Page 1
EDKVF9383
.EXz
Global Drive
Montageanleitung
Mounting Instructions
Ä.EXzä
9300 vector 250 ... 400 kW
Instructions de montage
EVF9381 ... EVF9383
Frequenzumrichter
Frequency Inverter
Convertisseur de fréquence
Page 2

Lesen Sie erst diese Anleitung, bevor Sie mit den Arbeiten beginnen!
Beachten Sie die enthaltenen Sicherheitshinweise!
Ausführliche Informationen finden Sie im Systemhandbuch zum Frequenzumrichter
9300 vector.
Read these Instructions before you start working!
Observe the safety instructions given therein!
More detailed information can be found in the System Manual for the 9300 vector
frequency inverter.
Veuillez lire attentivement cette documentation avant toute action !
Les consignes de sécurité doivent impérativement être respectées !
Pour une description complète, consulter le manuel du convertisseur de fréquence
9300 vector.
Page 3
3
45
2
DC rail +
6
DC rail –
7
89:
?
@
;
<
=
>
./
01
X1
X3
LO HI
GNDA1A2A3A4ST1ST25934763
28E1E32
E2E4E5391
X4
X5
7
62
34
33
K32
K31
5
1
X6
X11
X8
5
1
+UGL1 L2 L3 BR1 BR2 U V W-UG+UGL1 L2 L3 BR1 BR2 U V W-UG
1
5
X9
X10
9300vec069
Page 4

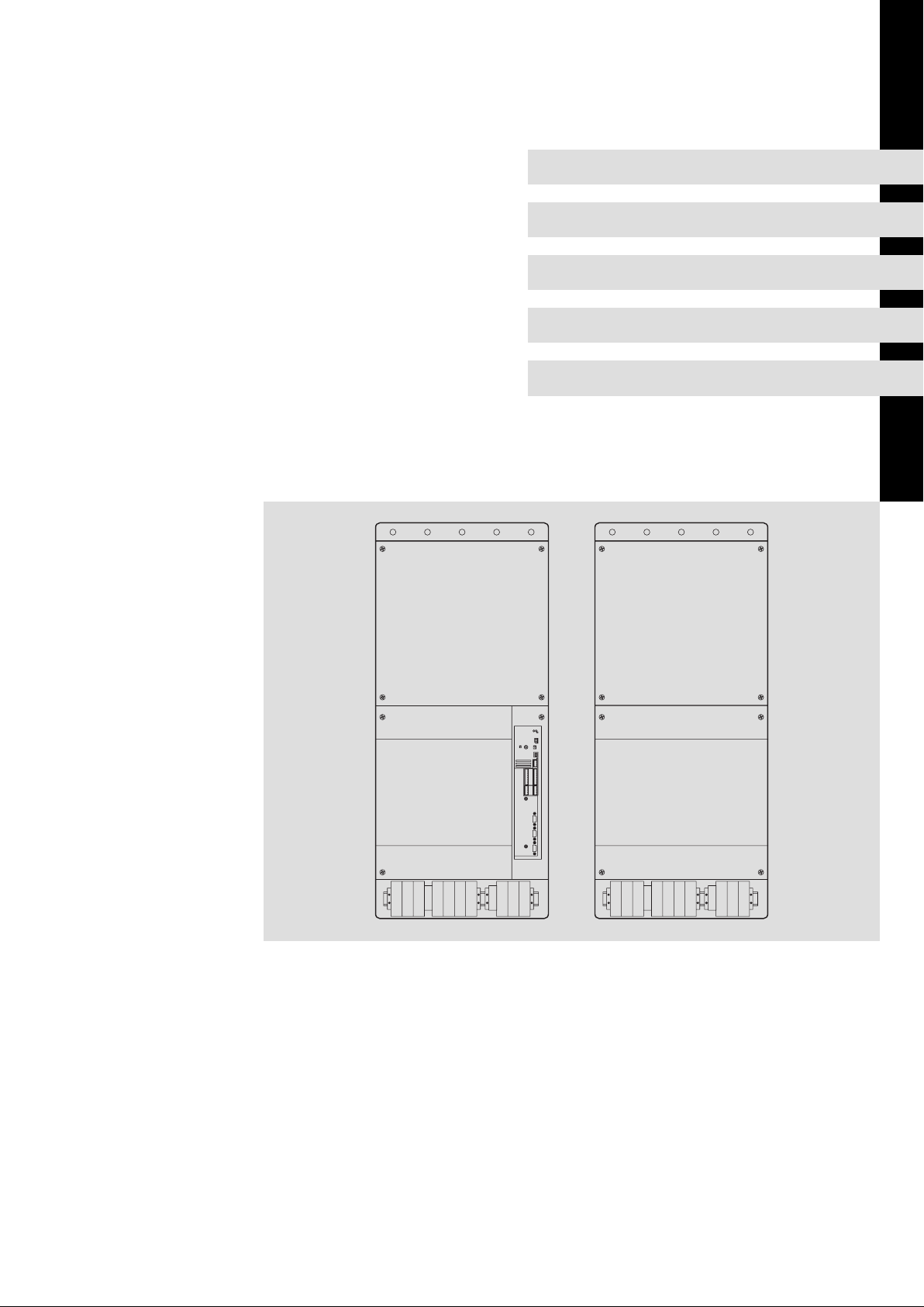
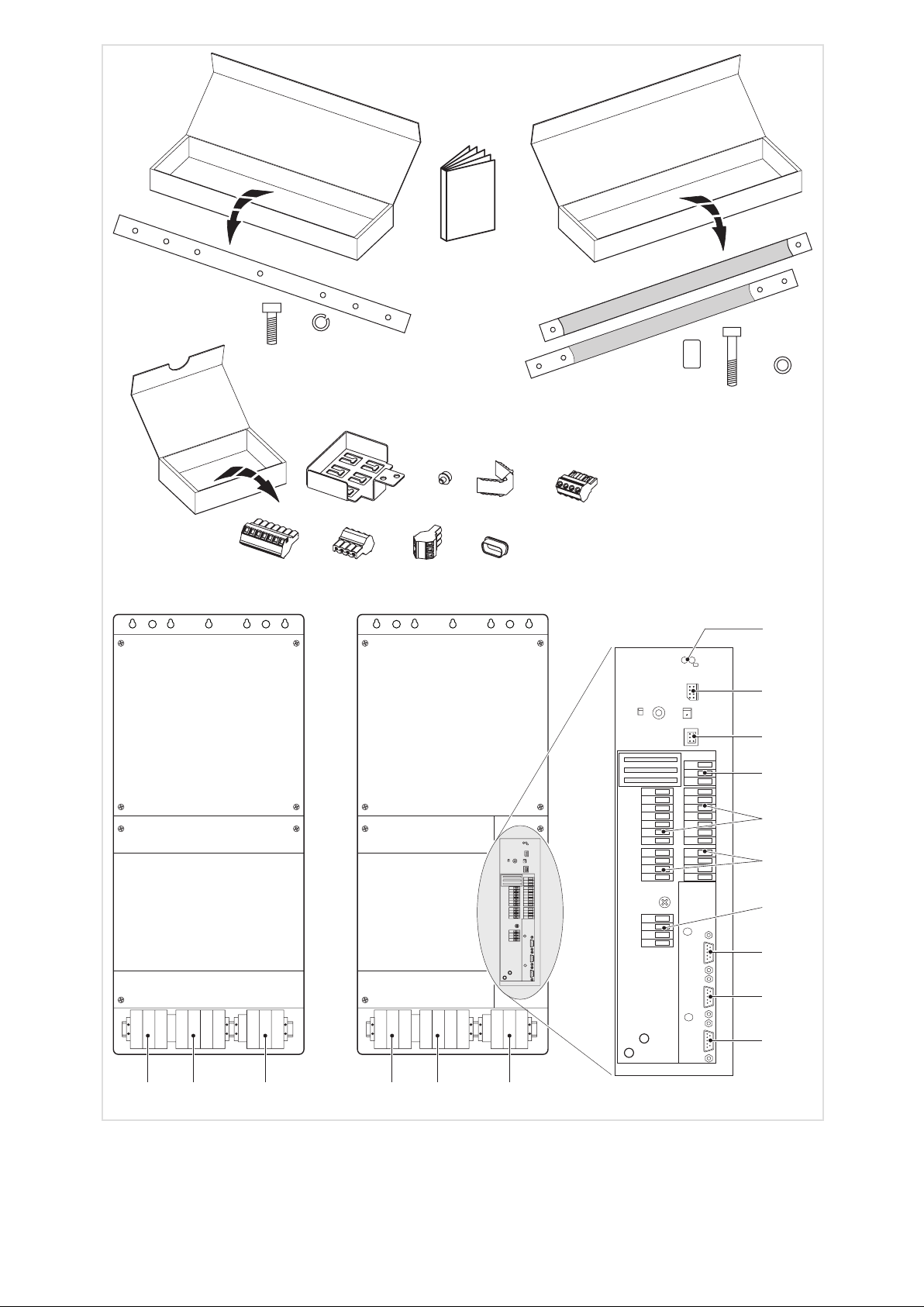
Lieferumfang
Beschreibung Verwendung Anzahl
Frequenzumrichter 9300 vector ˘ Master 1
Frequenzumrichter 9300 vector ˘ Slave 1
Montageanleitung 1
Montageschiene 4
Innensechskantschraube M8 × 25 mm
Federring M8 24
DC−Verbindungsschiene für +U
DC−Verbindungsschiene für −U
Distanzhülse M8
Innensechskantschraube M8 × 45 mm 6
U−Scheibe M8 6
EMV−Schirmblech für geschirmte Steuerleitungen 1
Kreuzschlitzschraube M4 × 12 mm Befestigung EMV−Schirmblech 2
Schirmklammer Anbindung der Leitungsschirme am Schirmblech 3
Klemmenleiste 4−polig Sicherheitsrelais KSR an X11 1 44
Klemmenleiste 7−polig Digitale Eingänge und Ausgänge an X5 2 42
Klemmenleiste 4−polig Analoge Eingänge und Ausgänge an X6 2 42
Klemmenleiste 3−polig Systembus (CAN) an X4 1 50
Schutzabdeckung Schutz für nicht verwendete Sub−D−Buchsen 4
G
G
Befestigung des Antriebsreglers mit der Montageschiene auf der Montageplatte
+UG−Verbindung zwischen Master und Slave 1
−UG−Verbindung zwischen Master und Slave 1
Befestigung der DC−Schienen im Master und
Slave
25
24
29
6
42
Anschlüsse und Schnittstellen
Beschreibung Funktion
Leistungsklemmen
Leistungsklemmen Anschluss an den DC−Zwischenkreis 35
Leistungsklemmen Motoranschluss 38
X1 Steuerschnittstelle Steckplatz für z. B. Keypad
X3 Jumper Einstellung analoges Eingangssignal an X6/1, X6/2 49
X4 Steuerklemmen Systembus (CAN) 50
X5 Steuerklemmen Digitale Eingänge und Ausgänge 42
X6 Steuerklemmen Analoge Eingänge und Ausgänge 42
X8 Sub−D−Buchse Inkrementalgebereingang 52
X9 Sub−D−Buchse
X10 Sub−D−Buchse Leitfrequenzausgang 54
X11 Steuerklemmen Sicherheitsrelais K
Netzanschluss Antriebsregler für 400 V 33
Netzanschluss Antriebsregler für 500 V 34
Inkrementalgebereingang 53
Leitfrequenzeingang 54
SR
Statusanzeigen
Position LED rot LED grün Betriebszustand
aus ein Antriebsregler freigegeben
ein ein Netz eingeschaltet und automatischer Start gesperrt
aus blinkt langsam Antriebsregler gesperrt
aus ein Motordaten−Identifizierung ist aktiv
blinkt schnell aus Unterspannung oder Überspannung
blinkt langsam aus Störung aktiv
0Abb. 0Tab. 0
44
4
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 5

Inhalt i
1 Über diese Dokumentation 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1 Dokumenthistorie 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2 Zielgruppe 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 Informationen zur Gültigkeit 8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4 Verwendete Konventionen 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5 Verwendete Hinweise 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Sicherheitshinweise 11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 Allgemeine Sicherheits− und Anwendungshinweise für Lenze−Antriebsregler 11 . .
2.2 Motor thermisch überwachen 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.1 Beschreibung 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.2 Parametrieren 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Restgefahren 17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Technische Daten 18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 Allgemeine Daten und Einsatzbedingungen 18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Sicherheitsrelais KSR 20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Bemessungsdaten 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3.1 Antriebsregler für 400 V Netzspannung 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3.2 Antriebsregler für 400 V / 500 V Netzspannung 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.4 Abmessungen 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Mechanische Installation 24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1 Bohrungen an der Montageplatte durchführen 24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 Montageschienen an der Montageplatte befestigen 25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3 Antriebsregler auf der Montageplatte befestigen 26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Elektrische Installation 27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1 EMV−gerechte Installation (Aufbau des CE−typischen Antriebssystems) 27 . . . . . . .
5.2 Master und Slave verbinden 29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.1 Wichtige Hinweise 29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.2 Vorbereitende Arbeiten 29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.3 Montage der DC−Verbindungsschienen 30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.4 Anschluss der Steuerleitungen zwischen Master und Slave 31 . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.5 Abschließende Arbeiten 32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3 Netzanschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V Netzspannung 33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4 Versorgungs− und Lüfteranschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V/500V
Netzspannung 33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4.1 Netzanschluss 34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4.2 Anschluss an den DC−Zwischenkreis (+UG, −UG) 35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4.3 Lüfteranschluss 35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
5
Page 6

Inhalti
5.5 Motoranschluss 38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.5.1 Motortemperatur−Überwachung verdrahten 40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6 Steueranschlüsse 42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6.1 Wichtige Hinweise 42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6.2 Mit aktiver Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment" 44 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6.3 Mit deaktivierter Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment" 47 . . . . . . . .
5.6.4 Klemmenbelegung 49 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.7 Systembus (CAN) verdrahten 50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8 Rückführsystem verdrahten 51 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8.1 Wichtige Hinweise 51 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8.2 Inkrementalgeber mit TTL−Pegel an X8 52 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8.3 Inkrementalgeber mit HTL−Pegel an X9 53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.9 Leitfrequenzeingang / Leitfrequenzausgang verdrahten 54 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Abschließende Arbeiten 56 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.1 Installation überprüfen 56 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.2 Inbetriebnahme vorbereiten 57 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 7

1 Über diese Dokumentation
1.1 Dokumenthistorie
Was ist neu / was hat sich geändert?
Materialnummer Version Beschreibung
.EXz 4.0 03/2011 TD23 Überarbeitung: Ergänzungen für Softwarestand 8.1
13219330 3.0 04/2008 TD23/35/32Überarbeitung, Fehlerbereinigung
13146181 2.0 10/2006 TD23 Überarbeitung, Fehlerbereinigung
00487687 1.0 06/2004 TD23 Erstausgabe
Tipp!
Informationen und Hilfsmittel rund um die Lenze−Produkte finden Sie im
Download−Bereich unter
http://www.Lenze.com
Über diese Dokumentation
Dokumenthistorie
eingefügt
1
1.2 Zielgruppe
Diese Dokumentation richtet sich an qualifiziertes Fachpersonal nach IEC 60364.
Qualifiziertes Fachpersonal sind Personen, die für die auszuführenden Tätigkeiten bei der
Aufstellung, Montage, Inbetriebsetzung und dem Betrieb des Produkts über entsprechende Qualifikationen verfügen.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
7
Page 8
1
Über diese Dokumentation
Informationen zur Gültigkeit
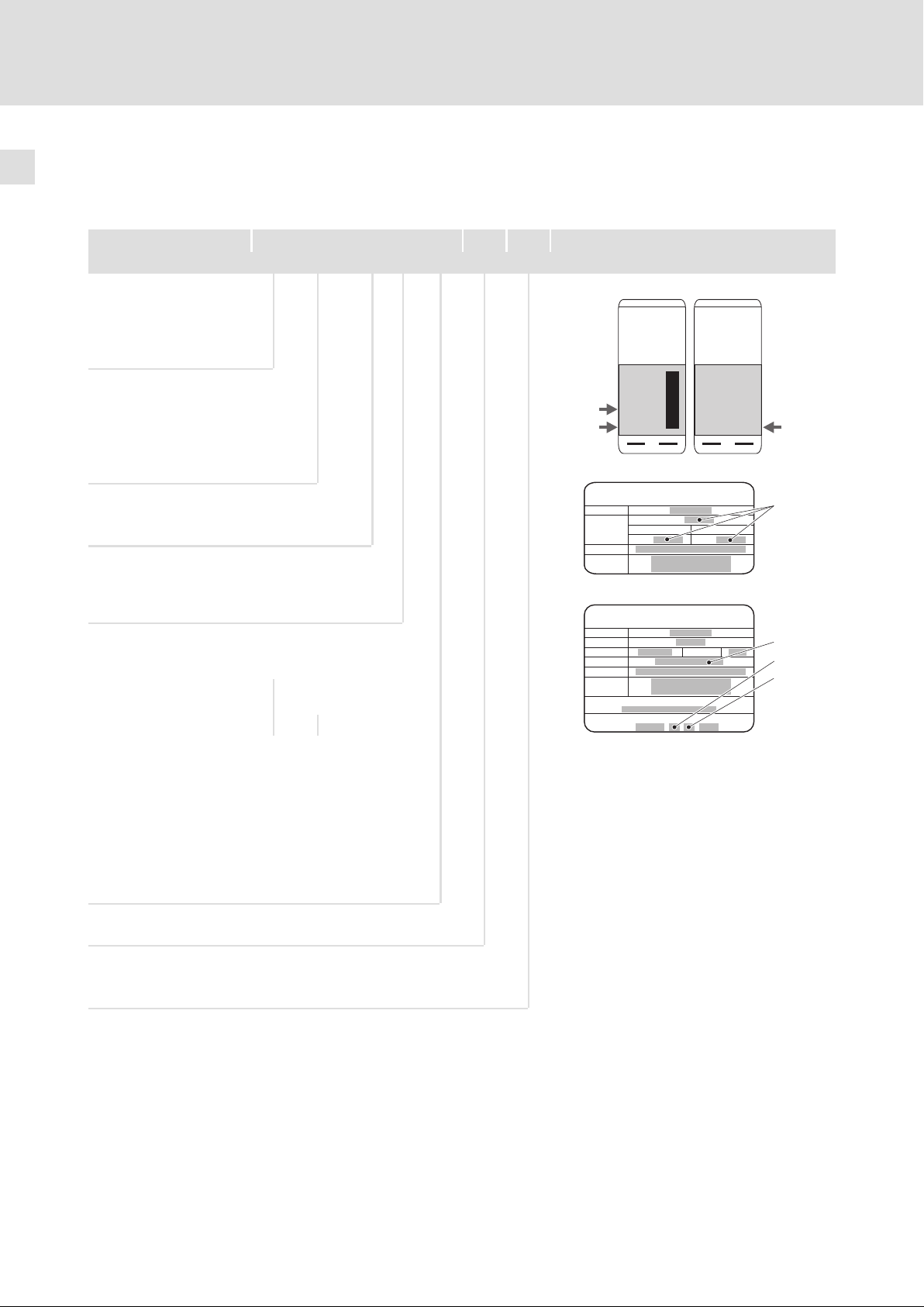
1.3 Informationen zur Gültigkeit
Diese Dokumentation ist gültig für Frequenzumrichter 9300 vector ab dem Gerätestand
EVF 93xx ˘ E V Vxxx 1x 8x
Produktreihe
EVF Frequenzumrichter
EVM: Master von EVF
EVL: Slave von EVF
Typ Nr. / Leistung
400 V 500 V
9381
250 kW
9382
315 kW
9383
400 kW
Bauart
E Einbaugerät
Ausführung
V Vectorgeregelter Frequenzumrichter
X: Slave
Variante Funkentstörfilter A
– 400 V – –
V030 400 V · –
V060 400 V – ·
V110 400 V ··
V210 400 V / 500 V – –
V240 400 V / 500 V · –
V270 400 V / 500 V – ·
V300 400 V / 500 V ··
315 kW
400 kW
500 kW
integriert
Bremstransistor
integriert
Typenschild
EVM... EVL...
0
1
0
L
Inverter
Type:
Input:
Output:
1
L
Inverter
Id.-No.:
Prod.-No.:
Type:
Input:
Output:
0045042000129567000005
33 . 9335VE . 1A . 70 . V030
Hans-Lenze-Strasse1
D-31855Aerzen
Madein EC
EVF
Master Slave
EVM
Hans-Lenze-Strasse1
D-31855Aerzen
Madein EC
Ser.-No.:
33.9335VE.1A.70
EVL
1
Hardwarestand
Softwarestand
– Slave (kein Softwarestand)
8
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 9

Über diese Dokumentation
Verwendete Konventionen
1
1.4 Verwendete Konventionen
Diese Dokumentation verwendet folgende Konventionen zur Unterscheidung verschiedener Arten von Information:
Informationsart Auszeichnung Beispiele/Hinweise
Zahlenschreibweise
Dezimaltrennzeichen sprachabhängig Als Dezimaltrennung werden die für die
Warnhinweise
UL−Warnhinweise
UR−Warnhinweise
Textauszeichnung
Programmname » « PC−Software
Symbole
Seitenverweis Verweis auf eine andere Seite mit zusätzli-
jeweilige Zielsprache üblichen Zeichen verwendet.
Zum Beispiel: 1234.56 oder 1234,56
Werden nur in der englischen Sprache verwendet.
Zum Beispiel: »Engineer«, »Global Drive
Control« (GDC)
chen Informationen
Zum Beispiel: 16 = siehe Seite 16
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
9
Page 10

1
Über diese Dokumentation
Verwendete Hinweise
1.5 Verwendete Hinweise
Um auf Gefahren und wichtige Informationen hinzuweisen, werden in dieser Dokumentation folgende Piktogramme und Signalwörter verwendet:
Sicherheitshinweise
Aufbau der Sicherheitshinweise:
Gefahr!
(kennzeichnet die Art und die Schwere der Gefahr)
Hinweistext
(beschreibt die Gefahr und gibt Hinweise, wie sie vermieden werden kann)
Piktogramm und Signalwort Bedeutung
Gefahr!
Gefahr!
Stop!
Gefahr von Personenschäden durch gefährliche elektrische
Spannung
Hinweis auf eine unmittelbar drohende Gefahr, die den Tod oder
schwere Verletzungen zur Folge haben kann, wenn nicht die
entsprechenden Maßnahmen getroffen werden.
Gefahr von Personenschäden durch eine allgemeine Gefahrenquelle
Hinweis auf eine unmittelbar drohende Gefahr, die den Tod oder
schwere Verletzungen zur Folge haben kann, wenn nicht die
entsprechenden Maßnahmen getroffen werden.
Gefahr von Sachschäden
Hinweis auf eine mögliche Gefahr, die Sachschäden zur Folge
haben kann, wenn nicht die entsprechenden Maßnahmen getroffen werden.
Anwendungshinweise
Piktogramm und Signalwort Bedeutung
Hinweis!
Tipp!
Wichtiger Hinweis für die störungsfreie Funktion
Nützlicher Tipp für die einfache Handhabung
Verweis auf andere Dokumentation
10
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 11

Sicherheitshinweise
Allgemeine Sicherheits− und Anwendungshinweise für Lenze−Antriebsregler
2 Sicherheitshinweise
2.1 Allgemeine Sicherheits− und Anwendungshinweise für Lenze−Antriebsregler
(gemäß Niederspannungsrichtlinie 2006/95/EG)
Zu Ihrer persönlichen Sicherheit
Wenn Sie die folgenden grundlegenden Sicherheitsmaßnahmen missachten, kann dies zu
schweren Personenschäden und Sachschäden führen:
ƒ Das Produkt ausschließlich bestimmungsgemäß verwenden.
ƒ Das Produkt niemals trotz erkennbarer Schäden in Betrieb nehmen.
ƒ Das Produkt niemals unvollständig montiert in Betrieb nehmen.
ƒ Keine technischen Änderungen am Produkt vornehmen.
ƒ Nur das für das Produkt zugelassene Zubehör verwenden.
2
ƒ Nur Original−Ersatzteile des Herstellers verwenden.
ƒ Alle am Einsatzort geltenden Unfallverhütungsvorschriften, Richtlinien und Gesetze
beachten.
ƒ Nur qualifiziertes Fachpersonal die Arbeiten zum Transport, zur Installation, zur
Inbetriebnahme und zur Instandhaltung ausführen lassen.
– IEC 364 bzw. CENELEC HD 384 oder DIN VDE 0100 und IEC−Report 664 oder
DIN VDE 0110 und nationale Unfallverhütungsvorschriften beachten.
– Qualifiziertes Fachpersonal im Sinne dieser grundsätzlichen Sicherheitshinweise
sind Personen, die mit Aufstellung, Montage, Inbetriebsetzung und Betrieb des
Produkts vertraut sind und die über die ihrer Tätigkeit entsprechenden
Qualifikationen verfügen.
ƒ Alle Vorgaben dieser Dokumentation beachten.
– Dies ist Voraussetzung für einen sicheren und störungsfreien Betrieb sowie für das
Erreichen der angegebenen Produkteigenschaften.
– Die in dieser Dokumentation dargestellten verfahrenstechnischen Hinweise und
Schaltungsausschnitte sind Vorschläge, deren Übertragbarkeit auf die jeweilige
Anwendung überprüft werden muss. Für die Eignung der angegebenen Verfahren
und Schaltungsvorschläge übernimmt Lenze Automation GmbH keine Gewähr.
ƒ Lenze−Antriebsregler (Frequenzumrichter, Servo−Umrichter, Stromrichter) und
zugehörige Komponenten können während des Betriebs − ihrer Schutzart
entsprechend − spannungsführende, auch bewegliche oder rotierende Teile haben.
Oberflächen können heiß sein.
– Bei unzulässigem Entfernen der erforderlichen Abdeckung, bei unsachgemäßem
Einsatz, bei falscher Installation oder Bedienung besteht die Gefahr von schweren
Personen− oder Sachschäden.
– Weitere Informationen entnehmen Sie der Dokumentation.
ƒ Im Antriebsregler treten hohe Energien auf. Deshalb bei Arbeiten am Antriebsregler
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
unter Spannung immer eine persönliche Schutzausrüstung tragen (Körperschutz,
Kopfschutz, Augenschutz, Gehörschutz, Handschutz).
11
Page 12

2
Sicherheitshinweise
Allgemeine Sicherheits− und Anwendungshinweise für Lenze−Antriebsregler
Bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung
Antriebsregler sind Komponenten, die zum Einbau in elektrische Anlagen oder Maschinen
bestimmt sind. Sie sind keine Haushaltsgeräte, sondern als Komponenten ausschließlich
für die Verwendung zur gewerblichen Nutzung bzw. professionellen Nutzung im Sinne der
EN 61000−3−2 bestimmt.
Bei Einbau der Antriebsregler in Maschinen ist die Inbetriebnahme (d. h. die Aufnahme des
bestimmungsgemäßen Betriebs) solange untersagt, bis festgestellt wurde, dass die Maschine den Bestimmungen der EG−Richtlinie 2006/42/EG (Maschinenrichtlinie) entspricht; EN 60204 beachten.
Die Inbetriebnahme (d. h. die Aufnahme des bestimmungsgemäßen Betriebs) ist nur bei
Einhaltung der EMV−Richtlinie (2004/108/EG) erlaubt.
Die Antriebsregler erfüllen die Anforderungen der Niederspannungsrichtlinie
2006/95/EG. Die harmonisierte Norm EN 61800−5−1 wird für die Antriebsregler angewendet.
Die technischen Daten und die Angaben zu Anschlussbedingungen entnehmen Sie dem
Leistungsschild und der Dokumentation. Halten Sie diese unbedingt ein.
Warnung: Die Antriebsregler sind Produkte, die nach EN 61800−3 in Antriebssysteme der
Kategorie C2 eingesetzt werden können. Diese Produkte können im Wohnbereich Funkstörungen verursachen. In diesem Fall kann es für den Betreiber erforderlich sein, entsprechende Maßnahmen durchzuführen.
Transport, Einlagerung
Beachten Sie die Hinweise für Transport, Lagerung und sachgemäße Handhabung.
Halten Sie die klimatischen Bedingungen gemäß den technischen Daten ein.
Aufstellung
Sie müssen die Antriebsregler nach den Vorschriften der zugehörigen Dokumentation aufstellen und kühlen.
Die Umgebungsluft darf den Verschmutzungsgrad 2 nach EN 61800−5−1 nicht überschreiten.
Sorgen Sie für sorgfältige Handhabung und vermeiden Sie mechanische Überlastung. Verbiegen Sie bei Transport und Handhabung weder Bauelemente noch ändern Sie Isolationsabstände. Berühren Sie keine elektronischen Bauelemente und Kontakte.
Antriebsregler enthalten elektrostatisch gefährdete Bauelemente, die Sie durch unsachgemäße Handhabung leicht beschädigen können. Beschädigen oder zerstören Sie keine
elektrischen Komponenten, da Sie dadurch Ihre Gesundheit gefährden können!
12
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 13

Sicherheitshinweise
Allgemeine Sicherheits− und Anwendungshinweise für Lenze−Antriebsregler
Elektrischer Anschluss
Beachten Sie bei Arbeiten an unter Spannung stehenden Antriebsreglern die geltenden
nationalen Unfallverhütungsvorschriften (z. B. VBG 4).
Führen Sie die elektrische Installation nach den einschlägigen Vorschriften durch (z. B. Leitungsquerschnitte, Absicherungen, Schutzleiteranbindung). Zusätzliche Hinweise enthält die Dokumentation.
Die Dokumentation enthält Hinweise für die EMV−gerechte Installation (Schirmung, Erdung, Anordnung von Filtern und Verlegung der Leitungen). Beachten Sie diese Hinweise
ebenso bei CE−gekennzeichneten Antriebsreglern. Der Hersteller der Anlage oder Maschine ist verantwortlich für die Einhaltung der im Zusammenhang mit der EMV−Gesetzgebung geforderten Grenzwerte. Um die am Einbauort geltenden Grenzwerte für Funkstöraussendungen einzuhalten, müssen Sie die Antriebsregler in Gehäuse
(z. B. Schaltschränke) einbauen. Die Gehäuse müssen einen EMV−gerechten Aufbau ermöglichen. Achten Sie besonders darauf, dass z. B. Schaltschranktüren möglichst umlaufend metallisch mit dem Gehäuse verbunden sind. Öffnungen oder Durchbrüche durch
das Gehäuse auf ein Minimum reduzieren.
Lenze−Antriebsregler können einen Gleichstrom im Schutzleiter verursachen. Wird für den
Schutz bei einer direkten oder indirekten Berührung an einem 3−phasig versorgten Antriebsregler ein Differenzstromgerät (RCD) verwendet, ist auf der Stromversorgungsseite
des Antriebsreglers nur ein Differenzstromgerät (RCD) vom Typ B zulässig. Wird der Antriebsregler 1−phasig versorgt, ist auch ein Differenzstromgerät (RCD) vom Typ A zulässig.
Neben der Verwendung eines Differenzstromgerätes (RCD) können auch andere Schutzmaßnahmen angewendet werden, wie z. B. Trennung von der Umgebung durch doppelte
oder verstärkte Isolierung oder Trennung vom Versorgungsnetz durch einen Transformator.
2
Betrieb
Sie müssen Anlagen mit eingebauten Antriebsreglern ggf. mit zusätzlichen Überwachungs− und Schutzeinrichtungen gemäß den jeweils gültigen Sicherheitsbestimmungen
ausrüsten (z. B. Gesetz über technische Arbeitsmittel, Unfallverhütungsvorschriften). Sie
dürfen die Antriebsregler an Ihre Anwendung anpassen. Beachten Sie dazu die Hinweise
in der Dokumentation.
Nachdem der Antriebsregler von der Versorgungsspannung getrennt ist, dürfen Sie spannungsführende Geräteteile und Leistungsanschlüsse nicht sofort berühren, weil Kondensatoren aufgeladen sein können. Beachten Sie dazu die entsprechenden Hinweisschilder
auf dem Antriebsregler.
Halten Sie während des Betriebs alle Schutzabdeckungen und Türen geschlossen.
Hinweis für UL−approbierte Anlagen mit eingebauten Antriebsreglern: UL warnings sind
Hinweise, die nur für UL−Anlagen gelten. Die Dokumentation enthält spezielle Hinweise zu
UL.
Sicherheitsfunktionen
Bestimmte Varianten der Antriebsregler unterstützen Sicherheitsfunktionen (z. B. "Sicher
abgeschaltetes Moment", ehem. "Sicherer Halt") nach den Anforderungen der EG−Richtlinie "Maschinen" 2006/42/EG. Beachten Sie unbedingt die Hinweise in der Dokumentation zur integrierten Sicherheitstechnik.
Wartung und Instandhaltung
Die Antriebsregler sind wartungsfrei, wenn die vorgeschriebenen Einsatzbedingungen
eingehalten werden.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
13
Page 14

2
Sicherheitshinweise
Allgemeine Sicherheits− und Anwendungshinweise für Lenze−Antriebsregler
Entsorgung
Metalle und Kunststoffe zur Wiederverwertung geben. Bestückte Leiterplatten fachgerecht entsorgen.
Beachten Sie unbedingt die produktspezifischen Sicherheits− und Anwendungshinweise
in dieser Anleitung!
14
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 15

2.2 Motor thermisch überwachen
2.2.1 Beschreibung
Hinweis!
Ab Softwarestand 8.1 verfügen die Antriebsregler 9300 vector über eine
2
I
xt−Funktion, um den angeschlossenen Motor sensorlos thermisch zu
überwachen.
ƒ Die I
ƒ Die berechnete Motorauslastung wird beim Netzschalten gespeichert.
ƒ Die I
2
xt−Überwachung basiert auf einem mathematischen Modell, das aus
den erfassten Motorströmen eine thermische Motorauslastung berechnet.
2
xt−Überwachung ist trotzdem kein Motorvollschutz, da andere
Einflüsse auf die Motorauslastung nicht erfasst werden können, wie
veränderte Kühlungsbedingungen (z. B. Kühlluftstrom unterbrochen oder zu
warm).
Sicherheitshinweise
Motor thermisch überwachen
Beschreibung
2
2
× t−Belastung des Motors wird vom Antriebsregler kontinuierlich berechnet und in
Die I
C0066 angezeigt.
2
Die I
x t−Überwachung ist so ausgelegt, dass bei einem Motor mit einer thermischen Mo-
tor−Zeitkonstante von 5 min, einem Motorstrom von 1,5 x I
und einer Auslöseschwelle
r
von 100 % die Überwachung nach 179 s auslöst.
Durch zwei einstellbare Auslöseschwellen können Sie unterschiedliche Reaktionen festlegen.
ƒ Einstellbare Reaktion OC8 (TRIP, Warnung, Aus).
– Die Reaktion wird in C0606 eingestellt.
– Die Auslöseschwelle wird in C0127 eingestellt.
– Die Reaktion OC8 kann beispielsweise für eine Vorwarnung genutzt werden.
ƒ Feste Reaktion OC6−TRIP.
– Die Auslöseschwelle wird in C0120 eingestellt.
Verhalten der I2 x t−Überwachung Bedingung
Die I2 x t−Überwachung wird deaktiviert.
Es wird C0066 = 0 % und
MCTRL−LOAD−I2XT = 0,00 % gesetzt.
Die I2 x t−Überwachung wird angehalten.
Der aktuelle Wert in C0066 und am Ausgang MCTRL−
LOAD−I2XT wird eingefroren.
Die I2 x t−Überwachung ist deaktiviert.
Die Motorauslastung wird in C0066 angezeigt.
Bei C0120 = 0 % und C0127 = 0 % die Reglersperre setzen.
Bei C0120 = 0 % und C0127 = 0 % die Reglerfreigabe
erteilen.
C0606 = 3 (Off) und C0127 > 0 % setzen.
Hinweis!
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Eine Fehlermeldung OC6 oder OC8 lässt sich erst zurücksetzen, wenn die
I2 × t−Belastung die eingestellte Auslöseschwelle um 5 % unterschritten hat.
15
Page 16

2
Sicherheitshinweise
Motor thermisch überwachen
Parametrieren
2.2.2 Parametrieren
Parametrierung
Codestelle Bedeutung Wertebereich Lenze−Einstellung
C0066 Anzeige der I2xt−Auslastung des Motors 0 ... 250 % −
C0120 Schwelle: Auslösung Fehler "OC6" 0 ... 120 % 0 %
C0127 Schwelle: Auslösung Fehler "OC8" 0 ... 120 % 0 %
C0128 Thermische Zeitkonstante des Motors 0.1 ... 50.0 min 5.0 min
C0606 Reaktion auf Fehler "OC8" Trip, Warnung, Off Warnung
Auslösezeit berechnen
ȡ
t +*(C0128) @ ln
ȧ
Ȣ
ƒ Die thermische Belastungsfähigkeit des Motors wird durch die thermische
1 *
ǒ
I
M
I
r
y ) 1
Ǔ
2
@ 100
ȣ
ȧ
Ȥ
IMAktueller Motorstrom
I
Motor−Bemessungsstrom
r
y C0120 oder C0127
Motor−Zeitkonstante (C0128) ausgedrückt. Entnehmen Sie den Wert den
Bemessungsdaten des Motors oder fragen Sie den Hersteller des Motors.
Auslösezeit im Diagramm ablesen
Diagramm zur Ermittlung der Auslösezeiten bei einem Motor mit einer thermischen Motor−Zeitkonstante von 5 min:
2
I t [%]
120
100
50
Abb. 2−1 I2 × t−Überwachung: Auslösezeiten bei unterschiedlichen Motorströmen und Auslöseschwellen
I =3×I
mot r
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
I =2×I
mot r
Imot Motorstrom
Motor−Bemessungsstrom
I
r
2
I
tI2t−Belastung
t Zeit
I =1.5×I
mot r
I=1×I
mot r
1000
t [s]
9300std105
16
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 17

2.3 Restgefahren
Personenschutz
ƒ Überprüfen Sie vor Arbeiten am Antriebsregler, ob alle Leistungsklemmen
spannungslos sind:
– Nach dem Netzabschalten führen die Leistungsklemmen U, V, W, +U
BR2 und 101 ... 104 noch mindestens 5 Minuten gefährliche Spannung.
– Bei gestopptem Motor führen die Leistungsklemmen L1, L2, L3, U, V, W, +U
BR1, BR2 und 101 ... 104 gefährliche Spannung.
ƒ Der Ableitstrom gegen Erde (PE) ist >3,5 mA. Nach EN 61800−5−1 ist eine
Festinstallation erforderlich.
ƒ Die Betriebstemperatur des Kühlkörpers am Antriebsregler ist > 80 °C:
– Berührung mit dem Kühlkörper führt zu Verbrennungen.
ƒ Während des Parametersatztransfers können die Steuerklemmen des
Antriebsreglers undefinierte Zustände annehmen.
– Deshalb unbedingt vor dem Transfer die Stecker X5 und X6 abziehen. Dadurch ist
sichergestellt, dass der Antriebsregler gesperrt ist, und alle Steuerklemmen den
fest definierten Zustand LOW" haben.
Sicherheitshinweise
Restgefahren
, −UG, BR1,
G
G
2
, −UG,
Geräteschutz
ƒ Häufiges Netzschalten (z. B. Tipp−Betrieb über Netzschütz) kann die
Eingangsstrombegrenzung des Antriebsreglers überlasten und zerstören:
– Deshalb müssen zwischen zwei Einschaltvorgängen mindestens 5 Minuten
vergehen.
– Verwenden Sie bei häufigen sicherheitsbedingten Abschaltungen die
Sicherheitsfunktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment" (STO).
Motorschutz
ƒ Bei bestimmten Einstellungen am Antriebsregler kann der angeschlossene Motor
überhitzt werden:
– Z. B. längerer Betrieb der Gleichstrombremse.
– Längerer Betrieb eigenbelüfteter Motoren bei kleinen Drehzahlen.
Schutz der Maschine/Anlage
ƒ Antriebe können gefährliche Überdrehzahlen erreichen (z. B. Einstellung hoher
Ausgangsfrequenzen bei dafür ungeeigneten Motoren und Maschinen):
– Die Antriebsregler bieten keinen Schutz gegen solche Betriebsbedingungen. Setzen
Sie dafür zusätzliche Komponenten ein.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
17
Page 18

3
Technische Daten
Allgemeine Daten und Einsatzbedingungen
3 Technische Daten
3.1 Allgemeine Daten und Einsatzbedingungen
Allgemeine Daten
Konformität und Approbation
Konformität
CE 2006/95/EG Niederspannungsrichtlinie
Personenschutz und Geräteschutz
Schutzart
Erdableitstrom IEC/EN 61800−5−1 > 3.5 mA Bestimmungen und Sicherheits-
Isolierung von Steuerschaltkreisen
Isolationsfestigkeit IEC/EN 61800−5−1
Schutzmaßnahmen Gegen Kurzschluss, Erdschluss (erdschlussfest im Betrieb,
EN 60529
NEMA 250 Berührschutz nach Typ 1
IEC/EN 61800−5−1 Sichere Trennung vom Netz durch doppelte (verstärkte) Iso-
IP20
lierung für die Klemmen X1 und X5.
Basisisolierung (einfache Trennstrecke) für die Klemmen X3,
X4, X6, X8, X9, X10 und X11.
< 2000 m Aufstellhöhe: Überspannungskategorie III
> 2000 m Aufstellhöhe: Überspannungskategorie II
eingeschränkt erdschlussfest beim Netzeinschalten), Überspannung, Kippen des Motors, Motor−Übertemperatur (Eingang für PTC oder Thermokontakt)
hinweise beachten!
EMV
Störaussendung EN 61800−3
Störfestigkeit IEC/EN 61800−3 Kategorie C3
Leitungsgeführt, bis 50 m Motorleitungslänge mit Funkentstörfilter: Kategorie C2.
Strahlung, mit Funkentstörfilter und Einbau im Schaltschrank: Kategorie C2
18
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 19
Technische Daten
Allgemeine Daten und Einsatzbedingungen
Einsatzbedingungen
Umgebungsbedingungen
Klimatisch
Lagerung
Transport IEC/EN 60721−3−2 2K3 (−25 ... +70 °C)
Betrieb IEC/EN 60721−3−3 3K3 (0 ... +50 °C)
Verschmutzung EN 61800−5−1 Verschmutzungsgrad 2
Aufstellhöhe < 4000 m üNN
Interner Lüfter 975 m3/h Volumenstrom je Gerät
Mechanisch
Rüttelfestigkeit EN 61800−5−1
Elektrisch
Netzanschluss
Netzsystem
TT, TN
(mit geerdetem
Sternpunkt)
DC−Verbundbetrieb Möglich bei den Varianten V210, V240, V270, V300
Motoranschluss
Länge der Motorleitung
Geschirmt 100 m
Ungeschirmt 200 m
IEC/EN 60721−3−1
1K3 (−20 ... +60 °C) < 6 Monate
1K3 (−20 ... +40 °C) > 6 Monate
> 2 Jahre: Zwischenkreis−Kondensatoren formieren
> +40 °C den Ausgangs−Bemessungsstrom um 2,5 %/°C reduzieren.
> 1000 m üNN den Ausgangs−Bemessungsstrom um
5 %/ 1000 m reduzieren.
Betrieb uneingeschränkt erlaubt.
Bei Netz−Bemessungsspannung und Schaltfrequenz £ 2 kHz
ohne zusätzliche Ausgangsfilter.
Müssen EMV−Bedingungen eingehalten werden, können sich
die zulässigen Leitungslängen ändern.
3
Montagebedingungen
Einbauort
Einbaulage Vertikal
Einbaufreiräume
Abmessungen
Gewichte
Im Schaltschrank
24
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
19
Page 20
3
Technische Daten
Sicherheitsrelais KSR
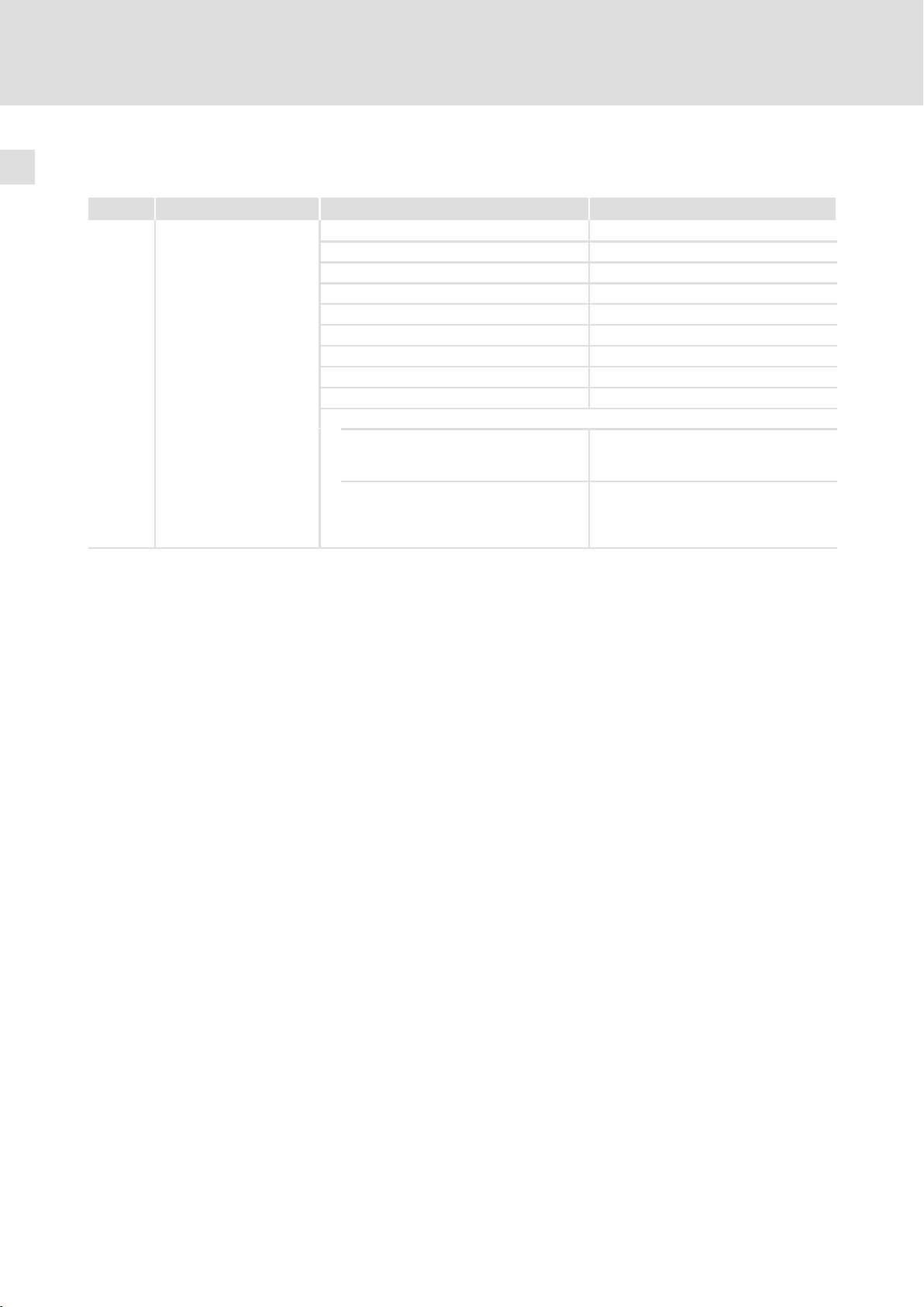
3.2 Sicherheitsrelais K
Klemme Beschreibung Bereich Werte
X11/K32
X11/K31
X11/33
X11/34
Sicherheitsrelais K
1. Abschaltpfad
SR
SR
Spulenspannung bei +20 °C DC 24 V (20 ... 30 V)
Spulenwiderstand bei +20 °C 823 W ±10 %
Bemessungsleistung der Spule ca. 700 mW
Max. Schaltspannung AC 250 V, DC 250 V (0,45 A)
Max. Schaltleistung AC 1500 VA
Max. Schaltstrom (ohmsche Last) AC 6 A (250 V), DC 6 A (50 V)
Empfohlene Minimallast > 50 mW
Max. Schalthäufigkeit 6 Schaltungen pro Minute
Mechanische Lebensdauer 107 Schaltspiele
Elektrische Lebensdauer
bei AC 250 V
(ohmsche Last)
bei DC 24 V
(ohmsche Last)
105 Schaltspiele bei 6 A
6
10
7
10
6 × 103 Schaltspiele bei 6 A
6
10
1,5 × 10
7
10
Schaltspiele bei 1 A
Schaltspiele bei 0,25 A
Schaltspiele bei 3 A
6
Schaltspiele bei 1 A
Schaltspiele bei 0,1 A
20
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 21

Technische Daten
Bemessungsdaten
Antriebsregler für 400 V Netzspannung
3
3.3 Bemessungsdaten
3.3.1 Antriebsregler für 400 V Netzspannung
Typ Leistung Netzspannung Netzstrom Ausgangsstrom
EVF9381−EV
EVF9381−EVV030
EVF9381−EVV060
EVF9381−EVV110
EVF9382−EV
EVF9382−EVV030
EVF9382−EVV060
EVF9382−EVV110
EVF9383−EV
EVF9383−EVV030
EVF9383−EVV060
EVF9383−EVV110
I
N
250 kW
315 kW 570 A 600 A 900 A 320 kg 350 kg
400 kW 713 A 750 A 1125 A 400 kg 430 kg
Gewicht ohne Funkentstörfilter A
Gewicht mit integriertem Funkentstörfilter A
1)
bei Netz−Bemessungsspannung und Schaltfrequenz 2 kHz
3/PE AC 400 V
340 V − 0 % ... 456 V + 0 %
45 Hz − 0 % ... 65 Hz + 0 %
475 A 500 A 750 A 320 kg 350 kg
I
max
1)
(60 s)
Gewicht
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
21
Page 22
3
Technische Daten
Bemessungsdaten
Antriebsregler für 400 V / 500 V Netzspannung
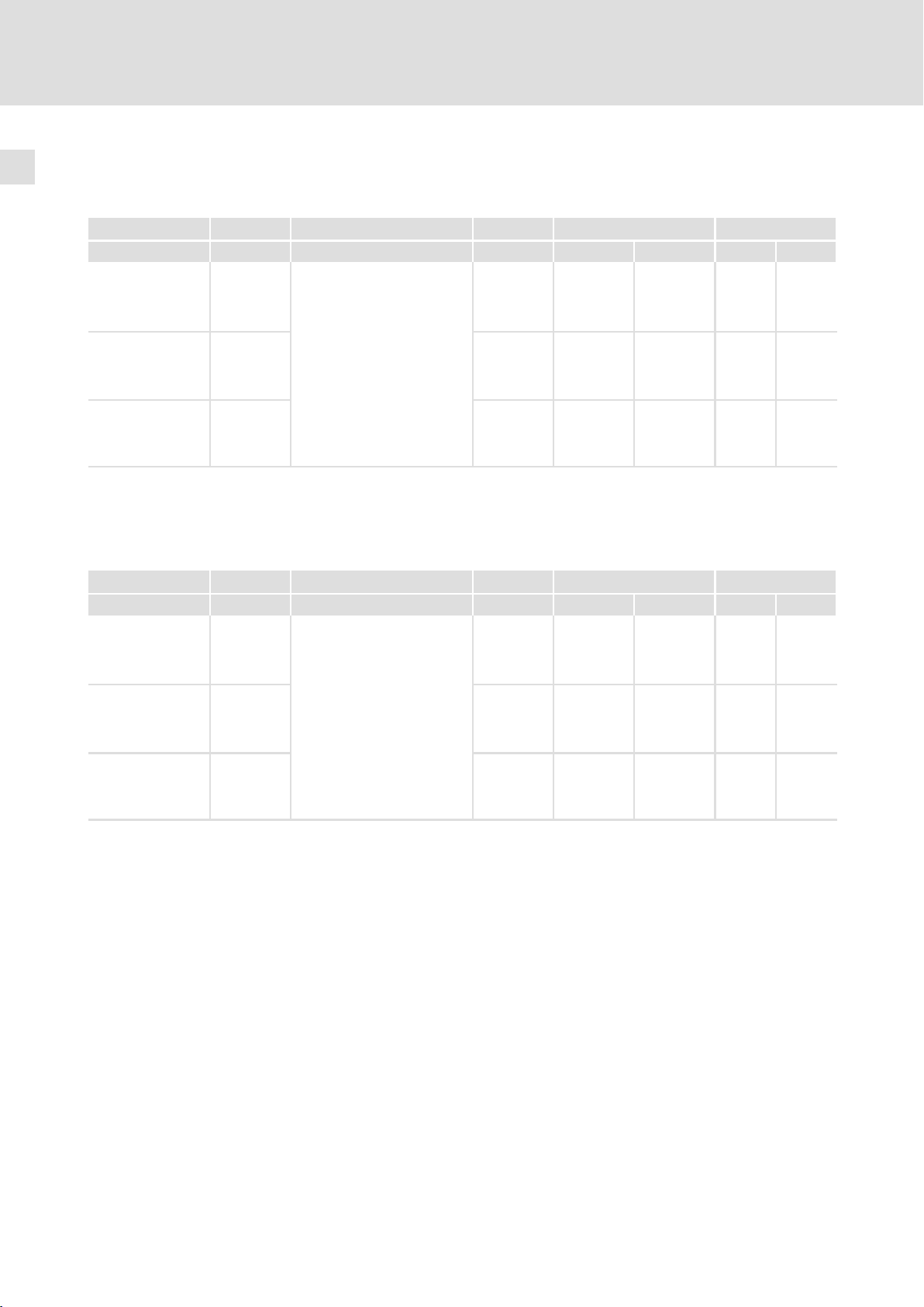
3.3.2 Antriebsregler für 400 V / 500 V Netzspannung
Bemessungsdaten bei 400 V Netzspannung
Typ Leistung Netzspannung Netzstrom Ausgangsstrom
I
N
EVF9381−EVV210
EVF9381−EVV240
EVF9381−EVV270
EVF9381−EVV300
EVF9382−EVV210
EVF9382−EVV240
EVF9382−EVV270
EVF9382−EVV300
EVF9383−EVV210
EVF9383−EVV240
EVF9383−EVV270
EVF9383−EVV300
250 kW
3/PE AC 400 V
340 V − 0 % ... 577 V + 0 %
315 kW 570 A 600 A 900 A 320 kg 350 kg
400 kW 713 A 750 A 1125 A 400 kg 430 kg
45 Hz − 0 % ... 65 Hz + 0 %
alternativ:
DC 565 V
DC 480 V − 0 % ... 800 V + 0 %
Gewicht ohne Funkentstörfilter A
Gewicht mit integriertem Funkentstörfilter A
1)
bei Netz−Bemessungsspannung und Schaltfrequenz 2 kHz
475 A 500A 750 A 320 kg 350 kg
Bemessungsdaten bei 500 V Netzspannung
Typ Leistung Netzspannung Netzstrom Ausgangsstrom
I
N
EVF9381−EVV210
EVF9381−EVV240
EVF9381−EVV270
EVF9381−EVV300
EVF9382−EVV210
EVF9382−EVV240
EVF9382−EVV270
EVF9382−EVV300
EVF9383−EVV210
EVF9383−EVV240
EVF9383−EVV270
EVF9383−EVV300
315 kW
3/PE AC 500 V
340 V − 0 % ... 577 V + 0 %
45 Hz − 0 % ... 65 Hz + 0 %
400 kW 570 A 600 A 900 A 320 kg 350 kg
alternativ:
DC 705 V
DC 480 V − 0 % ... 800 V + 0 %
500 kW 713 A 750 A 1125 A 400 kg 430 kg
475 A 500 A 750 A 320 kg 350 kg
1)
I
(60 s)
max
1)
I
(60 s)
max
Gewicht
Gewicht
22
Gewicht ohne Funkentstörfilter A
Gewicht mit integriertem Funkentstörfilter A
1)
bei Netz−Bemessungsspannung und Schaltfrequenz 2 kHz
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 23
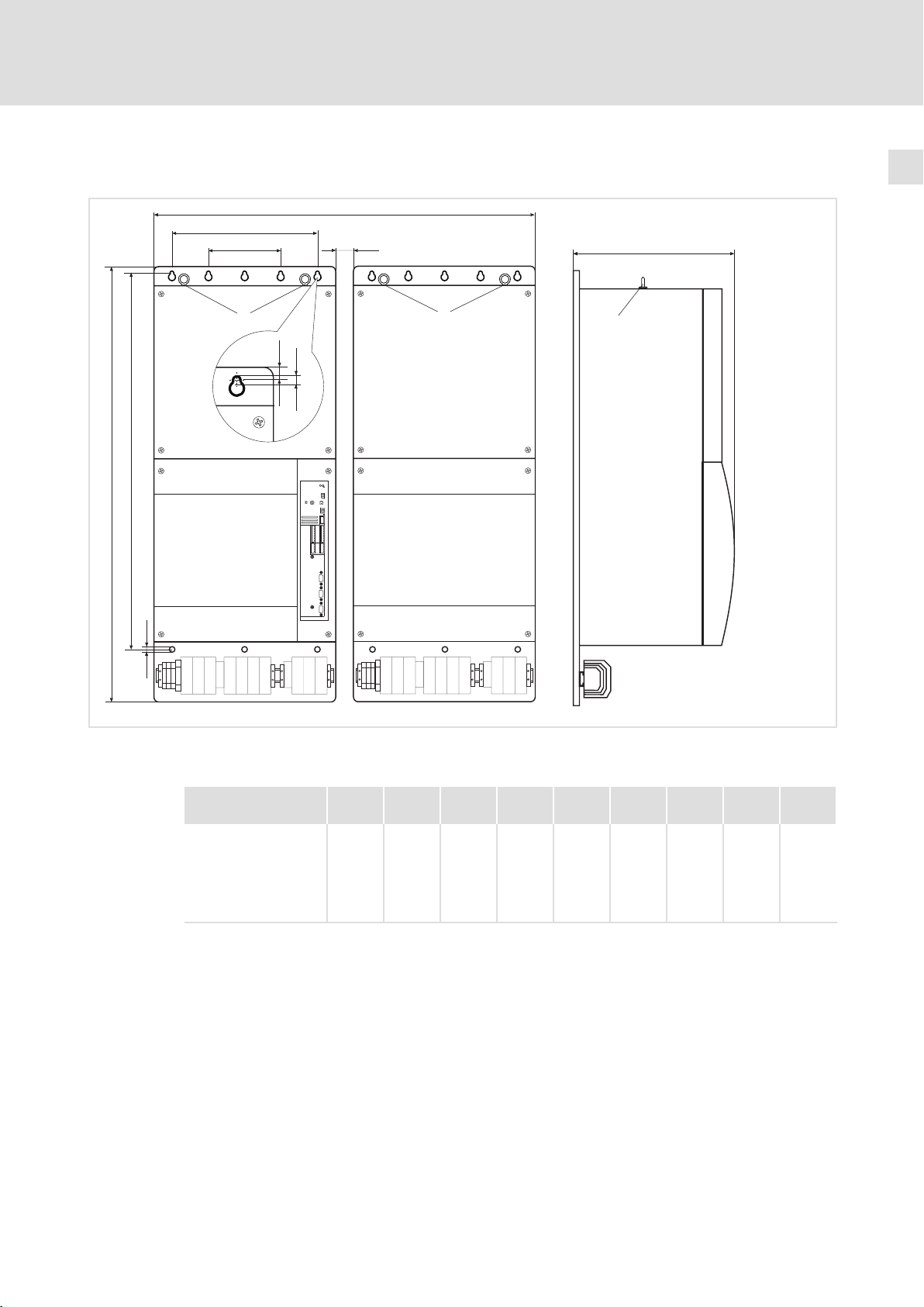
3.4 Abmessungen
b2
d
a1
a2
Technische Daten
3
Abmessungen
a
a3
c
0
b1
b
d
Abb. 3−1 Abmessungen
Ringösen
0
0
9300VEC039
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Typ a
[mm]a1[mm]a2[mm]a3[mm]b[mm]b1[mm]b2[mm]c[mm]d[mm]
EVF9381−EV
EVF9381−EVVxxx
EVF9382−EV
EVF9382−EVVxxx
EVF9383−EV
EVF9383−EVVxxx
1050 450 225 50 1145 1005 15 436
9
(16×)
23
Page 24
4
Mechanische Installation
Bohrungen an der Montageplatte durchführen
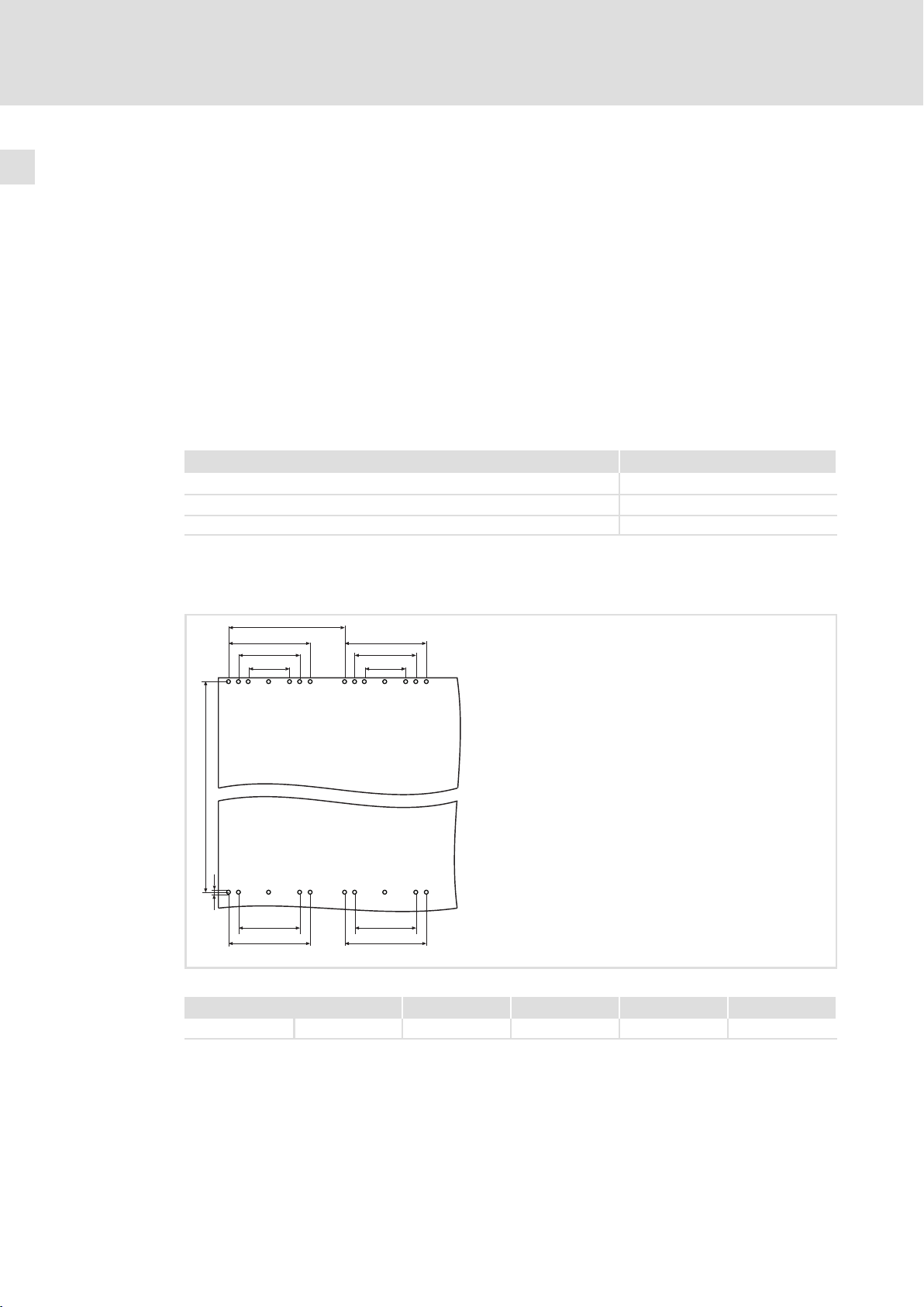
4 Mechanische Installation
Tipp!
ƒ Lenze empfiehlt den Einbau einer Luftschleuse. Mit der Luftschleuse wird
die erwärmte Kühlluft direkt aus dem Schaltschrank abgeführt.
– Best.−Nr. E93ZWL2
ƒ Eine Bohrschablone zum Markieren der Bohrlöcher steht als dxf−Datei im
Internet zur Verfügung, im Bereich "Downloads" unter www.Lenze.de.
4.1 Bohrungen an der Montageplatte durchführen
Freiraum Mindestabstand
Links/rechts zu einem anderen Antriebsregler 30 mm
Links/rechts zu einer nicht wärmeableitenden Wand 100 mm
Oben/unten 200 mm
Halten Sie die angegebenen Freiräume ein, um eine ausreichende Kühlung des Antriebsreglers sicherzustellen. Beim Einsatz einer Luftschleuse gelten andere Freiräume (siehe
Montageanleitung zur Luftschleuse).
a
a1 a1
a2 a2
a3
b
d
a2 a2
a1 a1
Abb. 4−1 Bohrungen in der Montageplatte zur Befestigung des Antriebsreglers
a3
93vec079
24
a a1 a2 a3 b d
550 mm 450 mm 340 mm 225 mm 1005 mm 9 mm (24x)
1. Entsprechend der Abbildung die Bohrungen auf der Montageplatte markieren.
2. Löcher in die Montageplatte bohren.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 25

Mechanische Installation
Montageschienen an der Montageplatte befestigen
4.2 Montageschienen an der Montageplatte befestigen
(ab Hardwarestand 1x)
4
0
22
33
1
0
33
22
Abb. 4−2 Montageschienen an der Montageplatte befestigen
Montageschiene
Montageplatte
Innensechskantschraube M8 × 25 mm
Federring M8
9300vec080
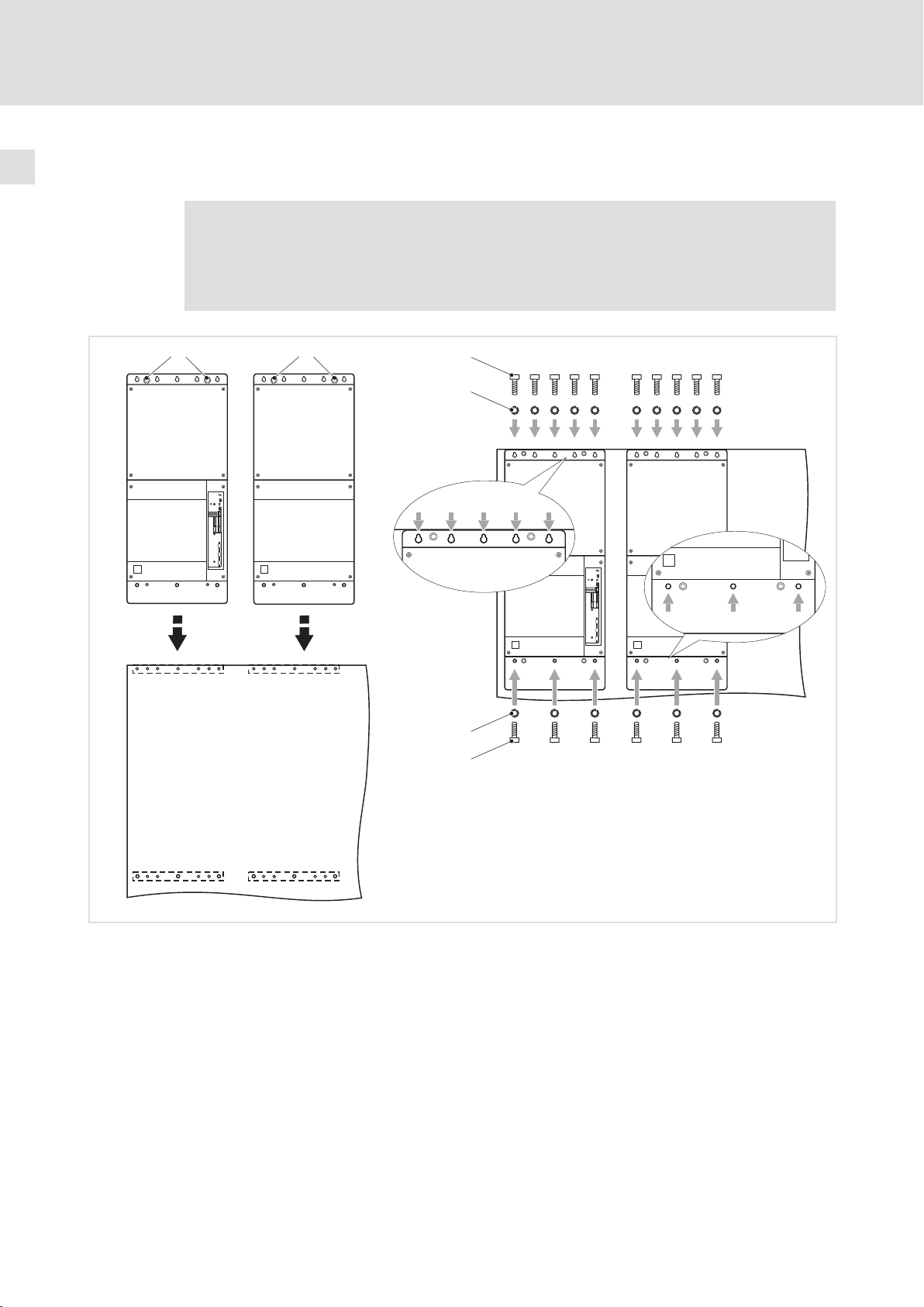
1. Montageschienen hinter die Montageplatte halten.
2. Montagesschienen mit je 2 Innensechskantschrauben und Federringen genau an
den gezeigten Punkten festschrauben.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
25
Page 26
4
Mechanische Installation
Antriebsregler auf der Montageplatte befestigen
4.3 Antriebsregler auf der Montageplatte befestigen
Gefahr!
Verletzungsgefahr durch hohes Gewicht des Antriebsreglers.
Transportieren Sie den Antriebsregler ausschließlich an den Ringösen und mit
geeignetem Hebezeug.
00
12
4
5
3
5
4
9300vec081
Abb. 4−3 Antriebsregler auf der Montageplatte befestigen
Ringösen Montageplatte
Master 16 Innensechskantschrauben M8 × 25 mm
Slave 16 Federringe M8
1. Master und Slave auf die Montageplatte legen.
2. Master und Slave oben jeweils mit 5 und unten jeweils mit
3 Innensechskantschrauben und Federringen genau an den gezeigten Punkten
festschrauben.
26
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 27

Elektrische Installation
EMV−gerechte Installation (Aufbau des CE−typischen Antriebssystems)
5 Elektrische Installation
Stop!
Der Antriebsregler enthält elektrostatisch gefährdete Bauelemente.
Vor Arbeiten im Bereich der Anschlüsse muss sich das Personal von
elektrostatischen Aufladungen befreien.
5.1 EMV−gerechte Installation (Aufbau des CE−typischen Antriebssystems)
ƒ Motorleitungen immer getrennt von Netzleitungen und Steuerleitungen verlegen.
ƒ Die Motorleitung möglichst rechtwinklig mit Netzleitungen und Steuerleitungen
kreuzen.
ƒ Optimal wird die Motorleitung frei von Unterbrechungen verlegt.
ƒ Alle Komponenten (Antriebsregler, Drosseln) an einen zentralen Erdungspunkt
(PE−Schiene) anschließen.
5
ƒ Schirme immer großflächig auf die Montageplatte auflegen bzw. die geräteseitigen
Schirmauflagen benutzen.
ƒ Legen Sie den Schirm der Motorleitung immer beidseitig auf − am Antriebsregler und
am Motor.
ƒ Die Leitungen der analogen und digitalen Ein− und Ausgänge geschirmt ausführen.
Wenn kurze (bis 200 mm) nicht abgeschirmte Leitungen verwendet werden, diese
immer verdrillen.
ƒ Die Schirmauflagen der Steuerleitungen sollen min. 50 mm Abstand zu den
Schirmanschlüssen der Motor− und DC−Leitungen aufweisen.
ƒ Bei den digitalen Leitungen muss die Schirmauflage zweiseitig erfolgen.
ƒ Bei den analogen Leitungen muss die Schirmauflage einseitig auf der Umrichterseite
erfolgen.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
27
Page 28
5
Elektrische Installation
EMV−gerechte Installation (Aufbau des CE−typischen Antriebssystems)
L1
L2
L3
N
PE
F1 … F3
K10
PES
+
DC 24 V
PES
PES PES
IN1
Z5
IN2
IN3
IN4
–
PE
PESPES
PES
PES
101 101102 102103 103104 104
X11
K31
K32
33
34
X5
28
E1
E2
E3
E4
E5
ST1
ST2
39
A1
A2
A3
A4
59
EVM9381-EV …
EVM9383-EV
T1 T2
UU
PE PE
VVWW
PE
PES
PES
J>
PE
M
3~
L3
PE PE
L1 L1L2 L2
DC+
DC–
PES
X6
63
7
62
7
4
3
2
1
PES
BR1 BR1BR2 BR2
+UG +UG-UG -UG
PE
X8/8
X8/5
KTY
M
PE
3~
PE
PES
EVL9381-EV …
EVL9383-EV
PE
PES
PES
F4 … F6
K10
S2
S1
L3
PES PES PES
Z2Z1
PES PES
PE
RB2
RB1PE
RB
K10
T2T1
JRB
Z3
PE
RB2
RB1PE
RB
JRB
K10
PES
T2T1
Z4
9300VEC082
Abb. 5−1 Beispiel für eine EMV−gerechte Verdrahtung
F1 ... F3, F4 ... F6 Absicherung
K10 Netzschütz
Z1, Z2 Motordrossel
Z3, Z4 Bremswiderstand
Z5 Speicherprogrammierbare Steuerung (SPS)
S1 Netzschütz einschalten
S2 Netzschütz ausschalten
+U
, −U
G
G
Anschluss DC−Zwischenkreis
PES HF−Schirmabschluss durch großflächige Anbindung an PE
28
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 29
5.2 Master und Slave verbinden
5.2.1 Wichtige Hinweise
Gefahr!
Gefahr von Personenschäden! Zerstörung des Antriebsreglers!
Durch beschädigte Steuerleitungen im Antriebsregler (Master und Slave) kann
die Endstufe fehlerhaft angesteuert werden.
Mögliche Folgen:
ƒ Beim Einschalten der Netzspannung können sich hohe Energien
explosionsartig entladen.
ƒ Explosionsgeräusche können Hörschäden verursachen. Ein Schreck durch
unerwartet lauten Knall kann Distress auslösen.
ƒ Der Antriebsregler wird zerstört.
Schutzmaßnahmen:
ƒ Achten Sie bei der Arbeit mit den DC−Verbindungsschienen darauf, dass Sie
keine internen Steckverbinder und Leitungen beschädigen.
ƒ Bevor Sie die Haube wieder aufsetzen:
– Alle in Abb. 5−5 markierten Stecker auf Beschädigung und korrekten Sitz
prüfen.
– Alle zugehörigen Leitungen auf Beschädigungen prüfen.
– Sitzen Stecker nicht korrekt, sind Stecker oder Leitungen beschädigt, ist die
Inbetriebnahme untersagt. Wenden Sie sich an den Lenze−Service.
Elektrische Installation
Master und Slave verbinden
Wichtige Hinweise
5
5.2.2 Vorbereitende Arbeiten
0 1
Abb. 5−2 Befestigung der Hauben am Master und am Slave
ƒ Obere Haube am Master und am Slave entfernen, um Zugang zu den
Leistungsteilen zu erhalten. Jede Haube ist mit 4 Schrauben befestigt.
9300vec164
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
29
Page 30
5
Elektrische Installation
Master und Slave verbinden
Montage der DC−Verbindungsschienen
5.2.3 Montage der DC−Verbindungsschienen
0
1
2
3
DC-
4
8
5
6
7
Abb. 5−3 +DC/−DC−Verbindungsschienen montieren
4
5
6
DC+
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
4
5
6
9300VEC024
So montieren Sie die DC−Verbindungsschienen
1. +DC−Verbindungsschiene montieren:
– Innensechskantschrauben M8 entfernen.
– Verbindungsschiene im Master und im Slave positionieren.
– Verbindungsschiene im Master und im Slave mit je 1 Innensechskantschraube
M8 × 45 mm , U−Scheibe und Distanzhülse befestigen.
– Innensechskantschrauben festziehen (Anzugsmoment: 10,9 Nm).
2. −DC−Verbindungsschiene montieren:
– Innensechskantschrauben M8 entfernen.
– Beide Verbindungskabel beiseite legen.
– Verbindungsschiene im Master und im Slave positionieren.
– Im Master und im Slave je 2 Innensechskantschrauben M8 × 45 mm mit
U−Scheibe erst durch Bohrungen der Verbindungsschiene und dann durch die
Distanzhülsen führen.
– Innensechskantschrauben im Master und im Slave in die Gewindebohrungen
drehen.
– Im Master und im Slave jeweils das Verbindungskabel mit Kabelschuh zwischen
Verbindungsschiene und U−Scheibe legen.
– Innensechskantschrauben festziehen (Anzugsmoment: 10,9 Nm).
30
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 31

Elektrische Installation
Master und Slave verbinden
Anschluss der Steuerleitungen zwischen Master und Slave
5.2.4 Anschluss der Steuerleitungen zwischen Master und Slave
5
0
2
4
Abb. 5−4 Steuerleitungen zwischen Master und Slave anschließen
1
DC+
DC-
5
0
1
0
1
3
9300VEC028
So schließen Sie die Steuerleitungen an
1. Flachbandleitung verlegen und anschließen:
Im Auslieferungszustand befindet sich die Flachbandleitung im Master. Der Stecker
ist am Drive Board bereits aufgesteckt.
– Flachbandleitung vom Master bis zum Anschluss am Drive Board im Slave führen.
Dabei die Flachbandleitung in die Kabelführungen legen.
– Im Slave den Stecker der Flachbandleitung in die Buchse am Drive Board
stecken.
2. 2−adrige Leitung mit Stecker verlegen und anschließen:
Im Auslieferungszustand befindet sich die Leitung im Master. Die entsprechende Lei-
tung mit Buchse befindet sich im Slave.
– 2−adrige Leitung vom Master bis zur Buchse im Slave führen.
– Im Slave 2−poligen Stecker mit 2−poliger Buchse verbinden.
3. 10−adrige Leitung mit Stecker verlegen und anschließen:
Im Auslieferungszustand befindet sich die Leitung im Master. Die entsprechende Lei-
tung mit Buchse befindet sich im Slave.
– 10−adrige Leitung vom Master bis zur Buchse im Slave führen.
– Im Slave 10−poligen Stecker mit 10−poliger Buchse verbinden.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
31
Page 32

5
5.2.5 Abschließende Arbeiten
Elektrische Installation
Master und Slave verbinden
Abschließende Arbeiten
Abb. 5−5 Steuerleitungen im Master und Slave
1. Steuerleitungen (Stecker und Leitungen) auf korrekten Sitz und Beschädigungen
prüfen. ()
– Sitzen Stecker nicht korrekt, sind Stecker oder Leitungen beschädigt, ist die
Inbetriebnahme untersagt. Wenden Sie sich an den Lenze−Service.
9300vec163
0 1
9300vec164
Abb. 5−6 Befestigung der Hauben am Master und am Slave
2. Schließen Sie die Gehäuse mit den Hauben !. Befestigen Sie die Hauben jeweils
mit den 4 Schrauben.
32
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 33

Elektrische Installation
Netzanschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V Netzspannung
Abschließende Arbeiten
5.3 Netzanschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V Netzspannung
Stop!
Eine ausreichende Zugentlastung liegt in der Verantwortung des Anwenders!
ƒ Die Einspeisung muss am Master und am Slave erfolgen!
0 1
5
BR2 BR2
PE PE
M8 M8
25-30 Nm 25-30 Nm
L1, L2,
L3
221-264 lb-in 221-264 lb-in
PE PE
Abb. 5−7 Vorschlag Netzanschluss
BR1 BR1
40 mm 40 mm
M6 M6
15-20 Nm 15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in 133-176 lb-in
BR1, BR2 Betrieb mit Bremswiderstand nur möglich bei Varianten V060 und V110
Anschlussklemmen Master
Anschlussklemmen Slave
UUVVWWL1 L1L2 L2L3 L3
PE PE
L1, L2,
L3
Anschluss siehe Systemhandbuch 9300 vector
Sicherungen und Leitungsquerschnitte für die Netzeinspeisung
Master Slave Master Slave Master Slave
EVF9381−EV
EVF9381−EVVxxx
EVF9382−EV
EVF9382−EVVxxx
EVF9383−EV
EVF9383−EVVxxx
1)
2)
Nationale und regionale Vorschriften beachten
Mehrleiter; beide Leiter müssen den gleichen Querschnitt haben
Lenze empfiehlt Sicherungen der Betriebsklasse gRL
315 315
315 315
400 400
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
9300VEC013
1)
1)
1)
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
95 95
95 95
150 150
5.4 Versorgungs− und Lüfteranschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V/500V Netzspannung
Stop!
Eine ausreichende Zugentlastung liegt in der Verantwortung des Anwenders!
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
33
Page 34

5
Elektrische Installation
Versorgungs− und Lüfteranschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V/500V Netzspannung
Netzanschluss
5.4.1 Netzanschluss
ƒ Die Einspeisung muss am Master und am Slave erfolgen!
0 1
PE PE
L3 L3
L1 L1
L2 L2
103
102
101
104
M8
25-30 Nm
L1, L2,
L3
221-264 lb-in
PE
M6
15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in
PE PE
BR2 BR2BR1 BR1+UG +UG-UG -UG
40 mm 40 mm
U U
V VW W
Abb. 5−8 Vorschlag Netzanschluss
BR1, BR2 Betrieb mit Bremswiderstand nur möglich bei Varianten V270 und V300
Anschluss siehe Systemhandbuch 9300 vector
Anschlussklemmen Master
Anschlussklemmen Slave
Sicherungen und Leitungsquerschnitte für die Netzeinspeisung
Typ Installation nach EN 60204−1
Schmelzsicherung
Master Slave Master Slave Master Slave
EVF9381−EVV210
EVF9381−EVV240
EVF9381−EVV270
EVF9381−EVV300
EVF9382−EVV210
EVF9382−EVV240
EVF9382−EVV270
EVF9382−EVV300
EVF9383−EVV210
EVF9383−EVV240
EVF9383−EVV270
EVF9383−EVV300
1)
2)
Nationale und regionale Vorschriften beachten
315 A
315 A 315 A
400 A 400 A
Mehrleiter; beide Leiter müssen den gleichen Querschnitt haben
Lenze empfiehlt Sicherungen der Betriebsklasse gRL
315 A
103
102
101
104
M8
25-30 Nm
L1, L2,
L3
221-264 lb-in
2)
L1, L2, L3 [mm2] PE [mm2]
150
1)
2 × 50
150
1)
2 × 50
240
1)
2 × 95
M6
15-20 Nm
PE
133-176 lb-in
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
9300VEC035
1)
1)
1)
95 95
95 95
150 150
34
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 35

Elektrische Installation
Versorgungs− und Lüfteranschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V/500V Netzspannung
Anschluss an den DC−Zwischenkreis (+UG, −UG)
5.4.2 Anschluss an den DC−Zwischenkreis (+UG, −UG)
ƒ Zur Einhaltung der EMV−Bestimmungen empfiehlt Lenze den Einsatz geschirmter
DC−Zwischenkreisleitungen.
ƒ Schirmschellen sind nicht im Lieferumfang enthalten.
ƒ Die Einspeisung muss am Master und am Slave erfolgen!
5
0
PE PE
L3 L3
L1 L1
L2 L2
103
102
101
104
22
M6
15-20 Nm
PE
133-176 lb-in
40 mm 40 mm
Abb. 5−9 Vorschlag Anschluss an +UG und −U
Sicherungen und Leitungsquerschnitte für den Anschluss an den DC−Zwischenkreis
EVF9381−EVV2xx
EVF9381−EVV300
EVF9382−EVV2xx
EVF9382−EVV300
EVF9383−EVV2xx
EVF9383−EVV300
M8 M8
25-30 Nm 25-30 Nm
+U
G
221-264 lb-in 221-264 lb-in
-U
G
BR1, BR2 Betrieb mit Bremswiderstand nur möglich bei Varianten V270 und V300
Anschlussklemmen Master
Anschlussklemmen Slave
Schirm der DC−Zwischenkreisleitungen großflächig auf leitender
Metallisch leitende Fläche
Achten Sie auf richtige Polung!
1)
Mehrleiter; beide Leiter müssen den gleichen Querschnitt haben
2)
Nur Sicherungen der Betriebsklasse gRL verwenden
Nationale und regionale Vorschriften beachten
PE PE
BR2 BR2BR1 BR1+UG +UG-UG -UG
max.
300 mm
U U
V VW W
33
Anschluss siehe Systemhandbuch 9300 vector
Schaltschrank−Montageplatte auflegen und mit Schirmschellen festschrauben
Master Slave Master Slave Master Slave
350 350
400 400
500 500
1
103
102
101
104
max.
300 mm
M6
15-20 Nm
PE
133-176 lb-in
G
+U
G
-U
G
9300VEC083
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
95 95
95 95
150 150
5.4.3 Lüfteranschluss
Hinweis!
Schließen Sie den Lüfter am Master und am Slave an.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
35
Page 36

5
Elektrische Installation
Versorgungs− und Lüfteranschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V/500V Netzspannung
Lüfteranschluss
Lüfteranschluss bei Versorgung des Antriebsreglers mit Netzspannung
Brücke legen zwischen den Klemmen bei Betrieb des Antriebsreglers an einem Netz
AC 340 ... 440 V AC 440 ... 577 V
(Auslieferungszustand)
L1 L2
101
102
103
104
9300vec044 9300vec045
101
L1 L2
102
103
104
Lüfteranschluss bei Versorgung des Antriebsreglers über den DC−Zwischenkreis
Gefahr!
Bei externer Spannungsversorgung des Lüfters führt Klemme L2 gefährliche
Netzspannung!
Wenn der Antriebsregler über den Zwischenkreis gespeist wird, muss der Lüfter separat
mit Netzspannung versorgt werden (siehe ). Entfernen Sie in diesem Fall die Brücke zwi-
schen den Klemmen 102 und 103 (siehe ).
Brücke entfernen
0
101
102
103
104
}
1
L1 L2
101
AC 340…440V
9300vec160 9300vec046 9300vec047
Netzanschluss für den Betrieb des Lüfters an
AC 340 ... 440 V AC 440 ... 577 V
1
L1 L2
102
103
104
101
AC 440 … 577 V
L1 L2
102
103
104
36
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 37

Elektrische Installation
Versorgungs− und Lüfteranschluss beim Antriebsregler für 400 V/500V Netzspannung
Lüfteranschluss
Defekte Sicherung wechseln
Bei externer Spannungsversorgung wird der Lüfter über eine in Klemme 104 integrierte Sicherung geschützt.
0
1
L1 L2
101
102
103
104
Abb. 5−10 Absicherung des Lüfters
Sicherungshalter öffnen.
Defekte Sicherung aus der Halterung nehmen und durch folgenden Typ ersetzen:
Typ: 500V SA 2A 6.32
Ref. Nr.: P098131
Hersteller: Ferraz Shawmut
5
9300vec161
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
37
Page 38

5
Elektrische Installation
Motoranschluss
Lüfteranschluss
5.5 Motoranschluss
ƒ Zur Einhaltung der EMV−Bestimmungen empfiehlt Lenze den Einsatz geschirmter
Motorleitungen.
ƒ Schirmschellen sind nicht im Lieferumfang enthalten.
Stop!
Motorseitige Parallelschaltung von Master und Slave
Um die beiden Motorleitungen vom Master und vom Slave an den Motor anzuschließen,
müssen die Ausgänge parallel geschaltet werden.
Bei der Parallelschaltung der Umrichterausgänge ist es wichtig, daß die Ausgänge durch
eine Induktivität zwischen Master und Slave entkoppelt werden. Die Länge der Motorleitungen entscheidet, ob die Induktivität der Leitungen für eine Entkopplung ausreicht.
Es gibt 2 Varianten für den Motoranschluss, um eine ausreichende Entkopplung zu gewährleisten:
ƒ Entkopplung über Motordrosseln
Wenn die einfache Motorleitungslänge £ 10 m ist, müssen Sie Master und Slave motorseitig über Drosseln parallel schalten, um eine ausreichende Entkopplung zwischen
Master und Slave zu erhalten.
ƒ Entkopplung über die Motorleitung
Wenn die einfache Motorleitungslänge > 10 m ist können Sie die Motorleitungen vom
Master und Slave am Motor parallel schalten. Die Induktivität der Motorleitungen
reicht aus, um eine ausreichende Entkopplung zwischen Master und Slave zu erhalten.
Eine ausreichende Zugentlastung liegt in der Verantwortung des Anwenders!
Entkopplung über Motordrosseln Entkopplung über die Motorleitung
UU
PE PE
VVWW
PE
£10 m
Z1 Z2
PE PE
M
PE
3~
9300VEC026 9300VEC008
Abb. 5−11 Varianten für die motorseitige Parallelschaltung von Master und Slave
Z1, Z2 Motordrossel für Antriebsregler
ELM3−0003H275 EVF9381
ELM3−0002H320 EVF9382
ELM3−0002H410 EVF9383
>10 m
PEUVW
PE
PE
PE
M
3~
PEUVW
38
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 39

Anschluss Motor
Elektrische Installation
Motoranschluss
Lüfteranschluss
5
0
UUVVWW
BR2 BR2BR1 BR1
40mm 40mm
22
PE
Abb. 5−12 Vorschlag Motoranschluss
PE PE
max.
300 mm
M8
25-30 Nm
M6
15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in
BR1, BR2 Betrieb mit Bremswiderstand nur möglich bei Varianten V060, V110, V270 und V300
Anschlussklemmen Master
Anschlussklemmen Slave
Schirm der Motorleitungen großflächig auf leitender Schaltschrank−Montageplatte
Metallisch leitende Fläche
Achten Sie auf richtige Polung!
Halten Sie die maximale Motorleitungslänge ein!
U, V, W
221-264 lb-in
Anschluss siehe Systemhandbuch 9300 vector
auflegen und mit Schirmschellen festschrauben
33
PE
1
M6
15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in
U, V, W
M8
25-30 Nm
221-264 lb-in
max.
300 mm
9300VEC036
Leitungsquerschnitte für den Motoranschluss
Typ Installation nach EN 60204−1
U, V, W [mm2] PE [mm2]
Master Slave Master Slave
EVF9381−EV
EVF9381−EVxxxx
EVF9382−EV
EVF9382−EVxxxx
EVF9383−EV
EVF9383−EVxxxx
1)
Nationale und regionale Vorschriften beachten
Mehrleiter; beide Leiter müssen den gleichen Querschnitt haben
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
95 95
95 95
150 150
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
39
Page 40

5
Elektrische Installation
Motoranschluss
Motortemperatur−Überwachung verdrahten
5.5.1 Motortemperatur−Überwachung verdrahten
Der Antriebsregler hat 2 Anschlüsse für die Motortemperatur−Überwachung:
ƒ Klemmen T1, T2 zum Anschluss eines Kaltleiters (PTC) oder Thermokontakts
(Öffner).
ƒ Pin X8/5 und X8/8 des Inkrementalgeber−Eingangs (X8) zum Anschluss eines
Temperatursensors KTY.
Inkrementalgeber−Eingang (X8) Klemmen T1, T2
Anschließbarer Temperatursensor
Auslösepunkt l Warnung: Einstellbar
Bemerkungen l Die Überwachung ist in der Lenze−Ein-
Linearer Temperatursensor (KTY) l Kaltleiter (PTC)
l Fehler (TRIP): Fest bei 150 °C
stellung nicht aktiv.
l Der KTY wird auf Unterbrechung und
Kurzschluss überwacht.
– Kaltleiter−Temperatursensor mit de-
finierter Auslösetemperatur (nach
DIN 44081 und DIN 44082)
l Thermokontakt (Öffner)
– Temperaturschalter als Öffner
l Fest (abhängig vom PTC/Thermokon-
takt)
l PTC: RJ
l Konfigurierbar als Warnung oder Feh-
l Die Überwachung ist in der Lenze−Ein-
l Wenn Sie keinen Lenze−Motor einset-
> 1600 W
ler (TRIP)
stellung nicht aktiv.
zen, empfehlen wir als Kaltleiter einen PTC bis 150 °C.
Anschluss am Inkrementalgeber−Eingang (X8)
Hinweis!
Lenze−Systemleitungen für die Motorrückführung enthalten zusätzliche Adern
für die Temperaturrückführung. Die Leitungen sind für eine EMV−gerechte
Verdrahtung ausgelegt.
B
B
A
A
V
CC5_E
GND
Z
KTY
Abb. 5−13 Anschluss am Inkrementalgeber−Eingang (X8)
X8/5, X8/8 Anschluss Temperatursensor KTY
Z
+KTY
-KTY
X8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
9300VEC068
40
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 41

Elektrische Installation
Motortemperatur−Überwachung verdrahten
Anschluss an die Klemmen T1, T2
Stop!
ƒ Keine Fremdspannung an die Klemmen T1, T2 anschließen. Die Steuerung
des Antriebsreglers wird beschädigt.
ƒ Verwenden Sie die Klemmen T1, T2 nicht für sicherheitsrelevante
Verschaltungen. Störungsmeldungen über diesen Eingang werden erst
nach 2 s verarbeitet.
Klemmen T1, T2 am Antriebsregler Eingangsschaltung für T1, T2
15 V
7.4 k
3.3 k
T2
J
2.7 k
T1
5
Motoranschluss
MONIT-OH8
T1
T2
9300STD328 9300VEC017
Abb. 5−14 Anschluss an die Klemmen T1, T2
T1, T2 Anschluss Kaltleiter (PTC) oder Thermokontakt (Öffner)
93xx
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
41
Page 42

5
5.6 Steueranschlüsse
5.6.1 Wichtige Hinweise
Elektrische Installation
Steueranschlüsse
Wichtige Hinweise
Stop!
Die Steuerkarte wird zerstört, wenn
ƒ die Spannung zwischen X5/39 und PE oder X6/7 und PE größer 50 V ist,
ƒ bei Versorgung über eine externe Spannungsquelle die Spannung zwischen
Spannungsquelle und X6/7 größer 10 V (Gleichtakt) ist.
Begrenzen Sie die Spannung bevor Sie den Antriebsregler einschalten:
ƒ Legen Sie X5/39, X6/2, X6/4 und X6/7 direkt auf PE oder
ƒ setzen Sie spannungsbegrenzende Bauelemente ein.
ƒ Für einen störungsfreien Betrieb müssen Sie die Steuerleitungen abschirmen:
– Bei Leitungen für die digitalen Eingänge und Ausgänge den Schirm zweiseitig
auflegen.
– Bei Leitungen für die analogen Eingänge und Ausgänge den Schirm einseitig am
Antriebsregler auflegen.
– Ab 200 mm Länge nur geschirmte Leitungen für die analogen und digitalen
Eingänge und Ausgänge verwenden. Unter 200 mm Länge können ungeschirmte,
aber verdrillte Leitungen verwendet werden.
42
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 43

Schirm auflegen
10
Elektrische Installation
Steueranschlüsse
Wichtige Hinweise
2
5
3
Abb. 5−15 Anbindung des Leitungsschirms mit Schirmklammer und Zugentlastung mit Kabelbinder
Schirmblech
Schirmblech mit 2 Schrauben M4 × 12 mm an der Steuerkarte unten festschrauben
Leitungsschirm mit Schirmklammer am Schirmblech anbinden
Steuerleitung mit Kabelbinder am Schirmblech zugentlasten
Daten der Anschlussklemmen
Stop!
ƒ Klemmenleisten nur bei vom Netz getrenntem Antriebsregler aufstecken
oder abziehen!
ƒ Klemmenleisten erst verdrahten, dann aufstecken!
ƒ Unbenutzte Klemmenleisten ebenfalls aufstecken, um die Kontakte zu
schützen.
Leitungstyp Aderendhülse Maximaler Leitungs-
starr — 2,5 mm
flexibel ohne Aderendhülse 2,5 mm
flexibel
flexibel
Aderendhülse ohne
Kunststoffhülse
Aderendhülse mit
Kunststoffhülse
querschnitt
2
(AWG 14)
2
(AWG 14)
2
2,5 mm
2,5 mm
(AWG 14)
2
(AWG 14)
Anzugsmoment Abisolier-
länge
0,5 ... 0,6 Nm
(4.4 ... 5.3 lb−in)
9300vec063
5 mm
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
43
Page 44

5
Elektrische Installation
Steueranschlüsse
Mit aktiver Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
5.6.2 Mit aktiver Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
(ab Hardwarestand 1x)
Sicherheitshinweise für die Installation der Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
ƒ Nur qualifiziertes Personal darf die Funktion Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
installieren und in Betrieb nehmen.
ƒ Alle sicherheitsrelevanten Leitungen (z. B. Steuerleitung für das Sicherheitsrelais,
Rückmeldekontakt) außerhalb des Schaltschranks unbedingt geschützt verlegen,
z. B. im Kabelkanal. Kurzschlüsse zwischen den einzelnen Leitungen müssen sicher
ausgeschlossen sein.
ƒ Die Verdrahtung des Sicherheitsrelais K
Leitungen ist unbedingt notwendig.
ƒ Der elektrische Bezugspunkt für die Spule des Sicherheitsrelais K
Schutzleitersystem verbunden sein (DIN EN 60204−1 Abs. 9.4.3). Nur so ist der Schutz
gegen fehlerhaften Betrieb durch Erdschlüsse gewährleistet.
mit isolierten Aderendhülsen oder starren
SR
muss mit dem
SR
44
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 45

K31K32 33 34
X11
Elektrische Installation
Steueranschlüsse
Mit aktiver Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
Versorgung über interne Spannungsquelle
ƒ Wird ein frei belegbarer digitaler Ausgang (z. B. X5/A1) fest auf HIGH−Pegel gelgt,
dient er als interne Spannungsquelle. Ein Ausgang ist mit maximal 50 mA belastbar.
– Über einen digitalen Ausgang können Sie das Relais K
(X5/28 und z. B. X5/E1) mit Spannung versorgen.
– Für die maximale Beschaltung (Relais K
und X5/E1 ... X5/E5, X5/ST1) müssen Sie
SR
zwei digitale Ausgänge parallel schalten und fest auf HIGH−Pegel legen.
ƒ Für die Versorgung der analogen Eingänge (X6/1, X6/2 und X6/3, X6/4) müssen Sie
einen frei belegbaren analogen Ausgang (z. B. X6/63) fest auf HIGH−Pegel legen.
GND2 +24V+5 V
+
K
SR
X5
3k
3k
28
E1 E2 E3 E4
3k
3k
3k
E5
50mA
50mA
50mA
3k
39
A1
A2 A3 A4 ST1
50mA
47k
ST2
59
und zwei digitale Eingänge
SR
1
2
3
X3
4
5
6
242R
3.3nF
X6
100k
100k
12
100k
100k
GND1 GND1
3
4
7762
63
5
IN1 IN2
AIN1 AIN2
13247
10k 10k
IN3
IN4
S1 S2
DIGOUT4
Z1
Abb. 5−16 Verdrahtung digitale und analoge Eingänge/Ausgänge mit aktiver Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes
Moment" und interner Spannungsquelle
S1 Impulssperre aufheben (1. Abschaltpfad)
S2 Antriebsregler freigeben (2. Abschaltpfad)
Z1 Speicherprogrammierbare Steuerung (SPS)
Die SPS übernimmt die Überwachung der Funktion ˜Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment˜
X5/A4 Rückmeldung über einen digitalen Ausgang (z. B. DIGOUT4)
Schließer oder Öffner
Z
Verbraucher
Für den Betrieb notwendige Mindestverdrahtung
Klemmenbelegung in der Lenze−Einstellung: 49
AOUT1
AOUTx
AOUT2
9300vec135
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
45
Page 46

5
X11
Elektrische Installation
Steueranschlüsse
Mit aktiver Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
Versorgung über externe Spannungsquelle
+
K
SR
K31K32 33 34
X5
3k
3k
28
E1 E2 E3 E4
GND2 +24V+5 V
1
2
3
X3
50mA
50mA
50mA
3k
3k
3k
3k
E5
39
A1
A2 A3 A4 ST1
50mA
47k
ST2
59
4
5
6
242R
X6
3.3nF
100k
100k
12
100k
100k
GND1 GND1
3
7762
4
63
IN1 IN2
AIN1 AIN2
13247
10k 10k
IN3
IN4
S1 S2
–
+
DC 24 V
(+18 V … +30 V)
DIGOUT4
Z1
Abb. 5−17 Verdrahtung digitale und analoge Eingänge/Ausgänge mit aktiver Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes
Moment" und externer Spannungsquelle
S1 Impulssperre aufheben (1. Abschaltpfad)
S2 Antriebsregler freigeben (2. Abschaltpfad)
Z1 Speicherprogrammierbare Steuerung (SPS)
Die SPS übernimmt die Überwachung der Funktion ˜Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment˜
X5/A4 Rückmeldung über einen digitalen Ausgang (z. B. DIGOUT4)
Schließer oder Öffner
Z
Verbraucher
Für den Betrieb notwendige Mindestverdrahtung
Klemmenbelegung in der Lenze−Einstellung: 49
AOUT1
AOUTx
AOUT2
9300vec136
46
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 47

Elektrische Installation
Steueranschlüsse
Mit deaktivierter Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
5
5.6.3 Mit deaktivierter Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
Hinweis!
Wenn Sie die Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment" nicht nutzen, müssen
K31K32 33 34
X11
Sie das Sicherheitsrelais K
Leistungsendstufe mit Spannung versorgt werden.
Versorgung über interne Spannungsquelle
ƒ Wird ein frei belegbarer digitaler Ausgang (z. B. X5/A1) fest auf HIGH−Pegel gelgt,
dient er als interne Spannungsquelle. Ein Ausgang ist mit maximal 50 mA belastbar.
– Über einen digitalen Ausgang können Sie das Relais K
(X5/28 und z. B. X5/E1) mit Spannung versorgen.
– Für die maximale Beschaltung (Relais K
zwei digitale Ausgänge parallel schalten und fest auf HIGH−Pegel legen.
ƒ Für die Versorgung der analogen Eingänge (X6/1, X6/2 und X6/3, X6/4) müssen Sie
einen frei belegbaren analogen Ausgang (z. B. X6/63) fest auf HIGH−Pegel legen.
GND2 +24V+5 V
+
K
SR
X5
3k
3k
28
E1 E2 E3 E4
3k
3k
3k
3k
E5
39
permanent bestromen, damit die Treiber der
SR
und X5/E1 ... X5/E5, X5/ST1) müssen Sie
SR
1
2
3
X3
50mA
50mA
50mA
A1
A2 A3 A4 ST1
50mA
47k
ST2
59
4
5
6
und zwei digitale Eingänge
SR
100k
100k
100k
100k
GND1 GND1
3
4
7762
63
X6
242R
3.3nF
12
S1
AIN1 AIN2
13247
10k 10k
AOUT1
AOUTx
Abb. 5−18 Verdrahtung digitale und analoge Eingänge/Ausgänge mit deaktivierter Funktion "Sicher
abgeschaltetes Moment" bei interner Spannungsquelle
S1 Antriebsregler freigeben
Schließer oder Öffner
Z
Verbraucher
Für den Betrieb notwendige Mindestverdrahtung
Klemmenbelegung in der Lenze−Einstellung: 49
AOUT2
9300vec0137
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
47
Page 48

5
X11
Elektrische Installation
Steueranschlüsse
Mit deaktivierter Funktion "Sicher abgeschaltetes Moment"
Versorgung über externe Spannungsquelle
+
K
SR
K31K32 33 34
X5
3k
3k
28
E1 E2 E3 E4
GND2 +24V+5 V
1
2
3
X3
50mA
50mA
50mA
3k
3k
3k
3k
E5
39
A1
A2 A3 A4 ST1
50mA
47k
ST2
59
4
5
6
X6
242R
3.3nF
100k
100k
12
100k
100k
GND1 GND1
3
4
7762
63
S1
–
+
DC 24 V
(+18 V … +30 V)
AIN1 AIN2
13247
10k 10k
AOUT1
AOUTx
Abb. 5−19 Verdrahtung digitale und analoge Eingänge/Ausgänge mit deaktivierter Funktion "Sicher
abgeschaltetes Moment" bei externer Spannungsquelle
S1 Antriebsregler freigeben
Schließer oder Öffner
Z
Verbraucher
Für den Betrieb notwendige Mindestverdrahtung
Klemmenbelegung in der Lenze−Einstellung: 49
AOUT2
9300vec138
48
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 49

5.6.4 Klemmenbelegung
Elektrische Installation
Steueranschlüsse
Klemmenbelegung
5
Klemme
X11/K32
X11/K31
X11/33 – Spule Sicherheitsrelais K
X11/34 + Spule Sicherheitsrelais K
X5/28 Reglersperre
X5/E1
X5/E2 Linkslauf / Quickstop aufheben HIGH
X5/E3 Festfrequenz 1 aktivieren (JOG1) HIGH
X5/E4 Fehlermeldung setzen (TRIP SET) LOW
X5/E5 Fehlermeldung zurücksetzen
X5/ST1
X5/ST2
X5/A1
X5/A2 Schaltschwelle Q
X5/A3 Betriebsbereit (DCTRL−RDY) HIGH
Sicherheitsrelais K
SR
1. Abschaltpfad
(DCTRL−CINH)
2. Abschaltpfad
Digitale Ein-
gänge
(frei belegbar)
Digitale Ausgänge
(frei belegbar)
Funktion
Fettdruck = Lenze−Einstellung
Rückmeldung Impulssperre
SR
SR
Antriebsregler freigeben und sperren LOW: Regler gesperrt
Rechtslauf / Quickstop aufheben HIGH
(TRIP RESET)
Zusätzlicher digitaler Eingang (E6) HIGH
Fehlermeldung vorhanden LOW
: Istdrehzahl < Soll-
drehzahl in C0017
MIN
Pegel / Zustand Technische Daten
Kontakt geöffnet: Impulssperre aufgehoben (Betrieb)
Kontakt geschlossen: Impulssperre aktiv
Spule nicht bestromt: Impulssperre aktiv
Spule bestromt: Impulssperre
aufgehoben (Betrieb)
HIGH: Regler freigegeben
LOW−HIGH−Flanke
LOW
Siehe Kapitel "Technische Daten"
LOW: 0 ... +3 V
HIGH: +12 ... +30 V
Eingangsstrom bei
+24 V:
8 mA pro Eingang
Einlesen und Bearbeitung der Eingangssignale
1/ms (Mittelwert)
LOW: 0 ... +3 V
HIGH: +12 ... +30 V
Belastbarkeit:
Max. 50 mA pro Ausgang
(Lastwiderstand mindestens 480
W bei +24 V)
X5/A4 Maximalstrom erreicht (DCTRL−IMAX) HIGH
X5/39 – GND2, Bezugspotenzial für digitale Si-
X5/59 – Anschluss externe Spannungsquelle für
X6/1
X6/2
X6/3
X6/4
X6/62 Analoger Aus-
X6/63 Analoger Aus-
X6/7 – GND1, Bezugspotenzial für analoge Sig-
Analoger Eingang 1
Analoger Eingang 2
gang 1
gang 2
gnale
den Stützbetrieb des Antriebsreglers bei
Netzausfall
Eingangsbereich
Spannung
Hauptsollwert
Eingangsbereich
Strom
Eingangsbereich
Spannung
Nicht aktiv
Monitor 1
Drehzahl−Istwert
Monitor 2
Motorstrom−Istwert
nale
6
4
2
Jumper X3
6
4
2
Jumper X3
Jumper X3 hat keinen Einfluss
– Potenzialgetrennt zu
DC 24 V (+18 ... +30 V) Stromaufnahme:
−10 V ... +10 V Auflösung:
5
3
1
−20 mA ... +20 mA Auflösung: 20 mA
5
3
1
−10 V ... +10 V Auflösung: 5 mV
−10 V ... +10 V;
max. 2 mA
−10 V ... +10 V;
max. 2 mA
– –
Aktualisierung der Ausgangssignale 1/ms
GND1
Max. 1 A bei 24 V
5 mV (11 Bit + Vorzeichen)
(10 Bit + Vorzeichen)
(11 Bit + Vorzeichen)
Auflösung: 20 mV
(9 Bit + Vorzeichen)
Auflösung: 20 mV
(9 Bit + Vorzeichen)
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
49
Page 50

5
Elektrische Installation
Systembus (CAN) verdrahten
5.7 Systembus (CAN) verdrahten
Verdrahtung
A
1
93XX 93XX 93XX
GND GND GND GNDLO LO LO LOHI HI HI HIX4 X4 X4PE PE PE PE
120 120
Abb. 5−20 Prinzipielle Verdrahtung des Systembus (CAN)
A
1
A
2
A
3
A
n
X4/GND CAN−GND: Systembus−Bezugspotenzial
X4/LO CAN−LOW: Systembus LOW (Datenleitung)
X4/HI CAN−HIGH: Systembus HIGH (Datenleitung)
A
2
Busteilnehmer 1 (Antriebsregler)
Busteilnehmer 2 (Antriebsregler)
Busteilnehmer 3 (Antriebsregler)
Busteilnehmer n (z. B. SPS), n = max. 63
A
3
A
n
Stop!
Schließen Sie einen 120 W Abschlusswiderstand am ersten und letzten
Bus−Teilnehmer an.
Wir empfehlen CAN−Kabel nach ISO 11898−2 zu verwenden:
CAN−Kabel nach ISO 11898−2
Kabeltyp Paarverseilt mit Abschirmung
Impedanz 120 W (95 ... 140 W)
Leitungswiderstand/−querschnitt
Kabellänge £ 300 m £ 70 mW/m / 0.25 0.34 mm2 (AWG22)
Kabellänge 301 1000 m £ 40 mW/m / 0.5 mm2 (AWG20)
Signallaufzeit £ 5 ns/m
9300VEC054
50
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 51

5.8 Rückführsystem verdrahten
5.8.1 Wichtige Hinweise
ƒ Sie können entweder am Eingang X8 oder am Eingang X9 einen Inkrementalgeber
anschließen:
– Inkrementalgeber mit TTL−Pegel schließen Sie an X8 an.
– Inkrementalgeber mit HTL−Pegel schließen Sie an X9 an.
ƒ Das Inkrementalgebersignal kann am Leitfrequenzausgang X10 für Folgeantriebe
ausgegeben werden.
Hinweis!
ƒ Wir empfehlen, für die Verdrahtung Lenze−Systemleitungen zu verwenden.
ƒ Bei selbstkonfektionierten Leitungen nur Leitungen mit paarweise
verdrillten und abgeschirmten Adern verwenden.
Elektrische Installation
Rückführsystem verdrahten
Wichtige Hinweise
5
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
51
Page 52

5
Elektrische Installation
Rückführsystem verdrahten
Inkrementalgeber mit TTL−Pegel an X8
5.8.2 Inkrementalgeber mit TTL−Pegel an X8
Technische Daten
Bereich Werte
Anschluss am Antriebsregler Steckverbinder: Stift, 9−polig, Sub−D
Anschließbare Inkrementalgeber Inkrementalgeber mit TTL−Pegel
Eingangsfrequenz 0 ... 500 kHz
Stromaufnahme 6 mA pro Kanal
Interne Spannungsquelle
(X8/4, X8/5)
Verdrahtung
<50m
KTY
l Geber mit zwei um 90° elektrisch versetzten 5V−Komplementärsigna-
len
l Anschluss der Nullspur möglich (optional)
DC 5 V / max. 200 mA
X8
1
2
3
4
A
5
A
6
B
7
B
8
Z
Z
9
V
GND
+KTY
-KTY
B
B
A
A
CC
Z
Z
Abb. 5−21 Anschluss Inkrementalgeber mit TTL−Pegel (RS−422)
Signale bei Rechtslauf
Paarweise verdrillte Adern
X8 − Inkrementalgeber mit TTL−Pegel
Steckverbinder: Stift, 9−polig, Sub−D
Pin 1
Signal B A A V
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
GND (−KTY) Z Z +KTY B
CC
0,14 mm2 (AWG 26) 1 mm2 (AWG 18) 0,14 mm2 (AWG 26)
9300VEC018
52
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 53

Elektrische Installation
Rückführsystem verdrahten
Inkrementalgeber mit HTL−Pegel an X9
5
5.8.3 Inkrementalgeber mit HTL−Pegel an X9
Technische Daten
Bereich Werte
Anschluss am Antriebsregler Steckverbinder: Stift, 9−polig, Sub−D
Anschließbare Inkrementalgeber Inkrementalgeber mit HTL−Pegel
l Zweispurig mit inversen Signalen und Nullspur
l Zweispurig ohne inverse Signale und Nullspur
Eingangsfrequenz 0 ... 200 kHz
Stromaufnahme 5 mA pro Kanal
Versorgung Inkrementalgeber Externe Spannungsquelle
Interne Spannungsquelle
(X9/4, X9/5)
DC 5 V / max. 200 mA
Summenstrom an X9/4, X9/5 und X10/4, X10/5: max. 200 mA
Verdrahtung
<50m
B
B
A
A
GND
Z
Z
+
–
Abb. 5−22 Anschluss Inkrementalgeber mit HTL−Pegel
Signale bei Rechtslauf
Externe Spannungsquelle für den Inkrementalgeber
Paarweise verdrillte Adern
X9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
A
B
B
Z
Z
9300VEC020
X9 − Inkrementalgeber mit HTL−Pegel
Steckverbinder: Stift, 9−polig, Sub−D
Pin 1
Signal B A A +5 V GND Z Z − B
Hinweis!
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0,14 mm2 (AWG 26) 1 mm2 (AWG 18) 0,14 mm2 (AWG 26)
Anschluss zweispuriger Inkrementalgeber ohne inverse Signale
(bei HTL−Pegel):
ƒ Legen Sie das Signal A auf Pin X9/2 (A) und das Signal B auf Pin X9/9 (B).
ƒ Verdrahten Sie Pin X9/3 (A) und X9/1) (B) mit dem Pluspol der externen
Spannungsquelle für den Inkrementalgeber.
53
Page 54

5
Elektrische Installation
Leitfrequenzeingang / Leitfrequenzausgang verdrahten
5.9 Leitfrequenzeingang / Leitfrequenzausgang verdrahten
Technische Daten
Bereich Leitfrequenzausgang X10
Anschluss am Antriebsregler Steckverbinder: Buchse, 9−polig, Sub−D
Pinbelegung Abhängig von der gewählten Grundkonfiguration
Ausgangsfrequenz 0 ... 500 kHz
Signal Zweispurig mit inversen 5 V−Signalen (RS422) und Nullspur
Belastbarkeit Max. 20 mA pro Kanal
(bis zu 3 Folgeantriebe anschließbar)
Besonderheiten Das Ausgangssignal "Enable" an X10/8 schaltet auf LOW, wenn der An-
Interne Spannungsquelle
(X10/4, X10/5)
Bereich Leitfrequenzeingang X9
Anschluss am Antriebsregler Steckverbinder: Stift, 9−polig, Sub−D
Eingangsfrequenz TTL−Pegel: 0 ... 500 kHz
Signal Zweispurig mit inversen Signalen und Nullspur
Auswertung der Signale Über Code C0427
Stromaufnahme Max. 5 mA
Besonderheiten Bei aktivierter Überwachung SD3 wird TRIP oder Warnung ausgelöst,
triebsregler nicht betriebsbereit ist (z. B. vom Netz getrennt). Dadurch
kann beim Folgeantrieb die Überwachung SD3 ausgelöst werden.
DC 5 V / max. 50 mA
Summenstrom an X9/4, X9/5 und X10/4, X10/5: max. 200 mA
HTL−Pegel: 0 ... 200 kHz
Zweispurig ohne inverse Signale und Nullspur (nur bei HTL−Pegel)
wenn das Eingangssignal "Lamp Control" an X9/8 auf LOW schaltet.
Dadurch kann der Antriebsregler reagieren, wenn der Master−Antrieb
nicht betriebsbereit ist.
54
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 55

Elektrische Installation
Leitfrequenzeingang / Leitfrequenzausgang verdrahten
Verdrahtung
Hinweis!
ƒ Wir empfehlen, für die Verdrahtung Lenze−Systemleitungen zu verwenden.
ƒ Bei selbstkonfektionierten Leitungen nur Leitungen mit paarweise
verdrillten und abgeschirmten Adern verwenden.
<50m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
X9X10
Lamp
control (LC)
A
A
B
B
Z
Z
Paarweise verdrillte Adern
B
1
2
3
B
A
A
4
GND
Z
Z
Enable (EN)
5
6
7
8
9
Abb. 5−23 Anschluss Leitfrequenzeingang (X9) / Leitfrequenzausgang (X10)
X9 Folgeantrieb (Slave) Signale bei Rechtslauf
X10 Leitantrieb (Master)
5
9300VEC019
X9 − Leitfrequenzeingang
Steckverbinder: Stift, 9−polig, Sub−D
Pin 1
Signal B A A +5 V GND Z Z LC B
X10 − Leitfrequenzausgang
Steckverbinder: Buchse, 9−polig, Sub−D
Pin 1
Signal B A A +5 V GND Z Z EN B
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0,14 mm
(AWG 26)
0,14 mm
(AWG 26)
2
(AWG 20)
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2
(AWG 20)
0,5 mm
0,5 mm
2
2
0,14 mm
(AWG 26)
0,14 mm
(AWG 26)
2
2
0,5 mm
(AWG 20)
0,5 mm
(AWG 20)
2
2
0,14 mm
(AWG 26)
0,14 mm
(AWG 26)
2
2
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
55
Page 56

6
Abschließende Arbeiten
Installation überprüfen
6 Abschließende Arbeiten
6.1 Installation überprüfen
Stop!
Zerstörung der digitalen Ausgänge (X5/A1 X5/A4).
Die digitalen Ausgänge sind nicht gegen Fremdspannung geschützt.
Mögliche Folgen:
ƒ Beim Anlegen einer Fremdspannung an X5/A1 X5/A4 können die digitalen
Ausgänge beschädigt werden. Die Steuerkarte funktioniert nicht mehr
fehlerfrei.
Schutzmaßnahmen:
ƒ Niemals Fremdspannung an die Klemmen X5/A1 X5/A4 legen.
Überprüfen Sie nach Abschluss der Installation ...
ƒ die Verdrahtung auf Vollständigkeit, Kurzschluss und Erdschluss
ƒ die Versorgung des internen Lüfters (nur 500 V Typen)
– die Position der Brücke ist abhängig von der angelegten Netzspannung
ƒ den Leistungsanschluss:
– Einspeisung über Klemmen L1, L2 und L3 (direkter Netzanschluss)
ƒ den phasenrichtigen Anschluss des Motors (Drehrichtung)
ƒ den Inkrementalgeber (Drehrichtung), falls vorhanden
Hinweis!
Der nächste Schritt ist die Inbetriebnahme. Informationen dazu finden Sie im
Systemhandbuch zum Antriebsregler.
ƒ Lesen Sie das Systemhandbuch, bevor Sie den Antriebsregler einschalten!
ƒ Führen Sie die Inbetriebnahme nach den Anweisungen im Systemhandbuch
durch!
ƒ Wenn Sie die Funktion "Sicherer Halt" verwenden, müssen Sie die Funktion
der Schaltung prüfen!
56
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 57

6.2 Inbetriebnahme vorbereiten
Für die Inbetriebnahme mit Keypad benötigen Sie:
ƒ Ein Keypad EMZ9371BC
Für die Inbetriebnahme mit PC benötigen Sie:
ƒ Einen Computer mit Windows®−Betriebssystem XP
ƒ Die Lenze PC−Software »Global Drive Control (GDC)«
ƒ Eine Verbindung mit dem Antriebsregler über eine Schnittstelle:
Antriebsregler Verbindung PC
Schnittstelle PC−Adapter Schnittstelle
Integrierter Systembus oder
Kommunikationsmodul CANopen
EMF2175IB
Kommunikationsmodul LECOMA/B
EMF2102IBCV001
Kommunikationsmodul LECOM−LI
EMF2102IBCV003
Systembuskabel
(liegt den Systembusadaptern bei)
Serielles Kabel
EWL0020
EWL0021
LWL
EWZ0006
EWZ0007
Abschließende Arbeiten
Inbetriebnahme vorbereiten
Systembusadapter
EMF2173IB
Systembusadapter
EMF2177IB
Für LECOM−B werden benötigt:
l Ein handelsüblicher
RS232/RS485−Umsetzer
l Ein RS485−Verbindungskabel
Lichtwellenleiter−Adapter
EMF2125IB
EMF2126IB
6
Parallel
USB
Seriell (RS232)
Außerdem benötigen Sie:
ƒ Das Systemhandbuch für den verwendeten Antriebsregler
ƒ Ggf. das Kommunikationshandbuch (KHB) zum Netzwerk der
Automatisierungsplattform
ƒ Netzspannung oder 24−V−Spannungsversorgung für die Steuerelektronik des
Antriebsreglers
Folgen Sie den Anleitungen der Software und/oder lesen Sie die Dokumentation.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
57
Page 58

Scope of supply
Description Use Amount
9300 vector frequency inverter ˘ master 1
9300 vector frequency inverter ˘ slave 1
Mounting Instructions 1
Mounting rail 4
Hexagon socket screw M8 × 25 mm
Spring washer M8 24
DC busbar for +U
DC busbar for −U
Distance sleeve M8
Hexagon socket screw M8 × 45 mm 6
Plain washer M8 6
EMC shield sheet for shielded control cables 1
Recessed head screw M4 × 12 mm Fastening of EMC shield sheet 2
Shield clip Connection of the cable shields to the shield sheet 3
4−pole terminal strip Safety relay KSR at X11 1 97
7−pole terminal strip Digital inputs and outputs at X5 2 95
4−pole terminal strip Analog inputs and outputs at X6 2 95
3−pole terminal strip System bus (CAN) at X4 1 103
Protective cover Protection for unused Sub−D sockets 4
G
G
Fastening of the controller with the mounting rail
on the mounting plate
+UG connection between master and slave 1
−UG connection between master and slave 1
Fastening of the DC busbars in the master
and slave
78
24
82
6
95
Connections and interfaces
Description Function
Power terminals
Power terminals Connection to the DC bus 88
Power terminals Motor connection 91
x1 Control interface Plug−in station, e.g. for keypad
X3 Jumper Setting of analog input signal at X6/1, X6/2 102
X4 Control terminals System bus (CAN) 103
X5 Control terminals Digital inputs and outputs 95
X6 Control terminals Analog inputs and outputs 95
X8 Sub−D socket Incremental encoder input 105
X9 Sub−D socket
X10 Sub−D socket Digital frequency output 107
X11 Control terminals Safety relay K
Controller mains connection for 400 V 86
Controller mains connection for 500 V 87
Incremental encoder input 106
Digital frequency input 107
SR
Status displays
Position LED red LED green Operating status
Off On Controller is enabled
On On Mains is switched on and automatic start is inhibited
Off Blinking slowly Controller is inhibited
Off On Motor data identification is active
Blinking quickly Off Undervoltage or overvoltage
Blinking slowly Off Active fault
0Fig. 0Tab. 0
97
58
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 59

Contents i
1 About this documentation 61 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1 Document history 61 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2 Target group 61 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 Validity information 62 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4 Conventions used 63 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5 Notes used 64 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Safety instructions 65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 General safety and application notes for Lenze controllers 65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2 Thermal motor monitoring 68 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.1 Description 68 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2.2 Parameter setting 69 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Residual hazards 70 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Technical data 71 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 General data and operating conditions 71 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Safety relay KSR 73 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Rated data 74 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3.1 Controller for a mains voltage of 400 V 74 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3.2 Controller for a mains voltage of 400 V / 500 V 75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.4 Dimensions 76 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Mechanical installation 77 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1 Drilling the holes into the mounting plate 77 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 Fastening the mounting rails to the mounting plate 78 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3 Fastening the controller on mounting plate 79 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Electrical installation 80 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1 Installation according to EMC (installation of a CE−typical drive system) 80 . . . . . . .
5.2 Master and slave connection 82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.1 Important notes 82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.2 Preliminary works 82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.3 Installation of the DC−busbars 83 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.4 Connection of the control cables between master and slave 84 . . . . . . . . .
5.2.5 Final works 85 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3 Controller mains connection for a mains voltage of 400 V 86 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4 Supply and fan connection at the controller for a mains voltage of 400 V/500V 86
5.4.1 Mains connection 87 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4.2 Connection to the DC bus (+UG, −UG) 88 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4.3 Fan connection 88 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
59
Page 60

Contentsi
5.5 Motor connection 91 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.5.1 Wiring of motor temperature monitoring 93 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6 Control terminals 95 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6.1 Important notes 95 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6.2 With function "Safe torque off" active 97 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6.3 With function "Safe torque off" deactivated 100 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6.4 Terminal assignment 102 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.7 Wiring of the system bus (CAN) 103 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8 Wiring of the feedback system 104 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8.1 Important notes 104 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8.2 Incremental encoder with TTL level at X8 105 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8.3 Incremental encoder with HTL level at X9 106 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.9 Wiring of digital frequency input / digital frequency output 107 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Final works 109 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.1 Installation check 109 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.2 Preparing the commissioning procedure 110 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
60
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 61

1 About this documentation
1.1 Document history
What is new / what has changed?
Material number Version Description
.EXz 4.0 03/2011 TD23 Revision: Supplements for software version 8.1
13219330 3.0 04/2008 TD23/35/32Revision, error correction
13146181 2.0 10/2006 TD23 Revision, error correction
00487687 1.0 06/2004 TD23 First edition
Tip!
Information and auxiliary devices around the Lenze products can be found in
the download area at
http://www.Lenze.com
About this documentation
Document history
inserted
1
1.2 Target group
This documentation is directed at qualified skilled personnel according to IEC 60364.
Qualified skilled personnel are persons who have the required qualifications to carry out
all activities involved in installing, mounting, commissioning, and operating the product.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
61
Page 62

1
About this documentation
Validity information
1.3 Validity information
This documentation applies to 9300 frequency inverters as of version:
EVF 93xx ˘ E V Vxxx 1x 8x
Product series
EVF Frequency inverter
EVM: Master of EVF
EVL: Slave of EVF
Type no. / power
400 V 500 V
9381
250 kW
9382
315 kW
9383
400 kW
Type
E Built−in unit
Design
V Vector−controlled frequency inverter
X: Slave
Variant Integrated RFI filter
– 400 V – –
V030 400 V · –
V060 400 V – ·
V110 400 V ··
V210 400 V / 500 V – –
V240 400 V / 500 V · –
V270 400 V / 500 V – ·
V300 400 V / 500 V ··
315 kW
400 kW
500 kW
A
Nameplate
Integrated brake
transistor
EVM... EVL...
0
1
0
L
Inverter
Type:
Input:
Output:
Master Slave
EVM
1
L
Inverter
Id.-No.:
Prod.-No.:
Type:
Input:
Output:
0045042000129567000005
33.9335VE.1A.70
33 . 9335VE . 1A . 70 . V030
Hans-Lenze-Strasse1
D-31855Aerzen
Madein EC
EVF
EVL
Hans-Lenze-Strasse1
D-31855Aerzen
Madein EC
Ser.-No.:
1
Hardware version
Software version
– Slave (no software version)
62
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 63

About this documentation
Conventions used
1
1.4 Conventions used
This documentation uses the following conventions to distinguish between different
types of information:
Type of information Identification Examples/notes
Spelling of numbers
Decimal separator language−dependentIn each case, the signs typical for the target
Warnings
UL warnings
UR warnings
Text
Program name » « PC software
Icons
Page reference Reference to another page with additional
language are used as decimal separators.
For example: 1234.56 or 1234,56
Are only given in English.
For example: »Engineer«, »Global Drive
Control« (GDC)
information
For instance: 16 = see page 16
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
63
Page 64

1
About this documentation
Notes used
1.5 Notes used
The following pictographs and signal words are used in this documentation to indicate
dangers and important information:
Safety instructions
Structure of safety instructions:
Danger!
Pictograph and signal word Meaning
Danger!
Danger!
Stop!
(characterises the type and severity of danger)
Note
(describes the danger and gives information about how to prevent dangerous
situations)
Danger of personal injury through dangerous electrical voltage.
Reference to an imminent danger that may result in death or
serious personal injury if the corresponding measures are not
taken.
Danger of personal injury through a general source of danger.
Reference to an imminent danger that may result in death or
serious personal injury if the corresponding measures are not
taken.
Danger of property damage.
Reference to a possible danger that may result in property
damage if the corresponding measures are not taken.
Application notes
Pictograph and signal word Meaning
Note!
Tip!
Important note to ensure troublefree operation
Useful tip for simple handling
Reference to another documentation
64
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 65

Safety instructions
General safety and application notes for Lenze controllers
2 Safety instructions
2.1 General safety and application notes for Lenze controllers
(in accordance with Low−Voltage Directive 2006/95/EC)
For your personal safety
Disregarding the following safety measures can lead to severe injury to persons and
damage to material:
ƒ Only use the product as directed.
ƒ Never commission the product in the event of visible damage.
ƒ Never commission the product before assembly has been completed.
ƒ Do not carry out any technical changes on the product.
ƒ Only use the accessories approved for the product.
2
ƒ Only use original spare parts from Lenze.
ƒ Observe all regulations for the prevention of accidents, directives and laws
applicable on site.
ƒ Transport, installation, commissioning and maintenance work must only be carried
out by qualified personnel.
– Observe IEC 364 and CENELEC HD 384 or DIN VDE 0100 and IEC report 664 or
DIN VDE 0110 and all national regulations for the prevention of accidents.
– According to this basic safety information, qualified, skilled personnel are persons
who are familiar with the assembly, installation, commissioning, and operation of
the product and who have the qualifications necessary for their occupation.
ƒ Observe all specifications in this documentation.
– This is the condition for safe and trouble−free operation and the achievement of
the specified product features.
– The procedural notes and circuit details described in this documentation are only
proposals. It’s up to the user to check whether they can be transferred to the
particular applications. Lenze Automation GmbH does not accept any liability for
the suitability of the procedures and circuit proposals described.
ƒ Depending on their degree of protection, some parts of the Lenze controllers
(frequency inverters, servo inverters, DC speed controllers) and their accessory
components can be live, moving and rotating during operation. Surfaces can be hot.
– Non−authorised removal of the required cover, inappropriate use, incorrect
installation or operation, creates the risk of severe injury to persons or damage to
material assets.
– For more information, please see the documentation.
ƒ High amounts of energy are produced in the controller. Therefore it is required to
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
wear personal protective equipment (body protection, headgear, eye protection, ear
protection, hand guard).
65
Page 66

2
Safety instructions
General safety and application notes for Lenze controllers
Application as directed
Controllers are components which are designed for installation in electrical systems or
machines. They are not to be used as domestic appliances, but only for industrial purposes
according to EN 61000−3−2.
When controllers are installed into machines, commissioning (i.e. starting of the operation
as directed) is prohibited until it is proven that the machine complies with the regulations
of the EC Directive 2006/42/EC (Machinery Directive); EN 60204 must be observed.
Commissioning (i.e. starting of the operation as directed) is only allowed when there is
compliance with the EMC Directive (2004/108/EC).
The controllers meet the requirements of the Low−Voltage Directive 2006/95/EC. The
harmonised standard EN 61800−5−1 applies to the controllers.
The technical data and supply conditions can be obtained from the nameplate and the
documentation. They must be strictly observed.
Warning: Controllers are products which can be installed in drive systems of category C2
according to EN 61800−3. These products can cause radio interferences in residential areas.
In this case, special measures can be necessary.
Transport, storage
Please observe the notes on transport, storage, and appropriate handling.
Observe the climatic conditions according to the technical data.
Installation
The controllers must be installed and cooled according to the instructions given in the
corresponding documentation.
The ambient air must not exceed degree of pollution 2 according to EN 61800−5−1.
Ensure proper handling and avoid excessive mechanical stress. Do not bend any
components and do not change any insulation distances during transport or handling. Do
not touch any electronic components and contacts.
Controllers contain electrostatic sensitive devices which can easily be damaged by
inappropriate handling. Do not damage or destroy any electrical components since this
might endanger your health!
66
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 67

Safety instructions
General safety and application notes for Lenze controllers
Electrical connection
When working on live controllers, observe the applicable national regulations for the
prevention of accidents (e.g. VBG 4).
The electrical installation must be carried out according to the appropriate regulations
(e.g. cable cross−sections, fuses, PE connection). Additional information can be obtained
from the documentation.
This documentation contains information on installation in compliance with EMC
(shielding, earthing, filter, and cables). These notes must also be observed for CE−marked
controllers. The manufacturer of the system is responsible for compliance with the limit
values demanded by EMC legislation. The controllers must be installed in housings (e.g.
control cabinets) to meet the limit values for radio interferences valid at the site of
installation. The housings must enable an EMC−compliant installation. Observe in
particular that e.g. the control cabinet doors have a circumferential metal connection to
the housing. Reduce housing openings and cutouts to a minimum.
Lenze controllers may cause a DC current in the PE conductor. If a residual current device
(RCD) is used for protection against direct or indirect contact for a controller with
three−phase supply, only a residual current device (RCD) of type B is permissible on the
supply side of the controller. If the controller has a single−phase supply, a residual current
device (RCD) of type A is also permissible. Apart from using a residual current device (RCD),
other protective measures can be taken as well, e.g. electrical isolation by double or
reinforced insulation or isolation from the supply system by means of a transformer.
2
Operation
If necessary, systems including controllers must be equipped with additional monitoring
and protection devices according to the valid safety regulations (e.g. law on technical
equipment, regulations for the prevention of accidents). The controllers can be adapted to
your application. Please observe the corresponding information given in the
documentation.
After the controller has been disconnected from the supply voltage, all live components
and power connections must not be touched immediately because capacitors can still be
charged. Please observe the corresponding stickers on the controller.
All protection covers and doors must be shut during operation.
Notes for UL−approved systems with integrated controllers: UL warnings are notes that
only apply to UL systems. The documentation contains special UL notes.
Safety functions
Certain controller versions support safety functions (e.g. "Safe torque off", formerly "Safe
standstill") according to the requirements of the EC Directive 2006/42/EC. The notes on
the integrated safety system provided in this documentation must be observed.
Maintenance and servicing
The controllers do not require any maintenance if the prescribed operating conditions are
observed.
Disposal
Recycle metal and plastic materials. Ensure professional disposal of assembled PCBs.
The product−specific safety and application notes given in these instructions must be
observed!
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
67
Page 68

2
Safety instructions
Thermal motor monitoring
Description
2.2 Thermal motor monitoring
2.2.1 Description
Note!
From software version 8.1 onwards, the 9300 vector controllers are provided
with an I
motor.
ƒ I
thermal motor utilisation from the detected motor currents.
ƒ The calculated motor utilisation is saved when the mains is switched off.
ƒ Nevertheless, I
because other influences on the motor utilisation such as changes in the
cooling conditions (e.g. cooling air flow interrupted or too warm) cannot be
detected.
2
xt function for sensorless thermal monitoring of the connected
2
xt monitoring is based on a mathematical model which calculates a
2
xt monitoring does not provide full motor protection
2
× t−load of the motor is constantly calculated by the drive controller and displayed
The I
in C0066.
2
The I
x t−monitoring is designed in a way, that a motor with a thermal motor time factor
of 5 min, a motor current of 1.5 x I
and a trigger threshold of 100 % releases the
r
monitoring after 179 s.
You can set different reactions with two adjustable trigger thresholds.
ƒ Adjustable reaction OC8 (TRIP, Warning, Off).
– The reaction is set in C0606.
– The trigger threshold is set in C0127.
– The reaction OC8 can be used for example for an advance warning.
ƒ Fixed reaction OC6−TRIP.
– The trigger threshold is set in C0120.
Response of the I2 x t−monitoring Condition
The I2 x t−monitoring is deactivated.
C0066 = 0 % and
MCTRL−LOAD−I2XT = 0,00 % is set.
The I2 x t−monitoring is stopped.
The actual value in C0066 and at the MCTRL−LOAD−I2XT
output is held.
The I2 x t−monitoring is deactivated.
The motor load is displayed in C0066.
Set the controller inhibit at C0120 = 0 % and
C0127 = 0 %.
Allow controller release at C0120 = 0 % and
C0127 = 0 %.
Set C0606 = 3 (Off) and C0127 > 0 %.
68
Note!
An OC6 or OC8 error message can only be reset if the I2 × t−monitoring has
fallen below the set trigger threshold by 5 %.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 69

2.2.2 Parameter setting
Parameter setting
Code Meaning Value range Lenze setting
C0066 Display of the I2xt utilisation of the motor 0 ... 250 % −
C0120 Threshold: Triggering of an "OC6" error 0 ... 120 % 0 %
C0127 Threshold: Triggering of an "OC8" error 0 ... 120 % 0 %
C0128 Thermal time constant of the motor 0.1 ... 50.0 min 5.0 min
C0606 Response to "OC8" error Trip, warning, off Warning
Calculating the release time
Safety instructions
Thermal motor monitoring
Parameter setting
2
ȡ
t +*(C0128) @ ln
ȧ
Ȣ
ƒ The thermal capacity of the motor is expressed by the thermal motor time factor
1 *
ǒ
I
M
I
r
y ) 1
Ǔ
2
@ 100
ȣ
ȧ
Ȥ
IMActual motor current
I
Rated motor current
r
y C0120 or C0127
(C0128). Please see the rated data of the motor for the value or ask the
manufacturer of the motor.
Reading the release time off the diagram
Diagram for the determination of the release times of a motor with a thermal motor time
factor of 5 min:
2
I t [%]
120
100
50
Fig. 2−1 I2 × t−monitoring: Release times for different motor currents and trigger thresholds
I =3×I
mot r
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
I =2×I
mot r
Imot Motor current
I
r
2
I
tI
T Time
I =1.5×I
mot r
Rated motor current
2
t load
I=1×I
mot r
1000
t [s]
9300std105
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
69
Page 70

2
2.3 Residual hazards
Safety instructions
Residual hazards
Protection of persons
ƒ Before working on the controller, check that no voltage is applied to the power
terminals:
– The power terminals U, V, W, +U
least five minutes after disconnecting from the mains.
– The power terminals L1, L2, L3, U, V, W, +U
live when the motor is stopped.
ƒ The leakage current to earth (PE) is >3.5 mA. EN 61800−5−1 requires a fixed
installation.
ƒ The heatsink of the controller has an operating temperature of > 80 °C:
– Direct skin contact causes burns.
ƒ During the parameter set transfer, the control terminals of the controller can
assume undefined states.
– For this reason, the connectors X5 and X6 have to be unplugged before the
transfer is executed. This ensures that the controller is inhibited and all control
terminals are in the defined state LOW".
, −UG, BR1, BR2 and 101 ... 104 remain live for at
G
, −UG, BR1, BR2 and 101 ... 104 remain
G
Device protection
ƒ Frequent mains switching (e.g. inching mode via mains contactor) can overload and
destroy the input current limitation of the controller.
– Thus, at least five minutes have to pass between two switch−on processes.
– In case of frequent, safety−related disconnections use the "safe torque off" safety
function (STO).
Motor protection
ƒ Certain drive controller settings can overheat the connected motor:
– E. g. long−time operation of the DC injection brake.
– Long−time operation of self−ventilated motors at low speeds.
Protection of the machine/system
ƒ Drives can reach dangerous overspeeds (e. g. setting of high output frequencies in
connection with motors and machines not suitable for this purpose):
– The drive controllers do not provide protection against such operating conditions.
For this purpose, use additional components.
70
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 71

General data and operating conditions
3 Technical data
3.1 General data and operating conditions
General data
Conformity and approval
Conformity
CE 2006/95/EC Low−Voltage Directive
Protection of persons and equipment
Type of protection
Earth leakage current IEC/EN 61800−5−1 > 3.5 mA Observe stipulations and safety
Insulation of control
circuits
Insulation resistance IEC/EN 61800−5−1
Protective measures Against short circuit, earth fault (earth−fault protected during
EN 60529
NEMA 250 Protection against accidental contact according to type 1
IEC/EN 61800−5−1 Safe mains isolation by double (reinforced) insulation for the
Technical data
IP20
instructions!
terminals X1 and X5.
Basic insulation (single isolating distance) for the terminals
X3, X4, X6, X8, X9, X10 and X11.
< 2000 m site altitude: overvoltage category III
> 2000 m site altitude: overvoltage category II
operation, limited earth−fault protection during mains
power−up), overvoltage, motor stalling, motor
overtemperature (input for PTC or thermal contact)
3
EMC
Noise emission EN 61800−3
Interference immunity IEC/EN 61800−3 Category C3
Cable−guided, up to 50 m motor cable length with RFI filter:
Category C2.
Radiation, with RFI filter and installation in control cabinet:
Category C2
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
71
Page 72

3
Technical data
General data and operating conditions
Operating conditions
Ambient conditions
Climatic
Storage
Transport IEC/EN 60721−3−2 2K3 (−25 ... +70 °C)
Operation IEC/EN 60721−3−3 3K3 (0 ... +50 °C)
Pollution EN 61800−5−1 Degree of pollution 2
Site altitude < 4000 m amsl
Internal fan 975 m3/h volume flow per device
Mechanical
Vibration resistance EN 61800−5−1
Electrical
Mains connection
Power system
TT, TN
(with earthed
neutral)
DC−bus operation Possible for the variants V210, V240, V270, V300
Motor connection
Length of the motor
cable
shielded 100 m
unshielded 200 m
IEC/EN 60721−3−1
1K3 (−20 ... +60 °C) < 6 months
1K3 (−20 ... +40 °C) > 6 months
> 2 years: form DC bus
capacitors
> +40 °C: reduce the rated output current by 2.5 %/°C.
> 1000 m amsl: reduce the rated output current by
5 %/ 1000 m.
Operation is permitted without restrictions.
At rated mains voltage and a switching frequency of £ 2 kHz
without additional output filter.
For compliance with EMC regulations, the permissible cable
lengths may change.
Mounting conditions
Mounting place In the control cabinet
Mounting position Vertical
Free spaces
Dimensions
Weights
77
72
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 73

Technical data
Safety relay KSR
3
3.2 Safety relay K
Terminal Description Field Values
X11/K32
X11/K31
X11/33
X11/34
Safety relay K
1st disconnecting path
SR
SR
Coil voltage at +20 °C DC 24 V (20 ... 30 V)
Coil resistance at +20 °C 823 W ±10 %
Rated coil power Approx. 700 mW
Max. switching voltage AC 250 V, DC 250 V (0.45 A)
Max. AC switching capacity 1500 VA
Max. switching current (ohmic load) AC 6 A (250 V), DC 6 A (50 V)
Recommended minimum load > 50 mW
Max. switching rate 6 switchings per minute
Mechanical service life 107 switching cycles
Electrical service life
at 250 V AC
(ohmic load)
at 24 V DC
(ohmic load)
105 switching cycles at 6 A
6
10
7
10
6 × 103 switching cycles at 6 A
6
10
1.5 × 10
7
10
switching cycles at 1 A
switching cycles at 0.25 A
switching cycles at 3 A
6
switching cycles at 1 A
switching cycles at 0.1 A
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
73
Page 74

3
Technical data
Rated data
Controller for a mains voltage of 400 V
3.3 Rated data
3.3.1 Controller for a mains voltage of 400 V
Type Power Mains voltage Mains
EVF9381−EV
EVF9381−EVV030
EVF9381−EVV060
EVF9381−EVV110
EVF9382−EV
EVF9382−EVV030
EVF9382−EVV060
EVF9382−EVV110
EVF9383−EV
EVF9383−EVV030
EVF9383−EVV060
EVF9383−EVV110
250 kW
315 kW 570 A 600 A 900 A 320 kg 350 kg
400 kW 713 A 750 A 1125 A 400 kg 430 kg
Weight without RFI filter A
Weight with integrated RFI filter A
1)
At rated mains voltage and a switching frequency of 2 kHz
3/PE AC 400 V
340 V − 0 % ... 456 V + 0 %
45 Hz − 0 % ... 65 Hz + 0 %
current
475 A 500 A 750 A 320 kg 350 kg
Output current
iN I
max
1)
(60 s)
Weight
74
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 75

Technical data
Rated data
Controller for a mains voltage of 400 V / 500 V
3
3.3.2 Controller for a mains voltage of 400 V / 500 V
Rated data at a mains voltage of 400 V
Type Power Mains voltage Mains
EVF9381−EVV210
EVF9381−EVV240
EVF9381−EVV270
EVF9381−EVV300
EVF9382−EVV210
EVF9382−EVV240
EVF9382−EVV270
EVF9382−EVV300
EVF9383−EVV210
EVF9383−EVV240
EVF9383−EVV270
EVF9383−EVV300
250 kW
3/PE AC 400 V
340 V − 0 % ... 577 V + 0 %
315 kW 570 A 600 A 900 A 320 kg 350 kg
400 kW 713 A 750 A 1125 A 400 kg 430 kg
45 Hz − 0 % ... 65 Hz + 0 %
alternatively:
DC 565 V
DC 480 V − 0 % ... 800 V + 0 %
Weight without RFI filter A
Weight with integrated RFI filter A
1)
At rated mains voltage and a switching frequency of 2 kHz
current
475 A 500 A 750 A 320 kg 350 kg
Rated data at a mains voltage of 500 V
Type Power Mains voltage Mains
EVF9381−EVV210
EVF9381−EVV240
EVF9381−EVV270
EVF9381−EVV300
EVF9382−EVV210
EVF9382−EVV240
EVF9382−EVV270
EVF9382−EVV300
EVF9383−EVV210
EVF9383−EVV240
EVF9383−EVV270
EVF9383−EVV300
315 kW
3/PE AC 500 V
340 V − 0 % ... 577 V + 0 %
45 Hz − 0 % ... 65 Hz + 0 %
400 kW 570 A 600 A 900 A 320 kg 350 kg
alternatively:
DC 705 V
DC 480 V − 0 % ... 800 V + 0 %
500 kW 713 A 750 A 1125 A 400 kg 430 kg
current
475 A 500 A 750 A 320 kg 350 kg
Output current
iN I
Output current
iN I
max
max
1)
(60 s)
1)
(60 s)
Weight
Weight
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Weight without RFI filter A
Weight with integrated RFI filter A
1)
At rated mains voltage and a switching frequency of 2 kHz
75
Page 76

3
b2
d
Technical data
Dimensions
3.4 Dimensions
a1
a2
a
a3
c
0
b1
b
d
Fig. 3−1 Dimensions
Eyebolts
0
0
9300VEC039
76
Type a
[mm]a1[mm]a2[mm]a3[mm]b[mm]b1[mm]b2[mm]c[mm]d[mm]
EVF9381−EV
EVF9381−EVVxxx
EVF9382−EV
EVF9382−EVVxxx
EVF9383−EV
EVF9383−EVVxxx
1050 450 225 50 1145 1005 15 436
9
(16×)
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 77

Drilling the holes into the mounting plate
4 Mechanical installation
Tip!
ƒ Lenze recommends to install an air lock. The air lock serves to dissipate the
heated cooling air directly from the control cabinet.
– Order no. E93ZWL2
ƒ A drilling jig for marking the bore holes is available as dxf−file in the
Internet in the "Download" area under www.Lenze.de.
4.1 Drilling the holes into the mounting plate
Assembly space Minimum clearance
Left/right of other controllers 30 mm
Left/right of a non−heat−conducting wall 100 mm
Top/bottom 200 mm
Mechanical installation
4
Comply with the clearances given to ensure a sufficient cooling of the controller. When
using an air lock, different clearances apply (see Mounting Instructions for the air lock).
a
a1 a1
a2 a2
a3
b
d
a2 a2
a1 a1
Fig.4−1 Bore holes in the mounting plate for fixing the controller
a a1 a2 a3 b d
550 mm 450 mm 340 mm 225 mm 1005 mm 9 mm (24x)
a3
93vec079
1. Mark the bore holes on the mounting plate according to the figure.
2. Drill the holes into the mounting plate.
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
77
Page 78

4
4.2 Fastening the mounting rails to the mounting plate
Mechanical installation
Fastening the mounting rails to the mounting plate
(from hardware version 1x)
0
22
33
1
0
33
22
Fig.4−2 Fastening the mounting rails on the mounting plate
Mounting rail
Mounting plate
Hexagon socket screw M8 × 25 mm
Spring washer M8
9300vec080
1. Hold the mounting rails behind the mounting plate.
2. Fasten the mounting rails exactly at the illustrated points using 2 hexagon socket
screws and spring washers on each side.
78
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 79

Mechanical installation
Fastening the controller on mounting plate
4
4.3 Fastening the controller on mounting plate
Danger!
Risk of injury due to the high weight of the controller.
The controller has to be carried using the eyebolts and an adequate lifting tool.
00
12
4
5
3
5
4
Fig.4−3 Fastening the controller on mounting plate
Eyebolts Mounting plate
Master 16 hexagon socket screws M8 × 25 mm
Slave 16 spring washers M8
1. Put master and slave on the mounting plate.
2. Fasten the master and slave each with five hexagon socket screws and spring
washers at the top and 3 hexagon socket screws and spring washers at the bottom
exactly at the marked point.
9300vec081
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
79
Page 80

5
Electrical installation
Installation according to EMC (installation of a CE−typical drive system)
5 Electrical installation
Stop!
The drive controller contains electrostatically sensitive components.
The personnel must be free of electrostatic charge when carrying out assembly
and service operations.
5.1 Installation according to EMC (installation of a CE−typical drive system)
ƒ Always separate motor cables from mains cables and control cables.
ƒ Cross the motor cable at right angles with mains cables and control cables.
ƒ Ideally the motor cable should be installed without interruptions.
ƒ Connect all components (controller, choke) to a central earthing point (PE rail).
ƒ Always connect the shields to the mounting plate with a contact surface as large as
possible or use the shield connections on the device side.
ƒ Always connect the motor cable shield to both sides − to the controller and to the
motor.
ƒ The cables of the analog and digital inputs and outputs must be shielded. Short
(up to 200 mm), unshielded cables must always be twisted.
ƒ The shield connections of the control cables must have a distance of at least 50 mm
to the shield connections of the motor and DC cables.
ƒ Digital cables require a double−sided shield connection.
ƒ Analog cables require a single−sided shield connection on the inverter side.
80
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 81

Electrical installation
5
Installation according to EMC (installation of a CE−typical drive system)
L1
L2
L3
N
PE
F1 … F3
K10
PES
+
DC 24 V
PES
PES PES
IN1
Z5
IN2
IN3
IN4
–
PE
PESPES
PES
PES
101 101102 102103 103104 104
X11
K31
K32
33
34
X5
28
E1
E2
E3
EVM9381-EV …
E4
EVM9383-EV
E5
ST1
ST2
39
A1
A2
A3
A4
59
T1 T2
UU
PE PE
VVWW
PE
PES
PES
J>
PE
M
3~
L3
PE PE
L1 L1L2 L2
DC+
DC–
PES
X6
63
7
62
7
4
3
2
1
PES
BR1 BR1BR2 BR2
+UG +UG-UG -UG
PE
X8/8
X8/5
KTY
M
PE
3~
PE
PES
EVL9381-EV …
EVL9383-EV
PE
PES
PES
F4 … F6
K10
S2
S1
L3
PES PES PES
Z2Z1
PES PES
PE
RB2
RB1PE
RB
K10
T2T1
JRB
Z3
PE
RB2
RB1PE
RB
JRB
K10
PES
T2T1
Z4
9300VEC082
Fig. 5−1 Example for wiring in accordance with EMC regulations
F1 ... F3, F4 ... F6 Fuses
K10 Mains contactor
Z1, Z2 Motor choke
Z3, Z4 Brake resistor
Z5 Programmable logic controller (PLC)
S1 Mains contactor on
S2 Mains contactor off
+U
, −U
G
G
DC−bus connection
PES HF shield termination through large−surface connection to PE
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
81
Page 82

5
5.2 Master and slave connection
5.2.1 Important notes
Electrical installation
Master and slave connection
Important notes
Danger!
Danger of personal injury! Destruction of the controller!
Damaged control cables in the controller (master and slave) may cause a faulty
control of the output stage.
Possible consequences:
ƒ When switching on the mains voltage, high energies may discharge like an
explosion.
ƒ Explosive noises may damage your hearing. A shock by an unexpected and
loud explosion may cause distress.
ƒ The controller will be destroyed.
Protective measures:
ƒ When working with the DC busbars, make sure that you do not damage any
internal connectors and cables.
ƒ Before attaching the cover again:
– Check all plugs selected in Fig. 5−5 for damage and correct fit.
– Check all cables involved for damages.
– If the plugs do not fit correctly, or the plugs or cables are damaged,
commissioning is prohibited. Contact the Lenze service.
5.2.2 Preliminary works
Fig. 5−2 Fastening the covers to the master and slave
ƒ Remove the upper cover from the master and the slave to access the power
sections. Each cover is fastened with 4 screws.
0 1
9300vec164
82
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 83

5.2.3 Installation of the DC−busbars
0
1
2
3
4
8
5
6
7
Fig. 5−3 Mounting of +DC/−DC busbars
4
5
6
DC-
Electrical installation
Master and slave connection
Installation of the DC−busbars
0
1
2
3
DC+
4
5
6
7
8
4
5
6
5
9300VEC024
How to mount the DC busbars
1. Mount +DC busbar :
– Remove hexagon socket screws M8 .
– Position the DC busbar in the master and the slave.
– Fasten the DC busbar in the master and the slave with 1 hexagon socket screw
M8 × 45 mm , 1 plain washer and 1 distance sleeve each.
– Tighten the hexagon socket screws (tightening torque: 10.9 Nm).
2. Mount −DC busbar :
– Remove hexagon socket screws M8 .
– Put both connecting cables aside.
– Position the DC busbar in the master and the slave.
– Insert 2 hexagon socket screws M8 × 45 mm each with plain washers into the
bore holes of the DC busbar, finally passing them through the distance sleeves .
– Screw the hexagon socket screws into the threaded holes in the master and
slave.
– Lay the connecting cable in the master and slave with cable lug between the
busbar and plain washer .
– Tighten the hexagon socket screws (tightening torque: 10.9 Nm).
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
83
Page 84

5
Electrical installation
Master and slave connection
Connection of the control cables between master and slave
5.2.4 Connection of the control cables between master and slave
0
2
4
Fig. 5−4 Connection of the control cables between master and slave
1
DC+
DC-
5
0
1
0
1
3
9300VEC028
How to connect the control cables
1. Installation and connection of the ribbon cable :
By default the ribbon cable is inside the master. The plug is already attached to the
Drive Board.
– Route the ribbon cable from the master to the Drive Board connection in the slave,
inserting the ribbon cable into the cable ducts .
– Plug the ribbon cable plug into the socket at the Drive Board.
2. Laying and connecting 2−core cables with plugs :
By default the cable is inside the master. The corresponding cable with socket is in the
slave.
– Lay the two−core cable from the master to the socket in the slave.
– Connect the 2−pole plug with the 2−pole socket in the slave.
3. Laying and connecting 10−core cables with plugs :
By default the cable is inside the master. The corresponding cable with socket is in the
slave.
– Lay the two−core cable from the master to the socket in the slave.
– Connect the 10−pole plug with the 10−pole socket in the slave.
84
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 85

5.2.5 Final works
Fig. 5−5 Control cables in the master and slave
1. Check the control cables (plugs and cables) for correct fit and possible damages. ()
– If the plugs do not fit correctly, or the plugs or cables are damaged, commissioning
is prohibited. Contact the Lenze service.
Electrical installation
Master and slave connection
Final works
5
9300vec163
0 1
Fig. 5−6 Fastening the covers to the master and slave
2. Close the housings using the covers !. Fasten the covers with 4 screws each.
9300vec164
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
85
Page 86

5
Electrical installation
Controller mains connection for a mains voltage of 400 V
Final works
5.3 Controller mains connection for a mains voltage of 400 V
Stop!
The user is responsible for sufficient strain relief!
ƒ Both, the master and the slave must be supplied!
0 1
BR2 BR2
PE PE
M8 M8
25-30 Nm 25-30 Nm
L1, L2,
L3
221-264 lb-in 221-264 lb-in
PE PE
Fig. 5−7 Mains connection example
BR1 BR1
40 mm 40 mm
M6 M6
15-20 Nm 15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in 133-176 lb-in
BR1, BR2 Brake resistor can only be operated with the variants V060 and V110
Master terminals
Slave terminals
UUVVWWL1 L1L2 L2L3 L3
PE PE
L1, L2,
L3
For connection see System Manual of 9300 vector
Fuses and cable cross−sections for the mains supply
Master Slave Master Slave Master Slave
EVF9381−EV
EVF9381−EVVxxx
EVF9382−EV
EVF9382−EVVxxx
EVF9383−EV
EVF9383−EVVxxx
1)
2)
Observe the national and regional legislation
Multiple conductor; both conductors must have the same cross−section
Lenze recommends to use fuses of the gRL utilisation category
315 315
315 315
400 400
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
9300VEC013
1)
1)
1)
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
95 95
95 95
150 150
5.4 Supply and fan connection at the controller for a mains voltage of 400 V/500V
Stop!
The user is responsible for sufficient strain relief!
86
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 87

Supply and fan connection at the controller for a mains voltage of 400 V/500V
5.4.1 Mains connection
ƒ Both, the master and the slave must be supplied!
0 1
Electrical installation
Mains connection
5
PE PE
L3 L3
L1 L1
L2 L2
103
102
101
104
M8
25-30 Nm
L1, L2,
L3
221-264 lb-in
PE
M6
15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in
PE PE
BR2 BR2BR1 BR1+UG +UG-UG -UG
40 mm 40 mm
U U
V VW W
Fig. 5−8 Mains connection example
BR1, BR2 Brake resistor can only be operated with the variants V270 and V300
For connection see System Manual of 9300 vector
Master terminals
Slave terminals
Fuses and cable cross−sections for the mains supply
Type Installation to EN 60204−1
2)
Fuse
Master Slave Master Slave Master Slave
EVF9381−EVV210
EVF9381−EVV240
EVF9381−EVV270
EVF9381−EVV300
EVF9382−EVV210
EVF9382−EVV240
EVF9382−EVV270
EVF9382−EVV300
EVF9383−EVV210
EVF9383−EVV240
EVF9383−EVV270
EVF9383−EVV300
1)
2)
Observe the national and regional legislation
315A
315A 315A
400 A 400 A
Multiple conductor; both conductors must have the same cross−section
Lenze recommends to use fuses of the gRL utilisation category
315A
103
102
101
104
M8
25-30 Nm
L1, L2,
L3
221-264 lb-in
PE
M6
15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in
L1, L2, L3 [mm2] PE [mm2]
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
9300VEC035
95 95
95 95
150 150
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
87
Page 88

5
Electrical installation
Supply and fan connection at the controller for a mains voltage of 400 V/500V
Connection to the DC bus (+UG, −UG)
5.4.2 Connection to the DC bus (+UG, −UG)
ƒ For compliance with EMC requirements, Lenze recommends to use shielded DC−bus
cables.
ƒ Shield clamps are not included in the scope of supply.
ƒ Both, the master and the slave must be supplied!
0
PE PE
L3 L3
L1 L1
L2 L2
103
102
101
104
22
M6
15-20 Nm
PE
133-176 lb-in
40 mm 40 mm
Fig. 5−9 Connection example to +UG and −U
Fuses and cable cross−sections for DC−bus connection
EVF9381−EVV2xx
EVF9381−EVV300
EVF9382−EVV2xx
EVF9382−EVV300
EVF9383−EVV2xx
EVF9383−EVV300
M8 M8
25-30 Nm 25-30 Nm
+U
G
221-264 lb-in 221-264 lb-in
-U
G
BR1, BR2 Brake resistor can only be operated with the variants V270 and V300
Master terminals
Slave terminals
Connect the DC−bus cable shield with a surface as large as possible to the control
Conductive surface
Ensure to have the poles right!
1)
Multiple conductor; both conductors must have the same cross−section
2)
Only use fuses of the gRL utilisation category
Observe the national and regional legislation
PE PE
BR2 BR2BR1 BR1+UG +UG-UG -UG
max.
300 mm
U U
V VW W
33
For connection see System Manual of 9300 vector
cabinet mounting plate by using the clamps.
Master Slave Master Slave Master Slave
350 350
400 400
500 500
1
103
102
101
104
max.
300 mm
M6
15-20 Nm
PE
133-176 lb-in
G
150
1)
2 × 50
240
1)
2 × 95
240
1)
2 × 95
+U
-U
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
240
2 × 95
G
G
9300VEC083
1)
1)
1)
95 95
95 95
150 150
5.4.3 Fan connection
Note!
Connect the fan to the master and the slave.
88
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 89

Electrical installation
Supply and fan connection at the controller for a mains voltage of 400 V/500V
Fan connection
Fan connection when controller is supplied with mains voltage
Lay a bridge between the terminals when a controller is operated on a mains.
AC 340 ... 440 V AC 440 ... 577 V
(when being delivered)
5
L1 L2
101
102
103
104
9300vec044 9300vec045
101
L1 L2
102
103
104
Fan connection when controller is supplied via the DC bus
Danger!
When the fan is externally supplied with voltage, the terminal L2 carries
dangerous mains voltage!
When the controller is supplied via the DC bus, the fan must be separately supplied with
mains voltage (see ). In this case, the bridge between the terminals 102 and 103 must be
removed (see ).
Remove bridge
0
101
102
103
}
L1 L2
104
AC 340…440V
9300vec160 9300vec046 9300vec047
Mains connection for the operation of the fan on
AC 340 ... 440 V AC 440 ... 577 V
1
L1 L2
101
102
103
104
1
101
102
103
104
AC 440 … 577 V
L1 L2
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
89
Page 90

5
Electrical installation
Supply and fan connection at the controller for a mains voltage of 400 V/500V
Fan connection
Exchange defect fuse
In case of an external voltage supply the fan is protected by a fuse integrated in terminal
104.
0
1
L1 L2
101
102
103
104
9300vec161
Fig. 5−10 Fusing of the fan
Open the fuse holder.
Remove the defect fuse from the support and replace it by the following type:
Type: 500V SA 2A 6.32
Ref. no.: P098131
Manufacturer: Ferraz Shawmut
90
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 91

Electrical installation
Motor connection
Fan connection
5
5.5 Motor connection
ƒ To comply with the EMC regulations, Lenze recommends to use shielded motor
cables.
ƒ Shield clamps are not included in the scope of supply.
Stop!
The user is responsible for sufficient strain relief!
Parallel connection of master and slave (motor side)
In order to connect the motor cables of master and slave to the motor, the outputs must
be connected in parallel.
It is important for the parallel connection of the inverter outputs that the outputs are
decoupled by means of an inductance between master and slave. The length of the motor
cables determine whether the inductance of the cables is sufficient for a decoupling.
2 motor connections ensure sufficient decoupling.
ƒ Decoupling via motor chokes
If the single motor cable length is £ 10 m, master and slave must be connected in parallel
via chokes on the motor side to achieve a sufficient decoupling between master and
slave.
ƒ Decoupling via motor cables
If the single motor cable length is > 10 m, the motor cables of master and slave can be
connected in parallel at the motor to achieve a sufficient decoupling between master
and slave.
Decoupling via motor chokes Decoupling via motor cables
UU
PE PE
VVWW
PE
£10 m
Z1 Z2
PE PE
PEUVW
PE
>10 m
M
PE
3~
9300VEC026 9300VEC008
Fig. 5−11 Variants for parallel connection of master and slave (motor side)
Z1, Z2 Motor choke for controller
ELM3−0003H275 EVF9381
ELM3−0002H320 EVF9382
ELM3−0002H410 EVF9383
PE
PEUVW
PE
M
3~
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
91
Page 92

5
Electrical installation
Motor connection
Fan connection
Motor connection
0
UUVVWW
BR2 BR2BR1 BR1
40mm 40mm
22
PE
Fig. 5−12 Motor connection example
PE PE
max.
300 mm
M8
25-30 Nm
M6
15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in
BR1, BR2 Brake resistor can only be operated with the variants V060, V110, V270 and V300
Master terminals
Slave terminals
Connect the motor cable shield with a surface as large as possible to the control
Conductive surface
Ensure to have the poles right!
Do not exceed the maximum motor cable length!
U, V, W
221-264 lb-in
For connection see System Manual of 9300 vector
cabinet mounting plate by using the clamps.
33
PE
1
M6
15-20 Nm
133-176 lb-in
U, V, W
M8
25-30 Nm
221-264 lb-in
max.
300 mm
9300VEC036
Cable cross−sections for the motor connection
Type Installation to EN 60204−1
U, V, W [mm2] PE [mm2]
Master Slave Master Slave
EVF9381−EV
EVF9381−EVxxxx
EVF9382−EV
EVF9382−EVxxxx
EVF9383−EV
EVF9383−EVxxxx
1)
Observe the national and regional legislation
Multiple conductor; both conductors must have the same cross−section
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
150
2 × 50
150
2 × 50
240
2 × 95
1)
1)
1)
95 95
95 95
150 150
92
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 93

Electrical installation
Motor connection
Wiring of motor temperature monitoring
5
5.5.1 Wiring of motor temperature monitoring
The drive controller features 2 connections for motor temperature monitoring:
ƒ Terminals T1, T2 for connecting a PTC thermistor or thermal contact (NC contact).
ƒ Pin X8/5 and X8/8 of the incremental encoder input (X8) for connecting a KTY
thermal sensor.
Incremental encoder input (X8) Terminals T1, T2
Connectable thermal
sensor
Tripping point l Warning: Adjustable
Notes l Monitoring is not active in the Lenze
Linear thermal sensor (KTY) l PTC thermistor
l Error (TRIP): Fixed at 150 °C
setting.
l The KTY is monitored with regard to
interruption and short circuit.
– PTC thermistor with defined
operating temperature (to
DIN 44081 and DIN 44082)
l Thermal contact (NC contact)
– Temperature switch as NC contact
l Fixed, (depending on the PTC/thermal
contact)
l PTC: RJ
l Configurable as warning or error
l Monitoring is not active in the Lenze
l If you do not use a Lenze motor, we
> 1600 W
(TRIP)
setting.
recommend a PTC thermistor up to
150°C.
Connection to incremental encoder input (X8)
Note!
Lenze system cables for motor feedback include additional cores for
temperature feedback. The cables are designed for wiring according to EMC.
B
B
A
A
V
CC5_E
GND
Z
KTY
Fig. 5−13 Connection to incremental encoder input (X8)
X8/5, X8/8 Connection of KTY thermal sensor
Z
+KTY
-KTY
X8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
9300VEC068
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
93
Page 94

5
Electrical installation
Motor connection
Wiring of motor temperature monitoring
Connection to the terminals T1, T2
Stop!
ƒ Do not connect an external voltage to the terminals T1, T2. The controller
will be damaged.
ƒ Do not use the terminals T1, T2 for safety−relevant wiring. Fault messages
via this input are only processed after 2 s.
Terminals T1, T2 at the controller Input circuit for T1, T2
15 V
7.4 k
3.3 k
T2
J
2.7 k
T1
MONIT-OH8
T1
T2
9300STD328 9300VEC017
Fig. 5−14 Connection to the terminals T1, T2
T1, T2 Connection of PTC thermistor or thermal contact (NC contact)
93xx
94
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 95

5.6 Control terminals
5.6.1 Important notes
Stop!
The control card will be damaged if
ƒ the voltage between X5/39 and PE or X6/7 and PE is greater than 50 V,
ƒ the voltage between voltage source and X6/7 exceeds 10 V (common mode)
in case of supply via external voltage source.
Limit the voltage before switching on the drive controller:
ƒ Connect X5/39, X6/2, X6/4 and X6/7 directly to PE or
ƒ use voltage−limiting components.
ƒ For trouble−free operation, the control cables must be shielded:
– Connect the shield of digital input and output cables at both ends.
– Connect the shield of analog input and output cables at one end (at the drive
controller).
– For lengths of 200 mm and more, use only shielded cables for analog and digital
inputs and outputs. Under 200 mm, unshielded but twisted cables may be used.
Electrical installation
Control terminals
Important notes
5
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
95
Page 96

5
Electrical installation
Control terminals
Important notes
How to connect the shield
10
2
3
Fig. 5−15 Connection of the cable shield with shield clip and strain relief with cable binder
Shield sheet
Fasten shield sheet with two screws M4 × 12 mm at the bottom of the control card
Connect cable shield with shield clip to the shield sheet
Provide a strain relief of the control cable at the shield sheet by means of a cable binder
Terminal data
Stop!
ƒ Connect or disconnect the terminal strips only if the controller is
disconnected from the mains!
ƒ Wire the terminal strips before connecting them!
ƒ Unused terminal strips must also be plugged on to protect the contacts.
Cable type Wire end ferrule Maximum cable
Rigid — 2.5 mm
Flexible
Flexible
Flexible
Without wire end
ferrule
Wire end ferrule
without plastic sleeve
Wire end ferrule with
plastic sleeve
cross−section
2
(AWG 14)
2
2.5 mm
2.5 mm
2.5 mm
(AWG 14)
2
(AWG 14)
2
(AWG 14)
Tightening torque Stripping
0.5 ... 0.6 Nm
(4.4 ... 5.3 lb−in)
9300vec063
length
5 mm
96
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 97

Electrical installation
Control terminals
With function "Safe torque off" active
5
5.6.2 With function "Safe torque off" active
(from hardware version 1x)
Safety instructions for the installation of the "Safe torque off" function
ƒ The installation and commissioning of the Safe torque off" function must be
carried out by skilled personnel only.
ƒ All safety−relevant cables (e.g. control cable for the safety relay, feedback contact)
outside the control cabinet must be protected, for instance by a cable duct. Short
circuits between the single cables must be ruled out!
ƒ Wiring of the safety relay K
absolutely vital.
ƒ The electrical reference point for the coil of the safety relay K
with the protective conductor system (DIN EN 60204−1 paragraph 9.4.3). Only this
measure guarantees that the operation is protected against earth faults.
with insulated wire end ferrules or rigid cables is
SR
must be connected
SR
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
97
Page 98

5
X11
Electrical installation
Control terminals
With function "Safe torque off" active
Supply via internal voltage source
ƒ If a freely assignable digital output (e.g. X5/A1) is assigned permanently to HIGH
ƒ For the supply of the analog inputs (X6/1, X6/2 and X6/3, X6/4) you have to set a
+
K
SR
K31K32 33 34
level, it serves as an internal voltage source. Every output has a maximum load
capacity of 50 mA.
– The relay K
and two digital inputs (X5/28 and e.g. X5/E1) can be supplied with
SR
voltage via a digital output.
– Two digital outputs must be connected in parallel and assigned permanently to
HIGH level in order to obtain the maximum wiring (relays K
and X5/E1 ... X5/E5,
SR
X5/ST1).
freely assignable analog output (e. g. X6/63) permanently to HIGH level.
GND2 +24V+5 V
1
2
3
X5
3k
3k
28
E1 E2 E3 E4
X3
50mA
50mA
50mA
3k
3k
3k
3k
E5
39
A1
A2 A3 A4 ST1
50mA
47k
ST2
59
4
5
6
242R
3.3nF
X6
100k
100k
12
100k
100k
GND1 GND1
3
7762
4
63
IN1 IN2
AIN1 AIN2
13247
10k 10k
IN3
Z1
S1 S2
IN4
DIGOUT4
Fig. 5−16 Wiring of digital and analog inputs/outputs with active "Safe torque off" function and internal
voltage source
S1 Deactivate pulse inhibit (1st disconnecting path)
S2 Enable controller (2nd disconnecting path)
Z1 Programmable logic controller (PLC)
The PLC monitors the ˜Safe torque off˜ function
X5/A4 Feedback via a digital output (e. g. DIGOUT4)
NO contact or NC contact
Z
Load
Minimum wiring required for operation
Terminal assignment in the Lenze setting: 102
AOUT1
AOUTx
AOUT2
9300vec135
98
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
Page 99

K31K32 33 34
X11
Supply via external voltage source
+
K
SR
X5
3k
3k
28
E1 E2 E3 E4
3k
3k
3k
3k
E5
Electrical installation
5
Control terminals
With function "Safe torque off" active
GND2 +24V+5 V
1
2
3
39
50mA
A1
50mA
50mA
50mA
A2 A3 A4 ST1
47k
ST2
59
X3
4
5
6
242R
X6
3.3nF
100k
100k
12
100k
100k
GND1 GND1
3
7762
4
63
IN1 IN2
AIN1 AIN2
13247
10k 10k
IN3
IN4
S1 S2
–
+
DC 24 V
(+18 V … +30 V)
DIGOUT4
Z1
Fig. 5−17 Wiring of digital and analog inputs/outputs with active "Safe torque off" function and external
voltage source
S1 Deactivate pulse inhibit (1st disconnecting path)
S2 Enable controller (2nd disconnecting path)
Z1 Programmable logic controller (PLC)
The PLC monitors the ˜Safe torque off˜ function
X5/A4 Feedback via a digital output (e. g. DIGOUT4)
NO contact or NC contact
Z
Load
Minimum wiring required for operation
Terminal assignment in the Lenze setting: 102
AOUT1
AOUTx
AOUT2
9300vec136
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
99
Page 100

5
Electrical installation
Control terminals
With function "Safe torque off" deactivated
5.6.3 With function "Safe torque off" deactivated
Note!
If the function "Safe torque off" is not made use of, the safety relay KSR must
be energised permanently to ensure the tension supply of the power output
stage.
Supply via internal voltage source
ƒ If a freely assignable digital output (e.g. X5/A1) is assigned permanently to HIGH
level, it serves as an internal voltage source. Every output has a maximum load
capacity of 50 mA.
– The relay K
voltage via a digital output.
– Two digital outputs must be connected in parallel and assigned permanently to
HIGH level in order to obtain the maximum wiring (relays K
X5/ST1).
ƒ For the supply of the analog inputs (X6/1, X6/2 and X6/3, X6/4) you have to set a
freely assignable analog output (e. g. X6/63) permanently to HIGH level.
and two digital inputs (X5/28 and e.g. X5/E1) can be supplied with
SR
and X5/E1 ... X5/E5,
SR
K31K32 33 34
X11
GND2 +24V+5 V
1
+
K
SR
X5
3k
28
S1
3k
3k
3k
E1 E2 E3 E4
3k
E5
50mA
50mA
50mA
3k
39
A1
A2 A3 A4 ST1
50mA
47k
ST2
59
X3
2
3
4
5
6
100k
100k
242R
3.3nF
12
X6
AIN1 AIN2
13247
10k 10k
100k
100k
GND1 GND1
3
4
7762
AOUT1
AOUT2
AOUTx
Fig. 5−18 Wiring of digital and analog inputs/outputs with function "Safe torque off" deactivated, given an
internal voltage source
S1 Controller enable
NO contact or NC contact
Z
Load
Minimum wiring required for operation
Terminal assignment in the Lenze setting: 102
63
9300vec0137
100
EDKVF9383 DE/EN/FR 4.0
 Loading...
Loading...