Page 1

2010
Kenworth T440/T470
Body Builder Manual
®
Page 2

2010 Emissions
Kenworth T440/T470
Body Builder Manual
Page 3

T470/T440 Body Builder
Manual Contents
SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION 1-1
SECTION 2: SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE 2-1
SAFETY SIGNALS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETYSTANDARDS COMPLIANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
SECTION 3: DIMENSIONS 3-1
DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
ABBREVIATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
TURNING RADIUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
KENWORTH AXLE TRACK/TIRE WIDTH SUMMARY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
OVERALL DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
T470 FIXED GRILLE HOOD W/O EXTENDED FRONT FRAME . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
T440 DAYCAB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
T470 FIXED GRILLE HOOD WITH EXTENDED FRONT FRAME . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
38” AEROCAB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-10
RIDE HEIGHTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-12
REAR SUSPENSION LAYOUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-14
REYCO 79KB SINGLE REAR AXLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
REYCO 102 TANDEM REAR AXLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-15
NEWAY AD 123 SINGLE REAR AXLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-16
NEWAY AD 246 TANDEM SUSPENSION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-17
HENDRICKSON PRIMAAX TANDEM SUSPENSION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
HENDRICKSON HMX TANDEM SUSPENSION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-19
HENDRICKSON RT TANDEM SUSPENSION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-20
KENWORTH AG 380 TANDEM SUSPENSION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-22
KENWORTH AG 400/460 TANDEM SUSPENSION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-23
KENWORTH AG 400L TANDEM SUSPENSION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-24
KENWORTH AG 460 TANDEM SUSPENSION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-25
CHALMERS 856-46 TANDEM SUSPENSION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-26
PUSHER AXLES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-27
PTO CLEARANCES. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-32
SECTION 4: EXHAUST AND AFTERTREATMENT 4-1
EXHAUST AND AFTER-TREATMENT INFORMATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR DEF SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS AND DIMENSIONS FOR DEF SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . 4-3
MEASUREMENT REFERENCE POINTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
GENERAL EXHAUST INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-10
EXHAUST INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-19
SECTION 5: FRAME LAYOUTS 5-1
FRAME LAYOUTS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
COMMON OPTIONAL COMPONENTS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
FRAME LAYOUT INDEX. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
CHARTS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
SECTION 6: BODY MOUNTING 6-1
FRONT FRAME DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
FRAME INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
BODY MOUNTING USING BRACKETS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
MOUNTING HOLES. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
BODY MOUNTING USING U–BOLTS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
12/09
iv
Page 4

T470/T440 Body Builder
Manual Contents
SECTION 7: FRAME MODIFICATIONS 7-1
FRAME MODIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
MODIFYING FRAME LENGTH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
CHANGING WHEELBASE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
CROSSMEMBERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
WELDING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
TORQUE REQUIREMENTS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
SECTION 8: ELECTRICAL 8-1
ELECTRICAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
MULTIPLEX INSTRUMENTATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
ACCESSING GAUGES AND SWITCHES. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-9
TELLTALE SYMBOLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-17
SPARE RELAYS BODY BUILDER INSTALLED(FOR LOADS EXCEEDING 20 AMPS) . . . 8-23
ADDITIONAL SPARE CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-25
REMOTE PTO/THROTTLE HARNESS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-27
MULTIFUNCTION TURN SIGNAL STALK, CHASSIS NODE & CHASSIS LOAD CENTER .8-28
CHASSIS LOAD CENTER DIMENSIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-30
2010 ELECTRICAL HARDWARE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-31
TRAILER CABLE CONNECTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-35
FACTORY INSTALLED SNOW PLOW LIGHT WIRING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-37
SECTION 9: ROUTING 9-1
ROUTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
ROUTING REQUIREMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
APPENDIX A: VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION A-1
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION LABELS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
v
12/09
Page 5

Figures
FIGURE 2-1: INCOMPLETE VEHICLE CERTIFICATION DOCUMENT . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
FIGURE 2-2: LOCATIONS OF CERTIFICATION LABELS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
FIGURE 2-3: WEST COAST MIRROR OAT SENSOR, . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
FIGURE 2-4: AERODYNAMIC MIRROR OAT SENSOR LOCATION. . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
FIGURE 2-5: INSTRUMENT CLUSTER FOR T440/T470 USED WITH
EPA2010 EMISSION COMPLIANT ENGINES. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
FIGURE 3-1: PROSPECTOR TURN CIRCLE ANALYSIS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
FIGURE 4-1: MEASUREMENT LOCATION OF DEF SUPPLY MODULE (PUMP). . . . . 4-4
FIGURE 4-2: MEASUREMENT LOCATION OF DEF DOSING MODULE (INJECTOR) . . 4-4
FIGURE 4-3: ORIENTATION OF DOSING MODULE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
FIGURE 4-4: RH UNDER CAB EXHAUST WITH SMALL, MEDIUM, OR LARGE TANKS. 4-5
FIGURE 4-5: VERTICAL EXHAUST WITH SMALL, MEDIUM, OR LARGE TANKS.. . . . 4-6
FIGURE 4-6: RH UNDER CAB EXHAUST WITH CLEAR BACK OF CAB TANK. . . . . . 4-7
FIGURE 4-7: VERTICAL WITH CLEAR BACK OF CAB TANK. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
FIGURE 4-8: ROUTING DEF LINES AND DEF TRAP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
FIGURE 4-9: SUPPLY MODULE ALLOWED CLOCKING ANGLES . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
FIGURE 4-10: ISOMETRIC VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR
WITH SINGLE SOC TAILPIPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
FIGURE 4-11: TOP VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR
WITH SINGLE SOC TAILPIPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
FIGURE 4-12: RIGHT VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR
WITH SINGLE SOC TAILPIPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
FIGURE 4-13: BACK VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR
WITH SINGLE SOC TAILPIPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
FIGURE 4-14: ISOMETRIC VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR
WITH SINGLE BACK OF CAB TAILPIPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-13
FIGURE 4-15: TOP VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR
WITH SINGLE BACK OF CAB TAILPIPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-13
FIGURE 4-16: RIGHT VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR
WITH SINGLE BACK OF CAB TAILPIPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-14
FIGURE 4-17: BACK VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR
WITH SINGLE BACK OF CAB TAILPIPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-14
FIGURE 4-18: ISOMETRIC VIEW OF VERTICAL DPF AND SCR . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
FIGURE 4-19: TOP VIEW OF VERTICAL DPF AND SCR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-15
FIGURE 4-20: RIGHT VIEW OF VERTICAL DPF AND SCR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-16
FIGURE 4-21: BACK VIEW OF VERTICAL DPF AND SCR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-16
FIGURE 4-22: ISOMETRIC VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR ON
AEROCAB WITH SINGLE SOC TAILPIPE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-17
FIGURE 4-23: TOP VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR ON
AEROCAB WITH SINGLE SOC TAILPIPE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-17
FIGURE 4-24: RIGHT VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR ON
AEROCAB WITH SINGLE SOC TAILPIPE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-17
FIGURE 4-25: BACK VIEW OF RIGHT HAND UNDER DPF AND SCR ON
AEROCAB WITH SINGLE SOC TAILPIPE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-18
FIGURE 5-1: DEF TANK DIMENSIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
FIGURE 6-1: MINIMUM CLEARANCE BETWEEN TOP OF REAR TIRES
AND BODY STRUCTURE OVERHANG.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
FIGURE 6-2: MINIMUM BACK OF CAB CLEARANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
FIGURE 6-3: SPACER BETWEEN FRAME SILL AND BODY RAIL . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
FIGURE 6-4: HIGH COMPRESSION SPRING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
FIGURE 6-5: RUBBER SPACER BETWEEN BRACKETS BETWEEN THE
MOUNTING BOLT AND UPPER BRACKET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
12/09
vi
Page 6

Figures
FIGURE 6-6: CROSSMEMBER-GUSSET HOLE PATTERN REQUIREMENTS.. . . . . . 6-5
FIGURE 6-7: ACCEPTABLE U-BOLT MOUNTING WITH WOOD AND
FABRICATED SPACERS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
FIGURE 6-8: CLEARANCE SPACE FOR AIR LINES AND CABLES . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
FIGURE 6-9: EXAMPLE OF FISHPLATE BRACKET AT REAR END OF BODY,
USED WITH U-BOLTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
FIGURE 7-1: DETAIL OF FRAME EXTENSION AND JOINT WELDING. . . . . . . . . . 7-2
FIGURE 7-2: FRAME INSERT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
FIGURE 7-3: COMPARISON OF ORIGINAL, SHORTENED, AND
EXTENDED WHEELBASES.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
FIGURE 7-4: CROSSMEMBER ADDED WHEN DISTANCE
EXCEEDS 60 INCHES (1524 MM). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
FIGURE 8-1: KENWORTH T440/T470 DASH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
FIGURE 8-2: DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID GAUGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
FIGURE 8-3: MULTIPLEXED INSTRUMENTATION BLOCK DIAGRAM.. . . . . . . . . . 8-3
FIGURE 8-4: CECU LOCATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
FIGURE 8-5: INSTRUMENT CLUSTER COMPONENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-5
FIGURE 8-6: CVSG GAUGES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-6
FIGURE 8-7: FIREWALL AIR JUNCTION BLOCK (VIEW FROM INSIDE OF CAB). . . . 8-7
FIGURE 8-8: AIR FILTER RESTRICTION SENSOR ON FIREWALL
AIR JUNCTION BLOCK (VIEW FROM ENGINE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-7
FIGURE 8-9: FUEL FILTER RESTRICTION PRESSURE GAUGE SENSOR LOCATION
(TYPICAL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-8
FIGURE 8-10: TELLTALE SYMBOL STANDARD CARDS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-17
FIGURE 8-11: BLANK TELLTALE CARD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-18
FIGURE 8-12: TELLTALE ICONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-19
FIGURE 8-13: KENWORTH SPARE SWITCHES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-20
FIGURE 8-14: SPARE SWITCH HARNESS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-21
FIGURE 8-15: SPECIALTY SWITCHES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-22
FIGURE 8-16: SPARE RELAY CONNECTORS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-23
FIGURE 8-17: SPARE RELAY HARNESSES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-24
FIGURE 8-18: SPARE BULLET CONNECTORS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-25
FIGURE 8-19: SPARE PIGTAIL CONNECTOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-26
FIGURE 8-21: CHASSIS POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . .8-30
FIGURE 8-22: DAYCAB HARDWARE LOCATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-31
FIGURE 8-23: AEROCAB STANDARD HARDWARE LOCATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-31
FIGURE 8-25: CHASSIS NODE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-32
FIGURE 8-25: SAE J560 TRAILER CONNECTOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FIGURE 8-26: ISO 3731 TRAILER CONNECTOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-35
FIGURE 8-27: JUNCTION BOX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-36
FIGURE 8-31: SNOW PLOW ICON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-37
FIGURE 8-32: CIRCUIT LOCATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-37
FIGURE 9-1: CLAMP AND BUTTERFLY CLAMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
FIGURE 9-2: BUTTERFLY TIE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
FIGURE 9-3: TIE STRAP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
FIGURE 9-4: HEAVY DUTY (HD) MOUNT.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
FIGURE 9-5: DEFINITION OF MEASUREMENTS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
FIGURE A-1: VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
FIGURE A-2: DRIVERS DOOR AND DOOR FRAME LABELS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
FIGURE A-4: FRONT AXLE IDENTIFICATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-4
FIGURE A-5: REAR AXLE IDENTIFICATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-4
vii
12/09
Page 7

Tables
TABLE 3-1: ABBREVIATIONS USED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
TABLE 3-2: TURNING RADIUS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
TABLE 3-3: AXLE TRACK. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
TABLE 3-4: RIDE HEIGHTS IN INCHES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-12
TABLE 3-5: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-14
TABLE 3-6: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-15
TABLE 3-7: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-16
TABLE 3-8: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-17
TABLE 3-9: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-18
TABLE 3-10: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-19
TABLE 3-11: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
TABLE 3-13: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
TABLE 3-14: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
TABLE 3-15: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-24
TABLE 3-16: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-25
TABLE 3-17: REAR SUSPENSION OPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-26
TABLE 3-18: GROUND CLEARANCE FOR FUEL TANKS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-29
TABLE 3-19: GROUND CLEARANCE FOR BATTERY BOXES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-30
TABLE 3-20: GROUND CLEARANCE FOR BATTERY BOXES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-31
TABLE 5-1: ABBREVIATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
TABLE 5-2: FUEL TANK OVERALL LENGTH (IN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
TABLE 5-3: BATTERY BOX CENTERFRAME LENGTHS (IN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
TABLE 5-4: DEF TANKS SYSTEMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
TABLE 6-1: SINGLE STEEL RAILS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
TABLE 6-2: INSERTED STEEL RAILS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
TABLE 7-1: CUSTOMARY GRADE 8 UNF OR UNC.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
TABLE 7-2: U.S. CUSTOMARY – GRADE 8. METRIC CLASS 10.9 . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
TABLE 8-1: TELLTALES POSITION AND COLOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-18
TABLE 8-3: CHASSIS NODE GUIDELINE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-28
TABLE 8-4: WIRE NUMBER GENERAL CATEGORIES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-33
TABLE 8-6: SAE J560 CONNECTOR. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-34
TABLE 8-7: ISO 3731 CONNECTOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-35
TABLE 9-1: EXHAUST – SYSTEM CLEARANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
TABLE A-1: MODEL YEAR (CODE) DESIGNATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
12/09
viii
Page 8

Section 1
Introduction
This manual was created to provide body builders with appropriate information and guidelines
useful in the body planning and installation process. This information will be helpful when installing
bodies or other associated equipment.
This manual contains appropriate dimensional information, guidelines for mounting bodies, guidelines for modifying frames, electrical wiring information, and other information useful in the body
installation process. This manual is specifi c to chassis with 2010 engines.
The Body Builder Manual can be very useful when specifying a vehicle, particularly when the body
builder is involved in the vehicle defi nition and ordering process. Early in the process, professional
body builders can often contribute valuable information that reduces the ultimate cost of the body
installation.
In the interest of continuing product development, Kenworth reserves the right to change specifi cations or products at any time without prior notice. It is the responsibility of the user to ensure
that he is working with the latest released information. Check Kenworth.com for the latest released
version.
If you require additional information or reference materials, please contact your local Kenworth
dealer.
1-1
12/09
Page 9

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
SAFETY SIGNALS
We’ve put a number of alerting messages in this book. Please read and follow them. They are there for your protection
and information. These alerting messages can help you avoid injury to yourself or others and help prevent costly damage to the vehicle.
Key symbols and “signal words” are used to indicate what kind of message is going to follow. Pay special attention to
comments prefaced by “WARNING”, “CAUTION”, and “NOTE.” Please don’t ignore any of these alerts.
Warnings, cautions, and notes
WARNING
Example:
WARNING! Be sure to use a circuit breaker designed to meet liftgate amperage requirements. An incorrectly specifi ed circuit breaker could result in a electrical overload or fi re situation. Follow the liftgate
installation instructions and use a circuit breaker with the recommended capacity.
CAUTION
Example:
CAUTION: Never use a torch to make a hole in the rail. Use the appropriate drill bit.
NOTE
When you see this word and symbol, the message that follows is especially vital. It signals a
potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
This message will tell you what the hazard is, what can happen if you don’t heed the warning,
and how to avoid it.
Signals a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury or damage to the vehicle.
Provides general information: for example, the note could warn you on how to avoid damaging
your vehicle or how to drive the vehicle more effi ciently.
Example:
Note: Be sure to provide maintenance access to the battery box and fuel tank fi ll neck.
Please take the time to read these messages when you see them, and remember:
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Signals a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate
injury or damage to the vehicle.
NOTE
Useful information that is related to the topic being discussed.
2-1
12/09
Page 10

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETY
STANDARDS COMPLIANCE
As an Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM), Kenworth Truck Co. ensures that our products comply with all applicable
U.S. or Canadian Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. However, the fact that this vehicle has no fi fth wheel and that a
Body Builder (Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer) will be doing additional modifi cations means that the vehicle was
incomplete when it left the build plant. See next section and Appendix A for additional information.
Incomplete V ehicle Certifi cation
An Incomplete Vehicle Document is shipped with the vehicle, certifying that the vehicle is not complete. See Figure 2–1.
In addition, affi xed to the driver’s side door frame or edge is an Incomplete Vehicle Certifi cation label. See Figure 2–2. For
further information on Vehicle Certifi cation and Identifi cation, see APPENDIX A “VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION.”
NOTE
These documents list the U.S. or Canadian Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard regulations that the
vehicle complied with when it left the build plant. You should be aware that if you add, modify or alter any
of the components or systems covered by these regulations, it is your responsibility as the Intermediate or
Final Stage Manufacturer to ensure that the complete vehicle is in compliance with the particular regulations upon completion of the modifi cations.
U.S. EPA Noise Label (U.S. registered vehicles only)
Final Stage Manufacturer
Label to be Installed by
Final Stage Manufacturer
Chassis Serial
Number
FIGURE 2-1. Incomplete Vehicle Certifi cation Document
Tire, Rim and
Weight Rating
Data label
Safety Mark (Canadian
Registry Only)
Incomplete Vehicle
Certifi cation Label
Major Components and
Weights Label
FIGURE 2-2. Locations of Certifi ca-
tion Labels - Driver’s Door and Frame
As the Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer, you should retain the Incomplete Vehicle Document for your records. In
addition, you should record and retain the manufacturer and serial number of the tires on the vehicle. Upon completion
of the vehicle (installation of the body and any other modifi cations), you should affi x your certifi cation label to the vehicle
as required by Federal law. This tag identifi es you as the “Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer” and certifi es that the
vehicle complies with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. (See Figure 2–2.) Be advised that regulations affecting the
intermediate and fi nal stage manufacturer may change without notice. Ensure you are referencing the most updated copy
of the regulation during the certifi cation and documentation processes.
In part, if the fi nal stage manufacturer can complete and certify the vehicle within the instruction in the incomplete vehicle
document (IVD) the certifi cation label would need a statement that reads, “This vehicle has been completed in accordance
with the prior manufacturers‚ IVD where applicable. This vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards [and Bumper and Theft Prevention Standards if applicable] in effect in (month, year).”
However, if the vehicle can not be completed and certifi ed with in the guidance provided in the IVD, the fi nal stage manu-
facturer must ensure the vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS). The fi nal
stage manufactures certifi cation label would need a statement that reads, “This vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal
Motor Vehicle Safety Standards [and Bumper and Theft Prevention Standards if applicable] in effect in (month, year).”
12/09
2-2
Page 11

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
These statements are just part of the changes to the new certifi cation regulation. Please refer to the Feb 15, 2005
fi nal rule for all of the details related to this regulation. You can contact NTEA Technical Services Department at
1-800-441-NTEA for a copy of the fi nal rule (DocID 101760).
For Canadian fi nal stage manufacturers see:
http://www.gazette.gc.ca/archives/p2/2002/2002-02-13/html/sor-dors55-eng.html; and
http://www.tc.gc.ca/acts-regulations/regulations/crc-c1038/menu.htm for the regulations.
Or contact:
Transport Canada
Tower C, Place de Ville, 330 Sparks Street
Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0N5
(613) 990-2309
TTY: 1-888-675-6863
Noise and Emissions Requirements
NOTE
For Cummins Contact: Please call 1-800-DIESELS or contact your local Cummins Distributor Reference •
AEB 21.102.
It is possible to relocate the DEF tank, however the relocation requirements need to be followed. Any variance from the
relocation requirements may cause the emissions control components/systems to operate improperly potentially resulting
in engine de-rate. See page 4-3 for relocation requirements.
NOTE
This truck may be equipped with specifi c emissions control components/systems* in order to
meet applicable Federal and California noise and exhaust emissions requirements. Tampering
with these emissions control components/systems* is against the rules that are established by the
U.S Code of Federal Regulations, Environment Canada Regulations and California Air Resources
Board (CARB). These emissions control components/systems* may only be replaced with original
equipment parts.
Modifying (i.e. altering, substituting, relocating) any of the emissions control components/systems defi ned above will affect the noise and emissions performance/certifi cation. If modifi cations
are required, they must fi rst be approved by the engine manufacturer. Unapproved modifi cations
could negatively effect emissions performance/certifi cation. There is no guarantee that proposed
modifi cations will be approved.
Contact the engine manufacturer for any requirements and restrictions prior to any modifi cations.
Some 2010 engine emissions certifi ed vehicles will be equipped with an On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) system. The OBD system is designed to detect malfunctions of any engine or vehicle
component that may increase exhaust emissions or interfere with the proper performance of the
OBD system itself.
The OBD system consists of computer program on one or more of the vehicle’s Electronic Control
Units (ECUs). This program uses information from the control system and from additional sensors
to detect malfunctions. When a malfunction is detected, information is stored in the ECU(s) for
diagnostic purposes. A Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) is illuminated in the dash to alert the
driver of the need for service of an emission-related component or system.
2-3
12/09
Page 12

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
To ensure compliance to emissions regulations, the fi nal confi guration of certain features of the completed vehicle
must meet specifi c requirements. This section describes requirements relevant for only the most common or critical modifi -
cations done by body builders. For a complete description of acceptable modifi cations, see the application
guidance available from the manufacturer of the engine installed in the chassis.
Fuel System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
The overall system restriction may not exceed the restriction limitations set forth by the engine manufacturer for both
supply and return.
Ensure that fuel lines are not pinched or can potentially be damaged when installed between body and frame•
Fuel lines must be routed and secured without dips or sags•
There must be easy access to fi lter(s) and fi ll cap•
The tank vent may not obstructed•
Added accessories (heaters, generators) cannot introduce air into system•
Fuel tank must be located so that the full level is not above cylinder head•
“Ultra Low Sulfur Fuel Only” labels must be present on the dash and fuel fi ll •
Modifi cation of the pressure side secondary fi lter and plumbing is not allowed without engine manufacturer •
approval
Body installation of fuel tank or routing of lines must not cause signifi cant increase in fuel temperature•
Fuel hoses shall meet or exceed OEM supplied hose material construction specifi cations•
Compressed Air System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
Air system modifi cation must meet applicable FMVSS regulations•
Compressed Air tank may not be modifi ed (exception – addition or removal of fi ttings or relocation of the tank) •
Added devices or bodywork may not interfere with or rub air lines•
Air supply to the engine doser may not be restricted or disconnected•
Air lines should be routed, protected from heat, and properly secured to prevent damage from other •
components
Care should be taken so that air lines do not rub against other components•
Care should be taken to protect the air system from heat sources.•
Exhaust and Exhaust After-treatment System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
The following after-treatment and exhaust system components may not be modifi ed:•
DPF assembly•
SCR Catalyst assembly•
Exhaust pipes between the engine and after-treatment devices (DPF, SCR Catalyst) and between •
after-treatment devices
12/09
2-4
Page 13

NO•
Sensor
x
The following modifi cations may only be done within the guidelines of the “DEF System Relocation Guide.”•
Modifi cations to Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) throttle, suction, or pressure lines•
Modifi cation or relocation of the DEF tank•
Modifi cation of coolant lines to and from the DEF tank•
All DEF and coolant lines should be routed, protected, and properly secured to prevent damage during vehicle •
operation or other components
If relocation of the DCU or ACM is necessary, use existing frame brackets and mount inside of frame fl anges •
where necessary. Do not extend the harnesses
Exhaust pipes between the engine and after-treatment devices or between after-treatment devices may not be •
modifi ed or replaced
The DPF, the SCR catalyst, or their mounting may not be modifi ed•
Section 2
Safety & Compliance
The NO•
Exhaust pipes used for tailpipes/stacks must be properly sized, and must prevent water from entering the •
exhaust system
Ensure adequate clearance between the exhaust and body panels, hoses, and wire harnesses•
The body in the vicinity of the DPF must be able to withstand temperatures up to 400°C (750°F)•
Do not add thermal insulation to the external surface of the DPF•
The SCR water drain hole may not be blocked•
Allow adequate clearance (25mm (1 inch)) for servicing the DPF sensors, wiring, and clamped joints•
Drainage may not come in contact with the DPF, SCR catalyst, sensors or wiring•
Allow suffi cient clearance for removing sensors from DPF. Thermistors require four inches. Other sensors •
require one inch
Wiring should be routed, protected from heat, and properly secured to prevent damage from •
other components
The exhaust system from an auxiliary power unit (APU) must not be connected to any part of the vehicle •
after-treatment system or vehicle tail pipe.
sensor may not been relocated or altered in any way
x
Cooling System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
Modifi cations to the design or locations of fi ll or vent lines, heater or defroster core, and surge tank are not •
recommended
With the exception of post-thermostat installation, additional accessories plumbed into the engine cooling •
system are not permitted, and may void vehicle warranty
Coolant level sensor tampering will void warranty•
When installing auxiliary equipment in front of the vehicle, or additional heat exchangers, ensure that •
adequate air fl ow is available to the vehicle cooling system. Refer to engine manufacturer application
guidelines for further detail
When installing FEPTO drivelines, the lower radiator anti-recirculation seal must be retained with FEPTO •
driveline clearance modifi cation only
2-5
12/09
Page 14

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
Changes made to cooling fan circuit and controls are not allowed, with the exception of AC minimum fan on •
time parameter
See owner’s manual for appropriate winter front usage•
Electrical System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
Electrical harnesses providing battery power and electronic control signals to engine and emissions control/•
vehicle OBD components including datalinks may not be spliced. These emissions control/vehicle OBD
components include the following:
throttle pedal•
vehicle speed sensor•
after-treatment wiring•
If the alternator or battery is substituted, it must meet the requirements of the engine manufacture’s guide-•
lines. This includes alternator ground voltage drop and alternator ground cable effectiveness. See the engine
manufacture’s guidelines for recommended test procedure. Additionally the maximum voltage differential and
the peak-peak voltage differential between the engine ECM block ground stud and battery negative terminal
may not exceed 500 mV under any combination of loads or operating conditions.
Installation of aftermarket transfer-cases must address the vehicle speed sensor position. The standard posi-•
tion of the speed sensor is at the transmission tail shaft. When a transfer-case is added it is best to relocate
the sensor to the axle side output shaft of the transfer-case. This is typically accomplished by adding a tone
wheel into the driveline yoke assembly.
Wiring extensions for the after-treatment wiring are available for relocating the DEF tank from your dealer via •
Paccar Parts. For relocation of DEF tank, refer to the after-treatment section of this manual.
The emission system requires an accurate Outside Air Temperature (OAT) reading in order to properly run •
its control algorithms. The OAT sensor is located in the driver’s side mirror assembly on Kenworth trucks and
is shown in the fi gures below. If the body builder needs to modify the mirror assembly in any way, it is im-
portant the OAT sensor stay positioned on the mirror assembly. Running the vehicle without the OAT sensor
connected will cause the MIL lamp to illuminate. If needed, a replacement sensor can be ordered from your
Kenworth dealer.
FIGURE 2-3: West Coast Mirror OAT sensor, located in overmold on mirror harness.
12/09
2-6
Page 15
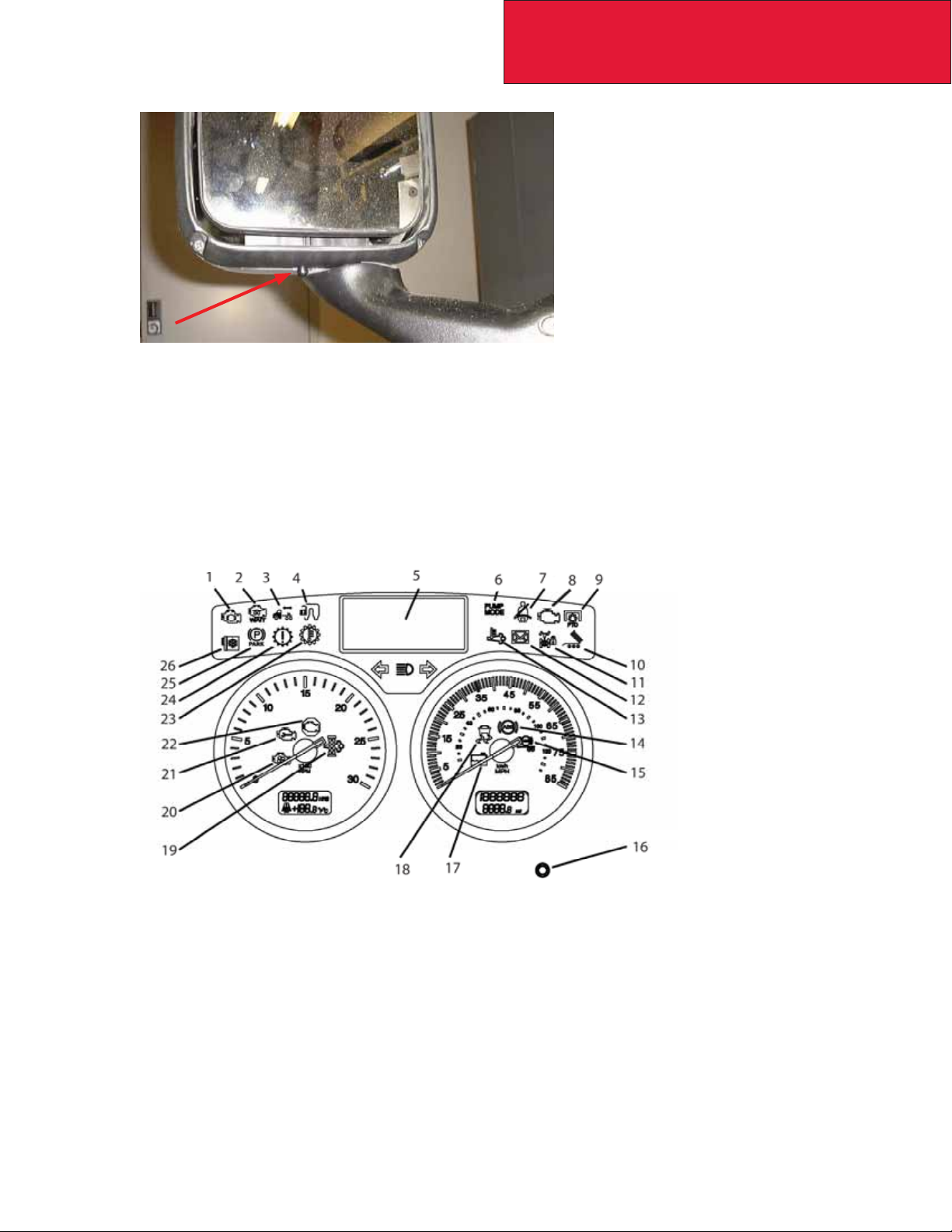
FIGURE 2-4: Aerodynamic Mirror OAT Sensor Location
Coolant Sensor considerations are given in the Cooling section above•
The OBD/Diagnostic connector port is located below the dash to the left of the steering wheel. This connector •
or its location may not be changed.
Section 2
Safety & Compliance
Vehicles using EPA 2010 compliant engines must be equipped with a Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) lamp. •
This lamp is required to be an engine outline symbol as defi ned by ISO (International Standards Organiza-
tion). The fi gure below shows the instrument cluster and MIL lamp position. Note this lamp location is fi xed
with respect to the controls and its location may not be changed if you are updating the warning lamp cards.
FIGURE 2-5: Instrument Cluster for T440/T470 used with EPA2010 Emission compliant
engines. The Check Engine lamp is symbol 21 and the MIL is symbol 8.
In addition to the sensors and lamps above, the emission system also depends on signals from the exhaust •
DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter), SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction), and NOx sensor. Wiring between these
devices, the Dosing Control Unit (DCU) and engine ECM should not be tampered with or altered in any way.
2-7
12/09
Page 16

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
Air Intake System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
The air intake screen may not be blocked, either fully or partially•
Modifi cation to the air intake system may not restrict airfl ow. For example, pipe diameter may not be reduced•
All sensors must be retained in existing locations•
To retain system seal, proper clamp torque must be used. Refer to service manual for proper clamp torque•
Charge Air Cooler System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
The Charge Air Cooler may not be modifi ed •
The installation of engine overspeed shutdown devices must not introduce restriction in the intake system•
All plumbing associated with the charge air cooler may not be modifi ed•
12/09
2-8
Page 17
Section 3
Dimensions
DIMENSIONS
This section has been designed to provide enough information to successfully layout chassis in the body planning
process. Optional equipment may not be depicted. Please contact your local Kenworth dealer if more dimensional
information is desired.
ABBREVIATIONS
Throughout this section, and in other sections as well, abbreviations are used to describe certain characteristics on your
vehicle. The chart below lists the abbreviated terms used.
TABLE 3-1. Abbreviations Used
AF AFTER FRAME – FRAME RAIL OVERHANG BEHIND REAR AXLE OR MEASURED FROM CENTERLINE OF TANDEM
CA BACK OF CAB TO CENTERLINE OF REAR AXLE OR CENTERLINE OF TANDEMS ON TANDEM SUSPENSION
EOF FRAME RAIL OVERHANG BEHIND REAR AXLE – MEASURED FROM THE CENTERLINE OF TANDEMS
FS FRONT SUSPENSION HEIGHT
RS REAR SUSPENSION HEIGHT
WB WHEELBASE
SOC SIDE OF CAB
BOC BACK OF CAB
TURNING RADIUS
Approximate turning radius specifi cations are listed in the following tables as a general guide. It is important to note that
optional components may alter the results.
TABLE 3-2. Turning Radius
Model Steering Gear Front Axle Front Wheel Front Tire
T440/T470
Single
TAS 65
Dana Spicer
E-1202I 12K
Accuride 28487
22.5 X 8.25
Bridgestone
R287
295/75R22.5
Rear
Suspension
Tandem
52” Axle
Spacing
Wheel Base
181 28
193 29.5
201 30.5
213 32
220 33
232 34.5
240 35.5
252 37
260 38
272 39.5
280 40.5
291 42
303 43.5
323 46
331 47
Est Curb to
Curb T urning
Radius (ft)
3-1
TABLE 3-2 CONTINUES ON NEXT PAGE…
12/09
Page 18
Section 3
Dimensions
TABLE 3-2 CONTINUED
Model Steering Gear Front Axle Front Wheel Front Tire
T440/T470
Dual
TAS 65
Dana Spicer
D2000 20K
Standard T rac k
Alcoa 82365
22.5 X 12.25
Bridgestone
M844
425/65R22.5
Rear
Suspension
Tandem
52” Axle
Spacing
Wheel Base
181 31.5
193 33.5
201 34.5
213 36.5
220 37.5
232 39
240 40
252 42
260 43
272 45
280 46
291 47.5
303 49.5
323 52.5
331 53.5
Est Curb to
Curb T urning
Radius (ft)
12/09
3-2
Page 19
Section 3
Dimensions
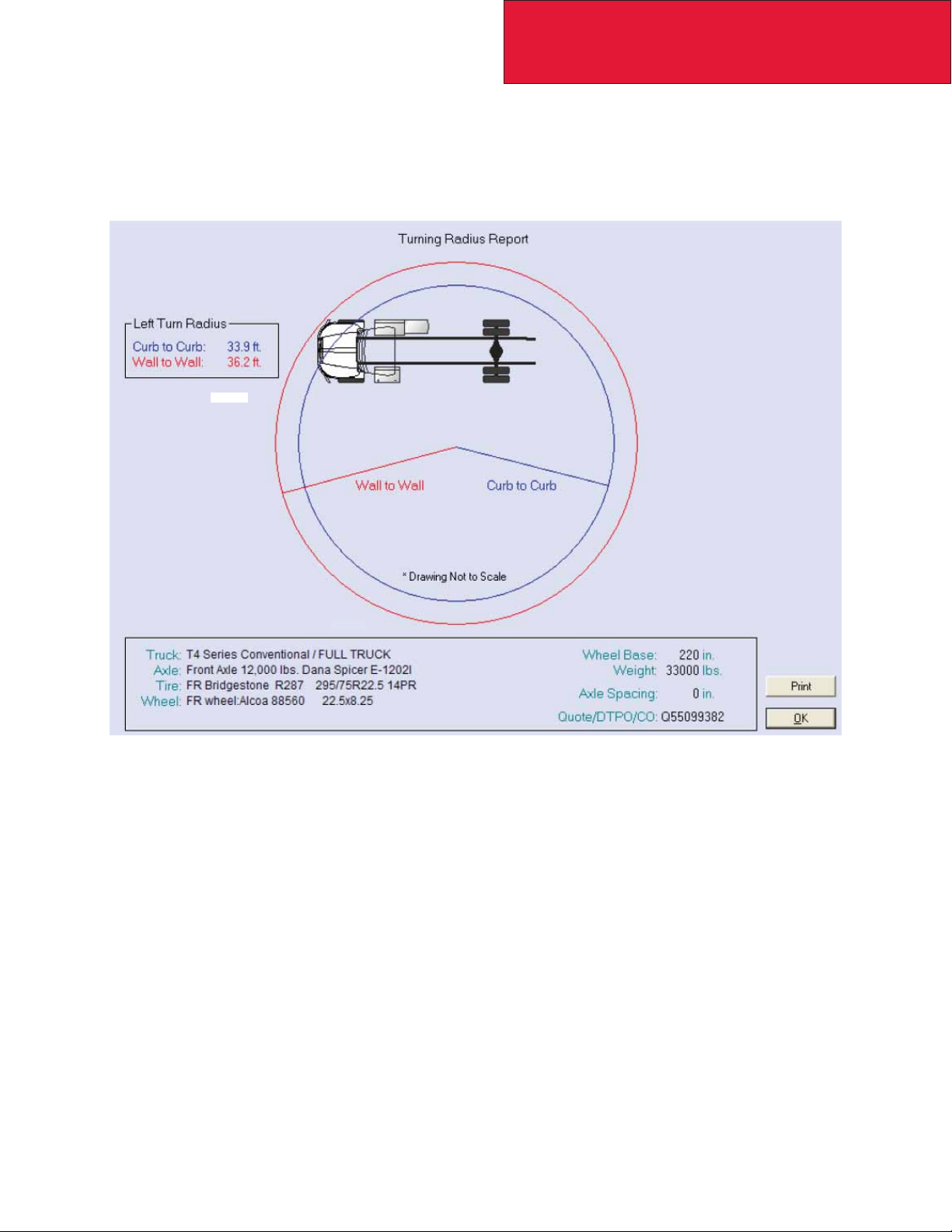
Prospector Turn Circle Analysis:
Please see Figure 3-2 as an example of Kenworth’s turn circle calculation made in Prospector for your specifi c chassis.
Your local Kenworth dealer can provide this information to you.
T470
T470
FIGURE 3-1. Prospector Turn Circle Analysis
Please consult your local Kenworth Dealer for this information, as it is chassis specifi c.
3-3
12/09
Page 20
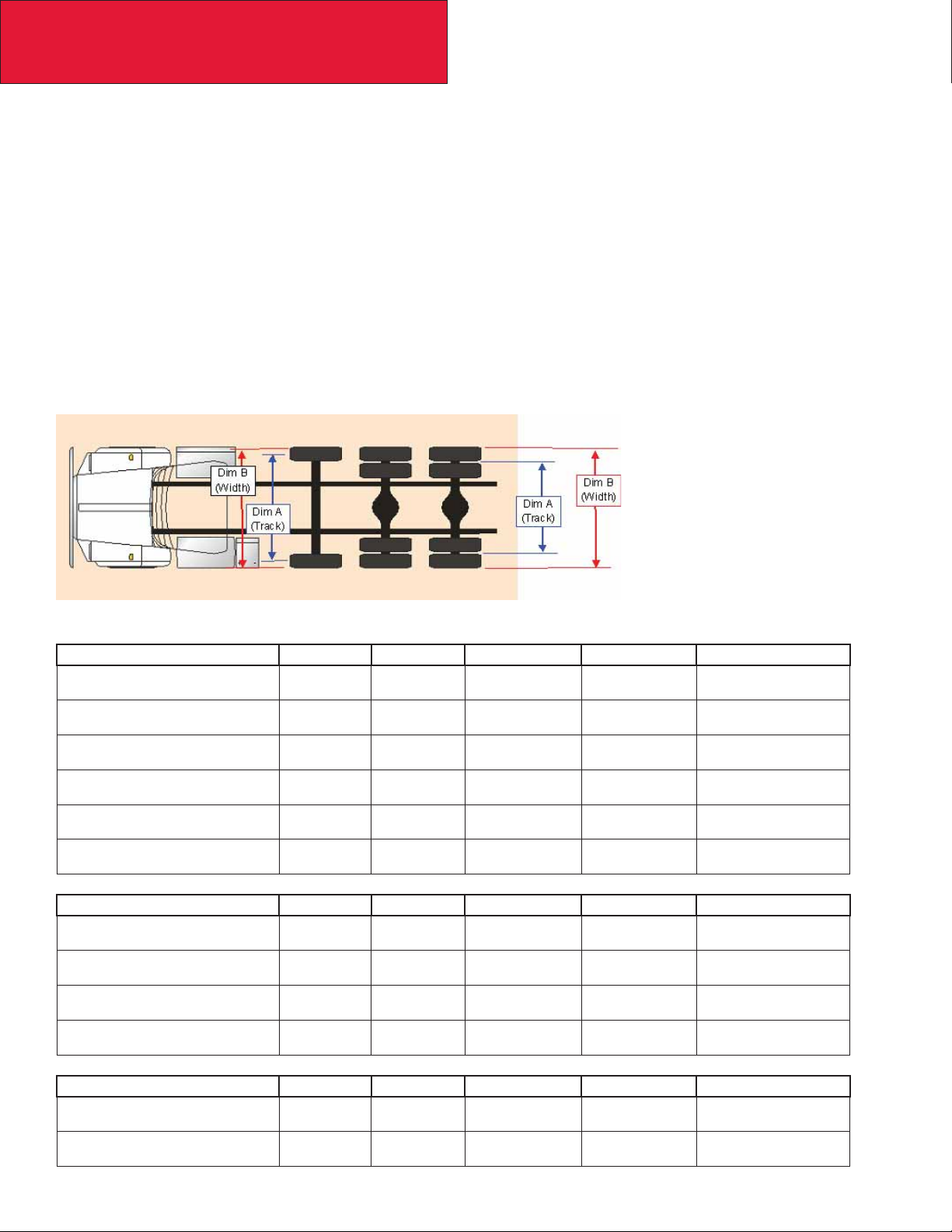
Section 3
Dimensions
AXLE TRACK AND TIRE WIDTH
The dimensions provided in this section are representative of some typical product combinations. The purpose of this section is to demonstrate some of the typical dimensions.
Axle Track: The distance between the dual tire centerlines on a dual tire arrangement or the distance between the tire •
centerlines on a single tire arrangement.
Width: The distance over the outermost tire sidewall to sidewall.•
These dimensions may be signifi cant to the following:
Appearance relative to other tires and chassis mounted equipment.•
Load carrying capacity. Different wheel disc offset can have a positive or negative impact on the axle carrying capac-•
ity of the axle.
KENWORTH AXLE TRACK/TIRE WIDTH SUMMARY
TABLE 3-3. Axle Track
Axle - Drive Wheel Tire Confi guration Track Dim ”A” Overall Width Dim ”B”
Dana Spicer D46-170(H)(P)
46K Dual
Dana Spicer D46-170(H)(P)
46K Dual
Dana Spicer D46-170W(H)(P)
46K Dual Wide Track
Dana Spicer D46-170W(H)(P)
46K Dual Wide Track
Dana Spicer D46-170(H)(P)
46K Dual
Dana Spicer D46-170W(H)(P)
46K Dual Wide Track
Axle - Steer Wheel Tire Brake Drum Type Track Dim ”A” Overall Width Dim ”B”
Dana Spicer E-1322I 13.2K Alcoa 98364
Dana Spicer E-1322W 13.2K Alcoa 98364
Dana Spicer D2000 20K Alcoa 82365
Dana Spicer D2000 20K Alcoa 82364
Alcoa 88364
22.5X8.25
Alcoa 98364
24.5X8.25
Alcoa 88364
22.5X8.25
Alcoa 98364
24.5X8.25
Alcoa 82360
22.5X12.25
Alcoa 82360
22.5X12.25
24.5X8.25
24.5X8.25
24.5X12.25
24.5X12.25
BR M726EL
11R22.5
BR M726EL
11R24.5
BR M726EL
11R22.5
BR M726EL
11R24.5
BR M844F
425/65R22.5
BR M844F
425/65R22.5
BR R250F
11R24.5
BR R250F
11R24.5
BR M844F
425/65R22.5
BR M844F
425/65R22.5
4-4 73.3” 97.8”
4-4 73.6” 98.0”
4-4 79.2” 103.7”
4-4 79.5” 103.9”
2-4 72.7” 88.9”
2-4 78.7” 94.9”
Cast 80.2” 91.0”
Cast 82.2” 93.0”
Cast 86.5” 102.7”
Cast 82.6” 98.8”
Axle - Pusher Non-Steerable Wheel Tire Wheel Orientation “Track Dim ”A” “Overall Width Dim ”B”
NS PSHR: WCAL ATLAS
Std Track (72.5”) 16K GAWR
NS PSHR: WCAL ATLAS
Wide T rac k (77.5”)
12/09
Alcoa 82365
24.5X12.25
“Alcoa 82365
24.5X12.25
BR M844F
425/65R22.5
BR M844F
425/65R22.5
3-4
Default-
Same as RR
Option
Same as FR
79.4” 95.6”
71.1” 87.3”
Page 21

Section 3
Dimensions
OVERALL DIMENSIONS
This section includes drawings and charts. The Extended Day Cab is also included.
On the pages that follow, detail drawings show particular views of each vehicle, all dimensions are in inches (in). They
illustrate important measurements critical to designing bodies of all types. See the “Contents” at the beginning of the
manual to locate the drawing that you need.
Note: To determine overall height please locate the chart Table 3-4 on page 3-8 and 3-9 and add that value to the height.
All heights are given from the bottom of the frame rail.
Kenworth also offers .dxf fi les and frame layouts of ordered chassis four weeks prior to build. Please speak with your
salesman to request this feature when specifying your chassis.
3-5
12/09
Page 22
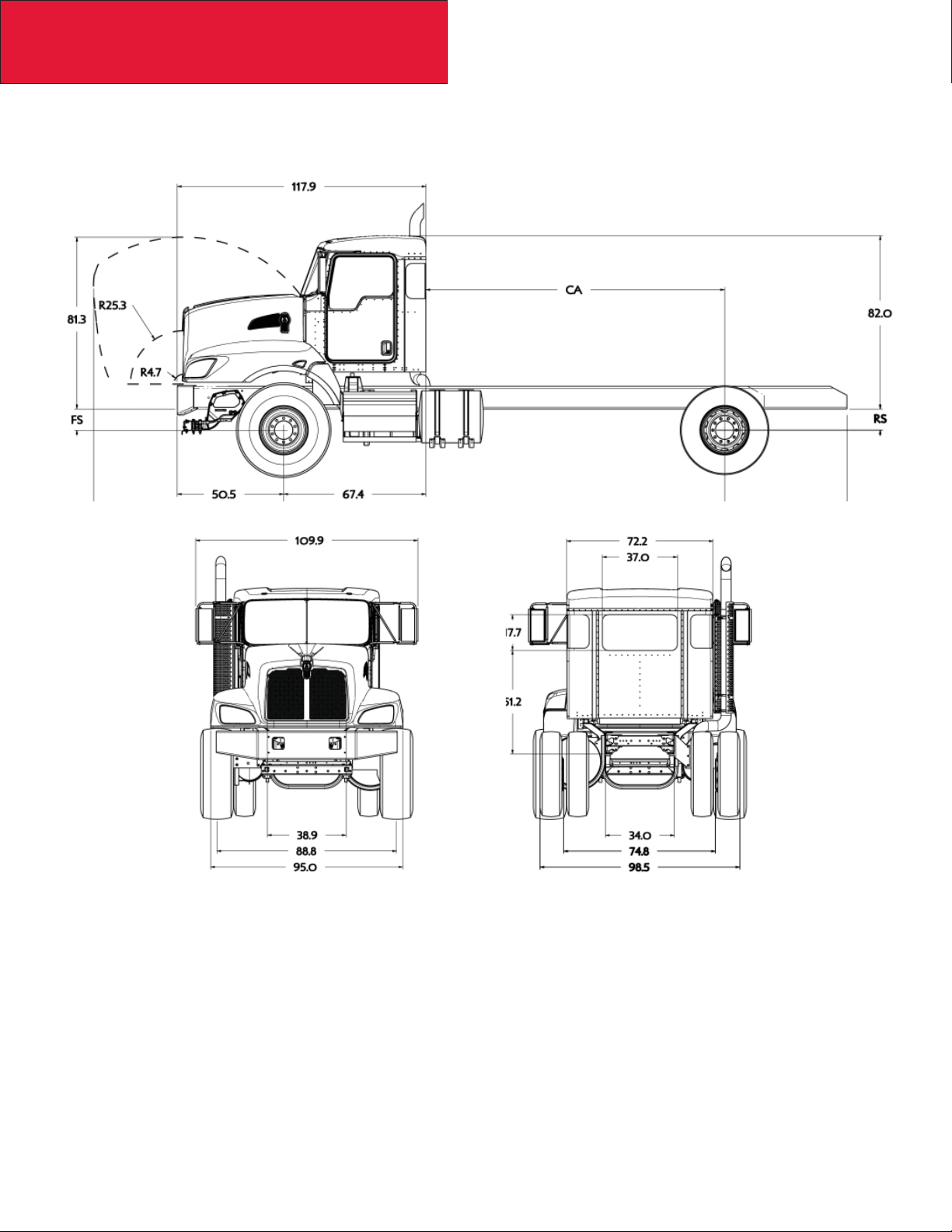
Section 3
Dimensions
T470 FIXED GRILLE HOOD W/O EXTENDED FRONT FRAME
The following drawings are shown with standard chassis components and the T470 fi xed grille hood.
12/09
3-6
Page 23
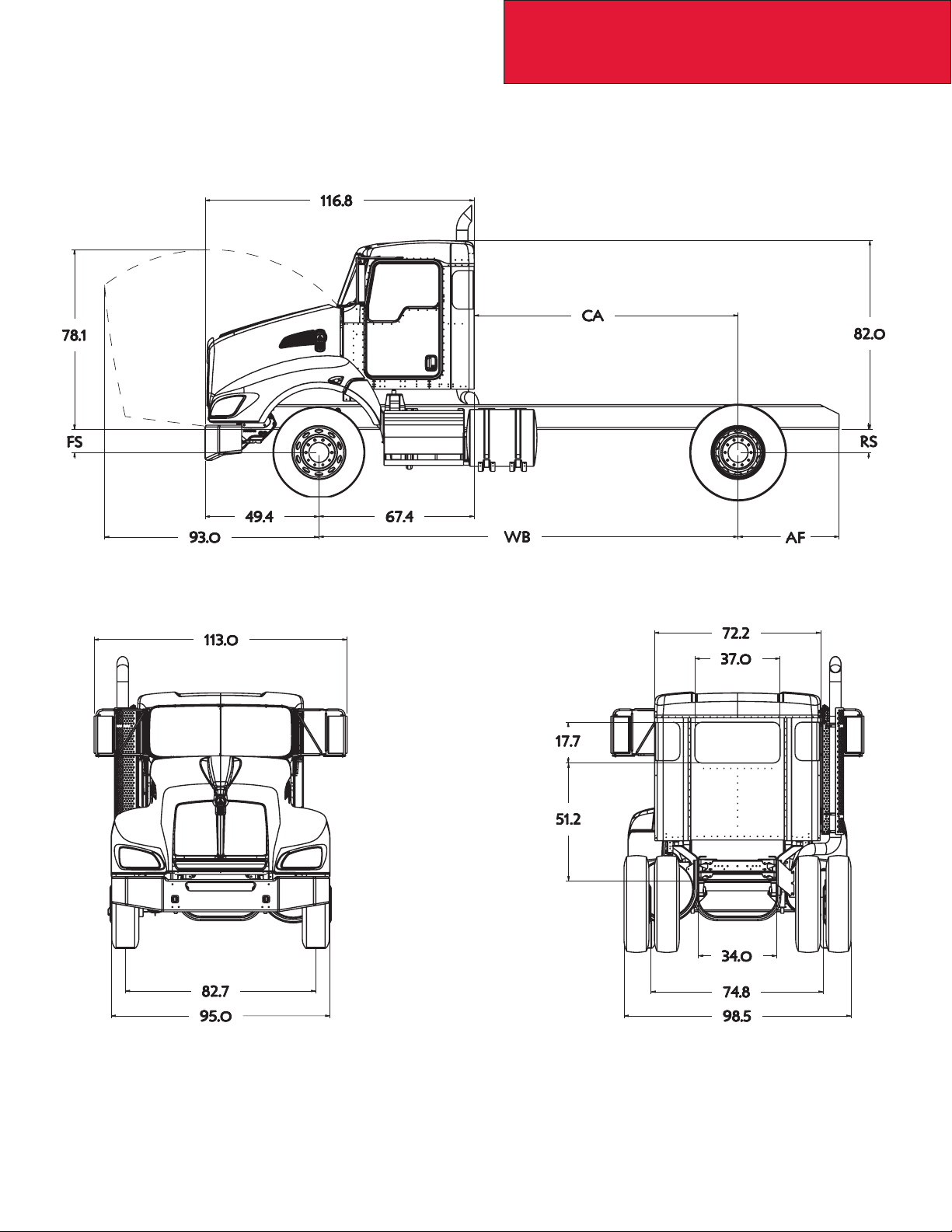
Section 3
Dimensions
T440 DAYCAB
The following drawings are shown with standard chassis components and the T440 daycab.
3-7
12/09
Page 24
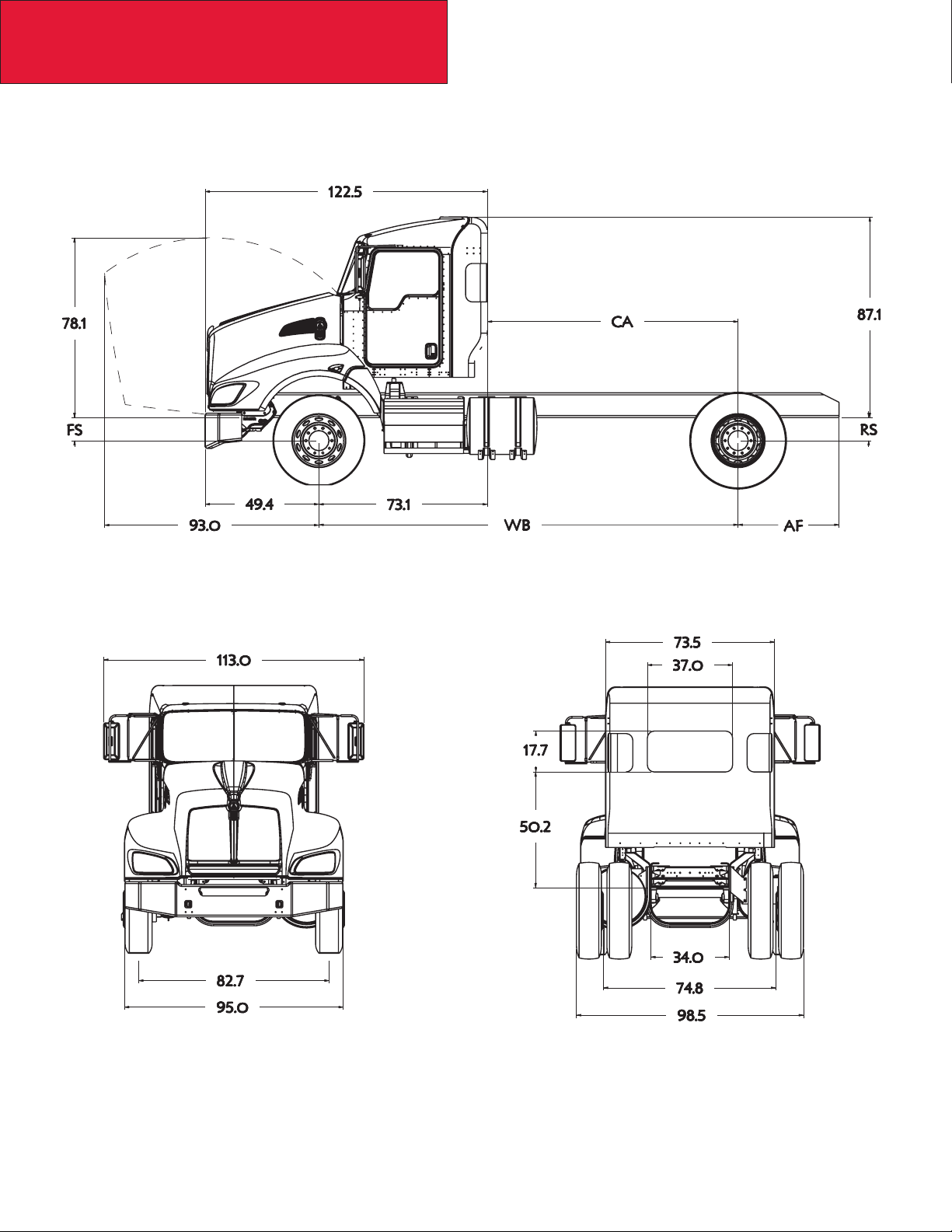
Section 3
Dimensions
T440 EXTENDED DAYCAB
The following drawings are shown with standard chassis components and the T440 extended daycab.
12/09
3-8
Page 25
Section 3
Dimensions
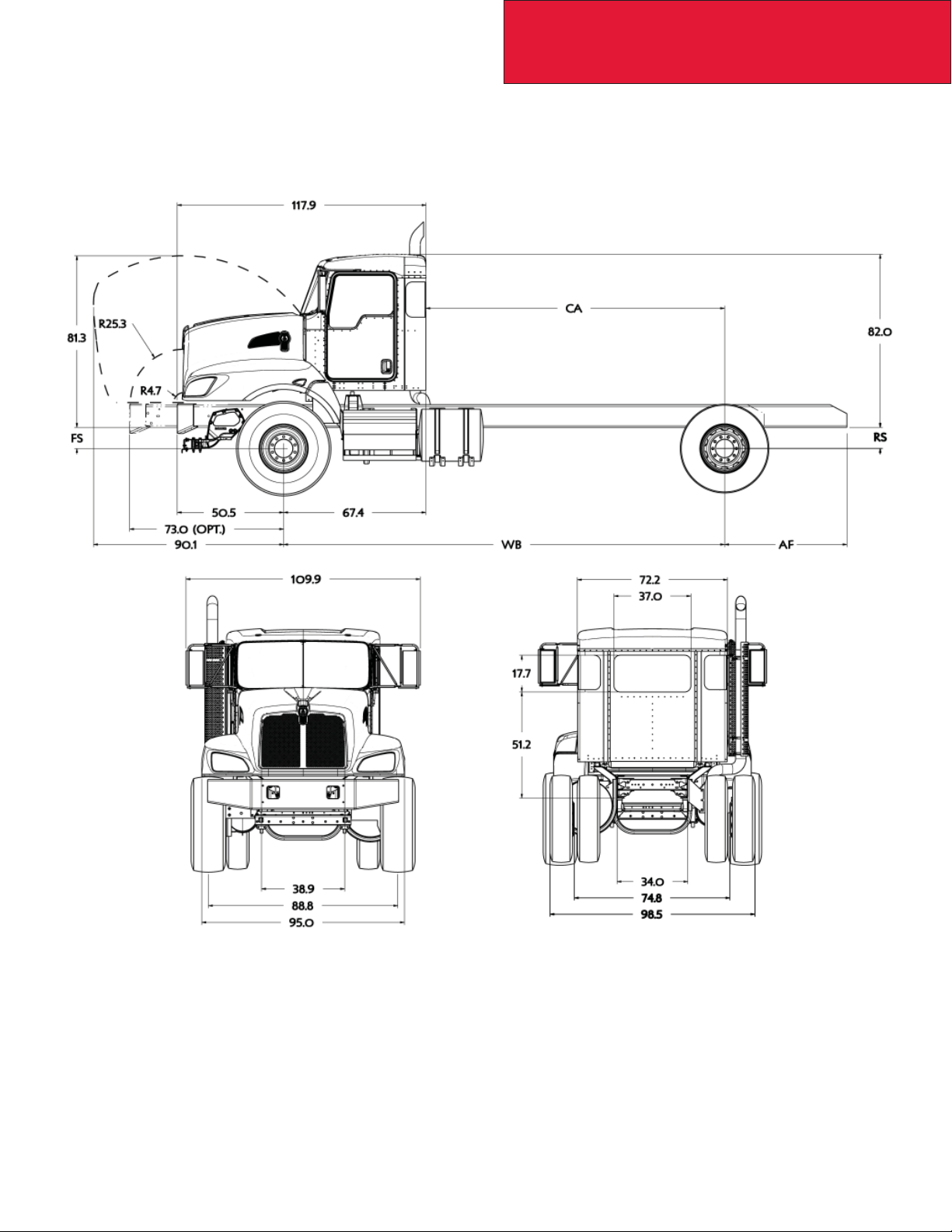
T470 FIXED GRILLE HOOD WITH EXTENDED FRONT FRAME
The following drawings are of a T470 fi xed grille hood with the optional extended front frame. These extended frame rails
can be used with or without FEPTO adapters.
3-9
12/09
Page 26
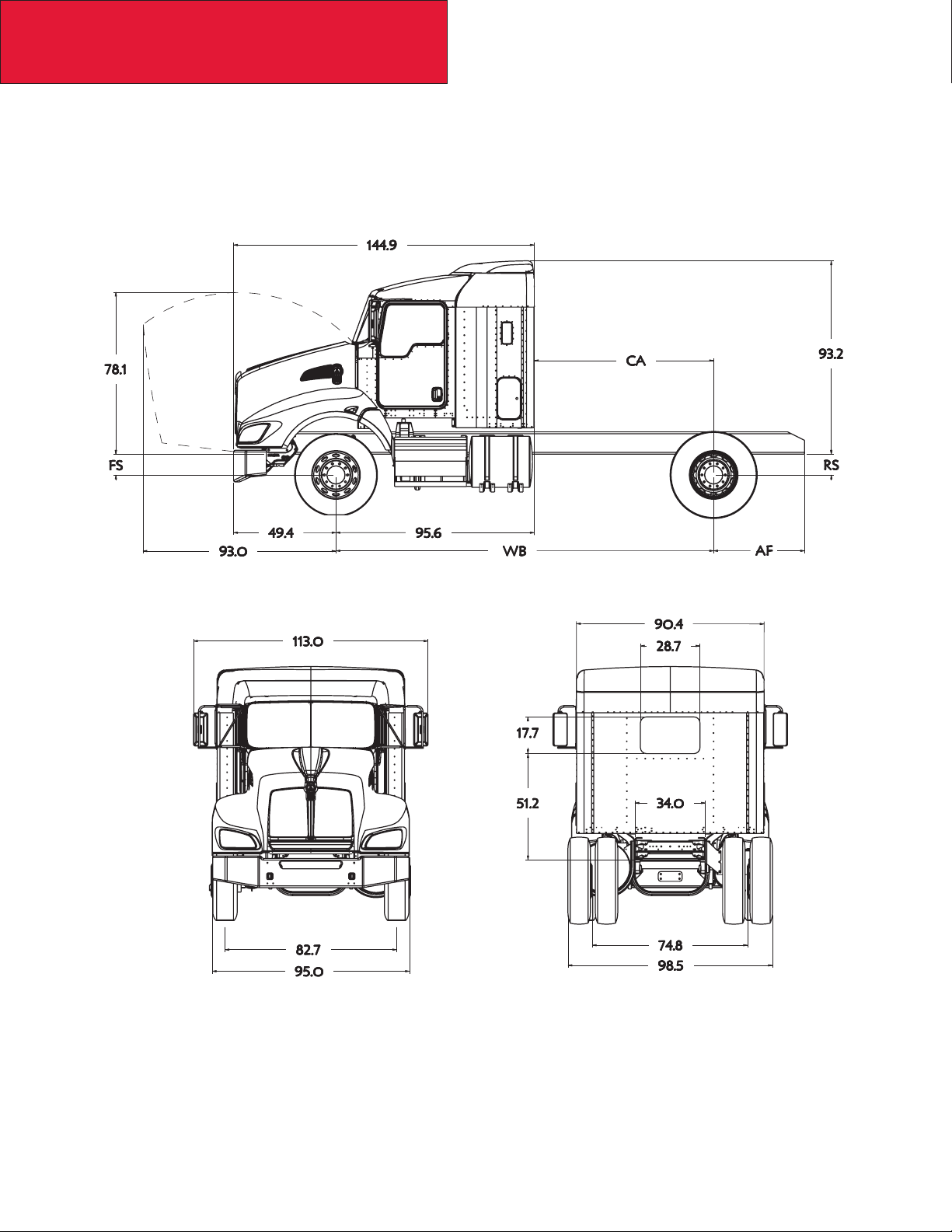
Section 3
Dimensions
38” AEROCAB
The 38” Aerocab is shown on a standard T440 chassis. It is important to note that the 38” will increase any of the models
bumper to back of cab dimension and front axle to back of cab dimension by 28”. The height (from the bottom of the frame
rail) will be 93.2” across the models.
12/09
3-10
Page 27
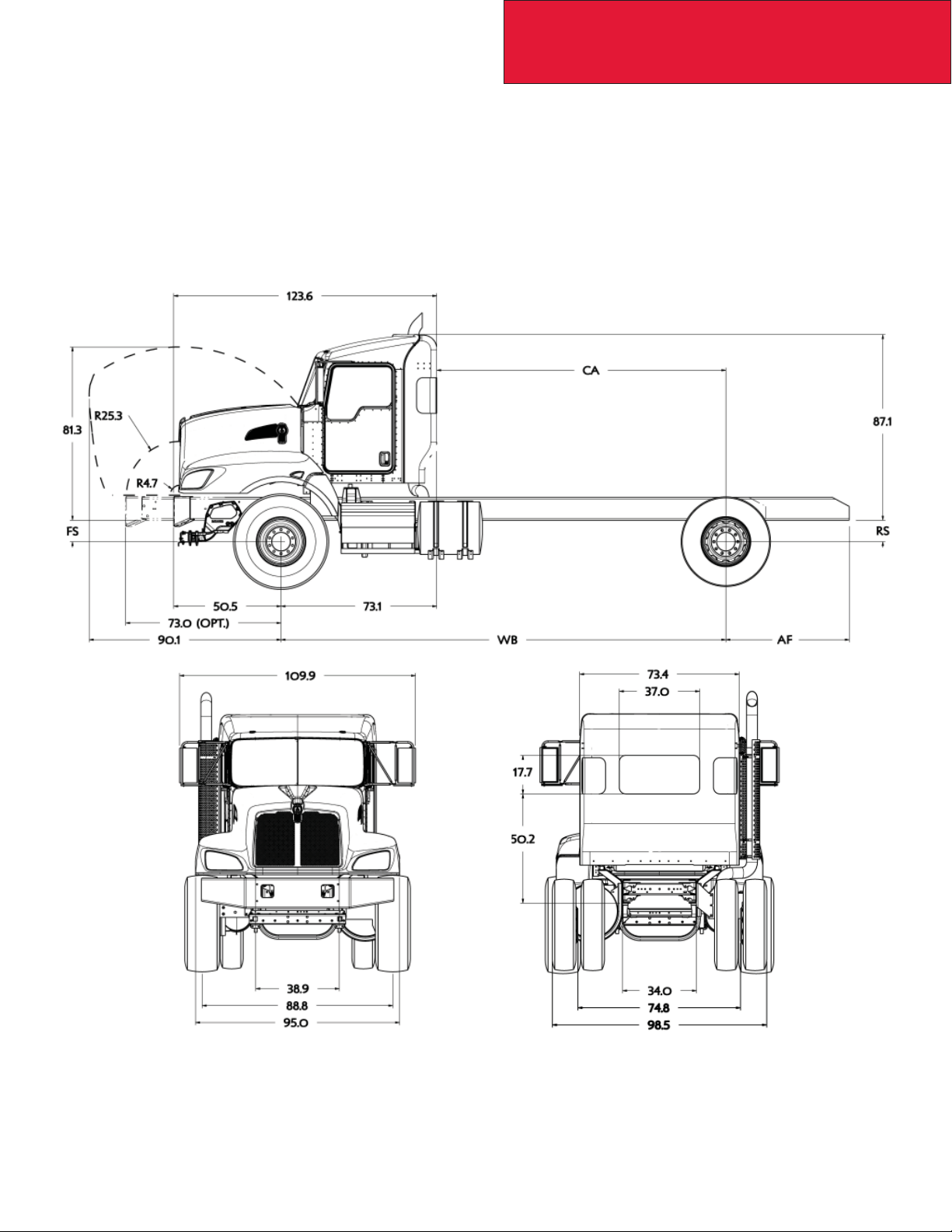
Section 3
Dimensions
EXTENDED DAY CAB
It is important to note that the Extended Day Cab will increase any of the models bumper to back of cab dimension and
front axle to back of cab dimension by 5.7”. The height (from the bottom of the frame rail) will be 86.9”. Below drawings
shown with T470 fi xed grille hood.
Suspension heights are measured from the centerlines of the axle spindle to the bottom of the frame rail. Add the tire
radius dimension to determine overall height to the bottom of the frame rail. Note: The frame rail height itself will not affect
the overall cab height as all components are located from the bottom of the frame rail.
3-11
12/09
Page 28
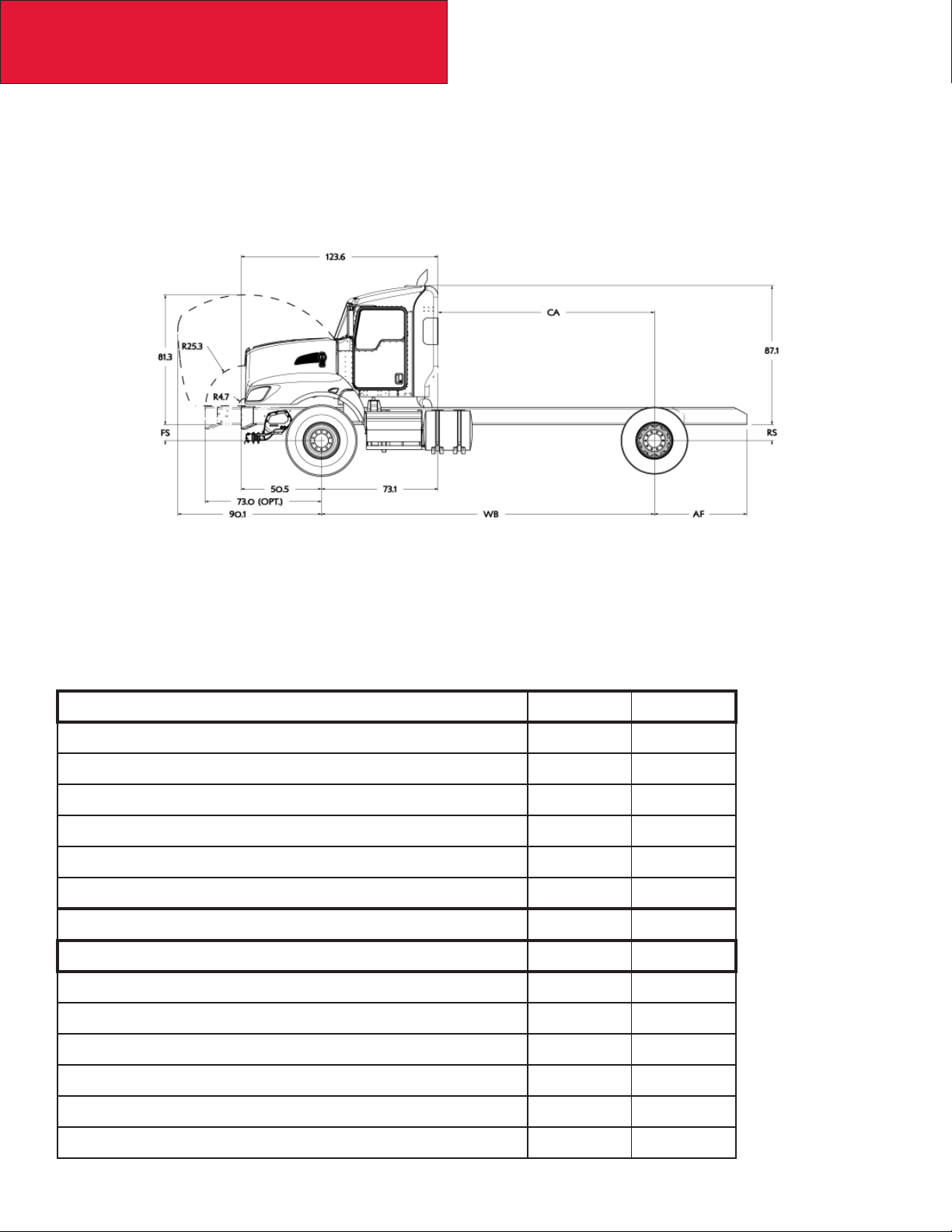
Section 3
Dimensions
RIDE HEIGHTS
The front (FS) and rear (RS) suspension ride heights are provided as a basic tool to determine the overall height of the
cab, height of exhaust components, and frame heights. The heights are all calculated from the centerlines of the axles,
please be sure to include the tire radius dimension to determine overall height. Note: the frame rail height itself will not
affect the overall height as all components are located from the bottom of the frame rail. Ride height information is also
available in Prospector.
TABLE 3-4. Ride Heights In Inches
To calculate Frame Heights use the following formula:
Front Frame Height = FS + 1/2 Front Tire Diameter
Rear Frame Height = RS + 1/2 Rear Tire Diameter
Front Suspension Laden Unladen
12K Taperleaf 10.3” 11.5”
13.2K Taperleaf 10.3” 11.5”
14.6K Taperleaf 10.3” 11.7”
16K Taperleaf 10.6” 12.3”
20K Taperleaf 10.4” 11.9”
22K Multi-stage Taperleaf 10.7” 12.7”
Rear Suspensions
Kenworth AG380 38K Rating 8.5” 8.5”
Kenworth AG400L 40K Rating 8.5” 8.5”
Kenworth AG400 40K Rating 9.0” 9.0”
Kenworth AG460 46K Rating 10.5” 10.5”
Reyco 79KB 21K Rating 6.6” 9.0”
Reyco 79KB 23K Rating 8.3” 10.8”
12/09
3-12
Page 29
Section 3
Dimensions
Reyco 79KB 26K Rating 8.2” 11.3”
Reyco 102 38K Rating 9.2” 10.8”
Reyco 102 40 K Rating 9.2” 10.8”
Chalmers 854-40-L-HS 40K Rating 9.6” 11.0”
Chalmers 854-40-H-HS 40K Rating 10.9” 12.4”
Chalmers 854-46-L 46K Rating 8.9” 11.3”
Chalmers 854-46-L-HS 46K Rating 9.6” 11.3”
Chalmers 854-46-H 46K Rating 10.1” 12.4”
Chalmers 854-46-H-HS 46K Rating 10.9” 12.5”
Chalmers 860-46-H-HS 46K Rating 10.9” 12.5”
Chalmers 872-46-H-HS 46K Rating 11.0” 12.5”
Hendrickson HAS 230 23K Rating 10.0” 10.0”
Hend HMX460 16.5” Saddle 46K Rating 9.5” 10.6”
Hend HMX460 17.5” Saddle 46K Rating 10.5” 11.6”
Hend HMX460 18.5” Saddle 46K Rating 11.5” 12.6”
Hendrickson Primaax 46K Rating 10.0” 10.0”
Hendrickson RT403 40K Rating 9.7” 10.7”
Hendrickson RT463 6.0” Saddle 46K Rating 10.0” 11.1”
Hendrickson RT463 7.19 Saddle 46K Rating 11.2” 12.5”
Hendrickson RT463 7.94 Saddle 46K Rating 11.9” 13.3”
Neway AD123 23K Rating 10.0” 10.0”
Neway AD126 26K Rating 10.0” 10.0”
Neway AD246 46K Rating 10.0” 10.0”
3-13
12/09
Page 30

Section 3
Dimensions
REAR SUSPENSION LAYOUTS
The rear suspension layouts are provided as a tool to help layout bodies prior to arrival. Be sure to check the axle spacing
that is shown, as alternate spacings may exist and could change some of the dimensions. The dimensions shown below
are the most typical installations, in special cases some hole locations will move. If you are planning on using the holes
shown for your body installation, please confi rm with your local KW dealer that the drawing below will be the installation
used on your specifi c truck. Ensure that proper torque is used to reinstall any suspension components. See Tables 5-1 and
5-2 on page 5-7.
It would be a good idea in this case to order the frame layout of your chassis along with your truck order. This can be done
on any Kenworth truck, and will be provided 4 weeks ahead of the build schedule.
If there are hole locations that are not detailed please work with your local Kenworth Dealer to request that information.
Additionally optional axle spacings are shown in the charts, if you would like details on the frame drilling with optional
spacings, please contact your local Kenworth dealer.
12/09
3-14
Page 31

KENWORTH AG 380 TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with a 52” Axle Spacing
Section 3
Dimensions
Kenworth AG 380 Suspension Data
TABLE 3-5. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
AG 380 38K 52” 8.5” 8.5”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
3-15
12/09
Page 32

Section 3
Dimensions
KENWORTH AG 400/460 TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with a 52” Axle Spacing
Optional Kenworth Tandem Suspensions
TABLE 3-6. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Kenworth AG 400 40K 52” 9” 9”
Kenworth AG 400 40K 54” 9” 9’
Kenworth AG 460 46K 54” 10.5” 10.5”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
12/09
3-16
Page 33

KENWORTH AG 400L TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with a 52” Axle Spacing
Section 3
Dimensions
Optional Kenworth Tandem Suspensions
TABLE 3-7. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Kenworth AG 400L 40K 52” 8.5” 8.5”
Kenworth AG 400L 40K 54” 8.5” 8.5”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
3-17
12/09
Page 34

Section 3
Dimensions
KENWORTH AG 460 TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with a 60” Axle Spacing
Optional Kenworth Tandem Suspensions
TABLE 3-8. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Kenworth AG 460 46K 60” 10.5” 10.5”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
12/09
3-18
Page 35

REYCO 79KB SINGLE REAR AXLE
Section 3
Dimensions
Optional Reyco 79KB Suspensions
TABLE 3-9. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Reyco 79KB single 21K - 8.3” 10.8”
Reyco 79KB single 23K - 8.3” 10.8”
Reyco 79KB single 26K - 8.2” 11.3”
Reyco 79KB single 30K - 8.9” 11.7”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
3-19
12/09
Page 36

Section 3
Dimensions
REYCO 102 TANDEM REAR AXLE
Shown with a 52” Axle Spacing
Reyco 102 Suspension Data
TABLE 3-10. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing Laden Ride Height
Reyco 102 Tandem 38K 52” 9.2” 10.8”
Reyco 102 Tandem 40K 52” 9.2” 10.8”
Unladen Ride
Height
12/09
3-20
Page 37

NEWAY AD 123 SINGLE REAR AXLE
Section 3
Dimensions
Optional Neway AD Single Suspensions
TABLE 3-11. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Neway AD123 single 23K - 10” 10”
Neway AD126 single 26K - 10” 10”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
3-21
12/09
Page 38

Section 3
Dimensions
NEWAY AD 246 TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with a 54” Axle Spacing
Optional Neway AD Tandem Suspensions
TABLE 3-12. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Neway AD246 tandem 46K 54” 10” 10”
Neway AD246 tandem 46K 60” 10” 10”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
12/09
3-22
Page 39

HENDRICKSON PRIMAAX TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with 54” Axle Spacings
Section 3
Dimensions
Optional Hendrickson Primaax Tandem Suspensions
TABLE 3-13. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Hendrickson Primaax Tandem 46K 54” 10” 10”
Hendrickson Primaax Tandem 46K 60” 10” 10”
Hendrickson Primaax Tandem 46K 72” 10” 10”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
3-23
12/09
Page 40

Section 3
Dimensions
HENDRICKSON HAS 230 SINGLE REAR SUSPENSION
Optional Hendrickson HAS 230 Suspensions
TABLE 3-14. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Hendrickson HAS 230 23K – 10.0” 10.0”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
12/09
3-24
Page 41

HENDRICKSON HMX TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with 54” Axle Spacing
Section 3
Dimensions
Optional Hendrickson HMX Tandem Suspensions
TABLE 3-15. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Hendrickson HMX400 16.5” saddle 40K 54” 9.5” 10.6”
Hendrickson HMX400 17.5” saddle 40K 54” 10.5” 11.6”
Hendrickson HMX460 16.5” saddle 46K 54” 9.5” 10.6”
Hendrickson HMX460 17.5” saddle 46K 54” 10.5” 11.6”
Hendrickson HMX460 18.5” saddle 46K 54” 11.5” 12.6”
Hendrickson HMX460 18.5” saddle 46K 60” 11.5” 12.6”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
3-25
12/09
Page 42

Section 3
Dimensions
HENDRICKSON RT TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with a 54” Axle Spacing Without Track Rods
Optional Hendrickson RT Tandem Suspensions
TABLE 3-16. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Hendrickson RT463 6” saddle 46K 54” 10.0” 11.1”
Hendrickson RT463 7.19” saddle 46K 54” 11.2” 12.5”
Hendrickson RT463 7.94” saddle 46K 54” 11.9” 13.3”
Hendrickson RT463 6” saddle 46K 60” 10.0” 11.1”
Hendrickson RT403 7.19” saddle 40K 52” 9.7” 10.7”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
12/09
3-26
Page 43

CHALMERS 856-46 TANDEM SUSPENSION
Shown with a 54” Axle Spacing
Section 3
Dimensions
Optional Chalmers Tandem Suspensions
TABLE 3-17. Rear Suspension Options
Suspension Type Rating Axle Spacing
Chalmers 854-40-H 40K 54” 10.2” 12.4”
Chalmers 854-40-L 40K 54” 8.9” 11.1”
Chalmers 854-40-L-HS 40K 54” 9.6” 11.1”
Chalmers 854-40-H-HS 40K 54” 10.9” 12.4”
Chalmers 854-40-H-SR 40K 54” 10.5” 12.4”
Chalmers 854-40-L-SR 40K 54” 9.2” 11.1”
Chalmers 854-46-L 46K 54” 8.9” 11.3”
Chalmers 854-46-L-HS 46K 54” 9.6” 11.3”
Chalmers 854-46-L-SR 46K 54” 9.2” 11.3”
Chalmers 854-46-H 46K 54” 10.1” 12.5”
Chalmers 854-46-H-HS 46K 54” 10.9” 12.5”
Chalmers 854-46-H-SR 46K 54” 10.5” 12.2”
Laden Ride
Height
Unladen Ride
Height
Chalmers 860-46-H 46K 60” 10.1” 12.5”
Chalmers 860-46-H-HS 46K 60” 10.9” 12.5”
Chalmers 872-46-H-HS 46K 72” 11.0” 12.5”
3-27
12/09
Page 44

Section 3
Dimensions
PUSHER AXLES
The rear pusher axle layouts are provided as a tool to help layout bodies prior to arrival. When using the pusher layouts to
determine available frame space please be aware that clearances required are not shown. For information that may not be
detailed in these drawings work with your local Kenworth Dealer to request that information.
Watson & Chalin Tru Track Alumilite 13.2K Steerable Pusher
Watson & Chalin Tru Track 20K Steerable Pusher
12/09
3-28
Page 45

Dimensions
Watson & Chalin Atlas 22.5K Non-Steerable Pusher
Section 3
3-29
12/09
Page 46

Section 3
Dimensions
GROUND CLEARANCE
This information is provided as a reference, not all optional equipment is included. In order to calculate the height on your
specifi c chassis, please use the ride height information provided on page 3-14. For comparison the FS value shown is
11.4” unladen and 10.4” laden.
A
TABLE 3-18. Ground Clearance for Fuel Tanks
Front
Suspension
20K Taperleaf Spring
Front Tires
M844F
425/65R22.5
Tires
Rear
Suspension
Hendrickson
HMX 460
17.5” Saddle
Height
Rear Tires Component
11R24.5
M711
B
Dimension
“A”
Distance
from
Bottom of
Frame Rail
(in)
22” Fuel Tank 16.3 17.2 14.9
24.5” Fuel
Tank
18.2 15.3 13
Dimension “B” Ground
Clearance (in)
Unladen Laden
12/09
3-30
Page 47

Section 3
Dimensions
A
B
TABLE 3-19. Ground Clearance for Battery Boxes
Front
Suspension
20K Taperleaf Spring
Front Tires
M844F
425/65R22.5
Tires
Rear
Suspension
Hendrickson
HMX 460
17.5” Saddle
Height
Rear Tires Component
M711
11R24.5
Battery Box
with Air Tanks
Vocational
Battery Box
with Air Tanks
Single DPF
Box
Dimension
“A”
Distance
from
Bottom of
Frame Rail
(in)
17.3 16.2 13.9
17.8 15.7 13.4
15.5 17.9 15.6
Dimension “B” Ground
Clearance (in)
Unladen Laden
3-31
12/09
Page 48

Section 3
Dimensions
A
B
TABLE 3-20. Ground Clearance for Battery Boxes
Dimension
“A”
Front
Suspension
20K Taperleaf Spring
1
Dimensions shown are for daycabs with high route exhaust. Sleeper ground clearance is reduced by 1.3 inches.
Front Tires
M844F
425/65R22.5
Tires
Rear
Suspension
Hendrickson
HMX 460
17.5” Saddle
Height
Rear Tires Component
Battery Box
with Air Tanks
M711
11R24.5
Vocational
Battery Box
with Air Tanks
1
Box 15.6 17.8 15.5
DPF
Distance
from
Bottom of
Frame Rail
(in)
17.3 16.2 13.9
17.8 15.7 13.4
Dimension “B” Ground
Clearance (in)
Unladen Laden
12/09
3-32
Page 49

Section 3
Dimensions
PTO CLEARANCES
The following visuals are provided to help aid in determining PTO locations and clearances. For specifi c dimensions
please work through your local Kenworth dealer. Multiple PTO’s are shown for layout purposes only. Power equipment,
i.e., drive shafts & power pumps are not included. Body builders should select the appropriate PTO for their application
and customer requirements. NOTE: Installations depict multiple PTOs. PTO locations shown below are for reference only.
Some PTOs may interfere with frame rail and/or other components.
In order to ensure the PTO area remains clear of air equipment, electrical and emissions equipment, Kenworth recommends always ordering PTO controls, even when installing the PTO aftermarket. Kenworth does offer a variety of factory
installed PTOs. Contact your local dealer for assistance.
Manual T ransmission:
3-33
12/09
Page 50

Section 3
Dimensions
Allison T ransmission:
12/09
3-34
Page 51

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
EXHAUST AND AFTER-TREATMENT INFORMATION
The following section is designed to give you information regarding the exhaust and after-treatment systems on Kenworth
chassis.
All Kenworth’s equipped with 2010 emission level engines will utilize Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR). SCR is a
process in which Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) is injected into the exhaust down stream of the engine. DEF is converted to
ammonia by the heat of the exhaust system. Inside of the SCR canister a catalyst causes a chemical reaction to occur
between the ammonia and NOx, turning it into water and nitrogen. For more information on the specifi c details of how
SCR works, please contact your local Kenworth dealer.
DEF System Schematic:
On most Kenworth chassis the DEF Supply Module (or pump) is integrated into the DEF tank. Kenworth does not allow
relocation of this pump. The following schematic details how the DEF lines route to the after-treatment system.
DEF T ank
(10-gallon shown)
DEF Return Line
(Backfl ow from
Supply Module)
Coolant Draw
(from Draw Tee)
DEF Draw Line
(Inlet to Supply Module)
See Detail A
Coolant Return
(to Coolant Valve)
Detail A
Scale 1:2
DEF Return Line (Backfl ow)
DEF Draw Line (Inlet)
DEF Supply Module
(Pump)
DEF Pressure Line
(Outlet)
DEF Dosing Module
(Injector)
4-1
12/09
Page 52

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
DEF will freeze at approximately 11° F. In order to keep DEF from freezing all tanks will be heated with engine coolant.
The following schematic shows the routing of these lines. The coolant lines that run to and from the SCR system must not
be tampered with, or used for a source of heat and/or cooling for other components on the chassis. It is critical that the
system is not compromised in any manner.
DEF T ank
(Small T ank Shown)
5/8” Coolant Hose
(Green - Draw)
Return T ee Draw Tee
DEF T ank
Heating
Element
3/8” Coolant Hose
(Blue - Return)
Draw Port Return Port
2/2 Coolant
Valve
3/8” Coolant Hose
(Green - Draw)
DEF Dosing Module
(Injector)
Coolant
Bulkhead
(Framemounted)
5/8” Coolant Hose
(Blue - Return)
12/09
4-2
Page 53

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR DEF SYSTEM
The installation of the DEF tank is a critical component of the SCR system. While Kenworth does not recommended relocating the DEF tank, there are applications and body installations that will require it. The guidelines below must be strictly
followed by any entity relocating the tank. Failure to follow the guidelines completely and accurately may result in engine
shutdown situations.
Kenworth offers a variety of DEF tank sizes to meet every application. The DEF tank volume is regulated by the E.P.A.
Kenworth advises against modifying the tank volume after the truck has been delivered from the factory.
• Total DEF capacity must meet or exceed 6% of the usable fuel capacity on the truck. The calculation to determine DEF capacity is:
Minimum DEF Tank Volume = Useable Fuel Capacity (gal) x 0.06
Example: For a truck with 200 useable gallons of fuel, the equation is
DEF required = 200 x 0.06 = 12 gallons or more of DEF.
PACCAR-approved DEF hoses are required when retrofi tting for system to function properly. The use of unapproved hoses
for DEF lines will void warranty and may cause engine shutdown situations. The DEF pump (or Supply Module) can not be
relocated from the DEF tank.
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS AND DIMENSIONS FOR DEF SYSTEM
When relocating any DEF system components, the locations must meet the guidelines below. Failure to comply may result
in non-conformance to EPA standards and engine shutdown.
DEF piping relative heights: In order to ensure proper functionality of DEF system, the height differences in the guidelines
below must be followed during line routing and component placement.
With all relocating procedures, general clearances and routing guidelines must be followed. See section 9 of this manual
for general routing guidelines.
When relocating the components the maximum pressure DEF hose length, from Supply module to Dosing Module, is 3
meters (118”).
Maintain a minimum of 3” clearance to shielded exhaust components when routing DEF lines to prevent possible melting.
If the DEF tank is relocated the coolant lines will need to be modifi ed. During this process if the tank is moved forward on
the chassis (ie closer to the engine) it is necessary to remove excess coolant lines and maintain the original routing path.
If the tank is moved rearward on the chassis the additional length of cooling line required to complete the installation must
be installed in a straight section of the existing coolant routing lines. This process will minimizes the change in coolant fl ow
by minimizing changes in restrictions. Increases in restriction occur with excessive line length and bends. Work with your
local Kenworth dealer if you are unsure about the coolant line modifi cations.
4-3
12/09
Page 54

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
MEASUREMENT REFERENCE POINTS
For all relocation procedures, the measurement points referenced in the guidelines are taken from the following specifi c
points:
Supply Module: The supply module is commonly called a pump. The measurement point on the supply module is the top
of the DEF fl uid pressure line. See Figure 4-1.
FIGURE 4-1: Measurement Location of DEF Supply Module (Pump)
Dosing Module: The dosing module is commonly called an injector, this injector is located on the SCR mixing pipe which
is between the DPF and SCR canister. The measurement point on the dosing module is the top of the DEF fl uid pressure
line. See Figure 4-2.
FIGURE 4-2: Measurement Location of DEF Dosing Module (Injector)
The following relocation guidelines are dependant on exhaust confi guration and DEF tank type and location.
The Dosing Module should not need to be relocated. However if it is removed for any reason, it is critical that the module
be reinstalled at the correct orientation. Figure 4-3 below illustrates the correct installation orientations. The angle references the vertical plane.
12/09
4-4
Page 55

FIGURE 4-3: Orientation of Dosing Module
Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Small, Medium, or Large DEF Tanks
FIGURE 4-4: RH Under Cab Exhaust with Small, Medium, or Large Tanks.
The height differential between the supply module and dosing module can not exceed one meter. The supply module is
integrated into the DEF tank assembly, separation of the module from the tank is not allowed.
When relocating the components the maximum pressure DEF hose length, from Supply module to Dosing Module, is 3
meters (118”).
DEF Pressure hose must include a “trap” in the routing if Dosing Module is below the highest point of the Supply Module
(See Figure 4-9 on page 4-9).
4-5
12/09
Page 56

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Horizontal (Crossover) DPF and SCR with Rectangular Small or Medium DEF T anks
FIGURE 4-5: Horizontal Exhaust with Small or Medium Tanks.
The height differential between the supply module and dosing module cannot e xceed one meter. The supply module is
integrated into the DEF tank assembly, separation of the module frm the tank is not allowed.
When relocating the components the maximum pressure DEF hose length, from Supply module to Dosing Module is
3 meters (118”).
Vertical DPF and SCR with Rectangular Small or Medium DEF Tanks
FIGURE 4-6: Vertical Exhaust with Small or Medium Tanks.
The height differential between the supply module and dosing module can not exceed one meter. The supply module is
integrated into the DEF tank assembly, separation of the module from the tank is not allowed.
When relocating the components the maximum pressure DEF hose length, from Supply module to Dosing Module, is 3
meters (118”).
12/09
4-6
Page 57

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Clear Back of Cab DEF Tank
FIGURE 4-7: RH Under Cab Exhaust with Clear Back of Cab Tank.
The installation and design of the Clear Back of Cab (CBOC) tank is highly integrated into the chassis and cooling system.
Kenworth does not allow relocation of this tank, only relocation of the supply module.
The height differential between the supply module and dosing module can not exceed one meter. The CBOC tank does
not have an integrated supply module. The standard KW installation is a supply module located inside of the frame rail.
When relocating either the supply module or the tank, the maximum height differential between the supply module and the
bottom of the tank is one meter. The maximum line length is 2 meters between supply module and DEF tank sending unit.
When relocating the components the maximum pressure DEF hose length, from Supply module to Dosing Module, is 3
meters (118”).
DEF Pressure hose must include a “trap” in the routing if Dosing Module is below the highest point of the Supply Module
(See Figure 4-8 on page 4-9).
4-7
12/09
Page 58

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Vertical DPF and SCR with Clear Back of Cab DEF Tank
FIGURE 4-7: Vertical with Clear Back of Cab Tank
The installation and design of the Clear Back of Cab (CBOC) tank is highly integrated into the chassis and cooling system.
Kenworth does not allow relocation of this tank, only relocation of the supply module.
The height differential between the supply module and dosing module can not exceed one meter. The Clear Back of Cab
(CBOC) tank does not have an integrated supply module. The standard KW installation is a supply module located inside
of the frame rail. When relocating either the supply module or the tank, the maximum height differential between the supply module and the bottom of the tank is one meter. The maximum line length is 2 meters between supply module and
DEF tank sending unit.
When relocating the components the maximum pressure DEF hose length, from Supply module to Dosing Module, is 3
meters (118”).
Routing to the Dosing Module (Injector)
It is important for the function of the dosing module to ensure that the dosing module is not routed downstream of DEF
lines or components. If this is unavoidable (for example on RH under exhaust systems) a routing trap must be installed. A
minimum of 12” of line length must be routed below the dosing module, in order to catch any leftover DEF when system is
purged.
12/09
4-8
Page 59

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Minimum 12” Line
Length Below
Dosing Module
FIGURE 4-8: Routing DEF Lines and DEF Trap
Clear Back of Cab Supply Module
The CBOC Supply Module (or Pump) standard mounting location is inside of the frame rail back of cab. Body builders
may need to relocate this component, and should follow the location and length restrictions above. Additionally the
mounting and the orientation of the Supply Module must not exceed 45° (from vertical) in two directions as shown in
Figure 4-9 below.
FIGURE 4-9: Supply Module Allowed Clocking Angles
4-9
12/09
Page 60

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
GENERAL EXHAUST INFORMATION
Kenworth will offer two main DPF and SCR exhaust systems on T440/T470 chassis in 2010. A Right Hand Under DPF
and SCR system, in which both canisters are located underneath the cab access step, and an Independent DPF and SCR
located vertically back of cab on stanchion brackets.
RH Under DPF and SCR Independent Back of Cab
The following images depict the typical exhaust routings for each system, and can be used to determine exhaust routing
paths for systems you choose. Dimensional information can be found in Section 5 of this manual.
Body Builders must not modify (including altering, substituting, and relocating) the DPF and SCR canisters. The exhaust
piping after it exits the SCR canister may be modifi ed, however using smaller diameter piping or piping with numerous
bends is not recommend as the backpressure requirements of the system may be exceeded.
12/09
4-10
Page 61

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Right Hand Under DPF and SCR on Daycab with Single Side of
Cab T ailpipe
FIGURE 4-10: Isometric View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single SOC Tailpipe
FIGURE 4-11: Top View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single SOC Tailpipe
4-11
12/09
Page 62

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
FIGURE 4-12: Right View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single SOC Tailpipe
FIGURE 4-13: Back View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single SOC Tailpipe
12/09
4-12
Page 63

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single Back of Cab Tailpipe
FIGURE 4-14: Isometric View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single Back of Cab Tailpipe
FIGURE 4-15: Top view of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single Back of Cab Tailpipe
4-13
12/09
Page 64

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
FIGURE 4-16: Right view of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single Back of Cab Tailpipe
FIGURE 4-17: Back view of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single Back of Cab Tailpipe
12/09
4-14
Page 65

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Vertical Independent DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe
FIGURE 4-18: Isometric View of Vertical DPF and SCR
FIGURE 4-19: Top View of Vertical DPF and SCR
4-15
12/09
Page 66

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
FIGURE 4-20: Right View of Vertical DPF and SCR
FIGURE 4-21: Back View of Vertical DPF and SCR
12/09
4-16
Page 67

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
Right Hand Under DPF and SCR on Aerocabs with Single Side of
Cab T ailpipe
FIGURE 4-22: Isometric View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR on Aerocab with Single SOC Tailpipe
FIGURE 4-23: Top View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR on Aerocab with Single SOC Tailpipe
4-17
12/09
Page 68

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
FIGURE 4-24: Right View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR on Aerocab with Single SOC Tailpipe
FIGURE 4-25: Back View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR on Aerocab with Single SOC Tailpipe
12/09
4-18
Page 69

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
EXHAUST INFORMATION
This section includes information on how to calculate tailpipe heights, and reference information for PTO clearance.
Optional equipment is not shown.
Tailpipe Stack Height Calculation
TABLE 4-1. Stack Height
Dimension A
Tailpipes side of Aerocab, RH
under DPF
Tailpipes independent back of
sleeper, RH under DPF
DPF mounted independent back
of cab or sleeper
Tailpipes side of cab mount,
DPF RH under
Tailpipes back of cab mount, w/
side extenders, DPF RH under
Tailpipes back of cab mount, w/o
side extenders, DPF RH under
DIMENSION “B” IS THE T AILPIPE LENGTH.
Cummins
(not ISL)
78.0”
75.0”
75.0”
Cummins
ISL
75.0”
68.5”
68.0”
TABLE 4-2. Unladen Stack Height
For approximate unladen stack height (12,000 pound springs) use the following frame heights:
Tire Size Top of Rail Ft. Suspension
11R24.5
11R22.5
285/75R24.5
295/75R22.5
425/65R22.5
385/65R22.5
43.5” 12K
42.5” 12K
42” 12K
41.5” 12K
43.2 20K
42.4 20K
*Use Prospector frame heights for more accurate results.
Sample: Tailpipe height 13’6” = Desired overall stack height = 162.0”
(–) Prospector frame height (–) 43.5”
(+) Frame rail depth (+) 10.6”
(–) Dimension ‘A’ from chart (–) 68.6”
= Tail pipe length = 60.5”
4-19
12/09
Page 70

Section 4
Exhaust & Aftertreatment
This page intentionally left blank.
12/09
4-20
Page 71

Section 5
Frame Layouts
FRAME LAYOUTS
The dimensions in the frame layout section are intended to aid in layout of the chassis, and to help determine the best
possible combination of fuel tanks, battery boxes, the diesel particulate fi lter (DPF), SCR canister, and Diesel Exhaust
Fluid (DEF) tank. For your application, the layouts focus on the under cab area, with appropriate dimensional information
included for pertinent back of cab components. Not all optional equipment is included in this section. Additional components may be placed on the rail behind components shown. The Back of Cab components are shown primarily for reference. For more specifi c requirements please work with your local Kenworth Dealer. Please read the instructions carefully.
The following dimensions are consistent across the entire section to aid in the comparison of one layout option versus
another.
TABLE 5-1.
B = Battery box
D = DEF tank
E = Exhaust
F1 = Fuel Tank RHS
F2 = Fuel Tank LHS
T = Tool Box
The layouts are organized by type, specifi cally the arrangement of under cab components. The visual index that follows
will give you a quick overview of the layouts that are included. Using the index locate the layout that you are interested in,
then turn to the specifi ed pages. The charts that follow are then model specifi c. It is important that the correct chart is used
for accurate dimensional information.
Visual Index
Symbol Description Symbol Description
RHUC DPF/SCR Tool Box
Vertical DPF/SCR DEF Tank
Parallel Battery Box, Standard Length Clear BOC DEF Tank
In Cab Battery Box Fuel Tank
Cantilever Battery Box
5-1
12/09
Page 72

Section 5
Frame Layouts
COMMON OPTIONAL COMPONENTS
The frame layouts that follow contain the minimum frame requirements to be operational (fuel tanks, battery
box, and after-treatment components). All layouts are shown with standard length battery boxes unless otherwise noted. Dimensions for these components have been provided below to help complete the frame layout for
chassis with more fuel tanks, additional tool boxes, etc.
TABLE 5-2. Fuel Tank Overall Length (in)
Fuel Tank Overall Length (in)
Fuel T ank Diameter
Gallons 22” 24.5”
45 N/A 23.0
56 35.6 N/A
60 38.0 30.6
75 47.3 38.5
90 N/A 45.5
100 62.2 50.0
105 N/A N/A
110 N/A 55.0
120 74.3 60.6
135 N/A 67.2
150 N/A 74.5
177 N/A N/A
TABLE 5-3. Battery Box Centerframe Lengths (in)
Battery Box Centerframe Lengths (in)
T440/T470
Parallel Short 34.8
Parallel Extended 42.0
Parallel BOC 34.8
Cantilever 17.8
Vocational 15.2
12/09
5-2
Page 73

Section 5
Frame Layouts
FIGURE 5-1. DEF Tank Dimensions.
TABLE 5-4. DEF Tanks Systems
Description
Small DEF Tank 9
Medium DEF Tank 18
Large DEF Tank 27
Usable V olume,
Gallons
Fuel T ank
Diameter
22” 27.4 15.3
24.5” 27.4 15.8
22” 27.7 15.0
24.5” 27.7 15.5
22” 27.7 15.0
24.5” 27.7 15.5
AB
Acronyms Index
Throughout the Frame Layout section you will see these acronyms. They are defi ned here to help you decode
the layouts.
BOC Back Of Cab DSOC Dual Side Of Cab
BOS Back Of Sleeper LHUC Left Hand Under Cab
CBOC Clear Back Of Cab RHUC Right Hand Under Cab
DEF Diesel Exhaust Fluid SOAC Side Of AeroCab
DSOAC Dual Side Of AeroCab SOC Side Of Cab
5-3
12/09
Page 74

Section 5
Frame Layouts
FRAME LAYOUT INDEX
Day Cab Chassis Layout Options
D1 is used with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC fuel tank, RH BOC DEF tank, and LH BOC cantilever battery box. Chart located
on page 5–8.
D2 is used with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC fuel tank, RH BOC cantilever battery box, and LH BOC DEF tank. Chart
located on page 5–9.
D3 is used with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC battery box, RH BOC DEF tank, and LH BOC fuel tank. Chart located on
page 5–10.
D4 is used with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC battery box, LH BOC DEF tank, and RH BOC fuel tank. Chart located on
page 5–11.
D5 is used with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC fuel tank, RH BOC DEF tank, and in cab battery box. Chart located on
page 5–12.
12/09
5-4
Page 75

Section 5
Frame Layouts
D6 is used with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC fuel tank, Clear BOC DEF tank, and in cab battery box. Chart located on
page 5–13.
D7 is used with Vertical-Vertical DPF/SCR, LH vertical tailpipe, RHUC fuel tank, LHUC battery box, and LH BOC DEF
tank. Charts located on page 5–14.
D8 is used with Vertical-Vertical DPF/SCR, LH vertical tailpipe, RHUC fuel tank, LHUC battery box, and RH BOC DEF
tank. Chart located on page 5–15.
D9 is used with Vertical-Vertical DPF/SCR, LH vertical tailpipe, LHUC & RHUC fuel tanks, RH BOC cantilever battery box,
and LH BOC DEF tank. Chart located on page 5–16.
D10 is used with Vertical-Vertical DPF/SCR, LH vertical tailpipe, LHUC fuel tank, RHUC battery box, and Clear BOC DEF
tank. Charts located on page 5–17.
5-5
12/09
Page 76

Section 5
Frame Layouts
Sleeper Chassis Layout Options
S1 is used with 38” AeroCab sleeper with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC fuel tank, RH BOC DEF tank, and LH BOC cantilever
battery box. Chart located on page 5–18.
S2 is used with 38” AeroCab sleeper with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC fuel tank, LH BOC DEF tank, and RH BOC cantilever
battery box. Chart located on page 5–19.
S3 is used with 38” AeroCab sleeper with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC battery box, RH BOC DEF tank, and LH BOC fuel tank.
Chart located on page 5–20.
S4 is used with 38” AeroCab sleeper with RHUC DPF/SCR, LHUC battery box, LH BOC DEF tank, and RH BOC fuel tank.
Chart located on page 5–21.
S5 is used with 38” AeroCab sleeper with Vertical-Vertical DPF/SCR, LH vertical tailpipe, RHUC fuel tank, LHUC battery
box, and LH BOC DEF tank. Chart located on page 5–22.
12/09
5-6
Page 77

Section 5
Frame Layouts
S6 is used with 38” AeroCab sleeper with Vertical-Vertical DPF/SCR, LH vertical tailpipe, RHUC fuel tank, LHUC battery
box, and RH BOC DEF tank. Chart located on page 5–23.
S7 is used with 38” AeroCab sleeper with Vertical-Vertical DPF/SCR, LH vertical tailpipe, RHUC & LHUC fuel tanks, LH
BOC DEF tank and RH BOC cantilever battery box. Chart located on page 5–24.
5-7
12/09
Page 78

Section 5
Frame Layouts
D1—Use with the following models: T470/T440
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR)* = 0.4in
TABLE 5-5.
T470/T440
Fuel T ank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in)
56 35.5 -3.7 17.0
22”
Diameter
Tank
24.5”
Diameter
Tank
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A CANTILEVER SIZED BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL BOXES WILL AFFECT THIS DIMENSION.
60 38.0 -1.2 19.5
75 47.3 8.1 28.8
100 62.2 23.0 43.7
120 74.2 35.0 55.7
60 30.5 -8.7 12.0
75 38.5 -0.7 20.0
90 45.5 6.3 27.0
100 50.0 10.8 31.5
110 54.9 15.7 36.4
120 60.5 21.3 42.0
135 67.2 28.0 48.7
150 74.5 35.3 56.0
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel Tank,
Daycab* (in)
Dimension B
BOC to Battery Box,
Daycab* (in)
BOC to DEF Tank, Daycab* (in)
Small Medium Large
18.4 24.8 32.9
Dimension D
DEF T ank Size
12/09
5-8
Page 79

D2—Use with the following models: T470/T440
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR)* = 0.4in
Dimension B (BOC to Cantilever Battery Box)* = 21.8in
Section 5
Frame Layouts
TABLE 5-6.
T470/T440
Dimension D
Fuel T ank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Large
56 35.5 -3.7 7.4 17.1 25.2
60 38.0 -1.2 10.1 19.3 27.4
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A CANTILEVER SIZED BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL BOXES WILL AFFECT THIS DIMENSION.
75 47.3 8.1 23.9 28.2 36.2
100 62.2 23.0 34.9 44.7 52.8
120 74.2 35.0 46.0 55.7 63.8
60 30.5 -8.7 1.9 11.6 19.7
75 38.5 -0.7 10.1 19.3 27.4
90 45.5 6.3 18.4 28.2 36.2
100 50.0 10.8 23.9 30.9 39.0
110 54.9 15.7 29.4 36.4 44.5
120 60.5 21.3 34.9 42.0 50.0
135 67.2 28.0 40.5 47.5 55.5
150 74.5 35.3 46.0 55.7 63.8
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel Tank,
Daycab* (in)
BOC to DEF Tank* (in)
DEF T ank Size
5-9
12/09
Page 80

Section 5
Frame Layouts
D3—Use with the following models: T470/T440
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR)* = .04in
Dimension B (BOC to Battery Box)* = -4.5in
TABLE 5-7.
T470/T440
Dimension D
Fuel T ank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Large
56 35.5 33.0
60 38.0 35.5
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
NOTE: DIMENSIONS “B” AND “F” ARE CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE
DIMENSIONS “B” AND “F”
75 47.3 44.8
100 62.2 59.7
120 74.2 71.7
60 30.5 28.0
75 38.5 36.0
90 45.5 43.0
100 50.0 47.5
110 54.9 52.4
120 60.5 58.0
135 67.2 64.7
150 74.5 72.0
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel Tank,
Daycab* (in)
BOC to DEF Tank, Daycab* (in)
DEF T ank Size
18.4 24.8 32.9
12/09
5-10
Page 81

D4—Use with the following models: T470/T440
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR)* = 0.4in
Dimension B (BOC to Battery Box)* = -4.5in
Section 5
Frame Layouts
TABLE 5-8.
T440/T470
Fuel T ank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Large
56 35.5 38.6
60 38.0 41.1
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
NOTE: DIMENSIONS “B” AND “D” ARE CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE
DIMENSIONS “B” AND “D”
75 47.3 50.4
100 62.2 65.3
120 74.2 77.3
60 30.5 33.6
75 38.5 41.6
90 45.5 48.6
100 50.0 53.1
110 54.9 58.0
120 60.5 63.6
135 67.2 70.3
150 74.5 77.6
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel Tank,
Daycab* (in)
BOC to DEF Tank, Daycab* (in)
7.4 17.1 25.2
Dimension D
DEF T ank Size
5-11
12/09
Page 82

Section 5
Frame Layouts
D5—Use with the following models: T470/T440 and In-cab battery box.
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR)* = 0.4in
TABLE 5-9.
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Large
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
Fuel T ank Size
56 35.5 -3.7
60 38.0 -1.2
75 47.3 8.1
100 62.2 23.0
120 74.2 35.0
60 30.5 -8.7
75 38.5 -0.7
90 45.5 6.3
100 50.0 10.8
110 54.9 15.7
120 60.5 21.3
135 67.2 28.0
150 74.5 35.3
T440/T470
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel Tank,
Daycab* (in)
Dimension D
BOC to DEF Tank, Daycab* (in)
DEF T ank Size
18.4 24.8 32.9
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
12/09
5-12
Page 83

Frame Layouts
D6—Use with the following models: T470/T440 and In-cab battery box.
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR)* = 0.4in
Dimension D (BOC to DEF tank)* = 0.7in
Section 5
TABLE 5-10.
T440/T470
Fuel Tank Size Dimension F
Diameter Gallons Length (in)
56 35.5 -3.7
60 38.0 -1.2
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
75 47.3 8.1
100 62.2 23.0
120 74.2 35.0
60 30.5 -8.7
75 38.5 -0.7
90 45.5 6.3
100 50.0 10.8
BOC to Fuel Tank,
Daycab* (in)
5-13
12/09
Page 84

Section 5
Frame Layouts
D7—Use with the following models: T470/T440
Dimension B (BOC to Battery Box)* = -4.5in
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR) = 19.6in
TABLE 5-11.
T440/T470
Fuel T ank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Small Medium
56 35.5 -3.7
22”
Diameter
Tank
24.5”
Diameter
Tank
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
NOTE: DIMENSIONS “B” AND “D” ARE CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE
DIMENSIONS “B” AND “D”
60 38.0 -1.2 -6.9
75 47.3 8.1 2.4
100 62.2 23.0 17.3
120 74.2 35.0 29.3
60 30.5 -8.7 -14.4
75 38.5 -0.7 -6.4
90 45.5 6.3 0.6
100 50.0 10.8 5.1
110 54.9 15.7 10.0
120 60.5 21.3 15.6
135 67.2 28.0 22.3
150 74.5 35.3 29.6
Dimension F
BOC to
Fuel T ank,
Daycab (in)
BOC to DEF Tank, Daycab (in)
Dimension D
DEF T ank Size DEF Tank Size
7.4 39.2
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel
Tank, Ext.
Daycab (in)
-9.4
BOC to DEF Tank, Ext. Daycab (in)
Dimension D
1.7 39.0
12/09
5-14
Page 85

D8—Use with the following models: T470/T440
Dimension B (BOC to Battery Box)* = -4.5in
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR) = 19.6in
Section 5
Frame Layouts
TABLE 5-12.
T440/T470
Fuel Tank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Small Medium
56 35.5 -3.7 18.4 39.2 -9.4 18.2 39.0
22”
Diameter
Tank
24.5”
Diameter
Tank
60 38.0 -1.2 18.4 39.2 -6.9 18.2 39.0
75 47.3 8.1 29.4 39.2 2.4 18.2 39.0
100 62.2 23.0 34.9 42.6 17.3 29.2 36.9
120 74.2 35.0
60 30.5 -8.7 18.4 39.2 -14.4 18.2 39.0
75 38.5 -0.7 18.4 39.2 -6.4 18.2 39.0
90 45.5 6.3 18.4 39.2 0.6 18.2 39.0
100 50.0 10.8 29.4 39.2 5.1 18.2 39.0
110 54.9 15.7 29.4 39.2 10.0 29.2 39.0
120 60.5 21.3 34.9 42.6 15.6 29.2 36.9
135 67.2 28.0
150 74.5 35.3 46.0 55.7 29.6 40.3 50.0
Dimension F
BOC to
Fuel Tank,
Daycab (in)
BOC to DEF Tank, Daycab (in)
Dimension D
DEF Tank Size DEF Tank Size
46.0 55.7
40.5 55.7
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel
Tank, Ext.
Daycab (in)
29.3
22.3
BOC to DEF Tank, Ext. Daycab (in)
Dimension D
40.3 50.0
34.8 50.0
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE DIMENSION “B”
5-15
12/09
Page 86

Section 5
Frame Layouts
D9—Use with the following models: T470/T440
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR) = 19.6in
TABLE 5-13.
T440/T470
Dimension
Fuel Tank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Small Medium
F1 & F2
BOC to
Fuel Tank,
Daycab (in)
Dimension B
BOC to
Battery Box,
Daycab (in)
BOC to DEF Tank, Daycab (in)
Dimension D
DEF Tank Size DEF Tank Size
Dimension
F1 & F2
BOC to Fuel
Tank, Ext.
Daycab (in)
Dimension B
BOC to
Battery Box,
Ext Daycab (in)
56 35.5 -3.7 24.1 7.4 39.2 -9.4 24.1 1.7 39.0
22”
Diameter
Tank
60 38.0 -1.2 24.1 18.4 39.2 -6.9 24.1 4.4 39.0
75 47.3 8.1 29.6 29.4 39.2 2.4 24.1 18.2 39.0
100 62.2 23.0 43.7 34.9 44.7 17.3 29.3 29.2 39.0
120 74.2 35.0 55.7
46.0 55.7
29.3 50.0
60 30.5 -8.7 24.1 1.9 39.2 -14.4 24.1 -3.8 39.0
75 38.5 -0.7 24.1 18.4 39.2 -6.4 24.1 4.4 39.0
90 45.5 6.3 29.6 18.4 39.2 0.6 29.6 18.2 39.0
24.5”
Diameter
Tank
100 50.0 10.8 35.1 29.4 39.2 5.1 29.6 18.2 39.0
110 54.9 15.7 36.4 29.4 39.2 10.0 35.1 29.2 39.0
120 60.5 21.3 42.0 34.9 42.0 15.6 35.1 29.2 39.0
135 67.2 28.0 48.7
40.5 47.5
22.3 43.0
150 74.5 35.3 56.0 46.0 55.7 29.6 50.3 40.2 50.0
Dimension D
BOC to DEF Tank,
Ext. Daycab (in)
40.3 50.0
34.8 41.8
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A CANTILEVER SIZED BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL BOXES WILL AFFECT THIS DIMENSION.
12/09
5-16
Page 87

D10—Use with the following models: T470/T440
Dimension B (BOC To Battery Box)* = -4.5in
Dimension E (BOC to DPF/SCR) = 19.6in
Dimension D (BOC to DEF tank)* = 0.7in
Section 5
Frame Layouts
TABLE 5-14.
T440/T470
Fuel T ank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in)
56 35.5 -3.7 -9.4
60 38.0 -1.2 -6.9
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
*Subtract 5.7 inches for the extended Daycab.
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE DIMENSION “B”
75 47.3 8.1 2.4
100 62.2 23.0 17.3
120 74.2 35.0 29.3
60 30.5 -8.7 -14.4
75 38.5 -0.7 -6.4
90 45.5 6.3 0.6
100 50.0 10.8 5.1
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel Tank,
Daycab (in)
Dimension F
BOC to Fuel Tank,
Extended Daycab (in)
5-17
12/09
Page 88

Section 5
Frame Layouts
S1—Use with the following models: T470/T440 38”
Dimension E (BOS to DPF/SCR) = -17..9in.
TABLE 5-15.
T440/T470 38”
Fuel T ank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Large
56 35.5 -31.7 0.9
60 38.0 -29.2 0.9
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A CANTILEVER SIZED BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL BOXES WILL AFFECT THIS DIMENSION.
75 47.3 -19.9 0.9
100 62.2 -5.0 18.4
120 74.2 7.0 27.7
60 30.5 -36.7 -16.0
75 38.5 -28.7 0.9
90 45.5 -21.7 0.9
100 50.0 -17.2 18.4
110 54.9 -12.3 18.4
120 60.5 -6.7 18.4
135 67.2 0.0 18.4
150 74.5 7.3 28.0
Dimension F
BOS to
Fuel T ank (in)
Dimension B
BOS to
Battery Box (in)
12.7 17.0 25.1
Dimension D
BOS to DEF Tank (in)
DEF T ank Size
12/09
5-18
Page 89

S2—Use with the following models: T470/T440 38”
Dimension E (BOS to DPF/SCR) = -17.9in
Dimension B (BOS to Cantilever Battery Box) = 2.9in
Section 5
Frame Layouts
TABLE 5-16.
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Large
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
Fuel T ank Size
56 35.5 -31.7 -20.6 -10.9 25.1
60 38.0 -29.2 -15.1 17.0 25.1
75 47.3 -19.9 12.7 17.0 25.1
100 62.2 -5.0 12.7 17.0 25.1
120 74.2 7.0 18.0 27.7 35.8
60 30.5 -36.7 -26.1 -16.4 25.1
75 38.5 -28.7 -15.1 17.0 25.1
90 45.5 -21.7 12.7 17.0 25.1
100 50.0 -17.2 12.7 17.0 25.1
110 54.9 -12.3 12.7 17.0 25.1
120 60.5 -6.7 12.7 17.0 25.1
135 67.2 0.0 12.7 19.5 27.5
150 74.5 7.3 18.0 27.7 35.8
T440/T470 38”
Dimension F
BOS to Fuel Tank (in)
Dimension D
BOS to DEF Tank (in)
DEF T ank Size
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A CANTILEVER SIZED BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL BOXES WILL AFFECT THIS DIMENSION.
5-19
12/09
Page 90

Section 5
Frame Layouts
S3—Use with the following models: T470/T440 38”
Dimension E (BOS to DPF/SCR) = -17.9in
Dimension B (BOS to Battery Box) = -32.5in
TABLE 5-17.
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Large
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
Fuel T ank Size
56 35.5 5.0
60 38.0 7.5
75 47.3 16.8
100 62.2 31.7
120 74.2 43.7
60 30.5 0.0
75 38.5 8.0
90 45.5 15.0
100 50.0 19.5
110 54.9 24.4
120 60.5 30.0
135 67.2 36.7
150 74.5 44.0
T440/T470 38”
Dimension F
BOS to Fuel Tank (in)
Dimension D
BOS to DEF Tank (in)
DEF T ank Size
12.7 17.0 25.1
NOTE: DIMENSIONS “B” AND “F” ARE CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE
DIMENSIONS “B” AND “F”
12/09
5-20
Page 91

S4—Use with the following models: T470/T440 38”
Dimension E (BOS to DPF/SCR) = -17.9in
Dimension B (BOS to Battery Box) = -32.5in
Section 5
Frame Layouts
TABLE 5-18.
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium Large
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
Fuel T ank Size
56 35.5 20.3
60 38.0 22.8
75 47.3 32.1
100 62.2 47.0
120 74.2 59.0
60 30.5 15.3
75 38.5 23.3
90 45.5 30.3
100 50.0 34.8
110 54.9 39.7
120 60.5 45.3
135 67.2 52.0
150 74.5 59.3
T440/T470 38”
Dimension F
BOS to Fuel Tank (in)
Dimension D
BOS to DEF Tank (in)
DEF T ank Size
-20.6 -10.9 -2.8
NOTE: DIMENSIONS “B” AND “D” ARE CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE
DIMENSIONS “B” AND “D”
5-21
12/09
Page 92

Section 5
Frame Layouts
S5—Use with the following models: T470/T440 38”
Dimension B (BOS to Battery Box) = -32.5in
Dimension E (BOS to DPF/SCR) = 19.6in
TABLE 5-19.
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
Fuel T ank Size
56 35.5 -31.7
60 38.0 -29.2
75 47.3 -19.9
100 62.2 -5.0
120 74.2 7.0
60 30.5 -36.7
75 38.5 -28.7
90 45.5 -21.7
100 50.0 -17.2
110 54.9 -12.3
120 60.5 -6.7
135 67.2 0.0
150 74.5 7.3
T440/T470 38”
Dimension F
BOS to Fuel Tank (in)
Dimension D
BOS to DEF Tank (in)
DEF T ank Size
-20.6 -10.9
NOTE: DIMENSIONS “B” AND “D” ARE CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE
DIMENSIONS “B” AND “D”
12/09
5-22
Page 93

S6—Use with the following models: T470/T440 38”
Dimension B (BOS to Battery Box) = -32.5in
Dimension E (BOS to DPF/SCR) = 19.6in
Section 5
Frame Layouts
TABLE 5-20.
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium
22” Diameter Tank
24.5” Diameter Tank
Fuel T ank Size
56 35.5 -31.7 -20.6 -9.4
60 38.0 -29.2 -17.9 -9.4
75 47.3 -19.9 29.3 39.0
100 62.2 -5.0 29.3 39.0
120 74.2 7.0 29.3 39.0
60 30.5 -36.7 -26.1 -9.4
75 38.5 -28.7 -17.9 -9.4
90 45.5 -21.7 29.3 39.0
100 50.0 -17.2 29.3 39.0
110 54.9 -12.3 29.3 39.0
120 60.5 -6.7 29.3 39.0
135 67.2 0.0 29.3 39.0
150 74.5 7.3 29.3 39.0
T440/T470 38”
Dimension F
BOS to Fuel Tank (in)
Dimension D
BOS to DEF Tank (in)
DEF T ank Size
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A STANDARD BATTERY BOX. OPTIONAL EXTENDED BOXES WILL CHANGE DIMENSION “B”
5-23
12/09
Page 94

Section 5
Frame Layouts
S7—Use with the following models: T470/T440 38”
Dimension E (BOS to DPF/SCR) = 19.6in
TABLE 5-21.
T440/T470 38”
Fuel T ank Size
Diameter Gallons Length (in) Small Medium
56 35.5 -31.7 0.9 -20.6 -10.9
22” Diameter
Tank
24.5” Diameter
Tank
60 38.0 -29.2 0.9 -17.9 39.0
75 47.3 -19.9 0.9 18.2 39.0
100 62.2 -5.0 37.1 18.2 39.0
120 74.2 7.0 37.1 18.2 39.0
60 30.5 -36.7 -16.0 -26.1 -16.4
75 38.5 -28.7 0.9 -17.9 39.0
90 45.5 -21.7 0.9 18.2 39.0
100 50.0 -17.2 37.1 18.2 39.0
110 54.9 -12.3 37.1 18.2 39.0
120 60.5 -6.7 37.1 18.2 39.0
135 67.2 0.0 37.1 18.2 39.0
150 74.5 7.3 37.1 18.2 39.0
Dimension F1 & F2
BOS to
Fuel T ank (in)
Dimension B
BOS to
Battery Box (in)
Dimension D
BOS to DEF Tank (in)
DEF T ank Size
NOTE: DIMENSION “B” IS CALCULATED USING A CANTILEVER SIZED BATTERY BO X. OPTIONAL BOXES WILL AFFECT THIS DIMENSION.
12/09
5-24
Page 95

Section 6
Body Mounting
FRONT FRAME DIMENSIONS
This section includes drawings of the T470 extended front frame (73”) and standard (50.5”) front frame settings. All
dimensions are in inches (in). They illustrate measurements useful to the installation of front frame equipment and
bumpers. Kenworth also offers .dxf fi les and frame layouts of ordered chassis four weeks prior to build. Please work with
your Kenworth sales representative to request this feature when specifying your chassis.
Extended Front Frame Standard Front Frame
44.8” 44.8” 27.0”27.0”
10.2”
72.8”
50.3”
10.2”
Extended Front Frame Standard Front Frame
6-1
12/09
Page 96

Section 6
Body Mounting
FRAME INFORMATION
Frame information provided is per rail, some specifi cations are written for RBM requirements per pair of rails. Make sure
to know the requirement before deciding on the frame rail.
TABLE 6-1. Single Steel Rails
Rail Height Flange Width Web Thickness Section Modulus RBM (in lbs) Weight (lbs/in)*
H W T S R W
10 - 5/8” x 3 -1/2” x 5/16” 14.80 1,776,000 2.90
10 - 3/4” x 3 -1/2” x 3/8” 17.80 2,132,000 3.46
10 - 11/16” x 3 -1/2” x 1/2” 22.35 2,683,000 4.53
11 - 5/8” x 3 -7/8” x 3/8” 21.43 2,572,000 3.80
* Per pair of rails.
TABLE 6-2. Inserted Steel Rails
Rail Height Insert Material Section Modulus RBM (in lbs) Weight (lbs/in)*
10 - 5/8” Single 9-7/8”x 2-7/8” x 1/4” 24.37 2,925,000 4.96
10 - 3/4” Single 9-7/8”x 2-7/8” x 1/4” 27.33 3,280,000 5.53
11 - 5/8” Single 10-3/4”x 3-1/2” x 3/8” 39.20 4,704,000 7.28
* Per pair of rails.
CRITICAL CLEARANCES
Rear Wheels and Cab
CAUTION:
Normal suspension movement could cause contact between the tires and the body. To prevent this, mount the body so
that the minimum clearance between the top of the tire and the bottom of the body is 8 inches (203 mm). This should be
measured with the body empty. See Figure 6–1.
Insuffi cient clearance between rear tires and body structure may cause damage to the
body during suspension movement. Allow at least 8 inches clearance (See Figure 6–1.)
FIGURE 6-1. Minimum Clearance Between Top Of Rear Tires And Body Structure Overhang.
CAUTION:
12/09
Maintain adequate clearance between back of cab and the front (leading edge) of mounted
body. Failure to comply may result in equipment damage. See Figure 6–2.
6-2
Page 97

Section 6
Body Mounting
Note:
FIGURE 6-2. Minimum Back of Cab Clearance
Be sure to provide maintenance access to battery box and fuel tank fi ll neck.
4”
WARNING:
If the frame rail fl anges are modifi ed or damaged, the rail may fail prematurely and cause
an accident. When mounting a body to the chassis, DO NOT drill holes in the upper or
lower fl ange of the frame rail. Mount the body using body mounting brackets or U–bolts.
Failure to comply may result in personal injury, death, equipment or property damage.
BODY MOUNTING USING BRACKETS
CAUTION:
Installation of a spacer between the body subframe and the top fl ange of the frame rail will help prevent premature wear of
the components due to chafi ng or corrosion.
Always install a spacer between the body subframe and the top fl ange of the frame
rail. Failure to do so may result in corrosion due to dissimilar materials and equipment
damage.
6-3
12/09
Page 98

Section 6
Body Mounting
Frame Sill
If the body is mounted to the frame with brackets, we recommend that the frame sill spacer be made from a strip of rubber or plastic (delrin or nylon). These materials will not undergo large dimensional changes during periods of high or low
humidity. The strip will be less likely to fall out during extreme relative motion between body and chassis. See Figure 6–3.
Body Subframe
(Rail)
Spacer
Chassis Frame
(Rail) Sill
FIGURE 6-3. Spacer Between Frame Sill and Body Rail - Rubber or Plastic
Brackets
When mounting a body to the chassis with brackets, we recommend designs that offer limited amount of relative movement, bolted securely but not too rigid. Brackets should allow for slight movement between the body and the chassis. For
instance, Figure 6–4 shows a high compression spring between the bolt and the bracket.
Spring
Rubber Spacer
FIGURE 6-4. High Compression Spring FIGURE 6-5. Rubber Spacer Between Brackets
Between the Mounting Bolt and Upper Bracket
Another possibility is mounting a rubber spacer between the brackets. See Figure 6–5.
These designs will allow relative movement between the body and the chassis during extreme frame racking situations.
Extreme frame racking, and mountings that are too rigid, could cause damage to the body. This is particularly true with
tanker installations.
12/09
6-4
Page 99

Section 6
Body Mounting
MOUNTING HOLES
When installing the lower bracket on frame rails the mounting holes in the chassis frame bracket and frame rail must comply with the general spacing and location guidelines illustrated in Figure 6–6. The hole diameter should not exceed the bolt
diameter by more than .060 inches (1.5 mm).
5.63
(143mm)
2.0
(50mm)
4 HOLES
4 HOLES
.63 IN. DIA.
.5 IN. DIA.
(12.7mm)
(16mm)
5.5
(140mm)
6 HOLES
6 HOLES
.63 IN. DIA.
.5 IN. DIA.
(12.7mm)
11.0
(279mm)
(16mm)
(140mm)
FIGURE 6-6. Crossmember-Gusset Hole Pattern Requirements. [inch (mm)]
Frame Drilling
WARNING:
When mounting a body to the chassis, DO NOT drill holes in the
upper or lower fl ange of the frame rail. If the frame rail fl anges are
modifi ed or damaged, the rail may fail prematurely. Mount the body us-
ing body mounting brackets or U–bolts. Failure to comply may result
in personal injury, death, equipment or property damage.
5.5
5.63
(143mm)
2.0
(50mm)
WARNING:
WARNING:
Use care when drilling the frame web so the wires and air lines routed inside the rail are
not damaged, failure to do so may cause an inoperable electrical or air system circuit.
Failure to comply may result in personal injury, death, equipment or property damage.
Do not drill closely spaced holes in the frame rail. Hole centers of two adjacent holes
should be spaced no less than twice the diameter of the largest hole. Closer spacing may
induce a failure between the holes. Failure to comply may result in personal injury, death,
equipment or property damage.
6-5
12/09
Page 100

Section 6
Body Mounting
BODY MOUNTING USING U–BOLTS
Spacers
If the body is mounted to the frame with U–bolts, use a hardwood sill (minimum 1/2 inch (12 mm) thick) between the frame
rail and body frame to protect the top surface of the rail fl ange.
WARNING:
Use a hardwood spacer between the bottom fl ange and the U–bolt to prevent the U–bolt from notching the frame fl ange.
See Figure 6–7.
Wood Sill 0.5 (12) Minimum
Frame Rail Spacer
(Fabricated Steel or
FIGURE 6-7. Acceptable U-Bolt Mounting with Wood and Fabricated Spacers [inch (mm)]
Do not allow the frame rails or fl anges to deform when tightening the U–bolts. It will weak-
en the frame. Use suitable spacers made of steel or hardwood on the inside of the frame
rail to prevent collapse of the frame fl anges. Failure to comply may result in personal
injury, death, equipment or property damage.
Body Structure
Truck Frame
Hardwood)
U-Bolt
U-Bolt Spacer (Hardwood)
WARNING:
CAUTION:
12/09
Do not allow spacers and other body mounting parts to interfere with brake lines, fuel
lines, or wiring harnesses routed inside the frame rail. Crimped or damaged brake lines,
fuel lines, or wiring may result in loss of braking, fuel leaks, electrical overload or a fi re.
Carefully inspect the installation to ensure adequate clearances for air brake lines, fuel
lines, and wiring. Failure to comply may result in personal injury, death, equipment or
property damage. See Figure 6–8.
Mount U–bolts so they do not chafe on frame rail. Failure to do so may result in
premature wear of the U-bolt or frame rail.
6-6
 Loading...
Loading...