Kenwood TK-2118 Service manual

VHF FM TRANSCEIVER / VHF FM手持机
TK-2118
SERVICE MANUAL /
Helical Antenna
(T90-0757-05)
Knob
(VOL)
(K29-5442-03)
Knob(ENC)
(K29-5443-03)
维修手册
© 2001-8 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-8575-00 (S) 668
Knob
(PTT, MONI)
(K29-9027-03)
TK-2118
Panel assy
(A62-0932-03)
Key top
(DIAL, SCAN)
(K29-9026-13)
Key top(DTMF)
(K29-9028-13)
Cabinet assy
(Front)
(A02-3512-13)
CONTENTS
GENERAL.................................................................. 2
REALIGNMENT......................................................... 3
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ......................................... 11
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA....................................... 17
DESCRIPTION OF COMPONENTS........................ 19
TERMINAL FUNCTION ........................................... 21
PARTS LIST............................................................. 22
EXPLODED VIEW ................................................... 29
PACKING ................................................................. 30
ADJUSTMENT......................................................... 31
PC BOARD VIEWS
DISPLAY UNIT (X41-3583-00)............................ 37
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6233-00) ................................ 39
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM.......................................... 51
BLOCK DIAGRAM .................................................. 55
LEVEL DIAGRAM ................................................... 57
BC-20, PB-40, PB-41, BT-12 ................................... 58
SPECIFICATIONS ................................BACK COVER

TK-2118
目录目录
目录
目录目录
概述. ............................................................................ 2
模式组合 ...................................................................... 3
电路说明 .................................................................... 11
半导体数据 ................................................................18
元件说明 .................................................................... 19
端子功能 .................................................................... 21
零件表 ....................................................................... 22
部件分解图 ................................................................29
包装 ........................................................................... 30
GENERAL / 概述
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians
familiar with similar types of commercial grade
communications equipment. It contains all required service
information for the equipment and is current as of the
publication date. Changes which may occur after publication
are covered by either Service Bulletins or Manual Revisions.
These are issued as required.
调整 ........................................................................... 31
PC板视图
显示单元 (X41-3583-00) ....................................... 37
发射-接收单元 (X57-6233-00) ............................. 39
原理图 ....................................................................... 51
方块图 ....................................................................... 55
电平图 ....................................................................... 57
BC-20, PB-40, PB-41, BT-12 ............................... 58
规格 ........................................................................ 背面
引言
本手册的范围
本手册是提供给熟悉通信专业并且具有维修经验的技术人员
使用的。它包括了维修该设备所需要的全部资料和现行出版日
期。在出版后可能发生变动,如果需要,可以使用《维修通
报》或《手册修订本》进行补充。
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment
information, the full part identification number should be
included. This applies to all parts : components, kits, or
chassis. If the part number is not known, include the chassis or
kit number of which it is a part, and a sufficient description of
the required component for proper identification.
PERSONAL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personal
safety :
• DO NOT transmit until all RF connectors are verified secure
and any open connectors are properly terminated.
• SHUT OFF and DO NOT operate this equipment near
electrical blasting caps or in an explosive atmosphere.
• This equipment should be serviced by a qualified
technician only.
SERVICE
This radio is designed for easy servicing. Refer to the
schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and
alignment procedures contained within.
Destnation Number of CH RF power output
C505W/2W
替换零件的订购
当订购替换零件或设备信息时,应注明完整的零件识别号
码。所有的零件均有识别号码:元件、组件或机壳。如果不知
道零件的号码,为了正确地识别,必须注明此元件所属的机壳
或组件的号码,并对元件进行充分的说明。
个人安全
为了个人的安全,请注意下列事项:
• 在没有认真核实所有射频插头之前或有任何一个打开的插头
没有连接到相应端子上的情况下,均不要发射。
• 在电爆管附近或在易燃性气体环境中,必须关掉电源,不要
操作本设备。
• 本设备只应该由有资格的技术人员来维修。
维修服务
为了便于维修本设备,建立了完整的维修服务体系,提供了
包括原理图、印刷线路板图和调整步骤在内的资料供参考。
型式 信道号码 射频功率输出
C50 5W/2W
TK-260 :K, K2
2
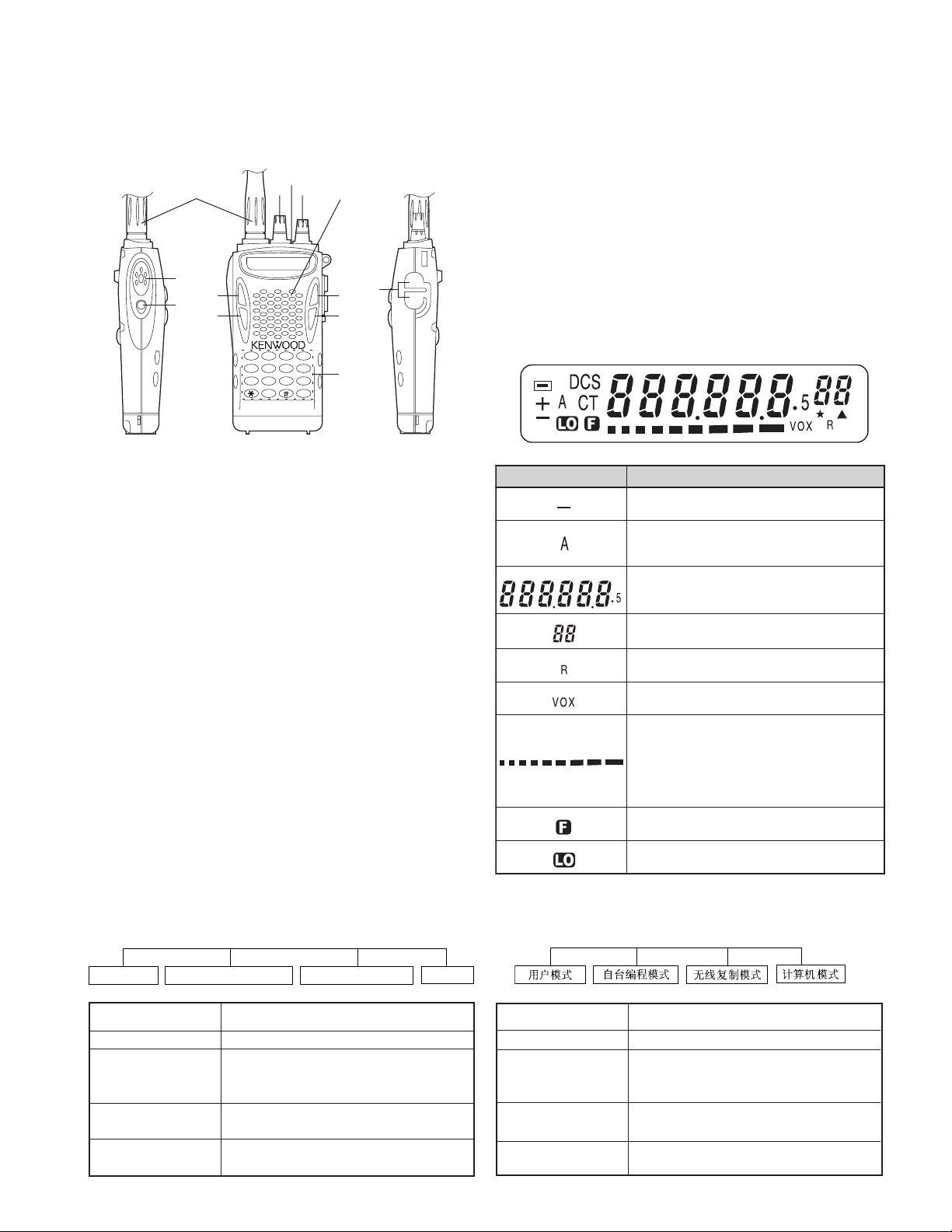
REALIGNMENT/ 模式组合
TK-2118
1. 各部分介绍
扬声器-
天线
r
PTT
MONI
qq
q Power(电源)开关/Volume(音量)控制器
qq
t
y
u
按顺时针方向转动时,接通对讲机的电源。旋转调节音
量。关闭对讲机电源时,按逆时针方向旋转到底。
ww
w LED 指示灯
ww
发射中时点亮红色,接收中时点亮绿色。接收符合对您的
对讲机设定的代码静噪、选择呼叫代码或者 DTMF 信号中
时,闪烁橙色。在发射中电池电压变低时闪烁红色。当电
池电压降低时闪烁红色。
ee
e 旋转编码器
ee
旋转选择频道。进行调节电平设定时,也配合其他功能使
用。
rr
r PTT(按下通话)开关
rr
按下后对着麦克风讲话进行发射。
tt
t MONI(监听)键
tt
根据如何对本键的编程,按下后监听选择的频道。此
外也与
yy
y DIAL(拨号)键
yy
FUNC
键配合使用变更频道 QT 代码。
用于存储、确认、发射和删除 DTMF 号码。此外也与
键配合使用锁定对讲机的键。
uu
u FUNC(功能)键
uu
按下或者按住本键开启对讲机键的其他功能。
ii
i SCAN(扫描)键
ii
按下本键开始或者停止扫描功能。此外也与
w
q
V
H
F
F
M
T
R
A
N
S
O
C
M
E
R
I
V
E
D
IA
L
F
U
N
C
123A
456B
789C
0
e
麦克风
8
1
1
2
-
K
T
L
E
D
SCAN
LOW
i
o
!1
MIC SP
!0
D
FUNC
FUNC
键配合
使用,暂时将频道闭锁在扫描之外,并且设定对讲机的显
示屏照明灯的条件。
oo
o LOW 键
oo
按下本键切换输出功率的高和低。也可以同时使用 FUNC
键设定静噪电平和 VOX 增益。
!0!0
!0 DTMF(双音多频)键盘
!0!0
用于存储和发射 DTMF 号码。
!1!1
!1 MIC-SP 插孔
!1!1
连接另购的扬声器/麦克风。
■ 显示屏
图标 说明
监听频道时出现(静噪关闭)。
当选择的频道包括在扫描序列中时显
示。扫描闭锁的频道不显示本图标。
显示工作频率或频道数码、选单设定以
及其他功能选择。
根据所选择的机能,显示各种数字。
当倒频功能接通时显示。
当 VOX 功能接通时显示。
接收时,该条形显示表示呼叫信号的强
度(条形越多,信号越强)。发射时,
表示电池电压(条形越多,电池的剩余
电量越多)。
按下 FUNC 键进入功能模式后显示。
使用低功率发射时显示。
注:以上未说明的图标在本对讲机中不使用。
2. Modes
Self Programming ModeUser Mode Wireless Clone Mode
MODE FUNCTION
User Mode For normal use.
Self Programming You can Program the RF frequency,
Mode QT/DQT and other functions using only
the radio.
Wireless Clone Mode
Used to transfer programming data
from one radio to another.
PC Mode Used for communication between the
TK-260 :K, K2
radio and a PC
PC Mode
2.模式
模式类型 功能
用户模式 用于一般操作。
自台编程模式 只用手持对讲机便可编程发射接收频
率、QT/DQT和其它功能。
无线复制模式 用于从一个手持机编程数据复制到另一
个手持机。
计算机模式 用于手持机与计算机之间的通信。
3
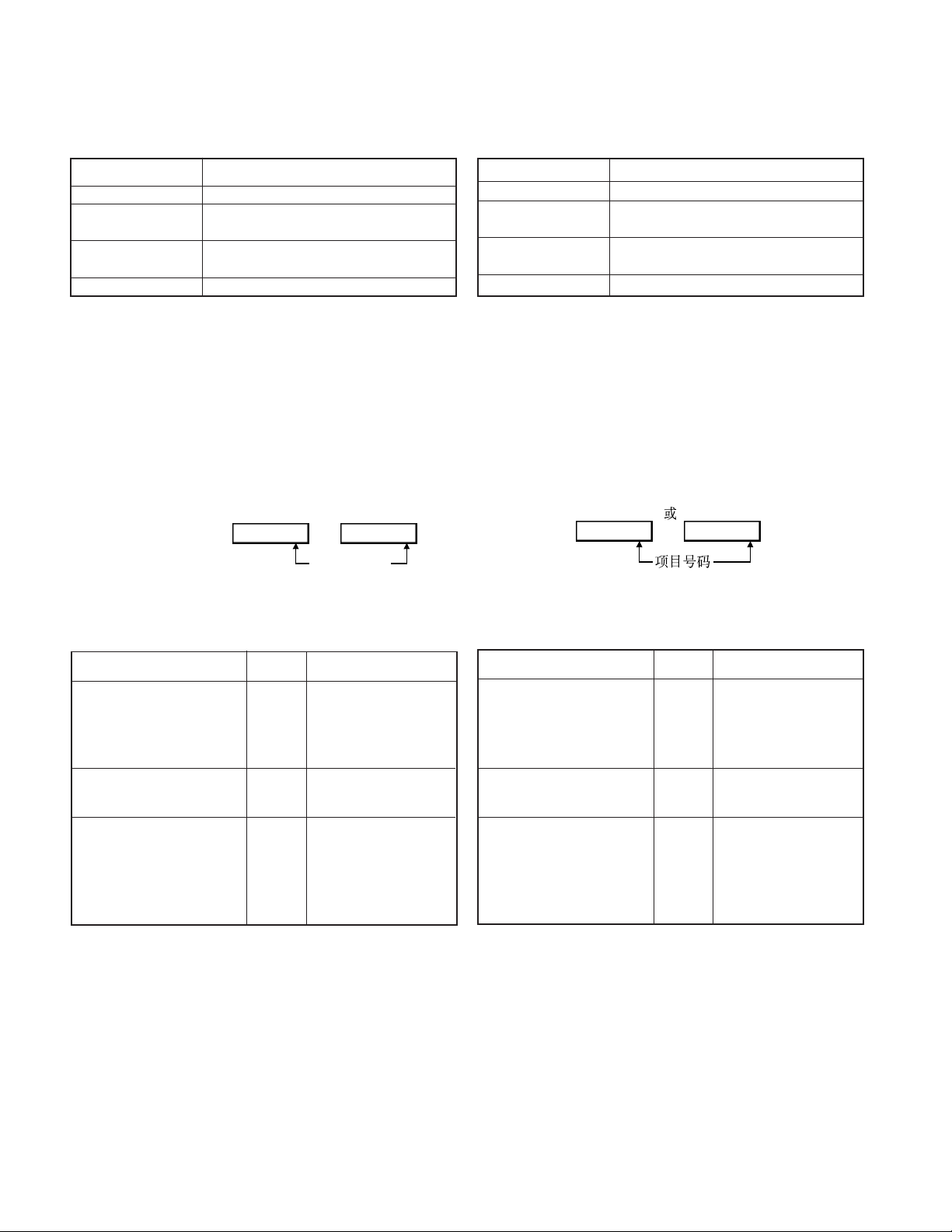
TK-2118
000 0
ON 1
(1) (2)
REALIGNMENT/ 模式组合
3.How to enter each mode
MODE PROCEDURE
User Mode Power ON
Self Programming [MONI] + [DIAL] + POWER ON
Mode (More than 2 sec)
Wireless Clone mode
PC Mode received commands from PC
[MONI] + [LOW] + POWER ON
(More than 2 sec)
4.Self Programming mode
After entering self-programming Mode, the radio allows 3
types of operation:
Function setting / Channel setting / All Reset
When self-programming is disable through using the FPU, self
programming mode cannot be turned ON.
1) Function setting
You can program 3 settings.
Operation:
After entering Self-Programming Mode Press the [SCAN] key.
The LCD changes to
(1) (2)
000 0
If your radio is programmed with the selective call function,
the LCD changes to (1).
When you press the PTT switch after setting the data, you
continue to the next item. (Refer to page 7 item 5)
Selecting the setting items
Setting the Selective Call
Code
(3 Digit)
Setting the BEEP ON or OFF
Setting the [MONI] Key
Assignment
Display
(Example)
(
000 0
(
ON 1
(
or
ON 1
Item number
Setting contents
You can enter 3 digit code
)
(000 to 999) using the DTMF
keys.
This feature is available only
when "Selective Call" has
been activated in the radio.
OFF: No, ON: Yes
)
This item is selected using
the channel selector.
0: Squelch OFF,
0 2
)
1: Monitor Toggle,
2: Monitor Momentary,
OFF: OFF
You can select from
among the above settings.
This item is selected using
the channel selector.
3. 如何进入每一种模式
模式类型 操作步骤
用户模式 电源ON
自台编程模式 [MONI]+[DIAL]+电源ON (高于2秒)
无线复制模式 [MONI]+[LOW]+电源ON (高于2秒)
计算机模式 从计算机接收指令
4. 自台编程模式
进入自台编程模式后,手持机允许三类操作:
功能设置/信道设置/全部复位
当使用FPU设置禁止自台编程时,便不能进入自台编程模式。
1) 功能设定
您可编程三个设置。
操作:
进入自台编程模式后按[SCAN]键。
LCD变为
如果您的手持机编程选择呼叫功能,则LCD变为 (1)。
当您在设置数据后按下PTT开关,您便可继续到下一个项目。
(请翻阅7页项目5)
选择设置项目
设置选择呼叫编码。
(3位数字)
设置峰鸣声ON或OFF
设置监听[MONI]按键赋值
(例如)
(
000 0
(
(
显示
ON 1
0 2
)
)
)
设置内容
您可使用DTMF键输入3
位代码(000-999)。
只有当“选择呼叫功
能”已在手持机中设定
有效时该功能才可用。
OFF: 否, ON: 是
该项目使用信道选择器
选择。
0: 静噪关闭,
1: 监听器触发,
2: 监听器瞬时,
OFF: 关
您可从上述设置中选择。
该项目使用信道选择器选择。
TK-260 :K, K2
4
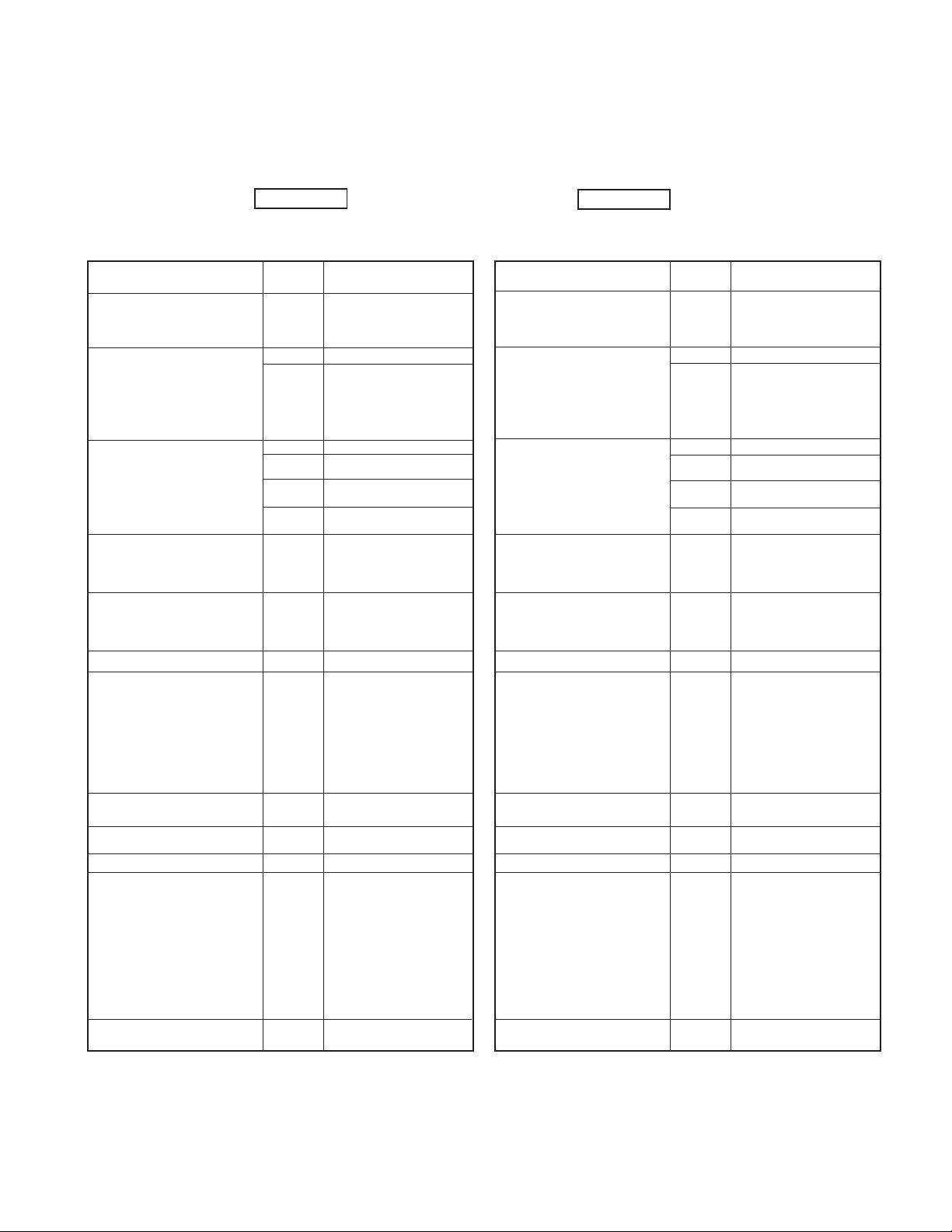
TK-2118
…
REALIGNMENT/ 模式组合
2) Channel setting
Operation:
After entering Self-Programming Mode Press the [LOW] key.
The LCD changes to
CH 1 1
When you press the PTT switch after setting the data, you
can continue to the next Item. (Refer to page8 item 6)
Selecting the setting items
Setting the channel number
When a channel number is not
set, the following items will not
be selected.
Setting the receive frequency
When a receive frequency is not
set ("blank" is set), the following
items will not be selected. (Item
numbers 3 to 12 are not selected.)
When "blank" is set, you will return
to "setting the channel number".
Setting the receive QT/DQT
When a channel number is not set,
this item will be skipped.
Setting the transmit frequency
Setting the transmit QT/DQT
When a transmit frequency is not
set, this item will be skipped.
Setting the option signalling
Setting the BUSY CH Lockout
(BCL)
Setting the Beat Shift
function ON or /OFF
Setting Scan DELETE / ADD
Setting Wide / Narrow
Setting the SP Unmute
When option signaling is set
to "0" (None), this item will be
skipped.
Setting the transmit power
Display
(Example)
(
CH 1 1
(
…… 2
(
150.000 2
(
(
q 100.0 3
(
(
Same as
RX Display
(This is item
number "4".)
Same as
RX Display
(This is item
number "5".)
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
OFF 3
d 023 3
d -023 3
0 6
OFF 7
OFF 8
Add 9
0 10
0 11
H 12
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
Setting contents
Channel range from 1 to
50.
Blank
100.00000MHz~549.99500MHz
(VHF: 5kHz(Default) /
6.25kHz Step)∗1
Default (C): 150.000MHz
(C2): 140.000MHz
OFF
QT(QT frequencies
table)∗2: 67.0Hz ~ 250.3Hz
DQT(DQT Normal/Inverse table)
∗2: 023 ~ 754 Normal setting
DQT(DQT Normal/Inverse table)
∗2: -023 ~ -754 Inverse setting
Same content as "Setting
the received frequency"
Same content as
"Setting the receive QT/
DQT"
0: None 1: DTMF
OFF: OFF 1: Carrier
2: QT/DQT 3: DTMF
For setting number
"3"(DTMF), if of Option
Signaling is changed from
"DTMF" to "None" before the
BCL setting is entered, the
BCL setting contents will be
automatically set to "OFF"
(OFF).
OFF: No ON: Yes
del: Scan DELETE
Add: Scan ADD
0: Narrow 1: Wide
0: Carrier or QT/DQT
1: Carrier + DTMF or QT/
DQT + DTMF
For setting number "1"
(Carrier + DTMF or QT/DQT +
DTMF), if Option Signaling is
changed from "DTMF" to
"None" before the SP Unmute
setting item is entered, the SP
Unmute setting contents will
be automatically set to "0"
(Carrier or QT/DQT).
H: High power
L: Low power
∗1 Step change for setting the frequency
MHz step: Routed the Channel selector while pressing the
[1] key.
5kHz or 6.25kHz step: Press the [SCAN] key
2) 信道设定
操作:
进入自台编程模式后按[LOW]键。
LCD变为
CH 1 1
当您在设置数据后按下PTT开关,您便可继续到下一项。
(请翻阅8页项目6)
选择设置项目
设置信道编号
当未设置信道号时,将不选
择以下项目。
设置接收频率
当未设置接收频率时(设置为
"空白"),将不选择以下项目。
(不选择项目编号3-12。)
当设置为"空白"时,您将返回
到"设置信道号"。
设置接收 QT/DQT
当未设置信道号时,该项目
将跳过。
设置发射频率
设置传送 QT/DQT
当未设置发射频率时,该项目
将跳过。
设置可选信令
设置繁忙信道锁定 (BCL)
设置差拍偏移功能ON或OFF
设置扫描删除/添加扫描
设置宽/窄带
设置SP不静音
当选择信令的选择被设置到
"0" (无)时,该项目将跳过。
设置发射功率
显示
(例如)
(
CH 1 1
(
……
2
(
150.000 2
(
OFF 3
(
q 100.0 3
(
d 023 3
(
d -023 3
与接收显示
相同(该项目
号为编号"4".)
与接收显示
相同(该项目
号为编号"5".)
(
0 6
(
OFF 7
(
OFF 8
(
Add 9
(
0 10
(
0 11
(
H 12
设置内容
)
信道范围1-50。
)
空白
100.00000MHz~549.99500MHz
)
(VHF: 5kHz(缺省) /6.25kHz
Step)*1
缺省 (C): 150.000MHz
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
(C2): 140.000MHz
OFF
QT(QT 频率表)*2:
67.0Hz ~ 250.3Hz
DQT(DQT 正常/反向表)*2:
023 ~ 754 正常设置
DQT(DQT 正常/反向表)*2:
-023 ~ -754 反向设置
与 "接收频率" 内容相同。
与 "设置接收 QT/DQT"内
容相同。
0: 无 1: DTMF
OFF: 关 1: 载波
2: QT/DQT 3: DTMF
对于设置 "3" (DTMF),如
果在输入BCL 设置之前可
选信令设置从"DTMF"变
为"无",则BC L 设置内容
将自动设置为 "OFF"
(关)。
OFF: 否 ON: 是
del: 扫描删除
Add: 扫描添加
0: 窄带 1: 宽带
0: 载波或 QT/DQT
1: 载波 + DTMF或
QT/DQT + DTMF
对于设置编号"1"(载波+
DTMF或QT/DQT+DTMF),
如果在输入S P 不静音设置
项目之前可选信令设置从
"DTMF"变为 "无",则SP不
静音设置内容将自动设置
为"0" (载波或QT/ DQT)。
H: 高功率
L: 低功率
∗1 设置频率的步进
MHz档:按下[1]键的同时确定信道选择器的方向。
5kHz或6.25kHz档: 按下[SCAN]键
TK-260 :K, K2
5
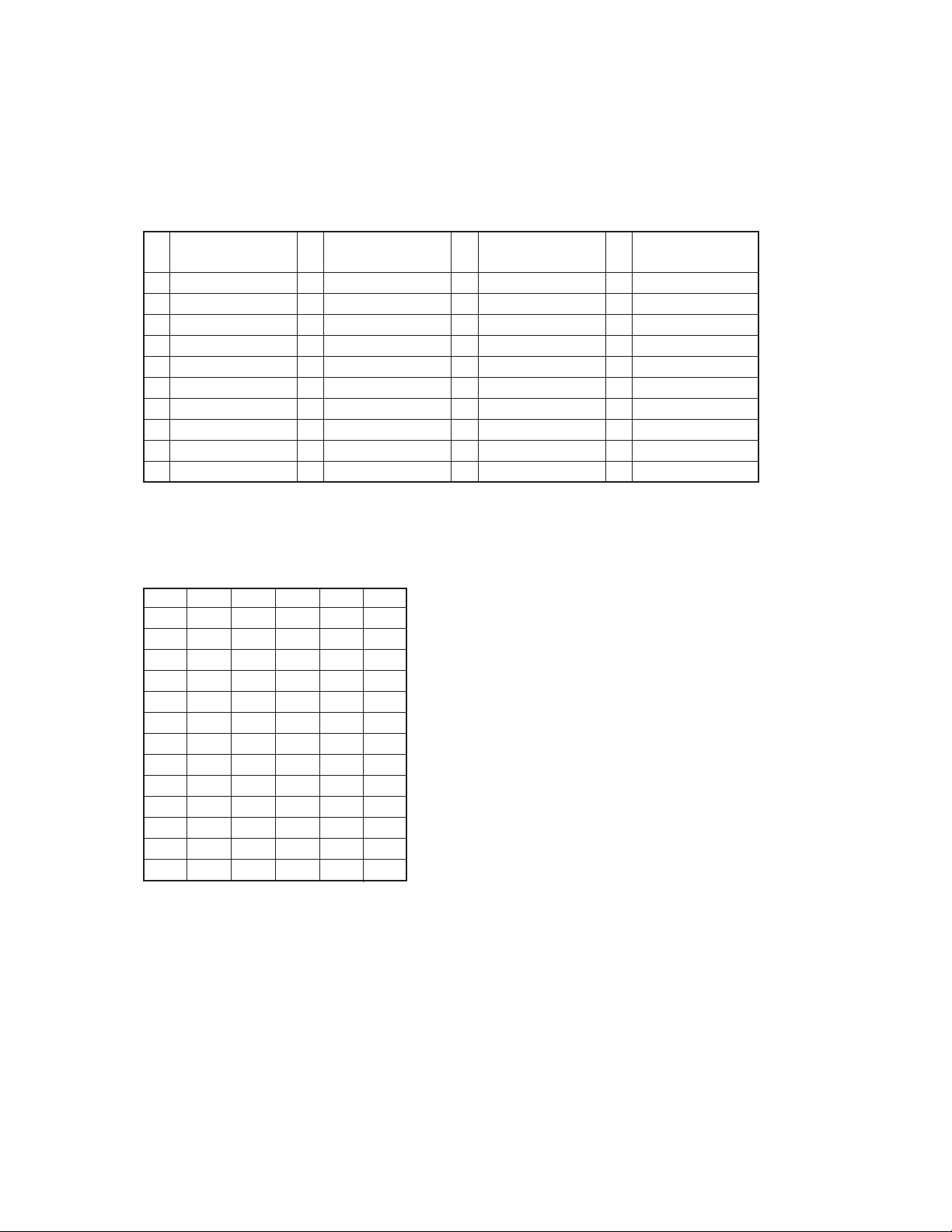
TK-2118
REALIGNMENT/ 模式组合
∗2 QT/DQT frequency table
OFF/ QT/ DQT: Press the [LOW] key
DQT Normal/ Inverse: Press the [DIAL] key
• QT frequencies (39 frequencies table) / QT频率 (39个频率表)
QT Frequency [Hz]
No.
1 67.0
2 69.3
3 71.9
4 74.4
5 77.0
6 79.7
7 82.5
8 85.4
9 88.5
10 91.5
频率
[Hz]
QT Frequency [Hz]
No.
11 94.8
12 97.4
13 100.0
14 103.5
15 107.2
16 110.9
17 114.8
18 118.8
19 123.0
20 127.3
• DQT table (83 codes) Normal/ Inverse / DQT (83 代码) 正常/反向表
频率
[Hz]
∗2 QT/DQT频率表
OFF/ QT/ DQT: 按下[LOW]键
DQT正常/反向: 按下[DIAL]
QT Frequency [Hz]
No.
21 131.8
22 136.5
23 141.3
24 146.2
25 151.4
26 156.7
27 162.2
28 167.9
29 173.8
30 179.9
频率
[Hz]
QT Frequency [Hz]
No.
31 186.2
32 192.8
33 203.5
34 210.7
35 218.1
36 225.7
37 233.6
38 241.8
39 250.3
频率
[Hz]
023 114 174 315 445 631
025 115 205 331 464 632
026 116 223 343 465 654
031 125 226 346 466 662
032 131 243 351 503 664
043 132 244 364 506 703
047 134 245 365 516 712
051 143 251 371 532 723
054 152 261 411 546 731
065 155 263 412 565 732
071 156 265 413 606 734
072 162 271 423 612 743
073 165 306 431 624 754
074 172 311 432 627
TK-260 :K, K2
6
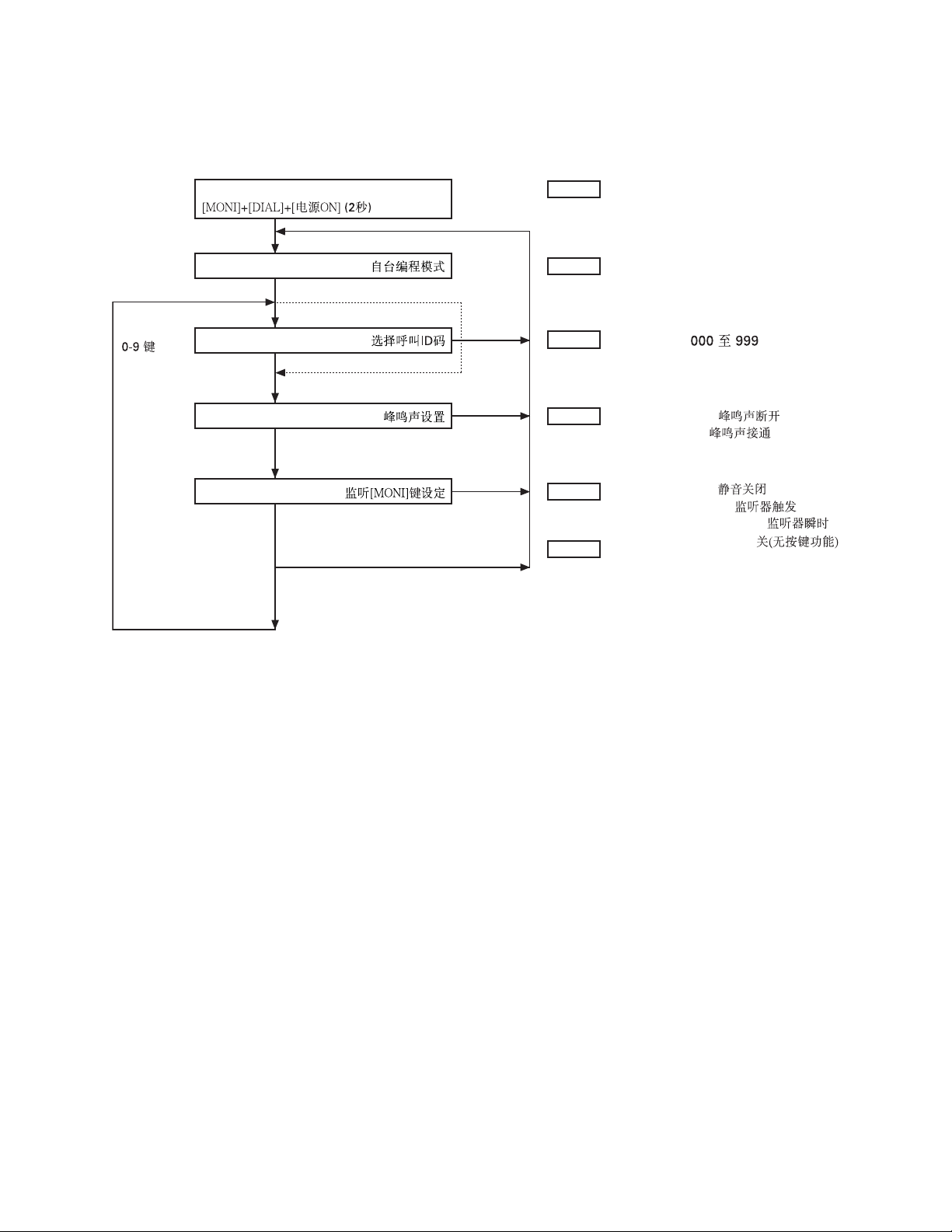
REALIGNMENT/ 模式组合
5. Function setting / 功能设定
TK-2118
0-9 key /
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
[MONI]+[DIAL]+[POWER ON](2sec) /
Self programming mode
[SCAN]
Selective call ID
[PTT]
Beep setting
[PTT]
[MONI] key assignment
[PTT]
[PTT]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
display
SELF
000 0
ON 1
0 2
END
000 to 999 /
OFF:BEEP OFF /
ON:BEEP ON /
0:Squelch OFF /
1:Monitor Toggle /
2:Monitor Momentary /
OFF: no key function /
Notes:
• If you radio is not programmed with the selective call
function, the Selective call ID setting will be skipped.
注释:
• 如果您的手持机未选择呼叫编码功能,则选择呼叫ID码设置
将被跳过。
TK-260 :K, K2
7
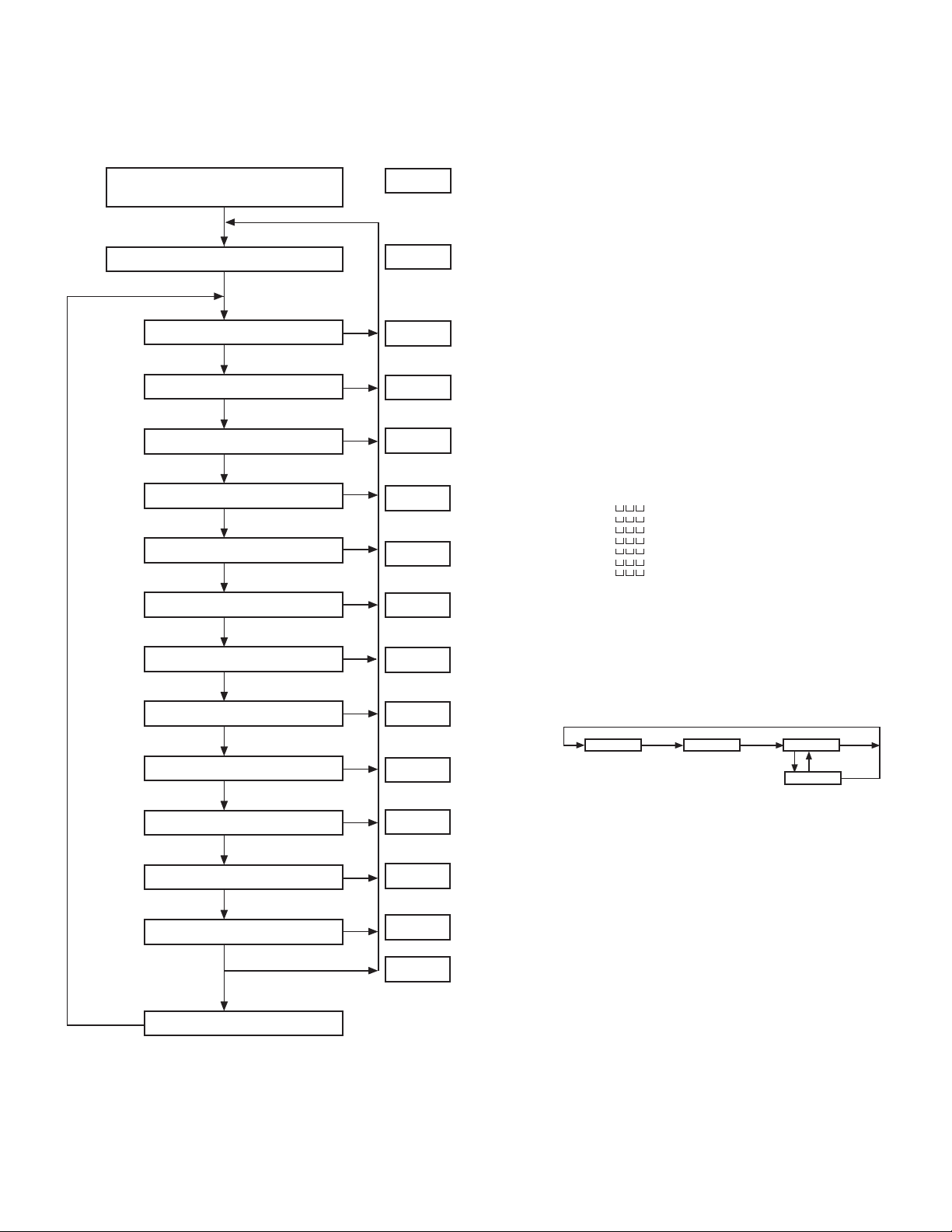
TK-2118
6. Channel Setting / 信道设定
REALIGNMENT/ 模式组合
[MONI]+[DIAL]+[POWER ON] (2sec) /
Self programming mode
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
CH Selector /
信道选择器
[监听]+[拨号]+[电源ON] (2秒)
自台编程模式
[LOW]
Channel select
[PTT]
RX frequency
[PTT]
RX signaling
[PTT]
TX freguency
[PTT]
TX signaling
[PTT]
Option signaling
[PTT]
Busy channel lockout
[PTT]
Beat Shift
[PTT]
Scan DEL /ADD
[PTT]
Wide/Narrow
[PTT]
SP Un mute
[PTT]
TX Power HI/LOW
[PTT]
[PTT]
UP Channel
繁忙信道封闭
删除/ 添加扫描
射频功率 高/低
信道选择
接收频率
接收信令
发射频率
发射信令
可选信令
拍频偏移
宽/窄
SP不静音
优先信道
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
[FUNC]
display
SELF
CH 1 1
150.000 2
q 67.0 3
150.000 4
q 67.0 5
0 6
OFF 7
OFF 8
Add 9
0 10
0 11
H 12
END
Select channel
1 to 50 channel
选择信 1至 50
Select RX frequency*
选择接收频率
Select RX signalling
选择接收信令
Select TX frequency*
选择发射频率
Select TX signalling
选择发射信令
0: None / 无
1: DTMF / DTMF
OFF: off / 关
1: Carrier / 载波
2: QT/DQT
3: DTMF
OFF: no shift / 不偏移
On: shift / 偏移
Add: Scan ADD
添加扫描
Del: Scan DEL
删除扫描
0: Narrow /窄
1: Wide /宽
0: Carrier or QT/DQT
载波或QT/DQT
1: Carrier+DTMF or QT/DQT+DTMF
载波+DTMF或QT/DQT+DTMF
H: High Power / 高功率
L: Low Power / 低功率
Note:
注释:
1. RX TX Frequency set
设置接收发射频率
MHz step Press the [1] key and
MHz 档 按下 [1] 键并旋转信道选择器
5kHz/6.25kHz step Press the [SCAN] key
5kHz/6.25kHz 档 按下 [SCAN] 键
*6.25KHz step indication
clear/default Press [LOW] key
清除/缺省 按下 [LOW] 键
2. RX TX signalling set
设置接收发送信令
OFF QT DQT select Press the [LOW] key
OFF QT DQT 选择 按下 [LOW] 键
DQT Normal / Inverse Press the [DIAL] key
DQT 正常/反向 按下 [DIAL] 键
OFF 3 q 67.0 3 d 023 3
turn the Channel Selector
. 000
. 006
. 0125
. 018
. 025
. 031
. 0375
……
[LOW] [LOW] [LOW]
[DIAL]
[DIAL]
d -023 3
[LOW]
TK-260 :K, K2
8
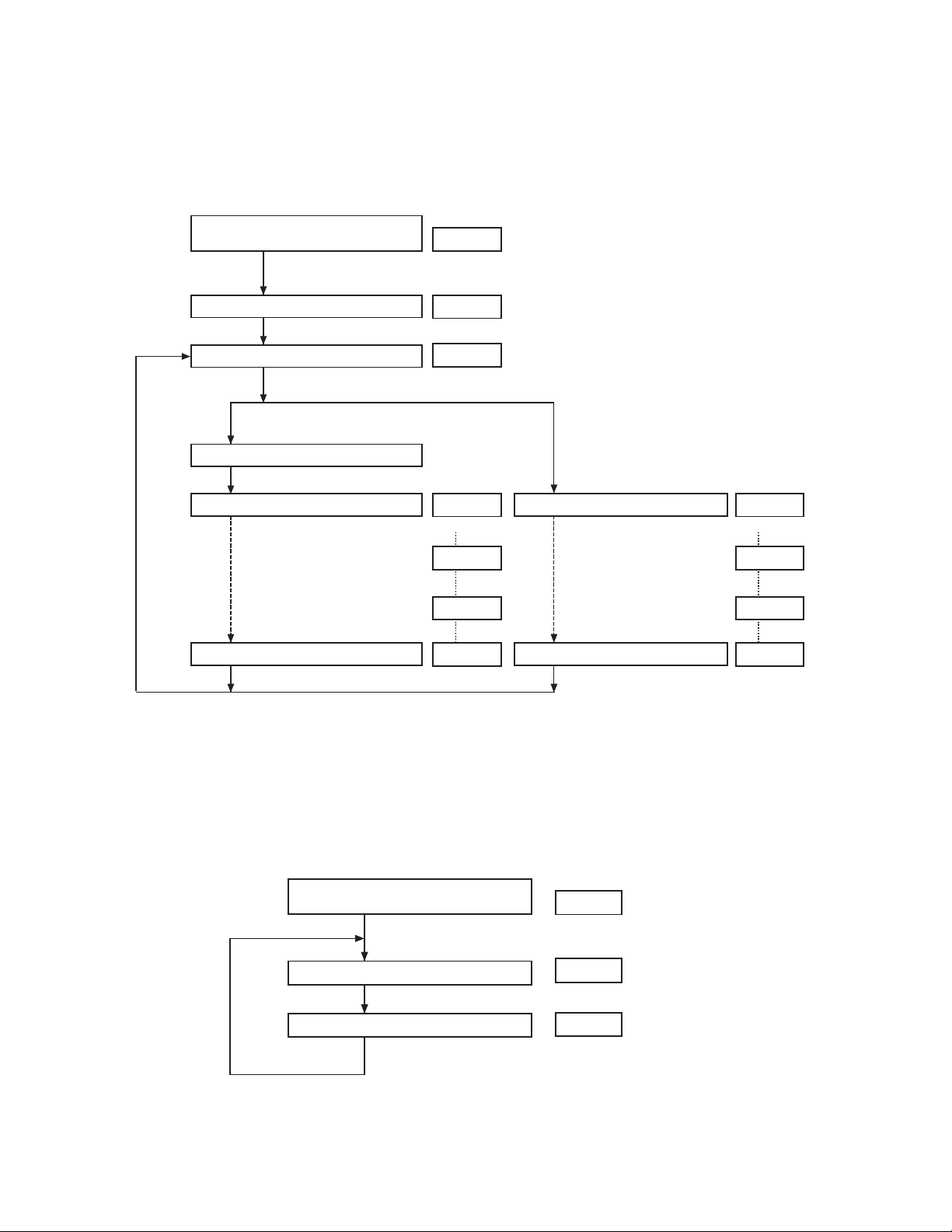
REALIGNMENT/ 模式组合
TK-2118
7. Wireless Clone Mode
The TK-2118 has a wireless Clone function.
When the wireless clone function is disabled through using
the FPU, clone mode cannot be turned ON.
[MONI]+[LOW]+[POWER ON](2sec)
[MONI]+[LOW]+[电源ON] (2秒)
Clone mode
Select freguency
Master /
Press PTT
Transmit data
主机
复制模式
选择频率
按下PTT
传送数据
RED LED / 红灯
display
150.000
154.000
CLOnE 0
CLOnE 20
7. 无线复制模式
TK-2118具有无线复制功能。
当使用FPU禁止无线复制功能时,不可接通复制模式。
Default freqency / 缺省频率
You must select a frequency
within this radio's range /
您必须从该手持机的范围中选择频率
Note: You can clone the programmed data
between the transceiver frequency
version must be same
注释: 用户可以在手持机之间复制下表列出的
编程数据。频率必须一致
Slave / 子机
Receive data
接收数据
CLOnE 0
Green LED / 绿灯
CLOnE 20
CLOnE 95
All date is transmitted
[MONI]
所有数据已传送
END
Notes:
• Remove the antenna from the master radio.
•Attach the antenna to the slave radio.
• During cloning do not perform any action which
might interrupt the cloning, such as cutting off the
power to the transceiver.
8. ALL RESET / 全部复位
[MONI]+[DIAL]+[POWER ON](2sec) /
[MONI]+[DIAL]+[电源ON] (2秒)
Self programming mode
PTT(first press)+[LOW]
自台编程模式
PTT(第一按下)+[LOW]
CLOnE 95
All date is received
注释注释
::
注释
:
注释注释
::
将天线从主机拆下。将天线从主机拆下。
•
将天线从主机拆下。
将天线从主机拆下。将天线从主机拆下。
将天线装到子机上。将天线装到子机上。
•
将天线装到子机上。
将天线装到子机上。将天线装到子机上。
在复制过程中不要执行可能中断复制的任何动作,如关在复制过程中不要执行可能中断复制的任何动作,如关
•
在复制过程中不要执行可能中断复制的任何动作,如关
在复制过程中不要执行可能中断复制的任何动作,如关在复制过程中不要执行可能中断复制的任何动作,如关
掉手持机的电源。掉手持机的电源。
掉手持机的电源。
掉手持机的电源。掉手持机的电源。
display
SELF
rESEt
所有数据已接收
END
Notes:
• If you use this function, the Radio data is returned
to the default conditions.
TK-260 :K, K2
• Some items cannot be programmed using the self
programming mode.
注释注释
注释:
注释注释
如果您使用该功能,则手持机数据返回至缺省状态。如果您使用该功能,则手持机数据返回至缺省状态。
•
如果您使用该功能,则手持机数据返回至缺省状态。
如果您使用该功能,则手持机数据返回至缺省状态。如果您使用该功能,则手持机数据返回至缺省状态。
有的项目不可通过使用自台编程模式来编程。有的项目不可通过使用自台编程模式来编程。
•
有的项目不可通过使用自台编程模式来编程。
有的项目不可通过使用自台编程模式来编程。有的项目不可通过使用自台编程模式来编程。
9
TK-2118
REALIGNMENT/ 模式组合
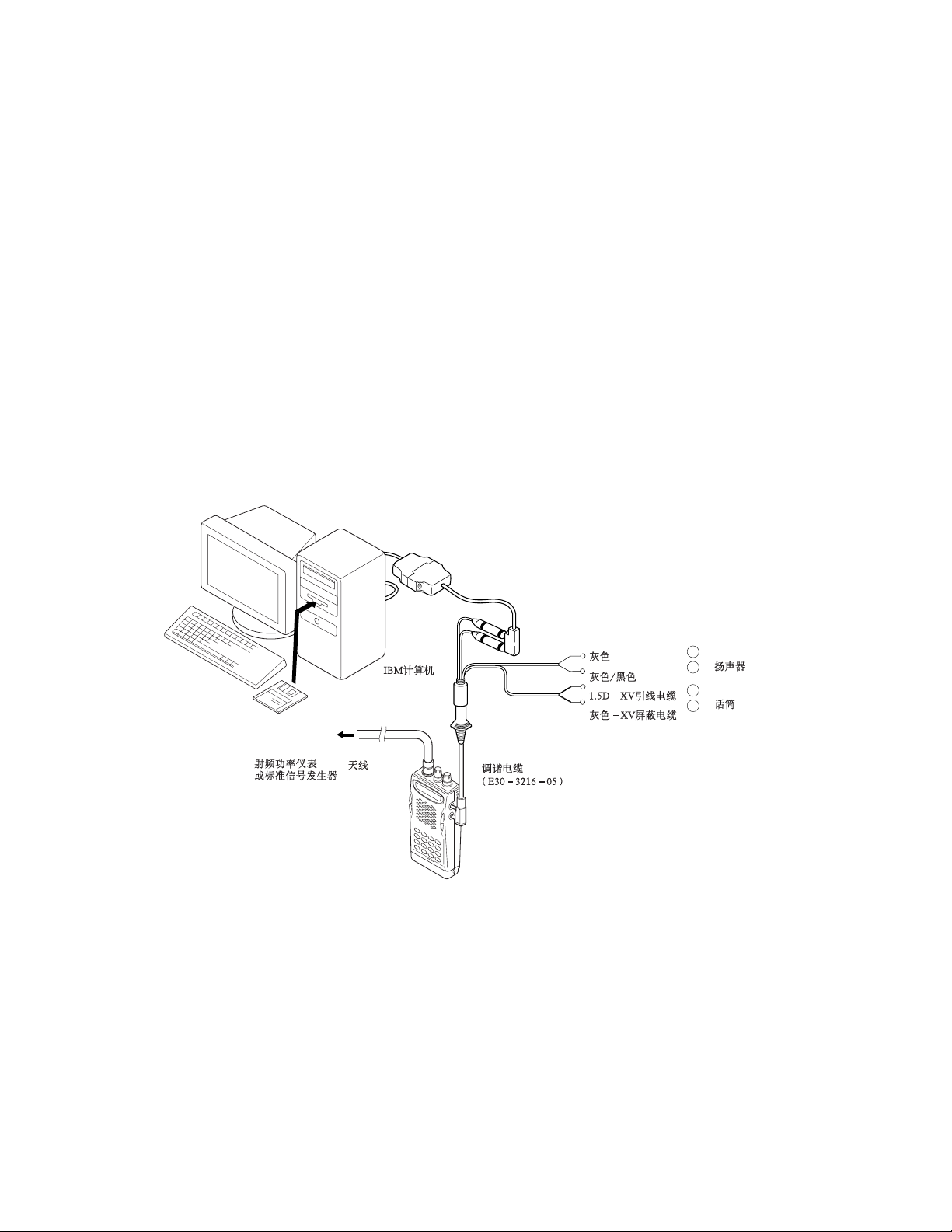
9.PC MODE
Preface
The TK-2118 transceiver can be programmed using a
personal computer, A programming interface cable (KPG-22)
and programming software.
The programming software can be used on an IBM PC or
compatible. Fig-1 shows the setup of a PC for programming.
Caution:
When removing or installing the KPG-22 cable,
first switch off the radio power.
Additionally, be sure to disable the VOX function,
if its enabled, as it can sometimes activate from
connection noise.
Connenction procedure
1. Connect the TK-2118 to the personal Computer using the
interface cable.
2. When the POWER is switched ON, you can enter user
mode.
9. 计算机模式
前言
TK-2118手持机可使用计算机,编程接口电缆(KPG-22)和编
程软件来编程。
编程软件可在IBM计算机或兼容机上使用。图1表示一台计
算机的编程设置过程。
注意注意
::
注意
:
注意注意
::
当拆卸或安装当拆卸或安装
当拆卸或安装
当拆卸或安装当拆卸或安装
另外,一定要禁止另外,一定要禁止
另外,一定要禁止
另外,一定要禁止另外,一定要禁止
动,它有时可被噪音连接激活。动,它有时可被噪音连接激活。
动,它有时可被噪音连接激活。
动,它有时可被噪音连接激活。动,它有时可被噪音连接激活。
连接步骤
1. 使用接口电缆将TK-2118与个人电脑连接。
2. 当接通电源时,您可进入用户模式。
KPG-22KPG-22
KPG-22
KPG-22KPG-22
电缆时,首先关闭手持机的电源。电缆时,首先关闭手持机的电源。
电缆时,首先关闭手持机的电源。
电缆时,首先关闭手持机的电源。电缆时,首先关闭手持机的电源。
VOX(VOX(
VOX(
VOX(VOX(
声控增益声控增益
声控增益
声控增益声控增益
))
功能,如果它被启功能,如果它被启
)
功能,如果它被启
))
功能,如果它被启功能,如果它被启
IBM-PC
KPG-69D
RF Power meter
or SSG
ANT
• KPG-22 description
(PC programming interface cable: Option)
The KPG-22 cable is required to interface the TK-2118 to a
computer. It has a circuit in its D-sub connector (25) pin case
that converts the RS-232C logic level to TTL.
The KPG-22 connects the SP/MIC connector of the TK-2118
to the Computer's RS-232C serial port.
• Programming software description
The software (KPG-69D) allows a user to program the TK2118 radios via the programming interface cable.
KPG-22
Fig. 1 / 图1
Gray
Gray/Black
1.5D-XV Lead wire
Gray-XV Shield wire
Tuning cable
(E30-3216-05)
+
SP
}
-
+
MIC
}
-
• KPG-22说明
(计算机编程接口电缆:可选件)
KPG-22电缆用于将TK-2118与电脑连接。在其D型副插座(25
芯)中有一个电平转换电路,此电路可以把RS-232C逻辑电平
转换为晶体管逻辑电平。
KPG-22将TK-2118的扬声器/ 话筒接头连接到计算机的R S 232C串行端口。
• 编程软件说明
软件(KPG-69D)允许用户通过编程接口电缆来编程TK-2118手
持机。
• Programming with IBM PC
TK-260 :K, K2
If data is transferred to the transceiver from a PC with the
KPG-69D, the destination data (basic radio information) for
each set can be modified.
10
• 使用IBM计算机编程
如果数据从装有KPG-69D的计算机传送到对讲机,则可修改
每组的目标数据(手持机基本设置)。
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION / 电路说明
ANT
ANT SW
RF
AMP
MCF
CF
IF SYSTEM
AF
AMP
RX
TX
PA
AMP
TX
AMP
PLL
VCO
MIC
AMP
TCXO
X4
multiply
51.65MHz
450kHz
51.2MHz
12.8MHz
SP
MIC
ANT
D24, D25
D26, D27
BPF
APC
TUNE
RF AMP
Q20
BPF
MIXER
Q12
MCF
XF1
IF AMP
Q6
CF1
IF, MIX, DET
IC2
AF AMP
LPF, HPF
IC306
AF PA AMP
IC309
SP
WIDE/NARROW SW
Q316
X4
multiply
Q2
IC300
MPU
TCXO
1st Local OSC
(PLL)
ANT SW
TK-2118
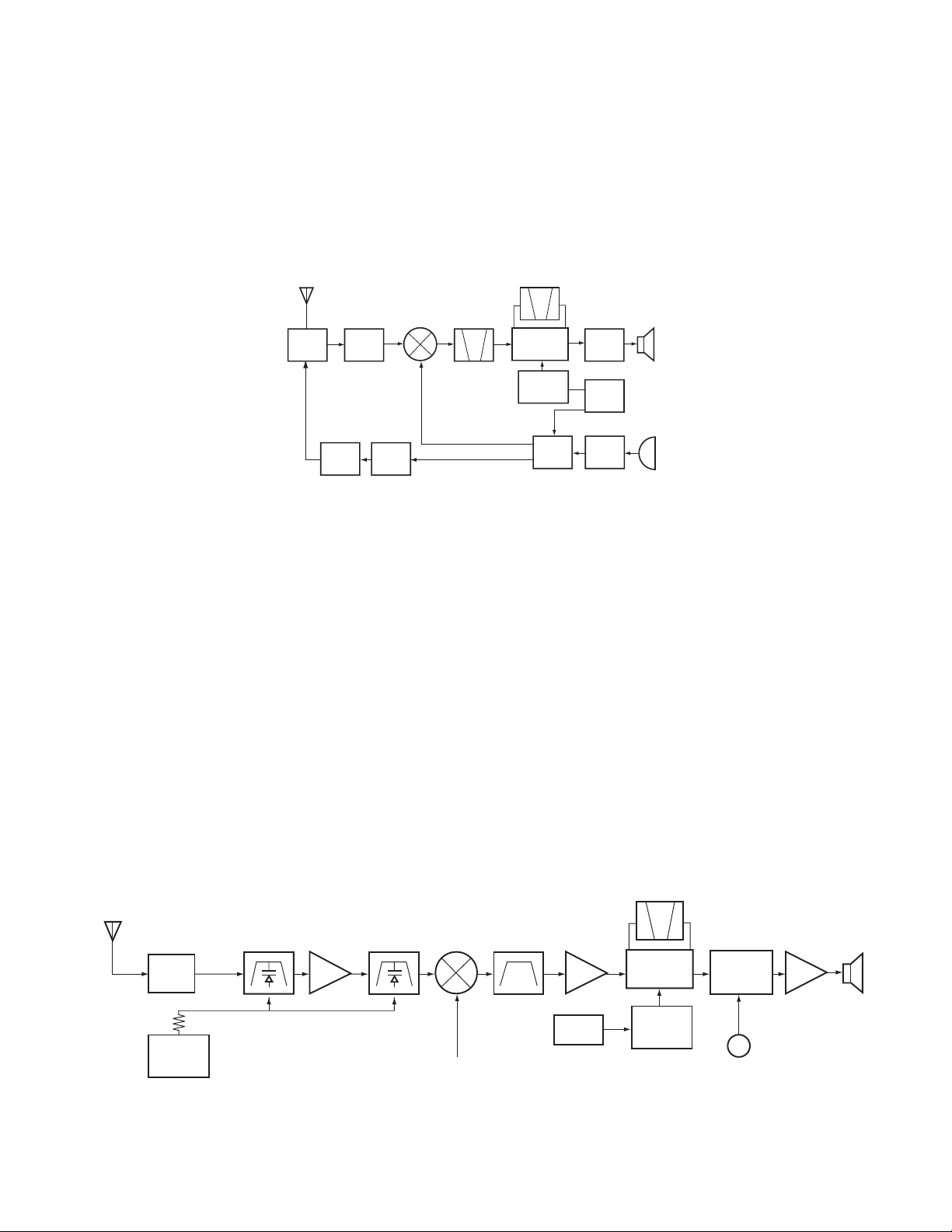
1.Frequency configuration
The receiver utilizes double conversion. The first IF is
51.65MHz and the second IF is 450kHz. The first local
oscillator signal is supplied from the PLL circuit.
The PLL circuit in the transmitter generates the necessary
frequencies. Fig. 1 shows the frequencies.
Fig. 1 Frequency configuration / 图1 电路构成
2.Receiver
The receiver is double conversion superheterodyne,
designed to operate in the frequency range of 150 to 174MHz
(C type), 136 to 150MHz (C2 type).
The frequency configuration is shown in Fig. 1.
1) Front - end RF amplifier
An incoming signal from the antenna is applied to an RF
amplifier (Q20) after passing through a transmit/receive switch
circuit (D24, D25, D26, AND D27 are off) and a band pass
filter (L44, L47 and L49). After the signal is amplified (Q20),
the signal is filtered through a band pass filter (L34 and L40) to
eliminate unwanted signals before it is passed to the first
mixer. Band pass filters (L44, L47, L49, L34 and L40) have
varactor diodes (D21, D22, D23, D16 and D20).
The voltage of these diodes are controlled by to track the
MPU (IC300) center frequency of the band pass filter. (See
Fig. 2)
1. 频率构成
接收部采用二次变频超外差方式。第一中频为51.65MHz·第
二中频为450KHz。第一本振频率信号由锁相环电路(PLL)提
供。
发射部由锁相环电路直接产生所需要的频率。图1显示各种频
率。
2.接收部
接收部为二次变频超外差方式,设计操作的频率范围是150-
174MHz (C),136-150MHz (C2)。
1) 前端射频放大器
从天线输入的信号经过收发转换电路 (D24, D25, D26和D27断
开) 和带通滤波器 (L44, L47和L49) 后,在射频放大器 (Q20) 处放
大。信号被放大后 (Q20),在通过第一混频器之前,经过带通
滤波器 (L34和L40) 滤波来消除不要的信号。带通滤波器(L44,
L47, L49, L34和L40) 有变容二极管 (D21, D22, D23, D16和D20)。
这些变容二极管的电压由带通滤波器的MPU (IC300) 中心频
率控制。(参见图2)
TK-260 :K, K2
Fig. 2 Receiver section configuration / 图2 接收部构成
11
TK-2118
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION / 电路说明
2) First Mixer
The signal from the RF amplifier is heterodyned with the
first local oscillator signal from the PLL frequency synthesizer
circuit at the first mixer (Q12) to create a 51.65MHz first
intermediate frequency (1st IF) signal. The first IF signal is
then fed through two monolithic crystal filters (MCFs : XF1) to
further remove spurious signals.
3) IF amplifier
The first IF signal is amplified by Q6, and then enters IC2
(FM processing IC). The signal is heterodyned again with a
second local oscillator signal within IC2 to create a 450kHz
second IF signal. The second IF signal is then fed through a
450kHz ceramic filter (CF1) to further eliminate unwanted
signals before it is amplified and FM detected in IC2.
XF1:L71-0585-05
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency 51.650MHz
Pass band width ±5.0kHz or more at 3dB
35dB stop band width ±20.0kHz or less
Ripple 1.0dB or less
Insertion loss 4.0dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 70dB or more at fo-910kHz
Te r minal impedance 400Ω/ 2.5PF
2) 第一混频器
来自射频放大器的信号与来自锁相环频率合成器电路的第一
本振信号在第一混频器 (Q12) 处混频并生成51.65MHz的第一中
频 (1st IF) 信号。第一中频信号通过两个单片晶体滤波器 (MCFs:
XF1) 进一步消除邻道的杂波信号。
3) 中频放大器
第一中频信号通过Q6放大,然后进入芯片IC2 (调频处理芯
片)。信号在IC2中与第二本振信号再次混频生成一个450kHz的
第二中频信号。在芯片I C 2 中第二本振信号被放大和鉴频之前,
通过一个450kHz陶瓷滤波器 (CF1) 滤除无用杂散信号。
XF1:L71-0585-05
项目 额定值
标称中心频率 51.650MHz
通频带宽 ±5.0kHz或更大 在3dB内
35dB止频带宽 ±20.0kHz或更小
脉动 1.0dB或更小
插入损耗 4.0dB或更小
保证衰减 70dB或更大 在fo-910kHz
终端阻抗 400Ω / 2.5PF
CF1:L72-0958-05
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency 450kHz
6dB band width ±6.0kHz or more
50dB band width ±12.5kHz or less
Ripple 2.0dB or less at fo ± 4kHz
Insertion loss 6.0dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 35.0dB or more at fo ± 100kHz
Te r minal impedance 2.0 kΩ
4) AF amplifier
The recovered AF signal obtained from IC2 is amplified by
IC306 (1/4), filtered by the IC306 low-pass filter (2/4) and
IC306 high-pass filter (3/4) and (4/4), and de-emphasized by
R404 and C363. The AF signal is then passed through a
WIDE/NARROW switch (Q316). The processed AF signal
passes through an AF volume control and is amplified to a
sufficient level to drive a loud speaker by an AF power
amplifier (IC309).
CF1:L72-0958-05
项目 额定值
标称中心频率 450MHz
6dB频带宽度 ±6.0kHz或更大
50dB频带宽度 ±12.5kHz或更小
脉动 2.0dB或更小
插入损耗 6.0dB或更小
保证衰减 35.0dB或更大
终端阻抗 2.0kΩ / 3PF
4) 音频放大器
在IC2中鉴频解调出的音频信号通过IC306 (1/4) 放大,通过
IC306低通滤波器 (2/4) 以及IC306高通滤波器 (3/4) 和 (4/4) 滤
波,并且通过R404和C363去加重。然后音频信号通过一个宽/
窄转换开关 (Q316)。经过处理的音频信号通过音量控制电路再
经过音频功率放大器 (IC309) 放大后、驱动扬声器。
TK-260 :K, K2
12
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION / 电路说明
TK-2118
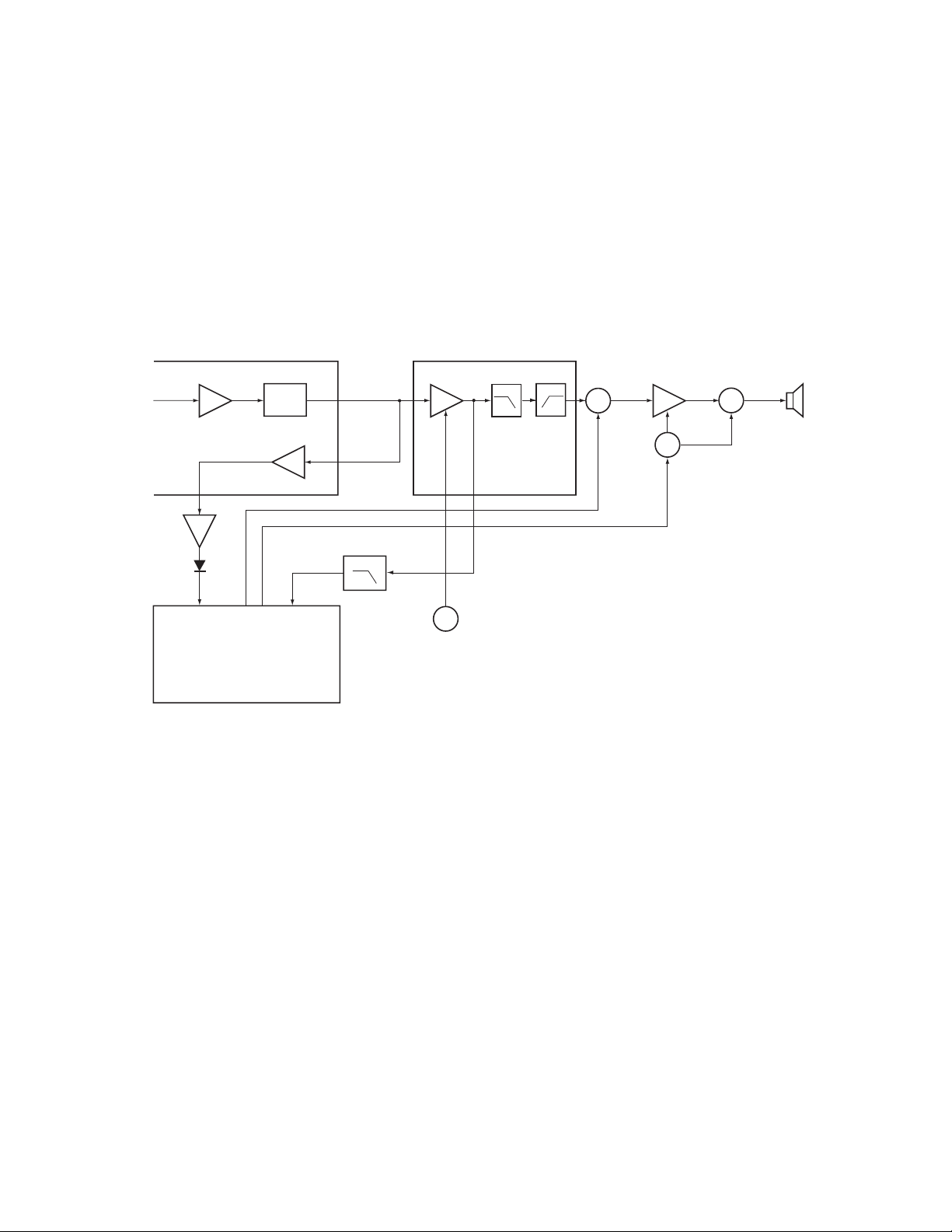
5) Squelch
Part of the AF signal from the IC enters the FM IC again, and
the noise component is amplified and rectified by a filter outside
amplifier Q1, and produce DC level by D1 corresponding to the
noise level.
The DC signal from the FM IC goes to the analog port of the
microprocessor (IC300). IC300 determines whether to output
sounds from the speaker by checking whether the input
voltage is higher or lower than the preset value.
To output sounds from the speaker, IC300 sends a high signal
to the MUTE and AFCO Iines and turns IC309 on through
Q313, Q320, Q321, Q323 and Q324.(See Fig. 3)
IC306
AF AMP
Q316
W/N SW
IF AMP DET
Q1
D1
6
BUSY
FM IF IC
56
MUTE
IC2
55
AFCO
HPF
AMP
5
IC307
LPF
TI
QT/DQT
5) 噪音抑制电路
来自FM IC的部分音频信号再次输入到FM IC,在放大器Q1
出来由滤波器对噪音部分进行放大和整流,并由相应于噪音电
平的D1产生直流电平。
直流信号进入微处理器的模拟端口 (IC300)。IC300通过检测输
入电压是否高于或低于预设值来决定是否通过扬声器输出声
音。
要通过扬声器输出声音,IC300向静音和自动频率控制振荡器
连线发送一个高电平信号并开启IC309通过Q313, Q320, Q321,
Q323和Q324。(参见图3)
LPF HPF
Q313
SW
IC309
AF PA AMP
Q324
SW
Q321, 323, 320
SW
SP
IC300
MPU
Fig. 3 AF Amplifier and squelch / 图3 音频放大器和噪音抑制电路
6) Receive signaling
QT/DQT
300 Hz and higher audio frequencies of the output signal
from IF IC are cut by a low-pass filter (IC307). The resulting
signal enters the microprocessor (IC300). IC300 determines
whether the QT or DQT matches the preset value, and
controls the MUTE and AFCO and the speaker output sounds
according to the squelch results.
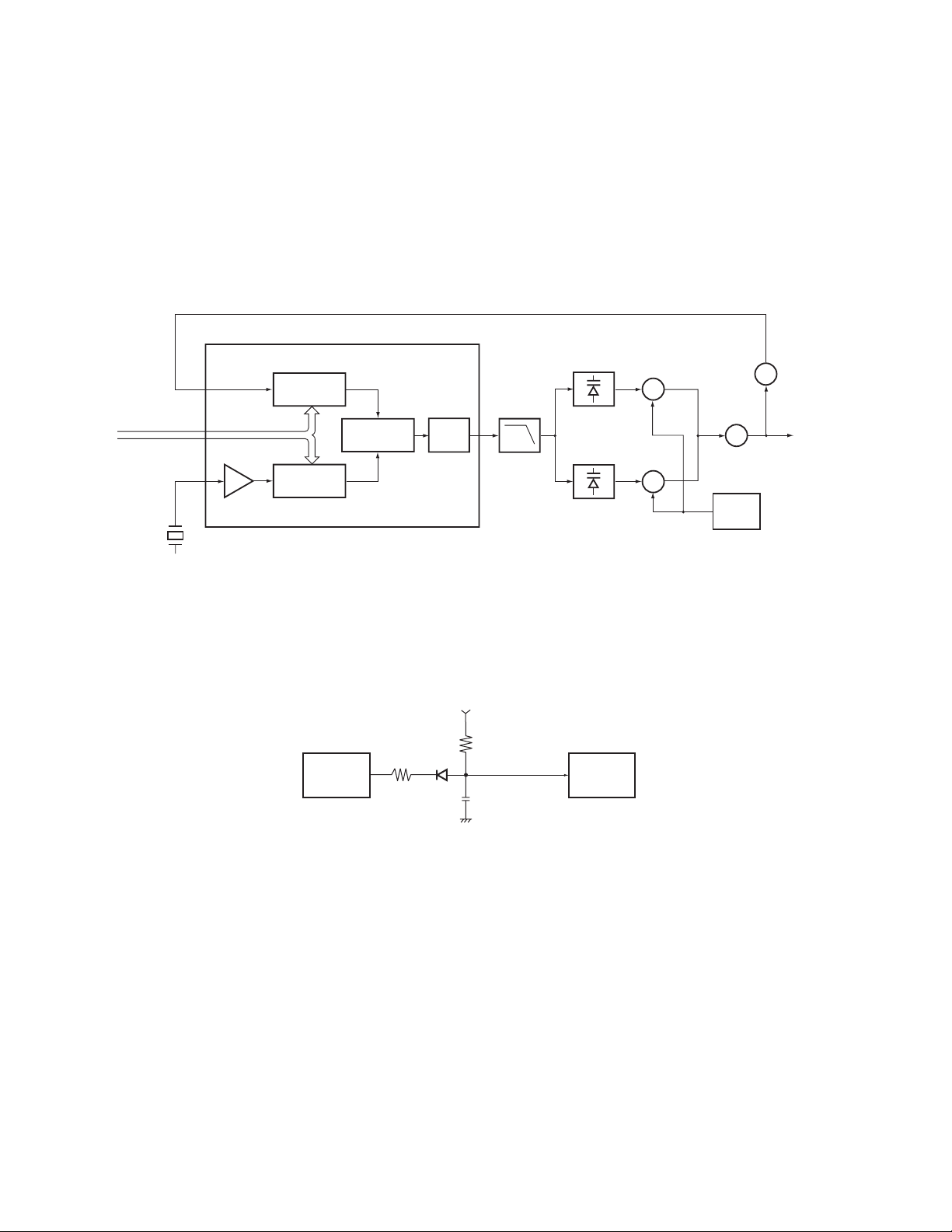
3.PLL frequency synthesizer
The PLL circuit generates the first local oscillator signal for
reception and the RF signal for transmission.
1) PLL
The frequency step of the PLL circuit is 5 or 6.25kHz.
A 12.8MHz reference oscillator signal is divided at IC1 by a fixed
counter to produce the 5 or 6.25kHz reference frequency. The
voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) output signal is buffer
amplified by Q7, then divided in IC1 by a dual-module
programmable counter . The divided signal is compared in phase
with the 5 or 6.25kHz reference signal in the phase comparator in
IC1. The output signal from the phase comparator is filtrered
through a low-pass filter and passed to the VCO to control the
TK-260 :K, K2
oscillator frequency. (See Fig.4)
6) 接受信令
QT/DQT
来自于中频芯片输出信号的300Hz和更高的音频被低频滤波
器 (Q307) 截断。所得到的信号输入微处理器 (IC300)。IC300确
定QT或DQT是否匹配预设置,并且根据噪声抑制电路的结果控
制MUTE和AFCO以及扬声器输出声音。
3. 锁相环频率合成器
锁相环电路生成用于接收的第一本振信号和用于发送的射频
载波信号。
1) 锁相环电路
锁相环电路的步进频率为5或6.25kHz。12.8MHz的参考振荡
器信号通过一个混合计数器在IC1中被分频并生成5或6.25kHz的
参考频率。压控振荡器 (VCO) 输出的信号通过Q7缓冲放大器,
然后在I C 1 中被可编程脉冲吞除计数器分频。被分频的信号在
带有5或6.25kHz参考信号的相位比较器的IC1中被比较。从相位
比较器输出的信号进入一个低通滤波器后,并通过压控振荡器
来控制振荡频率。(参见图4)
13
TK-2118
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION / 电路说明
2) VCO
The operating frequency is generated by Q5 in transmit
mode and Q4 in receive mode. The oscillator frequency is
controlled by applying the VCO control voltage, obtained from
the phase comparator, to the varactor diodes (D4, D6, D8 and
D9 in transmit mode and D5, D7, D10 and D11 in receive
mode). The T/R pin is set high in receive mode causing Q8
and Q9 to turn Q5 off, and turn Q4 on . The T/R pin is set low
in transmit mode. The outputs from Q4 and Q5 are amplified
by Q7 and sent to the buffer amplifiers.
PLL IC IC1
5kHz/6.25kHz
I/N
PLL DATA
REF OSC
I/M
12.8MHz
PHASE
COMPARATOR
5kHz/6.25kHz
CHARGE
PUMP
Fig. 4 PLL circuit / 图4 锁相环电路
3) UNLOCK DETECTOR
If a pulse signal appears at the LD pin of IC1, an unlock
condition occurs, and the DC voltage obtained from D2, R4,
and C12 causes the voltage applied to the UL pin of the
microprocessor to go low. When the microprocessor detects
this condition, the transmitter is disabled, ignoring the push-totalk switch input signal. ( See Fig.5)
2) 压控振荡器
在发射模式中通过Q 5 产生操作频率,在接收模式中通过Q 4
产生操作频率。通过相位比较器到变容二极管 ( 在发射模式中
为D4, D6, D8和D9,在接收模式中为D5, D7, D10和D11) 采用压
控振荡器控制电压来控制振荡频率。在接收模式中,由于Q8和
Q9切断Q5并且导通Q 4,所以发射/接收管脚设置为高电平。在
发射模式中,发射/ 接收管脚设置为低电平。Q 4和Q5 的输出通
过Q7被放大并被发送到缓冲放大器。
D4, 6, 8, 9
LPF
D5, 7, 10, 11
Q5
TX VCO
Q4
RX VCO
Q7
BUFF AMP
Q8, 9
T/R SW
Q3
RF AMP
3) 失锁检测器
如果IC1的LD管脚上出现高电平,则产生失锁状态,并从D2,
R4获得直流电压,且C12产生的提供给微处理器UL管脚的电压
降低。当微处理器检测到此情况时,不能进行发射,无视通话
转换开关输入信号。(参见图5)
5C
IC1
LD
PLL IC
Fig. 5 Unlock detector circuit / 图5 失锁检测器电路
4. Transmitter
1) Transmit audio
The modulation signal from the microphone is amplified by
IC308 (A/4), passes through a preemphasis circuit, and
amplified by the other IC308 (B/4) to perform IDC operation.
The signal then passes through a low-pass filter (splatter fiIter)
IC308 (C/4and D/4) and cuts 3kHz and higher frequencies.
The resulting signal goes to the VCO through the VCO
modulation terminal for direct FM modulation. (See Fig. 6)
2) QT/DQT encoder
A necessary signal for QT/DQT encoding is generated by
IC300 and FM-modulated to the PLL reference signal. Since
the reference OSC does not modulate the loop characteristic
frequency or higher, modulation is performed at the VCO side
TK-260 :K, K2
by adjusting the balance. (See Fig. 6)
14
R4
D2
C12
IC300
UL
MPU
4. 发射部
1) 发射音频
来自于话筒的调制信号通过IC308 (A/4) 被放大,经过一个预
加重电路,并通过另一个IC308 (B/4) 放大后进行IDC处理。然
后信号通过一个低通滤波器 (分离滤波器) IC308 (C/4和D/4) 并滤
除比3kHz频率更高的部分。得到的信号进入压控振荡器直接进
行调频调制。(参见图6)
2) QT/DQT编码器
QT/DQT编码所需的信号通过IC300产生,被锁相环电路的基
准频率调整。由于基准振荡器不能对频率环路特性外的频率进
行调制,因此通过分配器在压控振荡器一侧进行调制。(参见图
6)
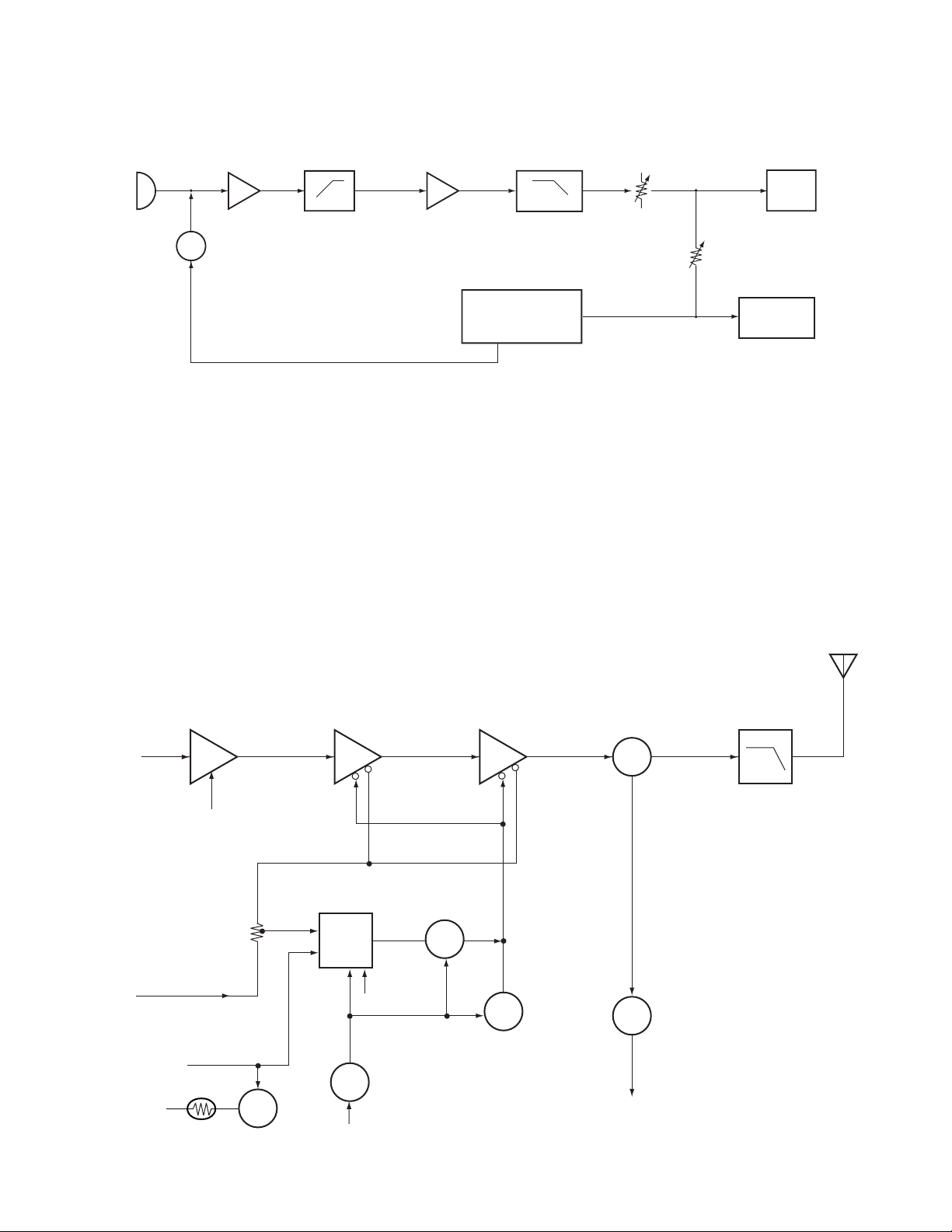
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION / 电路说明
AMP
Q15
DRIVE AMP
Q18
5T
B
DET
IC3
APC
5T
Q23
SW
Q16
SW
APC
5T
Q17
SW
RX
D25, 26
ANT SW
FINAL AMP
Q22
ANT SW
D24, 27
LPF
ANT
5T
SW
Q14
TH1
TK-2118
MIC
IC308 (A/4)
MIC
AMP
Q322
SW
PREEMPHASIS
IC308 (B/4)
IDC
MUTE
Fig. 6 Transmit audio QT/DQT / 图6 发射音频QT/DQT
3) VCO and RF amplifier
The transmit signal obtained from the VCO buffer amplifier
Q11, is amplified by Q15. This amplified signal is passed to
the power amplifier, Q18 and Q22, which consists of a 2-stage
FET amplifier and is capable of producing up to 5W of RF
power. (See Fig.7)
4) ANT switch and LPF
The RF amplifier output signal is passed through a lowpass filter network and a transmit/receive switching circuit
before it is passed to the antenna terminal. The transmit/
receive switching circuit is comprised of D24, D25, D26 and
D27. D25 and D26 turned on (conductive) in transmit mode
and off (isolated) in receive mode.
IC308(C/4, D/4)
LPF
(SPLATTER FILTER)
IC300
TO
QT/DQT
VR302
MAX
DEV
VR301
BALANCE
REFERENCE
VCO
X1, IC1
OSC
(TCXO)
3) 压控振荡器和射频放大器
从压控振荡缓冲放大器(Q11)接收到的发送信号通过Q15被放
大。这个放大信号通过功率放大器,Q18和Q22 (包括一个二级
场效应管放大器),并能产生5W射频功率。(参见图7)
4) 天线转换开关和LPF
在其到达天线终端之前,射频放大器输出信号通过一个低通
滤波器网络和一个发射/ 接收转换电路。发射/ 接收转换电路由
D24, D25, D26和D27构成。D25和D26在发射模式下开启 (通
导),在接收模式下关闭 (隔离)。
TK-260 :K, K2
Fig. 7 APC system / 图7 自动功率控制系统
15
 Loading...
Loading...