LG 47LW6500 Schematic

LED LCD TV
SERVICE MANUAL
CAUTION
BEFORE SERVICING THE CHASSIS,
READ THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS IN THIS MANUAL.
CHASSIS : LA12C
MODEL : 47LW6500
47LW6500-UA
North/Latin America http://aic.lgservice.com
Europe/Africa http://eic.lgservice.com
Asia/Oceania http://biz.lgservice.com
Internal Use Only
Printed in KoreaP/NO : MFL66980407 (1103-REV00)

LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 2 -
CONTENTS
CONTENTS .............................................................................................. 2
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ......................................................................... 3
SPECIFICATION....................................................................................... 6
ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTION .............................................................. 12
EXPLODED VIEW .................................................................................. 20
SVC. SHEET ...............................................................................................
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 3 -
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis have special safety-related characteristics. These parts are identified by in the
Schematic Diagram and Exploded View.
It is essential that these special safety parts should be replaced with the same components as recommended in this manual to prevent
Shock, Fire, or other Hazards.
Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
General Guidance
An isolation Transformer should always be used during the
servicing of a receiver whose chassis is not isolated from the AC
power line. Use a transformer of adequate power rating as this
protects the technician from accidents resulting in personal injury
from electrical shocks.
It will also protect the receiver and it's components from being
damaged by accidental shorts of the circuitry that may be
inadvertently introduced during the service operation.
If any fuse (or Fusible Resistor) in this TV receiver is blown,
replace it with the specified.
When replacing a high wattage resistor (Oxide Metal Film Resistor,
over 1W), keep the resistor 10mm away from PCB.
Keep wires away from high voltage or high temperature parts.
Before returning the receiver to the customer,
always perform an AC leakage current check on the exposed
metallic parts of the cabinet, such as antennas, terminals, etc., to
be sure the set is safe to operate without damage of electrical
shock.
Leakage Current Cold Check(Antenna Cold Check)
With the instrument AC plug removed from AC source, connect an
electrical jumper across the two AC plug prongs. Place the AC
switch in the on position, connect one lead of ohm-meter to the AC
plug prongs tied together and touch other ohm-meter lead in turn to
each exposed metallic parts such as antenna terminals, phone
jacks, etc.
If the exposed metallic part has a return path to the chassis, the
measured resistance should be between 1MΩ and 5.2MΩ.
When the exposed metal has no return path to the chassis the
reading must be infinite.
An other abnormality exists that must be corrected before the
receiver is returned to the customer.
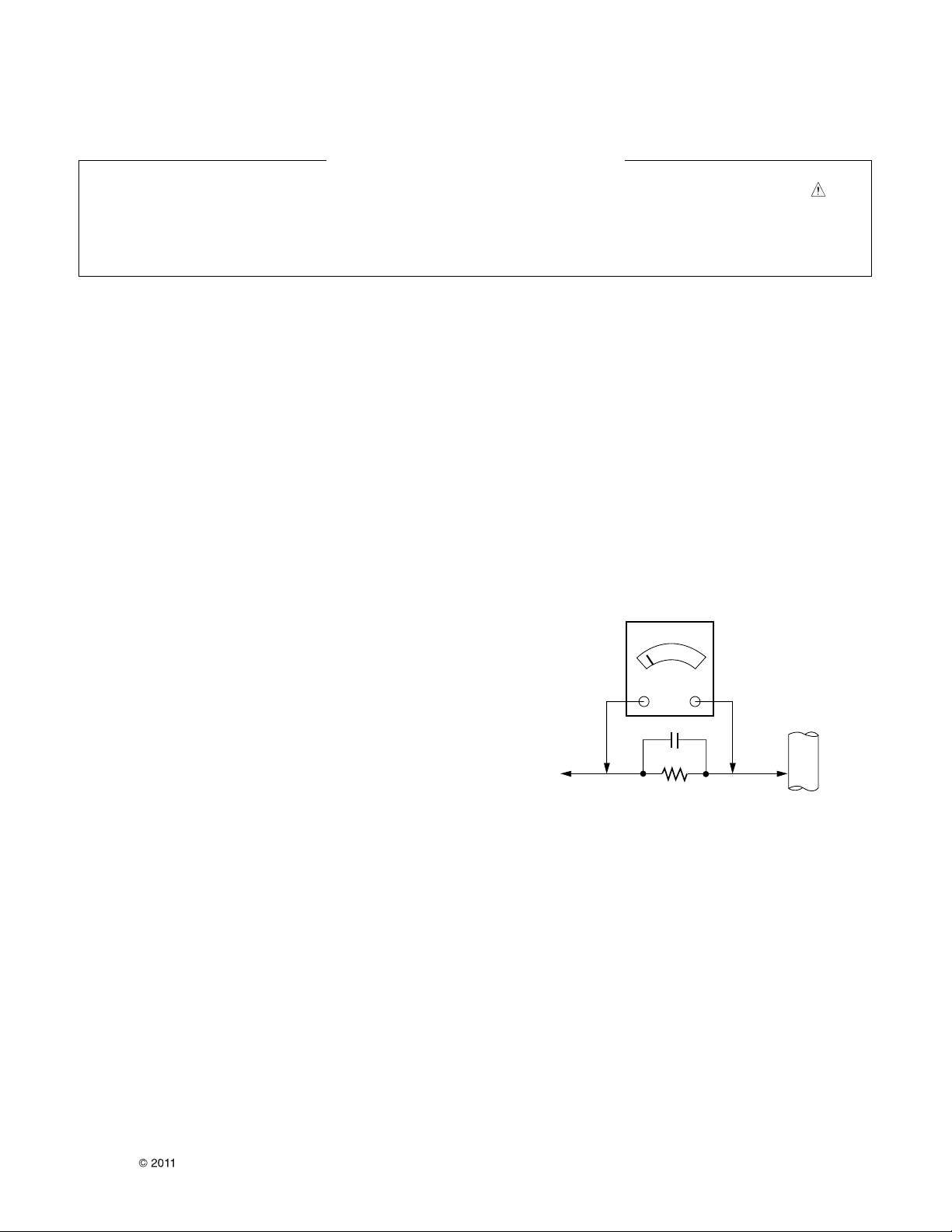
Leakage Current Hot Check (See below Figure)
Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet.
Do not use a line Isolation Transformer during this check.
Connect 1.5K/10watt resistor in parallel with a 0.15uF capacitor
between a known good earth ground (Water Pipe, Conduit, etc.)
and the exposed metallic parts.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor using AC voltmeter
with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity.
Reverse plug the AC cord into the AC outlet and repeat AC voltage
measurements for each exposed metallic part. Any voltage
measured must not exceed 0.75 volt RMS which is corresponds to
0.5mA.
In case any measurement is out of the limits specified, there is
possibility of shock hazard and the set must be checked and
repaired before it is returned to the customer.
Leakage Current Hot Check circuit
1.5 Kohm/10W
To Instrument's
exposed
METALLIC PARTS
Good Earth Ground
such as WATER PIPE,
CONDUIT etc.
AC Volt-meter
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
0.15uF

LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 4 -
CAUTION: Before servicing receivers covered by this service
manual and its supplements and addenda, read and follow the
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS on page 3 of this publication.
NOTE: If unforeseen circumstances create conflict between the
following servicing precautions and any of the safety precautions on
page 3 of this publication, always follow the safety precautions.
Remember: Safety First.
General Servicing Precautions
1. Always unplug the receiver AC power cord from the AC power
source before;
a. Removing or reinstalling any component, circuit board
module or any other receiver assembly.
b. Disconnecting or reconnecting any receiver electrical plug or
other electrical connection.
c. Connecting a test substitute in parallel with an electrolytic
capacitor in the receiver.
CAUTION: A wrong part substitution or incorrect polarity
installation of electrolytic capacitors may result in an
explosion hazard.
2. Test high voltage only by measuring it with an appropriate high
voltage meter or other voltage measuring device (DVM,
FETVOM, etc) equipped with a suitable high voltage probe.
Do not test high voltage by "drawing an arc".
3. Do not spray chemicals on or near this receiver or any of its
assemblies.
4. Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, clean
electrical contacts only by applying the following mixture to the
contacts with a pipe cleaner, cotton-tipped stick or comparable
non-abrasive applicator; 10% (by volume) Acetone and 90% (by
volume) isopropyl alcohol (90%-99% strength)
CAUTION: This is a flammable mixture.
Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, lubrication of
contacts in not required.
5. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage interlocks with which
receivers covered by this service manual might be equipped.
6. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and/or any of its
electrical assemblies unless all solid-state device heat sinks are
correctly installed.
7. Always connect the test receiver ground lead to the receiver
chassis ground before connecting the test receiver positive
lead.
Always remove the test receiver ground lead last.
8. Use with this receiver only the test fixtures specified in this
service manual.
CAUTION: Do not connect the test fixture ground strap to any
heat sink in this receiver.
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid-state) devices can be damaged easily
by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES
devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques
should be used to help reduce the incidence of component
damage caused by static by static electricity.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or
semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any electrostatic
charge on your body by touching a known earth ground.
Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available
discharging wrist strap device, which should be removed to
prevent potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the
unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES
devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as
aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or
exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES
devices.
4. Use only an anti-static type solder removal device. Some solder
removal devices not classified as "anti-static" can generate
electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate
electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective
package until immediately before you are ready to install it.
(Most replacement ES devices are packaged with leads
electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil
or comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the
leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
CAUTION: Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit,
and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged
replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as
the brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your
foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity
sufficient to damage an ES device.)
General Soldering Guidelines
1. Use a grounded-tip, low-wattage soldering iron and appropriate
tip size and shape that will maintain tip temperature within the
range or 500°F to 600°F.
2. Use an appropriate gauge of RMA resin-core solder composed
of 60 parts tin/40 parts lead.
3. Keep the soldering iron tip clean and well tinned.
4. Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be soldered. Use a mall wirebristle (0.5 inch, or 1.25cm) brush with a metal handle.
Do not use freon-propelled spray-on cleaners.
5. Use the following unsoldering technique
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach normal temperature.
(500°F to 600°F)
b. Heat the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly draw the melted solder with an anti-static, suction-
type solder removal device or with solder braid.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuit
board printed foil.
6. Use the following soldering technique.
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach a normal temperature
(500°F to 600°F)
b. First, hold the soldering iron tip and solder the strand against
the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly move the soldering iron tip to the junction of the
component lead and the printed circuit foil, and hold it there
only until the solder flows onto and around both the
component lead and the foil.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuit
board printed foil.
d. Closely inspect the solder area and remove any excess or
splashed solder with a small wire-bristle brush.
SERVICING PRECAUTIONS

LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 5 -
IC Remove/Replacement
Some chassis circuit boards have slotted holes (oblong) through
which the IC leads are inserted and then bent flat against the
circuit foil. When holes are the slotted type, the following technique
should be used to remove and replace the IC. When working with
boards using the familiar round hole, use the standard technique
as outlined in paragraphs 5 and 6 above.
Removal
1. Desolder and straighten each IC lead in one operation by gently
prying up on the lead with the soldering iron tip as the solder
melts.
2. Draw away the melted solder with an anti-static suction-type
solder removal device (or with solder braid) before removing the
IC.
Replacement
1. Carefully insert the replacement IC in the circuit board.
2. Carefully bend each IC lead against the circuit foil pad and
solder it.
3. Clean the soldered areas with a small wire-bristle brush.
(It is not necessary to reapply acrylic coating to the areas).
"Small-Signal" Discrete Transistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Remove the defective transistor by clipping its leads as close as
possible to the component body.
2. Bend into a "U" shape the end of each of three leads remaining
on the circuit board.
3. Bend into a "U" shape the replacement transistor leads.
4. Connect the replacement transistor leads to the corresponding
leads extending from the circuit board and crimp the "U" with
long nose pliers to insure metal to metal contact then solder
each connection.
Power Output, Transistor Device
Removal/Replacement
1. Heat and remove all solder from around the transistor leads.
2. Remove the heat sink mounting screw (if so equipped).
3. Carefully remove the transistor from the heat sink of the circuit
board.
4. Insert new transistor in the circuit board.
5. Solder each transistor lead, and clip off excess lead.
6. Replace heat sink.
Diode Removal/Replacement
1. Remove defective diode by clipping its leads as close as
possible to diode body.
2. Bend the two remaining leads perpendicular y to the circuit
board.
3. Observing diode polarity, wrap each lead of the new diode
around the corresponding lead on the circuit board.
4. Securely crimp each connection and solder it.
5. Inspect (on the circuit board copper side) the solder joints of
the two "original" leads. If they are not shiny, reheat them and if
necessary, apply additional solder.
Fuse and Conventional Resistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Clip each fuse or resistor lead at top of the circuit board hollow
stake.
2. Securely crimp the leads of replacement component around
notch at stake top.
3. Solder the connections.
CAUTION: Maintain original spacing between the replaced
component and adjacent components and the circuit board to
prevent excessive component temperatures.
Circuit Board Foil Repair
Excessive heat applied to the copper foil of any printed circuit
board will weaken the adhesive that bonds the foil to the circuit
board causing the foil to separate from or "lift-off" the board. The
following guidelines and procedures should be followed whenever
this condition is encountered.
At IC Connections
To repair a defective copper pattern at IC connections use the
following procedure to install a jumper wire on the copper pattern
side of the circuit board. (Use this technique only on IC
connections).
1. Carefully remove the damaged copper pattern with a sharp
knife. (Remove only as much copper as absolutely necessary).
2. carefully scratch away the solder resist and acrylic coating (if
used) from the end of the remaining copper pattern.
3. Bend a small "U" in one end of a small gauge jumper wire and
carefully crimp it around the IC pin. Solder the IC connection.
4. Route the jumper wire along the path of the out-away copper
pattern and let it overlap the previously scraped end of the good
copper pattern. Solder the overlapped area and clip off any
excess jumper wire.
At Other Connections
Use the following technique to repair the defective copper pattern
at connections other than IC Pins. This technique involves the
installation of a jumper wire on the component side of the circuit
board.
1. Remove the defective copper pattern with a sharp knife.
Remove at least 1/4 inch of copper, to ensure that a hazardous
condition will not exist if the jumper wire opens.
2. Trace along the copper pattern from both sides of the pattern
break and locate the nearest component that is directly
connected to the affected copper pattern.
3. Connect insulated 20-gauge jumper wire from the lead of the
nearest component on one side of the pattern break to the lead
of the nearest component on the other side.
Carefully crimp and solder the connections.
CAUTION: Be sure the insulated jumper wire is dressed so the
it does not touch components or sharp edges.

LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 6 -
SPECIFICATION
NOTE : Specifications and others are subject to change without notice for improvement.
1. Application range
This spec sheet is applied LCD TV with LA12C chassis.
2. Requirement for Test
Each part is tested as below without special appointment.
1) Temperature:
20ºC ± 5 ºC
2) Relative Humidity: 65 % ± 10 %
3) Power Voltage : Standard input voltage(100-240V~, 50/60Hz)
* Standard Voltage of each product is marked by models
4) Specification and performance of each parts are followed
each drawing and specification by part number in
accordance with BOM.
5) The receiver must be operated for about 20 minutes prior to
the adjustment.
3. Test method
1) Performance: LGE TV test method followed
2) Demanded other specification
- Safety : UL, CSA, IEC specification
- EMC : FCC, ICES, IEC specification
- Wireless : WirelessHD Specification (Option)
No Item Specification Remark
1. Receiving System 1) ATSC / NTSC-M OK
2. Available Channel 1) VHF : 02~13 OK
2) UHF : 14~69
3) DTV : 02-69
4) CATV : 01~135
5) CADTV : 01~135
3. Input Voltage 1) AC 100 ~ 240V~, 50/60Hz OK 110V, 50/60Hz on the label
4. Market North America OK
5. Screen Size 47/55/65 inches
6. Aspect Ratio 16:9 OK
7. Tuning System FS OK
8. Module LC470EUF-SDF1 LGD 47LW6500-UA
LC550EUF-SDF1 LGD 55LW6500-UA
T645HW05-V0 AUO 65LW6500-UA
9. Operating 1) Temp : 0 ~ 40 deg OK
Environment 2) Humidity : ~ 80 %
10. Storage Environment 1) Temp : -20 ~ 60 deg OK
2) Humidity : ~ 85 %
3. General specifications

- 7 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
4. Component Video Input (Y, CB/PB, CR/PR)-2D
5. RGB Input (PC)
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(kHz) Pixel clock Proposed
1. 720*480 15.73 60 13.5135 SDTV ,DVD 480I
2. 720*480 15.73 59.94 13.5 SDTV ,DVD 480I
3. 720*480 31.50 60 27.027 SDTV 480P
4. 720*480 31.47 59.94 27.0 SDTV 480P
5. 1280*720 45.00 60.00 74.25 HDTV 720P
6. 1280*720 44.96 59.94 74.176 HDTV 720P
7. 1920*1080 33.75 60.00 74.25 HDTV 1080I
8. 1920*1080 33.72 59.94 74.176 HDTV 1080I
9. 1920*1080 67.500 60 148.50 HDTV 1080P
10. 1920*1080 67.432 59.94 148.352 HDTV 1080P
11. 1920*1080 27.000 24.000 74.25 HDTV 1080P
12. 1920*1080 26.97 23.976 74.176 HDTV 1080P
13. 1920*1080 33.75 30.000 74.25 HDTV 1080P
14. 1920*1080 33.71 29.97 74.176 HDTV 1080P
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(kHz) Pixel clock Proposed
PC DDC
1. 640*350 31.468 70.09 25.17 EGA X
2. 720*400 31.469 70.08 28.32 DOS O
3. 640*480 31.469 59.9 25.17 VESA(VGA) O
4. 800*600 37.879 60.31 40.00 VESA(SVGA) O
5. 1024*768 48.363 60.00 65.00 VESA(XGA) O
6. 1360*768 47.712 60.015 5.50 VESA(WXGA) X
7. 1920*1080 66.587 59.934 138.5 HDTV 1080P O

LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 8 -
6. HDMI input (PC/DTV)
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(kHz) Pixel clock Proposed
PC DDC
1 640*350 31.468 70.09 25.17 EGA X
2 720*400 31.469 70.08 28.32 DOS O
3 640*480 31.469 59.94 25.17 VESA(VGA) O
4 800*600 37.879 60.31 40.00 VESA(SVGA) O
5 1024*768 48.363 60.00 65.00 VESA(XGA) O
6 1360*768 47.712 60.015 85.50 VESA (WXGA) O
7 1280*1024 63.981 60.020 108.00 VESA (SXGA) O
8 1920*1080 67.5 60 148.5 HDTV 1080P O
DTV
1 720*480 31.50 60 27.027 SDTV 480P
2 720*480 31.47 59.94 27.00 SDTV 480P
3 1280*720 45.00 60.00 74.25 HDTV 720P
4 1280*720 44.96 59.94 74.176 HDTV 720P
5 1920*1080 33.75 60.00 74.25 HDTV 1080I
6 1920*1080 33.72 59.94 74.176 HDTV 1080I
7 1920*1080 67.500 60 148.50 HDTV 1080P
8 1920*1080 67.432 59.939 148.352 HDTV 1080P
9 1920*1080 27.000 24.000 74.25 HDTV 1080P
10 1920*1080 26.97 23.976 74.176 HDTV 1080P
11 1920*1080 33.75 30.000 74.25 HDTV 1080P
12 1920*1080 33.71 29.97 74.176 HDTV 1080P

- 9 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
8. HDMI Input - 3D
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(Hz)
Pixel clock(MHz
) 3D input proposed mode Proposed
1 1920*1080 Side by Side HDTV 1080I
Top & Bottom
2 1280*720 Side by Side HDTV 720P
Top & Bottom
9. RGB-PC Input - 3D
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(Hz)
Pixel clock(MHz
) 3D input proposed mode Proposed
1 1920*1080 67.50 60 148.50 Side by Side HDTV 1080P
Top & Bottom
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(Hz)
Pixel clock(MHz
) 3D input proposed mode Proposed
1 1280*720 90.00 60.00 148.50 HDMI 3D Frame Packing 1.4a HDTV 720P
2 1280*720 45.00 60.00 74.25 Side by Side 1.3 HDTV 720P
Top & Bottom 1.4a HDTV 720P
HDMI 3D Top & Bottom
3 1920*1080 33.75 60.00 74.25 Side by Side , 1.3 HDTV 1080I
Top & Bottom
HDMI 3D Side by Side 1.4a HDTV 1080I
(Half)
4 1920*1080 67.50 60 148.50 Side by Side 1.3 HDTV 1080P
Top & Bottom
Checkerboard
Single Frame Sequential
5 1920*1080 54.00 24.000 148.50 HDMI 3D Frame Packing 1.4a HDTV 1080P
6 1920*1080 27.00 24.000 74.25 Side by Side 1.3 HDTV 1080P
Top & Bottom
Checkerboard
HDMI 3D Top & Bottom 1.4a HDTV 1080P
7 1920*1080 67.50 30.000 148.50 HDMI 3D Frame Packing 1.4a HDTV 1080P
8 1920*1080 33.75 30.000 74.25 Side by Side 1.3 HDTV 1080P
Top & Bottom
Checkerboard
7. RF Input - 3D

- 10 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
No Side by Side Top & Bottom Checkerboard
Single Frame Sequential
Frame Packing
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(Hz)
Pixel clock(MHz
) 3D input proposed mode Proposed
1 1920*1080 33.75 30.000 74.25 Side by Side HDTV 1080P
Top & Bottom
Checkerboard
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(Hz)
Pixel clock(MHz
) 3D input proposed mode Proposed
1 1920*1080 33.75 30.000 74.25 Side by Side HDTV 1080P
Top & Bottom
Checkerboard
10. USB Input - 3D
11. DLNA Input - 3D
12. 3D Input
- 11 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
13. Optical specs for LCD Module.
0.334
0.307
GREEN
0.606
0.152
BLUE
0.058
0.279
WHITE
-0.05
0.292
+0.05
0.630
RED
0.330
0.320
GREEN
0.620
0.150
BLUE
0.040
0.280
WHITE
Typ.
-0.05
0.290
Typ.
+0.05
T645HW05-V0
1,100:1 1,600:1 LGD Module
3 Contrast ratio
3,200:1 4,000:1 AUO Module (32LW5700/65LW6500)
4 3D Crosstalk 1 3 %
5 Luminance Uniformity 1.3 % 2D Only
Response Time(Gray to Gray) 5 6 ms
Response Time(MPRT) 6 9 ms
Response Time(Uniformity / MPRT) 1
6
Response Time(Uniformity / G to G) 1
No Item Min Typ Max Unit Remark
320 400 cd/m
100 250 cd/m
T315HB01-V0
320 400 cd/m
120 150 cd/m
LC420EUF-SDF1
320 400 cd/m
120 150 cd/m
LC470EUF-SDF1
320 400 cd/m
120 150 cd/m
LC550EUF-SDF1
2D
3D
2D
3D
2D
3D
2D
3D
2D
3D
360 450 cd/m
1
Max Luminance
(Center 1-point /
Full White Pattern)
100 125 cd/m
T645HW05-V0
0.630
RED
0.330
0.320
GREEN
0.620
0.150
BLUE
0.040
0.280
WHITE
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Y
X
Typ.
-0.03
0.290
Typ.
+0.03
T315HB01-V0
0.650
RED
0.333
0.307
GREEN
0.604
0.150
BLUE
0.059
0.279
WHITE
Typ.
-0.05
0.292
Typ.
+0.05
LC420EUF-SDF1
0.648
RED
0.332
0.306
GREEN
0.606
0.150
BLUE
0.058
0.279
WHITE
Typ.
-0.05
0.292
Typ.
+0.05
LC470EUF-SDF1
2 Color
coordinate
(Default)
RED Typ. 0.648 Typ. LC550EUF-SDF1

LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 12 -
ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTION
1. Application range
This spec. sheet applies to LA12C Chassis applied LCD TV
all models manufactured in TV factory .
2. Specification
2.1 Because this is not a hot chassis, it is not necessary
to use an isolation transformer. However, the use of
isolation transformer will help protect test instrument.
2.2 Adjustment must be done in the correct order.
2.3 The adjustment must be performed in the
circumstance of 25±5°C of temperature and 65±10%
of relative humidity
2.4 The input voltage of the receiver must keep
100~240V~, 50/60Hz.
2.5 The receiver must be operated for about 5 minutes
prior to the adjustment when module is in the
circumstance of over 15. In case of keeping module
is in the circumstance of 0°C, it should be placed in
the circumstance of above 15°C for 2 hours In case
of keeping module is in the circumstance of below 20°C, it should be placed in the circumstance of
above 15°C for 3 hours.
• Caution
When a still image is displayed for 20 minutes or longer
(especially where W/B scale is strong. Digital pattern 13ch
and/or Cross hatch pattern 09ch), there can some
afterimage in the black level area.
3. Adjustment items
3.1 Main PCBA Adjustments
(1) ADC adjustment: Component 480i, 1080p / RGB-PC 1080p
(2) EDID downloads for HDMI and RGB-PC
• Remark
- Above adjustment items can be also performed in Final
Assembly if needed. Adjustment items in both PCBA and
final assembly stages can be checked by using the
INSTART Menu 1.ADJUST CHECK.
3.2 Final Assembly adjustment
(1) White Balance adjustment
(2) RS-232C functionality check
(3) Factory Option setting per destination
(4) Shipment mode setting (IN-STOP)
(5) GND and HI-POT test
3.3. Appendix
(1)Tool option menu, USB Download (S/W Update, Option
and Service only)
(2) Manual adjustment for ADC calibration and White balance.
(3) Shipment conditions, Channel pre-set
4. MAIN PCBA Adjustments
4.1. ADC Calibration
4.1.1. Overview
• ADC adjustment is needed to find the optimum black level
and gain in Analog-to-Digital device and to compensate RGB
deviation.
4.1.2. Equipment & Condition
1) Jig (RS-232C protocol)
2) MSPG-925 Series Pattern Generator(MSPG-925FS)
- Resolution : 480i Comp1 (MSPG-925FS: model-209,
pattern-65)
- Resolution : 1080p Comp1 (MSPG-925FS: model-225,
pattern-65)
- Resolution : 1080p RGB (MSPG-925FS: model-225,
pattern-65)
- Pattern : Horizontal 100% Color Bar Pattern
- Pattern level : 0.7±0.1 Vp-p
- Image
4.1.3. Adjustment
4.1.3.1 Adjustment method
• Using RS-232, adjust items listed in 3.1 in the other
shown in “4.1.3.3”
4.1.3.2 Adj. protocol
Ref.) ADC Adj. RS232C Protocol_Ver1.0
4.1.3.3. Adj. order
• aa 00 00 [Enter ADC adj. mode]
• xb 00 40 [Change input source to Component1
(480i/1080p)]
• ad 00 10 [Adjust 480i//1080p Comp1]
• xb 00 60 [Change input source to RGB(1920*1080)]
• ad 00 10 [Adjust 1920*1080 RGB]
• ad 00 90 End adj.
Chassis Model Name Module type Local dimming THX Remark
47/55/65LW6500-UA
32/42/47/55LW5700-UE
42/47/55LW5600-UA
42/47/55LW5700-NA
LA12C
42/47/55LW6500-NB
Edge LED
O
(Except AUO)
X 1 point W/B adjustment
Protocol Command Set ACK
Enter adj. mode aa 00 00 a 00 OK00x
Source change xb 00 40
xb 00 60
b 00 OK40x (Adjust 480i/1080p Comp1 )
b 00 OK60x (Adjust 1920*1080 RGB)
Begin adj. ad 00 10
Return adj. result OKx (Case of Success)
NGx (Case of Fail)
Read adj. data (main)
ad 00 20
(sub )
ad 00 21
(main)
000000000000000000000000007c007b006dx
(Sub)
000000070000000000000000007c00830077x
Confirm adj. ad 00 99 NG 03 00x (Fail)
NG 03 01x (Fail)
NG 03 02x (Fail)
OK 03 03x (Success)
End adj. aa 00 90 a 00 OK90x

- 13 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
4.2. MAC Address, ESN Key and Widevine
Key download
4.2.1. Equipment & Condition
1) Play file: keydownload.exe
4.2.2. Communication Port connection
1) Key Write: Com 1,2,3,4 and 115200(Baudrate)
2) Barcode: Com 1,2,3,4 and 9600(Baudrate)
4.2.3. Download process
1) Select the download items
2) Mode check: Online Only
3) Check the test process
- US, Canada models: DETECT->MAC_WRITE->
WIDEVINE_WRITE
- Korea, Mexico models: DETECT->MAC_WRITE->
WIDEVINE_WRITE
4) Play: START
5) Check of result: Ready, Test, OK or NG
6) Printer out (MAC Address Label)
4.2.4. Communication Port connection
1) Connect: PCBA Jig RS-232C Port == PC RS-232C Port
4.2.5. Download
1) US, Canada models (11Y LCD TV + MAC + Widevine +
ESN Key)
2) Korea, Mexico models (11Y LCD TV + MAC + Widevine
Only)
4.1.6. Inspection
- In INSTART menu, check these keys.
4.3. LAN port Inspection (Ping Test)
4.3.1. Equipment setting
1) Play the LAN Port Test PROGRAM.
2) Input IP set up for an inspection to Test Program.
4.3.2. LAN PORT inspection (PING TEST)
1) Play the LAN Port Test Program.
2) Connect each other LAN Port Jack.
3) Play Test (F9) button and confirm OK Message.
4) Remove LAN CABLE

- 14 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
4.4. EDID Download
4.4.1. Overview
• It is a VESA regulation. A PC or a MNT will display an
optimal resolution through information sharing without any
necessity of user input. It is a realization of “Plug and Play”.
4.4.2. Equipment
• Since embedded EDID data is used, EDID download JIG,
HDMI cable and D-sub cable are not need.
• Adjust remocon.
4.3.3 Download method
1) Press Adj. key on the Adj. R/C,
2) Select EDID D/L menu.
3) By pressing Enter key, EDID download will begin
4) If Download is successful, OK is display, but If Download is
failure, NG is displayed.
5) If Download is failure, Re-try downloads.
* Caution) When EDID Download, must remove RGB/HDMI
Cable.
4.4.4. EDID DATA
4.4.4.1. For North America (PCM)
# HDMI 1(C/S : 7F6F)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255 [80H-FFH]
# HDMI 2(C/S : 7F5F)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255 [80H-FFH]
# HDMI 3(C/S : 7F4F)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255 [80H-FFH]
# HDMI 4(C/S : 7F3F)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255 [80H-FFH]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 80 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 39
60 | 3F 1F 52 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 01 7F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
________________________________________________
0 | 02 03 2E F1 48 10 22 20 05 84 03 02 01 23 09 07
10 | 07 78 03 0C 00 10 00 B8 2D 20 C0 0E 01 40 00 14
20 | 08 10 18 10 28 10 38 10 48 10 E3 05 03 01 02 3A
30 | 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C 04 05 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E
40 | 01 1D 80 18 71 1C 16 20 58 2C 25 00 A0 5A 00 00
50 | 00 9E 01 1D 00 72 51 D0 1E 20 6E 28 55 00 A0 5A
60 | 00 00 00 1E 26 36 80 A0 70 38 1F 40 30 20 25 00
70 | A0 5A 00 00 00 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 6F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 80 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 39
60 | 3F 1F 52 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 01 7F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
0 | 02 03 2E F1 48 10 22 20 05 84 03 02 01 23 09 07
10 | 07 78 03 0C 00 20 00 B8 2D 20 C0 0E 01 40 00 14
20 | 08 10 18 10 28 10 38 10 48 10 E3 05 03 01 02 3A
30 | 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C 04 05 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E
40 | 01 1D 80 18 71 1C 16 20 58 2C 25 00 A0 5A 00 00
50 | 00 9E 01 1D 00 72 51 D0 1E 20 6E 28 55 00 A0 5A
60 | 00 00 00 1E 26 36 80 A0 70 38 1F 40 30 20 25 00
70 | A0 5A 00 00 00 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 5F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 80 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 39
60 | 3F 1F 52 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 01 7F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 02 03 2E F1 48 10 22 20 05 84 03 02 01 23 09 07
10 | 07 78 03 0C 00 30 00 B8 2D 20 C0 0E 01 40 00 14
20 | 08 10 18 10 28 10 38 10 48 10 E3 05 03 01 02 3A
30 | 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C 04 05 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E
40 | 01 1D 80 18 71 1C 16 20 58 2C 25 00 A0 5A 00 00
50 | 00 9E 01 1D 00 72 51 D0 1E 20 6E 28 55 00 A0 5A
60 | 00 00 00 1E 26 36 80 A0 70 38 1F 40 30 20 25 00
70 | A0 5A 00 00 00 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 4F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 80 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 39
60 | 3F 1F 52 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 01 7F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 02 03 2E F1 48 10 22 20 05 84 03 02 01 23 09 07
10 | 07 78 03 0C 00 40 00 B8 2D 20 C0 0E 01 40 00 14
20 | 08 10 18 10 28 10 38 10 48 10 E3 05 03 01 02 3A
30 | 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C 04 05 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E
40 | 01 1D 80 18 71 1C 16 20 58 2C 25 00 A0 5A 00 00
50 | 00 9E 01 1D 00 72 51 D0 1E 20 6E 28 55 00 A0 5A
60 | 00 00 00 1E 26 36 80 A0 70 38 1F 40 30 20 25 00
70 | A0 5A 00 00 00 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 3F

- 15 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
# RGB(C/S : 98)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
4.4.4.2. For Korea (AC3)
# HDMI 1(C/S : 7FFD)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255 [80H-FFH]
# HDMI 2(C/S : 7FED)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255 [80H-FFH]
# HDMI 3(C/S : 7FDD)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255 [80H-FFH]
# HDMI 4(C/S : 7FCD)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
EDID Block 1, Bytes 128-255 [80H-FFH]
# RGB(C/S : 98)
EDID Block 0, Bytes 0-127 [00H-7FH]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 68 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 3A
60 | 3E 1E 53 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 98
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 80 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 39
60 | 3F 1F 52 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 01 7F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
10 | 50 09 07 07 78 03 0C 00 10 00 B8 2D 20 C0 0E 01
20 | 40 00 14 08 10 18 10 28 10 38 10 48 10 E3 05 03
30 | 01 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C 04 05 A0 5A 00
40 | 00 00 1E 01 1D 80 18 71 1C 16 20 58 2C 25 00 A0
50 | 5A 00 00 00 9E 01 1D 00 72 51 D0 1E 20 6E 28 55
60 | 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 26 36 80 A0 70 38 1F 40 30
70 | 20 25 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 FD
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 80 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 39
60 | 3F 1F 52 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 01 7F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 02 03 31 F1 48 10 22 20 05 84 03 02 01 26 15 07
10 | 50 09 07 07 78 03 0C 00 20 00 B8 2D 20 C0 0E 01
20 | 40 00 14 08 10 18 10 28 10 38 10 48 10 E3 05 03
30 | 01 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C 04 05 A0 5A 00
40 | 00 00 1E 01 1D 80 18 71 1C 16 20 58 2C 25 00 A0
50 | 5A 00 00 00 9E 01 1D 00 72 51 D0 1E 20 6E 28 55
60 | 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 26 36 80 A0 70 38 1F 40 30
70 | 20 25 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 ED
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 80 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 39
60 | 3F 1F 52 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 01 7F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 02 03 31 F1 48 10 22 20 05 84 03 02 01 26 15 07
10 | 50 09 07 07 78 03 0C 00 30 00 B8 2D 20 C0 0E 01
20 | 40 00 14 08 10 18 10 28 10 38 10 48 10 E3 05 03
30 | 01 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C 04 05 A0 5A 00
40 | 00 00 1E 01 1D 80 18 71 1C 16 20 58 2C 25 00 A0
50 | 5A 00 00 00 9E 01 1D 00 72 51 D0 1E 20 6E 28 55
60 | 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 26 36 80 A0 70 38 1F 40 30
70 | 20 25 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 DD
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 80 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 39
60 | 3F 1F 52 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 01 7F
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 02 03 31 F1 48 10 22 20 05 84 03 02 01 26 15 07
10 | 50 09 07 07 78 03 0C 00 40 00 B8 2D 20 C0 0E 01
20 | 40 00 14 08 10 18 10 28 10 38 10 48 10 E3 05 03
30 | 01 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C 04 05 A0 5A 00
40 | 00 00 1E 01 1D 80 18 71 1C 16 20 58 2C 25 00 A0
50 | 5A 00 00 00 9E 01 1D 00 72 51 D0 1E 20 6E 28 55
60 | 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 26 36 80 A0 70 38 1F 40 30
70 | 20 25 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 CD
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
_________________________________________________
0 | 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 01 00 01 01 01 01
10 | 01 15 01 03 68 10 09 78 0A EE 91 A3 54 4C 99 26
20 | 0F 50 54 A1 08 00 71 40 81 C0 81 00 81 80 95 00
30 | 90 40 A9 C0 B3 00 02 3A 80 18 71 38 2D 40 58 2C
40 | 45 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 66 21 50 B0 51 00 1B 30
50 | 40 70 36 00 A0 5A 00 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 3A
60 | 3E 1E 53 10 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 | 00 4C 47 20 54 56 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 98

- 16 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
5. Final Assembly Adjustment
5.1. White Balance Adjustment
5.1.1. Overview
5.1.1.1. W/B adj. Objective & How-it-works
(1) Objective: To reduce each Panel’s W/B deviation
(2) How-it-works: When R/G/B gain in the OSD is at 192, it
means the panel is at its Full Dynamic Range. In order to
prevent saturation of Full Dynamic range and data, one of
R/G/B is fixed at 192, and the other two is lowered to find
the desired value.
(3) Adj. condition: normal temperature
1) Surrounding Temperature: 25±5°C
2) Warm-up time: About 5 Min
3) Surrounding Humidity: 20% ~ 80%
4) Before White balance adjustment, Keep power on status,
don’t power off
5.1.1.2. Adj. condition and cautionary items
(1) Lighting condition in surrounding area surrounding lighting
should be lower 10 lux. Try to isolate adj. area into dark
surrounding.
(2) Probe location: Color Analyzer (CA-210) probe should be
within 10cm and perpendicular of the module surface
(80°~ 100°)
(3) Aging time
1) After Aging Start, Keep the Power ON status during 5
Minutes.
2) In case of LCD, Back-light on should be checked using no
signal or Full-white pattern.
5.1.2. Equipment
(1) Color Analyzer: CA-210 (NCG: CH 9 / WCG: CH12 / LED:
CH14)
(2) Adj. Computer (During auto adj., RS-232C protocol is
needed)
(3) Adjust Remocon
(4) Video Signal Generator MSPG-925F 720p/204-Gray
(Model: 217, Pattern: 49)
• Color Analyzer Matrix should be calibrated using CS-1000
5.1.3. Equipment connection
5.1.4. Adjustment Command (Protocol)
(1) RS-232C Command used during auto-adj.
(2) Adjustment Map
5.1.5. Adjustment method
5.1.5.1 Auto WB calibration
(1) Set TV in ADJ mode using P-ONLY key (or POWER ON
key)
(2) Place optical probe on the center of the display
- It need to check probe condition of zero calibration before
adjustment.
(3) Connect RS-232C Cable
(4) Select mode in ADJ Program and begin a adjustment.
(5) When WB adjustment is completed with OK message,
check adjustment status of pre-set mode (Cool, Medium,
Warm)
(6) Remove probe and RS-232C cable.
• W/B Adj. must begin as start command “wb 00 00” , and
finish as end command “wb 00 ff”, and Adj. offset if need
5.1.6 Reference (White Balance Adj. coordinate and color
temperature)
(1) Luminance: 204 Gray, 80IRE
(2) Standard color coordinate and temperature using CS-1000
(over 26 inch)
Colo r Analyzer
Comp ut er
Pattern Ge n e r ator
RS-232C
RS-232C
RS-232C
Probe
Signal Source
* If TV internal pattern is used, not needed
Connection Diagram of Automatic Adjustment
RS-232C COMMAND
Meaning
[CMD ID DATA]
wb 00 00 Begin White Balance adj.
wb 00 ff End White Balance adj.(Internal pattern disappeared)
ITEM Command Data Range Default
(Hex.) (Decimal)
Cmd 1 Cmd 2 Min Max
Cool R-Gain j g 00 C0
G-Gain j h 00 C0
B-Gain j i 00 C0
R-Cut
G-Cut
B-Cut
Medium R-Gain j a 00 C0
G-Gain j b 00 C0
B-Gain j c 00 C0
R-Cut
G-Cut
B-Cut
Warm R-Gain j d 00 C0
G-Gain j e 00 C0
B-Gain j f 00 C0
R-Cut
G-Cut

- 17 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
5.1.7. Reference (White Balance Adj. coordinate and color
temperature)
• Luminance: 204 Gray
• Standard color coordinate and temperature using CS-1000
(over 26 inch)
• Standard color coordinate and temperature using CA-
210(CH 14)
• Standard color coordinate and temperature using CA-
210(CH-14) – by aging time
*Only LGD Module (Except 32LW5700-UE/65LW6500-UA)
5.2. Tool Option setting & Inspection per
countries
5.2.1. Overview
(1) Tool option selection is only done for models in Non-USA
North America due to rating
(2) Applied model: LA02D and LA02E Chassis applied to
CANADA and MEXICO
5.2.2. Country Group selection
(1) Press ADJ key on the Adj. R/C, and then select Country
Group Menu
(2) Depending on destination, select KR or US, then on the
lower Country option, select US, CA, MX. Selection is
done using +, - KEY
5.2.3. Tool Option Inspection
(1) Press Adj. key on the Adj. R/C, and then check Tool
option.
5.3. Local Dimming Inspection
(1) Press ‘TILT” key of the Adj. R/C and check moving
patterns. The black bar patterns moves from top to bottom.
If a local dimming function does not work, a whole screen
shows full white.
* Except 32LW5700-UE / 55LW6500-UA (AUO / No local-
dimming)
Mode Color Coordination Temp ∆UV
xy
COOL 0.269 0.273 13000K 0.0000
MEDIUM 0.285 0.293 9300K 0.0000
WARM 0.313 0.329 6500K 0.0000
Mode Color Coordination Temp ∆UV
xy
COOL 0.269±0.002 0.273±0.002 13000K 0.0000
MEDIUM 0.285±0.002 0.293±0.002 9300K 0.0000
WARM 0.313+0.002 0.329±0.002 6500K 0.0000
Cool Medium Warm
x y x y x y
GP2G
Aging time
(Min)
269 273 285 293 313 329
1 0-2 276 285
2 3-5 274 282
3 6-9 273 280
4 10-19 272 278
5 20-35 271 276
6 36-49 269 274
7 50-79 269 273
8 Over 80 269 273
292 305 315 334
290 302 313 332
289 300 312 330
288 298 311 328
287 296 310 326
286 294 309 324
286 293 308 323
285 293 308 323
Model Tool 1 Tool 2 Tool 3 Tool 4 Tool 5 Tool 6
47LW6500-UA 33032 4161 7295 21897 47693 667
55LW6500-UA 33035 4161 7295 21897 47693 667
65LW6500-UA 37132 65 7295 21642 14925 667
32LW5700-UE 37284 65 5247 21898 14933 667
42LW5700-UE 33190 65 5247 21897 14933 667
47LW5700-UE 33192 65 5247 21897 14933 667
55LW5700-UE 33195 65 5247 21897 14933 667
42LW5700-NA 33190 4161 3327 22281 47661 665
47LW5700-NA 33192 4161 3327 22281 47661 665
55LW5700-NA 33195 4161 3327 22281 47661 665
42LW5600-UA 33174 4161 7295 21897 14925 667
47LW5600-UA 33176 4161 7295 21897 14925 667
55LW5600-UA 33179 4161 7295 21897 14925 667
42LW6500-NB 33030 4161 3327 22281 47661 665
47LW6500-NB 33032 4161 3327 22281 47661 665
55LW6500-NB 33195 4161 3327 22281 47661 665

- 18 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
5.4. EYE-Q Check
Step 1) Turn on the TV.
Step 2) Press EYE button in adjust remote control.
Step 3) Stay 6 seconds with Eye Q sensor hidden located on
the front of the set.
Step 4) Check the “Sensor Data” on the screen and check
whether the value is lower thanafter 6 seconds, the
value does not go below 10, Eye Q sensor is not
working properly. Then, change the sensor.
Step 5) Remove hand from the Eye Q II sensor and stay for 6
seconds.
Step 6) Check whether the “Back Light (xxx)” value has risen
on the screen. If after 6 seconds and the value still
does not go high, the eye Q II sensor is not working
properly. Replace the sensor.
5.5. Magic Motion remote controller Check
5.5.1. Test equipment
- RF-remote controller for check, IR-KEY-CODE remote
controller.
- Check AA battery before test. A recommendation is that a
tester change battery every lots.
5.5.2. Test
(1) Make pairing with TV set by pressing “Mute (START) key”
on RCU.
(2) Check a cursor on screen by pressing ‘ENTER” or “OK”
key of RCU
(3) Stop paring with TV set by pressing “VOL+ (STOP) key.
5.6. 3D pattern test
5.6.1. Test equipment
(1) Pattern Generator MSHG-600 or MSPG-6100 (HDMI 1.4
support)
(2) Pattern: HDMI mode (model No. 872, pattern No. 83)
5.6.2. Test method
(1) Input 3D test signal as Fig.1.
<Step1> <Step2> <Step3>
<Step4> <Step5>
O
K
O K
Fig.1
<HDMI Mode 872, Pattern No.83
Fig.2

- 19 -
LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
5.7. HDMI ARC Function Inspection
5.7.1. Test equipment
- Optic Receiver Speaker
- MSHG-600 (SW: 1220
↑)
- HDMI Cable (for 1.4 version)
5.7.2. Test method
(1) Insert the HDMI Cable to the HDMI ARC port from the
master equipment (HDMI1)
(2) Check the sound from the TV Set
(3) Check the Sound from the Speaker or using AV & Optic
TEST program (It’s connected to MSHG-600)
* Remark: Inspect in Power Only Mode and check SW version
in a master equipment

LGE Internal Use OnlyCopyright LG Electronics. Inc. All right reserved.
Only for training and service purposes
- 20 -
LV1
LV2
¿˝¿¸∏µ ø‹∫¿‘∑
§ø§
¿‘√øµªÛ
3D
TV
¿∑
¿ß¡¨
Ω∏∆ TV
¿Ã¿¸
∞∆º¡§
3D ø…º«
≥∞±
»Æ¿Œ
«ˆ¿Áπº¤
πº¤æ»≥ ¡§∫«•Ω
≥»
º±»£√≥
∆¿Ã¡ˆ
øµªÛ√≥∏∑
¡øλ˜
º±≈
¡ˆøÚ
«—/øµ/º˝¿⁄
ó
»√∞
¿Ã¿¸√≥
A2
A23
A13
A5
A10
300
200
500
120
510
511
810
900
910
800
530
540
521
400
710
EXPLODED VIEW
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis have special safety-related characteristics. These
parts are identified by in the Schematic Diagram and EXPLODED VIEW.
It is essential that these special safety parts should be replaced with the same components as
recommended in this manual to prevent X-RADIATION, Shock, Fire, or other Hazards.
Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE

P101
4
1
P5201
P3503
P1701
SPK_Woofer_R-
SPK_Woofer_R+
SPK_Woofer_L-
SPK_Woofer_L+
R502
Q501
R508
Q502
R110
R109
C106
R5202
41
R5201
R139
R150
SW5201
81
R3507
R3506
R3509
R3510
L1702
C1775
R1738
1
L1701
R1739
L1706
R1740
5
R1741
C1776
C519
C508
L503
L504
51523
24V
GNDGND
GNDGND
PWR ON24V
24V
Pb Free
Soldering
L514
6
5
C1723
R1711
R564
C557
IC505
R550
R549
R548
C522
C515
R1710
24
C1761
C1777
C565
C537
C525
R578
R1709
R1708
C1711
C1710
C1708
R1716
R1755
R1756
1
R572
R525
C516
R1712
C1700
R1754
C567
R570
R571
7
5
C530
M21
C1709
L1709
R1753
C1797
C1762
L1708
SPK_R-
IC506
L513
M20
C1799
C1712
R1713
48
SPK_R+
L515
L509
C5413
C5415
121
C1737
SPK_L-
8
1
C545
R5401
C5409
R5403
C5403
C5411
R5410
C5418
R5416
C1744
L1707
R1745
4
SPK_L+
R146
R182
R181
R184
R183
R176
R175
R177
R178
C5419
R1707
C1778
L516
C568
8
IC507
1
45
C546
BAR CODE
BAR CODE
JH
C506
P501
3.5V
3.5V
3.5V
3.5V
C528
1
4
L507
C523
L505
C524
L501
C503
R156
R166
C1759
L1705
C1763
C1764
94V-0
C1758
C505
C1741
48
C1742
36
R1752
Q503
C1740
C1738
Q508
10
1
IC501
C1765
C1739
C1736
24
121
C1733
C1731
C1735
R1720
R1702
C1701
R1704
C1743
IC1702
C513
IC1701
C1726
R1718
36
L1703L1704
L502
P502
12V
12VINV ON
12V
GND
GND/
P.DIM2
GND GND
Err
OUT
GND/
V-sync
A.DIM
P.DIM1
C1230
JK1202
D1206
R286
C1214
C1212
C114
C113
R228
R240
R253
R186
R189
R185
IC1203
R220
NAPRT
R215
R216
R263
C1216
R1229
8
R1222
R1220
1
45
R191
C1223
8
IC103
IC101
R224
R285
R227
AR5306
BCDEFGHJKLM
C1217
R190
48
AH
R411
R563
C555
45
R326
R328
R231R232
L5401
R5412
R5411
4
R5413
IC5403
5
R5414
R5415
L1204
C1219
C564
R569
R567
R568
LA12C
C535
BCM35230
EAX63969204(0)
C534
10.12.16 Y.Y.U.
IC102
1
R149
R107
C102
C101
R103
24
X101
R327
R329
R283
R223
R214
R162
R153
R147
R159
R194
R163
R281
R282
C105
R108
R261
R262
R251
R252
C5401
45
1
C5405
IC5402
8
L5404
C5417
C5416
1
8
C5421
C5420
C1724
R1719
C1728
C1734
R1721
C1732
C1766
IC5301
R1744
R1742
R1743
R5307
P1702
R3514
AR5309
P3502
20
10
1
JK1201
R173
R172
R169
R174
R130
R144
R145
R101
R195
UAVWY
IC401
AR5308
1
R5234
2836
R1207
R5233
R203
R1205
R209
R260
R208
C403
C1211
C1213
C1224
R1208
R1216
R206
R205
R207
R250
R280
R413
R412
R5235
D1205
X1201
R204
R5231R5232
R129
R287
C401
R5230
R5238
L1205
R1209
R1214
C109
R131
C110
BCDEFGHJKLMNPRT
123 789
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
R5225
R5236
R5239
R5240
8
1
IC1204
C1218
R1215
R1212
L1203
R301
C301
12345678910111213141516171819202122
2324 2526 2728
IC402
R5227 R5228
R5226
R5241
R5250
R5251
D1204
IC1202
9
10 18
19 27
45
1
R151
25
AA
AB
ACADAEAFAG
R402
R406
123 789
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
R5311
123 789
AR5307
R5312
R5313
R5314
R5315
R5316
R5320
R5321
REVERSE
40
30
41
FOR CABLE
R1213
C302
R213
C421
R5224
R5253
1414
4
C1215
R302
R106
1234567891011121314151617
D1203
5
C216
R5229
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
IC5201
1
R1231
R1221
R1230
C419
R419
R418
R5221
C5242
R5237
C1231
C1220
R1223
R5220
C5241
10
R212
C218
C217
R5223
C320
C321
C327
C328
C322
C323
C329
C330
C336
C335
C303
C325
C317
C312
C311
C306
C305
R422
R423
C5210
R5222
P3501
R718
R717
R706
C710
C828
R868
20
C702
R712
R707
C709
C708
R705
C705
C591
C594
C5211
R711
R826
L804
IC508
X5201
L5403
37
54
5572
R777
C825
C826
10
16
1
C816
C817
R233
C227
C332
C331
C334
C333
R242
R241
C304
R325
C326
C318
C313
C307
R592R593
R595
C593
8
5
1
4
R591
L517
C590
L5205
C5201
C5412
8
IC5401
1
C5406
C5404
30
FOR CABLE
C818
C533
R528
R306
40
R708
R703
C704
IC701
5
C819
R234
C231
5
4
C829
R869
IC804
8
1
C5414
R5404
C5407
C5410
R5408
L5402
50
R825
L805
M22
R544
C527
L506
R5405
R5402
R5407
51
C539
5
4
R5409
C5408
R5406
C5402
19 36
18
1
M23
C538
R545
IC504
C531
JK704
19110
R2166
C2112
C2113
C2177
JH
JK1001
12
R606
X601
R629
R630
R626
R628
R631
R632
R633
R627
D1201
D1202
R621
C1234
L1202
C2105
C2103
R2128
R1007
R1008
C602
C2121
C2126
R2121
R2169
TU2102
TU2101
C1004
C603
C605
121
R636
R638
C1233
4
P1201
R304
R640
R1139
C1104
L1112
R321
P601
C1110
C1109
R316
R2124
R2125
20
10
L1001
1
R607
R617
4837
C1232
1
R1108
ZD1113
R1109
C1106
R1136
C1108
R1144
C1107
R1143
C2131
R2136
R2163
R2101
R2123
R2712
R2713
R1005
R1006
D1001
D1002
R615
IC602
ZD1115
D1108
R1111
[A]
D1107
R1110
C2128
C2167
L2112
R2122
IC2702
15
20
28
Q1002
R1003
Q1001
1
R610
2413
D903D904
19110
JK702
14
10
302940
R2722
C1002
R1001
36
R648
R649
25
R935
R936
L2116
R2721
R1002
C606
R643
R646
R902
R929
R2702
1
C2733
C2734
JK1105
X602
C607
R642
SW1
C608
R645
R647
R903
Q901
R908
R909
C911
12
C2120
C2125
C2124
42
R644
R905
R904
Q902
R2720
P901
C2140
C2104
56
50
43
R2719
Q601
C2115
C2183
L2115
C2102
JK805
IC803
R916
R920
C903
D901 D902
D907
R928
P902
JK701
C2149
L2103
C2144
C2141
C2117
C2182
L2114
C2111
C2116
R2715
IC2701
AR2702
3625
AR2701
R2709
C2708
C2715
R2714
C2723
X2702
C2724
C2718
R2716
R1118
C1120
R1140
ZD1101
ZD1102
R303
1
C812
C814
C815
89
R915
R919
C901
R933
R934
D905D906
1151
C2181
C2106
D1111
16
19110
R1128
R1129
R862
R864
R1326
R2167
C2711
C2179
4837
R2708
X2701
R2135
L2110
13 24
IC2103
C2134
121
C2709
R833
R834
R1324
R1320
R1325
P1302
JK703
C2706
C2705
C2704
R2706
R2703
R2705
R2704
IC2703
JK1104
RDWHYL RDWHYL
RDWHRDGN BL
D814
D813
R1321
R1317
C2127
R1316
C1103
R1315
C1102
R1137
R1107
R1138
C1127
R311
R317
R312
D1406
D1404
L1303
112
VR703
R1106
R1105
ZD1111
R847
R848
C1126
R310
R1114
C804
C805
C832
C831
C830
R819
R820
R851
IC801
19110
R730
R737
C714
R728
R821
R822
C1125
L1110
L1111
D1101
[A]
JK802
C801
R866R867
D801
R804
R324
1
45
D802
R805
C802
IC802
8
C809
C810
D807
L808
R813
D806
L807
R811
D808
L806
R812
D812
D805
R808
C808
D804
R807
C807
14
1
R850
R852
8
7
R1401
D1402
D1401
JK1401
ZD1117
ZD1116
R2102
R853
VR706
JK803
JK1101
JK1102
C2101
JK801
JK804

R3505
C260
C253
L202
C298
C259
C222
C220
C215
C255
C314
C316
C2716
JP
R5259
R5258
L218
C295
C213
C281
R211
C315
C2717
C309
C310
C308
C2728
C2722
C2729
L2702
R3513
R3508
C2721
JP
JP
R407
R404
C2731
C425
JP
R3504
JP
JP
M8
C1788
JP
C1780
R1731
JP
JH
R1725
C1770
C1707
R432
R403
R410
C267
C263
C261
L205
JK1104
JP
R409
R405
C433
C410
R431
C402
C436
C432
C437
R1141
C1118
R1116
D1109
R416
R428
R1142
C1119
R1117
D1110
R417
R427
C252
JP
R323
C1123
R5219
R5243
C416
C439
R426
L203
C251
C1130
JP
C1124
R5255
C5212
R420
R414
R141
M4
C407
C423
C277
R408
R401
C205
C405
L210
M6
JP
JP
C1721
C415
R415
C435
R421
C450
R1130
L1108
R1134
JP
C1128
L1109
C1115
R1124
R1119
C1719
Q5202
C417
AR404
L1107
R1127
C1116
R1125
R1120
JP
C1725
R1760
C412
C426
C451
R318
C1117
C1129
R1759
R5262
R1133
JP
JP
C1752
C1717
R1758
M3
D1114
R1724
C1748
C1798
AR403
C452
R1135
L1103
C1113
R1122
C1779
C1769
R1757
Q5201
C203
AR406
C438
C442
R430
R429
C441
AR402
R424
R425
C409
AR405
C1121
R817
C1787
R1730
R1762
AR401
L1104
C1114
R1123
D1113
JP
C1782
R5254
R5256
R1121
ZD1107
ZD1106
C1122
D1112
C1790
R1733
C440
R1126
ZD1108
ZD1105
ZD1103
ZD1104
R1132
R322
R1131
D810
P1701
C1768
R1723
C404
C406
C408
C411
JK1105
R815
R814
6
JP
R1722
IC5202
R5245
C453
C455
C454
1
11
C1767
8
1
C1781
C5303
C5305
R5252
R5208
R5204
R536
M10
C1789
R1732
C1795
L1711
C1796
L1710
C1722
C1720
C1706
C1705
C1704
C1703
C1718
R1717
R1761
C1702
R1706
R1703
R1705
Q1701
R1701
C5304
C5213
R5308
C5306
R5303
R5304
C5302
C5310
C5311
AR5304
R5322
AR5303
R5244
45
R5246
R5207
C5225
R5203
R5249
R5248
R5216
R5215
R5247
C5243
R5211
R5212
C5219
C5214
C5208
C5207
L5202
C5203
L5203
C5204
R619
R616
8
IC601
1
45
R601
JK805
1
R801
R802
D809
JK804
D811
5
10
15
C5307
C5308
C5245
C5205
C5206
R838
C1727
C5309
R5317
AR5305
C5228
C5217
JP
JP
R5305
R5318
L5201
C5202
C1754
C1751
C5240
C604
R639
C813
C5315
C5312C5313
R5319
C5234
C5232
C5233
D1405
R5310
R5309
AR5301
C5239
C5238
L5204
L5206
R611
R612
R513
C580
R5301
R5302
C5301
C5231
C5216
C5209
C5246
R625
R603
R602
IC503
C5314
C5247
C5244
C5223
C5236
R604
R860
R863
R510 R511
R516
C581
R519
IC502
R515
R522
R517
R520
C520
R512
JP
R573
R574
R1729
C1784
C1774
R1735
JP
C1792
C1773
R1734
R1728
C1786
R1737
R1727
C1793
C1772
JP
C1771
R1726
R1736
C1785
AR5302
R5217
R5218
R5213
R5214
R5209
R5210
R5205
R5206
R5242
C5220
C5227
R553
R555
R558
C552
C560
Q507
C550
C551
R605
R623
R906
R637
R622
R624
R641
C609
Q903
R910
R613
R913
R614
R861
R865
L1401
C1401
D2210D3
1D1D4 11
JP
JP
P501
P502
JP JP
JP
C1791
JP
C1783
JP
JP
C1794
JP
R554
L511
JP
R911
R917
R921
JP
JP
JK1401
Q505
Q905
JP
R3512
R3501
R3502
Q506
R576
JP
JP
Q906
R918
JP
JP
JP
JP
M9
R557
R3511
R559
R575
JP
JP
JP
R914
JP
JP
D1403
C563
L3501
R922
JP
JP
JPJP
JP
R551
R547
R552
R518
R531
R538
R529
JP
R523
JP
JP
P1702
R3503
C3502
C3503
JP
JP
Q904
JP
R1402
R907
R912
JP
C3501
L902
C902
C905
JP
JP
L901
C904
C912
C913
R541
R546
R543
Q504
R535
R533
R532
R537
R524
R527
R540
R526
R1323
R1319
R1318
R1322
P101
JP
JP
JP
M1
C570
C559
R566
R542
C532
C571
R565
C558
JP
JP
M7
R168
R111
R117
R160
R170
R192
R164
R113R114
R115
R179
R157
R161
R158
R118
R165
R112
R180
R171
R193
R116
JP
JP
R1227
D708
M11
C1209
C713
C706
C2109
L2101
C2154
D707
JP
R1226
C1210
R1225
R1224
C701
R2145
ZD1110
C1208
C703
C2142
IC2102
C718
R779
R781
R780
M2
C2151
C2157
R1206
C720
R778
C2145
ZD1112
R1228
C1207
JP
L701
C2147
L2104
C2152
C2153
C2176
JP
C712
C711
L2111
C2180
JP
C719
C707
C2178
ZD1114
R1112
R1113
D1105
R2142
L2107
JP
JP
R2116
R2143
L2105
R315
R2138
L2109
L2108
JP
R2114
R2112
R2134
C2165
C2163
JP
M12
D1208
C1204
JP
C1206
C1205
R1204
JP
JP
D1207
JP
JP
R741
R754
Q710
D713
R721
R724
D711
R727
VR708
R729
C717
R735
VR707
R716
R714
R731
VR705
R726
C716
R739
VR702
R723
D710
R720
R725
R736
VR701
R740
C715
VR704
C730
R713
R715
R775
R776
JP
JP
R2120
Q2105
C2166
L2106
R2107
Q2101
C2168
R2117
C2123
C2159
C2169
R2161
Q2104
C2160
R2106
C2162
R2139
C2129
R2133
R2104
JP
34
R2113
R2168
20
R2140
R2137
C2161
C2107
18918 23
1892318
Q801
C2118
C2122
C2108
R837
R842
C107
R121
R126
C108
R843
R844
R196
Q102
C118
Q101
C821
R828
C823
33 19
3536
R827
R198
C119
R135
R136
R823
R824
L803
C824
M5
C822
R201
R199
R197
R202
C103
R105
R104
R142
C284
L214
C285
R1233
JH
R119
R167
R187
R1232
R122
C104
R143
R577
R120
R127
R154
R123
R188
C278
L217
C294
C297
R210
C201
C274
TU2102
R128
C288
C247
R155
C250
L204
R132
R124
L216
C291
L209
JP
R507
R503
C504
C509
C338
C221
C223
R125
C283
L212
C293
C280
L213
C287
L215
C290
C254
C257
TU2101
R266
R256
R257
R267
R265
R255
R254
R264
C510
C337
C286
R501
R505
C507
R504
C339
R148
C111
R313
R506
R140
C2713
C2701
R2707
C340
C276
C273
C225
C244
C112
C289
R314
C2727
C803
C319
R305
R5261
R5260
R226
R218
R235
R221
R222
C272
C262
C270
C266
R230
R284
R225
C209
C234
C238
C204
C207
C211
L220
C242
C233
C279
L211
C264
L2703
L207
C324
C210
C282
C268
R320
L2704
C2720
C208
C206
R319
JK802
C226
C232
C248
C212
C202
C224
C236
C214
C271
C258C5215
C275
C256
C296
C299
L219
C229
C269
L201
C265
C292
C249
L206
C2712
C2714
C2707
C2726
C2710
R2711
C2719
C2702
D803
R2701
C2732
JP
C2730
JP
R806
R803
R2710
L2701
C2725
C2703
JPJP
NAND FLASH MEMORY 8Gbit
+3.3V_Normal
NC_1
NC_2
NC_3
NC_4
NC_5
16Gbit
NC_6
0
RY/BY
RE
CE
NC_7
0
NC_8
VCC_1
VSS_1
NC_9
NC_10
CLE
ALE
WE
WP
NC_11
NC_12
NC_13
NC_14
NC_15
LGE35230(BCM35230KFSBG)
B5
HDMI0_CLKN
C5
HDMI0_CLKP
A4
HDMI0_D0N
B4
HDMI0_D0P
A3
HDMI0_D1N
B3
HDMI0_D1P
A2
HDMI0_D2N
B2
HDMI0_D2P
W2
CEC
V4
DDC0_SCL
W4
DDC0_SDA
V3
HDMI0_HTPLG_IN
V2
HDMI0_HTPLG_OUT
D13
HDMI0_ARC
E6
HDMI0_RESREF
R106
3K
NAND_RBb
NAND_REb
NAND_CEb
NAND_CEb2
NAND_CLE
NAND_ALE
NAND_WEb
Write Protection
- High : Normal Operation
- Low : Write Protection
FLASH_WP
+3.3V_Normal
R101
R105
R104
4.7K
4.7K
4.7K
R195
4.7K
R148
+3.3V_Normal
R103
HDMI_CLK-
HDMI_CLK+
HDMI_RX0-
HDMI_RX0+
HDMI_RX1-
HDMI_RX1+
HDMI_RX2-
HDMI_RX2+
HDMI_ARC
2.7KR107
4.7K
R149
16Gbit
OPT
C102
4700pF
C101
0.1uF
TC58DVG3S0ETA00
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
IC101
NON_BCM_CAP
LT0VCAL_MONITOR
IC102
NAND_8Gbit
TXOUT0_L0N
TXOUT0_L0P
TXOUT0_L1N
TXOUT0_L1P
TXOUT0_L2N
TXOUT0_L2P
TXCLK_LN
TXCLK_LP
TXOUT0_L3N
TXOUT0_L3P
TXOUT0_L4N
TXOUT0_L4P
TXOUT0_U0N
TXOUT0_U0P
TXOUT0_U1N
TXOUT0_U1P
TXOUT0_U2N
TXOUT0_U2P
TXCLK_UN
TXCLK_UP
TXOUT0_U3N
TXOUT0_U3P
TXOUT0_U4N
TXOUT0_U4P
TXOUT1_L0N
TXOUT1_L0P
TXOUT1_L1N
TXOUT1_L1P
TXOUT1_L2N
TXOUT1_L2P
TXCLK1_LN
TXCLK1_LP
TXOUT1_L3N
TXOUT1_L3P
TXOUT1_L4N
TXOUT1_L4P
TXOUT1_U0N
TXOUT1_U0P
TXOUT1_U1N
TXOUT1_U1P
TXOUT1_U2N
TXOUT1_U2P
TXCLK1_UN
TXCLK1_UP
TXOUT1_U3N
TXOUT1_U3P
TXOUT1_U4N
TXOUT1_U4P
GPIO_BL_ON
BL_PWM/GPIO
AE27
AE28
AF27
AF28
AG27
AG28
AE26
AF26
AH27
AG26
AF25
AE25
AH26
AG25
AE24
AD24
AH25
AF24
AE23
AD23
AG24
AF23
AC22
AD22
AG23
AH23
AE22
AE21
AF22
AH22
AG22
AF21
AG21
AF20
AD21
AC21
AG20
AH20
AD19
AE19
AF19
AH19
AE18
AD18
AG19
AF18
AG18
AF17
AC18
AH16
AG16
+3.3V_Normal
R153
1K
SRST
Strap Setting
+3.3V_Normal
R157
R154
10K
10K
OPT
OPT
R155
R158
10K
10K
NAND_DATA[0]:
0: System is LITTLE endian (O)
1: System is BIG endian
0: Disable EDID automatic Downloading from Flash (O)
1: Enable EDID automatic Downloading from Flash
0: Differential Oscillators TVM not bypassed (O)
R156
R159
1K
1K
CI_ADDR[7]:
NAND_DATA[6] :
0: Disable OSC clock output on chip Pin (O)
1: Enable OSC clock output on chip pin.
0: Host MIPS run at 500 MHz (O)
1: Differential Oscillators TVM bypassed
0: 27MHz TVM Crystal Frequency
1: 54MHz TVM Crystal Frequency (O)
R162
1K
CI_ADDR[6]:
1: Host MIPS run at 250 MHz
NAND_CLE:
NAND_DATA[4]:
R166
1K
R163
1K
R160
10K
OPT
R161
10K
R167
R164
10K
10K
OPT
OPT
R165
R168
10K
10K
NVRAM
+3.3V_Normal
R169
0
54MHz X-TAL
C113
12pF
50V
X-TAL_2
C114
12pF
50V
R175
R170
10K
10K
OPT
R176
R171
10K
10K
OPT
0: RESETOUTb (in On/Off only) stay asserted until software releases them.
1: Fix amount of delay for de-assertion on RESETOUTb (in On/IOff only)
M24M01-HRMN6TP
OPT
4.7K
4.7K
R173
R174
NC
E1
E2
VSS
OPT
4.7K
R172
2
3
GND_1
4
GND_2
1
X-TAL_1
54MHz
X101
CRYSTAL_BCM_Sunny
EAW58812611
SUNNY ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
R187
R179
R177
10K
10K
OPT
R180
R178
10K
10K
OPT
CI_ADDR[9],CI_ADDR[11],CI_ADDR[12],CI_ADDR[13]
TVM Crystal oscillator bias/gain control
0101, 0110, 1001, 1010, 1011, 1100, 1101, 1110: Reserved
0: MIPS will boot from external flash (O)
BCM_NVM_1M
IC103
1
8
2
7
A8’h
3
6
4
5
R183
R181
10K
10K
OPT
R182
10K
0000: 210uA
0001: 390uA
0010: 570uA
0011: 730uA
0100: 890uA (O)
0111: 1290uA
1000: 1416uA
1111: 2196uA
CI_ADDR[8]:
at end of RESETb pulse (O)
NAND_DATA[3]:
1: MIPS will boot from ROM
NAND_DATA[5]:
0: FLASH MODE (O)
1: BSC_SLAVE(BBS) MODE
VCC
WP
SCL
SDA
0R185
R189
1M
OPT
0R186
R184
10K
OPT
+3.3V_Normal
54MHz_XTAL_N
54MHz_XTAL_P
10K
OPT
R188
10K
R192
10K
OPT
R193
10K
- Low : Normal Operation
- High : Write Protection
NAND_DATA[0]
CI_ADDR[7]
NAND_DATA[6]
CI_ADDR[6]
NAND_CLE
NAND_DATA[4]
CI_ADDR[9]
CI_ADDR[11]
CI_ADDR[12]
CI_ADDR[13]
CI_ADDR[8]
NAND_DATA[3]
NAND_DATA[5]
BCM_NVM_256K
IC103-*1
AT24C256C-SSHL-T
A0
1
A1
2
A2
3
GND
4
Write Protection
33R190
33R191
X101-*2
54MHz
X-TAL_1
1
GND_1
2
CRYSTAL_BCM_KDS
EAW58239604
DAISHINKU CORPORATION.
X101-*1
54MHz
X-TAL_1
1
GND_1
2
CRYSTAL_BCM_Lihom
EAW60763703
LIHOM CO., LTD.
VCC
8
WP
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
SCL3_3.3V
SDA3_3.3V
GND_2
4
X-TAL_2
3
GND_2
4
X-TAL_2
3
16Gbit
IC102-*1
TH58DVG4S0ETA20
NC_1
1
NC_28
48
NC_27
47
NC_26
46
NC_25
45
I/O8
44
NAND_DATA[7]
I/O7
43
NAND_DATA[6]
I/O6
42
NAND_DATA[5]
I/O5
41
NAND_DATA[4]
NC_24
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
PSL
NC_23
VCC_2
VSS_2
NC_22
NC_21
NC_20
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
NC_19
NC_18
NC_17
NC_16
16Gbit
R151
+3.3V_Normal
C104
NAND_DATA[3]
NAND_DATA[2]
NAND_DATA[1]
NAND_DATA[0]
TXB4P
TXB4N
TXB3P
TXB3N
TXBCLKP
TXBCLKN
TXB2P
TXB2N
TXB1P
TXB1N
TXB0P
TXB0N
TXA4P
TXA4N
TXA3P
TXA3N
TXACLKP
TXACLKN
TXA2P
TXA2N
TXA1P
TXA1N
TXA0P
TXA0N
TXD4P
TXD4N
TXD3P
TXD3N
TXDCLKP
TXDCLKN
TXD2P
TXD2N
TXD1P
TXD1N
TXD0P
TXD0N
TXC4P
TXC4N
TXC3P
TXC3N
TXCCLKP
TXCCLKN
TXC2P
TXC2N
TXC1P
TXC1N
TXC0P
TXC0N
0
10uF
10V
C103
0.1uF
+3.3V_Normal
R194
2.7K
NAND_DATA[0-7]
RGB_DDC_SDA
RGB_DDC_SCL
BBS CONNECT
P101
TJC2508-4A
10KR108
C105
2.2uF
10V
RY/BY2
RY/BY1
VCC_1
VSS_1
NC_10
NC_11
NC_12
NC_13
Q101
BSS83
Q102
BSS83
+3.3V_Normal
VCC
1
SCL
2
SDA
3
GND
4
A_DIM
NC_2
NC_3
NC_4
NC_5
NC_6
NC_7
NC_8
NC_9
SBD
G
SBD
G
RE
CE1
CE2
CLE
ALE
WE
WP
C106
4.7uF
DEV_NAND_16Gbit
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
+3.3V_Normal
R196
10K
C118
0.1uF
16V
+3.3V_Normal
R198
10K
C119
0.1uF
16V
R110
R109
1.5K
1.5K
DVB_S Option: apply EU Satellite model
APPLY ONLY WHEN CONNECT TO PULL-UP GPIO
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
SDA0_3.3V
SCL0_3.3V
SCL2_3.3V
SDA2_3.3V
FOR HDMI STANDARD
NC_26
NC_25
NC_24
NC_23
I/O8
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
NC_22
PSL
NC_21
VCC_2
VSS_2
NC_20
NC_19
NC_18
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
NC_17
NC_16
NC_15
NC_14
22R199
22R197
+3.3V_Normal
R121
1.2K
DVB_S
+3.3V_Normal
+3.3V_Normal
Boot ROM Device Select - (FA4,FAD7,FAD2,FAD1)
+3.3V_Normal
R117
R113
10K
10K
OPT
R118
R114
10K
10K
OPT
R122
10K
R123
10K
OPT
R127
10K
OPT
R128
10K
CI_ADDR[4]
NAND_DATA[7]
NAND_DATA[2]
NAND_DATA[1]
NAND ECC (FA3, FA2, FALE)
+3.3V_Normal
R115
R111
10K
OPT
R112
10K
10K
R116
10K
OPT
R119
10K
OPT
R120
10K
CI_ADDR[3]
CI_ADDR[2]
NAND_ALE
DUAL COMPONENT
IC102 1ST : EAN61000101 2ND : T-TH58DVG4S0ETA20
IC102-*1
LGE35230(BCM35230KFSBG)
AG6
AF6
V5
AB4
Y4
AA4
Y5
AB2
AB5
U3
U2
Y2
Y1
AA3
33
AA2
33R136
H3
H2
H4
H5
F25
4.7KR141
W5
OPT
U5
22R142
U4
22R143
OPT
OPT
W3
22R144
W1
22R145
OPT
AB6
Y6
0R139
Y3
G24
J6
W6
F7
E7
R140
560
1%
BCM REFRENCE is 562ohm
C107
33pF
50V
R124
1K
OPT
R125
1K
R126
1.2K
C108
33pF
50V
DVB_S
R129
1.2K
C109
33pF
50V
5V_HDMI_3
R130
OPT
2K
+3.3V_Normal
R131
1.2K
C110
33pF
50V
PCM_5V_CTL
5V_HDMI_1
5V_HDMI_2
5V_HDMI_4
SOC_RESET
54MHz_XTAL_P
54MHz_XTAL_N
LNB_INT
BCM_RX
BCM_TX
+3.3V_Normal
4.7KR132
SRST
0.01uFC111
0.1uFC112
SC_ID
R135
NON_BCM_CAP
TVM_XTALIN
TVM_XTALOUT
IRRXDA
FP_IN0
FP_IN1
SPARE_ADC1
SPARE_ADC2
FS_IN1
FS_IN2
VGA_SDA
VGA_SCL
RDA
TDA
BSCDATAA
BSCCLKA
RDB/GPIO
TDB/GPIO
BSC_S_SCL
BSC_S_SDA
NMIB
POWER_CTRL
AON_HSYNC
AON_VSYNC
AON_GPIO_36
AON_GPIO_37
AON_RESETOUTB
TVM_BYPASS
RESETB
RESETOUTB
TMODE
TESTEN
VDAC_VREG
VDAC_RBIAS
0000: ST Micro M25P or compatible Serial Flash
0010: 8-bit 512Mbit 512B page SLC NAND Flash devices
0100: 8-bit 128, 256Mbit 512B page SLC NAND Flash devices
0110: 8-bit 1Gbit 2KB page SLC NAND Flash devices
1000: 8-bit 2Gbit, 4Gbit, 8Gbit 2KB page SLC NAND Flash devices
1010: 8-bit 16Gbit, 32Gbit 4KB page SLC NAND Flash devices (O)
0001: 8-bit 8/16/32Gbit 2KB page MLC NAND Flash devices
0011: 8-bit 16/32Gbit 4KB page MLC NAND Flash devices
0101: 8-bit 32Gbit 8KB page MLC NAND Flash devices
0111: 3B dual IO Serial Flash
1001: BB dual IO Serial Flash
1011: fast Serail Flash > 50Mhz
1100: OneNAND Flash (always 16-bit)
1110: Reserved
1101, 1111: Reserved
000 = ECC disabled
001 = ECC 1-bit repair
010 = ECC 4-bit BCH (O)
011 = ECC 8-bit BCH, 27 byte spare
100 = ECC 12-bit BCH, 27 byte spare
101 = ECC 8-bit BCH, 16 byte spare
110, 111 = Reservedd
IC101
AB1
AB3
AC1
AC2
AC3
AD2
AD3
AE2
AG1
AF1
AC5
AE6
AG5
AF3
AG2
AE3
AA5
AF2
AE1
AC4
AD5
AD4
AE4
AE5
AD6
AH3
AF4
AH4
AG4
AF5
AG3
AH2
AH5
AD15
AF14
AH14
AD14
AG14
AC16
AH7
AG7
AD7
AF7
AH8
C6
D7
NAND_DATA[7]
NAND_DATA[6]
NAND_DATA[5]
NAND_DATA[4]
NAND_DATA[3]
NAND_DATA[2]
NAND_DATA[1]
NAND_DATA[0]
NAND_ALE
NAND_CEb
NAND_CEb2
/CI_CE1
/CI_CE2
FLASH_WP
NAND_WEb
NAND_REb
/PCM_WAIT
NAND_CLE
NAND_RBb
CI_ADDR[2]
CI_ADDR[3]
CI_ADDR[4]
CI_ADDR[5]
CI_ADDR[6]
CI_ADDR[7]
CI_ADDR[8]
CI_ADDR[9]
CI_ADDR[10]
CI_ADDR[11]
CI_ADDR[12]
CI_ADDR[13]
CI_ADDR[14]
10KR146
TDI/GPIO
TMS/GPIO
TCK/GPIO
DINT/GPIO
AVS_VFB
AVS_VSENSE
AVS_RESETB
AVS_NDRIVE_1
AVS_PDRIVE_1
VDAC_1
VDAC_2
FAD_7
FAD_6
FAD_5
FAD_4
FAD_3
FAD_2
FAD_1
FAD_0
FCEB_0
FCEB_1
FCEB_2
FCEB_3
NFWPB
FRDYB
FA_10
FA_11
FA_12
FA_13
FA_14
FA_15
TRSTB
FALE
FA_0
FA_1
FA_2
FA_3
FA_4
FA_5
FA_6
FA_7
FA_8
FA_9
FWE
FRD
TDO
NAND_DATA[0-7]
R147
1K
DTV/MNT_V_OUT
CI_ADDR[2-14]
R150
1K
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FILRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFATURES SPECFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
BCM35230
MAIN & NAND FLASH
2010.09.18
1

+3.3V_Normal
1K
R252
1K
R262
FE_TS_DATA[0-7]
R253
OLED
LCD
R263
BCM
internal
FRC
0011
1100
HIGH
Support
CHBO_TS_CLK
CHBO_TS_SERIAL
CHBO_TS_SYNC
CHBO_TS_VAL_ERR
FHD
1K
R251
1K
R250
FRC2/URSA5
BCM_FRC/URSA5
1K
R260
NO_FRC/BCM_FRC
1K
R261
NO_FRC/FRC2
HD
MODEL OPTION
MODEL_OPT_0
MODEL_OPT_1
MODEL_OPT_2
MODEL_OPT_3
MODEL_OPT_4
MODEL_OPT_5
MODEL_OPT_6
MODEL_OPT_7 Enable Disable
NO_FRC
DDR speed
T2 Tuner
S Tuner
PHM
POWER 2.5V
+2.5V_BCM35230
C244
C220
0.1uF
+3.3V_Normal
R232
URSA_RESET
6.3V
GND
4.7K
OUTIN
R233
1.2K
C227
33pF
50V
R232-*1
C222
0.01uF
+0.9V_CORE
+3.3V_Normal
+1.5V_DDR
R234
1.2K
C231
33pF
50V
FRC2_RESET
C247
22uF
C248
10uF
10V
SDA1_3.3V
SCL1_3.3V
NON_NTP
FRC_RESET
+2.5V_BCM35230
Place Cap
Very close to R22 Ball
+0.9V_CORE
C225
C221
0.1uF
C17
B17
D15
B16
A16
A15
C16
G28
G26
W14
W15
W13
J5
R5
V6
H6
AE15
AF15
AG15
AF16
AD16
AE16
AG17
AH17
AE17
AD17
AB13
AC15
AB12
AB11
AE14
AG13
AH13
AF13
AE13
AD12
AF12
AG10
AF10
AE10
AD10
AE9
AE8
AC10
AC11
AC8
AB8
AC14
AG12
AH10
AB7
AG11
AD11
AE11
AD13
AE12
AC12
AC13
AH11
AF11
C223
0.01uF
C203
10uF
10V
Non_CHB
R212
1K
closed to soc
+3.3V_Normal
R280
22
R221
R222
R283
22
R235
R225
C205
10uF
10V
close to soc
C217
16V
0.1uF
C218
0.1uF
2KR213
M_REMOTE_RX
CI_DET
M_RFModule_RESET
EPHY_ACTIVITY
EPHY_LINK
22R214
22R215
22R281
22R282
22R216
INSTANT_MODE
22R218
22R220
22
22
22R223
22R284
22R224
100
0
22R226
22R227
0.22uF
6.3V
1K
R254
1K
OPT
R264
1K
LG FRC2
LOW
HDFHD
LCDOLED
16001333
Not Support
Not SupportSupport
1K
SIDE_USB_OCD1
SIDE_USB_OCD2
T2_TUNER
NO_T2_TUNER
external
URSA5
R201
PCM_MDI[0-7]
R255
R265
F/NIM_EU_CN
1K
1K
PCM_TS_DATA[0-7]
OPT
0
R202
0
1K
R256
S_TUNER
1K
R266
NO_S_TUNNER
+3.3V_Normal
TU_TS_CLK
FE_TS_DATA[0]
FE_TS_DATA[1]
FE_TS_DATA[2]
FE_TS_DATA[3]
FE_TS_DATA[4]
FE_TS_DATA[5]
FE_TS_DATA[6]
FE_TS_DATA[7]
WIFI
R286
10K
PHM
NO_PHM
R287
10K
WIFI
R257
R267
1K
1K
R203
R204
R205
R206
R207
R208
R209
C201
100pF
OPT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
PCM_MDI[0]
PCM_MDI[1]
PCM_MDI[2]
PCM_MDI[3]
PCM_MDI[4]
PCM_MDI[5]
PCM_MDI[6]
PCM_MDI[7]
R211
6.04K
R210
4.87K
1%
SIDE_USB_DM
SIDE_USB_DP
SIDE_USB_CTL1
SIDE_USB_CTL2
PCM_TS_CLK
PCM_TS_DATA[0]
PCM_TS_DATA[1]
PCM_TS_DATA[2]
PCM_TS_DATA[3]
PCM_TS_DATA[4]
PCM_TS_DATA[5]
PCM_TS_DATA[6]
PCM_TS_DATA[7]
PCM_TS_SYNC
PCM_TS_VAL
F/NIM_EU_CN
F/NIM_EU_CN
F/NIM_EU_CN
F/NIM_EU_CN
F/NIM_EU_CN
F/NIM_EU_CN
F/NIM_EU_CN
TU_TS_SYNC
TS_VAL_ERR
PCM_MCLKI
PCM_MISTRT
PCM_MIVAL_ERR
EPHY_TDP
EPHY_TDN
EPHY_RDP
EPHY_RDN
WIFI_DM
WIFI_DP
/PCM_IRQA
MODEL_OPT_0
MODEL_OPT_1
MODEL_OPT_2
MODEL_OPT_3
MODEL_OPT_4
MODEL_OPT_5
MODEL_OPT_6
MODEL_OPT_7
LGE35230(BCM35230KFSBG)
F26
EPHY_VREF
D26
EPHY_RDAC
F27
EPHY_TDP
F28
EPHY_TDN
E27
EPHY_RDP
E26
EPHY_RDN
F5
USB_MONCDR
E5
USB_RREF
C2
USB_PORT1DN
D1
USB_PORT1DP
E1
USB_PWRFLT_1/GPIO
D2
USB_PWRON_1/GPIO
B1
USB_PORT2DN
C1
USB_PORT2DP
C3
USB_PWRFLT_2/GPIO
C4
USB_PWRON_2/GPIO
M4
TCLKA/GPIO
L5
TDATA_0/GPIO
M5
TDATA_1/GPIO
L6
TDATA_2/GPIO
N3
TDATA_3/GPIO
N1
TDATA_4/GPIO
N2
TDATA_5/GPIO
M3
TDATA_6/GPIO
M2
TDATA_7/GPIO
L4
TSTRTA/GPIO
N4
TVLDA/GPIO
K6
TCLKD/GPIO
J4
TDATD_0/GPIO
K5
TDATD_1/GPIO
J2
TDATD_2/GPIO
J3
TDATD_3/GPIO
K2
TDATD_4/GPIO
K1
TDATD_5/GPIO
K3
TDATD_6/GPIO
L1
TDATD_7/GPIO
L3
TSTRTD/GPIO
L2
TVLDD/GPIO
P4
MPEG_CLK/GPIO
T2
MPEG_D_0/GPIO
R3
MPEG_D_1/GPIO
R2
MPEG_D_2/GPIO
P3
MPEG_D_3/GPIO
P2
MPEG_D_4/GPIO
P1
MPEG_D_5/GPIO
R6
MPEG_D_6/GPIO
N5
MPEG_D_7/GPIO
T4
MPEG_SYNC/GPIO
P5
MPEG_DATA_EN/GPIO
R4
MCIF_RESET/GPIO
U1
MCIF_SCLK/GPIO
T3
MCIF_SCTL/GPIO
T1
MCIF_SDI/GPIO
T5
MCIF_SDO/GPIO
IC101
NON_BCM_CAP
VI_IFP0
VI_IFM0
VDDR_AGC
AGC_SDM_2
AGC_SDM_1
PCI_VIO_0
PCI_VIO_1
PCI_VIO_2
GPIO_70
GPIO_71
GPIO_72
GPIO_73
GPIO_74
GPIO_75
GPIO_76
GPIO_77
GPIO_78
GPIO_79
PCI_AD05
PCI_AD06
PCI_AD07
PCI_AD08
PCI_AD09/GPIO
PCI_AD10/GPIO
PCI_AD11/GPIO
PCI_AD12/GPIO
PCI_AD13/GPIO
PCI_AD14/GPIO
PCI_AD15/GPIO
PCI_AD16/GPIO
PCI_AD17/GPIO
PCI_AD18/GPIO
PCI_AD19/GPIO
PCI_AD20/GPIO
PCI_AD21/GPIO
PCI_AD22
PCI_AD23
PCI_AD24
PCI_AD25
PCI_CBE00
PCI_CBE01/GPIO
PCI_CBE02/GPIO
PCI_CBE03
PCI_DEVSELB/GPIO
PCI_FRAMEB/GPIO
PCI_IRDYB/GPIO
PCI_PAR/GPIO
PCI_PERRB/GPIO
PCI_REQ1B
PCI_SERRB/GPIO
PCI_STOPB/GPIO
PCI_TRDYB/GPIO
GPIO_0
GPIO_1
GPIO_2
GPIO_3
GPIO_4
GPIO_5
GPIO_6
GPIO_7
16V
BCM_L/DIM
BCM_L/DIM
OPT
22R285
C207
4.7uF
10V
100
R241
100
R242
IF_AGC
0.01uFC216
3D_SYNC
MODEL_OPT_0
DTV_ATV_SELECT
RF_SWITCH_CTL_2
MODEL_OPT_1
MODEL_OPT_2
MODEL_OPT_3
AV2_CVBS_DET
ERROR_OUT
NFM18PS105R0J
C233
6.3V
OUTIN
GND
C232
4.7uF
10V
C209
4.7uF
10V
IF_P
IF_N
SC_DET/COMP2_DET
CHB_RESET
TW9910_RESET
RF_BOOSTER_CTL
DSUB_DET
PCM_RST
MODEL_OPT_4
DC_MREMOTE
DD_MREMOTE
L/DIM0_MOSI
L/DIM0_SCLK
COMP1_DET
MODEL_OPT_5
3D_GPIO_0
MODEL_OPT_6
MODEL_OPT_7
RF_SWITCH_CTL
3D_GPIO_1
3D_GPIO_2
C234
0.1uF
C211
0.1uF
+3.3V_Normal
BCM_L/DIM
NFM18PS105R0J
C204
6.3V
GND
C236
0.1uF
C213
0.1uF
+3.3V_Normal
BLM18PG121SN1D
R240
2.7K
22R228
22R230
FRC2_RESET
URSA_RESET
OUTIN
NFM18PS105R0J
C238
4.7uF
10V
C215
0.01uF
L201
C229
0.1uF
+3.3V_Normal
0R231-*1
100R231
NON_NTP
PWM_DIM
L/DIM0_VS
4.7K
BLM18PG121SN1D
C249
10uF
10V
BLM18PG121SN1D
+2.5V_BCM35230
BLM18PG121SN1D
C250
4.7uF
10V
Place Cap
C242
0.1uF
+3.3V_Normal
L202
L203
C251
0.1uF
16V
L204
+1.5V_DDR
Very close to R22 Ball
MLG1005S22NJT
L220
C253
10uF
10V
EPHY_VDD25
C252
4.7uF
10V
VAFE3_VDD25
C254
4.7uF
C224
1uF
25V
OPT
+0.9V_CORE
AADC_AVDD25
C256
0.1uF
C255
0.1uF
C257
0.1uF
+0.9V_CORE
C226
0.1uF
16V
OPT
+3.3V_Normal
+2.5V_BCM35230
L205
BLM18PG121SN1D
C258
0.1uF
+2.5V_BCM35230
C259
10uF
10V
+2.5V_BCM35230
+2.5V_BCM35230
NON_BCM_CAP
VDDC_1
VDDC_2
VDDC_3
VDDC_4
VDDC_5
VDDC_6
VDDC_7
VDDC_8
VDDC_9
VDDC_10
VDDC_11
VDDC_12
VDDC_13
VDDC_14
VDDC_15
VDDC_16
VDDC_17
VDDC_18
VDDC_19
VDDC_20
VDDC_21
VDDC_22
VDDC_23
VDDC_24
VDDC_25
VDDC_26
VDDC_27
VDDC_28
VDDC_29
VDDC_30
VDDC_31
VDDC_32
VDDC_33
VDDC_34
VDDC_35
VDDC_36
VDDC_37
VDDC_38
VDDC_39
VDDC_40
VDDC_41
VDDC_42
POR_VDD
VDDR1_1
VDDR1_2
VDDR1_3
VDDR1_4
VDDR1_5
VDDR1_6
VDDR1_7
VDDR1_8
VDDR1_9
VDDR1_10
VDDR1_11
VDDR1_12
DDR_LDO_VDDO
VDDR3_1
VDDR3_2
VDDR3_3
VDDR3_4
VDDR3_5
VDDR3_6
VDDR3_7
VDDR3_8
VDDR3_9
VDDR3_10
VDDR3_11
AON_VDDC_1
AON_VDDC_2
AON_POR_VDD
AON_VDDR3
AON_VDDR10_1
AON_VDDR10_2
IC101
LGE35230(BCM35230KFSBG)
V12
V7
M10
N10
P10
R10
T10
U10
V10
W10
V13
L11
M11
N11
P11
R11
T11
U11
V11
W11
V14
L18
M18
N18
P18
R18
T18
U18
V18
W18
V15
L19
M19
N19
P19
R19
T19
U19
V19
W19
V16
V17
L10
L22
AA28
V28
R28
M28
J28
K23
M22
T22
T23
U22
Y22
R22
G15
H22
G23
AB9
K7
AB15
L7
AB14
M7
N6
P6
AA6
AA7
Y7
U7
T7
T6
C260
4.7uF
BLM18PG121SN1D
BLM18PG121SN1D
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSS_13
VSS_14
VSS_15
VSS_16
VSS_17
VSS_18
VSS_19
VSS_20
VSS_21
VSS_22
VSS_23
VSS_24
VSS_25
VSS_26
VSS_27
VSS_28
VSS_29
VSS_30
VSS_31
VSS_32
VSS_33
VSS_34
VSS_35
VSS_36
VSS_37
VSS_38
VSS_39
VSS_40
VSS_41
VSS_42
VSS_43
VSS_44
VSS_45
VSS_46
VSS_47
VSS_48
VSS_49
VSS_50
VSS_51
VSS_52
VSS_53
VSS_54
VSS_55
VSS_56
VSS_57
VSS_58
VSS_59
VSS_60
VSS_61
VSS_62
VSS_63
VSS_64
VSS_65
VSS_66
VSS_67
VSS_68
VSS_69
VSS_70
VSS_71
VSS_72
VSS_73
VSS_74
VSS_75
VSS_76
VSS_77
VSS_78
VSS_79
VSS_80
VSS_81
VSS_82
VSS_83
VSS_84
C261
10uF
10V
L206
L207
C263
4.7uF
C262
10uF
PLL_VAFE_AVDD25
K10
K11
K12
L12
M12
N12
P12
R12
T12
U12
W12
K13
L13
M13
N13
P13
R13
T13
U13
W16
K14
L14
M14
N14
P14
R14
T14
U14
K15
L15
M15
N15
P15
R15
T15
U15
K16
L16
M16
N16
P16
R16
T16
U16
K17
L17
M17
N17
P17
R17
T17
U17
W17
K18
K19
H7
G14
AB16
R7
M6
AB23
P7
W7
J7
N7
AB10
AC23
AC6
G19
AA22
J23
J22
K22
J25
N22
N23
M25
P22
R25
V22
W22
W23
V25
AA25
ADAC_AVDD25
C266
4.7uF
VAFE2_VDD25
C265
4.7uF
C264
4.7uF
C267
0.1uF
C270
0.1uF
C269
0.1uF
C268
0.1uF
C271
0.01uF
C272
0.01uF
CORE 0.9V
+0.9V_CORE
+0.9V_CORE
+0.9V_CORE
L209
BLM18PG121SN1D
C274
22uF
L210
BLM18PG121SN1D
L211
BLM18PG121SN1D
HDMI_AVDD
PLL_AUD_AVDD
C277
4.7uF
PLL_VAFE_AVDD
POWER 3.3V
+3.3V_Normal
BLM18PG121SN1D
VAFE2_VDD25
Place as close as possible to the pad
VAFE3_VDD25
use only for A0/B0 chip
C210-*1
220pF
50V
BCM_A0/B0
PLL_VAFE_AVDD
PLL_VAFE_AVDD25
+0.9V_CORE
C202
390pF
50V
Place as close as possible to the pad
+0.9V_CORE
L214
BLM18PG121SN1D
C280
0.1uF
C281
0.1uF
C279
C282
0.1uF
4.7uF
USB_AVDD33
L212
VAFE2_DVDD
VAFE3_DVDD
C208
390pF
50V
Place as close as possible to the pad
C206
390pF
50V
+0.9V_CORE
C283
0.1uF
+3.3V_Normal
+2.5V_BCM35230
+2.5V_BCM35230
VDAC_AVDD33
BCM_C0
PLL_MIPS_AVDD
C273
0.1uF
C284
22uF
BLM18PG121SN1D
L213
BLM18PG121SN1D
ADAC_AVDD25
EPHY_VDD25
HDMI_AVDD33
C275
0.1uF
OPT
USB_AVDD
USB_AVDD33
C212
390pF
50V
C210
390pF
50V
PLL_MAIN_AVDD
C276
0.01uF
OPT
L215
AADC_AVDD25
PLL_AUD_AVDD
USB_AVDD
C285
C288
0.1uF
4.7uF
VAFE3_DVDD
C287
4.7uF
+3.3V_Normal
BLM18PG121SN1D
VDAC_AVDD33
C286
4.7uF
LGE35230(BCM35230KFSBG)
F19
D25
D24
E24
F24
E25
HDMI_AVDD
D5
D4
AE20
AD20
AC20
AB20
D14
E4
D3
D6
D18
E17
D16
C214
390pF
D17
50V
D9
D8
E8
E9
G25
K4
AD25
D11
D12
AE7
+3.3V_Normal
U6
C278
0.1uF
C290
0.1uF
L216
C289
0.1uF
AADC_AVDD25
ADACA_AVDD25
ADACC_AVDD25
ADACD_AVDD25
EPHY_BVDD25
EPHY_AVDD25
HDMI0_AVDD
HDMI0_AVDD33
LT0VDD25_1
LT0VDD25_2
LT0VDD25_3
LT0VDD25_4
SPDIF_IN_AVDD25
USB_AVDD
USB_AVDD33
VDAC_AVDD33
VAFE2_DVDD
VAFE2_AVDD25_1
VAFE2_AVDD25_2
VAFE2_DVDD25
VAFE3_DVDD
VAFE3_AVDD25_1
VAFE3_AVDD25_2
F9
VAFE3_AVDD25_3
VAFE3_DVDD25
F8
POR_VDD25
PLL_AUD_AVDD
PLL_MAIN_AVDD
PLL_MIPS_AVDD
PLL_VAFE_AVDD
PLL_VAFE_AVDD25
TVM_OSC_AVDD
AUX_AVDD33
+0.9V_CORE
+0.9V_CORE
+0.9V_CORE
HDMI_AVDD33
C291
4.7uF
NON_BCM_CAP
L219
BLM18PG121SN1D
C292
22uF
L217
BLM18PG121SN1D
L218
BLM18PG121SN1D
C293
0.1uF
IC101
AADC_AVSS
ADACA_AVSS
ADACC_AVSS
ADACD_AVSS
EPHY_AVSS
HDMI0_AVSS_1
HDMI0_AVSS_2
SPDIF_IN_AVSS
USB_AVSS_1
USB_AVSS_2
VDAC_AVSS
VAFE2_VSS_1
VAFE2_VSS_2
VAFE2_VSS_3
VAFE2_VSS_4
VAFE2_VSS_5
VAFE2_VSS_6
VAFE2_VSS_7
VAFE3_VSS_1
VAFE3_VSS_2
VAFE3_VSS_3
VAFE3_VSS_4
VAFE3_VSS_5
VAFE3_VSS_6
PLL_MIPS_AVSS
TVM_OSC_AVSS
PLL_MAIN_AVDD
LT0VSS_1
LT0VSS_2
LT0VSS_3
LT0VSS_4
LT0VSS_5
LT0VSS_6
LT0VSS_7
VAFE2_DVDD
C296
4.7uF
C294
4.7uF
PLL_MIPS_AVDD
C295
4.7uF
F20
G22
G21
F22
F23
F6
G6
AB22
AB21
AB19
AC19
AB18
AB17
AC17
F15
G7
G8
G9
G20
E18
G18
G17
F18
G16
F16
G13
G12
F12
G11
G10
F10
AD26
AC7
C297
0.1uF
C298
0.1uF
C299
0.1uF
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FILRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFATURES SPECFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
BCM35230
MAIN POWER
2
50

AV2_CVBS_IN
INCM_VID_AV2
AV1_CVBS_IN
INCM_VID_AV1
COMP1_Pr
COMP1_Pb
INCM_VID_COMP1
R303
36
TU_CVBS
TU_SIF
DSUB_R+
COMP1_Y
0.1uFC303
0.1uFC304
EU
R325-*1
10
INCM_R
DSUB_B+
INCM_B
R304
36
R311
36
R312
36
R310
0
SC_R/COMP2_Pr
SC_G/COMP2_Y
SC_B/COMP2_Pb
INCM_VID_SC/COMP2
SC_CVBS_IN
INCM_VID_SC
NON_EU
INCM_TUNER
R306
75
1%
OPT
0.1uFC317
0.1uFC318
+2.5V_BCM35230
R305
240
OPT
INCM_SIF
NON_BCM_CAP
VI_R
VI_INCM_R
VI_G
VI_INCM_G
VI_B
VI_INCM_B
HSYNC_IN
VSYNC_IN
VI_Y1
VI_PR1
VI_PB1
VI_INCM_COMP1
VI_SC_R1
VI_SC_G1
VI_SC_B1
VI_INCM_SC1
VI_FB_1/GPIO
VI_FS1
VI_SC_R2
VI_SC_G2
VI_SC_B2
VI_INCM_SC2
VI_FB_2/GPIO
VI_FS2
VI_L1
VI_C1_1
VI_INCM_LC1_1
VI_C1_2
VI_INCM_LC1_2
VI_CVBS1
VI_INCM_CVBS1
VI_CVBS2
VI_INCM_CVBS2
VI_CVBS3
VI_INCM_CVBS3
VI_CVBS4
VI_INCM_CVBS4
VI_SIF1_1
VI_INCM_SIF1_1
VI_SIF1_2
VI_INCM_SIF1_2
IC101
Near
Near
Near
Near
Near
Near
Near
Near
P801
P801
P801
JK1101
JK1104
TU2101/2
TU2201/2/3
JK1102
JK1103
JK2501
VIDEO INCM
Run Along DSUB_R Trace
Run Along DSUB_G Trace
Run Along DSUB_B Trace
Run Along COMP_Y_IN,COMP_Pr_IN,COMP_Pb_IN Trace
Run Along AV2_CVBS Trace
Run Along TUNER_CVBS_IF_P Trace
Run Along AV1_CVBS Trace
Run Along COMP_Y_IN,COMP_Pr_IN,COMP_Pb_IN/SC R,G,B Trace
INCM_R
INCM_G
INCM_B
INCM_VID_COMP1
INCM_VID_AV2
INCM_TUNER
INCM_VID_AV1
INCM_VID_SC/COMP2
BCM35230_with_CAP_220pF
IC101-*1
LGE35230
B6
BCM_CAP
VI_R
A6
VI_INCM_R
C7
VI_G
A7
VI_INCM_G
B7
VI_B
C8
VI_INCM_B
C13
HSYNC_IN
A13
VSYNC_IN
C9
VI_Y1
A9
VI_PR1
B9
VI_PB1
B8
VI_INCM_COMP1
C11
VI_SC_R1
A10
VI_SC_G1
B10
VI_SC_B1
C10
VI_INCM_SC1
D10
VI_FB_1/GPIO
F13
VI_FS1
A12
VI_SC_R2
C12
VI_SC_G2
B12
VI_SC_B2
B11
VI_INCM_SC2
E12
VI_FB_2/GPIO
E14
VI_FS2
E15
VI_L1
F17
VI_C1_1
E16
VI_INCM_LC1_1
F14
VI_C1_2
E11
VI_INCM_LC1_2
C18
VI_CVBS1
B18
VI_INCM_CVBS1
A18
VI_CVBS2
C19
VI_INCM_CVBS2
A19
VI_CVBS3
B19
VI_INCM_CVBS3
C20
VI_CVBS4
B20
VI_INCM_CVBS4
E19
VI_SIF1_1
D19
VI_INCM_SIF1_1
E10
VI_SIF1_2
F11
VI_INCM_SIF1_2
0.1uFC320
0.1uFC321
DSUB_G+
INCM_G
0.1uFC322
0.1uFC323
0R325
R316
36
R313
10K
0.1uFC319
R314
12K
R315
120
OPT
+2.5V_BCM35230
0.1uFC327
0.1uFC328
R317
36
DSUB_HSYNC
DSUB_VSYNC
R318
0
SC_FB
0.1uFC325
0.1uFC326
R319
10K
OPT
0.1uFC324
R320
12K
OPT
LGE35230(BCM35230KFSBG)
C13
A13
0.1uFC329
0.1uFC330
0.1uFC331
0.1uFC332
C11
0.1uFC333
A10
0.1uFC334
B10
0.1uFC335
C10
0.1uFC336
D10
F13
A12
C12
B12
B11
E12
E14
E15
F17
E16
F14
E11
C18
B18
A18
C19
A19
B19
C20
B20
E19
D19
E10
F11
B6
A6
C7
A7
B7
C8
C9
A9
B9
B8
SCL3_3.3V
SDA3_3.3V
+3.3V_Normal
R301
1.2K
C301
33pF
50V
PHONE JACK
INCM_AUD_SC/COMP2
R302
1.2K
M_REMOTE_TX
C302
33pF
50V
AV1_R_IN
INCM_AUD_AV1
AV2_R_IN
INCM_AUD_AV2
SC/COMP2_L_IN
SC/COMP2_R_IN
PC_L_IN
PC_R_IN
AV1_L_IN
AV2_L_IN
LGE35230(BCM35230KFSBG)
B15
SPDIF_INC_P
C15
SPDIF_INC_N
C14
SPDIF_IND_P
B14
SPDIF_IND_N
G4
I2SSCK_IN/GPIO
F4
I2SWS_IN
G5
I2SSD_IN/GPIO
1uF 10VC305
1uF 10VC306
1uF 10VC307
1uF 10VC308
1uF 10VC309
1uF 10VC310
1uF 10VC311
1uF 10VC312
1uF 10VC313
1uF 10VC314
1uF 10VC315
1uF 10VC316
C25
B24
A24
E22
E23
D23
C24
C23
B23
E21
D21
D22
B22
C22
A22
F21
D20
E20
A21
C21
B21
AADC_LINE_L1
AADC_LINE_R1
AADC_INCM1
AADC_LINE_L2
AADC_LINE_R2
AADC_INCM2
AADC_LINE_L3
AADC_LINE_R3
AADC_INCM3
AADC_LINE_L4
AADC_LINE_R4
AADC_INCM4
AADC_LINE_L5
AADC_LINE_R5
AADC_INCM5
AADC_LINE_L6
AADC_LINE_R6
AADC_INCM6
AADC_LINE_L7
AADC_LINE_R7
AADC_INCM7
IC101
NON_BCM_CAP
I2SSCK_OUTA/GPIO
I2SWS_OUTA/GPIO
I2SSD_OUTA0/GPIO
I2SSOSCK_OUTA/GPIO
I2SSD_OUTA1/GPIO
I2SSD_OUTA2/GPIO
I2SSCK_OUTC/GPIO
I2SWS_OUTC/GPIO
I2SSD_OUTC/GPIO
I2SSOSCK_OUTC/GPIO
I2SSCK_OUTD/GPIO
I2SWS_OUTD/GPIO
I2SSD_OUTD/GPIO
I2SSOSCK_OUTD/GPIO
SPDIF_OUTA/GPIO
AUDMUTE_0/GPIO
AUDMUTE_1
ADAC_AL_N
ADAC_AL_P
ADAC_AR_N
ADAC_AR_P
ADAC_CL_N
ADAC_CL_P
ADAC_CR_N
ADAC_CR_P
ADAC_DL_N
ADAC_DL_P
ADAC_DR_N
ADAC_DR_P
TU_RESET_SUB
HP_DET
AV1_CVBS_DET
TU_RESET
SC_RE1
SC_RE2INCM_AUD_PC
/RST_HUB
S2_RESET
SPDIF_OUT
HP_LOUT_N
HP_LOUT_P
HP_ROUT_N
HP_ROUT_P
SCART1_Lout_N
SCART1_Lout_P
SCART1_Rout_N
SCART1_Rout_P
100R326
100R327
100R328
100R329
C337
22pF
OPT
C338
22pF
OPT
C339
22pF
OPT
AUD_SCK
AUD_LRCK
AUD_LRCH
AUD_MASTER_CLK
C340
33pF
OPT
AUDIO INCM
Route Between AV1_L_IN & AV1_R_IN Trace
Near
Near
Near
Near
Near
JK1102
JK1103
JK2501
JK1104
JK801
TU2101/2
TU2201/2/3
0R321
Route Between SC/COMP2_L_IN & SC/COMP2_R_IN Trace
0R322
Route Between AV2_L_IN & AV2_R_IN Trace
0R323
Route Between PC_L_IN & PC_R_IN Trace
0R324
Route Along With TUNER_SIF_IF_N
INCM_AUD_AV1
INCM_AUD_SC/COMP2
INCM_AUD_AV2
INCM_AUD_PC
INCM_SIF
AF8
AF9
AG9
AC9
AD8
AD9
E2
F2
E3
F3
G2
G3
G1
H1
B13
AG8
E13
C28
C27
D28
D27
C26
A27
B27
B28
B25
A25
A26
B26
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FILRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFATURES SPECFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
BCM35230
MAIN AUDIO/VIDEO
3
50

DDR STRAP
R401
4.7K
DDR_1333
R403
4.7K
R405
4.7K
DDR_1333
R407
4.7K
DDR_DQ[0]
DDR_DQ[1]
DDR_DQ[2]
DDR_DQ[3]
DDR_DQ[4]
R409
4.7K
OPT
10101 : DDR3-1600K (CasL=11) (O)
JEDEC Types : DDR_DQ[0:4]
00001 : DDR3-1333H (CasL=9)
DUAL COMPONENT
IC401,IC402 1ST : EAN61667501, 2ND : EAN61570701
IC401-*1
IC402-*1
1ST : T-K4B2G1646B_HCK0, 2ND : T-H5TQ2G63BFR-PBC
NFM18PS105R0J
C410
C403
2.2uF
C405
10uF
C407
2.2uF
6.3V
OUTIN
GND
+1.5V_DDR
C417
470pF
C421
2.2uF
C423
10uF
C425
10uF
NFM18PS105R0J
C432
6.3V
GND
+1.5V_DDR
OUTIN
DDR_DQ[10]
DDR_DQ[9]
DDR_DQ[7]
DDR_DQ[8]
DDR_DQ[6]
DDR_DQ[5]
R402
R432
4.7K
4.7K
OPT
OPT
DDR_DQ[0-7]
DDR_DQ[0]
DDR_DQ[1]
DDR_DQ[2]
DDR_DQ[3]
DDR_DQ[4]
DDR_DQ[5]
DDR_DQ[24]
DDR_DQ[25]
DDR_DQ[26]
DDR_DQ[27]
DDR_DQ[28]
DDR_DQ[29]
DDR_DQ[30]
DDR_DQ[31]
DDR_DM[0]
DDR_DM[1]
DDR_DM[2]
DDR_DM[3]
DDR_QS0
DDR_QS0b
DDR_QS1
DDR_QS1b
DDR_QS2
DDR_QS2b
DDR_QS3
DDR_QS3b
DDR_DQ[6]
DDR_DQ[7]
DDR_DQ[8]
DDR_DQ[9]
DDR_DQ[10]
DDR_DQ[11]
DDR_DQ[12]
DDR_DQ[13]
DDR_DQ[14]
DDR_DQ[15]
DDR_DQ[16]
DDR_DQ[17]
DDR_DQ[18]
DDR_DQ[19]
DDR_DQ[20]
DDR_DQ[21]
DDR_DQ[22]
DDR_DQ[23]
DDR_DQ[8-15]
DDR_DQ[16-23]
DDR_DQ[24-31]
DDR_DM[0-3] DDR_QS3
R406
4.7K
OPT
NON_BCM_CAP
DDR_DQA_0
DDR_DQA_1
DDR_DQA_2
DDR_DQA_3
DDR_DQA_4
DDR_DQA_5
DDR_DQA_6
DDR_DQA_7
DDR_DQA_8
DDR_DQA_9
DDR_DQA_10
DDR_DQA_11
DDR_DQA_12
DDR_DQA_13
DDR_DQA_14
DDR_DQA_15
DDR_DQA_16
DDR_DQA_17
DDR_DQA_18
DDR_DQA_19
DDR_DQA_20
DDR_DQA_21
DDR_DQA_22
DDR_DQA_23
DDR_DQA_24
DDR_DQA_25
DDR_DQA_26
DDR_DQA_27
DDR_DQA_28
DDR_DQA_29
DDR_DQA_30
DDR_DQA_31
DDR_DMA_0
DDR_DMA_1
DDR_DMA_2
DDR_DMA_3
DDR_DQSA_P_0
DDR_DQSA_N_0
DDR_DQSA_P_1
DDR_DQSA_N_1
DDR_DQSA_P_2
DDR_DQSA_N_2
DDR_DQSA_P_3
DDR_DQSA_N_3
R408
4.7K
IC101
DDR_ADA_ALT_4
DDR_ADA_ALT_5
DDR_ADA_ALT_6
DDR_ADA_10
DDR_ADA_11
DDR_ADA_12
DDR_ADA_13
DDR_ADA_14
DDR_RASA_N
DDR_CASA_N
DDR_WEA_N
DDR_CKA01_P
DDR_CKA01_N
DDR_CKA23_P
DDR_CKA23_N
DDR_VREFA
R404
4.7K
OPT
LGE35230(BCM35230KFSBG)
U26
R26
U27
R27
V27
P26
U25
P27
R24
N24
T25
M23
R23
N25
T24
N26
L26
H27
L27
J26
M27
G27
M26
H26
L23
H25
L24
J24
M24
H23
L25
H24
T26
P25
J27
K24
T27
T28
P24
P23
K27
K28
K25
K26
R410
4.7K
OPT
DDR_ADA_0
DDR_ADA_1
DDR_ADA_2
DDR_ADA_3
DDR_ADA_4
DDR_ADA_5
DDR_ADA_6
DDR_ADA_7
DDR_ADA_8
DDR_ADA_9
DDR_BAA_0
DDR_BAA_1
DDR_BAA_2
DDR_CKEA
DDR_RST_N
DDR_ZQ
V23
AB27
Y23
Y26
AB26
Y24
AC26
AB24
AC25
AC24
AB25
AD28
Y25
AA27
AC27
AA26
AA24
AD27
Y27
AB28
W24
V24
W25
V26
U24
W27
W28
N28
N27
U23
AA23
W26
IC401-*2
NT5CB128M16BP-CG
DDR_1333_NANYA
N3
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
A3
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
A6
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
A9
L7
A10/AP
R7
A11
N7
A12
T3
NC_6
M7
NC_5
M2
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
J7
CK
K7
CK
K9
CKE
L2
CS
K1
ODT
J3
RAS
K3
CAS
L3
WE
T2
RESET
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
C7
DQSU
B7
DQSU
E7
DML
D3
DMU
E3
DQL0
F7
DQL1
F2
DQL2
F8
DQL3
H3
DQL4
H8
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
D7
DQU0
C3
DQU1
C8
DQU2
C2
DQU3
A7
DQU4
A2
DQU5
B8
DQU6
A3
DQU7
Bus Width : DDR_DQ[10]
0 - 16b
1 - 32b (O)
Chip Width : DDR_DQ[8]
0 - 8b
1 - 16b (O)
Chip Size : DDR_DQ[6:5]
00 - 4Gbit
01 - 2Gbit (O)
10 - 1Gbit
11 - 512Mbit
DDR_AA0
DDR_AA1
DDR_AA2
DDR_AA3
DDR01_AA4
DDR01_AA5
DDR01_AA6
DDR23_AA4
DDR23_AA5
DDR23_AA6
DDR_AA7
DDR_AA8
DDR_AA9
DDR_AA10
DDR_AA11
DDR_AA12
DDR_AA13
DDR_AA14
DDR_BAA0
DDR_BAA1
DDR_BAA2
DDR_RASb
DDR_CASb
DDR_WEb
DDR_CKE
DDR01_CLK
DDR01_CLKb
DDR23_CLK
DDR23_CLKb
DDR_VREFA
DDR_RESETb
240
R411
1%
M8
VREFCA
H1
VREFDQ
L8
ZQ
B2
VDD_1
D9
VDD_2
G7
VDD_3
K2
VDD_4
K8
VDD_5
N1
VDD_6
N9
VDD_7
R1
VDD_8
R9
VDD_9
A1
VDDQ_1
A8
VDDQ_2
C1
VDDQ_3
C9
VDDQ_4
D2
VDDQ_5
E9
VDDQ_6
F1
VDDQ_7
H2
VDDQ_8
H9
VDDQ_9
J1
NC_1
J9
NC_2
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
T7
NC_7
A9
VSS_1
B3
VSS_2
E1
VSS_3
G8
VSS_4
J2
VSS_5
J8
VSS_6
M1
VSS_7
M9
VSS_8
P1
VSS_9
P9
VSS_10
T1
VSS_11
T9
VSS_12
B1
VSSQ_1
B9
VSSQ_2
D1
VSSQ_3
D8
VSSQ_4
E2
VSSQ_5
E8
VSSQ_6
F9
VSSQ_7
G1
VSSQ_8
G9
VSSQ_9
IC402-*2
NT5CB128M16BP-CG
DDR_1333_NANYA
N3
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
A3
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
A6
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
A9
L7
A10/AP
R7
A11
N7
A12
T3
NC_6
M7
NC_5
M2
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
J7
CK
K7
CK
K9
CKE
L2
CS
K1
ODT
J3
RAS
K3
CAS
L3
WE
T2
RESET
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
C7
DQSU
B7
DQSU
E7
DML
D3
DMU
E3
DQL0
F7
DQL1
F2
DQL2
F8
DQL3
H3
DQL4
H8
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
D7
DQU0
C3
DQU1
C8
DQU2
C2
DQU3
A7
DQU4
A2
DQU5
B8
DQU6
A3
DQU7
C453
1uF
6.3V
DDR01_CLK
DDR01_CLKb
R412
56
1%
C401
1000pF
DDR_DQ[0-7]
DDR_DQ[8-15]
IC401-*3
NT5CB128M16BP-DI
DDR_1600_NANYA
M8
VREFCA
H1
VREFDQ
L8
ZQ
B2
VDD_1
D9
VDD_2
G7
VDD_3
K2
VDD_4
K8
VDD_5
N1
VDD_6
N9
VDD_7
R1
VDD_8
R9
VDD_9
A1
VDDQ_1
A8
VDDQ_2
C1
VDDQ_3
C9
VDDQ_4
D2
VDDQ_5
E9
VDDQ_6
F1
VDDQ_7
H2
VDDQ_8
H9
VDDQ_9
J1
NC_1
J9
NC_2
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
T7
NC_7
A9
VSS_1
B3
VSS_2
E1
VSS_3
G8
VSS_4
J2
VSS_5
J8
VSS_6
M1
VSS_7
M9
VSS_8
P1
VSS_9
P9
VSS_10
T1
VSS_11
T9
VSS_12
B1
VSSQ_1
B9
VSSQ_2
D1
VSSQ_3
D8
VSSQ_4
E2
VSSQ_5
E8
VSSQ_6
F9
VSSQ_7
G1
VSSQ_8
G9
VSSQ_9
N3
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
A3
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
A6
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
A9
L7
A10/AP
R7
A11
N7
A12
T3
NC_6
M7
NC_5
M2
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
J7
CK
K7
CK
K9
CKE
L2
CS
K1
ODT
J3
RAS
K3
CAS
L3
WE
T2
RESET
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
C7
DQSU
B7
DQSU
E7
DML
D3
DMU
E3
DQL0
F7
DQL1
F2
DQL2
F8
DQL3
H3
DQL4
H8
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
D7
DQU0
C3
DQU1
C8
DQU2
C2
DQU3
A7
DQU4
A2
DQU5
B8
DQU6
A3
DQU7
M8
VREFCA
H1
VREFDQ
L8
ZQ
B2
VDD_1
D9
VDD_2
G7
VDD_3
K2
VDD_4
K8
VDD_5
N1
VDD_6
N9
VDD_7
R1
VDD_8
R9
VDD_9
A1
VDDQ_1
A8
VDDQ_2
C1
VDDQ_3
C9
VDDQ_4
D2
VDDQ_5
E9
VDDQ_6
F1
VDDQ_7
H2
VDDQ_8
H9
VDDQ_9
J1
NC_1
J9
NC_2
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
T7
NC_7
A9
VSS_1
B3
VSS_2
E1
VSS_3
G8
VSS_4
J2
VSS_5
J8
VSS_6
M1
VSS_7
M9
VSS_8
P1
VSS_9
P9
VSS_10
T1
VSS_11
T9
VSS_12
B1
VSSQ_1
B9
VSSQ_2
D1
VSSQ_3
D8
VSSQ_4
E2
VSSQ_5
E8
VSSQ_6
F9
VSSQ_7
G1
VSSQ_8
G9
VSSQ_9
NT5CB128M16BP-DI
DDR_1600_NANYA
N3
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
A3
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
A6
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
A9
L7
A10/AP
R7
A11
N7
A12
T3
NC_6
M7
NC_5
M2
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
J7
CK
K7
CK
K9
CKE
L2
CS
K1
ODT
J3
RAS
K3
CAS
L3
WE
T2
RESET
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
C7
DQSU
B7
DQSU
E7
DML
D3
DMU
E3
DQL0
F7
DQL1
F2
DQL2
F8
DQL3
H3
DQL4
H8
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
D7
DQU0
C3
DQU1
C8
DQU2
C2
DQU3
A7
DQU4
A2
DQU5
B8
DQU6
A3
DQU7
IC402-*3
R413
56
1%
+1.5V_DDR
C455
C454
1uF
1uF
6.3V
6.3V
DDR_AA0
DDR_AA1
DDR_AA2
DDR_AA3
DDR01_AA4
DDR01_AA5
DDR01_AA6
DDR_AA7
DDR_AA8
DDR_AA9
DDR_AA10
DDR_AA11
DDR_AA12
DDR_AA13
DDR_BAA0
DDR_BAA1
DDR_BAA2
DDR_CKE
+1.5V_DDR
DDR_RASb
DDR_CASb
DDR_WEb
10KR414
DDR_RESETb
DDR_QS0
DDR_QS0b
DDR_QS1
DDR_QS1b
DDR_DM[0]
DDR_DM[1]
DDR_DQ[0]
DDR_DQ[1]
DDR_DQ[2]
DDR_DQ[3]
DDR_DQ[4]
DDR_DQ[5]
DDR_DQ[6]
DDR_DQ[7]
DDR_DQ[8]
DDR_DQ[14]
DDR_DQ[13]
DDR_DQ[12]
DDR_DQ[9]
DDR_DQ[10]
DDR_DQ[15]
DDR_DQ[11]
M8
VREFCA
H1
VREFDQ
L8
ZQ
B2
VDD_1
D9
VDD_2
G7
VDD_3
K2
VDD_4
K8
VDD_5
N1
VDD_6
N9
VDD_7
R1
VDD_8
R9
VDD_9
A1
VDDQ_1
A8
VDDQ_2
C1
VDDQ_3
C9
VDDQ_4
D2
VDDQ_5
E9
VDDQ_6
F1
VDDQ_7
H2
VDDQ_8
H9
VDDQ_9
J1
NC_1
J9
NC_2
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
T7
NC_7
A9
VSS_1
B3
VSS_2
E1
VSS_3
G8
VSS_4
J2
VSS_5
J8
VSS_6
M1
VSS_7
M9
VSS_8
P1
VSS_9
P9
VSS_10
T1
VSS_11
T9
VSS_12
B1
VSSQ_1
B9
VSSQ_2
D1
VSSQ_3
D8
VSSQ_4
E2
VSSQ_5
E8
VSSQ_6
F9
VSSQ_7
G1
VSSQ_8
G9
VSSQ_9
N3
P7
P3
N2
P8
P2
R8
R2
T8
R3
L7
R7
N7
T3
M7
M2
N8
M3
J7
K7
K9
L2
K1
J3
K3
L3
T2
F3
G3
C7
B7
E7
D3
E3
F7
F2
F8
H3
H8
G2
H7
D7
C3
C8
C2
A7
A2
B8
A3
NFM18PS105R0J
K4B2G1646C
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10/AP
A11
A12/BC
A13
NC_5
BA0
BA1
BA2
CK
CK
CKE
CS
ODT
RAS
CAS
WE
RESET
DQSL
DQSL
DQSU
DQSU
DML
DMU
DQL0
DQL1
DQL2
DQL3
DQL4
DQL5
DQL6
DQL7
DQU0
DQU1
DQU2
DQU3
DQU4
DQU5
DQU6
DQU7
C402
6.3V
GND
IC401
DDR_1333_SS
OUTIN
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VDDQ_5
VDDQ_6
VDDQ_7
VDDQ_8
VDDQ_9
NC_1
NC_2
NC_3
NC_4
NC_6
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
VSSQ_6
VSSQ_7
VSSQ_8
VSSQ_9
C412
1uF
+1.5V_DDR
+1.5V_DDR
R416
4.99K
1%
M8
H1
L8
R415
ZQ
B2
D9
G7
K2
K8
N1
N9
R1
R9
A1
A8
C1
C9
D2
E9
F1
H2
H9
J1
J9
L1
L9
T7
A9
B3
E1
G8
J2
J8
M1
M9
P1
P9
T1
T9
B1
B9
D1
D8
E2
E8
F9
G1
G9
C415
0.01uF
C416
0.01uF
1%
240
R417
4.99K
1%
DDR_AA14
DDR_VREFA
+1.5V_DDR
DDR23_CLK
DDR23_CLKb
DDR_DQ[16-23]
DDR_DQ[24-31]
R418
DDR23_AA4
DDR23_AA5
DDR23_AA6
DDR_AA10
DDR_AA11
DDR_AA12
DDR_AA13
DDR_BAA0
DDR_BAA1
DDR_BAA2
DDR_CKE
R419
56
56
1%
1%
C419
1000pF
+1.5V_DDR
DDR_RASb
DDR_CASb
DDR_WEb
DDR_RESETb
DDR_QS2b
DDR_QS3b
DDR_DM[2]
DDR_DM[3]
DDR_DQ[24]
DDR_DQ[30]
DDR_DQ[29]
DDR_DQ[28]
DDR_DQ[25]
DDR_DQ[26]
DDR_DQ[31]
DDR_DQ[27]
DDR_AA0
DDR_AA1
DDR_AA2
DDR_AA3
DDR_AA7
DDR_AA8
DDR_AA9
DDR_QS2
DDR_DQ[16]
DDR_DQ[17]
DDR_DQ[18]
DDR_DQ[19]
DDR_DQ[20]
DDR_DQ[21]
DDR_DQ[22]
DDR_DQ[23]
NFM18PS105R0J
C433
6.3V
GND
10KR420
N3
P7
P3
N2
P8
P2
R8
R2
T8
R3
L7
R7
N7
T3
M7
M2
N8
M3
J7
K7
K9
L2
K1
J3
K3
L3
T2
F3
G3
C7
B7
E7
D3
E3
F7
F2
F8
H3
H8
G2
H7
D7
C3
C8
C2
A7
A2
B8
A3
OUTIN
K4B2G1646C
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10/AP
A11
A12/BC
A13
NC_5
BA0
BA1
BA2
CK
CK
CKE
CS
ODT
RAS
CAS
WE
RESET
DQSL
DQSL
DQSU
DQSU
DML
DMU
DQL0
DQL1
DQL2
DQL3
DQL4
DQL5
DQL6
DQL7
DQU0
DQU1
DQU2
DQU3
DQU4
DQU5
DQU6
DQU7
C426
1uF
IC402
DDR_1333_SS
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VDDQ_5
VDDQ_6
VDDQ_7
VDDQ_8
VDDQ_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
VSSQ_6
VSSQ_7
VSSQ_8
VSSQ_9
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
NC_1
NC_2
NC_3
NC_4
NC_6
+1.5V_DDR
+1.5V_DDR
R422
4.99K
1%
M8
H1
L8
R421
ZQ
B2
D9
G7
K2
K8
N1
N9
R1
R9
A1
A8
C1
C9
D2
E9
F1
H2
H9
J1
J9
L1
L9
T7
A9
B3
E1
G8
J2
J8
M1
M9
P1
P9
T1
T9
B1
B9
D1
D8
E2
E8
F9
G1
G9
C435
0.01uF
C436
0.01uF
1%
240
DDR_AA14
R423
4.99K
1%
DDR_VREFA
+1.5V_DDR
K4B2G1646C-HCK0
N3
A0
P7
A1
P3
A2
N2
A3
P8
A4
P2
A5
R8
A6
R2
A7
T8
A8
R3
A9
L7
A10/AP
R7
A11
N7
A12/BC
T3
A13
M7
NC_5
M2
BA0
N8
BA1
M3
BA2
J7
CK
K7
CK
K9
CKE
L2
CS
K1
ODT
J3
RAS
K3
CAS
L3
WE
T2
RESET
F3
DQSL
G3
DQSL
C7
DQSU
B7
DQSU
E7
DML
D3
DMU
E3
DQL0
F7
DQL1
F2
DQL2
F8
DQL3
H3
DQL4
H8
DQL5
G2
DQL6
H7
DQL7
D7
DQU0
C3
DQU1
C8
DQU2
C2
DQU3
A7
DQU4
A2
DQU5
B8
DQU6
A3
DQU7
IC401-*1
DDR_1600_SS
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VDDQ_5
VDDQ_6
VDDQ_7
VDDQ_8
VDDQ_9
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
VSSQ_6
VSSQ_7
VSSQ_8
VSSQ_9
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
ZQ
NC_1
NC_2
NC_3
NC_4
NC_6
DDR_RESETb
DDR_AA13
DDR_AA14
DDR_AA2
DDR_AA11
DDR_AA3
DDR_AA7
DDR_AA9
DDR_AA8
DDR_AA0
DDR_AA1
DDR_BAA0
DDR_BAA2
DDR_BAA1
DDR_AA10
DDR_AA12
DDR_WEb
DDR23_AA6
DDR23_AA4
DDR23_AA5
DDR01_AA6
DDR01_AA4
DDR01_AA5
DDR_CASb
DDR_RASb
M8
H1
L8
B2
D9
G7
K2
K8
N1
N9
R1
R9
A1
A8
C1
C9
D2
E9
F1
H2
H9
J1
J9
L1
L9
T7
A9
B3
E1
G8
J2
J8
M1
M9
P1
P9
T1
T9
B1
B9
D1
D8
E2
E8
F9
G1
G9
DDR_CKE
R425
K4B2G1646C-HCK0
N3
P7
P3
N2
P8
P2
R8
R2
T8
R3
L7
R7
N7
T3
M7
M2
N8
M3
J7
K7
K9
L2
K1
J3
K3
L3
T2
F3
G3
C7
B7
E7
D3
E3
F7
F2
F8
H3
H8
G2
H7
D7
C3
C8
C2
A7
A2
B8
A3
+1.5V_DDR
R430
4.7K
OPT
R429
82
C442
R428
82
IC402-*1
DDR_1600_SS
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10/AP
A11
A12/BC
A13
NC_5
BA0
BA1
BA2
CK
CK
CKE
CS
ODT
RAS
CAS
WE
RESET
DQSL
DQSL
DQSU
DQSU
DML
DMU
DQL0
DQL1
DQL2
DQL3
DQL4
DQL5
DQL6
DQL7
DQU0
DQU1
DQU2
DQU3
DQU4
DQU5
DQU6
DQU7
100pF
R431
C437
4.7K
100pF
OPT
56R424
56
OPT
C438
56AR401
56AR402
56AR403
56AR404
56AR405
56AR406
56R426
56R427
VREFCA
VREFDQ
VDD_1
VDD_2
VDD_3
VDD_4
VDD_5
VDD_6
VDD_7
VDD_8
VDD_9
VDDQ_1
VDDQ_2
VDDQ_3
VDDQ_4
VDDQ_5
VDDQ_6
VDDQ_7
VDDQ_8
VDDQ_9
VSS_1
VSS_2
VSS_3
VSS_4
VSS_5
VSS_6
VSS_7
VSS_8
VSS_9
VSS_10
VSS_11
VSS_12
VSSQ_1
VSSQ_2
VSSQ_3
VSSQ_4
VSSQ_5
VSSQ_6
VSSQ_7
VSSQ_8
VSSQ_9
1uF
0.1uF
C404
0.1uFC406
C450
0.1uF
C408
0.1uF
C439
1uF
C409
0.1uF
0.1uF
C451
0.1uF
C411
C440
1uF
0.1uF
C452
1uFC441
M8
H1
L8
ZQ
B2
D9
G7
K2
K8
N1
N9
R1
R9
A1
A8
C1
C9
D2
E9
F1
H2
H9
J1
NC_1
J9
NC_2
L1
NC_3
L9
NC_4
T7
NC_6
A9
B3
E1
G8
J2
J8
M1
M9
P1
P9
T1
T9
B1
B9
D1
D8
E2
E8
F9
G1
G9
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FILRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFATURES SPECFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
BCM35230
MAIN DDR
4
50

FROM LIPS & POWER B/D
RL_ON
+3.5V_ST
+12V
#16/#20/#23
LD - GND OR USE
LE(N.L.D.) - OPEN
LE(L.D.) - USE
R502
10K
B
MLB-201209-0120P-N2
MLB-201209-0120P-N2
C506
0.1uF
50V
L501
C508
0.1uF
16V
C
E
Q501
2SC3052
L503
+3.5V_ST
R508
4.7K
RT1P141C-T112
Q502
1
2
3
PWR ON
GND/P.DIM2
24V
GND
GND
3.5V
3.5V
GND
GND
12V
12V
12V
SMAW200-H24S2
NORMAL_26~55
P502
FW20020-24S
1
1
3
3
5
5
7
7
9
9
11
11
13
13
15
15
17
17
19
19
21 22
21
23 24
23
SLIM_32~55
25
P501
2
2
4
4
6
6
8
8
10
10
12
12
14
14
16
16
18
18
20
20
22
24
24V
24V
GND
GND
3.5V
3.5V
GND
GND/V-sync
INV ON
A.DIM
P.DIM1
Err OUT
L504
MLB-201209-0120P-N2
POWER_16_URSA_SCAN
POWER_16_BCM_SCAN
0
R518
POWER_16_GND
R574
R573
C519
0.1uF
50V
Power_DET
PD_+20V
R510-*4
5.6K
1%
PD_+20V
R511-*4
1.3K
1%
PD_+18.5V
R510-*3
4.7K
1%
PD_+18.5V
R511-*3
1.21K
1%
+12V
1.21K
1%
PD_+12V
R512
2.7K
1%
NON_PD_+3.5V
R513
+24V
+3.5V_ST
PD_24V
R510
8.2K
1%
PD_24V
R511
1.5K
1%
PD_+3.5V
R515
0
5%
VCC
C580
0.1uF
16V
VCC
C581
0.1uF
16V
NON_PD_+3.5V
R517
100K
IC503
NCP803SN293
3
1
GND
NON_PD_+3.5V
R516
100K
NON_PD_+3.5V
IC502
NCP803SN293
3
1
GND
+3.5V_ST
R522
10K
OPT
R520
RESET
2
RESET
2
100
R519
100
NON_PD_+3.5V
+0.9V_CORE_BCM35230
+12V
L502
BLM18PG121SN1D
Placed on SMD-TOP
C505
C503
10uF
10uF
16V
16V
POWER_ON/OFF2_2
R503
C504
100pF
50V
0.9V_CORE_FB
R501
12K
1/16W
1%
R2
1K
R504
2K
+3.3V_Normal
TEST
C507
1000pF
50V
R505
6.8K
10K
R506
330
R1
R507
50VC509
220pF
OPT
C510
0.01uF
50V
ENABLE
FB
COMP
VDD
PGD
C513
0.1uF
16V
0.9V_CORE_FB
IC501
TPS40192DRCR
1
2
3
4
5
EP_GND
HDRV
10
SW
11
9
THERMAL
8
7
6
BOOT
LDRV
BP5
C515
0.47uF
C516
25V
4.7uF
10V
Vout=0.591*(1+R1/R2)
4.7R577
THE SYMBOL MARK OF THIS SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM INCORPORATES
SPECIAL FEATURES IMPORTANT FOR PROTECTION FROM X-RADIATION.
FILRE AND ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARDS, WHEN SERVICING IF IS
ESSENTIAL THAT ONLY MANUFATURES SPECFIED PARTS BE USED FOR
THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN THE SYMBOL MARK OF THE SCHEMETIC.
Max 7350 mA
Q503
AON7430
4G
5D
3 S_3
2 S_2
1 S_1
4G
4.7R578
5D
3S_3
2S_2
1S_1
AON7200
Q508
Switching freq: 600K
+24V
0
0
ESD
C520
0.1uF
16V
not to RESET at 8kV ESD
ST_3.5V-->3.5V
L505
1uH
L_VS
L/DIM0_VS
INV_CTL_18
A_DIM_20
PWM_DIM_22
ERROR_OUT_24
POWER_DET
15V-->3.6V
20V-->3.5V
24V-->3.48V
12V-->3.58V
C522
22uF
10V
OPT
C523
22uF
10V
C524
47uF
10V
PANEL_CTL
+12V
L511
12V_PANEL
MLB-201209-0120P-N2
+3.5V_ST
L517
BLM18PG121SN1D
C590
10uF
10V
OPT
R554
10K
R553
47K
B
POWER_ON/OFF1
PANEL_POWER
22K
R558-*1
5V_PANEL
2.7K
R559-*1
5V_PANEL
R557
C551
0.1uF
50V
R558
10K
12V_PANEL
1.8K
R559
12V_PANEL
B
22K
C
E
R555
22K
Q505
2SC3052
0.01uF
C550
50V
+1.5V_DDR
AP7173-SPG-13 HF(DIODES)
R591
10K
IC508
IN
1
PG
VCC
EN
2
3
4
9
THERMAL
1.5A
Vout=0.8*(1+R1/R2)
C
E
Q506
2SC3052
8
7
6
5
[EP]
OUT
FB
SS
GND
C552
10uF
TYP 1450mA
PANEL_VCC
Q507
AO3407A
S
D
1uF
25V
G
25V
C560
OPT
PANEL_DISCHARGE_REG
2K
1/8W
R575
R576
PANEL_DISCHARGE_REG
1/8W
C563
2K
0.1uF
50V
Max 800mA
+1.5V_DDR
R595
R1
4.3K
C593
560pF
50V
R593
3.9K
1%
R592
1K
1%
1%
R2
22uF
C594
10V
C591
0.1uF
16V
Q501,Q504,
Q505,Q506
Q502
Q507
IC502,IC503
OS Module OPT
INV_CTL_18
A_DIM_20
PWM_DIM_22
ERROR_OUT_24
0
R524
POWER_22_PWM_DIM
POWER_24_PWM_DIM
POWER_24_GND
DUAL COMPONENT
1ST : 0TRIY80001A 2ND : 0TR387500AA
1ST : 0TRIH80004A, 2ND : EBK61012501, 3RD : 0TR102009AM
1ST : EBK60752501, 2ND : EBK61011501
1ST : EAN61151001, 2ND : EAN60670101
R532
POWER_18_INV_CTL
100
POWER_18_A_DIM
POWER_20_ERROR_OUT
R526
0
0
R527
R529
R533
POWER_20_A_DIM
R531
POWER_20_PWM_DIM
R538
0
POWER_22_A_DIM
R535
NON_OPC/NON_IOP
POWER_24_INV_CTL
R541
POWER_24_ERROR_OUT
R540
100
0
0
0
0
0
R537
0
+3.3V_Normal
ERROR_OUT_PULL_UP
R523
4.7K
A_DIM
PWM_DIM
ERROR_OUT
PWM_DIM
ERROR_OUT
<OS MODULE PIN MAP>
PIN No
18
20
22
24
LGD
INV_ON
V4:VBR-A
V5:NC
PWM_DIM
Err_out
LED:GND
CMO(09)
A-DIM
PWM_DIM
INV_ON
AUO
INV_ON
Err_out
NC
A-DIM
PWM_DIM
A_DIM
A_DIM
SHARP
INV_ON
Err_out
PWM_DIM
GND
R543
6.8K
OPT
+3.3V_Normal
C
E
R546
1K
B
Q504
2SC3052
R547
10K
+3.5V_ST
R551
10K
OPT
INV_CTL
R552
10K
OPT
CHECK PWR/MODULE PIN MAP
+5V_Normal
Vout=0.8*(1+R1/R2)
+12V
L507
BLM18PG121SN1D
C528
10uF
16V
R525
13K
C530
3300pF
50V
+3.3V_NORMAL
OPT
C532
0.1uF
16V
COMP
R542
10K
VIN
EN
6
4A
IC505
FB
4
AOZ1024DI
5
EAN60660601
3
AGND
2
1
PGND
LX
7
POWER_ON/OFF2_2
L509
3.6uH
C534
22uF
10V
C535
22uF
10V
C537
OPT
R2
MAX 2.8A
+3.3V_Normal
R1
27K1%R548
50V
1%
4.7K
R549
+12V
L514
BLM18PG121SN1D
Placed on SMD-TOP
C546
10uF
16V
AOZ1073AIL-3
PGND
VIN
AGND
FB
IC507
L516
1
2
3A
3
4
LX_2
8
LX_1
7
EN
6
COMP
5
R564
3.6uH
NR8040T3R6N
POWER_ON/OFF2_1
R566
10K
OPT
C559
0.1uF
12K
16V
2200pF C557
Vout=0.8*(1+R1/R2)
10K1%R550
+5V_USB+WIFI
+0.9V_CORE
Vout=0.8*(1+R1/R2)
OPT
C525
10uF
10V
+2.5V_BCM35230
+3.5V_ST
OPT
C527
10uF
6.3V
120-ohm
POWER_ON/OFF2_1
L506
+5V_Normal
C531
1uF
R528
10K
C533
0.1uF
OPT
OPT
R536
10K
AP2132MP-2.5TRG1
VCTRL
IC504
1
PG
2
EN
3
VIN
4
2A
EAN61387601
9
THERMAL
8
7
6
5
[EP]
GND
ADJ
VOUT
NC
Max 960 mA
R544
18K
1%
R545
56K
1%
R2
R1
Switching freq: 500K
+2.5V_BCM35230
C539
C538
10uF
47uF
10V
6.3V
+12V
L513
BLM18PG121SN1D
Placed on SMD-TOP
C545
10uF
16V
AOZ1073AIL-3
PGND
1
VIN
2
AGND
3
FB
4
Vout=0.8*(1+R1/R2)
IC506
3A
L515
2700pF C555
3.6uH
NR8040T3R6N
R565
10K
OPT
C558
0.1uF
16V
POWER_ON/OFF2_1
R568
51K1%R567
1.5K
10K1%R569
LX_2
8
LX_1
7
EN
6
COMP
5
R563
12K
MAX 1A
51K1%R570
3.6K1%R571
OPT
C565
100pF
10K1%R572
R1
1/16W
50V
R2
C568
22uF
10V
Switching freq: 500K
MAX 1.9A
C567
R1
22uF
1%
10V
OPT
C564
100pF
50V
R2
Switching freq: 500K
C570
22uF
16V
C571
22uF
16V
OPT
+5V_Normal
+5V_USB
Vout=0.6*(1+R1/R2)
BCM35230
POWER
5
58
 Loading...
Loading...