
800MHz/900MHz FM TRANSCEIVER
TK-480/48 1
SERVICE MANUAL
REVISED II
This service manual applies to products with 30100001 or
subsequent serial numbers.
Whip antenna
(T90-0636-25) : TK-480
(T90-0640-25) : TK-481
Knob (ENC)
(K29-5232-03)
Knob (VOL)
(K29-5231-03)
Panel assy
(A62-0981-04)
Badge
(B43-1139-04)
Knob (PTT)
(K29-5157-03)
Cabinet assy
(A02-3659-03) : K2
Packing
(G53-0841-02) : K2
© 2001-3 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-8408-20 (N) 1015
CONTENTS
GENERAL ............................................................ 2
SYSTEM SET-UP ................................................ 2
OPERATING FEATURES .................................... 3
REALIGNMENT................................................. 11
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.................................... 14
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA................................ 20
DESCRIPTION OF COMPONENTS .................. 23
PARTS LIST ....................................................... 24
EXPLODED VIEW ............................................. 30
PACKING ........................................................... 31
ADJUSTMENT .................................................. 32
TERMINAL FUNCTION .................................... 40
PC BOARD VIEWS
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX) .................... 41
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX) ......................... 47
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................... 53
BLOCK DIAGRAM............................................. 57
LEVEL DIAGRAM (TK-480) .............................. 59
LEVEL DIAGRAM (TK-481) .............................. 60
KNB-16A/17A (Ni-Cd BATTERY) ..................... 61
KPG-36 (PROGRAMMING INTERFACE CABLE)
KSC-19 (CHARGER) .......................................... 61
SPECIFICATIONS.............................................. 62
.... 61
Photo is TK-480/481 K2 type.
(Produced in Singapore)
CAUTION
When using an external power connector,
please use with maximum final module protection of 9V.
TK-480/481
GENERAL / SYSTEM SET-UP
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians familiar with similar types of commercial grade communications equipment. It contains all required service information for the equipment and is current as of this publication date. Changes which may occur after publication are
covered by either Service Bulletins or Manual Revisions,
which are issued as required.
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment information, the full part identification number should be included.
This applies to all parts : components, kits, and chassis. If
the part number is not known, include the chassis or kit
number of which it is a part and a sufficient description of
the required component, for proper identification.
PERSONNEL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personnel safety :
• DO NOT transmit until all RF connectors are secure and
any open connectors are properly terminated.
• SHUT OFF this equipment when near electrical blasting
caps or while in an explosive atmosphere.
• This equipment should be serviced by only qualified technicians.
SERVICE
This radio is designed for easy servicing. Refer to the
schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and alignment procedures contained within.
NOTE
WE CANNOT guarantee oscillator stability when using
channel elements manufactured by companies other than
KENWOOD or its authorized agents.
You must use the KPG-49D to program TK-480/481 trans-
ceivers with a serial number of 30100001 or greater. You
cannot use the KPG-35D for those radios.
TK-480/481 transceivers with a serial number of
30100001 or greater have a red triangle in the KENWOOD
logo label (B43-1139-04) on the front panel. You will also
find the model name plate marked as “Ver 2.0” on the rear
of the transceiver.
Unit TX-RX unit Display unit
Model &
destination 0-10 0-11 0-10 0-11
TK-480
TK-481
Note X57-5630-XX/X54-3210-XX : Produced in Singapore
X57-5630-XX X54-3210-XX
K ✓✓
K2 ✓✓ LOC : 44.395MHz ✓
K ✓✓
K2 ✓✓ LOC : 44.395MHz ✓
Frequency range Remarks QT/DQT DTMF Charger Battery 16 key
806~870MHz
896~941MHz
SYSTEM SET-UP
Merchandise received
License and frequency allocated by FCC
Choose the type of transceiver
Transceiver programming
IF1 : 44.85MHz
IF1 : 44.85MHz
Frequency range (MHz) RF power Type
TX 806~825 2.5W TK-480 K,K2
851~870
RX 851~870
TX 896~902 TK-481 K,K2
935~941
RX 935~941
A personal computer (IBM PC or compatible), programming
interface (KPG-36), and programming software (KPG-49D) are
required for programming.
(The frequency, trunked system features, conventional system
features, TX power HI/LOW, and signaling data are programmed
for the transceiver.)
✓✓Option ✓
✓✓Option ✓
–
–
Are you using the speaker microphone?
NO
Delivery
YES
KMC-25
Speaker microphone
(Option)
2
OPERATING FEATURES
TK-480/481
1. Operation Features
The TK-480/481 is an 800/900MHz band EFJ LTR™-compatible trunked radio designed to operate in both trunked
and conventional modes. The programmable features are
summarized.
Model Trunking mode
Conventional mode
This model can handle up to 32 systems with up to 250
groups in each system. The transceiver can be used in both
trunked mode and conventional mode. Systems, groups,
and their functions are programmed.
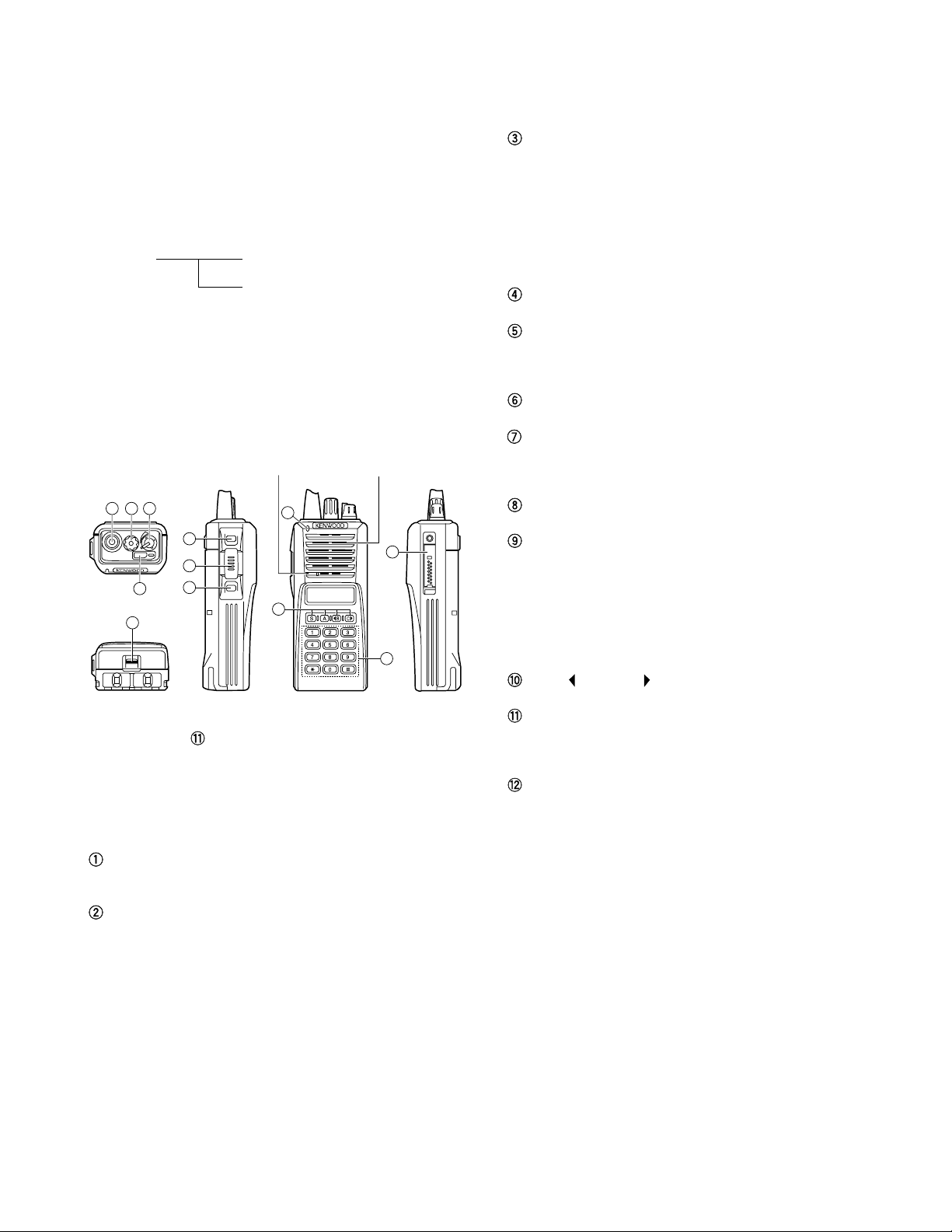
2. Transceiver Controls and Indicators
2-1. Physical Layout
Microphone Speaker
1 2 3
4
5
6
7
8
9
12
10
11
Volume/Power switch
Transceiver Power and Volume switch. Turn clockwise to
switch On the transceiver. Turn counterclockwise fully to
switch OFF the transceiver. Also adjusts the volume
level. When the power is switched off, all the parameters, such as the system and group, are stored in
memory. When the power is switched on again, the system returns to the previous conditions.
Auxiliary (orange) key (Programmable)
Battery pack release catch
Push down to release the battery pack. See Installing the
Ni-Cd Battery Pack.
MONITOR key* (Programmable)
PTT (Push-To-Talk) key
Press this key, then speak into the microphone to call a
station.
LAMP key* (Programmable)
TX/BATT indicator
This red LED lights during transmission (it does not light
during busy or when transmit is prohibited). If the battery
voltage falls below the programmed voltage during transmission, the brightness of this indicator decreases at intervals of about one second, so it can be used as the battery voltage alert function.
S, A, B, and C key (Programmable)
Note : The transceiver is also available without the DTMF
keypad (
).
2-2. Panel controls
The key on the top and front panel is momentary-type
push buttons. The functions of these keys and knob are explained below.
Antenna connector
Connect the supplied antenna here.
System or Group selector knob (Programmable)
Turning the system (or group) selector knob clockwise
increases the system (or group) number by one. Turning
the knob in the counterclockwise direction decreases the
system (or group) number by one.
After the system number (or group number) reaches the
highest system number (or group number), it goes back
to lowest system number (or group number).
System numbers (or group numbers) not set are skipped.
Caution : The FPU (KPG-49D) allows selecting between
system selector and group selector.
DTMF keypad (keypad model only)
Press the keys on the telephone keypad to send DTMF
tones.
Universal connector
Connect the external KMC-25 speaker/ microphone (optional) here. Otherwise, keep the supplied cover in place.
* : MONITOR and LAMP are arbitrary names chosen for
these buttons. They can be used for any of the auxiliary
functions.
2-3. Programmable keys
The FPU (KPG-49D) enables programmable keys to se-
lect the following functions.
Auto Tel, AUX(only when Voice Scrambler is not selected), DTMF ID (BOT), DTMF ID (EOT), Display Character,
Emergency (only AUX key), Function, Group Down, Group
Up, Home Group, Key Lock, Lamp, Memory (RCL/STO),
Memory (RCL), Memory (STO), Monitor A, Monitor B, Monitor C, Monitor D, Redial, RF Power Lo, Scan, Scan Del/Add,
Scan Temporary Delete, Scrambler (Only when Voice
Scrambler is selected), SP Attenuation (Only MIC switch),
System Down, System Up, TEL Disconnect and none.
These functions the FPU programs to the function keys
are described in the following sections.
3

TK-480/481
OPERATING FEATURES
■ Auto TEL
Automatically connects available repeaters that are connected to telephone circuits when operating as LTR system.
The time allocated to search for available repeaters is 60
seconds, after which connection failure occurs, a DTMF
tone is output and the function terminates.
If connection to an available circuit is made, only ID 253,
EOT or hang-up time-out can terminate the function.
■ AUX
This function can be programmed when the voice scrambler board is not installed.
If this key is pressed, an underscore (“_”) appears at the
extreme right of the LCD and AUX port which is inside of the
transceiver turns to the active level. If pressed again, the
underscore disappears and the AUX ports turns to the
deactive level.
■ DTMF ID (BOT)
Pressing this key in Conventional mode, automatically
sends the preset Connect ID.
■ DTMF ID (EOT)
Pressing this key in Conventional mode, automatically
sends the preset Disconnect ID.
■ Display character
This key switches the LCD display between the system/
group number and system/group name.
■ Emergency
Pressing this key for longer than the programmed “Emergency Key Delay Time” causes the transceiver to enter the
emergency mode. The transceiver jumps to the programmed “Emergency System/Group” and transmits for
the programmed “Active Time”.
The transceiver disables mic mute while transmitting.
After finishing transmission, the transceiver receivers for
the programmed “Interval Time”. The transceiver mutes
the speaker while receiving. Following the above sequence,
the transceiver continues to transmit and receive.
If “Man Down Switch” has been programmed on the radio and the switch is activated, the radio enters Emergency
mode after the specified “Man Down Delay Time” expires.
■ Key lock
Pressing this key causes the transceiver to accept entry
of only the [Function], [Key Lock], [PTT], [Lamp], [Monitor A],
[Monitor B], [Monitor C], [Monitor D], and [Emergency] keys.
The locked keys also include the tuning control.
■ Lamp
This key illuminates the LCD and keys on the front panel.
When the key is pressed, the LED lamp goes on.
When it is released, the lamp goes off after about five
seconds. If any key is pressed while the LED lamp is on, the
lamp is kept on for five seconds.
■ Memory
This key allows DTMF memory data to be recalled; up to
32 memories each with a memory dial of up to 16 digits and
an A/N of up to 10 digits per memory.
■ Monitor
Used to release signalling or squelch when operating as a
conventional. It is also used to reset option signalling.
■ Redial
Pressing this key when System/Group is shown, displays
the previously transmitted DTMF code. Pressing [PTT] at
this time, transmits the code that is currently displayed.
■ RF power low
Used to temporarily switch transmission output to low
power. Turning the function on enables:
Hi→Low, Low→Low
Key states are backed up, except in the PC mode when
they are reset.
■ Scan
Press this key starts scanning. Pressing this key stops
scanning.
■ Scan Del/Add
Used to select whether system scan routines are used
during system scan. Each pressing of the key (to ON)
toggles between lockout and lock. The scan routine is
started when on lock. The DEL indicator flashes when the
system is on lockout.
■ Function
Pressing this key causes the transceiver to display
“FCN”. Then, pressing a DTMF key causes the corresponding programmed function to start. This key may be convenient when using many functions with the 12-key keypad
(K2 type).
■ Group up/down
When the key is pressed each time, the group number to
be selected is incremented/decremented and repeats if held
for one second or longer.
■ Home group
Each pressing of the key selects a preset system/group.
4
■ Scan temporary delete
This key is temporarily deleted a system being scanned.
If you press this key when scan is stopped (when a call is
being received from another station), the system is temporarily deleted and scanning restarts.
This key operates even when “Scan Type” is set to “List
Type System Scan”.
■ Scrambler
If a scrambler code (1 to 4) has been set in the FPU, an
underscore (“_”) appears at the extreme right of the LCD
display when scrambler is active. Pressing this key changes
ON/OFF of scramble operation.
Holding this key down for 2 seconds sets Scramble Code
Select Mode.

OPERATING FEATURES
TK-480/481
■ System up/down
When the key is pressed each time, the system number
to be selected is incremented/decremented and repeats if
held for one second or longer.
■ Telephone disconnect
Pressing this key ends an RIC connection (disconnects
the telephone line).
■ None
Sounds error operation beep, and no action will occur.
Use this function when the transceiver is required to be
more simple operated.
2-4. Display
P
9
Sub display
Displays the system, channel and group numbers. Also
displays various functions, such as TA.
Alphanumeric display
The twelve-character dot matrix alphanumeric display
shows the system and group numbers. You can program
system and group names with up to ten characters in
place of these numbers. The left display is used as a delete indicator (
call (
) or scrambler ( _ ) function. The delete/add indicator shows the systems locked out of the scanning sequence. Selective call and scrambler are optional functions that can be programmed.
) and the right is used for the selective
3. Scan Operating
3-1. System scan
System scan can be selected with the “Scan” key by pro-
gramming the scan feature. When the “Scan” key is
pressed and the “SCN”’ mark appears, scan mode in entered. Scanning starts from the system following the currently displayed system. When a call is received, scanning
stops, and the system and group are displayed.
When the system knob or programming key is touched
during scanning, the scan stops and the revert system or
group can be changed. Scanning resumes one second after
the key is released.
System scan consists of the following 2 types.
■ Fix system scan
All the set systems except locked-out ones are scanned.
If the DEL/ADD feature is assigned to the programmable
key, it can be controlled from the front panel.
P (Priority) indicator
The P indicator ( ) appears when a selected channel is
programmed as priority, in conventional operation.
MON (Monitor) indicator
The MON indicator appears when the button programmed as MONITOR is pressed.
SVC (Service) indicator
This icon is not used on this transceiver.
SCN (Scan) indicator
The SCN indicator appears when using Scan mode.
LO indicator
Appears when low power is selected.
Handset indicator
The handset indicator ( ) appears when the selected
group is programmed as telephone IDs.
MAIL indicator
Flashes when a status message (FleetSync™) is received. Lights when a status message is stored in the
stack memory.
■ List type system scan
A scan list can be set for each system.
The list to be scanned can be changed by changing the
display system.
If many system have been set, the scan speed can be
increased by narrowing the systems to be scanned with
scan lists.
3-2. System lockout
The system lockout feature is used to lock systems out
of the scan sequence, and can be selected by programming
in the following two ways:
■ Fixed lockout
The system to be locked out is selected by programming.
When a locked system is selected, the Delete (
appears on the left of the SYSTEM indicator. The revert system is scanned even if it is locked out. If there is a locked
system, the Delete (
ning.
) indicator flashes during fixed scan-
) indicator
■ User selectable lockout
If the scan lockout feature is programmed to a key, the
user can lock systems out of the scan sequence with the
key. To lock a system out of the scan sequence, press the
key when the system is displayed. The Delete (
is displayed on the left of the SYSTEM indicator.
) indicator
5

TK-480/481
OPERATING FEATURES
To unlock a system, select the system and press the key.
The Delete (
tem has returned to the scan sequence. The revert system
is scanned even if it is locked out. If there a locked system,
the Delete (
systems are locked out, the scan stops and only the revert
system is received.
) indicator disappears to indicate that the sys-
) indicator flashes during fixed scanning. If all
3-3. Drop-out delay time (Scan resume time)
If a call is received during scan, the scan stops. The scan
resume time can be programmed as 0 to 300 seconds in
one-second increments. The default value is 3 seconds.
3-4. Dwell time
The dwell time is the time after transmission ends until
the scan resumes in scan mode. It can be set 0 to 300 seconds by programming. The default value is 3 seconds.
3-5. System/Group revert
System/Group revert can be programmed for one of the
following;
■ Last called revert
The system or group changes to the revert system or
group when a call is received with the system or group being scanned.
■ Last used revert
If a system/group call is received during scanning and the
PTT button is pressed for transmission and response within
the drop out delay time, the system or group is assigned as
the new revert system or group.
■ Selected revert
If the system/group was changed while scanning, the
newly selected system/group.
■ Selected + Talkback
If the system/group was changed while scanning, the
newly selected system/group. The transceiver “talks back”
on the current receive group.
3-6. Scan message wait
The time for staying with the home repeater that receives a signal during system scan and monitoring data
messages can be programmed. If there is no signal from the
home repeater, the system is scanned for about 50ms. If
there is a signal, three data messages are monitored. Normally, three data messages are monitored for each system,
and it can be increased in multiples of three data messages
per line to up to eight lines.
If the repeater data message indicates that there is no
call, data monitoring is terminated and the home repeater of
the next system is scanned.
3-7. Group scan operation
Group scan can be programmed for each group. In addition to the ID codes of the selected group, the ID codes of
the other groups that are permitted for group scan are decoded. (The two fixed ID and block decode codes are always
decoded.)
If, during group scanning, a call is received with one of
the selectable group ID codes for which group scan is enabled, the group display indicates the group number that the
call came in with. That group then becomes the new selected group. Group scan resumes after the specified dropout delay time or dwell time shared by the system scan
elapses.
3-8. In Conventional system.
If QT or DQT is set for the channel, the channels, including signalling, are scanned.
In case of the priority group is set in conventional system, if a group scan (including group scan during a system
scan) temporarily stops (receiving) in a group that does not
have priority, a look back is performed to the priority group.
Look back is performed according to the look back time A
and B settings. If a call is received on the priority group, reception immediately switches to the priority group.
4. Details of Features
4-1. Time-out timer
The time-out timer can be programmed in 15 seconds
increments from 15 seconds to ten minutes. If the transmitter is keyed continuously for longer than the programmed
time, the transmitter is disabled and a warning tone sounds
while the PTT button is held down. The alert tone stops
when the PTT button is released.
4-2. Sub LCD
You can use 3-digit the display to display the system
number, channel number or group number. It is useful when
the main (12-digit) display indicates system, group or channel name or other functions.
4-3. Selective Call Alert LED
You can select whether or not the LED on the transceiver
flashes in an orange color when selective call was occurred.
4-4. PTT ID
PTT ID provides a DTMF ANI or MSK ID to be sent with
every time PTT (connect ID at beginning of transmission,
disconnect ID at end of transmission, or both).
You can program PTT ID “on” or “off” for each group
channel (DTMF). The contents of ID are programmed for
each transceiver.
The transceiver is capable to have ID. The format is
DTMF. The timing that the transceiver sends ID is programmable.
BOT : Connect ID is sent on beginning of transmission.
EOT : Disconnect ID is sent on end of transmission.
Both : Connect ID is sent on beginning of transmission
and disconnect ID is sent on end of transmission.
There is also “PTT ID” setting for each channel.
6

OPERATING FEATURES
TK-480/481
4-5. Radio password
When the password is set in the transceiver, user can not
use the transceiver unless enter the correct password.
This code can be up to 6 digits from 0 to 9 and input with
the keypad or selector, and “S” key.
4-6. Battery Warning
This transceiver has battery warning feature. If the low
voltage is detected during transmission, the transceiver
warns it by flashing red “LED”.
Then more low voltage is detected during transmission,
the transceiver stops transmission and warns it by flashing
red “LED” and beep.
Please notice “standard” for the battery exchange,
charging time by flashing red LED and beep.
4-7. Minimum Volume
The minimum volume is programmable (off (0) to 31).
The transceiver remains the minimum volume level however the mechanical volume position is set to zero.
4-8. Call indicator
The call indicator can be programmed for each group. In
trunked system, it can be set to respond to a selectable decode ID or one of two fixed IDs, except block IDs. When a
call is received with a selectable decode ID, the call indicator
flashes. When a call is received with a fixed ID, the call indicator lights continuously.
On a conventional system, the call indicator can be programmed to light for each QT or DQT code. It keeps flashing
while a call is being received. It is turned off by pressing any
front panel key.
4-9. Free system ringback
This feature is available only when a telephone interconnected ID code is selected. If a busy tone sounds when the
PTT button is pressed, the transceiver enters this mode automatically.
When the PTT button is released, a beep sounds for
400ms to indicate that the mode has been entered. If the
scan is on, it is resumed (the “SCN” mark goes on). When
any repeater becomes available, a ringing tone sounds and
this mode ends.
The mode is terminated when the system, group, scan,
PTT, key is changed.
4-10. System search
This feature can be programmed to automatically access
other programmed systems when the selected system cannot be accessed. If an intercept tone sounds when the PTT
button is pressed after setting the mode, the transceiver
has entered the mode.
If the group ID is a telephone interconnect ID, the transceiver then attempts to access, in succession, other systems that have a telephone interconnect ID in the revert
group location. If the group ID is a dispatch ID, the transceiver attempts to access other systems that have a dispatch ID programmed in the revert group location.
If there is no system to be accessed, an intercept tone
sounds, the mode is terminated, and the transceiver returns
to the first system. If the access is successful, the mode is
terminated, and the searched system becomes the new selected system (If during scanning, the scan stops).
4-11. Transpond
This feature can be programmed to turn on and off for
each group. If the ID of the group for which transpond is
enabled is received, two data messages (transmit ID and
turn-off code) are automatically transmitted if the PTT button is not pressed as a response within the time set (0 to
300 seconds in 1-second increments). If the PTT button is
pressed within the time, the transpond is not preformed.
4-12. Transmit inhibit
The transceiver can be programmed with a transmit inhibit block of ID codes. If an ID code within this block is decoded the preset time before the PTT button is pressed,
transmission is inhibited. The BUSY indicator lights and a
busy tone sounds until the PTT button is released to indicate
that transmission is not possible (except clear-to talk mode).
Transmission with the group for which the encode ID is
not set is inhibited, and the busy tone is output while the
PTT button is held down, regardless of the clear-to -talk setting.
4-13. Auto TEL
A telephone interconnect call can be made by simply
pressing the key by assigning this feature to the key. This
feature accesses the TEL channel of the available system
automatically.
When the key is pressed, a queue tone is output, and the
“AUTO TEL” appears on the alphanumeric display along
with a flashing handset indicator (
mode has been entered. If the TEL ID is set for the revert
system, the TEL channel of that system is accessed. If all
TEL channels are busy, an attempt is made to access the
TEL channels of another system in which the TEL ID code
has been programmed. It is repeated for 60 seconds until
the access succeeds. If the access succeeds, a dial tone
returns from the repeater. If the key is pressed again when
the queue tone is sounding, this mode is canceled.
If the access fails after 60 seconds, a deny tone is output
and this mode is terminated. When the talk ends, the revert
system/group returns. When the scan mode is effective, the
scan resumes. The Auto TEL feature can be programmed to
turn on or off for each system.
) to indicate that this
■ ARQ mode
If affects Trunking mode only. Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) mode is a manner to minimize the air traffic of
data communication. Also, it enables to occupy the trunking
repeater channel for the data communication period.
■ Data TX with QT/DQT
Whether programmed QT/DQT is modulated or not with
a data transmission except for Selcall. A radio unit can receive a data message regardless of QT/DQT if the receiving
unit is not scanning.
7

TK-480/481
OPERATING FEATURES
5. Option Signalling
5-1. DTMF
Built-in DTMF decoder is available for option signalling.
It is possible to use individual call, group call, D.B.D.
(Dead Beat Disable). D.B.D. is used with DTMF only.
If the option signalling matches, a predetermined action
will occur.
If option signalling matches on a group which is set up
with option signalling, the option signalling indicator (
flash and option signalling will be released. The transpond
or alert tone will sound.
If the selective call alert LED is set up, the orange LED
will flash.
While option signalling matches (or if option signalling is
deactivated when you are transmitting), you can mute or
unmute ID/QT/DQT/Carrier.
■ AND/OR
You can select AND or OR for option signalling match
conditions.
Alert/Transpond
AND QT/DQT/ID+DTMF; Option matches = Action
OR QT/DQT/ID+DTMF; Option matches = Action
AF mute open
AND QT/DQT/ID+DTMF; Option matches = Action
OR QT/DQT/ID; Signalling only matches = Action
) will
■ AND/OR
AND : QT/DQT/ID + MSK to unmute. MSK matches =
alert tone
OR : QT/DQT/ID to unmute. MSK matches = alert tone
6.
Alphanumeric Two-way Paging Function
(FleetSync™)
6-1. General
The Alphanumeric Two-way Paging Function
(FleetSync™) is a Kenwood proprietary protocol. It enables
a variety of paging functions.
6-2. ID Construction
A radio unit ID is defined by a combination of 3-digit Fleet
and 4-digit ID numbers. Each radio unit must be assigned its
own Fleet and ID numbers.
6-3. PTT ID
A pre-programmed unique ID (Own) can be sent at the
beginning of transmission and/or the end of transmission to
identify which radio unit is on air.
When selecting (Sel) for MSK ID, the radio calls the specific Fleet user the same as selective call.
6-4. Selective Call (SELCALL)
This is a voice call to a particular individual or group of
stations.
With OR set up, alert/transpond will not function with
only DTMF.
With OR set up, AF mute will not release when only
DTMF matches.
With a conventional group not set up with QT or DQT,
only the carrier is considered when signalling matches.
■ Auto Reset
If option signalling matches a group set up with option
signalling, option signalling is released. After matching option signalling, option signalling will temporarily reset automatically.
■ Dead Beat Disable
If the D.B.D. code matches, a predetermined action will
occur. Whether option signalling is activated or not, when
D.B.D. matches on any group, the transceiver will become
TX inhibited or TX/RX inhibited. While D.B.D. is active, if the
D.B.D. code + “#” code is received, D.B.D. will disactivate.
When D.B.D. matches, transpond will function. Alert will
not be output, and option signalling match icon will not appear.
5-2. MSK
Built-in MSK (FleetSync™ : Fleet-ID) decoder is available
for option signalling. When the group ID matches, squelch
remains muted while the station waits for reception of
proper MSK signal. When MSK signal matches, squelch
unmutes.
■ Example of call types;
[100][ALL ] : <Group Call>
All the units whose fleet number is “100” are called.
[100][1000] : <Individual Call>
The unit, whose the fleet number is “100” and ID number is “1000”, is called.
[ALL][ALL ] : <Broadcast Call>
All the units are called.
[ALL][1000] : <Supervisor Call>
All ID “1000” are called regardless of their fleet number.
■ Unit ID Encode Block
Encode ID Block can be set to limit manual dial ID. The
radio unit will not accept an ID other than these IDs which
are entered from the keypad. If Inter-fleet Call is enabled,
block ID setting affects each fleet group.
6-5. Status Message
Using a 2-digit number, you can send and receive a Status message which may be decided in your talk group. Each
Status may be displayed with 16 alphanumeric characters if
programmed in the radio. A maximum of 9 received messages can be stored in the stack memory, and it can be reviewed after reception. If the message memory becomes
full, the oldest one will be erased. The stack memory will be
cleared by turning radio power off.
8

OPERATING FEATURES
TK-480/481
■ Status 80~99 (Special)
Status numbers from 80 to 99 are reserved for special
purposes. Entering these statuses from the DTMF keypad
can be inhibited.
Please notice that the following status numbers are used
for special purposes;
80~87 : Reserved for future use.
88 : Terminates to emergency mode.
89 : Request for hornalert (For Mobile).
90 : Remote stun on. Disable the received radio unit’s
TX.
91 : Remote stun on. Disable the received radio unit’s
TX/RX.
92 : Cancel remote stun. Enable the received radio unit’s
TX/RX.
93 : Acknowledgement status sent when the radio unit is
in stun mode (TX disabled).
94 : Acknowledgement status sent when the radio unit is
in stun mode (TX/RX disabled).
95~97 : Reserved for future use.
98 : Man Down Emergency status.
99 : Emergency Status.
Note : Remote stun works with DTMF D.B.D. function also.
■ Automatic Status Response
If you pre-select a status number and leave the radio in
the Status Mode, it can automatically respond with the selected status number upon request from the base station.
(The request function is initiated by serial control on the
base station (Optional).)
6-6. Short Message (Optional)
A maximum of 48 characters can be sent (External equipment is required). Received Short Messages will be displayed in the same manner as a Status Message. A maximum of 4 received messages can be stored in the stack
memory. In the Stack Mode, 3-digit LCD indicates the received Short Message as “M01”~”M04".
6-7. Long Message (Optional)
A maximum of 1024 characters can be sent (External
equipment is required). Received Long Message will not be
displayed or stacked in the radio memory but is output
through the COM (Data) port.
6-8. Emergency Function
Emergency status 99 will be sent at the beginning of
each emergency transmission.
■ FleetSync™ Baud Rate
MSK data baud rate setting. The same rate must be set
as a communication partner.
1200bps :
Data communication is made in 1200bps. The communication area is much wider than 2400bps. Recommended
for repeater operation.
2400bps :
Data communication is made in 2400bps. The communication area is narrower than 1200bps, but it will decrease
the data traffic. Data rate 2400bps may not work properly depending on the repeater’s characteristic.
■ Message Mode Timer
Message Mode Timer is a delay timer returning from
message/stack mode to Normal mode.
■ Status/Short/Long Message on Data Group
Status/Short/Long Message transmission is made
whether on the Data System/Group.
■ Status/Short/Unit ID Message Serial Output
(Option)
Whether a received Status/Short message or PTT ID is
output or not from serial port.
■ Call Alert (Continuous)
The radio can provide the alert tone repeatedly until next
operation.
■ PTT ID Sidetone
This function allows a single beep sound after the PTT ID
(MSK) for FleetSync singalling is encoded.
■ Caller ID Stack
The radio stores the last 3 received caller IDs to volatile
memory.
■ Caller ID Display
PTT ID is displayed on LCD.
6-10. Parameters
■ GTC Count
Number of Go To data Channel messages to be sent before transmitting a data message if it is being made on Data
System/ Group. If a radio unit receives a GTC message, it
will move to the Data System/Group of the current system.
Increase this item to make sure the called radio unit moves
to the Data System/Group.
■ Emergency Status response
“Alert” can be selected for the called radio unit’s response to reception of status 99 which is used as an emergency status.
6-9. Other Functions
■ Manual Dial
Fleet, ID and Status numbers can be entered from DTMF
keypad. (DTMF microphopne is required.)
■ Random Access (Contention)
When a channel (or all the repeater channels for Trunking
mode) is busy, radio unit will not transmit (depending on its
Busy Channel Lockout setting in conventional mode). As
soon as a channel is cleared, some transmissions may
crash. Random access is used to avoid this by employing a
random transmission sequence.
9

TK-480/481
OPERATING FEATURES
■ Number of Retries
Number of Retries is the maximum number of retry
transmission when no acknowledgement is received in the
Maximum ACK Wait Time. Increase this item to improve
data communication reliability.
■ TX Busy Wait Time
TX Busy Wait Time is the maximum amount of time before giving up the data transmission when the channel (or all
the repeater channels for Trunking mode) is busy. Also, this
timer affects if it expires during Random Access period.
■ Maximum ACK Wait Time
Maximum ACK Wait Time is the maximum amount of
time to wait for an acknowledgement from the called radio
unit. It is used as an interval time of retries. It must be set
greater than the ACK Delay Time of the called radio unit.
■ ACK Delay Time
ACK Delay Time is the amount of time from the end of
receiving a data to the beginning of sending an
acknowledgement. It should be adjusted as the repeater’s
hang-up delay time. Also, it must be set less than the Maximum ACK Wait Time of the calling radio unit.
■ TX Delay Time (RX Capture)
TX Delay Time is the amount of unmodulated transmission to let the called unit stop scanning or exit its battery
save mode. It is used only when starting a data communication sequence.
■ Data TX Modulation Delay Time
Data TX Modulation Delay Time is the amount of time
from the beginning of transmission to the beginning of a
data modulation. It is used every time data is transmitted.
It must be set to more than 300ms if data communication is
made in Trunking Mode.
7. Audible User Feedback Tones
The transceiver outputs various combinations of tones to
notify the user of the transceiver operating state. The main
tones are listed below.
The high tone is 1477Hz, the mid tone is 941Hz, and the
low tone is 770Hz.
7-1. Power On Tone
This tone is output when the transceiver is turned on.
(The high tone is output for 500ms.)
7-2. Alert Tone
This tone is output when the transceiver is TX inhibition
for TOT and PLL unlocked. It is output until the PTT button
is released. (The 697Hz tone is output.)
7-3. DBD On Tone
When a D.B.D. code is received, transpond tone sounds.
7-4. DBD Off Tone
When a D.B.D. release code is received, transpond tone
sounds.
7-5. Password Agreement Tone
When the correct password is entered, the tone sounds.
The optional feature's control tone can be set to yes or no.
7-6. PTT Release Tone
When you release the PTT switch, the PTT release tone
sounds.
7-7. Busy Tone
Sounds in LTR mode, when you cannot use a repeater
(system busy or TX inhibit). Sounds in conventional mode,
when busy channel lockout is functioning. You can select
yes or no for the optional feature's warning tone.
7-8. Group Call Tone
Sounds when a group call with the correct DTMF option
signalling is received, repeats 7 times. You can select yes or
no for the optional feature's warning tone.
7-9. Individual Call Tone
Sounds when an individual call with the correct DTMF
option signalling is received. You can select yes or no for
the optional feature's warning tone.
7-10. Key Press Tone [A]
Sounds when a key is pressed. For toggle keys, sounds
when toggle function is turned on (key press tone [B]
sounds when it is turned off). You can select yes or no for
the optional feature's control tone.
7-11. Key Press Tone [B]
Sounds when a key is pressed. For toggle keys, sounds
when the toggle function is turned off (key press tone [A]
sounds when it is turned on). You can select yes or no for
the optional feature's control tone.
7-12. Key Press Tone [C]
Sounds when a key is pressed. Also sounds when storing data, adding a DTMF code to memory, and when changing test mode settings. You can select yes or no for the
optional feature's control tone.
7-13. Key Input Error Tone
Sounds when a key is pressed but that key cannot be
used. You can select yes or no for the optional feature's
warning tone.
7-14. Roll Over Tone
Sounds at the smallest system/group. You can select
yes or no for the optional feature's control tone.
7-15. Transpond Tone
Sounds when an individual call with the correct LTR/
DTMF option signalling is received. For group calls, only the
group tone will sound, not the transpond tone.
10
TK-480/481
User mode
Panel test mode
PC mode
Firmware programming mode
Panel tuning mode
Data programming mode
PC test mode PC tuning mode
Clone mode
OPERATING FEATURES / REALIGNMENT
7-16. Intercept Tone
This tone indicates that the transceiver is out of range. It
indicates that the PTT button is pressed, and transmission
has started, but the repeater cannot be connected and talking is not possible. It is output until the PTT button is released. (The mid tone and low tone are output alternately in
200ms intervals.)
7-17. Delay Tone
This tone is output when the PTT button is pressed and
the repeater is accessed three times or more to indicate
connection with the repeater is delayed. This tone is the
same as the busy tone. (It is not output of clear to talk has
been set to yes.)
7-18. Proceed Tone
This tone is output when the PTT button is pressed,
transmission starts, and the repeater is connected to indicate that the user can talk if the clear to talk function has
been set. (The high tone is output for 100ms.)
7-19. Queue Tone
This tone is output until the auto TEL function is set and
the TEL channel is accepted successfully. (The mid tone on
for 50ms, off for 50ms, and on for 50ms in 1 second intervals.)
7-20. Deny Tone
This tone is output if the auto TEL function is set, the
queue tone is output, but the TEL channel cannot be accessed within 60 seconds. It is similar to the intercept tone.
(The mid tone and low tone are output alternately in 150ms
intervals.)
7-21. Free System Ringback Mode Tone, System
Search Mode Tone
This tone indicates that the transceiver is free system
ringback mode or system search mode. (The mid tone is
output for 400ms.)
7-22. Ringing Tone
This tone indicates that the transceiver can use the repeater in free system ringback mode. (The mid tone and no
tone are output eight cycles alternately in 50ms intervals.)
7-23. System Search Tone
Sounds when the system changes during system search.
You can select yes or no for the optional feature's warning
tone.
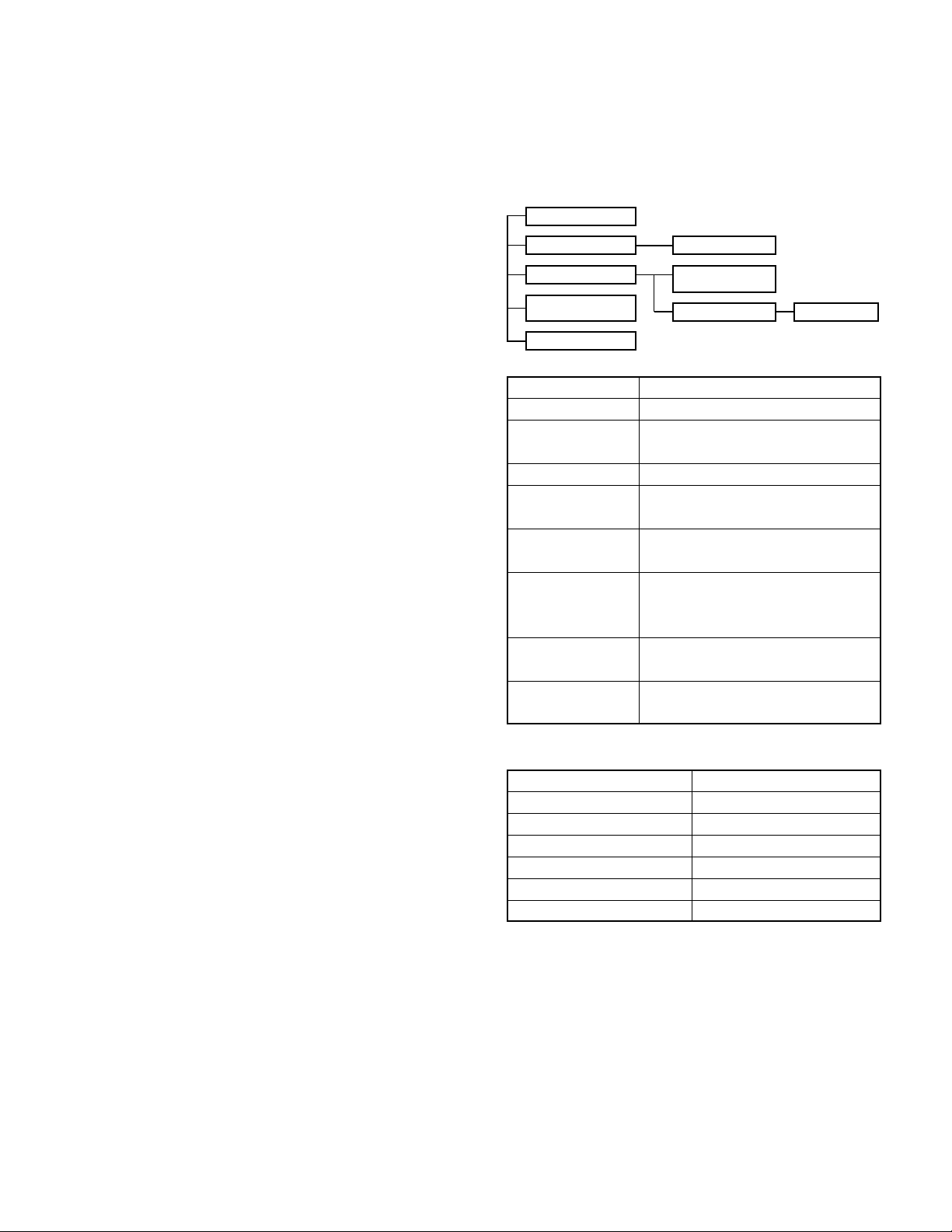
REALIGNMENT
1. Modes
Mode Function
User mode For normal use.
Panel test mode Used by the dealer to check the funda-
mental characteristics.
Panel tuning mode Used by the dealer to tune the radio.
PC mode Used for communication between the
radio and PC (IBM compatible).
Data program- Used to read and write frequency data
ming mode and other features to and from the radio.
PC test mode Used to check the radio using the PC.
This feature is included in the FPU.
See panel tuning.
Firmware program- Used when changing the main program
ming mode of the flash memory.
Clone mode Used to transfer programming data from
one radio to another.
2. How to Enter Each Mode
Mode Operation
User mode Power ON
Panel test mode [A]+Power ON (Two seconds)
PC mode Received commands from PC
Panel tuning mode [Panel test mode]+[S]
Firmware programming mode [S]+Power ON (Two seconds)
Clone mode [C]+Power ON (Two seconds)
3. Panel Test Mode
Setting method refer to ADJUSTMENT.
7-24. System Search End Tone
Sounds when a possible connection to a repeater in system search is not mode. You can select yes or no for the
optional feature’s warning tone.
4. Panel Tuning Mode
Setting method refer to ADJUSTMENT.
11
TK-480/481
REALIGNMENT
5. PC Mode
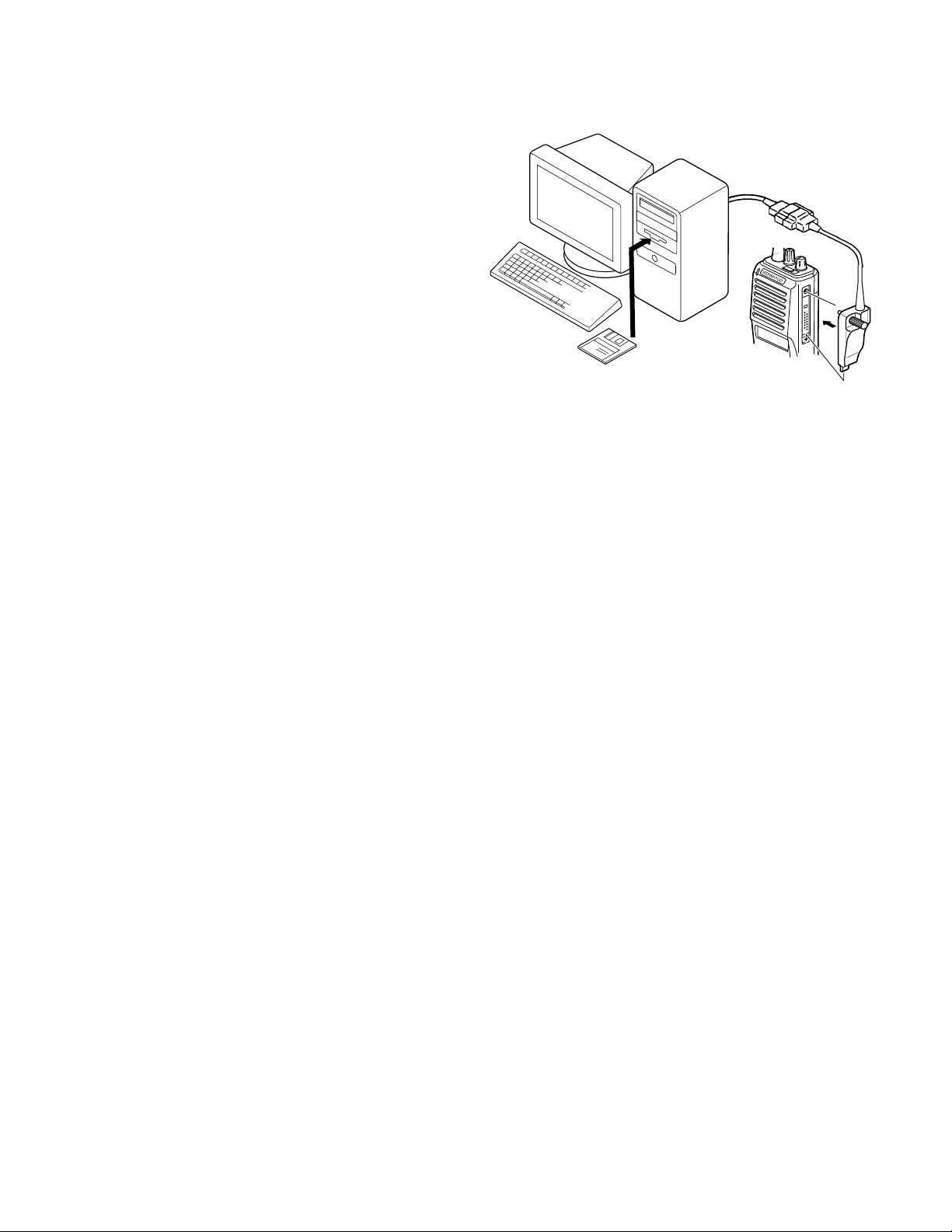
5-1. Preface
The TK-480/481 transceiver is programmed by using a
personal computer, programming interface (KPG-36) and
programming software (KPG-49D).
The programming software can be used with an IBM PC
or compatible. Figure 1 shows the setup of an IBM PC for
programming.
5-2. Connection procedure
1. Connect the TK-480/481 to the personal computer with
the interface cable.
2. When the POWER switch on, user mode can be entered
immediately. When PC sends command the radio enter
PC mode, and “PROGRAM” is displayed on the LCD.
When data transmitting from transceiver, the red LED is
blinking.
When data receiving to transceiver, the green LED is
blinking.
Notes:
• The data stored in the personal computer must match
model type, when it is written into the flash memory.
• Change the TK-480/481 to PC mode, then attach the interface cable.
5-3. KPG-36 description
(PC programming interface cable: Option)
The KPG-36 is required to interface the TK-480/481 to the
computer. It has a circuit in its D-subconnector (25-pin) case
that converts the RS-232C logic level to the TTL level.
The KPG-36 connects the universal connector of the TK-
480/481 to the computers RS-232C serial port.
5-4. Programming software description
The KPG-49D programming disk is supplied in 3-1/2" disk
format. The software on this disk allows a user to program
TK-480/481 radios via programming interface cable (KPG-
36).
5-5. Programming with IBM PC
If data is transferred to the transceiver from an IBM PC
with the KPG-49D, the destination data (basic radio information) for each set can be modified. Normally, it is not necessary to modify the destination data because their values are
determined automatically when the frequency range (frequency type) is set.
The values should be modified only if necessary. Data
can be programmed into the flash memory in RS-232C format via the universal connector.
KPG-49D instruction manual parts No. : B62-1096-XX
IBM-PC
KPG-36
KPG-49D
Fig. 1
6. Firmware Programming Mode
6-1. Preface
Flash memory is mounted on the TK-480/481. This allows
the TK-480/481 to be upgraded when new features are released in the future. (For details on how to obtain the firmware, contact Customer Service.)
6-2. Connection procedure
Connect the TK-480/481 to the personal computer (IBM
PC or compatible) with the interface cable (KPG-36). (Connection is the same as in the PC Mode.)
6-3. Programming
1. Start up the programming software (KPG-49D), select
“firmware program” in the “Program” item, and press
the Return key on the personal computer. This starts up
the firmware programmer.
2. The top screen is displayed. Press any key to advance to
the next screen.
3. Set the communications speed (normally, 57600 bps)
and communications port in the Setup item.
4. Set the firmware to be updated by File select (=F1).
5. Turn the TK-480/481 power ON with the [S] switch held
down. Hold the switch down for two seconds until the
display changes to “PROG 57600”. When “PROG
57600” appears, release your finger from the switch.
6. Check the connection between the TK-480/481 and the
personal computer, and make sure that the TK-480/481 is
in the Program mode.
7. Press F10 on the personal computer. A window opens on
the display to indicate progress of writing. When the TK-
480/481 starts to receive data. the [P] icon is blinking.
8. If writing ends successfully. the LED on the TK-480/481
lights and the checksum is displayed.
9. If you want to continue programming other TK-480/481 s,
repeat steps 5 to 8.
12
REALIGNMENT
TK-480/481
Notes:
• To start the Firmware Programmer from KPG-49D, the
Fpro path must be set up by KPG-49D Setup.
• This mode cannot be entered if the Firmware Programming mode is set to Disable in the Programming software (KPG-49D).
• When programming the firmware, it is recommend to
copy the data from the floppy disk to your hard disk before update the radio firmware.
Directry copying from the floppy disk to the radio may not
work because the access speed is too slow.
6-4. Function
1. If you press the [MON] switch (top of left side) while
“PROG 57600” is displayed, the checksum is displayed.
If you press the [MON] switch again while the checksum
is displayed, “PROG 57600” is redisplayed.
2. If you press the [LAMP] switch (bottom of left side) while
“PROG 57600” is displayed, the display changes to
“PROG 19200” to indicate that the write speed is low
speed (19200 bps). If you press the [LAMP] switch again
while “PROG 19200” is displayed, the display changes to
“PROG 38400”, and the write speed becomes the
middle-speed mode (38400 bps). If you press the [LAMP]
switch again while “PROG 38400” is displayed, the display returns to “PROG 57600”.
How to enter the password with the encoder;
If the encoder is rotated while “CLONE LOCK” is displayed, numbers (0 to 9) are displayed flashing. When
you press the [S] key, the currently selected number is
determined. If you press the [S] key after entering the
password in this procedure, “CLONE MODE” is displayed if the entered password is correct. If the password is incorrect, “CLONE LOCK” is redisplayed.
4. Power on the slave TK-480/481.
5. Connect the cloning cable (No. E30-3325-05) to the universal connectors on the master and slave.
6. Press the [S] key on the master while the master displays
“CLONE MODE”. The data of the master is sent to the
slave. While the slave is receiving the data, “PROGRAM”
is displayed. When cloning of data is completed, the master displays “END”, and the slave automatically operates
in the User mode. The slave can then be operated by the
same program as the master.
7. The other slave can be continuously cloned. When the [S]
key on the master is pressed while the master displays
“END”, the master displays “CLONE MODE”. Carry out
the operation in step 4 to 6.
Note:
Only the same models can be cloned together.
Note:
Normally, write in the high-speed mode.
7. Clone Mode
Programming data can be transferred from one radio to
another by connecting them via their external universal connectors. The operation is as follows (the transmit radio is the
master and the receive radio is a slave).
1. Turn the master TK-480/481 power ON with the [C] key
held down. If the password is set to the TK-480/481, the
TK-480/481 displays “CLONE LOCK”. If the password is
not set, the TK-480/481 displays “CLONE MODE”.
2. When “CLONE LOCK” is displayed, only the knob (en-
coder) and [S], and [0] to [9] keys can be accepted. When
you enter the correct password, and “CLONE MODE” is
displayed, the TK-480/481 can be used as the cloning
master. The following describes how to enter the pass-
word.
3. How to enter the password with the keypad;
If you press a key while “CLONE LOCK” is displayed.
The number that was pressed is displayed on the TK-480/
481. Each press of the key shifts the display in order to
the left. When you enter the password and press the [S]
key, “CLONE MODE” is displayed if the entered pass-
word is correct. If the password is incorrect, “CLONE
LOCK” is redisplayed.
Cloning cable
(E30-3325-05)
Fig. 2
13
TK-480/481
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
1. Overview
This transceiver is an 800/900MHz band EFJ LTR™
trunked system compatible FM portable transceiver that can
be programmed to operate on both LTR and conventional
systems.
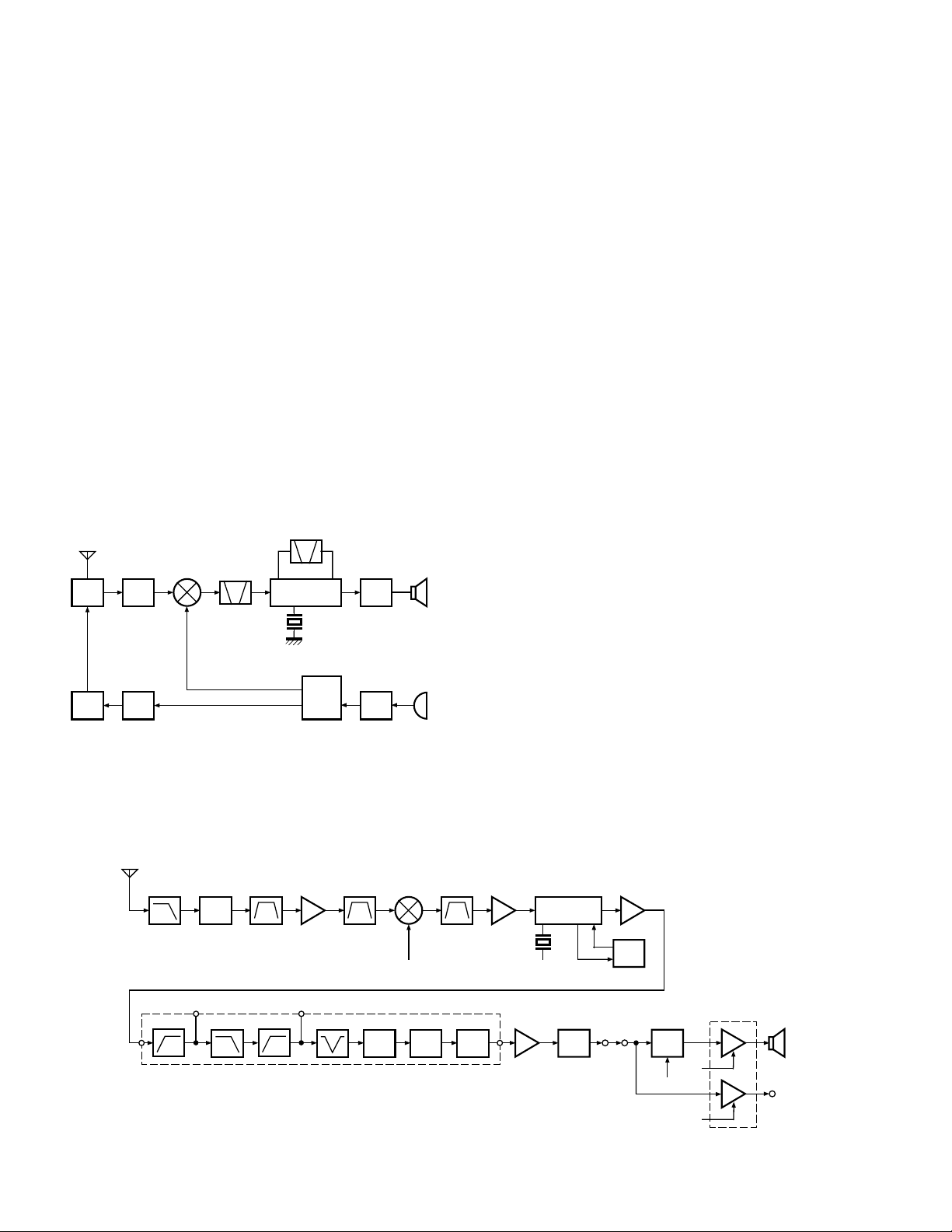
2. Circuit Configuration by Frequency
The receiver is a double-conversion superheterodyne
with a first intermediate frequency (IF) of 44.85MHz and a
second IF of 455kHz. Incoming signals from the antenna are
mixed with the local signal from the PLL to produce the first
IF of 44.85MHz.
This is then mixed with the 44.395MHz second local os-
cillator output to produce the 455kHz second IF. This is detected to give the demodulated signal.
The transmit signal frequency is generated by the PLL
VCO, and modulated by the signal from the microphone. It
is then amplified and sent to the antenna.
TK-480
TX 806~825MHz
851~870MHz
RX 851~870MHz
ANT
ANT
SW
PA
AMP
RF
AMP
TX
AMP
TK-481
TX 896~902MHz
935~941MHz
RX 935~941MHz
1st MIX
44.85MHz
TK-480 :
806.15~825.15MHz
TK-481 :
890.15~896.15MHz
TK-480
806~825MHz
851~870MHz
MCF
TK-481
896~902MHz
935~941MHz
CF
455kHz
IF SYSTEM
44.395
MHz
PLL
VCO
AF
AMP
MIC
AMP
SP
MIC
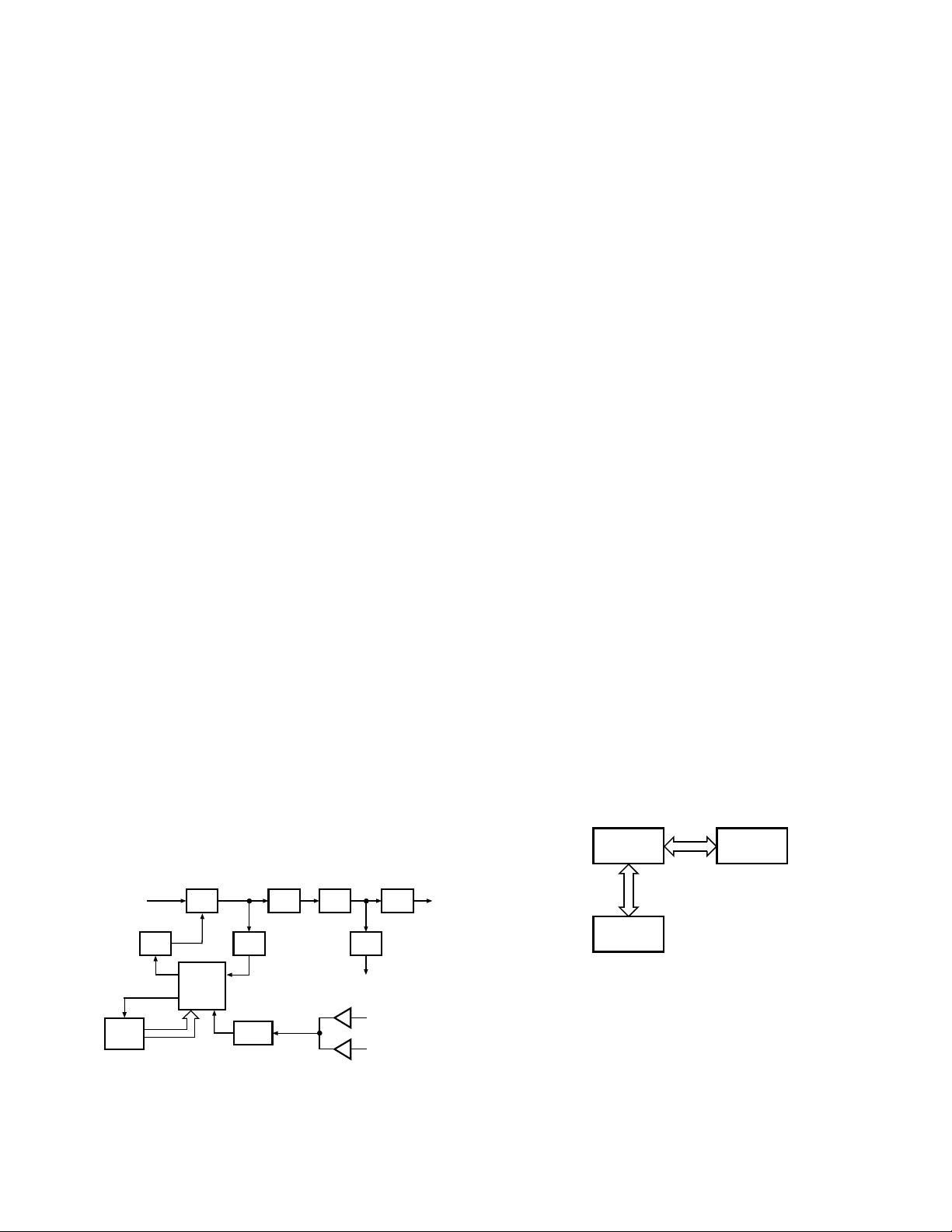
3. Receiver System
3-1. RF unit
An incoming RF signal from the antenna terminal is
passed through the antenna switch (D7, D9, and D10 are
off) and then the bandpass filter (L11). The signal is amplified by RF amplifier Q9, and passed through the bandpass
filter (L20) to remove the spurious signal again. The resulting signal is applied to the first mixer (Q6), where it is mixed
with the first local oscillator signal output from the frequency synthesizer to produce the first IF (44.85MHz).
3-2. IF unit
The first IF signal is passed through a four-pole monolithic crystal filter (XF1) to remove a adjacent channel signal.
The filtered first IF signal is amplified by the first IF amplifier
(Q5) and then applied to the IF system IC (IC9). The IF system IC provides a second mixer, second local oscillator, limiting amplifier, quadrature detector and RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator). The second mixer mixes the first IF
signal with the 44.395MHz of second local oscillator output
(crystal unit X1) and produces the second IF signal of
455kHz.
The second IF signal is passed through the ceramic filter
(CF1,2) to more remove the adjacent channel signal. The
filtered second IF signal is amplified by the limiting amplifier
and demodulated by the quadrature detector with ceramic
discriminator (CD1). The demodulated signal is routed to
the audio circuit.
14
Fig. 1 Frequency configuration
ANT
IC12
5
L30 D9,D10
HPF
ANT
SW
2
LPF
L11
BPFQ9RF AMP
1
HPF BEF
L20
BPFQ61st MIX
1st local
OSC (PLL)
DE-
EMP
EXP
XF1
MCFQ51st IF
MUTE
41
Fig. 2 Receiving system
X1
2nd local
OSC
IC3 (2/2)
AF AMP
IC9
MIX,DET,IF
IC4
VOL
IC8 (2/2)
AF AMP
AF AF
CF1
CF2
Q310
SW
SSW
VC1
VC2
IC300
AF PA
EXT.
SP
INT.
SP
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
SQ voltage
ANT input level
SQ close
SQ open
RSSI voltage
ANT input level
Preset
value
Preset
value
TK-480/481
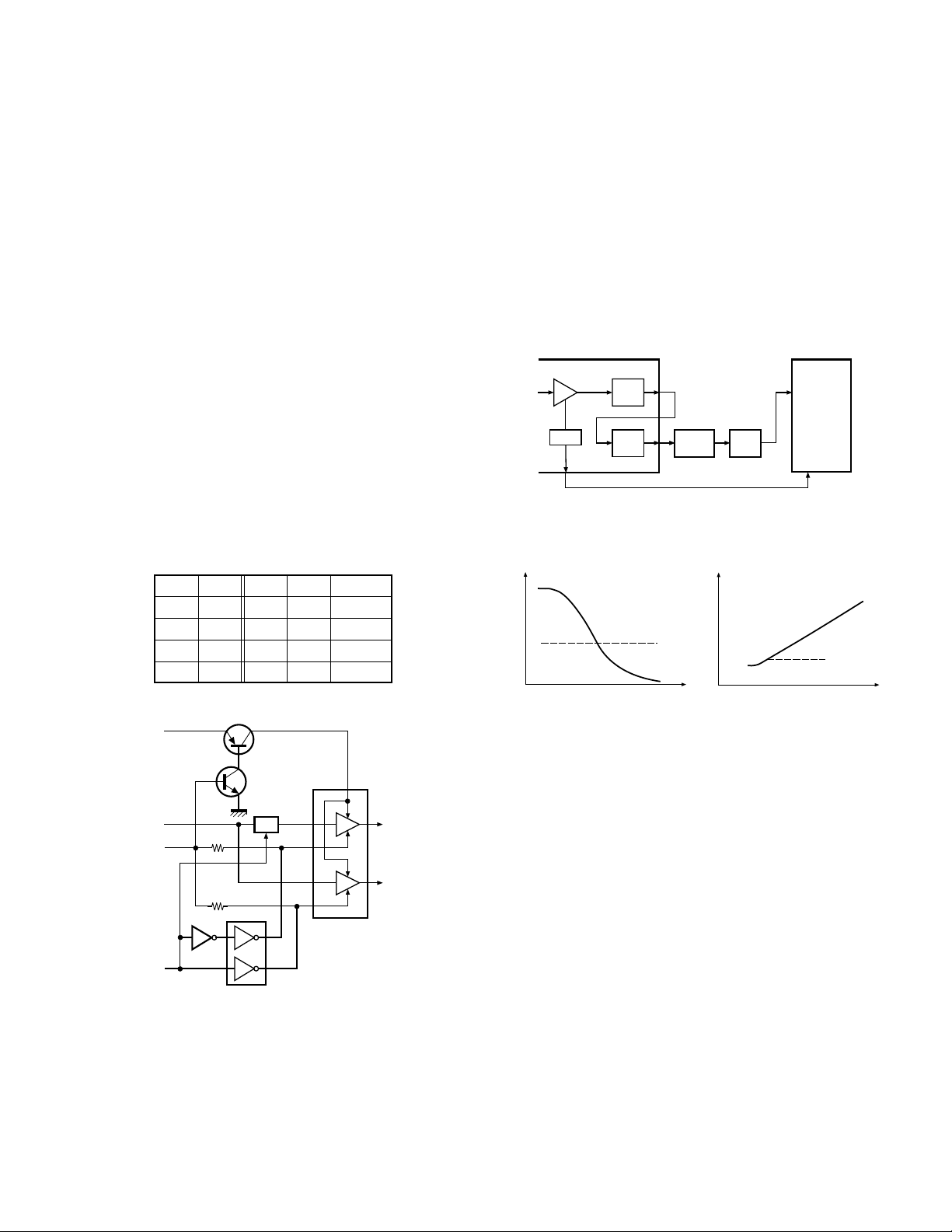
3-3. Audio amplifier circuit
The demodulated signal from IC9 is amplified by IC8 (2/
2), high-pass filtered, low-pass filtered, high-pass filtered,
band-eliminate filtered,and de-emphasized by IC12.
The signal then goes through an AF amplifier IC3 (2/2), an
electronic volume control (IC4), and an AF switch (Q310 is
on), and is routed to audio power amplifier (IC300), where it
is amplified and output to the internal speaker.
The audio mute signal (AM) from the microcomputer becomes Low in the standby and Q304, Q305 which are
power supply circuit for IC300 turn off. Also, IC12 is set to
the power down mode according to data from microprocessor, and the AF signal is muted. When the audio is output,
AM becomes High to turn Q304, Q305 ON, and voltage is
supplied to power terminal VP of IC300. Also, IC12 is canceled out of the power down mode.
The speaker is switched by the logic of speaker switching terminal SSW on the universal connector. When SP-MIC
is not attached, the logic of SSW becomes High and SW
(Q310) is turned ON, and the AF signal is input to both amplifiers of IC300.
When SP-MIC is attached, SSW is connected to GND at
inside of SP-MIC. For this reason, Q310 is turned OFF, and
the AF signal is input only to amplifier for EXT SP of IC300.
Change of INT/EXT SP refer to Fig. 3.
AM SSW VC1 VC2 SP
H H H L INT
H L L H EXT
L H L L MUTE
L L L L MUTE
3-4. Squelch circuit
The output from IC9 enters FM IC again, then passed
through a band-pass filter. The noise component output
from IC9 is amplified by Q19 and rectified by D3 to produce
a DC voltage corresponding to the noise level. The DC voltage is sent to the analog port of the CPU (IC15). And IC9
outputs a DC voltage (RSSI) corresponding to the input of
the IF amplifier. The CPU reads the RSSI signal via pin 24.
IC15 determines whether to output sounds from the
speaker by comparing the input voltage of pin 28 and pin 24
with the preset value.
IC9 : FM IF IC
IF AMP
DET
RSSI BPF
12
AMP
7
Q19 D3
NOISE
AMP
DET
28
IC15
CPU
24
Fig. 4 Squelch circuit
SB
AF
AM
SSW
Q301
Q308
Q305
Q304
SW
VC1
2
VC2
8
Fig. 3 Audio amplifier circuit
VP
IC300
Fig. 5
5
INT. SP
4. Transmitter System
Squelch and RSSI voltage vs ANT input level
4-1. Microphone amplifier
EXT. SP
The signal from the internal microphone goes through
the mute switch (Q300).
When the SP-MIC is not attached, the microphone
switching terminal (MSW) on the universal connector becomes High, and mute switch (Q300) is turned ON. When
the SP-MIC is attached, MSW is connected to GND at inside
of SP-MIC. For this reason, Q300 is turned OFF, the internal
microphone is muted, and only the input of the external microphone is supplied to the microphone amplifier of the TXRX unit.
15
TK-480/481
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The signal from microphone passes through the limitter
circuit in D11, and through the high-pass filter, the ALC circuit, the low-pass filter, the high-pass filter, and pre-emphasis/IDC circuit in IC12. When encoding DTMF, mute switch
(Q7) is turned OFF for muting the microphone input signal.
The signal passes through the D/A converter (IC4) for the
maximum deviation adjustment, and enters the summing
amplifier consisting of IC3 (2/2), and is mixed with the low
speed data from the CPU (IC15).
The output signal from the summing amplifier passes
through the D/A converter (IC4) again for the TA maximum
deviation adjustment,and the AF switch (Q21 is off in TX),
and goes to the VCO modulation input.
The other output signal from the summing amplifier
passes through the D/A converter (IC4) again for the BAL
adjustment,and the buffer amplifier (IC1 (2/2)), and goes to
the VCXO modulation input.
EXT.
MIC
Q300
MIC
SW
MIC
D11
LIMIT
12
HPF ALC
4-2. Drive and Final amplifier
The signal from the T/R switch (D5 is on) is amplified by
the pre-drive (Q11) and drive amplifier (Q12) to 50mW.
The output of the drive amplifier is amplified by the RF
power amplifier (IC30) to 2.5W (1W when the power is low).
The RF power amplifier consists of two stages MOS FET
transistor. The output of the RF power amplifier is then
passed through the harmonic filter (LPF) and antenna switch
(D7 is on) and applied to the antenna terminal.
4-3. APC circuit
The APC circuit always monitors the current flowing
through the RF power amplifier (IC30) and keeps a constant
current. The voltage drop at R127, R128 and R129 is caused
by the current flowing through the RF power amplifier and
this voltage is applied to the differential amplifier (IC21 1/2).
IC21 (2/2) compares the output voltage of IC21 (1/2) with
the reference voltage from IC4, and the output of IC21 (2/2)
controls the VGG of the RF power amplifier to make the
both voltages to same voltage.
The change of power high/low is carried out by the
change of the reference voltage. Q14,15 and 18 are turned
on in transmit and the APC circuit is active.
DTMF
98IC12
19
PRE EMP
IDC
6
Q7
15
16
COMP LPF HPF
MUTE
SW
18
MSW
Q301
IC4
D/A
I5
O5
LSD
IC3 (2/2)
SUM
AMP
IC4
D/A
O2
I2
IC4
D/A
O1
I1
Fig. 6 Microphone amplifier
From
T/R SW
(D5)
+B
REF
VOL
(IC4)
Q11
Pre-DRIVE
AMP
R127
R128
R129
Q12
DRIVE
AMP
IC21
(1/2)
IC30
RF
POWER AMP
VDD VGG
IC21
(2/2)
LPF
Fig. 7 Drive and final amplifier and APC circuit
Q21
AF
MUTE
5R
IC1
BUFF
AMP
D7
ANT
SW
IC14
VCO
X2
VCXO
ANT
16
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-480/481
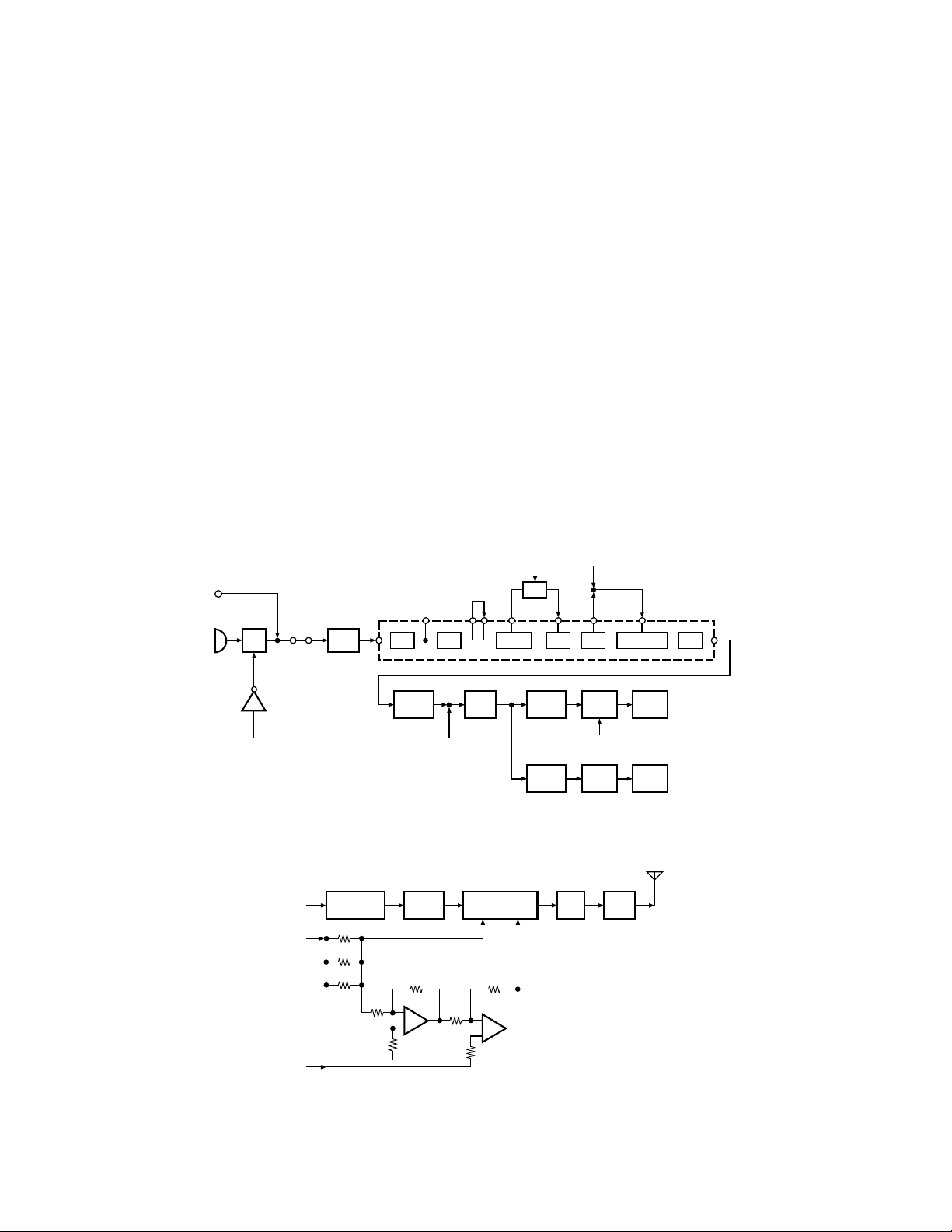
5. Frequency Synthesizer Unit
5-1. Frequency synthesizer
The frequency synthesizer consists of the VCXO (X2),
VCO (IC14), PLL IC (IC11) and buffer amplifiers.
The VCXO generates 16.8MHz. The frequency stability is
1.5ppm within the temperature range of –30 to +60°C. The
frequency tuning and modulation of the VCXO are done to
apply a voltage to pin 1 of the VCXO. The output of the
VCXO is applied to pin 8 of the PLL IC.
The TK-480’s VCO covers a dual range of the 806~
825MHz, and the 851~870MHz. The VCO generates
806.15~825.15MHz for providing to the first local signal in
receive. In TA mode, the pin 1 of the VCO goes low and the
VCO generates 851~870MHz.
The TK-481’s VCO covers a dual range of the 896~
902MHz, and the 935~941MHz. The VCO generates
890.15~896.15MHz for providing to the first local signal in
receive. In TA mode, the pin 1 of the VCO goes low and the
VCO generates 935~941MHz.
The output of the VCO is amplified by the buffer amplifier
(Q8) and routed to the pin 5 of the PLL IC. Also the output of
the VCO is amplified by the two-buffer amplifier (Q10, Q17)
and routed to the next stage according to T/R switch (D4,
D5).
The PLL IC consists of a prescaler, fractional divider, reference divider, phase comparator, charge pump. This PLL
IC is fractional-N type synthesizer and performs in the
100kHz reference signal which is eighth of the channel step
(12.5kHz). The input signal from the pins 1 and 5 of the PLL
IC is divided down to the 100kHz and compared at phase
comparator. The pulsed output signal of the phase comparator is applied to the charge pump and transformed into
DC signal in the loop filter (LPF). The DC signal is applied to
the pin 3 of the VCO and locked to keep the VCO frequency
constant.
PLL data is output from DT (pin 52), CP (pin 64) and EP
(pin 69) of the microprocessor (IC15). The data are input to
the PLL IC when the channel is changed or when transmission is changed to reception and vice versa. A PLL lock condition is always monitored by the pin 21 (UL) of the microprocessor. When the PLL is unlocked, the UL goes low.
6. Control Circuit
The control circuit consists of microprocessor (IC15) and
its peripheral circuits. It controls the TX-RX unit and transfers data to and from the display unit. IC15 mainly performs
the following;
1) Switching between transmission and reception by PTT
signal input.
2) Reading system, group, frequency, and program data
from the memory circuit.
3) Sending frequency program data to the PLL.
4) Controlling squelch on/off by the DC voltage from the
squelch circuit.
5) Controlling the audio mute circuit by decode data input.
6) Transmitting tone and encode data.
6-1. Memory circuit
Memory circuit consists of the CPU (IC15) and a flash
memory (IC17), a flash memory has a capacity of 2M bits
that contains the transceiver control program for the CPU
and data such as transceiver channels and operating features.
This program can be easily written from an external devices. The data, such as operating status, is programmed
into the EEPROM (IC16).
• Flash Memory
Note : The flash memory holds data such as written with
the FPU (KPG-49D), firmware program (User mode, Test
mode, Tuning mode, etc.) This data must be rewritten when
replacing the flash memory.
• EEPROM
Note : The EEPROM stores tuning data (Deviation, Squelch,
etc.).
Realign the transceiver after replacing the EEPROM.
IC15
CPU
IC16
EEPROM
TA
(TA : Low)
UL
CPU
IC15
BUFF
VCXO
Q10
BUFF
Q8
MB
TA
LPF
DT,CP,EP
18
IC14
VCO
IC11
PLL
CV
5
8
Fig. 8 PLL block diagram
Q17
BUFF
IC1
SW
To mixer
FC
BAL
D4
D5
SW
To
drive
amp
FLASH
IC17
Fig. 9 Memory circuit
17

TK-480/481
BUFF
AMP
VCXO
MB
X2IC1
AF
MUTE
VCO
MD
IC14Q21
LPF
35
HSD
OUT
IC23
R111 R107
C141
C138
R148
LSD
OUT
IC15
CPU
I3
I2
IC4
D/A (ADJ)
SUM
MIC IN
SUM
IC3 (1/2)
O2
I1
O1
IC12
AF AMPSUM
O5
I5
O3
36
O6
I6
IC3 (2/2)
RX audio
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
6-2. Low battery warning
The battery voltage is monitored by the microprocessor
(IC15). When the battery voltage falls below the voltage set
by the Low Battery Warning adjustment, the red LED
flashes to notify the operator that it is time to replace the
battery. If the battery voltage falls even more (approx. 5.8V),
a beep sounds and transmission is stopped.
Low battery warning Battery condition
The red LED flashes during The battery voltage is low but
transmission the transceiver is still usable.
The red LED flashes and The battery voltage is low and
continuous beep sounds the transceiver is not usable to
while PTT pressed make calls.
6-3. Key input
If the clock is supplied to CLK terminal when the RES
terminal (CPU pin 53) of the decade counter (IC301) is set to
Low, Q0 to Q7 become High sequentially. Normally, KI1 and
KI2 are Low (pulled down). When any key is pressed, KI1 or
KI2 become High. The CPU detects which key is pressed,
according to the voltage of KI1 and KI2 and clock timing.
Q5
Q1
Q0
Q2
Q6
Q7
Q3
Vss
CK
KRST
IC301
Vdd
RES
CLK
CL
CA
Q9
Q4
Q8
KI1
KI2
IC15
CPU
7. Signalling Circuit
7-1. Encode
• Low-speed data (QT,DQT,LTR)
Low-speed data is output from pin 36 of the CPU. The
signal passes through a low-pass CR filter, and goes to the
summing amplifier (IC3 1/2). The signal is mixed with the
audio signal and goes to the VCO (IC14) and VCXO (X2)
modulation input after passing through the D/A converter
(IC4) for BAL adjustment.
• High-speed data (DTMF)
High-speed data is output from pin 35 of the CPU. The
signal passes through a low-pass filter consisting of IC23,
and provides a TX DTMF tone and a RX DTMF tone including
a beep tone. The TX DTMF tone is passed to the D/A convertor (IC4) for DTMF deviation adjustment, and then applied to the audio processor (IC12).
The signal is mixed with the audio signal and goes to the
VCO and VCXO. The RX DTMF tone is passed a summing
amplifier (IC3 2/2), the D/A convertor (IC4) for audio control,
audio power amplifier and then to the speaker.
• MSK
MSK signal is output from pin 6 of IC12. The signal
passes through the D/A converter (IC4) for the MSK deviation adjustment, and is routed to the VCO. When encoding
MSK, the microphone input signal is muted.
18
RESET
CLOCK
CLOCK
INHIBIT
CARRY
OUT
16 keys
Fig. 10 Key input
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
Fig. 11 Decade counter timing chart
Fig. 12 Encode

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-480/481
7-2. Decode
• Low-speed data (QT,DQT,LTR)
The demodulated signal from the IF IC (IC9) is amplified
by IC8 (1/2) and passes through a low-pass filter (IC10) to
remove audio components. The signal is input to pin 23 of
the CPU.
The CPU digitizes this signal, performs processing such
as DC restoration, and decodes the signal.
• High-speed data (DTMF)
The DTMF input signal from the IF IC is amplified by IC8
(1/2) and goes to IC13, the DTMF decoder. The decoded information is then processed by the CPU. During transmission and standby, the DTMF IC is set to the power down
mode when the PD terminal is High. When the line is busy,
the PD terminal becomes Low, the power down mode is
canceled and decoding is carried out.
• MSK
The MSK input signal from the IF IC is amplified by IC8 (1/
2) and goes to pin 5 of IC12. The signal is demodulated by
MSK demodulator in IC12. The demodulated data goes to
the CPU for processing.
23
IC8
AMP
IC12
XOUT
IC10
LPF
IC13
DTMF
DECODE
OSC1
PD
DCK,SD,STD
LSD
IN
IC15
CPU
DT,CK,CE
7
IC19
Fig. 13 Decode
8. Power Supply Circuit
Battery +B is supplied via a 3A fuse from the battery terminal connected to the TX-RX unit. After passing through
the power switch, power supply (SB) is applied to the three
AVRs. IC5 supplies 5V (5M) to the control circuit, and IC7
supplies 5V (5C) to common circuits. IC6 supplies to the TX
circuit and the RX circuit. During transmission, 5TC becomes Low and Q2 is turned ON to supply 5V (5T) to the TX
circuit. During reception, 5RC becomes Low and Q1 is
turned ON to supply 5V (5R) to the RX circuit.
F1
+B
ON/OFF
VOL
Display unit
RF power amp (IC30)
SB
IC5
IC7
IC6
Q1
5M
5C
Q2
5T
5TC
5R
5RC
Fig. 14 Power supply circuit
9. Optional Board Terminal
Terminals for mounting the option board are provided at
the bottom edge of the TX-RX unit. The table below shows
the correspondence between the board and terminals.
R422, R32, R250, R259, R147, R276, R421 may have to be
removed depending on the type of option board being used.
Name Function
SB Battery (7.5V)
GND Ground
TXD Serial data
RXD Serial data
SQ Busy: high
LOK Link acquired : low (TX mode)
DI/ANI Modulation (ANI) input
DEO Detect output
TXAI/MUTE Modulation output from board or mic mute: low
TXAO Modulation input to board
RXAI Received signal input to board
RXAO Received signal output from board
D1 Binary 1
D2 Binary 2
OPT Scramble, Emergency: low
PTTIN PTT switch signal input to board (TX: low)
5CNS Battery (5V)
DI9 9600 bps data output
RXEMAO
RXEMAI
PTTOUT PTT switch signal output from board (TX: low)
MONI Busy: low
LAMP Busy: low
AAC
Audio Beep Beep signal output from board
AUX TXD Serial data
AUX RXD/EXTSW
Table 1 Terminal name and function
Received signal output from board (after de-emphasis)
Received signal input to board (after de-emphasis)
Audio Amp Control signal output from board (Busy: high)
Serial data/Option switch port
19

TK-480/481
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
Microprocessor : 30622M8A-4F9GP (TX-RX Unit IC15)
■ Pin function
Pin No. Port name I/O Function
1 LSDOUT O Low speed data output.
2 HSDOUT O High speed data output.
3 HSDIN I Not used.
4 DTMSTD I DTMF decode IC data detect input.
5 SELF I Not used.
6 BYTE I +5V.
7 CNVSS I GND.
8 SFTOE O Shift register output enable.
9 LCDCS O LCD driver chip select output.
10 RESET I Microcomputer reset input.
11 XOUT - 9.8304MHz (System clock).
12 VSS - GND.
13 XIN - 9.8304MHz (System clock).
14 VCC - +5V
15 AUX I AUX switch input.
16 AFTRD I MSK modulation data output timing
pulse input.
17 AFRTM I MSK demodulation data input timing
pulse input.
18 EN2 I Encoder pulse input 2.
19 PLLCLK O PLL IC clock output.
20 BEEP O Beep data output.
21 AFRDT I MSK demodulation data input.
22 AFREG1 O AF IC register switching data output 1.
23 AFREG2 O AF IC register switching data output 2.
24 EEPDAT O EEPROM data output.
25 DACSTB O D/A converter IC data strobe output.
26 AFCLR O MSK flame reset output.
27 SAVE O Not used.
28 LAMP I LAMP switch input.
29 AUXTXD O External Serial interface output.
30 AUXRXD I External Serial interface input.
31 PLLUL I PLL unlock detect input.
32 AFMSKE O
33 TXD O Serial interface output (ex. PC).
34 RXD I Serial interface input (ex. PC).
35 AFDAT O MSK data output.
36 PTT I PTT switch input.
37 RDY - Not used.
38 ALE - Not used.
MSK modulation enable (Enable active “H”).
Pin No. Port name I/O Function
39 HOLD - Not used.
40 HLDA - Not used.
41 BLCK - Not used.
42 RD - Flash memory RD bus.
43 BHE - Not used.
44 WR - Flash memory WR bus.
45 DTMCLK O DTMF decode IC clock output.
46 CNTCLK O Common clock output.
47 PLLSTB O PLL IC data strobe output.
48 CS0 O Flash memory chip enable.
49 A19 - Not used.
50~59 A18~A9 - Flash memory address bus.
60 VCC - +5V
61 A8 - Flash memory address bus.
62 VSS - GND.
63~70 A7~A0 - Flash memory address bus.
71 MONI I Monitor switch input.
72 EN4 I Not used.
73 EN3 I Not used.
74 EN1 I Encoder pulse input 1.
75 MINDAT O Common data output.
76 KEY2 I Key scan input 2.
77 KEY1 I Key scan input 1.
78 RESET O Key scan IC reset output..
79~86 D7~D0 - Flash memory data bus.
87 DTMDAT I DTMF decode IC data input.
88 PF I PF switch input.
89 VOL I Volume level input.
90 BATT I Battery voltage input.
91 ANLSQL I Squelch level input.
92 TEMP I Not used.
93 RSSI I
94 AVSS - GND.
95 LSDIN I Low speed data input.
96 VREF - +5V
97 AVCC - +5V
98 SFTSTB1 O Shift register data strobe output.
99 W/N O Not used.
100 AFSTB O AF IC data strobe output.
Received signal strength indicator input
(RSSI).
20

SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
TK-480/481
Shift Register 1 : BU4094BCFV (TX-RX Unit IC18)
Pin No.
Port
Port name
Function
1 STRB ES Strobe
2 DATA DAT Data
3 CLK CK Clock
4 Q1 LEDR Red LED. H : On, L : Off
5 Q2 LEDG Green LED. H : On, L : Off
6 Q3 KEYBLT Key backlight. H : On, L : Off
7 Q4 MMUTE MIC mute. H : Unmute, L : Mute
8 VSS GND.
9 QS IC18 data output.
10 Q’S NC
11 Q8 DTMPD DTMF decode IC power down.
H : Power down, L : Busy
12 Q7 Not used.
13 Q6 5TC TX power control. H : RX, L : TX
14 Q5 5RC RX power control. H : TX, L : RX
15 OE OE Output enable.
16 VDC 5M +5V.
Shift Register 2 : BU4094BCFV (TX-RX Unit IC19)
Pin No.
Port
Port name
Function
1 STRB ES Strobe
2 DATA DAT Data
3 CLK CK Clock
4 Q1 AM1 Audio mute 1. H : Unmute, L : Mute
5 Q2 LOK
Link complete (Programmable active H/L).
6 Q3 TA Talk around. H : Off, L : On
7Q4 NC
8 VSS GND
9QS NC
10 Q’S NC
11 Q8 SQ
External squelch (Programmable active H/L).
12 Q7 CODE2 Option board data 2.
13 Q6 CODE1 Option board data 1.
14 Q5 OPT Option board control.
Please set option board type in the
KPG-49D. H : On, L : Off
Auxiliary signal outut. Please set key
function in the KPG-49D (Program-
mable active H/L).
15 OE OE Output enable.
16 VDC 5M +5V.
VCO System : KCH31, KCH32 (TX-RX Unit IC14)
■ Circuit diagram
D1
Q1
C3
C2 C8
L2
C4
C13
R2
D2
C6
D1 : HVC350B
D2 : HVC202A
D3 : MA2S077
C5
D3
C7
R6
R4
R7
R3
R5
3
CV
2
MD
1
TA
Q1 : 2SK1824
Q2 : 2SC4226(R25)
Q3 : 2SC5008
L1
C1
R1
C16
C10
C9
C11
Q2 Q3
C12
R8
R9
L4
C14
4 OUT
C15
C17
L3
5 GND
6
5C
21

TK-480/481
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
PLL System : SA7025DK (TX-RX Unit IC11)
■ Block diagram
CLOCK
DATA
STROBE
Vss
RF
RF
TEST
V
CCP
REF
AUX
V
Serial input + Program latches
PR NM1
FBEM
2
IN
IN
IN
IN
EM÷EA
EA
64/65/72
Prescaler
EM
SM
2
NR
12
Reference divider
SA
2
EA
PA NA
12
1/4
Prescaler
NM2
NM3
2
12 8
Main dividers
Main phase
detector
Main
reference
select
÷2 ÷2 ÷2
Auxiliary
reference
select
Auxiliary
phase
detector
Auxiliary divider
FMOD NF
Fractional
accumulator
FRD
CN
CK
3
8
CL
2
4
2
Prescaler
modulus control
Normal output
charge pump
Speed-up
output
charge pump
Integral output
charge pump
Auxiliary output
charge pump
FB
DD
RF
RN
PHP
PHI
RA
PHA
LOCK
V
DDA
V
SSA
■ Pin description
Pin No.
Symbol Description
1 CLOCK Serial clock input.
2 DATA Serial data input.
3 STROBE Serial strobe input.
4VSS Digital ground.
5RFIN Prescaler positive input.
6RFIN Prescaler negative input.
7VCCP Prescaler positive supply voltage. This pin supplies power to the prescaler and RF input buffer.
8 REFIN Reference divider input.
9 RA Auxiliary current setting; resistor to VSSA.
10 AUXIN Auxiliary divider input.
11 PHA Auxiliary phase detector output.
12 VSSA analog ground.
13 PHI Integral phase detector output.
14 PHP Proportional phase detector output.
15 VDDA
Analog supply voltage. This pin supplies power to the charge pumps, Auxiliary prescaler, Auxiliary and Reference buffers.
16 RN Main current setting; resistor to VSSA.
17 RF
Fractional compensation current setting; resistor to V
SSA
.
18 LOCK Lock detector output.
19 TEST Test pin; connect to VDD.
20 VDD Digital supply voltage. This pin supplies power to the CMOS digital part of the device.
22

DESCRIPTION OF COMPONENTS
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX)
Ref. No.
IC300 IC Audio power amplifier
IC301 IC Counter / Key scan
Q300 FET DC switch / INT MIC on/off
Q301 FET DC switch
Q302 Transistor DC switch / LED (Red) driver
Q303 Transistor DC switch / LED (Green) driver
Q304 Transistor DC switch
Q305 Transistor Current driver / Audio amp AVR
Q306 Transistor DC switch
Q307 Transistor Current driver /
Q308 FET DC switch / SP INT/EXT
Q309 Transistor Temperature compensation
Q310 FET Mute switch
D300 Zener diode Surge absorption
D301 LED LED / Red, Green
D302 Diode Quick discharge / AF mute
D303 Zener diode Voltage reference
D304 Diode Voltage reference
D305~310 LED LCD back light
D315~318 Diode Reverse current prevention
D319~321 Zener diode Surge absorption
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX)
Ref. No.
IC1 IC Buffer amplifier
IC2 IC Voltage detector / Reset
IC3 IC Summing amplifier
IC4 IC D/A converter (Adjustment)
IC5 IC Voltage regulator / 5M
IC6 IC Voltage regulator / 5V
IC7 IC Voltage regulator / 5C
IC8 IC Buffer amplifier
IC9 IC FM IF system
IC10 IC Active filter / For LSDin
IC11 IC PLL system
IC12 IC Audio processor
IC13 IC DTMF decoder
IC14 IC VCO system
Use/ Function
Use/ Function
Operation/Condition
LCD back light LED AVR
Operation/Condition
TK-480/481
Ref. No.
IC15 IC Microprocessor / 16-bit+1M flash
IC16 IC EEPROM
IC17 IC AND gate
IC18,19 IC Shift register / Output expander
IC21 IC Comparator (APC)
IC23 IC Active filter / For HSDout
IC30 IC Power module
Q1 FET DC switch / 5R
Q2 Transistor DC switch / 5T
Q3 Transistor Ripple filter / 5CV
Q4 Transistor TX/RX switch
Q5 Transistor IF amplifier
Q6 FET Mixer
Q7 FET Mute switch / MIC line mute
Q8 Transistor RF amplifier
Q9 FET RF amplifier
Q10 Transistor Buffer amplifier
Q11,12 Transistor RF amplifier / TX driver
Q13 FET DC switch
Q14,15 Transistor DC switch
Q16 Transistor AF mute switch
Q17 Transistor RF amplifier
Q18 FET DC switch
Q19 Transistor Noise amplifier / Squelch
Q20 Transistor Switch
Q21 FET AF mute switch
Q22 FET DC switch
Q23 FET Mute switch
D1 Diode Reverse protection
D2 Diode Overload protection
D3 Diode Noise detection
D4,5 Diode TX/RX switch
D6 Diode Overload protection
D7 Diode ANT switch
D8 Diode Reverse current prevention
D9,10 Diode ANT switch
D11 Diode Voltage clamp
D12 Diode DC switch
D17,18 Diode Surge absorption
Use/ Function
Operation/Condition
23

TK-480/48 1
PARTS LIST
✽ New Parts.
Parts without Parts No. are not supplied.
Les articles non mentionnes dans le Parts No. ne sont pas fournis.
Teile ohne Parts No. werden nicht geliefert.
TK-480/481
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX)
Ref. No.
indicates safety critical components.
New
Address
parts
Parts No. Description
TK-480/481
11A✽ A02-3658-03 CABINET ASSY (4KEY) A,B-K
11A✽ A02-3659-03 CABINET ASSY (16KEY) A,B-K2
22B✽ A62-0981-04 PANEL ASSY
4 2C B09-0363-03 CAP (SP/MIC) ACSY
5 2A B38-0810-05 LCD ASSY
61B✽ B43-1139-04 BADGE (KENWOOD)
7 1C B46-0470-00 WARRANTY CARD
92C✽ B62-1483-00 INSTRUCTION MANUAL
10 3A ✽ B72-1968-04 MODEL NAME PLATE A-K,K2
10 3A ✽ B72-1969-04 MODEL NAME PLATE B-K,K2
12 3B E04-0406-05 RF COAXIAL RECEPTACLE (SMA)
15 2B E23-1049-04 TERMINAL (ANT)
51 3A ✽ E23-1166-04 RELAY TERMINAL
16 2A E37-0672-05 FLAT CABLE (C0NT-TX-RX)
17 3A E37-0673-05 LEAD WIRE WITH CONNECTOR (PTT)
18 1A E37-0674-15 LEAD WIRE WITH CONNECTOR (SP)
19 3B E58-0440-05 SQUARE SOCKET (SP/MIC)
52 3A E72-0412-13 TERMINAL BLOCK
54 2A F10-2248-13 SHIELDING CASE (VC0)
55 2A F10-2253-03 SHIELDING PLATE (BAND PASS)
56 2A F10-2255-04 SHIELDING PLATE (P-MODULE)
57 2A F10-2310-03 SHIELDING PLATE (LCD)
- F20-1192-04 INSULATING SHEET
- F20-3303-04 INSULATING SHEET (MIC/GND)
21 1A G01-0881-04 COIL SPRING
22 1B G09-0418-05 KNOB SPRING (VOL,ENC)
23 1B G10-0799-04 FIBROUS SHEET (SP)
24 3A G11-0800-04 SHEET (PTT)
61 3A G11-2544-04 SHEET (CHASSIS)
62 2A G13-1731-04 CUSHION (LCD)
63 3A,3B G13-1762-04 CUSHION (VOL/CHASSIS)
64 3A ✽ G13-1834-04 CUSHION (TERMINAL)
26 3B G53-0811-03 PACKING (TOP)
25 1A G53-0840-02 PACKING (4KEY) A,B-K
25 1A G53-0841-02 PACKING (16KEY) A,B-K2
65 3A ✽ G53-1510-04 PACKING (BATT+)
66 3A ✽ G53-1520-24 PACKING (TERMINAL)
28 2D H12-3014-02 PACKING FIXTURE
29 3D ✽ H52-1096-12 ITEM CARTON CASE A-K,K2
29 3D ✽ H52-1097-12 ITEM CARTON CASE B-K,K2
31 1A J19-1572-04 HOLDER
68 2A J21-8321-03 HARDWARE FIXTURE (P-MODULE)
32 2C J29-0658-05 HOOK ACSY
33 3B J82-0045-05 FPC (VOL,ENC)
34 3B J82-0046-05 FPC (SOCKET)
38 1B K29-5157-03 KNOB (PTT)
39 1B K29-5158-03 KEY TOP (PTT)
40 1A K29-5165-03 LEVER KNOB
36 1B K29-5231-03 KNOB (VOL)
37 1B K29-5232-03 KNOB (ENC)
A 2B N14-0569-04 CIRCULAR NUT (VOL,ENC)
Destination
L : Scandinavia K : USA P : Canada
Y : PX (Far East, Hawaii) T : England E : Europe
Y : AAFES (Europe) X: Australia M: Other Areas
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
PAN HEAD SEMS SCREW W (P-MODULE)
PAN HEAD TAPTITE SCREW (TERMINAL)
VARIABLE RESISTOR (POWER SW/VOL)
Ref. No.
B 3B N30-2605-46 PAN HEAD MACHINE SCREW (ANT)
C 3A N30-2610-46 PAN HEAD MACHINE SCREW (CASE)
D 2A N67-2606-46
F3A✽ N79-2025-46
E 2A,1B N83-2005-46 PAN HEAD TAPTITE SCREW (UNIT)
42 2C N99-2004-05 SCREW SET ACSY
44 3B R31-0617-05
S300 - S70-0414-05 TACT SWITCH
46 1A T07-0714-05 SPEAKER
47 2C ✽ T90-0636-25 WHIP ANTENNA (800MHZ) ACSY A-K,K2
47 2C ✽ T90-0640-25 WHIP ANTENNA (900MHZ) ACSY B-K,K2
MIC300 1A T91-0579-05 MIC ELEMENT
49 2B W02-1814-05 ENCODER
50 1D ✽ W09-0900-35 BATTERY ASSY ACSY
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX) -10 : K -11 : K2
D301 B30-2019-05 LED (RE/GR) (BUSY/TX)
D305-310 B30-2171-05 LED (BACKLIGHT) A,B-K2
D305,306 B30-2171-05 LED (BACKLIGHT)
C301 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C302 C92-0560-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 6.3WV
C304 CK73FB1C474K CHIP C 0.47UF K
C305 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C307 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C308 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C309 CK73FB1C474K CHIP C 0.47UF K
C310 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C311 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C312 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C313 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
C314 C92-0647-05 CHIP-TAN 3.3UF 4WV
C315 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C316,317 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C318 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C321-333 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C335-339 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C340 CK73GB1E153K CHIP C 0.015UF K
C341-344 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
CN300 E40-5891-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR (24P)
CN301 E40-5892-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR (14P)
CN302 E40-5662-05 PIN ASSY SOCKET (SP)
CN303 E40-5887-05 PIN ASSY (PTT)
CN304 E40-5823-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR (LCD)
L300,301 L92-0141-05 FERRITE CHIP
L302,303 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L304,305 L92-0141-05 FERRITE CHIP
L306,307 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L308,309 L92-0141-05 FERRITE CHIP
CP300,301 R90-0723-05 MULTI-COMP 47K X2
CP302 R90-0724-05 MULTI-COMP 1K X4 A,B-K2
CP303 R90-0724-05 MULTI-COMP 1K X4
Desti-
nation
24
A : TK-480 (K,K2)
B : TK-481 (K,K2)

PARTS LIST
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description Ref. No.
Ref. No.
R300 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R301 RK73FB2A101J CHIP R 100 J 1/10W
R302 RK73GB1J470J CHIP R 47 J 1/16W
R303 RK73GB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R304 RK73GB1J182J CHIP R 1.8K J 1/16W
R305 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R306 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R307 RK73GB1J821J CHIP R 820 J 1/16W
R308 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W
R309 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R310 RK73GB1J331J CHIP R 330 J 1/16W
R311 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R312 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R313,314 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R315 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R316 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R317 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R318 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R319 RK73GB1J820J CHIP R 82 J 1/16W
R320,321 RK73GB1J820J CHIP R 82 J 1/16W A,B-K2
R324 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R325 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W A,B-K2
R326 RK73GB1J124J CHIP R 120K J 1/16W
R327 RK73GB1J563J CHIP R 56K J 1/16W
R328 RK73GB1J124J CHIP R 120K J 1/16W
R331 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R332 RK73GB1J272J CHIP R 2.7K J 1/16W
R333 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R336 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R337 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R338-341 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
Destination
TK-480/48 1
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX)
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX)
New
Address
Parts No. Description
parts
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX) -10 : TK-480 -11 : TK-481
C1,2 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C3,4 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C5 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C6 C92-0507-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 6.3WV
C7 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C8 CK73GB1E223K CHIP C 0.022UF K
C9 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C10 C92-0507-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 6.3WV
C11 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C12,13 C92-0507-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 6.3WV
C14 C92-0576-05 CHIP-TAN 1.0UF 6.3WV
C15 CC73GCH1H100D CHIP C 10PF D
C16,17 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C18 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C19-23 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C24 C92-0507-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 6.3WV
C25 CK73FB1A105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
C26 CK73GB1E123K CHIP C 0.012UF K
C27 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C28-30 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C31 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C32 CK73GB1H472K CHIP C 4700PF K
C33 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C34 C92-0560-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 6.3WV
C35 CK73GB1C333K CHIP C 0.033UF K
C36 CC73GCH1H820J CHIP C 82PF J
C37 C92-0560-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 6.3WV
C38 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C39 CC73GCH1H221J CHIP C 220PF J
C40 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
Destination
S301-303 S70-0457-05 TACT SWITCH (PTT)
D300 NNCD6.8G ZENER DIODE
D302 1SS373 DIODE
D303 015AZ2.4-X ZENER DIODE
D304 MA2S111 DIODE
D315 IMN10 DIODE A,B-K2
D316 MA2S111 DIODE A,B-K2
D317 MA2S111 DIODE
D318 IMN10 DIODE
D319-321 015AZ6.8 ZENER DIODE
IC300 TDA7053AT IC (AUDIO AMP)
IC301 ✽ TC74HC4017AF IC (COUNTER)
Q300 2SJ243 FET
Q301 UPA672T FET
Q302-304 2SC4617(S) TRANSISTOR
Q305 2SB798(DL,DK) TRANSISTOR
Q306 2SC4617(S) TRANSISTOR
Q307 2SB1132(Q,R) TRANSISTOR
Q308 UPA672T FET
Q309 2SC4617(S) TRANSISTOR
Q310 2SK1824 FET
TH300 TN10-3S154JT THERMISTOR
A : TK-480 (K,K2)
B : TK-481 (K,K2)
C41 CK73FB1C334K CHIP C 0.33UF K
C42 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C43 C92-0513-05 CHIP-TAN 3.3UF 6.3WV
C44 C92-0662-05 CHIP-TAN 15UF 6.3WV
C45 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C46 CC73GCH1H221J CHIP C 220PF J
C47 CK73GB1E223K CHIP C 0.022UF K
C48 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C49,50 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C51 CK73GB1E223K CHIP C 0.022UF K
C52-54 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C55 CC73GCH1H150J CHIP C 15PF J
C56 CK73GB1H222K CHIP C 2200PF K
C57 CK73GB1E153K CHIP C 0.015UF K
C58 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C59 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C60 CC73GCH1H100D CHIP C 10PF D
C61 CC73GCH1H040C CHIP C 4.0PF C B-K,K2
C62 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C63 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C64 CC73GCH1H271J CHIP C 270PF J
C65 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C66 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C67 CK73GB1H122J CHIP C 1200PF J
C68 CC73GCH1H040C CHIP C 4.0PF C B-K,K2
C69 C92-0559-05 CHIP-TAN 6.8UF 6.3WV
C70-72 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C73 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
25

TK-480/48 1
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX)
Ref. No.
C74 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C75 CK73GB1C333K CHIP C 0.033UF K
C76 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C77 CK73GB1H562J CHIP C 5600PF J
C78 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
Address
New
Parts No. Description Ref. No.
parts
PARTS LIST
Destination
C137 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C138 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C139 CC73GCH1H030C CHIP C 3.0PF C A-K,K2
C139 CC73GCH1H020C CHIP C 2.0PF C B-K,K2
C140 CK73FB1A105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
Destination
C79 CC73GCH1H121J CHIP C 120PF J
C80 CK73GB1C683K CHIP C 0.068UF K
C81 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C82,83 CK73GB1H562J CHIP C 5600PF J
C84 CC73GCH1H150J CHIP C 15PF J
C85 CK73GB1H272J CHIP C 2700PF J
C86 CK73GB1C333K CHIP C 0.033UF K
C87 CC73GCH1H030C CHIP C 3.0PF C
C88 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C89,90 CK73GB1H272J CHIP C 2700PF J
C91 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C92 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C93 CC73GCH1H151J CHIP C 150PF J
C94 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C95 C92-0504-05 CHIP-TAN 0.68UF 20WV A-K,K2
C95 C92-0003-05 CHIP-TAN 0.47UF 25WV B-K,K2
C96 CK73GB1H122K CHIP C 1200PF K A-K,K2
C96 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K B-K,K2
C97 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C98 CC73GCH1H030C CHIP C 3.0PF C
C99 CC73GCH1H1R5B CHIP C 1.5PF B
C100 CC73GCH1H391J CHIP C 390PF J A-K,K2
C100 CK73GB1H821K CHIP C 820PF K B-K,K2
C101 C92-0560-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 6.3WV
C102 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C103,104 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C105 CK73GB1C473K CHIP C 0.047UF K
C106-108 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C109 C92-0507-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 6.3WV
C110 CC73GCH1H1R5B CHIP C 1.5PF B
C141 CK73GB1H472K CHIP C 4700PF K
C142,143 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C144 CK73GB1C273K CHIP C 0.027UF K
C145,146 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C147,148 CK73HB1C103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C149 CC73GCH1H040C CHIP C 4.0PF C
C150,151 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C152 CC73GCH1H020C CHIP C 2.0PF C
C153 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C154 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C155 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C156 C92-0507-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 6.3WV
C157 CC73GCH1H680J CHIP C 68PF J
C158 CC73GCH1H270J CHIP C 27PF J
C159 CK73FB1H563K CHIP C 0.056UF K
C160,161 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C162 CC73GCH1H270J CHIP C 27PF J
C163 CK73FB1C474K CHIP C 0.47UF K
C164,165 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C166 CC73GCH1H010C CHIP C 1.0PF C A-K,K2
C166 CC73GCH1HR75C CHIP C 0.75PF C B-K,K2
C167 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C168 CC73GCH1H020C CHIP C 2.0PF C
C169-172 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C173 CC73GCH1H020C CHIP C 2.0PF C
C174 CC73GCH1H1R5C CHIP C 1.5PF C
C175 CC73GCH1H030C CHIP C 3.0PF C
C176 CC73GCH1H010C CHIP C 1.0PF C A-K,K2
C176 CC73GCH1HR75C CHIP C 0.75PF C B-K,K2
C177 CK73GB1C473K CHIP C 0.047UF K
C111,112 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C113 CK73GB1C473K CHIP C 0.047UF K
C114,115 CK73GB1H472K CHIP C 4700PF K A-K,K2
C114,115 CK73GB1H332K CHIP C 3300PF K B-K,K2
C116 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C117 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C118 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C119 CC73GCH1HR75C CHIP C 0.75PF C
C120 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C121 CK73GB1E153K CHIP C 0.015UF K
C122 CC73GCH1H1R5C CHIP C 1.5PF C A-K,K2
C122 CC73GCH1H030C CHIP C 3.0PF C B-K,K2
C123 C92-0507-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 6.3WV
C124 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C125 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C126 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C127-129 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C130 CC73GCH1H100D CHIP C 10PF D
C131 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C132 CC73GCH1H010C CHIP C 1.0PF C A-K,K2
C132 CC73GCH1HR75C CHIP C 0.75PF C B-K,K2
C133 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C134 CC73GCH1H010B CHIP C 1.0PF B A-K,K2
C135 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C136 CC73GCH1H030C CHIP C 3.0PF C
26
C178-180 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C181,182 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C183 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C184 CC73GCH1H030C CHIP C 3.0PF C
C185 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C186 CC73GCH1H1R5C CHIP C 1.5PF C
C187 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C188-191 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C192 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C193 CC73GCH1H020C CHIP C 2.0PF C A-K,K2
C193 CC73GCH1H1R5C CHIP C 1.5PF C B-K,K2
C194-199 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C200 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C201 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C202 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C203 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C204 C92-0003-05 CHIP-TAN 0.47UF 25WV
C205,206 CK73HB1C103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C207 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C208,209 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C261,262 CK73HB1C103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C263 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
CN1 E40-5823-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR (10P)
CN2 E40-9517-05 PIN ASSY SOCKET (4P)
A : TK-480 (K,K2)
B : TK-481 (K,K2)

PARTS LIST
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description Ref. No.
CRYSTAL RESONATOR (3.579545MHZ)
Ref. No.
CN3 E40-5890-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR (24P)
CN4-9 E23-1002-05 TERMINAL
CN10 E23-0342-05 TEST TERMINAL
CN11,12 E23-1002-05 TERMINAL
F1 F53-0130-05 FUSE (3A)
F1 F53-0217-05 FUSE (3A)
CD1 L79-1072-05 TUNING COIL
CF1,2 L72-0924-05 CERAMIC FILTER (455KHZ) A-K,K2
CF1,2 L72-0939-05 CERAMIC FILTER (455KHZ) B-K,K2
L1 L92-0149-05 FERRITE CHIP
L3 L40-1095-34 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (1UH)
L4 L40-4791-37 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (4.700UH)
L5 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L6,7 L40-3985-45 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (0.39UH)
L8 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L9 L40-1075-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10NH) A-K,K2
L9 L40-6865-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (6.8NH) B-K,K2
L10 L40-8265-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (8.2NH) A-K,K2
L10 L40-6865-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (6.8NH) B-K,K2
L11 L79-1464-05 DIELECTRIC FILTER (860MHZ) A-K,K2
L11 L79-1466-05 DIELECTRIC FILTER (938MHZ) B-K,K2
L12 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L13,14 L40-1075-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10NH)
L15 L40-5663-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (5.6NH) A-K,K2
L15 L40-2763-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (2.7NH) B-K,K2
L16 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L17 L40-1075-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10NH) A-K,K2
L17 L40-8265-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (8.2NH) B-K,K2
L18 L40-2275-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (22NH) A-K,K2
L18 L40-6865-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (6.8NH) B-K,K2
L19 L40-1075-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10NH) A-K,K2
L19 L40-1275-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (12NH) B-K,K2
L20 L79-1465-05 DIELECTRIC FILTER (860MHZ) A-K,K2
L20 L79-1467-05 DIELECTRIC FILTER (938MHZ) B-K,K2
L21 L40-6865-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (6.8NH) A-K,K2
L21 L40-5663-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (5.6NH) B-K,K2
L22,23 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L24 L40-6865-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (6.8NH) A-K,K2
L24 L40-5663-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (5.6NH) B-K,K2
L25 L92-0149-05 FERRITE CHIP
L26 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L27 L40-6875-54 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (68NH)
L28 L33-0761-05 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L29 L40-1075-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10NH)
L30 L79-1468-05 FILTER MODULE (870MHZ) A-K,K2
L30 L79-1469-05 FILTER MODULE (960MHZ) B-K,K2
L31 L33-0760-05 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L32 L40-6875-54 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (68NH)
L34 L40-8265-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (8.2NH) A-K,K2
L34 L40-1075-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10NH) B-K,K2
L35 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L53-56 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
X1 L77-1760-15 CRYSTAL RESONATOR (44.395MHZ)
X2 L77-1699-15 VCXO (16.8MHZ)
X3 L77-1708-05
X4 L78-0462-05 RESONATOR (9.8304MHZ)
XF1 L71-0501-05 MCF (44.85MHZ) A-K,K2
XF1 L71-0502-05 MCF (44.85MHZ) B-K,K2
A : TK-480 (K,K2)
B : TK-481 (K,K2)
Destination
TK-480/48 1
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX)
New
Address
CP1 R90-0718-05 MULTI-COMP 4.7K X4
CP3 R90-0743-05 MULTIPLE RESISTOR
CP5 R90-0743-05 MULTIPLE RESISTOR
CP6-21 R90-0741-05 MULTIPLE RESISTOR
CP22 R90-0743-05 MULTIPLE RESISTOR
CP24 R90-0743-05 MULTIPLE RESISTOR
R1,2 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R3 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R4 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
R5 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R6 RK73GB1J184J CHIP R 180K J 1/16W
R7 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R8 RK73GB1J183J CHIP R 18K J 1/16W A-K,K2
R8 RK73GB1J273J CHIP R 27K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R9 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
R10 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R11 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W A-K,K2
R11 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R12 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R13 RK73GB1J683J CHIP R 68K J 1/16W
R14 RK73GB1J394J CHIP R 390K J 1/16W
R15 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R16 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R17 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R18 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R19 RK73GB1J152J CHIP R 1.5K J 1/16W
R20 RK73GB1J683J CHIP R 68K J 1/16W
R21 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
R22 RK73GB1J182J CHIP R 1.8K J 1/16W
R23 RK73GB1J563J CHIP R 56K J 1/16W A-K,K2
R23 RK73GB1J124J CHIP R 120K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R24 RK73GB1J274J CHIP R 270K J 1/16W
R25 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R26 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R27 RK73GB1J222J CHIP R 2.2K J 1/16W
R28 RK73GB1J220J CHIP R 22 J 1/16W
R29 RK73GB1J183J CHIP R 18K J 1/16W A-K,K2
R29 RK73GB1J123J CHIP R 12K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R31 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R32 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R33 RK73GB1J123J CHIP R 12K J 1/16W
R34 RK73GB1J334J CHIP R 330K J 1/16W
R35 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R36 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R37 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R38 RK73GB1J151J CHIP R 150 J 1/16W
R39 RK73GB1J560J CHIP R 56 J 1/16W
R40 RK73GB1J272J CHIP R 2.7K J 1/16W
R41 RK73GB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R42,43 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R44 R92-0670-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R45 RN73GH1J913D CHIP R 91K D 1/16W
R46 RN73GH1J683D CHIP R 68K D 1/16W
R47 RN73GH1J913D CHIP R 91K D 1/16W
R48 RN73GH1J333D CHIP R 33K D 1/16W
R49 RK73GB1J684J CHIP R 680K J 1/16W
R50 RK73GB1J564J CHIP R 560K J 1/16W
R51 RK73GB1J331J CHIP R 330 J 1/16W
R53 RN73GH1J274D CHIP R 270K D 1/16W
R54 RK73GB1J334J CHIP R 330K J 1/16W
Parts No. Description
parts
Destination
27

TK-480/48 1
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX)
Ref. No.
R55 RN73GH1J913D CHIP R 91K D 1/16W
R56 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R57 RK73GB1J334J CHIP R 330K J 1/16W
R58 RN73GH1J682D CHIP R 6.8K D 1/16W
R59 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
Address
New
Parts No. Description Ref. No.
parts
PARTS LIST
Destination
R112 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R113 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W A-K,K2
R113 RK73GB1J220J CHIP R 22 J 1/16W B-K,K2
R114 RK73GB1J152J CHIP R 1.5K J 1/16W
R115 RK73GB1J681J CHIP R 680 J 1/16W
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
Destination
R60 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R61 RK73GB1J155J CHIP R 1.5M J 1/16W
R62 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R63 RN73GH1J683D CHIP R 68K D 1/16W
R64 RK73GB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R65 RK73GB1J560J CHIP R 56 J 1/16W
R66 RN73GH1J682D CHIP R 6.8K D 1/16W
R67,68 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R69 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W A-K,K2
R69 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R70 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W
R71 RK73GB1J224J CHIP R 220K J 1/16W
R72 RK73GB1J152J CHIP R 1.5K J 1/16W A-K,K2
R72 RK73GB1J222J CHIP R 2.2K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R73 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R74 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R75 RK73GB1J152J CHIP R 1.5K J 1/16W
R76 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R77 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W
R78 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R79 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R80 RK73GB1J394J CHIP R 390K J 1/16W A-K,K2
R80 RK73GB1J684J CHIP R 680K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R81 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R82 RK73GB1J333J CHIP R 33K J 1/16W A-K,K2
R82 RK73GB1J393J CHIP R 39K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R83 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R84 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R85 RK73GB1J681J CHIP R 680 J 1/16W
R86 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
R116 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R117 RK73GB1J470J CHIP R 47 J 1/16W
R118 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R120 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R121 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R122 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R123 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R124,125 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R126 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R127-129 RK73EB2ER39K CHIP R 0.39 K 1/4W
R130-135 RN73GH1J154D CHIP R 150K D 1/16W
R136,137 RK73GB1J271J CHIP R 270 J 1/16W
R138 RK73HB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R139 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R140 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R141,142 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R143 RK73GB1J105J CHIP R 1.0M J 1/16W
R144 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R145 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R146 RK73GB1J222J CHIP R 2.2K J 1/16W
R147 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R148 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R149 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R150 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R151 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R152 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R153 RK73GB1J123J CHIP R 12K J 1/16W
R154 RK73GB1J221J CHIP R 220 J 1/16W
R155 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R156 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R87 RK73GB1J470J CHIP R 47 J 1/16W
R88 RK73GB1J220J CHIP R 22 J 1/16W
R89 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R90 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R91 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R92,93 RK73GB1J150J CHIP R 15 J 1/16W
R94 RK73GB1J272J CHIP R 2.7K J 1/16W
R95 RK73GB1J150J CHIP R 15 J 1/16W
R96 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R97 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R98 RK73GB1J184J CHIP R 180K J 1/16W
R99 RK73GB1J121J CHIP R 120 J 1/16W A-K,K2
R100 RK73GB1J820J CHIP R 82 J 1/16W A-K,K2
R100 RK73GB1J221J CHIP R 220 J 1/16W B-K,K2
R101 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R102 RK73GB1J182J CHIP R 1.8K J 1/16W
R103 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R104 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R105 RK73GB1J122J CHIP R 1.2K J 1/16W
R106 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R107 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R108 RK73GB1J682J CHIP R 6.8K J 1/16W
R109 RK73GB1J470J CHIP R 47 J 1/16W
R110 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R111 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
28
R157 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R158 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R159,160 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R161,162 RK73GB1J184J CHIP R 180K J 1/16W
R163 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R164 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R165 RK73GB1J150J CHIP R 15 J 1/16W A-K,K2
R165 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM B-K,K2
R166 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W B-K,K2
R167 RK73GB1J123J CHIP R 12K J 1/16W
R168 RK73GB1J333J CHIP R 33K J 1/16W
R169 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R170 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R171 RK73GB1J823J CHIP R 82K J 1/16W
R200-207 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R211 RK73HB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R218 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R248 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R250 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R259 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R276 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R297,298 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R408 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R417 RK73GB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R418 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
A : TK-480 (K,K2)
B : TK-481 (K,K2)

PARTS LIST
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description Ref. No.
Ref. No.
R419-422 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R423 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
D1 1SR154-400 DIODE
D2 MA2S111 DIODE
D3 MA742 DIODE
D4,5 MA2S077 DIODE
D6 ✽ UDZS4.7B ZENER DIODE
D7 HVU131 DIODE
D8 MA2S111 DIODE
D9,10 MA2S077 DIODE
D11 MA742 DIODE
D12 MA2S111 DIODE B-K,K2
D17,18 DA221 DIODE
IC1 TA75W01FU IC (BUFFER AMP)
IC2 RN5VL42C IC (VOLTAGE DETECTOR/RESET)
IC3 TC75W51FU IC (SUMMING AMP)
IC4 M62364FP IC (D/A CONVERTER)
IC5 S-81350HG-KD IC (VOLTAGE REGULATOR/5M)
IC6 NJU7201U50 IC (VOLTAGE REGULATOR/5V)
IC7 TK11250BM IC (VOLTAGE REGULATOR/5C)
IC8 TC75W51FU IC (BUFFER AMP)
IC9 TA31136FN IC (FM IF SYSTEM)
Destination
Address
TK-480/48 1
New
Parts No. Description
parts
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX)
Destination
IC10 TA75W01FU IC (ACTIVE FILTER)
IC11 SA7025DK IC (PLL SYSTEM)
IC12 TC35453F IC (AUDIO PROCESSOR)
IC13 LC73872M IC (DTMF DECODER)
IC14 KCH31 HIC (VCO SYSTEM) A-K,K2
IC14 KCH32 HIC (VCO SYSTEM) B-K,K2
IC15 ✽ 30622M8A-4F9GP IC (MICROPROCESSOR)
IC16 AT2408N10SI2.5 IC (EEPROM)
IC17 AT29C020-90TI IC (AND GATE)
IC17 ✽ W29C020C90 IC (AND GATE)
IC18,19 BU4094BCFV IC (SHIFT REGISTER)
IC21 NJM2904V IC (COMPARATOR)
IC23 TA75S01F IC (ACTIVE FILTER)
IC30 M68757L IC (POWER MODULE) A-K,K2
IC30 M68757H IC (POWER MODULE) B-K,K2
Q1 2SJ243 FET
Q2 2SA1832(GR) TRANSISTOR
Q3,4 2SC4617(S) TRANSISTOR
Q5 2SC4619 TRANSISTOR A-K,K2
Q5 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR B-K,K2
Q6 ✽ 3SK318 FET
Q7 2SK1824 FET
Q8 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q9 3SK274 FET
Q10,11 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q12 2SC4988 TRANSISTOR
Q13 2SK1824 FET
Q14 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q15 DTA144EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q16 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q17 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q18 2SK1824 FET
Q19 2SC4617(S) TRANSISTOR
Q20 DTC144EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q21-23 2SK1824 FET
TH2 157-503-65001 THERMISTOR
A : TK-480 (K,K2)
B : TK-481 (K,K2)
29

TK-480/481
EXPLODED VIEW
A
6
B
37
36
1
22x2
23
1
21x2
38
46
40
18
39
31
25
Ex2
MIC300
5
E
Ex2
Display unit (A/2)
16
E
55
62
2
54
E
E
E
E
D
68
D
A : N14-0569-04
B M2.6 x 5 : N30-2605-46
C M2.6 x 10 : N30-2610-46
D M2.6 x 6 : N67-2606-46
E M2 x 5 : N83-2005-46
F M2 x 2.5 : N79-2025-46
When you repair or
exchange the display
unit, please exchange
the sheet (24) as well.
Display unit
(B/2)
3
57
24
701 (Chassis)
TX-RX unit
Ex2
17
C
61
63
65
C
703
51
51
F
S/No. label
15
E
56
49
44
2
A
A
52
Bx2
64
33
F
12
63
34
26
When you repair or exchange
the square socket (19), please
exchange FPC (34) as well.
64
19
10
66
30
Parts with the exploded numbers larger than 700 are not supplied.

PACKING
TK-480/481
C
1
7 Warranty card
(B46-0470-00)
9 Instruction manual
(B62-1483-00)
4 Cap (SP/MIC)
(B09-0363-03)
D
50 Battery assy
(W09-0900-35)
Insulation sheet
2
32 Hook
(J29-0658-05)
3
42 Screw set
(N99-2004-05)
28 Packing fixture
(H12-3014-02)
47 Whip antenna
(T90-0636-25) : TK-480
(T90-0640-25) : TK-481
29 Item carton case
(H52-1096-12) : TK-480
(H52-1097-12) : TK-481
31

TK-480/481
ADJUSTMENT
Test Equipment Required for Alignment
Test Equipment Major Specifications
1. Standard Signal Generator Frequency Range 800 to 950MHz
(SSG) Modulation Frequency modulation and external modulation
Output 0.1µV to greater than 1mV
2. Power Meter Input Impedance 50Ω
Operation Frequency 800 to 950MHz or more
Measurement Capability Vicinity of 10W
3. Deviation Meter Frequency Range 800 to 950MHz
4. Digital Volt Meter Measuring Range 10mV to 10V DC
(DVM) Input Impedance High input impedance for minimum circuit loading
5. Oscilloscope DC through 30MHz
6. High Sensitivity Frequency Range 10Hz to 1000MHz
Frequency Counter Frequency Stability 0.2ppm or less
7. Ammeter 5A
8. AF Volt Meter Frequency Range 50Hz to 10kHz
(AF VTVM) Voltage Range 1mV to 10V
9. Audio Generator (AG) Frequency Range 50Hz to 5kHz or more
Output 0 to 1V
10. Distortion Meter Capability 3% or less at 1kHz
Input Level 50mV to 10Vrms
11. Voltmeter Measuring Range 10mV to 10V DC or less
Input Impedance 50kΩ/V or greater
12. 16Ω Dummy Load Approx. 16Ω, 3W
13. Regulated Power Supply 5V to 10V, approx. 5A
Useful if ammeter requipped
■ The following parts are required for adjustment
1. Antenna connector adapter
The antenna connector of this radio uses an SMA termi-
nal.
Use an antenna connector adapter [SMA(f) – BNC(f) or
SMA(f) – N(f)] for adjustment. (The adapter is not provided
as an option, so buy a commercially-available one.)
Note
When the antenna connector adapter touches the knob,
draw out the knob to mount the connector.
2. Universal connector
Use the interface cable (KPG-36) for PC tuning or the lead
wire with plug (E30-3287-18) and screw (N08-0535-08) for
panel tuning. Connct the plug to the universal connector of
the radio and tighten the screw.
The lead wire with plug (E30-3287-18) and screw (N080535-08) terminals are as follows. Numbers are universal
connector terminal numbers.
Caution
1. When connecting the plug to the universal connector of
the radio, a short circuit may occur. To prevent this, be
sure to turn the radio POWER switch off.
2. Since the RX AF output is a BTL output, there is a DC
component. Isolate this with a capacitor or transformer
as shown in the figure.
3. Do not connct an instrument between red or black and
GND.
• Universal connector
1: SSW
3: SP–
5: EMC
7: PTT
9: NC
11: 5M
13: RXD
2: SP+
4: MSW
6: ME
8: PF
10: E
12: TXD
14: NC
32

ADJUSTMENT
TK-480/481
• Panel tuning
SCREW
TUBE
BLU (7)
BRN (10)
RED (2)
BLK (3)
2: RED (RX AF OUTPUT)
3: BLACK (RX AF OUTPUT)
5: WHITE (MIC INPUT)
6: BROWN (MIC GND)
7: BLUE (PTT SW) GND → ON
8: YELLOW (PF SW)
10: BROWN (GND)
11: GREEN (5M)
PTT SWTo Radio
100µ 10V
+
16Ω
100µ 10V
WHT
(5)
10µ 10V
BRN (6)
+
+
AF Voltmeter
Audio generator
Repair Jig (Chassis)
Use jig (part No. : W05-0825-00) for repairing the TK-480/
481.
The jig facilitates the voltage check and protects the
module when the voltage on the flow side of the TX-RX unit
is checked during repairs.
Battery terminal (+)
Power
module
TX-RX unit
Jig
• PC tuning
Connect the wires to the PCB in the connector case of
interface cable.
For output the wires out of the connector case, need to
process the connector case.
KPG-36
Remove the
screw
PCB layout
16Ω
Shield
100µ 10 V
+
100µ 10 V
+
10µ 10 V
+
Connector case
AF voltmeter
Audio generator
How to Remove the Flat Cable
1. Gently draw out both sides of the connector lever uni-
formly in the direction of the arrow with tweezers.
(CN300, CN301)
Tweezers
Flat cable
Lever
2. Gently prise up the connector lever in the direction of the
arrow with a fine regular screwdriver or tweezers.
(CN1, CN3, CN304)
Regular screwdriver
Flat cable
Lever
33

TK-480/481
ADJUSTMENT
Test Mode
■ Test mode operating features
This transceiver has a test mode.
press [A] key and turn power on. Hold [A] key until test
channel No. and test signalling No. appears on LCD.
mode can be inhibited by programming. To exit test mode,
switch the power on again. The following functions are available in test mode.
• Controls
Controls “FCN” appears “FCN” not appears
[PTT] Used when making a Used when making
transmission. a transmission.
[AUX] Unused Unused.
[MON] Monitor ON and OFF. Monitor ON and OFF.
[LAMP] Lights the lamp for five Unused.
seconds.
Lighting is extended for
a further five seconds by
pressing any key while
the lamp is lit.
[S] MSK 1200 bps and Sets to the Tuning
2400 bps mode.
[A] Function OFF Function ON.
[B] Compander function RF power HIGH and
ON and OFF. LOW.
[C] Beat shift ON and OFF Changes group.
[0] to [9], Used as the DTMF Used as the DTMF
and [#], keypad. If a key is keypad. If a key is
[*] pressed during trans- pressed during trans-
mission, the DTMF mission, the DTMF
corresponding to the corresponding to the
key that was pressed key that was pressed
is sent. (keypad model) is sent. (keypad model)
[ENCODER]
Changes system. Changes system.
Note : If a [S], [A], [B], [C] key is pressed during transmission, the DTMF corresponding to the key that was pressed
is sent.
• LCD indicator
“SCN” Unused
“
” Lights at Compander ON.
“LO” Lights at RF Power Low.
“P” Unused
“MON” Lights at moniter ON.
“SVC” Unused
“
” Lights at MSK 2400 bps.
• LED indicator
Red LED Lights during transmission. Blinks at the
low battery voltage warning.
Green LED Lights when there is a carrier.
To enter test mode,
Test
• Sub LCD indicator
“FCN” Appears at Function ON.
■ Frequency and signalling
The set has been adjusted for the frequencies shown in
the following table. When required. re-adjust them following
the adjustment procedure to obtain the frequencies you
want in actual operation.
Frequency (MHz)
SYS No.
RX (TX : TA) TX RX (TX : TA) TX
1 851.0500 806.0500 935.0250 896.0250
2 851.5500 806.5500 935.0500 896.0500
3 860.0000 815.0000 938.0000 899.0000
4 860.5000 815.5000 938.0250 899.0250
5 865.9875 820.9875 939.9875 900.9875
6 869.4000 824.4000 940.4000 901.4000
7 869.9000 824.9000 940.9000 901.9000
8 855.4000 810.4000 936.2500 897.2500
9 865.6000 820.6000 939.3000 900.3000
10 867.5000 822.5000 936.7500 897.7500
11~16 ––––
TK-480 TK-481
Signalling
Group No. RX TX
1 None None
2 None 100Hz square
3 LTR data LTR data
4 QT 67.0Hz QT 67.0Hz
5 QT 151.4Hz QT 151.4Hz
6 QT 210.7Hz QT 210.7Hz
7 QT 250.3Hz QT 250.3Hz
8 DQT D023N DQT D023N
9 DQT D754I DQT D754I
10 DTMF DEC, (159D) DTMF DEC, (159D)
11 None DTMF tone 9
12 None None
13 Single tone 1200Hz Single tone 1200Hz
14 None MSK
15 MSK code MSK code
• Preparations for tuning the transceiver
Before attempting to tune the transceiver, connect the
unit to a suitable power supply.
Whenever the transmitter is turned, the unit must be
connected to a suitable dummy load (i.e. power meter).
The speaker output connector must be terminated with a
16Ω dummy load and connected to an AC voltmeter and an
audio distortion meter or a SINAD measurement meter at all
times during tuning.
34

ADJUSTMENT
TK-480/481
• Transceiver tuning
(To place transceiver in tuning mode)
System appears on LCD. Set system according to tuning
requirements.
LCD display (Test mode)
–
1
1
Group No.System No.
Press [S], now in tuning mode. Use [ B] button to write
tuning data through tuning modes, and channel selector
knob to adjust tuning requirements (1 to 256 appears on
LCD).
Use [C
] button to select the adjustment item through
tuning modes. Use [A] button to adjust 3 point tuning.
LCD display (Tuning mode)
FREQ
Adjustment (1~256)Adjustment item
1
3-point tuning frequency (MHz)
Test CH
Low 851.05000 806.05000 935.02500 896.02500
Center 860.50000 815.50000 938.02500 899.02500
High 869.90000 824.90000 940.90000 901.90000
TK-480 TK-481
RX TX RX TX
Adjustment Points
TX-RX unit (X57-5630-XX) Component side view
■ Tuning mode
Panel test mode
System/Group No.
[S]
FREQ : Frequency adj.
[S]
HPOW : High power
[S]
THPW : High power (T/A)
[S]
[S]
TLPW : Low power (T/A)
[S]
BAL : DQT balance
[S]
MAX : Max deviation L MAX
[S]
TMAX : Max deviation (T/A)
[S]
NMAX : Max deviation (NPSPAC)
[S]
[S]
[S]
[S]
DTMF : DTMF deviation
[S]
FMSK : MSK deviation
[S]
TONE : Tone deviation
[S]
[S]
[S]
[C]
[C]
[C]
LPW : Low power
[C]
[C]
[C]
[C]
[C]
(TK-480)
[C]
FQT : Fine QT
[C]
FDQT : Fine DQT
[C]
FLTR : LTR
[C]
[C]
[C]
[C]
SQL : Squelch
[C]
BATT : Battery
[C]
[C] [C]
[A]
L TMAX C TMAX H TMAX
[A]
L NMAX C NMAX H NMAX
[A]
C MAX H MAX
[C] [C]
[C] [C]
[A]
[C]
[A]
[C]
[A]
[C]
VC
IC30
IC14
35

TK-480/481
Common Section
1. Setting 1) BATT terminal voltage : 7.5V
Standard modulation
MOD : 1kHz
DEV : ±3kHz (TK-480)
±1.5kHz (TK-481)
Measurement
Test-
equipment
ADJUSTMENT
Unit Terminal
Unit Parts Method
Adjustment
Specifications/RemarksConditionItem
2. VCO lock 1) SYS – GRP : 1 – 1
voltage DVM
2) SYS – GRP : 7 – 1 4.3V or less.
PTT : ON
3) SYS – GRP : 7 – 1
TA mode : ON
PTT : ON
Power meter
TX-RX VC Check 0.5V or more.
Transmitter Section
Measurement
Test-
equipment
1. Frequency 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽ f. counter Panel ANT Panel
adjustment Select FREQ ✽ ✽ ✽ knob : 815.500MHz
in tuning mode. TK-481
PTT : ON : 899.025MHz
2. Maximum 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
power check Select HPOW 256
in tuning mode. Ammeter Panel ANT
PTT : ON
3. TX high 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽ Panel
power Select HPOW ✽ ✽ ✽ knob 1.7A or less
adjustment in tuning mode.
PTT : ON
Power meter
Unit Terminal
Unit Parts Method
Adjustment
Encoder
TK-480 ±100Hz
Check 3.0W or more
Encoder
2.5W ±0.1W
Specifications/RemarksConditionItem
4. TX T/A 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
high power Select THPW ✽ ✽ ✽
adjustment in tuning mode.
PTT : ON
5. TX high 1) SYS – GRP : 1 – ✽, 7 – ✽ Check 2.0~3.0W
power check TA mode : OFF and ON
(Press [A] key, then [C] key) 1.7A or less
PTT : ON
6. TX low 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽ Panel
power Select LPW ✽ ✽ ✽ knob 1.2A or less
adjustment in tuning mode.
PTT : ON
7. TX T/A 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
low power Select TLPW ✽ ✽ ✽
adjustment in tuning mode.
PTT : ON
8. TX low 1) SYS – GRP : 1 – ✽, 7 – ✽ Check 0.5~1.5W
power check Low power (Press [B] key) 1.2A or less
TA mode : OFF and ON
(Press [A] key, then [C] key)
PTT : ON
Encoder
1.0W ±0.1W
36

ADJUSTMENT
TK-480/481
Measurement
Test-
equipment
9. DQT BAL 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
adjustment Select BAL ✽ ✽ ✽ Deviation knob lation waves into
in tuning mode. meter square waves.
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 3kHz
HPF : OFF AG
PTT : ON AF VTVM
10. MAX DEV 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
adjustment Select MAX ✽ ✽ ✽ TK-481 : 1.75kHz
in tuning mode. (According to the
AG : 1kHz/150mV larger +, –.)
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 15kHz
HPF : OFF
Adjustment item
L MAX ✽ ✽ ✽ →C MAX ✽ ✽ ✽
→H MAX ✽ ✽ ✽
PTT : ON
11. T/A MAX 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
DEV Select TMAX ✽ ✽ ✽
adjustment in tuning mode.
AG : 1kHz/150mV
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 15kHz
HPF : OFF
Adjustment item
L TMAX ✽ ✽ ✽ →C TMAX ✽ ✽ ✽
→H TMAX ✽ ✽ ✽
PTT : ON
Power meter
Oscilloscope
Unit Terminal
Panel ANT Panel
Universal
Unit Parts Method
Adjustment
Encoder
Make the demodu-
TK-480 : 3.8kHz ±50Hz
Specifications/RemarksConditionItem
12. NPSPAC 1) SYS – GRP : 10 – ✽ TK-480 : 2.9kHz ±50Hz
MAX DEV Select NMAX ✽ ✽ ✽ (According to the
adjustment in tuning mode. larger +, –.)
AG : 1kHz/150mV
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 15kHz
HPF : OFF
Adjustment item
L NMAX ✽ ✽ ✽ →C NMAX ✽ ✽ ✽
→H NMAX ✽ ✽ ✽
PTT : ON
13. MIC 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – 1 Check TK-480 : 2.2~3.6kHz
sensitivity AG : 1kHz/15mV (TK-480) TK-481 : 0.6~1.0kHz
check AG : 1kHz/8mV (TK-481)
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 15kHz
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
14. T/A MIC 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – 1
sensitivity TA mode : ON
check (Press [A] key, then [C] key)
AG : 1kHz/15mV (TK-480)
AG : 1kHz/8mV (TK-481)
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 15kHz
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
37

TK-480/481
ADJUSTMENT
Measurement
Test-
equipment
15. QT DEV 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
adjustment MIC input : OFF Deviation knob TK-481 : 0.45kHz
Select FQT ✽ ✽ ✽ meter
in tuning mode.
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 3kHz AG
HPF : 50Hz AF VTVM
De-emphasis : 750µs
PTT : ON
16. DQT DEV 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
adjustment Select FDQT ✽ ✽ ✽
in tuning mode.
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 3kHz
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
17.LTR DEV 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽ TK-480 : 1.00kHz ±0.10kHz : TK-480
adjustment Select FLTR ✽ ✽ ✽ TK-481 : 0.75kHz ±0.05kHz : TK-481
in tuning mode.
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 3kHz
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
Power meter
Oscilloscope
Unit Terminal
Panel ANT Panel
Unit Parts Method
Adjustment
Encoder
TK-480 : 0.75kHz ±0.05kHz
Specifications/RemarksConditionItem
18. DTMF DEV 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽ TK-480 : 3.00kHz ±0.15kHz : TK-480
adjustment Select DTMF ✽ ✽ ✽ TK-481 : 1.50kHz ±0.10kHz : TK-481
in tuning mode.
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 15kHz
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
19. MSK DEV 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽
adjustment Select FMSK ✽ ✽ ✽
in tuning mode.
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 15kHz
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
20. TONE DEV 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽ 2.5kHz ± 0.1kHz
adjustment Select TONE ✽ ✽ ✽
in tuning mode.
Deviation meter filter setting
LPF : 15kHz
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
21. BATT 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽ After pressing the BATT terminal voltage : 6.2V
detection Select BATT ✽ ✽ ✽ PTT switch, confirm
writing in tuning mode. that one predeter-
PTT : ON mined numeric in
the range 1 to 256
appears and then
press [B] key.
That numeric will be
stored in memory.
38

ADJUSTMENT
TK-480/481
Measurement
Test-
equipment
22. BATT 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – 1
detection BATT terminal voltage : 5.7V Deviation knob LED (TX) blinks.
check PTT : ON meter
2) BATT terminal voltage : 6.5V Transmit
PTT : ON AG
Note : When the CPU is changed these adjustment values will become suitable values for NPSPAC, the deviations except MAX DEV in NPSPAC band
are automatically adjusted.
Power meter
Oscilloscope
AF VTVM
Unit Terminal
Panel ANT Panel
Unit Parts Method
Adjustment
Encoder
Check Can not transmit.
Specifications/RemarksConditionItem
Receiver Section
Measurement
Test-
equipment
1. Sensitivity 1) SYS – GRP : 1 – 1 SSG Panel ANT Check 12dB SINAD or more.
check SSG output : –116dBm
MOD : 1kHz AF VTVM
DEV : ±3kHz (TK-480)
:±1.5kHz (TK-481) Distortion
2. Squelch 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – ✽ Panel
adjustment Select SQL ✽ ✽ ✽ knob closing squelch.
in tuning mode.
SSG output : 3dB below to
12dB SINAD level
Oscilloscope
meter
Unit Terminal
Unit Parts Method
Adjustment
Encoder
Specifications/RemarksConditionItem
Adjust to point of
3. Squelch 1) SYS – GRP : 4 – 1 Check Squelch must be opened.
check
See Note. 2) SSG output : OFF Squelch must be closed.
Note : When squelch is adjusted, the microcomputer simultaneously reads and writes the RSSI level. Do not write adjustment values without the SSG
connected.
SSG output : 12dB SINAD level
39

TK-480/481
TERMINAL FUNCTION
CN No. Pin No.
CN1 1 B O
CN2 1 MON I
for X54-
SW 3 PTT I
section
CN3 1 AF O Audio output.
for 3 NC – Not use.
X54- 4 PF I External PF signal input.
Display
unit 6 RXD I Serial control signal input.
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX A/2) : DISPLAY section
CN300
for 3 ME – MIC GND.
X57- 4 LBL I Backlight LED control.
TX-RX Normally:0V, lighting:5V.
unit 5 LG I
Name I/O Function
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX) : TX-RX section
Power input after passing through the fuse.
2B O
3 SB I Power output after power switch.
4 SB I Power output after power switch.
5 5M O 5V.
6 VOL I Volume level input for audio control.
7E – GND
8 EN2 I Encoder pulse input.
9E – GND
10 EN1 I Encoder pulse input.
2 LAMP I
4 GND – GND
2 AFE – Audio GND.
5 CK O Clock data output.
7 TXD O Serial control signal output.
8DT O
9 KRS O Key scan IC reset output.
10 KI1 I KEY input
11 KI2 I KEY input
12 GND - GND
13 5M O 5V.
14 AM O Audio mute signal output.
15 CS O LCD driver chip select output.
16 NC – Not use.
17 PTT I PTT signal input.
18 AUX I AUX key input.
19 LR O
20 LG O
21 LBL O Backlight LED control.
22 ME – MIC GND.
23 MIC I MIC signal input.
24 SB O Power output after power switch.
1 SB I Power input after power switch.
2 MIC O MIC signal output.
6LR I
7 AUX O AUX key output.
Power input after passing through the fuse.
Normally;5V, MON when connected GND.
Normally;5V, LAMP when connected GND.
Normally;5V, transmit when connected GND.
Data output for LCD driver/decade counter.
Mute:”L”, Unmute:”H”
TX LED control. Normally:0V, lighting:5V.
RX LED control. Normally:0V, lighting:5V.
Normally:0V, lighting:5V.
RX LED control. Normally:0V, lighting:5V.
TX LED control. Normally:0V, lighting:5V.
CN No. Pin No.
CN301
CN302
CN304
CN303
for x57-
TX-RX 3 PTT O
unit 4 GND – GND
Name I/O Function
8 PTT O PTT signal output.
9NC – Not use.
10 CS I LCD driver chip select input.
11 AM I Audio mute signal input.
Mute:”L”, Unmute:”H”
12 5M I 5V.
13 GND – GND
14 KI2 O KEY output
15 KI1 O KEY output
16 KRS I Key scan IC reset input
17 DT I
18 TXD I Serial control signal input.
19 RXD O Serial control signal output.
20 CK I Clock data input.
21 PF O External PF signal output.
22 NC – Not use.
23 AFE – Audio GND.
24 AF I Audio input.
1 SSW I EXT/INT speaker switch input.
2 SP+ O BTL output + for external speaker.
3 SP- O BTL output - for external speaker.
4 MSW I EXT/INT MIC switch input.
5 EMC I External microphone input.
6ME – External microphone ground.
7 PTT I External PTT input.
8 PF I Programmable function key input.
9NC – Not use.
10 E – GND
11 5M O 5V output
12 TXD O Serial data output.
13 RXD I Serial data input.
14 NC – Not use
1 SP O Output for internal speaker.
2E – GND
1NC – Not use.
2 LEDK I Backlight LED control.
3 LEDA O Backlight LED control.
4 VCI O LCD power supply.
5 SOD O Serial data output for LCD driver.
6 SID I Serial data input for LCD driver.
7 SCLK O Clock data output for LCD driver.
8 CS O LCD driver chip select output.
9 Vcc O 5V
10 GND – GND
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX B/2) : SW section
1 MON O
2 LAMP O
Data input for LCD driver/decade counter.
Normally;5V, MON when connected GND.
Normally;5V, LAMP when connected GND.
Normally;5V, transmit when connected GND.
40

SRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX) -10 : K -11 : K2 Component side view
S301
MON
C330
C338
C337C329
C336
SP+
1
CN302
S302
PTT
SP–
2
C316
C317
J72-0517-22
LCD ASSY
S303
LAMP
PC BOARD VIEWS TK-480/481
1
2
3
4
5
C
D306
3
6
9
#
6
D301
+
–
MIC300
D308
B
D310
7
2
5
8
0
8
A
D305
S
D307
D309
9
741
*
10
J72-0517-22
11
Ref No. Address
D301 10A
D305 9K
D306 6K
D307 9N
D308 7N
Pattern 1
Pattern 2
Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Component side
Foil side
D309 9Q
D310 7Q
41 42
12
13
14

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S
TK-480/481 PC BOARD VIEWS
1
2
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX) -10 : K -11 : K2 Foil side view
ME
R300
R302
R304
R305
C327
SSW
J72-0517-22
D321
EMC
R303
+
C302
Q300
C301
S300
AUX
CN303
4
GND
PTT
1
LAMP
MON
3
4
5
6
7
J72-0517-22
C340
L302
1
24
R325
R324
R332
C318
AF
IC301
AE
PF
NC
CP300
R331
C312
C339
C331
PTT
CN301
E
NC
C328
MSW
SP+
ME
PF
SSW
EMC
PTT
SP–
TXD
NC
RXD
5M
MSW
D319
R339
R312R311
L309
L308
R301
C332
D300
R340
R341
14
R338
CN300
GND
5M
Q310
AUX
AM
5M
CS
R318
3 4
G
D
S
NC
AM
C343
ME
SB
LG
1
MIC
PTT
LBL
LR
R306
SB
Q301
1
Q308
1
6
3 4
1
6
IC300
R314
D320
L305
L304
16
C333
C344
RXD
KI1
DT
TXD
KRS
KI2
CK
R315
C307
16
C326
C335
1
D316
D302
C309
Q307
CP301
8
C311 R309
Q305
R316
R308
E
C
B
E
C
B
Q304
C341 C342
+
C313
C304
R319
D304
R336
R317
C308
Q306
9
L301
R313
L306
R326
TH300
L307
L300
R327
R333
Q309
R328
D303
10
11
8
8
D318
D317
9
D315
9
CP303
R320
R321
CP302
C310
12
13
43 44
14
+
C314
C321
SP+
SP–
L303
LEDK
VCC
SCLK
SOD
LEDA
NC
1
CN304
10
CS
R337
C323
C324
C325
C322
+MIC
C315
Ref No. Address
IC300 7I
IC301 8G
Q300 5P
Q301 6H
Q302 11R
Q303 10R
Q304 9H
Q305 9H
+
MIC
–
Ref No. Address
Q306 11H
Q307 11H
Q308 7H
Q309 9J
Q310 7G
D300 6M
D302 9G
D303 9I
Ref No. Address
D304 10H
D315 9G
D316 9G
D317 9F
D318 9F
D319 5L
D320 6I
D321 4P
Q303
Q302
R310
C305
R307
Component side
Pattern 1
Pattern 2
Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Foil side
GND
CS
SID
VCI

SRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3210-XX) -10 : K -11 : K2 Component side view + Foil side
J72-0517-22
S300
S301
MON
D321
R300
EMC
R303
C302
C301
AUX
R302
C326
R304
R305
C335
+
C327
Q300
SSW
ME
C338
1
CN301
C330
C337C329
MSW
SP+
SSW
EMC
SP–
ME
PF
PTT
C336
C328
TXD
E
5M
NC
SP+
SP–
1
2
NC
CN302
RXD
C331
PTT
14
R338
S302
PTT
C316
C339
C332
C317
R340
R341
D319
R339
R301
R312
R311
D300
L309
MSW
L308
LCD ASSY
S303
LAMP
PC BOARD VIEWS TK-480/481
1
2
CN303
1
LAMP
MON
4
GND
PTT
3
4
CN300
GND
AUX
ME
SB
C
1
MIC
Q301
6
4
B
LBL
SB
1
3
1
D306
R306
L305
L304
C333
C344
D320
R314
16
IC300
AM
NC
LG
PTT
5M
CS
LR
AM
R318
Q308
1
3 4
6
Q310
G
D
S
C343
5M
RXD
KI1
DT
AE
PF
TXD
KRS
KI2
CP300
C307
R315
16
24
3
NC
CK
AF
R325
R324
C340R331
C312
R332
C318
IC301
2
D308
L302
1 8
6
5
9
D310
8
#
0
5
6
7
D301
R310
C305
R307
Q303
Q302
+
–
MIC300
C315
+MIC
R337
C323
C324
C325
C322
CS
CP301
89
SP+
SP–
GND
VCC
10
SID
CS
SCLK
CN304
LEDK
VCI
L303
NC
LEDA
SOD
1
+
C314
C321
Q309
L301
L300
R327
R328
R326
TH300
R333
L307
C311
D303
R313
L306
D305
R319
R336
A
R309
+
C313
S
R317
C308
Q306
Ref No. Address
IC300 7K
IC301 8N
Q300 5D
Q301 6L
Q302 11B
Q303 10B
Q304 9L
Q305 9L
Q305
CE
B
Q304
C341 C342
C304
D304
Ref No. Address
Q306 11L
Q307 11L
Q308 7L
Q309 9J
Q310 7M
D300 6G
D301 10A
D302 9M
R316
R308
C309
Q307
E
C
B
9
D315
D302
D316
CP303CP302
R320
C310
R321
Ref No. Address
D303 9K
D304 10L
D305 9K
D306 6K
D307 9N
D308 7N
D309 9Q
D307
D318
D317
741
Ref No. Address
D315 9M
D316 9M
D317 9N
D318 9N
D319 5H
D320 6K
D321 4D
D309
*
J72-0517-22
Component side
Pattern 1
Pattern 2
Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Foil side
Connect 1 and 4
D310 7Q
8
9
10
11
12
13
45 46
14

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S
TK-480/481 PC BOARD VIEW
1
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX) -10 : TK-480 -11 : TK-481 Component side view
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
GND
SQ
D2
D1
OPT
5C
LOK
AAC
RXEMAI
RXWMAO
RXD
TXD
AUXRXD
AUXTXD
SB
AUDIOBEEP
RSSI
MONI
LAMP
DEO
DI9
RXAO
RXAI
PTTOUT
TXAO
PTTIN
TXAI/MUTE
DI/ANI
R419
R420
C111
C112
Q22
R87
+
C107
R423
C100
R11
R8
R148
C138
4
R88
C123
G
D
S
+
+
R9
C10
GND
C120
S
D
G
R98
C109
C263
R13
+
1
R164
1
4
AF
CN2
PTT
C191
Q7
IC3
LAMP
C200
24
1
R86
C58
R422
8
5
C188
D18
R4
R5
R3
C197
1
4 5
IC1
+
8
R6
C92
C6
VC
1 2 3 4
X2
1
3 4
1
MON
C11
C195
R7
C201
R99
+
D6
IC4
1213
R417 R14
C18
C9
R12
F1
CN10
L1
B
C196
R32
C189
C190
R157
GND
KI2
KI1
KRSDTTXD
RXDCKPFNCAFE
R122
R250
PTTNCCSAM5M
R147
SB
MICMELBLLGLR
AUX
C80
R161
R162
R59
C26
8
IC10
C5
1
C79
R57
C199
C75
C15
C60
C56
R56
8
R21
45
1
R54
R16
C28
CF1
R25
R23
IC8
C53
L4
IC14
C37
+
45
6
CD1
C61
C156
24
CN3
D17
CF2
C55
R40
C62
R51
Q 5
R49
C155
C154
L20
XF1
IC30
C163
L25 C160
R129
R128
C175
C173
ANT
C169
D7
C134
R127
L27
C167
R136
R137
L30
C166
L28
L31
L32
C174
D10
C40
D9
C168
C176
L29 CN1
C143
1
R156
C3C2C1
+B
EN1EEN2EVOL5MSBSB+B
10
L11
C7 C16
R10
C8
5
IC2
1
34
C68
R2
C4
R17
R1
D2
C19
+
C12
IC5
O
C22
G
I
R103
J72-0812-02
10
DTA144EE
2SB1132
IMN10
2SB798
2SC4988
DA221
DTC114EE
11
DTC144EE
2SA1832
2SC4617
2SC4619
2SC5108
12
MA742
3SK318
3SK274
UPA672T
2SJ243
S-81350HG-KD
2SK1824
13
I
G
O
47 48
14
Ref No. Address
IC1 4H
IC2 8R
IC3 7F
IC4 5G
IC5 9S
IC8 7I
IC10 7I
Ref No. Address
IC14 6K
IC30 3O
Q5 9L
Q7 5F
Q22 6F
D2 9R
D6 5M
Ref No. Address
D7 5P
D9 6Q
D10 6R
D17 9G
D18 9F
Component side
Pattern 1
Pattern 2
Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Pattern 5
Pattern 6
Foil side

SRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX) -10 : TK-480 -11 : TK-481 Foil side view
IC6
CN12
C29
C13
O
I
G
C25
+
Q4
C21
C38
6
IC7
1
34
C30 C31
CN11
R130
R132
C20
C17
C164
R36
R131
R133
R37
C161
+
L19
C34
L18
C139
G1
Q9
G2
C135
R101
R96
C129
R134
C165
R135
R145 R144
C133
S
C132
R94
D
R91
C125
R140
1
IC21
4 5
C170
C198
Q14
R100
L14
L15
C127
C122
R169
C172
Q15
8
R141
Q20
R170
C209
CN4
Q18
C171
R15
Q1
R76
R151
R60
R146
R143
S
D
G
C145
D
G
D 4
L9
L6
R113
S
Q2
C99
G2
D
C84
R27
Q13
D
G
S
C153
R142
C140
D5
Q17
C193
R105
Q6
G1
S
C150 L23
C146
R108
C110
L7
L21
Q 11
R154
L34
L10
R65
C91
C152
L24
Q12
R114
C149
C192
C94
C78
C81
R62
R115
C142
R152
R153
C136
R155
C208
R165
R109
C194
R102
R167
C63
E
C
B
R168
Q10
L17
R97
PC BOARD VIEW TK-480/481
1
2
R53
C74
C67
R50
R106
R110
R83
C118
C108
R89
R259
R77
CP1
34
44
1 11
R55
C76
R61 R64
C77
C82
R44
R58
R63
Q16
R66
R126
C144
C203
R112
C83
C159
X3
R67
IC12
C85
C90
C86
C98
C106
C89
C93
R71
R73
C96
16
IC19
16
9
4 5
IC18
1
IC16
3
L22
C261
8
16
4
1
C87
R111
C141
R107
R276
R421
89
1
R408
8
L53
17
R118
CN8
IC17
R81
2333
22
12
C102
L54
C103
+
C101
CN9
R74
R84
R80
C115
C126
C97
C121C114
R82
CP21
R125
R124
R123
R201
R202
R203
R204
R205
R206
R207
R139
R116
C147
L16
R418
32
R200
CP18
CP20
CP22
CP19
CP17
CP16
76
IC15
100
1 25
C207
C205
R120
R138
CP3
R211
C148
C262
C206
CP11
CP13
CP12
CP5
R149
R104
1
CP14
CP15
5175
50
R150
CP10
CP9
CP8
R297
R298
CP7
CP6
CP24
26
R218
R248
D11
X4
C157
C162
C158
L26
5
6
7
8
9
78
IC13
C187
C52
C105
R75R78
C88
C57
L8
L12
C59
C182
R69
C181
R70
R42
20
IC11
1
R117
C151
C185
R159
R43
D12
C180
C183
C177
R72
R68
1011
C178
R38
+
C95
R35
C69
+
L5
C179
C73
R166
R90
C130
R92
C186
R85
Q8
R95
R93
C44
C131 C137
+
C128
R31
Q3
L13
C119
C117
C116
R79
+
C104
C184
C14
R39
+
C24
G
S
D
Q21
CN6
D3
C33
Q23
G
S
D
C202
C36
CN5
C35
R29 R34
C32 C39 C54
R158
R22
R24
IC9
C48
C46
89
1
C45
C51
R41
C27
+
C43
R18
R19
16
C42
C50
C47
L35
Q19
R26
R28
X1
CN7
TH2
R121
14
1
C124 C113
L55
L56
C66
R45
R47
D1
C72
C70
R48
C71
R46
C23
R171
R20
R163
D8
C41
R160
+
C204
C64
1
3 4
IC23
5
C49
R33
L3
J72-0812-02
C65
TK11250BM
TC35453F
30622M8A-4F9GP
M68757H
M68757L
AT29C020-90TI
W29C020C90
SA7025DK
AT2408N10SI2.5
NJU7201U50
TC74HC4017AF
BU4094BCFV
49
Ref No. Address
IC6 6B
IC7 7B
IC9 9I
IC11 5J
IC12 6N
IC13 3L
IC15 7Q
IC16 3R
IC17 5Q
IC18 3Q
IC19 3P
IC21 5D
IC23 9L
Q1 7E
Ref No. Address
Q2 7E
Q3 7I
Q4 6C
Q6 8F
Q8 6H
Q9 7D
Q10 7G
Q11 6F
Q12 5F
Q13 5F
Q14 6D
Q15 5E
Q16 8N
Q17 7F
Ref No. Address
Q18 6E
Q19 8J
Q20 7E
Q21 7J
Q23 8H
D1 6K
D3 8K
D4 7E
D5 7F
D8 8L
D11 9N
D12 6I
Pattern 1
Pattern 2
Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Pattern 5
Pattern 6
Component side
Foil side
10
11
12
13
50
14

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S
TK-480/481 PC BOARD VIEW
1
TX-RX UNIT (X57-5630-XX) -10 : TK-480 -11 : TK-481 Component side view + Foil side
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
16
GND
SQ
D2
D1
OPT
1
5C
CP14
LOK
CP15
AAC
50
R150
RXEMAI
CP10
RXWMAO
CP9
RXD
CP8
TXD
R297
R298
AUXRXD
CP7
AUXTXD
SB
CP6
AUDIOBEEP
CP24
26
1
9
4 5
IC16
8
8
L22
L53
C261
16
IC18
89
1
R408
IC17
C206
CP18
CP13
CP16
CP17
CP19
CP22
CP11
CP12
51 75
IC15
RSSI
R218
CP5
R149
R104
CP3
C262
R138
R211
C148
R248
L26
C157
C158
C162
X4
CP20
125
C205
IC19
17
32
76
100
R276
R421
R200
R120
16
1
CP21
R125
R124
R123
R201
R202
R203
R204
R205
R206
R207
R139
R116
C147
C207
R418
MONI
LAMP
DEO
CN8
DI9
RXAO
RXAI
PTTOUT
CN9
L16
TXAO
PTTIN
TXAI/MUTE
DI/ANI
R419
R420
X3
4
C98
C87
C106
R87
R67
GND
R89
C120
R88
R111
C141
R107
R118
CP1
+
R81
23 33
22
12
C102
+
C101
R80
C115
C121C114
R82
C123
G
S
C107
R11
R8
C89
C10
R148
C138
C96
D
IC12
+
+
R9
R64
C85
R66
C86
C159
S
D
G
R98
C109
C263
R13
C83
+
C90
1
R164
1
R61
4
R63
AF
C203
C111
C112
Q22
R423
C100
L54
C103
C93
R71
R73
R74
R84
C126
C97
D11
CN2
PTT
C191
Q7
IC3
C82
LAMP
C200
24
1
R86
C58
R422
8
5
C77
C188
Q16
CN3
D18
C118
111
C189
RXDCK PFNCAFE
R83
MON
C201
34
44
C76
R126
R259
C18
R32
C190
R44
KRSDTTXD
C144
1
C108
R77
C11
IC4
R53
C9
R55
R12
R58
GND
KI2
KI1
R106
D17
R110R112
C74
R417
C67
R14
C196
L55
L56
C72
R157
7 8
IC13
R4
R5
4 5
IC1
1
C124C113
C195
R7
C66
C70
R48
C71
R46
C23
R50
F1
CN10
L1
R250
AUX
PTTNCCSAM5M
C64
1
3 4
IC23
5
C65
1
14
8
R6
C92
R122
R3
C197
R45
1213
B
MICMELBLLGLR
R160
R121
+
C6
R38
+
C95
X2
R35
CN7
L5
R47
R161
R162
R59
C26
C80
D1
C15
C60
C56
R56
R25
R23
8
IC10
C5
1
8
+
IC8
R21
45
C24
1
R171
R54
R16
C199
C79
R57
D8
C75
R163
TH2
R20
R147
SB
C41
24
+
C204
C28
D3
L35
CF1
X1
J72-0812-02
C187
C52
IC30
C105
C88
C57
L8
C182
1
20
R69
C181
R70
1
R42
R159
R43
R166
R85
C117
Q3
6
CN6
R29R34
R22
C46
8 9
CF2
1
C45
L3
VC
C186
C128
R158
IC9
C48
1 2 3 4
R130
C135
L28
L18
L11
L30
R101
CN11
C166
C20
R36
R37
C40
D9
C168
C17
+
C34
C163
L24
L21
Q 11
C192
L34
L10
R65
C91
C94
C78
C81
R62
C150
C155
L23
C146
R108
R154
Q17
C110
L7
Q13
D
S
C154
C140
D5
C193
R105
G1
Q6
S
XF1
G
C153
R142
Q2
L20
C84
R27
R146
L25
R143
R129
R113
C99
G2
D
CN4
Q18
S
D
G
C171
C145
S
Q1
D
G
D 4
R76
L9
L6
R60
C172
Q15
R128
R15
R151
C160
R141
R144
Q20
R170
C209
L12
3 4
C185
C59
IC14
R90
C130
R92
Q8
R165
E
C
B
D6
R114
R109
C152
+
C156
Q12
C149
R115
C142
R117
R99
C151
R95
R93
C44
C194
R152
R31
Q10
C131 C137
Q23
R153
C136
R97
L17
R102
R155
C208
R167
R168
C61
CN5
R51
C63
16
+
C32C39C54
R18
R19
C55
C49
CD1
C33
G
S
D
C202
C36
C35
R40
C62
Q 5
R49
8
R127
C170
R169
IC21
C68
C122
C167
C198
L14
L15
R140
R145
R100
C132
C127
R134
C165
D7
1
45
L27
R136
Q14
C133
R94
C125
R135
R137
C161
R91
R132
C169
C134
C164
R131
R133
C139
S G1
Q9
D
G2
R96
C129
L19
C175
C173
ANT
L31
CN12
L32
R156
C174
+
D10
C13
Q4
C176
O
L29 CN1
C21
I
C143
+B
IC6
1
G
C38
C29
C25
6
IC7
1
34
C30C31
C7 C16
R10
C8
5
IC2
1
34
R17
D2
C22
R2
C4
C19
R1
R103
C3C2C1
EN1EEN2EVOL5MSBSB+B
10
+
C12
IC5
O
G
I
R33
C177
R75 R78
R72
R68
C37
+
1011
C53
C178
S
Q21
C180
R39
C184
C14
IC11
C183
D12
C104
L13
C119
C116
+
C69
+
L4
C179
C73
G
D
45
R79
C50
C47
R24
Q19
C51
R41
R26
C27
C42
R28
+
C43
10
NJM2904V
M62364FP
TA75W02FU
TDA7053AT
TC75W51FU
11
12
RN5VL42C
TA31136FN
LC73872M
TA75S01F
13
51 52
14
Ref No. Address
IC1 4H
IC2 8R
IC3 7F
IC4 5G
IC5 9S
IC6 6R
IC7 7R
IC8 7I
IC9 9K
IC10 7I
IC11 5J
IC12 6F
IC13 3H
IC14 6K
IC15 7C
Ref No. Address
IC16 3B
IC17 5C
IC18 3C
IC19 3D
IC21 5P
IC23 9H
IC30 3O
Q1 7O
Q2 7O
Q3 7K
Q4 6Q
Q5 9L
Q6 8N
Q7 5F
Q8 6L
Ref No. Address
Q9 7P
Q10 7M
Q11 6N
Q12 5N
Q13 5N
Q14 6P
Q15 5O
Q16 8F
Q17 7N
Q18 6O
Q19 8J
Q20 7O
Q21 7J
Q22 6F
Q23 8L
Ref No. Address
D1 6I
D2 9R
D3 8I
D4 7O
D5 7N
D6 5M
D7 5P
D8 8H
D9 6Q
D10 6R
D11 9F
D12 6K
D17 9G
D18 9F
Component side
Pattern 1
Pattern 2
Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Pattern 5
Pattern 6
Foil side
Connect 1 and 6

OMKIGECA
SQ
TRPNLJHFDB
Note : Components marked with a dot (·) are parts of pattern 1.
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM TK-480/481
1
2
3
4
5
6
56
7

TK-480/48 1TK-480/481
BLOCK DIAGRAM
57

VCO
IC14
*
C131
PLL
Q10
C136
Q17
C193
Q11
D5
C149
Q12
C152
Power
module
D7 C169
L30
ANT
2.5W
–11.7dBm
(Q10 open)
–7.8dBm
(Q17 open)
–1.9dBm
(D5 open)
+7.1dBm
(Q12 open)
+17.5dBm
(C152 open)
RF (815.50MHz)
EMC
MIC
12
LPF
ALC
COMP
SW
IDC
6
DAC
I5
O5
DAC
I2
O2
13
15 16
18
19
9
8
IC12
16.6mVrms
17.2mVrms 39.2mVrms 331mVrms 320mVrms
310mVrms
IC4 IC3 (1/2) IC4
*
487mVrms 179mVrms 311mVrms 154mVrms
AF
5
43
41
DAC
*
IC12
C58
IC3
IC4
AF
AMP
IC300
SP
500mW
(BTL)
203mVrms 287mVrms 419mVrms 135mVrms 29mVrms
AF
C169
L30
ANT
C143
L11
C139
Q9 C122
L20
C110
Q6
R60
XF1
R51
Q5
C55
FM IF
SYSTEM
CF1,2
IC8
AMP
*
–118.0dBm –119.0dBm –119.4dBm –120.4dBm –107.0dBm –110.3dBm –106.8dBm –116.4dBm
–109.6dBm
(C55 open)
241mVrms 265mVrms
–79.2dBm –80.2dBm
RF (860.50MHz)
IF1 (44.85MHz)
IF2
(455kHz)
AF
To make measurements in the AF section,
connect the oscilloscope proves directly.
(ANT input : –47dBm, 1kHz FM, 3kHz dev.)
In the RF section, use a 1000pF coupling capacitor.
(The display shows the SSG input value required
to obtain 12dB SINAD.)
AG is set to the MIC input
becomes 3kHz Dev at 1kHz MOD.
To make measurements in the
AF section, connect the
oscilloscope proves directly.
In the RF section, use a 1000pF
coupling capacitor.
TK-480/481
LEVEL DIAGRAM (TK-480)
RX Section
TX Section
59

TK-480/481
VCO
IC14
*
C131
PLL
Q10
C136
Q17
C193
Q11
D5
C149
Q12
C152
Power
module
D7 C169
L30
ANT
2.5W
–10.2dBm
(Q10 open)
–7.4dBm
(Q17 open)
–0.4dBm
(D5 open)
+5.3dBm
(Q12 open)
+17.8dBm
(C152 open)
RF (899.00MHz)
EMC
MIC
12
LPF
ALC
COMP
SW
IDC
6
DAC
I5
O5
DAC
I2
O2
13
15 16
18
19
9
8
IC12
16.1mVrms
16.7mVrms 41.2mVrms 353mVrms 338mVrms
318mVrms
IC4 IC3 (1/2) IC4
*
530mVrms 133mVrms 109mVrms 54mVrms
AF
5
43
41
DAC
*
IC12
C58
IC3
IC4
AF
AMP
IC300
SP
500mW
(BTL)
188mVrms 254mVrms 376mVrms 132mVrms 29mVrms
AF
C169
L30
ANT
C143
L11
C139
Q9 C122
L20
C110
Q6
R60
XF1
R51
Q5
C55
FM IF
SYSTEM
CF1,2
IC8
AMP
*
–118.0dBm –118.4dBm –118.4dBm –118.0dBm –108.3dBm –106.6dBm –105.5dBm –117.0dBm
–107.5dBm
(C55 open)
115mVrms 268mVrms
–58dBm –55dBm
RF (938.00MHz)
IF1 (44.85MHz)
IF2
(455kHz)
AF
To make measurements in the AF section,
connect the oscilloscope proves directly.
(ANT input : –47dBm, 1kHz FM, 1.5kHz dev.)
In the RF section, use a 1000pF coupling capacitor.
(The display shows the SSG input value required
to obtain 12dB SINAD.)
AG is set to the MIC input
becomes 1.5kHz Dev at 1kHz MOD.
To make measurements in the
AF section, connect the
oscilloscope proves directly.
In the RF section, use a 1000pF
coupling capacitor.
LEVEL DIAGRAM (TK-481)
RX Section
60
TX Section

TK-480/481
KNB-16A/17A (Ni-Cd BATTERY) /
KPG-36 (PROGRAMMING INTERFACE CABLE) / KSC-19 (CHARGER)
KNB-16A KNB-17A
External View External View
KNB-16A KNB-17A
Circuit Diagram Circuit Diagram
Discharge pin side
+
Breaker
(80±5°C)
Breaker
(70±5°C)
Discharge pin side
+
Breaker
(80±5°C)
–
Breaker
(70±5°C)
KPG-36 External View
KSC-19 External View
–
Diode
Thermister
+ –
Charge pin side
T
Diode
Thermister
+
Charge pin side
T
KNB-16A Specifications
Voltage ....................................... 7.2V (1.2V x 6)
Charging current ........................ 1100mAh
Dimensions (mm) ...................... 58 W x 110.8 H x 17.2 D
(Projections included)
Charger and charging time
KSC-19 (Normal Charger) ...... Approx. 8 hours
KSC-20 (Rapid charger) ......... Approx. 1 hour
Weight ....................................... 180g
KNB-17A Specifications
Voltage ....................................... 7.2V (1.2V x 6)
Charging current ........................ 1500mAh
Dimensions (mm) ...................... 58.0 W x 110.8 H x 20.0 D
(Projections included)
Charger and charging time
KSC-19 (Normal Charger) ...... Approx. 8 hours
KSC-20 (Rapid charger) ......... Approx. 1.3 hour
Weight ....................................... 220g
–
KSC-19 Charging
KNB-16A
Voltage ................................................. 7.2V
Battery capacity ................................... 1100mAh
Charging time ....................................... Approx. 8 hours
KNB-17A
Voltage ................................................. 7.2V
Battery capacity ................................... 1500mAh
Charging time ....................................... Approx. 8 hours
61

TK-480/481
General
Frequency Range
RX ......................................................... TK-480 : 851 to 870MHz TK-481 : 935 to 941MHz
TX ......................................................... TK-480 : 806 to 825MHz (851 to 870MHz : Talk-Around)
Systems .................................................... Maximum 32
Groups ...................................................... Maximum 250
Conventional Channels ............................. Maximum 600
Channel Spacing ....................................... TK-480 : 25kHz (PLL channel step 12.5kHz)
Battery Voltage ......................................... DC 7.5V
Battery Life ............................................... More than 8 hours at 5-5-90 duty cycle with KNB-16A battery
Temperature Range .................................. –30°C to +60°C (–22°F to +140°F)
Dimensions and Weight
With KNB-16A (1100mAh battery) ...... 135 (5.33) H x 58 (2.29) W x 34 (1.34) D mm (inch) 1.01lbs (460g)
(Dimensions not including protrusions, weight includes antenna and belt hook)
Receiver (Measurements made per TIA/EIA-603)
RF Input Impedance ................................. 50Ω
Sensitivity
12dB SINAD* ....................................... 0.30µV
Selectivity* ............................................... TK-480 : 70dB±25kHz TK-481 : 63dB±12.5kHz
Intermodulation* ...................................... TK-480 : 65dB±25/50kHz TK-481 : 60dB±12.5/25kHz
Spurious (Except for IF 1/2)* .................... 70dB
Frequency Stability ................................... TK-480 : ±0.00025% (–30°C to +60°C)
Channel Spread......................................... TK-480 : 19MHz TK-481 : 6MHz
Audio Power Output ................................. 500mW at 16Ω less than 5% distortion
SPECIFICATIONS
TK-481 : 896 to 902MHz (935 to 941MHz : Talk-Around)
TK-481 : 12.5kHz (PLL channel step 12.5kHz)
TK-481 : ±0.00015% (–30°C to +60°C)
62
* : Typical specifications
Transmitter (Measurements made per TIA/EIA-603)
RF Power Output
High ...................................................... 2.5W
Low ...................................................... 1W
RF Output Impedance .............................. 50Ω
Spurious .................................................... –60dB
Modulation ................................................ TK-480 : 16K0F3E, 16K0F1D, 15K0F2D, 14K0F3E, 14K0F1D, 13K0F2D
TK-481 : 11K0F3E, 11K0F1D, 10K5F2D
FM Noise .................................................. TK-480 : –45dB TK-481 : –40dB
Audio Distortion ........................................ 5.0% or less
Frequency Stability ................................... TK-480 : ±0.00025% (–30°C to +60°C)
TK-481 : ±0.00015% (–30°C to +60°C)
Channel Spread......................................... TK-480 : 64MHz TK-481 : 45MHz

TK-480/481
63

TK-480/481
KENWOOD CORPORATION
14-6, Dogenzaka 1-chome, Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 150-8501, Japan
KENWOOD SERVICE CORPORATION
P.O. BOX 22745, 2201 East Dominguez Street, Long Beach, CA 90801-5745, U.S.A.
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS CANADA INC.
6070 Kestrel Road, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L5T 1S8
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Rembrücker Str. 15, 63150 Heusenstamm, Germany
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS BELGIUM N.V.
Mechelsesteenweg 418 B-1930 Zaventem, Belgium
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS FRANCE S.A.
13, Boulevard Ney, 75018 Paris, France
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS U.K. LIMITED
KENWOOD House, Dwight Road, Watford, Herts., WD1 8EB United Kingdom
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS EUROPE B.V.
Amsterdamseweg 37, 1422 AC Uithoorn, The Netherlands
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS ITALIA S.p.A.
Via G. Sirtori, 7/9 20129 Milano, Italy
KENWOOD IBERICA S.A.
Bolivia, 239-08020 Barcelona, Spain
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS AUSTRALIA PTY. LTD.
(A.C.N. 001 499 074)
16 Giffnock Avenue, Centrecourt Estate, North Ryde, N.S.W. 2113 Australia
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS (HONG KONG) LTD.
Unit 3712-3724, Level 37, Tower one Metroplaza, 223 Hing Fong Road, Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGIES(S) PTE LTD.
Sales Marketing Division
1 Ang Mo Kio Street 63, Singapore 569110
 Loading...
Loading...