Page 1

EDS Device Servers/Terminal Servers
User Guide
EDS4100
EDS8PS
EDS16PS
EDS8PR
EDS16PR
EDS32PR
Part Number 900-433
Revision I April 2011
Page 2
Copyright & Trademark
© 2011 Lantronix. All rights reserved. No part of the contents of this book may be transmitted or
reproduced in any form or by any means without the written permission of Lantronix. Printed in the
United States of America.
Ethernet is a trademark of XEROX Corporation. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open
Group. Windows is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Warranty
For details on the Lantronix warranty replacement policy, please go to our web site at
www.lantronix.com/support/warranty
Contacts
Lantronix Corporate Headquarters
167 Technology Drive
Irvine, CA 92618, USA
Phone:949-453-3990
Fax:949-450-7249
Technical Support
Online: www.lantronix.com/support
.
Sales Offices
For a current list of our domestic and international sales offices, go to the Lantronix web site at
www.lantronix.com/about/contact
Disclaimer
Note: This product has been designed to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of FCC and EN5502 2:1998 Rules when pr operly enclosed and
grounded. These limits are designed to provide reasonable pro tection against radio
interference in a residential installation. This equipment genera tes, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with this guide, may
cause interference to radio communications. See “Appendix C - Compliance” on
page 155 for additional information.
The information in this guide may change without notice. The manufacturer assumes no
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this guide.For the latest revision of this product
document, please check our online documentation at www.lantronix.com/support/documentation
.
.
EDS User Guide 2
Page 3
Revision History
Date Rev. Comments
March 2006 A Initial Document
October 2006 B EDS16PR and EDS32PR products added.
December 2006 D German and English TUV certification added.
January 2007 E EDS8PR product added.
November 2007 F Added LPD, Terminal Host, RSS, and RT pages; updated XML and
other pages.
November 2008 G EDS8PS and EDS16PS products added.
May 2009 H Updated for EDS8/16/32PR and EDS4100 v4.1.0.2.
April 2011 I Updated for firmware version 5.2.0.0R24. Added support for Modbus
protocol for EDS4100, configurable MTU, and additional VIP tunnel
connect protocols; as well as improvements to SNMP, logging, and SSL.
EDS User Guide 3
Page 4

Table of Contents
List of Figures ____________________________________________________________10
List of Tables _____________________________________________________________12
1: About This Guide 14
Chapter and Appendix Summaries ____________________________________________14
Additional Documentation ___________________________________________________15
2: Introduction 16
EDS8PS and EDS16PS Overview ____________________________________________17
Features _ _________________________________________________________17
EDS4100 Overview ________________________________________________________18
Features _________________________________________________________18
EDS8PR, EDS16PR, and EDS32PR Overview __________________________________19
Features _ _________________________________________________________19
Applications ______________________________________________________________20
Protocol Support _________________________________________________________20
Evolution OS™ ___________________________________________________________20
Additional Features ________________________________________________________21
Modem Emulation ______________________________________________________21
Web-Based Configuration and Troubleshooting _______________________________21
Command-Line Interface (CLI) ____________________________________________21
VIP Access ___________________________________________________________21
SNMP Management ____________________________________________________21
XML-Based Architecture and Device Control _________________________________21
Really Simple Syndication (RSS) __________________________________________21
Enterprise-Grade Security _______________________________________________21
Terminal Server/Device Management ______________________________________22
Troubleshooting Capabilities ____________ _________________________________22
Configuration Methods _____________________________________________________22
Addresses and Port Numbers ________________________________________________23
Hardware Address _____________________________________________________23
IP Address ___________________________________________________________23
Port Numbers _________________________________________________________23
Product Information Label ___________________________________________________24
3: Installation of EDS8PS and EDS16PS 25
Package Contents _________________________________________________________25
User-Supplied Items _______________________________________________________25
Identifying Hardware Components ____________________________________________26
Serial Ports ___________________________________________________________26
EDS User Guide 4
Page 5

Console Port __________________________________________________________26
Ethernet Port _________________________________________________________27
LEDs ________________________________________________________________27
Reset Button __________________________________________________________27
Reboot the device: __________________________________________________27
Restore factory defaults: _____________________________________________28
Installing the EDS8/16PS ____________ _______________________________________28
Finding a Suitable Location ______________________________________________28
Connecting the EDS8/16PS ______________________________________________28
Connect the EDS8/16PS to one or more serial devices. _____________________28
4: Installation of EDS4100 30
Package Contents _________________________________________________________30
User-Supplied Items _______________________________________________________30
Identifying Hardware Components ____________________________________________30
Serial Ports ___________________________________________________________31
Ethernet Port _________________________________________________________32
Terminal Block Connector _______________________________________________33
LEDs ________________________________________________________________33
Reset Button __________________________________________________________33
Physically Installing the EDS4100 _____________________________________________34
Finding a Suitable Location ______________________________________________34
Connecting the EDS4100 ________________________________________________34
Connect the EDS4100 to one or more serial devices. _______________________34
5: Installation of EDS8PR, EDS16PR and EDS32PR 36
Package Contents _________________________________________________________36
User-Supplied Items _______________________________________________________36
Identifying Hardware Components ____________________________________________37
Serial Ports ___________________________________________________________37
Console Port __________________________________________________________37
Ethernet Port _________________________________________________________38
LEDs ________________________________________________________________38
Reset Button __________________________________________________________39
Installing the EDS8/16/32PR _________________________________________________39
Finding a Suitable Location ______________________________________________39
Connecting the EDS8/16/32PR ___________________________________________39
6: Using DeviceInstaller 41
Accessing EDS Using DeviceInstaller __________________________________________41
Device Details Summary ____________________________________________________41
EDS User Guide 5
Page 6

7: Configuration Using Web Manager 43
Accessing Web Manager ___________________________________________________43
Device Status Page ____________________________________________________44
Web Manager Page Components _____________________________________________45
Navigating the Web Manager ________________________________________________46
8: Network Settings 48
Network 1 (eth0) Interface Status _____________________________________________48
Network 1 (eth0) Interface Configuration _______________________________________49
Network 1 Ethernet Link ____________________________________________________51
9: Line and Tunnel Settings 52
Line Settings _____________________________________________________________52
Line Statistics _________________________________________________________52
Line Configuration _____________________________________________________53
Line Command Mode ___________________________________________________55
Tunnel Settings __________________________________________________________ 56
Tunnel – Statistics _____________________________________________________57
Tunnel – Serial Settings _________________________________________________59
Tunnel – Packing Mode _________________________________________________60
Tunnel – Accept Mode __________________________________________________63
Tunnel – Connect Mode _________________________________________________66
Connecting Multiple Hosts ____________________________________________70
Host List Promotion _________________________________________________70
Tunnel – Disconnect Mode _______________________________________________71
Tunnel – Modem Emulation ______________________________________________72
10: Terminal and Host Settings 75
Terminal Settings _________________________________________________________75
Line Terminal Configuration ______________________________________________75
Network Terminal Configuration ___________________________________________77
Host Configuration ________________________________________________________78
11: Service Settings 79
DNS Settings _____________________________________________________________79
SNMP Settings ___________________________________________________________80
FTP Settings ____________________________________________________________81
TFTP Settings ___________________________________________________________83
Syslog Settings ___________________________________________________________84
HTTP Settings ____________________________________________________________85
HTTP Statistics ________________________________________________________85
HTTP Configuration ____________________________________________________86
EDS User Guide 6
Page 7

HTTP Authentication ___________________________________________________88
RSS Settings _____________________________________________________________89
LPD Settings _____________________________________________________________90
LPD Statistics _________________________________________________________90
LPD Configuration _____________________________________________________91
12: Security Settings 93
SSH Settings _____________________________________________________________93
SSH Server Host Keys _________________________________________________94
SSH Server Authorized Users ____________________________________________98
SSH Client Known Hosts _______________________________________________100
SSH Client Users _____________________________________________________101
SSL Settings ____________________________________________________________103
SSL Cipher Suites ____________________________________________________103
SSL Certificates ______________________________________________________104
SSL RSA or DSA _____________________________________________________104
SSL Certificates and Private Keys ________________________________________104
SSL Utilities _________________________________________________________105
OpenSSL ___ _____________________________________________________105
Steel Belted RADIUS _______________________________________________105
Free RADIUS _____________________________________________________105
SSL Configuration ____________________________________________________106
13: Modbus 109
Serial Transmission Mode __________________________________________________109
Modbus Statistics ________________________________________________________110
Modbus Configuration _____________________________________________________111
14: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings 112
Filesystem Settings _______________________________________________________112
Filesystem Statistics ___________________________________________________112
Filesystem Browser ___________________________________________________113
Protocol Stack Settings ____________________________________________________115
TCP Settings ________________________________________________________115
IP Settings __________________________________________________________116
ICMP Settings ________________________________________________________116
ARP Settings ________________________________________________________118
SMTP Settings _______________________________________________________119
IP Address Filter _________________________________________________________120
Query Port _____________________________________________________________121
Diagnostics __ ___________________________________________________________122
Hardware ___ ________________________________________________________122
EDS User Guide 7
Page 8

MIB-II Statistics _______________________________________________________123
IP Sockets __________________________________________________________124
Ping __ _____________________________________________________________124
Traceroute __ ________________________________________________________126
Log ___ _____________________________________________________________127
Memory _____________________________________________________________129
Buffer Pools _________________________________________________________129
Processes ___ ________________________________________________________130
Real Time Clock _________________________________________________________132
System Settings _________________________________________________________132
15: Advanced Settings 134
Email Settings ___________________________________________________________134
Email Statistics _______________________________________________________134
Email Configuration ___________________________________________________135
Command Line Interface Settings ____________________________________________137
CLI Statistics _________________________________________________________137
CLI Configuration _____________________________________________________137
XML Settings ____________________________________________________________139
XML: Export Configuration ______________________________________________140
XML: Export Status ____________________________________________________141
XML: Import Configuration ______________________________________________142
Import Configuration from External File _________________________________142
Import Configuration from the Filesystem _______________________________143
Import Line(s) from Single Line Settings on the Filesystem __________________145
16: VIP Settings 147
Obtaining a Bootstrap File __________________________________________________147
Importing the Bootstrap File ________________________________________________147
Enabling VIP ____________________________________________________________148
Configuring Tunnels to Use VIP _____________________________________________148
Virtual IP (VIP) Statistics ___________________________________________________148
Virtual IP (VIP) Counters ___________________________________________________149
Virtual IP (VIP) Configuration _______________________________________________149
17: Branding the EDS 150
Web Manager Customization _______________________________________________150
Short and Long Name Customization _________________________________________150
18: Updating Firmware 151
Obtaining Firmware _______________________________________________________151
Loading New Firmware ____________________________________________________151
EDS User Guide 8
Page 9

Appendix A - Technical Support 152
Technical Support US ______________________________________________152
Technical Support Europe, Middle East, Africa ___________________________152
Appendix B - Binary to Hexadecimal Conversions 153
Converting Binary to Hexadecimal ________________________________________153
Conversion Table __________________________________________________153
Scientific Calculator ________________________________________________154
Appendix C - Compliance 155
Lithium Battery Notice _____________________________________________________156
Installationsanweisungen __ ________________________________________________156
Rackmontage ___ _____________________________________________________156
Energiezufuhr ___ _____________________________________________________157
Erdung __ ___________________________________________________________157
Installation Instructions ____________________________________________________157
Rack Mounting _______________________________________________________157
Input Supply _________________________________________________________157
Grounding ___ ________________________________________________________157
Appendix D - Lantronix Cables and Adapters 158
Index 159
EDS User Guide 9
Page 10

List of Figures
Figure 2-1 EDS8PS Device Server___________________________________________________17
Figure 2-2 EDS4100 4 Port Device Server_____________________________________________18
Figure 2-3 EDS16PR Device Server__________________________________________________19
Figure 2-4 Sample Hardware Address ________________________________________________23
Figure 2-5 Product Label___________________________________________________________24
Figure 3-1 Front View of the EDS8PS ________________________________________________26
Figure 3-2 Back View of the EDS8PS_________________________________________________26
Figure 3-3 RJ45 Serial Port_________________________________________________________27
Figure 3-5 Example of EDS8/16PS Connections ________________________________________29
Figure 4-1 Front View of the EDS4100 _______________________________________________31
Figure 4-2 Back View of the EDS4100 ________________________________________________31
Figure 4-3 RS-232 Serial Port Pins (Serial Ports 1, 2, 3, 4) ________________________________32
Figure 4-4 RS-422/RS-485 Serial Port Pins ____________________________________________32
Figure 4-5 Terminal Block Connector Pin Assignments ___________________________________33
Figure 4-7 Example of EDS4100 Connections __________________________________________35
Figure 5-1 Front View of the EDS16PR _______________________________________________37
Figure 5-2 Back View of the EDS16PR _______________________________________________37
Figure 5-3 RJ45 Serial Port_________________________________________________________38
Figure 5-5 Example of EDS16PR Connections _________________________________________40
Figure 7-1 Web Manager Home Page ________________________________________________44
Figure 7-2 Components of the Web Manager Page ______________________________________45
Figure 8-1 Network 1 (eth0) Interface Status ___________________________________________48
Figure 8-2 Network 1 (eth0) Interface Configuration______________________________________49
Figure 8-4 Network 1 Ethernet Link __________________________________________________51
Figure 9-1 Line 1 Statistics _________________________________________________________52
Figure 9-2 Line 1 Configuration______________________________________________________53
Figure 9-4 Line 1 Command Mode ___________________________________________________55
Figure 9-6 Tunnel 1 Statistics _______________________________________________________58
Figure 9-7 Tunnel 1 Serial Settings___________________________________________________59
Figure 9-9 Tunnel 1 Packing Mode (Mode = Disable) ____________________________________60
Figure 9-10 Tunnel 1 Packing Mode (Mode = Timeout) ___________________________________61
Figure 9-11 Tunnel 1 Packing Mode (Mode = Send Character) _____________________________61
Figure 9-13 Tunnel 1 Accept Mode___________________________________________________64
Figure 9-15 Tunnel 1 Connect Mode _________________________________________________67
Figure 9-17 Host 1, Host 2, Host 3 Exchanged__________________________________________70
Figure 9-18 Tunnel 1 Disconnect Mode _______________________________________________71
Figure 9-21 Tunnel 1 Modem Emulation_______________________________________________74
Figure 10-1 Terminal on Line Configuration____________________________________________75
Figure 10-3 Terminal on Network Configuration _________________________________________77
Figure 10-5 Host Configuration______________________________________________________78
Figure 11-1 DNS Settings __________________________________________________________79
Figure 11-2 SNMP Configuration ____________________________________________________80
Figure 11-4 FTP Configuration ______________________________________________________82
Figure 11-6 TFTP Configuration _____________________________________________________83
Figure 11-8 Syslog _______________________________________________________________84
Figure 11-10 HTTP Statistics _______________________________________________________85
Figure 11-11 HTTP Configuration____________________________________________________86
Figure 11-13 HTTP Authentication ___________________________________________________88
Figure 11-15 RSS ________________________________________________________________89
Figure 11-17 LPD Statistics ________________________________________________________90
EDS User Guide 10
Page 11

Figure 11-18 LPD Configuration _____________________________________________________91
Figure 12-1 SSH Server: Host Keys (Upload Keys) ______________________________________94
Figure 12-3 SSH Server: Host Keys (Upload Keys) ______________________________________96
Figure 12-5 SSH Server: Host Keys (Create New Keys) __________________________________97
Figure 12-7 SSH Server: Authorized Users ____________________________________________99
Figure 12-9 SSH Client: Known Hosts _______________________________________________100
Figure 12-11 SSH Client: Users ____________________________________________________101
Figure 12-14 SSL _______________________________________________________________106
Figure 13-3 Modbus Statistics______________________________________________________110
Figure 13-4 Modbus Configuration __________________________________________________111
Figure 14-1 Filesystem Statistics ___________________________________________________112
Figure 14-2 Filesystem Browser ____________________________________________________113
Figure 14-4 TCP Protocol _________________________________________________________115
Figure 14-6 IP Protocol __________________________________________________________116
Figure 14-8 ICMP Protocol ________________________________________________________117
Figure 14-10 ARP Protocol Page ___________________________________________________118
Figure 14-12 SMTP______________________________________________________________119
Figure 14-14 IP Address Filter Configuration __________________________________________120
Figure 14-16 Query Port Configuration_______________________________________________121
Figure 14-17 Diagnostics: Hardware_________________________________________________122
Figure 14-18 MIB-II Network Statistics _______________________________________________123
Figure 14-20 IP Sockets __________________________________________________________124
Figure 14-21 Diagnostics: Ping_____________________________________________________124
Figure 14-23 Diagnostics: Traceroute________________________________________________126
Figure 14-25 Diagnostics: Log _____________________________________________________127
Figure 14-26 Diagnostics: Log (Filesystem) ___________________________________________127
Figure 14-27 Diagnostics: Log (Line 1)_______________________________________________128
Figure 14-28 Diagnostics: Memory__________________________________________________129
Figure 14-29 Diagnostics: Buffer Pools_______________________________________________130
Figure 14-30 Diagnostics: Processes ________________________________________________131
Figure 14-31 Real Time Clock Page_________________________________________________132
Figure 14-33 System_____________________________________________________________133
Figure 15-1 Email Statistics _______________________________________________________134
Figure 15-2 Email Configuration ____________________________________________________135
Figure 15-4 CLI Statistics _________________________________________________________137
Figure 15-5 CLI Configuration______________________________________________________138
Figure 15-7 XML: Export Configuration_______________________________________________140
Figure 15-9 XML: Export Status ____________________________________________________141
Figure 15-11 XML: Import Configuration______________________________________________142
Figure 15-12 XML: Import Configuration from External File _______________________________142
Figure 15-13 XML: Import from Filesystem ___________________________________________143
Figure 15-14 XML: Import Configuration from Filesystem ________________________________144
Figure 15-15 XML: Import Line(s) from Single Line Settings on the Filesystem________________145
Figure 16-1 VIP Status ___________________________________________________________148
Figure 16-2 VIP Counters _________________________________________________________149
Figure 16-4 VIP Configuration Page _________________________________________________149
Figure 18-1 Update Firmware ______________________________________________________151
EDS User Guide 11
Page 12

List of Tables
Table 3-4 Front Panel LEDs ________________________________________________________27
Table 4-6 Back Panel LEDs ________________________________________________________33
Table 5-4 Back Panel LEDs ________________________________________________________39
Table 6-1 Device Details Summary___________________________________________________41
Table 7-3 Summary of Web Manager Pages ___________________________________________46
Table 8-3 Network Interface Configuration _____________________________________________49
Table 8-5 Network 1 Ethernet Link ___________________________________________________51
Table 9-3 Line Configuration________________________________________________________54
Table 9-5 Line Command Mode _____________________________________________________55
Table 9-8 Tunnel - Serial Settings____________________________________________________59
Table 9-12 Tunnel Packing Mode ____________________________________________________62
Table 9-14 Tunnel Accept Mode_____________________________________________________64
Table 9-16 Tunnel Connect Mode____________________________________________________68
Table 9-19 Tunnel Disconnect Mode _________________________________________________71
Table 9-20 Modem Emulation Commands and Descriptions _______________________________72
Table 9-22 Tunnel Modem Emulation_________________________________________________74
Table 10-2 Terminal on Line 1 Configuration ___________________________________________76
Table 10-4 Terminal on Network Configuration _________________________________________77
Table 10-6 Host Configuration ______________________________________________________78
Table 11-3 SNMP ________________________________________________________________81
Table 11-5 FTP Settings ___________________________________________________________82
Table 11-7 TFTP Server ___________________________________________________________83
Table 11-9 Syslog ________________________________________________________________84
Table 11-12 HTTP Configuration ____________________________________________________86
Table 11-14 HTTP Authentication____________________________________________________88
Table 11-16 RSS_________________________________________________________________90
Table 11-19 LPD Configuration______________________________________________________91
Table 12-2 SSH Server Host Keys Settings - Upload Keys Method__________________________95
Table 12-4 SSH Server Host Keys Settings - Upload Keys Method__________________________96
Table 12-6 SSH Server Host Keys Settings - Create New Keys Method ______________________97
Table 12-8 SSH Server Authorized User Settings _______________________________________99
Table 12-10 SSH Client Known Hosts _______________________________________________100
Table 12-12 SSH Client Users _____________________________________________________102
Table 12-13 Supported Cipher Suites________________________________________________103
Table 12-15 SSL ________________________________________________________________107
Table 13-1 6 Byte Header of Modbus Application Protocol _______________________________109
Table 13-2 Modbus Transmission Modes_____________________________________________109
Table 13-5 Modbus Configuration___________________________________________________111
Table 14-3 Filesystem Browser_____________________________________________________114
Table 14-5 TCP Protocol Settings___________________________________________________115
Table 14-7 IP Protocol Settings ____________________________________________________116
Table 14-9 ICMP Settings_________________________________________________________117
Table 14-11 ARP Settings_________________________________________________________118
Table 14-13 SMTP Settings _______________________________________________________119
Table 14-15 IP Address Filter Settings _______________________________________________120
Table 14-19 Requests for Comments (RFCs)__________________________________________123
Table 14-22 Diagnostics: Ping _____________________________________________________125
Table 14-24 Diagnostics: Traceroute ________________________________________________126
Table 14-32 Real Time Clock Settings _______________________________________________132
Table 14-34 System _____________________________________________________________133
EDS User Guide 12
Page 13

Table 15-3 Email Configuration_____________________________________________________135
Table 15-6 CLI Configuration ______________________________________________________138
Table 15-8 XML Export Configuration________________________________________________140
Table 15-10 XML Export Status ____________________________________________________141
Table 15-16 XML: Import Line(s) from Single Line Settings _______________________________146
Table 16-3 VIP Counters__________________________________________________________149
Table 20-1 Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion Table____________________________________153
EDS User Guide 13
Page 14
1: About This Guide
This guide provides the information needed to configure, use, and update the EDS™ Device
Server. It is intended for software developers and system integrators who are installing the EDS in
their designs.
Chapter and Appendix Summaries
A summary of each chapter is provided below.
Chapter Description
Chapter 2: Introduction Main features of the product and the protocols it supports.
Includes technical specifications.
Chapter 3: Installation of EDS8PS and EDS16PS Instructions for installing the EDS8PS and the EDS16PS
device servers.
Chapter 4: Installation of EDS4100 Instructions for installing the EDS4100 device server.
Chapter 5: Installation of EDS8PR, EDS16PR and
EDS32PR
Chapter 6: Using DeviceInstaller Instructions for viewing the current configuration using
Chapter 7: Configuration Using Web Manager Instructions for accessing Web Manager and using it to
Chapter 8: Network Settings Instructions for using the web interface to configure
Chapter 9: Line and Tunnel Settings Instructions for using the web interface to configure line and
Chapter 10: Terminal and Host Settings Instructions for using the web interface to configure terminal
Chapter 11: Service Settings Instructions for using the web interface to configure settings
Chapter 12: Security Settings Instructions for using the web interface to configure SSH
Chapter 13: Modbus Instructions for using the web interface to configure
Instructions for installing the EDS8PR, the EDS16PR, and
the EDS16PR device server.
DeviceInstaller.
configure settings for the device.
Ethernet settings.
tunnel settings.
and host settings.
for DNS, SNMP, FTP, and other services.
and SSL security settings.
Modbus.
Modbus is only available on the EDS4100 and
Note:
is not supported on the EDS8PR, EDS16PR,
EDS32PR, EDS8PS and EDS16PS.
Chapter 14: Maintenance and Diagnostics Settings Instructions for using the web interface to maintain the
device, view statistics, files, and logs, and diagnose
problems.
Chapter 15: Advanced Settings Instructions for using the web interface to configure email,
CLI, and XML settings.
Chapter 16: VIP Settings Information about Virtual IP (VIP) features available on the
device and instructions for using the web interface to
configure the VIP settings.
Chapter 17: Branding the EDS Instructions for customizing the device.
EDS User Guide 14
Page 15
1: About This Guide
Chapter 18: Updating Firmware Instructions for obtaining the latest firmware and updating
the device.
Appendix A - Technical Support Instructions for contacting Lantronix Technical Support.
Appendix B - Binary to Hexadecimal Conversions Instructions for converting binary values to hexadecimals.
Appendix C - Compliance Lantronix compliance information.
Appendix D - Lantronix Cables and Adapters Lantronix cables and adapters for use with the EDS devices
are listed here according to part number and application.
Additional Documentation
Visit the Lantronix web site at www.lantronix.com/support/documentation for the latest
documentation and the following additional documentation.
Document Description
EDS4100 Quick Start,
EDS8/16PS Quick Start, or
EDS8/16/32PR Quick Start
EDS Command Reference Instructions for accessing Command Mode (the command line
DeviceInstaller Online Help Instructions for using the Lantronix Windows-based utility to locate
Com Port Redirector
Quick Start and Online Help
Information about the EDS hardware installation and initial
configuration of your EDS device.
interface) using a Telnet connection or through the serial port.
Detailed information about the commands. Also provides details for
XML configuration and status.
the device and to view its current settings.
Instructions for using the Lantronix Windows-based utility to create
virtual com ports.
Secure Com Port Redirector
User Guide
Instructions for using the Lantronix Windows-based utility to create
secure virtual com ports.
EDS User Guide 15
Page 16

2: Introduction
This chapter introduces the Lantronix EDS family of device servers. It provides an overview of the
products, lists their key features, and describes the applications for which they are suited.
EDS is a unique, hybrid Ethernet terminal and multi-port device server product designed to
remotely access and manage virtually all of your IT/networking equipment and servers. It is also
designed to provide connectivity for edge devices such as medical equipment, kiosks, POS/retail
terminals, security equipment, and more.
EDS device servers contain all the components necessary to deliver full network connectivity to
virtually any kind of serial device. They boast a reliable TCP/IP protocol stack, a variety of remote
management capabilities, and an innovative design based on the leading-edge Lantronix
Evolution OS™.
Delivering a data center-grade, programmable device computing and networking platform for
integrating edge equipment into the enterprise network. Rack-mountable EDS models are
available in 8, 16, and 32 port configurations. Desk top EDS models are available in 4, 8, and 16
port configurations.
This chapter contains the following sections:
EDS8PS and EDS16PS Overview
EDS4100 Overview
EDS8PR, EDS16PR, and EDS32PR Overview
Applications
Protocol Support
Evolution OS™
Additional Features
Configuration Methods
Addresses and Port Numbers
Product Information Label
EDS User Guide 16
Page 17

EDS8PS and EDS16PS Overview
The EDS8PS (8 serial ports) and EDS16PS (16 serial ports) are compact desktop device servers
that give you the ability to network-enable asynchronous RS-232 serial devices. They provide fully
transparent RS-232 point-to-point connections without requiring modifications to existing software
or hardware in your application.
Figure 2-1 EDS8PS Device Server
2: Introduction
Features
Key features of the EDS8PS and EDS16PS include:
Dual-purpose Ethernet terminal server and device server design.
8 (EDS8PS) or 16 (EDS16PS) serial ports with hardware handshaking signals.
RS-232 support.
An RJ45 Ethernet port.
8 MB Flash memory.
32 MB random access memory (RAM).
Lantronix Evolution OS™.
A dedicated console port.
AES, SSH, or SSL secure data encryption.
Three convenient configuration methods (Web, command line, and XML).
Print server functionality (LPR/LPD).
See Chapter 3: Installation of EDS8PS and EDS16PS for installation instructions.
EDS User Guide 17
Page 18

EDS4100 Overview
Figure 2-2 EDS4100 4 Port Device Server
The EDS4100 is a compact device
server that allows you to networkenable asynchronous RS-232 and
RS-422/485 serial devices. It can
deliver fully transparent RS-232/
422 point-to-point connections and
RS-485 multi-drop connections
without requiring modifications to
existing software or hardware in
your application.
Ports 1 through 4 support
RS-232 devices.
Ports 1 and 3 also support
RS-422/485.
Note: RS-485 circuits support 32 full-load devices or 128 quarter-load devices. Each
RS-485 port, however, counts as one device, l eaving up to 31 fu ll-load or 127 qua rter-load
devices that can be connected to the RS-485 circuit.
2: Introduction
The EDS4100 device server supports the Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) standard. With PoE, power
is supplied to the EDS over the Ethernet cable, by either an Ethernet switch or a midspan device.
Being able to draw power through the Ethernet cable eliminates power supply and cord clutter. It
also allows the EDS to be located in areas where power is not typically available.
Features
The key features of the EDS4100 include:
Dual-purpose Ethernet terminal server and device server design.
Four serial ports with hardware handshaking signals.
RS-232 and RS-422/485.
One RJ45 Ethernet port.
IEEE 802.3af standard for Power-over-Ethernet (PoE).
8 MB Flash memory.
32 MB Random Access Memory (RAM).
Lantronix Evolution OS™.
AES, SSH, or SSL secure data encryption.
Three configuration methods (Web, command line, and XML).
Print server functionality (LPR/LPD).
See Chapter 4: Installation of EDS4100 for installation instructions.
EDS User Guide 18
Page 19

EDS8PR, EDS16PR, and EDS32PR Overview
The EDS8PR (8 serial ports), EDS16PR (16 serial ports), and EDS32PR (32 serial ports) are
compact easy-to-use, rack-mountable device servers that give you the ability to network-enable
asynchronous RS-232 serial devices. They provide fully transparent RS-232 point-to-point
connections without requiring modifications to existing software or hardware components in your
application.
Figure 2-3 EDS16PR Device Server
2: Introduction
Features
The key features of the EDS8PR, EDS16PR, and EDS32PR include:
Dual-purpose Ethernet terminal server and device server design.
8 (EDS8PR), 16 (EDS16PR) or 32 (EDS32PR) serial ports with hardware handshaking
signals.
RS-232 support.
One RJ45 Ethernet port.
8 MB Flash memory.
32 MB Random Access Memory (RAM).
Lantronix Evolution OS™.
A dedicated console port.
AES, SSH, or SSL secure data encryption.
Three configuration methods (Web, command line, and XML).
Print server functionality (LPR/LPD).
See Chapter 5: Installation of EDS8PR, EDS16PR and EDS32PR, for installation instructions.
EDS User Guide 19
Page 20

Applications
The EDS device server connects serial devices such as those listed below to Ethernet networks
using the IP protocol family.
ATM machines
Data display devices
Security alarms and access control devices
Modems
Time/attendance clocks and terminals
Patient monitoring equipment
Medical instrumentation
Industrial Manufacturing/Automation systems
Building Automation equipment
Point of Sale Systems
2: Introduction
Protocol Support
The EDS device server contains a full-featured TCP/IP stack. Supported protocols include:
ARP, IP, UDP, TCP, ICMP, BOOTP, DHCP, AutoIP, Telnet, DNS, FTP, TFTP, HTTP/HTTPS,
SSH, SSL/TLS, SNMP, SMTP, RSS and Syslog for network communications and
management.
TCP, UDP, TCP/AES, UDP/AES, Telnet, SSH and SSL/TLS for tunneling to the serial port.
TFTP, FTP, and HTTP for firmware upgrades and uploading files.
Evolution OS™
The EDS incorporates the Lantronix Evolution OS™. Key features of the Evolution OS™ include:
Built-in Web server for configuration and troubleshooting from Web-based browsers
CLI configurability
SNMP management
XML data transport and configurability
Really Simple Syndication (RSS) information feeds
Enterprise-grade security with SSL and SSH
Comprehensive troubleshooting tools
EDS User Guide 20
Page 21

Additional Features
Modem Emulation
In modem emulation mode, the EDS can replace dial-up modems. The unit accepts modem AT
commands on the serial port, and then establishes a network connection to the end device,
leveraging network connections and bandwidth to eliminate dedicated modems and phone lines.
Web-Based Configuration and Troubleshooting
Built upon Internet-based standards, the EDS enables you to configure, manage, and troubleshoot
through a browser-based interface accessible anytime from anywhere. All configuration and
troubleshooting options are launched from a web interface. You can access all functions via a Web
browser, for remote access. As a result, you decrease downtime (using the troubleshooting tools)
and implement configuration changes (using the configuration tools).
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Making the edge-to-enterprise vision a reality, the EDS with the Evolution OS™ uses industrystandard tools for configuration, communication, and control. For example, the Evolution OS™
uses a Command Line Interface (CLI) whose syntax is very similar to that used by data center
equipment such as routers and hubs.
2: Introduction
VIP Access
Virtual IP Access is the Lantronix technology that solves the access-through-firewall problem. With
VIP Access, the EDS can act as a ManageLinx DSC and provide direct access to your equipment
behind a firewall.
SNMP Management
The EDS supports full SNMP management, making it ideal for applications where device
management and monitoring are critical. These features allow networks with SNMP capabilities to
correctly diagnose and monitor EDS.
XML-Based Architecture and Device Control
XML is a fundamental building block for the future growth of M2M networks. The EDS supports
XML-based configuration setup records that make device configuration transparent to users and
administrators. The XML is easily editable with a standard text or XML editor.
Really Simple Syndication (RSS)
The EDS supports Really Simple Syndication (RSS) for streaming and managing on-line content.
RSS feeds all the configuration changes that occur on the device. An RSS aggregator then reads
(polls) the feed. More powerful than simple email alerts, RSS uses XML as an underlying Web
page transport and adds intelligence to the networked device, while not taxing already overloaded
email systems.
Enterprise-Grade Security
Evolution OS™ provides the EDS the highest level of networking security possible. This ‘data
center grade’ protection ensures that each device on the M2M network carries the same level of
security as traditional IT networking equipment in the corporate data center.
EDS User Guide 21
Page 22

2: Introduction
By protecting the privacy of serial data transmitted across public networks, users can maintain
their existing investment in serial technology, while taking advantage of the highest data-protection
levels possible.
SSH and SSL are able to do the following:
Verify the data received came from the proper source
Validate that the data transferred from the source over the network has not changed when it
arrives at its destination (shared secret and hashing)
Encrypt data to protect it from prying eyes and nefarious individuals
Provide the ability to run popular M2M protocols over a secure SSH or SSL connection
In addition to keeping data safe and accessible, the EDS has robust defenses to hostile Internet
attacks such as denial of service (DoS), which can be used to take down the network. Moreover,
the EDS cannot be used to bring down other devices on the network.
You can use the EDS with the Lantronix Secure Com Port Redirector (SCPR) to encrypt COM
port-based communications between PCs and virtually any electronic device. SCPR is a Windows
application that creates a secure communications path over a network between the computer and
serial-based devices that are traditionally controlled via a COM port. With SCPR installed at each
computer, computers that were formerly “hard-wired” by serial cabling for security purposes or to
accommodate applications that only understood serial data can instead communicate over an
Ethernet network or the Internet.
Terminal Server/Device Management
Remote offices can have routers, PBXs, servers and other networking equipment that require
remote management from the corporate facility. The EDS easily attaches to the serial ports on a
server, Private Branch Exchange (PBX), or other networking equipment to deliver central, remote
monitoring and management capability.
Troubleshooting Capabilities
The EDS offers a comprehensive diagnostic toolset that lets you troubleshoot problems quickly
and easily. Available from the Web Manager, CLI, and XML interfaces, the diagnostic tools let you:
View critical hardware, memory, MIB-II, buffer pool, and IP socket information.
Perform ping and traceroute operations.
Conduct forward or backup DNS lookup operations.
View all processes currently running on the EDS, including CPU utilization and total stack
space available.
Configuration Methods
After installation, the EDS requires configuration. For the unit to operate correctly on a network, it
must have a unique IP address on the network. There are four basic methods for logging into the
EDS and assigning IP addresses and other configurable settings:
DeviceInstaller: Configure the IP address and related settings and view current settings on the
using a Graphical User Interface (GUI) on a PC attached to a network. See Using DeviceInstaller
(on page 41).
EDS User Guide 22
Page 23

Web Manager: Through a web browser, configure the EDS settings using the Lantronix Web
Manager. See Configuration Using Web Manager (on page 43).
Command Mode: There are two methods for accessing Command Mode (CLI): making a Telnet
connection or connecting a terminal (or a PC running a terminal emulation program) to the unit’s
serial port. (See the EDS Command Reference Guide for instructions and available commands.)
XML: The EDS supports XML-based configuration and setup records that make device
configuration transparent to users and administrators. XML is easily editable with a standard text
or XML editor. (See the EDS Command Reference Guide for instructions and commands.)
Addresses and Port Numbers
Hardware Address
The hardware address is also referred to as the Ethernet address or MAC address. The first three
bytes of the Ethernet address are fixed and read 00-20-4A, identifying the unit as a Lantronix
product. The fourth, fifth, and sixth bytes are unique numbers assigned to each unit.
Figure 2-4 Sample Hardware Address
00-20-4A-14-01-18 or 00:20:4A:14:01:18
2: Introduction
IP Address
Every device connected to an IP network must have a unique IP address. This address references
the specific unit.
Port Numbers
Every TCP connection and every UDP datagram is defined by a destination and source IP
address, and a destination and source port number. For example, a Telnet server commonly uses
port number 23.
The following is a list of the default server port numbers running on the EDS:
TCP Port 22: SSH Server (Command Mode configuration)
TCP Port 23: Telnet Server (Command Mode configuration)
TCP Port 80: HTTP (Web Manager configuration)
TCP Port 443: HTTPS (Web Manager configuration)
UDP Port 161: SNMP
TCP Port 21: FTP
UDP Port 69: TFTP
UDP Port 514: Syslog
TCP Port 515: LPD
UDP Port 30718: LDP (Lantronix Discovery Protocol) port
TCP/UDP Port 10001: Tunnel 1
EDS User Guide 23
Page 24

Note: Multi-port products include one or more additional supported ports and tunnels
Bar Code
Product Revision
Hardware/MAC Address
Manufacturing Date Code
with default sequential numbering. For instance: TCP/UDP Port 10002: Tunnel 2, TCP/
UDP Port 10003: Tunnel 3, etc.
Product Information Label
The product information label on the unit contains the following information about the specific unit:
Bar Code
Product Revision
Hardware Address (MAC Address or Serial Number)
Manufacturing Date Code
2: Introduction
Figure 2-5 Product Label
EDS User Guide 24
Page 25

3: Installation of EDS8PS and EDS16PS
This chapter describes how to install the EDS8PS and EDS16PS device servers.
Package Contents
Your EDS package includes the following items:
One EDS device server (EDS8PS or EDS16PS)
One RJ45-to-DB9F serial cable
One power cord
User-Supplied Items
To complete your EDS8/16PS installation, you need the following items:
RS-232 serial devices that require network connectivity. Each EDS8/16PS serial port supports
a directly connected RS-232 serial device.
A serial cable for each serial device to be connected to the EDS8/16PS. All devices attached
to the device ports support the RS-232C (EIA-232) standard. Category 5 cabling with RJ45
connections is used for the device port connections.
Note: To connect an EDS8/16PS serial port to a DTE device, you need a DTE cable,
such as the one supplied in your EDS8/16PS package, or an RJ45 patch cable and DTE
adapter. To connect the EDS8/16PS serial port to a DCE device, you need a DCE
(modem) cable, or an RJ45 patch cable and DTE adapter. For a list of the Lantronix
cables and adapters you can use with the EDS8/16PS, see the Appendix D - Lan tronix
Cables and Adapters (on page 158).
An available connection to your Ethernet network and an Ethernet cable.
A working power outlet.
EDS User Guide 25
Page 26
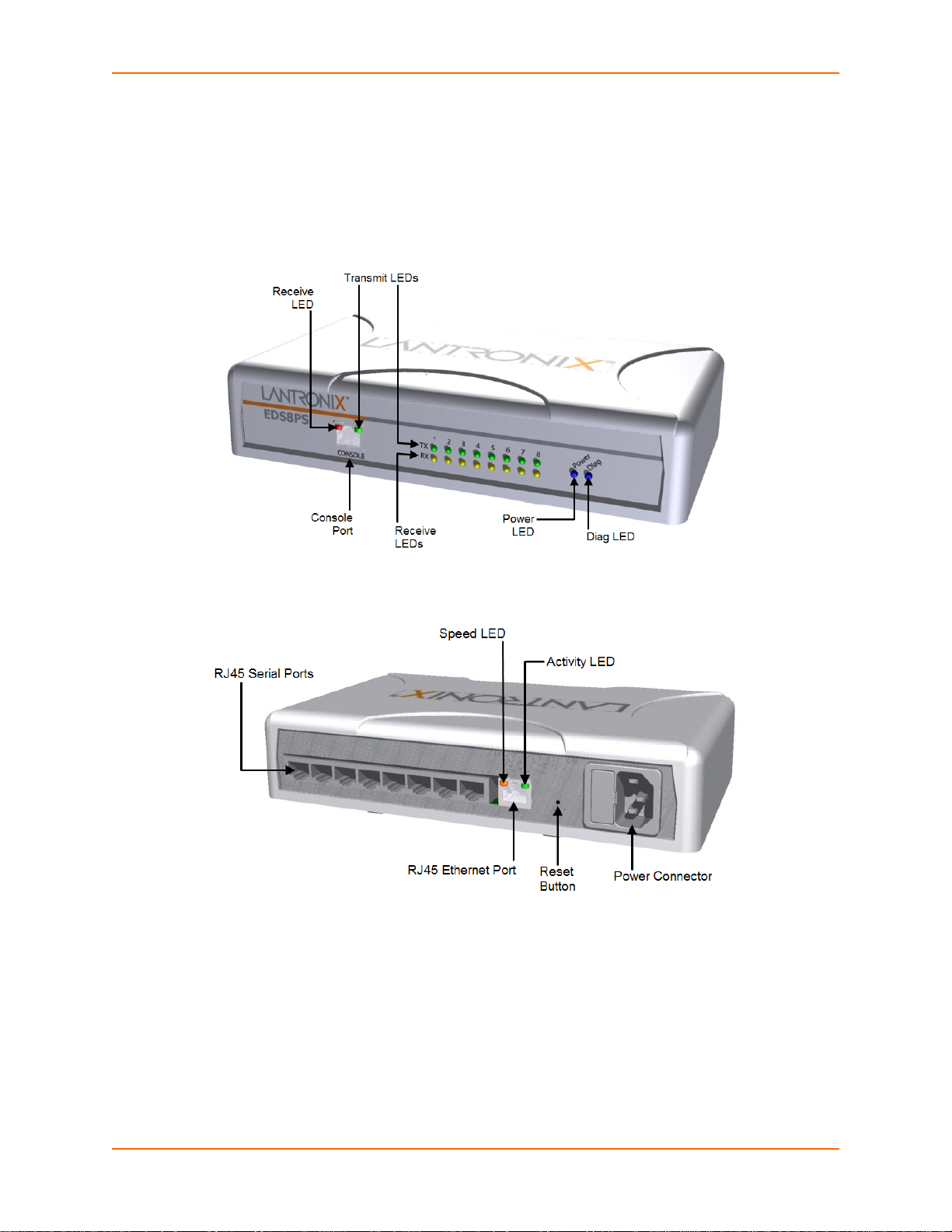
Identifying Hardware Components
Figure 3-1 shows the front of the EDS8PS. Figure 3-2 shows the back of the EDS8PS.
Figure 3-1 Front View of the EDS8PS
3: Installation of EDS8PS and EDS16PS
Figure 3-2 Back View of the EDS8PS
Serial Ports
The EDS8PS has 8 serial ports and the EDS16PS has 16 serial ports on the back panel. All are
configured as DTE and support up to 230,400 baud.
Console Port
The front panel of the EDS8/16/32PR provides an RJ45 Console port, configured as DTE and
supports baud rates up to 230,400 baud.
Note: The console port cannnot be used as a serial port.
EDS User Guide 26
Page 27

3: Installation of EDS8PS and EDS16PS
Figure 3-3 RJ45 Serial Port
Ethernet Port
The back panel of the EDS8/16PS provides a network interface via the right most RJ45 port. This
port can connect to an Ethernet (10 Mbps) or Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps) network. The Speed LED
on the back of the EDS8/16PS shows the connection of the attached Ethernet network. The EDS8/
16PS can be configured to operate at a fixed Ethernet speed and duplex mode (half- or fullduplex). Otherwise by default, the EDS8/16PS auto-negotiates the connection to the Ethernet
network.
LEDs
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on the front panel show status information.
Each serial port plus the console port have a Transmit and a Receive LED. The Ethernet port
has Speed, Activity, Power, and Status LEDs.
The table below describes the LEDs on the front of the EDSPS.
Table 3-4 Front Panel LEDs
LED Description
Transmit (green) Blinking = EDS is transmitting data on the serial port.
Receive (yellow) Blinking = EDS is receiving data on the serial port.
Power (blue) On = EDS is receiving power.
Diag (green) Fast blink = initial startup (loading OS).
Slow blink (once per second) = operating system startup.
On = unit has finished booting.
Speed (yellow) On = EDS is connected to a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet network.
Off = EDS is connected to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network.
Activity (green) Blink = EDS is sending data to or receiving data from the Ethernet network.
Reset Button
The reset button is on the rear of the device to the right of the Ethernet port, accessible through a
hole in the case. You can use it to reboot the unit or to reload factory defaults.
Reboot the device:
EDS User Guide 27
Page 28

1. Press and hold the reset button for about 3 seconds. The status LED blinks quickly.
2. When the fast blinks stop, release the button. When the unit reboots, the status LED changes
from a fast blink to a solid ON.
Restore factory defaults:
1. Press and hold the reset button for about 11 seconds. The LED blinks quickly for about 3
seconds, then comes on for about 5 seconds, then blinks slowly for about 2 seconds.
2. When the slow blinks stop, release the button.
Installing the EDS8/16PS
Finding a Suitable Location
You can install the EDS8/16PS either in a shelf or as a desktop unit.
If using AC power, avoid outlets controlled by a wall switch.
3: Installation of EDS8PS and EDS16PS
Connecting the EDS8/16PS
All EDS serial ports support RS-232 devices.
Connect the EDS8/16PS to one or more serial devices.
1. Power off the serial devices.
2. Attach a CAT 5 serial cable between the EDS8/16PS and your serial device. See the
Appendix D - Lantronix Cables and Adapters (on page 158), for a list of cables and adapters
you can use.
3. Connect an Ethernet cable between the EDS8/16PS Ethernet port and your Ethernet network.
4. Insert the power cord into the back of the EDS8/16PS. Plug the other end into an AC wall
outlet.
5. Power up the serial devices.
EDS User Guide 28
Page 29

3: Installation of EDS8PS and EDS16PS
Figure 3-5 Example of EDS8/16PS Connections
EDS User Guide 29
Page 30

4: Installation of EDS4100
This chapter describes how to install the EDS4100 device server.
Package Contents
Your EDS4100 package includes the following items:
One EDS4100 device server.
One DB9F-to-DB9F null modem cable.
A printed Quick Start Guide.
Your package may also include a power supply.
User-Supplied Items
To complete your EDS4100 installation, you need the following items:
RS-232 and/or RS-422/485 serial devices that require network connectivity:
A serial cable for each serial device. One end of the cable must have a female DB9 connector
for the EDS4100 serial port.
To connect an EDS4100 serial port to another DTE device, you will need a null modem cable,
such as the one supplied in your EDS4100 package.
To connect the EDS4100 serial port to a DCE device, you will need a straight-through
(modem) cable.
An available connection to your Ethernet network and an Ethernet cable.
A working power outlet if the unit will be powered from an AC outlet.
Identifying Hardware Components
The following two figures show the front and back of the EDS4100.
EDS User Guide 30
Page 31

Figure 4-1 Front View of the EDS4100
4: Installation of EDS4100
Figure 4-2 Back View of the EDS4100
Serial Ports
The front of the EDS4100 has four male DB9 serial ports. These ports allow you to connect up to
four standard serial devices:
All four serial ports support RS-232 devices. See Figure 4-3 for pin assignments.
Serial ports 1 and 3 also support RS-422 and RS-485 serial devices. See Figure 4-4 for pin
assignments.
All four serial ports are configured as DTE.
EDS User Guide 31
Page 32

Ports 1 & 3 support up to 921600
R-422/485 4-wire
pin assignments
(serial ports 1 and 3)
R-485 2-wire
pin assignments
(serial ports 1 and 3)
Ports 2 & 4 support up to 230400
Figure 4-3 RS-232 Serial Port Pins (Serial Ports 1, 2, 3, 4)
4: Installation of EDS4100
Figure 4-4 RS-422/RS-485 Serial Port Pins
Note: Multi-drop connections are supported in 2-wire mode only.
Ethernet Port
The back panel of the EDS4100 provides an RJ45 Ethernet port. This port can connect to an
Ethernet (10 Mbps) or Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps) network. The Speed LED on the back of the
EDS4100 shows the connection of the attached Ethernet network. The EDS4100 can be
configured to operate at a fixed Ethernet speed and duplex mode (half- or full-duplex) or otherwise
(by default) auto-negotiate the connection to the Ethernet network.
EDS User Guide 32
Page 33

4: Installation of EDS4100
Terminal Block Connector
The back of the EDS4100 has a socket for a terminal block screw connector (not included) for
attaching to an appropriate power source, such as those used in automation and manufacturing
industries. The terminal block connector supports a power range from 42 VDC to 56 VDC. It can
be used with the EDS4100's barrel power connector and PoE capabilities as a redundant power
source to the unit. Vendors who do supply this connector can be found by doing a web search for
part 'Phoenix 1803581 MC 1,5/ 3-ST-3,81'.
Figure 4-5 Terminal Block Connector Pin Assignments
Pin Signal
Top V+
Middle V-
Bottom Ground
LEDs
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on the front and back panels show status information.
Back panel - Each serial port has a Transmit and a Receive LED. The Ethernet connector has
Speed and Activity LEDs. In addition, the back panel has a Power LED and a Status LED.
Front panel - The front panel has a green Power LED.
The table below describes the LEDs on the back of the EDS4100.
Table 4-6 Back Panel LEDs
LED Description
Transmit (green) Blinking = EDS is transmitting data on the serial port.
Receive (yellow) Blinking = EDS is receiving data on the serial port.
Power (green) On = EDS receiving power.
Status (yellow) Fast blink = initial startup (loading OS).
Slow blink (once per second) = operating system startup.
On = unit has finished booting.
Speed (yellow) On = EDS is connected to a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet network.
Off = EDS is connected to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network
Activity (green) Blink = EDS sending data to or receiving data from the Ethernet network.
Reset Button
The reset button is on the back of the EDS4100, to the left of the power connector. Pressing this
button reboots the EDS4100 and terminates all serial and Ethernet port data activity.
EDS User Guide 33
Page 34

Physically Installing the EDS4100
Finding a Suitable Location
Place the EDS4100 on a flat horizontal or vertical surface. The EDS4100 comes with
mounting brackets installed for vertically mounting the unit, for example, on a wall.
If using AC power, avoid outlets controlled by a wall switch.
Connecting the EDS4100
Observe the following guidelines when attaching serial devices:
All four EDS4100 serial ports support RS-232 devices.
Alternatively, ports 1 and 3 support RS-422/485 devices.
To connect an EDS4100 serial port to another DTE device, use a null modem cable.
To connect the EDS4100 serial port to a DCE device, use a straight-through (modem) cable.
Connect the EDS4100 to one or more serial devices.
1. Power off the serial devices.
4: Installation of EDS4100
2. Attach a serial cable between the EDS4100 and each serial device.
3. Connect an Ethernet cable between the EDS4100 Ethernet port and your Ethernet network.
4. Power-up the EDS4100. Use one or more of the following methods.
These power-up methods can be used in combination to provide redundant backup power to
the unit.
PoE: Power is supplied over the Ethernet cable by an Ethernet switch or a mid-span
device.
Barrel power connector: The barrel power connector supports a power range of 9 to 30
VDC. Insert the round end of the supplied power cord into the barrel power connector on
the back of the EDS4100. Plug the other end into an AC wall outlet.
Terminal block connector: The terminal block connector supports a power range of 42
VDC to 56 VDC. Attach the power source to the terminal block connector on the back of
the EDS4100.
As soon as you plug it in, the EDS4100 powers up automatically, the self-test begins, and
Evolution OS™ starts.
5. Power up the serial devices.
EDS User Guide 34
Page 35

Figure 4-7 Example of EDS4100 Connections
4: Installation of EDS4100
EDS User Guide 35
Page 36

5: Installation of EDS8PR, EDS16PR and EDS32PR
This chapter describes installing the EDS8PR, EDS16PR and EDS32PR device servers.
Package Contents
Your EDS package includes the following items:
One EDS device server (EDS8PR, EDS16PR or EDS32PR).
One RJ45-to-DB9F serial cable.
A printed Quick Start guide.
Your package may also include a power supply.
User-Supplied Items
To complete your EDS8/16/32PR installation, you need the following items:
RS-232 serial devices that require network connectivity. Each EDS8/16/32PR serial port
supports a directly connected RS-232 serial device.
A serial cable for each serial device. All devices attached to the EDS device ports must
support the RS-232C (EIA-232) standard. Category 5 cabling with RJ45 connections is used
for the device port connections.
Note: To connect an EDS8 /16/32PR serial port to a DTE device , you need a DTE cable,
such as the one supplied in your EDS8/16/32PR package, or an RJ45 patch cable and
DTE adapter. To connect the EDS8/16/32PR serial po rt to a DCE device, you need a DCE
(modem) cable, or an RJ45 patch cable and DTE adapter.
For a list of the Lantronix cables and adapters you can use with the EDS8/16/32PR, see Appendix
C: Lantronix Cables and Adapters.
An available connection to your Ethernet network and an Ethernet cable.
A working power outlet.
EDS User Guide 36
Page 37

Identifying Hardware Components
The following two figures show the components on the front and back of the EDS16PR.
Figure 5-1 Front View of the EDS16PR
5: Installation of EDS8PR, EDS16PR and EDS32PR
Figure 5-2 Back View of the EDS16PR
Serial Ports
All EDS serial ports are configured as DTE and support up to 230,400 baud.
The EDS8PR has 8 serial ports.
The EDS16PR has 16 serial ports.
The EDS32PR has 32 serial ports.
Console Port
The front panel has an RJ45 Console port configured as DTE and supports up to 230,400 baud.
EDS User Guide 37
Page 38

5: Installation of EDS8PR, EDS16PR and EDS32PR
Figure 5-3 RJ45 Serial Port
Ethernet Port
The back panel has an RJ45 Ethernet port. This port can connect to an Ethernet (10 Mbps) or Fast
Ethernet (100 Mbps) network.
The Speed LED on the back panel shows the connection speed of the connected Ethernet
network.
You can configure the EDS to operate at a fixed Ethernet speed and duplex mode (half- or fullduplex) or auto-negotiate the connection to the Ethernet network.
LEDs
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on the front and back panels show status information.
Front panel. The front panel has a green Power LED.
Back panel. Each serial port has a Transmit and a Receive LED. The Ethernet connector has
Speed and Activity LEDs. There is also a Power LED and a Status LED.
EDS User Guide 38
Page 39

5: Installation of EDS8PR, EDS16PR and EDS32PR
The table below describes the LEDs on the back of the EDS.
Table 5-4 Back Panel LEDs
LED Description
Transmit (green) Blinking = EDS is transmitting data on the serial port.
Receive (yellow) Blinking = EDS is receiving data on the serial port.
Power (green) On = EDS is receiving power.
Status (yellow) Fast blink = initial startup (loading OS).
Slow blink (once per second) = operating system startup.
On = unit has finished booting.
Speed (yellow) On = EDS is connected to a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet network.
Off = EDS is connected to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network.
Activity (green) Blink = EDS is sending data to or receiving data from the Ethernet
network.
Reset Button
The reset button is on the back of the EDS, to the left of the power connector.
Pressing this button for 2-to-3 seconds reboots the EDS8/16/32PR and terminates all data activity
occurring on the serial and Ethernet ports.
Installing the EDS8/16/32PR
Finding a Suitable Location
You can install the EDS8/16/32PR either in an EIA-standard 19-inch rack (1U tall) or as a desktop
unit. If using AC power, avoid outlets controlled by a wall switch.
Connecting the EDS8/16/32PR
1. Power off the serial devices that will be connected to the EDS8/16/32PR.
2. Attach a CAT 5 serial cable between the EDS8/16/32PR and your serial device. For a list of
cables and adapters you can use with the EDS8/16/32PR, see Appendix C: Lantronix Cables
and Adapters.
3. Connect an Ethernet cable between the EDS8/16/32PR Ethernet port and your Ethernet
network.
4. Insert the power cord into the back of the EDS8/16/32PR. Plug the other end into an AC wall
outlet. After power-up, the self-test begins.
5. Power up the serial devices.
EDS User Guide 39
Page 40

5: Installation of EDS8PR, EDS16PR and EDS32PR
Figure 5-5 Example of EDS16PR Connections
EDS User Guide 40
Page 41

6: Using DeviceInstaller
This chapter covers the steps for locating a device and viewing its properties and details.
DeviceInstaller is a free utility program provided by Lantronix that discovers, configures, upgrades
and manages Lantronix Device Servers. It can be downloaded from the Lantronix website at
www.lantronix.com/support/downloads.html
the IP address, related settings or for more advanced features, see the DeviceInstaller online help.
Note: AutoIP generates a random IP address in the range of 169.254.0.1 to
169.254.255.254 if no BOOTP or DHCP server is found.
Accessing EDS Using DeviceInstaller
Note: Make note of the MAC address. It is needed to locate the EDS using
DeviceInstaller.
1. Click Start > All Programs > Lantronix > DeviceInstaller > DeviceInstaller.
When DeviceInstaller starts, it will perform a network device search.
2. Click Search to perform additional searches, as desired.
3. Expand the EDS folder by clicking the + symbol next to the EDS folder icon. The list of
available Lantronix EDS devices appears.
. For instructions on using DeviceInstaller to configure
4. Select the EDS unit by expanding its entry and clicking on its hardware (MAC) address to view
its configuration.
5. On the right page, click the Device Details tab. The current EDS configuration appears. This
is only a subset of the full configuration; the complete configuration may be accessed via Web
Manager, CLI, or XML.
Device Details Summary
Note: The settings are Display Only in this table unless otherwise noted.
Table 6-1 Device Details Summary
Current Settings Description
Name Name identifying the EDS.
DHCP Device Name Shows the name associated with the EDS’ current IP address, if
Group Configurable field. Enter a group to categorize the EDS. Double-
Comments Configurable field. Enter comments for the EDS. Double-click the
the IP address was obtained dynamically.
click the field, type in the value, and press Enter to complete. This
group name is local to this PC and is not visible on other PCs or
laptops using DeviceInstaller.
field, type in the value, and press Enter to complete. This
description or comment is local to this PC and is not visible on
other PCs or laptops using DeviceInstaller.
EDS User Guide 41
Page 42

6: Using DeviceInstaller
Device Family Shows the EDS device family type as “EDS”.
Type Shows the specific device type, such as “EDS8PS”.
ID Shows the EDS ID embedded within the unit.
Hardware Address Shows the EDS hardware (MAC) address.
Firmware Version Shows the firmware currently installed on the EDS.
Extended Firmware Version Provides additional information on the firmware version.
Online Status Shows the EDS status as Online, Offline, Unreachable (the EDS is
on a different subnet), or Busy (the EDS is currently performing a
task).
IP Address Shows the EDS current IP address. To change the IP address,
click the Assign IP button on the DeviceInstaller menu bar.
IP Address was Obtained Displays “Dynamically” if the EDS automatically received an IP
address (e.g., from DHCP). Displays “Statically” if the IP address
was configured manually.
If the IP address was assigned dynamically, the following fields
appear:
Obtain via DHCP with value of True or False.
Obtain via BOOTP with value of True or False.
Subnet Mask Shows the subnet mask specifying the network segment on which
the EDS resides.
Gateway Shows the IP address of the router of this network. There is no
default.
Number of Ports Shows the number of serial ports on this EDS.
Supports Configurable Pins Shows False, indicating configurable pins are not available on the
EDS.
Supports Email Triggers Shows True, indicating email triggers are available on the EDS.
Telnet Enabled Indicates whether Telnet is enabled on this EDS.
Telnet Port Shows the EDS port for Telnet sessions.
Web Enabled Indicates whether Web Manager access is enabled on this EDS.
Web Port Shows the EDS port for Web Manager configuration.
Firmware Upgradable Shows True, indicating the EDS firmware is upgradable as newer
versions become available.
EDS User Guide 42
Page 43

7: Configuration Using Web Manager
This chapter describes how to configure the EDS using Web Manager, the Lantronix browserbased configuration tool. The unit’s configuration is stored in nonvolatile memory and is retained
without power. All changes take effect immediately, unless otherwise noted. It contains the
following sections:
Accessing Web Manager
Web Manager Page Components
Navigating the Web Manager
Table 7-3 Summary of Web Manager Pages
Accessing Web Manager
Note: You can also access the Web Manager by selecting the Web Configuration tab on
the DeviceInstaller window.
To access Web Manager, perform the following steps:
1. Open a standard web browser. Lantronix supports the latest version of Internet Explorer,
Mozilla Suite, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Chrome or Opera.
2. Enter the IP address of the EDS in the address bar. The IP address may have been assigned
manually using DeviceInstaller (see the EDS Quick Start Guide) or automatically by DHCP.
3. Enter your username and password.The factory-default username is “admin” and the factorydefault password is “PASS.” The Device Status web page shown in Figure 7-1 displays
configuration, network settings, line settings, tunneling settings, and product information.
Note: The Logout button is available on any web page. Logging out of the web page
would force re-authentication to take place the next time the web page is accessed.
EDS User Guide 43
Page 44

7: Configuration Using Web Manager
Device Status Page
The Device Status page is the first page that appears after you log into the Web Manager. It also
appears when you click Status in the Main Menu.
Figure 7-1 Web Manager Home Page
EDS User Guide 44
Page 45

Web Manager Page Components
Header
Links to Subpages
Menu Bar
Configuration
& Status Area
Footer
Information,
Instructions
& Help
Logout Link
The layout of a typical Web Manager page is below.
Figure 7-2 Components of the Web Manager Page
7: Configuration Using Web Manager
The menu bar always appears at the left side of the page, regardless of the page shown. The
menu bar lists the names of the pages available in the Web Manager. To bring up a page, click it in
the menu bar.
The main area of the page has these additional sections:
At the very top, many pages, such as the one in the example above, enable you to link to
sub pages. On some pages, you must also select the item you are configuring, such as a
line or a tunnel.
In the middle of many pages, you can select or enter new configuration settings. Some
pages show status or statistics in this area rather than allow you to enter settings.
At the bottom of most pages, the current configuration is displayed. In some cases, you
can reset or clear a setting.
The information or help area shows information or instructions associated with the page.
A Logout link is available at the upper right corner of every web page. In Chrome or
Safari, it is necessary to close out of the browser to logout. If necessary, reopen the
browser to log back in.
EDS User Guide 45
Page 46

The footer appears at the very bottom of the page. It contains copyright information and a
link to the Lantronix home page.
Navigating the Web Manager
The Web Manager provides an intuitive point-and-click interface. A menu bar on the left side of
each page provides links you can click to navigate from one page to another. Some pages are
read-only, while others let you change configuration settings.
Note: There may be times when you must reboot the EDS for the new configuration
settings to take effect. The chapters that follow indicate when a change requires a reboo t.
Table 7-3 Summary of Web Manager Pages
7: Configuration Using Web Manager
Web Manager
Page
Status Shows product information and network, line, and tunneling
CLI Shows Command Line Interface (CLI) statistics and lets you
Diagnostics Lets you perform various diagnostic procedures. 122
DNS Shows the current configuration of the DNS subsystem and the
Email Shows email statistics and lets you clear the email log, configure
Filesystem Shows file system statistics and lets you browse the file system to
FTP Shows statistics and lets you change the current configuration for
Host Lets you view and change settings for a host on the network. 78
HTTP Shows HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) statistics and lets you
IP Address Filter Lets you specify all the IP addresses and subnets that are allowed
Line Shows statistics and lets you change the current configuration and
LPD Shows LPD (Line Printer Daemon) Queue statistics and lets you
Modbus Shows the current connection status of the Modbus servers
Network Shows status and lets you configure the network interface. 48
Description See
Page
52
settings.
137
change the current CLI configuration settings.
79
DNS cache.
134
email settings, and send an email.
112
view a file, create a file or directory, upload files using HTTP, copy
a file, move a file, or perform TFTP actions.
81
the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server.
85
change the current configuration and authentication settings.
120
to send data to this device.
52
Command mode settings of a serial line.
90
configure the LPD and print a test page.
109
listening on the TCP ports and lets you configure the Modbus
settings for EDS4100.
Protocol Stack Lets you perform lower level network stack-specific activities. 115
Query Port Lets you change configuration settings for the query port. 121
EDS User Guide 46
Page 47

7: Configuration Using Web Manager
Web Manager Page
(continued)
RSS Lets you change current Really Simple Syndication (RSS)
SNMP Lets you change the current Simple Network Management
SSH Lets you change the configuration settings for SSH server host
SSL Lets you upload an existing certificate or create a new self-signed
Syslog Lets you specify the severity of events to log and the server and
System Lets you reboot device, restore factory defaults, upload new
Terminal Lets you change current settings for a terminal. 75
TFTP Shows statistics and lets you change the current configuration for
Tunnel Lets you change the current configuration settings for a tunnel. 56
VIP Lets you configure Virtual IP addresses to be used in Tunnel
XML Lets you export XML configuration and status records, and import
Description See
Page
89
settings.
80
Protocol (SNMP) configuration settings.
93
keys, SSH server authorized users, SSH client known hosts, and
SSH client users.
103
certificate.
84
ports to which the syslog should be sent.
132
firmware, and change the device long and short names.
83
the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server.
147
Accept Mode and Tunnel Connect Mode.
139
XML configuration records.
EDS User Guide 47
Page 48

8: Network Settings
This chapter describes how to access, view, and configure network settings from the Network web
page. The Network web page contains sub-menus that enable you to view and configure the
Ethernet network interface and link.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Network 1 (eth0) Interface Status
Network 1 (eth0) Interface Configuration
Network 1 Ethernet Link
Network 1 (eth0) Interface Status
This page shows the status of the Ethernet network interface.
To view the network interface status:
1. Select Network on the menu bar. The Network web page appears.
2. Select Interface > Status submenus at the top of the page. The Network 1 (eth0) Interface
Status page appears.
Figure 8-1 Network 1 (eth0) Interface Status
EDS User Guide 48
Page 49

Network 1 (eth0) Interface Configuration
This page shows the configuration settings for the Ethernet connection and lets you change these
settings.
To view and configure network interface settings:
1. Select Network on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Network web page.
2. Select Interface > Configuration submenus at the top of the page. The Network 1 (eth0)
Interface Configuration page appears.
Figure 8-2 Network 1 (eth0) Interface Configuration
8: Network Settings
3. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 8-3 Network Interface Configuration
Network 1 Interface
Configuration
Settings
BOOTP Client Select On or Off. At boot up, the device will attempt to obtain an IP address from a
Description
BOOTP server.
Notes:
Overrides the configured IP address, network mask, gateway, hostname, an d
domain.
When DHCP is On, the system automatically uses DHCP, regardless of whether
BOOTP Client is On.
EDS User Guide 49
Page 50

8: Network Settings
Network 1 Interface
Description
Configuration
Settings
DHCP Client Select On or Off. At boot up, the device will attempt to lease an IP address from a DHCP
server and maintain the lease at regular intervals.
Note: Overrides BOOTP, the configured IP address, network mask, gateway,
hostname, and domain.
IP Address Enter the device static IP address.
You may enter it alone, in CIDR format, or with an explicit mask.
The IP address consists of four octets separated by a period and is used if BOOTP and
DHCP are both set to Off. Changing this value requires you to reboot the device.
Note: When DHCP is enabled, the device tries to obtain an IP address from DHCP. If it
cannot, the device uses an AutoIP address in the range of 169.254.xxx.xxx.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the router for this network. Or, clear the field (appears as
<None>). This address is only used for static IP address configuration.
Hostname Enter the device hostname. It must begin with a letter, continue with a sequence of
letters, numbers, and/or hyphens, and end with a letter or number.
Domain Enter the device domain name.
DHCP Client ID Enter the ID if the DHCP server uses a DHCP ID. The DHCP server’s lease table shows
IP addresses and MAC addresses for devices. The lease table shows the Client ID, in
hexadecimal notation, instead of the device MAC address.
Primary DNS IP address of the primary name server. This entry is required if you choose to configure
DNS (Domain Name Server) servers.
Secondary DNS IP address of the secondary name server.
MTU When DHCP is enabled, the MTU size is (usually) provided with the IP address. When
not provided by the DHCP server, or using a static configuration, this value is used. The
MTU size can be from 576 to 1500 bytes.
4. Click Submit to save changes. Some changes to the following settings require a reboot for the
changes to take effect:
BOOTP Client
DHCP Client
IP Address
DHCP Client ID
Note: If DHCP or BOOTP fails, AutoIP intervenes and a ssigns an address.A new DHCP
negotiation is attempted every 5 minutes to obtain a new IP address. When the DHCP is
enabled, any configured static IP address is ignored.
EDS User Guide 50
Page 51

Network 1 Ethernet Link
This page shows the current negotiated Ethernet settings and lets you change the speed and
duplex settings.
To view and configure the Ethernet link:
1. Select Network on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Network web page.
2. Select the Link submenu.
8: Network Settings
Figure 8-4 Network 1 Ethernet Link
The Status table shows the current negotiated settings. The Configuration table shows the
current range of allowed settings.
3. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 8-5 Network 1 Ethernet Link
Network 1-Ethernet Link
Settings
Speed Select the Ethernet link speed. Default is Auto.
Duplex Select the Ethernet link duplex mode. Default is Auto.
Description
4. Click Submit. The changes take effect immediately.
EDS User Guide 51
Page 52

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Note: The number of lines and tunnels
available for viewing and configuration differ
between Lantronix DeviceLinx products. For
example, an XPort Pro and EDS1100 support
only one line while other device networking
products (such as EDS2100, EDS4100, XPort
AR, EDS8/16PS and EDS8/16/32PR) provide
additional lines and tunnels.
This chapter describes how to view and
configure lines and tunnels. It contains the
following sections:
Line Settings
Tunnel Settings
Line Settings
View statistics and configure serial interfaces by using the Line web page. Serial interfaces are
referred to as lines in this user guide, and a different number of lines, from 1 to 32, may be
available for selection depending on your product.
The following sub-menus may be used for a selected line number:
Line Statistics—Displays statistics for the selected line number. For example, the bytes
received and transmitted, breaks, flow control, parity errors, etc.
Line Configuration—Enables the change of the name, interface, protocol, baud rates, and
parity, etc.
Line Command Mode—Enables the types of modes, wait time, serial strings, signon
message, etc.
The following sections describe the steps to view and configure specific line number settings.
These instructions also apply to additional line instances of the device.
Line Statistics
This read-only web page
shows the status and
statistics for the serial line
selected at the top of this
page.
1. Select Line on the menu
bar. The Line web page
appears.
2. Select a line number at
the top of the page.
3. Select Statistics. The
Line Statistics page for
the selected line appears.
4. Repeat above steps as
desired, according to
additional line(s)
available on your
EDS User Guide 52
product.
Figure 9-1 Line 1 Statistics
Page 53

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Note: The Interface
option is only supported
in XPort Pro, EDS4100,
EDS1100 and
EDS2100.
Line Configuration
This page shows the configuration settings for the serial line selected at the top of the page and
lets you change the settings for that serial line.
To configure a specific line:
1. Select Line on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Line web page.
2. Select a line number at the top of the page.
3. Select Configuration. The Configuration page for the selected line appears.
Figure 9-2 Line 1 Configuration
EDS User Guide 53
Page 54

4. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 9-3 Line Configuration
9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Line - Configuration
Settings
Name If the Terminal Login Menu feature is being used, enter the name for the
Interface Select the interface type from the drop-down menu. The default is RS232.
State Indicates whether the current line is enabled. To change the status, select
Protocol Select the protocol from the drop-down menu. The default is Tunnel.
Baud Rate Select the baud rate from the drop-down menu. The default is 9600.
Parity Select the parity from the drop-down menu. The default is None.
Data Bits Select the number of data bits from the drop-down menu. The default is 8.
Stop Bits Select the number of stop bits from the drop-down menu. The default is 1.
Flow Control Select the flow control from the drop-down menu. The default is None.
Xon Char Specify the character to use to start the flow of data when Flow Control is
Xoff Char Specify the character to use to stop the flow of data when Flow Control is
Gap Timer The driver forwards received serial bytes after the Gap Timer delay from
Threshold The driver will also forward received characters after Threshold bytes have
Description
line. Leaving this field blank will disable this line from appearing in the
Terminal Login Menu. The default Name is blank. See Terminal and Host
Settings on page 75 for related configuration information.
Note: This option is only supported in XPort Pro, EDS4100, EDS1100 and
EDS2100.
Enabled or Disabled from the drop-down menu.
set to Software. Prefix a decimal character with \ or a hexadecimal
character with 0x, or provide a single printable character. The default Xon
char is 0x11.
set to Software. Prefix a decimal character with \ or a hexadecimal
character with 0x, or provide a single printable character. The default Xoff
char is 0x13.
the last character received. By default, the delay is four character periods at
the current baud rate (minimum 1 ms).
been received.
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional line(s) available on your product.
EDS User Guide 54
Page 55

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Line Command Mode
Setting the Command Mode
enables the CLI on the serial
line.
To configure Command
Mode on a specific line:
1. Select Line on the menu
bar, if you are not already
in the Line web page.
2. Select a line number at the
top of the page.
3. Select Command Mode.
The Command Mode page
for the selected line
appears.
Figure 9-4 Line 1 Command Mode
4. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 9-5 Line Command Mode
Line – Command Mode
Settings
Mode Select the method of enabling Command Mode or choose to disable
Wait Time Enter the wait time for the serial string during boot-up in milliseconds.
Serial String Enter the serial string characters. Select a string type.
Echo Serial String Select Yes to enable echoing of the serial string at boot-up.
Description
Command Mode.
Always = immediately enables Command Mode for the serial line.
Use Serial String = enables Command Mode when the serial string is
read on the serial line during boot time.
Disabled = turns off Command Mode.
Text = string of bytes that must be read on the Serial Line during boot
time to enable Command Mode. It may contain a time element in x
milliseconds, in the format {x}, to specify a required delay.
Binary = string of characters representing byte values where each
hexadecimal byte value starts with \0x and each decimal byte value starts
with \.
EDS User Guide 55
Page 56

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Line – Command Mode
Settings (continued)
Signon Message Enter the boot-up signon message. Select a string type.
Description
Text = string of bytes sent on the serial line during boot time.
Binary = one or more byte values separated by commas. Each byte value
may be decimal or hexadecimal. Start hexadecimal values with 0x.
Note: This string will be output on the serial port at boot, regardless of
whether command mode is enabled or not.
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional line(s) available on your product.
Tunnel Settings
Note: The number of lines and tunnels available for viewing and configuration differ
between Lantronix DeviceLinx products. For example, an XPort Pro and EDS1100
support only one line while other device networking products (such as EDS2100,
EDS4100, XPort AR, EDS8/16PS and EDS8/16/32PR) provide addition a l lines an d
tunnels.
Tunneling allows serial devices to communicate over a network, without “being aware” of the
devices which establish the network connection between them. Tunneling parameters are
configured using the Web Manager or Command Mode Tunnel Menu. See Configuration Using
Web Manager (on page 43) or the EDS Command Reference for the full list of commands.
The EDS supports two tunneling connections simultaneously per serial port. One of these
connections is Connect Mode; the other connection is Accept Mode. The connections on one
serial port are separate from those on another serial port.
Connect Mode: the EDS actively makes a connection. The receiving node on the network
must listen for the Connect Mode’s connection. Connect Mode is disabled by default.
Accept Mode: the EDS listens for a connection. A node on the network initiates the
connection. Accept Mode is enabled by default.
Disconnect Mode: this mode defines how an open connection stops the forwarding of data.
The specific parameters to stop the connection are configurable. Once the EDS Disconnect
Mode observes the defined event occur, it will disconnect both Accept Mode and Connect
Mode connections on that port.
When any character comes in through the serial port, it gets copied to both the Connect Mode
connection and the Accept Mode connection (if both are active).
View statistics and configure a specific tunnel by using the Tunnel web page. When you select
Tunnel from the Main Menu, tunnels available for your product will display. Select a specific tunnel
to configure.
The following sub-menus listed may be used to configure a specific tunnel:
Tunnel – Statistics
Tunnel – Serial Settings
Tunnel – Packing Mode
EDS User Guide 56
Page 57

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel – Accept Mode
Tunnel – Connect Mode
Tunnel – Disconnect Mode
Tunnel – Modem Emulation
The following sections describe the steps to view and configure specific tunnel number settings.
These instructions also apply to additional tunnel menu options.
Tunnel – Statistics
Displays statistics for the specific tunnel. For example, Completed Accepts, Completed Connects,
Disconnects, Dropped Accepts, Dropped Connects, etc. The EDS logs statistics for tunneling.
The Dropped statistic shows connections ended by the remote location. The Disconnects
statistic shows connections ended by the EDS.
To display statistics for a specific tunnel:
1. Select Tunnel on the menu bar. The Tunnel web page appears.
2. Select a tunnel number at the top of the page.
3. Select Statistics. The Tunnel Statistics page for the specific tunnel appears.
If a particular tunnel is connected, the following becomes available:
Identifying information about the tunnel connection (i.e., “Connect 1 Counters”)
Address of connection (i.e., “local:10001 -> 172.22.22.22.10001”)
Kill Connection(s) link: Click this link to terminate this active tunnel connection, as
desired.
Octets forwarded from Serial
Octets forwarded form Network
Uptime
EDS User Guide 57
Page 58

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Additional information
appears for each active
tunnel connection including
a link allowing you to
terminate the connection.
Figure 9-6 Tunnel 1 Statistics
4. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional tunnel(s) available on your product.
EDS User Guide 58
Page 59

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel – Serial Settings
Serial line settings are configurable for the corresponding serial line of the specific tunnel.
Configure the buffer size to change the maximum amount of data the serial port stores. For any
active connection, the device sends the data in the buffer.
The modem control signal DTR on the selected line may be continuously asserted or asserted only
while either an Accept Mode tunnel or a Connect Mode tunnel is connected.
To configure serial settings for a specific tunnel:
1. Select Tunnel on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Tunnel web page.
2. Select a tunnel number at the top of the page.
3. Select Serial Settings. The Serial Settings page for the specific tunnel appears.
Figure 9-7 Tunnel 1 Serial Settings
4. View or modify the following settings:
Table 9-8 Tunnel - Serial Settings
Tunnel - Serial Settings Description
Line Settings (display only) Current serial settings for the line.
Protocol (display only) The protocol being used on the line. In this case, Tunnel.
DTR Select when to assert DTR.
Unasserted = never asserted
TruPort = asserted whenever either a connect or an accept mode tunnel
connection is active with the Telnet Protocol RFC2217 saying that the
remote DSR is asserted.
Asserted while connec ted = asserted whenever either a connect or an
accept mode tunnel connection is active.
Continuously asserted = asserted regardless of the status of a tunnel
connection.
EDS User Guide 59
Page 60

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional tunnel(s) available on your product.
Tunnel – Packing Mode
Packing Mode takes data from the serial port, packs it together, and sends it over the network.
Packing can be configured based on threshold (size in bytes, timeout (milliseconds), or a single
character.
Size is set by modifying the threshold field. When the number of bytes reaches the threshold, a
packet is sent immediately.
The timeout field is used to force a packet to be sent after a maximum time. The packet is sent
even if the threshold value is not reached.
When Send Character is configured, a single printable character or control character read on the
Serial Line forces the packet to be sent immediately. There is an optional trailing character
parameter which can be specified. It can be a single printable character or a control character.
To configure the Packing Mode for a specific tunnel:
1. Select Tunnel on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Tunnel web page.
2. Select a tunnel number at the top of the page.
3. Select Packing Mode. The Packing Mode page for the specific tunnel appears.
Figure 9-9 Tunnel 1 Packing Mode (Mode = Disable)
Depending on the Mode selection, different configurable parameters for the specific tunnel
number are presented to the user. The following figures show the display for each of the three
packing modes.
EDS User Guide 60
Page 61

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Figure 9-10 Tunnel 1 Packing Mode (Mode = Timeout)
Figure 9-11 Tunnel 1 Packing Mode (Mode = Send Character)
4. Enter or modify the following settings:
EDS User Guide 61
Page 62

Table 9-12 Tunnel Packing Mode
9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel - Packing Mode
Description
Settings
Mode Select Disable to disable Packing Mode completely.
Select Timeout to send data after the specified time has
elapsed.
Select Send Character to send the queued data when the send
character is received.
Threshold
(Appears for both Timeout
and Send Character
Modes)
Timeout
(Appears for Timeout
Mode)
Send the queued data when the number of queued bytes reaches
the threshold. When the buffer fills to this specified amount of data
in bytes (and the timeout has not elapsed), the device packs the
data and sends it out; applies only if the Packing Mode is not
Disabled.
Enter a time, in milliseconds, for the device to send the queued
data after the first character was received. Specifies the time
duration in milliseconds; applies only if the Packing Mode is
Timeout.
Send Character
(Appears for Send
Character Mode)
Enter the send character (single printable or control). Upon
receiving this character, the device sends out the queued data.
The data is packed until the specified send character is
encountered. Similar to a start or stop character, the device packs
the data until it sees the send character. The device then sends the
packed data and the send character in the packet. Applies only if
the Packing Mode is Send Character.
Trailing Character
(Appears for Send
Character Mode)
Enter the trailing character (single printable or control). This
character is sent immediately following the send character. This is
an optional setting. If a trailing character is defined, this character is
appended to data put on the network immediately following the
send character.
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional tunnel(s) available on your product.
EDS User Guide 62
Page 63

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel – Accept Mode
Controls how a specific tunnel number behaves when a connection attempt originates from the
network. In Accept Mode, the EDS waits for a connection from the network. The configurable local
port is the port the remote device connects to for this connection. There is no remote port or
address. The default local port is 10001 for serial port 1 and increases sequentially for each
additional serial port, if supported.
Accept Mode supports the following protocols:
SSH (the EDS is the server in Accept Mode). When using this protocol, the SSH server
host keys and at least one SSH authorized user must be configured.
SSL
TCP
AES encryption over TCP
Telnet (The EDS supports IAC codes. It drops the IAC codes when Telnetting and does
not forward them to the serial port).
Accept Mode has the following states:
Disabled (never a connection)
Enabled (always listening for a connection)
Active if it receives any character from the serial port
Active if it receives a specific (configurable) character from the serial port (same start
character as Connect Mode’s start character)
Modem control signal
Modem emulation
To configure the Accept Mode of a specific tunnel:
1. Select Tunnel on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Tunnel web page.
2. Select a tunnel number at the top of the page.
3. Select Accept Mode. The Accept Mode page for the specific tunnel appears.
EDS User Guide 63
Page 64

Figure 9-13 Tunnel 1 Accept Mode
Note: The CP Output
option is only supported in
XPort Pro and XPort AR.
9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel - Accept Mode
Settings
Mode Select the method used to start a tunnel in Accept mode. Choices are:
Local Port Enter the port number for use as the local port. The defaults are port 10001 for
Protocol Select the protocol type for use with Accept Mode. The default protocol is TCP. If
TCP Keep Alive Enter the time, in seconds, the device waits during a silent connection before
4. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 9-14 Tunnel Accept Mode
Description
Disabled = do not accept an incoming connection.
Always = accept an incoming connection (default)
Any Character = start waiting for an incoming connection when any
character is read on the serial line.
Start Character = start waiting for an incoming connection when the start
character for the specific tunnel is read on the serial line.
Modem Control Asserted = start waiting for an incoming connection as long
as the Modem Control pin (DSR) is asserted on the serial line until a
connection is made.
Modem Emulation = start waiting for an incoming connection when triggered
by modem emulation AT commands. Connect mode must also be set to
Modem Emulation.
Tunnel 1. Additional tunnels, if supported, increase sequentially.
you select TCP AES you will need to configure the AES keys.
checking if the currently connected network device is still on the network. If the
unit then gets no response after 8 attempts, it drops that connection.
EDS User Guide 64
Page 65

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel - Accept Mode
Settings (continued)
Flush Serial Data Select Enabled to flush the serial data buffer on a new connection.
Block Serial Data
Block Network
Password Enter a password that clients must send to the device within 30 seconds from
Email on Connect Select whether the device sends an email when a connection is made. Select
Email on Disconnect Select whether the device sends an email when a connection is closed. Select
Description
Select On to block, or not tunnel, serial data transmitted to the
Select On to block, or not tunnel, network data transmitted to the
opening a network connection to enable data transmission.
The password can have up to 31 characters and must contain only alphanumeric
characters and punctuation. When set, the password sent to the device must be
terminated with one of the following: (a) 0x0A (LF), (b) 0x00, (c) 0x0D 0x0A (CR
LF), or (d) 0x0D 0x00.
None if you do not want to send an email. Otherwise, select the Email profile to
use for sending.
None if you do not want to send an email. Otherwise, select the Email profile to
use for sending.
device.
device.
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional tunnel(s) available on your product.
EDS User Guide 65
Page 66

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Note: While in the “Any Character” or “Start
Character” connection modes, the EDS
waits and retries the connection if the
connection cannot be made. Once it makes
a connection and then disconnects, it will
not reconnect until it sees another character
or the start character again (depending on
the configured setting).
Tunnel – Connect Mode
Connect Mode defines how the device makes an outgoing connection through a specific tunnel.
When enabled, Connect Mode is always on and attempting a network connection if the connection
mode condition warrants it. For Connect Mode to function, it must:
Be enabled
Have a remote host configured
Have a remote port configured
Enter the remote host address as an IP address or DNS name. The EDS device will make a
connection only if it can resolve the address. For DNS names, the EDS will re-evaluate the
address after being established for 4 hours. If re-evaluation results in a different address, it will
close the connection.
Connect Mode supports the following protocols:
TCP
AES encryption over TCP and UDP
When setting AES encryption, both the encrypt key and the decrypt key must be specified.
The encrypt key is used for data sent out. The decrypt key is used for receiving data. Both of
the keys may be set to the same value.
SSH
To configure SSH, the SSH client username must be configured. In Connect Mode, the EDS is
the SSH client. Ensure the EDS SSH client username is configured on the remote SSH server
before using it with the EDS.
SSL
UDP
Is only available in Connect Mode because it is a connectionless protocol. For Connect Mode
using UDP, the EDS accepts packets from any device on the network. It will send packets to
the last device that sent it packets.
Telnet
Note: The Local Port in Connect Mode is independent of the port configured in Accept
Mode.
There are six different connect modes:
Disable
No connection is attempted.
Always
A connection is always attempted.
Any Character
A connection is attempted if it detects any
character from the serial port.
Start Character
EDS User Guide 66
A connection is attempted if it detects a specific and configurable character from the serial
port.
Page 67

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Note: The VIP and Host
Mode options are supported
in all products except XPort
AR.
The CP Output option is
only supported in XPort Pro
and XPort AR.
Figure 9-15 Tunnel 1 Connect Mode
Modem Control Asserted
A connection is attempted when the modem control pin is asserted in the serial line.
Modem Emulation
A connection is attempted by an ATD command.
To configure Connect Mode for a specific tunnel:
1. Select Tunnel on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Tunnel web page.
2. Select a tunnel number at the top of the page.
3. Select Connect Mode. The Connect Mode page for the specific tunnel appears.
EDS User Guide 67
Page 68

4. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 9-16 Tunnel Connect Mode
9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel – Connect Mode
Description
Settings
Mode Select the method to be used to attempt a connection to a remote host or
device. Choices are:
Always = a connection is attempted until one is made. If the connection gets
disconnected, the EDS retries until it makes a connection. (default)
Disable = an outgoing connection is never attempted.
Any Character = a connection is attempted when any character is read on
the serial line.
Start Character = a connection is attempted when the start character for the
specific tunnel is read on the serial line.
Modem Control Asserted = a connection is attempted as long as the
Modem Control pin (DSR) is asserted, until a connection is made.
Modem Emulation = a connection is attempted when triggered by modem
emulation AT commands.
Local Port Enter the port for use as the local port. A random port is selected by default.
Once you have configured a number, click the Random link in the Current
Configuration to switch back to random.
Host
Click <None> in the Host field to configure the Host parameters.
VIP = Enabling the VIP directs the tunnel to connect to a remote Lantronix
Virtual IP identified by the VIP Name. When VIP is enabled, the Host 2 field
displays. Default is Disabled.
VIP Name = Displays configured VIP name. Used only if VIP is enabled.
Address = Enter the remote Host Address as an IP address or DNS name. It
designates the address of the remote host to connect to. Displays configured
IP address or DNS address, used only if VIP is disabled.
Port = Enter the port for use as the Host Port. It designates the port on the
remote host to connect to. Displays configured Port.
Protocol = Select the protocol type for use with Connect Mode. The default
protocol is TCP. Additional fields may need to be completed depending on
protocol chosen for the host.:
For SSH, also enter an SSH Username.
For SSL, also select Enabled or Disabled for Validate Certificate.
Note: If security is a
concern, it is highly
recommended that SSH
be used. When using SSH,
both the SSH Server Host
Keys and SSH Server
Authorized Users must be
configured.
For SSL, TCP, TCP AES and Telnet, use the TCP Keep Alive field to
adjust the value.
For TCP AES, enter the AES Encrypt and AES Decrypt Keys. Both of
keys may be set to the same value.
For UDP, there are no additional fields to complete. In this mode, the
device accepts packets from any device on the network and sends
packets to the last device that sent it packets.
For UDP AES, enter the AES Encrypt and AES Decrypt Keys.
SSH Username = Displays configured username, used only if SSH protocol
is selected.
TCP Keep Alive = Default is 45000 milliseconds. Enter zero to disable and
blank the value to restore the default.
AES Encrypt/Decrypt Key = Displays presence of key, used only if protocol
with AES is selected.
EDS User Guide 68
Page 69

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel – Connect Mode
Description
Settings (continued)
Host Mode Select the host mode if you have more than one host configured:
Sequential
Simultaneous
Note: See Connecting Multiple Hosts on page 70 for more information.
Reconnect Timer Enter the reconnect time in milliseconds. The device attempts to reconnect after
this amount of time after failing a connection or exiting an existing connection.
This behavior depends upon the Disconnect Mode.
Note:
When you configure Tunnel - Connect Mode, you can specify a number
of milliseconds to attempt to reconnect after a dropped connection has
occurred. The default is 1500 milliseconds.
The Reconnect Timer only applies if a Disconnect Mode is configured.
With a Disconnect Mode set, the device server maintains a connection
until the disconnect mode condition is met (at which time the device server
closes the connection). If the tunnel is dropped due to conditions beyond
the device server, the device server attempts to re-establish a failed
connection when the specified reconnect interval reaches its limit.
Any network-side disconnect is considered an error and a reconnect is
attempted without regard to the Connect Mode settings. Simultaneous
Connect Mode connections require some Disconnect Mode
configurations or the connections will never terminate. See Tunnel –
Disconnect Mode on page 71 for more information about the parameters.
If Disconnect Mode is disabled and the network connection is dropped,
then the re-establishment of a tunnel connection is governed by the
configured Connect Mode settings.
Flush Serial Data Select whether to flush the serial line when a connection is made. Choices are:
Enabled = flush the serial line when a connection is made.
Disabled = do not flush the serial line. (default)
Block Serial Select Enabled to block (not tunnel) serial data transmitted to the device. This
is a debugging tool that causes serial data sent to the device to be ignored.
Block Network Select Enabled to block (not tunnel) network data transmitted to the device.
This is a debugging tool that causes network data sent to the device to be
ignored.
Email on Connect Select whether the device sends an email when a connection is made. Select
None if you do not want to send an email. Otherwise, select the Email profile to
use.
Email on Disconnect Select whether the device sends an email when a connection is closed. Select
None if you do not want to send an email. Otherwise, select the Email profile to
use.
5. Click Submit. The host is configured. A second host appears underneath the newly
configured host.Repeat these steps to configure additional hosts as necessary. EDS supports
configuration of up to sixteen hosts.
EDS User Guide 69
Page 70

Connecting Multiple Hosts
Note: The CP Output option is only supported in
XPort Pro and XPort AR.
Figure 9-17 Host 1, Host 2, Host 3 Exchanged
If more than one host is
configured, a Host Mode option
appears. Host Mode controls
how multiple hosts will be
accessed. For EDS, the
Connect Mode supports up to
sixteen Hosts. Hosts may be
accessed sequentially or
simultaneously:
Sequential – Sequential
host lists establish a
prioritized list of tunnels.
The host specified as Host
1 will be attempted first. If
that fails, it will proceed to
Host 2, 3, etc, in the order
they are specified. When a
connection drops, the cycle
starts again with Host 1 and
proceeds in order.
Establishing the host order
is accomplished with host
list promotion (see Host List
Promotion on page 70).
Sequential is the default
Host Mode.
9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Simultaneous – A tunnel
will connect to all hosts
accepting a connection.
Connections occur at the
same time to all listed
hosts. The device can
support a maximum of 64
total aggregate
connections.
Host List Promotion
This feature allows Host IP promotion of individual hosts in the overall sequence.
To promote a specific Host:
1. Click the icon in the desired Host field, for example Host 2 and Host 3.
2. The selected Host(s) exchanges its place with the Host above it.
3. Click Submit. The hosts change sequence.
EDS User Guide 70
Page 71

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Tunnel – Disconnect Mode
Relates to the disconnection of a specific tunnel. Disconnect Mode ends Accept Mode and
Connect Mode connections. When disconnecting, the EDS shuts down the specific tunnel
connection gracefully.
The following settings end a specific tunnel connection:
The EDS receives the stop character.
The timeout period has elapsed and no activity is going in or out of the EDS. Both Accept
Mode and Connect Mode must be idle for the time frame.
The EDS observes the modem control inactive setting.
Note: To clear data out of the serial buffers upon a disconnect, enable “Flush Serial Data”.
To configure the Disconnect Mode for a specific tunnel:
1. Select Tunnel on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Tunnel web page.
2. Select a tunnel number at the top of the page.
3. Select Disconnect Mode. The specific tunnel Disconnect Mode page appears.
Figure 9-18 Tunnel 1 Disconnect Mode
4. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 9-19 Tunnel Disconnect Mode
Tunnel – Disconnect
Mode Settings
Stop Character Enter the stop character in ASCII, hexadecimal, or decimal notation.
Modem Control Select Enabled to disconnect when the modem control pin is not
Timeout Enter a time, in milliseconds, for the device to disconnect on a Timeout.
Flush Serial Data Select Enabled to flush the serial data buffer on a disconnection.
Description
Select <None> to disable.
asserted on the serial line.
The value 0 (zero) disables the idle timeout.
EDS User Guide 71
Page 72

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional tunnel(s) available on your product.
Tunnel – Modem Emulation
A tunnel in Connect Mode can be initiated using modem commands incoming from the Serial Line.
This page enables you to configure the modem emulation settings when you select Modem
Emulation as the Tunnel Connect Mode type.
The Modem Emulation Command Mode supports the standard AT command set. For a list of
available commands from the serial or Telnet login, enter AT?. Use ATDT, ATD, and ATDP to
establish a connection. All of these commands behave like a modem. For commands that are valid
but not applicable to the EDS, an “OK” message is sent (but the command is silently ignored).
The EDS attempts to make a Command Mode connection as per the IP/DNS/port numbers
defined in Connect Mode. It is possible to override the remote address, as well as the remote port
number.
The following table lists and describes the available commands.
Table 9-20 Modem Emulation Commands and Descriptions
Command Description
+++ Switches to Command Mode if entered from serial port during connection.
AT? Help.
ATDT<Address Info> Establishes the TCP connection to socket (<ipaddress>:<port>).
ATDP<Address Info> See ATDT.
ATD Like ATDT. Dials default Connect Mode remote address and port.
ATD<Address Info> Sets up a TCP connection. A value of 0 begins a command line interface
session.
ATO Switches to data mode if connection still exists. Vice versa to '+++'.
ATEn Switches echo in Command Mode (off - 0, on - 1).
ATH Disconnects the network session.
ATI Shows modem information.
ATQn Quiet mode (0 - enable results code, 1 - disable results code.)
ATVn Verbose mode (0 - numeric result codes, 1 - text result codes.)
ATXn Command does nothing and returns OK status.
ATUn Accept unknown commands. (n value of 0 = off. n value of 1 = on.)
AT&V Display current and saved settings.
AT&F Reset settings in NVR to factory defaults.
AT&W Save active settings to NVR.
ATZ Restores the current state from the setup settings.
EDS User Guide 72
Page 73

9: Line and Tunnel Settings
Table 9-20
Command (continued) Description
ATS0=n Accept incoming connection.
ATA Answer incoming connection (if ATS0 is 2 or greater).
A/ Repeat last valid command.
Modem Emulation Commands and Descriptions (continued)
N value of 0—Disable
N value of 1—Connect automatically
N value of 2+—Connect with ATA command.
For commands that can take address information (ATD, ATDT, ATDP), the destination address
can be specified by entering the IP Address, or entering the IP Address and port number. For
example, <ipaddress>:<port>. The port number cannot be entered on its own.
For ATDT and ATDP commands less than 255 characters, the EDS replaces the last segment of
the IP address with the configured Connect Mode remote station address. It is possible to use the
last two segments also, if they are under 255 characters. For example, if the address is
100.255.15.5, entering “ATDT 16.6” results in 100.255.16.6.
When using ATDT and ATDP, enter 0.0.0.0 to switch to the Command Line Interface (CLI). Once
the CLI is exited by using the CLI exit command, the EDS reverts to modem emulation mode. By
default, the +++ characters are not passed through the connection. Turn on this capability using
the modem echo pluses command.
To configure modem emulation for a specific tunnel:
1. Select Tunnel on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Tunnel web page.
2. Select a tunnel number at the top of the page.
3. Select Modem Emulation. The Modem Emulation page for the specific tunnel appears.
EDS User Guide 73
Page 74

Figure 9-21 Tunnel 1 Modem Emulation
9: Line and Tunnel Settings
4. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 9-22 Tunnel Modem Emulation
Tunnel- Modem
Emulation Settings
Echo Pluses Select Enabled to echo +++ when entering modem Command Mode.
Echo Commands Select Enabled to echo the modem commands to the console.
Verbose Response Select Enabled to send modem response codes out on the serial line.
Response Type Select the type of response code: Text or Numeric.
Error Unknown
Commands
Incoming
Connection
Connect String Enter the connect string. This modem initialization string prepares the modem for
Display Remote IP Selects whether the incoming RING sent on the Serial Line is followed by the IP
Description
Select whether an ERROR or OK response is sent in reply to unrecognized AT
commands. Choices are:
Enabled = ERROR is returned for unrecognized AT commands.
Disabled = OK is returned for unrecognized AT commands. Default is Disabled.
Select whether Incoming Connection requests will be disabled, answered
automatically, or answered manually. Default is Disabled.
communications. It is a customized string sent with the “CONNECT” modem
response code.
address of the caller. Default is Disabled.
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional tunnel(s) available on your product.
EDS User Guide 74
Page 75

10: Terminal and Host Settings
This chapter describes how to view and configure the Terminal Login Connect Menu and
associated Host configuration. It contains the following sections:
Terminal Settings
Host Configuration
The Terminal Login Connect Menu feature allows the EDS device to present a menu of predefined
connections when the device is accessed via telnet, ssh, or a serial port. From the menu, a user
can choose one of the presented options and the device automatically makes the predefined
connection.
The Terminal page controls whether a Telnet, SSH, or serial port connection presents the CLI or
the Login Connect Menu. By default, the CLI is presented when the device is accessed. When
configured to present the Login Connect Menu, the hosts configured via the Hosts page, and
named serial lines are presented.
Terminal Settings
This page shows configuration settings for each terminal connection method. You can configure
whether each serial line or the telnet/SSH server presents a CLI or a Login Connect menu when a
connection is made.
Line Terminal Configuration
To configure a specific line to support an attached terminal:
1. Select Terminal on the menu bar. The Terminal web page appears.
2. Select the line number at the top of the page connected to the terminal you want to configure.
The default is Line 1.
Figure 10-1 Terminal on Line Configuration
3. Enter or modify the following settings:
EDS User Guide 75
Page 76

Table 10-2 Terminal on Line 1 Configuration
10: Terminal and Host Settings
Terminal on Line
Description
Configuration Settings
Terminal Type Enter text to describe the type of terminal. The text will be sent to a host via IAC.
Note: IAC means, “interpret as command.” It is a way to send commands over
the network such as send break or start echoing.
Login Connect Menu Select the interface to display when the user logs in. Choices are:
Enabled = shows the Login Connect Menu.
Disabled = shows the CLI
Exit Connect Menu Select whether to display a choice for the user to exit the Login Connect Menu
and reach the CLI. Choices are:
Enabled = a choice allows the user to exit to the CLI.
Disabled = there is no exit to the CLI.
Send Break Enter a Send Break control character, e.g., <control> Y, or blank to disable.
When the Send Break control character is received from the network on its way to
the serial line, it is not sent to the line; instead, the line output is forced to be
inactive (the break condition).
Break Duration Enter how long the break should last in milliseconds.
Echo Applies only to Connect Mode Telnet connections, not to Accept Mode. Only
disable Echo if your terminal echoes, in which case you will see double of each
character typed.
4. Click Submit to save changes.
5. Repeat above steps as desired, according to the additional line(s) available on your product.
EDS User Guide 76
Page 77

10: Terminal and Host Settings
Network Terminal Configuration
To configure menu features applicable to CLI access via the net work:
1. Select Terminal on the menu bar, if you are not already in the Terminal web page.
2. Select Network at the top of the page. The Configuration submenu is automatically selected.
The Terminal Configuration page appears for the network.
Figure 10-3 Terminal on Network Configuration
3. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 10-4 Terminal on Network Configuration
Terminal on Network
Configuration Settings
Terminal Type Enter text to describe the type of terminal. The text will be sent to a host via IAC.
Login Connect Menu Select the interface to display when the user logs in. Choices are:
Exit Connect Menu Select whether to display a choice for the user to exit the Login Connect Menu
Echo Applies only to Connect Mode Telnet connections, not to Accept Mode. Only
Description
Note: IAC means, “interpret as command.” It is a way to send commands over
the network such as send break or start echoing.
Enabled = shows the Login Connect Menu.
Disabled = shows the CLI
and reach the CLI. Choices are:
Enabled = a choice allows the user to exit to the CLI.
Disabled = there is no exit to the CLI.
disable Echo if your terminal echoes, in which case you will see double of each
character typed.
4. Click Submit to save changes.
EDS User Guide 77
Page 78

Host Configuration
This Host web page is where you may view and modify current settings for a selected remote host.
To configure a selected remote host:
1. Select Host on the menu bar. The Host web page appears.
2. Select a specific host number at the top of the page. The Host Configuration page for the
selected host appears.
10: Terminal and Host Settings
Figure 10-5 Host Configuration
3. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 10-6 Host Configuration
Host Settings Description
Name Enter a name for the host. This name appears on the Login Connect
Menu. To leave a host out of the menu, leave this field blank.
Protocol Select the protocol to use to connect to the host. Choices are:
Telnet
SSH
Note: SSH keys must be loaded or created on the SSH page for the
SSH protocol to work.
SSH Username Appears if you selected SSH as the protocol. Enter a username to
select a pre-configured Username/Password/Key (configured on the
SSH: Client Users page), or leave it blank to be prompted for a
username and password at connect time.
Remote Address Enter an IP address for the host to which the device will connect.
Remote Port Enter the port on the host to which the device will connect.
4. Click Submit to save changes.
5. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional host(s) available on your product.
EDS User Guide 78
Page 79

11: Service Settings
This chapter describes the available services and how to configure each. It contains the following
sections:
DNS Settings
SNMP Settings
FTP Settings
TFTP Settings
Syslog Settings
HTTP Settings
RSS Settings
LPD Settings
DNS Settings
The primary and secondary domain name system (DNS) addresses come from the active
interface. The static addresses from the Network Interface Configuration page may be overridden
by DHCP or BOOTP. The DNS web page enables you to view the status and cache.
When a DNS name is resolved using a forward lookup, the results are stored in the DNS cache
temporarily. The EDS checks this cache when performing forward lookups. Each item in the cache
eventually times out and is removed automatically after a certain period, or you can delete it
manually.
To view the DNS status:
1. Select DNS on the menu bar. The DNS page appears.
Figure 11-1 DNS Settings
EDS User Guide 79
Page 80

To find a DNS Name or IP Address:
1. Enter either a DNS name or an IP address.
2. Click Lookup.
When a DNS name is resolved, the results appear in the DNS cache.
When an IP address is resolved, the results appear in a text below the Lookup field.
To clear cache entries:
1. Click Remove All to remove all listed cache entries.
2. Click Delete next to a specirfic cache entry to remove only that one.
SNMP Settings
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a network management tool that monitors
network devices for conditions that need attention. The SNMP service responds to SNMP
requests and generates SNMP Traps.
This page is used to configure the SNMP agent.
11: Service Settings
To configure SNMP:
1. Select SNMP on the menu bar. The SNMP page opens and shows the current SNMP
configuration.
Figure 11-2 SNMP Configuration
2. Enter or modify the following settings:
EDS User Guide 80
Page 81

11: Service Settings
Table 11-3 SNMP
SNMP Settings Description
State Select Enabled to enable SNMP.
Read Community Enter the SNMP read-only community string.
Write Community Enter the SNMP read/write community string.
System Contact Enter the name of the system contact.
System Name Enter the system name.
System Description Enter the system description.
System Location Enter the system location.
Traps State Select Enabled to enable the transmission of SNMP Traps.
The Cold Start trap is sent on device boot up, and the
Linkdown trap is sent when the device is rebooted from
software control.
Traps Primary Destination Enter the primary SNMP trap host.
Traps Secondary
Destination
Enter the secondary SNMP trap host.
3. Click Submit.
FTP Settings
The FTP web page shows the current File Transfer Protocol (FTP) configuration and various
statistics about the FTP server.
To configure FTP:
1. Select FTP on the menu bar. The FTP page opens to display the current configuration.
EDS User Guide 81
Page 82

Figure 11-4 FTP Configuration
2. Enter or modify the following settings:
11: Service Settings
Table 11-5 FTP Settings
FTP Settings Description
State Select Enabled to enable the FTP server.
Admin Username Enter the username to use when logging in via FTP.
Admin Password Enter the password to use when logging in via FTP.
3. Click Submit.
EDS User Guide 82
Page 83

TFTP Settings
In the TFTP web page, you can configure the server and view the statistics about the Trivial File
Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server.
To configure TFTP:
1. Select TFTP on the menu bar. The TFTP page opens to display the current configuration.
11: Service Settings
Figure 11-6 TFTP Configuration
2. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 11-7 TFTP Server
TFTP Settings Description
State Select Enabled to enable the TFTP server.
Allow TFTP File Creation Select whether to allow the creation of new files stored on the TFTP server.
Allow Firmware Update Specifies whether or not the TFTP Server is allowed to accept a firmware
update for the device. An attempt to update firmware is recognized based
on the name of the file.
Note: TFTP cannot authenticate the client, so the device is open to
malicious update.
Allow XCR Import Specifies whether the TFTP server is allowed to accept an XML
configuration file for update. An attempt to import configuration is
recognized based on the name of the file.
Note: TFTP cannot authenticate the client, so the device is open to
malicious update.
3. Click Submit.
EDS User Guide 83
Page 84

Syslog Settings
The Syslog web page shows the current configuration and statistics of the system log.
To configure the Syslog:
Note: The syslog file is always saved to local storage, but it is not retained through
reboots. Saving the syslog file to a server that supports remote logging services (see RFC
3164) allows the administrator to save the complete syslog history. The default port is 514.
1. Select Syslog on the menu bar. The Syslog page opens to display the current configuration.
11: Service Settings
Figure 11-8 Syslog
2. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 11-9 Syslog
Syslog Settings Description
State Select to enable or disable the syslog.
Host Enter the IP address of the remote server to which system logs are sent
for storage.
Local Port Enter the number of the local port on the device from which system logs
are sent.
Remote Port Enter the number of the port on the remote server that supports logging
services. The default is 514.
Severity Log Level From the drop-down box, select the minimum level of system message
the device should log. This setting applies to all syslog facilities. The
drop-down list is in descending order of severity (e.g., Emergency is
more severe than Alert.)
3. Click Submit.
EDS User Guide 84
Page 85

HTTP Settings
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the transport protocol for communicating hypertext
documents on the Internet. HTTP defines how messages are formatted and transmitted. It also
defines the actions web servers and browsers should take in response to different commands.
HTTP Authentication enables the requirement of usernames and passwords for access to the EDS
device.
This page has three links at the top for viewing statistics and for viewing and changing
configuration and authentication settings.
HTTP Statistics—Viewing statistics such as bytes received and transmitted, bad requests,
authorizations required, etc.
HTTP Configuration—Configuring and viewing the current configuration.
HTTP Authentication—Configuring and viewing the authentication.
HTTP Statistics
To view HTTP statistics:
This page shows various statistics about the HTTP server.
1. Select HTTP on the menu bar and then Statistics at the top of the page. The HTTP Statistics
page appears.
11: Service Settings
Figure 11-10 HTTP Statistics
Note: The HTTP log is a scrolling log, with the last Max Log Entries cached and
viewable. You can change the maximum number of entries that can be viewed on the
HTTP Configuration Page.
EDS User Guide 85
Page 86

11: Service Settings
HTTP Configuration
On this page you may change HTTP configuration settings.
To configure HTTP:
1. Select HTTP on the menu bar and then Configuration at the top of the page. The HTTP
Configuration page opens.
Figure 11-11 HTTP Configuration
2. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 11-12 HTTP Configuration
HTTP Configuration
Settings
State Select Enabled to enable the HTTP server.
Port Enter the port for the HTTP server to use. The default is 80.
Secure Port Enter the port for the HTTPS server to use. The default is 443. The HTTP
Description
server only listens on the HTTPS Port when an SSL certificate is
configured.
EDS User Guide 86
Page 87

11: Service Settings
HTTP Configuration
Description
Settings (continued)
Secure Protocols Select to enable or disable the following protocols:
SSL3 = Secure Sockets Layer version 3
TLS1.0 = Transport Layer Security version 1.0. TLS 1.0 is the successor
of SSL3 as defined by the IETF.
TLS1.1 = Transport Layer Security version 1.1
The protocols are enabled by default.
Note: A server certificate and associated private key need to be installed in
the SSL configuration section to use HTTPS.
Max Timeout Enter the maximum time for the HTTP server to wait when receiving a
request. This prevents Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks. The default is 10
seconds.
Max Bytes Enter the maximum number of bytes the HTTP server accepts when
receiving a request. The default is 40 kB (this prevents DoS attacks).
Logging State Select Enabled to enable HTTP server logging.
Max Log Entries Sets the maximum number of HTTP server log entries. Only the last Max
Log Entries are cached and viewable.
Log Format Set the log format string for the HTTP server. Follow these Log Format
rules:
%a - remote IP address (could be a proxy)
%b - bytes sent excluding headers
%B - bytes sent excluding headers (0 = '-')
%h - remote host (same as '%a')
%{h}i - header contents from request (h = header string)
%m - request method
%p - ephemeral local port value used for request
%q - query string (prepend with '?' or empty '-')
%t - timestamp HH:MM:SS (same as Apache '%(%H:%M:%S)t' or
'%(%T)t')
%u - remote user (could be bogus for 401 status)
%U - URL path info
%r - first line of request (same as '%m %U%q <version>')
%s - return status
Authentication
Timeout
The timeout period applies if the selected authentication type is either
Digest or SSL/Digest. After this period of inactivity, the client must
authenticate again.
3. Click Submit.
EDS User Guide 87
Page 88

11: Service Settings
HTTP Authentication
HTTP Authentication enables you to require usernames and passwords to access specific web
pages or directories on the EDS' built-in web server.
To configure HTTP authentication settings:
1. Select HTTP on the menu bar and then Authentication at the top of the page. The HTTP
Authentication page opens.
Figure 11-13 HTTP Authentication
2. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 11-14 HTTP Authentication
HTTP Authentication
Settings
URI Enter the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI).
Realm Enter the domain, or realm, used for HTTP. Required with the
Description
Note: The URI must begin with ‘/’ to refer to the filesystem.
URI field.
EDS User Guide 88
Page 89

11: Service Settings
HTTP Authentication
Settings (continued)
Auth Type Select the authentication type:
Username
Description
None = no authentication is necessary.
Basic = encodes passwords using Base64.
Digest = encodes passwords using MD5.
SSL = the page can only be accessed over SSL (no password
is required).
SSL/Basic = the page is accessible only over SSL and
encodes passwords using Base64.
SSL/Digest = the page is accessible only over SSL and
encodes passwords using MD5.
Note: When changing the parameters of Digest or SSL Digest
authentication, it is often best to close and reopen the browser to
ensure it does not attempt to use cached authentication
information.
Enter the Username used to access the URI. More than one
Username per URI is permitted.
Click Submit and enter the next Username as necessary.
Password Enter the Password for the Username.
3. Click Submit.
4. To delete the URI and users, click Delete in the current configuration table.
Note: The URI, realm, username, and password are user-specified, free-form fields. The
URI must match the directory created on the EDS file system.
RSS Settings
Really Simple Syndication (RSS) (sometimes referred to as Rich Site Summary) is a method of
feeding online content to Web users. Instead of actively searching for EDS configuration changes,
RSS feeds permit viewing only relevant and new information regarding changes made to the EDS
via an RSS publisher. The RSS feeds may also be stored to the file system cfg_log.txt file.
To configure RSS settings:
1. Select RSS on the menu bar. The RSS page opens and shows the current RSS configuration.
Figure 11-15 RSS
EDS User Guide 89
Page 90

2. Enter or modify the following settings:
RSS Settings Description
RSS Feed Select On to enable RSS feeds to an RSS publisher.
Persistent Select On to enable the RSS feed to be written to a file (cfg_log.txt)
Max Entries Sets the maximum number of log entries. Only the last Max Entries
3. Select Submit.
4. In the Current Status table, view and clear stored RSS Feed entries, as necessary.
LPD Settings
The EDS device acts as a print server if a printer gets connected to one of its serial ports.
Selecting the Line Printer Daemon (LPD) link in the Main Menu displays the LPD web page. The
LPD web page has three sub-menus for viewing print queue statistics, changing print queue
configuration, and printing a test page. Because the LPD lines operate independently, you can
specify different configuration settings for each.
11: Service Settings
Table 11-16 RSS
and to be available across reboots.
are cached and viewable.
LPD Statistics
This read-only page shows various statistics about the LPD server.
To view LPD statistics for a specific LPD line:
1. Select LPD on the menu bar. The LPD web page appears.
2. Select an LPD line at the top of the page.
3. Select Statistics. The LPD Statistics page for the selected LPD line appears.
4. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional LPD(s) available on your product.
Figure 11-17 LPD Statistics
EDS User Guide 90
Page 91

11: Service Settings
LPD Configuration
Here you can change LPD configuration settings.
To configure LPD settings for a specific LPD line:
1. Select LPD on the menu bar, if you are not already at the LPD web page.
2. Select a LPD line at the top of the page.
3. Select Configuration. The LPD Configuration for the selected LPD line appears.
Figure 11-18 LPD Configuration
4. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 11-19 LPD Configuration
LPD Configuration
Settings
Banner Select Enabled to print the banner even if the print job does not specify to do so. Selected
Binary Select Enabled for the device to pass the entire file to the printer unchanged. Otherwise,
Start of Job Select Enabled to print a "start of job" string before sending the print data.
End of Job Select Enabled to send an "end of job" string.
Formfeed Select Enabled to force the printer to advance to the next page at the end of each print job.
Description
by default.
the device passes only valid ASCII and valid control characters to the printer. Valid control
characters include the tab, linefeed, formfeed, backspace, and newline characters. All
others are stripped. Disabled by default.
EDS User Guide 91
Page 92

11: Service Settings
LPD Configuration
Settings (continued)
Convert Newlines Select Enabled to convert single newlines and carriage returns to DOS-style line endings.
SOJ String If St art of Job (above) is enabled, enter the string to be sent to the printer at the beginning
EOJ String If En d of Job (above) is enabled, enter the string to send at the end of a print job. The limit
Queue Name To change the name of the print queue, enter a new name. The name cannot have white
Description
of a print job. The limit is 100 characters.
Indicate whether the string is in text or binary format.
is 100 characters. Indicate whether the string is in text or binary format.
space in it and is limited to 31 characters. The default is LPDQueueX (for line number X)
5. Click Submit
6. Repeat above steps as desired, according to additional LPD lines available on your product.
EDS User Guide 92
Page 93

12: Security Settings
The EDS device supports Secure Shell (SSH) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). SSH is a network
protocol for securely accessing a remote device. SSH provides a secure, encrypted
communication channel between two hosts over a network. It provides authentication and
message integrity services.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a protocol that manages data transmission security over the
Internet. It uses digital certificates for authentication and cryptography against eavesdropping and
tampering. It provides encryption and message integrity services. SSL is widely used for secure
communication to a web server. SSL uses certificates and private keys.
Note: The EDS supports SSLv3 and its successors, TLS1.0 and TLS1.1. An incoming
SSlv2 connection attempt is answered with an SSlv3 response. If the initiator also
supports SSLv3, SSLv3 handles the rest of the connection.
This chapter contains the following sections:
SSH Server Host Keys
SSH Server Authorized Users
SSH Client Known Hosts
SSH Client Users
SSL Cipher Suites
SSL Certificates
SSL RSA or DSA
SSL Certificates and Private Keys
SSL Utilities
SSL Configuration
SSH Settings
SSH is a network protocol for securely accessing a remote device over an encrypted channel. This
protocol manages the security of internet data transmission between two hosts over a network by
providing encryption, authentication, and message integrity services.
Two instances require configuration: when the EDS is the SSH server and when it is an SSH
client. The SSH server is used by the CLI (Command Mode) and for tunneling in Accept Mode.
The SSH client is for tunneling in Connect Mode.
To configure the EDS as an SSH server, there are two requirements:
Defined Host Keys: both private and public keys are required. These keys are used for the
Diffie-Hellman key exchange (used for the underlying encryption protocol).
Defined Users: these users are permitted to connect to the EDS SSH server.
This page has four links at the top for viewing and changing SSH server host keys, SSH server
authorized keys, SSH client known hosts, and SSH client users.
EDS User Guide 93
Page 94

12: Security Settings
SSH Server Host Keys
SSH Host Keys can be obtained in a few different ways:
Uploading keys via PUTTY or other tools which generate RFC4716 format keys.
Creating keys through the EDS.
The steps for creating or uploading keys is described below.
To upload SSH server host keys generated from PuTTY:
1. Create the keys with puttygen.exe. The keys are in PuTTY format.
2. Use puttygen.exe again to convert the private key to Open SSH format as follows:
a. Import the private key using "Conversions…Import key."
b. Create a new file using "Conversions…Export OpenSSH key."
3. Use ssh-keygen to convert the public key to OpenSSH format.
ssh-keygen -i -f putty_file > openssh_file
4. Select SSH on the menu bar and SSH Server: Host Keys at the top of the page. The SSH
Server Host Keys page appears.
Figure 12-1 SSH Server: Host Keys (Upload Keys)
5. Enter or modify the following settings in the part of the screen related to uploading keys:
EDS User Guide 94
Page 95

12: Security Settings
Table 12-2 SSH Server Host Keys Settings - Upload Keys Method
SSH Server: Host Keys
Settings (continued)
Private Key Enter the path and name of the existing private key you
Public Key Enter the path and name of the existing public key you want
Key Type Select a key type to use for the new key:
Description
want to upload or use the Browse button to select the key.
Be sure the private key will not be compromised in transit.
This implies the data is uploaded over some kind of secure
private network.
to upload or use the Browse button to select the key.
RSA = use this key with the SSH1 and SSH2 protocols.
DSA = use this key with the SSH2 protocol.
6. Click Submit.
To upload SSH server host RFC4716 format keys:
1. Use any program that can produce keys in the RFC4716 format.
2. Use ssh-keygen to convert the format to OpenSSH.
ssh-keygen -i -f RFC4716_file > output_file
Note: If the keys do not exist, follow directions under To create new SSH server host
keys (on page 97).
3. Select SSH on the menu bar and SSH Server: Host Keys at the top of the page. The SSH
Server Host Keys page appears.
EDS User Guide 95
Page 96

Figure 12-3 SSH Server: Host Keys (Upload Keys)
12: Security Settings
4. Enter or modify the following settings in the part of the screen related to uploading keys:
Table 12-4 SSH Server Host Keys Settings - Upload Keys Method
SSH Server: Host Keys
Settings (continued)
Private Key Enter the path and name of the existing private key you
Public Key Enter the path and name of the existing public key you want
Key Type Select a key type to use for the new key:
Description
want to upload or use the Browse button to select the key.
Be sure the private key will not be compromised in transit.
This implies the data is uploaded over some kind of secure
private network.
to upload or use the Browse button to select the key.
RSA = use this key with the SSH1 and SSH2 protocols.
DSA = use this key with the SSH2 protocol.
5. Click Submit.
Note: SSH keys may be created on another computer and uploaded to the EDS. For
example, use the following command using Open SSH to create a 1024-bit DSA key pair:
ssh-keygen –b 1024 –t dsa
EDS User Guide 96
Page 97

12: Security Settings
To create new SSH server host keys
Note: Generating new keys with large bit size results in longer key generation times.
1. Select SSH on the menu bar and SSH Server: Host Keys at the top of the page. The SSH
Server Host Keys page appears.
Figure 12-5 SSH Server: Host Keys (Create New Keys)
2. Enter or modify the following settings in the part of the screen related to creating new keys:
Table 12-6 SSH Server Host Keys Settings - Create New Keys Method
SSH Server: Host Keys
Settings
Key Type Select a key type to use:
Description
RSA = use this key with SSH1 and SSH2 protocols.
DSA = use this key with the SSH2 protocol.
Note: RSA is more secure.
EDS User Guide 97
Page 98

12: Security Settings
SSH Server: Host Keys
Settings (continued)
Bit Size Select a bit length for the new key:
Description
512
768
1024
Using a larger bit size takes more time to generate the key.
Approximate times are:
10 seconds for a 512 bit RSA Key
15 seconds for a 768 bit RSA Key
1 minute for a 1024 bit RSA Key
30 seconds for a 512 bit DSA Key
1 minute for a 768 bit DSA Key
2 minutes for a 1024 bit DSA Key
Note: Some SSH clients require RSA host keys to be at
least 1024 bits long. This device generates keys up to 1024
bits long. It can work with larger keys (up to 2048 bit) if they
are imported or otherwise created.
3. Click Submit.
Note: SSH Keys from other programs may be converted to the required EDS format.
Use Open SSH to perform the conversion.
SSH Server Authorized Users
On this page you can change SSH server settings for Authorized Users. SSH Server Authorized
Users are accounts on the EDS that can be used to log into the EDS using SSH. For instance,
these accounts can be used to SSH into the CLI or open an SSH connection to a device port.
Every account must have a password.
The user's public keys are optional and only necessary if public key authentication is required.
Using public key authentication allows a connection to be made without the password being
asked.
Under Current Configuration, User has a Delete User link, and Public RSA Key and Public
DSA Key have View Key and Delete Key links. If you click a Delete link, a message asks whether
you are sure you want to delete this information. Click OK to proceed or Cancel to cancel the
operation.
To configure the SSH server for authorized users:
1. Select SSH on the menu bar and then Server Authorized Users at the top of the page. The
SSH Server: Authorized Users page appears.
EDS User Guide 98
Page 99

Figure 12-7 SSH Server: Authorized Users
12: Security Settings
2. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 12-8 SSH Server Authorized User Settings
SSH Server:
Authorized Users
Settings
Username Enter the name of the user authorized to access the SSH server.
Password Enter the password associated with the username.
Public RSA Key Enter the path and name of the existing public RSA key you want
Public DSA Key Enter the path and name of the existing public DSA key you want
Description
to use with this user or use the Browse button to select the key. If
authentication is successful with the key, no password is required.
to use with this user or use the Browse button to select the key. If
authentication is successful with the key, no password is required.
3. Click Submit.
Note: When uploading the security keys, ensure the keys are not compromised in
transit.
EDS User Guide 99
Page 100

12: Security Settings
SSH Client Known Hosts
On this page you can change SSH client settings for known hosts.
Note: You do not have to complete the fields on this page for communication to occur.
However, completing them adds another layer of security that protects against Man-InThe-Middle (MITM) attacks.
To configure the SSH client for known hosts:
1. Select SSH on the menu bar and then Client Known Hosts at the top of the page. The SSH
Client: Known Hosts page appears.
Figure 12-9 SSH Client: Known Hosts
2. Enter or modify the following settings:
Table 12-10 SSH Client Known Hosts
SSH Client:
Known Hosts Settings
Server Enter the name or IP address of a known host. If you enter a server name,
Public RSA Key Enter the path and name of the existing public RSA key you want to use
Public DSA Key Enter the path and name of the existing public DSA key you want to use
Description
the name should match the name of the server used as the Remote
Address in Connect mode tunneling.
with this known host or use the Browse button to select the key.
with this known host or use the Browse button to select the key.
Note: These settings are not required for communication. They protect against Man-In-
The-Middle (MITM) attacks.
3. Click Submit.
4. In the Current Configuration table, delete currently stored settings as necessary.
EDS User Guide 100
 Loading...
Loading...