Page 1

GBR-4001
4-WAN Gigabit Broadband VPN Router
User Manual
V1.0
Digital Data Communications Asia Co., Ltd.
http://www.level1.com
Page 2

Table of Contents
Table of Contents ........................................................................................................................ II
Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 1
0.1 Factory settings ............................................................................................................. 1
0.2 Contact Us ................................................................................................................... 1
Chapter 1. Product Overview ............................................................................................. 2
1.1 Key characteristics ........................................................................................................ 2
1.2 Specifications ............................................................................................................... 3
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation........................................................................................ 4
2.1 Panel description ........................................................................................................... 4
2.2 Precaution for installation .............................................................................................. 5
2.3 Preparing for installation ............................................................................................... 5
2.4 Hardware Installation .................................................................................................... 6
2.5 Hardware connection ..................................................................................................... 7
Chapter 3. Login to the device ........................................................................................... 8
3.1 Configuring the correct network settings ......................................................................... 8
3.2 Login to the device ........................................................................................................ 9
Chapter 4. Configuration Wizard ..................................................................................... 12
4.1 WAN1 Port Configuration - Dynamic IP access ............................................................. 12
4.2 WAN1 port configuration - Static IP access ................................................................... 13
4.3 WAN1 configuration -- PPPoE access ........................................................................... 13
Chapter 5. Start menu ....................................................................................................... 15
5.1 Configuration Wizard .................................................................................................. 15
5.2 Interface status ............................................................................................................ 15
5.3 Interface Traffic .......................................................................................................... 16
5.4 Restart Device ............................................................................................................ 17
Chapter 6. Network parameters ....................................................................................... 18
6.1 Configuration of WAN port .......................................................................................... 18
6.1.1 Network interface configuration ........................................................................... 18
6.1.2 Internet Connection List ....................................................................................... 22
6.2 Line combination ........................................................................................................ 24
6.2.1 Description of line combination function ............................................................... 25
6.2.2 Global Settings .................................................................................................... 26
6.2.3 Load Balancing List............................................................................................. 28
6.2.4 Detection and Bandwidth ..................................................................................... 28
6.2.5 Identity Binding .................................................................................................. 29
6.3 Configuration of LAN port .......................................................................................... 30
6.4 DHCP server .............................................................................................................. 31
6.4.1 DHCP server configuration .................................................................................. 31
6.4.2 Static DHCP ....................................................................................................... 33
Page 3

6.4.3 DHCP auto binding ............................................................................................. 35
6.4.4 DHCP client list .................................................................................................. 35
6.4.5 Case of DHCP configuration ................................................................................ 36
6.5 DDNS Settings ........................................................................................................... 38
6.5.1 DDNS authentication ........................................................................................... 39
6.6 UPnP ......................................................................................................................... 40
Chapter 7. Advanced Configuration ................................................................................ 41
7.1 NAT and DMZ configuration ....................................................................................... 41
7.1.1 Description of NAT functions ............................................................................... 41
7.1.2 Port Forwarding .................................................................................................. 42
7.1.3 NAT rules ........................................................................................................... 45
7.1.4 DMZ .................................................................................................................. 47
7.1.5 NAT and DMZ configuration instances ................................................................. 48
7.2 Static Route Settings ................................................................................................... 50
7.3 Policy routing ............................................................................................................. 52
7.3.1 Enable policy routing ........................................................................................... 53
7.3.2 Policy routing configuration ................................................................................. 53
7.4 Anti-NetSniper ........................................................................................................... 55
7.5 Port mirroring ............................................................................................................. 55
7.6 Port VLAN ................................................................................................................. 56
7.7 SYSLOG configuration ............................................................................................... 58
Chapter 8. User management ........................................................................................... 59
8.1 User status .................................................................................................................. 59
8.2 IP/MAC binding ......................................................................................................... 61
8.2.1 IP/MAC binding list ............................................................................................ 62
8.2.2 IP/MAC binding configuration ............................................................................. 63
8.2.3 IP/MAC binding instances ................................................................................... 64
8.3 PPPoE Server ............................................................................................................. 67
8.3.1 PPPoE introduction ............................................................................................. 67
8.3.2 PPPoE global Settings ......................................................................................... 68
8.3.3 PPPoE account configuration ............................................................................... 70
8.3.4 PPPoE user status ................................................................................................ 72
8.3.5 Export PPPoE Accounts ....................................................................................... 73
8.3.6 Import PPPOE Accounts ...................................................................................... 74
8.3.7 Instance of PPPoE server configuration ................................................................. 75
8.4 WEB authentication .................................................................................................... 77
8.4.1 WebAuth Global Settings ..................................................................................... 77
8.4.2 Web Authentication Account List .......................................................................... 78
8.4.3 WEB Authentication Client Status ........................................................................ 80
8.5 User Group Settings .................................................................................................... 81
Chapter 9. App Control ..................................................................................................... 82
9.1 Schedule Settings ........................................................................................................ 82
Page 4

9.2 Application Control ..................................................................................................... 83
9.2.1 Application Management List ............................................................................... 84
9.2.2 Internet Application Management Settings ............................................................. 84
9.2.3 Internet Application Management ......................................................................... 86
9.3 QQ white list .............................................................................................................. 88
9.4 TM Whitelist .............................................................................................................. 90
9.5 Notification ................................................................................................................ 91
9.5.1 Daily Routine Notification ................................................................................... 92
9.5.2 Account expiration notification ............................................................................. 93
9.6 Application Audit ........................................................................................................ 94
9.7 Policy Database .......................................................................................................... 95
Chapter 10. QoS ............................................................................................................... 97
10.1 Fixed Rate Limiting .................................................................................................... 97
10.2 Flexible bandwidth ...................................................................................................... 98
10.3 Session Limiting ....................................................................................................... 100
Chapter 11. Firewall ....................................................................................................... 102
11.1 Attack Prevention ..................................................................................................... 102
11.2 Access control .......................................................................................................... 103
11.2.1 Access Control Rule .......................................................................................... 104
11.2.2 Access control list ............................................................................................. 105
11.2.3 Access Control Settings ..................................................................................... 106
11.2.4 Access Control Settings instance ......................................................................... 112
11.3 Domain filtering ........................................................................................................ 115
11.3.1 Domain filtering Settings .................................................................................... 115
11.3.2 Domain Block Notification ................................................................................. 116
11.4 MAC Address Filtering .............................................................................................. 118
11.4.1 MAC Address Filtering ....................................................................................... 119
11.4.2 MAC Address Filtering Settings ......................................................................... 120
Chapter 12. VPN ............................................................................................................. 122
12.1 PPTP ....................................................................................................................... 122
12.1.1 PPTP overview .................................................................................................. 122
12.1.2 PPTP list ........................................................................................................... 123
12.1.3 PPTP server configuration .................................................................................. 124
12.1.4 PPTP client Settings .......................................................................................... 126
12.1.5 PPTP configuration instance ............................................................................... 128
12.2 IPSec ....................................................................................................................... 133
12.2.1 IPSec Overview ................................................................................................ 133
12.2.2 IPSec list .......................................................................................................... 140
12.2.3 IPSec Settings ................................................................................................... 140
12.2.4 IPSec configuration instance .............................................................................. 146
Chapter 13. System ....................................................................................................... 154
13.1 Administrator ........................................................................................................... 154
Page 5

13.2 Language ................................................................................................................. 155
13.3 Time ........................................................................................................................ 155
13.4 Configuration ........................................................................................................... 157
13.5 Firmware Upgrade .................................................................................................... 158
13.6 Remote Management ................................................................................................. 159
13.7 Scheduled task .......................................................................................................... 160
Chapter 14. System ....................................................................................................... 162
14.1 Interface Status ......................................................................................................... 162
14.2 System information ................................................................................................... 162
14.3 System log ............................................................................................................... 163
14.3.1 System log information ...................................................................................... 163
14.3.2 Log Management Settings .................................................................................. 165
Chapter 15. Customer service ...................................................................................... 166
Appendix A Configuration of LAN computers ............................................................ 167
Appendix A FAQ ............................................................................................................. 170
B-1. How ADSL users go online? ...................................................................................... 170
B-2. How the Fixed IP access users go online? .................................................................... 171
B-3. How the Dynamic IP (Cable Modem) access users go online? ....................................... 171
B-4. How to restore the device to its factory settings? .......................................................... 172
Appendix B Figure Index ............................................................................................... 174
Appendix C LICENSE STATEMENT / GPL CODE STATEMENT ................................. 178
Page 6

Type of interfaces
IP address/subnet mask
LAN port
192.168.1.1/255.255.255.0
WAN port
Dynamic IP access
Introduction
Tip: In order to achieve the best results, it is proposed to upgrade Windows Internet Explorer
browser to Version 6.0 or above.
0.1 Factory settings
1. The factory settings of interfaces are shown in Table 0-1.
Table 0-1 Factory settings of interfaces
2. The factory user name of the system administrator is admin, and the factory password is
admin (case-sensitive).
0.2 Contact Us
If you have any questions during installation or use, please contact us in the following manners.
Customer service: 0800-011-110
LEVELONE discussions: http://www.level1.com
E-mail support: support@level1.com
http://www.level1.com Page 1
Page 7

Chapter 1. Product Overview
1.1 Key characteristics
Support DSL, FTTX+LAN and Cable Modem and other access modes
Support the configuration of dynamic WAN port
Support traffic load balancing and line backup
Support policy routing
Support intelligent bandwidth management function
Support fine speed limit
Support the DHCP server function
Support virtual server and DMZ
Support the PPPoE server functions, and provide a fixed IP allocation, account billing and
other functions
Support routine business notification, due account notification functions
Support WEB authentication function
Support Internet behavior management for users, and provide a wealth of controlling policies
Support SYSLOG configuration
Support the Internet behavior audit function
Support URL, MAC address, keyword filtering and other firewall policies
Support QQ, MSN white list
Support internal/external network attack and defense
Support network vanguard
Support port mirroring
Support port VLAN
Support user groups, time management
Support multiprotocol VPN (PPTP, IPSec)
http://www.level1.com Page 2
Page 8

Support UPnP
Support dynamic domain names (3322. org, iplink. com. cn)
Support HTTP remote management
Support the WEB upgrading mode
Support backup and import of WEB configuration files
Support filtering of MAC addresses
1.2 Specifications
Meets IEEE802.3 Ethernet and IEEE802.3u Fast Ethernet standards.
Supports TCP/IP, DHCP, ICMP, NAT, PPPoE, static routes and other protocols.
The physical ports support auto negotiation function, and support the MDI/MDI - X adapter
function.
Provide status indicators.
Operating environment: Temperature: 0 ± 40℃
Height: 0-4000m
Relative humidity: 10%-90%, no condensation
http://www.level1.com Page 3
Page 9

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
LED
lights
Description
Function
PWR
Power indicator
It is constantly on when the power supply is working properly.
SYS
System status
indicator
Flashes in the frequency of 2 times per second, and the flashing
frequency declines when the system burden is heavy; Defective
often light or often.
Link/Act
Port status
indicator
When a device is properly connected to a port, the status LED
that corresponds to the port stays lit, and it will flash if there is
flow.
100M
Port rate LED
When a device is connected to a port and after the success of
100M negotiation, the LED corresponding to the port stays lit.
Interface
Meaning
Notes
Remarks
LAN
LAN
interface
Integrated with multiple switched
Ethernet ports.
Some products are provided with
only one LAN port.
LAN/WAN are all RJ-45
ports, and support the
adapter function.
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation
2.1 Panel description
Figure 2_1 Front Panel - GBR-4001
1. LED description
2. Description of interfaces
Figure 2_2 Rear Panel - GBR-4001
Table 2_1 LED description
http://www.level1.com Page 4
Page 10

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
WAN
WAN
interface
The number of WAN interfaces
depends upon product model.
Console
Serial port
Asynchronous communication serial
ports that meet the RS232 standard
Some products support the
Console port.
Table 2_2 Description of interfaces
3. Reset button
Reset button can be used to recover the device's factory settings when you forget the administrator
password. Method: In the process of charged operation, hold down the Reset button for more
than 5 seconds, and then release the button. The device will be returned to its factory settings after
operation, and automatically restart.
Note: The above operations will delete all the original device configurations; please use it
with care!
2.2 Precaution for installation
1. Make sure to install the workbench and ensure the stability of the rack.
2. Do not place any heavy objects on the device.
3. Make sure that the device is stored in a dry and ventilated area with proper heat dissipation,
and do not put it in a dirty and damp place.
4. Avoid exposing the device directly to the sunlight and keep it far away from heating
elements;
5. Please use the original power cord.
2.3 Preparing for installation
1. We have applied to local operators (ISP, such as China Telecom, China Unicom, etc.) for
broadband services.
2. Preparation of related devices:
1) Modem (This item is not required when connected directly to Ethernet).
2) Hub or switch.
http://www.level1.com Page 5
Page 11

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
3) The PC with Ethernet card and Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) installed.
4) Power socket.
3. Preparation of tools and cables: Phillips screwdriver, network cable.
2.4 Hardware Installation
Before installing the device, make sure the broadband service is normal. If you cannot access,
please contact operators (ISP) to resolve the problem. After successfully accessing to the network,
follow these steps to install the device. The power plug must be removed during installation.
1. Installed on the work bench
Place the device on a stable workbench, and the installation steps are as follows:
1. Place the device on a sufficiently large, stable and properly grounded workbench, with its bottom
up;
2. Remove the adhesive protective paper from the foot pad, and stick the 4 pads in the 4 round slots
at the bottom of the casing respectively.
3. Flip over the device, and place it on the workbench stably.
2. Install on the standard rack
Install the device on a 19-inch standard rack, and the installation steps are as follows:
1. Check the grounding and stability of the rack.
2. Install the two L-shaped brackets in the accessories on both sides of the device panel, and fix
them with the screws in the accessories.
Figure 2_3 Product rack installation drawing I
3. Place the device in the appropriate location in the rack, and support it using a tray.
4. Secure the L-shaped brackets on the guide slots (as shown in the figure below) fixed at both ends
of the rack.
http://www.level1.com Page 6
Page 12

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Figure 2_4 Product rack installation drawing II
2.5 Hardware connection
1. Establish a LAN connection
Connect the LAN port of the router or a PC or a hub or a switch in LAN with a network cable.
2. Establish a WAN connection
Connect the WAN port of the router to the Internet with a network cable, as shown in the figure
below.
3. Connect the power supply
Before connecting the power supply, make sure that both power supply and grounding are correct.
Figure 2_5 Establish a connection to LAN and WAN
Tip: The above network connection diagram is for reference only. Please configure the
network architecture according to the actual situation and needs.
http://www.level1.com Page 7
Page 13

Chapter 3 Logging Device
Chapter 3. Login to the device
This chapter describes how to configure the correct network settings for the network computers,
how to log on to the appliances and how to use shortcut icons to quickly link to the GBR-4001
website for product information and services.
3.1 Configuring the correct network settings
Before logging to the device through the WEB interface, you must correctly configure the network
computers in network settings.
First, connect your computer to the LAN port of the device, and then set the computer's IP
address.
The first step is to set the computer's TCP/IP. If it has been set correctly, skip this step.
The second step is to set the computer's IP address. You can use either of the following methods:
1. Set the computer's IP address as one of the addresses from 192.168.1.2 - 192.168.1.254, the
subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, and the default gateway is 192.168.1.1 (the LAN IP address of
the device), and the DNS server is the address provided by the local operator.
2. Set the computer's TCP/IP as "Obtain an IP address automatically". After setting, the
built-in DHCP server of the device will automatically assign IP addresses to computers.
The third step is to use the Ping command on your computer to check whether it is connected to
the device. In Start ->Operation, type in cmd, and click <OK> to open the command window.
Type in ping 192.168.1.1.
The following lists two kinds of results of executing the Ping command in the Windows XP
environment:
If the screen is shown as follows, it indicates that the computer has been successfully and a
connection is established on the device.
http://www.level1.com Page 8
Page 14
Chapter 3 Logging Device
Pinging 192.168.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Pinging 192.168.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
If the screen is shown as follows, it indicates that the connection between the computer and the
device fails.
When connection fails, please check the following items:
1. Hardware connections: The LEDs that correspond to the LAN port on the device panel and
the PC network card LED must be on.
2. Configuring TCP/IP properties of the computer: If the LAN IP address of the device is
192.168.1.1, then the calculated IP address must be any one of the free addresses from
192.168.1.2 - 192.168.1.254.
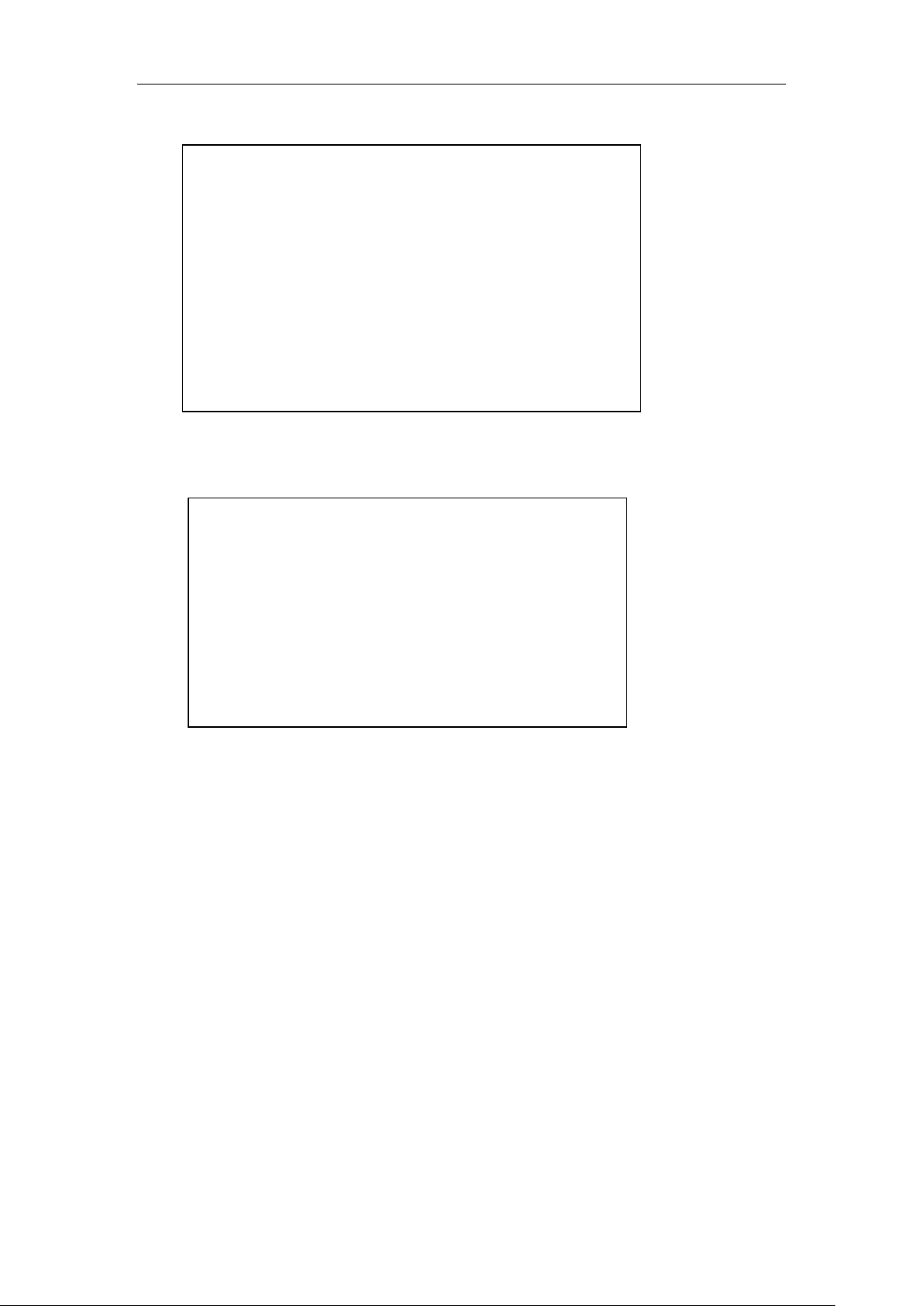
3.2 Login to the device
When MS Windows, Macintosh, Unix or Linux operating systems are used on the PC, the device
can be configured through browsers (such as Internet Explorer or Firefox).
Open the browser, and type in the IP address of the device's LAN port in the address bar, such as
http://192.168.1.1. After the connection is established, you will see a login interface as shown in
http://www.level1.com Page 9
Page 15
Chapter 3 Logging Device
Figure 3-1. In the first use, you should log in as a system administrator, that is, enter your
administrator username and password (the factory values of username, password are Admin, case
sensitive) on the login interface, and then click <OK>.
Figure 3_1 WEB login interface
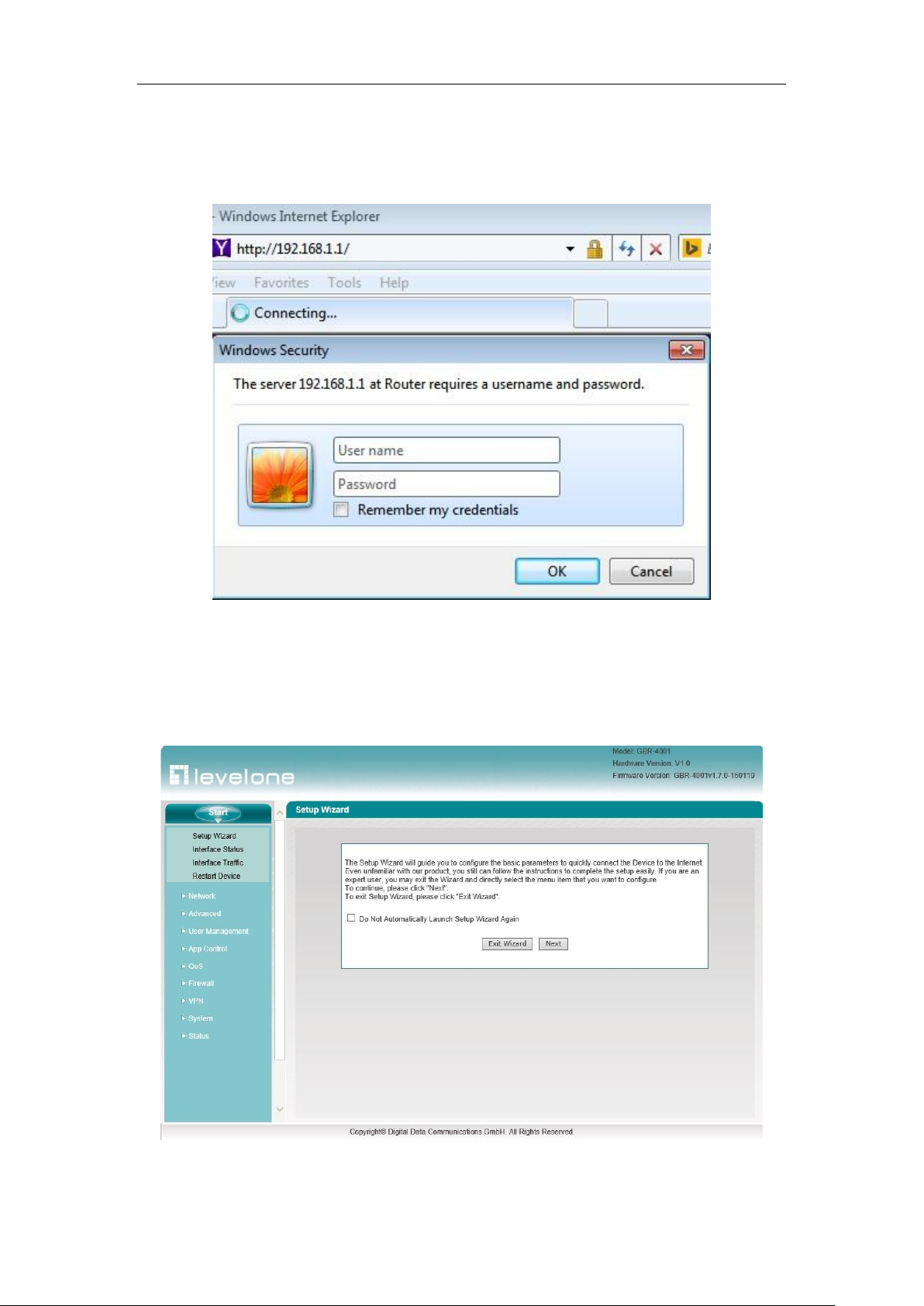
If user name and password are correct, the browser will display the homepage of the WEB
management interface, as shown in Figure 3-2. The top-right corner of the page displays device
model, software version, hardware version and other information.
Figure 3_2 Homepage of the WEB interface
http://www.level1.com Page 10
Page 16

Chapter 3 Logging Device
Homepage Description:
1. The top-right corner of the page displays device model, software version, hardware version
and three fast link icons. These 3 shortcut icons have the following functions:
1) Product Discussion– Link to the discussion forums of LEVELONE’s official website to
participate in discussions about the product.
2) Knowledge Base– Link to the knowledge base of LEVELONE’s official website for
searching related technical information.
3) Booking Service– Link to the booking service page of LEVELONE’s official website,
for advance reservation of the customer service in a certain working period.
2. This page displays the main menu bar on the left.
3. The main operating page is located on the right of the page, in which you can configure
various functions of the device, view the related configuration information and status
information, etc.
4. If this is the first time for you to log in the device, the main operation page will be linked
directly to the configuration wizard page. The next chapter describes how to configure the
basic parameters required for the normal running of the device in the Start -> Configuration
wizard page.
http://www.level1.com Page 11
Page 17

Chapter 4 Configuration Wizard
Chapter 4. Configuration Wizard
By reading this chapter, you can understand the basic network parameters required for the device
to access to the Internet, and these parameters are configured to connect the device to the Internet.
Before configuring "Internet Line" in the Configuration Wizard, you should properly configure the
network settings of the network computer. For specific methods, see Chapter 3 Logging in the
Device.
If this is the first time for you to log in the device, a configuration wizard homepage appears
directly in the main operating page. As shown in Figure 4_1:
Figure 4_1 Home page of configuration wizard
In logging next time, the wizard will no longer automatically pop up: When checking it, you
can go directly to the System Status page in logging next time;
Exit the wizard: Exits the Configuration Wizard and returns to the System Status page.
Next step: Enter the Selection of device access mode page.
4.1 WAN1 Port Configuration - Dynamic IP access
Configure the second page of the wizard to configure the WAN1 port address of the device. The
default WAN line access takes dynamic IP access, as shown in Figure 4-2. If your Internet access
mode is dynamic IP access, please click <Finish>, to complete the configuration of the Internet
line.
http://www.level1.com Page 12
Page 18

Chapter 4 Configuration Wizard
Figure 4_2 Configuration Wizard - Dynamic IP access
4.2 WAN1 port configuration - Static IP access
If your Internet access mode is fixed IP access, please select " Static IP access" in the drop-down
list box of Figure 4-3. The following describes the meaning of the parameters for configuration
of fixed IP access.
Figure 4_3 Configuration Wizard - Static IP access
IP address, subnet mask, gateway address, primary DNS server, secondary DNS server: Fill
in the WAN IP address, subnet mask, gateway address and DNS server address that ISP (Such
as China Telecom) offers you.
4.3 WAN1 configuration -- PPPoE access
If your Internet access mode is fixed IP access, please select "PPPoE access" in the drop-down list
http://www.level1.com Page 13
Page 19

Chapter 4 Configuration Wizard
box of Figure 4_4. The following describes the meaning of the parameters for PPPoE access.
Figure 4_4 Configuration wizard - PPPoE access
User name: Type in the user name the ISP provides you. If you have any questions, please
ask your ISP.
User name: Type in the password the ISP provides you. If you have any questions, please ask
your ISP.
Tip:
1. After configuring the Internet line for the WAN1 port, please click < Finish >, this
configuration will take effect.
2. For the multi-WAN device, if you need to configure more than one line for Internet access,
go to Network parameters->WAN port configuration page to configure other Internet lines.
http://www.level1.com Page 14
Page 20

Chapter 5 Start Menu
Chapter 5. Start menu
Start menu is located on the top of the Level 1 menu bar of the WEB interface, providing the
interface for 4 common pages, including: configuration wizard, running status, Interface Traffic ,
device reboot. In the Start menu, you can quickly configure the basic parameters required by the
device in working properly, view the information about the interfaces, and view the statistics data
of the devices' real-time traffics.
5.1 Configuration Wizard
The Start-> Configuration wizard pages can help you to quickly configure the basic parameters
required by some devices in working normally. For details, see Chapter 4 Configuration Wizard.
5.2 Interface status
This section describes the Start-> Interface status page, in which you can view the information
about the device's interfaces. As shown in the interface in Figure 5_1, the connection type,
connection status, IP address and other information about the interfaces can be viewed.
Figure 5_1 Information about Interface status
http://www.level1.com Page 15
Page 21

Chapter 5 Start Menu
5.3 Interface Traffic
This section describes the Start-> Interface Traffic page, as shown in Figure 5_2. You can view
the average, maximum, sum and the current real-time rate for the relevant ports to receive and
send data, and provide different units (kbit/s and KB/s) for them.
Tip:
If this page fails to display properly, please click the hyperlink "if it does not display properly,
please install svgviewer" to have the svgviewer plug-in installed.
Figure 5_2 Interface Traffic
WAN: WAN port of the device, click on the tab to view the dynamic figure of receiving,
sending traffic.
LAN: LAN port of the device, click on the tab to view the dynamic figure of receiving,
sending traffic.
Timeline: The x-coordinate in the flow chart. You can click on the timeline options (1x, 2x,
4x, 6x in the figure) in the figure to determine the display effect;
Flowline: The y-ordinate in the flow chart. You can choose the display effects as needed
(standardization, maximization as shown in the figure);
Display: Provides two display effect options, solid effect and hollow effect;
Color: It can be selected for display according to needs and preferences, such as red, blue,
http://www.level1.com Page 16
Page 22

Chapter 5 Start Menu
black etc.
Flip: Click the Flip bLeveloneon, and the colors can swap to receive and send data.
5.4 Restart Device
If you need to restart the device, just enter into the Start-> Restart device page to click <Restart>.
Figure 5_3 Restart device
Tip: Upon restarting, all users will be disconnected from the device.
http://www.level1.com Page 17
Page 23

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Chapter 6. Network parameters
In the network parameter menu, you can configure the basic network parameters for the device,
including WAN/LAN configuration, DHCP server, DDNS configuration, UPnP and WAN port
number configuration.
6.1 Configuration of WAN port
This section focuses on the configuration interface and methods of Network parameters —> WAN
configuration. In this page, you can configure not only the line information, modify or delete the
configured lines according to the actual needs, but also view the connection status of lines.
After completing the configuration of Internet line in Configuration Wizard, you can view the
connection and configuration of the line in this page, or modify the configuration as needed.
6.1.1 Network interface configuration
This section describes how to configure Internet access lines. Internet connection types include:
dynamic IP access, fixed IP access, PPPoE access.
Enter into the Network parameters ->WAN port configuration pages, and the configuration
interface is shown in Figure 6_1.
http://www.level1.com Page 18
Page 24

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_1 Configuration of WAN port
1. Dynamic IP access
As shown in Figure 6_1, the following describes the meaning of the parameters for dynamic IP
access.
Interface: Selects the appropriate interface for the device.
Access mode: Selects "Dynamic IP access" here.
Operator policy: Selects the operator of the interface, with the options as follows: Operator
policy, Telecom, China Unicom and China Mobile respectively.
Working mode: options include NAT and routing mode.
NAT mode: Network address translation. The router working in this mode can convert
the IP address of the Intranet (LAN side) to that of the external network (WAN side).
The router works in this mode by default.
Routing mode: The router working in this mode will not NAT-convert the IP address for
the Intranet (LAN side) to access to the external network (WAN side), and directly looks
up the routing table for forwarding.
Tip:
Both NAT mode and routing mode can take effect to a single line.
MAC address: The MAC address of the related interface, which usually requires no
http://www.level1.com Page 19
Page 25

Chapter 6 Network parameters
modification.
Interface mode: Sets the duplex mode and rate for interfaces. Options are: Auto (adaptive),
10M-FD (10M full duplex), 10M-HD (10M half duplex), 100M-FD (100M full duplex),
100M-HD (100M half duplex), 1000M-FD (1000M full duplex, supported by Gigabit
devices). The default is Auto, which is usually not required to be modified, and if there is any
compatibility issue, or the device used does not support auto negotiation function, then the
type of Ethernet negotiation can be set up here.
Tip:
1. When configuring the line, users can select the appropriate operator through "Operator
policy", and the system will generate a corresponding route based on the user's choice, you
can easily achieve the goal that Telecom traffic flows on the Telecom routes while Unicom
traffic flows on the Unicom routes.
2. Generally, it is not recommended to modify the MAC address of interfaces. However, in
some cases, the operator binds the MAC of the device, which results in the failure of the new
network device to dial up successfully, and at this time, the MAC address of the device needs
to be modified as that of the original network device.
2. Static IP access
Figure 6_2 Static IP access
The interface as shown in Figure 6_2 is the configuration interface for fixed IP access.
IP address, subnet mask, gateway address: Static IP address, subnet mask and gateway
address the operator provides to you.
http://www.level1.com Page 20
Page 26

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Primary DNS server, secondary DNS server: The DNS server address the operator provides
to you.
For the working mode in the advanced options, MAC address, interface mode, please refer to
the configuration of dynamic access.
3. PPPoE access
Figure 6_3 PPPoE access
The interface as shown in Figure 6_3 is the configuration interface for PPPoE access.
Access mode: Here, PPPoE access, ADSL virtual dial-up (or PPPoE dial-up of Ethernet
media) are selected, the device will obtain the IP address, subnet mask and gateway address
information through dial-up.
User name and password: The user name and password provided by the operator when it is
conducting services.
Password authentication mode: The way ISP uses to authenticate user names and passwords,
which is EITHER by default. In most areas, PAP is used, and CHAP mode is also used in a
few areas, NONE represents no username and password authentication is to be done,
EITHER means to negotiate with the peer device automatically as to the specific
authentication mode.
Dial-up type:
Auto dial-up: Automatic dial-up connection after the device is powered on or the
http://www.level1.com Page 21
Page 27

Chapter 6 Network parameters
previous dial-up disconnection occurs.
Manual dial-up: Users may click related bLeveloneons below the "Line connection
information list" of the Network parameters —>WAN configuration to manually
connect and hang up.
On-demand dialing: The device will connect automatically when there is Internet traffic
in the Intranet.
Dial-up mode: Selects the PPPoE dial-up mode, which is normal mode by default. If the
dial-up is not successful, try using other modes on the premise of using the correct user name
and password.
Idle time: The time length after there is no traffic of access and before automatic
disconnection, 0 means no automatic disconnection (Unit: minutes).
MTU: Maximum transmission unit, whose default value is 1480 bytes. The device will
automatically negotiate with the peer device. Do not modify it unless in special applications.
For the working mode in the advanced options, MAC address, interface mode, please refer to
the configuration of dynamic access.
6.1.2 Internet Connection List
In the " Internet Connection List ", you can view the configuration and status information for the
lines, as shown in Figure 6_4, Figure 6_5.
Figure 6_4 Internet Connection List
http://www.level1.com Page 22
Page 28

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_5 Internet Connection List information (Continued Figure 6_4)
Interface: This column displays the WAN port of the device.
Connection type: The connection type of the current Internet access lines, including fixed
access, dynamic access, PPPoE access.
Connection status: The current connection status of the lines. It is displayed as "Off" when
the connection is not successful or is not available, and displayed as "Connected" when the
connection is successful; for dynamic IP access and PPPoE access, it also displays the time
(Unit: hours: minutes: seconds) to maintain the connection when the connection is successful.
IP address, subnet mask, gateway address: IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address for
the WAN interface provided by ISP.
Downstream rate, upstream rate: The downlink/uplink average rate of the current line in the
time interval of two times of list refreshing. The unit is KB/s.
1. Dial-up and hang-up of PPPoE accesslines
If a line is PPPoE access, then click on the interface, the "Dial-up" and "Hang-up" bLeveloneons
will appear below the "Line connection information list", as shown in Figure 6_6, the WAN3
interface is PPPoE access, click on "WAN3", the following four bLeveloneons are displayed on
the lower right part of the line connection information list, and their functions are as follows:
Delete: Delete this line.
Dial-up: Establishes a connection with the PPPoE server. When the PPPoE connection
dial-up type is set to "Manual dial-up", and the PPPoE dial-up is required here.
Hang-up: Hangs up the current connection to the PPPoE server.
Refresh: Click this bLeveloneon to display the up-to-date information of line connection
information list.
http://www.level1.com Page 23
Page 29

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_6 Internet Connection List - PPPoE access
2. Update and release of dynamic IP accesslines
If a line is a dynamic IP access line, then click on the interface, the "Update" and "Release"
bLeveloneons are displayed below the "Line connection information list", as shown in Figure 6_7.
Figure 6_7 Internet Connection List - Dynamic IP access
Update: The system automatically complete the process of releasing the IP address, and then
obtaining an IP address again.
Release: Releases the currently obtained dynamic IP address.
6.2 Line combination
This section describes the Network parameter -> Line combination page.
In the line combination configuration, you can quickly configure line combination modes, and
other related parameters, and specify the detection interval, detection number, detection target IP
address and bandwidth of the lines.
http://www.level1.com Page 24
Page 30

Chapter 6 Network parameters
6.2.1 Description of line combination function
1. Line detection mechanism
Regardless of line combination modes, make sure that the network is not interrupted when the line
fails, which require that the device must be able to monitor line status in real time. To this end, we
designed a flexible automatic detection mechanism, and provide a variety of line detection
methods for users to choose, in order to meet the practical application needs.
To facilitate understanding, several related parameters are introduced first.
Detection interval: the time interval of sending inspection packets. One inspection packet is sent
per time, and the default value is 0 seconds. In particular, when the value is 0, it means not to
make line detection.
Detection times: The number of inspection packets sent within each detection cycle.
Destination IP address: The object of detection. The device will send inspection packets to the
pre-designated target to detect if the line is normal.
The following is an introduction of the device's line detection mechanism in two cases: line
normal and line failure.
When a line fails, the detection mechanism is described as follows: The device will send an
inspection packet to the detection target of the line at the specified detection interval. If all the
inspection packets sent have no response within a detection cycle, this line will be deemed to be
failed, and it will be shielded immediately. For example, if the 3 inspection packets that are sent
have no response within a detection cycle, the line is deemed to be failed by default.
When a line is normal, the detection mechanism is described as follows: Similarly, the device will
send an inspection packet to the detection target of the line at the specified detection interval. If
half of the inspection packets or above sent have response within a detection cycle, this line will
be deemed to be normal, and it will be restored. For example, if the 3 inspection packets that are
sent have response within a detection cycle, the line is deemed to be restored by default.
The device allows users to specify Internet lines for some hosts in the Intranet in advance, which
is realized by setting the "Internal starting IP address" and "Internal end IP address" of the line,
and the hosts whose IP addresses are within two address ranges will give priority to the use of the
specified line. For the hosts with the specified Internet line, they can only access to the Internet
through that line when the specified line is normal. However, when the specified line fails, they
will use other normal lines for Internet access.
Tip:Line detection is not enabled, then the "Detection interval" should be set to "0" second.
2. Line combination mode
The device provides 2 line groups: "Main line" group and "Backup line" group. For convenience's
sake, the lines in the "main line" group are collectively known as main line, and the lines in the
http://www.level1.com Page 25
Page 31

Chapter 6 Network parameters
"backup line" group are collectively known as backup line. All lines are main lines by default.
Users can divide some lines into the "Backup line" group as needed.
The device provides two line combination modes, "All line load balancing" and "Partial line load
balancing while the other backed up".
In the "All line load balancing" mode, all lines are used as main lines. Working principles are as
follows:
1. When all lines are normal, the Intranet hosts can use all lines for Internet access
simultaneously.
2. If a line fails, it should be shielded immediately, and the flow originally passing through the
line will be allocated to the other lines.
3. Once the fault line is restored to normal, the device will enable this line automatically, and
the flow is automatically redistributed.
In the "Partial line load balancing while the others backed up" mode, part of the lines are used as
main lines, the other part of the lines is used as backup lines. Working principles are as follows:
1. As long as the main line is normal, the Intranet hosts use main lines for Internet access.
2. If the main line fails, it will automatically switch to using the backup line for Internet access.
3. Once the fault lines are restored to normal once, they will be immediately switched back to
the main line.
Tip:
When a line is interrupted for line switching, some user applications (such as part of network
games) may be unexpectedly interrupted. This is determined by the TCP session property.
6.2.2 Global Settings
In these two line combination modes, "All line load balancing" and "Partial line load balancing
while the others backed up", the interface of global setting is different; therefore, their universal
setting parameters are described below respectively.
1. Full Load Balancing
http://www.level1.com Page 26
Page 32

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_8 Full Load Balancing
Line load balancing mode: " Full Load Balancing " is selected here.
Save: The line combination configuration parameters take effect.
Refill: Restores to the configuration parameters before modification.
Tip: Line combination mode is " Full Load Balancing " by default.
2. Partial Load Balancing
Figure 6_9 Partial Load Balancing
Line combination mode: " Partial Load Balancing " is selected here.
Main line: The list box represents the "main line" group, and all the lines in the list box are
used as the main lines.
Main line: The list box represents the "Backup line" group, and all the lines in the list box are
used as the backup lines.
==> (Right arrow), <== (Left arrow): Select one (or more) line in the "Main line" list box
first, and then click on "==>", and the selected lines are immediately moved to the "Backup
line" list box. Similarly, select one (or more) line in the "Backup line" list box first, and
then click on "<==", and the selected lines are immediately moved to the "Main line" list box.
http://www.level1.com Page 27
Page 33

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Save: The line combination configuration parameters take effect.
Refill: Restores to the configuration parameters before modification.
6.2.3 Load Balancing List
In the Network parameter -> Load Balancing -> Load Balancing List page, you can view the
information of configuration line.
Figure 6_10 Load Balancing List
Edit the line combination status information: Click on the interface of the line or the "Edit"
hyperlink corresponding to the line, to skip to the relevant page for change,
Refresh: Click <Refresh>, to get the latest status information of line combination.
6.2.4 Detection and Bandwidth
After configuring the line combination function, you also need to configure the detection
mechanism of the lines, and the configuration methods are as follows.
Enter the Network parameters -> Load Balancing -> Detection and Bandwidth page, or enter the
Line combination status information list line interface or edit the icon, enter the Detection and
bandwidth distribution page.
http://www.level1.com Page 28
Page 34

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_11 Detection and Bandwidth
Detection interval: The time interval for sending inspection packets, Unit: seconds, when you
enable line detection, the value range is 1-60 (the value is 0, which means not to enable the
line detection).
Detection times: The number of inspection packets sent within the detection cycle (one
detection packet is sent per time). The default value is 10.
Detection Target IP address: The IP address of the target to be detected.
Bandwidth: Sets the bandwidth ISP provides to the current line, and the Max custom value of
the Gigabit device is set to 1000M.
Internal starting and ending IP address: The address range of the hosts on the current line is to
be used in priority in Intranet.
Save: The above configuration parameters take effect.
Refill: Restores to the configuration parameters before modification.
Return: Returns to the line combination state information page.
6.2.5 Identity Binding
When the device has multiple WAN ports, you can enter the Network parameters -> Load
Balancing -> Identity Binding page to enable the identity binding function.
In the case of multi-line session load balancing, NAT sessions in the same application may be
distributed in different lines, which will cause such applications as online bank, QQ, etc. not to
work properly due to change of identity, and the identity binding function can address this issue by
binding the sessions in the same application from the same user on a line. For example, when a
user in the Intranet logs in the online bank, if the first session is assigned to WAN2 port
http://www.level1.com Page 29
Page 35

Chapter 6 Network parameters
connection line, all the online banking sessions of this user will go out from the WAN2 port until
the user logs out.
Figure 6_12 Enabling identity binding
Enable identity binding: Enables/disables the identity binding function. If multiple lines are
configured, please enable the device's identity binding function to make normal use of such
apps as QQ, online bank.
6.3 Configuration of LAN port
The device's LAN ports can be configured with 4 IP addresses, and the first default IP address of
the LAN port is 192.168.1.1. If you need to change the LAN IP address in order to adapt to the
existing network, enter the Network parameters > LAN port configuration page for
configuration.
Figure 6_13 Configuration of LAN port
http://www.level1.com Page 30
Page 36

Chapter 6 Network parameters
IP address: Sets the LAN IP addresses, and the first IP address is 192.168.1.1 by default,
while the other three IP addresses are 0.0.0.0 by default.
Subnet mask: Sets the subnet mask of the corresponding IP address, which is 255.255.255.0
by default.
MAC address: The MAC address of the LAN port. It is suggested not to modify the MAC
address of the LAN port freely.
Interface mode: Sets the duplex mode and rate for interfaces. Options are: Auto (adaptive),
10M-FD (10M full duplex), 10M-HD (10M half duplex), 100M-FD (100M full duplex),
100M-HD (100M half duplex), 1000M-FD (1000M full duplex, supported by Gigabit
devices). The default is Auto, which is usually not required to be modified, and if there is any
compatibility issue, or the device used does not support auto negotiation function, then the
type of Ethernet negotiation can be set up here.
Tip:
After modifying the LAN IP address, you must use a new IP address to log into the device, and the
IP for logging into the host must be on the same network segment!
6.4 DHCP server
This section mainly introduces the Network parameters -> DHCP server page, including DHCP
server settings, static DHCP and DHCP automatic binding and DHCP client list.
6.4.1 DHCP server configuration
Below is a description of the parameters for configuring the DHCP server functions.
http://www.level1.com Page 31
Page 37

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_14 Configuration of DHCP service
Enable DHCP server: Used to disable or enable the device's DHCP server function. Selecting
it means allow.
Start and end IP address: The IP address fields the DHCP server assigns to the network
computer automatically (which should be on the same network segment as the IP address of
the device LAN port).
Subnet mask: The subnet mask automatically assigned by the DHCP server to the network
computer (which should be consistent with that of the LAN port of the device).
Gateway address: The gateway IP address the DHCP server automatically assigns to the
network computer (which should be consistent with the LAN IP address of the device).
Leasing time: The leasing time for the network computers to obtain the IP address assigned
by the device (Unit: Seconds).
Primary DHCP server: The IP address of the primary DNS server automatically assigned by
the DHCP server to the network computers.
Secondary DNS server: The IP address of the secondary DNS server assigned by the DHCP
server to the network computers automatically.
Enable DNS proxy: Selecting it means enabled. The DNS proxy function of the device will
not take effect unless enabled. After enabling this function, the gateway address is assigned to
http://www.level1.com Page 32
Page 38

Chapter 6 Network parameters
a client as primary, secondary DNS servers.
Operator DNS servers 1, 2: The IP address of operator DNS server.
Tip:
1. If the device's DHCP server function is to be used, network computer's TCP/IP protocol can
be set to "obtain an IP address automatically".
2. If what's originally used by the user is a proxy server software (such as Wingate), and the
PC's DNS server is set as the IP address of the proxy server, then the LAN IP address of the
device only needs to be set to the same IP address, so that the user can switch to using the
device's DNS proxy function without having to change the PC setting after the device enables
the DNS proxy function.
6.4.2 Static DHCP
This section describes the static DHCP list and the way to configure a static DHCP.
Using the DHCP service to automatically configure TCP/IP properties for the network computers
is very convenient, but it can cause a computer to be assigned with different IP address at different
times. And some Intranet computers may need a fixed IP address, in this case, the static DHCP
function is required, to bind the computer's MAC address with an IP address, as shown in Figure
6_15. When a computer having this MAC address requests the address from the DHCP server
(device) , the device will find a corresponding fixed IP address based on its MAC address and
assign it to the computer.
1. Static DHCP list
http://www.level1.com Page 33
Page 39

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_15 Static DHCP list
2. Static DHCP configuration
Click <Add new entry> in the page as shown in Figure 6_15, to enter into the Static DHCP
configuration page as shown in the figure below. Below is a description of the meaning of the
parameters for configuring static DHCP.
Figure 6_16 Static DHCP configuration
User name: Configures the user name of the computer bound by this DHCP (custom, no
repeat is allowed).
IP address: The reserved IP address, which must be the valid IP address within the address
range specified by the DHCP server.
MAC address: The MAC address of the computer to use this reserved IP address in a fixed
way.
http://www.level1.com Page 34
Page 40

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Tip:
1. After the setting is successful, the device will assign the preset IP address for the specified
computer in a fixed way.
2. The assigned IP addresses must be within the range provided by the DHCP server.
6.4.3 DHCP auto binding
Below is the description of DHCP automatic binding function.
Figure 6_17 DHCP auto binding
Enable DHCP automatic binding: When DHCP automatic binding is enabled, the device will
scan the Intranet, and bind IP/MAC of intranet users who obtain an IP address dynamically,
and the device will bind any one IP address it assigns subsequently with the MAC address of
the client. Enabling this function can protect against network ARP spoofing. If it is not
enabled, no automatic binding operation is to be done.
Enable DHCP automatic deletion: When DHCP automatic deletion is enabled, it means that
the device will automatically delete the IP/MAC previously bound automatically after the
lease expires or the user releases the address actively; if it is not enabled, it means that no
automatic deleting operation is to be done.
6.4.4 DHCP client list
For the IP address already assigned to the network computer, its information can be viewed in the
DHCP client list. Information as shown in the figure below: The DHCP server assigns the IP
address of 192.168.1.100 in the address pool to the network computers whose MAC address is
6C:62:6D:E9:6D:13, and the rest of the time for the computer to lease this IP address is 86333
seconds.
http://www.level1.com Page 35
Page 41

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_18 DHCP client list
6.4.5 Case of DHCP configuration
Application requirements
In this example, the device must have the DHCP function enabled, and the starting address is
192.168.1.10, with a total number of 100 allocable addresses. The host with the MAC address
of00:21:85:9B:45:46 assigns the fixed IP address of 192.168.1.15, while the host with the MAC
address of00:1F:3C:0f:07:F4 assigns the fixed IP address of 192.168.1.10.
Configuration steps
The first step is to enter into the Network parameters -> DHCP server -> DHCP service settings
page.
The third step is to enable the DHCP function, configure the related DHCP service parameters (as
shown in Figure 6_19), and click <Save> after the end of configuration.
http://www.level1.com Page 36
Page 42

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_19 DHCP service settings - Instance
The third step is to enter the Network parameters -> DHCP server-> Static DHCP page, and click
<Add new entry>, to configure the two static DHCP instances in the request (such as Figure 6_20,
Figure 6_21).
Figure 6_20 Static DHCP configuration - Instance A
http://www.level1.com Page 37
Page 43

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Figure 6_21 Static DHCP configuration - Instance B
At this point, the configuration is complete, and you can view the information about 2 static
DHCP entries in the "Static DHCP information list", as shown in Figure 6_22. If configuration
errors are found, you can click the corresponding item's icon directly and enter into the Static
DHCP configuration page for modification and saving.
Figure 6_22 Static DHCP information list - Instance
6.5 DDNS Settings
This section describes the Network parameters -> DDNS Settings page and configuration
methods. Includes: application for DDNS account, configuration of DDNS service, DDNS
authentication.
http://www.level1.com Page 38
Page 44

Chapter 6 Network parameters
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a service to resolve a fixed domain name to a dynamic IP address (such
as ADSL dial-up Internet access) services. You need to apply to the DDNS service provider for
this service, and the specific service of DDNS is provided by various service providers according
to the actual situation. The DDNS service provider reserves the rights to change, interrupt or
terminate part or all of the network services. At present, the DDNS service is free of charge, when
the DDNS service provider may charge some fee for using DDNS services in providing network
services. In this case, LEVELONE will give a notice as soon as possible. If you refuse to pay such
expenses, you cannot use the related services. At the free stage, LEVELONE does not guarantee
the DDNS service must be able to meet the requirements, nor guarantee the service will not be
uninterrupted, nor guarantee the timeliness, safety, and accuracy of network services.
Interface: Selects the interface binding of the DDNS service.
6.5.1 DDNS authentication
You can use the Ping command (for example: ping avery12345.3322.org) in the DOS status of
intranet computers, to check if the DDNS update is successful. Upon seeing the correctly
parsed-out IP address (for example: 58.246.187.126), it indicates that domain name resolution is
correct. Note: Under normal circumstances, the device's IP address will not be pinged from the
Internet after NAT is used on the device but only the IP address for that domain name can be
parsed out.
1. Only when the IP address assigned by ISP (Such as China Telecom) to the WAN port
connection line can the domain name be sure to be accessed by Internet users.
2. The DDNS function can help the Dynamic IP use VPN and server mapping.
http://www.level1.com Page 39
Page 45

Chapter 6 Network parameters
6.6 UPnP
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is an architecture for common peer network connections used for
PCs and intelligent devices (or instruments). Using UPnP means simpler, more choices and more
innovative experiences. The network products supporting Universal Plug and Play needs only be
physically connected to the network, to begin to work.
This section describes the Network parameters ->UpnP page and configuration. When
configuring UPnP in this page, you need to simply enable or disable this feature.
Figure 6_23 UPnP configuration
Enable UPnP: Ticking the check box for enabling the UPnP feature.
Internal address: The host IP address when port translation is needed in the intranet.
Internal port: The port number provided by the host when port translation is required in the
intranet.
Protocol: The protocol used by the UPnP port in translation (TCP/UDP).
Peer address: The IP address of the peer host.
External ports: The port number of the device used for port translation. This port is the
service port the device provides to the Internet.
Description: The description information given when an application requests port translation
to the device through UPnP.
Tip: It is recommended not to enable the UPnP feature when this feature is not in use.
http://www.level1.com Page 40
Page 46

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
Chapter 7. Advanced Configuration
The features described in this chapter include: NAT and DMZ, route configuration, network
vanguard defense, port mirroring, port VLAN and SYSLOG configuration.
7.1 NAT and DMZ configuration
This section describes the features and configuration methods of the Advanced
Configuration->NAT and DMZ configuration page.
7.1.1 Description of NAT functions
NAT (network address translation) is a technology to map an IP address field (such as Intranet) to
another IP address field (such as the Internet). NAT was designed to solve the problem of
increasing shortage of IP addresses, NAT allows a private network to use the IP address in any
range internally, and for the public Internet, it is reflected as limited range of public network IP
addresses. Since the internal network can be effectively isolated from the outside world, so NAT
can also provide some assurance for network security.
LEVELONE routing products provide flexible NAT function. The following will detail its
characteristics.
1. NAT address space
In order to correctly conduct the NAT operation, any NAT device must maintain two address
spaces: one is the private IP addresses used internally by Intranet hosts, which is represented by
"Internal IP address" in the device. Another is the public network IP address for external use,
which is represented by "External IP address" in the device.
2. NAT Static mapping and virtual server (DMZ host)
After the NAT feature is enabled, the device blocks the access requests that originate outside.
However, in certain application environments, a computer in the external network hopes to access
to the Intranet server through the device, at this point, the static NAT mapping or virtual server
http://www.level1.com Page 41
Page 47

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
(DMZ host) needs to be set up on the device in order to achieve this objective.
With the static NAT mapping function, a one-to-one mapping relationship can be established
between<External IP address + External port>and<Internal IP address + Internal port>, so that
all the service requests for a specified port of the device will be forwarded to the matching intranet
server, and the computer in the external network can access to the services provided by this server.
In some cases, a network computer needs to be fully exposed to the Internet, in order to achieve
two-way communications, and at this time, you will need to set up this computer to a virtual
server (DMZ host). When an external user accesses to the public network address that is mapped
to the virtual server, the device will forward the packets directly to the virtual server.
Tip: The computer that is set to a virtual server will lose the firewall protection of the device.
The priority of NAT static mappings is higher than the virtual server. When the device receives a
request from an external network, it will first check to see if there is a matching NAT static
mapping based on the IP address and port number of the external access requests, and send the
request messages matching the static NAT mapping to the Intranet computers if any. If there are no
matching static mappings, it will check to see if there is a matching virtual server.
3. Two types of NAT rules
The device provides two NAT types: "Easy IP" and "One2One".
Easy IP: The translation of network port addresses. Multiple internal IP addresses are mapped to
the same external IP address. It can dynamically assign a port associated with a single external
address for each internal connection, and maintain the mapping of these internal connections to an
external port, thus enabling multiple users to use a public network address to communicate with
the external Internet.
One2One: The translation of static addresses. The internal IP and the external IP address are
subject to one-to-one mapping. In this mode, the port number will not change. It is typically
used to configure the extranet-access-to-intranet server: The network servers still use private
addresses, and provide the public IP address assigned to it to the external network users.
We refer to each specific NAT configuration as "NAT rules". The exit IP address and lines must be
specified when configuring the NAT rules. When there are multiple valid public network
addresses, each type of NAT rules can be configured with more than one. In practical application,
a mixture of different types of NAT rules often needs to be used.
7.1.2 Port Forwarding
This section describes the static NAT mapping functions of the device. Below is the description of
the meaning of the parameters for the static NAT mapping list and the static NAT mapping
configuration.
http://www.level1.com Page 42
Page 48

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
1. Port Forwarding list
Figure 7_1 Port Forwarding list
Tip:
After enabling certain functions of the system, the list displays some NAT static mapping entries
(A static mapping entry named as "admin" is added in the list after remote management is enabled
in Systems management -> Remote management page, they cannot be edited or deleted in this
page.
2. Static NAT mapping configuration
Click <Add new entry> in the page of Figure 7_1 to enter the Static NAT mapping configuration
page, as shown in Figure 7_2. Here, the meaning of the parameters of the static NAT mapping
configuration is described.
http://www.level1.com Page 43
Page 49

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
Figure 7_2 Port Forwarding Settings
Static mapping name: The name of static NAT mapping, which is custom and cannot be
repeated.
Enable this configuration: Selecting it indicates that the static NAT mapping takes effect, and
not selecting it means that the static NAT mapping does not take effect, but retains its
configuration.
Protocol: The protocol type of packets, the available options are: TCP, UDP and TCP/UDP.
When you are unable to confirm that the protocol used by the application is TCP or UDP,
select TCP/UDP.
External starting port: The starting service port the device provides to the Internet.
IP address: The IP address of the computer as a server in the Intranet.
Common port: The port number that corresponds to the common protocol type for users'
choice. When you are unable to confirm the protocol, select TCP/UDP.
Internal starting port: The starting port of the services enabled by the network server.
Number of ports: A segment of ports starting from the internal starting port, whose maximum
value is set to 500.
NAT binding: Selects the interface bound by the static NAT mapping.
http://www.level1.com Page 44
Page 50

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
7.1.3 NAT rules
The NAT rules features of the device are described below, including: NAT rule info lists, meaning
of Easy IP NAT rules configuration parameters, meaning of One2One NAT rules configuration
parameters.
1. List of NAT rules information
In NAT rules information list, you can see the configured NAT rules. As shown in Figure 7_3, it
has two NAT rules instances configured. The NAT type of an instance: EasyIP converts the
address with the intranet IP address of 192.168.1.20-192.168.1.25 to 200.200.202.20, and binds to
the WAN1 port to achieve Internet access. The NAT type of an instance: One2One converts the
address with the intranet IP address of 192.168.1.50-192.168.1-52 to 200.200.202.50,
200.200.202.51, 200.200.202.52, and binds to the WAN1 port to achieve Internet access.
Figure 7_3 List of NAT rules information
Tip: Multiple NAT rules are configured for the same object, and the rules configured last will
take effect first.
2. Easy IP
Click <Add new entry> in Figure 7_3 to enter the NAT rules configuration page. The following
describes the meaning of the parameters for configuring the NAT rules with the type of EasyIP.
http://www.level1.com Page 45
Page 51

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
Figure 7_4 Easy IP
Rule name: Customizes the name of the NAT rule.
NAT type: Selects EasyIP here, which means the internal IP address are mapped to the same
external IP address.
External IP address: In the NAT rule, the external IP address mapped to the internal IP
address.
Internal starting IP address, internal ending IP address: The IP address range for the
computers in the intranet that have the priority to use the NAT rules for Internet access.
Binding: Selects the interface bound by the static NAT mapping.
3. One2One
Select the NAT type as One2One in Figure 7_5. The meaning of the parameters for configuring
the NAT rules as One2One type is described here, and those parameters same as EasyIP are
repeated no longer here.
Figure 7_5 One2One
NAT type: Here, One2One is selected. The internal IP address and the external IP address are
http://www.level1.com Page 46
Page 52

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
subject to one-to-one mapping.
External starting IP address: In the NAT rule, the external starting IP address mapped to the
internal starting IP address.
Tip:
1. Each One2One rule can only bind 20 external addresses at maximum.
2. "External starting IP address" must be set, and the actually mapped external IP address is
gradually increased from the set value. For example, if "Internal starting IP address" is set to
192.168.1.50; "Internal ending IP address" is set to 192.168.1.52; "external starting address"
is set to 200.200.202.50, then 192.168.1.50, 192.168.1.51, 192.168.1.52 are in turn mapped
to 200.200.202.50, 200.200.202.51, 200.200.202.52.
7.1.4 DMZ
The DMZ functions of the device are described below.
Figure 7_6 DMZ configuration
Enable DMZ function: Enables or disable the DMZ function.
DMZ host IP address: The IP address of the network computer used as a virtual server (DMZ
host).
Tip:
The computer that is set to a DMZ host will lose the firewall protection of the device, which takes
effect to all WAN ports.
http://www.level1.com Page 47
Page 53

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
7.1.5 NAT and DMZ configuration instances
This section describes the specific instances of NAT and DMZ configuration. Includes: Static
NAT mapping instances, instances with the type of NAT rules as EasyIP, One2One.
I. Instances of Static NAT mapping configuration
Intranet computer 192.168.1.99 starts the TCP80 port services, and wants to access this service
through WAN1 port 80. It's configuration is as shown in Figure 7_7.
Figure 7_7 Port Forwarding Settings
II. EasyIP configuration instances
An Internet café uses a single line for Internet access, and the ISP has assigned 8 addresses for this
line: 218.1.21.0/29 -218.1.21.7/29, where 218.1.21.1/29 is the gateway address of the line, and
218.1.21.2/29 is the IP address of WAN1 port of the device. Note that 218.1.21.0/29 and
218.1.21.7/29 are respectively the related subnet number and broadcast address, which cannot be
used.
Now, Game B Zone (IP address range: 192.168.1.10/24-192.168.1.100/24) wishes to use
218.1.21.3/29 as a NAT mapping address for accessing to the Internet through the WAN port.
Configuration steps are follows:
The first step is to enter the Advanced configuration -> NAT and DMZ configurations ->NAT
rules page, and click <Add new entry>.
The second step is to enter the NAT rules configuration page, and fill in "Game Zone" in the
http://www.level1.com Page 48
Page 54

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
"Rule name".
The third step is to select "NAT type" as "EasyIP".
The fourth step is to fill in 218.1.21.3 in the "External IP address". Fill in 192.168.1.10 and
192.168.1.100 in "Internal starting IP address" and "Internal ending IP address" respectively.
The fifth step is to select the rule-bound interface as WAN1 port.
The sixth step is to click <Save>, and the NAT rule is configured successfully.
Figure 7_8 NAT rules Settings——EasyIP
Tip:
When configuring Easy IP, if the "External IP address" is not on the same network segment as the
IP address of the bound interface, a route must be configured on the upper router to the network
segment on which the "External IP address" resides or a 32-bit host route to the "external IP
address", and the next hop is set to the IP address of the bound interface.
III. One2One configuration instance
Demands
An enterprise applies for a line of Telecom, which adopts the fixed IP access method, and the
bandwidth is 6M. Telecom assigned 8 addresses to it: 202.1.1.128/29-202.1.1.1.135/29. Here,
202.1.1.129/29 is the gateway address of the line, and 202.1.1.130/29 is the IP address of the
device's WAN1. Note: 218.1.21.0/29 and 218.1.21.7/29 are respectively the related subnet number
and broadcast address, which cannot be used.
The company wants its people to access to the Internet via NAT by using 202.1.1.130/29 sharing.
Additionally, there are four servers that are in one-to-one NAT (One2One) and use
202.1.1.131/29-202.1.1.1.134/29 for providing services externally. The internal network address is
192.168.1.0/24, and the address for 4 servers is 192.168.1.200/24-192.168.1.203/24.
Analysis
Since the fixed IP access mode is used for Internet access on this line, it is necessary to configure
http://www.level1.com Page 49
Page 55

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
the fixed IP access to the default Internet line in Network parameters —> WAN port
configuration page, or directly enter the Start--> Configuration wizard > Network parameter
spage to configure the line. After the default Internet access line is configured correctly, the
system-reserved NAT rules corresponding to the default line will be automatically generated, and
the NAT function is automatically enabled.
And this enterprise provides four internal servers for external access, so it is also necessary to set
an NAT rule with the type of "One2One".
Configuration steps are follows:
The first step is to enter the Advanced configuration -> NAT and DMZ configurations ->NAT
rules page, and click <Add new entry>.
The second step is to enter the NAT rules configuration page, and fill in "Server" in the "Rule
name".
The third step is to select "NAT type" as "One2One".
The fourth step is to fill in202.1.1.131in the "External starting IP address". Fill
in192.168.1.200and 192.168.1.203 in "Internal starting IP address" and "Internal ending IP
address" respectively.
The fifth step is to select the rule-bound interface as WAN1 port.
The sixth step is to click <Save>, and the NAT rule is configured successfully.
Figure 7_9 NAT rule Settings —One2One
7.2 Static Route Settings
This section describes the Advanced Configuration-> Routing configuration page and
configuration methods.
http://www.level1.com Page 50
Page 56

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
Static route is manually configured by a network administrator, making the transmission of
packets to the specified destination network be realized according to the predetermined path.
Static routing does not change with changes in the structure of the network, therefore, when
network structure changes or there is a network failure, you need to manually modify the static
routing information in the routing table. Setting and using static routes correctly can improve
network performance and meet special requirements, such as implementing traffic control,
guaranteeing bandwidth for important applications and so on.
The following describes the list of routing configuration information and the meaning of the
parameters in the routing configuration.
Figure 7_10 Static Route List
Click <Add new entry> in the above figure, and enter the Route configuration page.
Figure 7_11 Static Route Settings
http://www.level1.com Page 51
Page 57

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
Routing name: The name of static routes (custom, no repetition).
Enable this configuration: Enables this static route. Selecting it means enabled, while
deselecting it means the route is disabled.
Destination network: The destination network number for this static route.
Subnet mask: The mask of the destination network for this static route.
Gateway address: The IP address of the next-hop router ingress. The device defines a line for
hopping to the next router through interface and gateway. Typically, the interface address and
the gateway must be on the same network segment.
Priority: Sets the priority of a static route. When the destination network, subnet mask are the
same, select the high priority routing for forwarding data, and the smaller the value is, the
higher the priority is.
Interface: The forwarding interface for the specified packets. The packets matching the static
route will be forwarded from the specified interface.
Tip:
When the destination network and priority of multiple routes are the same, the device will match
them in the principle of first matching for last establishment.
7.3 Policy routing
This section mainly describes Advanced Configuration—>Policy routing page and configuration
methods. In this page, you can define policy routing, and the packet are routed according to the
source IP addresses, protocols, destination addresses and destination ports.
http://www.level1.com Page 52
Page 58

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
7.3.1 Enable policy routing
Figure 7_12 Policy routing list
Enable policy routing: This is a global switch of policy routing. Only after it is enabled can
the configured policy routing can take effect.
Move to: Users can appropriately sort the policies using this bLeveloneon.
7.3.2 Policy routing configuration
Click <Add new entry> in the above figure, and enter the Policy routing configuration page.
http://www.level1.com Page 53
Page 59

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
Figure 7_13 Policy routing configuration
Interface: Sets the physical interface bound by the policy routing, and the packets that meet
the conditions of policy routing will be forwarded from the bound interface.
Policy route name: Customizes the name of the policy.
Source address: The source IP address of the packets following this policy route, which can
be configured in two ways.
Network segment: The starting IP address and the ending IP address following this
policy route.
User group: The user group following this policy route, click on "User group" to refer to
the source address for policy reference for the user group. Enter User management ->
User group configuration-> Add new entry to set up the source address field for the
policy routing to take effect.
Destination address: The destination address in the packet following this policy route, which
is configured in the same way as the source address.
Services: The services in the packets following this policy route, which can be configured in
the following manner.
Ports: Range 1-65535, the corresponding protocols are TCP and UDP; when the selected
http://www.level1.com Page 54
Page 60

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
protocol is ICMP, the port range needs not be configured.
Effective time setting: Selects the time period for the policy routing takes effect, and the
default date is "Every day". The time is "All day". You can go to Advanced settings —>
Configure policy route page to edit the time for the policy route to take effect.
Tip:
1. When all the packets match the defined source IP address, protocol and destination port,
they will be forwarded to the specified interface, but the packets that cannot find a
matching policy routes will go the normal route.
2. The execution order of policy routing: Static route to the LAN port > Policy routing >
Static route to the WAN port.
7.4 Anti-NetSniper
This section describes the Advanced Configuration -> Anti-NetSniper page and configuration
methods. Network vanguard defense is used to crack the shared detection set by the network
operator. Verify that the intranet is experiencing a sharing problem, or don't enable that function.
Figure 7_14 Anti-NetSniper
7.5 Port mirroring
This section describes the port mirroring function of the Advanced configuration -> Port
mirroring page. With the port mirroring function, you can copy the flow of the monitoring port to
the monitoring port, to provide the detailed information on the transmitting status of the monitored
ports, allowing network managers to make traffic monitoring, performance analysis and
troubleshooting.
Except HiPER
the default LAN1 port of monitoring port, and other LAN ports are monitored ports. The
TM
840G, the devices of HiPER series that support the port mirroring function have
http://www.level1.com Page 55
Page 61

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
configuration interface is shown in the figure below.
Figure 7_15 Port mirroring
Enable mirroring: Checking it to enable this feature.
When the HiPER
work.
Monitoring port: The port for monitoring the traffic of the monitored ports, which can be
only one.
Monitored port: Only one monitored port can be selected.
TM
840G device supports two or more LAN ports, the port mirroring function can
Tip: The monitored port cannot be the same port as the monitoring port.
7.6 Port VLAN
This section describes the port VLAN function of the Advanced configuration -> Port VLAN
page.
VLAN (virtual LAN) can split the network into several different broadcast domains logically. A
logical constitutes a logical broadcast domain. The members of the same VLAN share broadcast
and can communicate with each other. To achieve physical isolation between different VLANs,
the unicast, broadcast and multicast packets within a VLAN will not be forwarded to any other
VLAN, thereby helping to control traffic, simplify network management and enhance network
security.
3. Port VLAN list
http://www.level1.com Page 56
Page 62

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
Figure 7_16 Port VLAN list
VLAN group number: Displays the VLAN group number of the VLAN.
VLAN group name: Displays the VLAN group name of the VLAN.
VLAN members: Displays the members to the VLAN.
4. Port VLAN
Figure 7_17 Port VLAN settings
VLAN group number: Sets the VLAN group number.
VLAN group name: Sets the name of the VLAN group.
VLAN members: Selects the members to the VLAN group.
Tip:
1. The system has a default VLAN (VLAN 1), and it contains all physical ports by default, and
cannot be deleted.
http://www.level1.com Page 57
Page 63

Chapter 7 Advanced Configuration
2. A VLAN can contain more than one port, and one port can belong to more than one VLAN.
5. Instances of Port VLAN
Requirements: The host under the LAN1 port can communicate with the hosts under the LAN2,
LAN3 ports, but those under the LAN2 and LAN3 ports cannot access to each other.
Configuration steps:
1. Modify VLAN 1, whose member ports only include: 1, 2.
2. Create VLAN 2, whose member ports are: 1, 3.
Analysis: Both LAN1 port and LAN2 port belong to VLAN1, both LAN1 and LAN3 belong to
VLAN2; the hosts under the fixed LAN1 port can communicate with the hosts under LAN2,
LAN3 ports. Additionally, both LAN2 port and LAN3 port are not in the same VLAN, and the
hosts under LAN2 and LAN3 cannot access to each other.
7.7 SYSLOG configuration
This section describes the Advanced Configuration -> SYSLOG configuration page.
Figure 7_18 SYSLOG configuration
Enable Syslog service: After the syslog service feature is enabled, this feature will send a
large amount of information of device operation to a syslog server, which makes it easy for
administrators to analyze system conditions, and monitoring system activity.
Address of syslog server (domain name): Sets the address of the syslog server, which can be
an IP address or a domain name.
Port of Syslog server: Sets the service ports that are opened by the syslog server, whose
default value is 514.
Syslog message type: Sets the type of syslog message to be sent, whose default value is
Local0.
http://www.level1.com Page 58
Page 64

Chapter 8 User Management
Chapter 8. User management
This chapter describes the secondary menu under the primary menu of user management,
including: User state, IP/MAC binding, PPPoE server, WEB authentication, user group
configuration.
8.1 User status
This section describes the User management-> User status page. Administrators can understand
all intranet users' net behaviors, the traffic occupied by the net behaviors and the status of each
user, and so on by viewing, analyzing the pie charts and lists in this page.
Figure 8_1 User Status
Analysis of the current network traffic usage: analyzes the current percentage of network
traffic used by Intranet applications.
Analysis of current net behaviors: Analyzes the net behavior of all currently online users.
Clear data: The system counts the traffic and net behaviors from 00:00 every day. Clicking
this bLeveloneon will clear the historical data of the day and immediately begin to recount.
Disable identification statistics: Click this bLeveloneon to disable the identification function
for net behavior management. After doing this, the net behavior management function will be
http://www.level1.com Page 59
Page 65

Chapter 8 User Management
disabled.
The following describes the list of user status information, through checking of which,
administrators can learn about each online user's online time, real-time upload/download rate, total
uplink/downlink traffic, net behaviors, etc.
Figure 8_2 User status information list
The first column of user status information displays if each user's net behaviors are affecting work,
whose status includes: Severe (red), minor (yellow), normal (green). When an intranet user's
behavior of accessing shopping websites, social networking sites, using stock software and
playing online/web game accounts for a range of [100%, 70%] of all of its personal net behaviors,
this means seriously affecting work. When the range is (70%, 50%), it means minor. When the
range is (50%, 0%), it means normal.
User name: Displays the user name for Intranet users.
MAC address: Displays the MAC address of Intranet users.
Ways of authentication: Displays authentication of Intranet users (WEB and PPPoE)
IP address: Displays the IP address of Intranet users.
Upload, download rate: Displays the upload and download rate of Intranet users.
http://www.level1.com Page 60
Page 66

Chapter 8 User Management
Total uplink, downlink traffic: Displays the total uplink and downlink traffic of Intranet users.
Online time: Displays the user's online time.
Group: Displays the group to which the user belongs.
Net behavior: Displays the user's net behaviors.
Settings: Click the icon. If you want to clear the user's net behavior statistics, please click
"Clear data".
Note: Click on the icon to modify the description information of PPPoE dial-up user, WEB
authenticated user.
Automatic refreshing interval: This list supports automatic refreshing, with the interval of 1-5
seconds.
Stop automatic refreshing: Click this bLeveloneon and the list will stop automatic refreshing.
If you need to view the information of the entire list or modify the notes, etc., it is proposed
to stop automatic refreshing.
Start automatic refreshing: Click this bLeveloneon and the list will refresh the list at the
automatic refreshing interval.
8.2 IP/MAC binding
This section describes the User management->IP/MAC binding page and configuration method.
To implement network security management, you must first solve the identity problems of users
before you can carry out the necessary service authorization work. In Firewall -> Access control
policy, we will introduce how to implement the control of Intranet users' net behaviors. In this
section, we will describe how to solve the problem of user identification.
In the device, user's identification can be completed through the IP/MAC binding function. The
use of the bound IP/MAC address pair as the user's unique identity ID can protect the device and
network against IP spoofing attacks. IP spoofing attack means that a host attempts to use another
trusted host's IP address to connect to the device or pass through the device. This host's IP address
can be easily changed as a trusted IP address, but the MAC address is added by the manufacturer
to the Ethernet card, so it cannot be easily changed.
http://www.level1.com Page 61
Page 67

Chapter 8 User Management
8.2.1 IP/MAC binding list
Figure 8_3 IP/MAC binding global configuration
Allow non-IP/MAC bound user to connect to the device: Allows or disallows the
non-IP/MAC bound users to connect to the device, and access to other networks through the
device.
Allow: Ticking this check box means to allow the bound user to connect to the device, but
unchecking it means to disallow the bound user to connect to the device.
Modify the IP/MAC binding entries, click the Edit icon, to enter the IP/MAC binding
configuration page as shown in the figure below, and after change, click <Save>.
Export: This bLeveloneon is used to export the IP address, MAC address, user name in the
list of IP/MAC binding information.
Figure 8_4 Modification of IP/MAC instances
http://www.level1.com Page 62
Page 68

Chapter 8 User Management
Tip:
Before deciding to cancel the "Allow non-IP/MAC bound user to connect to the device" function,
you must make sure that the management computer has been added to the "IP/MAC binding
information list", otherwise it will cause the management computer to be unable to connect to the
device.
8.2.2 IP/MAC binding configuration
Figure 8_5 IP/MAC binding configuration
Network segment: The management IP address/subnet mask of the device by default.
Text box: Displays the scanned IP/MAC information, or the configured IP/MAC binding
information, whose input format is "IP+MAC+ username".
IP address, MAC address: The user's IP address, MAC address (which can be obtained
using the ipconfig /all command under DOS environment on Windows platforms).
User name: It can be ignored, because the system will automatically assign a name for
it.
Scan: Click <Scan> to display the ARP information dynamically learned by the device.
http://www.level1.com Page 63
Page 69

Chapter 8 User Management
Binding: Binds all the IP/MAC entries in the text box.
Tip:
1. In the above input format, there may be one or more spaces between the IP and MAC, MAC
and username.
2. For the invalid entries, the system will skip the invalid configuration entries in binding.
8.2.3 IP/MAC binding instances
Flexibly using the IP/MAC binding feature can configure "white list" and "black list" for Internet
access for Intranet users.
By configuring the "white list" for Internet access, only the users in "white list" are allowed to
access the Internet through the device, while prohibiting all other users from doing it. Therefore, if
only a few users in the intranet are allowed for accessing the Internet, a "white list" is to be
configured to achieve this goal.
By configuring the "black list" for Internet access, only the users in "black list" are prohibited
from accessing the Internet through the device, while allowing all other users to do it. Therefore, if
only a few users in the intranet are prohibited from accessing the Internet, a "black list" is to be
configured to achieve this goal.
In the device, the users in the "white list" are legal users - their IP and MAC address exactly
matches an entry in the "IP/MAC binding information list", and the entry selects "Allow".
The users in the "black list" are illegal users - their IP and MAC address exactly matches an entry
in the "IP/MAC binding information list", and the entry does not select "Allow". Or, there is only
one entry in their IP and MAC address matches the corresponding information of a bound entry.
1. Configure "white list" of Internet access for Intranet users, following these steps:
First, Specify legal users by configuring the IP/MAC binding entries, and use the IP address and
MAC address of the host with the permission to access the Internet as the IP/MAC address
binding pair, and add it to the "IP/MAC-binding information list", and "Allow" needs also be
selected, that is, allow the users exactly matching the IP/MAC address to access the Internet.
Next, deselect the "Allow non-IP/MAC binding user to connect to the device", so that all other
hosts not included in the "IP/MAC binding information list" will not be able to access the Internet.
For example, if you want to allow a host with the IP address of 192.168.1.2, and the MAC address
of0021859b4544to connect to and pass the device, you can add an IP/MAC address binding entry,
enter the host's IP address and MAC address, and select "Allow", as shown in Figure 8_6.
http://www.level1.com Page 64
Page 70

Chapter 8 User Management
Figure 8_6 IP/MAC binding information list – Instance I
2. Configure "Black list" of Internet access for intranet users, following these steps:
First, specify the illegal user by configuring the IP/MAC binding entries, and there are two
methods:
1. Use the IP address of the host that is prohibited from Internet access and the MAC address of
any of the non-intranet adapter as the IP/MAC address binding pair, and add it into the
"IP/MAC-binding information list".
2. You can use the IP and MAC addresses of the host that is prohibited from Internet access as
the IP/MAC address binding pair, and deselect "Allow" (no "√" in the box), namely, to
prohibit the users that exactly match the IP/MAC address from accessing to the Internet.
Next, select the "Allow non-IP/MAC binding user to connect to the device", so that all other hosts
whose IP addresses and MAC addresses are not included in the "IP/MAC binding information list"
will be able to access the Internet.
For example, if you want to prohibit a host with the IP address (for example, 192.168.1.3) from
accessing and connecting to the device, you can add a IP/MAC address binding pair, enter the IP
address, and the MAC address is set to the MAC address of any non- intranet adapter, as shown in
the table below.
http://www.level1.com Page 65
Page 71

Chapter 8 User Management
Figure 8_7 IP/MAC binding information list – Instance II
For example, if you want to prohibit a host with the IP address of 192.168.1.30 and the MAC
address of 0021859b2564 from connecting and passing the device, you can add an IP/MAC
address binding pair, enter the host's IP address and MAC address, and deselect "Allow" (no "√"
in the box), as shown in Figure 8_8.
Figure 8_8 IP/MAC binding information list – Instance III
http://www.level1.com Page 66
Page 72

Chapter 8 User Management
PPPoE Client
PPPoE Server
PADI
PADO
PADR
PADS
8.3 PPPoE Server
This section describes the device's PPPoE function, including: PPPoE introduction, PPPoE global
configuration of device, configuration of PPPoE accounts and viewing of PPPoE connection
status.
8.3.1 PPPoE introduction
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet). It allows a host on the Ethernet to connect to the
Internet through a simple access device. PPPoE protocol uses Client/Server, which encapsulates
PPP packets in an Ethernet frame, and provides the point-to-point connection over Ethernet.
PPPoE dial-up connections include two stages, Discovery (discovery) and Session (PPP session).
The following will introduce these two stages.
1. Discovery stage
This stage is used to establish a connection. When a user host wants to start a PPPoE session, it
must first implement the discovery stage to identify the Ethernet MAC address of PPPoE Server,
and establish a PPPoE session ID (Session ID).
Figure 8_9 Basic workflow of Discovery stage
As shown in the figure above, Discovery stage consists of four steps. The following describes the
basic workflow.
PADI: If you want to set up a PPPoE connection, PPPoE client should first send a PADI
(PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation) packet as a broadcast. The PADI packet includes the
services the client requests.
PADO: When the PPPoE server receives a PADI packet, it will determine if it is able to
provide services, and if so, it will send to the client a PADO (PPPoE Active Discovery Offer)
packet to respond. PADO packets include the PPPoE server name and the service name
http://www.level1.com Page 67
Page 73

Chapter 8 User Management
same as that in the PADI packet. If the PPPoE server cannot provide services to PADI, it is
not allowed to use the PADO packet to respond.
PADR: Since PADI is sent as a broadcast, the PPPoE client may receive more than one
PADO packet, and it will review all the PADO packets received and choose a PPPoE server
based on the server name in it or the services provided, and then send a PADR (PPPoE Active
Discovery Request) packet to the selected server. PADR packet includes the services
requested by the client.
PADS: When PPPoE server receives the PADR packet sent by the client, it is ready to start a
PPPoE session, and creates a unique PPPoE session ID for PPPoE session, and sends to the
client a PADS (PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation) package as a response.
When the discovery stage ends normally, both ends of the communication obtain the session ID
and their MAC addresses, and they define a PPPoE session together uniquely.
2. PPP session stage
When PPPoE enters the PPP session stage, the client and the server will conduct a standard PPP
negotiation, and after this, the data is sent over PPP encapsulation. The PPP packets are
encapsulated as the payload of PPPoE frame in an Ethernet frame, and sent to the peer end of the
PPPoE link. Session ID must be the ID determined in the Discovery stage, and remains unchanged
during the session. The MAC address must be that of the peer end.
At any time during the session stage, both PPPoE server and client can send PADT (PPPoE Active
Discovery Terminate) to each other, notifying the other side of ending the session. When receiving
PADT, it is not allowed to use the session to send the PPP traffic. After sending or receiving a
PADT packet, even the conventional PPP end packet is not allowed to be sent. Normally, both
parties of PPP communication end the PPPoE session using the PPP itself, but can end the session
using PADT if PPP cannot be used.
8.3.2 PPPoE global Settings
Enter User management->PPPoE server page to configure the PPPoE server function. The
configuration parameters are described as follows.
http://www.level1.com Page 68
Page 74

Chapter 8 User Management
Figure 8_10 PPPoE Global Settings
Enable PPPoE server: Enables/disables the PPPoE server function of the device. Select it to
enable.
Forcing PPPoE authentication: Enabling it means to only allow the users who pass the
intranet PPPoE authentication to access the Internet.
Exception address group: After the device enables the forcing PPPoE authentication, the
users of the address group can communicate with external network without dial-up
authentication, and the address group needs to be configured in the User management ->
User group configuration page.
Starting IP address: The starting IP address the PPPoE server automatically assigns to the
network computers.
Primary DNS server: The IP address of the primary DNS server automatically assigned by
the PPPoE server to the network computers.
Secondary DNS server: The IP address of the secondary DNS server automatically assigned
by the PPPoE server to the network computers.
Allow users to modify the dial-up password: Checking it means to allow intranet PPPoE
dial-up users to modify dial-up password on their own.
Password authentication mode: The way PPPoE authenticates username and password. The
device provides three authentication modes, PAP, CHAP and AUTO, and the default value is
AUTO, which means that the system automatically selects one of PAP and CHAP to
authenticate the dial-in users, and generally does not need to be set.
Maximum number of sessions: The maximum number of PPPoE sessions supported by the
http://www.level1.com Page 69
Page 75

Chapter 8 User Management
system to be established.
Tip:
1. The steps that PPPoE users change the dial-up password:
1) Users open the dial-up client, and dial up using the user name, password.
2) After a successful dial-up, log into the self-service page, whose address is:
http://192.168.1.1/poeUsers.asp (the address is the LAN IP address for the device).
3) In the change password page, enter your user name, old password, new password, and
confirming password.
4) Click "Submit" to display "Operation is successful", and the password is successfully
changed.
2. Users can modify their password 5 times a day on their own.
3. The administrator can use the Behavior management -> Electronic notification page to
configure the Routine business notification for informing users of how to modify the
PPPoE dial-up password.
8.3.3 PPPoE account configuration
Enter the User management ->PPPoE account ->PPPoE server configuration page (as shown in
Figure 9_11) to view the PPPoE account info list. Click <Add new entry> in the page to enter into
the page as shown in Figure 8_12:
Figure 8_11 PPPoE account info list
http://www.level1.com Page 70
Page 76

Chapter 8 User Management
User name: The user name of PPPoE dial-up users.
Enable: If the user is allowed to access the Internet. Checking it means allow.
Fixed IP address: Displays the IP address bound to that user name.
Charging mode: When the charging feature is enabled, the "by date" will be displayed (which
currently supports charged by date).
User status: The using status of the user will be displayed after the charging feature is
enabled, including: normal, to be expired, expired.
To be expired: This parameter is controlled through "Account Days Remaining" in the
account expiration notification feature (Here, the account expiration notification feature,
please go to Behavior management -> Electronic notification page for configuration).
Expired: Means that the account is not in the effective date of account.
Date of account opening, date of account disabling: When the charging feature is enabled, the
effective date of the account will be displayed.
Upload rate limit, download rate limit: The maximum upload and download rates of PPPOE
(0 means unlimited rate).
Maximum number of sessions for account: Displays the number of users who can
simultaneously use the account for PPPoE connection.
MAC address: Displays the MAC address bound by the account.
Upload rate limit, download rate limit: Sets rate limit in batch for the accounts checked in the
PPPoE account info list (0 means unlimited rate).
Rate limit: Click on this bLeveloneon, to bring the upload speed, download rate limit in
force.
Figure 8_12 PPPoE account settings
http://www.level1.com Page 71
Page 77

Chapter 8 User Management
User name: The account (custom, not repeatable) used by users in initiating PPPoE
connections for the PPPoE server to authenticate, the value range is: 1-31 characters.
Password: The password used by users in initiating PPPoE connections for the PPPoE server
to authenticate.
MAC binding: Chooses to bind the user name with the corresponding MAC address. If
binding, only the hosts with the corresponding MAC address can use the account for
accessing to the Internet.
No binding: Means no user name/MAC binding is to be done.
Automatic binding: After the user dials up successfully for the first time, the device will
automatically bind the user name with the dial-up user's MAC address.
Manual binding: Manually enters the MAC address in the MAC address bar for user
name/MAC binding.
Maximum number of sessions for account: Sets the number of users who can simultaneously
use the account for PPPoE connection.
Fixed IP address: The fixed IP address assigned for the PPPoE dial-up user, which must be
within the scope of address pool.
Added to the account groups: the user name will be added to the appropriate account group,
which must be configured in the User management -> User group configuration page.
Charging mode: Checking it means that the PPPoE charging feature is enabled. Here, the
account expiration notification feature is configured in the Behavior management ->
Electronic notification page.
Date of account opening, date of account disabling: Sets the effective date for the dial-up user
using the account.
Upload rate limit, download rate limit: The maximum upload and download rates of the
PPPOE account (0 means unlimited rate).
Note: Fill in the information to be noted. When Note Information is long, the page displays
only 5 characters, and when you position the mouse pointer over the content of the note, the
page will automatically display all the contents of the note.
Tip:
If the PPPoE account is configured with the upload and download rate, then the account will
no longer match the fine rate limit.
8.3.4 PPPoE user status
Enter the User management ->PPPoE server ->PPPoE user connection status page, on which
http://www.level1.com Page 72
Page 78

Chapter 8 User Management
you can view the account information used; if users use the configured user name to connect to the
PPPoE server, we can see such information of the IP addresses, the user's MAC address, online
time of PPPoE connections, upload/download rates, etc. the PPPoE server assigns to the user in
the list.
Figure 8_13 PPPoE User Status List
Tip:
When the account of the network dial-up user expires, dial-up can be made successfully, and the
user can access to the device, but cannot access the Internet.
8.3.5 Export PPPoE Accounts
http://www.level1.com Page 73
Page 79

Chapter 8 User Management
Figure 8_14 Export PPPoE Accounts
Export account: Click this bLeveloneon to export all PPPoE accounts in the list, including the
user name, password for the account, in the. txt format.
8.3.6 Import PPPOE Accounts
Figure 8_15 Import PPPOE Accounts
Tip:
1. When configuring PPPOE accounts to be imported and bound in batch, its input format is
"Account + password", for example, test 123456, each row can have only one configuration
item entered.
2. In the above input format, there may be one or more spaces between the account and the
password.
http://www.level1.com Page 74
Page 80

Chapter 8 User Management
8.3.7 Instance of PPPoE server configuration
1. Demand: Only the users authenticated by the Intranet can access the Internet.
Now, 3 accounts are configured for intranet users, and their user names are test1, test2, and test3
respectively. Initial passwords are: password1, password2, password3, in which test1, test2 are
separately bound with 10.0.0.1, 10.0.0.2 and the charging feature is enabled (the using period of
the account is from October 1, 2012 to December 31, 2013) and a notification is issued 15 days
prior to account expiration; the maximum number of sessions of test3 is set to 5.
2. Configuration steps:
1) Configure the PPPoE server. Log on to the device, enter the User management ->PPPoE
server page, configure the content as shown in the figure below, and enable the forced PPPoE
authentication and allow users to modify the dial-up password (The password change
message can be given to users by configuring the routine business notification feature).
Figure 8_16 Instance - PPPoE Global Settings
2) Configuration of PPPoE account. Enter the PPPoE account Settings. Click on the <Add
new entry>, configure a PPPoE account, bind the account with the IP address, and enable the
charging feature. The configured content with the user name of test1 is as shown in the figure
below:
http://www.level1.com Page 75
Page 81

Chapter 8 User Management
Figure 8_17 PPPoE account Settings
3) Repeat Step 2, and configure the account with the PPPoE user name as test2. Bind it with
10.0.0.2. Configure the account of test3, and set the maximum number of sessions for its
account to 5.
Figure 8_18 Instance - PPPoE User Status List
4) Configure the account expiration notification feature. Enter the Behavior management->
Electronic notification-> Account expiration notification page, to configure the account
expiration notification feature, here, the "Send days of expiration notification in advance" is
set to 15 days.
5) Create a client on the Intranet user's computer.
http://www.level1.com Page 76
Page 82

Chapter 8 User Management
8.4 WEB authentication
8.4.1 WebAuth Global Settings
Enter the User management->WEB certification page to configure the WEB authentication
feature of the device. WEB Authentication is used to authenticate Intranet users as to having
permission to access the Internet, that is, after enabling this feature, the intranet users cannot
access to the Internet unless passing the WEB authentication.
Figure 8_19 WebAuth Global Settings
Enable WEB authentication: Checking it means that the intranet users cannot access the
Internet unless passing the WEB authentication.
Enable background image: Check it to enable this feature.
Allow users to modify authentication password: Checking it means to allow the WEB
authentication users to modify the authentication password on their own.
Exception address group: After the device enables the forced PPPoE authentication, the users
of the address group can communicate with external network without WEB authentication,
and the address group needs to be configured in the User management -> User group
Settings page.
http://www.level1.com Page 77
Page 83

Chapter 8 User Management
Window title: The title of the custom WEB authentication pop-up window.
Window tip text: Tip texts for custom WEB authentication pop-up window.
Network image link: Enters the network link to the picture, to make this picture as the
background of the WEB authentication pop-up window.
8.4.2 Web Authentication Account List
Figure 8_20 Web Authentication Account List
Figure 8_21 Web Authentication Account List - Add new entry
http://www.level1.com Page 78
Page 84

Chapter 8 User Management
User name: Displays/configures the user name of the WEB authentication user.
Concurrent number: Displays the number of users using the same WEB authentication.
User status: Displays the connection status of the WEB authentication users, including: not
used, in use.
Charging mode: Displaying/checking it means to enable the charging mode.
Account opening/expiry date: Displays/configures the time period for the WEB authenticated
user to use the account.
Total time: Restricts the total time for the WEB authenticated user to use the account. 0
means no limit.
Used time: Displays the time the currently authenticated account used accumulatively.
Description: Displays/configures that described content.
Password: Configures the password of the WEB authentication user.
Maximum number of sessions for the account: Configures the maximum number of sessions
for the account.
Hang up: Clicks this bLeveloneon to hang up the connection to the user.
Add new entry: Click this bLeveloneon to enter the Figure 8_21 page to configure the
information WEB authentication account.
Delete all entries: Click this bLeveloneon to delete all information configured on the page.
Tip:
1. Steps that the WEB authenticated users modify the authentication password:
1) Users open the browser for authentication using the user name, password.
2) After a successful authentication, click to change the password in the dialog box for
successful authentication that opens.
3) On the password change page, enter the user name, old password, new password and
confirming password.
4) Click "Submit" to display "Operation is successful", and the password is successfully
changed.
5) Users can modify their password 5 times a day on their own.
6) The administrator can use the Behavior management -> Electronic notification page to
configure the Routine business notification for informing users of how to modify the
PPPoE dial-up password.
http://www.level1.com Page 79
Page 85

Chapter 8 User Management
2. How the WEB authenticated users to go off line safely
1) Users open the browser for authentication using the user name, password.
2) After successful authentication, the dialog box for successful authentication that opens,
click Go off line safely.
3) Click OK in the web page message dialog box that opens.
8.4.3 WEB Authentication Client Status
Figure 8_22 WEB Authentication Client Status
User name: Displays the user name of the users who are using the WEB authentication.
IP address: Displays the IP address of the users who are using the WEB authentication.
Tip:
The user names and IP addresses in the WEB authentication connection status list are those of the
users who are using WEB authentication.
http://www.level1.com Page 80
Page 86

Chapter 8 User Management
8.5 User Group Settings
In the User management -> User Group Settings page, and click <Add new entry> in the "User
group configuration list", to enter the page as shown in Figure 8_24.
Figure 8_23 User group list
Figure 8_24 User group Settings
Group name: Customizes the group name of the user group.
Group type: It consists of address group and account group. Here, account group refers to the
PPPoE authentication accounts, WEB authentication accounts.
Tip:
The depth of the user group cannot be greater than 2, for instance: Address A contains Address
Group B, and now it is configured with Address Group C, it is not allowed to make it contain
Address Group A.
http://www.level1.com Page 81
Page 87

Chapter 9 App Control
Chapter 9. App Control
The features described in this chapter are include time period, net behavior management, QQ
white list, MSN white list, electronic notifications.
9.1 Schedule Settings
Enter the App Control -> Schedule Settings page, and click "Add new entry" to enter into the
configuration page as shown in Figure 9_2. Time period defines the effective time for related
features, one time period can define the three time units.
Figure 9_1 Schedule list
The meaning of time configuration parameters is described below.
Time period name: Customizes the name of time period.
Effective date of time period: Configures the effective date for this time period.
Time unit: The effective date unit configured in the effective time.
http://www.level1.com Page 82
Page 88

Chapter 9 App Control
Figure 9_2 Schedule Settings
9.2 Application Control
This section describes the net behavior management list and net behavior management
configuration in the App Control -> Application Control page.
http://www.level1.com Page 83
Page 89

Chapter 9 App Control
9.2.1 Application Management List
Enter the Behavior management-> Net behavior management page, to enable the net behavior
management feature in this page, and view the net behavior management information configured
in the list of net behavior management information.
Figure 9_3 Application Management List
Enable net behavior management: Checking it means to enable the net behavior management
feature.
9.2.2 Internet Application Management Settings
Click <Add new entry> on the above image to enter the Net behavior management configuration
page, to manage intranet users' net behavior.
Group name: Customizes the group name for the instances of the net behavior management,
which must be unique.
Select net behavior management object: Fills out the address field or user group on which the
behavior management instance takes effect.
The net behavior management supported by the device: Chat software, P2P software, stock
software, web video, online game, shopping web sites, social networking sites, web games,
http://www.level1.com Page 84
Page 90

Chapter 9 App Control
messages, forums, etc.
Effective time setting: Sets the time when the net behavior management instance takes effect.
Tip:
When a net behavior management feature does not take effect, make sure that this policy library is
up-to-date. In the Behavior management-Policy library page, click <Update> hyperlink to
update the corresponding policy library.
http://www.level1.com Page 85
Page 91

Chapter 9 App Control
Figure 9_4 Internet Application Management Settings
9.2.3 Internet Application Management
1. Demands
In order to control its employees' net behavior, a company prescribes according to their actual
needs, to prohibit QQ, MSN and other chat software, stocks and game software, checking stocks
and game site information, and access to the shopping website during the working time. In the
rest of the time, all operations are opened up.
Here, the users at the management level (address: 192.168.1.5 and 192.168.1.9) are not subject to
any restrictions in net behavior.
Sales and customer service staff, whose addresses are 192.168.1.70-192.168.1.99 and
192.168.1.50 - 192.168.1.69 respectively, must use chat software to communicate with customers
as required by their work.
http://www.level1.com Page 86
Page 92

Chapter 9 App Control
The R & D Department (address: 192.168.1.100-192.168.1.129) prohibits the use of chat software.
The company's working hours are: Monday-Friday, 9 o'clock -18 o'clock.
2. Analysis
From above, 2 net behavior management policies are configured based on the requirements of the
company's net behavior management.
1) Configure the net behavior management policies for sales and customer service staff to
enable the chat software feature. However, other features are disabled.
2) Configure the net behavior management policies for R&D staff by only prohibiting the use of
chat software.
3. Configuration steps
1) Enter the Behavior management-> Net behavior management page, to enter the Net
behavior management configuration page.
2) Configure behavior management policies for sales department, customer service department:
Group name: IM
Starting IP address, ending IP address: 192.168.1.50, 192.168.1.99.
Behavior management: Checks the "Select All" box of stock software, online video, online
games, shopping sites, social networking sites, Web games, mails, forums and others.
Effective time period: Monday to Friday, from 9:00-18:00. Click <Save>.
3) Configure the behavior management policies for the R&D Department:
Group name: yanfa
Starting IP address, ending IP address: 192.168.1.100, 192.168.1.129.
Behavior management: Just checks the "Select All" box of the chat software.
Effective time period: Monday to Friday, from 9:00-18:00. Click <Save>.
4. View the configuration list
http://www.level1.com Page 87
Page 93

Chapter 9 App Control
Figure 9_5 Internet Application Management
Figure 9_6 Internet Application Management (Continued Figure 9_5)
9.3 QQ white list
QQ white list refers to the QQ users who are defined to be allowed to log on after QQ is
http://www.level1.com Page 88
Page 94

Chapter 9 App Control
prohibited in the Net behavior management page.
Enter the App Control-> QQ white list page, after the QQ white list feature is enabled, click "Add
new entry" to add QQ white list users in the QQ white list configuration page.
Figure 9_7 QQ white list
Allow 400/800 Business QQ: Checks to allow 400/800 Business QQ.
Enable QQ white list: Checks to enable the QQ white list feature.
Export account: Click this bLeveloneon to export the QQ accounts in the QQ white list entry.
Import account: Click this bLeveloneon to import QQ to the QQ white list entries.
http://www.level1.com Page 89
Page 95

Chapter 9 App Control
Figure 9_8 Import QQ Accounts
Tip:
The maximum number of QQ numbers supported by this version is 4294967295
9.4 TM Whitelist
Aliwangwang White List refers to the Aliwangwang users allowed to log in after Aliwangwang is
prohibited in the Net behavior management
Enter the App Control -> TM Whitelist page, and after the Aliwangwang white list feature is
enabled, click "Add new entry" to enter into the Aliwangwang white list configuration page to add
Aliwangwang white list users.
http://www.level1.com Page 90
Page 96

Chapter 9 App Control
Figure 9_9 Trademanager Whitelist
Enabled Aliwangwang white list: Checks to enable Aliwangwang white list feature.
9.5 Notification
Enter the App Control -> Notification page to configure routine business notification and account
expiration notification.
Notification is a notice sent by the device to users in the form of Web pages when the Intranet
users access to the website. Upon receipt of the notification, Intranet users can access the
website normally by entering the corresponding address in the browser address bar again.
http://www.level1.com Page 91
Page 97

Chapter 9 App Control
9.5.1 Daily Routine Notification
Figure 9_10 Daily Routine Notification
Enable: Checks to enable the Routine business notification feature.
Notification network segment: Sets the address range of routine business notification, which
can only contain 65535 addresses at maximum.
Notification title, content: Sets the title and content of the routine business notification.
Redirecting time: Redirects to the specified page according to the specified time.
Redirecting URL: Automatically redirects to the specified URL address.
Setting of effective date: Sets the date when the routine business notification takes effect.
http://www.level1.com Page 92
Page 98

Chapter 9 App Control
Effective frequency: Sets the frequency of routine business notification.
Preview page: Click this bLeveloneon to preview the configured notification contents.
Save: After click <Save>, the specified users in the Intranet will receive a routine business
notification sent by the device when it accesses to the web page for the first time with the
effective time period.
Tip:
When the routine business notification only involves the change of "Notification title",
"Notification content", click <Save> and the notification will not take effect.
9.5.2 Account expiration notification
Figure 9_11 Account expiration notification
Enable: Checks to enable the account expiration notification feature.
Days for sending expiration notices in advance: Sets the effective number of days for sending
expiration notification. When this parameter is set to 10, the user will receive the expiration
http://www.level1.com Page 93
Page 99

Chapter 9 App Control
notification sent by the device when it dials up successfully and accesses to the website for
the first time starting from 10 days before the expiration of the account.
Notification title, content: Sets the title and content of the account expiration notification.
Preview page: Click this bLeveloneon to preview the configured notification contents.
Tip:
When the account of the network dial-up user expires, dial-up can be made successfully, and the
user can access to the device, but cannot access the Internet. Meanwhile, it will receive an
expiration notification sent by the device in accessing the website.
9.6 Application Audit
The section describes the net behavior audit feature. Enter the App Control -> Application Audit
-> Log Management page, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 9_12 Log management
Enable web logs: Enables the web log to view the records of Intranet users' access to
webpages in the Behavior audit page. Such as “2012-12-03 15:07:47 srcip=10.0.0.10;
url=www.Levelone.com.cn”, which means that the users whose Intranet IP address is
10.0.0.10 at 15:07 on December 3, 2012 visited www.Levelone.com.cn.
Enable QQ online/offline logs: Enable the QQ online/offline logs to view the online/offline
logs of the Intranet user QQ in the Behavior audit.
Enable MSN online/offline logs: Enable the MSN online/offline logs to view the
online/offline logs of the Intranet user MSN in the Behavior audit.
Enable mail audit logs: Enable the mail audit logs to view the records of Intranet user mails
in the Behavior audit page.
http://www.level1.com Page 94
Page 100

Chapter 9 App Control
Enable behavior-blocking log: Enable the behavior-blocking log to view the user records
filtered by the behavior management PDB.
Figure 9_13 Internet Audit
Note: Net behavior audit can record the latest 400 log information.
9.7 Policy Database
This section describes the App Control - Policy Database page and operating procedures. The
system provides 11 different types of policies at present, including: emails, IM, P2P, STOCK,
online video, online games, shopping websites, social networking sites, web games, forums, etc.
Users can bring the behavior management referencing these policies into force by updating one
policy or all policies.
http://www.level1.com Page 95
 Loading...
Loading...