Page 1
PREFACE
This Service Manual describes the
technical features and servicing
procedures for the KYMCO DINK
CLASSIC 200.
Section 1 contains the precautions for
all operations stated in this manual.
Read them carefully before any
operation is started.
Section 2 is the removal/installation
procedures for the frame covers which
are subject to higher removal/installation
frequency during maintenance and
servicing operations.
Section 3 describes the inspection/
adjustment procedures, safety rules and
service information for each part, starting
from periodic maintenance.
Sections 5 through 13 give instructions
for disassembly, assembly and adjustment
of engine parts. Section 14 is the
removal/ installation of chassis. Section
16 states the testing and measuring
methods of electrical equipment. Section
20 provides the maintenance instructions
of the exhaust emission control system.
Most sections start with an assembly or
system illustration and troubleshooting
for the section. The subsequent pages
give detailed procedures for the section.
KWANG YANG MOTOR CO., LTD.
OVERSEAS SALES DEPARTMENT
OVERSEAS SERVICE SECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION
1
EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
2
INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3
LUBRICATION SYSTEM
4
ENGINE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
5
CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6
CYLINDER/PISTON
7
DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/KICK
STARTER
8
FINAL REDUCTION
9
A.C. GENERATOR/STARTER CLUTCH
10
CRANKCASE/CRANKSHAFT
11
COOLING SYSTEM
12
FUEL SYSTEM/CARBURETOR/FUEL
PUMP
13
STEERING HANDLEBAR/FRONT
WHEEL/FRONT BRAKE/FRONT
SHOCK ABSORBER/FRONT FORK
14
REAR BRAKE/REAR FORK/REAR
WHEEL/REAR SHOCK ABSORBER`
15
BATTERY/CHARGING SYSTEM
16
IGNITION SYSTEM
17
STARTING SYSTEM
18
SWITCHES/HORN/FUEL UNIT/
T HERMO-STATIC
SWITCH/TEMPERATURE
GAUGE/INSTRUMENTS/ LIGHTS
19
E/M
EXHAUST EMISSION CONT ROL SYST EM
20
The information and contents included in
this manual may be different from the
motorcycle in case specifications are
changed.
CHASSIS
EQUIPMENT
ENGINE
Page 2

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-0
DINK 20 0
1
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER
1
Location of Engine Serial Number
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER
----
1-0 TOOLS
-----------------------------
1-11
SPECIFICATION
-----------------
1-1 LUBRICATION POINTS
--------
1-12
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
------
1-2 WIRING DIAGRAM
--------------
1-14
TORQUE VALUES
---------------
1-9 CABLE & HARNESS ROUTING-1-19
TROUBLESHOOTING
-----------
1-20
Page 3
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-1
DINK 20 0
SPECIFICATIONS
Name & Model No.
SH40AA
Motorcycle Name & Type
Dink Classic 200
Overall length
1907mm
Overall width
750mm
Overall height
1170mm
Wheel base
1390mm
Engine type
Water cooled 4-stroke,
OHC engine
Displacement
176cc
Fuel Used
92# nonleaded gasoline
Front wheel
53
Net weight (kg)
Rear wheel
77
Total
130
Front wheel
58
Gross weight(kg)
Rear wheel
85
Total
143
Front wheel
120/70-12
Rear wheel
130/70-12
Ground clearance
155mm
Perform
-
Braking distance (m)
7.9m(40km/hr)
ance
Min. turning radius
2350mm
Starting system
Starting motor &
Kick starter
Type
Gasoline, 4-stroke
Cylinder arrangement
Single cylinder
Combustion chamber t ype
Semi-sphere
Valve arrangement
O.H.C.& Center
Pivot
Bore x stroke (mm)
62 x 58.2
Compression ratio
10.9:1
Compression pressure
(kg/cm_-rpm)
15
Max. output (ps/rpm)
15.2/7250
Max. torque (kg-m/rpm)
1.4/6500
Intake
Open
BTDC 12°
Port
(1mm)
Close
ATDC 35°
timin
g
Exhaust
Open
BDDC 28°
(1mm)
Close
0°
Valve
Intake
0.1
clearance (cold)
Exhaust
0.1
Idle speed (rpm)
1700rpm
Lubrication type
Forced pressure &
wet sump
Oil pump type
Inner/outer rotor
type
Oil filter type
Full-flow filtration
Oil capacity
1.1 liters
Cooling Type
Water cooling
Air cleaner type & No
Paper element, wet
Fuel capacity
10 liters
Type
VE
Piston dia.
26
Venturi dia.
22equivalent
Throttle type
Butterfly type
Type
CDI
Ignition timing
Repeatedly
Contact breaker
Non-contact point
type
Spark plug
NGK
DPR7EA-9
Spark plug gap
0.7mm
Battery
Capacity
12V8AH
Clutch
Type
CVT
Type
Non-stage transmission
Operation
Automatic
centrifugal
type
Type
Two-stage reduction
Reduction
1st
2.8-1.0
ratio
2nd
(46/16)x(46/15)=8.8
2
Front
Caster angle
Axle
Connecting rod
Tire pressure
Front
1.75
(kg/cm_)
Rear
2.0~2.25
Turning
Left
42.5°
angle
Right
42.5°
Front
Disk brake
Brake system
type
Rear
Disk brake
Front
Telescope
Suspension
type
Rear
Double swing
Shock absorber
Front
Telescope
type
Rear
Double swing
Frame type
Under bone
Tires
Engine
System
Fuel System
Carburetor
Electrical
Ignition System
Power Drive System
Transmis-
sion Gear
Reduction
Gear
Moving Device
Damping
Device
Page 4

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-2
DINK 20 0
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
Make sure to install new gaskets, O-rings,
circlips, cotter pins, etc. when
reassembling.
When tightening bolts or nuts, begin with
larger-diameter to smaller ones at several
times, and tighten to the specified torque
diagonally.
Use genuine parts and lubricants.
When servicing the motorcycle, be sure to
use special tools for removal and
installation.
After disassembly, clean removed parts.
Lubricate sliding surfaces with engine oil
before reassembly.
Page 5
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-3
DINK 20 0
Apply or add designated greases and
lubricants to the specified lubrication
points.
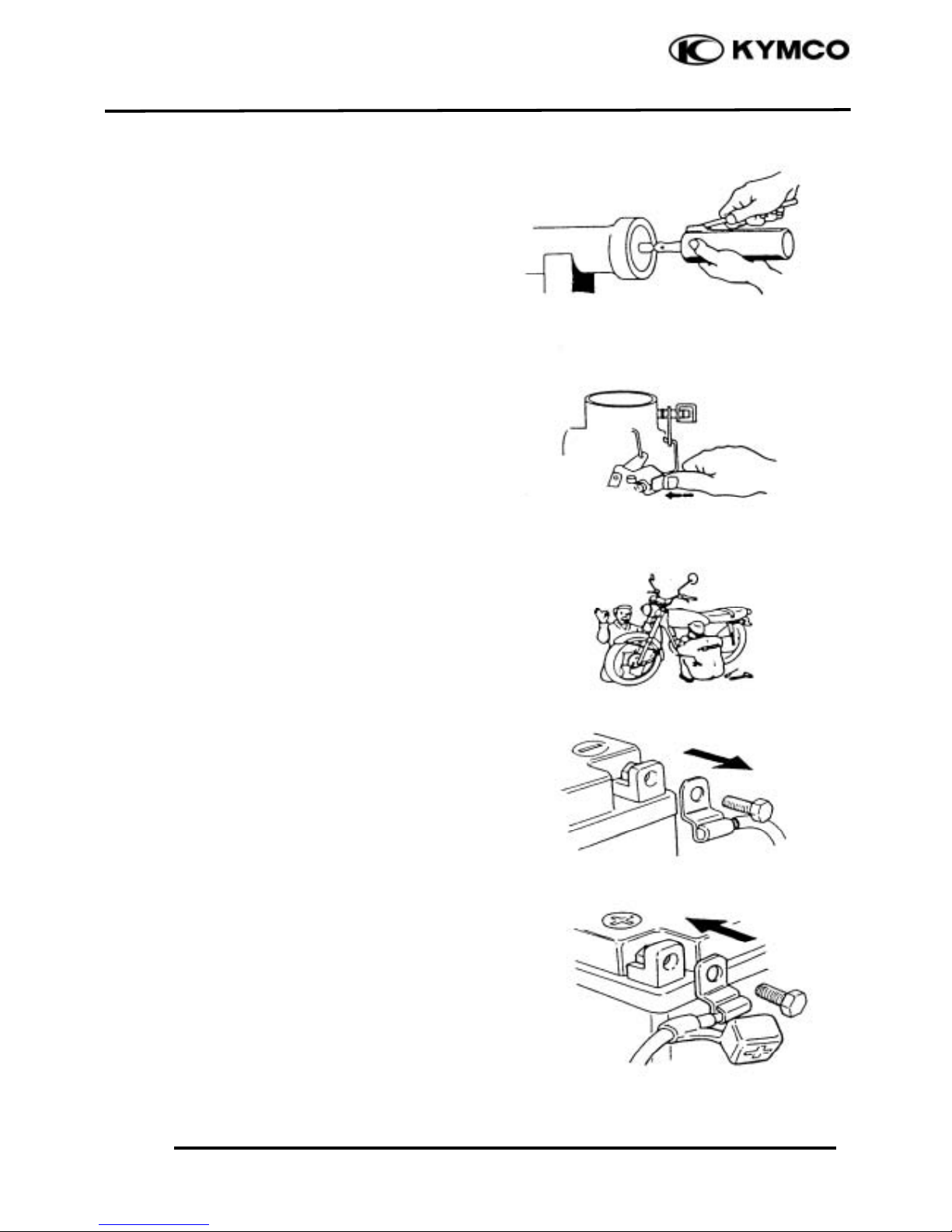
After reassembly, check all parts for
proper tightening and operation.
When two persons work together, pay
attention to the mutual working safety.
Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal
before operation.
When using a spanner or other tools, make
sure not to damage the motorcycle surface.
After operation, check all connecting
points, fasteners, and lines for proper
connection and installation.
When connecting the battery, the positive
(+) terminal must be connected first.
After connection, apply grease to the
battery terminals.
Terminal caps shall be installed securely.
Page 6
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-4
DINK 20 0
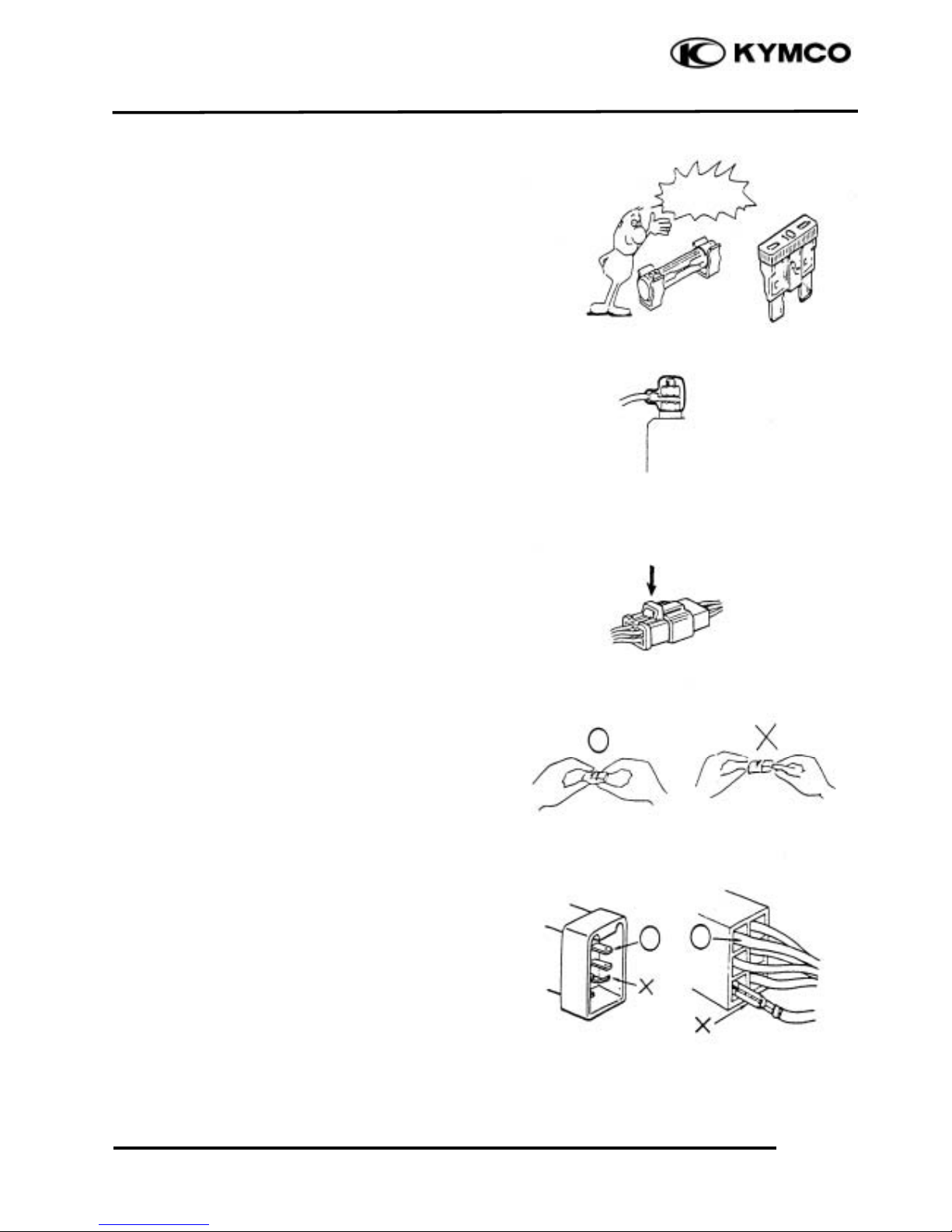
If the fuse is burned out, find the cause and
repair it. Replace it with a new one
according to the specified capacity.
After operation, terminal caps shall be
installed securely.
When taking out the connector, the lock on
the connector shall be released before
operation.
Hold the connector body when connecting
or disconnecting it.
Do not pull the connector wire.
Check if any connector terminal is bending,
protruding or loose.
Confirm
Capacity
Page 7
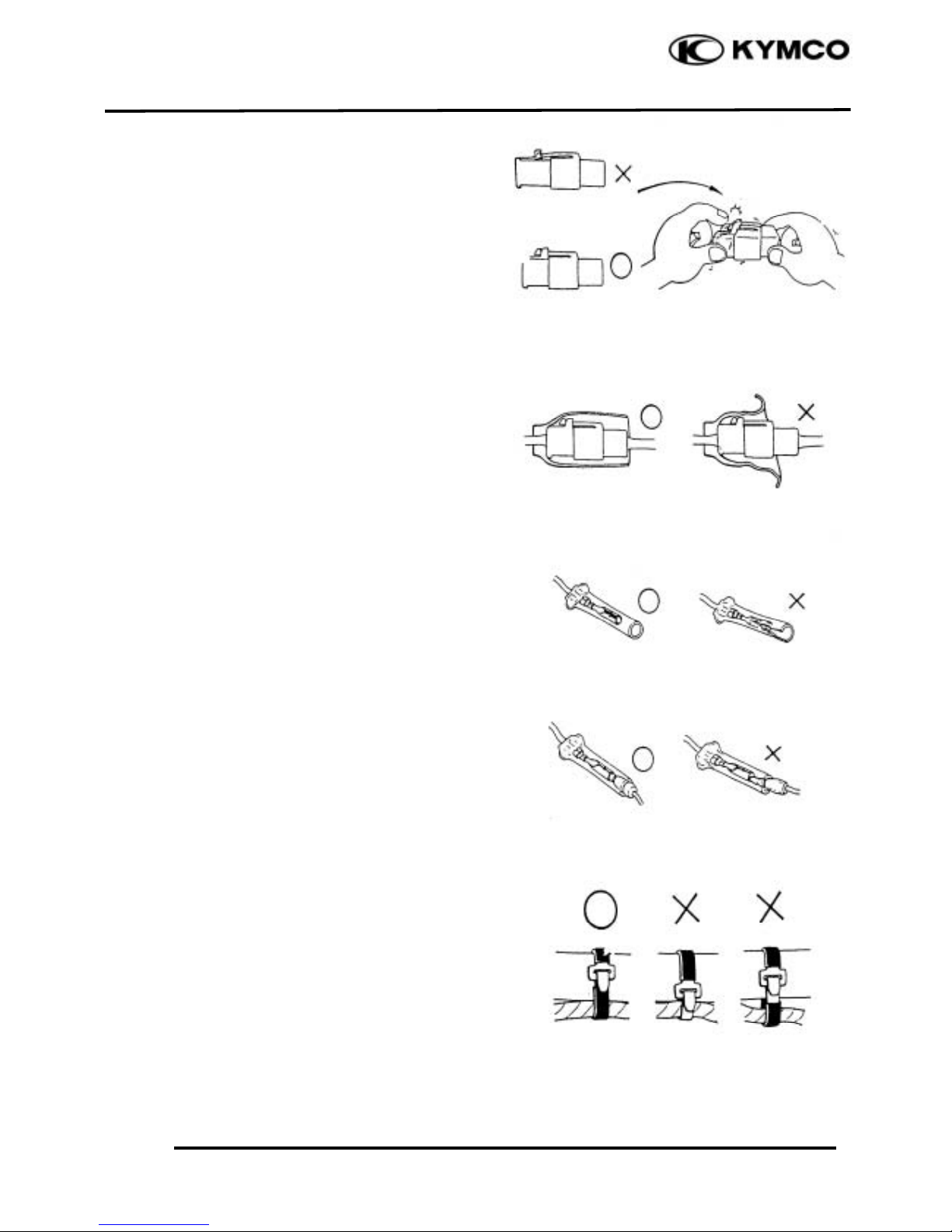
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-5
DINK 20 0
The connector shall be inserted
completely.
If the double connector has a lock, lock
it at the correct position.
Check if there is any loose wire.
Before connecting a terminal, check for
damaged terminal cover or loose negative
terminal.
Check the double connector cover for
proper coverage and installation.
Insert the terminal completely.
Check the terminal cover for proper
coverage.
Do not make the terminal cover opening
face up.
Secure wire harnesses to the frame with
their respective wire bands at the
designated locations.
Tighten the bands so that only the
insulated surfaces contact the wire
harnesses.
Snapping!
Page 8
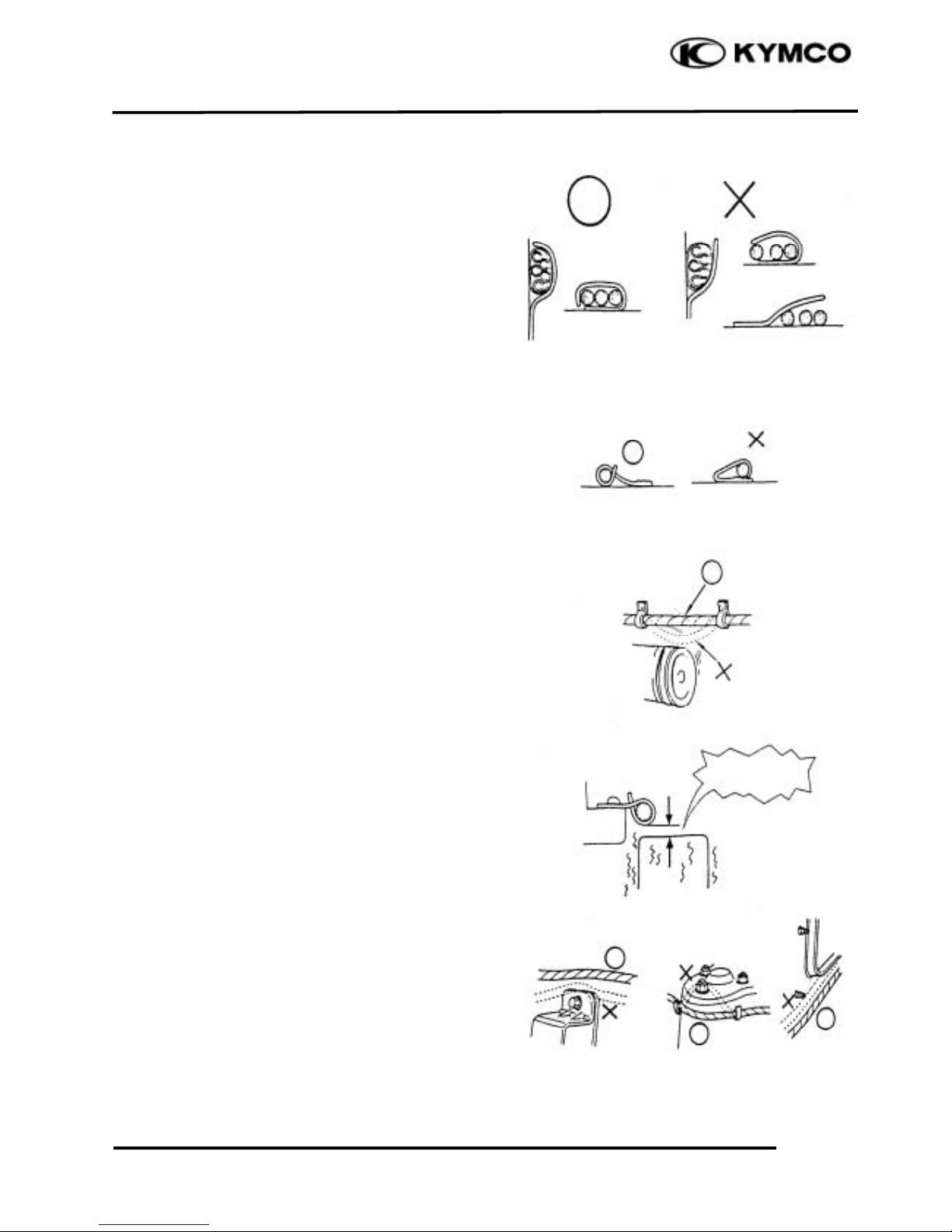
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-6
DINK 20 0
After clamping, check each wire to make
sure it is secure.
Do not squeeze wires against the weld or
its clamp.
After clamping, check each harness to make
sure that it is not interfering with any
moving or sliding parts.
When fixing the wire harnesses, do not
make it contact the parts which will
generate high heat.
Route wire harnesses to avoid sharp edges
or corners. Avoid the projected ends of
bolts and screws.
Route wire harnesses passing through the
side of bolts and screws. Avoid the
projected ends of bolts and screws.
No Contact !
Page 9
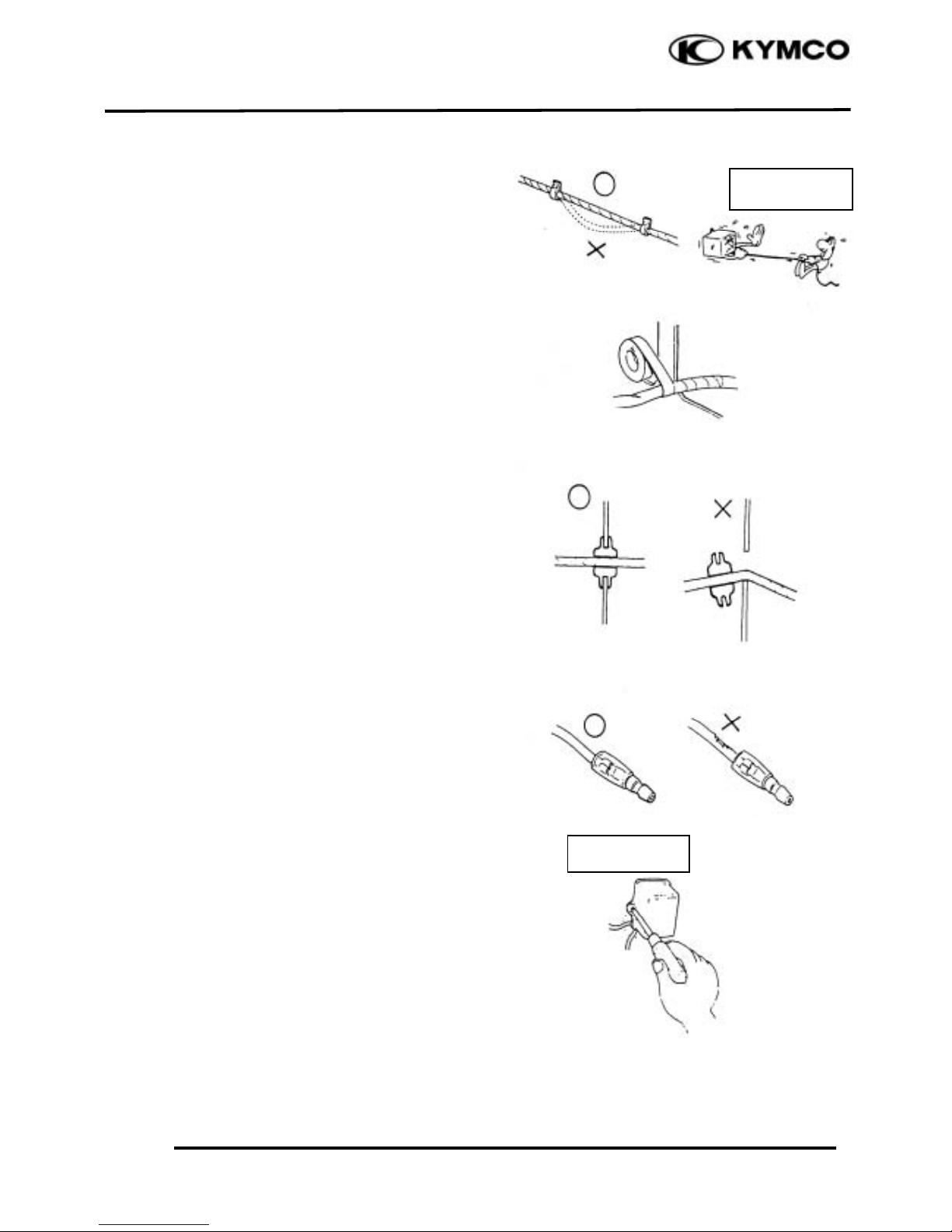
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-7
DINK 20 0
Route harnesses so they are neither
pulled tight nor have excessive slack.
Protect wires and harnesses with electrical
tape or tube if they contact a sharp edge or
corner.
When rubber protecting cover is used to
protect the wire harnesses, it shall be
installed securely.
Do not break the sheath of wire.
If a wire or harness is with a broken sheath,
repair by wrapping it with protective tape
or replace it.
When installing other parts, do not press or
squeeze the wires.
Do not pull too
tight!
Do not press or
squeeze the wire.
Page 10
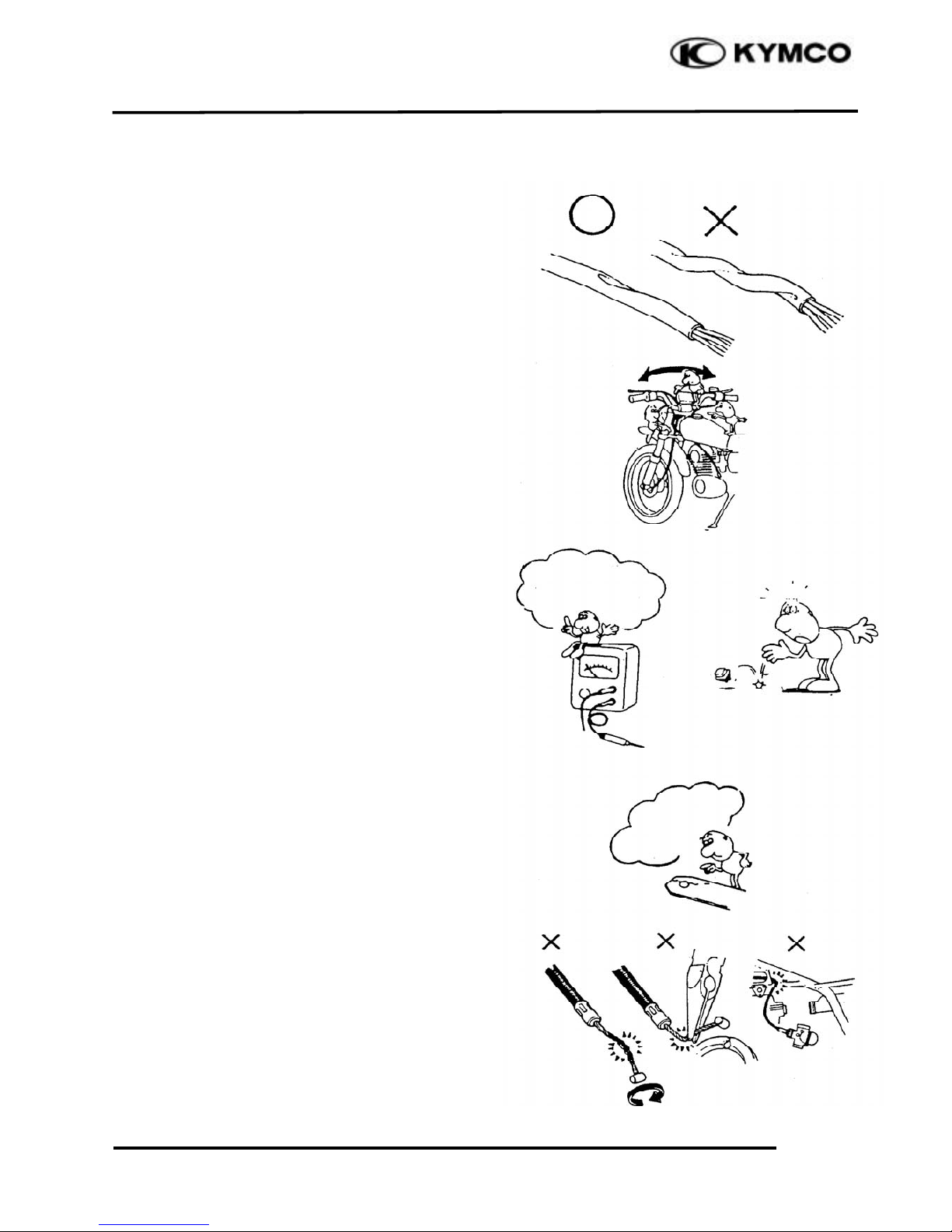
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-8
DINK 20 0
After routing, check that the wire harnesses
are not twisted or kinked.
Wire harnesses routed along with handlebar
should not be pulled tight, have excessive
slack or interfere with adjacent or
surrounding parts in all steering positions.
When a testing device is used, make sure to
understand the operating methods
thoroughly and operate according to the
operating instructions.
Be careful not to drop any parts.
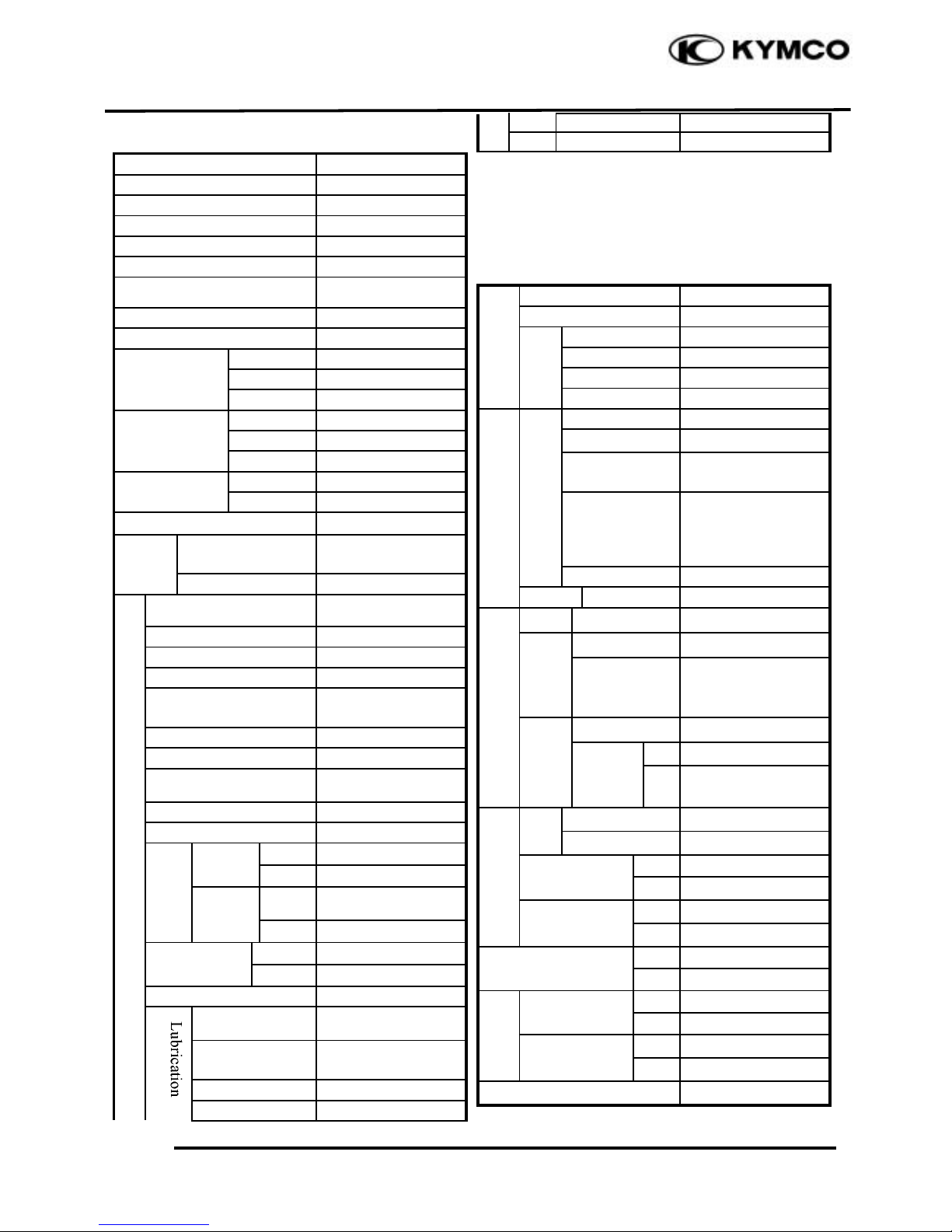
When rust is found on a terminal, remove
the rust with sand paper or equivalent
before connecting.
Do not bend or twist control cables.
Damaged control cables will not operate
smoothly and may stick or bind.
Do you understand
the instrument?
Remove Rust!
Page 11
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-9
DINK 20 0
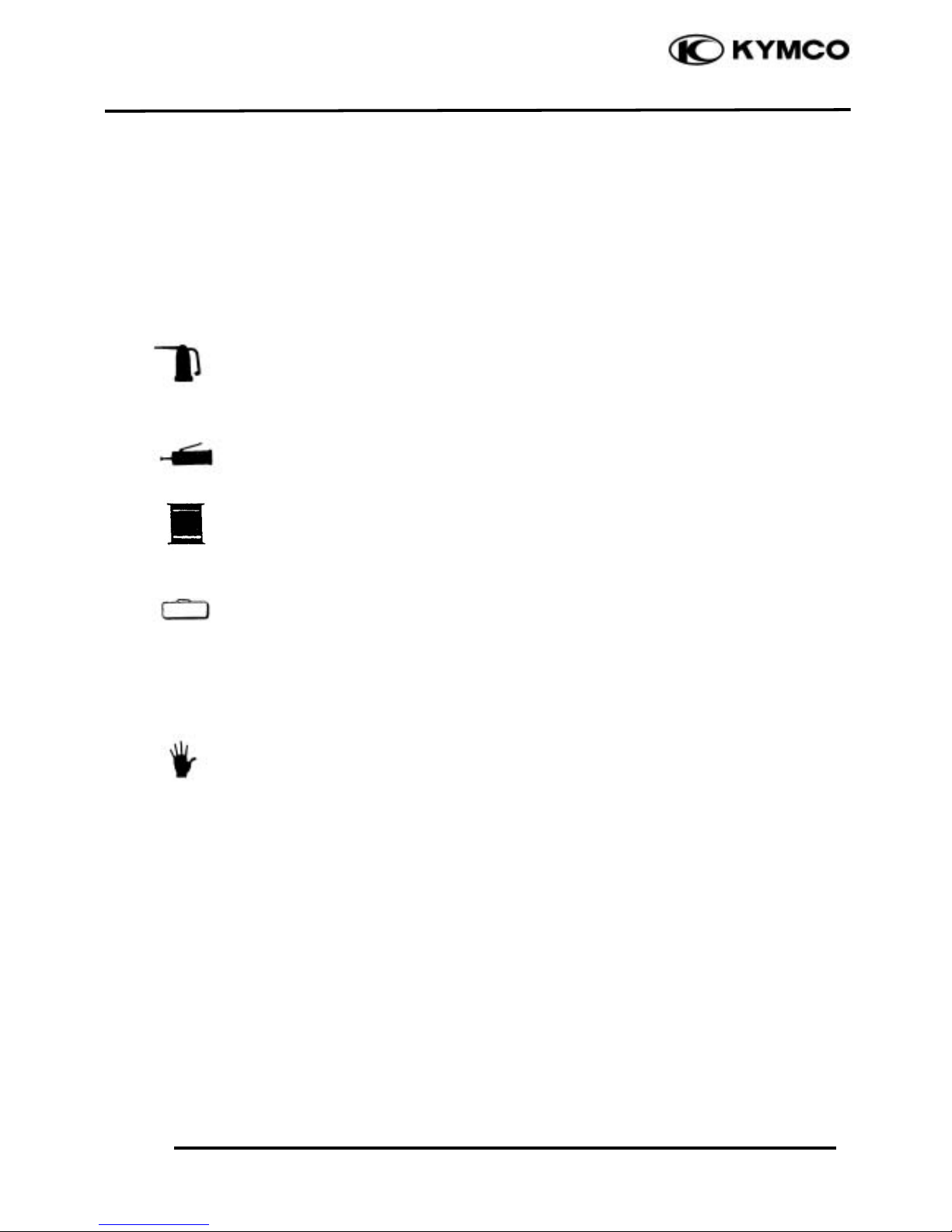
Symbols:
The following symbols represent the
servicing methods and cautions included in
this service manual.
: Apply engine oil to the
specified points. (Use
designated engine oil for
lubrication.)
: Apply grease for lubrication.
: Transmission Gear Oil (90#)
: Use special tool.
: Caution
: Warning
Special
Engine Oil
Grease
Gear Oil
*
Page 12

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-10
DINK 20 0
TORQUE VALUES
STANDARD TORQUE VALUES
Item
Torque (kg-m)
Item
Torque (kg-m)
5mm bolt, nut
6mm bolt, nut
8mm bolt, nut
10mm bolt, nut
12mm bolt, nut
0.5
1.0
2.2
3.5
5.5
5mm screw
6mm screw, SH bolt
6mm flange bolt, nut
8mm flange bolt, nut
10mm flange bolt, nut
0.4
0.9
1.2
2.7
4.0
Torque specifications listed below are for important fasteners.
ENGINE
Item
Q‘ty
Thread dia.(mm)
Torque (kg-m)
Remarks
Cylinder head bolt A
Cylinder head bolt B
Oil filter screen cap
Exhaust muffler joint lock nut
Cylinder head cap nut
Valve adjusting lock nut
Cam chain tensioner slipper bolt
Oil bolt
Clutch outer nut
Clutch drive plate nut
Flywheel nut
Oil pump bolt
Cylinder head cover bolt
Spark plug
Cam chain tensioner bolt
Water pump impeller
2
2
1
2
4
2
1
1
1
1
1
2
4
1
1
1
8
8
30
8
8
5
6
12
12
12
14
5
6
10
6
8
2.2
2.2
1.5
0.9
2.2
0.9
0.9
1.3
5.5
5.5
5.5
0.4
1.2
1.2
0.9
1.4
Double end bolt
Double end bolt
Apply oil to
threads
Left hand threads
FRAME
Item
Q‘ty
Thread dia.(mm)
Torque (kg-m)
Remarks
Steering stem lock nut
Front axle nut
Rear axle nut
Rear shock absorber upp er bolt
Rear shock absorber lower bolt
Front shock absorber lock bolt
Engine hanger bolt
1
1
1
2
2
4
1
10
12
14
10
8
10
12
4.5
6.0
9.0
3.0
3.0
2.5
5.5
U-nut
U-nut
U-nut
Page 13
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-11
DINK 20 0
SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool Name
Tool No.
Remarks
Ref. Page
Valve guide driver
Valve guide removal/installation
Valve guide reamer
Valve guide grinding
Valve spring compressor
Valve removal
Lock nut wrench, 39mm
Clutch disassembly
Bearing driver
Bearing removal
Bearing remover, 12mm
Bearing removal
Remover shaft
Bearing removal
Remover weight
Bearing removal
Bearing remover, 15mm
Bearing removal
Bearing driver
Bearing removal
Clutch spring compressor
Clutch disassembly
Ball race remover extension
Ball race removal
Ball race remover
Ball race removal
Spring compressor
Spring removal
Mechanical seal driver
Water pump mechanical seal
removal/installation
Kick starter spring remover
Kick starter spring removal
Gear remover
Starter gear removal
Valve adjuster
Tapper adjustment
Float level gauge
Carburetor fuel level check
Valve seat cutter 45°
Valve seat refacing
Valve seat cutter 32°
Valve seat refacing
Valve seat cutter 60°
Valve seat refacing
Cutter clip, 5mm
Universal holder
Holding clutch for removal
Bearing driver (32x35mm)
Bearing installation
Pilot, 12mm
Bearing installation
Pilot, 15mm
Bearing installation
Pilot, 17mm
Bearing installation
Flywheel puller
A.C. generator flywheel removal
Rear shock absorber compressor
Rear shock absorber disassembly
Steering head bearing remover
Steering head bearing removal
Kick starter spring remover
Kick starter spring installation
Flywheel holder
A.C. generator flywheel holding
Reamer clip
Fuel unit wrench
Fuel unit removal
Page 14
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-12
DINK 20 0
LUBRICATION POINTS
ENGINE
Lubrication Points
Lubricant
Valve guide/valve stem movable part
Camshaft protruding surface
Valve rocker arm friction surface
Camshaft drive chain
Cylinder lock bolt and nut
Piston surroundings and piston ring grooves
Piston pin surroundings
Cylinder inside wall
Connecting rod/piston pin hole
Connecting rod big end
Crankshaft
Crankshaft one-way clutch movable part
Oil pump drive chain
Starter reduction gear engaging part
Countershaft gear engaging part
Final gear engaging part
Bearing movable part
O-ring face
Oil seal lip
•Genuine KYMCO Engine Oil (SAE15W-40)
•API SE, SF or SG Engine Oil
Starter idle gear
Friction sp ring movable part/shaft movable p art
Shaft movable grooved part
Starter spindle movable part
High-temperature resistant grease
Starter one-way clutch threads
Thread locking agent
A.C. generator connector
Transmission case breather tube
Adhesive
Page 15
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-13
DINK 20 0
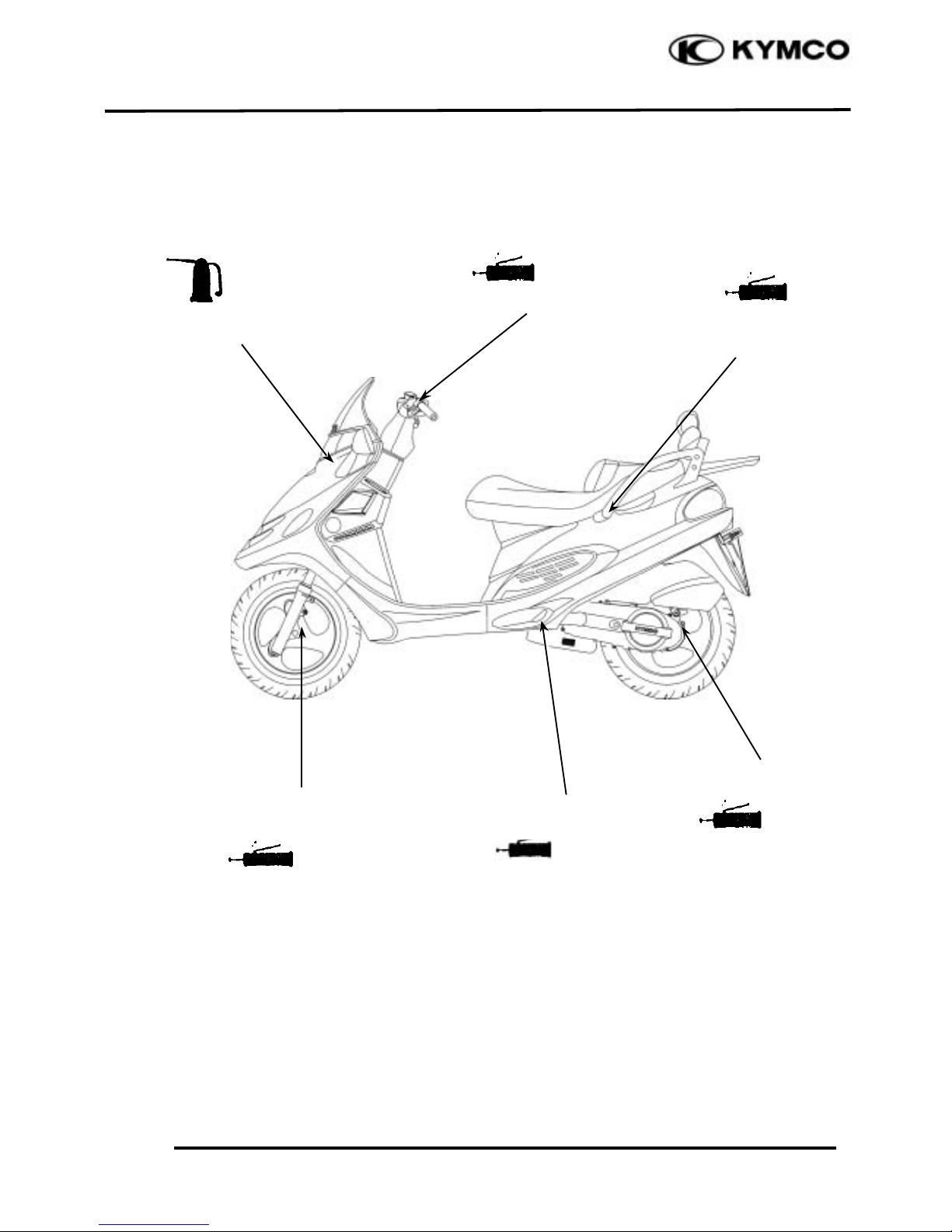
FRAME
The following is the lubrication points for the frame.
Use general purpose grease for parts not listed.
Apply clean engine oil or grease to cables and movable parts not specified. This will avoid
abnormal noise and rise the durability of the motorcycle.
Seat Lock
Rear Wheel Bearing
Grease
Speedometer Cable
Throttle Cable
Main Stand Pivot
Side Stand Pivot
Speedometer Gear/
Front Wheel Bearing
Engine Oil
Grease
Grease
Grease
Grease
Front Brake Lever Pivot
Page 16

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-14
DINK 20 0
CABLE & HARNESS ROUTING
Front Stop Switch
Rear Stop Switch
Throttle Cable
Fuel Vapor
Recovery Tube
Wire Connectors
Radiator
Front Brake Fluid Tube
Rear Brake Fluid Tube
Speedometer Cable
Horn
Water Hose
Fuel Vapor
Recovery Tube
Pressure Type
Radiator Cap
Page 17

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-15
DINK 20 0
Fuel Vapor
Recovery Tube
Radiator Air Vent Tube
Front Brake Fluid Tube
Rear Brake Fluid Tube
Fuel Tank
Inlet Tube
Water Hose
Ignition Switch
Fuel Filler
Water Hoses
Thermostatic
Switch
Fuel Tank
Breather Tube
Page 18

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-16
DINK 20 0
Throttle Cable
Speedometer Cable
Fuel Vapor
Recovery Tube
Rear Brake Fluid
Tube
Fuel Tank Inlet
Tube
Water Hose
Fuel Filler
Fuel Tank
Breather Tube
Throttle Cable
Front Stop
Switch
Wire Harness
Fuel Unit
Page 19
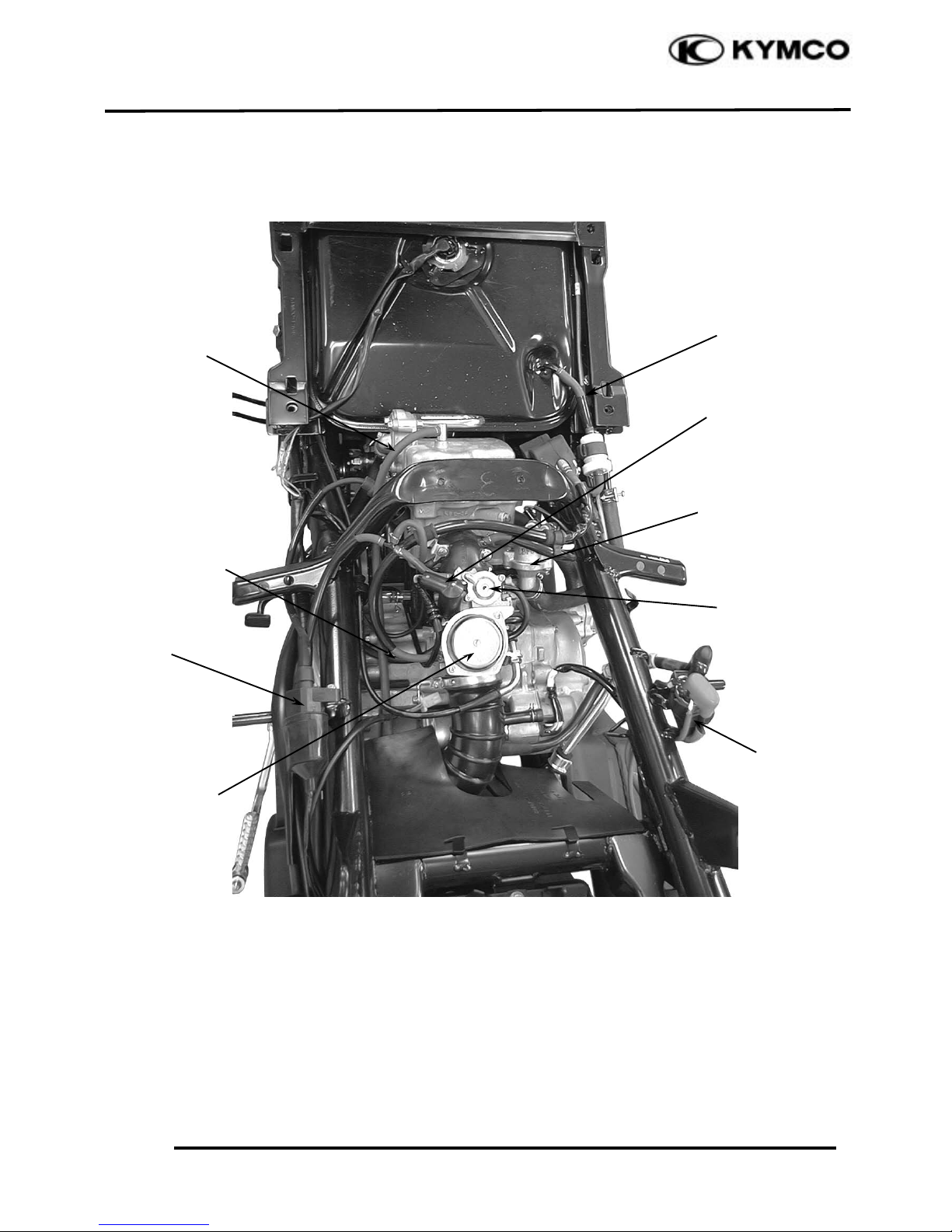
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-17
DINK 20 0
Starter Relay
Oil Vapor
Recovery Tube
Carburetor
Fuel Tube
Ignition Coil
Auto Bystarter Wire
Thermostat
Carburetor
Overflow Tube
Air Cut-off
Valve (A.C.V.)
Page 20
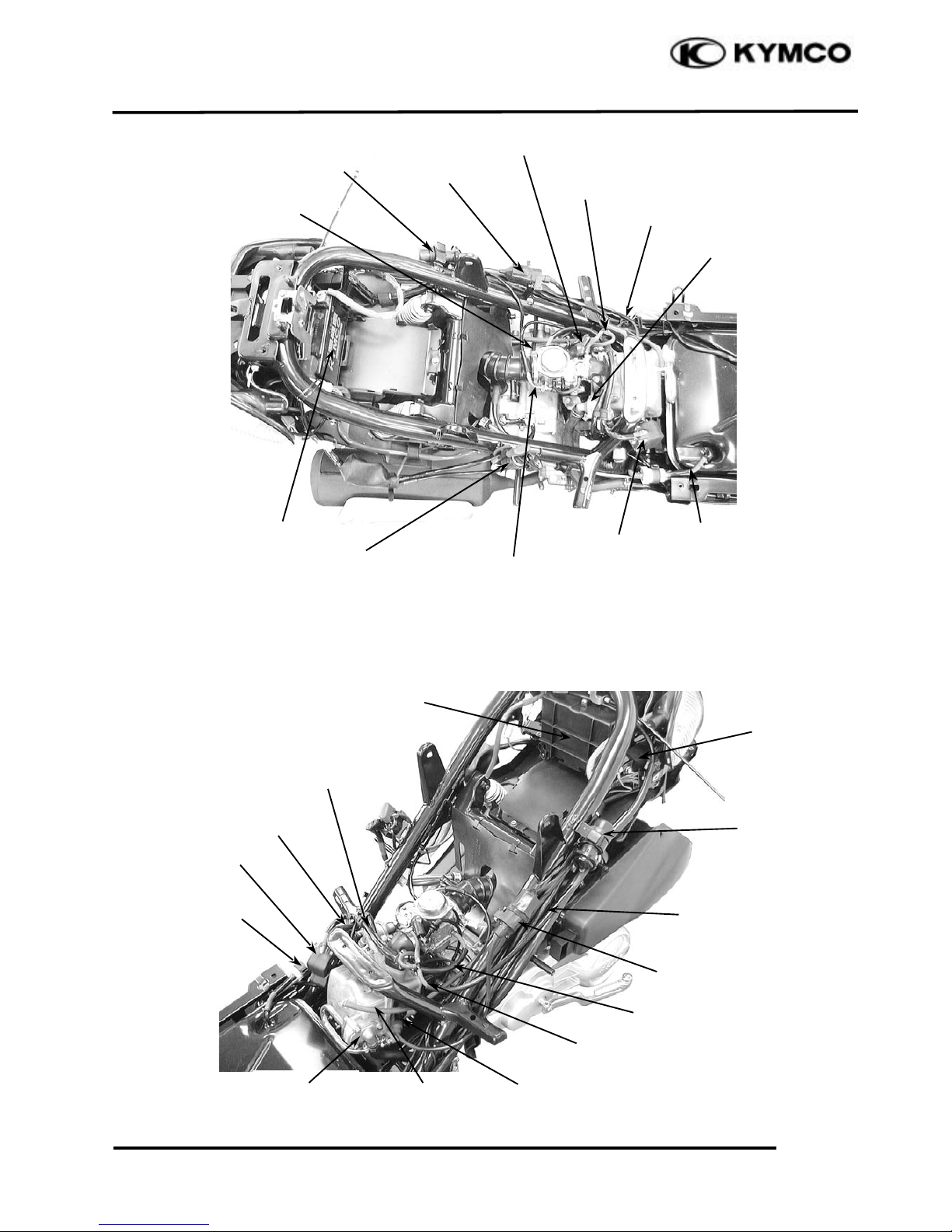
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-18
DINK 20 0
Starter Relay
Fuel Tube
Battery
Ignition Coil
Thermostat
Air Injection Air
Cleaner
Fuel Tube
CDI Unit
Auto Bystarter
Spark Plug Cap
Battery
Fuel Pump
Fuel Tube
Wire Harness
Spark Plug Cap
Throttle Cable
Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV)
Vacuum Tee
Vacuum Tee
Fuel Pump
Ground Wire
Fuel Pump Vacuum Tube
Fuel Filter
Air Injection
Air Cleaner
Ignition Coil
Reed Valve
Page 21
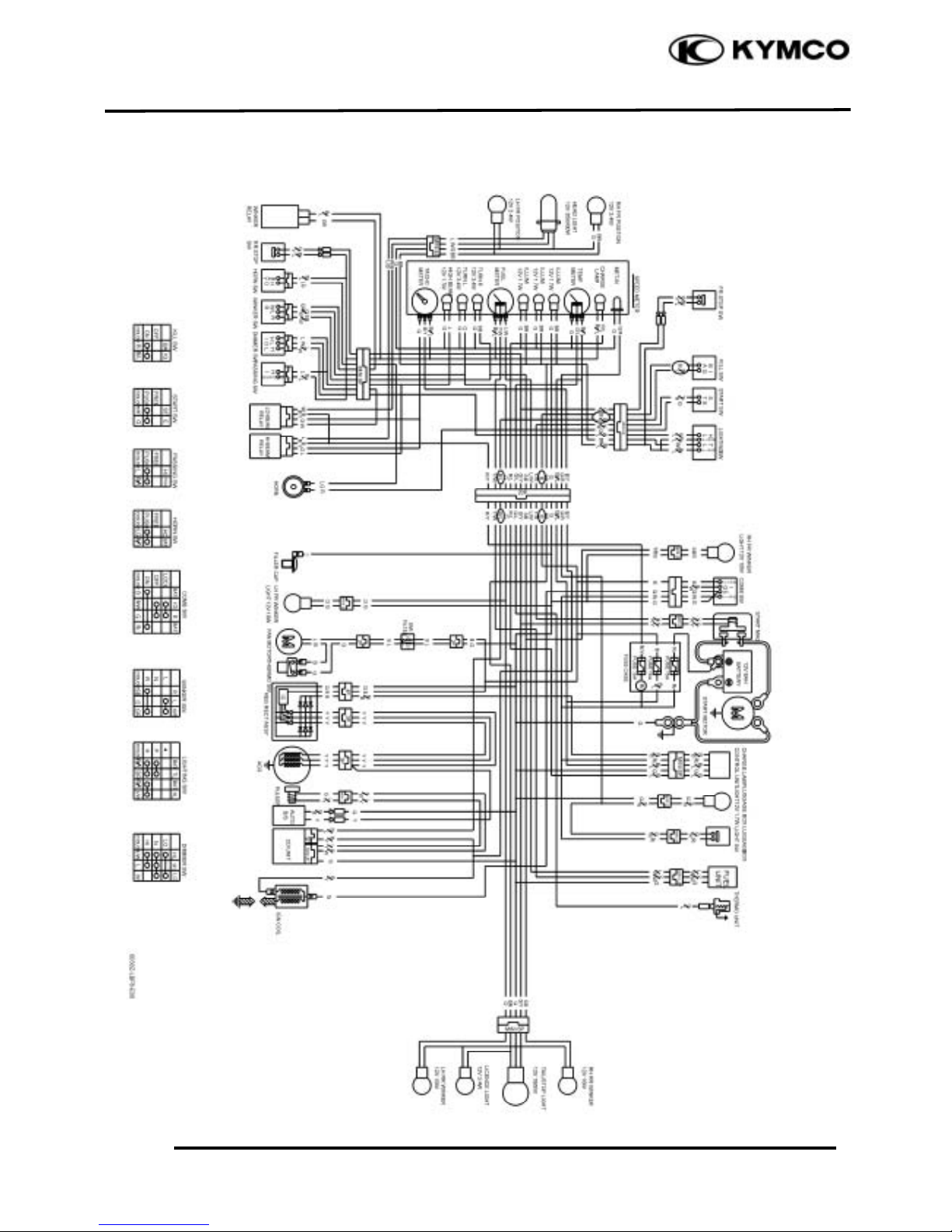
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-19
DINK 20 0
WIRING DIAGRAM
Page 22
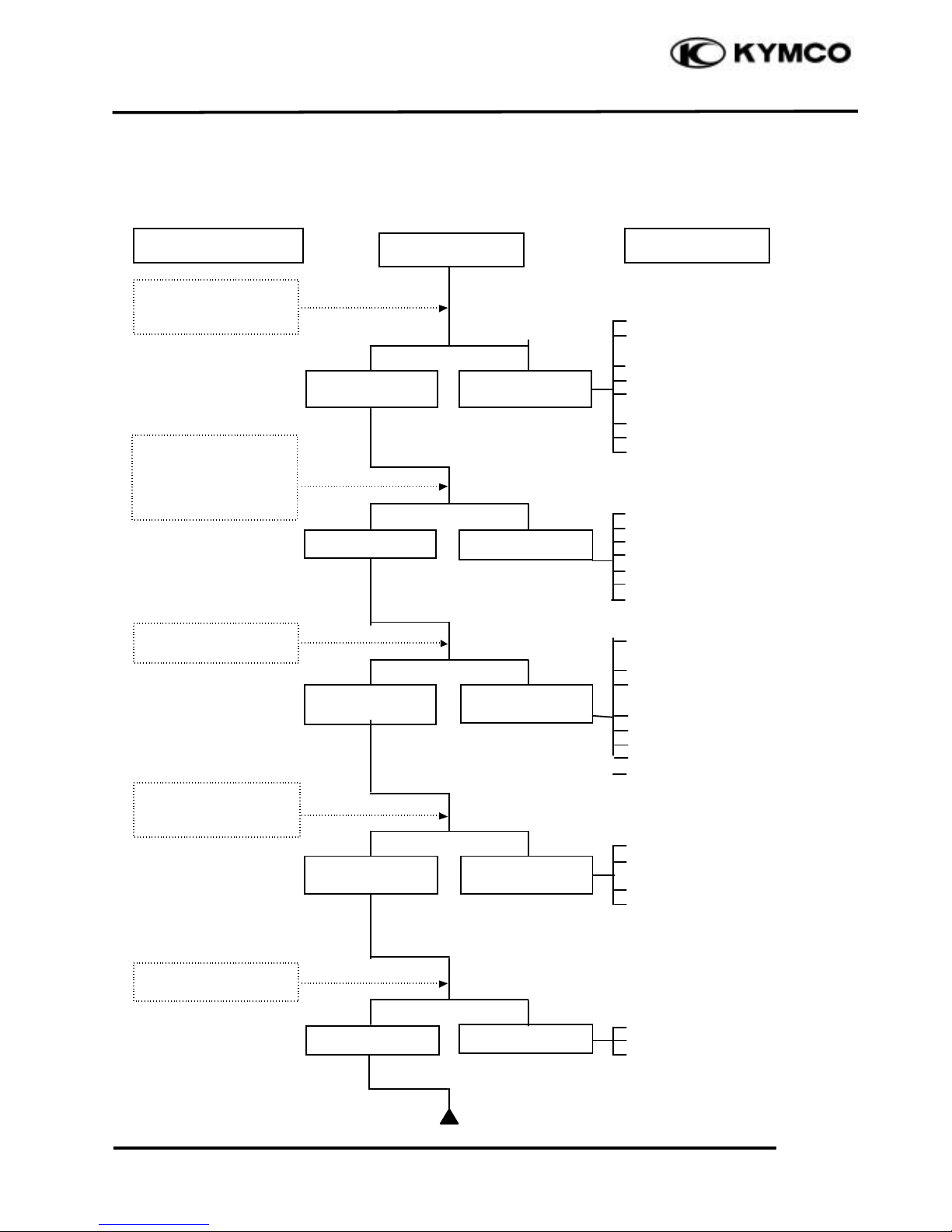
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-20
DINK 20 0
TROUBLESHOOTING
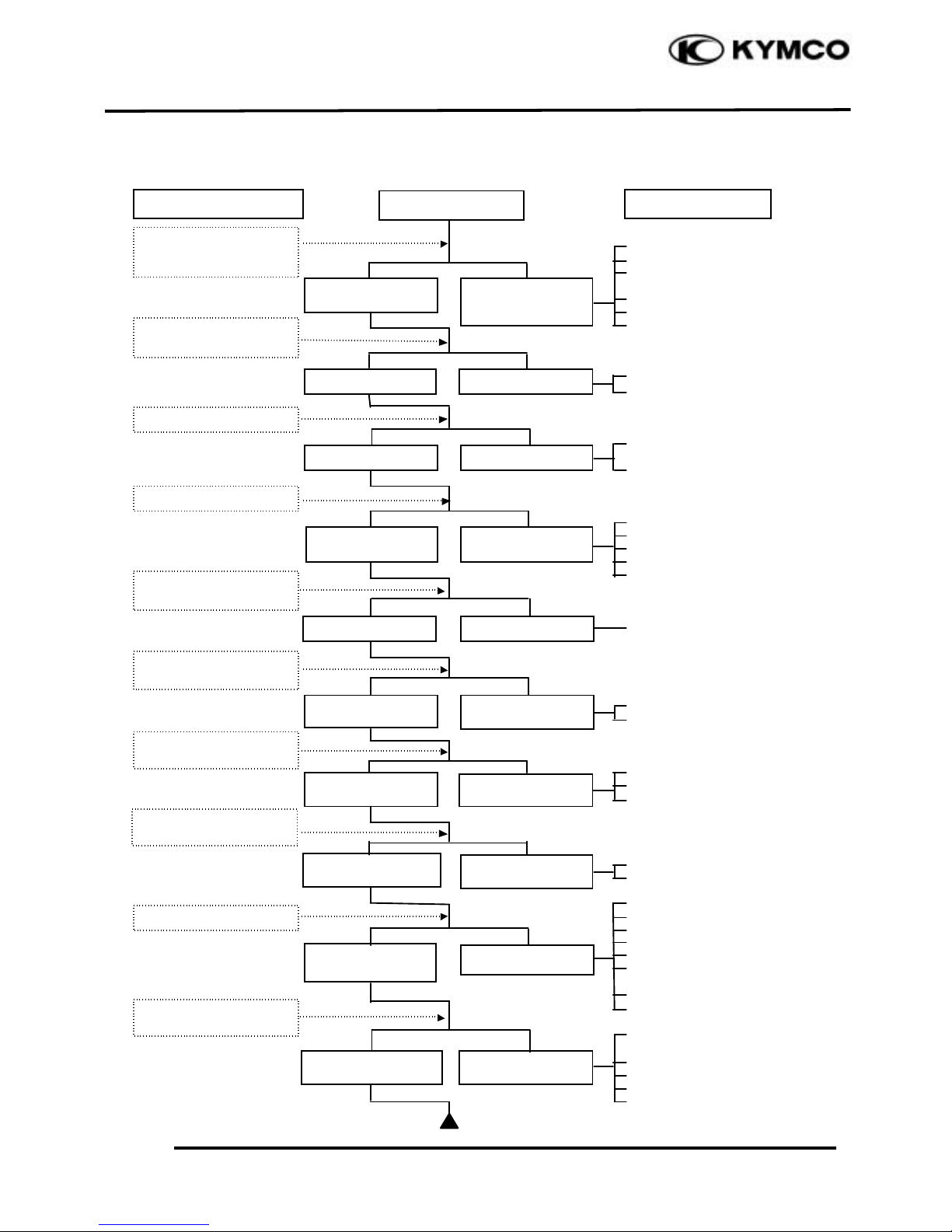
ENGINE WILL NOT START OR IS HARD TO START
Empty fuel tank
Clogged carburetor fuel inlet
tube, vacuum tube or fuel tube
Clogged auto fuel valve
Clogged float oil passage
Clogged fuel tank cap
breather hole
Clogged fuel strainer
Clogged fuel filter
Faulty fuel pump
Faulty spark plug
Fouled spark plug
Faulty CDI unit
Faulty A.C. generator
Broken or shorted ignit ion coil
Broken or shorted exciter
coil
Faulty ignition switch
Starter motor idles but
crankshaft does not rotate
Valve clearance too small
Improper valve and seat
contact
Worn cylinder and piston rings
Blown cylinder head gasket
Flaws in cylinder head
Seized valve
Improper valve timing
Faulty auto bystarter
Air leaking through intake
pipe
Incorrect ignition timing
Incorrectly adjusted pilot
screw
Flooded carburetor
Faulty auto bystarter
Throttle valve excessively
open
Check if fuel reaches
carburetor by
loosening drain screw
Remove spark plug
and install it into
spark plug cap to test
spark by connecting it
to engine ground
Inspection/Adjustment
Probable Cause
Spark jumps
Normal
compression
Engine does not
fire
Weak or no spark
Low or no
compression
Engine fires but
does not start
Test cylinder
compression
Start engine by following normal starting
procedure
Remove spark plug and
inspect again
Symptom
Fuel reaches
carburetor
Fuel does not
reach carburetor
Wet spark plug
Dry spark plug
Page 23
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-21
DINK 20 0
ENGINE LACKS POWER
Clogged air cleaner
Restricted fuel flow
Clogged fuel line between fuel
tank and carburetor
Clogged exhaust muffler
Faulty auto bystarter
Split carburetor vacuum piston
diaphragm
Faulty CDI unit
Faulty A.C. generator
Improper valve clearance
adjustment
Worn valve seat (valve stem too
protruding
Improper valve and seat contact
Worn cylinder and piston rings
Blown cylinder head gasket
Flaws in cylinder head
Improper valve timing
Clogged carburetor jets
Fouled spark plug
Incorrect heat range plug
Oil level too high
Oil level too low
Oil not changed
Clogged oil pipe
Faulty oil pump
Insufficient coolant
Faulty thermostat
Worn cylinder and piston rings
Mixture too lean
Poor quality fuel
Excessive carbon buildup in
combustion chamber
Ignition timing too early
Air in cooling system
Excessive carbon build-up in
combustion chamber
Poor quality fuel
Clutch slipping
Mixture too lean
Ignition timing too early
Start engine and accelerate
lightly for observation
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Engine speed
increases
Correct timing
Engine speed does
not increase
sufficiently
Incorrect timing
Check ignition timing
(using a timing light)
Test cylinder compression
Check carburetor for
clogging
Rapidly accelerate or run
at high speed
Remove spark plug and
inspect
Check if engine overheats
Check valve clearance
Correct
Incorrect
Normal
compression
Abnormal
compression
Not Clogged
Clogged
Remove oil dipstick and
check oil level and condition
Remove cylinder head oil
pipe bolt and inspect
Engine overheats
Engine does not
overheats
Plug not fouled or
discolored
Plug fouled or
discolored
Correct and not
contaminated
Incorrect or
contaminated
Valve train lubricated
properly
Valve train not
lubricated properly
Engine does not knock
Engine knocks
Page 24

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-22
DINK 20 0
POOR PERFORMANCE (ESPECIALLY AT IDLE AND LOW SPEEDS)
Faulty CDI unit
Faulty A.C. generator
Mixture too rich (turn screw
out)
Mixture too lean (turn screw
in)
Damaged insulator rubber
Carburetor not securely
tightened
Faulty intake manifold
gasket
Deformed carburetor O-ring
Faulty or fouled spark plug
Faulty CDI unit
Faulty A.C. generator
Faulty ignition coil
Broken or shorted high
tension wire
Faulty ignition switch
Damaged air cut-off valve
diaphragm
Damaged air cut-off valve
spring
Remove spark plug
and install it into
spark plug cap to test
spark by connecting it
to engine ground
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Check ignition timing
Check carburetor air
cut-off valve
Check carburetor
gasket for air leaks
Check carburetor pilot
screw adjustment
Correct timing
Incorrect timing
Correctly adjusted
No air leak
Air leaks
Good spark
Weak or inter mittent spark
Good
Faulty
Incorrectly adjusted
Page 25
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-23
DINK 20 0
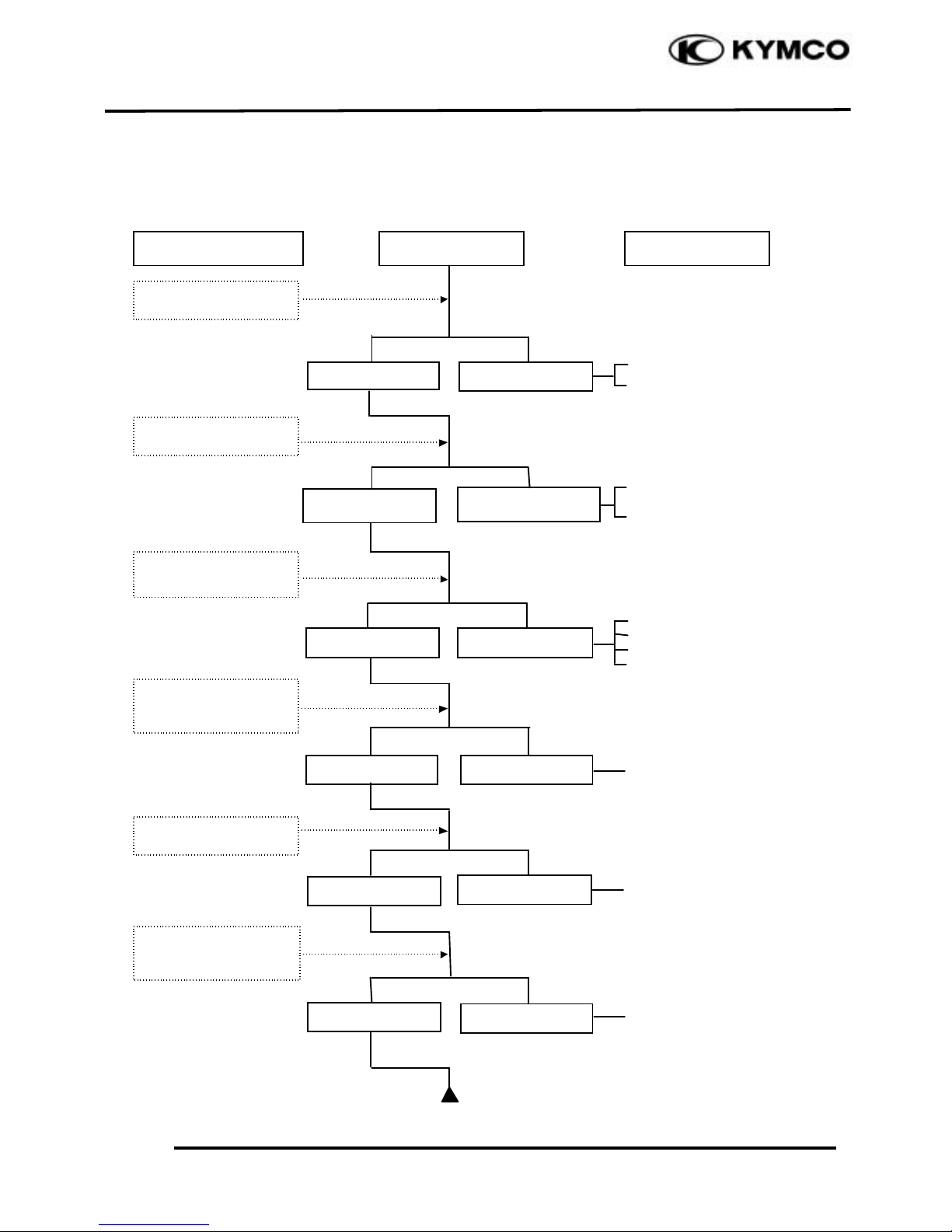
POOR PERFORMANCE (AT HIGH SPEED)
Faulty CDI unit
Faulty A.C. generator
Improperly adjusted valve
clearance
Worn valve seat
Empty fuel tank
Clogged fuel tube or filter
Faulty fuel pump
Cracked fuel pump vacuum
tube
Clean and unclog
Cam timing gear aligning
marks not aligned
Faulty spring
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Check ignition timing
Check carburetor jets
for clogging
Check fuel pump for
fuel supply
Correct timing
Incorrect timing
Check valve spring
tension
Check valve clearance
Fuel flows freely
Fuel flow rest ricted
Correct
Incorrect
Not clogged
Clogged
Correctly adjusted
Incorrectly adjusted
Not weakened
Weak spring
Check valve timing
Page 26
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-24
DINK 20 0
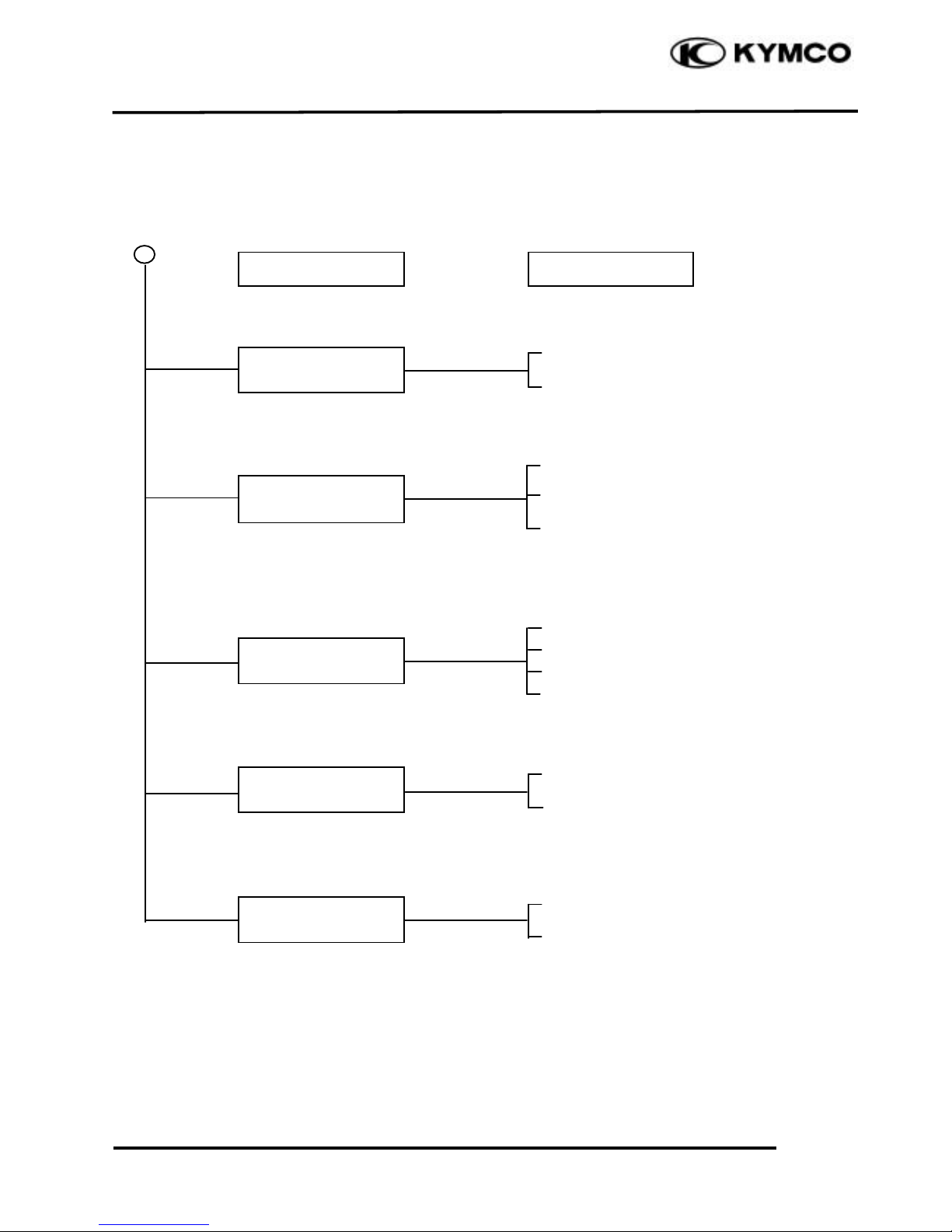
ENGINE NOISE
Valve clearance too large
Worn camshaft lobe
Worn piston rings
Worn piston pin and connecting rod
small end
Excessive carbon build-up in combustion
chamber
Damaged cam chain tensioner
Worn cam gear teeth
Worn or damaged cam chain
Extended cam chain
Faulty crankshaft bearing
Worn crank pin bearing
Worn or damaged final reduction gears
Worn final reduction gear shaft splines
Valve noise
Symptom
Probable Cause
Crankshaft noise
Gear noise
Piston noise
Cam chain noise
Page 27
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-25
DINK 20 0
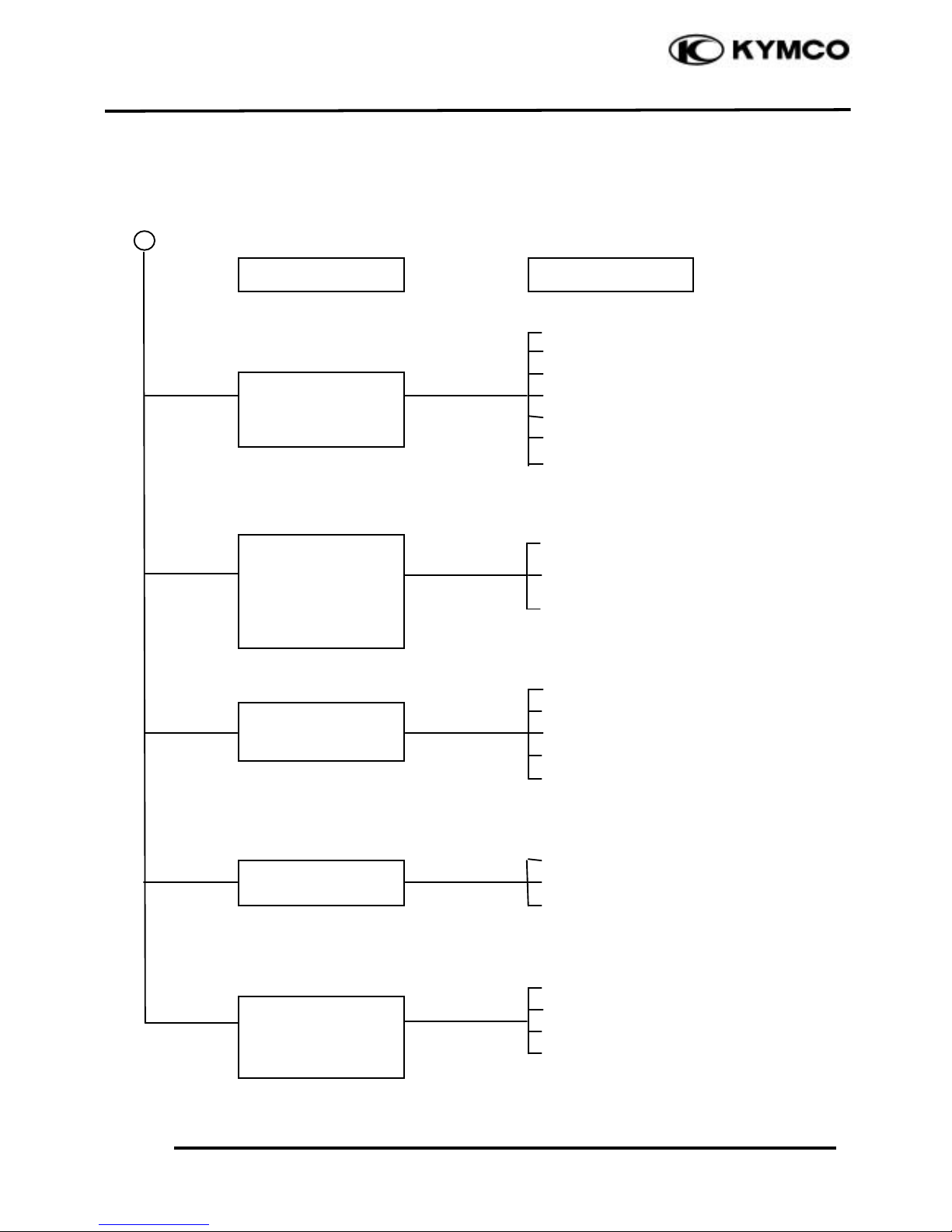
CLUTCH, DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS
Worn or slipping drive belt
Broken ramp plate
Broken drive face spring
Separated clutch lining
Damaged driven pulley shaft splines
Damaged final gear
Seized final gear
Broken shoe spring
Clutch outer and clutch weight stuck
Seized pivot
Worn or slipping drive belt
Worn weight rollers
Seized drive pulley bearings
Weak driven face spring
Worn or seized driven pulley bearings
Worn or slipping drive belt
Worn weight rollers
Worn or seized driven pulley bearings
Oil or grease fouled drive belt
Worn drive belt
Weak driven face spring
Worn or seized driven pulley bearings
Engine starts but
motor-cycle does not
move
Engine lacks power at
start of a grade(poor
slope performance)
Symptom
Probable Cause
Engine lacks power at
high speed
There is abnormal
noise
or smell while running
Motorcycle creeps or
engine starts but soon
stops or seems to rush
out (Rear wheel
rotates when engine
idles)
Page 28
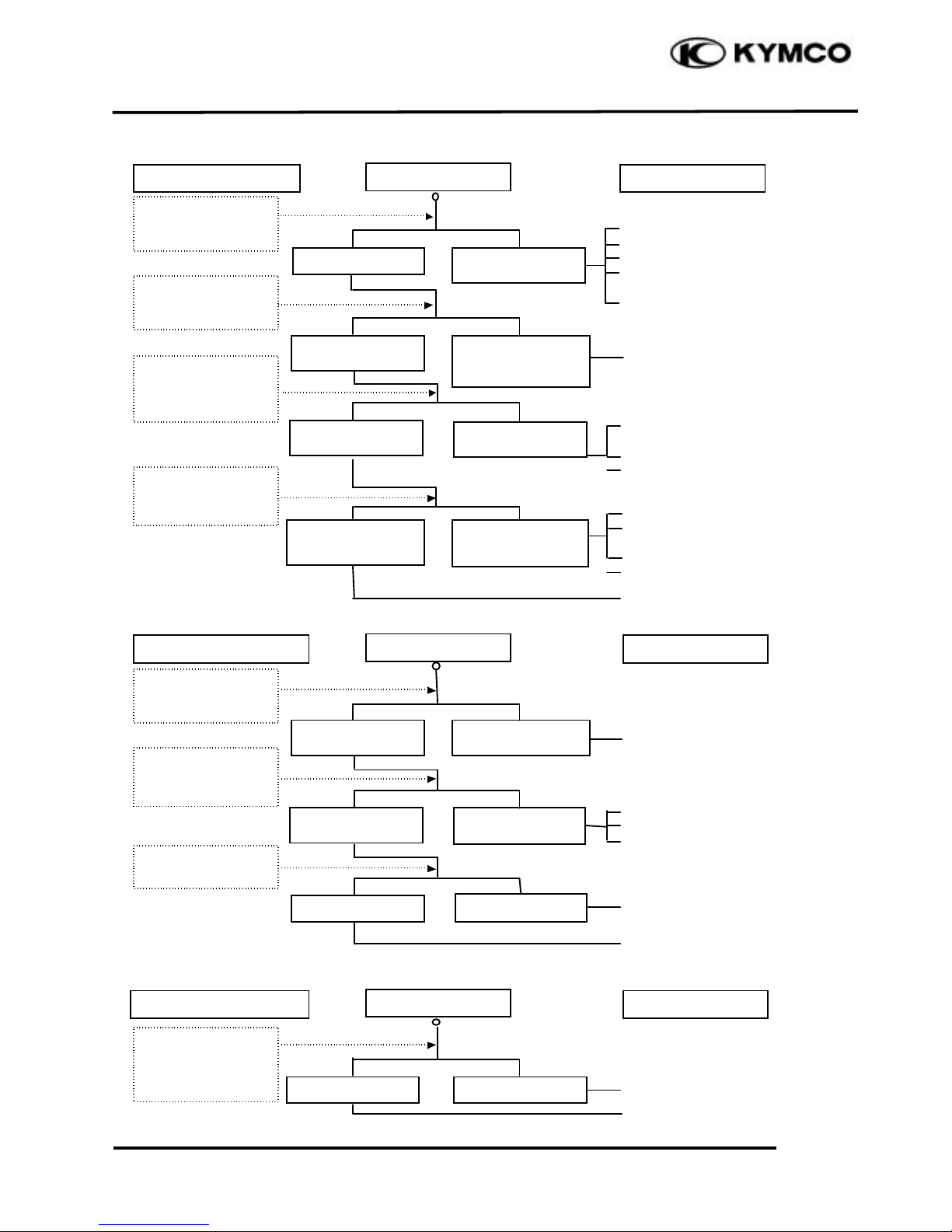
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-26
DINK 20 0
STARTER MOTOR
1. Starter motor won‘t turn
Burned out fuse
Weak or dead battery
Faulty stop switch
Loose or disconnected
connectors
Broken or shorted ignition
switch wire
Faulty or weak battery
Poor starter button
connection
Open or shorted starter relay
Loose or disconnected
connectors
Worn brushes
Open or shorted wires or
rotor
Open starter motor cable
Loose connectors
Open wire harness
2. Starter motor turns slowly or idles
Weak or dead battery
Loose connector or terminal
Poor contact in starter relay
Faulty starter clutch
Seized cylinder
Broken or shorted starter
motor cable
3. Starter motor does not stop turning
Faulty starter pinion
Starter relay shorted or stuck
Inspection/Adjustment
Inspection/Adjustment
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Check operation of
stop switch by
applying brake
Stoplight does not
come on
Stoplight comes
Check battery
circuit by operating
turn signals
Check battery
circuit by operating
turn signals
Turn ignition
switch
OFF
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Signals operate
properly
Signals dim, remain
on or don‘t
operate
Check operation of
starter relay by
depressing starter
button
Connect starter
motor directly to
battery
Connect starter
motor directly to
battery
Starter motor
turns slowly
Starter motor
turns normally
Signals operate
properly
Signals dim, remain
on or don‘t operate
Not stopped
Stopped
Rotate crankshaft
Starter motor
turns
St arter does not
turn
Relay operates
properly
Relay does not
operate
Turns easily
Hard to turn
Page 29
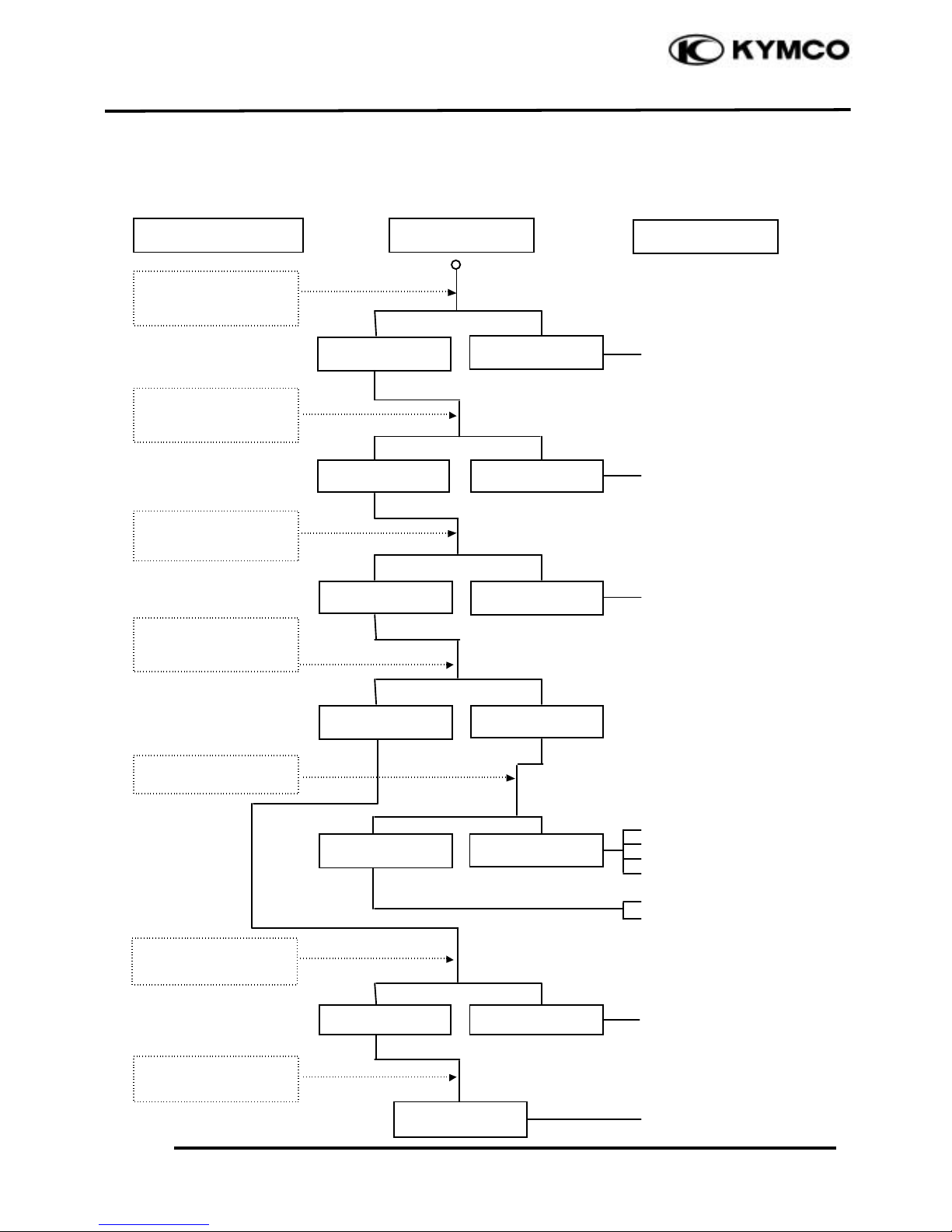
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-27
DINK 20 0
closed
NO SPARK AT SPARK PLUG
Faulty spark plug
Faulty spark plug
Poorly connected coupler
Faulty ignition switch
Faulty exciter coil
Faulty pulser coil
Faulty ignition coil
Broken wire harness
Poorly connected coupler
Faulty CDI unit
Faulty ignition coil
Replace with a new
spark plug and inspect
again
Check CDI unit
coupler for looseness
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Normal
Abnormal
Normal
Abnormal
Normal
Abnormal
Abnormal
Measure resistance
between terminals of
CDI unit coupler
Check related parts
Check ignition coil
with a CDI unit tester
Weak or no spark
Not loose
Good spark
Loose
Good
Good
Check spark plug cap
and high-tension wire
for looseness
Check CDI unit with a
CDI unit tester
Page 30
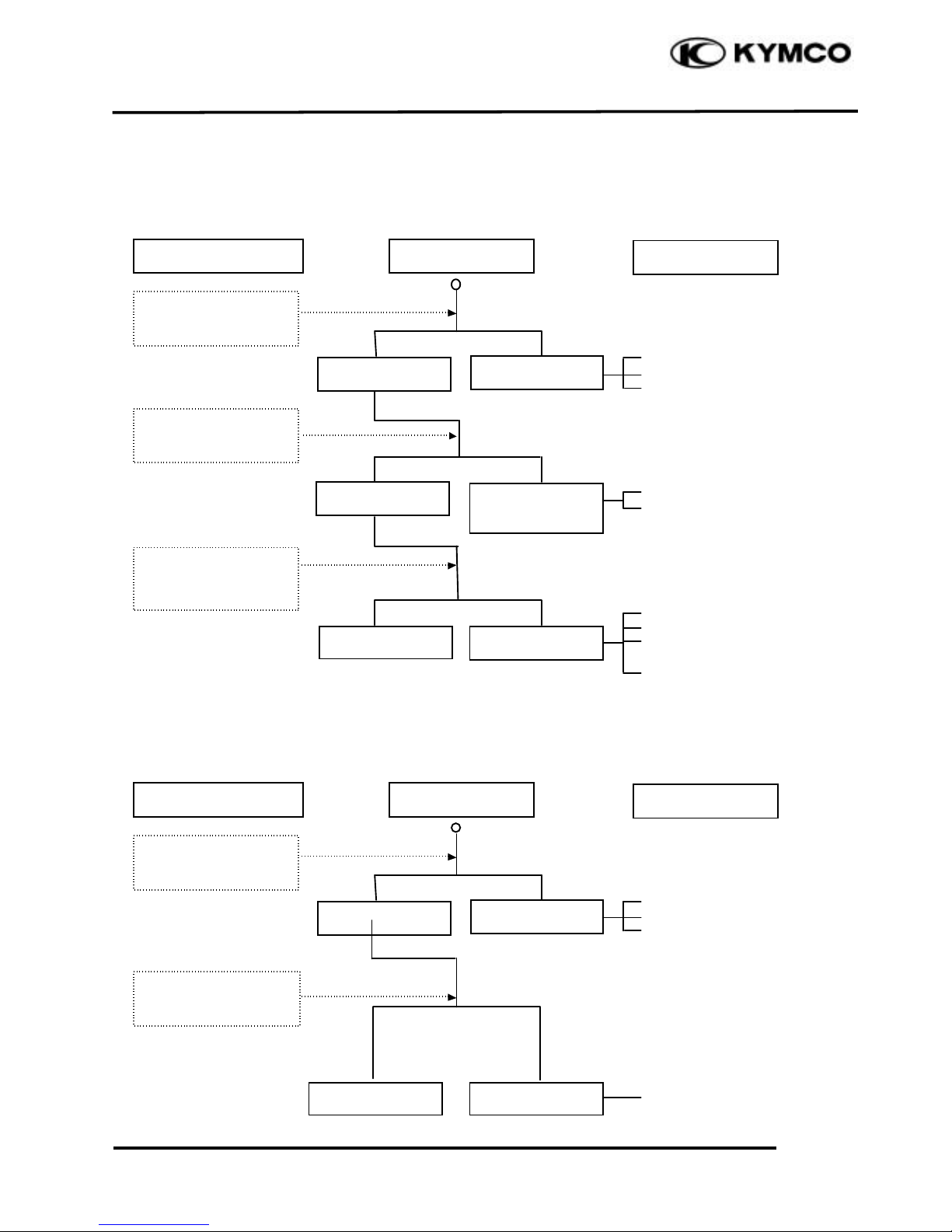
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-28
DINK 20 0
POOR CHARGING (BATTERY OVER DISCHARGING OR OVERCHARGING)
Undercharging
Faulty AC generator
Faulty regulator/rectifier
Faulty battery
Shorted AC generator coil
Open circuit between AC
generator 3 yellow wires
Faulty regulator/rectifier
Faulty AC generator
Loose regulator/rectifier
coupler
Limit voltage too high
Overcharging
Faulty battery
Faulty regulator/rectifier
Broken or poorly
connected
regulat or/rectifier black wire
Limit voltage too high
Start engine and test
limit voltage of
battery terminals
Measure battery limit
voltage with an
electric tester
Test output voltage of
regulator/rectifier
coupler red wire
Inspection/Adjustment
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Symptom
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Normal voltage
Normal
Normal
Voltage does not
increase
Abnormal
Resistance too
low
Normal voltage
No voltage
Measure resistance
between AC generator
coil terminals
Check resistance
between regulator/
rectifier terminals
Normal
Abnormal
Page 31

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-29
DINK 20 0
FUEL GAUGE
1. Pointer does not register correctly (Ignition switch ON)
Burned out fuse
Weak or dead battery
Faulty ignition switch
Loose or disconnected
connectors
Broken wire harness
Faulty float
Broken or shorted fuel
unit wire
Disconnected connector
Incorrectly connected
connector
Broken or shorted wire in
fuel gauge
2. Pointer fluctuates or swings (Ignition switch ON)
Burned out fuse
Weak or dead battery
Faulty ignition switch
Loose or disconnected
connector
Broken wire harness
Poor contact in fuel unit
Insufficient damping oil in
fuel gauge
Loose or disconnected
connector
Broken or shorted wire in
fuel gauge
Inspection/Adjustment
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Symptom
Remove fuel unit and
check operation of
pointer by moving
float up and down
Remove fuel unit and
check operation of
pointer by moving
float up and down
Signals operate
properly
Signals dim, remain
on or don‘t
operate
Signals operate
properly
Signals dim,
remain
Check battery circuit
by operating turn
signals
Check battery circuit
by operating turn
signals and horn
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Pointer does not
move
Pointer moves
Pointer moves
Pointer does not
move
Check operation of
pointer by opening and
shorting fuel unit
terminal on wire
harness side
Move float up and
down rapidly (1 round
/sec.) to check the
operation of pointer
Pointer does not
move
Pointer moves
Pointer does not
move in accordance with float
Pointer moves in
accordance with
float
Good
Faulty
Check connectors for
proper connection
Check connectors for
proper connection.
Good
Faulty
Float up: Full
Float down: Empty
Page 32

1. GENERAL INFORMATION
1-30
DINK 20 0
STEERING HANDLEBAR DOES NOT TRACK STRAIGHT
(Front and rear tire pressures are normal)
Steering stem nut too tight
Broken steering steel balls
Excessive wheel bearing play
Bent rim
Loose axle nut
Misaligned front and rear wheels
Bent front fork
POOR SUSPENSION PERFORMANCE
(Front and rear tire pressures are normal)
Weak shock spring
Excessive load
Shock damper oil leaking
Bent fork tube or shock rod
Fork tube and slider binding
Fork spring and slider binding
Damaged shock stopper rubber
Loose steering stem nut
POOR BRAKE PERFORMANCE
Worn brake linings
Foreign matter on brake linings
Rough brake drum contacting area
Worn brake linings
Foreign matter on brake linings
Rough brake drum contacting area
Worn brake linings
Worn brake cam contacting area on
Worn brake linings
Foreign matter on brake linings
Sluggish or elongated brake cables
Brake shoes improperly contact
Water and mud in brake system
Oil or grease on brake linings
Steering is heavy
Suspension is too soft
Soft brake lever
Hard brake lever
Poor brake
performance
Front or rear wheel is
wobbling
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
St eering handlebar pulls
to one side
Suspension is too hard
Suspension is noisy
Brake squeaks
Hard to brake
Page 33

2. EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
2-0
DINK 20 0
2
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
__________________________________________________________________________________
SCHEMATIC DRAWING ---------------------------------------------- 2-1
SERVICE INFORMATION -------------------------------------------- 2-2
TROUBLESHOOTING ------------------------------------------------- 2-2
FRAME COVERS REMOVAL----------------------------------------- 2-3
EXHAUST MUFFLER REMOVAL ----------------------------------- 2-6
2
Page 34

2. EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
2-1
DINK 20 0
SCHEMATIC DRAWING
Page 35

2. EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
2-2
DINK 20 0
SERVICE INFORMATION
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
• When removing frame covers, use care not to pull them by force because the cover joint claws
may be damaged.
• Make sure to route cables and harnesses according to the Cable & Harness Routing.
TORQUE VALUES
Exhaust muffler lock bolt 3.5kg-m
Exhaust muffler joint lock nut 1.2kg-m
TROUBLESHOOTING
Noisy exhaust muffler
• Damaged exhaust muffler
• Exhaust muffler joint air leaks
Lack of power
• Caved exhaust muffler
• Clogged exhaust muffler
• Exhaust muffler air leaks
Page 36

2. EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
2-3
DINK 20 0
FRAME COVERS REMOVAL
REAR CARRIER & HAND RAIL
REMOVAL
Remove the met-in box:
First remove the two bolts and two nuts
attaching the met-in box.
Remove the bolt attaching the center cover.
Remove the met-in box.
Remove the hand rail right and left lock bolts.
Remove the two hex bolts and one stay bolt
attaching the rear carrier.
Disconnect the third stoplight wire connector
on the rear carrier.
Remove the rear carrier and hand rail.
FRAME BODY COVER REMOVAL
Remove the two screws on the bottom of the
center cover.
Remove the center cover.
Remove the two screws attaching the front
part of the frame body cover.
Remove the two screws attaching the rear
protective cover.
Remove the rear protective cover.
Remove the two screws attaching the rear
ends of the right and left side rails.
Center Cover Bolt
Screws
Screws
Bolts/Nuts
Hex Bolts
Lock Bolts
Frame Body Cover
Center Cover
Rear Protective Cover
Screws
Screws
Page 37

2. EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
2-4
DINK 20 0
Remove the screws attaching the right and left
side covers.
Remove the right and left side covers by
pulling them backward.
Remove the right and left screws on the rear
part of the frame body cover.
Disconnect the seat lock wire.
Remove the frame body cover.
FLOOR BOARD REMOVAL
Remove the floor mat.
Remove the center cover. (2-3)
Remove the eight screws and two bolts
attaching the front right and left side covers.
Remove the two bottom cover adjusting
screws.
Remove the front right and left side covers.
Remove the six bolts attaching the floor
board.
Remove the floor board .
The installation sequence is the reverse of
removal.
Screws
Side Cover
Seat Lock Wire
Screws
Floor Board
Bolts
Page 38

2. EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
2-5
DINK 20 0
FRONT UPPER COVER REMOVAL
Remove the right and left rearview mirrors.
Remove the two screws on the back of the
front upper cover.
Remove the two bolts on the front of the
front upper cover.
Disconnect the headlight wire connector.
Remove the front upper cover.
The installation sequence is the reverse of
removal.
FRONT LOWER COVER REMOVAL
First remove the front upper cover.
Remove the two screws attaching the front
lower cover.
Remove the four screws on the back of the
front lower cover.
Disconnect the right/left turn signal light wire
connectors.
Remove the front lower cover
The installation sequence is the reverse of
removal.
LEG SHIELD REMOVAL
Remove the front upper cover.
Remove the front lower cover.
Remove the four screws attaching the leg
shield and instruments and remove the fuse
box.
Remove the nut attaching the leg shield.
Remove the adjusting screw which combines
the leg shield with instruments.
Remove the leg shield.
The installation sequence is the reverse of
removal.
Screws
Screws
Screws
Adjusting Screw
Screws
Bolts
Page 39

2. EXHAUST MUFFLER/FRAME COVERS
2-6
DINK 20 0
HANDLEBAR COVER REMOVAL
First remove the four screws attaching the
handlebar front cover.
Remove the handlebar front cover.
Remove the two screws and one bolt
attaching the handlebar rear cover.
Remove the handlebar rear cover.
The installation sequence is the reverse of
removal.
BOTTOM COVER REMOVAL
Remove the side stand.
Remove the four bolts attaching the bottom
cover.
Remove the bottom cover.
FRONT INNER FENDER A/B REMOVAL
Remove the front upper cover. (2-5)
Remove the front lower cover. (2-5)
Remove the screws which combines inner
fender A with inner fender B.
Remove the two bolts attaching the inner
fender A.
Separate inner fenders A and B.
The installation sequence is the reverse of
removal.
EXHAUST MUFFLER REMOVAL
Remove the two exhaust muffler joint lock
nuts.
Remove the two exhaust muffler lock bolts to
remove the exhaust muffler.
Remove the exhaust muffler joint packing
collar.
The installation sequence is the reverse of
removal.
Torque:
Exhaust muffler joint lock nut: 1.2kg-m
Exhaust muffler lock bolt: 3.5kg-m
Screws
Screws
Screws
Bolt
Lock Bolts
Bolts
Bolt
Bottom Cover
Joint Lock Nut
Page 40

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-0
DINK 20 0
3
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
__________________________________________________________________________________
SERVICE INFORMATION -------------------------------------------- 3- 1
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE ---------------------------------------- 3- 2
FUEL LINE/FUEL FILTER ------------------------------------------- 3- 2
THROTTLE OPERATION --------------------------------------------- 3- 2
ENGINE OIL ------------------------------------------------------------ 3- 4
AIR CLEANER ---------------------------------------------------------- 3- 5
SPARK PLUG ----------------------------------------------------------- 3- 5
VALVE CLEARANCE ------------------------------------------------- 3- 6
CARBURETOR IDLE SPEED ----------------------------------------- 3- 6
IGNITION TIMING----------------------------------------------------- 3- 7
CYLINDER COMPRESSION ------------------------------------------ 3- 7
FINAL REDUCTION GEAR OIL ------------------------------------- 3- 8
DRIVE BELT ------------------------------------------------------------ 3- 8
HEADLIGHT AIM ------------------------------------------------------ 3- 9
CLUTCH SHOE WEAR ------------------------------------------------ 3-10
COOLING SYSTEM ---------------------------------------------------- 3-10
BRAKE SYSTEM ------------------------------------------------------- 3-10
NUTS/BOLTS/FASTENERS------------------------------------------- 3-11
WHEELS/TIRES -------------------------------------------------------- 3-11
STEERING HANDLEBAR--------------------------------------------- 3-11
SUSPENSION ----------------------------------------------------------- 3-11
3
Page 41

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-1
DINK 20 0
SERVICE INFORMATION
GENERAL
°I WARNING
•Before running the engine, make sure that the working area is well-ventilated.
Never run the engine in a closed area. The exhaust contains poisonous carbon
monoxide gas which may cause death to people.
•Gasoline is extremely flammable and is explosive under some conditions. The
working area must be well-ventilated and do not smoke or allow flames or
sparks near the working area or fuel storage area.
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE
Throttle grip free play : 2_ 6mm
Spark plug : NGK: DP7EA9
Spark plug gap : 0.8_ 1.0mm
Valve clearance : IN: 0.1mm EX: 0.1mm
Idle speed : 1500±100rpm
(SH25AA: 1700±100rpm)
Engine oil capacity: Cylinder compression : 15±2kg/cm_
At disassembly : 1.1 liter Ignition timing : BTDC 10°±3°/1500rpm
At change : 0.8 liter Coolant capacity : 1165cc
Gear oil capacity : Radiator capacity : 825cc
At disassembly : 0.2 liter Reserve tank capacity : 340cc
At change : 0.195 liter
CHASSIS
Front/rear brake free play: 20_ 30mm
TIRE
1 Rider
2 Riders
Front
1.75kg/cm_
1.75kg/cm_
Rear
2.00kg/cm_
2.25kg/cm_
TIRE SPECIFICATION:
Front : 100/90–10
Rear : 120/70–10
TORQUE VALUES
Front axle nut : 5.0_ 7.0kg-m
Rear axle nut : 11.0_ 13.0kg-m
Page 42

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-2
DINK 20 0
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
Perform the periodic maintenance at each scheduled maintenance period.
I: Inspect, and Clean, Adjust, Lubricate or Replace if necessary.
A: Adjust C: Clean R: Replace T : Tighten
Regular Service Mileage (km)
Frequency
Item
comes
first
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
11000
12000
Engine oil
R
New
motorcycle
300km
RRRRRRRRRRR
Engine oil filter screen
C
C
Fuel filter screen
R
Gear oil
Note 3
R
New
motorcycle
300km
R
R
Valve clearance
AAA
A
Carburetor
I
I
Air Cleaner
Note 2,3
IRR
Spark plug
Clean at every 3000km and replace if necessary
Brake system
IIIIIIIIIII
I
Drive belt
I
Suspension
III
Nut, bolt, fastener
I
TireII
I
Steering head bearing
III
I
Brake fluid
Perform pre-ride inspection daily
Radiator coolant
Replace every year or at every 10000km (R)
Radiator core
I
I
Radiator cap
I
I
Brake lever
I
I
Brake shoe wear
I
I
Shock absorber
I
I
• In the interest of safety, we recommend these items be serviced only by an authorized
KYMCO motorcycle dealer.
Note: 1. For higher odometer readings, repeat at the frequency interval established here.
2. Service more frequently when riding in dusty or rainy areas.
3. Service more frequently when riding in rain or at full throttle.
Whichever
Page 43

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-3
DINK 20 0
FUEL LINE/FUEL FILTER
Remove the center cover.
Check the fuel tube replace any parts which
show signs of deterioration, damage or
leakage.
Check for dirty or clogged fuel filter and
replace with a new one if it is clogged.
THROTTLE OPERATION
Check the throttle grip for smooth movement.
Measure the throttle grip free play.
Free Play: 2_ 6mm
Major adjustment of the throttle grip free
play is made with the adjusting nut at the
carburetor side. Adjust by loosening the lock
nut and turning the adjusting nut.
Minor adjustment is made with the adjusting
nut at the throttle grip side.
Slide the rubber cover out and adjust by
loosening the lock nut and turning the
adjusting nut.
Lock Nut
Adjusting Nut
Fuel Filter
• Do not smoke or allow flames or
sparks in your working area.
°Ø
Fuel Tube
Lock Nut
Adjusting Nut
Page 44

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-4
DINK 20 0
ENGINE OIL
OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
Stop the engine and support the motorcycle
upright on level ground.
Wait for 2_ 3 minutes and check the oil level
with the dipstick. Do not screw in the
dipstick when making this check.
OIL CHANGE
Remove the oil drain bolt to drain the engine
oil.
Install the aluminum washer and tighten the
oil drain bolt.
Torque: 1.5kg-m
Pour the recommended oil through the oil
filler hole.
Oil Capacity:
At disassembly: 1.1 liter
At change: 0.8 liter
Recommended Oil:
SAE: 15W40#
API: SG/CD
Start the engine and check for oil leaks.
Stop the engine and recheck the oil level.
OIL FILTER SCREEN INSPECTION
Drain the engine oil.
Remove the oil filter screen and spring.
Clean the oil filter screen.
Install the oil filter screen, spring, and filter
screen cap.
Fill the engine with recommended engine oil.
• Drain the oil while the engine is warm.
°Ø
• Replace the aluminum washer with a
new one if it is deformed or damaged.
°Ø
Oil Dipstick
Oil Filter Screen Cap
Spring
Oil Filter Screen
Page 45

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-5
DINK 20 0
AIR CLEANER
Remove the seven air cleaner case cover
screws and the cover.
Remove the air cleaner element.
Check the element and replace it if it is
excessively dirty or damaged.
CHANGE INTERVAL
More frequent replacement is required when
riding in unusually dusty or rainy areas.
SPARK PLUG
Remove the frame center cover.
Remove the spark plug cap and spark plug.
Check the spark plug for wear and fouling
deposits.
Clean any fouling deposits with a spark plug
cleaner or a wire brush.
Specified Spark Plug: NGK: DP7EA9
Measure the spark plug gap.
Spark Plug Gap: 0.8_ 1.0mm
Torque: 0.8_ 1.0kg-m
Spark Plug
Screws
Air Cleaner Case Cover
Air Cleaner Element
°b
Gap
Wear
Fouling
Deposits
Cracks
Damage
Deformation
0.9mm
• The air cleaner element has a
viscous type paper element. Do not
clean it with compressed air.
• Be sure to install the air cleaner
element and cover securely.
°Ø
• When installing, first screw in the spark
plug by hand and then tighten it with a
spark plug wrench.
°Ø
Page 46

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-6
DINK 20 0
VALVE CLEARANCE
Remove the center cover and the secondary
air inlet tube bolt.
Remove the cylinder head cover.
Turn the A.C. generator flywheel to the top
dead center (TDC) on the compression stroke
so that the “T” mark on the flywheel aligns
with the index mark on the left crankcase
cover.
Inspect and adjust valve clearance.
Valve Clearance: IN: 0.1mm
EX: 0.1mm
Loosen the lock nut and adjust by turning the
adjusting nut
Valve Wrench
CARBURETOR IDLE SPEED
Lift up the seat and remove the inspection
cover.
Warm up the engine before this operation.
Start the engine and connect a tachometer.
Turn the throttle stop screw to obtain the
specified idle speed.
Idle Speed: 1500±100rpm
When the engine misses or run erratic, adjust
the pilot screw.
Throttle Stop Screw
Pilot Screw
Feeler Gauge
• Inspect and adjust valve clearance while
the engine is cold (below 35¢J).
°Ø
• Check the valve clearance again after
the lock nut is tightened.
°Ø
• The engine must be warm for accurate
idle speed inspection and adjustment.
°Ø
Cylinder Head Cover
Bolts
“T” Mark
Top Dead Center
Special
Page 47

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-7
DINK 20 0
IGNITION TIMING
Remove the timing hole cap.
Check the ignition timing with a timing light.
When the engine is running at the specified
idle speed, the ignition timing is correct if the
“F” mark on the flywheel aligns with the
index mark on the crankcase cover.
Also use a timing light to check the advance.
Raise the engine speed to 4,000rpm.
The index mark should be between the
advance marks.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
Warm up the engine before compression test.
Remove the center cover and spark plug cap.
Remove the spark plug .
Insert a compression gauge.
Open the throttle valve fully and push the
starter button to test the compression.
Compression: 15±2kg/cm_
If the compression is low, check for the
following:
_Leaky valves
_Valve clearance to small
_Leaking cylinder head gasket
_Worn pistons
_Worn piston/cylinder
If the compression is high, it indicates that
carbon deposits have accumulated on the
combustion chamber and the piston head.
Compression Gauge
Timing Light
• The CDI unit is not adjustable.
• If the ignition timing is incorrect, check
the ignition system,
°Ø
Timing Hole Cap
“F” Mark
Page 48

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-8
DINK 20 0
FINAL REDUCTION GEAR OIL
Stop the engine and remove the oil check bolt.
The oil level shall be at the oil check bolt hole.
If the oil level is low, add the recommended
oil SAE90# to the proper level.
Install the oil check bolt.
OIL CHANGE
Remove the oil check bolt.
Remove the oil drain bolt and drain the oil
thoroughly.
Install the oil drain bolt.
Torque: 1.0kg-m
Fill the final reduction with the recommended
oil SAE90#.
Gear Oil Capacity:
At disassembly : 200cc
At change : 195cc
Reinstall the oil check bolt and check for oil
leaks.
DRIVE BELT
Remove the left crankcase cover.
Inspect the drive belt for cracks or excessive
wear.
Replace the drive belt with a new one if
necessary and in accordance with the
Maintenance Schedule.
Drive Belt
Oil Check Bolt Hole/Oil Filler
• Place the motorcycle on its main stand
on level ground.
°Ø
Oil Drain Bolt/Sealing Washer
• Make sure that the sealing washer is in
good condition.
°Ø
• Make sure that the sealing washer is in
good condition.
°Ø
Page 49

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-9
DINK 20 0
HEADLIGHT AIM
Turn the ignition switch ON.
Turn on the headlight switch.
Adjust the headlight aim by turning the
headlight aim adjusting bolt.
CLUTCH SHOE WEAR
Start the engine and check the clutch
operation by increasing the engine speed
gradually.
If the motorcycle tends to creep, or the engine
stalls, check the clutch shoes for wear and
replace if necessary.
COOLING SYSTEM
COOLANT LEVEL INSPECTION
Place the motorcycle on its main stand on
level ground.
Check the coolant level of the reserve tank
and the level should be between the upper
and lower level lines.
If necessary, fill the reserve tank with
recommended coolant to the “F” level line.
Recommended Coolant: SIGMA Coolant
(Standard Concentration 30%)
COOLANT REPLACEMENT
Remove the front cover.
Remove the radiator cap.
Remove the drain bolt to drain the coolant
and tilt the motorcycle to the right and the
coolant will drain more easily.
Drain the coolant in the reserve tank.
Reinstall the drain bolt.
Fill the radiator with the specified coolant.
Lower Line
Headlight Aim Adjusting Bolt
Upper Line
Radiator Cap
• The coolant level does not change no
matter the engine is warm or cold. Fill
to the “F” (upper) line.
°Ø
• The coolant freezing point should be
5¢J lower than the temperature of the
riding area.
°Ø
• Perform this operation when the engine
is cold.
°Ø
Reserve Tank
Page 50

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-10
DINK 20 0
Coolant capacity : 1165cc
Radiator capacity : 825cc
Reserve tank capacity :340cc
Start the engine and check if there is no
bubbles in the coolant and the coolant level is
stable. Reinstall the radiator cap.
If there are bubbles in the coolant, bleed air
from the system.
Fill the reserve tank with the recommended
coolant up to the upper line.
BRAKE SYSTEM
BRAKE LEVER
Measure the front and rear brake lever free
plays.
BRAKE FLUID
Turn the steering handlebar upright and check
if the front/rear brake fluid level is at the
upper limit. If the brake fluid is insufficient,
fill to the upper limit.
Specified Brake Fluid: DOT-3
BRAKE DISK/BRAKE PAD
Check the brake disk surface for scratches,
unevenness or abnormal wear.
Check if the brake disk runout is within the
specified service limit.
Check if the brake pad wear exceeds the wear
indicator line.
Drain Bolt
Rear Brake Reservoir
Brake Disk
Front Brake Reservoir
• The brake fluid level will decrease if the
brake pads are worn.
°Ø
• Keep grease or oil off the brake disk to
avoid brake failure.
°Ø
Page 51

3. INSPECTION/ADJUSTMENT
3-11
DINK 20 0
NUTS/BOLTS/FASTENERS
Check all important chassis nuts and bolts for
looseness.
Tighten them to their specified torque values
if any looseness is found.
WHEELS/TIRES
Check the tires for cuts, imbedded nails or
other damages.
Check the tire pressure.
Tire Pressure
1 Rider
2 Riders
Front
1.75kg/cm_
1.75kg/cm_
Rear
2.00kg/cm_
2.25kg/cm_
STEERING HANDLEBAR
Raise the front wheel off the ground and
check that the steering handlebar rotates
freely.
If the handlebar moves unevenly, binds, or
has vertical movement, adjust the steering
head bearing.
SUSPENSION
Check the action of the front/rear shock
absorbers by compressing them several times.
Check the entire shock absorber assembly for
oil leaks, looseness or damage.
Jack the rear wheel off the ground and move
the rear wheel sideways with force to see if
the engine hanger bushings are worn.
Replace the engine hanger bushings if there is
any looseness.
• Tire pressure should be checked when
tires are cold.
°Ø
Pressure Gauge
Page 52

4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
4-0
DINK 20 0
4
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
LUBRICATION SYSTEM
__________________________________________________________________________________
LUBRICATION SYSTEM DIAGRAM-------------------------------- 4-1
SERVICE INFORMATION -------------------------------------------- 4-2
TROUBLESHOOTING ------------------------------------------------- 4-2
ENGINE OIL/OIL FILTER -------------------------------------------- 4-3
OIL PUMP REMOVAL------------------------------------------------- 4-4
OIL PUMP DISASSEMBLY ------------------------------------------- 4-4
OIL PUMP INSPECTION ---------------------------------------------- 4-5
OIL PUMP ASSEMBLY------------------------------------------------ 4-6
OIL PUMP INSTALLATION------------------------------------------ 4-6
4
Page 53

4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
4-1
DINK 20 0
LUBRICATION SYSTEM
Oil Pump
Oil Filter Screen
Crankshaft
Rocker Arm Shaft
Page 54

4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
4-2
DINK 20 0
SERVICE INFORMATION
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
• The maintenance of lubrication system can be performed with the engine installed in the frame.
• Drain the coolant before starting any operations.
• Use care when removing and installing the oil pump not to allow dust and foreign matters to enter
the engine and oil line.
• Do not attempt to disassemble the oil pump. The oil pump must be replaced as a set when it
reaches its service limit.
• After the oil pump is installed, check each part for oil leaks.
SPECIFICATIONS
OIL PUMP
Standard (mm)
Service Limit (mm)
Inner rotor-to-outer rotor clearance
0.15
0.20
Outer rotor-to-pump body clearance
0.15_ 0.20
0.25
Rotor end-to-pump body clearance
0.04_ 0.09
0.12
ENGINE OIL
Engine Oil Capacity
At disassembly: 1.1 liter At change: 0.9 liter
Recommended Oil
SAE15W40# API: SG/CD
TROUBLESHOOTING
Oil level too low Poor lubrication pressure
• Natural oil consumption • Oil level too low
• Oil leaks • Clogged oil filter or oil passage
• Worn piston rings • Faulty oil pump
• Worn valve guide
• Worn valve guide seal
Oil contamination
• Oil not changed often enough
• Faulty cylinder head gasket
• Loose cylinder head bolts
Page 55

4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
4-3
DINK 20 0
ENGINE OIL/OIL FILTER
Remove the oil dipstick and check the oil
level with the oil dipstick.
If the level is near the lower level, fill to the
upper level with the recommended engine oil.
OIL CHANGE
Remove the oil drain bolt located at the left
side of the engine to drain the engine oil.
After the oil has been completely drained,
install the aluminum washer and tighten the
oil drain bolt.
Torque: 14.7N-m
Pour the recommended oil through the oil
filler hole.
OIL FILTER SCREEN
Drain the engine oil.
Remove the oil filter screen cap.
Remove the oil filter screen and spring.
Check the oil filter screen for clogging or
damage and replace if necessary. Check the
filter screen O-ring for damage and replace if
necessary.
Install the oil filter screen, spring, O-ring and
filter screen cap.
Torque: 14.7N-m
Recommended Oil: SAE15W40# API: SG/CD
Oil Capacity:
At disassembly: 1.1 liter
At change: 0.9 liter
Start the engine and check for oil leaks. Start
the engine and let it idle for few minutes, then
recheck the oil level.
Oil Dipstick
Oil Drain Bolt
Oil Filter Screen Cap
• Place the motorcycle upright on
level ground for engine oil level check.
• Run the engine for 2_ 3 minutes
and check the oil level after the engine is
stopped for 2_ 3 minutes.
°Ø
• The engine oil will drain more
easily while the engine is warm.
°Ø
Page 56

4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
4-4
DINK 20 0
Circlip
Bolts
Oil Pump Driven Gear
Oil Separator
OIL PUMP REMOVAL
First drain the coolant.
Remove the right crankcase cover. (10-3)
Remove the A.C. generator starter driven
gear. (10-4)
Remove the attaching bolt and oil separator
cover.
Pry the circlip off and remove the oil pump
driven gear, then remove the oil pump drive
chain.
Remove the two oil separator bolts to remove
the oil pump.
OIL PUMP DISASSEMBLY
Remove the screw and disassemble the oil
pump as shown.
Oil Separator Cover
Oil Pump
Page 57

4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
4-5
DINK 20 0
Outer Rotor
Inner Rotor
Outer Rotor
Outer Rotor
Inner Rotor
Dowel Pin
Pump Body
Rotor End
Pump Body
Pump Shaft
OIL PUMP INSPECTION
Measure the pump body-to-outer rotor
clearance.
Service Limit: 0.25mm replace if over
Measure the inner rotor-to-outer rotor
clearance.
Service Limit: 0.20mm replace if over
Measure the rotor end-to-pump body
clearance.
Service Limit: 0.12mm replace if over
OIL PUMP ASSEMBLY
Install the outer rotor, inner rotor and pump
shaft into the pump body.
There is one mark on the surface of the inner
rotor and outer rotor.
The mark is upside.
Insert the pump shaft by aligning the flat
on the shaft with the flat in the inner
rotor. Install the dowel pin.
°Ø
Pump Body
Page 58

4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM
4-6
DINK 20 0
Screw
Bolts
Oil Separator Cover
Pump Driven Gear
Bolt
Install the pump cover by aligning the hole in
the cover with the dowel pin.
Tighten the screw to secure the pump cover.
Make sure that the pump shaft rotates freely
without binding.
OIL PUMP INSTALLATION
Install the oil pump and oil separator and
tighten the two bolts.
Make sure that the pump shaft rotates freely.
The arrow of oil pump is upside.
Install the pump drive chain and driven gear,
then set the circlip securely on the pump
shaft.
Install the oil separator cover properly.
Install the A.C. generator starter driven gear.
(10-5)
Circlip
Fit the tab of the separator cover into the
slit in the separator.
°Ø
Oil Separator
Pump Drive Chain
Arrow Mark
Page 59

5. ENGINE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
5-0
DINK 20 0
5
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
ENGINE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
__________________________________________________________________________________
SCHEMATIC DRAWING ---------------------------------------------- 5-1
SERVICE INFORMATION -------------------------------------------- 5-2
ENGINE REMOVAL --------------------------------------------------- 5-3
ENGINE INSTALLATION -------------------------------------------- 5-5
5
Page 60

5. ENGINE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
5-1
DINK 20 0
SCHEMATIC DRAWING
3.0kg-m
5.0kg-m
4.0kg-m
Page 61

5. ENGINE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
5-2
DINK 20 0
SERVICE INFORMATION
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
• A floor jack or other adjustable support is required to support and maneuver the engine. Be
careful not to damage the motorcycle body, cables and wires during engine removal.
• Use shop towels to protect the motorcycle body during engine removal.
• Drain the coolant before removing the engine.
• After the engine is installed, fill the cooling system with coolant and be sure to bleed air from the
water jacket. Start the engine to check for coolant leaks.
• Before removing the engine, the rear brake caliper must be removed first. Be careful not to bend
or twist the brake fluid tube.
SPECIFICATIONS
Engine dry weight: 30kg
Engine oil capacity: at disassembly: 1.1 liter
Coolant capacity:
Total capacity : 1165cc
Radiator capacity : 825cc
Reserve tank capacity : 340cc
TORQUE VALUES
Engine mounting bolt 5.0kg-m
Rear shock absorber upper mount bolt 4.0kg-m
Page 62

5. ENGINE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
5-3
DINK 20 0
ENGINE REMOVAL
Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Remove the frame body cover. (2-3)
Disconnect the engine negative cable.
Disconnect all of the A.C. generator, auto
bystarter, spark plug, thermosensor wire
couplers and connectors.
Disconnect the engine fuel tube.
Drain the coolant. (3-9)
Disconnect the water hose.
Disconnect the starter motor wire that goes to
the starter relay.
Disconnect the fuel tube and vacuum tube
that go to the carburetor from the fuel pump.
Disconnect the vacuum tube from the air
injection cut-off valve (AICV).
Disconnect the throttle cable from the
carburetor.
Remove the brake fluid tube bolt of the rear
brake caliper.
Remove the rear brake caliper bolt and the
rear brake caliper.
Starter Relay
Wire Connectors
Fuel Tube
Throttle Cable
Fuel Pump Vacuum Tube
Brake Fluid Tube
Rear Brake Caliper
Page 63

5. ENGINE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
5-4
DINK 20 0
Remove the right/left rear shock absorber
upper mount bolts.
Remove the two engine mounting bolts and
pull out the engine with the engine hanger
backward.
ENGINE HANGER REMOVAL
Remove the engine hanger bolts to remove the
engine hanger.
Inspect the engine hanger bushings and
stopper rubber for wear or damage.
Engine Mounting
Bushings
Rear Shock Absorber Upper Mount Bolts
Stopper Rubber
Bolt
Engine Hanger
Page 64

5. ENGINE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
5-5
DINK 20 0
ENGINE INSTALLATION
Install the engine in the reverse order of
removal.
Tighten the engine mounting bolts.
Torque: 5.0kg-m
Tighten the rear shock absorber upper mount
bolts.
Torque: 4.0kg-m
After installation, inspect and adjust the
following:
• Throttle grip free play (3-3)
• Fill the rear brake reservoir with brake fluid
and bleed air from the rear brake.
• Fill the cooling system with coolant and
start the engine to bleed air from the
system.
Engine Mounting Nuts
Engine Hanger Bolt
Rear Shock Absorber Upper Mount Bolts
Page 65

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-0
DINK 20 0
6 .
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
__________________________________________________________________________________
SCHEMATIC DRAWING ---------------------------------------------- 6- 1
SERVICE INFORMATION -------------------------------------------- 6- 2
TROUBLESHOOTING ------------------------------------------------- 6- 3
CYLINDER HEAD COVER REMOVAL ----------------------------- 6- 4
CAMSHAFT REMOVAL----------------------------------------------- 6- 4
CYLINDER HEAD REMOVAL --------------------------------------- 6- 6
CYLINDER HEAD DISASSEMBLY --------------------------------- 6- 7
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY -------------------------------------- 6- 8
CYLINDER HEAD INSTALLATION -------------------------------- 6- 9
CAMSHAFT INSTALLATION---------------------------------------- 6-10
CYLINDER HEAD COVER INSTALLATION ---------------------- 6-11
6
Page 66

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-1
DINK 20 0
SCHEMATIC DRAWING
Page 67

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-2
DINK 20 0
SERVICE INFORMATION
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
• The cylinder head can be serviced with the engine installed in the frame. Coolant in the radiator
and water jacket must be drained first.
• When assembling, apply molybdenum disulfide grease or engine oil to the valve guide movable
parts and valve arm sliding surfaces for initial lubrication.
• The valve rocker arms are lubricated by engine oil through the cylinder head engine oil passages.
Clean and unclog the oil passages before assembling the cylinder head.
• After disassembly, clean the removed parts and dry them with compressed air before inspection.
• After removal, mark and arrange the removed parts in order. When assembling, install them in the
reverse order of removal.
SPECIFICATIONS
Standard (mm)
Service Limit (mm)
Item
SH40AA
SH40AA
IN
0.10
EX0.10
Cylinder head compression pressure
15kg/cm_
Cylinder head warpage
0.05IN30.8763
30.75EX30.4081
30.26IN10.00_ 10.018
10.10EX10.00_ 10.018
10.10
Valve rocker arm shaft
IN
9.972_ 9.987
9.9
O.D.
EX
9.972_ 9.987
9.9IN1.2
1.8EX1.2
1.8IN4.990_ 4.975
4.925EX4.970_ 4.955
4.915IN5.00_ 5.012
5.03EX5.00_ 5.012
5.03
Valve stem-to-guide
IN
0.010_ 0.037
0.08
clearanceEX0.030_ 0.057
0.10
TORQUE VALUES
Cylinder head cap nut 19.6N-m Apply engine oil to threads
Valve clearance adjusting nut 8.8N-m Apply engine oil to threads
Cylinder head cover bolt 7.8_ 11.8N-m
SPECIAL TOOLS
Valve spring compressor
Valve seat cutter, 24.5mm 45° IN-EX
Valve seat cutter, 25mm Plane cutter 37.5° EX
Valve seat cutter, 22mm Plane cutter 37.5° EX
Valve seat cutter, 26mm Plane cutter 63.5° IN/EX
Cutter clip
Valve guide driver
Valve guide reamer
Valve clearance (cold)
Camshaft cam height
Valve rocker arm I.D.
Valve seat width
Valve stem O.D.
Valve guide I.D.
Page 68

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-3
DINK 20 0
TROUBLESHOOTING
• The poor cylinder head operation can be diagnosed by a compression test or by tracing engine
top-end noises.
Poor performance at idle speed White smoke from exhaust muffler
• Compression too low • Worn valve stem or valve guide
• Damaged valve stem oil seal
Compression too low
• Incorrect valve clearance adjustment Abnormal noise
• Burned or bend valves • Incorrect valve clearance adjustment
• Incorrect valve timing • Sticking valve or broken valve spring
• Broken valve spring • Damaged or worn camshaft
• Poor valve and seat contact • Worn cam chain tensioner
• Leaking cylinder head gasket • Worn camshaft and rocker arm
• Warped or cracked cylinder head
• Poorly installed spark plug
Compression too high
• Excessive carbon build-up in combustion
chamber
Page 69

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-4
DINK 20 0
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
Remove the center cover. (2-3)
Remove the met-in box. (2-3)
Remove the cylinder head cover four bolts
and then remove the cylinder head cover.
CAMSHAFT REMOVAL
Turn the A.C. generator flywheel so that the
“T” mark on the flywheel aligns with the
index mark on the crankcase.
Hold the round hole on the camshaft gear
facing up and the location is the top dead
center on the compression stroke.
Remove the two bolts attaching cam chain
tensioner and the tensioner.
First remove the two bolts between the
cylinder head and cylinder.
Then, remove the four cap nuts attaching the
cylinder head.
Remove the camshaft holder and dowel pins.
Cylinder Head Cover
Bolt
Cam Chain Tensioner
Round Hole
Camshaft Holder
Bolts
Camshaft Holder
Cap Nuts
• Diagonally loosen the cylinder head
cap nuts in 2 or 3 times.
°Ø
Page 70

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-5
DINK 20 0
Remove the camshaft gear from the cam chain
to remove the camshaft.
CAMSHAFT INSPECTION
Check each cam lobe for wear or damage.
Measure the cam lobe height.
Service Limits:
SH40AA
IN: 30.75mm replace if below
Check each camshaft bearing for play or
damage. Replace the camshaft assembly with
a new one if the bearings are noisy or have
excessive play.
CAMSHAFT HOLDER DISASSEMBLY
Take out the valve rocker arm shafts using a
6mm bolt and screwdriver.
Remove the valve rocker arms.
Cam Chain
Camshaft Gear
Camshaft Bearings
Valve Rocker Arms
Rocker Arm Shafts
Screwdriver
Page 71

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-6
DINK 20 0
CAMSHAFT HOLDER INSPECTION
Inspect the camshaft holder, valve rocker
arms and rocker arm shafts for wear or
damage.
Measure the I.D. of each valve rocker arm.
Service Limits: IN: 10.10mm replace if over
EX: 10.10mm replace if over
Measure each rocker arm shaft O.D.
Service Limits: IN: 9.90mm replace if below
EX: 9.90mm replace if below
CYLINDER HEAD REMOVAL
First drain the coolant from the radiator and
water jacket, then remove the thermostat
water hose.
Remove the camshaft. (6-4)
Remove the carburetor and intake manifold.
Remove the bolt attaching the thermostat
housing and the thermostat housing.
Remove the cylinder head.
Remove the dowel pins and cylinder head
gasket.
Remove the cam chain guide.
Remove all gasket material from the cylinder
head mating surface.
Intake Manifold
Cam Chain Tensioner Slipper
Camshaft Holder
If the valve rocker arm contact surface is
worn, check each cam lobe for wear or
damage.
°Ø
Rocker Arm Shafts
Cylinder
Cylinder Head Gasket
Be careful not to drop any gasket
material into the engine.
°Ø
Page 72

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-7
DINK 20 0
CYLINDER HEAD DISASSEMBLY
Remove the valve spring cotters, retainers,
springs, spring seats and valve stem seals
using a valve spring compressor.
Remove carbon deposits from the exhaust
port and combustion chamber.
Valve Spring Compressor
Cylinder Head
• Be sure to compress the valve springs
with a valve spring compressor.
• Mark all disassembled parts to ensure
correct reassembly.
°Ø
Exhaust Port
Combustion Chamber
Be careful not to damage the cylinder
head mating surface.
°Ø
Page 73

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-8
DINK 20 0
INSPECTION
CYLINDER HEAD
Check the spark plug hole and valve areas for
cracks.
Check the cylinder head for warpage with a
straight edge and feeler gauge.
Service Limit: 0.05mm repair or replace if
over
VALVE SPRING FREE LENGTH
Measure the free length of the inner and outer
valve springs.
Service Limits:
Inner (IN, EX) : 29.3mm replace if below
Outer (IN, EX): 32.0mm replace if below
VALVE /VALVE GUIDE
Inspect each valve for bending, burning,
scratches or abnormal stem wear.
Check valve movement in the guide.
Measure each valve stem O.D.
Service Limits: IN: 4.925mm replace if
below
EX: 4.915mm replace if
below
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY
Install the valve spring seats and stem seals.
Lubricate each valve stem with engine oil and
insert the valves into the valve guides.
Be sure to install new valve stem seals.
Straight Edge
Feeler Gauge
Valve Spring Compressor
Page 74

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-9
DINK 20 0
Tap the valve stems gently with a plastic
hammer to firmly seat the cotters.
CYLINDER HEAD INSTALLATION
Install the cam chain guide.
Install the dowel pins and a new cylinder
head gasket.
Install the cylinder head and take out the cam
chain
Assemble the camshaft holder.
First install the intake and exhaust valve
rocker arms; then install the rocker arm shafts.
Gasket
Cam Chain Guide
Valve Rocker Arms
Plastic Hammer
Cam Chain
Cylinder Head
Camshaft Holder
Be careful not to damage the valves.
°Ø
Dowel Pins
• Install the exhaust valve rocker arm
shaft on the “EX” side of the camshaft
holder and the exhaust rocker arm shaft
is shorter.
• Clean the intake valve rocker arm shaft
off any grease before installation.
• Align the cutout on the exhaust valve
rocker arm shaft with the bolt of the
camshaft holder.
°Ø
Page 75

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-10
DINK 20 0
CAMSHAFT INSTALLATION
Turn the A.C. generator flywheel so that the
“T” mark on the flywheel aligns with the
index mark on the crankcase.
Keep the round hole on the camshaft gear
facing up and align the punch marks on the
camshaft gear with the cylinder head surface
(Position the intake and exhaust cam lobes
down.) and install the cam chain over the
camshaft gear.
Install the dowel pins.
Install the camshaft holder, washers and nuts
on the cylinder head.
Tighten the four cylinder head nuts and the
two bolts between the cylinder head and
cylinder.
Torque: Cylinder head cap nut: 19.6N-m
Cylinder & cylinder head bolt:
7.8_ 11.8N-m
Dowel Pins
Nut
Washer
Punch Marks
Bolts
Cam Chain
Round Hole
• Apply engine oil to the threads of the
cylinder head cap nuts.
• Diagonally tighten the cylinder head
cap nuts in 2_ 3 times.
• First tighten the cylinder head cap nuts
and then tighten the bolts between the
cylinder and cylinder head to avoid
cracks.
°Ø
Page 76

6. CYLINDER HEAD/VALVES
6-11
DINK 20 0
Install a new cam chain tensioner gasket.
Release the lock pawl and push the push rod
all the way in.
Install the cam chain tensioner and tighten the
two bolts.
Install the tensioner spring and tighten the
sealing bolt.
Torque: 2.9_ 5.8N-m
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
INSTALLATION
Adjust the valve clearance. (3-6)
Install a new cylinder head cover O-ring and
install the cylinder head cover.
Install and tighten the cylinder head cover
bolts.
Torque: 7.8_ 11.8N-m
Cam Chain Tensioner
Sealing Bolt
Bolt
Lock Pawl
Push Rod
Gasket
Cam Chain Tensioner
Spring
Cylinder Head Cover
O-ring
Be sure to install the O-ring into the
groove properly.
°Ø
Page 77

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-0
DINK 20 0
7
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
CYLINDER/PISTON
__________________________________________________________________________________
SCHEMATIC DRAWING ---------------------------------------------- 7-1
SERVICE INFORMATION -------------------------------------------- 7-2
TROUBLESHOOTING ------------------------------------------------- 7-2
CYLINDER REMOVAL------------------------------------------------ 7-3
PISTON REMOVAL ---------------------------------------------------- 7-3
PISTON INSTALLATION --------------------------------------------- 7-7
CYLINDER INSTALLATION----------------------------------------- 7-7
7
Page 78

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-1
DINK 20 0
SCHEMATIC DRAWING
Page 79

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-2
DINK 20 0
SERVICE INFORMATION
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
• The cylinder and piston can be serviced with the engine installed in the frame.
• When installing the cylinder, use a new cylinder gasket and make sure that the dowel pins are
correctly installed.
• After disassembly, clean the removed parts and dry them with compressed air before inspection.
SPECIFICATIONS
Standard (mm)
Service Limit (mm)
Item
SH40AA
SH40AA
I.D.
62.005_ 62.015
62.10
Warpage
0.01
0.05
Cylindricity
0.01
0.05
True roundness
0.01
0.05
Ring-to-groove
top
0.015_ 0.050
0.09
clearance
Second
0.015_ 0.050
0.09
top
0.15_ 0.30
0.50
Piston,
Ring end gap
Second
0.15_ 0.30
0.50
piston ring
Oil side rail
0.2_ 0.9
Piston O.D.
61.993_ 61.995
61.90
Piston O.D. measuring position
9mm from bottom of skirt
.
Piston-to-cylinder clearance
0.010_ 0.040
0.01
Piston pin hole I.D.
15.002_ 15.008
15.04
Piston pin O.D
14.994_ 15.000
14.96
Piston-to-piston pin clearance
0.002_ 0.014
0.02
Connecting rod small end I.D. bore
15.016_ 15.034
15.06
TROUBLESHOOTING
• When hard starting or poor performance at low speed occurs, check the crankcase breather for
white smoke. If white smoke is found, it means that the piston rings are worn, stuck or broken.
Compression too low or uneven
compression Excessive smoke from exhaust muffler
• Worn or damaged cylinder and piston rings • Worn or damaged piston rings
• Worn, stuck or broken piston rings • Worn or damaged cylinder and piston
Compression too high Abnormal noisy piston
• Excessive carbon build-up in combustion • Worn cylinder, piston and piston rings
chamber or on piston head • Worn piston pin hole and piston pin
• Incorrectly installed piston
Cylinder
Page 80

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-3
DINK 20 0
CYLINDER REMOVAL
Remove the cylinder head. (6-7)
Remove the water hose from the cylinder.
Remove the cylinder base bolt.
Remove the cam chain guide.
Remove the cylinder.
Remove the cam chain tensioner.
Remove the cylinder gasket and dowel pins.
Clean any gasket material from the cylinder
surface.
PISTON REMOVAL
Remove the piston pin clip.
Press the piston pin out of the piston.
Cylinder Base Bolt
Water Hose
Dowel Pins
Cam Chain Guide
Gasket
Shop Towel
Cylinder
Piston Pin
Piston
Piston Rings
Cam Chain Tensioner
Place a clean shop towel in the crankcase
to keep the piston pin clip from falling
into the crankcase.
*
Page 81

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-4
DINK 20 0
Inspect the piston, piston pin and piston
rings.
Remove the piston rings.
Clean carbon deposits from the piston ring
grooves.
Install the piston rings onto the piston and
measure the piston ring-to-groove clearance.
Service Limits:
Top: 0.09mm replace if over
2nd: 0.09mm replace if over
Remove the piston rings and insert each
piston ring into the cylinder bottom.
Measure the piston ring end gap.
Service Limit: 0.5mm replace if over
Measure the piston pin hole I.D.
Service Limit: 15.04mm replace if over
• Take care not to damage or break the
piston rings during removal.
*
• Use the piston head to push each
piston ring into the cylinder.
*
Page 82

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-5
DINK 20 0
Measure the piston pin O.D.
Service Limit: 14.96mm replace if below
Measure the piston O.D.
Service Limit: 61.90mm replace if below
Measure the piston-to-piston pin clearance.
Service Limit: 0.02mm replace if over
CYLINDER INSPECTION
Inspect the cylinder bore for wear or damage.
Measure the cylinder I.D. at three levels of
top, middle and bottom at 90° to the piston
pin (in both X and Y directions).
Service Limit: 62.10mm repair or replace if
below
Measure the cylinder-to-piston clearance.
Service Limit: 0.1mm repair or replace if
over
The true roundness is the difference between
the values measured in X and Y directions.
The cylindricity (difference between the
values measured at the three levels) is subject
to the maximum value calculated.
Service Limits:
True Roundness:0.05mm repair or replace
if over
Cylindricity: 0.05mm repair or replace if over
• Take measurement at 9mm from the
bottom and 90° to the piston pin hole.
*
Middle
Bottom
Top
Page 83

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-6
DINK 20 0
Inspect the top of the cylinder for warpage.
Service Limit: 0.05mm repair or replace if over
Measure the connecting rod small end I.D.
Service Limit: 15.06mm replace if over
PISTON RING INSTALLATION
Install the piston rings onto the piston.
Apply engine oil to each piston ring.
Second
Side Rail
Top
• Be careful not to damage the piston and
piston rings during assembly.
• All rings should be installed with the
markings facing up.
• After installing the rings, they should
rotate freely without sticking.
• Stagger the ring end gaps as the figure
shown.
*
Second
Top
Side Rail
Oil Ring
Page 84

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-7
DINK 20 0
PISTON INSTALLATION
Remove any gasket material from the
crankcase surface.
Install the piston, piston pin and a new
piston pin clip.
CYLINDER INSTALLATION
Install the dowel pins and a new cylinder
gasket on the crankcase.
Coat the cylinder bore, piston and piston
rings with clean engine oil.
Carefully lower the cylinder over the piston
by compressing the piston rings.
Gasket
Cylinder
Dowel Pin
• Be careful not to drop foreign matters
into the crankcase.
*
Piston
Piston Pin Clip
Piston Pin
• Be careful not to damage or break the
piston rings.
• The piston ring end gaps should not be
parallel with or at 90° to the piston pin.
*
• Position the piston “IN” mark on the
intake valve side.
• Place a clean shop towel in the
crankcase to keep the piston pin clip
from falling into the crankcase.
*
Page 85

7. CYLINDER/PISTON
7-8
DINK 20 0
Tighten the cylinder base bolt.
Install the cam chain guide.
Connect the water hose to the cylinder.
Install the cylinder head. (6-9)
Tighten the cylinder base bolt.
• Insert the tab on the cam chain guide
into the cylinder groove.
*
Cylinder Base Bolt
Cam Chain Guide
Page 86

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
DINK 20 0
8
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
__________________________________________________________________________________
SCHEMATIC DRAWING ---------------------------------------------- 8- 1
SERVICE INFORMATION -------------------------------------------- 8- 2
TROUBLESHOOTING ------------------------------------------------- 8- 2
LEFT CRANKCASE COVER ------------------------------------------ 8- 3
DRIVE PULLEY -------------------------------------------------------- 8- 4
CLUTCH/DRIVEN PULLEY ------------------------------------------ 8- 8
KICK STARTER -------------------------------------------------------- 8-15
8
Page 87

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
DINK 20 0
SCHEMATIC DRAWING
Page 88

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
DINK 20 0
SERVICE INFORMATION
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
• The drive pulley, clutch and driven pulley can be serviced with the engine installed.
• Avoid getting grease and oil on the drive belt and pulley faces. Remove any oil or grease from
them to minimize the slipping of drive belt and drive pulley.
SPECIFICATIONS
Item
Standard (mm)
Service Limit (mm)
Movable drive face bushing I.D.
33.000_ 33.025
33.06
Drive face collar O.D.
32.006_ 32.009
31.90
Drive belt width
19.0
17.5
Clutch lining thickness
3.963_ 4.037
2.0
Clutch outer I.D.
130.0_ 130.2
130.5
Driven face spring free length
88.3
83.2
Driven face O.D.
33.965_ 33.985
33.94
Movable driven face I.D.
34.00_ 34.025
34.06
Weight roller O.D.
16.99_ 17.00
16.00
TORQUE VALUES
Drive face nut 49.0_ 58.8N-m
Clutch outer nut 49.0_ 58.8N-m
Clutch drive plate nut 49.0_ 58.8N-m
SPECIAL TOOLS
Universal holder Clutch spring compressor
Bearing driver Lock nut wrench, 39mm
Kick starter spring remover
TROUBLESHOOTING
Engine starts but motorcycle won‘t move Lack of power
• Worn drive belt • Worn drive belt
• Broken ramp plate • Weak driven face spring
• Worn or damaged clutch lining • Worn weight roller
• Broken driven face spring • Faulty driven face
Engine stalls or motorcycle creeps
• Broken clutch weight spring
Page 89

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
DINK 20 0
LEFT CRANKCASE COVER
REMOVAL
Remove two bolts on the air cleaner.
Remove the air cleaner.
Remove the left crankcase cover bolts and left
crankcase cover.
Remove the seal rubber and dowel pins.
INSTALLATION
Install the dowel pins and the seal rubber.
Install the left crankcase cover.
Install the cable clamp to the specified
location. Install and tighten the left crankcase
cover bolts.
Kick Lever
Left Crankcase Cover
Air Cleaner
Bolts
Dowel Pins
Left Crankcase Cover
Bolts
Bolts
• Do not pull out the kick starter spindle.
Press in the kick starter spindle when
installing the left crankcase cover.
*
Page 90

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
DINK 20 0
Install the air cleaner and tighten the bolts.
DRIVE PULLEY
REMOVAL
Remove the left crankcase cover.
Hold the drive pulley using an universal
holder and remove the drive face nut.
Remove the drive pulley face.
Universal Holder
Remove the drive belt from the movable drive
face.
INSPECTION
Check the drive belt for cracks, separation or
abnormal or excessive wear.
Measure the drive belt width.
Service Limit: 17.5mm replace if below
Drive Pulley Face
Universal Holder
Movable Drive Face
Drive Belt
Bolts
• Use specified genuine parts for
replace-ment.
*
Special
Page 91

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
DINK 20 0
Remove the movable drive face assembly.
Remove the drive pulley collar.
DISASSEMBLY
Remove the ramp plate.
Remove the weight rollers.
INSPECTION
Check each weight roller for wear or damage.
Measure each weight roller O.D.
Service Limit: 16.00mm replace if below
Drive Pulley Collar
Ramp Plate
Weight Roller
Movable Drive Face Assembly
Page 92

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
DINK 20 0
Measure the movable drive face bushing
assemblyy I.D.
Service Limit: 27.20mm replace if over
Check the drive pulley collar for wear or
damage.
Measure the O.D. of the drive pulley collar
sliding surface.
Service Limit: 26.90mm replace if below
ASSEMBLY
Install the weight rollers into the movable
drive face.
Weight Roller
Page 93

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
8-7
DINK 20 0
Install the ramp plate.
Insert the drive pulley collar into the movable
drive face.
INSTALLATION
Install the movable drive face onto the
crankshaft.
Lay the drive belt on the driven pulley.
Set the drive belt on the drive pulley collar.
Drive Pulley Collar
Ramp Plate
Driven Pulley
Movable Drive Face Assembly
Drive Pulley Collar
Drive Belt
Page 94

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
8-8
DINK 20 0
Install the drive pulley face and drive face
nut.
Hold the drive pulley with the universal
holder and tighten the drive face nut.
Torque: 49.0_ 58.5N-m
Universal Holder
CLUTCH/DRIVEN PULLEY
Remove the left crankcase cover. (8-3)
Remove the drive pulley and drive belt. (8-
4)
Hold the clutch outer with the universal
holder and remove the clutch outer nut.
Universal Holder
Remove the clutch outer.
INSPECTION
Inspect the clutch outer for wear or damage.
Measure the clutch outer I.D.
Service Limit: 130.5mm replace if over
Drive Pulley Face
Special
• Do not get oil or grease on the
drive belt or drive pulley faces.
*
Clutch Outer
Drive Face Nut
Drive Pulley
Universal Holder
Universal Holder
Special
Page 95

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
8-9
DINK 20 0
Check the clutch shoes for wear or damage.
Measure the clutch lining thickness.
Service Limit: 2.0mm replace if below
CLUTCH/DRIVEN PULLEY
DISASSEMBLY
Hold the clutch/driven pulley assembly with
the clutch spring compressor.
Clutch Spring Compressor
Set the tool in a vise and remove the clutch
drive plate nut.
Lock Nut Wrench, 39mm
Loosen the clutch spring compressor and
disassemble the clutch/driven pulley
assembly.
Remove the seal collar.
Clutch/Driven Pulley
Special
Special
Clutch Spring Compressor
• Be sure to use a clutch spring
compressor to avoid spring damage.
*
Lock Nut Wrench
Page 96

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
8-10
DINK 20 0
Pull out the guide roller pins and guide rollers.
Remove the movable driven face from the
driven face.
Remove the oil seal from the movable driven
face.
INSPECTION
Measure the driven face spring free length.
Service Limit: 83.2mm replace if below
Check the driven face assembly for wear or
damage.
Measure the driven face O.D.
Service Limit: 33.94mm replace if below
Movable Driven Face
Guide Roller Pin
Guide Roller
Oil Seal
Page 97

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
8-11
DINK 20 0
Check the movable driven face for wear or
damage.
Measure the movable driven face I.D.
Service Limit: 34.06mm replace if over
DRIVEN PULLEY FACE BEARING
REPLACEMENT
Check the bearings for play and replace them
if they have excessive play.
Drive the inner needle bearing out of the
driven pulley face.
Remove the snap ring and drive the outer
bearing out of the driven face.
Apply grease to the outer bearing.
Drive a new outer bearing into the driven face
with the sealed end facing up.
Bearing Driver
Seat the snap ring in its groove.
Apply grease to the driven face bore areas.
Snap Ring
Inner Bearing
Outer Bearing
• Discard the removed bearing and
replace with a new one.
*
• Discard the removed bearing and
replace with a new one.
*
Special
Pack all bearing cavities with 9_ 9.5g
grease.
Page 98

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
8-12
DINK 20 0
Press a new needle bearing into the driven
face.
Bearing Driver
CLUTCH DISASSEMBLY
Remove the circlips and retainer plate to
disassemble the clutch.
Circlips
Retainer Plate
Special
• Keep grease off the clutch
linings.
*
Clutch Lining
Page 99

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
8-13
DINK 20 0
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
Install the damper rubbers on the drive plate
pins.
Install the clutch weights/shoes and clutch
springs onto the drive plate.
Install the retainer plate and secure with the
circlips.
CLUTCH/DRIVEN PULLEY AS SEMBLY
Clean the pulley faces and remove any grease
from them.
Apply grease to the O-rings and install them
onto the moveable driven face.
Circlips
Drive Plate
Movable Driven Face
Page 100

8. DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS/
KICK STARTER
8-14
DINK 20 0
Install the movable driven face onto the
driven face.
Apply grease to the guide rollers and guide
roller pins and then install them into the holes
of the driven face.
Install the seal collar.
Remove any excessive grease.
Set the driven pulley assembly, driven face
spring and clutch assembly onto the clutch
spring compressor.
Compress the tool and install the drive plate
nut.
Set the tool in a vise and tighten the drive
plate nut to the specified torque.
Torque: 49.0_ 58.8N-m
Clutch Spring Compressor
Outer Driver, 32x35mm
INSTALLATION
Install the clutch/driven pulley onto the drive
shaft.
• Be sure to clean the driven face
off any grease.
*
• Align the flat surface of the driven
face with the flat on the clutch drive plate.
*
• Keep grease off the drive shaft.
*
Movable Driven Face
Guide Roller Pin
Seal Collar
Guide Roller
Clutch/Driven Pulley
Driven Face
Clutch Spring Compressor
Lock Nut Wrench
• Be sure to use a clutch spring
compressor to avoid spring damage.
*
Special
 Loading...
Loading...