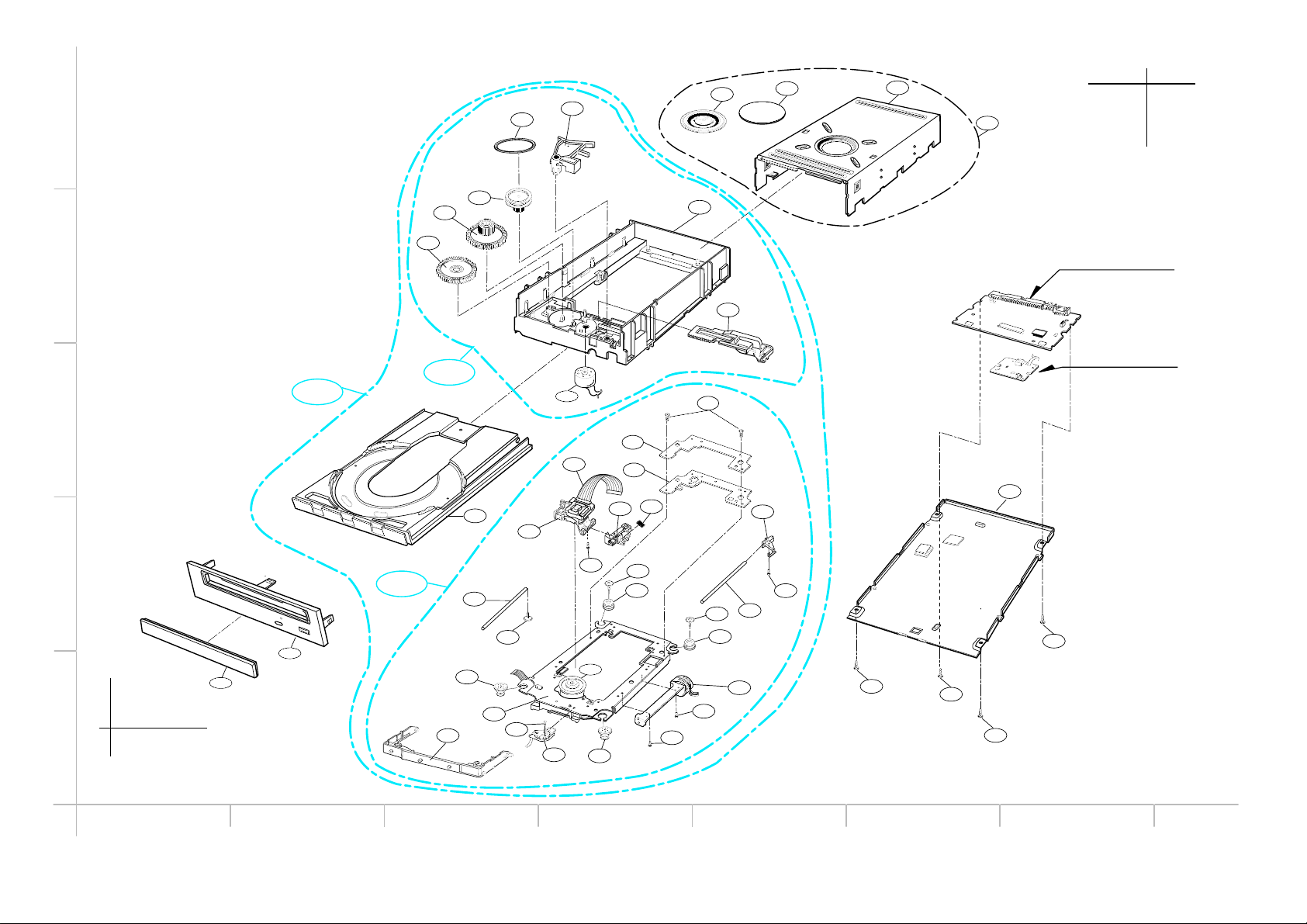
030
014
007
A02
A01
A03
021
028
028
452
032
452
020
021
050
430
005
035
004
006
A B C D E F GH
1
2
3
4
5
452
024
481
034
027
026
033
025
430
419
020
453
031
036
453
003
002
010
011
009
008
012
016
015
013
PBM00 (MAIN C.B.A)
PBF00 (FRONT C.B.A)
482
482
482
001
482
19 20
EXPLODED VIEW
Page 20
ATIP Absolute Time in Pre-groove. With an additional modulation of the “Wobble”, the “Groove” contains a time
code information.
Wobble The pre-groove in the Disc is not a perfect spiral but is wobbled.
With : – A typical amplitude of 30 nm
– A spatial peried of 54~64 µm
CW Continuous Wave. The laser light output is at a constant level.
DOW Direct Over-Write. The action in which new information is recored over previously recorded information in
CD-RW disc.
Overwrite
The action in which new information is recorded over previously recorded information.
(Pre-)Groove
The guidance track in which clocking and time code information is stored by means of an FM
modulated wobble.
Land Land is characterized in the following way:
When radial signals are concerned,land is defined as the area between the grooves.
When HF signal are concerned,land is defined as the area between the marks(pits) in tangential
direction.
Hybrid Disc A Multisession disc of which the first Session is mastered. On a hybrid disc, recorded and
mastered information may co-exist.
Mastered Information,stored as pits on the disc during the manufacturing process of the disc.
Information (when making the master)
OPC Optimum Power Control. Procedure is determined optimum recording power according to CD-
R/RW Media in recording start step.
ROPC Running OPC. The purpose is to continuously adjust the writing power to the optimum power
that is required.
When the optimum power may change because of changed conditions of disc and change in
operating temperature.
Jitter The 16 value of the time variation between leading and trailing edges of a specific (I3 … I11) pit
or land as measured by Time Interval Analysis.
Deviation The difference between a fixed value of Pit length and Land length.
TOC Table Of Contents : in the Lead-in Area the subcode Q-channel contains information about the
Tracks on the disc.
Packet A method of writing data on a CD in small increments.
Writing Two kinds of packets can be written : Fixed-length and Variable-length.
Write The shape of the HF write signal used to modulate the power of the laser.
Strategy The Write Strategy must be used for recordings necessary for disc measurements.
Information Wobble, ATIP, Disc Identification, Write Power, Speed Range OPC Parameters, etc are
Area recorded in the Information area of CD-RW Disc
Finalization The action in which (partially) unrecorded or logically erased tracks are finished and the Lead-in
and/or Lead-out areas are recorded or overwritten with the appropriate TOC subcode.
Logical Erase
A method to remove information from a disc area by overwriting it with an EFM signal containing
mode 0 subcode
A logically erased area is equivalent to an unrecorded
Physical Erase
The action in which previously recorded information is erased by overwriting with a CW laser
output.
After a Physical Erase action, the erased area on the CD-RW disc is in the unrecorded state
again.
Session
An area on the disc consisting of a Lead-in area, a Program area, a lead-out area.
Multi session
A session that contains or can contain more than one session composed Lead-in and Lead-out
GLOSSARY
24
Page 21

25
The differences of CD-R/CD-RW discs and General CD-ROM
1.Recording Layer
Recordable CD has a wobbled pre-groove on the surface of disc for laser beam to follow track.
2.Disc Specification
Read-only Disc
CD-R and CD-RW Disc
3~1 1T
1.6um
0.4~0.5 um
(Pit)Groove
Land
Track pitch(p)
Radial Direction
Iw
A
O
a
a
Groove
Land
Radial Error Signal
The Groove wobble
Average center
Actual center
CD-ROM (READ-ONLY DISC)
a=30nm
ITEM CD-ROM CD-R CD-RW
Standard Yellow Book Orange Book II Orange Book III
Record Not available Write once Re-Writeable
Tracking Signal I11/Itop > 0.6 > 0.6 0.55 > M11> 0.70
(HF Modulation)
Read Laser Power(mW) < 0.5 mW < 0.7 mW < 1.0 mW
Jitter < 35 nsec < 35 nsec < 35 nsec
Reflectivity (R
top) 70 % 65 % 15 % ~ 25 %
Remark)
Write Laser Power(mW) 14-65 mW 6-45 mW
Page 22

26
3.Disc Materials
1) CD-ROM disc
Laser Beam
Groove
Substrate
(Polycarbonate)
Organic Dye Layer
Reflective Layer
Protective Layer
Label Printing
2) CD-R disc
Pigment Reflective Layer Color
Phtalocyanine Gold/Silver Yellow/White
Cyanine Gold/Silver Dark Green/Bright Green
Azo Gold/Silver Dark Blue
• It is composed of Silver _ colored aluminum plate and Reflective layer.
• Groove (Pit) of aluminum plate make a track.
• Laser wavelength : 780 nm, Laser Power (Read): 0.5mW
• Signal is detected by the
difference of reflective beam
intensity between “pit” and
“Land” on the disc.
• It is so-called WORM (Write Once Read Many) CD.
• It is composed of polycarbonate layer, Organic dye layer, Reflective layer, and Protective
layer.Gold/Silver Reflective layer is used to enhance the reflectivity
• According to the kinds of Organic dye layer, it is divided by Green CD, Gold CD, Blue CD.
• Laser Wavelength : 780 nm, Laser Power (read) : 0.7 mW
• Recording Power : 8x(14~20mW), 16x(25~35mW)
• When some part of dye layer is exposed to laser heat, it’s color changs black.Therefore, writing and
reading is enabled by the difference of reflectivity between changed part and unchanged part.
• Polycarbonate layer has Pre_Groove which make a Track.
Laser Beam
Pit
Substrate
(Polycarbonate)
Reflective Layer
Protective Layer
Label Printing
Page 23

27
3) CD-RW Disc
4.
Reading process of Optical Disc
Laser Beam
Groove
Substrate
(Polycarbonate)
Recording Layer
Dielectric Layer(TL)
Dielectric Layer(UL)
Protective Layer
Label Printing
• It is composed of polycarbonate layer, alloy(silver, arsenic) layer, aluminum reflectivity layer, protective layer.
• An crystalized alloy layer is transformed into noncrystalized by the laser heat. Therefore, writing and reading
is enabled by the difference of reflectivity.
• It is possible to overwrite about 1000 times.
• Laser Wavelength : 780 nm, Laser Power (Read) : 1.0mW
• Recording Power : Erase (4~18mW), Write (6~45mW)
• When disc rewriting, new data is overwritten previously recorded data.
• Polycarbonate layer has a Pre-Groove which make a track.
Lens
H
D
Beam
Spot
Focusing
Lens
Laser Spot
at Constant
Read Intensity
Reflected
Light
Signal
Laser Spot
Position
(Time)
Previously Recorded Marks
Groove Land Mirror
I
3
I
top
I
11
I
G
I
L
I
0
Numerical aperture: NA=nsinθ,
n: Refractive index
Focus depth : H =
λ
/NA
laser spot diameter : D =
λ
/NA
2
θ
Page 24

28
5.Writing Process of CD-R Disc
a b c d e f g
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
Incident
Laser
Power
(Read)
(Read)
(Write)
Laser Spot
Position
(Time)
a b c d e f g
Laser Spot
Position
(Time)
Laser
Spot
Recorded
Mark
Reflected
Light
Signal
Reflected
Light
Signal
Below "ORP"– Mark Too Short
At Optimum Record Power ("ORP")
Above "ORP" – Mark Too Long
Time
6.Writing process of CD-RW Disc
Write Power
Erase Power
Read Power
Groove
Crystal
Amorphous
Amorphous
Recorded state
(lower reflectivity)
Melting/
quenching
Heating/
gradual cooling
Crystal phase
Erased state
(higher reflectivity)
Page 25
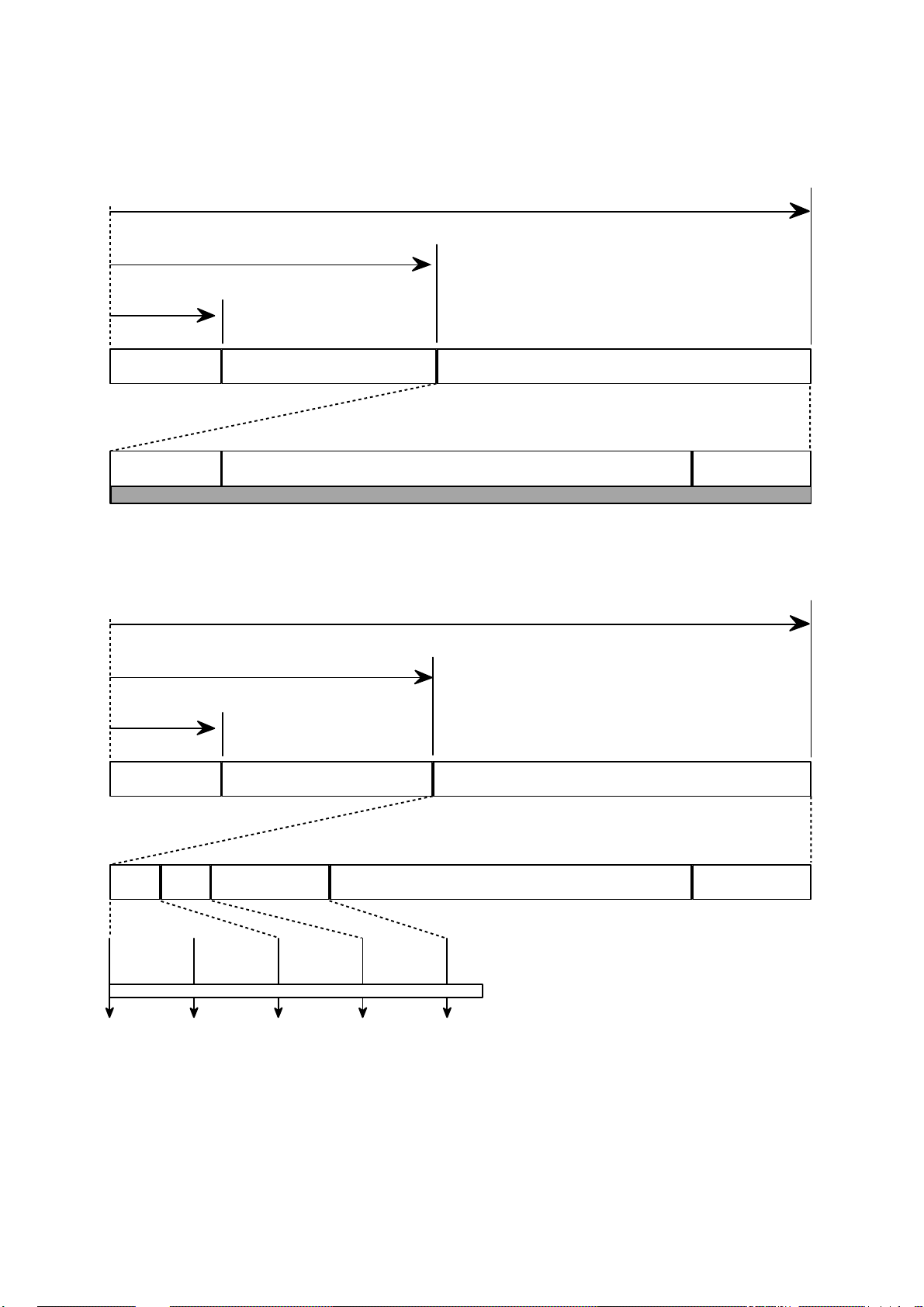
29
7.Organization of the PCA, PMA and Lead-in Area
1) Layout of CD-ROM disc
Center hole Clamping and Label Area Information Area
Lead-in Area
Lead-in Area
Diameter 15 mm
Diameter 46 mm
Diameter 120 mm
Program Area
Read Only Disc
Lead-out Area
Program Area Lead-out Area
Center hole
Clamping and Label Area
Information Area
PCA PMA
Test Area Count Area
Diameter 15 mm
Diameter 45 mm
Diameter 120 mm
Unrecorded Disc
Tsl-00:35:65 Tsl-00:15:05
Tsl-00:13:25
Tsl
99:59:74
00:00:00
in out
Test Area : for performing OPC procedures.
Count Area : to find the usable area immediately in T.A
Tsl : start time of the Lead-in Area, as encoded in ATIP
PMA : Program Memory Area
Disc Center
Disc Center
2) Layout of CD-R/RW disc
Page 26
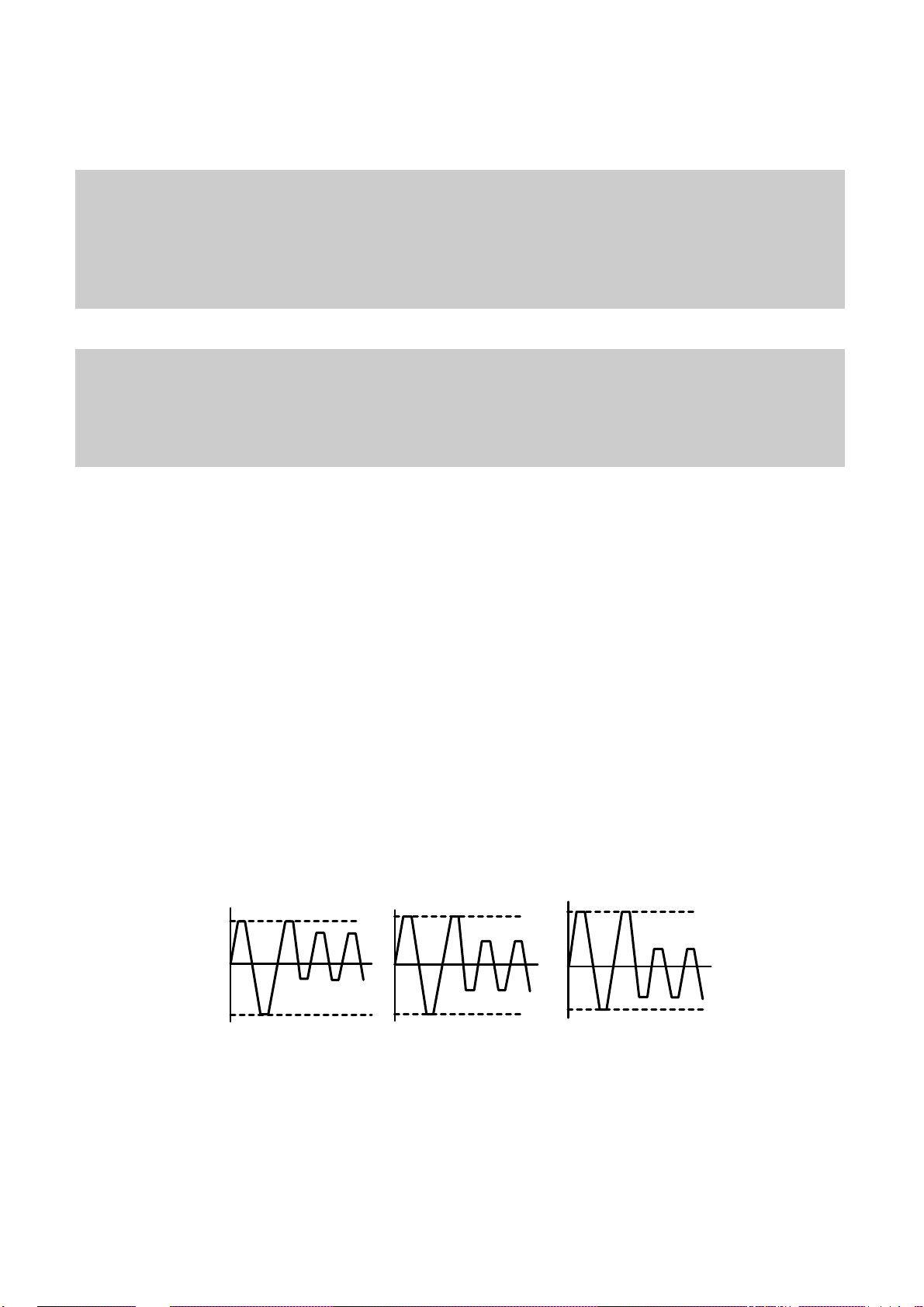
30
8. Function of PCA and PMA area
1) PCA (Power Calibration Area)
• PCA area is used to determine the correct Laser Power for a disc.
– Method 1 : PCA area is divided by a track.
– Method 2 : The previous Calibration value is referred.
– Method 3 : ROPC is used to determine Laser Power value automatically in data writing.
• CD-R Disc can write maximum 99 Tracks but CD-RW Disc can write unlimited tracks because it has a rewritable
function.
2) PMA (Program Memory Area)
• It has a track information (track No, track Start/End time) of every track before writing completed.
– PMA area has the last written point and the next writable point of a disc.
– In case of CD to CD copy, some writer may not write PMA area.
* When Disc is Finalized,
PMA information is transferred to the Lead_In area so that general Driver can read it.
* Because PCA and PMA area exist before Lead-In area, General CD Player or CD-ROM Drive can’t read
these areas.
9. OPC and ROPC
1) OPC (Optimum Power Control)
• This is the first step of writing process, because CD writer has its own laser power value and media have different
writing characteristics,
– This is determined by the Writing characteristic, speed, temperature, and humidity.
– Laser wavelength is determined by the environmental temperature (775~795nm) and Optical Laser Power is
determined by the test and retry.
• Asymmetry and optimum writing Power
– EFM signal Asymmetry is determined by the writing power.
Therefore, Optical Power which has the same value to the preset power value can be estimated by measuring
HF signal Asymmetry on the PCA area.
• Measurement of Asymmetry
* Parameter setting (Beta) : Using AC coupled HF signal before equalization
Beta = (A1+A2)/(A1-A2)
Time
P << Po
Time
P = Po
HF Signal
A1
0
A2
Time
P >> Po
Page 27
31
2) ROPC (Running Optimum Power Control)
• Variable primary factor of Optimum Power
– Change of Power sensitivity on the Disc. (limited to 0.05 *Po)
– Wavelength shift of the laser diode due to the operating temperature change.
– Change of the Spot aberration due to the Disc skew,
Substrate thickness, Defocus.
– Change of Disc or Optics conditions due to the long term OPC
==> It is necessary to adjust continuously to obtain the Optimum Power.
• Principle of Running OPC
– To meet the factors mentioned above,
a horizontal _ direction movement of a curve is uesd.
– Beta = f(B-level) = constant on the Recorded Disc
– Procedure of ROPC
a. Reference B-level is determined during OPC Procedure.
b. During Recording, B-level value is controlled to have a close
Reference B-level value.
c. Normalization of B-level is used to eliminate the effect of reflectivity fluctuation.
==> The reflected B-level value is normalized by the disc reflectivity itself.
CD-R/RW Media
Write Strategy
Determination
PCA Test Area
Program Area
PMA Area
Lead-In Area
Lead-out Area
OPC
PCA Count Area
ROPC
* Recording Capacity of CD-R/RW (74Minute Recording media)
• (2048 Byte/Sector) X (75 Sector/Second) X (60 Second/Minute) X 74 Minute
= 681,984,000 Bytes = 682 Mbytes
• But the actual recording capacity is about 650 Mbytes. (according to the ISO 9660 standard, approximately
30 Mbytes are used to make directory structure and volume names.)
Incident recording pulse
Reflected recording pulse
Sampled timing B
11T
Sample B-level (Write Power)
Level B
Sampled at timing B
Pwo decided by OPC
Recording Power
Level B with Pwo
normalized to recording power
Sample Disc Reflectivity
(Read power)
10. Writing Process of DISC
Page 28

32
The differences of DVD-R/RW , DVD+R/R W discs and DVD-ROM
1.Recording Layer
LPP
(Land Pre-Pit)
DVD+R/RW Disc
DVD-R/RW Disc
0.74
um
3
T
0.4 um
DVD-ROM (Read Only Disc)
Page 29

33
2.Disc Specification
3.Disc Materials
1) DVD-ROM
DVD-ROM
Media T ype
User data capacity
Single-Layer
Read Only
4.7GB
Dual-Layer
Read Only
8.54GB
DVD-R DVD-RW DVD+R DVD+RW
Dye Phase change Dye Phase change
4.7GB 4.7GB 4.7GB 4.7GB
Wavelength
650nm 650nm 650nm 650nm 650nm 650nm
Reflectivity
45~85% 18~30nm 45~85% 18~30% 45~85% 18~30nm
Track pitch
0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74
Minimum pit length
0.4 0.44 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4
Modulation
>0.6 >0.6 >0.6 >0.6 >0.6 >0.6
Channel bit-rate
26.16MHz 26.16MHz 26.16MHz 26.16MHz 26.16MHz 26.16MHz
Wobble Frequency
- - 140KHz 140KHz 817.4KHz 817.4KHz
Addressing
26.16MHz 26.16MHz Wobble & LPP Wobble & LPP Wobble(ADIP) Wobble(ADIP)
Read Power (mW)
0.7 0.1 0.7 0.1
Write Power (mW)
- -
JItter
<8% <8% <8% <8% <9% <9%
++
Bonding layer
Polycarbonate
Semi-reflective
Polycarbonate
Reflective layer
Label
Polycarbonate
Label
Bonding layer
Reflective layer
Polycarbonate
<Single Layer >
<Dual Layer >
Page 30

34
2) Recording format using organic dye material (DVD-R/DVD+R)
* The format that records data through the creation of recorded marks by changing the organic dye material
with a laser beam.
DVD-R
Adhesive layer
Protective layer
Reflective layer
Recording layer(dye)
Disc substrate
DVD+R
Adhesive layer
Protective layer
Reflective layer
Recording layer(dye)
Disc substrate
Adhesive layer
Protective layer
Reflective layer
Dye layer
Substrate
Laser beam
> Disc structure
> Disc structure
[Recording]
Recording is done by changing the organic dye layer and the substrate with a laser when a strong is
applied to a disc, the temperature of the ortanic dye material goes up, the dye is decomposed and the
substrate changes at the same time. At this time, a durable bit is created as is the case with a CD-ROM.
[Playback]
Signals are read with the differences of the reflection of a laser from pits.
Page 31

35
3) Recording format using phase-change recording material (DVD-RW/DVD+RW)
* Data is recorded by changing the recording layer from the amorphous status to the crystalline status, and
played back by reading the difference of the reflection coefficient.
[ Amorphous : Non-crystalline ]
Substrate
Laser beam
Recording data
(Melting/Quick cooling)
Erasing data
(Heating/Gradual cooling)
Data erased state
(High reflection coefficient)
Recorded state
(Low reflection coefficient)
Crystalline status
Amorphous status
DVD-RW
Adhesive layer
Protective layer
Reflective layer
Dielectric layer
Recording layer
(Phase change material)
Dielectric layer
Disc substrate
DVD+RW
Adhesive layer
Protective layer
Reflective layer
Dielectric layer
Recording layer
(Phase change material)
Dielectric layer
Disc substrate
> Disc structure
> Recording principles
[Recording]
When a high-power laser is applied to the recording material, it melts and then becomes amorphous with
a low reflection coefficient when it quickly cools off. When a mid-power laser is applied to heat gradually
the recording material and then gradually cools it off, it becomes crystal with a high reflection coefficient.
[Playback]
A low-power laser is used for playback. The amount of reflected light depends on the status (amorphous
or crystalline) of the recording material. This is detected by an optical sensor.
Page 32

36
4. Writing Pulse Wave Form of DVD+R
For different speed ranges, different write strategies can be used. This document specifies 2 options:
- a pulsed write strategy, where each single mark is created by a number of subsequent separated short
pulses.
- a blocked write strategy, where each single mark is created by one continuous pulse.
1) 1stMethod : Using Pulsed Write Strategy
* 3T :
NRZI
T = 3
2Tw
Ttop
dTtop
dTle
Pb
top
top le
Pp
Channel bits
N = 3 : only the top pulse(T ),
first pulse lead-time dT , dT
NRZI
T > 4
2Tw Tw
Ttop Tmp
Tmp
Tlp
dTtop
dTle
Pb
top
top
le
lp
mp
Pp
Channel bits
N > 4 : the top pulse (T ), multi-pulse (T ) and last pulse (T ),
first pulse lead-time dT , dT
Pp : Actual write power
Pb : Bias Power
* >
4T :
Page 33

37
2) 2stMethod : Using Blocked Write Strategy
NRZI
Channel bits
2Tw
Tw
dT
top
T
top
dT
le
P
p
P
b
T
mp
lp
T
dP
p
0mW
P
c
P
b
1.25T
w
3T mark
4T mark
5T mark
Etc.
dT
top,3
dP
p3
T
top,3
dT
le
1.25T
w
P
c
P
b
1.25T
w
1.25T
w
1.25T
w
dT
top,4
dP
p4
T
top,4
T
lp
T
top,4
T
top,4
T
mp
T
mp
T
lp
T
lpT
mp
N = 3 : T (cm = 3) can be optimized individually.
N > 4 : T (cm 4) + x (N-3) T + T , T = T
P shall be < 0.1mW
top
mp
lp
w
w
top
c
Pp : Actual write power
Pb : Bias Power
dPp : Additional power ( Only be applied for the 3T and 4T marks)
Pc : Cooling power (Especially at higher recording speeds, optimum cooling down of the
recording layer after writing a mark may be
needed.)
>
Page 34

38
5. Writing Pulse Wave Form of DVD+RW
NRZI
Channel bits
2Tw
Tw
Ttop
dTtop
P
p
Pe
T
mp
mp
T
dTera
Pp : Actual write power
Pe : E r as e Powe r
Pb : Bias
Power
Pb
0mW
T
mp
Page 35

6. Organization of the Inner Drive Area, Outer Drive Area, Lead-in Zone and
Lead-out Zone
1) Layout of DVD-ROM disc
39
Center
hole
1st transition area
2nd transition area
Clamping
Zone
3rd transtion
area
Information Zone
Lead-in Zone
Lead-in
Zone
Lead -out
Zone
Diameter 15 mm
Diameter 16 mm
Diameter 22 mm
Diameter 33 mm
Diameter 44 mm
Diameter 120 mm
Data Zone
Read Only Disc
Lead-out Zone
Data Zone
Outer Drive
Area
Inner Drive
Area
Inner Disc
Test Zone
Outer Disc
Test Zone
Unrecorded Disc
PSN: 23080H 27080H 27480H 28480H 2A480H 30000H 260540H 261940H 262940H
263940H
267940H
in OUT
Disc Center
Rim area
Center
hole
1st transition area
2nd transition area
Clamping
Zone
3rd transtion
area
Information Zone
Diameter 15 mm
Diameter 16 mm
Diameter 22 mm
Diameter 33 mm
Diameter 44 mm
Diameter 120 mm
Disc Center
Rim area
Inner Disc
Count Zone
Outer Disc
Count Zone
2) Layout of DVD+R disc
> Inner Disc Test Zone : for performing OPC procedures.
> Inner Disc Count Zone : for counting the number of OPC algorithm performed in IDT Zone.
> Outer Disc Test Zone : for performing OPC procedures.
> Outer Disc Count Zone : for counting the mumger of OPC algorithm performed in IDT Zone.
Page 36

3) Layout of DVD+RW disc
40
> Inner Disc Test Zone : for performing OPC procedures.
> Inner Disc Count Zone : for counting the number of OPC algorithm performed in IDT Zone.
> Outer Disc Test Zone : for performing OPC procedures.
> Outer Disc Count Zone : for counting the number of OPC algorithm performed in IDT Zone.
Lead-in Zone
Lead -out Zone
Data Zone
Inner Disc
Test Zone
Outer Disc
Test Zone
Unrecorded Disc
PSN: 2A480H 2A7C80H 2DC80H 30000H 260540H 262940H
265940H
266140H
in OUT
Center
hole
1st transition area
2nd transition area
Clamping
Zone
3rd transtion
area
Information Zone
Diameter 15 mm
Diameter 16 mm
Diameter 22 mm
Diameter 33 mm
Diameter 44 mm
Diameter 120 mm
Disc Center
Rim area
Inner Disc
Count Zone
Outer Disc
Count Zone
Page 37

41
LightScribe Media
1. LightScribe Media
Center Hole
Screen Printed Imaging Layer
Clear Protective Coating
Reflective/Thermal Layer
Dye Data Layer
Polycarbonate
Substrate
DiscOD
Label Zone
Control Feature Zone
Clamping/Logo Zone
Page 38

42
2. Hardware Block Diagram of LightScribe Label Printing
Host
PC
(Spindle)
uP
(DSP)
Power
Drive
Analog
Signal
Processor
MECHANISM
Optical
Pick-up
Optical
Encoder
(Sled)
(Track)
(Tilt)
(Focus)
RFOUT
Spindle Motor
Step Motor
Track Actuator
Tilt Actuator
Focus Actuator
Laser Power Reference
Write Strategy Control
Buffer
Memory
SERVO Signals
RF Cell Signals
Laser Power Monitor Signal
Optical FG
CIrcuit
Page 39

43
3. MD Assy For LightScribe
Optical Encoder Unit
OPU ID Movement Range : L=21um
Page 40

44
4. Optical Encoder Assy
Codewheel
Direction of
radial play
CODEWHEEL
OR
CODESTRIP
FFC
3PIN
SIGNAL
PROCESSING
CIRCUITRY
R
V
LED
V
CC
CH A
CH B
CH B
GND
GND
Vcc
OFG
Encoder PCB
PIN 6
VCC
PIN 5
CH A
PIN 4
GND
PIN 3
VLED
PIN 2
GND
PIN 1
CH B
PIN 6
VCC
PIN 5
CH A
PIN 4
GND
PIN 3
VLED
PIN 2
GND
PIN 1
CH B
Optical Encoder IC
Schematic of Enc PCB
Page 41

45
DVD & CD DATA PROCESSING
1.Data Processing Flow
Command
Data
Status
RF EQ & AGC
SERVO
DSP
Encoder & Decoder & CSS
RF data slice EFM demodulator
CiRC error correction
Audio DAC
Buffer/Memory controller
CSS controller
Atapi interface control
Data PLL
Servo ADC
Focus/tracking
control output
Sled control output
CAV Spindle control
P-up
Unit
(LPC-812R)
IC121
RF AMP
(AN22113A)
CD
DVD
IC201
(MN103SA6G)
TE/CSO GEN
FE GEN
IC261 DRAM
IC262
Flash ROM
SRAM
Page 42

46
MN103SA6G
HOST DVD
PLAYER
(EMPEG2 B/D)
Scrambled MPEG Data
Change the "KEY"
KEY Management Control
2. Copy Protection and Regional Code Management Block
Block Diagram
Brief Process
1. Regional Code for DVD Disc
– DVD-ROM drive transfers the regional code of the control data to host by the command of host, the DVD
player of host reads the regional code, and plays title in the case of allowed regional code only.
2. Management of DVD Disc for the scrambled of data
(1) DVD-ROM and DVD player of host generate the “KEY 1” respectively, transfer to opposite part, the
“KEY 2” is received, recognizes the data transfer or not with this value, and generates the bus key
encoded the data.
(2) Encoded “Disc Key” and “Title Key” host is transfer with the bus Key.
(3) DVD player of host reads the key value, and uses the value to restore the scrambled data.
* Refer to the next page for the details.
Page 43

47
3. About Prevention the DVD-ROM from to be copy
A data is able to encode and record in the disc, if a copyright holder wants to prevent the disc from copying.
In case of a disc enhanced movie of 3 titles......
DISC KEY (2048 Bytes) is used to encode the whole contents in the disc and TITLE
KEY (5 Bytes) is used to encode the title respectively.
So, the data is encoded and stored in a disc through the unknown algorithms
with a disc key and title key. (At this time, the disc key and title key are stored
in a disc.)
…As above, the disc is able to copy when the disc key and title key are
opened.
Then, ROM-DRIVE encodes the disc key and title key and transfers to MPEG2 board.
If you want to play the disc prevented from the copy......
First of all, ROM-DRIVE and MPEG-2 board identify with each other through the procedure as described
below.
1. Drive and host gives and takes the ID of 2bit. This ID is AGID (Authentication Grant ID).
The various decoder boards are attached to the host, in these, AGID sets the MPEG-2 board and drive.
2. After the AGID is set, MPEG-2 board generates the challenge key (10 Byte) and transfers to drive. The
board and drive generate key 1 (5Byte) with the challenge key respectively. (Of course, the Algorithm
generating the key 1 is not known.)
3. Compare with the generated key 1, if it corresponds each other, the first step of authentication is
completed. This is a course to identify the MPEG-2 board with a drive.
4. The second step of authentication is a course to identify a drive with the MPEG-2 board.
The dirve generates a challenge key and transfers it to the MPEG-2 board. The dirve and MPEG-2 board
generate the key 2 (5Byte) with the challenge key, compare with each other, and if it corresponds and the
secondary step of authentication is completed.
5. As above, the identification is completed.
6. The dirve and MPEG-2 board generate the Bus key with the key 1 and key 2 and own it.
7. Dirve encodes the disc key and title key with this Bus key and transfers to the MPEG-2 board.
8. The MPEG-2 board reads the encoded disc key and title key with the Bus key only.
9. MPEG-2 board lets data read from the drive to decode with the read disc key and title key and makes into
the video signal by decoding.
ROM-DRIVE
AGID
HOST
MPEG-2
BOARD
Challenge key
encoded disc key, title key
Page 44

48
4.About the DVD-ROM Regional Code
DISC ROM - DRIVE MPEG-2 BOARD VGA CARD
MONITOR
1
CAN
U.S.A
MIX
CUB
BHS
PRI. VIR
1
BMG
GRL
2
2
ZAF
ISO
SWZ
FIN
POI
FST
LTU
BIR
UKR
TUR
FGY
JRN
TKM
AFG
PAK
CHN
MMR
MNG
RUS
KOR
JPN
HKG
MAC
TWN
PHL
6
3
2
1
5
5
4
1
MDI
MNP
GUM
PLW
PNG
NZL
AUS
4
The disc has
the regional
code of 8 bit.
Example)
The disc
manufactured
in the U.S.A,
has the
number one.
Transfer to
MPEG-2 board
reading the
regional code.
Receiving
data from the
MPEG-2
board and
output
through the
monitor
If the board is setting to the regional
code 1 for the U.S.A. ...
Check the received regional code to
number 1, all or not, transfer the
data to VGA card in accordance with
only a case among the three case.
Regional code
Page 45

INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE PICK-UP
1.Block Diagram of the PICK-UP(LPC-812R)
49
7
RF- SW
EF3
C
VC
VCC
D
GND
RF+
EF2
B
A
EF1
EF4
VREF
VCC
GND
STB
SW
OUT
NC
CW
CW
CDO
DVDO
IN
ENA E3
VCC
SEL
DVD_LD CD_LD
VCC
OSC
NE4E4NE3
CXA2694N
PD4CI
CP0076AH
8
1
VC(PDIC)
2
VCC(PDIC)
3
GND(PDIC)
4
EF4
5
EF1
6
A
7
B
8
EF2
9
EF3
10
C
11
D
12
SW(PDIC)
13
RF+
14
RF-
15
SW(FM)
16
VCC(FM)
17
GND(FM)
18
VREF(FM)
19
FM_OUT
20
TEMP
21
GND
Themester
22
W1DISN
23
W1DIS
24
W2DISN
25
W2DIS
26
W3DISN
27
W3DIS
28
OSCEN
29
GND
30
GND
31
VCC
32
W3SET
33
W2SET
34
W1SET
35
RSET
36
OUTSET
37
ENABLE
38
VCC
39
GND
40
F+
Focus
Actuator
TILT
TRACK
41
F-
42
TILT+
43
TILT-
44
T+
45
T-
9
10
11
12
13
14
6
5
4
3
2
1
10 1
2
3
4
5
9
8
7
6
13
6
NE2
5
E2
4
ER
3
RFA
2
RFB
1
OUTB
14
RSA
15
GND
16
RSB
17
OUTA
18
12
19
VCC
20IR21I222
I3
I4
23
24
11
10
9
8
7
Page 46

2.Pick up Pin Assignment
50
No. Pin Name Signal Description
45 T- Tracking Actuator drive signal44 T+ Tracking Actuator drive signal+
43 Tilt- Tilting Actuator drive signal42 Tilt+ Tilting Actuator drive signal+
41 F- Focusing Actuator drive signal40 F+ Focusing Actuator drive signal+
39 GND(LDD) Ground connection for LDD
38 VCC(LDD) Power supply for LDD
37 ENABLE Disables output current regardless of OUTEN(ENABLE Low:No lout)
36 OUTSEL High:selects DVD LD, Low:CD LD
35 RSET Input voltage for current amplifier
34 W1SET Input voltage for current amplifier
33 W2SET Input voltage for current amplifier
32 W3SET Input voltage for current amplifier
31 VCC(LDD) Power supply for LDD
30 GND(LDD) Ground connection for LDD
29 GND(LDD) Ground connection for LDD
28 OSCEN TTL control for Oscillator Enable (High Enable)
27 W3DIS LVDS control for output current (High Enable)
26 W3DISN LVDS control for output current (Low Enable)
25 W2DIS LVDS control for output current (High Enable)
24 W2DISN LVDS control for output current (Low Enable)
23 W1DIS LVDS control for output current (High Enable)
22 W1DISN LVDS control for output current (Low Enable)
21 GND(FPD) Ground connection for PDIC, FPD, TEMP
20 TEMP Output voltage for controlling temperature
19 FPD-OUT APC amplifier output
18 VREF(FPD) APC amplifier reference voltage output
17 GND(TEMP) Ground connection for PDIC, FPD, TEMP
16 VCC(FPD) Power supply for FPD
15 SW2(FPD) FPD output gain Select (High : CD, Low:DVD)
14 RF- Signal PDIC RF negative differential output
13 RF+ Signal PDIC RF positive differential output
12 SW1(PDIC) PDIC output gain Select (L/M/H)
11 D Signal PDIC output D
10 C Signal PDIC output C
9 EF3 Signal PDIC output EF3
8 EF2 Signal PDIC output EF2
7 B Signal PDIC output B
6 A Signal PDIC output A
5 EF1 Signal PDIC output EF1
4 EF4 Signal PDIC output EF4
3 GND(PDIC) Ground connection for PDIC, FPD, TEMP, LDD
2 VCC(PDIC) Power supply for PDIC(+5V)
1 VC(PDIC) Reference voltage input for PDIC)
Page 47

3.Signal detection of the P/U
1) Focus Error Signal ==> (A+C)-(B+D)
This signal is generated in RF IC (IC121 : AN22113A) and controls the pick-up’s up and down to focus on
Disc.
2) Tracking Error Signal (DPP Method) ==> {(A+D)-(B+C)}- k x {(EF1+EF4)-(EF2+EF3)}
This signal is generated in RF IC (IC121 : AN22113A) and controls the pick-up’s left and right shift to find
to track on Disc.
3) RF Signal ==> (A+B+C+D)
This signal is converted to DATA signal in DSP IC (IC201 : MN103SA6G).
51
Pick-Up module
Photo Diode
Tracking
Focusing
Infrared Iaser
k[(F+H) - (E+G)]
(A+D) - (B+C)
(A+D) - (B+C) - k[(F+H) - (E+G)]
Offset
TE
Tp
Sub2
Main
Tp/2
Sub1
T rac k Center
F,E
D,C
A,B
H,G
Page 48

52
MN103SA6G
Write
Strategy
IC 201
CN 101
Optical
Pick-up
LPC-812R
LD PD
LDD
Serial
I/F
D/A
D/A
D/A
D/A
D/A
D/A
M
P
X
IC 121 AN22113A
APC
19
A/D
ADSC
S/H
Signal
FM
123
VPD
127
FPDM
124
VREFPD
40 41
42
SH1
SH2SH3
VGA
LPF
Ave
Erase
Space
VGA
S/H2
S/H3
S/H1
DESCRIPTION OF CIRCUIT
1. ALPC (Automatic Laser Power Control) Circuit
1-1. Block Diagram
1-2. ALPC (Automatic Laser Power Control) Circuit Operation
The ALPC block detects the laser output power of the front monitor. The power signal detected with the PD for front monitor
detection is input the voltage from the VPD pin(123Pin) or the FPDM pin(127Pin), the reference signal of the input signal is
input from the VREFPD pin(124Pin). The ALPC block generates the singals from the input laser power signals in the
following detection systems. This block has four detection paths:All average value path, multi pulse average/peak value
detection path, erase/bottom value detection path, space/playback power value detection path.
Page 49

53
2.Focus/Tracking/Sled Servo Circuit
2-1. Focus, Tracking & Sled Servo Process
F
E
DC
AB
H
G
Pick-up
Focus Error
Detector
Focus Error
Detector
A,B,C,D
A,B,C,D
E,F,G,H
A,B,C,D
E,F,G,H
IC121 AN22113A
FE
TE
IC201
Servo Control
MN103SA6G
TE FE
A/D
D
A
C
SLED
COMPENSATOR
A/D
PARALLEL
DIGITAL
COMPENSATOR
SDRV
60
64
66
67
STEP2
STEP1
IC301 BD7956FS
29
30
M
Stepping Motor
Logic
A+
37 38 40 39
A- B- B+
Tracking Focusing
Actuator
T- T+ F- F+
5
4
LEVEL SHIFT
FDRV
TDRV
LEVEL SHIFT
53 54 51 52
Focus, Tracking, Sled Servo
Page 50

54
2-2. Focus & Tracking Servo Process(using the LightScribe)
OPU
PDIC
S-DPWM 10bit
100/50 MHz
S-DPWM 10bit
100/50 MHz
ADC
INT
LPF
V ref
R
On/Off
BD7956
Drive IC
AN22113
FEP
MUX
Circuit
R
On/Off
16 bit
Timer
RXD
RFS_iNT
HC_CTL
RXD
RFOUT
Track
Focus
Internal u-P(F/W)
Need to change to 16bit
MN103SA6G
MECHANISM
Comparator
RFOUT
RXD/RFS_INT
Page 51

3. Spindle Servo Circuit
3-1. Spindle Servo Process
55
F
E
DC
AB
H
G
Pick-up
Wobble Signal
Generator
RF
IC121 AN22113A
WBLIN
EFM
SRF
SERVO DSP
Phase Controller
Frequency
Controller
68
SPDRV
IC201 MN103SA6G
IC301 BD7956FS
M
Spindle Motor
Level Shift
3-2. Spindle Servo
Spindle servo is as following ;
1) Wobble CLV 4x, 10x, 16x, 24x, 32x, 40x : Blank area in CD-R, CD-RW
2) Wobble CLV 1x, 2x, 2.4x, 4x, 8x : Blank area in DVD+/-R/RW
3) CD 15x CAV : Video CD, CD-DA(Audio out)
4) CD 32x CAV : CD-RW, CD-DA(DAE)
5) CD 40x CAV : CD-ROM/R
6) DVD 8x CAV : Single Layer DVD-ROM(Movie), Dual Layer DVD-ROM, DVD+RW, DVD-RW, DVD+R
Double Layer
7) DVD 10x CAV : DVD+R, DVD-R
6) DVD 16x CAV : Single layer DVD-ROM(Data)
-Spindle Servo is controlled by IC201(MN103SA6G) and servo signal is output via SP-DRV(Pin70).
Page 52

3-3. Spindle Servo Process(using the LightScribe)
56
MN103SA6G
MECHANISM
BSDA 12bit 100MHz
Internal u-P (F/W)
16bit Timer
Pre-scale
FEP
INT
X-TAL
16.9344MHz
TR
Optical
Encoder IC
5V
Optical FG
69
9
2 or 3
state
R
On/Off
BD7956
Drive IC
Motor
Optical
Encoder
Enc
Vcc
Page 53

MAJOR IC INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM AND PIN DESCRIPTION
IC121 (AN22113A) : FEP(RF) Analog Signal Processor
• Pin Assignment
57
CDRFP 97
CDRFN 98
CDHPF 99
DLY1 100
DLY2 101
GND2 102
FO1 103
FO2 104
TR1 105
TR2 106
TR3 107
TR4 108
109
110
VCC1 111
GND6 112
VREF 113
SVREF 114
VCC3 115
AIN 116
BIN 117
118
119
EIN 120
FIN 121
122
123
DACOUT 124
VREF08 125
VPD 126
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
VREFPD
127
GND3
128
1
ROPCIN
2
APCAAF1
3
APCAAF2
4
APCAAF3
5
CPCAPH
6
CPCABH
7
NC
NC
8
STMD
9
STMDN
10
11
CBDOF
12
CBDOS
13
CHPOFT
14
SEO121SEO2
22
MOUT023MOUT1
24
COFTR
15
VCC6
16
VHALF
17
CTC
18
CXDPH1
19
CXDPH2
20
MOUT2
25
GND1
26
PO0
27
PO128PO229PO330PO431PO5
32
PO6
33
STMOUT
39
TC
40
OFTR
41
BDO
42
VCC51
43
GND5
44
WTGT
45
PIO0
34
PIO1
35
PIO2
36
PIO3
37
FEPIDGT/SH6
46
NC
47
WIDGT/SH4
48
SH3
49
SH2
50
SH1
51
SH5
52
VCC4
53
SEN
54
SCK
55
SDAT
56
RSEN
57
RSDAT
58
VCC52
59
GND4
60
ASENV/LPPM
61
LPPS
62
WBL
63
CLUMPGT
64
PAD065
PAD166
PAD2
67
PAD3
65
PAD469
PAD5
70
PAD6
71
PAD772
CLPPPH
82
CLPPHPF
83
CBPFAGC
84
CWBLCMP
85
CRWAGC
87
CRWCMP
88
CWBLVGA2
89
CWBLVGA190
CWAGC2
91
CWAGC1
92
CWBLHPF2
93
CWBLHPF1
94
RFP
95
RFN
96
FLTAMP75
RFIN276
RFIN1
77
HDVREF
78
CWBLBUF
79
VCC2
80
EQOUTP
74
RFOUT
81
AIDENV/WBLDIF
86
EQOUTN
73
PIO4
38
AN22113A
(Top View)
128Pin TQFP
TQFP-128-P-1414A
Page 54

58
Input Block
TEC Block
LPOS Block
WBL/LPP Block
OFTR Block
OPC&ASENV
Block
RFEQ Block
JLINE Block
LOGIC Block
APC Block
MPX Block
FIN
STMD
STMDN
STMOUT
SE01 SE02
TC
WBLDIF
ASENV/
LPPM
LPPS
WBL
OFTR
VPD
FPDN
SDAT
SCK
SEN
RSDAT
RSEN
EIN
TR3
TR4
AIN/TR1
BIN/TR2
HIN/Fo1
GIN/Fo2
VREF
CD/DVD
Switch
S/H
&
VGA
MPX
MPX
MPX
MPX
MPX
MPX
MPX
DPD Block
TCTI Block
BDO Block
FOCUS
PPTE
Block
VREF
Block
RF Gene Block
GATE
Block
Operation Circuit
SMFEP
SDAAOUT
SDABOUT
SPLAOUT
SDACOUT
SDADOUT
SPLBOUT
SRFMA
SRFMD
SRFMB
SRFMC
SMTEP
SMTEN
CHP0FT
COFTR
SLP14
SLP23
SMFEPN
SSFEP
SSFEPN
SMTEP
SMTEN
SSTEP
SSTEN
SDAAOUT
SDABOUT
SDACOUT
SDADOUT
SDPDTEP
SRFMA
SRFMD
SRFMB
SRFMC
SDPDTEN
SPLAOUT
SPLBOUT
SPOF
TCOP
TCO
TCON
TIOP
TIO
SBDOAS
TION
VGA
VGA
COMP.
PK
ENV
PK
ENV
COMP.
VGA/
Bypass
VGA/
Bypass
M
P
X
M
P
X
DPD TE
Dtetction
TC/TI
Dtetction
HDVREF
VHALF
VREF08
RFP
CDRFP
RFN
CDRFN
BDO
RF OUT
RFIN1
RFIN2
EQOUTP EQOUTN
VREF
GATE
All
Sum
VG
A
Group delay
compensation
SW
To
Each Block
PK
ENV
VGA
COMP.
Lve1
Shift
LPF
MPX
TECENV
SLPOS2
SLP23
SLP14
LPF
SLPOS1
SSTEP
SSTEN
VGA S/H VGA
VGA
WBL
Detection
LPP
Detection
BAL
BAL
AGC/
Bypass
AGC/
Bypass
S/H VGA
Amp
COMP.
VGA
VGA
VGA
VGA
S/H VGA
LPF
Bypass
+
-
+
+
-
-
+
+
+
+
_
_
+
+
_
_
+
LPF
PK
ENV
BT
ENV
ATT
Amp EQ
0FST
To
Each Block
To Each Block
To MPX
JLINE
LOGIC
COMP.
CLMP.
-
VGA
VGA
VGA S/H
S/H
S/H
LPF/
Bypass
ATT
SEL
Block Diagram
Page 55

59
• Pin Assignment
Pin no. Pin Name Type Function
1 GND3 PS Ground pin for APC/OPC & ASENV
2 ROPCIN I Input pin after OPC addition
3 APCAAF1 I Capacitor connection pin for APC mark system AAF
4 APCAAF2 I Capacitor connection pin for APC average DC detection system AAF
5 APCAAF3 I Capacitor connection pin for APC bottom detection system AAF.
6 CPCAPH O External capacitor connection pin for PCA peak hold.
7 CPCABH O External capacitor connection pin for PCA bottom hold.
8NC --
9 STMD I PD input pin for STM
10 STMDN I PD input pin for STM
11 N.C - 12 CBDOF I Capactitor connection pin for BDO detection Fast Peak Env.
13 CBDOS I Capacitor connection pin for BDO detection LPF
14 CHPOFT O External capacitor connection pin for OFTR HPF
15 COFTR I External capacitor connection pin for OFTR
16 VCC6 PS Power supply pin for DPD & internal current source power supply pin(3.3V)
17 VHALF O 1/2 VCC(3.3V) output pin
18 CTC I Capacitor connection pin for TE binary floating
19 CXDPH1 I PH capacitor connection pin 1 for LPOS
20 CXDPH2 I PH capacitor connection pin 2 for LPOS
21 SEO1 O Output pin 1 after selection of each error signal
22 SEO2 O Output pin 2 after selection of each error signal
23 MOUT0 I Analog monitor 0
24 MOUT1 I/O Analog monitor 1
25 MOUT2 I/O Analog monitor 2
26 GND1 PS Ground pin for INPUT MATRIX/SERVO/VREF/DPD
27 PO0 O CMOS output pin 0
28 PO1 O CMOS output pin 1
29 PO2 O CMOS output pin 2
30 PO3 O CMOS output pin 3
31 PO4 O CMOS output pin 4
32 PO5 O CMOS output pin 5
33 PO6 O CMOS output pin 6
34 PIO0 I/O CMOS input pin or output pin 0
35 PIO1 I/O CMOS input pin or output pin 1
36 PIO2 I/O CMOS input pin or output pin 2
37 PIO3 I/O CMOS input pin or output pin 3
38 PIO4 I/O CMOS input pin or output pin 4
39 STMOUT O Encoder circuit comparator output
40 TC O Track cross signal output
Page 56

60
Pin no. Pin Name Type Function
41 OFTR O OFTR signal output
42 BDO O BDO output
43 VCC51 PS Power supply pin for CMOS I/F & internal current source power supply pin 1(3.3V)
44 GND5 PS Ground pin for CMOS I/F
45 WTGT I Light gate signal input (pull-down)
46 FEPIDGT/SH6 I CAPA through signal input pin/ servo sampling signal input pin(pull-dowm)
47 NC - 48 WIDGT/SH4 I VFO through signal input pin
ROPC mark detection sampling signal input pin (pull-down)
49 SH3 I PCA average detection, APC space detection/Playback power detection/
Erase detection sample timing signal input pin(pulldown)
50 SH2 I PCA peak/bottom detection, APC space detection/Playback power detection/
Erase detection sample timing signal input pin(pulldown)
51 SH1 I ROPC space detection, APC space detection/Playback power detection sample
timing signal input pin(pulldown)
52 SH5 I Sample-and-hold timing signal input pin of wobble S/H at recording (pull-down)
53 VCC4 PS Power supply pin for internal LOGIC(5.0V)
54 SEN I Serial enable input (pulldown)
55 SCK I Serial clock input (pullup)
56 SDAT I/O Serial signal data input
57 RSEN I Serial enable input for RF (pulldown)
58 RSDAT I Serial signal data input for RF
59 VCC52 PS Power supply pin for CMOS I/F & internal current source power supply pin2 (3.3V)
60 GND4 PS Ground pin for internal LOGIC
61 ASENV/LPPM O ASENV output/LPP mark output pin
62 LPPS O LPP space output pin
63 WBL O WBL binary output
64 CLUMPGT I RFAGC input bias circuit clamp setting input pin (pulldown)
65 PAD0 I A/D input pin 0
66 PAD1 I A/D input pin 1
67 PAD2 I A/D input pin 2
68 PAD3 I A/D input pin 3
69 PAD4 I A/D input pin 4
70 PAD5 I A/D input pin 5
71 PAD6 I A/D input pin 6
72 PAD7 I A/D input pin 7
73 EQOUTN O Equalizer filter ouptut N pin
74 EQOUTP O Equalizer filter output P pin
75 FLTAMP I FILTER final stage AMP reference voltage stabilization pin
Page 57

61
Pin no. Pin Name Type Function
76 RFIN2 I RFAGC signal input pin 2
77 RFIN1 I RFAGC signal input pin 1
78 HDVREF O 2.2V reference voltage output pin
79 CWBLBUF I Capacitor connection pin for WBLDIF
80 VCC2 PS Power supply pin for RFGene/RFEQ/WBL/LPP (5.0V)
81 RFOUT O RFGene signal output pin
82 CLPPPH I Capacitor connection pin for LPP peak hold
83 CLPPHPF I Capacitor connection pin for LPPHPF
84 CBPFAGC I AGC adjustment capacitor connection pin after WBL BPF
85 CWBLCMP I Floating Capacitor connection pin for VGA before WBL binary
86 AIDENV/WBLDIF O ASENV binary output/Differential signal output pin for ADIP detection
87 CRWAGC I AGC adjustment capacitor connection pin for +RW
88 CRWCMP I Floating Capacitor connection pin for VGA before WBLDIF AGC
89 CWBLVGA2 I Floating Capacitor connection pin 2 for VGA before SLR
90 CWBLVGA1 I Floating Capacitor connection pin 1 for VGA before SLR
91 CWAGC2 I AGC adjustment capacitor connection pin 2 for WBL extraction
92 CWAGC1 I AGC adjustment capacitor connection pin 1 for WBL extraction
93 CWBLHPF2 I Capacitor connection pin for N side HPF before WBLAGC
94 CWBLHPF1 I Capacitor connection pin for P side HPF before WBLAGC
95 RFP I DVD RF differential input + pin
96 RFN I DVD RF differential input - pin
97 CDRFP I CD RF differential input + pin
98 CDRFN I CD RF differential input - pin
99 CDHPF I Internal RF additional floating capacitor connection pin
100 DLY1 I Capacitor connection pin 1 for group delay correction
101 DLY2 I Capacitor connection pin 2 for group delay correction
102 GND2 PS Ground pin for RFGene/RFEQ/WBL/LPP
103 FO1/GIN I DVD focus signal input pin 1/CD sub signal input pin 3
104 FO2/HIN I DVD focus signal input pin 2/CD sub signal input pin 4
105 TR1 I DVD tracking signal input pin 1
106 TR2 I DVD tracking signal input pin 2
107 TR3 I DVD tracking signal input pin 3
108 TR4 I DVD tracking signal input pin 4
109 N.C - 110 N.C. - 111 VCC1 PS Power supply pin for INPUT MATRIX/SERVO/VREF (5.0V)
112 GND6 PS Ground pin for BG
113 VREF O 1.65V reference voltage output pin
114 SVREF I OEIC signal reference level input pin
115 VCC3 - Power supply pin for APC/OPC&ASENV(5.0V)
Page 58

62
Pin no. Pin Name Type Function
116 AIN I CD main signal input pin 1
117 BIN I CD main signla input pin 2
118 N.C. - 119 N.C. - 120 EIN I CD sub signal input pin 1
121 FIN I CD sub signll input pin 2
122 N.C. - 123 N.C. - 124 DACOUT O Wide Use DAC output pin
125 VREF08 O 0.8V referece Voltage output (for APC) pin
126 VPD I DVD front monitor signal input pin (for APC)
127 N.C. I 128 VREFPD I Front light system reference level input pin
I : Input pin O: Output pin I/O : I/O pin PS : Power supply/Ground pin N.C: Non Connection
Page 59

63
IC201 (MN103SA6G) : Encoder, Decoder & DSP Singal Processor
• Pin Assigment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
162
161
160
159
158
157
156
155
154
153
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
216
215
214
213
212
211
210
209
208
207
206
205
204
203
202
201
200
199
198
197
196
195
194
193
192
191
190
189
188
187
186
185
184
183
182
181
180
179
178
177
176
175
174
173
172
171
170
169
168
167
166
165
164
163
BSMD
NBSMD
PKMD
NPKMD
PK2MD
MPK2MD
PK3MD
NPK3MD
AVDD33D2
LOUT
ROUT
AVSSD2
RV1
VREFH
AVDD33D1
CPOP5
CPOP4
CPOP3
CPOP2
CPOP1
AVSSD1
SE01
SE02
AVSSA
AIDENV/WBLDIF
AVDD33A
REFMDLA
REFTOP
REFBTM
REGDRC
EQOUTN
EQOUTP
AVDD33DRC
CDA1
AVSSDRC
P02
FMSW/PO3
WTGT
WBL
FEPIDGT
SH5
WIDGT
SH3
SH2
SH1
TC
CLUMPGT
ASENV
POLGT
LPPS
OFTR
P04/GENE0/TRCDATA3/EXTRIG2
TGCHG/P05
LSEN
FADR3
FADR2
FADR1
MA4
MA3
MA5
MA2
MA6
MA1
MA7
MA0
VDD3
VSS
MA8
MA10
MA9
P15/TRCDATA3/EXTR1G2/MBA1
P14/TRCDATA2/EXTR1G1/MA11
MBA0
MCKB
MNRAS
MCLK
MNCAS
MDQMU
MNWE
MDQML
VDD3
VDD12
VSS
MDQ8
MDQ7
MDQ9
MDQ6
MDQ10
MDQ5
MDQ11
MDQ4
MDQ12
MDQ3
MDQ13
MDQ2
MDQ14
MDQ1
MDQ15
MDQ0
NDASP
NCS3FX
VDD3
VDD5
VSS
NCS1FX
DA2
DA0
NPDIAG
NRST
TRCST/P21
TRCCLK/P20
P17/TRCDATA2/EXTRIG1
VDD3
OSC0
OSC1
VSS
MSTPOL/TRCDATA1
DASPST/TRCDATA0
SCLOCK
SDATA
TRYLOAD/P26
NEJECT
TX/P16
NCE
NOE
FDT0
FDT8
FDT1
FDT9
FDT2
FDT10
FDT3
VDD12
FDT11
FDT4
FDT12
FDT5
FDT13
FDT6
FDT14
FDT7
FDT15
FADR16
FADR15
FADR14
FADR13
FADR12
FADR11
VDD3
VSS
FADR10
FADR9
NWE
FADR20/P25
FADR19/P24
FADR18
FADR17
FADR8
FADR7
FADR6
FADR5
FADR4
LSCK
LSDAT
P06/HFON
VSS
VDD3
VHALF/PO7
PWM0A
PWM0B/P10
PWM1A
PWM1B/P11
PWM2A/P27
PWM28/P12/TX
PWM3A
PWM3B/P15
PWM4
FG
SEN
SCK
SDAT
RSEN
RSDAT
BDO
MASTER/P23
NRESET
HDD7
HDD8
HDD6
VSS
VDD12
VDD3
HDD9
HDD5
HDD10
HDD4
HDD11
HDD3
HDD12
HDD2
HDD13
VSS
VDD3
HDD1
HDD14
HDD0
HDD15
DMARQ
WIOWR
NIORD
IORDY
NDMACK
INTRQ
N10/CS16/P22
DA1
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
798081
91
125
216
215
214
213
212
211
LDDENA
MN103SA6G
TOP VIEW
Page 60

• Block Diagram (SODC:MN103SA6G)
64
FEP
LDD
FEP
DRC
CD
SERVO
ADSC
CD
REC
PERIPHERAL
32 bit CPU
ANALOG
CPU
BCU
FMT
HOST
16.9MHz
SDRAM
16 Mbit
64 Mbit
Falsh
ROM
2 Mbyte
ECC
HOST
I/F
Page 61

65
• Pin Table
Pin Pin Name I/O Connection Description
Number
Target
1 BSMD O PU BIAS modulation signal differential current output
2 NBSMD O PU NBIAS modulation signal differential current output
3 PKMD O PU PEAK1 modulation signal differential current output
4 NPKMD O PU NPEAK1 modulation signl differential current output
5 PK2MD O PU PEAK2 modulation signal differential current ouptut
6 NPK2MD O PU NPEAK2 modulation signal differential current ouptut
7 PK3MD O PU PEAK3 modulation signal differential current ouptut
8 NPK3MD O PU NPEAK3 modulation signal differential current ouptut
9 AVDD33D2 Power supply Power supply Analog VDD(3.3V) for audio
10 LOUT O Audio AMP Analog audio output (Lch)
11 ROUT O Audio AMP Analog audio ouput (Rch)
12 AVSSD2 GND GND Analog Vss for audio
13 RV1 I/O Res Fixed current source for LVDS, WBL, and analog blocks
14 VREFH I FEP 2.2V reference voltage input
15 AVDD33D1 Power supply Power supply WOBBLE analog VDD(3.3V)
16 CPOP5 I/O Cap.Res Filter connection pin for wobble PLL
17 CPOP4 I/O Cap.Res Filter connection pin for wobble PLL
18 CPOP3 I/O Cap.Res Filter connection pin for wobble PLL
19 CPOP2 I/O Cap.Res Filter connection pin for wobble PLL
20 CPOP1 I/O Cap.Res Filter connection pin for wobble PLL
21 AVSSD1 GND GND WOBBLE analog Vpp
22 SEO1 I FEP Error signal output after selection analog input
23 SEO2 I FEP Error signla output after selection analog input
24 AVSSA GND GND Servo analog-to-digital converter analog Vss
25 AIDENV I FEP TE signal for DVD-RAM
WBLDIF ADIP detector signal input
26 AVDD33A Power supply Power supply Servo analog-to-digital converter analog VDD(3.3V)
27 REFMDLA O Cap Analog-to-digital converter reference voltage for ADIP
28 REFTOP O Cap Analog-to-digital converter reference voltage for DRC(TOP)
29 REFBTM O Cap Analog-to-digital converter reference voltage for DRC(BOTTOM)
30 REGDRC O Cap DRC analog-to-digital converter analog VDD(1.2V)
31 EQOUTN I FEP RF differential signal (NEG)
32 EQOUTP I FEP RF differential signal (POS)
33 AVDD33DRC Power supply Power supply DRC analog-to-digital converter analog VDD(3.3V)
34 CDA1 O Cap Smoothing capacitance for DRC-VCO
35 AVSSDRC GND GND DRC analog Vss
36 PO2 I/O - CPU external interrupt, general-purpose I/O, laser fault detect
signal
Page 62

66
Pin Pin Name I/O Connection Description
Number
Target
37 FMSW I/O PU Power monitor detector multiplier conversion signal
PO3 General-purpose I/O
38 WTGT O FEP Write gate
39 WBL I FEP Wobble binary signal
40 FEPIDGT O FEP CAPA punch out signal, main beam sampling signal
41 SH5 O FEP Write WOBBLE sample and hold sampling signal
42 WIDGT O FEP VFO punch out signal, ROPC mark detection sampling signal
43 SH3 O FEP Sample timing signal for PCA mean value detection, APC space
detection, read power detection, and erase detection
44 SH2 O FEP Sample timing signal for PCA peak, bottom detection, APC peak
detection, and mean value detection
45 SH1 O FEP Sample timing signal for ROPC, space detection, APC space
detection, and read power detection
46 TC I FEP Track crossing signal input
47 CLUMPGT O FEP RF AGC bias circuit clamp signal
48 ASENV I FEP ASENV/LPP mark input
49 POLGT O FEP CAPA polarity switch signal, sub beam sampling signal
50 LPPS I FEP LPP space input
51 OFTR I FEP Off track input
52 PO4 CPU external interrupt, general-purpose I/O
GENE0 I/O - Inner limit switch input
TRCDATA3 Trace data 3
EXTRIG2 Trigger 2
53 TGCHG I/O OEIC Write power switch signal
P05 General-purpose I/O
54 LSEN O PU LDD serial interface enable
55 LSCK O PU LDD serial interface clock
56 LSDAT I/O PU LDD serial interface data
57 LDDENA O PU LDD enable signal
58 P06 I/O - CPU external interrupt(5V input)
HFON General-purpose I/O for external high frequency module(HFM)
ON/OFF
59 VSS GND GND Digital Vss
60 VDD3 Power supply Power supply I/O pad VDD(3.3V)
61 VHALF I/O FEP Drive pin central reference voltage input
P07 General-purpose I/O
62 PWM0A O DRIVER Focus drive differential PWM+ output, focus drive BSDA output
63 PWMOB I/O DRIVER Focus drive differential PWM- output
P10 General-purpose I/O
Page 63

67
Pin Pin Name I/O Connection Description
Number
Target
64 PWM1A O DRIVER
Focus 2(tilt) drive differential PWM+ output, focus 2 drive BSDA output.
65 PWM1B I/O DRIVER Focus 2(tilt) drive differential PWM-output
P11 General-purpose I/O
66 PWM2A I/O DRIVER
Tracking drive differential PWM+ output, tracking drive BSDA output
P27 General-purpose I/O
67 PWM2B Tracking drive differential PWM-output
P12 I/O DRIVER General-purpose I/O, IEC958-compliant digital output
TX Debugging serial TX
68 PWM3A O DRIVER Traverse drive differential PWM+ output, stepper 1 drive output
69 PWM3B I/O DRIVER Traverse drive differential PWM- output, stepper 2 drive output
P13 General-purpose I/O
70 PWM4 O DRIVER Spindle drive output
71 FG I DRIVER Spindle FG input(5V input)
72 SEN O FEP FEP serial interface enable
73 SCK O FEP FEP serial interface clock
74 SDAT I/O FEP FEP serial interface data
75 RSEN O FEP FEP serial interface enable2(RF)
76 RSDAT O FEP FEP serial interface data2(RF)
77 BDO I FEP Dropout signal
78 MASTER I/O HOST ATAPI master/slave signal
P23 General-purpose I/O
79 NRESET I HOST ATAPI reset signal
80 HDD7 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
81 HDD8 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
82 HDD6 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
83 VSS GND GND Digital Vss
84 VDD12 Power supply Power supply Internal logic Vpp(1.2V)
85 VDD3 Power supply Power supply I/O pad VDD(3.3V)
86 HDD9 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
87 HDD5 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
88 HDD10 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
89 HDD4 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
90 HDD11 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
91 HDD3 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
92 HDD12 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
93 HDD2 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
94 HDD13 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
95 VSS GND GND Digital Vss
Page 64

68
Pin Pin Name I/O Connection Description
Number
Target
96 VDD3 Power supply Power supply I/O pad VDD(3.3)
97 HDD1 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
98 HDD14 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
99 HDD0 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
100 HDD15 I/O HOST ATAPI data I/O
101 DMARQ O HOST DMA request to ATAPI host
102 NIOWR I/O HOST ATAPI host write signal
103 NIORD I/O HOST ATAPI host read signal
104 IORDY O HOST Ready signal to ATAPI host
105 NDMACK I HOST ATAPI host DMA acknowledge signal
106 INTRQ O HOST Interrupt request to ATAPI host
107 NIOCS16 I/O HOST ATAPI data bus width select signal
P22 General-purpose I/O
108 DA1 I/O HOST ATAPI host address signal input
109 NPDIAG I/O HOST Diagnostic signal from ATAPI slave to master
110 DA0 I/O HOST ATAPI host address signal
111 DA2 I/O HOST ATAPI host address signal
112 NCS1FX I HOST ATAPI host chip select signal
113 VSS GND GND Digital Vss
114 VDD5 Power supply Power supply 5V reference power supply
115 VDD3 Power supply Power supply I/O pad VDD(3.3V)
116 NCS3FX I HOST ATAPI host chip select signal
117 NDASP I/O HOST ATAPI drive active slave signal
118 MDQ0 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
119 MDQ15 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
120 MDQ1 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
121 MDQ14 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
122 MDQ2 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
123 MDQ13 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
124 MDQ3 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
125 MDQ12 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
126 MDQ4 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
127 MDQ11 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
128 MDQ5 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
129 MDQ10 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
130 MDQ6 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
131 MDQ9 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
132 MDQ7 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
Page 65

69
Pin Pin Name I/O Connection Description
Number
Target
133 MDQ8 I/O SDRAM SDRAM data
134 VSS GND GND Digital Vss
135 VDD12 Power supply Power supply Internal logic Vpp(1.2V)
136 VDD3 Power supply Power supply I/O pad VDD(3.3V)
137 MDQML O SDRAM SDRAM DQML signal
138 MNWE O SDRAM SDRAM write enable signal
139 MDQMU O SDRAM SDRAM DQMU signal
140 MNCAS O SDRAM SDRAM CAS signal
141 MCLK I/O SDRAM SDRAM clock
142 MNRAS O SDRAM SDRAM RAS signal
143 MCKE O SDRAM SDRAM clock enable signal
144 MBA0 O SDRAM SDRAM bank switch 0
P14 General-purpose I/O
145 TRCDATA2 I/O SDRAM Debugging trace data
EXTRIG1 Trigger
MA11 SDRAM address
P15 General-purpose I/O
146 TRCDATA3 I/O SDRAM Debugging trace data
EXTRIG2 Trigger
MBA1 SDRAM bank switch 1
147 MA9 O SDRAM SDRAM address
148 MA10 O SDRAM SDRAM address
149 MA8 O SDRAm SDRAM address
150 VSS GND GND Digital Vss
151 VDD3 Power supply Power supply I/O pad VDD(3.3V)
152 MA0 O SDRAM SDRAM address
153 MA7 O SDRAM SDRAM address
154 MA1 O SDRAM SDRAM address
155 MA6 O SDRAM SDRAM address
156 MA2 O SDRAM SDRAM address
157 MA5 O SDRAM SDRAM address
158 MA3 O SDRAM SDRAM address
159 MA4 O SDRAM SDRAM address
160 FADR1 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
161 FADR2 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
162 FADR3 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
163 FADR4 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
164 FADR5 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
Page 66

70
Pin Pin Name I/O Connection Description
Number
Target
165 FADR6 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
166 FADR7 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
167 FADR8 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
168 FADR17 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
169 FADR18 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
170 FADR19 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
P24 General-purpose I/O
171 FADR20 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
P25 General-purpose I/O
172 NWE O FLASH Flash ROM write enable signal
173 FADR9 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
174 FADR10 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
175 VSS GND GND Digital Vss
176 VDD3 Power supply Power supply I/O pad VDD(3.3V)
177 FADR11 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
178 FADR12 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
179 FADR13 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
180 FADR14 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
181 FADR15 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
182 FADR16 I/O FLASH Flash ROM address
183 FDT15 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
184 FDT7 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
185 FDT14 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
186 FDT6 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
187 FDT13 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
188 FDT5 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
189 FDT12 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
190 FDT4 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
191 FDT11 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
192 VDD12 Power supply Power supply Internal logic VDD(1.2V)
193 FDT3 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
194 FDT10 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
195 FDT2 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
196 FDT9 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
197 FDT1 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
198 FDT8 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
199 FDT0 I/O FLASH Flash ROM data
200 NOE O FLASH Flash ROM output enable signal
Page 67

71
Pin Pin Name I/O Connection Description
Number
Target
201 NCE O FLASH Flash ROM chip enable signal
202 TX I/O - IEC958-compliant digital output, debugging serial TX
P16 General-purpose I/O
203 NEJECT I/O Mecha Tray eject signal (SODC external interrupt)
204 TRYLOAD I/O Mecha Tray eject signal (SODC external interrupt)
P26 General-purpose I/O
205 SDATA I/O - Debugger data, DRC monitor 0
206 SCLOCK I/O - Debugger clock, DRC monitor 1
207 DASPST I/O - DASP setting
TRCDATA0 Trace data 0
208 MSTPOL I/O - MASTER pin polarity switch
TRCDATA1 Trace data 1
209 VSS GND GND Digital Vss
210 OSCI I Xtal Oscilator input (16.9344MHz)
211 OSCO O Xtal Oscilator output
212 VDD3 Power supply Power supply I/O pad V
DD(3.3V)
P17 General-purpose I/O
213 TRCDATA2 I/O - Trace data 2
EXTRIG1 External interrupt
214 TRCCLK I/O - Trace clock
P20 General-purpose I/O
215 TRCST I/O - Trace status
P21 General-purpose I/O
216 NRST I Reset IC Reset input (power on reset)
Page 68

IC301 (BD7956FS) : CD-ROM/DVD-ROM 7CH POWER DRIVER
• Block Diagram
LEVEL
SHIFT
LEVEL
SHIFT
BOTTOM
HOLD
Current
Limit
FF
FF
TSD
Tjmonitor
LIMIT
LIMIT
HB
PWM Hall matrix
50k
100k
50k
50k
100k
100k
100k
LEVEL
SHIFT
LEVEL
SHIFT
PRE
LOGIC
PRE
LOGIC
STBY/
BRAKE
CONTROL
FG
FG
fin
fin
OSC
50k
47k
33.6k
33.6k
1
54
LDO- ACO1+
53
ACO1-
52
ACO2+
51
ACO2-
50
ACO3+
49
ACO3-
48
AV
47
ACTIN3
46
LDIN
45
AGND
44
SPCNF
43
FG
42
V
41
fin
40
SLO1+
39
SLO1-
38
SLO2+
37
SLO2-
36
SLGND
35
CTL2
34
CTL1
33
SLRNF2
32
SLRNF1
31
SLV
DD
C
M
30
SLIN2
29
SLIN1
28
DVcc
2
LDO+
3
Vcc
4
ACTIN1
5
ACTIN2
6
TJMON
7
BTHC
8
SPVM_S
9
PGND1
10
PGND2
11
U
12
SPV 1
13
V
M
M
14
fin
15
PGND3
16
W
17
SPV 2
18
SPRNF
19
HB
20
HU+
21
HU-
22
HV+
23
HV-
24
HW+
25
HW-
26
SPIN
27
DGND
72
Page 69

73
No Symbol Description
1 LDO- Loading driver negative output
2 LDO+ Loading driver positive output
3 Vcc BTL pre and Loading power supply
4 ACTIN1 Actuator driver 1 input
5 ACTIN2 Actuator driver 2 input
6 TJMON monitor of chip temperature
7 BTHC Capacitor connection terminal for spindle
current bottom holding
8 SPVM
-S Spindle driver sense power supply
9 PGND1 Spindle driver power ground 1
10 PGND2 Spindle driver power ground 2
11 U Spindle driver output U
12 SPVM1 Spindle driver power supply 1
13 V Spindle driver output V
14 fin fin
15 PGND3 Spindle driver power ground 3
16 W Spindle driver output W
17 SPVM2 Spindle driver power supply 2
18 SPRNF Spindle driver current sense
19 HB Hall bias
20 HU+ Hall amp.U positive input
21 HU- Hall amp.U negative input
22 HV+ Hall amp.V positive input
23 HV- Hall amp.V negative input
24 HW+ Hall amp.W positive input
25 HW- Hall amp.W negative input
26 SPIN Spindle driver input
27 DGND PWM block pre-ground
No Symbol Description
54 ACO1+ Actuator driver 1 positive output
53 ACO1- Actuator driver 1 negative output
52 ACO2+ Actuator driver 2 positive output
51 ACO2- Actuator driver 2 negative output
50 ACO3+ Actuator driver 3 positive output
49 ACO3- Actuator driver 3 negative output
48 AV
M Actuator driver block power supply
47 ACTIN3 Actuator driver input 3
46 LDIN Loading driver input
45 AGND BTL driver block power ground
44 SPCNF Spindle driver feedback filter
43 FG Frequency generator output
42 Vc Reference voltage input
41 fin fin
40 SLO1+ Sled driver 1 positive output
39 SLO1- Sled driver 1 negative output
38 SLO2+ Sled driver 2 positive output
37 SLO2- Sled driver 2 negative output
36 SLGND Sled driver power ground
35 CTL2 Driver logic control 2 input
34 CTL1 Driver logic control 1 input
33 SLRNF2 Sled driver 2 current sense
32 SLRNF1 Sled driver 1 current sense
31 SLVDD Sled driver PowerMOS pre-supply
30 SLIN2 Sled driver 2 input
29 SLIN1 Sled driver 1 input
28 DVcc PWM block control power supply
• Pin Function
Page 70

Input/Output circuit diagram
74
Three-phase motor driver output
Hall signal input
Splindle driver feedback filter pin
PWM driver output SLED1, 2
BTL driver input ACT1,2,3,LD PWM driver input SLED1, 2 PWM driver input Spindle
BTL driver output FO, TK BTL driver output LD
Spindle driver current detection input Hall bias
FG signal output
12
109 15
17
16 13 11
22
20
28
28 28
28
28
24
23
21
25
32 33
38
40
27 36
37
39
49
51
53
48
48
48
50
52
54
45
2
3
3
3
45
1
19
28
43
28
5
4
46
47
3
3
50k
5pF
5k
10pP
Ω
Ω
Reference voltage input
BTHC terminal TJ output
29
30
28
28
47k
3pF
Ω
3
40kΩ
100
113
Ω
Ω
5kΩ
26
28
28
47k
5pF
Ω
5k
Ω
Control signal input
34
35
28
28
50kΩ
50kΩ
50kΩ
1
1
1
20
6
18
8
8
2kΩ
12.5k
7pF
Ω
50kΩ
18kΩ
50k
5pF
Ω
2.5kΩ
42
3
×4ch ×2ch
1kΩ
50kΩ
50kΩ
50kΩ
50kΩ
200kΩ
100Ω
200Ω
10kΩ 47kΩ
Page 71

TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
Are the pin 44 of
CN271+5V, pin41 of CN271+12V
respectively after the power cable
connecting?
Reset or Power Check.
• Check the power(5V/12V) short.
• Check the PC power cable.
• Repair the PC power supply.
• Check the IC401(3.3V regulator IC).
• Check the IC201, IC121.
Does the pin #1
(Reset) of IC271 change 0V to 3.3V
at the power supply initial input
mode?
<Power>
•
Is the pin 5 of IC401 3.3V?
<Reference>
•
1.65V(VREF) : Check pin113 of IC121?
• 2.2V(HDVREF): Check pin78 of IC121
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
75
Are the X201 oscillating?
• Check the X201(16.9MHz).
• Check the IC201.
NO
• Check the IC401.
NO
• Check the IC121.
NO
Check it after connecting the power cable
only on interface cable for NO Reset or
Power ON.
YES
OK
Page 72

76
System Check.
Go to “Tray operating is abnormal”
Load tray without inserting disc.
NO
Does Tray operate normally?
Does Pick-up move to inside?
Does Laser turn on?
After eject tray, Insert CD-ROM Disc
and check rotation.
Does Disc rotate
continuously and the drive recognize
the disc?
After eject tray, Insert Blank CD-R or
RW Disc and check rotation.
After eject the tray, Insert DVD Disc and
check rotation.
After eject the tray, Insert DVD+R/RW Disc
and check rotation.
Does Disc rotate
continuously and the drive recognize the
disc?
Does Disc rotate
continuously and the drive recognize the
disc?
Does Disc rotate
continuously and the drive recognize the
disc?
Go to “Sled operating is abnormal”
Go to “Laser operating is
abnormal”
Go to “Recognition fail Case1
(CD-ROM Disc)”
Go to “Recognition fail Case2
(Blank CD-R/RW)”
Go to :Recognition fail Case3
(DVD Disc)”
Go to :Recognition fail Case4
(Blank DVD+R/RW)”
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
Does Pickup lens move
up/down?
Go to “Focus Actuator operating is
abnormal”
NO
YES
OK
Page 73

77
Is the
input voltage 0V at IC201
pin203 when push the
EJECT SW?
Tray operating is abnormal.
Drive doesn’t work after tray
close
• Check the pull-up line(3.2V).
• Replace SW1.
• Check the pull-up line(3.3V).
• Replace SW1.
When CN303 is open, Is
there Tray drive signal
output?
• Check the connction of IC201 pin 203.
• Replace the EJECT SW.
• Check the connctor (CN303).
• Replace the IC301.
Is the input
voltage 0V at IC201
pin204(/OPENSW) when
push the SW1?
Is the input
voltage 0V at IC201
pin63(/LOADSW) when
push the SW1?
YES
NO
NO
• Check the connction of IC201 pin 66.
• Replace theIC201.
• Check the communication line
between IC201.
NO
YES
YES
YES
NO
Is there Tray
drive voltage output?
(IC301 pin 1,2)
Is there Tray
control signal input?
(IC301 pin 4)
YES
NO
YES
Tray open doesn’t work.
Page 74

78
Is there Sled
control signal output?
(IC201 pin 68,69)
Sled operating is abnormal.
Replace the IC301.
Replace the IC121.
Replace the IC201.
Is DRVMUTE2 signal ‘H’?
(IC301 pin 35)
• Check the R316, R317.
Check the connection of IC121
pin 32.
Is there
Sled drive voltage output ?
(CN302 pin 1,2,3,4)
Replace the Sled Motor.
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
•
Check the Connection CN302.
NO
Is there
Sled drive voltage input?
(IC301 pin 29,30)
YES
NO
Is there
Sled drive voltage output?
(IC301 pin37,38,39,40)
YES
NO
Page 75

79
Is there
Spindle control DSP output?
(IC201 pin70)
Spindle operating is abnormal
Is there
Spindle drive voltage output?
(IC301 pin 11, 13, 16)
Is there
Spindle drive voltage output?
(IC301 pin 1, 2, 3)
•
Check the Connection CN301.
•
Replace the Spindle Motor.
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
Is there
FG signal input?
(IC201 pin 71)
NO
YES
YES
• Check the output of IC301 pin 43.
• Check the connector CN301.
• Replace the IC301.
• Replace the IC201.
OK
Page 76

80
Focus Servo is unstable
Is FE signal
output normal in Focusing
Up/Down?
(IC121 pin25*)
Check Pickup Read Power
is 1.3~1.7mW?
YES
Replace the IC121.
Replace the Pick up.
Go to “Focus Actuator
operating is abnormal”
NO
NO
Is FDRV signal
output normal in Focusing
Up/Down?
(IC201 pin 62)
•
Replace the IC201.
NO
YES
Focus Actuator operating is
abnormal
Is there Focus
Search control signal input?
(IC301 pin5)
Is DRVMUTE2 signal “H”?
(IC301 pin 35)
• Replace the IC301.
• Check the connection CN101 pin40,41.
• Check the connection of IC121 pin 32.
• Replace the IC121.
NO
YES
Replace the Pick-Up.
Is there Focus
Search drive voltage output?
(IC301 pin 51,52)
NO
• Check the connection of IC201 pin 62.
• Check the communication line between
IC121 and IC201.
• Replace the IC201.
YES
NO
YES
* IC121 pin25 is MOUT2(FEP Monitor2).
After disc recognition action, Monitor port
is off. So, please check FE signal during
disc recognition.
Page 77

81
Track Servo is unstable
Is TE signal
output normal in Focusing
ON and Tracking OFF?
(IC121 pin 24*)
YES
•
Check the PICK UP FFC.
•
Replace the PICK UP.
Replace the IC121.
NO
Replace the IC201.
Check the Drive IC(IC301) and
P/U referring to “Focus Actuator
operating is abnormal”.
Is there TDRV
signal output in Tracking ON?
(IC201 pin66)
NO
Is PICK UP
(E, F, G, H) output normal?
(CN101 pin 8, 5, 9, 4)
YES
YES
NO
* IC121 pin24 is MOUT1(FEP Monitor1).
After disc recognition action, Monitor port
is off. So, please check TE signal during
disc recognition.
Page 78

82
Recognition Fail Case 1:
CD-ROM Fail
Check Pickup Read Power
was 1.3 ~1.7mW?
Check the Pick-up FFC and CN101.
Replace the Pick-up.
Go to “Focus Servo is unstable”.
NO
YES
Does Focus Servo
operate normally?
Check Pickup
RF signal IC121(Pin81)
RFOUT was 2~2.5V?
NO
Go to “LD CHECK”.
YES
NO
Replace IC121.
YES
Check EQOUTP
waveform (IC121 Pin 74) was
1.75~2.3V?
NO
Go to “Tracking Servo is unstable”.
YES
YES
Check after replacing IC201.
It is OK?
NO
Recognition Fail Case2 :
Blank CD-R/RW
Is there WBL (IC201 pin39)
signal?
Check the connection between
IC201 and IC121.
Replace IC121.
Replace the IC201.
NO
YES
Is there WBL (IC121 pin63)
signal?
NO
YES
OK
Page 79

83
Check Pick-up Read Power
was 1.1~1.3mW.
Recognition Fail Case 3 :
DVD Disc
Go to ‘LD CHECK’.
YES
YES
NO
Is there WBL
(IC121 pin63) Signal?
Recognition Fail Case 4 :
Blank DVD+R/RW
Replace IC201.
Replace IC121.
Check the connection
between IC121 and IC201.
YES
NO
NO
Is there WBL
(IC201 pin39) Signal?
YES
NO
Is there RF signal at IC121
Pin81?
YES
Replace the Pickup.
NO
Replace the IC121.
Is there
RF signal at IC121 Pin95(RFP)
and Pin96 (RFN)?
YES
NO
Replace the IC201.
Check again after the replace
IC121 It is OK?
OK
Page 80

84
In case of writing fail.
Normal Case
Check disc Label.
Finalized Disc?
Check the Media CD-R
or CD-RW or DVD+R or
DVD+
RW?
If CD-R disc, use new CD-R disc.
If CD-RW disc, erase the disc.
If DVD+R disc, use new DVD+R disc.
If DVD+RW disc, erase the disc.
Go to “Writing Part Check”
YES
NO
Remove the Dust, Fingerprint and
if the disc has long width
Scratch, change it.
Does the disc
have any Dust, Scratch,
Fingerprint...?
YES
NO
Use LG bundle Software
(Write Tool & Version)
Is the write
Tool(version) supported by
LG DVD+RW Drive?
YES
NO
NO
Check disc information on Writng Tool.
[If you get some data information with
“Non Recordable Disc” Message, the
disc is finalized -Finalized Disc :
unrecordable Disc any more]
Eject Disc.
YES
Page 81

85
No audio output
• Check and replace the IC121.
Audio Play : AUDMUTE ‘H’.
• Check and replace the IC201.
•
Check the connection of L/R OUT.
Insert the audio Disc.
NO
AUDMUTE : ‘L’?
(IC121 Pin 33)
DSP ROUT,LOUT signals output?
(IC201 Pin 10, 11)
Do audio Line
signals output? (CN271
pin 51, 54)
NO
NO
YES
YES
Normal
Page 82

86
Change the Media.
NO
LS Media Recognition Fail:
LS CD, DVD
Check the Cleanness of Media.
Check 3pin FFC and Q501.
Check Encoder IC Power.
NO
YES
Check Enc Assy’s Alignment and
Grease on it.
Check the OFG Signal.
NO
YES
Go to ‘LD CHECK’.
Check P/U Read Power
4.5~5.5mW.
NO
YES
Replace IC501, 502.
Check the RXD/RFS_INT Signal
On Recognizing LS Media..
NO
YES
OK
Page 83

87
A. Start
1. Install GWA-4164B –> PC Power ON –> Execute Windows.
2. Execute Dragon_JW3.exe on Windows (Dragon_JW3.exe & Dragon.cfg should be on same Directory).
3. If you use GWA-4164B, “Dragon(2005/04/08, 14:00)” will be displayed on the window Frame.
4. Select I/F Setup on the menu bar.
5. Select ATAPI I/F and then Click OK.
6. Select Target Device on the menu bar.
7. Select “DVDRRW GWA-4164B” on Target Device, and then Click OK.
• How to use Test Tool (Dragon)
[I/F Setup Menu]
[Target Device window]
Page 84

88
B. Check ALPC Parameters
1. Select About on the menu bar.
2. Click Addition Func. on About window -> New frame will be displayed.
3. Click ALPC Para tab and verify the specification.
[ALPC Parameters]
1) CD VRDC : 117~153
2) CD VWDC_NMP : 100~135
3) CD VWDC_MP : 100~137
4) CD VWDC_ERASE : 105~135
5) DVD VRDC : 115~157
6) DVD VWDC_NMP : 100~135
7) DVD VWDC_MP : 100~135
8) DVD VWDC_ERASE : 105~140
9) H.C. VWDC : 100~150
10) Default ALPC Para. used : 0xFF
4. Close window.
[ALPC Parameters Menu]
[Additional Function Menu]
Page 85

C. Laser Power Setup
1. Remove disc on the tray.
2. Select ALPC/OPC on the menu bar, and then select Setup Laser Power(Manual) menu.
3. First, select CD and setup wave length of LD Power meter (780nm)
(Wave Length : CD(780nm), DVD(660nm), Measure Range : 0.01mW unit).
4. Click VRDC button on the Laser Power Setup window. Laser beam will be emitted from LD.
5. Measure LD Power with LD Power meter. Type the result in the blank(Read Power box).
ex) 1.44mW -> 144, 0.99mW -> 99)
6. Click NMP button and measure LD Power with Power meter. Type the result in the blank(R NMP Power
box).
ex) 16.45mW -> 1645, 12.08mW -> 1208
7. Click MP button and measure LD Power with Power meter. Type the result in the blank(RW Erase Power
box).
8. Click ERASE button and measure LD Power with Power meter. Type the result in the blank(RW Erase
Power box).
9. Click LD Off button and then click Setup button, and result witll be displayed with OK or NG.
10. Select HC_CD and then click HC button.
11. Measure LD Power with Power meter. Type the result in the blank (HC Power).
12. Click LD Off button and then click Setup button, and result will be displayed with OK or NG.
13. Select DVD and change wave length of LD Power meter (660nm).
14. Follow above step 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
15. Close Laser Power Setup window.
89
[Laser Power Setup window]
[Laser Power Setup Frame]
Page 86

90
[CD Laser Power Setup Result]
[HC_CD Laser Power Setup Result]
[DVD Laser Power Setup Result]
Page 87

91
12V_source
3.3V
1.3V
Drive IC (spindle, sled, load) power
BD7956FS
RF IC (IC121)
AN22113A
DSP IC (IC201)
MN103SA6G
Pick-up
LPC-812R
BA3259
IC401
3.3/1.2V-Reg
5V_source
Reset IC (IC271)
BD5233
Drive IC (Actuator)
BD7956
RF IC (IC121)
AN22113A
DSP IC (IC201)
MN103SA6G
Pick-up
LPC-812R
AT22138A
IC101
SDRAM (IC261)
M12L16161A
Flash Memory (IC262)
EEPROM (IC201)
MN103SA6G
MX29LV160BBTC
Power Supply System Diagram
Page 88

Disc
Disc
Sled
motor
FCS/TRK/TILT
Sled Driver
LDD
ALPC
Gain/S/H
Matrix
OPC/ROPC
RF EQ
&
GCC
Wobble
JLINE
MPX
Write Strategy
LVDS
Serial I/F
ADC
Servo
ADSC
FMT
Servo
DRC
ECC
BCU
1M bit
DRAM
32bit
CPU
Host
I/F
Host PC
&
Authoring
Tool
Buffer
RAM
PWM
BSDA
-Controller
Serial
I/F
FEP(RF)
(AN22113A)
SODC(DSP)
(MN103SA6G)
I/V AMP
Spindle
motor
Spindle
Driver
92
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Page 89

94
Spindle motor
(LG-inotec)
Sled motor
(Mabuchi)
1chip(7ch)
Motor drive
(TBD)
serial
serial
16.9344MH
serial
P-up
(LPC-812R)
RV7 FEP AN22113A
DAC
WS
Input
Block
FOCUS
PPTE
Block
STM
Block
MPX
Block
WBL/LPP Block
OFTR Block
APC
Block
OPC &
ASENV
Block
DPD Block
TCTI Block
BDO Block
RFEQ
Block
JLINE
Block
LOGIC
Block
RF Gene Block
GATE
Block
To each
Block
VREF
Block
TEC Block
LPOS
Block
SDRAM
16/64Mb
Built-in System Controller
32Bit CPU
Flash ROM
AD
ADIP
DRC
CD
ADIP
FORMATTER
ECG
EEPROM
4KByte
AD
SRAM
ADSC
DA VCO
CIRC
CD PRE
ANALOG
SERVO DSP
32bit
CD REC
PERIPHERAL
BCU
A/D
AUTH
SYSIF
INTC TMR
KCGEN
MODEC
WDT
AM
DMA
ENC
DEC
HOST I/F
ATAPI I/F
MPEG I/F
RV7 MN103SA6G
Regulator
3.3v/1.3V
Power block
Regulator
12V
host
 Loading...
Loading...