Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
REFRIGERATOR
ATTENTION
Before start servicing, carefully read the safety instructions
in this manual
MODEL(S): GR-382R
LRTP1231W
Page 2

Contents
Safety Precautions ----------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------- 1
Service Precautions ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-3
Specifications ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4
Feature Chart ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5
Circuit Diagram ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 6-7
Cooling Systems ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8
Product Disassembly ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9-11
Doors ------------------------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------- 9
Door Switch ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9
Electronic Control Display PCB ----------------------------------------------------------------- --- 9
Freezer Fan ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10
Defrost Control ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 10
Lamp ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10
Refrigerator Control Box ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 11
Reversible Door --------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------- 12-13
Adjustments ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14-15
Compressor ---------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------ 14
PTC Starter----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
Overload Protector (OLP) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 15
Troubleshooting ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16-21
Compressor & Electrical Components ------------------------------------------------------------ 16
PTC & OLP ------------------------------------ ---------------------------------------------------------- 17
Other Electrical Components ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 18
Service Diagnosis Chart ------------------------------------------------------------- ----------------- 19
Refrigerant Cycle --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 20-21
MICOM circuit & operation --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 22-39
Refrigerator Exploded View-------------------------------------------------------------------------- 40-41
Service Parts list----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 42-43
Safety Precautions.
Read the following inst ructions before servicing your refrigerator.
1. Unplug the refrigerator before
servicing.
2. Visually inspect for gas leakage or
short circuit.
3. If testing with the refrigerator
plugged in, wear rubber gloves to
avoid electric shock.
4. Do not touch frozen metal parts;
your hands could freeze to the
surface. This
5. Be sure that no water is dripping
may cause frostbite.
towards electrical or metal parts.
6. If you check the bottom part of the
refrigerator while the freezer
door is open, be careful standing
up. You
could bump your head.
7. When you tilt your refrigerator be
sure to take out all metal, glass, or
other loose
parts.
8. When servicing the evaporator,
wear cotton gloves to prevent cutting
by any of
the evaporator fins.
1
Page 3

Service Precautions
Refrigerant Recharging
Test the compressor's operation before
recharging the refrigerant; this is very
important to detect failures and to
ensure the proper motor running, and
to identify failures immediately. If
failure has been detected, clean the
system from any other possible
R-134a residues by breaking the final
part of the compressor's service pipe
at it's thinnest part as shown in Fig. #1.
Replace the filter and any other part
that could be deteriorated. Unweld
and pull out the service pipe,
then place a new pipe extension with a
Hansen male connector and solder
the new pipe. See Fig. #2
0(absolute or -1 atm, -760 mm Hg.) It
is not recommend to run the vacuum
pump for more than 30 minutes. See
Figure 3.
In case there is a large leak and the
vacuum operation must stop,
you must add a small amount of
refrigerant to the system and check
with an electronic leak detector. If a
soldering failure is detected, open the
valve before soldering to equalize the
pressure and keep solder from being
blown out of the joint or sucked into
the piping.
It is necessary to open the valve
when soldering to allow the gases to
escape without forcing the molten
solder out of the joint. The extension
with the male Hansen connector
should be connected to a female type
connector to the vacuum pump's pipe.
See Fig. #3
System air evacuation starts as soon
as the pump begins to run. The
system must be kept under vacuum
until the low pressure gauge shows
As soon as the repair is completed,
charge the correct amount of
refrigerant into the system.
Remember that each system requires
a specific amount of refrigerant with a
tolerance of ±5 grams. See Figure 4.
Before performing this operation (if
the vacuum pump and charging
cylinder are still attached to the
system) be sure the valve between
the pump and the cylinder is closed to
2
Page 4
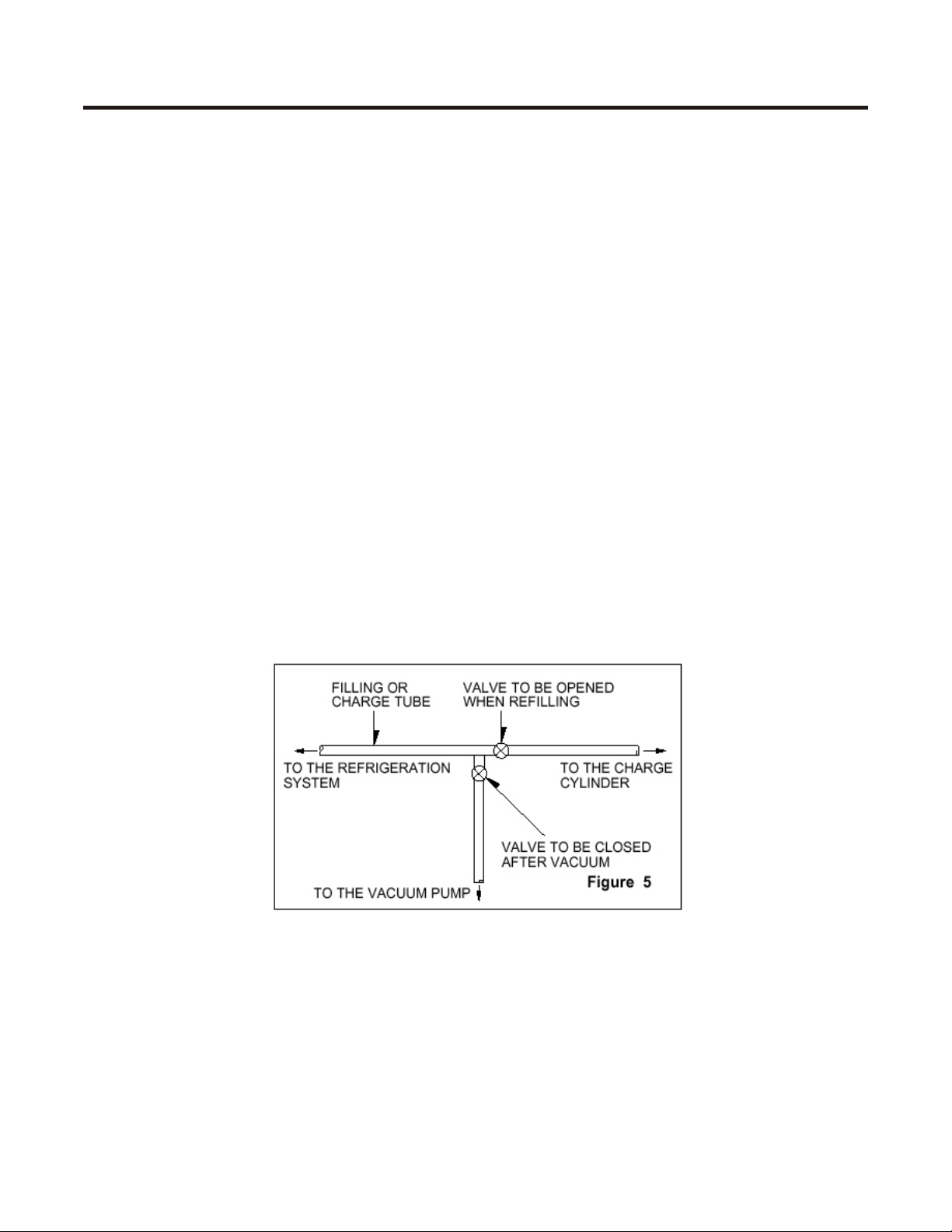
Service Precautions
keep refrigerant out of the system.
See Figure 5.
For gas charging, check the
graduated scale on the cylinder to see
the amount of refrigerant that it
contains and the amount that will be
pumped into the system. For
example, if you have 750 grams of
refrigerant in the cylinder and we
have to pump 165 grams to the
system, this amount will be reached
when the indicator reaches 585
grams; remember that the indicator
shows a lower level of meniscus.
Do this after choosing the scale
corresponding to the gas pressure
indicated on the pressure indicator
located on the upper part of the
column. To let R-134a flow into the
system, open the valve at the
recharging cylinder's base. The total
amount of refrigerant should not be
installed in one session, as it could
block the compressor. Install 20~30
grams at a time and close the valve.
The compressor will run and the
pressure will drop. Then open the
valve and install other 20~30 grams
of refrigerant. Repeat this procedure
until the entire amount has been
added to the system. Under operating
conditions, the system pressure
should stabilize between 0.3 and 0.6
atm.
3
Page 5

Page 6

Feature Chart
FREEZER
Temperature
Control
Shelf
Ice Trays
Twist´n Serve
REFRIGERATOR
Temperature
Control
Fresh Meat
Tray
Lamp
Shelves
(Plastic or Glass)
Deodorizer
(Absorbs
Odors)*
Multi Air Flow
Air flow distributor
Freezer
Door Baskets
Refrigerator
Door Baskets
Vegetable Tray
(Keeps fruits and
vegetables fresh)
MODEL(S): GR-382R
LRTP1231W
* This part is only included in model LRTP1231W
Magic Crisper
(Vegetable Tray cover
that control humidity)
5
Leveling
Screws
Page 7

Page 8

Graphic Circuit Diagram
Brown
Red
Pink
Yellow
Blue
Violeta
Whitte
White
White
White
Brown
Red
Red
Blue
Orange
Orange
Yellow
Blue
c
C
C
Brown
Red
Orange
Orange
Blue
Black
Switch
Violet
Yellow
Thermal Fuse
Defrost Resistance
Evaporator
Defrost Resistance
Fan
(Heater Cord)
Sensor
Lamp
Control
Sensor
Brown
Blue
Red
Blue
Sensor
CON2
Defrost and Temperature Electronic Control
CON1
Black
Yellow
Blue
Black
Fan
Motor
Blue
AC Current
Brown
Pink
Blue
Pink
Black
OLP
M
Running Capacitor
COMPRESSOR
7
Page 9
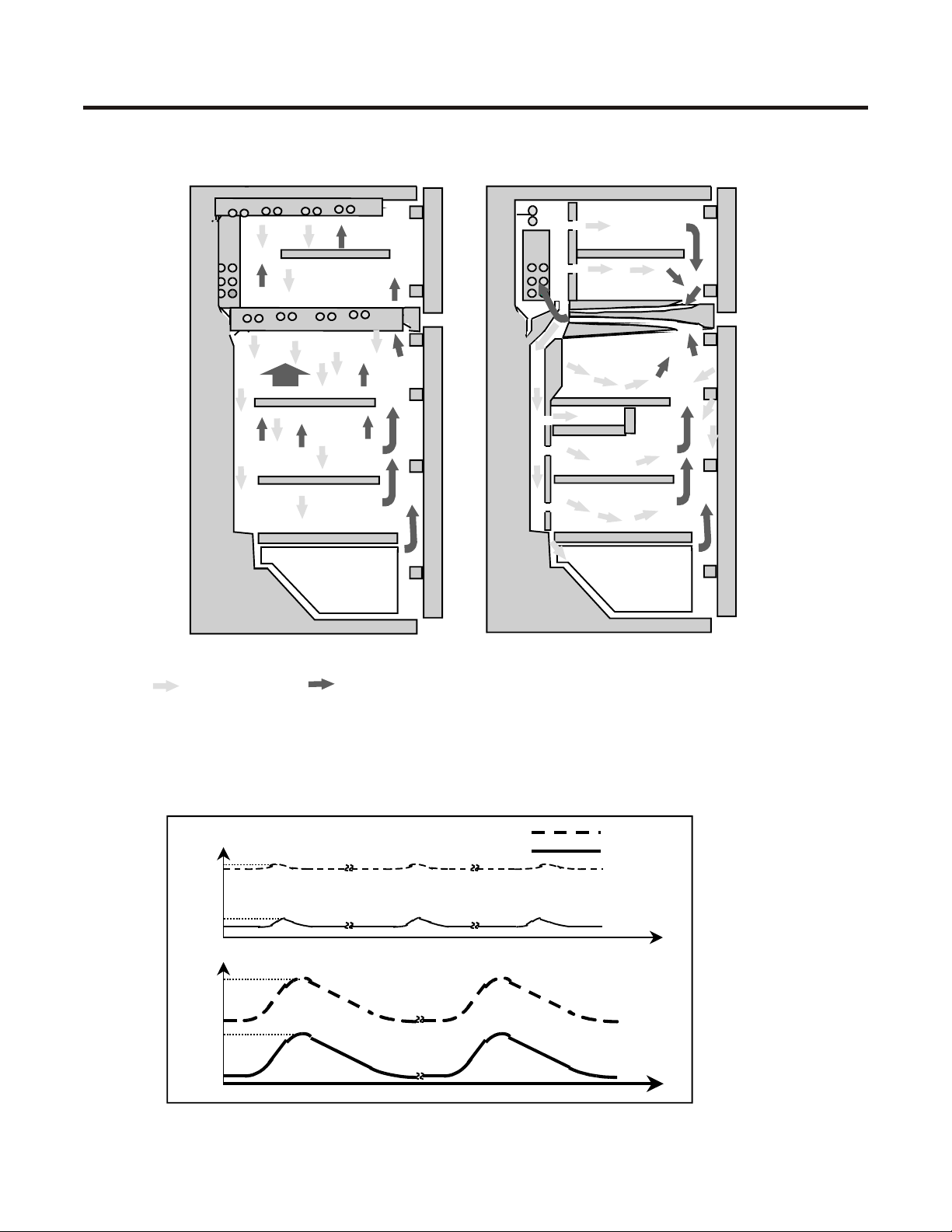
Cooling Systems
Direct System Indirect System
Important: Check that the air ducts are not
Cold Air
Temperature variation during defrosting time, depending upon the cooling system .
Temp.( ? )
4
3
-16
-18
Temp.( ? )
18
Warm Air
obstructed for a better cooling
performance.
Indirect System
Direct System
Refrigerator
Freezer
Tim
e
3
-3
-18
Tim
e
8
Page 10

3. Product Disassemble.
Doors
Freezer Door
1. Remove hinge cover by pulling it
upwards.
2. Loosen the hexagonal bolts that
hold the upper hinge in place. See
Figure 1.
3. Remove door. See Figure 2.
Figure 1
Figure 2
4. Pull gasket to remove it. See
Figures 3 and 4.
2. Disconnect all switche's cables.
See Figure 8
Figure 7
Figure 8
Control Circuit ( Display PWB)
1. Remove the lamp cover by
inserting a screwdriver in the lower
side's holes. See Figure 9.
2. Loosen and remove the 2 screws.
See Figure 10.
Figure 3
Figure 4
Refrigerator Door.
1. Loosen the hexagonal bolts that
hold the central hinge in place.
See Figure 5.
2. Remove refrigerator door. See
Figure 6.
3. Pull out the gasket to remove it
from the door. See Figure 4 from
Freezer door.
Figure 5
Figure 6
Door Switch
1. Pull out the door switch out using
a flat head screwdriver. See
Figure 7
Figure 9 Figure 10
3. Pull out the Control Box. See
Figure 11.
4. Disconnect the connector from the
cable terminal. See Figure 12.
5. Remove the EPS Multi air duct
(insulation) from the control box.
6. Detach the electronic control
(Display, PWB). See Figure 13.
Figure 11
Figure 12
9
Page 11

Figure 13
Fan and Fan Motor.
1. Remove freezer shelf.
3. Remove the ice bin assembly by
pulling it to the right side, until it
snaps out.
4. Remove Grill Fan screw cover.
See Figure 14.
5. Loosen the screw. See Figure 15.
6. Pull out the fan cover. Figure 16.
Defrost Control Assembly
1. The defrost control assembly
consists of one thermistor and a
fuse that melts with heat.
2. The termistor's function is to
sense the compartment's
temperature and automatically
stop the defrost. The termistor is
located beside of the evaporator
bracket.
3. The melting fuse is a safety device
to prevent an overheating of the
defrosting resistance when it
operates.
4. The fuse melts at 162° F and the
resistance heater stops.
5. To replace this components,
please follow the steps mentioned
at Figure 18.
Figure 14
Figure 15
6. Unplug the connector.
7. Remove the fan holder shroud.
Figure 17.
8. Remove fan and loosen both
screws that hold the bracket.
9. Remove the motor bracket and the
rubber parts. Pull out the fan
motor. See Figure 17.
Figure 16
Figure 17
1. Figure 18. Unplug the connector plugged to
Lamp.
Refrigerator Compartment Lamp
1. Remove the lamp cover with
a screwdriver or a similar tool.
See Figure 19.
2. Remove the lamp by unscrewing it
counterclockwise and replace it
with the same specifications
(125V,20W). Part Number
6912JB2002J.
10
Page 12

Figure 13
Figure 19
Refrigerator Control Box.
Remove the lamp cover as mentioned
before.
1. Loosen the screws.
2. Remove the entire control box.
See Figure 20.
3. Disconnect the control box
connector. See Figure 21.
Figure 20 Figure 21
11
Page 13

4. Reversible Door
PRECAUTION
1. Before reversing the doors, remove all foods and accesories,
like shelves or trays, which are not attached to the doors.
2. Use a Philips screwdriver, bolt driver, torque wrench, or spanner to
tighten and loosen the bolt.
3. Be careful not to drop the refrigerator or door when assembling or
disassembling lower hinge or the Adjustable Screw Assembly.
4. Don´t lay the refrigerator down to work on it. It will cause
malfunction.
5. The doors may be reversed to provide left or right opening, depending upon the customer´s
preference.
HOW TO REPLACE THE DOOR OPENING LEFT TO RIGHT
(when converting from left-opening to right opening)
12
Page 14

13 14
Page 15

5. Adjustments
1- COMPRESSOR
1-1 Function
The compressor sucks low pressure
evaporated gas from the evaporator
and compresses it into high
temperature/high pressure gas and
sends it to the condensor.
1-2 Composition
The compressor includes the
compressing system, a motor, and an
enclosure. The PTC (thermistor) and
OLP (Overload Protection Device) are
attached to its exterior. Handle and
repair the compressor with care. It
includes parts manufactured to 1
micron tolerance, and is hermetically
sealed to exclude dust or humidity
after fabrication. Dust, humidity, or
flux getting into the refrigeration cycle
could clog it or otherwise affect the
cooling.
1-3 Use notes.
(1) Protect your refrigerator from over
currents or overloads.
(2) Do not bump or jar the
compressor. If it is bumped or
forced (dropping or careless
handling,) it could damage the
compressor or cause noise or
undesirable operation.
(3) Use only exact replacement parts
when repairing the compressor. If
the terminals become corroded, it
could affect operation. If the
replacement parts are of incorrect
values, operation and safety will
be compromised.
2- PTC
2-1 PTC Composition
(1) The PTC (Thermistor) is a
semiconductive starting
component that is made with
BaTiO .
(2) The higher the temperature, the
higher the resistance value will be.
This characteristic is used for
starting the motor.
2-2 PTC Function
(1) The PTC is attached to the
hermetic compressor and its used
for its starting.
This household refrigerator uses a
single induction motor. During
normal operation, the motor starts
with current flowing through both
the main and the auxiliary
windings. After the motor starts,
current to the auxiliary winding is
cut off.
2-3 PTC- Electric Diagram
According to motor starting method.
3
Page 16

2-4 Motor restarting and PTC cooling.
(1) To restart normal operation after a
power interruption, wait 5 minutes
to let the pressure equalize and
the PTC to cool.
(2) During normal operation, the PTC
generates heat. If it has not had
time to cool after a power
interruption, the motor will not
restart until the PTC cools.
2-5 PTC OLP Relation
(3) If power is cut off during
compressor operation and then
restored before the PTC has
cooled down, it's resistance value
increases. As a result, the current
cannot flow to the auxiliary
winding and the motor cannot start
and the OLP operates due to the
current overflow through the main
winding.
(3) While the OLP repeats the
ON/OFF operation 3~5 times, the
PTC cools and the compressor
operates normally. If the OLP
does not operate when the PTC is
hot, the compressor motor will
overheat, causing a short circuit or
possibly a fire. Therefore, use a
fail-safe OLP.
2-6 Note on using the starting PTC
(1) Be careful not to cause an
overvoltage or short circuit.
(2) Do not force or bump it.
(3) Keep the OLP dry. If water or oil
gets into the OLP, the electrical
insulation can degrade and fail.
(4) Do not replace the PTC at your
own convenience. Do not
disassemble the PTC. If the PTC's
exterior is damaged, the
resistance value changes and
may cause failure during the
stating of the compressor's motor.
Use a PTC in good condition.
3- OLP
3-1 OLP Definition
(5) The OLP is a bimetallic, heat sensitive switch attached to the
compressor. Its function is to
protect the motor in the event of
overheating.
(6) When an overvoltage flows to the
motor, the bimetal reacts by
heating and activating (opening)
the OLP.
3-2 OLP Function
(7) Prevents the starting to the motor
winding.
(8) Do not turn the adjustment screw
during normal OLP operation.
(OLP connection diagram)
15
Page 17

6. Troubleshooting
6-1 COMPRESSOR AND ELECTRIC COMPONENTS
1
Power Source.
Remove the PTC-Starter
from the Compressor
(Rating Voltage
10%)
Go to Step 2
and measure the voltage
between Terminal C of
Compressor and
Terminals 5 or 6 of PTC.
No Voltage.
OLP disconnected?.
Replace OLP.
Check connection
condition.
Go to Step 5
Reconnect.
Consult a qualified
electrician.
NO
Replace
Compressor.
YES
Go to Step 5
Go to Step 3
Go to Step 3
2
Check the
resistance of
Motor
Compressor.
Applied voltage isnÿ´t in
the range of Rating
Voltage 10%.
Check the resistance
among M-C, S-C and M-S
in Motor Compressor.
4
5
3
Check the
resistance of
PTC-Starter.
Check OLP.
Check
starting state.
Check the resistance of
two terminals in PTCStarter.
Check if applying a
regular OLP.
Measure minimum starting
voltage after 5 min. for
balancing cycle pressure
and cooling the PTC.
OLP works within 30
seconds In forcible
OLP operation by
turning against power
on and off.
NO
Components start in
the voltage of Rating
Voltage 10% below.
Go to Step 4
Replacce
PTC-Starter.
NO
YES
YES
Replace OLP.
O.K.
NO
Go to Step 5
Go to Step 4
Go to Step 5
Go to Step 5
Go to Step 1
16
Page 18

6-2 PTC AND OLP
Normal operation of
Compressor is
impossible or poor.
Separates the PT
from Compressor and
measure the
resistance between
No. 5 and 6 (only
RSIR Type) or No. 4
and 5 of PTC with a
Tes ter or Wheatstone
Bridge (Figure 22).
Observation value is
220V/50Hz: 22 W ±30%
115V/60Hz: 6.8 W ±30%
240V/50Hz: 33 W ±30%
127,220V/60Hz:22 W ±30%
The Resistance value
is 0 or several
hundreds W
The value is ?
Check the other
electric components.
Replace PTC.
Separate the OLP
from Compressor and
check resistance value
between two terminals
of OLP with a Tester.
(Figure 23).
YES
NO
Check other electric
components.
Replace OLP
17
Page 19

6-3 OTHER ELECTRIC COMPONENTS
No Cooling
Compressor
doesn´t run.
Check if current flows to
the following components.
a. Starting Devices Shorted or Broken
b. OLP Poor contact or shorted.
c. Compressor coil Coil Shorted.
d. Circuit Parts Poor contact or shorted.
Cause
Replace each
component.
Running state of
Compressor is poor.
Fan Motor doesn´t
run.
Check starting
voltage.
Check if current
flows to starting
devices.
Check current
flowing in sub-coil
of Compressor.
Check capacity of
OLP.
The items
described above
are normal.
Checker current
flow of the door
switch.
Check current
flowing in the fan
motor.
Low Voltage
Poor contacting
and broken.
Shorted
Lack of Capacity
Compressor
Motor Coil.
Poor contact
Coil is shorted
Raise the voltage.
Replace the
defective
component.
Replace the
Compressor.
Replace the
defective
component.
Much frost is on the
evaporator.
Check current flow
of the following
components:
· Defrost Control
Check current flow
of the following
components:
· L-CORD, TE-PLATE
18
Shorted
Replace PTC.
Replace PTC.
Page 20

6-4 SERVICE DIAGNOSIS CHART
COMPLAINT POINTS TO BE CHECKED REMEDY
1. Is the power cord unplugged?
2. Check if the power switch is set to OFF.
No Cooling
Poor Cooling
Poor Freezing
Food in the refrigerator
is frozen
Moisture or ice forms in
the chamber of the set.
Moisture forms on the
outside
Abnormal Noise
Door doesn´t close well.
Ice and food smell
unpleasent.
3. Check if the fuse of power switch is
shorted.
4. Measure the voltage of power outlet.
1. Check if the refrigerator is placed close
to a wall.
2. Check if the refrigerator is placed close
to a stove, oven or in indirect sunlight.
3. Is the ambient temperature high or the
room door closed?
4. Check if putting in hot food.
5. Did you open the refrigerator door too
often?
1. Is the ambient temperature too low?
10°C (40°F).
3. Is food buckling the cooling air outlet?
4. Check if the PWB is set to MAX.
7. Is watery food kept?
8. Check if putting in hot food.
9. Did you open the refrigerator door too
often?
13. Check if ambient temperature and
humidity are high.
14. Is there a gap in the door gasket?
18. Is the refrigerator positioned in a firm
and even place?
19. Is something in the way behind the
refrigerator?
20. Check if the evaporating tray cover is
left off.
21. Check if the cover of mechanical room
in below and front sides is taken out.
26. Check if the door gasket area has
become dirty or contaminated.
27. Is the refrigerator placed in a firm and
even place?
28. Is too much food put in the refrigerator?
32. Check if the inside of the refrigerator
becomes dirty.
33. Did you keep fragrant foods without
wrapping?
34. It smells plastic.
In addition to the items described above, refer to the following to solve the complaint.
Check if frost forms
in the Freezer.
Defrosting is poor.
· Plug it to the outlet.
· Set the switch to ON.
· Replace a regular fuse.
· If the voltage is low, check the wiring or
call an electrician.
· Place the set with the space of about 10
cm.
· Place the set apart from these heat
sources.
· Is the ambient temeperature within spec?
(above 10°C or 40°F )
· Put food in after it cools.
· Don´t open the door too often and close it
firmly.
2. To make the freezer colder, set the COLD
AIR CONTROL to 7 and set the R control
button (PWB) to MAX.
5. Place food in high temperature section
(Front Part).
6. Set the button to MID.
10. Seal watery food with vinyl wrap.
11. Put food after it cools.
12. Don´t open the door too often and close it
firmly.
15. Wipe moisture with a dry cloth.
16. This does not occur if the temperature
and humidity are in the normal range.
17. Fix the gap.
22. Adjust the leveling screws. Position the
refrigerator properly.
23. Remove the objects.
24. Replace the tray.
25. Replace the cover.
29. Clean the door gasket.
30. Position the refrigerator in a firm place
and adjust the leveling screws.
31. Keep food from reaching to the door.
35. Clean the inside of the refrigerator.
36. Wrap fragrant food.
37. The new refrigerator smells of plastic, but
the odor will dissipate after a couple of
weeks.
Replace the
componets of the
defrosting circuit.
Check Refrigerating
Cycle.
The cycle is faulty.
19
Repair the cycle.
Page 21

6-5 REFRIGERATING CYCLE
Troubleshooting Chart
CAUSE
LEAKAGE
CLOGGED BY
DUST
PARTIAL
LEAKAGE
WHOLE
LEAKAGE
PARTIAL
CLOG
WHOLE
CLOG
REFRIGERAT
CONDITION
Freezer and
Refrigerator don´t
get cold normally.
Freezer and
Refrigerator don´t
get cold at all.
Freezer and
Refrigerator don´t
get cold normally.
Freezer and
Refrigerator don´t
get cold at all.
EVAPORATOR
CONDITION
Low flowing sound of
refrigerator is heard
and frost forms in inlet
only.
Flowing sound of
refrigerant is not heard
and frost isn´t formed.
Flowing sound of
refrigerant is heard and
frost forms in inlet only.
Flowing sound of
refrigerant is not heard
and frost isn´t formed.
TEMPERATURE
OF THE
COMPRESSOR
A little higher than
ambient temperature.
Equal to ambient
temperature.
A little higher than
ambient temperature
Equal to ambient
temperature.
REMARKS
1. A little refrigerator
has leaked.
2. Refrigerator runs
normally if you
recharge it.
3. No discharging of
refrigerant.
4. Refrigerator runs
normally if yoy
recharge it.
5. Normal discharginf
of refrigerant.
6. The capillary tube
is faulty.
7. Normal discharging
of refrigerant.
MOISTURE
Cooling operation
stops periodically.
Flowing sound of
refrigerant is not heard
and frost melts.
Lower than ambient
temperature.
CLOG
COMPRESSION
COMPRESSION
DEFECTIVE
Leakage Detection
Check for a leak which may be in the oil discharge in the compressor or in the evaporator.
Check if
Compressor runs.
Moisture clog
CO
COMPRESSION
Normal formed frost.
Freezer and
refrigerator don´t get
cold.
No compressing
operation.
YES
Faulty Compressor
Low flowing sound of
refrigerant is heard and
frost forms in inlet only.
Flowing sound of
refrigerant is not heard
and no frost.
Check if frost forms
on the evaporator.
Normal amount.
A little higher than
ambient temperature.
Equal to ambient
temperature.
No frost or forms in
inlet only.
Observe the
discharging amount
of refrigerant.
Large or small amount.
Recharge refrigerant to
compressor and check
cooling operation.
Check for oil leaks.
8. Cooling operation
restarts when
heating the inlet of
capillary tube.
9. Low pressure on
high side.
· No pressure of
high pressure side
in compressor.
YES
Check Compressor
Clogged by dust.
20
Slight frost forms on
Evaporator.
Refrigerant leakage.
(Locate and repair the leak.)
Page 22

General Control of Refrigerating Cycle.
NO. ITEMS CONTENTS AND
SPECIFICATIONS
1 WELDING ROD
2 FLUX
3 DRIER ASSEMBLY
1. H3O
Ag: 30%, Cu: 27%, Zn: 23%, Cd: 20%
Brazing Temperature: 710~840°C
2. BCuP2
Chemical Ingredients
Cu: About 93%
P: 6.8 %
Rest: within 0.2%
Brazing Temperature: 735~840°C
Ingredients and Preparation:
Borax 60%
Fluoridation Kalium: 35%
Water: 5%
· Assemble the drier within 30 minutes after unpacking.
· Keep the unpacked drier at the temperature of
80~100°C
Chemical Ingredients
REMARKS
1. Recommended H34 containing 34% Ag in the
Service Center.
2. Don´t store the drier outdoors, because humidity
damages it.
4 VACUUM
DRY AIR AND NITROGEN
5
GAS
6 NIPPLE AND COUPLER
7 PIPE
1. When measuring with pirant Vacuum gauge of charging
M/C, vacuum degree is within 1 Torr.
2. If the vacuum degree of the cycle inside is 10 Torr.
Below for low pressure and 20 Torr. For high pressure,
indicates no vacuum leakage state.
3. Vacuum degree of vacuum pump must be 0.05 Torr.
below after 5 minutes.
4. Vacuum degree must be the same of the value
described on item (2) above for more than 20 min.
· The pressure of dry air must be more than 12 ~6Kg/cm2.
· Temperature must be more than –20 ~ -70°C.
· Keep the pressure to 12~6Kg/cm2 also when
substituting dry air for Nitrogen gas.
1. Check if gas leaks with soapy water.
2. Replace Quick Coupler in case of leakage.
1. Put all joint pipe in a clean box and cover tightly with the
lid so dust or humidity do not contaminate.
3. Apply M/C Vacuum Gauge withou fail.
4. Perform vacuum operation until a proper vacuum
degree is built up.
5. If a proper vacuum degree is not built up, check the
leakage from the Cycle Pipe line parts and Quick
Coupler Connecting part.
6. Check if gas leaks from connecting part of coupler.
21
Page 23

7. MICOM Function & Circuit
7-1 FUNCTION
7-1-1 FUNCTION
1. When the appliance is plugged in, it is set to Medium. Each time the button is pushed, it cycles
through Medium Medium/High High Low Medium/Low Medium.
2. When the power is initially applied or restored after a power failure, it is automatically set to
Medium.
Temperature
Control
TEMP °F (° C)
ROOM REFRIGERATOR
Low
46.4 (8) 39.2 (4) 37.4 (3) 34.7 (1.5) 30.2 (-1)
Medium
Low
Medium
Medium
High
High
22
Page 24

7-1-2 DEFROSTING
1. The defrosting is performed each time when the total running time of the
compressor reaches 10 hours.
2. After the power is turned on (or restored after a power failure), the defrosting
starts when the total running time of the compressor reaches 4 hours.
3. When the temperature of the defrosting sensor reaches 13 °C or above, the
defrosting stops. If the temperature does not reach 13 °C in 2 hours after the
defrosting starts, the defrosting error code is displayed. (Refer to 7-1-4 Error
Diagnostic Mode).
4. With the defective defrosting sensor (cut or short-circuited wire), the defrosting
will not be performed.
7-1-3 SEQUENTIAL OPERATION OF ELECTRIC COMPONENTS
The electric components, such as the compressor, defrosting heater, and cooling
fan, starts sequentially to avoid noise and damage to the part which may result
from the simultaneous start of various components on turning the power on or after
the completion of a test.
23
Page 25

7-1-4 ERROR DIAGNOSTIC MODE
1. The error diagnostic mode indicates when a fault may affect the performance of
the product occurs while operating the product.
2. Even if a function control button is pushed when an error occurs, the function
will not be performed.
3. When the error is cleared while the error code is displayed due to a fault, the
refrigerator returns to the normal condition (Reset).
4. The error code is displayed by the refrigerator temperature indication LED on
the display of the refrigerator while the remaining LEDs are off.
24
Page 26

7-2 PCB FUNCTION
7-2-1 POWER CIRCUIT
The second part of the Transformer is composed of the power supply for the
display and relay drive (12 Vdc) and for the MICOM and IC (5 Vdc).
The voltage for each part is as follows:
VA1 prevents overvoltage and noise. When 175 V or higher power is a pplied, the
inside elements are short-circuited and broken, resulting in the blowout of the fuse
in order to protect the elements of the secondary part of the Transformer.
25
Page 27

7-2-2 OSCILLATION CIRCUIT
This circuit is to generate the base clock for calculating time and the synchro clock
for transmitting data to and from the inside logic elements of the IC1 (MICOM). Be
sure to use the exact replacement parts since the calculating time by the IC1 may
be changed or it will not work if he OSC1 SPEC is changed.
7-2-3 RESET CIRCUIT
The reset circuit is for allowing all the functions to start at the initial conditions by
initializing various parts including the RAM inside the MICOM (IC1) when the
power is initially supplied or the power supply to the MICOM is restored after a
momentary power failure. For the initial 10 ms of power supply, LOW voltage is
applied to the MICOM RESET terminal. During a normal operation, 5 V is applied
to the RESET terminal. (If trouble occurs in the RESET IC, the MICOM will not
work).
26
Page 28

7-2-4 LOAD DRIVE CIRCUIT
1. Load Drive Condition Check
FEEZER
FAN
COOLING
FAN
MELTING
FUSE
DEFROST
HEATER
Load Type
Measurement Location
Condition
Compressor, Freeze Fan
Motor
A B
ON 1 V or below
OFF 12 V
Defrosting Heater
27
Page 29

7-2-5 TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT
REFRIGERATOR-SENSOR
DEFROST-SENSOR
The upper CIRCUIT reads REFRIGERATOR temperature and DEFROST SENSOR temperature for defrosting into MICOM. OPENING or SHORT state of
each TEMPERATURE SENSOR are as follows:
SENSOR CHECK POINT NORMAL (-30 -50)
Refrigerator Sensor POINT A Voltage
0.5 V 4.5 V 0 V 5 V
Defrosting Sensor POINT B Voltage
SHORT-
CIRCUITED
OPEN
28
Page 30

7-2-6 TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION & OVERCOOLING/UNDERCOOLING
COMPENSATION CIRCUIT
1. Refrigerator Temperature Compensation
Refrigerator
Resistance
(RCR1)
180 KW
56 KW
33 KW
18 KW
12 KW
10 KW
8.2 KW
5.6 KW
3.3 KW
2 KW
470 KW
Temperature
Compensation
°F (°C)
41 (+5.0)
39.2 (+4.0)
37.4 (+3.0)
35.6 (+2.0)
35.24 (+1.8)
32 ( 0 )
30.2 ( -1.0 )
28.4 ( -2.0 )
26.6 ( -3.0 )
24.8 ( -4.0 )
23 ( -5.0 )
Remark
Compensation by raising
the temperature
Standard Temperature
Compensation by
lowering the temperature
Table of Temperature Compensation by adjusting the resistance (Difference with the current
temperature).
Example. If the refrigerator compensation resistance (RCR1) is changed from 10 K (the current
resistance) to 18 K (the adjustment resistance) of the refrigerator rises 33.8°F (+1°C).
29
Page 31

7.2.7 KEY BUTTON INPUT & DISPLAY LIGHT ON CIRCUIT
The circuit shown above is to determine whether a function control key on the operation display is
pushed and to turn on the corresponding function indication LED. The drive type is the scan type.
30
Page 32

7-3. RESISTANCE SPECIFICATION OF SENSOR
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
°F (°C)
RESISTANCE OF REFRIGERATOR
(DEFROST) SENSOR
-4 -20 77 KW
5 -15 66 KW
14 -10 47.3 KW
23 -5 38.4 KW
32 0 30 KW
41 +5 24.1 KW
50 +10 19.5 KW
59 +15 15.9 KW
68 +20 13 KW
77 +25 11 KW
86 +30 8.9 KW
104 +40 6.2 KW
122 +50 4.3 KW
1. The resistance of SENSOR HAS 5% common difference.
2. Measure the resistance of SENSOR after leaving it over 3 minutes in measuring temperature. This
postponing is necessary because of perceiving speed.
31
Page 33

7-4. TROUBLE SHOOTING
* Replace the PWB when there´s no trouble after checking the contents of trouble.
REMEDY
Certify Fuse.
Certify outlet voltage.
Use boosting
Transformer.
Reconnect
CONNECTOR.
Replace Transformer
Replace Compressor.
Replace OLP, PTC.
Replace MAIN PWB
(RY1).
Verify the black wire of
MAIN PWB
CONNECTOR
(CON1).
Repair the leak and
recharge the
refrigerant.
Replace FAN
MOTOR.
Replace DOOR
LINER.
Verify MOTOR and
the connection of the
black wire of MAIN
PWB CONNECTOR
(CON1).
See DEFROSTING
trouble
Replace SENSOR.
CONTENT
CHECKING
POINTS TO
STATE OF
METHOD
CHECK
TROUBLE
POWER SOURCE is
incorrect.
Is the voltage
correct? connector
connection is poor.
Transformer Fuse
open.
COMPRESSOR lock
or blocked.
OLP or PTC is
defective.
COMPRESSOR
RELAY is defective.
CONNECTING WIRE
is defective.
FREEZER/REFRIGE
RATOR door open.
Verify the correct bulb
is used.
Check the connector.
GERATOR.
MAIN PWB
CONNECTOR.
1. FREEZER/REFRI
2. LAMP is dim.
3. The connection of
Al the DISPLAY
LED OFF.·DISPLAY LED
represents
abnormal
operation.
·
Check the main PWB.
operate?
1. Does compressor
1. NO COOLING
Refrigerant leakage.
Measure the amount
of frost on Evaporator
and the surface
temperature of
condenser pipe.
2. Does refrigerant
leak.
FAN MOTOR is
defective.
DOOR LINER
contact.
CONNECTING WIRE
is defective.
Check the main PWB.
MOTOR operate?
1. Does FAN
Poor DEFROSTING.
Certify the amount of
frost on evaporator.
normal?
2. Is DEFROSTING
1. FREEZER
TEMPERATURE is
too warm.
SENSOR
RESISTANCE is
incorrect.
Check the SENSOR
resistance in the
refrigerator.
3. Is SENSOR
normal?
COOLING
POWER SOURCE
CLASSIFICATION
32
Page 34

REMEDY
CONTENT
CHECKING
METHOD
Be sure door closes.
Replace FAN MOTOR.
Remove Impurities.
See POOR
DEFROSTING.
FAN MOTOR is poor.
AIR FLOW blocked.
EVAPORATOR frozen.
See if FREEZER
TEMPERATURE Iis too
warm.
Check the amount and
speed of cool air being
supplied inside the
refrogerator.
Replace HEATER.
Replace
TEMPERATURE
FUSE.
Check evaporator
connection and wire of
MAIN PWB
CONNECTOR.
Replace DEF-
SENSOR.
Replace RY2 of MAIN
PWB.
HEATER disconnection.
TEMPERATURE FUSE
disconnection.
Poor Connection.
DEFROST SENSOR is
defective.
HEATER RELAY is
defective.
Check the main PWB.
Remove ice and
impurities.
Check HEATER
PLATE.
DRAIN PIPE is blocked.
Check DRAIN PIPE.
Reassemble DOOR.
Replace GASKET.
Attachment is incorrect.
DOOR sealing is
incorrect.
Check the attachin of
DEFROST-SENSOR.
Check the gap in the
door gasket.
CHECK
TEMPERATURE
normal?
MOTOR blow
POINTS TO
STATE OF
1. Is FREEZER
TROUBLE
REFRIGERATOR
enough cool air?
1. Does HEATER emit
2. Does the FAN
TEMPERATURE is too
warm.
POOR COOLING
heat?
2. Is the DRAIN PIPE
blocked?
NO DEFROSTING.
POOR DEFROSTING
3. Does ice remains
after DEFROSTING?
CLASSIFICATION
33
Page 35

7-4 MAIN PWB ASSEMBLY AND PARTS LIST.
7-4-1 MAIN PWB ASSEMBLY.
34
Page 36

Page 37

Page 38

Page 39

7.5 PWB DIAGRAM
REFRIGERATOR-LAMP
FREEZER FAN/MOTOR
COOLING FAN/MOTOR
MELTING
FUSE
DEFROSTHEATER
38
Page 40

REFRIGERATOR-SENSOR
DEFROST-SENSOR
39
Page 41

8. Exploded View
The parts of refrigerator and the shape of each part may vary by market area.
Capacitors and fuse are optional parts.
Optional parts:
40
Page 42

D
A
41
Page 43

9. Service parts list
Loc. Descripción GR-382R
Part Number
103A HANDLE,BACK
103B HANDLE,BACK
104C LEG ASSEMBLY
105A DRAIN,PIPE-Z
106A ADJUSTABLE LEG
106B ADJUSTABLE LEG
110A PWB(PCB) ASSY,DISPLAY
110B ICE TRAY GUIDE
REFRIGERATOR CONTROL BOX
120A
ASSEMBLY
120B REFRIGERATOR CONTROL BOX COVER
120E DUCT,INSULATION
120G DUCT,INSULATION
125A ICE TRAY
125H ICE TRAY SUPPORTER
125L ICE TRAY HOLDER
129A DUCT GUIDE
131A ICE BIN
149A FREEZER SHELF
149B MEAT TRAY
149C REFRIGERATOR SHELF ASSEMBLY
149E REFRIGERATOR SHELF ASSEMBLY
151A VEGETABLE TRAY
154A VEGETABLE TRAY COVER
158C LAMP COVER
200A FREEZER DOOR ASSEMBLY
201A FREEZER DOOR FOAM ASSEMBLY
203A FREEZER DOOR GASKET ASSEMBLY
205A DOOR BASKET
210A DOOR STOPPER
210B STOPPER GUIDE
212G NAME PLATE,P(H)
230A REFRIGERATOR DOOR ASSEMBLY
231A REFRIGERATOR DOOR FOAM ASSEMBLY
REFRIGERATOR DOOR GASKET
ASSEMBLY
233A
241A DOOR BASKET
241B DOOR BASKET
241C DOOR BASKET
241D DOOR BASKET
281A HINGE COVER
3650JJ2003A 3650JJ2003B
3650JJ2003E 3650JJ2003F
4981JA3006A 4981JA3006A
5250JA2009A 5250JA2009A
3J04686A
3J04686A 3J04686A
6871JB2036A 6871JB2036A
4974JJ1003A 4974JJ1003A
4995JJ1001E
4994JJ1001A
5208JJ1006A 5208JJ1006A
5208JJ1005A 5208JJ1005A
3390JJ1003A 3390JJ1003A
4980JJ1001A 4980JJ1001A
4930JJ3001A 4930JJ3001A
4974JJ1001A 4974JJ1001A
5074JJ1001A 5074JJ1001A
5026JJ1001B 5026JJ1001B
3390JJ1002A 3390JJ1002A
5027JJ2001A 5027JJ2003A
5027JJ2002A 5026JJ1002A
3390JJ1001A 3390JJ1001A
3550JJ1003B 3550JJ1003B
3550JJ1004B 3550JJ1004A
3581JJ8009B
5433JJ0011A
4987JJ1001A 4987JJ1001A
5004JJ1001B 5004JJ1001B
4620JJ2004A 4620JJ2001A
4974JA3031A J325-00033A
4140JD1020P
3581JJ8010A 3581JJ8002D
5433JJ0012B 5433JJ0005B
4987JJ1001C 4987JJ1001B
5004JJ1004B 5004JJ1004B
5004JJ1002B 5004JJ1002B
5004JJ1003B 5004JJ1003B
5004JJ1005B 5004JJ1005B
3550JJ2011A 3550JJ2004B
11Ft3
LRTP1231W
Part Number
3J04686A
4995JJ1001F
4994JL1001A
3581JJ8001D
5433JJ0003D
4140JD1020B
42
Page 44

11Ft3
Loc. Descripción GR-382R LRTP1231W
281B UPPER HINGE ASSEMBLY
282B CENTER HINGE ASSEMBLY
283B LOWER HINGE ASSEMBLY
301A EVAPORATOR ASSY
303A SPACER,INSULATION
303B SPACER AS SY
304A MECHANICAL AREA COVER
307A COMPRESSOR ASSEMBLY
308A PTC ASSEMBLY
309A OLP
310A PTC COVER
312A BUSHING
314A COMPRESSOR BUSHING
315A COMP BASE ASSY,STD
315B ROLLER
315C PIN
317A DRIER ASSY
318A DRIER HOLDER
319A DRIP TRAY
319C FAN GUIDE
323B CONDENSER ASSY,WIRE
327A BUSHING
328A BUSHING
329A FAN ASSEMBLY
329C FAN ASSEMBLY
330B FREEZER SHROUD ASSEMBLY
332A FAN GRILLE ASSEMBLY
401A DEFROST CONTROL ASSEMBLY
404A FAN MOTOR (MECHANICAL AREA)
405A MOTOR BRACKET
405C FAN MOTOR BUSHING
406B DOOR SWITCH
407A HEATER,PLATE
410H CAPACITOR[M/R]
411A CONNECTOR ASSEMBLY
418A HEATER,CORD
420A MOTOR(MECH),COOLING
501A MAIN PWB ASSEMBLY
501F PWB ASSEMBLY
604F DEODORIZER COVER
155J NAME PLATE,P(H)
409B LIGHT BULB
604G DEODORIZER
4775JA3015C 4775JA2001D
4775JA3009B 4775JA3009A
4775JA2020A 4775JA2023B
5421JA2359B 5421JA2359A
4826JJ2001A 4826JJ2001A
4827JJ3001A 4827JJ3001A
3551JJ2002A 3551JJ2002A
2521JA1006A 2521C-B5602
6748JA3001A 6748C-0004D
6750JA3001A 6750C-0005D
3550JA2158A 3550JA2087B
5040JA3044A 5040JA3021A
4J03277A 4J03277A
3103JJ2001C 3103JJ2001A
3J02312A 3J02312A
4J04238A 4J04238A
5851JJ2002A 5851JJ2002A
4930JJ3002A 4930JJ3002A
3390JJ0001A 3390JJ0001A
4974JJ1002A 4974JJ1002A
5403JA1039A 5403JA1039A
5040JJ3003A 5040JJ3003A
5040JJ3002A 5040JJ3002A
5901JJ1001A 5901JJ1001A
5901JJ1001B 5901JJ1001B
4999JJ1001A 4999JJ1001A
3531JJ1001A 3531JJ1001A
6615JB2005C 6615JB2005A
4680JB1033B 4680JB1033D
4810JA3007A 4810JA3007A
J756-00008B J756-00008B
6600JB1002K 6600JB1002K
5300JB1080F 5300JB1080F
0CZZJB2003G J513-00003C
6877JK3001A 6877JK1002A
5300JB1079F 5300JB1079C
4680JB1017Q 4680JB1017C
6871JB1115A 6871JB1115B
3550JJ2001B 3550JJ2001A
3550JJ2002A 3550JJ2002A
4140JJ2001A 4140JJ2001A
6912JB2002J 6912JB2002J
NO DEODORIZER 5986JA3007B
43
Page 45

P/No. 3828J8331B
Electronics Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...