Page 1

Page 2
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
• Read these instructions.
• Keep these instructions.
• Heed all warnings.
• Follow all instructions.
• Do not use this apparatus near water.
• Mains powered apparatus shall not be exposed to dripping or
splashing and that no objects filled with liquids, such as vases,
shall be placed on the apparatus.
• Clean only with dry cloth.
• Do not block any ventilation openings, install in accordance with
the manufacturer’s instructions.
• Do not install near any heat sources such as radiators, heat
registers, stoves, or other apparatus (including amplifiers) that
produce heat.
• Do not defeat the safety purpose of the polarized or groundingtype plug. A polarized plug has two blades with one wider than
the other. A grounding type plug has two blades and a third
grounding prong. The wide blade or the third prong are provided
for your safety. If the provided plug does not fit into your outlet,
consult an electrician for replacement of the obsolete outlet. (for
U.S.A. and Canada)
• Protect the power cord from being walked on or pinched
particularly at plugs, convenience receptacles, and the point
where they exit from the apparatus.
• Only use attachments/accessories specified by the
manufacturer.
• Unplug this apparatus during lightning storms or when unused
for long periods of time.
• Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. Servicing is
required when the apparatus has been damaged in any way,
such as power-supply cord or plug is damaged, liquid has been
spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus, the apparatus
has been exposed to rain or moisture, does not operate
normally, or has been dropped.
• Do not install this equipment on the far position from wall outlet
and/or convenience receptacle.
• Do not install this equipment in a confined space such as a box
for the conveyance or similar unit.
• Use only with the cart, stand, tripod, bracket, or table specified
by the manufacturer, or sold with the apparatus. When a cart is
used, use caution when moving the cart/apparatus combination
to avoid injury from tip-over.
The lightning flash with arrowhead symbol
within an equilateral triangle, is intended to
alert the user to the presence of uninsulated
“dangerous voltage” within the product’s
enclosure that may be of sufficient magnitude
to constitute a risk of electric shock to persons.
The exclamation point within an equilateral
triangle is intended to alert the user to the
presence of important operating and
maintenance (servicing) instructions in the
literature accompanying the product.
THE FCC REGULATION WARNING (for U.S.A.)
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device , pursuant to P art 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. How ev er, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different
from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
help.
Unauthorized changes or modification to this system can void the
user’s authority to operate this equipment.
CE mark for European Harmonized Standards
CE mark which is attached to our company’s products of AC mains
operated apparatus until December 31, 1996 means it conforms to
EMC Directive (89/336/EEC) and CE mark Directive (93/68/EEC).
And, CE mark which is attached after January 1, 1997 means it
conforms to EMC Directive (89/336/EEC), CE mark Directive (93/
68/EEC) and Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC).
Also, CE mark which is attached to our company’s products of
Battery operated apparatus means it conforms to EMC Directive
(89/336/EEC) and CE mark Directive (93/68/EEC).
ii
Page 3
Handling of the internal hard disk
Do not apply physical shock to this device. In particular,
you must never move this device or apply physical shock
while the power is turned on. This can cause part or all of
the data on disk to be lost, or may damage the hard disk
or interior components.
When this device is moved to a location where the temperature is radically different, water droplets may condense on the hard disk. If the device is used in this
condition, it may malfunction, so please allow several
hours to pass before operating the device.
Do not turn the power on and off repeatedly. This may
damage the D1600mkII.
This device begins to access the hard disk immediately
after the power is turned on.
Never turn off the power while the HDD access indicator
is lit or blinking. Doing so can cause all or part of the data
on hard disk to be lost, or may cause malfunctions such
as hard disk damage.
If the hard disk has been damaged due to incorrect
operation, power failure, or accidental interruption of
the power supply, a fee may be charged for replacement
even if this device is still within its warranty period.
Phantom Power
To prevent hazard or damage, ensure that only microphone cables and microphones designed to IEC-268-15A
are connected.
Data handling
Incorrect operation or malfunction may cause the contents of
memory to be lost, so we recommend that you save
important data on a CD or other media. Please be aware that
Korg will accept no responsibility for any damages which
may result from loss of data.
This product has been designed and manufactured
according to FDA regulations “title 21. CFR. chapter 1,
subchapter J. based on the radiation Control for Health
and Safety Act of 1968,” and is classified as a class 1 laser
product. There is no hazardous invisible laser radiation
during operation because invisible laser radiation emitted
inside of this product is completely confined in the
protective housings.
The label required in this regulation is shown below.
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Optical pickup
Type : SF-W35
Manufacturer : SANYO
Laser output : Operation condition: 37.5mW;
Maximum condition: 76.3mW
Wavelength : 783 +/-3nm
INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN.
AVOID DIRECT EXPOSURE TO BEAM.
UNSICHTBARE LASERSTRAHLUNG,
NICHT IN DEN STRAHL BLICKEN AUCH
NICHT MIT OPTISCHEN INSTRUMENTEN.
LASERSTRÅLING NÅR DEKSEL ÅPNES. STIRR IKKE INN I STARÅLEN.
LASERSTRÅLING VED ÅBNING. SE IKKE IND I STRÅLEN.
LASERSTRÅLNING NÄR DENNA DEL ÄR ÖPPNAD.
AVATTAESSA OLET ALTTIINA LASERSÄTEILYLLE.
DANGER
VORSICHT
WENN ABDECKUNG GEÖFFNET.
ADVARSEL
ADVARSEL
VARNING
STIRRA EJ IN I STRÅLEN.
VARO!
ÄLÄ TUIJOT A SÄTEESEEN.
COPYRIGHT WARNING
This professional device is intended only for use with
works for which you yourself own the copyright, for which
you have received permission from the copyright holder to
publicly perform, record, broadcast, sell, and duplicate, or
in connection with activities which constitute “fair use”
under copyright law. If you are not the copyright holder,
have not received permission from the copyright holder, or
have not engaged in fair use of the works, you may be violating copyright law, and may be liable for damages and
penalties. If you are unsure about your rights to a work,
please consult a copyright attorney. KORG TAKES NO
RESPONSIBILITY FOR ANY INFRINGEMENT COMMITTED THROUGH USE OF KORG PRODUCTS.
CLASS 1 LASER
CLASS 1 LASER
PRODUCT TO IEC
LASER KLASSE 1
NACH IEC 60825-1
* Company names, product names, and names of formats
etc. are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective owners.
iii
Page 4

Table of Contents
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS.................... ii
THE FCC REGULATION WARNING (for U.S.A.)....ii
CE mark for European Harmonized Standards..........ii
Data handling ...............................................iii
Introduction......................... 1
1. Main features...............................................................1
2. Printing conventions in this manual........................2
3. Included items.............................................................2
3. Record vocals on virtual tracks.............................. 22
4. Make insert effect settings.......................................24
Step 3: Mixdown ...........................................26
1. Apply effects............................................................. 26
2. Apply EQ (equalizer)............................................... 27
3. Apply master effects................................................ 28
Step 4: Mastering..........................................30
1. Apply an effect to the entire song.......................... 30
2. Create the master track............................................ 31
3. Write your song to a CD..........................................32
Basic operation................... 35
Parts and their function.....................................3
1. Top panel.....................................................................3
2. Front panel...................................................................5
3. Rear panel.................................................................... 6
Objects in the LCD screen and their functions ..........8
1. Objects in the LCD screen......................................... 8
2. Adjusting the LCD screen contrast.......................... 8
Basic operation ..............................................9
1. Selecting a mode......................................................... 9
2. Selecting a tab page.................................................... 9
3. Selecting and setting a parameter............................9
Preparations................................................ 10
1. Connections............................................................... 10
2. Turning the power on/off.......................................11
Listening to the demo song .............................. 12
Quick Start.........................13
Step 1: Quick Recording .................................. 13
1. Make connections..................................................... 13
2. Turn on the power....................................................13
3. Create a new song.................................................... 14
4. Rhythm.......................................................................14
5. Assign the input to a mixer channel...................... 15
6. Adjust the level.........................................................15
7. Check the sound....................................................... 16
8. Record........................................................................ 16
9. Play back.................................................................... 18
Step 2: Overdubbing....................................... 19
1. Record a guitar..........................................................19
2. Record a keyboard....................................................20
Creating/selecting a song.................................35
1. Creating a new song................................................ 35
2. Naming a song.......................................................... 35
3. Selecting another song............................................. 36
Assign audio inputs to the mixer ........................36
1. Analog inputs............................................................36
2. Digital input.............................................................. 38
3. Using the tuner......................................................... 39
Recording ...................................................39
1. Adjust the recording level, and record..................39
2. Recording on virtual tracks.....................................40
3. Playback while recording addition tracks:
Overdubbing............................................................. 40
4. Re-record part of a performance: Punch-in/out..40
5. Combining multiple tracks into two: Bounce...... 42
6. Other recording methods........................................ 43
Playback.....................................................45
1. Playback..................................................................... 45
2. Program play.............................................................45
3. Other playback options........................................... 45
Changing the time location...............................46
1. Switching the counter display................................ 46
2. Moving the current time location..........................46
3. Using scrub playback etc. to find a precise time
location....................................................................... 47
Using the mixer ............................................48
1. Adjusting the volume.............................................. 48
2. Adjusting the stereo position..................................48
3. Using EQ to adjust the tone.................................... 48
4. Pairing........................................................................ 49
5. Monitor settings........................................................49
6. Solo settings...............................................................50
iv
Page 5

7. Registering and playing scenes..............................50
Using effects................................................ 53
1. Overview of the effects............................................53
2. Insert effects...............................................................53
3. Master effects.............................................................55
4. Final effect..................................................................56
5. Editing an effect........................................................56
6. Controlling an effect from an external device......57
7. Using an external effect............................................58
Mixdown .................................................... 58
1. Creating an audio CD..............................................58
2. Recording to a master tape......................................60
3. Using the sub inputs.................................................60
Track editing................................................ 61
1. Track editing functions............................................61
2. Track editing examples............................................62
Song editing................................................ 69
1. Song editing operation.............................................69
2. Examples of song editing.........................................70
Rhythm/tempo settings ................................... 71
1. Specifying and playing a rhythm...........................71
2. Recording your performance while you listen to
the rhythm .................................................................72
3. Recording the rhythm..............................................72
4. Specifying the tempo................................................72
Data.......................................................... 75
1. Backing up and restoring song data......................75
2. Backing up and restoring effect user data.............77
3. Saving a WAV file.....................................................79
4. Data compatibility with other models in the
Digital Recording Studio series..................................81
Drive......................................................... 82
1. Checking the hard disk............................................82
2. Formatting the hard disk.........................................82
3. Erasing the data from a CD-RW.............................83
4. Using the drive capacity efficiently........................83
USB .......................................................... 85
1. Saving data to your computer................................85
Updating the system ...................................... 86
1. Downloading the system file..................................86
2. Updating the system................................................86
MIDI.......................................................... 87
1. MIDI connections......................................................87
2. MIDI messages used by the D1600mkII................87
3. Using MIDI................................................................87
Reference..........................91
1. COUNTER ................................................ 91
Counter: Counter display.............................................91
2. SYSTEM/USB............................................ 91
P1Control: Foot switch/control change device
(pedal/MIDI) settings..............................................91
P2MIDI: MIDI settings .................................................92
P3Sync: Synchronization settings ...............................92
P4MMC: MMC settings................................................93
P5B-U/Rst: Backup/restore using a removable disc93
P6DiskUtil: Managing drives ......................................96
3. RECORD.................................................. 99
P1RecMode: Selecting the recording mode...............99
P2Bounce: Settings for bounce recording..................99
4. TRACK...................................................100
P1Vtr1–8: Select virtual tracks 1–8............................100
P2Vtr9–16: Select virtual tracks 9–16........................100
P3EditTrk: Track editing............................................100
P4Import: Import a WAV file.................................... 106
P5Export: Export a WAV file.....................................107
5. SONG/CD................................................108
P1SelSong: Selecting a song.......................................108
P2EditSong: Song editing...........................................109
P3PrgPlay: Program playback of songs...................110
P4CDR/RW: Creating and playing CD-R/RW discs ..
110
6. STORE...................................................112
7. MARK....................................................113
P1Mark: Editing marks ..............................................113
8. SCENE ...................................................113
P1ReadDel: Scene playback on/off and editing.....113
P2MixView: Pan/fader scene display......................114
9. TEMPO/RHYTHM.......................................115
P1SetUp: Tempo and rhythm settings .....................115
P2TmpMap: Editing the tempo map........................116
P3TmpTrk: Create a tempo track..............................117
10. IN/LOC1, OUT/LOC2, TO/LOC3, END/LOC4.......118
Locate functions...........................................................118
11. AUTO PUNCH .........................................119
P1AtPunch: Settings for auto punch-in/out
recording..................................................................119
12. LOOP...................................................120
P1Loop: Loop playback/recording settings ...........120
v
Page 6

13. UNDO...................................................120
22. METER/TRACK VIEW................................ 133
14. TRIGGER...............................................121
P1Trigger: Settings to start trigger recording .........121
15. SCRUB .................................................122
16. ENTER..................................................122
17. INPUT/TUNER.........................................123
P1Ch1–8: Select the inputs for mixer channels 1–8 123
P2Ch9–16: Select the inputs for mixer channels 9–16..
124
P3InEq1–4: EQ settings for inputs 1–4 .....................124
P4InEq5–8: EQ settings for inputs 5–8 .....................124
P5Tuner: Tuner............................................................124
18. EQ/PHASE .............................................125
P1Eq1–4: EQ settings for mixer channels 1–4 ......... 125
P2Eq5–8: EQ settings for mixer channels 5–8 ......... 125
P3Eq9–12: EQ settings for mixer channels 9–12 ..... 125
P4Eq13–16: EQ settings for mixer channels 13–16 . 125
P5Phase: Phase settings for mixer channels............ 125
19. INSERT EFFECT.......................................126
P1InsAsn: Insert effect insertion location/type......126
P2InsEff1: Selection and settings for Insert Effect 1127
P3InsEff2: Selection and settings for Insert Effect 2128
P4InsEff3: Selection and settings for Insert Effect 3128
P5InsEff4: Selection and settings for Insert Effect 4128
P6Ins5–8: Selection and settings for Insert Effects 5–
8.................................................................................128
20. MASTER EFFECT/AUX ...............................129
P1MstEff1: Selection and settings for master effect 1 ..
129
P2MstEff2: Selection and settings for master effect 2 ..
129
P3EffSnd1: Send settings for effect 1........................129
P4EffSnd2: Send settings for effect 2........................130
P5AuxSend: External send settings.......................... 130
P6FinalEff: Selection and settings for the final effect...
130
23. TRACK STATUS...................................... 134
24. PAN.................................................... 134
25. FADER................................................. 134
26. TRANSPORT KEYS .................................. 135
Effect Parameter List ...........137
Insert Effect (2in2outx2)/Master Effect/Final Effect. 137
Reverb RV1 – RV7....................................................... 137
Delay DL1 – DL6 ......................................................... 137
Modulation MO1– MO7............................................. 139
Dynamics DY1 – DY7.................................................. 140
Special Effect SE1 – SE4..............................................142
Insert Effect (2in2outx2)/ Final Effect................. 143
Large size LS1 – LS7.................................................... 143
Insert Effect (1in2outx2) ................................ 144
GT1 – GT6..................................................................... 144
AS1 – AS3 ..................................................................... 144
PA1 ................................................................................ 145
EB1 – EB3...................................................................... 145
MS1................................................................................ 145
VO1 – VO2....................................................................145
Effects within multi-effect programs GT1–VO2, and
their parameters...................................................... 145
Insert Effect (1in1outx4) ................................ 148
Effects within multi-effect programs MM1–MM33,
and their parameters.............................................. 149
Insert Effect (1in1outx8) ................................ 150
Effect Control ............................................. 151
Appendices.......................153
21. SOLO/MONITOR ......................................131
P1Solo: Solo select.......................................................131
P2Monitor: Monitor settings .....................................132
vi
Troubleshooting.......................................... 153
Various messages ....................................... 157
About the hard disk and CD-R/RW drive.............. 159
1. Hard disk................................................................. 159
2. About the CD-R/RW drive................................... 160
3. Playing or recording from an audio CD ............. 161
Page 7

Specifications .............................................162
MIDI implementation chart..............................164
Block diagram.............................................165
Effect Program List.......................................166
Rhythm Pattern List (215 patterns) ....................168
vii
Page 8

viii
Page 9

Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Korg D1600mkII Digital
Recording Studio.
To ensure trouble-free enjoyment, please read this manual carefully and use the instrument as directed.
1. Main features
• 16-track digital recorder
The D1600mkII delivers studio-quality sound with
24-bit internal processing, 16/24-bit recording and
playback, and uncompressed recording at a sampling
frequency of 44.1 kHz. It allows a maximum of 16
tracks of simultaneous playback (16-bit) and up to 8
tracks of simultaneous recording. The recording time
is a maximum of approximately 122 hours (16-bit,
one track). Each track provides eight virtual tracks,
meaning that you can record 128 tracks per song.
• XLR input jacks with +48V phantom power supply, analog inputs, dedicated guitar input jack, and digital jacks
All analog inputs of the D1600mkII use high-performance balanced head amps that take full advantage of its all-digital audio quality. The four XLR
input jacks with +48V phantom power contain highquality mic preamps, allowing condenser mics to be
connected directly. All phone jack inputs ar e balanced
TRS-types. Unbalanced input is also supported. Levels from mic level to +16 dBu (higher than professional level) are supported, letting you directly
connect a wide variety of audio sources. There’s also
a dedicated guitar input jack. The S/P DIF digital
input contains a sampling rate converter , allowing 48
kHz or 32 kHz sources to be automatically converted
to 44.1 kHz for recording.
• Mixer section provides three-band EQ with sweepable
mid-range
• 100 scene memories, and mixer data transmission/
reception via MIDI
The D1600mkII’s 24-channel 8-bus mixer section provides 3-band EQ (high EQ and low EQ are shelving
types, and mid EQ is a peaking type with adjustable
center frequency) on every analog input and mixer
channel. Since EQ is applied separately to the inputs
and the mixer, you won’t have the problem of recording EQ settings being re-applied to the playback – a
mistake that’s easy to make with MTR systems that
have an analog internal mixer.
Mixer parameters such as fader, EQ, pan, and effect
settings can be stored as a scene, and each song can
contain one hundred scenes. Scenes can be switched
automatically as time progresses, or can be easily
recalled when desired as general-purpose settings.
Mixer data such as fader and pan can be transmitted
and received via MIDI, allowing the mixer to be automated from an external sequencer.
• Three independent effects usable simultaneously
The three independent built-in effects (Insert, Master,
and Final) use 44-bit internal processing. For each of
these three effects, you can choose an effect program
that consists of up to five effects taken from 98 types
of high-quality effect. 128 insert, 32 master, and 32
final effects (total 192) created by professional musicians and studio engineers are provided as preset
programs. You can edit these preset effect programs
and store 192 more of your own in the user area.
External MIDI controllers or an expression pedal
(EXP-2, XVP-10: sold separately) can control an insert
effect in realtime.
• Sophisticated editing
The non-destructive editing offered only by digital
recorders lets you edit without impairing the high
audio quality. You can use auto or manual punch-in/
out. The Undo function that lets you revert to the
state prior to a recording or editing operation, in conjunction with the Redo that cancels the Undo, lets
you step back through as many as 99 prior recording
or editing operations. Ten different track editing commands include the convenient Time Expansion/
Compression operation that lets you match phrases
of differing tempo after they have been recorded, and
Normalize that boosts low-level tracks to the appropriate level.
In each song you can assign 100 named Mark points
and four Locate points, letting you move immediately to the song location where you want to edit.
• Hard disk drive built-in
• Hard disk USB drive and USB connector
The D1600mkII contains a high-capacity 40 GB hard
disk drive. Of the total capacity, 2 GB are allocated as
a “USB drive*” that can be connected to your computer via the USB connector for sharing of data, and the
remaining capacity is used as a “song drive” for holding your songs. WAV files can be imported or
exported, making it easy to transfer audio data to or
from your computer.
* FAT 16 is supported
• Create audio CDs using the CD-R/RW drive
You can use the CD-R/RW drive to backup/restore
songs and effect data, import/export WAV files, and
create audio CDs. You can also insert an audio CD in
the drive, patch the sound to a mixer channel, and
record or play it.
An audio CD can be written in two ways; you can
write one song at a time using Track At Once, or you
can insert markers in a single song (e.g., recorded
from a live performance) and write each section as a
track of an audio CD by using the Disc At Once
method.
Parts and their functionObjects in the LCD screen
and their functions
Basic operationPreparationsListening to the demo song Introduction
1
Page 10
• Auto Save function automatically preserves your data at
power-off
The D1600mkII features an Auto Save function that
automatically saves your recorded or edited songs
and phrases to the hard disk whenever you switch
songs or turn off the power.
LCD screens
The parameter values shown in the LCD screens printed
in this manual are explanatory examples, and may not
necessarily match the displays that appear on your
D1600mkII.
What is ?
(Resonant structure and Electronic circuit Modeling System) is Korg’s proprietary technology for digitally recreating the numerous factors that produce
and influence a sound, ranging from the sound-production mechanisms of acoustic instruments and electric/electronic musical instruments, to the resonances
of an instrument body or speaker cabinet, the sound
field in which the instrument is played, the propagation route of the sound, the electrical and acoustic response of mics and speakers, and the changes
produced by vacuum tubes and transistors.
2. Printing conventions in this manual
Switches and knobs [ ]
Keys, dials, and knobs on the panel of the D1600mkII are
printed within [square brackets].
Parameters that appear in the LCD screen “ ”
Parameters that appear in the LCD screen are printed
inside “double quotation marks.” The terms ‘button’ and
‘cell’ refer to objects in the LCD screen.
The LCD screen of the D1600mkII is a touch panel. To
select a parameter, simply touch that parameter directly. Alternatively, you can use the [CURSOR] keys
to move the cursor to the desired parameter. Most of
the procedure examples given in this manual will use
the method of directly pressing the parameter in the
LCD screen to select it.
3. Included items
Make sure that the following included items are all
present.
• Owner’s manual (this document)
• Power cable
Bold-face type
Panel settings such as for faders or the [TRACK ST ATUS]
keys are printed in bold type, and parameter values are
printed in “bold type.”
Bold type also indicates content within the text that we
wish to emphasize.
Steps 1. 2. 3. …
Steps in a procedure are indicated as 1. 2. 3. …
p.■■
This indicates a page or parameter number for reference.
Symbols ,
These symbols respectively indicate points of caution and
notes of advice.
[...] “xx” tab page
This indicates a page displayed in the LCD screen. To
access this page, press the [...] key on the panel.
If there is more than one tab, the tab pages will be
selected successively each time you press the [...] key.
2
Page 11
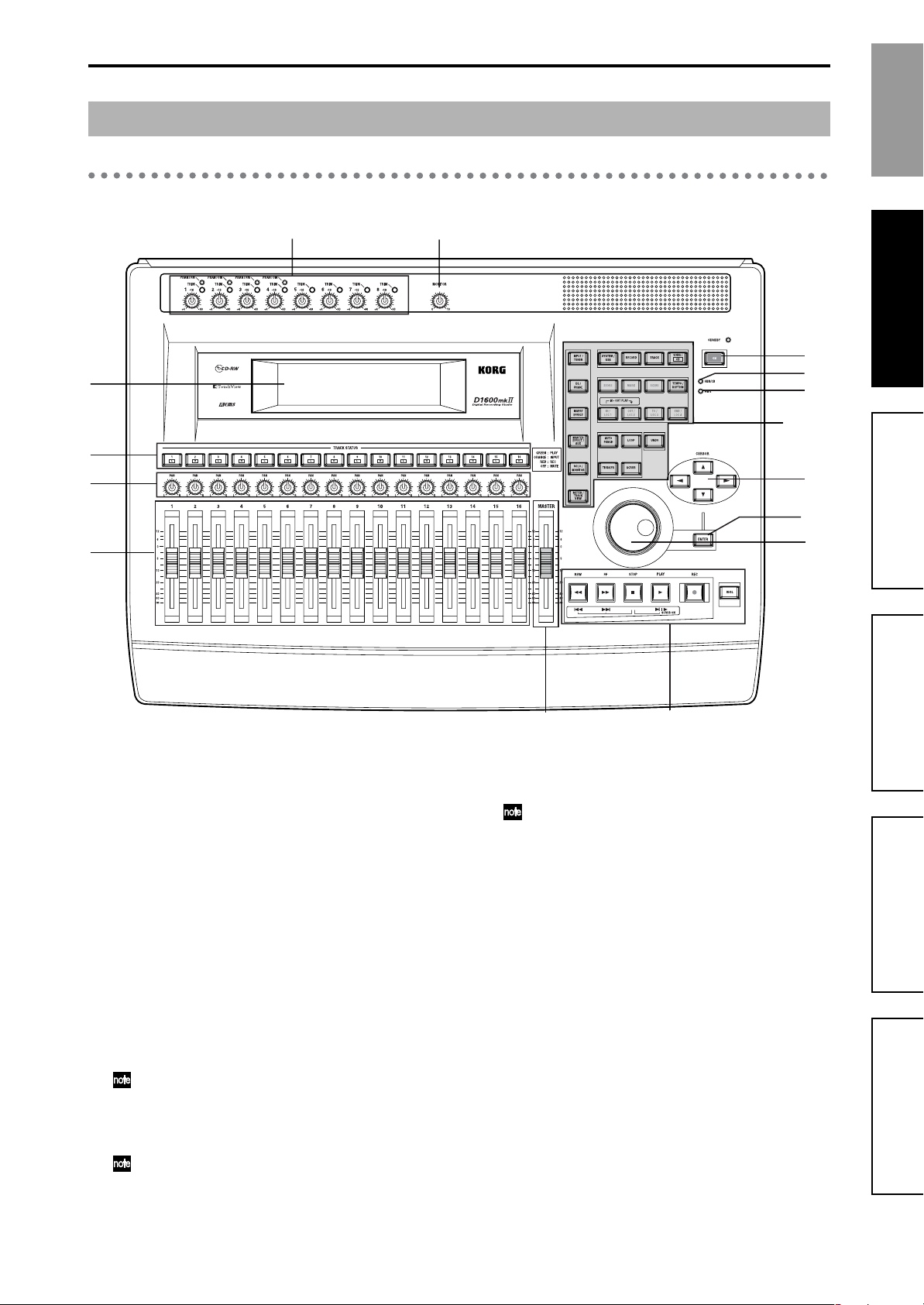
1. Top panel
Parts and their function
33 34
1
2
3
4
1 LCD screen
The D1600mkII uses a TouchView system based on a
touch panel screen. By pressing objects that are
shown in the LCD screen, you can select pages, tabs,
and parameters, and set their values.
Also displayed are the volume (level meters), time
locations (locate) during recording or playback, and
various other parameters.
2 [TRACK STATUS] keys
These keys are used to put each track into playback,
record, or to mute (silence) status. Each time you
press a key, the track setting will alternate.
•Green: PLAY
• Orange: INPUT
• Red: REC
• Dark: MUTE
When recording from analog/digital input, you can
arm up to eight recording tracks.
These settings can be paired.
3[PAN] knobs (Ch1…16)
These knobs adjust the stereo location of each channel.
These settings can be paired, and registered in a
scene.
5
4 [CHANNEL] faders (Ch1…16)
These faders adjust the recording/playback volume
of each channel.
These settings can be paired, and registered in a
scene.
5 [MASTER] fader
This adjusts the volume of all channels. During
bounce recording, this sets the recording level of the
bounce destination track.
6 TRANSPORT keys
[REC] key, [RHSL] key, [PLAY] key, [STOP] key,
[REW] key, [FF] key
These are used to perform recording operations such
as playback and record.
7[VALUE] dial
This is used to modify parameter values, and to move
the current time.
When the Scrub function is on, rotating the dial will
cause the track to play at the corresponding speed.
8 [CURSOR] key
This key moves the cursor.
6
9
10
11
12~31
8
32
7
Parts and their functionObjects in the LCD screen
Parts and their function
and their functions
Basic operationPreparationsListening to the demo song Introduction
3
Page 12
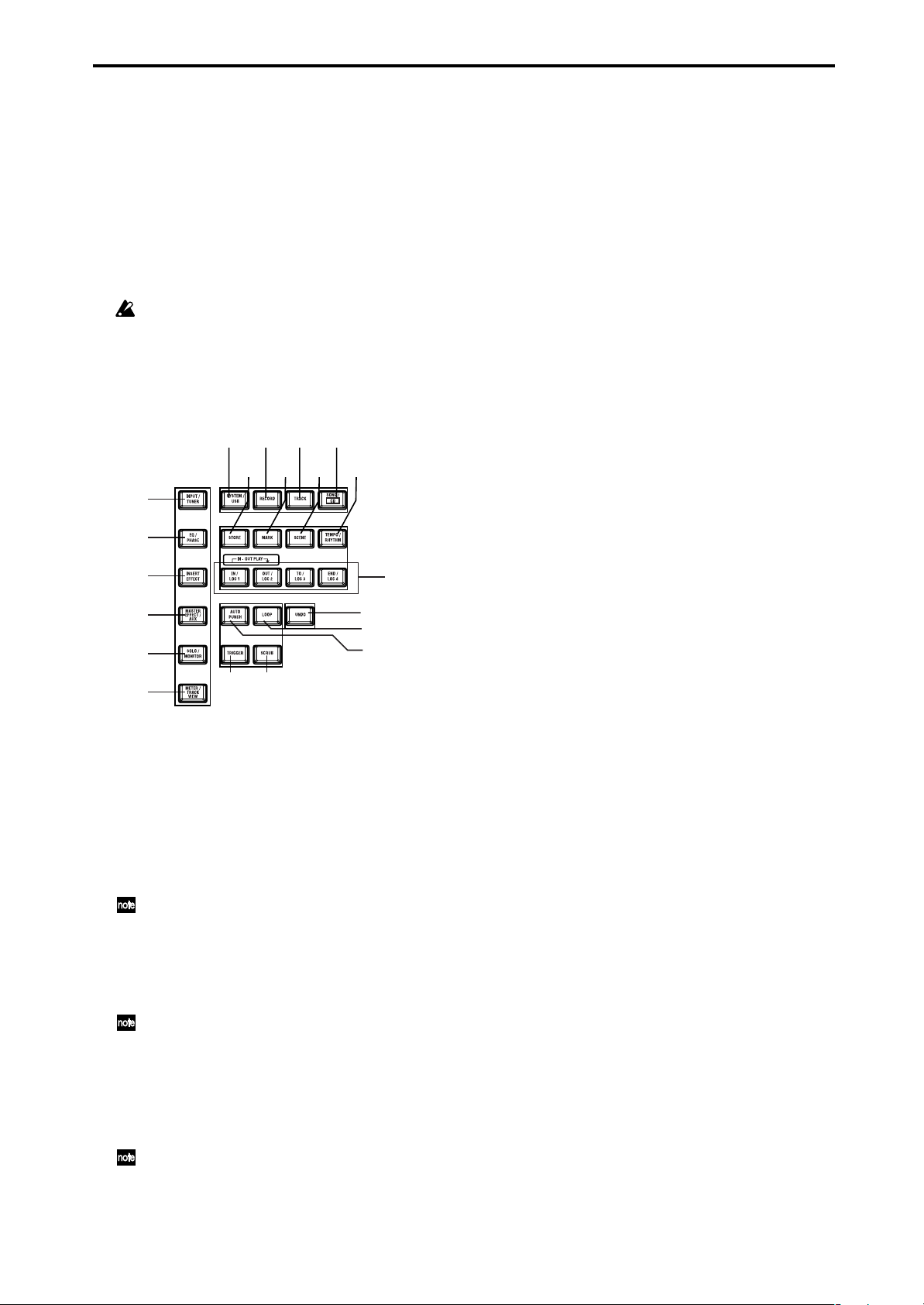
9 [POWER] key
This turns the power of the D1600mkII on/off. When
the D1600mkII is in standby mode, pressing the
[POWER] key will turn on the power. If the
D1600mkII is operating, pressing and holding the
[POWER] key for a while will cause it to shut down
and enter standby mode.
10 HDD/CD access indicator
This indicator will light when the internal hard disk
is being accessed for recording or playback, or when
the internal CD-R/RW drive is operating.
Never move the D1600mkII or apply physical
shock to it when this HDD/CD access indicator
is lit.
11 MIDI indicator
This indicator will light when MIDI messages are
received from the MIDI IN connector.
18
1923202421
22
25
16 [SOLO/MONITOR] key
This key is used to solo an individual channel, send,
or return. It is also used to select an audio source for
monitoring.
When solo is on, the LED will blink.
17 [METER/TRACK VIEW] key
This key is used to display volume data (level meters)
during recording and playback, and to view audio
event data in each track (track view).
18 [SYSTEM/USB] key
This lets you make settings for the foot switch and
MIDI functions, manage the disk drive, and backup/
restore data.
You can also connect the D1600mkII to your computer via the USB jack, and exchange data between your
computer and the D1600mkII’s USB drive.
19 [RECORD] key
Press this key to make recorder settings such as
selecting the recording source or the bounce recording method etc.
12
13
14
15
29
28
16
17
12 [INPUT/TUNER] key
This key is used to select the mixer channel to which
the audio signal from each input jack will be sent.
This is also used when adjusting the EQ (for recording) that is applied to the analog inputs.
In addition, this key is used to access the tuner.
13 [EQ/PHASE] key
This key is used to specify the EQ (for track playback)
and phase of each channel.
These settings can be paired, and registered in a
scene.
14 [INSERT EFFECT] key
This key is used to select the location of an insert
effect, to select the effect type, and to select and edit
effect programs.
These settings can be registered in a scene.
15 [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] key
This key is used to select and edit effect programs for
master effects 1 and 2, and to set the send levels from
each channel to the master effects. In addition, it is
used to set the send amount to an external effect, and
to select and edit effect programs for the final effects.
These settings can be registered in a scene. The
send settings can be paired.
30 31
27
20 [TRACK] key
This key is used to select the virtual track for each
track, to perform track editing operations such as
copy or delete, and when importing or exporting
WAV files.
26
21 [SONG/CD] key
Press this key to create a new song, rename/select a
song, perform a song editing operation such as copy
or move, perform program playback of songs, or produce an audio CD (a CD-R/RW drive is required).
22 [STORE] key
Press this key to register the time location for a locate
point, a mark, or a scene.
23 [MARK] key
This key registers the desired time location in a song
as a Mark, so that the registered time can be recalled
instantly.
It is also used to edit marks by renaming or deleting
them etc.
24 [SCENE] key
This key is used to register [CHANNEL] fader , [PAN]
knob, EQ or effect send settings as a scene at the specified time location in a song. If the Scene Read setting
is on during playback, the registered scenes will be
selected automatically at the corresponding times.
Scenes can also be sorted, renamed, or deleted.
This key will light when Scene Read is “On.”
25 [TEMPO/RHYTHM] key
This key is used to set the tempo for a song, create a
tempo map, and turn the rhythm function on/off.
This key will light when the Rhythm function is on.
26 [IN/LOC1] key, [OUT/LOC2] key, [TO/LOC3] key,
[END/LOC4] key
These keys are used to register a desired time location
within a song, or to instantly jump to a registered
time location.
4
Page 13
The time locations registered here are used as the
punch-in/out locations, and the editing range for
track editing operations such as copy or delete.
By holding down the [IN/LOC1] key and pressing
the [OUT/LOC2] key, you can listen to the audio
between the IN–OUT points.
27 [AUTO PUNCH] key
This key is used to turn the Auto Punch-in/out function on/off, to set the pre/post roll time, and to verify
the start/end locations.
This key will light when the Auto Punch-in/out function is on.
28 [LOOP] key
This key is used to turn the Loop function on/off for
playback or recording, and to verify the start/end
locations.
This key will light when the Loop function is on.
29 [UNDO] key
After recording or editing a track, you can use the
Undo function to return the data to its prior state,
and then (if desired) use the Redo function to cancel
the Undo and go back to the edited data.
Up to 99 prior recording or editing operations can be
undone. You can select from 1, 8, or 99 levels of undo.
This key will light when Undo or Redo is available.
30 [TRIGGER] key
This is the on/off key for the Trigger Recording func-
tion, which causes recording to begin automatically
in response to an audio input. This key is also used to
set the threshold level and pre-trigger time.
This key will light when the Trigger Recording function is on.
31 [SCRUB] key
This key turns the Scrub, Play To/From, and Slow
Play functions on/off. The key will light when the
Scrub function is “On.” These functions are used by
operating the [VALUE] dial or TRANSPORT keys.
32 [ENTER] key
This key is used to finalize a parameter selection, or
to turn a parameter on/off.
33 [TRIM] knob: –60...–10...+4 dBu
These knobs adjust the input level. The markings
indicate the input level.
The LEDs will show different colors to indicate the
following statuses.
• Lit green: input present
• Lit orange: correct level
• Lit red: excessive level
Adjust each [TRIM] knob appropriately, so that the
LEDs do not turn red when the connected instrument
is played at maximum volume.
The input level will depend on the instrument or performance, but the approximate ranges are as follows.
• –60 – –40 dBu: mic input
• –30 dBu: guitar, bass guitar
• –10 dBu: consumer audio devices such as a CD
player
• +4 dBu: keyboards or studio equipment
If the [TRIM] knob is raised when nothing is connected to an input, hum or noise may result.
34 [MONITOR OUT LEVEL] knob
This knob sets the volume level from the [MONITOR
OUT L/R] jacks.
Parts and their functionObjects in the LCD screen
Parts and their function
and their functions
2. Front panel
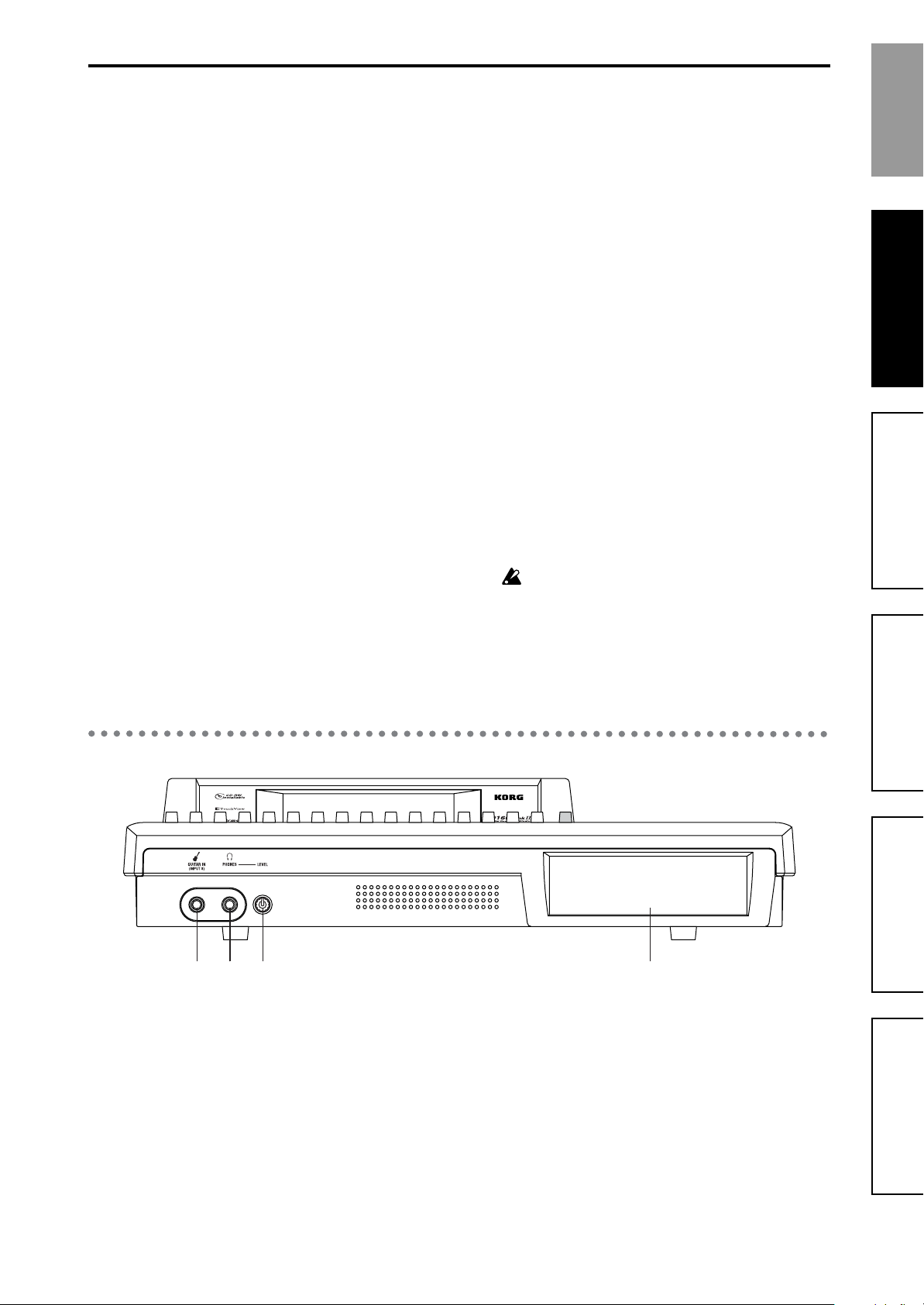
21 3 4
1 [GUITAR IN] jack
A guitar or bass guitar can be plugged in here.
This is an unbalanced 1/4" (6.3 mm) input jack with
1 M
Ω impedance.
2 [PHONES] jack
A set of headphones can be connected here.
This is a 1/4" stereo phone jack.
This outputs the same signal as the [MONITOR OUT
L/R] jacks.
3 [PHONES LEVEL] knob: 0...10
This knob sets the volume level of the headphones.
The volume will increase in correspondence to the
printed grid.
4 CD-R/RW drive bay
Use this to backup/restore data, and to play or write
audio CDs. For details on handling and inserting a
disc, refer to “2. About the CD-R/RW drive”
(
→p.160).
Basic operationPreparationsListening to the demo song Introduction
5
Page 14
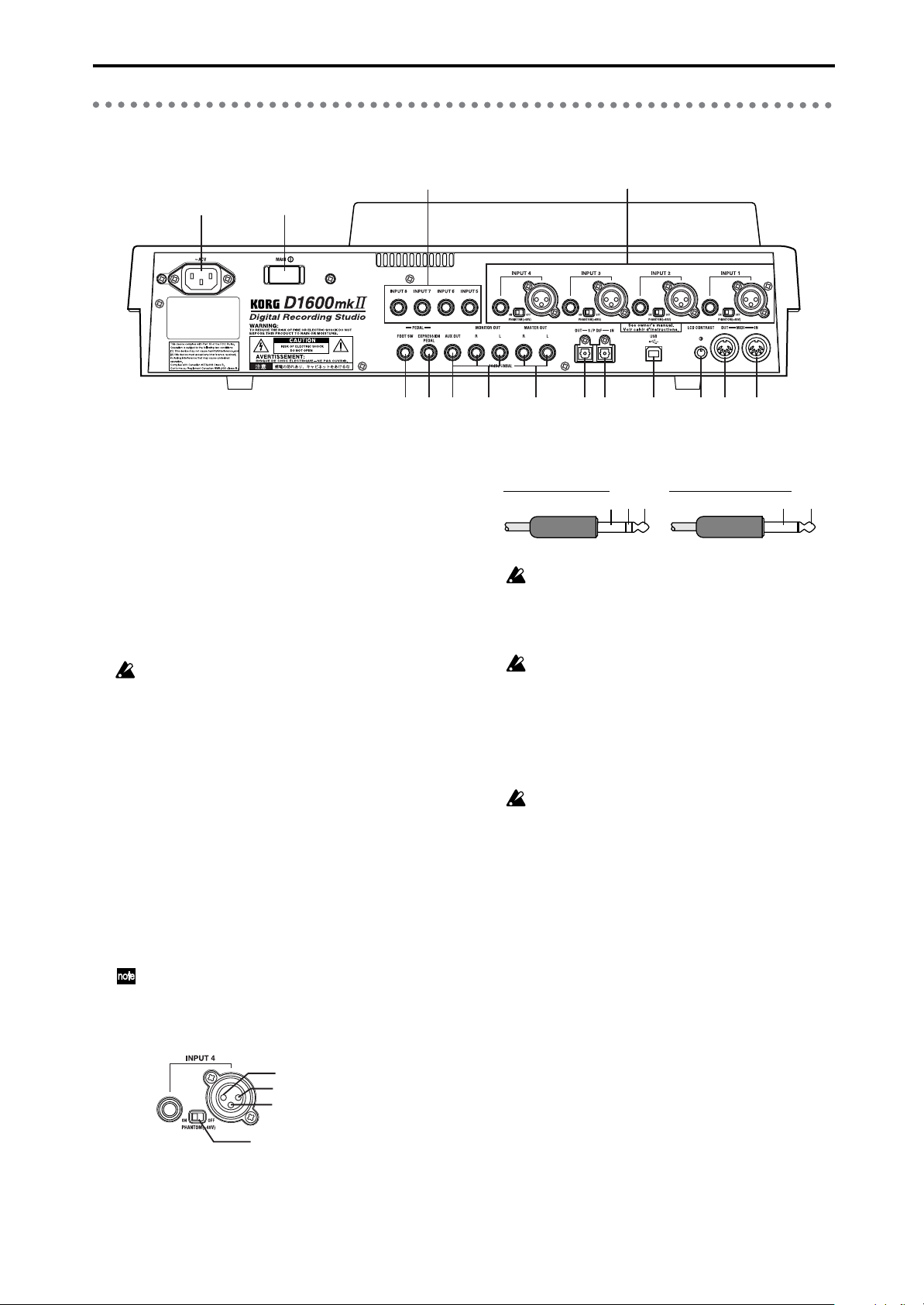
3. Rear panel
12
34
1 [AC] connector
Connect the included power supply cable here.
2 [Main power] switch
This turns the main power on/off.
When the [Main power] switch is turned on, the
D1600mkII will be in standby mode. In standby
mode, you can press the [POWER] key to turn on the
power of the D1600mkII. While the D1600mkII is
operating, you can use the [POWER] key to shut
down, and then turn the main power off to turn the
power off completely.
To turn off the power, you must first press the
[POWER] key to perform the shutdown operation. Never turn off the [Main power] switch or
disconnect the power cable until shutdown has
been completed.
If you turn off the [Main power] switch or disconnect the power cable before shutdown has
been completed, data and user settings may be
lost, or the hard disk may be damaged.
3 [INPUT 1], [INPUT 2], [INPUT 3], [INPUT 4] jacks
Audio sources such as mic or line (keyboard etc.) can
be connected here.
Both balanced XLR and balanced 1/4" TRS phone
jacks are provided.
Unbalanced phone plugs can also be connected.
+48V phantom power is provided on the XLR jacks
so that you can use condenser mics.
If you connect the phone jack, you will not be
able to input from the XLR jack. If you want to
use the XLR jack, don’t connect anything to the
phone jack.
2: HOT
1: GND
3: COLD
10
5
4 [INPUT 5], [INPUT 6], [INPUT 7], [INPUT 8] jacks
5 [FOOT SW] jack
6 [EXPRESSION PEDAL] jack
9876
Balanced phone plug Unbalanced phone plug
If a condenser mic is connected or disconnected
with the phantom power switch on, damage to
your equipment may occur. For this reason,
always turn the phantom power switch off before
connecting a condenser mic.
Never connect an unbalanced mic or device
when the phantom power switch is on. Doing so
may damage your equipment.
Mic/line (e.g., keyboard) sources can be input here.
These are balanced 1/4" TRS phone jacks.
Unbalanced phone jacks can also be connected.
If you connect a plug to the [GUIT AR IN] jack, no
input signal will be received from the [INPUT 8]
jack. If you wish to use the [INPUT 8] jack, disconnect the plug from the [GUITAR IN] jack.
When your hands are occupied with playing an
instrument, you can use a foot switch to control basic
operations of the D1600mkII recorder.
A foot switch can be used to start/stop the playback,
start/end manual punch-in recording, register a
mark, or to record tap tempo.
Connect the foot switch (optional PS-1) to this jack.
You can use a pedal to control a specified parameter
of an insert effect. You can control the parameter in
realtime while you play or record.
Connect an expression pedal (separately sold option,
EXP-2, XVP-10 etc.) to this jack.
11
GND
12
COLD HOT
13 14
15
GND HOT
Phantom power switch
6
Page 15

7 [AUX OUT] jack
Connect this to the input jack of an external effect
device.
This jack outputs the external send signal from each
mixer channel. This is a 1/4" phone jack.
8 [MONITOR OUT L/R] jacks
Connect your external monitor system to these jacks.
The bus that is sent to the monitor output is selected
in the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page.
These jacks output the same audio signal as
[PHONES].
This is a 1/4" phone jack.
9 [MASTER OUT L/R] jacks
These are analog outputs for the master LR bus which
combines the signals from each mixer channel, or for
the audio source that is selected by the Solo function.
The Solo selection is made in the [SOLO/MONITOR]
“Solo” tab page.
Connect your external monitor system or recording
device to these jacks. They output the same audio signal as the [S/P DIF OUT] jacks.
This is a 1/4" phone jack.
10 [S/P DIF OUT] jack
This is an optical-type S/PDIF format (IEC60958,
EIAJ CP-1201) digital output jack (stereo).
Use an optical cable to connect this jack to the optical
digital input of your DAT or MD.
This jack digitally outputs the same audio signal as
the [MASTER OUT L/R] jacks at a sampling rate of
44.1 kHz.
Parts and their functionObjects in the LCD screen
Parts and their function
and their functions
11 [S/P DIF IN] jack
This is an optical-type S/PDIF format (IEC60958,
EIAJ CP-1201) digital input jack (stereo).
Use an optical cable to connect this jack to the optical
digital output of your DAT or MD.
A sampling rate converter is built in. If the connected
source has a sampling rate of 48 kHz or 32 kHz
source, it will be converted automatically to 44.1 kHz.
12 [USB] connector
Use a USB cable to connect this to your computer.
You cannot connect USB peripheral devices such
as an external hard disk or CD-R/RW drive to
the D1600mkII.
13 [LCD CONTRAST] knob
This adjusts the contrast of the LCD screen.
The optimal setting will depend on the viewing
angle, so adjust the contrast as necessary. Looking
from the front panel, turning the knob toward the
right will darken the text, and turning it toward the
left will lighten the text.
14 [MIDI OUT] connector
MIDI messages are transmitted from this connector.
Use this when you wish to control a connected external MIDI device from the D1600mkII.
Basic operationPreparationsListening to the demo song Introduction
15 [MIDI IN] connector
MIDI messages are received at this connector. Use
this when you wish to control the D1600mkII from a
connected external MIDI device.
7
Page 16
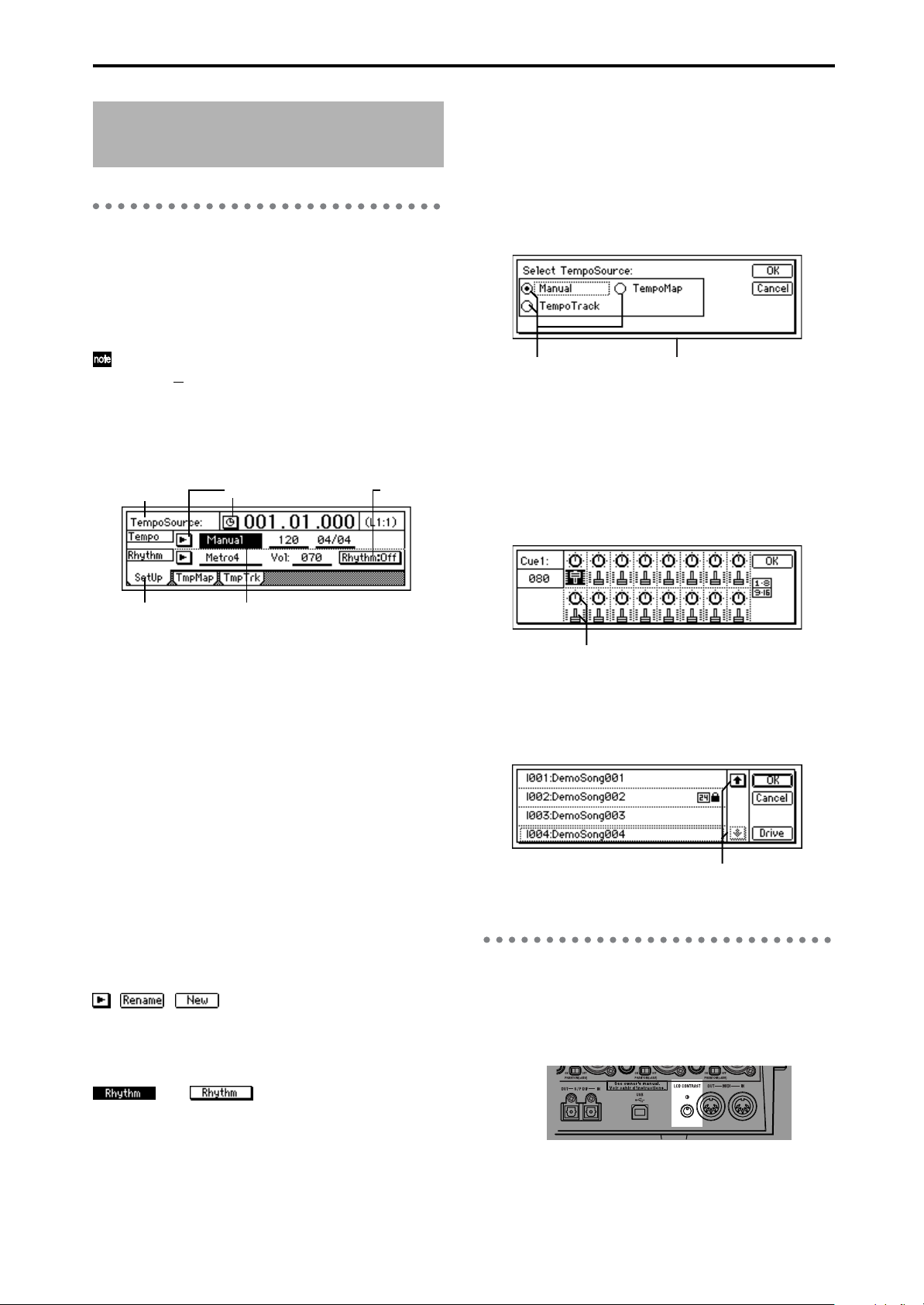
Objects in the LCD screen and
their functions
1. Objects in the LCD screen
The LCD screen of the D1600mkII features the Touch
View system, which uses a touch panel.
By pressing objects displayed in the LCD screen you can
perform operations such as selecting pages, setting
parameter values, moving the cursor location, or editing
settings.
In this manual, terms enclosed in “quotation marks”
such as “...
the LCD screen which you can operate. Terms
enclosed in square brackets such as [...] key, [...] knob,
[...] dial, or [...] fader refer to controls etc. located on
the top panel, front panel, or rear panel.
a:Current parameter
display
”, “...” button, or “...” tab refer to objects in
c:Popup
button
d:Toggle
button
e: Tab page
Each mode contains numerous parameters, which are
organized into pages. Each page is accessed by its own
tab.
f: Dialog box
To execute, press the “OK” button. To cancel, press the
“Cancel” button. The dialog box will close.
g: Radio buttons f: Dialog box
g: Radio buttons
These buttons are used to select one of multiple items.
Press one of the radio buttons.
h: Icons
These are objects shaped like faders or knobs. To modify
a value, select it and rotate the [VALUE] dial.
e: Tab
b: Edit cell
a: Current parameter display
This is the name of the parameter currently selected by
the edit cell.
For icon-type parameters such as EQ or fader, the value is
displayed at the right.
b: Edit cell
When you select a parameter in the LCD screen, the
parameter value will be highlighted in some cases. This
area is referred to as the edit cell, and your editing will
apply to the highlighted portion.
The parameter value in the edit cell can be modified using
the [VALUE] dial or by using the popup buttons in the
LCD screen.
c: Popup button
When you press this button, a dialog box (f) will appear.
To enter a parameter value, choose the desired value
from the dialog box.
, ,
d: Toggle button
Pressing this type of button will alternately switch a
function between on/off.
(on)/ (off)
h: Icons
i: Scroll buttons
These buttons are used to view parameter values that cannot be displayed in a single screen.
i: Scroll buttons
2. Adjusting the LCD screen contrast
Use the rear panel [LCD CONTRAST] knob to adjust the
contrast.
8
Page 17
Basic operation
1. Selecting a mode
To make settings in the LCD screen for the various functions of the D1600mkII, you must first press the key of the
mode that includes that function.
For the functions of each mode, refer to “Reference”
(→p.91–).
2. Selecting a tab page
Each mode contains numerous parameters, and these are
organized into pages. Pages are accessed by tabs.
1. Press the key for the desired mode.
The illustration below shows a tab page of TEMPO/
RHYTHM mode that will appear when you press the
[TEMPO/RHYTHM] key.
In this manual, this is referred to as the [TEMPO/
RHYTHM] “SetUp” tab page.
2. Select the desired tab page.
Each time you press the key of the currently selected
mode, you will cycle through the tab pages of that
mode.
Some pages contain only one tab.
Setting a parameter value
The method of setting a parameter value will differ depending on the type of parameter.
Underlined “___” parameters, and icons such as EQ
Either directly press the parameter displayed in the
LCD, or use the [CURSOR] keys to move the edit cell
so that the parameter is highlighted, and rotate the
[VALUE] dial to edit the value.
This is the typical method, and also applies for
underlined parameters such as “T
displayed as an icon such as EQ, and changes in
locate times.
Popup buttons and dialog boxes
Use the popup button to access the dialog box, and
set the parameter value.
• When you press a popup button shown in the
LCD screen, a dialog box will appear.
• Use the [CURSOR] keys to move the edit cell to
the popup button, and press the [ENTER] key to
access the dialog box.
Toggle buttons
These buttons are used to turn a function on/off.
• Each time you press a toggle button shown in the
LCD screen, the setting will alternate on/off.
• Use the [CURSOR] keys to select the parameter,
and press the [ENTER] key. The button will turn
on/off each time you press it.
Radio buttons
These buttons are used to select one of multiple
choices.
• When you press one of the radio buttons shown in
the LCD, it will be selected.
• Use the [CURSOR] keys to move the edit cell to
the desired button, and press the [ENTER] key.
Selecting an item from a list
•To select a song or mark, rotate the [VALUE] dial
to select the desired item.
•To select a song in a program play list, use the following procedure.
1. Select the playback list number.
2. Rotate the [VALUE] dial to select the song.
empo”, parameters
Parts and their functionObjects in the LCD screen
and their functions
and their functions
Objects in the LCD screen
Basic operationPreparationsListening to the demo song Introduction
Basic operation
3. Selecting and setting a parameter
Selecting a parameter
Use one of the following methods to select the parameter
that you wish to edit.
• In the LCD screen, press that parameter directly.
•Press the up/down/left/right [CURSOR] keys to
move the cursor to that parameter.
• In a list display screen, rotate the [VALUE] dial to
move the cursor.
9
Page 18
Preparations
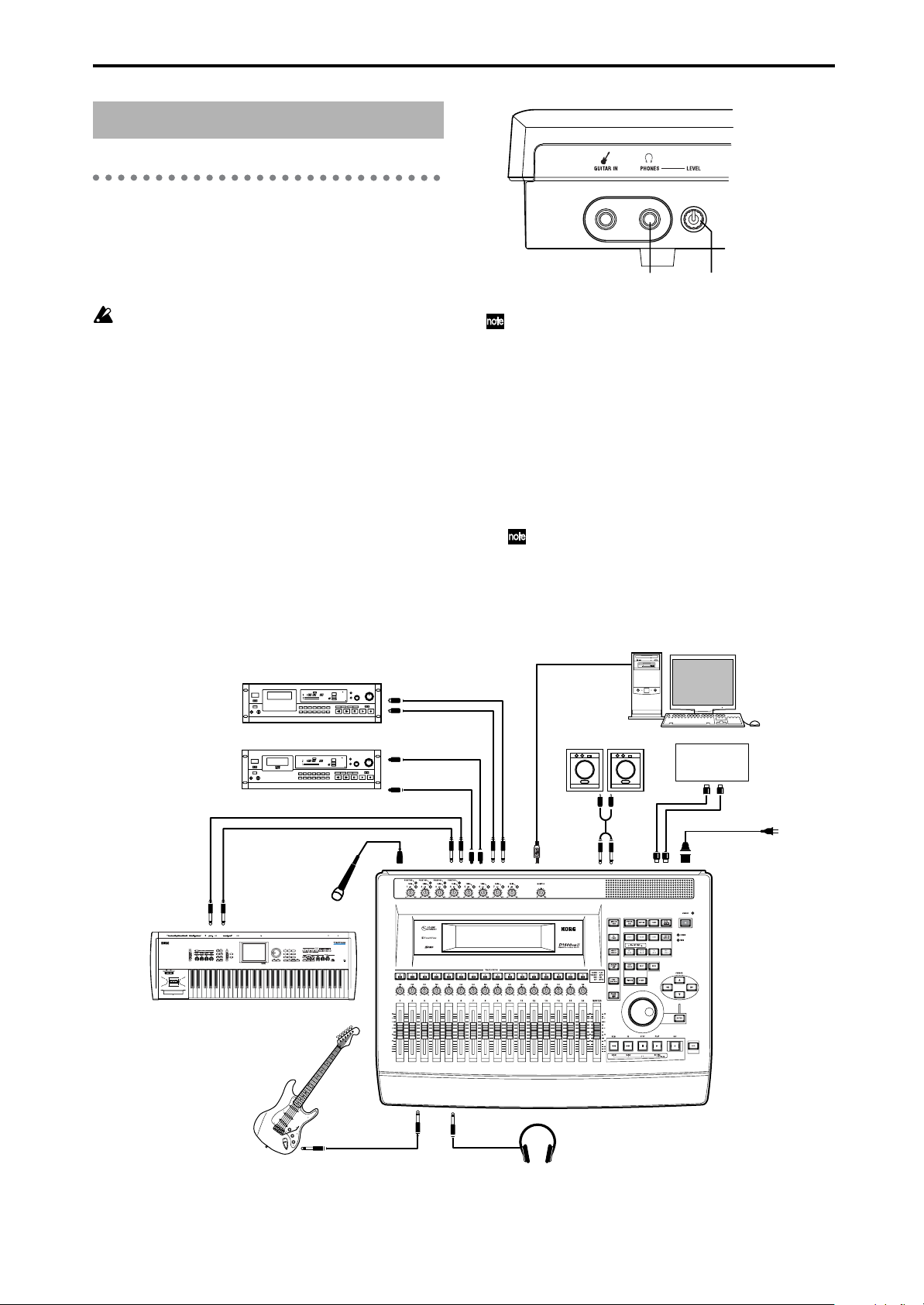
1. Connections
The diagram below shows a basic example of connections when using the D1600mkII to record. Make the
appropriate connections for your system, substituting
your own equipment as necessary for the equipment
shown here.
Be sure that the power is turned off while you are
making connections. If the power is on while connections are being made, your speaker system may be
damaged, or other malfunctions may occur.
1. Connect the included power supply cable.
Connect the power supply cable to the D1600mkII’s
[AC] connector. Then plug the other end into an electrical outlet.
2. Connect your audio monitoring system.
Use a phone cable to connect powered monitors etc.
to the [MONITOR OUT L/R] jacks.
If you will be monitoring through headphones, connect the 1/4" phone plug of your headphones to the
[PHONES] jack.
Use the [PHONES LEVEL] knob to adjust the
volume.
[PHONES LEVEL] knob[PHONES] jack
The audio signal that is output from the [MONITOR
OUT L/R] jacks and the [PHONES] jack is set in the
[SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page.
3. Connect your input devices.
To record analog signals
• Guitar/bass ↔ [GUITAR IN] jack
• Mic (XLR) ↔ [INPUT 1]–[INPUT 4] jacks
• Synthesizers, etc. ↔ [INPUT 1]–[INPUT 8] jacks
For details on specifying how the input audio signals
are sent to mixer channels, and how to monitor the
input sound, refer to “Assign audio inputs to the
mixer” (→p.36).
A guitar or bass guitar that is being sent through
a compact effect device can be connected to
[INPUT 1]–[INPUT 8].
OUTPUT
Keyboard
Master recorder (Analog: cassette tape recorder, etc.)
Master recorder (Digital: DAT, MD, etc.)
Mic
INPUT L/R
DIGITAL IN
DIGITAL OUT
INPUT
1–4
MASTER
OUT L/R
S/P DIF OUT
S/P DIF IN
INPUT
1–8
Powered monitors etc.
USB
MONITOR
OUT L/R
MIDI
IN/OUT
Computer
MIDI
sequencer
to the AC outlet
AC connector
MIDI
OUT/IN
10
Guitar
GUITAR IN
PHONES
Headphones
Page 19
When inputting in stereo, you should select two
adjacent inputs (1–2, 3–4) so that track editing
can be performed more efficiently.
If you are recording from a connected mic, locate
the mic at a sufficient distance from the
D1600mkII so that it does not pick up noise.
Connections for recording digital sources
• Optical digital (S/P DIF) output of a digital output
device such as DA T or MD ↔ [S/P DIF IN] jack of
the D1600mkII (use an optical digital cable for connection)
For details on assigning the audio inputs to mixer
channels and auditioning the input sound, refer to
“Assign audio inputs to the mixer” (→p.36)
4. Make other connections.
Connections for mixdown
Here’s how to make connections when the song created on the D1600mkII will be mixed down on an
external recording device (DAT, MD, tape recorder,
etc.)
• Optical digital (S/P DIF) input of a digital record-
ing device such as DAT or MD ↔ [S/P DIF OUT]
of the D1600mkII
• AUX IN inputs of an analog recor ding device such
as a cassette tape recorder ↔ [MASTER OUT L/R]
jacks of the D1600mkII
Connections when using external effects
If you wish to apply an external effect to the signal
from the [AUX OUT] send output, use the [INPUT
1]–[INPUT 8] jacks to receive the return signal(s).
In this case, you can choose whether the signal(s) will
be returned to the mixer channel(s) in the same way
as a conventional input, or sent directly to the master
bus. Refer to “7. Using an external effect” (→p.58).
Connections when using a foot switch to perform
manual punch recording, or playback/stop etc.
Connect the pedal switch (separately sold option: PS-
1) to the [FOOT SW] jack.
Connections when using a foot pedal to control
effects
Connect the expression pedal (separately sold option:
EXP-2, XVP-10) to the [EXPRESSION PEDAL] connector.
If a volume pedal is connected, it will not operate
correctly.
Connections when controlling effects or switching
scenes from an external MIDI device
Connect the MIDI OUT connector of the external
MIDI device ↔ [MIDI IN] connector of the
D1600mkII.
Connections for synchronizing the D1600mkII with
a MIDI sequencer
MIDI IN connector of your sequencer ↔ [MIDI OUT]
connector of the D1600mkII (use a MIDI cable for
connection)
MIDI OUT connector of your sequencer ↔ [MIDI IN]
connector of the D1600mkII
Connections for saving or backing-up data on your
computer
USB connector of your computer ↔ [USB] connector
of the D1600mkII (use a USB cable for connection)
2. Turning the power on/off
Turning the power on
Use the following procedure to turn on the power of the
D1600mkII and of the devices connected to it.
Before turning the power on, be sure to lower the volume of each device to the minimum position, and
turn the devices on beginning with the first device in
the signal chain (i.e., devices that produce audio signals).
1. Lower the D1600mkII’s [MASTER] fader to
the – ∞ position. Also turn down the volume of each connected device.
2. Turn on the power of the external input
device, such as a keyboard connected to the
D1600mkII.
3. Turn on the [Main power] of the
D1600mkII.
The ST ANDBY LED will light. The D1600mkII will be
in “standby” mode.
4. Press the [POWER] key of the D1600mkII to turn on
the power.
The opening message will appear in the LCD screen,
and then the [SONG/CD] “SelSong” tab page will
appear. The selected song will be the one that had
been selected when the power was last turned off.
5. Turn on the power of your external equipment, such
as the monitor system to which audio is being sent
from the D1600mkII.
Turning the power off
When you are finished playing or recording a song, turn
off the power. If you will not be using the D1600mkII for
an extended time (e.g., when you have finished work for
the day), be sure to turn off the main power so that the
power is turned off completely. Use the following procedure to turn off the power of the D1600mkII and of the
connected devices.
Before turning off the power, turn the volume of all
devices down to the minimum position, and turn off
the power switches beginning with the devices that
are at the end of the audio signal chain.
When you wish to turn off the power, you must perform the shutdown operation. Never turn off the
[Main power] switch or disconnect the power cable
until the shutdown has been completed. If you turn
off the main power or disconnect the power cable before shutdown is complete, data or user settings may
be lost, or you may damage the hard disk.
Audio that is recorded on the D1600mkII and the
mixer settings you make are saved automatically
when you select or switch songs, or when you shut
down. However, effects that you edit will be lost unless you save them.
1. If you wish to keep any effect settings that you
edited, save them. Refer to “5. Editing an effect”
(→p.56).
2. Lower the [MASTER] fader of the D1600mkII to the
–∞ position. Lower the volume of any external
devices to the minimum position.
Parts and their functionObjects in the LCD screen
and their functions
Basic operationPreparationsListening to the demo song Introduction
Preparations
11
Page 20

3. Turn off the power of the external output devices
(such as your monitor system) to which audio is
being sent from the D1600mkII.
4. Press and hold down the D1600mkII’s [POWER]
key to shut it down.
When you press and hold the [POWER] key, a dialog
box will ask you for confirmation. If you press the
“Yes” button, the song will be saved automatically,
and then the D1600mkII will shut down and enter
standby mode. If you press the “No” button, you will
return to the previous screen.
If you press the “Restart” button in the power-off
confirmation dialog box, the D1600mkII will restart.
By restarting, you can delete the Undo data and
recover the space it had occupied on the hard disk.
5. By pressing the D1600mkII [Main power] switch to
turn it off, you can turn the power off completely.
6. If an external drive is connected, turn off the power
of the external drive.
7. Turn off the power of external input devices, such as
keyboards.
Listening to the demo song
Here’s how to listen to the demo songs.
1. Move the D1600mkII’s [CHANNEL] faders to the 0
mark, and the [MASTER] fader to the –∞ mark.
2. Press the [SONG/CD] key to access the “SelSong”
tab page.
Make sure that “001: SISTER DANCE” is selected.
3. Make the [TRACK STATUS] key LED of all tracks
light green (PLAY).
If any are lit a different color or are dark, press the
key to make the LED light green.
4. Press the [PLAY] key to begin playback.
5. Slowly raise the [MASTER] fader to adjust the volume level.
6. When the demo song ends, press the [STOP] key to
stop playback.
12
Page 21
Quick Start
The Quick Start section consists of the following four steps.
We’ll begin our explanation by telling how to connect your equipment,
and take you all the way through to the final step of writing your performance to CD-R. Please take some time to work through this Quick
Start so that you can become familiar with the process of recording on the
D1600mkII.
Step 1: Quick Recording
Connect your guitar, record your performance on a track, and then play
it back.
Step 2: Overdubbing
While listening to the performance you recorded, record an additional
guitar performance. We’ll also explain how you can record a keyboard in
stereo, or record vocals using the virtual tracks.
Step 3: Mixdown
Apply effects to each track, and adjust the volume and EQ. Then use the
master effect to apply finishing touches to the entire song.
Step 4: Mastering
Create a two-track master from the song you mixed-down in Step 3. Then
write this stereo master track to CD-R to create your own original CD.
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Step 1: Quick Recording
1. Make connections
1. Turn the top panel [TRIM] knob to set the INPUT 8 input level to the
minimum position.
2. Connect your guitar to the front panel [GUITAR IN] jack.
3. Connect your headphones to the front panel [PHONES] jack. If you
are using monitor speakers, connect them to the rear panel [MONITOR OUT L/R] jacks.
2. Turn on the power
1. Connect the power cable to the D1600mkII, and then plug it into an
AC outlet.
2. Set the top panel [MASTER] fader to “–∞.”
3. Press the rear panel [POWER ON] key.
The D1600mkII will enter standby mode, and the STANDBY LED
will light.
4. Press the top panel [POWER] key.
The power will turn on, and the following display will appear.
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
Connection diagram (→p.10)
Before you turn off the power,
refer to “2. Turning the power
on/off” (→p.11).
13
Step 4: Mastering
Page 22
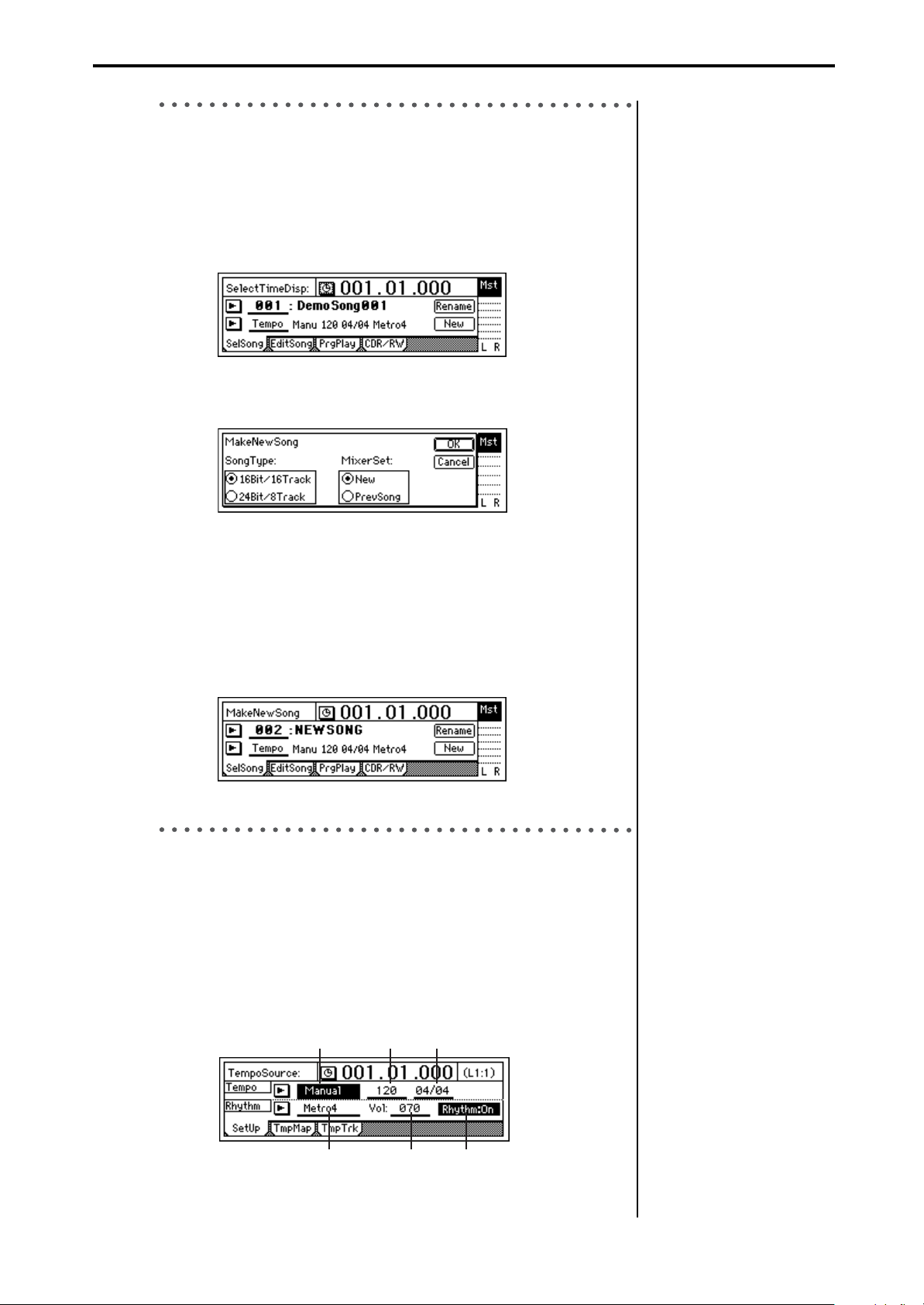
3. Create a new song
b
Before you can record a new composition, you must first create a new
“song” on the D1600mkII.
1. Press the [SONG/CD] key. Then press the “SelSong” tab to access the
[SONG/CD] “SelSong” tab page.
You can also access the “SelSong” tab page by pressing the [SONG/
CD] key several times.
2. Press the “New” button.
The “MakeNewSong” dialog box will appear.
3. Use “Song Type” to specify the bit depth and number of tracks for
the song you want to create, and use “Mixer Set” to specify the mixer
settings.
In this example, press the “Song Type” radio button “16Bit/16Track.”
In the “Mixer Set” area, press the “New” radio button.
4. Press the “OK” button.
This creates a song named “NEWSONG.” If any songs exist already,
the new song will be created following the existing songs.
You can press the “Rename”
utton and input a name for the
song. “2. Naming a song”
(→p.35)
4. Rhythm
Now let’s make rhythm settings so that you can listen to a rhythm pattern
while you record.
Rhythm settings
1. Press the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] key. Then press the “Setup” tab to
access the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “Setup” tab page.
You can also access the “Setup” tab page by pressing the [TEMPO/
RHYTHM] key several times.
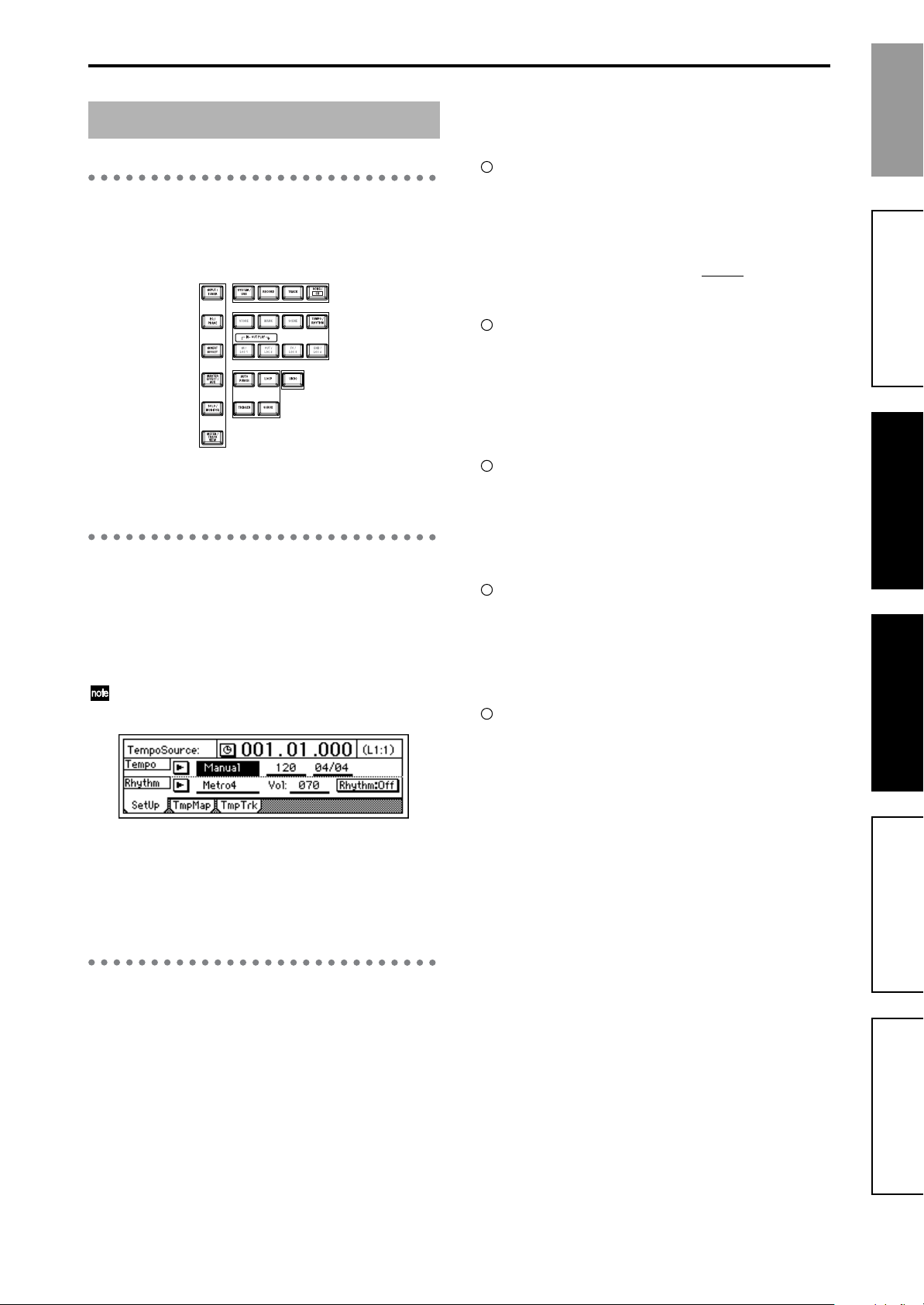
TempoSource Tempo Beat
SelRhythm RhythmVol
14
Page 23
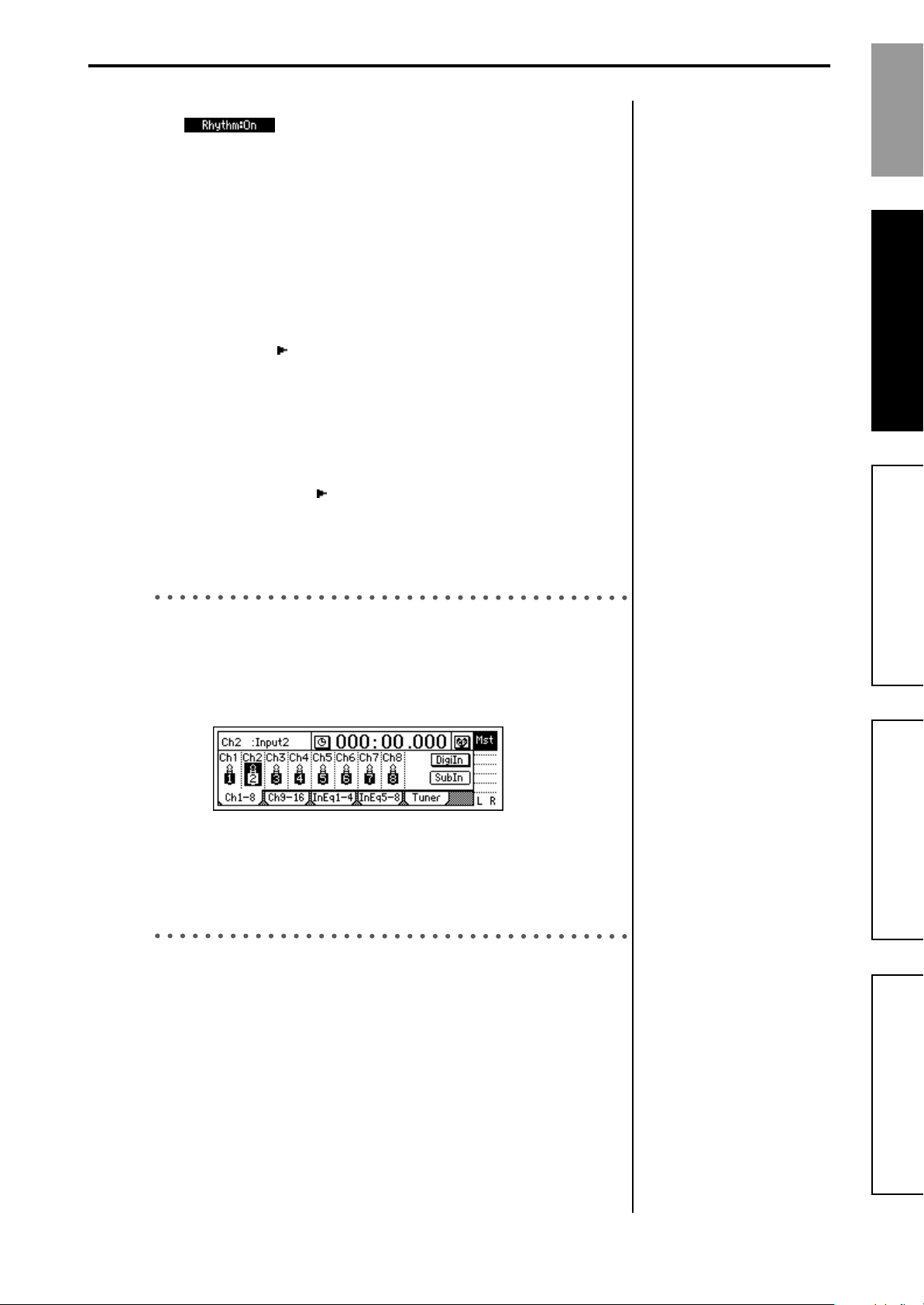
2. Press the “Rhythm” button to make the display read
“”.
The [TEMPO/RHYTHM] key will light.
3. Raise the [MASTER] fader and verify that you hear the rhythm. Use
the front panel [PHONES LEVEL] knob to adjust the volume of your
headphones, or use the top panel [MONITOR OUT LEVEL] knob to
adjust the volume of your monitor speakers.
Set the tempo, time signature, rhythm pattern, and rhythm volume
1. Select “TempoSource” and turn the [VALUE] dial to select the tempo
source.
For this example, select “Manual.”
You can select the tempo source in the dialog box that appears when
you press the “ ” button. Use the radio buttons to make your selection, and press the “OK” button.
2. Select “Tempo” and turn the [VALUE] dial to adjust the tempo.
3. Select “Beat” and turn the [VALUE] dial to specify the time signature.
4. Select “SelRhythm” and turn the [VALUE] dial to select the rhythm
pattern you want to use.
You can select the rhythm pattern in the dialog box that appears
when you press the “ ” button. Use the radio buttons to make your
selection, and press the “OK” button.
5. Select “Vol” and turn the [VALUE] dial to adjust the volume of the
rhythm.
If you want the tempo, time signature, and/or rhythm pattern
to change during the song, create a Tempo Map. (→p.72)
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Step 1: Quick Recording
5. Assign the input to a mixer channel
Assign the input to a mixer channel
1. Press the [INPUT/TUNER] key to access the [INPUT/TUNER]
“Ch1–8” tab page.
2. Select the “Ch 8” icon, and turn the [VALUE] dial to select “INPUT
8.”
Since the front panel [GUITAR IN] jack is “INPUT 8,” the input from
the [GUITAR IN] jack has been assigned to track channel 8.
6. Adjust the level
Adjust the level of the input signal while you watch the LCD screen.
[TRACK STATUS] key setting
Set the [TRACK STATUS] key to INPUT for the track you are using.
1. Press the front panel [TRACK STATUS] key of track 8 to select the
INPUT setting (LED lit orange).
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
15
Step 4: Mastering
Page 24

Pre-fader level display
2. Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key. From the screen that appears,
press the “ ” button to open the dialog box.
3. From the Select DisplayMode dialog box, press the “PreFaderLev”
radio button and press the “OK” button; the pre-fader screen will
appear.
The ch.8 level meter will move when you play your guitar.
4. While watching the level meter, adjust the INPUT 8 [TRIM] knob so
that the level meter goes as high as possible without reaching “CLP”
when you play your guitar most loudly.
Use the [TRIM] knob to set the input level so that the peak indicator
(the LED near the [TRIM] knob) lights when the volume is loudest.
7. Check the sound
Make settings so that you can hear the sound through your headphones
or monitor speakers.
1. Raise the front panel [CHANNEL 8] fader to unity gain (0 dB).
2. Press the [SOLO/MONITOR] key to access the [SOLO/MONITOR]
“Monitor” tab page.
3. Press the “MasterLR” button to select “ ”.
4. While you play your guitar, gradually raise the [MASTER] fader.
You will hear the sound of the guitar from your headphones or monitor speakers.
8. Record
Next you will record your guitar performance on track 8 while watching
the status of the recording track on the track view screen.
Let’s start by recording a backing guitar part.
[TRACK STATUS] key setting
Specify the track on which you will record.
1. Press the front panel track 8 [TRACK STATUS] key to choose REC
(LED lit red).
16
Page 25

Check the record mode
2. Press the [RECORD] key to access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab
page. Verify that “Select RecMode” is set to “Input.”
Track View settings
3. Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key.
4. Press the “ ” button to open the “Select DisplayMode” dialog box.
5. Press the “TrkView1–16” radio button, and then press the “OK” button to display the track view screen.
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Step 1: Quick Recording
Start recording
6. Make sure that the counter display is at the beginning of the song.
At the beginning of the song, the counter value will be “001.01.000”
or “000:00.000”.
7. Press the [REC] key.
The D1600mkII will be in record-ready mode, and the [REC] and
[PLAY] LEDs will blink.
8. When you are ready to perform, press the [PLAY] key.
Recording will begin; begin performing on your instrument. During
recording, the [REC] and [PLAY] LEDs will light.
In the track view screen, the bar will start moving at the point you
press the [PLAY] key.
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
For details on the counter display and how to move to a different time, refer to “Changing
the time location” (→p.46).
If you want to record the
rhythm, refer to “3. Recording
the rhythm” (→p.72).
If you want to use Trigger
Recording, refer to “6. Other
recording methods” (→p.43).
17
Step 4: Mastering
Page 26
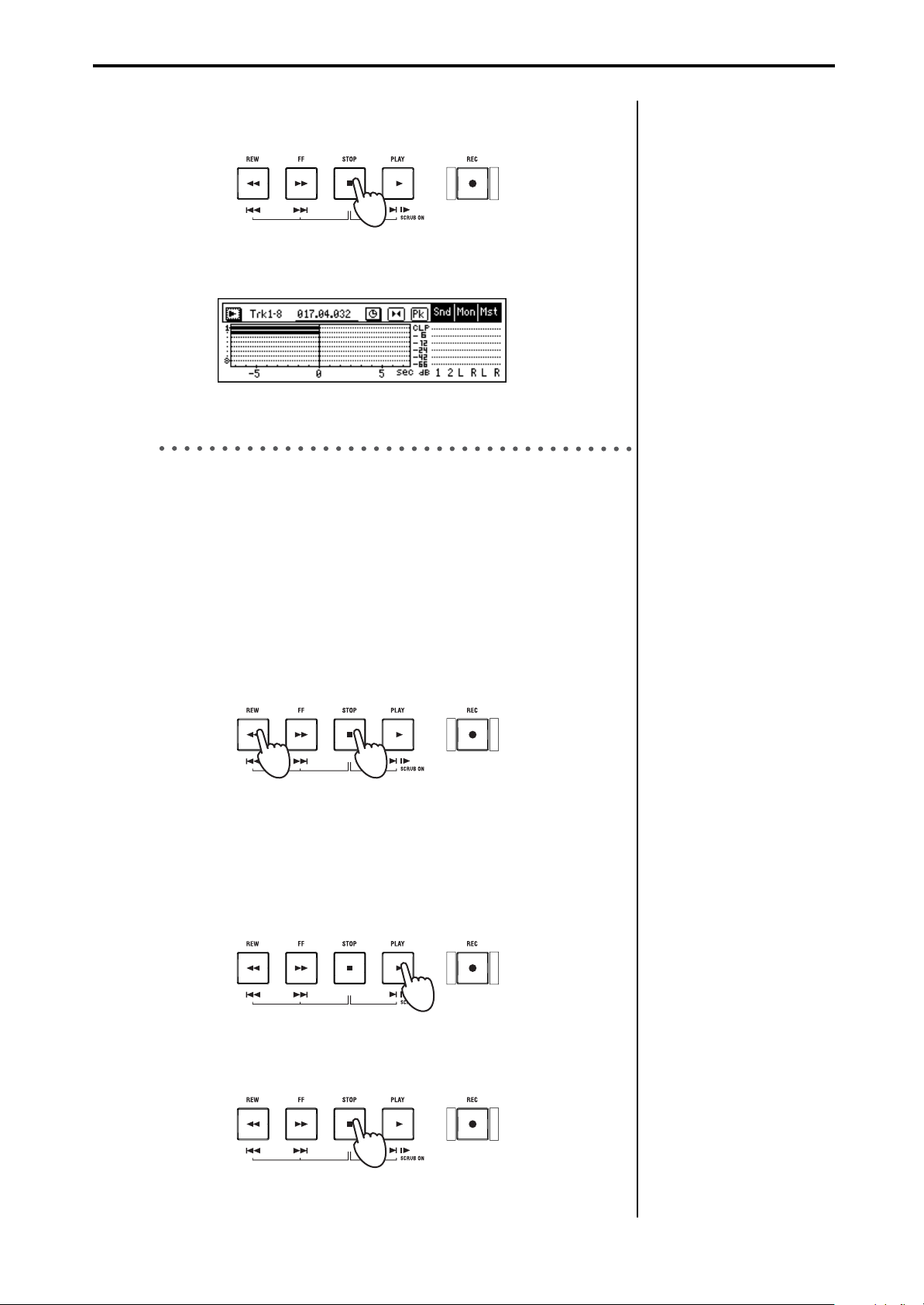
9. When you have finished performing, press the [STOP] key.
Recording will stop, and the [REC] and [PLAY] LEDs will go dark.
In the track view screen, the region from the beginning to the end of
your audio recording is displayed as a thick line.
Areas in which you did not perform are also displayed as a thick line.
9. Play back
Now we’ll play back the recorded song from the beginning.
[TRACK STATUS] key setting
Specify the track that you want to play back.
1. Press the front panel track 8 [TRACK STATUS] key to select PLAY
(LED lit green).
To stop the rhythm, access the
[TEMPO/RHYTHM] “Setup”
tab page and press the
“Rhythm” button to turn it
“Off.”
Playback
2. Hold down the [STOP] key and press the [REW] key.
The counter time will move to the beginning of the song.
3. Press the [PLAY] key.
Playback will begin, and the [PLAY] LED will light. Use the [MASTER] fader to adjust the volume.
You can use the front panel [PHONES] knob to adjust the volume of
your headphones, or the top panel [MONITOR OUT LEVEL] knob to
adjust the volume of your monitor speakers.
4. To stop playback, press the [STOP] key.
The [PLAY] LED will go dark.
For details on the counter display and how to change the
time location, refer to “Changing the time location” (→p.46).
18
Page 27
Step 2: Overdubbing
“Overdubbing” is the process of recording additional performances on
other tracks while you listen to the previously-recorded performance or
rhythm.
For this example we’ll overdub an additional performance on guitar or
keyboard while listening to the performance you recorded in Step 1.
We’ll also explain how to record your keyboard in stereo, and how to
record on a virtual track. We will also apply an effect to your keyboard.
1. Record a guitar
While listening to the performance you recorded in Step 1, you can play
a guitar phrases, riffs, or solos, and record them. In this example we’ll
overdub on track 7.
Assign the input to a mixer channel
Assign the input of the guitar connected to INPUT 8 to mixer channel 7.
1. Press the [INPUT/TUNER] key to access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch
1–8” tab page.
2. Select the “Ch 7” icon and use the [VALUE] dial to select “INPUT 8.”
Check the level
When recording on more than one track, you don’t have to readjust the
level each time if you are playing the same instrument in the same state;
if so, proceed to the next step. Adjust the level only if you have switched
sounds or instruments.
1. Press the track 7 [TRACK STATUS] key to select INPUT (LED lit
orange).
2. In the [METER/TRACK VIEW] page, select “PreFaderLev.”
3. Turn the INPUT 8 [TRIM] knob while watching the level meter.
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
Step 2: Overdubbing
Check the sound
1. Set the [CHANNEL 7] fader to unity gain (0 dB).
2. In the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page, make sure that the
“MasterLR” button is “On.”
3. While playing your guitar, slowly raise the [MASTER] fader and
check the sound in your headphones, etc.
[TRACK STATUS] key settings
You’ll need to select the appropriate status for the recording track, playback track, and other tracks.
1. Press the track 7 [TRACK STATUS] key to select REC (LED lit red).
2. Press the track 8 [TRACK STATUS] key to select PLAY (LED lit
green).
3. Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the other tracks to select MUTE
(LED dark).
Step 4: Mastering
19
Page 28
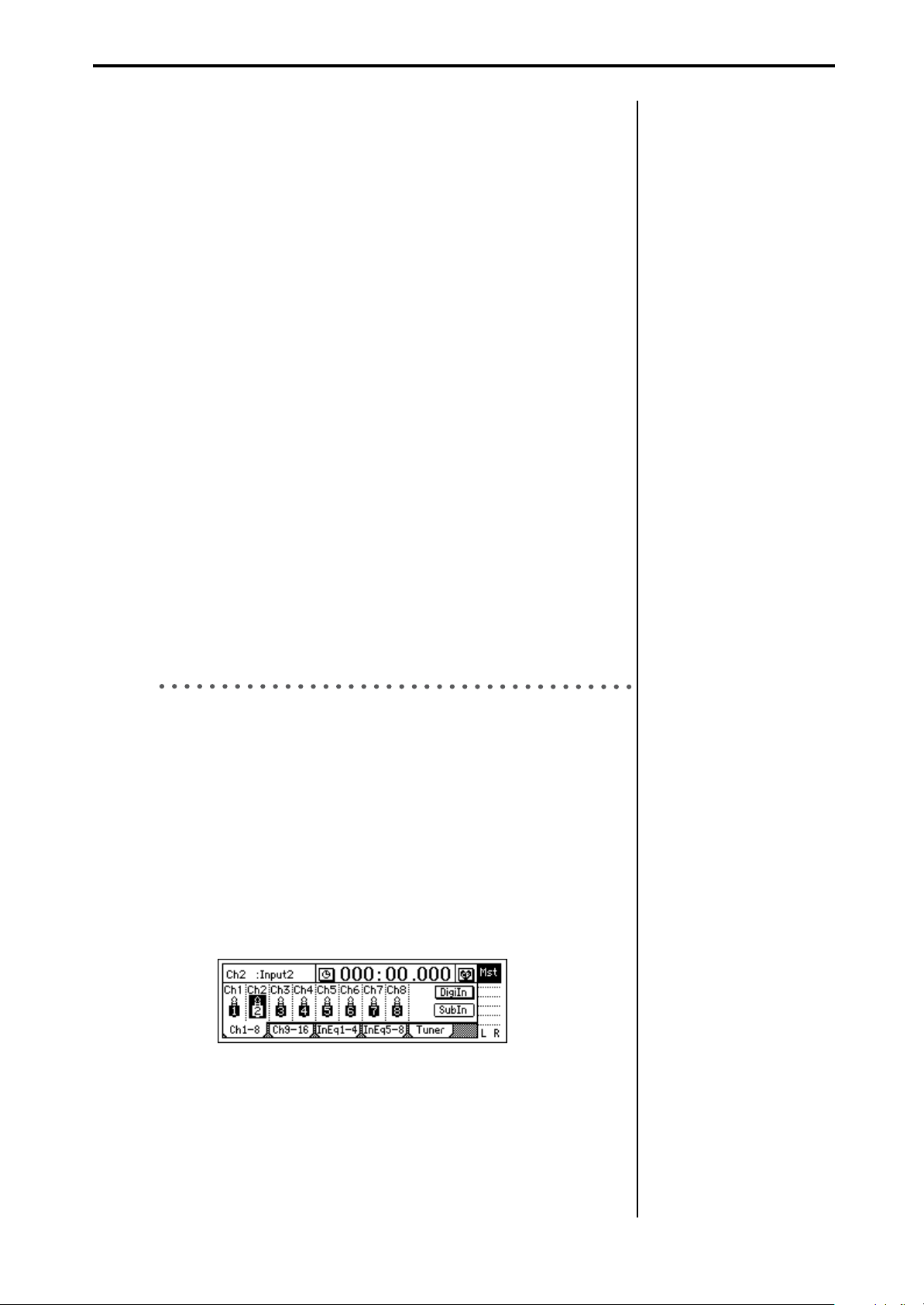
Check the recording mode
If you’ve already checked the recording mode, there’s no need to check it
again; if so, proceed to the next step.
1. Access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page, and make sure that
“Select RecMode” is set to “Input.”
Record
1. Set the recording-start location to the beginning of the song.
At the beginning of the song, the counter value will be “001.01.000”
or “000:00.000”.
To move to the beginning of the song, press the counter value and
turn the [VALUE] dial to the beginning of the song (“001.01.000” or
“000:00.000”).
Alternatively, you can hold down the [STOP] key and press the
[REW] key to move to the beginning of the song. However if you are
already at the beginning of the song, holding down the [STOP] key
and pressing the [REW] key will take you to the preceding song, so
check the current location before you use this method.
2. Hold down the [REC] key and press the [PLAY] key to begin recording.
3. When you have finished recording, press the [STOP] key.
Play back
1. Hold down the [STOP] key and press the [REW] key to return to the
beginning of the song.
2. Press the [TRACK STATUS] key to select PLAY for the track you just
recorded.
3. Press the [PLAY] key to play back.
For details on the counter display and moving the time location, refer to “Changing the time
location” (→p.46).
2. Record a keyboard
Here’s how to record a keyboard in stereo.
Connect your keyboard
1. Use the top panel [TRIM] knobs to set INPUT 5 and INPUT 6 to the
minimum setting (+4 dB).
2. Lower the [MASTER] fader, and connect your keyboard to the
[INPUT 5] and [INPUT 6] jacks.
Assign the inputs to mixer channels
1. Press the [INPUT/TUNER] key to access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch
1–8” tab page.
2. Select the “Ch 5” icon, and use the [VALUE] dial to select “INPUT 5.”
In the same way, select the “Ch 6” icon and use the [VALUE] dial to
select “INPUT 6.”
When using stereo input, you
will be able to edit tracks and
effects most efficiently if you
select an odd-numbered and
even-numbered pair of inputs
(1–2, 3–4) and assign them to
adjacent mixer channels.
20
Page 29

Check the level
Assign the audio from your keyboard to tracks, and check the levels.
1. Press the track 5 and 6 [TRACK STATUS] keys to select INPUT (LEDs
lit orange).
2. Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key. In the screen that appears,
press the “ ” button to open the dialog box.
3. In the Select DisplayMode dialog box, select the “Pr eFaderLev” radio
button and press the “OK” button.
When you play your keyboard, the channel 5 and 6 level meters will
move.
4. While watching the level meters, turn the INPUT 5 and 6 [TRIM]
knobs so that the level is as high as possible without allowing the
level meters to reach “CLP” when you play your keyboard most
loudly.
Set the input level by turning the [TRIM] knob so that the peak indicator (the LED near the [TRIM] knob) lights when the volume is
loudest.
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
Step 2: Overdubbing
Check the sound
1. Set the [CHANNEL 5, 6] faders to unity gain (0 dB).
2. In the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page, make sure that the
“MasterLR” button is “On.”
3. While playing your keyboard, slowly raise the [MASTER] fader.
You will hear the sound through your headphones or monitor speakers.
Set the [TRACK STATUS] keys
Set the status of the recording tracks, playback tracks, and other tracks.
1. Press the track 5 and 6 [TRACK STATUS] keys to select REC (LED lit
red).
2. Press the track 7 and 8 [TRACK STATUS] keys to select PLAY (LED
lit green).
3. Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the remaining tracks to select
MUTE (LED dark).
Make effect settings
Use the [INSERT EFFECT] “InsAsn,” “InsEff1,” and “InsEff2” tab pages
to make insert effect settings. For details on the procedure, refer to “4.
Make insert effect settings” (→p.24).
Step 4: Mastering
21
Page 30
Check the recording mode
If you have already checked the recording mode, there’s no need to check
it again; if so, proceed to the next step.
1. Access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page, and make sure that
“Select RecMode” is set to “Input.”
Record
1. Set the recording-start position to the beginning of the song.
At the beginning of the song, the counter value will be “001.01.000”
or “000:00.000”.
2. Press the [REC] key, and then press the [PLAY] key to start recording.
3. When you have finished recording, press the [STOP] key.
Play back
1. Hold down the [STOP] key and press the [REW] key to return to the
beginning of the song.
2. Press the [TRACK STATUS] key to set the recorded tracks to PLAY.
3. Press the [PLAY] key to play back.
3. Record vocals on virtual tracks
In this example, we’ll record several “takes” of vocals on the virtual
tracks of track 4.
For details on the counter display and on how to change the
time location, refer to “Changing the time location” (→p.46)
Connect a mic
1. Turn the top panel [TRIM] knob to set INPUT 4 to the minimum level
(+4 dB).
2. Lower the [MASTER] fader, and then connect your mic to the
[INPUT 4] jack. If you are using a condenser mic, you must connect
it to the [INPUT 4] jack and then turn the phantom power switch on.
Never turn on the phantom power switch before you connect the
mic. If you connect or disconnect a mic with the phantom power
turned on, you may damage your equipment.
Assign the input to a mixer channel
1. Press the [INPUT/TUNER] key to access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch
1–8” tab page.
2. Select the “Ch 4” icon, and use the [VALUE] dial to select “INPUT 4.”
Check the level
Assign the vocal signal to the track, and check the level.
1. Press the track 4 [TRACK STATUS] key to select INPUT (LED lit
orange).
2. Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key. In the screen that appears,
press the “ ” button to open the dialog box.
3. In the Select DisplayMode dialog box, select the “Pr eFaderLev” radio
button, and then press the “OK” button.
4. Turn the INPUT 4 [TRIM] knob while you watch the level meter.
22
Page 31

Check the sound
1. Set the [Channel 4] fader to unity gain (0 dB).
2. In the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page, make sure that the
“MasterLR” button is “On.”
3. Slowly raise the [MASTER] fader while you sing into the mic.
Check the sound in your headphones or monitor speakers.
[TRACK STATUS] key settings
Set the status for the recording track, playback tracks, and remaining
tracks.
1. Press the track 4 [TRACK STATUS] key to select REC (LED lit red).
2. Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the playback tracks to select
PLAY (LED lit green).
3. Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the remaining tracks to select
MUTE (LED dark).
Effect settings
If desired, make insert effect settings in the [INSERT EFFECT] “InsAsn,”
“InsEff1,” and “InsEff2” tab pages.
For details, refer to “4. Make insert effect settings” (→p.24).
Check the recording mode
If you have already checked the recording mode, there’s no need to check
it again; if so, proceed to the next step.
1. Access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page, and make sure that
“Select RecMode” is set to “Input.”
Select a virtual track
1. Press the [TRACK] key to access the [TRACK] “Vtr 1–8” tab page.
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
Step 2: Overdubbing
2. In the top line of the screen, press a virtual track number (“4a” in the
example shown here), and turn the [VALUE] dial to select “4b”.
The selected virtual track and the already-recorded virtual tracks are
highlighted. For details, refer to “2. Recording on virtual tracks”
(→p.40).
When you turn on the power, virtual tracks “1a,” “2a,” “3a”... are
selected automatically. In other words if you record a track without
selecting a virtual track, recording will occur on “1a,” “2a,” “3a”...
etc.
Record
1. Set the recording-start position to the beginning of the song.
At the beginning of the song, the counter value will be “001.01.000”
or “000:00.000”.
2. Press the [REC] key, and then press the [PLAY] key to start recording
on virtual track “4b”.
3. When you have finished recording, press the [STOP] key.
4. Select another virtual track as described in “Select a virtual track”
(above), and continue recording additional takes on other virtual
tracks.
For details on the counter display and on how to change the
time location, refer to “Changing the time location” (→p.46)
Step 4: Mastering
23
Page 32

Play back a virtual track
1. Hold down the [STOP] key and press the [REW] key to return to the
beginning of the song.
2. Press the [TRACK STATUS] key to set the recorded tracks to PLAY.
3. Press the [PLAY] key to play back.
At this time, the virtual tracks selected in the [TRACK] “Vtr 1–8” tab
page will play.
You can select different virtual tracks in the [TRACK] “Vtr 1–8” tab
page while you play back, and compare the different takes.
4. When you have finished listening, press the [STOP] key.
4. Make insert effect settings
If you want to apply effects while you record, make insert effect settings
as follows.
Select an insert effect
1. Press the [INSERT EFFECT] key to access the [INSERT EFFECT]
“InsAsn” tab page.
2. Press the “ ” button located at the right of “Assign” to open the
“Select EffectAssign” dialog box.
Here you will select whether the insert effect will apply to input or to
playback.
3. Select the “Input” radio button, and press the “OK” button.
Select the “Input” radio button when you want to apply the insert
effect to the input from an input jack.
4. Press the “ ” button located below “Select EffType” to open the
“Select Effect Type” dialog box.
5. Select the “2in2out x 2” radio button, and press the “OK” button.
“2in2out x 2” means that you can use two stereo-in/stereo-out
effects.
24
Page 33

Specify the destination for the processed sound
In this example we’ll explain how to apply an insert effect to a stereoconnected keyboard.
Connect your keyboard to the [INPUT 5] and [INPUT 6] jacks, and assign
the audio to mixer channels 5 and 6. For our example, we will place insert
effect 1 between [INPUT 5] jack and mixer channel 5, and between
[INPUT 6] jack and mixer channel 6.
1. Press the “ ” button below “InsertTo” to open the “Select
InsertEffect AssignChannel” dialog box.
Insert Effect
SelectChInput
In this dialog box you can specify the mixer channel to which the
sound processed by the insert effect will be sent.
For example, the dialog box shown above is set as follows.
The upper left indicates [INPUT 1] jack → insert effect 1 → mixer
channel 9. This means that the audio signal from the [INPUT 1] jack
is processed by insert effect 1 and sent to mixer channel 9.
The upper right indicates [INPUT 3] jack → insert effect 2 → mixer
channel Off. This means that the audio signal from the [INPUT 3]
jack is processed by insert effect 2, but not sent to a mixer channel. In
other words, insert effect 2 is not used.
2. Press the “SelectCh” field for insert ef fect 1, and use the [VALUE] dial
to select the destination.
For this example, select “5”.
Below it, [INPUT 6] jack → insert effect 1 → “6” will be selected automatically.
3. Press the “OK” button in the dialog box.
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
Step 2: Overdubbing
Select an effect program
1. Press the [INSERT EFFECT] key to access the [INSERT EFFECT]
“InsEff1” tab page.
EffectNumber
2. Press the “Ef fectNumber” button, and turn the [VALUE] dial to select
the effect program you want to use.
Effect Program List (→p.166)
Step 4: Mastering
25
Page 34

Step 3: Mixdown
“Mixdown” is the process of applying insert effects, master effects, and
EQ etc. to the sound of each track to adjust the overall balance, and
combining everything into two-track stereo data.
1. Apply effects
Here’s how to assign an insert effect to a mixer channel so that the effect
is applied to the playback of the track.
[TRACK STATUS] key settings
Specify the tracks that you want to play back.
1. Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the playback tracks to select
PLAY (LED lit green).
Make insert effect settings
1. Access the [INSERT EFFECT] “InsAsn” tab page.
2. Press the “ ” button at the right of “Assign” to open the “Select
EffectAssign” dialog box.
3. In the dialog box, press the “PlayTrack” radio button, and then press
the “OK” button.
Select the “PlayTrack” radio button when you want to apply the
insert effect to the output of the track channel during mixdown.
4. Press the “ ” button below “SelectEffType” to open the “Select
EffectType” dialog box.
5. In the dialog box, select an effect type and press the “OK” button.
For this example, select “1in1out x 4”.
“1in1out x 4” means you can use four monaural-in/monaural-out
effects.
Specify the destination of the processed sound
Here’s how to apply the insert effect to the recorded vocal.
1. Press the “ ” button below “InsertTo” to open the “Select Insert
Effect AssignChannel” dialog box.
Insert Effect
26
SelectTr
In this dialog box you can specify the track channel to which the
insert effect will be applied.
Page 35

For example, the dialog box shown above portrays the following settings.
The upper left indicates track channel 3 → ef fect 1 → mixer channel 3.
This means that the track 3 audio signal will be processed by effect 1,
and sent to mixer channel 3.
The upper right indicates Off → ef fect 2 → Off. This means that effect
2 is not used.
2. Press the effect 1 “SelectTr” field, and use the [VALUE] dial to select
the track channel to which you will apply the effect.
For this example, select “4”.
3. Press the “OK” button in the dialog box.
Select an effect program
1. Press the [INSERT EFFECT] key to access the [INSERT EFFECT]
“InsEff1” tab page.
2. Select the “EffectNumber” button, and use the [VALUE] dial to select
the effect program you want to use.
EffectNumber
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Effect Program List (→p.166)
You can also press the [PLAY] key and select an effect during playback.
2. Apply EQ (equalizer)
Here’s how to make EQ settings for each mixer channel.
1. Press the [EQ/PHASE] key, and from the [EQ] “Eq 1–4,” “Eq 5–8,”
and “Eq 9–12” tab pages, select the tab page that contains the EQ you
want to adjust.
Each channel has a three-band EQ with Lo, Mid, and High, and you
can adjust the frequency of the Mid range.
Low EQ gain (L)
High EQ gain (H)
Mid EQ gain (M)
Mid EQ center frequency (F)
2. Select each EQ icon and turn the [VALUE] dial to specify the value.
The numerical value is shown in the upper left of the screen.
Negative (–) gain settings will cut the corresponding frequency
range, and positive (+) gain settings will boost it.
Increasing the center frequency value will raise the center frequency,
and decreasing this value will lower the center frequency.
3. Adjust the EQ while the song plays back.
4. When you have finished making adjustments, press the [STOP] key.
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
EQ (→p.48)
Step 3: Mixdown
Step 4: Mastering
27
Page 36

3. Apply master effects
Here’s how you can apply master effects to the desired track channels.
The D1600mkII contains two master effects, letting you apply two differ-
ent effects simultaneously. This means that you can simulate complex
acoustic spaces that could not be created by a single effect. To regulate the
amount of the master effects, adjust the send and return controls.
In this example, we’ll apply the master effects “ReverbHall” and “Reverb
Room,” and adjust the depth of the effects by adjusting the send level
from each mixer channel, the return level, and the return balance.
Select master 1
1. Press the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] key to access the [MASTER
EFFECT/AUX] “MstEff1” tab page.
2. Press “EffectNumber” and turn the [VALUE] dial to select a master
effect.
For this example, select “M001” ReverbHall.
Master effect 1 send and return settings
1. In the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] “MstEff1” tab page, adjust the
“RetLev” (return level) and “RetBal” (return balance).
For this example, set “RetLev” to “100,” and “RetBal” to “CNT.”
The return level is the volume sent from master ef fect 1 to the master
bus. Raising this value will produce a deeper effect.
The return balance is the left/right volume balance of the sound
returned from master effect 1 to the master LR bus.
2. Access the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] “MstEff1” tab page.
3. Set the [CHANNEL] faders to unity gain (0 dB) for the mixer channels to which you want to apply the effect, and press the [PLAY] key
to play back the song.
4. In the screen, select the “Send” icon for each channel and turn the
[VALUE] dial to adjust the send level of that channel.
Watch the level meter in the screen, and make adjustments so that
“CLP” does not appear.
The send level is the amount of volume sent to master effect 1.
Effect Program List (→p.166)
28
Page 37

5. While you listen to the song, access the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX]
“MstEff1” tab page.
Watch the level meter in the screen, and adjust the return level so that
“CLP” does not appear.
6. When you have finished making adjustments, press the [STOP] key.
Select master effect 2, and make send and return settings
1. Access the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] “MstEff2” tab page.
2. Press “Ef fectNumber,” and use the [VALUE] dial to select the desired
master effect.
For this example, select “M003” ReverbRoom.
3. Adjust the master effect 2 send and return settings as described in
“Master effect 1 send and return settings.”
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
Step 3: Mixdown
29
Step 4: Mastering
Page 38

Step 4: Mastering
“Mastering” is the process of applying a final effect and EQ to the mixeddown song in order to make the overall volume and tone consistent.
We’ll also explain how you can use the CD-R/RW drive to create an audio CD of your song.
1. Apply an effect to the entire song
We’ll check the panning and volume for each track of the completed
song, and apply a final effect to the entire song.
As the final effect, you will normally use a dynamics-type effect program
(such as compression) to make the overall level consistent. By applying a
multi-band limiter or similar effect, you can give the sound a finishing
touch of quality.
[TRACK STATUS] key settings
Make settings for the playback tracks.
1. Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys for the playback tracks to select
PLAY (LED lit green).
Song adjustments
1. Play back the song from the beginning.
2. While you listen to the song, turn the [PAN] knob of each playback
track to adjust its stereo position. Use the [CHANNEL] faders to
adjust the levels.
If you want to see the meter for each fader in the LCD screen, press
the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key, press the “ ” button in the upper
left of the screen, select “PostFaderLev” in the dialog box that
appears, and press the “OK” button.
Final effect settings
1. Access the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] “FinalEff” tab page.
EffectNumber
2. Select “EffectNumber,” and use the [VALUE] dial to select the
desired final effect.
3. If you press the button located at the right of “EffectNumber,” the
structure of the final effect you selected will be displayed as icons.
You can press one of these icons to make detailed settings. When you
have finished making settings, press the “OK” button to return to the
[MASTER EFFECT/AUX] “FinalEff” tab page.
Check the song
1. Press the [PLAY] key to play back the song, and check how the effect
sounds.
2. If you want to edit the effect parameters, refer to step 3 of “Final
effect settings.” When you have finished editing, press the [STOP]
key.
Effect Program List (→p.166)
30
Page 39

2. Create the master track
When you create an audio CD, the data of track 1 and track 2 is
what will be written to the CD.
You will create the master track by combining the song data into tracks 1
and 2.
If your song consists of only one or two tracks, copy or swap the track
data into tracks 1 and 2.
If your song consists of multiple tracks, bounce the track data to combine
it into tracks 1 and 2. “Bounce” refers to the process of combining multiple tracks of data into a smaller number of tracks.
Here we will explain how to create the master track by bouncing the completed song to tracks 1 and 2.
For details on how to copy a track, refer to “Track editing” (→p.61).
[TRACK STATUS] key settings
Specify the status of the recording tracks, playback tracks, and the remaining tracks.
1. Press the track 1 and 2 [TRACK STATUS] keys to select REC (LED lit
red).
2. Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the playback tracks to select
PLAY (LED lit green).
3. Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the remaining tracks to select
MUTE (LED dark).
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
Adjust the recording level
The master track will be created with the level and volume balance you
specify here; this will be the data that is written to create the audio CD.
1. Play back the song from the beginning.
Make sure that all the tracks in the song sound as you intend.
If you used virtual tracks to record several takes, you will need to
select the virtual track that you want to use in the final version of the
song.
2. Use the [MASTER] fader to adjust the level.
Adjust the level so that the master LR level meter does not indicate
“CLP” at any point in the entire song.
Preparations for bounce-recording
1. Press the [RECORD] key to access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab
page.
2. In the “Select RecMode” field, choose “Bounce.”
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
31
Step 4: Mastering
Step 4: Mastering
Page 40

3. Access the [RECORD] “Bounce” tab page, and set “BounceMode” to
“16Tr→2Tr”.
“16Tr→2Tr” means that sixteen tracks will be bounced to two tracks.
4. Press the field at the right of “RecordVirtualTrack,” and turn the
[VALUE] dial to select “h”.
The bounced data will be placed in the virtual track you selected
here. In other words, you will be bounce-recording on virtual track
“1h” of track 1 and virtual track “2h” of track 2.
If tracks “1h” and “2h” already contain data, choose different virtual
tracks.
Bounce-record
1. Go to the beginning of the song.
2. Press the [REC] key and then the [PLAY] key to begin resampling.
3. When you are finished recording, press the [STOP] key.
Play back
1. Use the [TRACK STATUS] keys to set tracks 1 and 2 to PLAY. For all
tracks other than tracks 1 and 2, either lower the faders or set their
[TRACK STATUS] to MUTE.
2. In the [TRACK] “Vtr1–8” tab page, select virtual tracks “1h” and
“2h” for tracks 1 and 2.
If you selected virtual tracks other than “h” in “Preparations for
bounce-recording,” select those virtual tracks instead.
3. Play back the song from the beginning.
The final effect will be applied to the song in duplicate when you
play back here. This is because the final effect was applied to the
bounce-recorded data, and is also being applied to the playback
you are hearing. Set the final effect to NO EFFECT so that you can
hear the actual state of the song (i.e., as it was actually bouncerecorded).
If tracks “1h” and “2h” already
contain data, and you select “h”
here, the data in “1h” and “2h”
will play back during bouncerecording. If you want to keep
the data of tracks “1h” and “2h”,
choose different virtual tracks.
32
3. Write your song to a CD
Here’s how to create an original CD by writing your song to CD-R.
Since CD-RW discs may sometimes not be playable in an audio
CD player, we recommend that you use CD-R discs when creating audio CDs.
Creating an audio CD will require the same amount of free space on the
hard disk as occupied by your song (the total of the two tracks).
For example in order to write a five-minute stereo song to an audio CD,
there must be at least five minutes of stereo (ten minutes of monaural)
worth of recordable free space on the hard disk.
If there is no region of silence at the beginning of your song (the
“zero time” location), the beginning of your song may “drop out”
when you write it to a CD and play back. You can prevent this by
inserting a region of about 0.5 seconds of silence at the beginning
of the song. For details on how to do this, refer to “Inserting blank
data: Insert Track” (→p.63).
For details on how to check the
free space on the hard disk, refer
to “1. Select TimeDisp Type”
(→p.91) in “1. COUNTER.”
Page 41

Write to CD-R
When creating an audio CD, the virtual tracks that are currently selected
for tracks 1 and 2 will be used. To verify that the virtual tracks you intend
to write are selected, play back the song or access the [TRACK] “Vtr1–8”
tab page.
1. Insert a blank disc into the CD-R/RW drive.
By “blank disc” we mean an unused CD-R or CD-RW. A CD-RW that
has been used can also be completely erased and used as a blank
disc.
However since CD-RW discs may sometimes not be playable in an
audio CD player, we recommend that you use CD-R discs.
2. Access the [SONG/CD] “CDR/RW” tab page.
Press the “ ” button, and in the screen that appears,
press the “OK” button. Make sure that “CD-R/RW Information”
indicates “BlankDisc” or “song number .” The fr ee space on the disc is
displayed below this.
3. Press the “WriteCD” button.
A message of “Obey Copyright Rules” will appear.
Step 1: Quick Recording Quick Start
4. Select the writing speed.
Select the writing speed that is appropriate for the disc you are using.
For example if the disc you are using is marked as “supports 8x writing,” you can select the “8x” writing speed. “8x” means that the disc
will be written at eight times the conventional playback speed.
Depending on your system, it may not be possible to write at the
selected speed. If so, try a slower writing speed.
5. Carefully read the owner’s manual section “COPYRIGHT WARNING” (→p.iii), and press the “Yes” button if you accept the terms.
The D1600mkII will begin creating an image file.
You can stop creating the image file by pressing the “Abort” button during this time.
Then the D1600mkII will start writing the CD.
If you press the “Abort” button while data is being written to the
CD, the writing will stop. If you were writing a CD-R, that disc
will become unusable. If you were writing a CD-RW, you can
erase the entire disc and use it again as a blank disc.
When writing is completed, the display will indicate “Completed”.
Step 2: OverdubbingStep 3: Mixdown
“3. Erasing the data from a CDRW” (→p.83)
33
Step 4: Mastering
Step 4: Mastering
Page 42

6. Press the “No” button in the dialog box.
b
The [SONG/CD] “CDR/RW” tab page will appear.
If you want to create another
identical CD, press the “Yes”
utton.
If you want to write additional songs, select the next song and then
perform steps 1–6.
7. Press the “Final” button.
A message will ask you to confirm that you really want to finalize the
disc.
A CD is not completed as an audio CD (i.e., cannot be played back
by a CD player) until you finalize the disc.
You cannot write any more songs to a disc that has been finalized.
If you want to write more than one song to a CD, you must write
all of the songs to the disc before pressing the “Final” button to
finalize it.
8. If you are sure you want to finalize the disc, press the “OK” button.
When finalization is finished, a message of “Completed” will appear,
and the CD-R/RW tray will open.
If you want to write songs to
more than one CD, write the
songs to all the CDs, and then
finalize the CDs.
9. Remove the CD and press the “OK” button.
The original CD of your own performance is now completed.
Check the audio CD
1. Play back the CD in an audio CD player.
34
Page 43

Basic operation
Basic
operation
Creating/selecting a song
Here’s how to create a song, assign a name to it, and select songs.
1. Creating a new song
1. Press the [SONG/CD] key to access the “SelSong”
tab page.
2. Press the “New” button.
The “MakeNewSong” dialog box will appear.
3. Select the bit-depth, number of tracks, and mixer
settings for the song you want to create.
Use the “SongType” radio buttons to select the bit
depth and number of tracks.
16Bit/16Track: Create a song for 16-bit recording/
playback. Tracks 1–16 will be available.
24Bit/8Track: Create a song for 24-bit recording/
playback. Tracks 1–8 will be available.
Use the “Mixer Set” radio buttons to select the
desired mixer settings. (→p.109: “SongType,” “MixerSet”)
2. Naming a song
Songs on the D1600mkII have a song number and a song
name.
The song number is a number in the range of 001–100,
assigned in the order in which each song was created.
You can freely specify a song name of up to sixteen
characters.
A newly created song will have a name of “NEWSONG.” We recommend that you assign a different
name so that you will be able to distinguish it from
other songs.
1. Press the [SONG/CD] key to access the “SelSong”
tab page.
2. Press the “Rename” button.
The “RenameSong” dialog box will appear.
3. Modify the song name.
Use the “ “ “ ” buttons to move the cursor in the
song name to the character that you wish to change,
and rotate the [VALUE] dial to modify the name.
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
4. Press the “OK” button.
A song named “NEWSONG” will be created following the last song that currently exists.
The buttons in the LCD screen have the following
function.
“0...9”: Select numerals (e.g., “0”).
“A../a..”: Select alphabetical characters (e.g., “A”).
Press the button once again to select lowercase alphabetical characters (e.g., “a”).
“Symbol”: Select symbols.
“Insert”: Insert a space and move the subsequent
characters backward.
“Space”: Select a space (blank).
“Backsp”: Delete the character before the cursor loca-
tion.
“Delete”: Delete the character at the cursor location.
“ClearAll”: Erase the entire name.
4. Finalize the name.
If you are satisfied with the name you input, press the
“OK” button. To cancel without changing the name,
press the “Cancel” button.
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
35
MIDI
Page 44

3. Selecting another song
You can select an existing song in any of the following
three ways.
To select the preceding or following song
number
• If you hold down the [STOP] key and press the [FF]
key, you will move to the end of the current song.
Doing this at the end of the song will move to the
beginning of the next song.
• If you hold down the [STOP] key and press the [REW]
key while you are located at the beginning of the
current song (e.g., “000:00.000”), you will move to the
beginning of the preceding song. If you are in the
middle of the current song, you will move to the
beginning of the current song.
To make a major change in the song
number
1. Press the [SONG/CD] key to access the “SelSong”
tab page.
Assign audio inputs to the mixer
The D1600mkII has eight analog inputs and one (twochannel) digital input jack. Audio signals from devices
connected to these jacks can be assigned to the various
mixer channels and recorded. The D1600mkII’s rhythm
sounds or the sound from an audio CD played by the CDR/RW drive can also be assigned to the mixer channels.
Input 1
Input 2
Input 3
Input 4
Input 5
Input 6
Input 7
Input 8
L
Digital In
R
L
Rhythm
R
[INPUT/TUNER]“Ch1-8”, “Ch9-16”
L
CD
R
In this section we will explain how to assign each type of
input source to mixer channels, and audition the source.
Ch1: Track 1
Ch2: Track 2
Ch3: Track 3
Ch4: Track 4
Ch5: Track 5
Ch6: Track 6
Ch7: Track 7
Ch8: Track 8
Ch9: Track 9
Ch10: Track 10
Ch11: Track 11
Ch12: Track 12
Ch13: Track 13
Ch14: Track 14
Ch15: Track 15
Ch16: Track 16
2. Select (highlight) “SongNumber
,” and turn the
[VALUE] dial to select the desired song number.
To select from the song list
1. Press the [SONG/CD] key to access the “SelSong”
tab page.
2. Press the “ ” button at the left of the song number.
The song list will appear.
3. In the song list, turn the [VALUE] dial to select the
desired song, and press the “OK” button.
1. Analog inputs
Use the connections and settings most applicable to your
situation.
• Connect a guitar to the [GUITAR IN] jack, and assign it
to mixer channel 8
• Connect a condenser mic audio input source to
[INPUT 2], and assign it to mixer channel 2.
• Connect a keyboard to the [INPUT 3] and [INPUT 4]
jacks, and assign them to mixer channels 9 and 10
If you are using stereo input, you should use adjacent
inputs (1–2, 3–4), and input the signals to adjacent
mixer channels.
Before you proceed, create a new song as described in
“1. Creating a new song” (→p.35).
Connect a guitar to the [GUITAR IN] jack,
and assign it to mixer channel 8
1. Connect your guitar.
Set the [INPUT 8] ([GUITAR IN]) [TRIM] to the
minimum (+4 dB) and lower the [MASTER] fader
before connecting your guitar to the [GUITAR IN]
jack.
2. Select the input channel.
Access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch1–8” tab page.
36
Page 45

Select the “Ch8” icon, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
select “INPUT 8.”
The input from the [GUITAR IN] jack has now been
assigned to mixer channel 8.
3. Assign the input sound to mixer channel 8.
Press the track 8 [TRACK STATUS] key to set it to
INPUT (LED lit orange).
4. Use the trim to adjust the input level.
Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key. Press the “ ”
button to access the dialog box.
Press the “PreFaderLev” radio button, and press the
“OK” button.
Play your guitar to input sound, and the level meter
of Ch.8 will move accordingly. Adjust the INPUT 8
[TRIM] knob while watching the level meter. Raise
the [TRIM] as high as possible without the level
reaching CLP, while playing your guitar.
Connect a mic to [INPUT 2] and assign it to
mixer channel 2
1. Connect a mic.
Set the INPUT 2 [TRIM] to the minimum (+4 dB),
lower the D1600mkII’s [MASTER] fader , and connect
a mic to the [INPUT 2] jack.
If you are using a condenser mic, turn on phantom
power for [INPUT 2] after you connect the mic.
Turn phantom power on only if you are using a
condenser mic.
Phantom power must be turned on after connecting the condenser mic. If you connect or disconnect the mic with phantom power turned on,
your equipment may be damaged.
2. Specify the input channel.
Access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch1–8” tab page.
Select the “Ch2” icon, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
select “INPUT 2.”
The input from the [INPUT 2] has now been assigned
to mixer channel 2.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
5. Audition the sound.
Set the [MASTER] and [CHANNEL 8] faders to unity
gain (0 dB).
Access the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page.
Press the “MasterLR” button to turn it “On” (high-
lighted).
Gradually raise the [PHONES LEVEL] knob or
[MONITOR OUT LEVEL] knob, and listen to the
sound in your headphones or monitor system.
3. Assign the input sound to mixer channel 2.
Press the track 2 [TRACK STATUS] key to select
INPUT (the LED will light orange).
4. Use trim to adjust the input level.
Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key.
Press the “ ” button to access the dialog box. Choose
“PreFaderLev,” press the “OK” button.
When you input sound into the mic, the Ch2 level
meter will move accordingly.
Adjust the input 2 [TRIM] knob while you watch the
level meter. Raise the [TRIM] as high as possible.
Don’t allow the level to reach CLP when you produce
your loudest sound.
5. Audition the sound.
Set the [MASTER] and [CHANNEL 2] faders to unity
gain (0 dB).
Access the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page.
Press the “MasterLR” button to turn it “On” (high-
lighted).
Gradually raise the [PHONES LEVEL] knob or
[MONITOR OUT LEVEL] knob, and listen to the
sound in your headphones or monitor system.
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
37
the system
MIDI
Page 46

Connect a keyboard to the [INPUT 3] and
[INPUT 4] jacks, and assign them to mixer
channels 9 and 10.
1. Connect your keyboard.
Set the [INPUT 3] and [INPUT 4] trim to the minimum (+4 dB) and lower the [MASTER] fader before
connecting your keyboard to the [INPUT 3] and
[INPUT 4] jacks.
2. Select the input channels.
Access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch9–16” page tab.
Select the “Ch9” icon, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
select “INPUT 3.”
Select the “Ch10” icon, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
select “INPUT 4.”
The input from the [INPUT 3] and [INPUT 4] jacks
has now been assigned to mixer channels 9 and 10.
3. Assign the input sound to mixer channels 9 and 10.
Press the track 9/10 [TRACK STATUS] keys to set
each of them to INPUT (LED lit orange).
4. Use the trim to adjust the input level.
Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key.
Press the “ ” button to access the dialog box.
Choose “PreFaderLev” and press the “OK” button.
Play your keyboard to input sound, and the level
meters of Ch.9 and Ch.10 will move accordingly.
Adjust the INPUT 3 and 4 [TRIM] knobs while
watching the level meter. Raise the [TRIM] level as
high as possible, don’t allow the level to reach CLP
when you play your keyboard with maximum velocity.
5. Audition the sound.
Set the [MASTER], [CHANNEL 9] and [CHANNEL
10] faders to unity gain (0 dB).
Access the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page.
Press the “MasterLR” button to turn it “On” (high-
lighted). Gradually raise the [PHONES LEVEL] knob
or [MONITOR OUT LEVEL] knob, and listen to the
sound in your headphones or monitor system.
2. Digital input
The D1600mkII can record a digital audio signal that is
input via the S/P DIF jack.
If you are using the digital input, you will not be able
to use the input from an audio CD played in the CDR/RW drive.
The S/P DIF input has a built-in sampling rate converter .
Sources with sampling rates of 48 kHz or 32 kHz can be
connected directly, and will automatically be converted
to 44.1 kHz.
Inputting audio from a DA T connected to the
[S/P DIF] jack to mixer channels 1 and 2
1. Connect the digital output device.
Lower the [MASTER] fader of the D1600mkII, and
use an optical digital cable to connect the digital output of your DAT to the [S/P DIF IN] jack.
2. Enable the digital input.
Access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch1–8” tab page.
When you press the “DigiIn” button, a message of
“Obey Copyright Rules” will appear.
Carefully read the owner’s manual section “COPYRIGHT WARNING” (→p.iii). If you accept the terms,
press the “Yes” button for the “AreYouSure?”
prompt. Digital input will be enabled.
3. Specify the input channels.
Select the “Ch1” icon, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
select “S/PDIF L.”
In the same way, select “S/PDIF R” for “Ch2.”
The input from the [S/P DIF IN] jack has now been
assigned to channels 1 and 2.
4. Assign the input sound to mixer channels 1 and 2.
Play back the DAT, and press the [TRACK STATUS]
keys of tracks 1 and 2 to set them to INPUT (LED lit
orange).
5. Check the recording mode and input level, and
audition the sound.
Refer to steps 3, 4, and 5 of “Connect a guitar to the
[GUITAR IN] jack, and assign it to mixer channel 8”
(→p.36).
38
Page 47

3. Using the tuner
The D1600mkII has a built-in tuner function.
To tune an instrument
Connect the instrument you want to tune to the [INPUT
8/GUITAR IN] jack.
1. Use “SelectSource” to select the audio source you
want to tune.
In the [INPUT/TUNER] “Tuner” tab page, set
“SelectSource” to “Input8.”
2. Set “Calib
use.
Normally you will use “440 Hz.”
3. Input sound from your instrument, and tune it.
The display shows the note name closest to the pitch
you input. Tune your instrument so that the ●
symbol is located below the triangle (▼) in the
middle.
” to the reference frequency you want to
Recording
This section explains the basic recording procedure on
the D1600mkII.
1. Adjust the recording level, and record
Here’s how to record the audio that you specified in
“Assign audio inputs to the mixer” (→p.36).
If you wish to create a new song and record into it,
refer to “1. Creating a new song” (→p.35). Make sure
that the [RHSL] key is Off. (→p.135)
1. Check the recording mode.
Access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page.
Set “Select RecMode” to “Input” (i.e., the audio input
will be recorded).
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
Recording
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
The pitch difference is displayed in units of cents.
(100 cents = semitone, 1200 cents = 1 octave)
You cannot select this page while recording or
playing. Nor can you record while in this page.
So that the tuner can detect the pitch accurately,
effects will be automatically turned off while this
page is displayed.
To check the pitch of an already-recorded sound
To check the pitch of a desired track, set “SelectSource” to
“Track,” and select the track number in the field located
at the right. Move to the time location at which you want
to check the pitch, and press the [PLAY] key to play back.
The note name and pitch will be detected.
Use the [CHANNEL] fader to set the recording level.
Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key.
Press the “ ” button to select “PostFaderLev,” and
press the “OK” button.
Gradually raise the [CHANNEL] fader, and the level
meter of the input channel will change according to
the input. Raise the level as far as possible without
allowing the level bar to reach “CLP.”
2. Move the current time to the location where you
wish to begin recording.
Start recording from the beginning of the song
(“001.01.000” or “000:00.000”).
3. Press the [TRACK STATUS] key of the track that
you wish to record, to set the status to REC (LED lit
red).
4. Enter record-ready mode.
Press the [REC] key. (The [REC] and [PLAY] LEDs
will blink.)
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
39
the system
MIDI
Page 48

5. Start recording.
Press the [PLAY] key. (The [REC] and [PLAY] LEDs
will light.)
Begin playing.
6. Stop recording.
When you have finished playing, press the [STOP]
key. (The [REC] and [PLAY] LEDs will turn off.)
When you have finished recording, verify that
the performance was recorded correctly.
7. Move to the beginning of the song.
8. Specify the track(s) for playback.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] key of the track you
recorded, to set its status to PLAY (LED lit green).
9. Begin playback.
Press the [PLAY] key. (The [PLAY] LED will light.)
10. Stop playback.
When you are finished playing back, press the [STOP]
key. (The [PLAY] LED will turn off.)
2. Recording on virtual tracks
The D1600mkII has sixteen tracks, and each of these
tracks has eight virtual tracks.
For example when recording a solo part, you can switch
between several virtual tracks to record different
performances on each, and select the best performance
later. Or when using bounce (ping-pong) recording, you
can specify an unrecorded virtual track as the recording
destination, so that you can mixdown into two tracks
without erasing any of the sixteen tracks.
Recorded tracks
Selected track
3. Playback while recording addition tracks: Overdubbing
The process of listening to previously-recorded tracks
while you record additional tracks is called overdub-
bing. For example, this can be used to record a solo while
you listen to previously-recorded backing tracks.
1. Select the playback tracks.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the tracks that
you wish to play back, to set them to PLAY mode
(LED lit green).
2. Select the recording track.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] key of the track that you
wish to record, to set it to REC mode (LED blinking
red).
3. Lower the faders of tracks you are not using.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] key of the tracks that are
not being recorded or played, to set them to MUTE
(LED dark). This will silence the tracks that are not
being recorded or played.
4. Adjust the recording level of the input device, and
record.
Refer to “1. Analog inputs” and “1. Adjust the
recording level, and record” (→p.36, 39)
In the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page, set
“Select Rec Mode” to “Input.”
4. Re-record part of a performance: Punch-in/out
If you make a mistake during part of your recorded
performance, or are not completely satisfied with your
performance, you can re-record just the unsatisfactory
portion without having to record from the beginning of
the song.
“Punch-in” is when you switch the song from playback
to record, and “punch-out” is when you switch the song
from record back into playback.
Recording on a virtual track
1. Select the virtual track.
In the [TRACK] “Vtr1–8” or “Vtr9–16” tab page,
select the track that you wish to record, and use the
[VALUE] dial to select an open virtual track.
2. Adjust the recording level of the input device, and
record.
Refer to “1. Analog inputs” and “1. Adjust the recording level, and record” (→p.36, 39).
40
Manual punch-in/out
Manual punch-in/out is when you manually switch
between punch-in and punch-out.
On the D1600mkII, manual punch-in/out can be performed by pressing the [REC] key or a PS-1 foot switch
(separately sold option) during playback to begin recording, and pressing the [REC] key, [PLAY] key, or foot
switch to end recording.
1. Connect the input device, and adjust the recording
level.
Refer to “1. Analog inputs” and “1. Adjust the recording level, and record” (→p.36, 39).
Page 49

2. Make monitor output settings.
Access the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page.
Select the signal that you wish to monitor. (→p.132)
Turn the “AutoIn” button “On.”
If the “AutoIn” button is “Off”, you will always
hear the input signal that is assigned to the
recording track. If it is “On”, the sound recorded
on that track will be heard during playback, and
the assigned input signal will automatically be
heard during recording.
3. Move the current time to a location earlier than the
point where you wish to begin re-recording.
4. Press the [PLAY] key to begin playback.
The song will play back, and you will hear the sound
of the playback tracks and the track selected for
recording.
5. At the point where you wish to begin re-recording,
press the [REC] key.
Recording will begin (manual punch-in), and you
will begin hearing the external input signal.
6. At the point where you wish to stop re-recording,
press the [REC] key or [PLAY] key.
Recording will stop, and the track will switch back to
playback (manual punch-out). You will begin hearing the track playback.
7. Press the [STOP] key to stop.
After recording, move the current time to a point
earlier than where you began recording, and check
that the recording was satisfactory.
Manual punch-in/out using a foot switch
You can switch between playback and recording by
pressing a PS-1 foot switch (separately sold option).
This allows you to switch between playback and recording while you are performing on an instrument, or when
you are at a distance from the D1600mkII.
1. Connect a foot switch to the [FOOT SW] jack.
2. Access the [SYSTEM/USB] “Control” tab page.
3. Specify the function of the foot switch.
Select “Func (FootSwFunction
4. In “Manual punch-in/out” steps 5 and 6, perform
manual punch-in/out by pressing the foot switch
instead of the [REC] key (you may use either).
You can also use the foot switch to record from the
beginning of the song.
Set the “Func” parameter of step 3 to “Play/Stop.”
Press the [REC] key at the beginning of the song (LED
will blink), and press the foot switch to start recording.
)” to “PunchI/O.”
Auto punch-in/out
Auto punch-in/out is when punch-in and punch-out
occur automatically at pre-specified times.
1. Access the [AUTO PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab page.
2. Register IN (punch-in) as the time at which recording will begin, and OUT (punch-out) as the time at
which recording will end.
For details on registering the IN and OUT times, r efer
to p.46.
In the [AUTO PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab page, you can
press the “Wave” button to register the IN and OUT
points while viewing a waveform display.
The time locations you register will be
overwritten onto the [IN/LOC1] key and [OUT/
LOC2] key.
3. Connect the input device, and adjust the recording
level.
Refer to “1. Analog inputs” and “1. Adjust the recording level, and record” (→p.36, 39).
4. Make monitor output settings.
Refer to “Manual punch-in/out” step 2.
5. Specify the “pre-roll” – the length of playback that
will occur before the recording start location.
In the [AUTO PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab page, press
the “RolTime” button to access the “SetRollTime”
dialog box.
Set “Pr
eRoll” to the desired length of playback before
the beginning of recording. Set “PostRoll
desired length of playback after the end of recording.
Set “Unit
When you have finished making settings, press the
“OK” button to return to the previous page.
6. Turn on the auto punch-in/out function.
In the [AUTO PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab page, press
the “AutoPunch” button to turn it “On.” The [AUTO
PUNCH] key will light.
7. Begin recording.
When you press the [REC] key, the location will move
back from the specified record start time by the
length of the pre-roll time specified by “Pr
the D1600mkII will enter record-ready mode (LED
blinking).
When you press the [PLAY] key, playback will begin.
The track will play back during the pre-roll time, and
will switch to recording at the specified point (IN).
(The [REC] LED will light.)
When the specified end of recording is reached,
recording will end. (The [REC] LED will blink.)
8. Press the [STOP] key to stop.
9. Listen to the performance that you recorded.
” to the desired unit of pre/post-roll time.
After the post-roll time has elapsed, the
D1600mkII will stop and return to the beginning
of the pre-roll time.
” to the
eRoll,” and
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
Recording
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
MIDI
41
Page 50

5. Combining multiple tracks into two: Bounce
You can combine the performances of multiple tracks
into two tracks, thus freeing up the original tracks for
additional recording. This procedure is called bouncing.
You can use this when you wish to play back the performances of more than 16 tracks simultaneously.
You can use bounce recording to do the following things.
• Combine 16 tracks of audio, and overwrite-record
them onto two tracks.
• Combine 16 tracks of audio, and record them onto two
unused virtual tracks.
• Record 14 tracks of audio and two external input
signals onto the remaining two tracks.
• Combine multiple external input sources, and record
them on two tracks.
When you use a CD-R/RW drive to create an audio
CD, the data of tracks 1 and 2 will be written to the
CD, so you must combine your completed song into
tracks 1 and 2.
You can also mix down your completed song to two
tracks of the D1600mkII, instead of mixing down to
an external two-channel recorder.
Combining 16 tracks of audio and
overwriting them onto 2 tracks
As an example, here’s how to combine the audio of
tracks 1–16, and overwrite-record the result onto tracks 1
and 2.
1. Select bounce recording as the recording mode.
Access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page.
Select “Bounce” (bounce recording).
2. Select the bounce mode.
Access the [RECORD] “Bounce” tab page.
Set “BounceMode” to “16Tr→2Tr.”
3. Choose the currently selected tracks for recording.
Set “RecordVirtualTrack” to “Current.”
4. Select the tracks that you wish to record.
Set the status of the tracks to be recorded (tracks 1
and 2) to REC (LED lit red). Set the remaining tracks
(3–16) to PLAY (LED lit green).
5. Adjust the stereo positions of the playback tracks.
Press the [PLAY] key, and rotate the [PAN] knob to
adjust the stereo positions of channels 1–16.
6. Adjust the playback/recording levels.
Use the [CHANNEL] faders to adjust the playback
level.
Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key.
Press the “ ” button to access the dialog box. Select
“PostFaderLev” so that you can view the meter display for each fader.
7. Use the [MASTER] fader to adjust the recording
level.
When you are finished making adjustments, press the
[STOP] key.
8. Move the current location to the beginning of the
song.
9. Begin bounce recording.
Press the [REC] key to enter record-ready mode (LED
blinking), and then press the [PLAY] key to begin
recording (LED lit).
10. When recording is finished, press the [STOP] key to
stop.
11. Listen to the recording.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys of the recording
tracks (1 and 2) to set them to PLAY (LED lit green).
Either lower the faders of the other channels, or turn
the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Solo” tab page “1” and “2”
settings “On.”
Press the [PLAY] key to listen to the playback, and
then press the [STOP] key to stop.
Recording 16 tracks of audio to 2 virtual
tracks that are not currently selected
As an example, here’s how the audio of tracks 1–16
(virtual track “a” selected for all tracks) can be recorded
to virtual track “b” of tracks 1 and 2.
Perform bounce recording as described in “Combining 16 tracks of audio and overwriting them
onto 2 tracks”. However in step 3, change the
“Record Virtual Track” setting to “b,” so that the
recording will occur on virtual track “b.”
To listen to the result of the recording, select virtual
track “b.”
Access the [TRACK] “Vtr1–8” tab page, and set
“SelectVirtualTrack” to “1b” and “2b” for tracks 1
and 2.
Recording 14 tracks of audio and 2
external input sources on the remaining 2
tracks
Here’s how the audio of tracks 1–14 and the audio inputs
from INPUT 1 and 2 can be recorded on tracks 15 and 16.
1. Specify the input channels.
Access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch9–16” tab page.
Set “Ch15” to “INPUT1, and set “Ch16” to
“INPUT2.”
2. Set the recording mode to bounce recording.
Access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page.
Select “Bounce” (bounce recording).
3. Select the bounce mode.
Access the [RECORD] “Bounce” tab page.
Set “BounceMode” to “14Tr+2In→2Tr.”
4. Choose the currently selected tracks for recording.
Set “RecordVirtualTrack” to “Current.”
5. Select the tracks for playback and recording.
Press each [TRACK STATUS] key to set the playback
tracks (1–14) to PLAY (LED lit green) and the record-
ing tracks (15 and 16) to REC (LED lit red).
6. Adjust the stereo positions of the playback tracks
and the input sources.
Press the [PLAY] key, and rotate the [PAN] knob to
adjust the stereo positions of channels 1–14. Set channel 15 to the left, and channel 16 to the right.
42
Page 51

7. Adjust the playback/input levels.
Use the [CHANNEL] faders to adjust the playback
level and input level.
Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key.
Press the “ ” button to access the dialog box. Select
“PostFaderLev” so that you can view the meter display for each fader.
8. Adjust the recording level.
Use the [MASTER] fader to adjust the recording level.
When you are finished making adjustments, press the
[STOP] key.
9. Start bounce recording.
Refer to steps 8–11 of “Combining 16 tracks of audio
and overwriting them onto 2 tracks” (→p.42).
After recording or track editing, you can use Undo to
return the data to the state before recording or track
editing. After returning to the state before recording,
don’t forget to set tracks 15, 16 back to virtual track
“a.”
Record eight external input audio sources
onto two tracks
As an example, here’s how the audio sources being input
to INPUT 1–8 can be overwritten onto tracks 1 and 2.
1. Specify the input channels.
Access the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch1–8” tab page.
Assign “Ch1”–“Ch8” respectively to “INPUT1”–
“INPUT8.”
2. Select bounce recording as the recording mode.
Access the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page.
Select “Bounce” (bounce recording).
3. Select the bounce mode.
Access the [RECORD] “Bounce” tab page.
For “BounceMode,” select 14Tr+2In→2Tr.”
4. Record on the currently selected tracks.
Set “RecordVirtualTrack” to “Current.”
5. Select the tracks for recording and for audio input.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] key to set the recording
tracks (1 and 2) to REC (LED lit red), set the other
input tracks (3–8) to INPUT (LED lit orange), and set
the remaining tracks (9–16) to MUTE (LED dark).
6. Adjust the panning of the input sources.
Rotate the [PAN] knobs to adjust the stereo position
for 1–8.
7. Adjust the input levels.
Use the [CHANNEL] faders to adjust the input levels.
Press the [METER/TRACK VIEW] key.
Press the “ ” button to open the dialog box. In the
dialog box, select “PostFaderLev,” and you will be
able to view a meter display for each fader.
8. Adjust the volume level.
Use the [MASTER] fader to adjust the recording level.
9. Begin mix recording.
Refer to steps 8–11 of “Combining 16 tracks of audio
and overwriting them onto 2 tracks” (→p.42).
6. Other recording methods
Trigger recording
This is a function that uses the input level (trigger) to
initiate recording. Recording will begin at the instant that
sound is input to the D1600mkII.
1. Connect the input device, and set the recording
level.
Refer to “1. Analog inputs” and “1. Adjust the recording level, and record” (→p.36, 39).
2. Select trigger recording.
Access the [TRIGGER] “Trigger” tab page, and turn
“TriggerRec” On (the [TRIGGER] key will light).
3. Press the [REC] key to enter record-ready mode
(LED blinking).
4. Begin playing.
When the input level exceeds the threshold level
(“Threshold”), recording will begin automatically.
Refer to “Thr
(→p.121)
You can use the Rehearsal function to check the
threshold level.
5. When you have finished playing, press the [STOP]
key to stop.
eshold” and “PreTrigTime.”
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
Recording
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
43
the system
MIDI
Page 52

Loop recording
When using auto-punch recording, you can use Loop recording to record repeated takes over the same section,
and then use undo/redo to choose the best take.
If you turn “Loop” “On” during auto-punch recording,
the IN–OUT region will be recor ded r epeatedly (looped).
At this time, playback will occur before and after the IN–
OUT region for the lengths specified by the [AUTO
PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab page settings for “RolTime”
(“Pr
eRoll” and “PostRoll”).
1. Register the region (IN–OUT) that you wish to
record. (→p.46)
This setting can also be made using “Wave” in the
[LOOP] “Loop” or [AUTO PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab
pages.
2. Connect the input device, and adjust the recording
level.
Refer to “1. Analog inputs” and “1. Adjust the recording level, and record” (→p.36, 39).
3. Specify how the sound will be output for monitoring.
Refer to “Manual punch-in/out” step 2. (→p.40)
4. Set the pre-roll and post-roll.
In the [AUTO PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab page, select
“RolTime.”
Set “Pr
eRoll” to specify the length of playback prior
to the beginning of recording, and set “PostRoll
specify the length of playback after the end of recording. Set “Unit
post-roll times are set.
When you have made these settings, press the “OK”
button.
5. In the [AUTO PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab page, turn
“Auto Punch” “On.” (The [AUTO PUNCH] key will
light.)
6. In the [LOOP] “Loop” tab page, turn “Loop” “On.”
7. Begin recording.
When you press the [REC] key, the D1600mkII will
locate to the beginning of the pre-roll time preceding
the IN (recording start) point, and will enter recordready mode. (The [REC] key LED will blink.)
Press the [PLAY] key to begin playback.
Playback will occur for the pre-roll time, and record-
ing will begin at the IN time. (The [REC] key LED
will light.)
When the OUT time is reached, recording will end,
and playback will continue for the post-roll time.
(The [REC] key LED will blink.)
Then the D1600mkII will locate to the beginning of
the pre-roll time, and the same operations will be
repeated.
To stop, press the [STOP] key at a point outside of the
recording area (IN–OUT).
8. Listen to the recorded content.
Use the undo/redo function to select the best take.
” to select the units in which the pre/
” to
9. Press the [UNDO] key.
A list will show the latest and previous recordings.
10. Rotate the [VALUE] dial to select what you believe
to be the best take from the list.
11. Press the “Undo” button to execute the Undo.
The selected take will be recalled.
12. Play back, and verify that you selected the correct
take.
If the [AutoPunch] “AtPunch” tab page “AutoPunch” setting is “On” when you press the [PLAY]
key, the region between the recording start (IN) and
recording end (OUT) points will play back as a loop.
13. If you decide to cancel the Undo, press the “Redo”
button to return to the “Level00” take.
The undo operation you executed in step 11 will be
cancelled.
Press the “OK” button to return to the previous
screen.
In addition to the recording methods described above,
the following possibilities are available when recording
on the D1600mkII. For details refer to the page listed.
• Apply EQ to the audio being recorded. (→p.48)
• Apply effects to the audio being recorded. (→p.54)
• Listen to the internal rhythm while recording your per-
formance. (→p.72)
• Record the internal rhythm. (→p.72)
• Rehearse the recording. (→p.135)
44
Page 53

Playback
This section explains basic playback on the D1600mkII,
and also how to use program playback.
1. Playback
1. Select the track(s) for playback.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] keys for the tracks that
you wish to play, to put them in PLAY (LED lit
green).
2. Move to the time location from which you wish to
playback.
For details on changing the time location, refer to
p.46.
3. Begin playback.
Press the [PLAY] key. (The [PLAY] LED will light.)
4. Stop playback.
Press the [STOP] key. (The [PLAY] LED will turn off.)
You can also use a PS-1 foot switch (separately sold
option) to start and stop playback. (→p.91)
2. Program play
Here’s how you can play back multiple songs in the order you specify.
In addition to using this to play songs in a desired order,
this function is also convenient when mixing down to
DAT or MD.
Setting up a program
1. Access the [SONG/CD] “PrgPlay” tab page.
2. Select the first song.
Use the scroll buttons to select “01” in the program
play list, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to select a song.
If you wish to change the drive, press the “Drive”
button. Select the desired drive in the “Drive Select”
screen.
3. Select the second, third, and subsequent songs in
the same way.
To delete a song from the list, select the song and
rotate the [VALUE] dial to select “– – –.”
The program play list is maintained until you turn off
the power.
The program play list can be played only when the
“PrgPlay” tab page is displayed.
Playing the program Playlist
1. Access the [SONG/CD] “PrgPlay” tab page.
2. Press the [PLAY] key to begin playback.
Songs will be played in the order of the list, starting
with the first song of the program. During playback
you can press the [FF] key to skip to the next song, or
the [REW] key to skip to the beginning of the current
song or (if you are already at the beginning of the current song) to the beginning of the previous song.
3. Press the [STOP] key to stop playback.
3. Other playback options
Loop playback
This function repeatedly plays the IN–OUT region of the
song. This is convenient when you wish to audition that
region, and is also used in conjunction with auto punch
recording to perform loop recording.
1. Select the playback track.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] key of the playback
track(s) to select PLAY (LED lit green).
2. Register the desired region (IN–OUT) for loop playback. (→p.46)
You can also set this by using “Wave” in [LOOP]
“Loop” or [AUTO PUNCH] “AtPunch” tab page.
3. Access the [LOOP] “Loop” tab page, and turn the
“Loop” button “On.”
4. Begin loop playback.
When you press the [PLAY] key, playback will begin
from the IN location, and repeat over the IN–OUT
region.
5. Press the [STOP] key to stop.
In addition to the playback methods described above, the
following playback methods are also available on the
D1600mkII. For details refer to the page given.
• Apply EQ to the playback audio. (→p.48)
• Adjust the level and pan of the playback audio.
(→p.48)
• Apply effects to the playback audio. (→p.55)
• Play the built-in rhythms together with the playback.
(→p.71)
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
Playback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
45
the system
MIDI
Page 54

Changing the time location
This section explains how you can move the counter that
shows the current location within the song.
Using the [FF] or [REW] keys
Moving backward
Press the [REW] key to move toward the beginning
of the song. If you hold down the key, you will
rewind continuously.
You can also rewind during playback.
1. Switching the counter display
You can switch the time display type shown by the
counter.
1. Press the “ ” button located at the left of the
counter to access the “Select TimeDisp Type” dialog
box.
2. Select the type of time units that you wish to view,
press the “OK” button.
You can select one of the following four types of
display.
• ___.__.___ “measures” . “beats” . “1/96 of a beat”
• ___:__.___ “minutes” : “seconds” . “1/1000 of a second”
• ___:__.__F “minutes” : “seconds” . “1/30 of a second”
• ___.__ Free “minutes” . “seconds”
In order for the “__.__ Free” display to accurately
indicate the remaining time, you must set the
recording track [TRACK STATUS] to REC, and
set the counter display to “FreeTime.” When you
do so, the remaining recording time will be
displayed according to the number of tracks that
are set to REC.
(remaining available
recording time)
Moving forward
Press the [FF] key to move toward the end of the
song. If you hold down the key, you will fast-forward
continuously.
You can also fast-forward during playback.
Moving to the beginning of the song
While in the middle of the song, hold down the
[STOP] key and press the [REW] key to return to the
beginning of the song.
Moving to the end of the song
While in the middle of the song, hold down the
[STOP] key and press the [FF] key to jump to the end
of the song.
Using the locate keys to move
(LOC1, LOC2, LOC3, LOC4)
You can register specific times in the locate keys, and
jump instantly to those times.
Up to four locate points can be registered for each song.
Use the [IN/LOC1], [OUT/LOC2], [TO/LOC3], and
[END/LOC4] keys.
In addition to recalling the locate times that you register, these keys are also used to specify the time locations for auto punch recording (IN/OUT times) and
for track editing (the editing region). For details on
the various locate functions, refer to p.118.
Registering a locate point
1. Move the current time to the location that you wish
to register.
Use the counter (“Counter”) or the [FF]/[REW] keys
to change the current time.
2. Press the [STORE] key to capture the selected time
location.
2. Moving the current time location
Using the counter
1. Select a page in which the counter is displayed in
the upper part of the LCD screen, such as the
[SONG/CD] “SelSong” tab page.
2. Select the portion in the counter that you wish to
change to a new location.
3. Rotate the [VALUE] dial to change the time.
46
3. Register the time location you captured.
Press one of the [IN/LOC1], [OUT/LOC2], [TO/
LOC3], or [END/LOC4] keys to register the saved
location in that key. The registration will be completed as soon as you press the key.
Even if you perform steps 2 and following during playback or recording, the time location at
the moment you pressed the [STORE] key will be
preserved, and can be registered in a locate point.
Moving to a locate point
When you press a previously-registered [IN/LOC1],
[OUT/LOC2], [TO/LOC3], or [END/LOC4] key, you
will move to the registered location.
Page 55

Using marks to move the time location
You can register a specific location in a mark, and then
move instantly to the registered location.
A name can be assigned to each mark, and used to navigate within a song.
Up to 100 marks can be registered in each song.
Registering a mark
1. Move the current time to the location that you wish
to register as a mark.
Use the counter or the [FF]/[REW] keys to change the
current time.
2. Press the [STORE] key to capture the time location.
3. Register the time location you captured.
Press the [MARK] key to register the captured time
location as a mark. The registration will be completed
at the moment you press the key. Marks will be
renumbered in order of time.
Even if you perform steps 2 and following during playback or recording, the time location at
the moment you pressed the [STORE] key will be
captured, and can be registered in a mark.
3. Using scrub playback etc. to
find a precise time location
By using the Scrub function, the Play From/To function,
or the Slow Play function, you can accurately find the
location where an audio region begins, or set a locate
time or mark time with greater precision.
Using the Scrub function
1. Press the [TRACK STATUS] key of the track that
you wish to search, setting its track status to PLAY
(LED lit green).
2. Press the [SCRUB] key to turn the Scrub function
“On” (key lit).
3. Use “TrackSelect” to select the track that you wish
to play.
4. Select “Loc,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial to find the
location while listening to the audio.
The audio will play back in correspondence with the
rotation of the [VALUE] dial.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
time location
Changing the
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
Moving to a mark location
1. Access the [MARK] “Mark” tab page.
2. Use “MarkNumber
3. Press the “Recall” button to recall the mark.
You will move to the time location of that mark.
” to select the desired mark.
Deleting a mark
Undo is not available after deleting a mark.
1. Access the [MARK] “Mark” tab page.
2. Use “MarkNumber
wish to delete.
3. Press the “Delete” button to access the dialog box.
4. Verify the “mark number to be deleted” in the
upper left. If you wish to delete it, press the “Yes”
button to delete it. If you decide not to delete it,
press the “No” button.
To delete all marks, press the “SelectAll” button to
turn it “On.” Then press the “Yes” button to delete
the marks.
” to select the mark that you
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
Naming a mark
•Press the “Rename” button to access the “Rename-
Mark” dialog box. For the rename procedure, refer to
“2. Naming a song” (→p.35).
• When you have assigned a name, press the “OK” but-
ton.
the system
MIDI
47
Page 56

Using the mixer
Here you can adjust various mixer settings such as
volume, tone, pan, recording and playback, to create the
desired levels for your song.
For details on adjusting the effects, refer to p.53.
1. Adjusting the volume
The input or recording/playback volume is adjusted by
the [CHANNEL] faders. Raise or lower the faders to
adjust the volume. (→p.134)
The volume can be adjusted from silence (–∞) to unity
gain (0 dB) to +12 dB gain.
Normally, you should set the faders at unity gain (the
position where the input signal is output at the same
volume) and then lower the faders for any channels
that are too loud, rather than raising the faders of
channels that are too soft. This will reduce the possibility of clipping at the final stage, and is the most effective way to mix.
• When Pairing is on, use the odd-numbered channel
fader to make adjustments. (→p.49)
•Volume settings can be registered in a scene. (→p.50)
2. Adjusting the stereo position
Rotate the [PAN] knob to adjust the stereo position of
each channel.
Channel 1–16 [PAN] knobs
Rotating the knob toward the L position will place the
sound toward the left, and rotating it toward the R position will place the sound toward the right.
Normally, vocals and bass are located in the center,
guitar at the left or right, and piano at the opposite
side from guitar.
• When Pairing is on, use the odd-numbered channel
knob to make adjustments. (→p.49)
• These settings can be registered in a scene. (→p.50)
If the pan is paired (=Balance) for channels 1/2–15/
16, set the odd-numbered [PAN] of the paired channels to the center when you wish to input to tracks 1/
2–15/16 and record in stereo.
If you use EQ excessively by boosting the EQ gain of
a channel to the maximum setting, the overall mix
will become unbalanced. EQ can be used in the “cut”
(Minus) direction as well.
Applying EQ to the track playback
• When Pairing is on, use the odd-numbered channel
“Eq” to make adjustments. (→p.49)
• These settings can be registered in a scene. (→p.50)
1. Select the tab page that contains the EQ you wish to
adjust.
Select from the [EQ/PHASE] “Eq1–4,” “Eq5–8,”
“Eq9–12” and “Eq13–16” tab pages.
2. Select the desired EQ.
For each channel, the EQ controls are arranged as follows.
• High EQ gain (H): upper right icon
• Low EQ gain (L): upper left icon
• Mid EQ gain (M): lower right icon
• Mid EQ center frequency (F): lower left icon
3. Adjust the gain and center frequency.
Adjusting the gain in the negative (–) direction will
cut the signal, and adjusting it in the positive (+)
direction will boost it.
Increasing the center frequency value will raise the
frequency, and decreasing the value will lower the
frequency.
High EQ, Low EQ
• Select “Hi EQ Gain (H)” or “Low EQ Gain (L)” of
the channel you want to adjust, and turn the
[VALUE] dial to adjust the gain. The numerical
value is shown in the upper left of the screen.
Mid EQ
• Select “Mid EQ Center Frequency (F)” of the chan-
nel you want to adjust, and turn the [VALUE] dial
to specify the center frequency. The numerical
value is shown in the upper left of the screen.
• Select “Mid EQ Gain” of the channel you want to
adjust, and turn the [VALUE] dial to adjust the
gain. The numerical value is shown in the upper
left of the screen.
3. Using EQ to adjust the tone
The tone of each channel can be adjusted by a three-band
equalizer (EQ).
•To adjust the input sound (analog), use the Input EQ
([INPUT/TUNER] “InEq1–4,” “InEq5–8” tab pages).
This will affect the sound that is recorded.
•To adjust the track playback sound, use the EQ ([EQ/
PHASE] “Eq1–4,” “Eq5–8,” “Eq9–12,” “Eq13–16” tab
pages).
EQ can be used to cut a frequency range in which unwanted noise (hiss) is heard, or to boost/cut the low
or high range to correct the tone.
Normally, you should make EQ settings so that the
48
audio is heard more clearly.
Applying input EQ to the analog inputs/
Recording with input EQ
You can apply input EQ to the analog inputs (EQ cannot
be applied to the digital input), and record the sound that
has been adjusted by the EQ.
1. Access the page that includes the channel to which
you wish to apply EQ.
Select the [INPUT/TUNER] “InEq1–4” tab page.
Page 57

2. Input an audio signal, and adjust it to an appropriate level.
Refer to “1. Analog inputs” and “1. Adjust the recording level, and record” (→p.36, 39)
Verify that the level meter on the left side of the LCD
screen moves when you hear the sound.
3. For each “InputEQ,” select the gain settings and
mid EQ center frequency, and rotate the [VALUE]
dial to adjust them.
Refer to step 2 and step 3 of “Applying EQ to the
track playback” (→p.48).
4. Record the sound as adjusted by the EQ.
Refer to “1. Adjust the recording level, and record”
(→p.39).
4. Pairing
Adjacent odd and even-numbered channels (1–2, 3–4, 5–
6, 7–8, 9–10, 11–12, 13–14, 15–16) can be paired, so that
changing a value for the odd-numbered channel will
simultaneously change the value for both channels.
It is convenient to use mixer pairing for stereo-recorded
channels.
Pairing is valid for the following settings.
• [TRACK STATUS] keys
• EQ (channel EQ)
• EffSnd 1 + 2 (effect send)
• AuxSend (auxiliary send)
• [PAN] knobs
• [CHANNEL] faders
With the exception of the [TRACK STATUS] keys
and the [CHANNEL] faders, you can select whether
or not pairing will be enabled for a parameter. This
selection is made simultaneously for both Effect
Sends 1 and 2.
1. Access the “Select Pair” screen.
Press the “ ” (SelChPair) button found in the
[INPUT/TUNER], [EQ/PHASE], or [INSERT
EFFECT] pages to access the “Select ChannelPair”
screen.
2. Select the channels for which you wish to enable
pairing.
Press a “1 2”–“15 16” button to turn it “On” (highlighted as “ ”).
5. Monitor settings
In order to monitor the audio from the D1600mkII, you
will need to connect a set of powered monitor speakers
etc. to the [MONITOR OUT L/R] jacks, or connect headphones to the [PHONES] jack.
Select the signal for monitoring
1. Select the signal that you wish to monitor.
Access the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page.
Normally you will select “MasterLR.”
Press the “MasterLR” button to turn it “On” (high-
lighted).
If “Solo” is selected, the solo function will take
priority. Defeat “Solo” before you make your
selection.
2. Select input monitoring.
During playback you will hear the playback tracks of
mixer channels whose [TRACK STATUS] is set to
PLAY (LED lit green). For mixer channels whose
[TRACK ST ATUS] is REC (LED lit red), you will hear
the external input sound.
If you press the “AutoIn” button to turn it “On”,
mixer channels whose [TRACK STATUS] is REC
will monitor the track playback during playback,
and will automatically switch to monitoring the
external input sound when recording (and
rehearsing) and when stopped.
3. Adjust the monitor volume.
Use the [MONITOR OUT LEVEL] knob to adjust the
monitor volume of the [MONITOR OUT L/R] jacks,
and use the [PHONES LEVEL] knob to adjust the
monitor volume of the [PHONES] jack.
Adjusting the cue level
Since the [CHANNEL] faders of the D1600mkII adjust
both the recording level of the tracks and the volume
level of each channel, the recording level and the
monitoring level will be the same.
For this reason, a Cue Level function is provided so that
you can adjust the monitoring volume and pan for your
convenience while you record, independently of the master LR volume.
1. Select cue as the monitoring source.
In the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Monitor” tab page, turn
“On” the “Cue” button.
If “Solo” is selected, solo will be given priority.
Defeat “Solo” before you make your selection.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
mixer
Using the
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
3. Select the functions for which pairing will be
enabled.
Select the functions that will be paired for the channels you selected in “Select ChannelPair.”
From “Eq,” “
functions that you wish to enable to turn
tion. To finalize the settings, press the “OK” button.
Send
,” “
Aux
,” and “
Pan
,” press the
on
each func-
the system
MIDI
49
Page 58

2. Adjust the cue level.
Press the “Level” button to access the cue level
adjustment screen. Select the icons for each channel,
and rotate the [VALUE] dial to adjust the volume
level and pan displayed in the upper left.
6. Solo settings
Only the signals whose “Solo” button is “On” will be
sent to the monitor bus. Use this function when you wish
to hear a specific channel out of numerous sources, or to
audition the send audio, etc. The solo signal is output
from the [MONITOR OUT L/R] jacks and the [PHONES]
jack.
7. Registering and playing scenes
Mixer settings you make can be registered as a scene, and
selected automatically as playback progresses.
Frequently-used settings can also be registered and
recalled when desired to reproduce the mixer settings at
another time, or part of the settings can be modified and
overwritten.
Up to 100 scenes can be registered for each song.
The following settings can be registered in a scene.
•EQ
•Effect settings
•EffSnd (effect send)
• AuxSend (auxiliary send)
•[PAN] knob
• [CHANNEL] fader
Scene 1 Scene 2 Scene 3 Scene 4
Intro Verse Chorus Interlude
Select the signal for soloing
1. Select the signal for soloing, and turn Solo “On.”
Access the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Solo” tab page.
Press the desired “Solo” button(s) to turn Solo “On”
for that signal (it will be highlighted). If even one
selection is being soloed, the [SOLO/MONITOR] key
will blink.
You can select more than one signal to solo.
2. Adjust the monitor volume.
Use the [MONITOR OUT LEVEL] knob or [PHONES
LEVEL] knob to adjust the volume level.
To turn solo off
• Access the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Solo” tab page, and
turn the “Solo” button “Off.”
• By pressing the “ClearAll” button, you can turn off all
solo settings.
Outputting the solo signal from master LR
If desired, the solo signal can be output from [MASTER
OUT L/R]. Do this when you wish to output the solo
signal from a monitor system connected to the [MASTER
OUT L/R] jacks.
In the [SOLO/MONITOR] “Solo” tab page, turn the
“SoloToMstOut” button “On” (highlighted).
However, this will automatically be turned off when
you exit the [SOLO/MONITOR] page.
EG
Key
BASS
Chorus 1
Chorus 2
EG
Dr
Vo
Key
BASS
Vo
Chorus 1
Dr
Chorus 2
EG
Key
BASS
Chorus 1
Chorus 2
EG
Dr
Vo
Key
BASS
Vo
Chorus 1
Dr
Chorus 2
The faders and pan knob on the top panel do not
actually move, but you can watch the values change
in the [SCENE] “MixView” tab page.
Registering a scene
1. Move the current time to the location at which you
wish to register the scene.
Use the counter or [FF]/[REW] keys to move. (→p.46)
2. Adjust the mixer settings.
Adjust the [CHANNEL] faders, [P AN] knobs, EQ and
effect settings.
3. Register the scene.
Press the [STORE] key to capture the current time
location.
When you press the [SCENE] key, the registration
destination scene number “SCENE ***” will be
displayed, and the settings will be registered.
Registered scenes are assigned numbers sequentially, starting at the lowest unused number.
Even during playback or recording, you can use
step 3 above to register a scene.
50
Page 59

Automatically switching scenes while a
song plays: Scene Playback
Scenes you registered can be selected automatically during playback at the time locations you specify.
Register each scene at the time location where you
want the mixer settings to change. (→“Registering a
scene”)
1. Turn “SceneRead” “On.”
Access the [SCENE] “ReadDel” tab page.
Press the “SceneRead” button to turn it “On.” When
this is “On”, the [SCENE] key will light.
2. Play back the song.
Move to the desired location, and press the [PLAY]
key to begin playback.
When playback reaches the registered time, the scene
will change automatically.
Recalling a scene
Here’s how to recall mixer settings that you registered in
a scene.
1. Turn “SceneRead” “Off.”
Access the [SCENE] “ReadDel” tab page.
Press the “SceneRead” button to turn it “Off.” When
this is “Off”, the [SCENE] key will turn off.
If “SceneRead” is “On”, it will not be possible to
recall a scene that was registered at a different
time location.
2. Recall the scene.
In the [SCENE] “ReadDel” or “MixView” tab page,
move the cursor to “SceneNumber
[VALUE] dial to select the desired scene. The selected
scene will be recalled.
,” and rotate the
Re-registering a scene at another time
location
Here’s how you can re-register a previously registered
scene at a different time location.
1. Recall the scene that contains the mixer settings you
wish to re-register.
Select the scene as described in “Recalling a scene.”
2. Move the current time to the location at which you
wish to re-register the scene. (→p.46)
3. Register the scene.
Press the [STORE] key, and then the [SCENE] key.
Editing a scene and overwriting it
Here’s how you can modify part of a scene, and overwrite the settings back onto that scene.
1. Recall a scene.
As described in “Recalling a scene,” select the scene
that you wish to modify.
2. Modify the settings of the scene.
Adjust the [CHANNEL] faders, [PAN] knobs, EQ,
and effects as desired.
3. Overwrite the scene.
In the [SCENE] “ReadDel” tab page, make sure that
the number of the scene you modified is selected.
Press the “OvrWrt” button.
A dialog box will ask you for confirmation. When
you press the “Yes” button, the scene will be overwritten onto that number.
Deleting a scene
Here’s how to delete an unwanted scene.
Undo is not available for this operation.
1. Recall the scene.
As described in “Recalling a scene,” recall the scene
that you wish to delete. If you wish to delete all
scenes, select any of the scenes.
2. Delete the scene(s).
In the [SCENE] “ReadDel” tab page, press the
“Delete” button. Verify the “Delete scene number” in
the upper left, and if you wish to delete the scene,
press the “Y es” button to delete the scene. If you pr ess
the “No” button, the scene will not be deleted.
If you wish to delete all scenes, press the “SelectAll”
button to turn it “On.” Then press the “Yes” button to
delete all the scenes.
Moving a registered scene to another time
location
Here’s how to move a registered scene to another time location.
1. Recall the scene.
As described in “Recalling a scene,” recall the scene
that you wish to move.
2. Move the time location of the scene.
Press the “EditLoc” button.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
mixer
Using the
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
Specify the time location in the dialog box and press
the “OK” button to execute the move.
the system
MIDI
51
Page 60

Scene filtering
1. In the [SCENE] “ReadDel” tab page, press the
“Filter” button to display “Select SceneFilter.”
2. Select the parameters whose settings you wish to
disable.
There are two pages of settings, and you can use the
“Next” button to access the next page.
The first page contains settings for the parameters of
each channel. For example you can use the filter to
disable the pan settings for channels 5 and 6 by turning the “5,” “6,” and “Fader” buttons “On.”
The second page contains settings for overall parameters. As in the first page, turn on the parameters that
you wish to disable. Press the “OK” button to finalize
the settings.
3. In the [SCENE] “ReadDel” tab page, turn
“SceneRead” “Off.”
4. Transmit a program change from the external MIDI
device to recall a scene.
When the D1600mkII receives program change #0, it
will recall scene 001. Program changes #0–99 correspond to scene 001–100.
Using MIDI to control scenes
MIDI output
When the scene changes, a scene change message
(program change) will be transmitted. This message will
be transmitted in the following cases.
• When you use “SceneNumber” to switch scenes in the
[SCENE] “ReadDel” tab page
• When you press the [STORE] key and [SCENE] key to
register a scene
• When “SceneRead” is “On” and the scene changes
during playback or recording
MIDI input
If “SceneRead” is “Off”, scene change messages
(program changes) that are received will cause the
D1600mkII to select the scene of the corresponding
number.
If “SceneRead” is “On”, these messages will not be
received, regardless of whether the D1600mkII is
playing, recording, or stopped.
1. Connect the external MIDI device. (→p.87)
2. Make MIDI settings.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “MIDI” tab page, set
“GlobalCh
device that will be transmitting the messages.
To transmit MIDI messages, turn the [SYSTEM/USB]
“MIDI” tab page “ProgChange” “Trans” “On.”
To receive MIDI messages, turn the [SYSTEM/USB]
“MIDI” tab page “ProgChange” “Recv” “On.”
” to the channel of the external MIDI
52
Page 61

Using effects
1. Overview of the effects
On the D1600mkII, you can use up to eight insert effects
that can be inserted into an analog input or mixer channel, two master effects that can be applied to the send
from each channel, and a final effect that can be applied
to master LR as the last stage. Each of these effects are
independent, meaning that you can use a maximum of
eleven effect programs simultaneously.
•Effect algorithms
total of 98
•Effect programs
Presets (192) User (192)
Insert effects I000, I001–I128 U001–U128
Master effects M000, M001–M032 u001–u032
Final effects F000, F001–F032 u033–u064
Examples of using the insert effects
Various ways in which insert effects can be used for
recording or track playback are described below for each
effect type.
During recording
1 in 2 out x 2 (mono-in/stereo-out × 2)
While recording guitar and bass simultaneously, you
could apply Guitar Multi to the guitar and Bass Multi
to the bass as you record.
While recording two vocals simultaneously, you
could apply separate Vocal Multi programs to each
singer as you record.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
Preset effects contain effect programs created by professional musicians and studio engineers.
User effects can store your own effect programs that you
created by editing a preset effect.
It is not possible to rewrite a preset effect program.
2. Insert effects
The insert effects can be inserted into an analog input or
mixer channel, to apply an effect to the analog input
signal or playback track. Effects can also be applied to a
built-in rhythm sound that is input to a mixer channel.
There are four types of insert effects, as described below.
The available effect programs will depend on the effect
type you select.
The effect type selection is made in [INSERT EFFECT] “InsAsn” tab page “SelectEffType.”
1 in 2 out x 2
These are mono-in/stereo-out or mono-out effect
chains consisting of three to five effects. Two of these
chains can be used. These are ideal for adding spaciousness to a lead guitar or vocal.
2 in 2 out x 2
These are stereo-in/stereo-out effects such as reverb,
chorus, and delay. Two such effects can be used
simultaneously. These are ideal for stereo-input
sources such as keyboard.
While recording vocal and guitar simultaneously, you
could apply V ocal Multi to the vocal and Guitar Multi
to the guitar as you record.
2 in 2 out x 2 (stereo-in/stereo-out × 2)
While recording keyboard and rhythm machine
simultaneously, you could apply St.Chorus to the
keyboard and St.Comp to the rhythm machine as you
record.
Other examples are shown below.
mixer
Using the
Using
Using
effects
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
1 in 1 out x 4
These are mono-in/mono-out effect chains consisting
of two effects. Four such effects can be used simultaneously. These are ideal for sources whose stereo
location is fixed, such as rhythm guitar.
1 in 1 out x 8
Up to eight mono-in/mono-out effects can be used.
This is ideal for sounds with a fixed pan location,
such as drums.
the system
MIDI
53
Page 62

1 in 1 out x 4 (mono-in/mono-out × 4)
While recording four vocals simultaneously, you
could apply Exciter-Comp to voices that lack impact,
and apply Limiter-P4EQ to loud voices as you record.
Other examples are shown below.
1 in 1out x 8 (mono in/mono out × 8)
For example when using eight mics to simultaneously record each instrument of a drum set, you can
apply a separate effect program to each instrument,
such as a Limiter to the bass drum, a Gate to the
snare drum, and an Exciter to the tom while you
record.
During track playback
2 in 2 out x 2 (stereo-in/stereo-out × 2)
Two tracks containing stereo recorded drums etc.
could be processed by St.Comp or St.Limiter to adjust
the dynamics, or Reverb could be applied to create a
broader sense of space.
1 in 1 out x 4 (mono-in/mono-out × 4)
Exciter-Comp or Limiter-P4EQ could be applied to
individual recorded tracks to adjust the dynamics, or
P4EQ-Cho/Fln could be applied to add modulation.
1 in 1 out x 8 (mono-in/mono-out × 8)
Comp, Limiter , Gate, or Expander could be applied to
individual recorded tracks to adjust the dynamics, or
Chorus, Phaser, or Delay could be applied.
Applying the insert effects while you record
(analog/rhythm only)
While you record, effects can be applied to the input
from an instrument connected to the [INPUT 1] –
[INPUT 8/GUITAR IN] analog inputs, or to the built-in
rhythm sound that is input to a mixer channel, so that the
sound processed by the effect is recorded.
You can also apply effects to the sound of an audio
CD played back in the CD-R/RW drive.
As an example, here’s how to connect a guitar to the
[INPUT 8/GUITAR IN] jack, apply effects, and record
the sound on track 8.
1. Make connections, and select the track for recording.
Refer to “Connect a guitar to the [GUITAR IN] jack,
and assign it to mixer channel 8” (→p.36).
2. Access the [INSERT EFFECT] “InsAsn” tab page.
54
When using eight mics to record multiple instruments simultaneously, you could apply Gate to each
instrument to reduce crosstalk between the mics, or
apply Limiter to adjust the dynamics.
3. Press the “Assign: ” button, and select “Input(In).”
4. Press the “SelectEffType: ” button, and select the
effect type.
In the illustration for step 2, “1 in 1 out x 4” has been
selected.
5. Insert the effect between INPUT 8 (GUITAR IN)
and channel 8.
Press the “InsertTo: ” button.
For effect 1, use “SelectCh
After making the settings, press the “OK” button.
Input
indicator
Effect 1
” to set the channel to “8.”
SelectCh
channel selection
Page 63

6. Select the effect program.
Access the [INSERT EFFECT] “InsEff1” tab page.
Select “Ef
to select the desired effect program.
7. As described in “1. Adjust the recording level, and
record” (→p.39), adjust the record level and then
record.
fectNumber,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial
Applying an insert effect to a track during
playback
Here’s how an insert effect can be inserted into a mixer
channel, and applied to the track playback.
1. Select the track(s) that you wish to playback.
Press the [TRACK STATUS] key of one or more
recorded tracks to set their status to PLAY (LED lit
green).
2. Access the [INSERT EFFECT] “InsAsn” tab page.
3. Master effects
The D1600mkII contains two master effects (MstEff1 and
MstEff2) which can be used simultaneously. You can
adjust the send amount from each channel to change the
depth of the effect.
How the master effects can be used
The master effects are used mainly for spatial processing
(reverb etc.) to create an overall sense of depth and balance.
For example, you could use send 1 for ReverbHall and
send 2 for ReverbRoom, in order to use the effects to
simulate a complex spatial environment.
In this way, you can combine two different effects to
produce results that would not be possible when using
only a single effect.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
3. Press the “Assign: ” button. In the dialog box that
appears, select “PlayTrack (Trk).”
4. Press the “SelectEffType: ” button, and select the
effect type.
5. Specify the channel into which the effect will be
inserted.
Press the “InsertTo: ” button to open the dialog box.
For each effect, rotate the [VALUE] dial to set
“SelectCh
After making the settings, press the “OK” button.
6. Select an effect program.
Use the [INSERT EFFECT] “InsEff1” or “InsEff2” tab
page to select the effect that you wish to use.
Select “Ef
to select the desired effect program.
” to the input (output) channel.
fectNumber,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial
Using the master effects
1. Access the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] “MstEff1” or
“MstEff2” tab page.
2. Select an effect program.
Select “Ef
to select the desired effect program.
3. Set the return level from the master effect to the
master LR, and set the return balance.
For this example, set “RetLev” (return level) to “100,”
and set “RetBal” (return balance) to “CNT.”
4. Adjust the send levels.
Adjustments for Master Effect 1 are made in the
“EffSnd1” tab page, and for Master Effect 2 in the
“EffSnd2” tab page.
fectNumber,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial
Using
Using
effects
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
7. Press the [PLAY] key to begin playback.
You can also select effect programs while you listen to
the playback.
Select the appropriate “Send” icon knob, and rotate
the [VALUE] dial to adjust the send amount.
Play back to hear the output from master LR, and
audition the resulting effect.
Adjust the return level and send level so that CLP
does not appear in the master effect level meter.
the system
MIDI
55
Page 64

4. Final effect
One stereo-in stereo-out effect is provided as the final
effect. It applies to the master LR output (→diagram on
preceding page).
The final effect is used mainly for dynamics processing
(compression etc.) to make the overall level more consistent.
During mixdown, you can use the final effect to apply
mastering effects such as a multi-band limiter , in or der to
polish the mix for CD-quality results.
1. Access the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] “FinalEff” tab
page.
2. Select an effect program.
Select “Ef
to select the desired effect program.
Play back, and listen to the output from master LR to
hear the result of the effect.
fectNumber,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial
4. View the effects and chain that make up the program.
Press the “(EffectProgramName)” button to access
the “EffectAlgorithm” dialog box that displays the
structure of that effect program.
5. Turn individual effects on/off as desired.
Press the “(Effect On/Off)” button located below
each “(EffectIcon),” to turn it “On” (highlighted) or
“Off.”
6. Edit the settings of each effect.
Press the “(EffectIcon)” button of the effect that you
wish to edit. The screen shown below is the dialog
box when “St.Dly” is selected.
5. Editing an effect
You can edit (modify) the effect programs that are used
as insert effects, master effects, and final effects.
If you change the “Ef
power without saving, your edited effect settings will
be lost. If you wish to keep your edited settings, you
must execute the Store operation.
1. Access the page for the effect that you wish to edit.
This illustration shows the [INSERT EFFECT]
“InsEff1” tab page as an example.
2. Select an effect program.
Select “Ef
to select the desired effect program.
3. Listen to the sound produced by the effect program.
Press the “Bypass” button, and bypass will be turned
“On” (i.e., the effect will not be applied). Then press
the “Cancel” button to turn bypass “Off” (i.e., the
effect will be applied). Compare the effect and
bypassed sounds.
fectNumber,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial
fectNumber” or turn off the
Select the parameter, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
edit it. For details on each parameter, refer to “Effect
Parameter List” (→p.137).
You can use “Ef
box to turn the effect on/off. This on/off setting is
linked with the “(Effect On/Off)” button of step 5.
The setting of one will be reflected by the other.
After making settings, press the “OK” button.
If you wish to edit another effect, press the
“(EffectIcon)” button, and edit the parameters.
In the “EffectAlgorithm” dialog box, press the “OK”
button.
7. Assign a name to the edited effect program.
Press the “Rename” button to access the
“RenameEffect” dialog box. For details on the
renaming procedure, refer to “2. Naming a song”
(→p.35).
After assigning the name, press the “OK” button.
fect On/Off” in the top of the dialog
56
Page 65

8. Save the effect program.
If the song is playing, press the [STOP] key to stop it.
Press the “Store” button to access the “StoreEffect”
dialog box.
Specify the number for storing, press the “Exec.”
button to save the effect program.
When you save the effect program, it will be
overwritten onto that number, and the previous
settings of that number will be lost.
6. Controlling an effect from an external device
You can also control an insert effect in realtime by using
an expression pedal such as the EXP-2 (foot controller) or
an external MIDI controller.
For the effect parameters that can be controlled, refer to
“Effect Parameter List” (→p.137).
1. Connect an expression pedal (separately sold
option: EXP-2 foot controller) or external MIDI
controller. (→p.10)
2. Select the external device that will control the
effect.
Access the [SYSTEM/USB] “Control” tab page.
In “Device (CtrlChgDevice
wish to use an expression pedal, or select a MIDI
message if you wish to control via MIDI. (→p.91)
),” select “Pedal” if you
4. Select the effect program that you wish to control.
In the [INSERT EFFECT] “InsEff1”–“InsEff4” tab
pages, choose the insert effect that you selected in
step 3.
Select “Ef
to select the effect program.
If the selected effect includes a control function, and
the conditions allow the effect to be controlled, a “#”
symbol will be added at the end of the effect program
name.
5. Specify the parameter to be controlled, and the
range of control.
Press the “(Effect Program Name)” button.
The “Effect Algorithm” dialog box that makes up that
effect program will appear.
Press the “Cntrl Icon” button to access the “ControlDevice” dialog box.
fectNumber,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
Using
effects
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
If you set “Device (CtrlChgDevice
by a MIDI message other than “Pedal,” you must set
the [SYSTEM/USB] “MIDI” tab page “GlobalCh
(GlobalChannel
of the external MIDI device that is transmitting the
control messages.
3. Select the insert effect that you wish to control.
Use “Asn(#) (CtrlChgAssign
effect that will be controlled.
)” setting to match the MIDI channel
)” to be controlled
)” to select the insert
Select “Param
the parameter that you wish to control.
Rotate the [VALUE] dial to specify the maximum
value in “Max
When you have finished making settings, press the
“OK” button.
In the “EffectAlgorithm” dialog box, press the “OK”
button.
If you wish to save the above settings, save your
data as described on “5. Editing an effect” step 8
(→p.56).
6. Operate the expression pedal or external MIDI
controller to control the effect.
,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial to select
,” and the minimum value in “Min.”
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
57
MIDI
Page 66

7. Using an external effect
A send signal can be output from the [AUX OUT] jack,
and processed by an external effect. The output of the
external effect can then be returned to the [INPUT 1]–
[INPUT 8] jacks and sent to the desired channels or to the
master LR bus.
As an example, here’s how the playback sound can be
sent to an external effect, and returned to the master LR
bus via the [INPUT 3] and [INPUT 4] jacks.
1. Connect your external effect processor.
Connect the [AUX OUT] jack of the D1600mkII to the
INPUT jack of your external effect processor, and
connect the OUTPUT jacks of the external effect
processor to the [INPUT 3] and [INPUT 4] jacks of the
D1600mkII.
2. Send the playback sound to the external effect.
Access the [MASTER EFFECT/AUX] “AuxSend” tab
page.
Select “Aux” for the channel(s) that you wish to send
to the external effect, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
adjust the send amount.
3. Input the audio from the external effect processor.
Select the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch1–8” or “Ch9–16” tab
page.
Press the “SubIn” button to access the dialog box.
Select the “In3–4” “Fader” icon, and turn the
[VALUE] dial to set the return level.
Use the “Balance” icon to adjust the return balance.
Mixdown
You can use mixer settings such as EQ, faders, and effects
to adjust the audio from each recorded track, and
combine the result into two tracks to create your own CD
or record it on an external two-channel recorder (DAT
recorder, MD recorder, cassette recorder etc.) to create a
finished song. This process is called mixdown.
1. Creating an audio CD
You can use the CD-R/RW drive to create an original CD
from songs you record on the D1600mkII.
In order to create an audio CD, the hard disk must
have free space equivalent to the size (the total of the
two channels) of the song you are creating.
For example if you want to create an audio CD of a
five-minute stereo song, the D1600mkII’s hard disk
must have free space for at least five minutes of stereo
(ten minutes of monaural) recording. For details on
the free area of the hard disk, refer to “1. Select TimeDisp Type” (→p.91).
To write a song to CD
1. Check the completed song.
Use the faders and knobs to adjust the volume and
panning of each track, and play back the song to
check it.
If you want to enable the scenes you stored, go to
the [SCENE] “ReadDel” tab page and turn
“SceneRead” on.
2. Bounce-record your song to two tracks.
Bounce the song to two tracks as described in “5.
Combining multiple tracks into two: Bounce”
(→p.42).
If the song you write to CD contains no silence at
the beginning (“zero time”), the beginning of the
song may drop out when you play back from the
CD. To avoid this, you can insert approximately
0.5 seconds of silence at the beginning of the
audio data you mixed down to tracks 1 and 2.
For details, refer to “Inserting blank data: Insert
Track” (→p.63).
3. Insert a disc into the CD-R/RW drive.
Use a blank disc or a disc that has not yet been
finalized.
Since CD-RW discs will not play in some audio
CD players, we recommend that you use CD-R
media.
58
Page 67

4. Select the [SONG/CD] “CDR/RW” tab page.
Press the “ ” button, and in the screen
that appears, press the “OK” button. Make sure that
“CD-R/RW Information” shows “BlankDisc” or
“song number.” The free space on the disc is shown
below.
Make sure that the “DAO” (Disc At Once) button is
off.
5. Execute writing.
Press the “WriteCD” button, and the “Obey Copyright Rules” message will appear.
6. If you want to write other songs, perform steps 2, 4,
and 5.
The songs will be written on the disc in the order in
which you write them.
7. Finalize the disc.
If you want to play the newly created CD-R/RW in
an audio CD player, finalize the disc by pressing the
“Final” button when writing is completed.
No further songs can be written to a finalized
disc. This means that you should execute the
Finalize step after you have written all the songs
you want to write on that disc.
8. Check the written content.
Press the “CD Monitor” button, and then press the
“” button to play back the disc, and
check that it was written correctly.
9. Play back the disc in your audio CD player to check
it.
Play the disc in a CD player to verify that the audio
CD was created correctly.
CD-RW discs will not play in some audio CD
players.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
Carefully read the “COPYRIGHT WARNING” section of the manual (→p.iii). If you accept the terms,
select the writing speed. Select a writing speed that is
supported by the disc you are using.
Depending on your system, you may not be able
to write at the selected speed. If so, try a slower
writing speed.
Press the “Yes” button, and the D1600mkII will begin
creating an image file.
If you press the “Abort” button while the image
file is being created, creation of the image file will
be stopped.
Then the D1600mkII will begin writing the CD.
If you press the “Abort” button while the CD is
being written, writing will stop. If you were writing to CD-R, that disc will be unusable. However
if you were writing to CD-RW, you will be able to
erase that disc and use it again as a blank disc.
For details, refer to “3. Erasing the data from a
CD-RW” (→p.83).
When writing is finished, the display will indicate
“Completed”. If you want to write the same song to
another CD, press the “Yes” button. If not, press the
“No” button.
If you press the “Yes” button, the CD-R/RW tray will
open. When you insert a new blank disc or an
unfinalized disc and close the tray, writing to the CD
will begin automatically . Since the pr eviously-created
image file will be used in this case, the writing
process will be faster than the first time.
When writing is finished, the display will indicate
“Completed.” If you want to write the same song to
another CD, press the “Yes” button. If not, press the
“No” button.
If you press the “No” button, you can then press
the “CD Monitor” button to check the content
that was written to the CD.
Making an audio CD from a live recording
If you want to make an audio CD from a single item of
song data, such as a live recording or a long song, you
can use the Disc At Once method to write the disc. With
this method, the marks you register within the song will
be used to divide the tracks of the CD, letting you create
a live CD with no gap between tracks.
An audio CD created using Disc At Once can also be
used as a master CD for pressing.
When you write a disc using Disc At Once, it will be
finalized automatically; you will not be able to add
any further songs.
1. Check the song you want to record.
Use the faders and knobs to adjust the volume and
pan etc. of each track, and play back the song to check
it.
2. Register a mark at each time location where you
want to create a track division. (→p.46)
3. Select the [SONG/CD] “CDR/RW” tab page.
Turn on the “DAO” (Disc At Once) button.
4. Insert a disc into the CD-R/RW drive.
You must use a blank disc.
5. In the [SONG/CD] “CDR/RW” tab page, press the
“” button.
In the screen that appears, press the “OK” button.
Make sure that the “CD-R/RW Information” field
shows “BlankDisc.”
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
Mixdown
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
59
MIDI
Page 68

6. Execute writing.
Press the “WriteCD” button, and the “Obey Copyright Rules” message will appear.
Carefully read the “COPYRIGHT WARNING”
section of the manual (→p.iii).
If you accept the terms, select the writing speed and
press the “Yes” button. The disc will be written and
automatically finalized.
2. Recording to a master tape
1. Check the completed song.
Use the faders and knobs to adjust the volume and
pan etc. of each track, and play back the song to check
it.
2. Connect the D1600mkII to your external recording
device.
Connect your MD or DAT to the [S/P DIF OUT] jack
or to the [MASTER OUTPUT] jacks.
3. Record on your external recording device.
Play back the song on the D1600mkII, and adjust the
recording level on your external recorder.
Start recording on your external recorder, and play
back the D1600mkII.
By using the Program Play function you can
consecutively play back multiple songs in the desired
order. For details, refer to “2. Program play” (→p.45).
Press the “SubIn” button to access the sub input setting screen.
Turn the “M (mute)” button “Off” for the connected
input.
Select the “Fader” icon and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
raise the value so that the audio signal will be input.
If the input is mono, press the “Stereo/Mono” button
to select “Mono” so that the audio will be sent to both
L and R buses.
3. Using the sub inputs
You can use any of the analog inputs ([INPUT 1]–[INPUT
8/GUIT AR IN]) as a sub input to send the audio directly
to the master bus.
• If you have synchronized a sequencer to the completed
song, you can use this to input the sequenced sounds
via the sub inputs.
•You can use this to add the return audio from an exter-
nal effect processor connected to the [AUX OUT] jack.
1. Connect the external audio source to the analog
inputs.
Input the external source to [INPUT 1]–[INPUT 8/
GUITAR IN].
2. Make sub input settings.
Select the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch1–8” or “Ch9–16” tab
page.
60
Page 69

Track editing
1. Track editing functions
The following functions are provided for track editing.
• Copy Track: copy a track
• Insert Track: insert a blank space
• Erase Track: erase a track
• Delete Track: delete a track
• Reverse Track: reverse track audio end-to-end
• Optimize Track: optimize track data
• Swap Track: exchange tracks
• Expansion/Compression Track : expand or compress a
track
• Copy Whole Track: copy an entire track
• Swap Whole Track: exchange entire tracks
• Fade Track: fade-in/fade-out
• Normalize Track: optimize the level
In some cases, track editing functions may not be
usable if you have insufficient hard disk space. You
must allocate sufficient free space (equivalent to the
IN–OUT or TO–END time) for the track editing
operation.
Basic track editing procedure
1. Specify the region (time) that will be edited.
In order to edit a track, you must first specify the
region (area of time) that will be edited.
Move to the location that you wish to register.
Press the [STORE] key, and then press one of the
following keys to register the corresponding location.
[IN/LOC1] key: IN time
[OUT/LOC2] key: OUT time
[TO/LOC3] key: TO time
[END/LOC4] key: END time
For details, refer to “Using the locate keys to move”
(→p.46).
The IN, OUT , T O, and END times ar e used as follows
by each editing command.
How the editing commands use the IN, OUT, TO, and END times
IN OUT TO END
Copy Track
Insert Trac k
Erase T rac k
Delete T rac k
Swap T rac k
Reverse
Track
Optimize
Track
Expansion/
Compression T rac k
Fade Track
Normalize
Track
Copy source
start time
Blank insert
start time
Erase start
time
Delete start
time
Swap start
time
Reverse start
time
Optimize
start time
Expand/compress start
time
Fade start time F ade end time
Normalize
start time
Copy source
end time
Blank insert
end time
Erase end
time
Delete end
time
Swap end
time
Reverse end
time
Optimize end
time
Expand/compress end
time
Normalize
end time
Copy destination start time
– – – – – –
– – – – – –
– – – – – –
– – – – – –
Reversed copy
destination
start time
– – – – – –
Expand/com-
press result
copy destination start time
– – – – – –
– – – – – –
– – –
– – –
Expand/compress destination end
time
Depending on the “EditType,” the “Wave” button
may appear, allowing you to view the waveform as
you specify the location more precisely. (→p.101)
2. Access the [TRACK] “EditTrk” tab page.
3. Select the type of operation that you wish to execute
(copy, insert blank, etc.).
Select “EditType.” Select the area to the right of the
“” button, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to select the
desired editing operation.
Alternatively, you can press the “ ” button to display “Select EditTrack Type,” and select the type of
editing.
4. Select the track(s) that you wish to edit.
The LCD screen will differ depending on the “EditType.” The screen shown in step 2 is when “EditType” is set to “CopyTrack.”
For “CopyTrack,” use “SourceTrack” to specify the
copy source track, “DestTrack” to specify the copy
destination track, and “Times” to specify the number
of copies.
You can use “Wave” to view the waveform as
you specify the editing region.
DestTrack TimesSourceTrack
5. Execute the selected track editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button to execute the selected track
editing command.
In the example shown in step 4, the data in the IN–
OUT region of track 1 will be copied three times starting at the TO location of track 2.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
Track
editing
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
61
MIDI
Page 70

2. Track editing examples
Copying track data: Copy Track
The Copy Track command copies recorded track data
from the specified region (IN–OUT) to another location
(TO).
•You can copy the IN–OUT data not only once, but
multiple times in succession.
•You can copy not only a single track, but multiple
tracks simultaneously.
• By using the clipboard, you can copy track data to
another song.
This command can be used in the following ways.
•A phrase of several measures (such as a drum pattern)
can be copied repeatedly to create track data for the
entire song.
• The first verse of a song can be copied, and used to
create the second verse.
•A favorite phrase can be recorded on a track, and
copied for use on another track or song.
Procedure for copying a track within the same song
Here’s how to copy the IN–OUT region of track 1 to the
TO location of track 2 three times.
1. Register the IN, OUT, and TO times.
2. Select the Copy command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“CopyTrack.”
DestTrack TimesSourceTrack
3. Select the copy source track number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
4. Select the copy destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 2.
If you specify multiple tracks for the copy source,
you must specify the same number of tracks for
the copy destination.
5. Specify the number of times that the data will be
copied.
Set “Times” to 3.
6. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
The data will be overwritten onto the copy
destination track.
7. Verify the results.
Press the [TO/LOC3] key to play back from the TO
location, and verify that the copy was performed
correctly .
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
Procedure for copying to a track in a different song
Here’s how to copy the IN–OUT region of song 001 track
1 to the TO location of song 002 track 2, once.
1. Select song 001.
2. Register the IN and OUT times.
3. Select the Copy command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“CopyTrack.”
4. Select the copy source track number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
5. Select the clipboard as the copy destination track
number.
Set “DestTrack” to “Clip.”
6. Execute the copy command.
Refer to step 6 of “Procedure for copying a track
within the same song.”
The data in the clipboard will be overwritten.
7. Select song 002.
8. Register the TO time location.
9. Select the Copy command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“CopyTrack.”
10. Select the clipboard as the copy source track
number.
Set “SourceTrack” to “Clip 1.” The number indicates
the number of tracks in the clipboard.
11. Select the copy destination track num.
Set “DestTrack” to track 2.
12. Specify the number of times that the data will be
copied.
Set “Times” to 1.
13. Execute the copy.
Refer to step 6 of “Procedure for copying a track
within the same song.”
The data will be overwritten onto the copy destination track.
14. Verify that the data was copied correctly.
Press the [TO/LOC3] key to play back from the TO
location, and verify that the copy was performed
correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before
executing the command.
If you are using an external drive, the data in the
clipboard will be erased when you switch drives.
62
Page 71

Inserting blank data: Insert Track
The Insert Track command inserts blank space into the
specified region (IN–OUT) of the recorded track. Track
data located after the inserted blank will be moved
toward the end of the song.
•You can insert a blank into not only a single track, but
into multiple tracks simultaneously.
This command can be used in ways such as the following.
• This command can be used to add a phrase in the
middle of previously-recorded data, by inserting blank
space and recording your new data.
Inserting a blank (Insert)
Here’s how to insert a blank space into the IN–OUT
region of track 1.
1. Register the IN and OUT times.
2. Select the Insert command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“InsertTrack.”
DestTrack
3. Select the number of the track into which you wish
to insert blank space.
Set “DestTrack” to track 1.
4. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
5. Verify the results.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key to play back from the IN
location, and verify that the blank data was inserted
correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
Erasing data from a track: Erase Track
The Erase Track command erases the specified region
(IN–OUT) of recorded track data. When data is erased, a
blank space will be created in that region.
•You can erase data from not only one track, but from
the IN–OUT region of multiple tracks simultaneously.
Unlike the Delete Track command, the data that followed the OUT location will not be moved forward.
Procedure for erasing track data (Erase)
Here’s how to erase the IN–OUT region of track 1.
1. Register the IN and OUT times.
2. Select the Erase command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“EraseTrack.”
DestTrack
3. Select the number of the track from which you wish
to erase data.
Set “DestTrack” to track 1.
4. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
5. Verify the results.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key to play back from the IN
location, and verify that the data was erased correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
Deleting track data: Delete Track
The Delete Track command deletes data from the specified region (IN–OUT) of recorded track data. When data
is deleted, the data that followed (i.e., the data after the
OUT location) will be moved toward the beginning of the
song.
•You can delete data from not only one track, but from
the IN–OUT region of multiple tracks simultaneously.
Procedure for deleting track data (Delete)
Here’s how to delete the IN–OUT region of track 1.
1. Register the IN and OUT times.
2. Select the Delete command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“DeleteTrack.”
DestTrack
3. Select the number of the track from which you wish
to delete data.
Set “DestTrack” to track 1.
4. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
Track
editing
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
MIDI
63
Page 72

5. Verify the results.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key to play back from the IN
location, and verify that the data was deleted
correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
Reversing track data: Reverse Track
The Reverse T rack command copies a reversed version of
the specified region (IN–OUT) of recorded track data to
the TO location of another track.
• The IN–OUT region can be copied not just once, but
multiple times in succession.
• Data can be copied not only from one track, but from
multiple tracks simultaneously.
Procedure for reversing track data (Reverse)
Here’s how to reverse the IN–OUT region of track 1, and
copy it three times to the TO location of track 2.
1. Register the IN, OUT, and TO times.
2. Select the Reverse command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“ReverseTrack.”
Optimizing track data: Optimize Track
This operation optimizes the specified region (IN–OUT)
of recorded track data.
If you repeatedly record or edit short intervals of time,
the data on the hard disk will become fragmented,
requiring the D1600mkII to access the disk more
frequently, and making it more likely that skips will be
heard or that the “DiskBusy” message will appear,
possibly making it impossible to play back correctly. In
such cases, you can optimize the fragmented region so
that it will play back correctly.
Optimizing track data
Here’s how to optimize the IN–OUT region of track 1.
1. Store the IN and OUT locations.
Set IN at a point slightly ahead of where the “DiskBusy” messages begin appearing, and OUT to a point
at which these messages no longer appear.
2. Select the Optimize command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“OptimizeTrack.”
DestTrack TimesSourceTrack
3. Select the reverse source track number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
4. Select the reverse destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 2.
5. Specify the number of times the data will be copied.
Set “Times” to 3.
6. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
7. Verify the results.
Press the [TO/LOC3] key to play back from the TO
location, and verify that the data was edited correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
The longer the specified range (IN–OUT), the longer
this command will take to process until the
“Completed” display appears.
DestTrack
3. Select the track number that you want to optimize.
Find the track where you suspect that the data is fragmented (here we will assume that track 1 is the problem), and specify “DestTrack” as track “1”.
4. Execute the operation.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute the operation.
When the operation is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
5. Check the results.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key and play back from the IN
location. If playback occurs correctly without the
“Disk Busy” message appearing, the optimization
was successful.
You can use Undo to return to the state prior to
execution.
This operation will require a longer time for completion in proportion to the length of the specified region
(IN–OUT).
64
Page 73

Erasing audio events from silent areas
Here’s how you can erase audio events from silent areas
of the IN–OUT region of track 1. (These areas will become blank.)
1. Store the IN and OUT locations.
Set IN at a point slightly ahead of the silent areas you
want to erase, and OUT at a location after the end of
the silent areas.
2. Select the Optimize command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“OptimizeTrack.”
3. Select the optimize mode.
Press the “Mode” button to open the dialog box.
For this example, select “Erase Silence,” and press the
“Yes” button to return to the [TRACK] “EditTrk” tab
page.
4. Select the track number that you want to optimize.
For this example, set “DestTrack” to track “1”.
5. Execute the operation.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute the operation.
When the operation is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
6. Check the results.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key, play back from the IN location, and check the result of the operation.
You can use Undo to return to the state prior to
execution.
This operation will require a longer time for completion in proportion to the length of the specified region
(IN–OUT).
Erasing punch-noise
Here’s how you can erase punch-noise from the IN–OUT
region of track 1.
1. Store the IN and OUT locations.
Set IN at a point slightly ahead of the noise, and OUT
at a location after the end of the noise.
You cannot edit this to other than a transition
between events.
2. Select the Optimize command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“OptimizeTrack.”
3. Select the optimize mode.
Press the “Mode” button to open the dialog box.
For this example, select “Erase Punch Noise,” and
press the “Yes” button to return to the [TRACK]
“EditTrk” tab page.
4. Select the track number that you want to optimize.
For this example, set “DestTrack” to track “1”.
5. Execute the operation.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute the operation.
When the operation is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
6. Check the results.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key, play back from the IN location, and check the result of the operation.
You can use Undo to return to the state prior to
execution.
This operation will require a longer time for completion in proportion to the length of the specified region
(IN–OUT).
Swapping track data: Swap Track
This command exchanges (swaps) the specified region
(IN–OUT) of recorded track data with the same region of
another track.
• Data can be swapped not only between single tracks,
but also between multiple tracks simultaneously.
Procedure for swapping track data (Swap)
Here’s how to exchange the IN–OUT regions of track 1
and track 2.
1. Register the IN and OUT times.
2. Select the Swap command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“SwapTrack.”
DestTrackSourceTrack
3. Select the swap source track number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
4. Select the swap destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 2.
5. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
6. Verify that the data was exchanged correctly.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key to play back from the IN
location, and verify that the data was exchanged
correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
Track
editing
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
65
MIDI
Page 74

Expanding or compressing a track:
Expansion/Compression Track
This command expands or compresses the specified
region (IN–OUT) of recorded track data into the specified
region (TO–END) of a specified track.
• The original data is left unchanged, and the timeexpanded/compressed result is created on another
track.
•You can select whether or not the pitch will be
converted.
• Not only a single track, but multiple adjacent tracks of
data can be converted simultaneously.
• The converted data can be copied multiple times in
succession.
This command can be used in ways such as the following.
•Drum loops of different tempo can be changed to the
same tempo.
• Phrases can be made to fit into a specific time length.
Procedure for expanding (Expansion) or compressing (Compression) track data and copying it
Here’s how the IN–OUT range of track 1 can be converted to the length of the TO–END range of track 2, and
copied there three times.
1. Register the IN, OUT, TO, and END times.
2. Select the expansion/compression command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“Exp/CompTrack.”
When processing is completed, the display will indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
8. Verify that the data was processed correctly.
Press the [TO/LOC3] key to play back from the TO
location, and verify that the data was expanded/
compressed correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
The longer the specified range (IN–OUT), the longer
this command will take to process until the
“Completed” display appears.
Copying an entire track/Copying to a
virtual track: Copy Whole Track
This command copies an entire recorded track (from
beginning to end) to a different entire track.
•You can copy not only one track, but multiple tracks
simultaneously.
• The currently selected virtual track can be copied to
multiple virtual tracks.
This command can be used in ways such as the following.
• The same track can be copied to multiple virtual tracks,
and used to create multiple takes that are partially different.
Procedure for copying an entire track
Here’s how track 1 can be copied to virtual track “a”
(=currently selected) of track 2.
1. Select the Copy Whole command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“CopyWholeTrack.”
DestTrack TimesSourceTrack
3. Select the expansion/compression mode.
Press the “Mode” button to access the dialog box.
For this example, select “Fast” and “Fixed.” Then
press the “OK” button to return to the [TRACK]
“EditTrk” tab page.
4. Select the expansion/compression source track
number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
5. Select the expansion/compression destination track
number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 2.
6. Specify the number of times that the data will be
copied.
Set “Times” to 3.
7. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
DestTrack DestVTrackSourceTrack
2. Select the copy source track number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
3. Select the copy destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 2.
4. Select the copy destination virtual track.
Set “DestVTrack” to virtual track “a.”
5. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
6. Verify that the data was copied correctly.
Play back from the beginning of the song, and verify
that the data was copied correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
66
Page 75

Procedure for copying to a virtual track
Here’s how virtual track “a” (=currently selected) of
track 1 can be copied to virtual track “b” of track 1.
1. Verify the copy destination.
In the [TRACK] “Vtr1–8” tab page, make sure that
track 1 virtual track “b” is blank or is a track that may
be erased (overwritten). After you verify this, you
must return the setting to “a.”
2. Select the Copy Whole command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“CopyWholeTrack.”
3. Select the copy source track number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
4. Select the copy destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 1.
5. Select the copy destination virtual track.
Set “DestVTrack” to virtual track “b.”
6. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
7. In the [TRACK] “Vtr1–8” tab page, select virtual
track “b” for track 1.
8. Verify that the data was copied correctly.
Play back from the beginning of the song, and verify
that the data was copied correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
In this case, you must return track 1 to virtual track
“a.”
Exchanging entire tracks/virtual tracks:
Swap Whole Track
This command exchanges (swaps) the data of an entire
recorded track (from beginning to end) with the data of
another entire track.
• Not only individual tracks, but multiple tracks can be
swapped simultaneously.
This command can be used in ways such as the following.
• Recorded tracks can have their numbers re-ordered by
type.
• Data that is scattered across different virtual tracks can
be rearranged into virtual track “a” etc.
Procedure for exchanging an entire track
Here’s how track 1 can be exchanged with the currently
selected virtual track “a” of track 2.
1. Select the Swap Whole command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“SwapWholeTrack.”
DestTrack DestVTrackSourceTrack
2. Select the swap source track number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
3. Select the swap destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 2.
4. Select the swap destination virtual track.
Set “DestVTrack” to virtual track “a.”
5. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
6. Verify that the data was exchanged correctly.
Play back from the beginning of the song, and verify
that the data was exchanged correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
Procedure for exchanging with a virtual track
Here’s how currently selected virtual track “a” of track 1
can be exchanged with virtual track “b” of track 1.
1. Verify the copy destination.
In the [TRACK] “Vtr1–8” tab page, make sure that
track 1 virtual track “b” is the track that you wish to
exchange. After you verify this, you must return the
setting to “a.”
2. Select the Swap Whole command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“SwapWholeTrack.”
3. Select the swap source track number.
Set “SourceTrack” to track 1.
4. Select the swap destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 1.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
Track
editing
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
MIDI
67
Page 76

5. Select the swap destination virtual track.
Set “DestVTrack” to virtual track “b.”
6. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
7. In the [TRACK] “Vtr1–8” tab page, select virtual
track “b” for track 1.
8. Verify that the data was exchanged correctly.
Play back from the beginning of the song, and verify
that the data was exchanged correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
In this case, you must return track 1 to virtual track
“a.”
Fading-in/fading-out: Fade Track
This command fades-in or fades-out the specified region
(IN–OUT) of recorded track data. By using fade-in and
fade-out in conjunction with each other, you can create
cross-fades.
•You can fade-in or fade-out the IN–OUT region.
• Not only a single track, but multiple tracks of data can
be faded in or out simultaneously.
Procedure for fading-in
Here’s how to fade-in the IN–OUT region of track 1.
1. Register the IN and OUT times.
Register the start and end times of the desired fadein.
2. Select the fade-in command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“FadeTrack.”
DestTrack
3. Select the fade-in curve.
Press the “Mode” button to access the dialog box.
5. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
6. Verify that the data was faded correctly.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key to play back from the IN
location, and verify that the data was faded-in correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
The longer the specified range (IN–OUT), the longer
this command will take to process until the “Completed” display appears.
Procedure for fading-out
Here’s how to fade-out the IN–OUT region of track 1.
1. Register the IN and OUT times.
Register the start and end times of the desired fadeout.
2. Select the fade-out command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“FadeTrack.”
3. Select the fade-out curve.
Press the “Mode” button to access the dialog box.
For this example, select the “D” curve, press the
“OK” button to return to the [TRACK] “EditTrk” tab
page.
4. Select the fade-out destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 1.
5. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
6. Verify that the data was faded correctly.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key to play back from the IN
location, and verify that the data was faded-out correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
The longer the specified range (IN–OUT), the longer
this command will take to process until the “Completed” display appears.
For this example, select the “A” curve, press the
“OK” button to return to the [TRACK] “EditTrk” tab
page.
4. Select the fade-in destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 1.
68
Page 77

Boosting to the optimal level: Normalize
Track
This command boosts the specified region (IN–OUT) of
track data that was recorded at a lower than optimal
level, so that the level is raised to the maximum volume
without clipping.
• The peak of the audio data in the IN–OUT region is
detected, and the audio level of the IN–OUT region is
boosted so that the peak reaches the maximum allowable level.
•You can normalize either a single track, or adjacent
tracks simultaneously.
If data recorded at an extremely low level is normalized, any noise included in that region will also be
boosted.
Procedure for normalizing
Here’s how to normalize the IN–OUT region of track 1.
1. Register the IN and OUT times.
Register the start and end times of the region you
wish to normalize.
2. Select the normalize command.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“NormalizeTrack.”
Song editing
You can copy a song you recorded, change the order of
songs, or delete an unwanted song. You can also apply a
“protect” setting to prevent a song from being
accidentally deleted.
You cannot Undo song editing operations.
1. Song editing operation
The D1600mkII provides the following song editing
operations.
• Copy song: copy a song
• Move song: move a song
• Delete song: delete a song
• Protect song: protect a song
Basic song editing procedure
1. Select the song that you want to edit.
2. Access the [SONG/CD] “EditSong” tab page.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
DestTrack
3. Select the normalize destination track number.
Set “DestTrack” to track 1.
4. Execute the editing command.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?,” so press the
“Yes” button to execute the command.
When processing is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
5. Verify that the data was processed correctly.
Press the [IN/LOC1] key to play back from the IN
location, and verify that the data was normalized
correctly.
You can use Undo to return to the state before executing the command.
The longer the specified range (IN–OUT), the longer
this command will take to process until the
“Completed” display appears.
3. Select the desired type of song editing operation
(e.g., copy or delete).
Select “EditType.”
Select the field at the right of the “ ” button, and
turn the [VALUE] dial to select the type of editing
operation.
Alternatively, you can press the “ ” button to open
the “Select EditSong Type” dialog box and select the
editing operation.
4. Select the song that you want to edit.
The LCD screen display will differ depending on the
“EditType.”
The screen shown above is for when you select
“CopySong” as the “EditType.”
For the “CopySong” operation, the song you selected
in step 1 will appear as “Source Song.”
Use the “DestSong” field to specify the copydestination song.
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
Song
editing
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
DestSongSourceSong
the system
MIDI
69
Page 78

5. Execute the song editing operation.
Press the “Exec.” button to execute the song editing
operation.
In the case of the screen shown in step 4, song 1 will
be copied to song 2. Previously-existing song 2 and
any following songs will move backward (i.e., be
renumbered upward).
2. Examples of song editing
3. Verify the song you want to move.
Make sure that “SourceSong” is set to the desired
move-source song.
4. Select the move-destination song number.
Set “DestSong” to the move-destination song
number.
5. Execute the editing operation.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute the editing operation.
When the operation is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
Copying a song: Copy Song
This operation copies the selected song to the desired
song number.
You can use this when you want to create a different mix
or arrangement of the same song.
1. Select the copy-source song (“SourceSong”).
2. Select the Copy Song operation.
In the [SONG/CD] “EditSong” tab page, select
“CopySong” as the “EditType.”
DestSongSourceSong
3. Verify the song you want to copy.
Make sure that “SourceSong” is set to the desired
copy-source song.
4. Select the copy-destination song number.
Set “DestSong” to the copy-destination song number.
5. Execute the editing operation.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute the editing operation.
When the operation is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
Moving a song: Move Song
This operation moves the selected song to a different
song number.
You can use this to rearrange the order of the songs.
1. Select the move-source song (“SourceSong”).
2. Select the Move Song operation.
In the [SONG/CD] “EditSong” tab page, select
“MoveSong” as the “EditType.”
Deleting a song: Delete Song
This operation deletes the selected song.
1. Select the song you want to delete (“DestSong”).
2. Select the Delete Song operation.
In the [SONG/CD] “EditSong” tab page, select
“DeleteSong” as the “EditType.”
DestSong
3. Verify the song you want to delete.
Make sure that the song you want to delete is selected
as the “DestSong”.
4. Execute the editing operation.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute the editing operation.
When the operation is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “OK” button.
Protecting a song: Protect Song
This operation protects the selected song, so that it cannot be rewritten or deleted. It will not be possible to write
any parameters of that song. For example if you attempt
to record into a song for which Protect is turned on, an
error message will appear and recording will stop.
You can use this setting to prevent a completed song
from being accidentally overwritten or deleted.
1. Select the song you want to protect (“DestSong”).
2. Select the Protect Song operation.
In the [SONG/CD] “EditSong” tab page, select
“ProtectSong” as the “EditType.”
70
DestSongSourceSong
DestSong
Page 79

3. Make sure that the song you want to protect is
selected as the “DestSong”.
4. Turn the protect setting on or off.
Press the “Exec.” button. A lock symbol is displayed
to indicate a song for which Protect is turned on. The
setting will alternate on/off each time you press the
“Exec.” button.
Rhythm/tempo settings
The D1600mkII contains numerous rhythm patterns for a
variety of time signatures (→p.168 “Rhythm Pattern
List”).
When you have a sudden idea for a song, you can record
your performance immediately, using the built-in
rhythms as a guide.
By joining various rhythm patterns, you can also create
drum patterns for an entire song.
1. Specifying and playing a rhythm
Access the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “SetUp” tab page.
The settings described below are made in this page.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Turning the rhythm on/off
Press the “Rhythm” button to turn it “On” (highlighted).
The [TEMPO/RHYTHM] key will light, and the
rhythm will sound during playback or recording.
If you do not want to hear the rhythm during playback or recording, turn the “Rhythm” button “Off.”
Adjusting the rhythm volume
Select the “RhythmVol (Vol),” and rotate the
[VALUE] dial to adjust the volume.
Setting the tempo and time signature
1. Select the “TempoSource,” and select the tempo
source.
For this example, we will select “Manual” which will
use a single tempo, time signature, and rhythm pattern.
You can also press the “ ” button, and select
from a list.
If you wish to change the tempo, time signature, and
rhythm pattern during the song, you must create a
Tempo Map. (→p.72)
2. Select the “T
adjust the tempo.
3. Select the “Beat
the time signature.
empo,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial to set
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
settings
Rhythm/tempo
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
71
the system
MIDI
Page 80

Selecting the rhythm pattern
Select “SelRhythm,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
select the rhythm pattern that you wish to use.
You can also press the “ ” button, and select
from a list.
2. Recording your performance while you listen to the rhythm
You can record your performance while listening to the
built-in rhythm as a guide.
1. Make settings as described in “1. Specifying and
playing a rhythm.”
Turn “Rhythm” “On.”
Make other settings as necessary.
2. Connect your input device, and begin recording.
Refer to “1. Analog inputs” and “1. Adjust the recording level, and record” (→p.36, 39).
When you press the [REC] key to enter record-ready
mode, the rhythm will begin sounding. Recording
will begin when you press the [PLAY] key. You will
hear the selected rhythm pattern. Begin performing,
using the rhythm as a guide.
3. Recording the rhythm
Built-in rhythm patterns can be recorded on a track.
As an example, here’s how the rhythm pattern can be re-
corded on mixer channels 1 and 2.
1. Make settings as described in “1. Specifying and
playing a rhythm.”
Turn “Rhythm” “Off.”
If this is turned on, the sound will be output in
duplicate to the track and also to the master LR
bus.)
To set the volume, use the mixer channel that you are
inputting. Since “RhythmV
volume to the master LR bus, you do not need to set
it.
Make other settings as necessary.
2. Specify the input channels.
Select the [INPUT/TUNER] “Ch1–8” tab page.
Select the “Ch1” icon, and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
select “Rhythm L.” In the same way, set “Ch2” to
“Rhythm R.”
3. Check the record mode.
Select the [RECORD] “RecMode” tab page.
Select “Input” (= record the input).
4. Specify the recording tracks.
Press [TRACK STATUS] keys for tracks 1 and 2 to set
them to REC (LED lit red).
5. Adjust the recording level, and record.
Use the [CHANNEL] faders of tracks 1 and 2 to
adjust the level appropriately.
ol (Vol)” adjusts the send
4. Specifying the tempo
As an alternative to playing your entire song at the same
tempo, you can make the tempo change during the song,
or synchronize the tempo to an external MIDI device.
Choose one of the following tempo sources to control the
tempo of the song.
• Manual tempo: when the tempo is the same for the
entire song
• Tempo map: when you want the tempo to change dur-
ing the song
• Tempo track: when you want to use the tempo
recorded from MIDI Clock or Tap Tempo
The tempo source is set by the [TEMPO/RHYTHM]
“SetUp” tab page “T
Here’s how to use each type of tempo setting.
Manual tempo
When you use manual tempo, the song will play back
according to the “T
signature), and “SelRhythm
the tempo etc. will not change during the song.
Set the tempo source to Manual.
Access the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “SetUp” tab page.
Select “T
choose “Manual.”
For details on “T
settings, refer to “1. Specifying and playing a
rhythm” (→p.71).
empoSource,” and turn the [VALUE] dial to
Tempo map
The tempo map lets you specify tempo, time signature,
and rhythm pattern for each measure so that these will
change at the specified measure within the song.
1. Set the tempo source to Tempo Map.
Access the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “SetUp” tab page.
Select “T
choose “TempoMap.”
2. Make settings for the first tempo map event “001,”
which specifies the initial tempo at the beginning of
the song.
empoSource,” and turn the [VALUE] dial to
The tempo map for a song consists of tempo map
event “001” which specifies the initial tempo at
the beginning of the song, and tempo map events
“002”–“200” which you can specify to change the
tempo etc. at measures within the song.
empoSource” setting.
SelRhythm Tempo BeatTempoSource
empo” (tempo), “Beat” (time
” (rhythm pattern) settings;
empo,” “Beat,” and “SelRhythm”
72
Page 81

Access the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “TmpMap” tab
page.
Select “T
select tempo map event “001”.
Press the “Edit” button to open the “Select
TempoMap 001 Param” dialog box.
Use “Tempo” to set the tempo, “Beat” to set the time
signature, and “Rhythm” to specify the rhythm
pattern.
You cannot change the starting location (Start
Measure) of tempo map event “001”.
You can only specify the ending location (End
Measure).
When you have finished making settings, press the
“OK” button.
3. Add tempo map events to change the tempo, time
signature, and rhythm pattern during the song.
Press the “New” button to display “Select T empoMap
002 Param”.
Use “Meas” to specify the beginning (Start Measure)
and end (End Measure) of the tempo map event you
want to create. Use “Tempo” to specify the desired
tempo, “Beat” to specify the time signature, and
“Rhythm” to select a rhythm pattern. If you want to
overwrite the existing tempo map event, press the
“Insert” button to turn it off.
Press the “OK” button to add the tempo map event.
The tempo map events are renumbered from
beginning to end.
By adding tempo map events and using “Rhythm
change rhythm patterns, you can create drum
patterns for an entire song, including intro, fill-in,
and ending.
empoMap,” and turn the [VALUE] dial to
” to
To delete or modify a tempo map event
You can delete an unwanted tempo map event, or modify
its measure location or tempo settings etc.
1. Select the tempo map event that you want to delete
or modify.
Access the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “TmpMap” tab
page.
Select “T
select the appropriate tempo map event.
2. Delete or modify the tempo map event.
If you want to delete it, press the “Delete” button. A
message will ask you “AreYouSure?”
empoMap,” and turn the [VALUE] dial to
Press the “OK” button to delete the tempo map event
you selected in step 1. By turning the “SelectAll” button on (highlighted), you can delete all tempo map
events except for tempo map event “001”.
You cannot Undo this operation.
If you want to modify the tempo map event, press
the “Edit” button to open the dialog box. Edit the
parameters as desired.
Tempo track
The tempo track records MIDI clock data from an
external device such as a MIDI sequencer, or records tap
tempo.
Recording MIDI clock data from an external MIDI
sequencer, and using it as the tempo track
Here’s how MIDI clock tempo data from an external
MIDI sequencer can be recorded on the tempo track.
Use this when you wish to synchronize the D1600mkII
song with song data created on a MIDI sequencer in
which the tempo changes continuously.
1. Specify the time signature of the song.
If the time signature of the MIDI sequencer song data
changes during the song, you should create tempo
maps at the locations where the time signature
changes. (→“Tempo map”)
If the time signature changes during the song, it
will be detected as an incorrect tempo unless you
have created a tempo map that matches the
changes in time signature. There is no need to
specify the tempo.
2. Connect the MIDI OUT of your MIDI sequencer to
the [MIDI IN] connector of the D1600mkII.
3. Make settings on your MIDI sequencer so that it
will transmit MIDI clock messages.
Refer to the owner’s manual for your MIDI
sequencer.
4. Specify how tempo will be recorded.
In the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “TmpTrk” tab page,
select “MIDI Clock.”
5. Record the MIDI clock data.
Press the “RecStart” button to put the D1600mkII in
record-ready mode.
Start your MIDI sequencer.
When MIDI clock messages are received from the
MIDI sequencer, the display will indicate “ReceivingMIDIClock.”
6. When the MIDI sequencer finishes playing back,
stop the MIDI sequencer.
The D1600mkII will stop recording, and will display
“Complete.” Press the “OK” button.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
settings
Rhythm/tempo
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
MIDI
73
Page 82

7. Select the tempo track as the tempo source.
Select the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “SetUp” tab page.
Select “T
select “TempoTrk.”
If MIDI clock messages cannot be received correctly
from the MIDI sequencer, tempo recording may end
prematurely.
empoSource,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
5. Record the tap tempo.
Press the “RecStart” button to put the D1600mkII in
record-ready mode.
Press either the [PLAY] key or the foot switch, and
playback and recording will begin simultaneously.
While listening to the playback, press either the
[PLAY] key or the foot switch at the intervals you
selected in step 4, to record the tap tempo. A counter
will be displayed while tempo is being recorded.
Tap tempo
While playing back a song, you can press (tap) the
[PLAY] key at the beginning of each measure or beat to
record a tempo. Alternatively, you can use a foot switch
(separately sold option) instead of the [PLAY] key.
Tap tempo can be used to record the tempo after you
have recorded a song. By recording the tempo afterward
for a song that contains no tempo settings, you can do the
following things.
• Edit tracks in units of a measure
• Synchronize external MIDI devices
1. Prepare the audio for which you wish to record the
tempo.
First, the audio for which you wish to record tempo
data must be recorded from the beginning of the
song.
Trigger recording is a convenient way to record
from the beginning of the song. (→p.43)
2. Specify the time signature of the song.
If the time signature changes during the song, create
a tempo map event at each location where the time
signature changes (→p.72 “Tempo map”). You will
not be able to set the tempo of the tempo map event
in this case.
3. If you wish to use a foot switch to input the tap
tempo, connect a foot switch such as the PS-1
(separately sold option) to the [FOOT SW] jack of
the D1600mkII.
4. Select the tempo recording method.
In the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “TmpTrk” tab page,
select either “MeasTap” (tap at the beginning of each
measure), or “BeatTap” (tap at the beginning of each
beat).
When pressing the [PLAY] key to record taps, do
not strike the key with excessive force. Doing so
may cause the hard disk or other components to
malfunction.
6. Stop recording.
After entering the last tap, press the [STOP] key to
end.
For example if you are recording four measures of 4/
4 time, you would tap 4 times for “MeasTap” or 16
times for “BeatTap,” and press the [STOP] key at the
beginning of measure 5.
If you input taps only part-way through the song, the
tempo of the last-input measure or beat will be automatically copied until the end of the song.
7. Select the tempo track as the tempo source.
Access the [TEMPO/RHYTHM] “SetUp” tab page.
Select “T
select “TempoTrk.”
empoSource,” and rotate the [VALUE] dial to
74
Page 83

Data
When you switch songs or turn off the power, the
D1600mkII’s auto-save function automatically saves the
song you recorded or edited, and its parameters.
This means that it is not absolutely necessary for you to
explicitly perform a “save” operation.
If you edit an effect program and want to keep the results, you must save the effect.
You will use the data-saving operations described here
when you want to save important data created on the
D1600mkII on a CD-R/RW or your computer, for
example when you want to free up additional space by
deleting data from the hard disk.
If you want to save data on your computer, first save the
data to the USB drive of the D1600mkII’s hard disk, and
then save this data on your computer.
You can save the following data.
• Song data
•Effect user data
•WAV files (audio files in WAV format)
The various parameters of the song are not saved on
an audio CD you create. If you want to save the song
in a state in which it can be edited or remixed further,
you must make a backup of it.
Data save methods and the types of file that can be saved
Data save method
Backup1Song
BackupAllSongs
BackupUserData
Export
1 song + all user effects
All songs + all user effects
All user effects
Either the Insert, Master, or Final user effects
WAV-format files
File type
Save-destination
➞CD-R/RW ➞USB drive
To back up to CD-R/RW
Here’s how to back up all songs to CD-R/RW.
No further data can be written to a CD-R/RW disc
you use for a backup.
The CD-R/RW created by this backup operation is
not in ISO9660 format. You will not be able to load it
into a computer or play it on a CD player.
1. Insert a CD-R/RW disc into the CD-R/RW drive.
You must use a blank disc. To erase the contents of a
CD-RW disc so that it can be used as a blank disc,
refer to “3. Erasing the data from a CD-RW” (→p.83).
2. Select “BackupAllSongs.”
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “B-U/Rst” tab page, select “BU/RstType” and turn the [VALUE] dial to select
“BackupAllSongs.”
Alternatively, you can press the “ ” button to open
the “Select Backup/Restore Type” dialog box.
DestinationSource B-U/RstType
3. Verify the songs you want to back up.
Make sure that “Source” is set to “ALL.”
4. Select the backup-destination drive.
Press the “Drive” button to open the dialog box.
Select “C:CD” and press the “Yes” button.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
Filename extensions of files saved on the USB drive
Data save method
Backup1Song
BackupUserData
Export
File type
1 song
All user effects
Insert User Data [Ins001–Ins128]
Master User Data [Mst001–Mst032]
Final User Data [Fin033–Fin064]
WAV-format files
Extension
.DBK
.DFX
.DFI
.DFM
.DFF
.WAV
1. Backing up and restoring song
data
Backing up song data
You can back up song data in the following ways.
• Backup1Song: Back up the single selected song.
• BackupAllSongs: Back up all songs. (CD-R/RW only)
•Effect user data will also be saved.
•A backed up song cannot be played directly. In
order to play the song, you must first restore it into
the D1600mkII.
5. Check the backup-destination drive and the drive
information.
Make sure that “C:CD” is selected as the “Destination.” The number of CD-R/RW discs is displayed.
Make ready the appropriate number of discs.
If you are using more than one disc, we recommend that you number them beforehand.
6. Execute the backup.
Press the “Exec.” button to display the confirmation
screen. Here you can specify the writing speed.
Press the “Yes” button to begin the backup. Effect
user data will also be backed-up at this time.
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
Data
the system
75
MIDI
Page 84

If more than one disc is required, the following dialog
box will appear when the disc is full, requesting you
to insert the next disc. Insert the next disc, and press
the “Yes” button.
When the backup is finished, the display will indicate
“Completed.” Press the “Yes” button.
When backing up to CD-R/RW, the backed-up
data will automatically be compared to the original data to ensure that the backup CD is valid.
If you press the “Cancel” button while writing to
CD-R, writing will be halted and the disc will be
unusable. If you are writing to CD-RW, the data
that was being written will be erased.
To back up to the USB drive
Here’s how to back up the selected song to the USB
drive.
1. Select the song that you want to back up.
2. Select “Backup1Song.”
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “B-U/Rst” tab page, select “BU/RstType” and turn the [VALUE] dial to select
“Backup1Song.” Alternatively, you can press the
“” button to open the “Select Backup/Restore
Type” dialog box.
7. Execute the backup.
Press the “Exec.” button to open a confirmation
dialog box.
Here you can specify a date (timestamp) for the file.
Press the “Date” button to open the dialog box, select
the date and time fields, and turn the [VALUE] dial to
edit them.
Press the “Yes” button and the backup will begin.
Effect user data will also be backed up at this time.
Effect user data is saved under a name of
“(filename specified in steps 6 and 7).DFX”. You
cannot save if an identically-named file already
exists on the USB drive. You will need to change
the name.
Restoring song data
When backed-up song data is restored back into the
D1600mkII, the data will once again be playable.
To restore
1. If you are restoring from CD-R/RW, insert the disc
into the CD-R/RW drive.
DestinationSource B-U/RstType
3. Verify the song that you want to back up.
Make sure that the song you want to back up is
selected for “Source.”
4. Select the backup-destination drive.
Press the “Drive” button to open the dialog box.
Select “U:USB DOS” and press the “Yes” button.
5. Verify the backup-destination drive and filename.
The file name will be the name of the song you are
backing up.
Make sure that “U:(song name)” is selected as the
“Destination.”
6. Edit the file name.
If you want to change the file name, press the
“Rename” button. Edit the name in the “Rename
File” dialog box. (→p.35)
You cannot save if an identically-named file
already exists on the USB drive. You will need to
change the name. The file name can be a maximum of eight characters.
DestinationB-U/RstType
2. Select “Restore.”
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “B-U/Rst” tab page, select “BU/RstType,” and turn the [VALUE] dial to choose
“Restore.” Alternatively, you can press the “ ”
button to open the “Select Backup/Restore Type”
dialog box and make your selection there.
3. Select the restore-source drive.
Press the “Drive” button to open the dialog box.
Select “C:CD[B]” or “U:USB DOS,” and press the
“Yes” button.
4. Select the restore-source song.
Press the “ ” button to open the “Select
RestoreSong” dialog box, and select the song that you
want to restore.
When restoring from CD-R/RW
From the file list, select the song that you want to
restore.
76
If you want to restore all songs, turn on the “Select
All” button.
Select the desired song, and press the “Yes” button.
Page 85

When restoring from the USB drive
From the file list, select the song that you want to
restore.
You cannot restore all songs in a single operation.
Select the desired song, and press the “Yes” button.
5. If you are restoring a single song, select the restoredestination song.
Move the cursor to “Destination,” and use the
[VALUE] dial to select the restore-destination song
number.
6. Execute the restore.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute.
If you are restoring from a multi-disc backup, you
will be requested for the next disc when necessary.
When this occurs, insert the next disc and press the
“Yes” button. Insert the discs in the order in which
they were backed-up.
When the operation is finished, you can choose to
restore effect user data. If you do so, the effect user
data currently on the hard disk will be overwritten.
2. Backing up and restoring effect user data
Backing up effect user data
You can back up effect user data in the following ways.
• Back up all effect user data
• Back up individual effect user data (only to the USB
drive)
You can also save all effect user data as part of a song
data backup.
When you restore, the effect user data currently on
the hard disk will be overwritten.
Backing up to CD-R/RW
Here’s how to back up all effect user data to a CD-R/RW
disc.
1. Insert the CD-R/RW into the CD-R/RW drive.
2. Select “BackupUserData.”
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “B-U/Rst” tab page, select “BU/RstType,” and turn the [VALUE] dial to choose
“BackupUserData.” Alternatively, you can press the
“” button to open the “Select Backup/Restore
Type” dialog box and make your selection there.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
Press the “Yes” button.
The effect user data will be restored, overwriting the
effect user data on the hard disk.
If you press the “No” button, the effect user data will
not be restored.
When you restore from the USB drive, effect user
data will not be restored if there is no effect user
data file of the same name as the song you are
restoring.
7. When the operation is finished, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “Yes” button.
DestinationSource B-U/RstType
3. Select “C:CD” as the backup-destination drive.
Press the “Drive” button to open the dialog box.
Select “C:CD” and press the “Yes” button.
4. Make sure that “EffAll” is selected as the “Source.”
5. Make sure that “C:CD” is selected as the “Destination.”
6. Execute the backup.
Press the “Exec.” button, and a confirmation dialog
box will appear. Here you can specify the writing
speed.
Press the “Yes” button to begin the backup.
When execution is finished, the display will indicate
“Completed.” Press the “Yes” button.
When backing up to CD-R/RW, the backup is
automatically compared with the original data to
ensure that the backup CD is valid.
If you press the “Cancel” button while writing to
CD-R, writing will be stopped and an unusable
disc will result. If you are writing to CD-RW, the
data that was being written will be erased.
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
Data
the system
77
MIDI
Page 86

Backing up to the USB drive
Here’s how to back up user area insert effect “U055” to
the USB drive.
1. Select “BackupUserData.”
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “B-U/Rst” tab page, select “BU/RstType,” and turn the [VALUE] dial to select
“BackupUserData.” Alternatively, you can press the
“” button to open the “Select Backup/Restore
Type” dialog box and make your selection there.
DestinationSource B-U/RstType
Restoring effect user data
To restore
1. When restoring from CD-R/RW, insert the disc into
the CD-R/RW drive.
2. Select “Restore.”
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “B-U/Rst” tab page, select “BU/RstType,” and turn the [VALUE] dial to choose
“Restore.” Alternatively, you can press the “ ” button to display “Select Backup/Restore Type” and
make your selection.
2. Select “U:USB DOS” as the backup-destination
drive.
Press the “Drive” button to open the dialog box.
Choose “U:USB DOS” and press the “Yes” button.
3. Select the effect that you want to back up.
Move the cursor to “Source,” and use the [VALUE]
dial to select “Ins055.”
4. Verify the backup-destination drive and filename.
The name of the effect you are backing up will be the
filename. Make sure that “U:(effect name)” is selected
as the “Destination.”
5. Edit the filename.
Press the “Rename” button, and use the “RenameFile” dialog box to edit the filename. (→p.35)
If a file of the same name already exists on the
USB drive, you will not be able to save. Please
change the name.
If you select all effects “EffAll,” the name of the
currently selected song will be the name of the
effect user data file.
6. Execute the backup.
Press the “Exec.” button to display the confirmation
screen.
DestinationSource B-U/RstType
3. Select the restore-source drive.
Press the “Drive” button to open the dialog box.
Select “C:CD[B]” or “U:USB DOS,” and press the
“Yes” button.
4. If you are restoring from the USB drive, select the
effect user data that you want to restore.
Press the “ ” button.
From the “BackUpFileList,” select the effect that you
want to restore.
For details on the file types, refer to p.75.
Press the “Yes” button.
5. Verify the restore-destination.
If you are restoring all effect user data, the display
will indicate “***”.
If you are restoring individual effect user data, select
the restore-destination effect number. Move the
cursor to “Destination,” and use the [VALUE] dial to
make your selection.
6. Execute the restore.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?”, so press the
“Yes” button to execute.
7. When execution is completed, the display will
indicate “Completed.” Press the “Yes” button.
78
Here you can specify a date (timestamp) for the file.
Press the “Date” button to open the dialog box, select
the date and time fields, and use the [VALUE] dial to
edit them.
Press the “Yes” button and the backup will begin.
Page 87

3. Saving a WAV file
Importing a W AV file: You can load a W AV-format audio
file from CD-ROM/R/RW or the USB drive and paste it
into a track of a D1600mkII song.
You can use Undo to return to the previous state.
Exporting a WAV file: Audio data you copy to the
D1600mkII’s clipboard can be exported as a WAV-format
audio file to CD-R/RW or the USB drive.
6. Execute the import.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” If you want to
execute, press the “Yes” button.
The display will indicate “Completed” when the
operation is finished. Press the “Yes” button.
This operation will take a longer time in proportion
to the length of the file you are importing.
7. Move to the beginning of the song, and verify that
the data was imported correctly.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
Importing (loading) a WAV file
You can import WAV files of the following formats.
• Sampling frequency: 44.1 kHz
• Bit depth: 8-bit, 16-bit, 24-bit
• Number of channels: 1 (monaural), 2 (stereo)
If you want to import a WAV file from your compu-
ter, connect a USB cable and copy the WAV file from
your computer to the D1600mkII’s USB drive. Then
import the file from the USB drive.
Importing a WAV file into the beginning of a track
Here’s how to import a monaural WAV file from CD into
the beginning of track 1.
1. Insert the CD-R/RW disc containing the WAV file
into the CD-R/RW drive.
2. Select the Import operation.
Access the [TRACK] “Import” tab page.
DestTrackDriveList WavFileList
Importing a WAV file into the middle of a track
Here’s how to import a stereo WAV file from the USB
drive, and copy it once to the TO location (the time location stored in the [TO/LOC3] key) of the tracks 1 and 2.
1. Select the Import operation.
Access the [TRACK] “Import” tab page.
DestTrackDriveList WavFileList
2. Select the import-source drive.
Press the “DriveList” button to open the dialog box.
Select “U:USB DOS” and press the “Yes” button.
3. Select the WAV file that you want to import.
Press the “WavFileList” button to open the dialog
box.
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
3. Select the import-source drive.
Press the “DriveList” button to display the dialog
box.
Select “C:CD” and press the “Yes” button.
4. Select the WAV file that you want to import.
Press the “WavFileList” button to open the dialog
box.
You can press the “Prvw” (preview) button to audition the first two seconds of the selected WAV file.
Select the desired WAV file and press the “Yes”
button.
5. Select the import-destination track number.
For “DestTrack,” select track “1”.
Select a stereo WAV file and press the “Yes” button.
4. Select the clipboard as the import-destination track
number.
Select “Clip2” as the “DestTrack.”
The number indicates the number of tracks in the
clipboard. In the case of monaural data, this will
be “Clip 1”.
5. Execute the import.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute.
The display will indicate “Completed” when the
operation is finished. Press the “Yes” button.
This operation will take a longer time in proportion to the length of the file you are importing.
6. Store the TO location.
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
Data
the system
79
MIDI
Page 88

7. Select the Copy operation.
In the [TRACK] “EditTrk” tab page, select “CopyTrack” for “EditType.”
TimesSourceTrack DestTrack
8. Select the clipboard as the copy-source track
number.
Select “Clip2” for “SourceTrack.”
9. Select tracks 1 and 2 as the copy-destination track
numbers.
Select “1–2” for “DestTrack.”
10. Specify the number of times the data will be copied.
In the “Times” field, select “1” as the number of copies.
11. Execute the copy.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute.
The display will indicate “Completed” when the
operation is finished. Press the “Yes” button.
The data will be overwritten onto the copydestination track.
12. Press the [TO/LOC3] key, and play back from the
TO location to verify that the data was imported
correctly.
Exporting (writing) a WAV file
You can export data as a WAV file in the following formats.
• Sampling frequency: 44.1 kHz
• Bit-depth: 16-bit, 24-bit
• Number of channels: 1 (monaural), 2 (stereo)
When exporting to CD-R/RW, you can add more
data to the disc later if desired.
An exported WAV file can be loaded into the
D1600mkII or your computer even without finalizing
the disc.
When a WAV file is exported to CD-R/RW, it is written in ISO9660 level 1 format.
A file exported to the USB drive can then be saved on
your computer.
3. Copy the track data to the clipboard.
In the [TRACK] “EditT rk” tab page, set “EditType” to
“CopyTrack.”
Select tracks “1–2” as the “SourceTrack.”
Select “Clip2” as the “DestTrack.”
The number indicates the number of tracks in the
clipboard.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute.
The display will indicate “Completed” when the
operation is finished. Press the “Yes” button.
4. Choose the Export operation.
Access the [TRACK] “Export” tab page.
DriveList
5. Select the export-destination drive.
Press the “DriveTrack” button to open the dialog box.
Select “U:USB DOS” and press the “Yes” button.
6. Edit the name of the WAV file.
Press the “Rename” button, and edit the name in the
“RenameFile” dialog box. (→p.35)
When you export a stereo WAV file, the seventh
and eighth characters of the filename will auto-
matically be “ST”. For a monaural file, this will
be “MN”.
You cannot save the data if an identically-named
file already exists on the USB drive.
7. Specify the date and time of the WAV file.
Press the “Date” button to open the dialog box, select
the field you want to edit, and use the [VALUE] dial
to specify the date and time.
To export a WAV file
Here’s how to copy the IN–OUT region of tracks 1 and 2
from a 16-bit song to the clipboard, and export it as a
stereo WAV file to the USB drive.
1. Select a 16-bit song.
2. Store the IN and OUT time locations.
80
8. Execute the Export operation.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to execute.
The display will indicate “Completed” when the
operation is finished. Press the “Yes” button.
Page 89

4. Data compatibility with other models in the Digital Recording Studio series
This section discusses data compatibility between the
D1600mkII and the D12, D16 (version 2.0 and following),
D1200, D1600, and D1200mkII models of the Digital
Recording Studio series.
If you want to use D1600mkII data on the D16, you
must update the D16’s system to version 2 or later.
Effect programs
D1600mkII effect programs can also be used on the
D1200 or D1200mkII in the same way.
Some D1600mkII effect programs may not work in the
same way on the D12, D16, and D1600.
This is because the algorithms of the following three
D1600mkII effects differ from those of the D12, D16, and
D1600.
• 48: PA1: Pre Amp Simulator
• 49: EB1: Bass Multi1
• 52: MS1: Mic Multi
Be aware that if an effect program using these algorithms
is created on the D1600mkII, it will not produce the same
results when restored to the D12, D16, or D1600.
The opposite is also true.
Since insert effects can also be used in scenes, you will
not obtain the same results when D12, D16, or D1600
data is restored to the D1600mkII, or conversely.
Compatibility of data written to CD-R or CDRW
Data compatibility with the D12, D1200, and
D1200mkII
A CD-R or CD-RW created on the D12, D1200, or
D1200mkII can be used in the same way as
D1600mkII data. Song data and effect user data will
appear in the D1600mkII’s drive list as “D12[B]”.
A CD-R or CD-RW created on the D1600mkII can also
be used on these models. Song data and effect user
data will appear in the D12/D1200/D1200mkII drive
list as “D12[B]”. However, the data of tracks 13–16
cannot be restored.
As mentioned above, some D12 insert effects use
a different algorithm than the D1600mkII.
Compatibility of data saved to computer via
the USB connector
Data compatibility with the D1200 and D1200mkII
When data created on the D1200 or D1200mkII is
restored into the D1600mkII, it can be used in the
same way as D1600mkII data.
When D1600mkII data is restored into the D1200 or
D1200mkII, it can be used in the same way as D1200
or D1200mkII data. However, the song data of tracks
13–16 cannot be restored.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
Data
Data compatibility with the D16 and D1600
A CD-R or CD-RW created on the D16 or D1600 can
be used in the same way as D1600mkII data.
A CD-R or CD-RW created on the D1600mkII can also
be used by these devices.
the system
MIDI
81
Page 90

Drive
The D1600mkII’s internal hard disk is divided into a
“song drive” used to record and play back the songs you
record, and a “USB drive” used to exchange data with
your computer.
The size of the USB drive is fixed as 2 Gbytes of the
total hard disk capacity; the remainder of the hard
disk is the song drive.
Perform the following operations if you want to erase
data from a drive or CD-RW disc, or if error messages
appears.
1. Checking the hard disk
This operation detects and repairs errors on the song
drive of the hard disk. Execute this if error messages such
as “DiskBusy” start appearing frequently. After execution, you can continue using the song data if there were
no major errors.
1. Select “CheckDrive/S”.
Access the [SYSTEM/USB] “DiskUtil” tab page.
Choose “SelOperation,” and use the [VALUE] dial to
select “CheckDrive/S”.
2. Formatting the hard disk
Execute this operation if you want to erase data from the
entire song drive and/or USB drive, or if “DiskError”
messages start appearing frequently and executing the
CheckDrive operation did not help. You can format the
song drive and USB drive simultaneously or individually.
When you execute this Format operation, all data will
be erased from the disk, so be sure to check the contents of the disk before you execute.
If an unexpected accident such as a power failure
occurs during the format operation, the D1600mkII
may become unable to operate correctly. If this
occurs, please contact your Korg distributor.
1. Select the type of format operation.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “DiskUtil” tab page, choose
“SelOperation” and use the [VALUE] dial to select
the desired type of format.
• Format ALL: format the entire hard disk
• Format/S: format the song drive
• Format/U: format the USB drive
SelOperation
2. Execute the Format operation.
Press the “Exec.” button to open the dialog box.
SelOperation
2. Execute the Check Drive operation.
Press the “Exec.” button to open the dialog box.
Specify the area to be checked. In this example, select
“Unused.”
Press the “Yes” button to begin checking.
The display will indicate “Completed” when check-
ing is finished. Press the “Yes” button.
82
Use the “Quick” button to select the type of formatting.
Normally you will turn the “Quick” button on. This
will merely initialize the system management area, so
formatting will not require very much time.
If the “DiskError” message appears frequently, turn
the “Quick” button off. For example you would turn
this off if the D1600mkII failed to recognize the drive
even after it was formatted with “Quick” turned on.
Formatting with the “Quick” button turned off
will require a substantial length of time for
completion. For example to format 40 GB, the
time required will differ as follows depending on
whether the “Quick” button is on or off.
Off: approximately 10 hours and 30 minutes
On: approximately 7 seconds
If you turn on the “Force” button, formatting will be
executed even if the hard disk contains protected
songs.
If you execute formatting with the “Force” button
turned off, and the hard disk contains a protected
song, the “SongProtect” message will appear , and the
operation will be aborted.
Page 91

Press the “Yes” button to begin formatting.
The display will indicate “Completed” when the
operation is finished. Press the “Yes” button.
3. Erasing the data from a CD-RW
Here’s how you can erase the data from a CD-RW disc.
When you erase the data, that disc can again be used as a
blank disk.
When you execute “EraseCD-RW” all data on that
CD-RW disc will be erased.
You cannot execute “EraseCD-RW” on any drive other than the CD-RW.
SelOperation
1. Insert a CD-RW disc into the CD-R/RW drive.
2. Select “EraseCD-RW”.
Access the [SYSTEM/USB] “DiskUtil” tab page, and
use the [VALUE] dial to choose “SelOperation”.
3. Execute the Erase operation.
Press the “Exec.” button to open the dialog box.
4. Using the drive capacity
efficiently
You can use the following three operations or techniques
to make efficient use of the D1600mkII’s drive capacity.
• Execute the Optimize Track operation
• Erase the Undo data
• Share audio data
Executing the Optimize Track command
Here are three examples of executing the Optimize Track
operation. As you will see, there are some situations in
which this operation will recover additional drive
capacity, and other situations in which it will not. Read
this section, and execute the Optimize Track operation if
it will be useful in your situation.
There is no need for you to execute this Optimize
Track operation frequently. Execute it if the “DiskBusy” message appears, or if you want to recover
hard disk space after you have completed a song.
Example 1: You recorded an intro, solo, and ending
on a track
When you record an intro, solo, and ending on the track,
the regions between these will record silence (in reality, a
noise-level signal), unnecessarily occupying space on the
drive.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
Use the “Quick” button to select the type of erasure.
If this button is turned on, the CD-RW disc will be
erased at high speed. Normally you will select this
method.
If this button is turned off, the CD-RW disc will be
erased completely. Use this method if the disc is not
recognized even after being erased with the “Quick”
button turned on.
Press the “Yes” button to begin erasing the disc.
The display will indicate “Completed” when the
erasure is finished. Press the “Yes” button.
You can also erase data from a CD-RW in the
[SONG/CD] “CDR/RW” tab page.
Intro Solo EndingSilence
If you want to keep only the audio data of the intro,
solo, and ending
Execute the Optimize Track operation on the track
you recorded, from the beginning of the song to the
end. When executing, set the Optimize T rack “Mode”
to “Erase Silence.” This will leave only the actuallyused regions as audio data, so that only the intro,
solo, and ending will occupy space on the drive.
Intro Solo Ending
IN OUT
Intro Solo Ending
Silence
“OptimizeTrack”
After execution
Data erased
Silence
Silence
Data
erased
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
Drive
83
the system
MIDI
Page 92

Example 2: You recorded an intro, A, B, and solo on
the first take, and overwrite-recorded A’ and B’ on
the second take
When you play back the track, you will hear only the
intro, A’ and B’. However in actuality, the A and B data
you recorded on the first take will remain “underneath”
A’ and B’. This is because the first take is saved as one
piece of audio data, and the track is using the intro and
solo regions of this data. Thus, the audio data of the first
take and second take are occupying the drive.
First
take
Record the second take
First
Intro BA
take
Second
take
BA SoloIntro
Solo
B'A'
To erase A and B from the first take
Execute the Optimize Track operation on the track
you recorded, from the beginning of the song to the
end. This will create new audio data that contains the
intro from the first take, A’ and B’ from the second
take, and the solo from the first take. A and B from
the first take will be erased.
Intro
IN OUT
Intro
BA
B'A'
“OptimizeTrack”
B'A'
Solo
Solo
Example 3: You recorded A and B on the first take,
and intro, A’, B’, and solo on the second take
The A and B audio data you recorded on the first take
will remain in the track. However at the point you finish
recording the second take, the audio data of the first take
is not used at all, and thus the data of the first take will
not occupy space on the drive. In other words in this
case, there is no need for you to execute the Optimize
operation.
BA
First take
First
take
Second
Intro B'A' Solo
take
Erasing the Undo data
The D1600mkII lets you execute the Undo operation up
to 99 times. Old data is kept on the drive so that you can
do this.
If you want to erase this Undo data, simply restart the
D1600mkII. When you restart, all of the Undo data will
be erased, recovering the space on the hard disk.
Sharing audio data
When you execute Copy Track to copy track data into another track or song, the copy-source and copy-destination will share the same audio data. This means that no
additional space will be used on the drive.
Copy
Intro BA
Copy-destination track
Copy-source track
Intro BA
Intro BA
Shared data
However if new audio data is created because you
execute Optimize Track on the copy-destination or
copy-source, the data will no longer be shared. Be
aware that this will cause more drive space to be
occupied than before execution.
For example, suppose you record take 1 and copy it
to another track. Even if you record a second take on
the copy-source, the copy-source and copy-destination will still share the same audio data.
Copy-source track
Intro BA
Record a
second take
Intro BA
Second
take
A'
Copy
Intro BA
Shared data
If you then execute Optimize Track on the copysource, new audio data will be created for the copysource. This means that data will no longer be shared
with the copy-destination. In other words, executing
Optimize Track in this situation will cause a larger
amount of drive space to be occupied.
Copy-source track
Intro BA
Record a
second take
Copy
Copy
Shared dataShared data
Copy-destination track
Copy-destination track
84
Intro BA
A'
IN OUT
“OptimizeTrack”
Intro
A'
B
Copy-destination track
Intro BA
Shared data
Page 93

USB
2. Access the “USB Mode” screen.
Basic
operation
What is USB?
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, and is an interface
for transferring data between a computer and peripheral
devices.
You cannot connect USB peripherals such as external
hard disks or CD-R/RW drives to the D1600mkII.
By connecting the D1600mkII’s [USB] connector to your
computer, you can save data from the USB drive of the
D1600mkII’s hard disk onto your computer.
The following data can be saved to (or loaded from) your
computer via the USB drive.
Song data
Song data such as the data of each track, and pan and
effect settings etc.
Since this data is in the D1600mkII’s own format, it
cannot be played or edited as audio data on your
computer or another device. In order to play this
data, you must restore it into the D1600mkII.
Effect user data
Data stored in the effect program user area.
Since this data is in the D1600mkII’s own format, it
cannot be edited on your computer.
In order to edit this data, you must restore it into the
D1600mkII.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “DiskUtil” tab page, press the
“USB Mode” button.
Do not disconnect the USB cable or turn your
computer on/off while this screen is displayed.
3. A drive named “KORG D1600” will appear on your
computer.
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
WAV files: audio files in WAV format
This is audio track data that you copy to the clipboard.
1. Saving data to your computer
Do not format (initialize) the D1600mkII’s hard disk
from your computer. The hard disk may be formatted
only by the D1600mkII itself.
Windows users (Windows Me/2000 or
later)
In order to use the D1600mkII with Windows 98, you will
need to install a device driver. For details on obtaining
and installing the device driver, visit the Korg website
(http://www.korg.com).
The screens that appear will depend on the system
you are using. The screens shown here are for
Windows XP.
1. Use a USB cable to connect your computer.
Connect the USB cable to your computer , and connect
the other end to the [USB] connector of the
D1600mkII. Make sure that the connector is oriented
correctly, and push it all the way in.
Turn on your computer and start up your operating system before you do this.
4. Back up the data on your computer.
Open the “KORG D1600” drive that appeared in step
3, and you will see the contents of the USB drive on
the D1600mkII’s hard disk.
Copy the desired data into your computer. You can
also copy data from your computer into the USB
drive.
5. Disconnect the D1600mkII from your computer.
Left-click the icon shown in the right side of your
computer’s task bar.
5
From the menu that appears, left-click “Safely
remove USB Mass Storage Device (drive name).”
Make sure that a message of “You may now safely
remove the USB Mass Storage Device” appears.
Select the “USB Mode” “Exit” button and press
[ENTER]. When you have exited USB mode,
disconnect the USB cable from the D1600mkII.
If you are using Windows Me, “USB Mass
Storage Device” will appear as “USB Drive.”
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
USB
85
the system
MIDI
Page 94

Macintosh users (Mac OS 9.0.4 or later)
1. Use a USB cable to connect your computer.
Connect the USB cable to the [USB] connector of the
D1600mkII. Make sure that the connector is oriented
correctly, and push it all the way in.
2. Access the “USB Mode” screen.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “DiskUtil” tab page, press the
“USB Mode” button.
Do not disconnect the USB cable or turn off your
computer while this screen is displayed.
3. A drive named “KORG D1600” will appear on your
desktop.
When you connect the D1600mkII for the first
time, a device driver will be installed.
4. Back up the data on your computer.
Open “KORG D1600” that appeared in step 3, and
you will see the contents of the USB drive within the
D1600mkII’s hard disk. Copy the desired data into
your computer. You can also copy data from your
computer into the USB drive.
5. Drag the added drive into the trash.
To disconnect the D1600mkII, drag the drive from
your desktop into the “trash,” or select “Remove”
from the “Special” menu. In the “USB Mode” dialog
box, press the “Exit” button to exit the “USB Mode”
dialog box. Disconnect the USB cable from the
D1600mkII.
Updating the system
1. Downloading the system file
You can download the latest system file from the Korg
website (http://www.korg.com). For details, refer to the
Korg website.
Using a CD-ROM/R/RW
Insert the media containing the system file into the CDR/RW drive.
Using USB
Use a USB cable to connect the D1600mkII to your
computer, and copy the system file into the root level of
the USB drive (the same location as the KORG folder).
2. Updating the system
1. Load the system file.
In the “SelOperation” field of the [SYSTEM/USB]
“DiskUtil” tab page, choose “LoadSystem/C” if you
want to load from CD-ROM/R/RW, or
“LoadSystem/U” if you want to load from the USB
drive.
SelOperation
2. Execute loading.
Press the “Exec.” button.
The display will ask “AreYouSure?” Press the “Yes”
button to begin loading.
If the power is turned off while the system is
being loaded, the D1600mkII may stop operating
correctly. If this occurs, please contact your Korg
distributor.
3. When loading is completed, the D1600mkII will
check whether the system file was loaded correctly.
If the file was loaded correctly, the display will
indicate “Check sum = OK.” If not, the display will
indicate “Check sum = NG.”
If the display indicates “Check sum = NG,” restart
the D1600mkII and load the system file once again.
If the “Check sum = NG” message appears again, it is
possible that the D1600mkII has malfunctioned.
Please contact your Korg distributor.
86
Page 95

MIDI
What is MIDI?
MIDI stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface,
and is a world-wide standard that allows a variety of
musical information to be exchanged between electronic
musical instruments and computers.
About the MIDI implementation chart
The owner’s manual of each MIDI device contains a
MIDI implementation chart. This chart makes it easy for
you to verify the MIDI messages that the device can
transmit and receive. When using two MIDI devices
together, compare their MIDI implementation charts to
verify the types of MIDI message that they are able to
exchange.
• For more details on the MIDI specifications, refer to the
separate MIDI implementation. To obtain the MIDI
implementation, please contact your Korg distributor.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
1. MIDI connections
Special MIDI cables are used to transmit and receive
MIDI messages. Connect these cables between the MIDI
connectors of the D1600mkII and the MIDI connectors of
the external device with which you wish to exchange
data.
MIDI IN connector: MIDI messages from another MIDI
device are received here. Connect this to the MIDI OUT
connector of the external device.
MIDI OUT connector: The D1600mkII transmits MIDI
messages from this connector. Connect this to the MIDI
IN connector of the external device.
MIDI channel settings
MIDI allows information for multiple MIDI devices to be
conveyed over a single MIDI cable by using sixteen
MIDI channels, 1–16. If MIDI messages are being
transmitted on MIDI channel “1”, the messages will not
be received unless the receiving device is also set to MIDI
channel “1.”
2. MIDI messages used by the D1600mkII
Note, aftertouch, velocity, pitch bend: This data is used
by the D1600mkII to control effects.
Program change: This data is used by the D1600mkII to
select scenes.
Control change: This data is used by the D1600mkII to
control mixer parameters.
MMC (MIDI Machine Control): MMC messages can be
transmitted to control an external sequencer or recorder.
MMC messages can also be received to control the
D1600mkII from an external sequencer or recorder.
MTC (MIDI Time Code): MTC messages can be
transmitted to make an external sequencer or recorder
operate in synchronization with the D1600mkII. MTC
messages can also be received to synchronize the
D1600mkII with another device.
3. Using MIDI
Controlling the D1600mkII from a MIDI sequencer
Here’s how the MMC messages transmitted from a MIDI
sequencer can be used to stop/play/fast-forward/
rewind/record/locate the D1600mkII.
You must use a MIDI sequencer that supports MMC.
These following operations are not possible with a
sequencer that does not support MMC.
1. Make MIDI connections.
Use a MIDI cable to connect the MIDI OUT connector
of your MIDI sequencer to the [MIDI IN] connector of
the D1600mkII.
MIDI
IN
D1600mkII
2. Make settings on your MIDI sequencer so that it
will output MMC messages to control external
devices.
For details refer to the owner’s manual for your MIDI
sequencer.
3. Turn on MMC reception.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “MMC” tab page, set “SelectMMCMode” to “Receive.”
4. Set the device ID settings to match.
Set “MMCDevID
device ID of your MIDI sequencer.
Since the device ID specifications may differ
depending on the type of your MIDI sequencer , it
may not be necessary for the number to be the
same.
” to the same setting as the MMC
MIDI
OUT
MIDI Sequencer
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
Updating
the system
the system
87
MIDI
MIDI
Page 96

5. Operate your external MIDI sequencer.
When you perform stop/play/fast-forward/rewind/
record/locate operations on your MIDI sequencer,
the D1600mkII will be controlled accordingly. (For
details refer to the owner’s manual for your MIDI
sequencer.)
At this time, you can also make the D1600mkII
transmit MTC (MIDI Time Code) or MIDI Clock
messages to synchronize the MIDI sequencer, so
that the two devices will be synchronized as the
sequencer controls stop/play/fast-forward/
rewind/record/locate operations on the
D1600mkII.
Synchronizing two D1600mkII units
Here’s how you can synchronize two D1600mkII units.
One D1600mkII will be the master, and the other will be
the slave. Make connections as follows.
Using MIDI for mixer control
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “MIDI” tab page you can turn the
“Control Change: Trans” and “Recv” parameters “ON”
so that D1600mkII mixer parameters can be transmitted
and received.
Recording D1600mkII mixer control operations
Here’s how operations of the D1600mkII mixer can be
recorded on an external MIDI sequencer. Connect the
D1600mkII and your MIDI sequencer as follows.
MIDI
OUT
MIDI
IN
MIDI
OUT
MIDI
IN
MIDI
IN
MTC “MTC Slave”
MMC “Receive”
MTC “MTC Mstr”
MMC “Transmit”
MIDI
OUT
D1600mkII (Master) D1600mkII (Slave)
1. Make settings on the master D1600mkII.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “Sync” tab page, set “Select
MIDI SyncMode” to “MTC Mstr.” In the [SYSTEM/
USB] “MMC” tab page, set “Select MMC Mode” to
“Transmit.”
For this example, set “MMCDevID” to “10.”
2. Make settings on the slave D1600mkII.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “Sync” tab page, set “Select
MIDI SyncMode” to “MTC Slave.” In the [SYSTEM/
USB] “MMC” tab page, set “Select MMC Mode” to
“Receive.” For this example, set “MMCDevID” to
“10” (the same as the master).
If you do not want to receive mixer control data,
you can either turn the [SYSTEM/USB] “MIDI”
tab page “Control Change: Trans” parameter
“Off” on the master D1600mkII, or turn the
[SYSTEM/USB] “MIDI” tab page “Control
Change: “Recv” parameter “Off” on the slave
D1600mkII.
3. Press the [PLAY] key on the master D1600mkII.
When the slave D1600mkII receives time code and
establishes synchronization with the time code of the
master unit, the slave D1600mkII will begin playback.
Several seconds may be required in order for
synchronization to be established.
MIDI Sequencer
D1600mkII
1. Make synchronization settings for the D1600mkII
and your external MIDI sequencer.
Set the D1600mkII as the master and the external
MIDI sequencer as the slave. Make preparations so
that your MIDI sequencer will synchronize to the
MIDI Clock or MTC messages transmitted from the
D1600mkII. (→p.92)
2. Enable control change transmission on the
D1600mkII.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “MIDI” tab page, turn the
“Mixer Control” parameter “Control Change: Trans”
to “ON.”
3. Put the external MIDI sequencer in record-ready
mode.
The mixer control data of the D1600mkII will be
transmitted on MIDI channels 1–16 corresponding to
tracks 1–16. Make settings on your external MIDI
sequencer so that MIDI channels 1–16 will be
recorded. (For details refer to the owner’s manual of
your MIDI sequencer.)
For the parameters, refer to the MIDI implementation. To obtain the MIDI implementation, contact
your Korg distributor.
4. Begin recording.
When you press the D1600mkII’s [PLAY] key to start
playback, the external MIDI sequencer will begin
recording in synchronization. Now when you operate
the mixer parameters (fader, pan, EQ etc.), the
corresponding control change will be transmitted
from the D1600mkII, and recorded on the external
MIDI sequencer.
5. Stop the D1600mkII.
When you press the D1600mkII’s [STOP] key to stop
playback, the external MIDI sequencer will also stop
recording. The mixer operations of the D1600mkII
have been recorded on the external MIDI sequencer.
88
Page 97

Using MIDI to control the D1600mkII mixer
Here’s how the mixer control data recorded in
“Recording D1600mkII mixer control operations” can be
transmitted back to the D1600mkII to control its mixer.
Make the same connections as in “Controlling the
D1600mkII from a MIDI sequencer.”
1. Make synchronization settings for the D1600mkII
and the external MIDI sequencer.
Make the settings in step 1 of “Recording D1600mkII
mixer control operations.”
2. Enable control change reception on the D1600mkII.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “MIDI” tab page, turn the
“Mixer Control” parameter “Control Change: Recv”
to “ON.”
3. Put the external MIDI sequencer in playback-ready
mode.
4. Begin playback on the D1600mkII.
When you press the D1600mkII’s [PLAY] key to begin
playback, the external MIDI sequencer will also begin
playback in synchronization. The previouslyrecorded mixer control data will be transmitted from
the MIDI sequencer, causing the D1600mkII mixer
settings to change.
Basic
operation
Creating/
selecting a song
to the mixer
Assign audio inputs
RecordingPlayback
time location
Changing the
mixer
Using the
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
settings
Rhythm/tempo
DataDriveUSBUpdating
89
the system
MIDI
MIDI
Page 98

90
Page 99

1. COUNTER
Reference
2. SYSTEM/USB
Reference
COUNTER
USB
SYSTEM /
Counter: Counter display
The counter located in the upper right of each page shows the
current location of the recorder.
1
1. Select TimeDisp Type...................................................
This switches the counter display. When you press the
“” button at the left of the counter, the “Select TimeDisp Type” dialog box will appear.
Select the desired type of display, and press the “OK”
button.
MBT
MSF
___.__.___ (MBT): The current location will be shown in
measures from the beginning of the song.
From the left, the numbers indicate the Measure, Beat,
and Tick (1/96 beat).
___:__.___ (MSM): The current location will be shown as
an absolute time from the beginning of the song.
From the left, the numbers are Minutes: Seconds. Milliseconds (1/1000 second).
__:__.__F (MSF): The current location will be displayed
as the absolute time and the number of frames from the
beginning of the song. You will normally select this display type if you are using MTC synchronization.
From the left, the numbers are Minutes: Seconds. Frames
(1/30 second).
___.__Free (Free Time): The remaining time available
for recording on the currently selected drive will be
shown.
From the left, the numbers are Minutes. Seconds.
To change the current time of the counter, move the
cursor to the counter value, and use the [VALUE]
dial to change the value.
If the counter display is set to “Free,” the times in the
STORE, MARK, SCENE, A.PUNCH, LOOP, and
SCRUB pages will be displayed as absolute time
(MSM).
MSM
FreeTime
P1 Control: Foot switch/control
change device (pedal/MIDI)
settings
31 2 4 5
1. Pol(FootSwPolarity) ............................................[–, +]
This sets the polarity of the foot switch.
Connect a foot switch (such as the separately sold PS-1
option) to the front panel [FOOT SW] jack, and set this
parameter so that the polarity indicator “ ” is lit when
you press the foot switch.
2. Func(FootSwFunction) ..... [PunchI/O, Play/Stop, Mark]
Select the function that the foot switch will control.
PunchI/O: The foot switch will start/stop manual punch
recording.
Use the [TRACK STATUS] keys to set the desired track
to REC, begin playback, and press the foot switch at the
location where you wish to begin recording. Press the
foot switch again to stop recording.
Play/Stop: The foot switch will start/stop playback.
Press the foot switch to start playback, and press it again
to stop playback.
Mark: The foot switch will register a mark.
When you press the foot switch, a mark will be registered at that time location.
While this page is displayed, the foot switch will be
used only to verify the polarity, and the specified
function will be disabled. Also during tap recording,
the function you select here will be ignored, and the
foot switch will automatically function as a tap
marker.
3. Device(CtrlChgDevice).............[Pedal, A.Touch, P.Bend,
Velocity, NoteNum, CC#000…119]
Select the external device that will control the internal
effects of the D1600mkII. The effect selected by “Asn
can be controlled in real-time.
Pedal: An expression pedal can be used to control the
effect. Connect an expression pedal (separately sold
option: XVP-10, EXP-2 etc.) to the [EXPRESSION
PEDAL] jack, and operate the pedal to control the effect.
A.Touch, P.Bend, Velocity, NoteNum: MIDI aftertouch,
pitch bend, velocity, or note number data can be used to
control the effect.
Connect the MIDI OUT of your external MIDI device to
the [MIDI IN] connector on the D1600mkII, and transmit
the selected MIDI data from the external MIDI device to
control the effect.
”
RECORDTRACKSONG /
CD
STOREMARKSCENETEMPO /
RHYTHM
IN / LOC1...
END / LOC4
AUTO
PUNCH
LOOPUNDOTRIGGERSCRUBENTERINPUT /
TUNER
EQ /
PHASE
FX
INSERT
MASTER
FX / AUX
SOLO /
MONITOR
Tr VIEW
METER /
Tr STATUSPANFADER
91
TRANSPORT
Page 100

CC(Control Change) #000…119: MIDI control change
messages can be used to control the effect. Connect the
MIDI OUT of your external MIDI device to the [MIDI
IN] connector on the D1600mkII, and transmit the
selected MIDI control change message from the external
MIDI device to control the effect.
4. Asn(CtrlChgAssign).......................[ExpOff, InsEff1…4]
Select the insertion effect that will be controlled.
The insertion effect that you select here will be controlled
by the selected “
ExpOff: The insertion effect will not be controlled.
InsEff1, InsEff2, InsEff3, InsEff4: Insertion effect 1, 2, 3,
or 4 will be controlled respectively.
If the effect program that you are using does not provide control capability, it cannot be controlled.
Device
”.
5. Fan Control............................. [On, Rec&PlayOff, Off]
Control the operation of the internal fan.
On: The fan will operate constantly.
Rec&PlayOff: The fan will stop during recording and
playback.
Off: The fan will stop.
If the internal temperature rises, the fan will begin
operating automatically even if this setting is “Off.”
When the temperature falls to an acceptable level,
the fan will stop automatically.
A external sequencer connected via MIDI can record the
control changes transmitted from the D1600mkII.
5. ControlChange: Recv.................................... [On, Off]
Turn control change reception on/off.
Control change messages that were recorded on an
external MIDI sequencer can be received by the
D1600mkII to control the corresponding mixer parameters.
For the parameters that can be controlled, refer to the
MIDI implementation chart (→p.164).
P3 Sync: Synchronization settings
By synchronizing the D1600mkII with an external MIDI
sequencer, you can simultaneously play back tracks of audio
together with your external tone generator.
The action of making the D1600mkII operate at the same timing as a MIDI sequencer is called synchronization.
The device transmitting the synchronization clock is called
the master, and the device receiving the synchronization
clock is called the slave. The D1600mkII can operate either as
the master or slave.
2
P2 MIDI: MIDI settings
2
1 3
5
4
1. GlobalCh(GlobalChannel).............................[01…16]
Specify the global MIDI channel.
This setting is required in the following situations.
• When using MIDI messages to control an effect with
a “Device
• When using program change messages to transmit/
receive scene changes
To allow MIDI messages to be transmitted and
received, connect the external MIDI device to the
D1600mkII via MIDI, and set the MIDI channel of the
external device to match the “GlobalCh
D1600mkII.
2. ProgramChange: Trans................................. [On, Off]
Turn program change message transmission on/off.
Program changes are transmitted when you switch
scenes, or execute a Store or Recall operation.
3. ProgramChange: Recv.................................. [On, Off]
Turn program change reception on/off.
When a program change is received, the scene will
change.
4. ControlChange: Trans................................... [On, Off]
Turn control change message transmission on/off.
The corresponding control change message is transmitted when you modify a mixer parameter.
” setting other than “Pedal”
” of the
1
1. Select MIDISync Mode .............. [MTC Mstr, MTC Slave,
Clock Mstr, Off]
Select the synchronization messages that will be transmitted
and received from the [MIDI IN/OUT] connectors.
MTC Mstr: The D1600mkII will function as the master
device for MTC 30 NDF (MIDI time code 30 non-drop
frame) messages.
MTC Slave: The D1600mkII will function as the slave
device for MTC 30 NDF (MIDI time code 30 non-drop
frame) messages.
Clock Mstr: The D1600mkII will transmit MIDI Clock
messages.
Off: The D1600mkII will not transmit or receive synchronization messages.
2. MTC RecvErrorLevel.........................................[0...10]
Specify the MTC check level used if “SelectMIDISyncMode” is set to “MTC Slave.”
If, due to some problem, MTC messages are not sent
consecutively to the D1600mkII, the D1600mkII will
detect the abnormal MTC state and may stop synchronization and halt playback. In such cases, you can lower
the “MTC RecvErrorLevel” setting so that synchronized
playback will continue even if some problems occur
with MTC reception.
If this is set to “0,” synchronized playback will not
stop even if a problem occurs.
Depending on the compatibility between the two
devices when a device other than the D1600mkII is
used as the MTC master for synchronization, correct
synchronization may not be possible unless you start
from the beginning of the song.
92
 Loading...
Loading...