Kenworth T370, T270, T170, Hybrid Service Manual

Kenworth
T170 / T270 / T370 and Hybrid
2011 Body Builders Manual
®


Kenworth Medium Duty
Body Builders Manual
Models: T170/T270/T370 and Hybrid
For 2011 Model Year and Later with 2010 EPA Compliant Engines

Body Builder’s Manual
Contents
SECTION 1 — INTRODUCTION
SCOPE .................................................................1-1
SECTION 2 — SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
SAFETY SIGNALS ........................................................2-1
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes ........................................2-1
FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETYSTANDARDS COMPLIANCE .................2-2
Incomplete Vehicle Certication ........................................2-2
Noise and Emissions Requirements ....................................2-3
Fuel System .......................................................2-4
Compressed Air System ..............................................2-4
Exhaust and Exhaust After-treatment System .............................2-4
Cooling System ....................................................2-5
Electrical System ...................................................2-6
Air Intake System ...................................................2-8
Charge Air Cooler System ............................................2-8
SECTION 3 — DIMENSIONS
ABBREVIATIONS AND DEFINITIONS .........................................3-1
OVERALL DIMENSIONS ...................................................3-3
DETAIL VIEWS ...........................................................3-5
DETAIL VIEWS ...........................................................3-6
Back of Cab: Flush Mounted Flood Lamps – T270/370 ......................3-6
DETAIL VIEWS ...........................................................3-7
Crossmember Locations – T170 .......................................3-7
DETAIL VIEWS ...........................................................3-8
Crossmember Locations – T170 .......................................3-8
COMPONENTS ...........................................................3-9
Frame Rail Congurations - T170/270/370 ................................3-9
Battery Box – T270/370 .............................................3-10
Battery/Tool Box – T270/370 .........................................3-10
22-inch Fuel Tanks — T270/370 .......................................3-11
24.5-inch Fuel Tanks — T270/370 .....................................3-11
Rectangular Fuel Tank ..............................................3-12
Battery Box – T270/370 .............................................3-13
Battery/Access Step – T170 ..........................................3-13
Horizontal Exhaust/Mufer ...........................................3-14
Step/DPF Box Assembly RH Under Cab – T270/370. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Horizontal Mufer-Vertical Tailpipe on Cab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
RH Back of Cab Independent Mufer — T270/T370 .......................3-16
RIDE HEIGHTS ...................................................3-17
REAR SUSPENSION LAYOUTS .............................................3-19
KENWORTH AG210L SINGLE REAR AXLE ...................................3-19
KENWORTH AG400L TANDEM REAR AXLE ...................................3-20
REYCO 79KB SINGLE REAR AXLE ..........................................3-21
Optional Reyco 79KB Suspensions ....................................3-21
REYCO 102 TANDEM REAR AXLE ..........................................3-22
Optional Reyco 102 Suspension ......................................3-22
HENDRICKSON HAS SINGLE REAR AXLE ...................................3-23
Optional Hendrickson HAS Single Suspensions ..........................3-23
HENDRICKSON PRIMAAX SINGLE REAR AXLE ...............................3-24
Optional Hendrickson Promaax Single Suspensions .......................3-24
HENDRICKSON HAS TANDEM SUSPENSION .................................3-25
Optional Hendrickson HAS Tandem Suspensions .........................3-25
HENDRICKSON RT TANDEM SUSPENSION ..................................3-26
Optional Hendrickson RT Tandem Suspensions ..........................3-26
CHALMERS 854-40 TANDEM SUSPENSION ..................................3-27
Optional Chalmers Tandem Suspensions ...............................3-27
TIRE DATA ..............................................................3-28
FRAME AND CAB RELATED HEIGHTS .......................................3-28
12/11
I

GROUND CLEARANCES ..................................................3-28
PTO CLEARANCES ......................................................3-33
SECTION 4 — EXHAUST & AFTERTREATMENT
EXHAUST AND AFTER-TREATMENT INFORMATION ............................4-1
GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR DEF SYSTEM ...................................4-3
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS AND DIMENSIONS FOR DEF SYSTEM ............4-3
MEASUREMENT REFERENCE POINTS .......................................4-4
GENERAL EXHAUST INFORMATION .........................................4-9
EXHAUST INFORMATION .................................................4-18
SECTION 5 — FRAME LAYOUTS
FRAME LAYOUTS .........................................................5-1
COMMON OPTIONAL COMPONENTS ........................................5-2
FRAME LAYOUT INDEX ....................................................5-4
SECTION 6 — BODY MOUNTING
FRAME INFORMATION ....................................................6-1
CRITICAL CLEARANCES ...................................................6-1
Rear Wheels and Cab ...............................................6-1
Body Mounting Using Brackets ........................................6-2
Frame Sill .........................................................6-2
Brackets ..........................................................6-2
Mounting Holes ....................................................6-3
Frame Drilling ......................................................6-3
Hole Location Guidelines .............................................6-4
BODY MOUNTING USING U–BOLTS ..........................................6-4
Spacers ..........................................................6-4
Rear Body Mount ...................................................6-6
HYBRID CLEARANCES ....................................................6-6
Hybrid PEC .......................................................6-6
Hybrid Battery Box ..................................................6-7
Body Builder’s Manual
Contents
SECTION 7 — FRAME MODIFICATIONS
FRAME MODIFICATIONS ...................................................7-1
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
DRILLING RAILS ..........................................................7-1
Location and Hole Pattern ............................................7-1
MODIFYING FRAME LENGTH ...............................................7-2
Frame Insert .......................................................7-2
Changing Wheelbase ................................................7-3
Crossmembers .....................................................7-4
WELDING ...............................................................7-5
TORQUE REQUIREMENTS ..........................................7-7
SECTION 8 - ELECTRICAL
ELECTRICAL ............................................................8-1
ACCESSING GAUGES AND SWITCHES ......................................8-10
OPTIONAL SWITCHES, AIR VALVES AND GAUGES ............................8-20
ADDITIONAL SPARE CIRCUITS ............................................8-23
Additional Spare Circuits for Wiring ....................................8-23
OPTIONAL BODY BUILDER HARNESS .......................................8-24
Circuits Wired Through the Ignition ....................................8-26
Connecting Ignition Circuits ..........................................8-26
Circuits Wired to Battery .............................................8-26
BODY BUILDER POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER .............................8-29
INSTALLING A THIRD BATTERY (NOT AVAILABLE ON HYBRID) ..................8-30
II
12/11

Body Builder’s Manual
Contents
WIRING FOR A LIFTGATE .................................................8-31
Liftgate Power Source ..............................................8-31
Connecting the Liftgate Power ........................................8-32
270 AMP ALTERNATOR (RECOMMENDED HOOKUP) ...........................8-33
Engine Connections ................................................8-33
REMOTE PTO/THROTTLE HARNESS ........................................8-34
TRAILER CABLE CONNECTIONS ...........................................8-40
SECTION 9 - ROUTING
ROUTING ...............................................................9-1
ROUTING REQUIREMENTS ................................................9-2
Routing of Wires and Hoses near Exhaust System .........................9-4
APPENDIX A - VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION
VIN Location .......................................................A-1
Chassis Number Locations ...........................................A-1
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION LABELS ..........................................A-2
Tire/Rim and Weight Rating Data Label ..................................A-2
Incomplete Vehicle Certication Label ...................................A-2
Components and Weights Label .......................................A-2
Noise Emission Label ................................................A-3
Paint Identication Label .............................................A-3
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION .............................................A-3
Engine Identication .................................................A-3
Transmission Identication ............................................A-4
Front Axle Identication ..............................................A-4
Rear Axle Identication ..............................................A-4
III

Figures
FIGURES
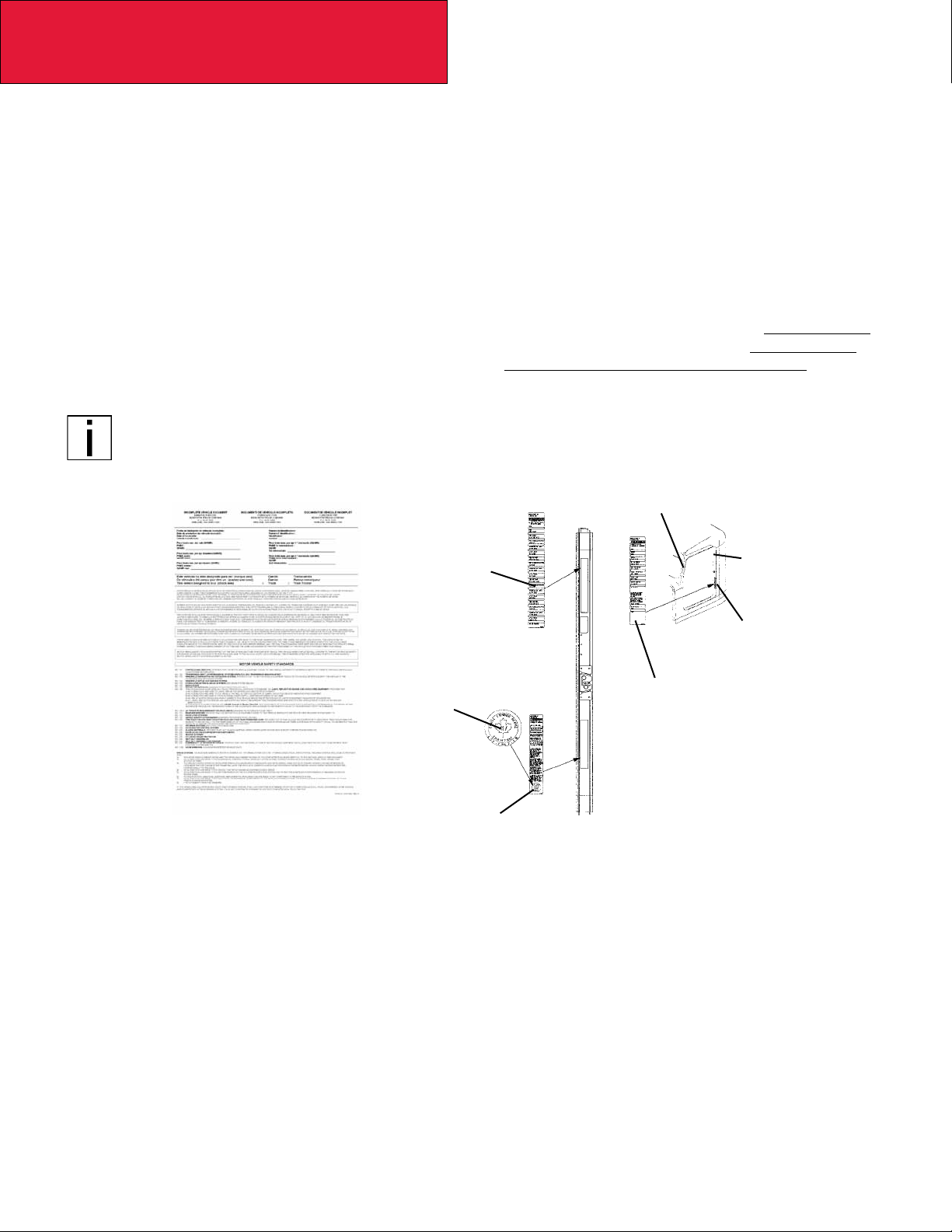
FIGURE 2-1. Incomplete Vehicle Certication Document ........................................2-2
FIGURE 2-2. Locations of Certication Labels - Driver’s Door and Frame ...........................2-2
FIGURE 2-3. West Coast Mirror OAT sensor, located in overmold on mirror harness. .................2-6
FIGURE 2-4. Aerodynamic Mirror OAT Sensor Location ........................................2-7
FIGURE 2-5. Instrument Cluster for T170/T270/T370 used with EPA2010 Emission compliant engines ....2-7
FIGURE 3-1. Prospector Turn Circle Analysis ................................................3-2
FIGURE 3-2. T170/T270/T370 Overall Height, and Length Dimensions ............................3-3
FIGURE 3-3. Top of Cab View, T270/T370, Roof Mounted Options ................................3-5
FIGURE 3-4. Side of Cab View, T270/370, Roof Mounted Options ................................3-5
FIGURE 3-5. Flush Mounted Flood Lamp Locations ...........................................3-6
FIGURE 3-6. T170 Crossmember Location ..................................................3-7
FIGURE 3-7. T170 Crossmember Location ..................................................3-8
FIGURE 3-8. Frame Rail Dimensions and Properties ..........................................3-8
FIGURE 3-9. T270/370 Battery Box Measurements] ..........................................3-10
FIGURE 3-10. T270/370 Battery/Tool Box Measurements ......................................3-10
FIGURE 3-11. T270/370 22” Fuel Tank Mounting Measurements ................................3-11
FIGURE 3-12. T270/370 24.5” Fuel Tank Mounting Measurements. With and without steps. ...........3-11
FIGURE 3-13. Rectangular Fuel Tank Measurements .........................................3-12
FIGURE 3-14. T270/370 Battery Box Measurements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
FIGURE 3-15. T170 Battery Box/Cab Access Step Measurements ...............................3-13
FIGURE 3-16. Horizontal Exhaust Mufer/DPF Measurements ..................................3-14
FIGURE 3-17. T270/T370 RH Step/DPF Box Assembly for Use with Vertical Tailpipe (left)
or Horizontal Tailpipe .................................................................3-15
FIGURE 3-18. T270/370 Vertical Tailpipe on Right Side of Cab ..................................3-15
FIGURE 3-19. T270/T370 with Vertical Mufer/DPF Behind RH Side of Cab .......................3-16
FIGURE 4-1. Measurement Location of DEF Supply Module (Pump) ..............................4-4
FIGURE 4-2. Measurement Location of DEF Dosing Module (Injector) .............................4-4
FIGURE 4-3. Orientation of Dosing Module ..................................................4-5
FIGURE 4-4. RH Under Cab Exhaust with Small or Medium Tanks. ...............................4-5
FIGURE 4-5. Horizontal Series Exhaust with Small or Medium Tanks. .............................4-6
FIGURE 4-6. Vertical Exhaust with Small or Medium Tanks. .....................................4-6
FIGURE 4-7. Horizontal Crossover Exhaust system with Small or Medium Tanks. ....................4-7
FIGURE 4-8. Routing DEF Lines and DEF Trap ...............................................4-8
FIGURE 4-9. Isometric View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single SOC Tailpipe ............4-10
FIGURE 4-10. Top View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single SOC Tailpipe ...............4-10
FIGURE 4-11. Right View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single SOC Tailpipe ..............4-11
FIGURE 4-12. Back View of Right Hand Under DPF and SCR with Single SOC Tailpipe ..............4-11
FIGURE 4-13. Isometric view of Horizontal DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe ...................4-12
FIGURE 4-14. Top view of Horizontal DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe .......................4-12
FIGURE 4-15. Right view of Horizontal DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe ......................4-13
FIGURE 4-16. Back view of Horizontal DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe ......................4-13
FIGURE 4-17. Isometric view of Horizontal (Series) DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe ............4-14
FIGURE 4-18. Top view of Horizontal (Series) DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe ................4-14
FIGURE 4-19. Right view of Horizontal (Series) DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe ...............4-15
FIGURE 4-20. Back view of Horizontal (Series) DPF and SCR with Horizontal Tailpipe ...............4-15
FIGURE 4-21. Isometric view of Vertical Independent DPF and SCR .............................4-16
FIGURE 4-22. Top view of Vertical Independent DPF and SCR ..................................4-16
FIGURE 4-23. Right view of Vertical Independent DPF and SCR ................................4-17
FIGURE 4-24. Back view of Vertical Independent DPF and SCR .................................4-17
FIGURE 5-1. DEF Tank Dimensions. .......................................................5-3
FIGURE 6-1. Minimum Clearance Between Top of Rear Tires and Body Structure Overhang ...........6-1
FIGURE 6-2. Minimum Back of Cab Clearance ...............................................6-1
FIGURE 6-3. Spacer Between Frame Sill and Body Rail - Rubber or Plastic .........................6-2
FIGURE 6-4. High Compression Spring .....................................................6-2
FIGURE 6-5. Rubber Spacer Between Brackets, Between the Mounting Bolt and Upper Bracket ........6-2
FIGURE 6-6. Crossmember-Gusset Hole Pattern Requirements ..................................6-3
IV
12/11

Tables
FIGURE 6-6. Hole Locations Guidelines for Frame Rail and Bracket ...............................6-3
FIGURE 6-7. Acceptable U-Bolt Mounting with Wood and Fabricated Spacers .......................6-4
FIGURE 6-8. Clearance Space for Air Lines and Cables ........................................6-5
FIGURE 6-9. Example of Fishplate Bracket at Rear End of Body, used with U-Bolts ..................6-6
FIGURE 6-10. Clearance zones around Hybrid Power Electronics Carrier (PEC) .....................6-6
FIGURE 6-11. Clearance zones around the Hybrid Battery Box located LH Under Cab ................6-7
FIGURE 7-1. Detail of Frame Extension and Joint Welding ......................................7-2
FIGURE 7-2. Frame Insert ...............................................................7-2
FIGURE 7-3. Comparison of Original, Shortened, and Extended Wheelbases .......................7-4
FIGURE 7-4. Crossmember Added when Distance Exceeds 60 inches (1524 mm) ...................7-4
FIGURE 7-5. Heat Treated Frame Rail Warning ...............................................7-5
FIGURE 8-1. J1939 Data link Wiring .......................................................8-1
FIGURE 8-2. Kenworth B-Cab Dash .......................................................8-2
FIGURE 8-3. Diesel Exhaust Fluid Gauge ...................................................8-2
FIGURE 8-4. Multiplexed Instrumentation Block Diagram. .......................................8-3
FIGURE 8-5. CECU Location.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
FIGURE 8-6. Main Instrument Panel .......................................................8-5
FIGURE 8-7. Instrumentation Harness Interface Diagram .......................................8-7
FIGURE 8-8. Firewall Air Junction Block (view from inside of cab) ................................8-8
FIGURE 8-9. Air Filter Restriction Sensor on Firewall Air Junction Block (view from inside of cab) ........8-8
FIGURE 8-10. Fuel Filter Restriction Pressure Gauge Sensor Location (typical) .....................8-9
FIGURE 8-11. Telltale Symbol Standard Cards ..............................................8-14
FIGURE 8-12. Blank Telltale Tray .........................................................8-16
FIGURE 8-13. Telltale Icons. (continued on page 8-18). .......................................8-17
FIGURE 8-14. Spare switches wired to Power ...............................................8-19
FIGURE 8-15. Optional Switches. .........................................................8-20
FIGURE 8-16. Switch and Wiring for Customer Installed Beacon Lamp in the Chassis Harness. .......8-21
FIGURE 8-17. Switch and Wiring for Customer Installed Beacon Lamp in the IP Harness. ............8-21
FIGURE 8-18. Switch and Wiring for Customer Installed Flood Lamp in the Chassis Harness.. . . . . . . . . . 8-22
FIGURE 8-19. Location of Standard Body Harness Connection .................................8-24
FIGURE 8-20. Body Junction Harness. . ....................................................8-25
FIGURE 8-21. ePTO Harness Location ....................................................8-28
FIGURE 8-22. Location of Body Builder Distribution Module on Hybrid ............................8-29
FIGURE 8-23. Detail of Body Builder Power Distribution Module .................................8-29
FIGURE 8-24. Adding a Third Battery .....................................................8-30
FIGURE 8-25. Adding a Third Battery .....................................................8-31
FIGURE 8-26. Liftgate Circuit Breaker Inside Battery Box ......................................8-32
FIGURE 8-27. P27-6180 Fuse Holder. .....................................................8-33
FIGURE 8-28. Battery Harness Jumper. ....................................................8-33
FIGURE 8-29. PACCAR PX-6 and PX-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-34
FIGURE 8-30. Wiring for Customer Installed Throttle Control at End of Frame. . .....................8-35
FIGURE 8-31. Cab Load Center (mPDC) ...................................................8-37
FIGURE 8-32. SAE J560 Trailer Connector .................................................8-40
FIGURE 8-33. ISO 3731 Trailer Connector ..................................................8-40
FIGURE 8-34. Junction Box .............................................................8-41
FIGURE 9-1. Clamp and Buttery Clamp ....................................................9-1
FIGURE 9-2. Buttery Tie ................................................................9-1
FIGURE 9-3. Tie Strap ..................................................................9-1
FIGURE 9-4. Heavy Duty (HD) Mount. ......................................................9-2
FIGURE 9-5. Denition of measurements. ...................................................9-4
FIGURE A-1. Vehicle Identication Number (VIN). .............................................A-1
FIGURE A-2. Drivers Door and Door Frame Labels ............................................A-2
FIGURE A-4. Front Axle Identication ......................................................A-4
FIGURE A-5. Rear Axle Identication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-4
V
V

Section 1
Introduction
SCOPE
This manual was created to provide body builders with appropriate information and guidelines useful in the body planning
and installation process. This information will be helpful when installing bodies or other associated equipment.
This manual contains appropriate dimensional information, guidelines for mounting bodies, guidelines for modifying
frames, electrical wiring information, and other information useful in the body installation process. This manual is specic
to chassis with 2010 engines.
The intended primary users of this manual are body builders who install bodies and associated equipment on Kenworth
T170/T270/T370 Medium Duty vehicles. Dealers who sell and service the vehicle will also nd this information useful.
This Body Builders’ Manual can be very useful when specifying a vehicle, particularly when the body builder is involved in
the vehicle denition and ordering process. Early in the process, professional body builders can often contribute valuable
information that reduces the ultimate cost of the body installation.
In the interest of continuing product development, Kenworth reserves the right to change specications or products at any
time without prior notice. It is the responsibility of the user to ensure that he is working with the latest update. The most
current update is available through your local Kenworth dealer.
If you require additional information or reference materials, please contact your local Kenworth dealer.
1-1
12/11

Section 1
Introduction
Page Intentionally Left Blank.
12/11

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
SAFETY SIGNALS
There are a number of alerting messages in this book. Please read and follow them. They are there for your protection
and information. These alerting messages can help you avoid injury to yourself or others and help prevent costly
damage to the vehicle.
Key symbols and “signal words” are used to indicate what kind of message is going to follow. Pay special attention to
comments prefaced by “WARNING”, “CAUTION”, and “NOTE.” Please do not ignore any of these alerts.
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes
When you see this word and symbol, the message that follows is especially vital. It
signals a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death
or serious injury. This message will tell you what the hazard is, what can happen if
you do not heed the warning, and how to avoid it.
WARNING
CAUTION
NOTE
Example:
WARNING! Be sure to use a circuit breaker designed to meet liftgate amperage
requirements. An incorrectly specied circuit breaker could result in an electrical
overload or re situation. Follow the liftgate installation instructions and use a circuit
breaker with the recommended capacity.
Signals a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor
or moderate injury or damage to the vehicle.
Example:
CAUTION: Never use a torch to make a hole in the rail. Use the appropriate drill bit.
Provides general information: for example, the note could warn you about how to
avoid damaging your vehicle or how to drive the vehicle more efciently.
Example:
Note: Be sure to provide maintenance access to the battery box and fuel tank ll
neck.
Signals the location of a high voltage electrical components
Example:
HAZARDOUS VOLTAGE: To reduce the risk of possible serious injury (Shock, Burn or
Death): Components marked with High Voltage should be avoided. Service must be
performed by qualied personnel only.
Please take the time to read these messages when you see them, and remember:
WARNING!
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION:
Signals a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor injury or
damage to the vehicle.
NOTE:
Useful information that is related to the topic being discussed.
2-1
12/11
Section 2
Safety & Compliance
FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETY
STANDARDS COMPLIANCE
As an Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM), Kenworth Truck Co. ensures that our products comply with all applicable
U.S. or Canadian Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. However, the fact that this vehicle has no fth wheel and that a
Body Builder (Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer) will be doing additional modications means that the vehicle was
incomplete when it left the build plant. See next section and Appendix A for additional information.
Incomplete Vehicle Certication
An Incomplete Vehicle Document is shipped with the vehicle, certifying that the vehicle is not complete. See Figure 2–1.
In addition, afxed to the driver’s side door frame or edge is an Incomplete Vehicle Certication label. See Figure 2–2. For
further information on Vehicle Certication and Identication, see APPENDIX A “VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION.”
NOTE
These documents list the U.S. or Canadian Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard regulations that the
vehicle complied with when it left the build plant. You should be aware that if you add, modify or alter any
of the components or systems covered by these regulations, it is your responsibility as the Intermediate or
Final Stage Manufacturer to ensure that the complete vehicle is in compliance with the particular regulations upon completion of the modications.
U.S. EPA Noise Label (U.S. registered vehicles only)
Final Stage Manufacturer
Label to be Installed by
Final Stage Manufacturer
Chassis Serial
Number
FIGURE 2-1. Incomplete Vehicle
Certication Document
Tire, Rim and
Weight Rating
Data label
Safety Mark (Canadian
Registry Only)
Incomplete Vehicle
Certication Label
Major Components and
Weights Label
FIGURE 2-2. Locations of Certication
Labels - Driver’s Door and Frame
As the Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer, you should retain the Incomplete Vehicle Document for your records. In
addition, you should record and retain the manufacturer and serial number of the tires on the vehicle. Upon completion
of the vehicle (installation of the body and any other modications), you should afx your certication label to the vehicle
as required by Federal law. This tag identies you as the “Intermediate or Final Stage Manufacturer” and certies that the
vehicle complies with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. (See Figure 2–2.) Be advised that regulations affecting the
intermediate and nal stage manufacturer may change without notice. Ensure you are referencing the most updated copy
of the regulation during the certication and documentation processes.
In part, if the nal stage manufacturer can complete and certify the vehicle within the instruction in the incomplete vehicle
document (IVD) the certication label would need a statement that reads, “This vehicle has been completed in accordance
with the prior manufacturers‚ IVD where applicable. This vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards [and Bumper and Theft Prevention Standards if applicable] in effect in (month, year).”
However, if the vehicle can not be completed and certied with in the guidance provided in the IVD, the nal stage manufacturer must ensure the vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS). The nal
stage manufactures certication label would need a statement that reads, “This vehicle conforms to all applicable Federal
Motor Vehicle Safety Standards [and Bumper and Theft Prevention Standards if applicable] in effect in (month, year).”
12/11
2-2

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
These statements are just part of the changes to the new certication regulation. Please refer to the Feb 15, 2005
nal rule for all of the details related to this regulation. You can contact NTEA Technical Services Department at
1-800-441-NTEA for a copy of the nal rule (DocID 101760).
For Canadian nal stage manufacturers see:
http://www.gazette.gc.ca/archives/p2/2002/2002-02-13/html/sor-dors55-eng.html; and
http://www.tc.gc.ca/acts-regulations/regulations/crc-c1038/menu.htm for the regulations.
Or contact:
Transport Canada
Tower C, Place de Ville, 330 Sparks Street
Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0N5
(613) 990-2309
TTY: 1-888-675-6863
Noise and Emissions Requirements
NOTE
It is possible to relocate the DEF tank, however the relocation requirements need to be followed. Any variance from the
relocation requirements may cause the emissions control components/systems to operate improperly potentially resulting
in engine de-rate. See page 4-3 for relocation requirements.
NOTE
2010 Automotive engines have been tested and EPA/CARB certied with a complex integrated system. This system is comprised of several emissions control devices including,
but not limited to, a Diesel Particulate lter (DPF) and a Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR)
system.
The body builder must not modify or relocate any devices included in the emissions
system. Doing so may result in the voiding of all warranties and the occurrence of an
emissions noncompliance event that may be considered tampering and punishable by the
assessment of penalties by the EPA and ARB as well as the need for remedial measures.
Modication of the emissions system can only be done with the preapproval of Cummins
and/or Kenworth. Body builders’ rst point of contact concerning emissions systems
modications will be Kenworth.
Some 2010 engine emissions certied vehicles will be equipped with an On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) system. The OBD system is designed to detect malfunctions of any engine or vehicle
component that may increase exhaust emissions or interfere with the proper performance of the
OBD system itself.
The OBD system consists of computer program on one or more of the vehicle’s Electronic Control
Units (ECUs). This program uses information from the control system and from additional sensors
to detect malfunctions. When a malfunction is detected, information is stored in the ECU(s) for
diagnostic purposes. A Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) is illuminated in the dash to alert the
driver of the need for service of an emission-related component or system.
To ensure compliance to emissions regulations, the nal conguration of certain features of the completed vehicle
must meet specic requirements. This section describes requirements relevant for only the most common or critical
modications done by body builders. For a complete description of acceptable modications, see the application
guidance available from the manufacturer of the engine installed in the chassis.
2-3
12/11

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
Fuel System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
The overall system restriction may not exceed the restriction limitations set forth by the engine manufacturer for both
supply and return.
• Ensure that fuel lines are not pinched or can potentially be damaged when installed between body and frame
• Fuel lines must be routed and secured without dips or sags
• There must be easy access to lter(s) and ll cap
• The tank vent may not obstructed
• Added accessories (heaters, generators) cannot introduce air into system
• Fuel tank must be located so that the full level is not above cylinder head
• “Ultra Low Sulfur Fuel Only” labels must be present on the dash and fuel ll
• Modication of the pressure side secondary lter and plumbing is not allowed without engine manufacturer
approval
• Body installation of fuel tank or routing of lines must not cause signicant increase in fuel temperature
• Fuel hoses shall meet or exceed OEM supplied hose material construction specications
Compressed Air System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• Air system modication must meet applicable FMVSS regulations
• Compressed Air tank may not be modied (exception – addition or removal of ttings or relocation of the tank)
• Added devices or bodywork may not interfere with or rub air lines
• Air supply to the engine doser may not be restricted or disconnected
• Air lines should be routed, protected from heat, and properly secured to prevent damage from other
components
• Care should be taken so that air lines do not rub against other components
• Care should be taken to protect the air system from heat sources.
Exhaust and Exhaust After-treatment System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
12/11
• The following after-treatment and exhaust system components may not be modied:
• DPF assembly
• SCR Catalyst assembly
• Exhaust pipes between the engine and after-treatment devices (DPF, SCR Catalyst) and between
after-treatment devices
• NOx Sensor
2-4

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
• The following modications may only be done within the guidelines of the “DEF System Relocation Guide.”
• Modications to Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) throttle, suction, or pressure lines
• Modication or relocation of the DEF tank
• Modication of coolant lines to and from the DEF tank
• All DEF and coolant lines should be routed, protected, and properly secured to prevent damage during vehicle
operation or other components
• If relocation of the DCU is necessary, use existing frame brackets and mount inside of frame anges where
necessary. Do not extend the harnesses
• The DPF, the SCR catalyst, or their mounting may not be modied
• The NO
• Exhaust pipes used for tailpipes/stacks must be properly sized, and must prevent water from entering the
exhaust system
• Ensure adequate clearance between the exhaust and body panels, hoses, and wire harnesses
• The body in the vicinity of the DPF must be able to withstand temperatures up to 400°C (750°F)
• Do not add thermal insulation to the external surface of the DPF
• The SCR water drain hole may not be blocked
• Allow adequate clearance (25mm (1 inch)) for servicing the DPF sensors, wiring, and clamped joints
• Drainage may not come in contact with the DPF, SCR catalyst, sensors or wiring
• Allow sufcient clearance for removing sensors from DPF. Thermistors require four inches. Other sensors
require one inch
• Wiring should be routed, protected from heat, and properly secured to prevent damage from
other components
• The exhaust system from an auxiliary power unit (APU) must not be connected to any part of the vehicle
after-treatment system or vehicle tail pipe.
sensor may not been relocated or altered in any way
x
Cooling System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• Modications to the design or locations of ll or vent lines, heater or defroster core, and surge tank are not
recommended
• With the exception of post-thermostat installation, additional accessories plumbed into the engine cooling
system are not permitted, and may void vehicle warranty
• Coolant level sensor tampering will void warranty
• When installing auxiliary equipment in front of the vehicle, or additional heat exchangers, ensure that
adequate air ow is available to the vehicle cooling system. Refer to engine manufacturer application guide-
lines for further detail
• When installing FEPTO drivelines, the lower radiator anti-recirculation seal must be retained with FEPTO
driveline clearance modication only
• Changes made to cooling fan circuit and controls are not allowed, with the exception of AC minimum fan on
time parameter
• See owner’s manual for appropriate winter front usage
2-5
12/11

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
Electrical System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• Electrical harnesses providing battery power and electronic control signals to engine and emissions control/
vehicle OBD components including datalinks may not be spliced. These emissions control/vehicle OBD
components include the following:
• throttle pedal
• vehicle speed sensor
• after-treatment wiring
• If the alternator or battery is substituted, it must meet the requirements of the engine manufacture’s guidelines. This includes alternator ground voltage drop and alternator ground cable effectiveness. See the engine
manufacture’s guidelines for recommended test procedure. Additionally the maximum voltage differential and
the peak-peak voltage differential between the engine ECM block ground stud and battery negative terminal
may not exceed 500 mV under any combination of loads or operating conditions.
• Installation of aftermarket transfer-cases must address the vehicle speed sensor position. The standard position of the speed sensor is at the transmission tail shaft. When a transfer-case is added it is best to relocate
the sensor to the axle side output shaft of the transfer-case. This is typically accomplished by adding a tone
wheel into the driveline yoke assembly.
• Wiring extensions for the after-treatment wiring are available for relocating the DEF tank from your dealer via
Paccar Parts. For relocation of DEF tank, refer to the after-treatment section of this manual.
• The emission system requires an accurate Outside Air Temperature (OAT) reading in order to properly run
its control algorithms. The OAT sensor is located in the driver’s side mirror assembly on Kenworth trucks and
is shown in the gures below. If the body builder needs to modify the mirror assembly in any way, it is important the OAT sensor stay positioned on the mirror assembly. Running the vehicle without the OAT sensor
connected will cause the MIL lamp to illuminate. If needed, a replacement sensor can be ordered from your
Kenworth dealer.
FIGURE 2-3: West Coast Mirror OAT sensor, located in overmold on mirror harness.
12/11
2-6
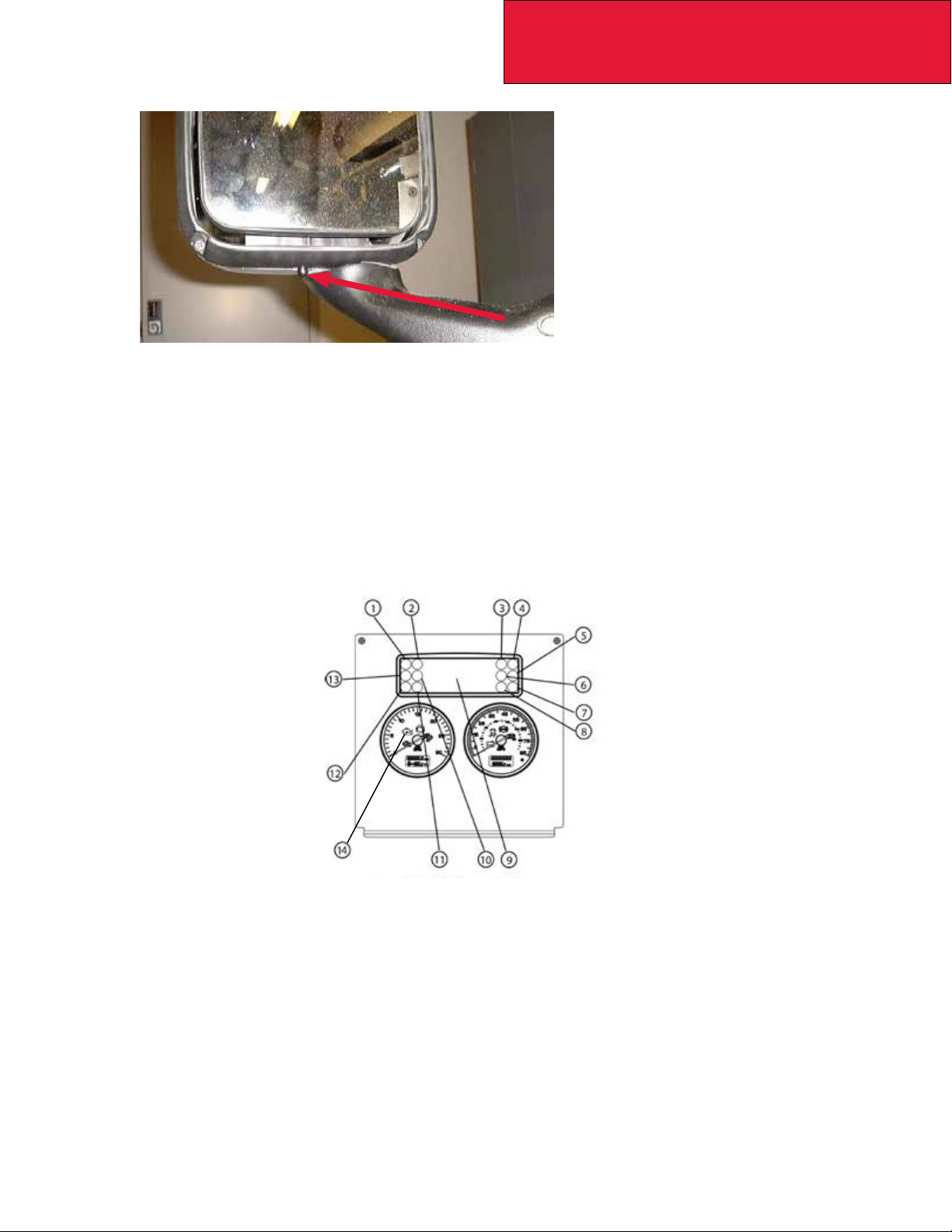
FIGURE 2-4: Aerodynamic Mirror OAT Sensor Location
• Coolant Sensor considerations are given in the Cooling section above
• The OBD/Diagnostic connector port is located below the dash to the left of the steering wheel. This connector
or its location may not be changed.
Section 2
Safety & Compliance
• Vehicles using EPA 2010 compliant engines must be equipped with a Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) lamp.
This lamp is required to be an engine outline symbol as dened by ISO (International Standards Organization). The gure below shows the instrument cluster and MIL lamp position. Note this lamp location is xed
with respect to the controls and its location may not be changed if you are updating the warning lamp cards.
The MIL lamp will not be used with Medium Duty vehicles until 2013.
1 PTO 5 High Exhaust System
Temperature (HEST)
2 Wait to Start 6 Fasten Seat Belts 11 High Beam
3 Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL)
4 Engine Brake 8 Park Brake 13 Check Transmission
7 RH Turn Signal 12 LH Turn Signal
9 Multi-Function Display 14 Check Engine Light
10 Brake Fail
FIGURE 2-5: Instrument Cluster for T170/T270/T370 used with EPA2010 Emission compliant
engines. The Check Engine lamp is symbol 21 and the MIL is symbol 8.
• In addition to the sensors and lamps above, the emission system also depends on signals from the exhaust
DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter), SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction), and NOx sensor. Wiring between these
devices, the Dosing Control Unit (DCU) and engine ECM should not be tampered with or altered in any way.
2-7
12/11

Section 2
Safety & Compliance
Air Intake System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• The air intake screen may not be blocked, either fully or partially
• Modication to the air intake system may not restrict airow. For example, pipe diameter may not be reduced
• All sensors must be retained in existing locations
• To retain system seal, proper clamp torque must be used. Refer to service manual for proper clamp torque
Charge Air Cooler System
The following are highlights of some of the more common or critical aspects of this system.
• The Charge Air Cooler may not be modied
• The installation of engine overspeed shutdown devices must not introduce restriction in the intake system
• All plumbing associated with the charge air cooler may not be modied
12/11
2-8
Section 3
Dimensions
DIMENSIONS
This section is designed to provide enough information to successfully layout chassis in the body planning process. Only
typical truck layouts and congurations are shown. Optional equipment may not be depicted. Please contact your local
Kenworth dealer if more information is desired.
ABBREVIATIONS AND DEFINITIONS
Throughout this section, and in other sections as well, abbreviations and specic terminology are used to describe certain
characteristics on your vehicle. The charts below list the abbreviated terms used and provide denitions for terminology
used.
TABLE 3-1. Abbreviations Used
AF After Frame – Frame rail overhang behind rear axle or measured from the centerline of tandem
BOC Back of Cab
BOF Bottom of Rail
CA Back of cab to centerline of rear axle or centerline of tandems on tandem suspension
FS Front suspension height from centerline of axle up to the bottom of the frame rail
OAL Overall Vehicle Length
SOC Side of Cab
RS Rear suspension height from centerline of axle up to the bottom of the frame rail
WB Centerline of front axle to centerline of rear axle or centerline of tandems on tandem suspension
TABLE 3-2. Denitions
GAWR The maximum allowable weight each axle assembly is designed to carry, as measured at the tires, there-
fore including the weight of the axle assembly itself. GAWR is established by considering the rating of each
of its components (tires, wheels, springs, axle and steering system), and rating the axle on its weakest link.
The GAWR assumes that the load is equal on each side.
LADEN This is the weight condition of the truck with the front and rear axles loaded to their Gross Axle Weight
Rating, GAWR.
UNLADEN This is the weight condition of the truck delivered from the PACCAR factory. This is without the following:
body, driver, and tools. It does include uids, but no fuel.
3-1
12/11
Section 3
Dimensions
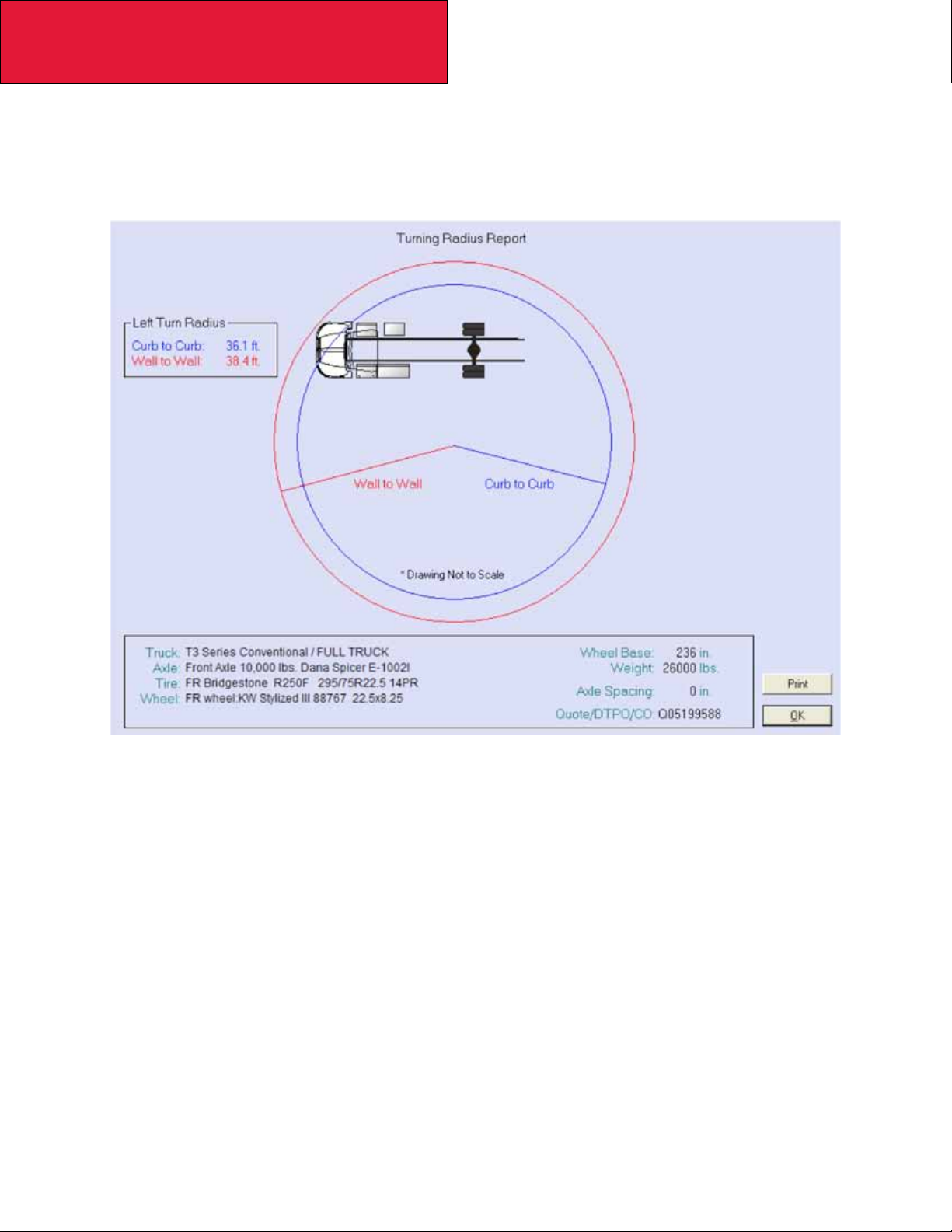
Prospector Turn Circle Analysis:
Please see Figure 3-1 as an example of Kenworth’s turn circle calculation made in Prospector for your specic chassis.
Your local Kenworth dealer can provide this information to you.
FIGURE 3-1. Prospector Turn Circle Analysis
Please consult your local Kenworth Dealer for this information, as it is chassis specic.
12/11
3-2
Section 3
Dimensions
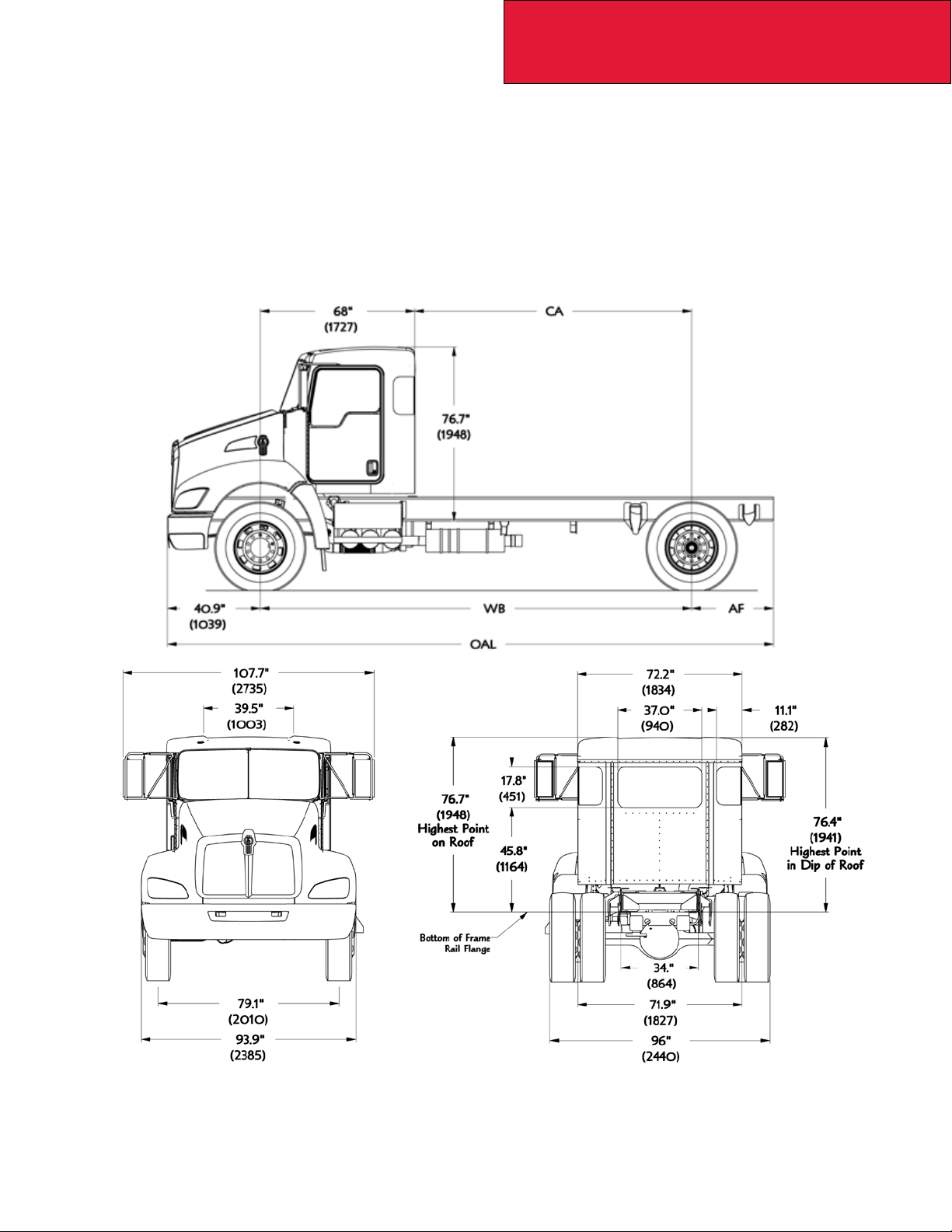
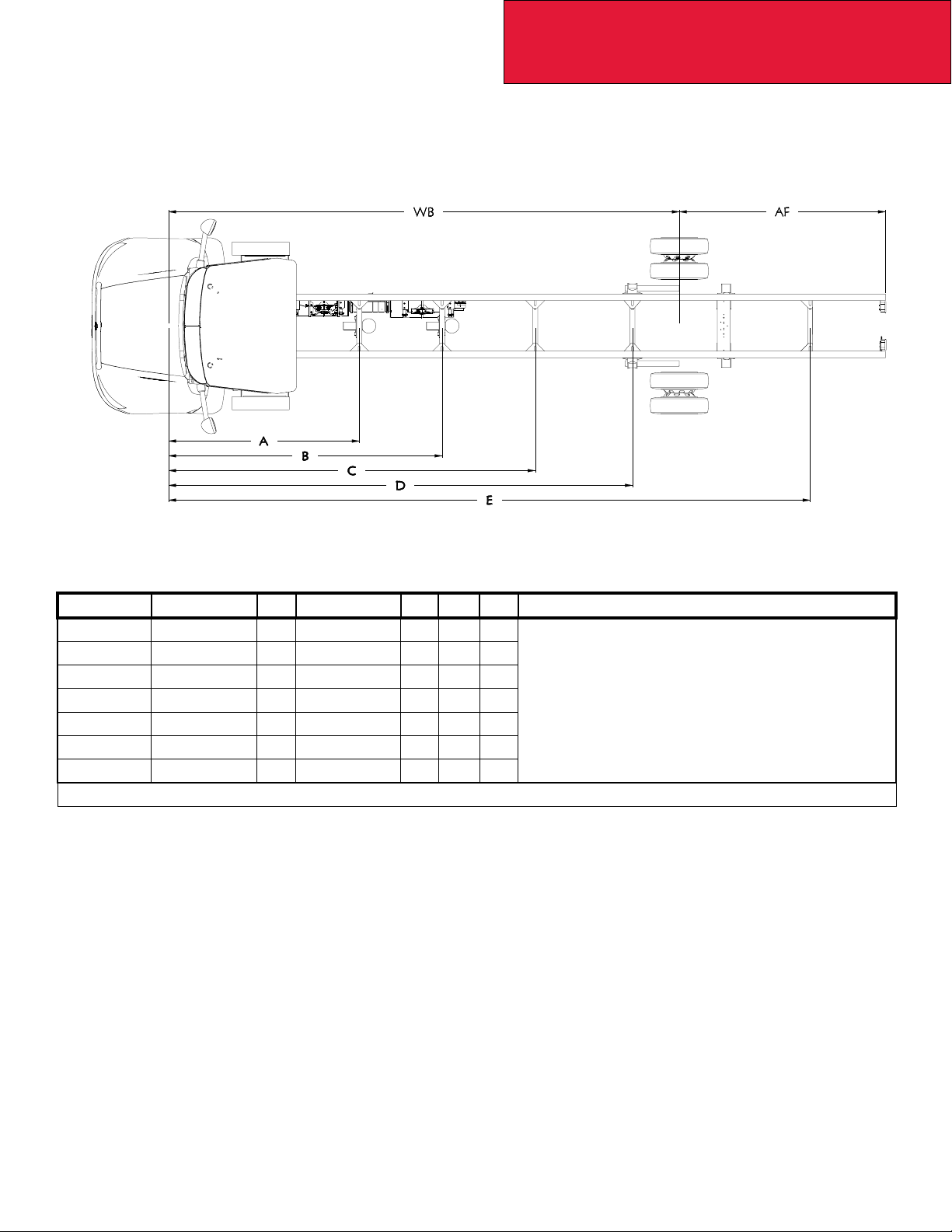
OVERALL DIMENSIONS
This section includes drawings and charts of the following medium duty models: T170, T270 and T370.
On the pages that follow, detail drawings show particular views of each vehicle with dimensions being in inches and (mm).
They illustrate important measurements critical to designing bodies of all types. See the “Table of Contents” at the beginning of the manual to locate the drawing that you need.
Kenworth also offers .dxf les and frame layouts of ordered chassis four weeks prior to build. Please speak to your sales
person to request this feature when specifying your chassis.
*
*
* Dimensions are typical. Measurements will vary with axle, brake
drum, tires and wheel selections
FIGURE 3-2. T170/T270/T370 Overall Height, and Length Dimensions [inches (mm)]
3-3
*
*
12/11
Section 3
Dimensions
TABLE 3-3. Hydraulic Brake Vehicles. T170 Single Rear Axle: Overall Fore-Aft Dimensions [inches (mm)]
WB OAL AF CA
153 (3886) 235.9 (5992) 55 (1397) 72 (1829)
162 (4115) 240.9 (6119) 55 (1397) 77 (1956)
176 (4470) 280.9 (7135) 64 (1626) 108 (2743)
188 (4775) 304.9 (7745) 76 (1930) 120 (3048)
206 (5232) 328.9 (8354) 82 (2083) 138 (3505)
218 (5537) 352.9 (8964) 94 (2388) 150 (3810)
236 (5994) 376.9 (9573) 100(2540) 168 (4267)
245 (6223) 384.9 (9777) 99 (2515) 177 (4496)
TABLE 3-4. Hydraulic Brake Vehicles. T270/370 with Single Rear Axle: Overall Fore-Aft Dimensions [inches
(mm)]
WB* OAL AF CA
153 (3886) 235.9 (5992) 55 (1397) 72 (1829)
162 (4115) 240.9 (6119) 55 (1397) 77 (1956)
176 (4470) 280.9 (7135) 64 (1626) 108 (2743)
188 (4775) 304.9 (7745) 76 (1930) 120 (3048)
206 (5232) 328.9 (8354) 82 (2083) 138 (3505)
218 (5537) 352.9 (8964) 94 (2388) 150 (3810)
236 (5994) 376.9 (9573) 100 (2540) 168 (4267)
245 (6223) 384.9 (9777) 99 (2515) 177 (4496)
254 (6452) 424.9 (10793) 130 (3302) 186 (4724)
260 (6604) 448.9 (11402) 148 (3759) 192 (4877)
272 (6909) 462.9 (11758) 150 (3810) 204 (5182)
* Air Brake Vehicles. T270/T370 wheelbases for Single Rear Axle begin at 140 inches. Tandem Rear axles begin at 175
inches. Wheelbase on Air Brake vehicles available in 1-inch increments.
12/11
3-4
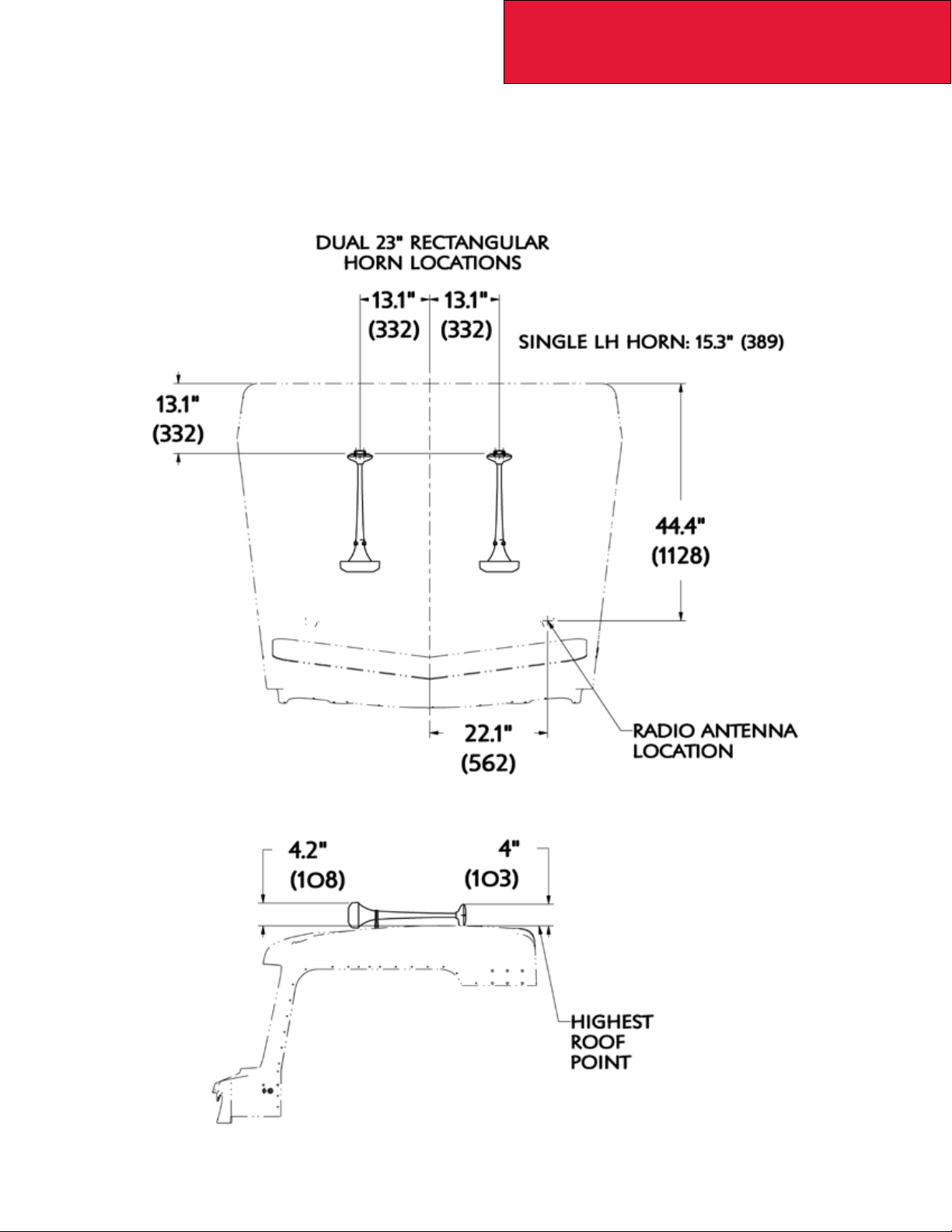
DETAIL VIEWS
Top of Cab: Roof Mounted Options – T270/370
Section 3
Dimensions
FIGURE 3-3. Top of Cab View, T270/T370, Roof Mounted Options
FIGURE 3-4. Side of Cab View, T270/370, Roof Mounted Options
3-5
12/11
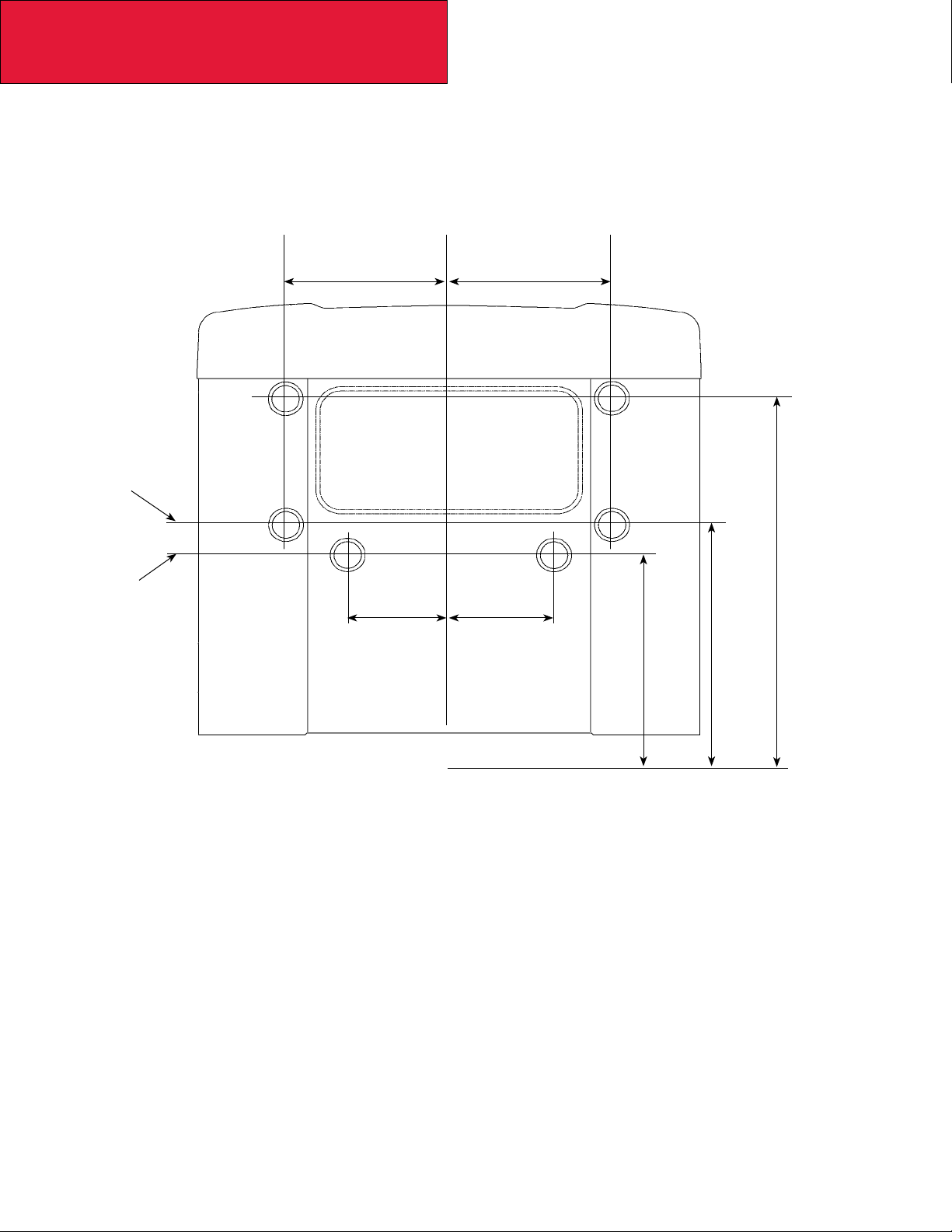
Section 3
Dimensions
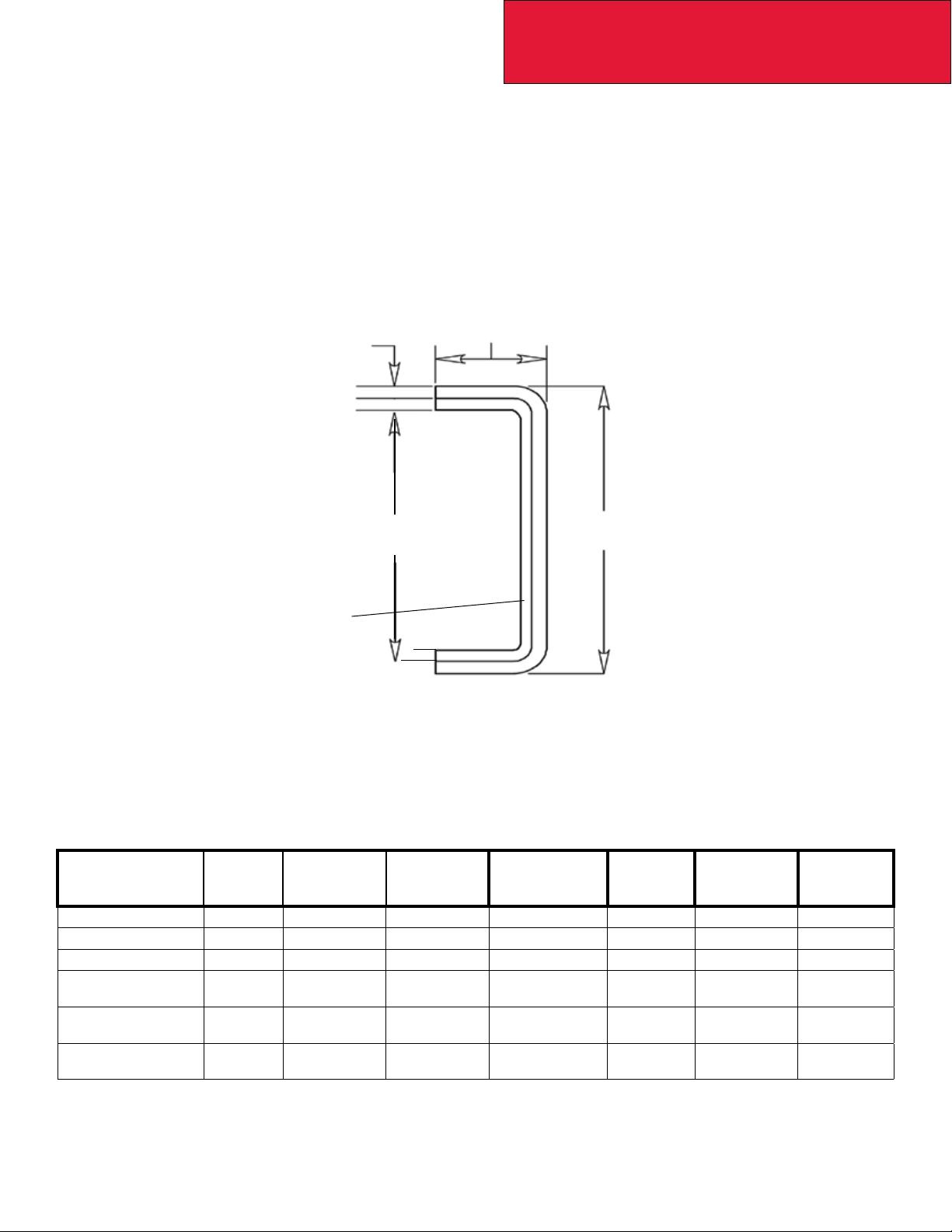
DETAIL VIEWS
Back of Cab: Flush Mounted Flood Lamps – T270/370
Mid Mount Flood
Lamp Elevations
Mid Mount Flood
Lamp Location for
Vertical Tailpipe
Back of Cab
25 (635)
14.4 (365) 14.4 (365)
C/L
25 (635)
High Mount Flood
Lamp Elevation
62.4
(1585)
43.7
(1110)
37.2
(945)
FIGURE 3-5. Flush Mounted Flood Lamp Locations [inches (mm)]
12/11
3-6
BOF
DETAIL VIEWS
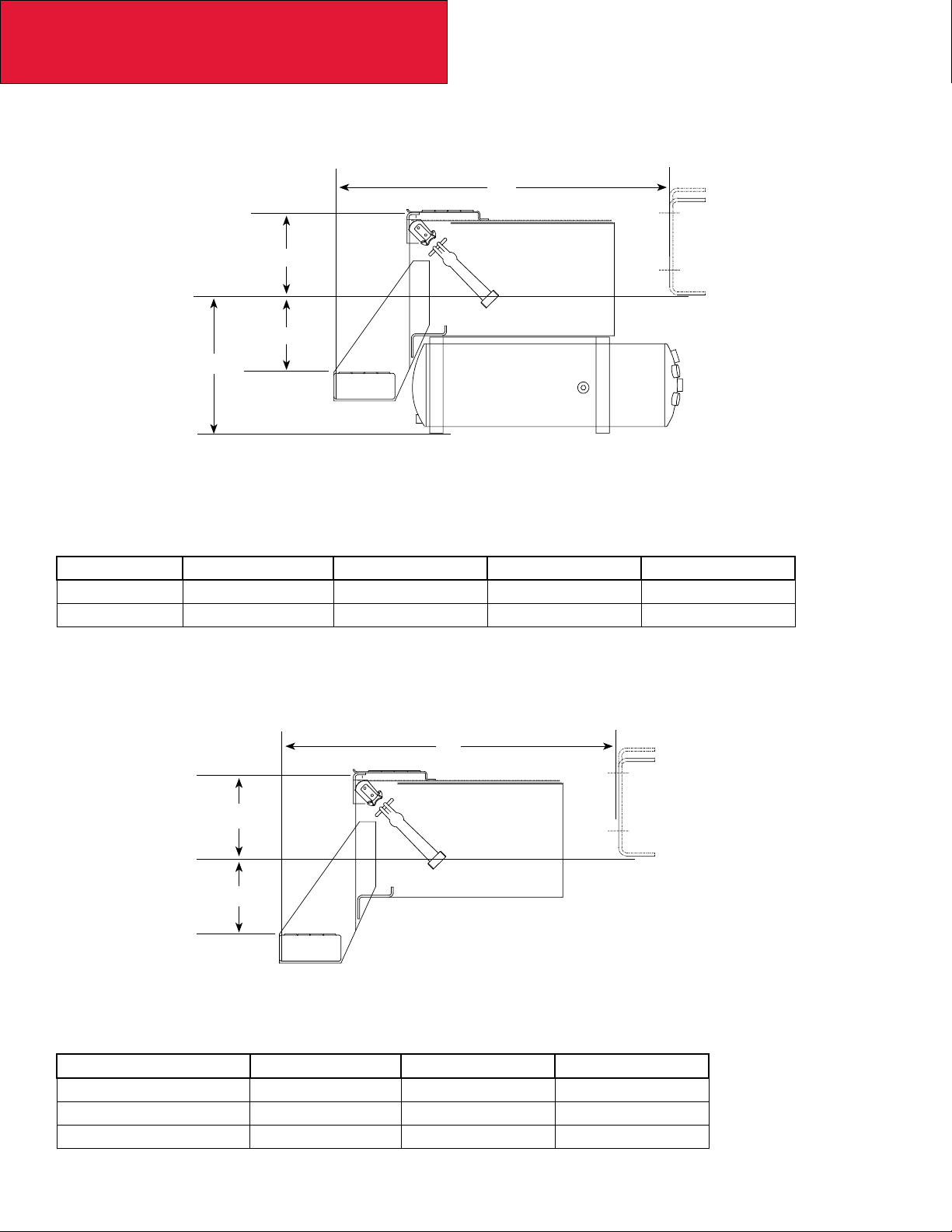
Crossmember Locations – T170
Section 3
Dimensions
FIGURE 3-6. T170 Crossmember Location
TABLE 3-5
WB A CB B CB C D E
206 101.8 (2585) Y 121.1(3075) Y 1.) For without a square end of frame cross-
218 101.8 (2585) Y 121.1(3075) Y
236 101.8 (2585) Y 121.1(3075) Y
245 101.8 (2585) Y 121.1(3075) Y
254 101.8 (2585) Y 162 (4125) Y
260 101.8 (2585) Y 162 (4125) Y
272 101.8 (2585) Y 162 (4125) Y
Y SPL100 Driveline centerbearing (CB) is mounted on this crossmember.
T170 Cross member. Location: measured from front axle centerlines [inches (mm)]
member with an AF range of 80 (2032)
to 125(3175) a crossmember is installed at:
E=WB+64.4”(1636mm)
2.) For AF range of 126 (3200) to 173(4394) a
2nd crossmember is installed at:
E=WB+112.4”(2855 mm)
3-7
12/11

Section 3
Dimensions
DETAIL VIEWS
Crossmember Locations – T170
FIGURE 3-7. T170 Crossmember Location
TABLE 3-6
WB A CB C D E
153 101.8 (2585) Y 1.) For without a square end of frame crossmember with an AF
162 101.8 (2585) Y
176 101.8 (2585) Y
188 101.8 (2585) Y
Y SPL100 Driveline center bearing (CB) is mounted on this cross member
T170 Cross member. Location: measured from front axle centerlines [inches (mm)]
range of 80 (2032)to 125(3175) a crossmember is installed at:
E=WB+64.4”(1636mm)
2.) For AF range of 126 (3200) to 173(4394) a 2nd crossmember is
installed at: E=WB+112.4”(2855 mm)
12/11
3-8
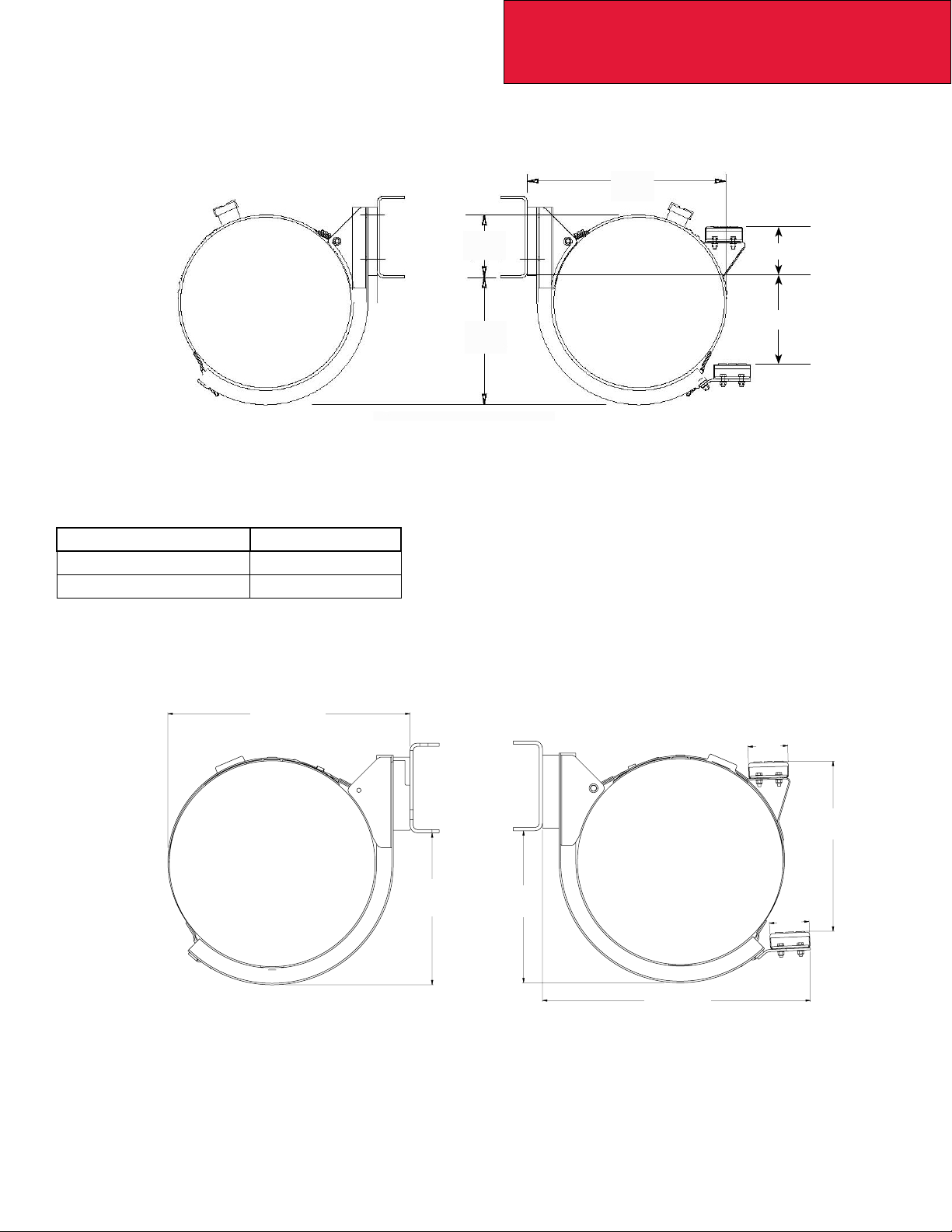
Section 3
Dimensions
COMPONENTS
This section includes detail drawings and charts showing particular vehicle components with dimensions in inches and
(millimeters). They illustrate important measurements critical to designing bodies of all types. See the “Table of Contents”
at the beginning of the manual to locate the drawing that you need.
Frame Rail Congurations - T170/270/370
Note: Bottom of frame rail is a reference point that you can use to determine estimated heights of components and ground
clearances.
W
T
Rail Heat
Treated
H
Optional
Insert, Heat
Treated
Shown
FIGURE 3-8. Frame Rail Dimensions and Properties [inches (mm)]
TABLE 3-7. Frame Rail Properties
Frame Rail or Insert
(1)(2)
9-7/8 Frame Rail T170/T270 9.88 1,251,767 2.10 9.88 (251) 3.46 (87.8) 0.25 (6.4)
10-5/8 Frame Rail T270/T370 14.8 1,776,000 2.90 10.63 (270) 3.46 (87.8) 0.31 (7.9)
10-3/4 Frame Rail T270/T370 17.8 2,132,000 3.50 10.75 (273) 3.46 (87.8) 0.38 (9.5)
9-7/8 Insert ONLY for
10-5/8 Frame Rail (2)(3)
10-5/8 Frame Rail with
9-7/8 Insert
10-3/4 Frame Rail with
9-7/8 Insert
(1) Yield Strength: 120,000 PSI
(2) Frame rails and inserts are heat treated.
(3) Full inserts start ahead of the steering gear and end at the end of frame.
(4) Partial inserts start 25 inches behind the center line of the front axle and end at the end of the frame.
Model
T270/T370 9.57 1,149,000 2.00 9.88 (251) 2.88 (73.0) 0.25 (6.4)
T270/T370 23.4 2,925,000 4.96 10.63 (270) 3.46 (87.8) 0.56 (14.3)
T270/T370 27.4 3,281,000 5.50 10.75 (273) 3.46 (87.8) 0.63 (15.9)
Section
Modulus per
Rail, cu.in.
RBM per Rail
lbs-Inch
Weight per Inch
per Pair, lbs
Height H,
inch (mm)
Flange Width
W, inch (mm)
Thickness T,
inch (mm)
3-9
12/11
Section 3
Dimensions
Battery Box – T270/370
Parallel Battery Box LH Under Cab for air braked truck or hydraulic braked truck with an accessory air system.
A
B
BOF
C
D
Rear View
FIGURE 3-9. T270/370 Battery Box Measurements [inches (mm)]
TABLE 3-8. T270/370 Battery Box Measurements [inches (mm)]
Type A, inch (mm) B, inch (mm) C, inch (mm) D, inch (mm)
Hybrid 33.4 (848) 6.7 (170) 9.5 (241) 15.8 (401)
Non-Hybrid 33.4 (848) 8.5 (215) 9.3 (236) 13.4 (354)
Battery/Tool Box – T270/370
Parallel Battery Box LH Under Cab for Hydraulic braked Truck without an Accessory Air System or Tool Box Under Cab.
C
A
B
Rear View
2.8 (70)
BOF
FIGURE 3-10. T270/370 Battery/Tool Box Measurements [inches (mm)]
TABLE 3-9. T270/370 Battery Box/Toolbox Dimensions [inches (mm)]
Type A, inch (mm) B, inch (mm) C, inch (mm)
Non-Hybrid Battery Box 8.5 (215) 9.4 (239) 33.4 (848)
Hybrid Battery Box 8.5 (215) 9.5 (241.6) 33.4 (848)
Toolbox 9.3 (236) 9.2 (233) 33 (848)
12/11
3-10
22-inch Fuel Tanks — T270/370
Round Fuel Tank Mounting
Section 3
Dimensions
25.9
(658)
11.0
(279)
BOF
A
REAR VIEW REAR VIEW
LEFT SIDE BEHIND CAB RIGHT SIDE UNDER CAB
FIGURE 3-11. T270/370 22” Fuel Tank Mounting Measurements [inches (mm)]
22” Fuel Tank Height A, inch (mm)
Standard 16.3 (416)
Raised 1 Inch 15.3 (389)
24.5-inch Fuel Tanks — T270/370
6.7 (169)
10.4 (265)
29.0 (790)
4.8
(122)
20.4
(518)
18.2
(462)
NO STEPS WITH STEPS
18.2
(462)
4.8
(122)
32.1 (815)
FIGURE 3-12. T270/370 24.5” Fuel Tank Mounting Measurements. With and without steps. [inches (mm)]
3-11
12/11
Section 3
Dimensions
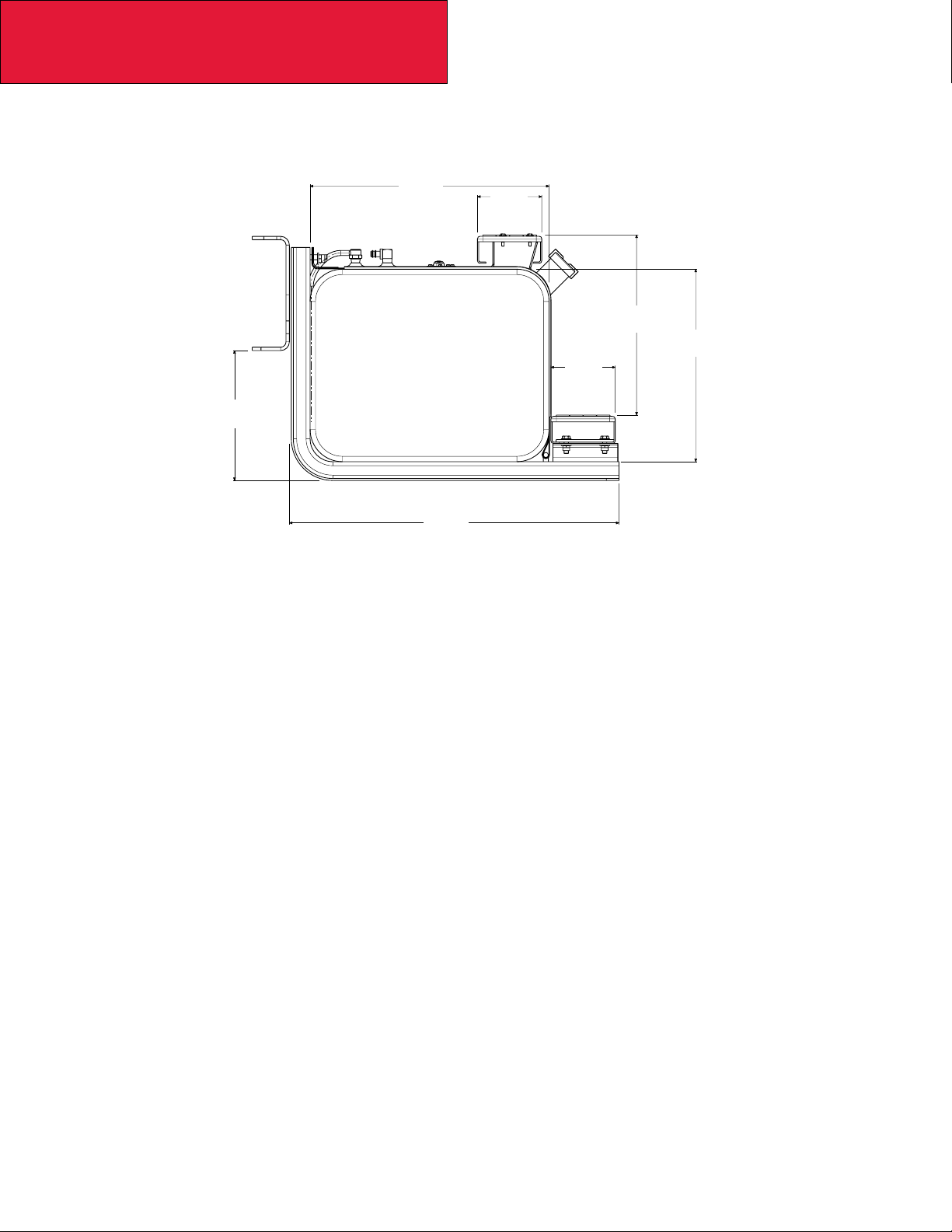
Rectangular Fuel Tank
Rectangular Fuel Tank Mounting
22.2
(564)
12.1
(307)
30.7
(780)
6.0
(152)
FIGURE 3-13. Rectangular Fuel Tank Measurements [inches (mm)]
6.0
(152)
16.8
(427)
17.9
(455)
12/11
3-12
 Loading...
Loading...