
VHF FM TRANSCEIVER
TK-2107
SERVICE MANUAL
Antenna
(T90-0733-05):M3
© 2000-05 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-8536-00(S) 200
Knob
(CHANNEL SELECTOR)
(K29-5278-03)
Knob(VOLUME)
(K29-5255-03)
TK-2107 (16 channels)
Cabinet assy
(A02-2448-13)
CONTENTS
GENERAL.................................................................. 2
REALIGNMENT......................................................... 2
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR................................... 4
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ........................................... 5
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA......................................... 9
DESCRIPTION OF COMPONENTS........................ 10
PARTS LIST............................................................. 11
EXPLODED VIEW ................................................... 17
P ACKING................................................................. 18
ADJUSTMENT......................................................... 19
PC BOARD VIEWS
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6020-21) ................................ 23
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .......................................... 27
BLOCK DIAGRAM .................................................. 31
LEVEL DIAGRAM ................................................... 33
KNB-15A (Ni-Cd BATTERY) ................................... 34
SPECIFICATIONS ................................ BACK COVER
TK-2107
GENERAL/REALIGNMENT
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians
familiar with similar types of commercial grade
communications equipment. It contains all required service
information for the equipment and is current as of the
publication data. Changes which may occur after publication
are covered by either Service Bulletins or Manual Revisions.
These are issued as required.
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment
information, the full part identification number should be
included. This applies to all parts : components, kits, or
chassis. If the part number is not known, include the chassis or
kit number of which it is a part, and a sufficient description of
the required component for proper identification.
REALIGNMENT
1 Modes
PC ModeUser Mode Manufacture Mode
MODE FUNCTION
User Mode Use this mode for normal operation.
PC Mode Use this mode, to make various
settings by means of the FPU through
the RS-232C port.
Manufacture Mode Use this mode, to realign the various
settings through the RS-232C port
during manufacture work.
2 How to enter each mode
MODE PROCEDURE
User Mode Power ON
PC Mode Connect to the IBM PC compatible
machine and controled by the FPU.
PERSONAL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personal
safety :
• DO NOT transmit until all RF connectors are verified secure
and any open connectors are properly terminated.
• SHUT OFF and DO NOT operate this equipment near
electrical blasting caps or in an explosive atmosphere.
• This equipment should be serviced by a qualified
technician only.
SERVICE
This radio is designed for easy servicing. Refer to the
schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and
alignment procedures contained within.
Destnation Number of CH RF power output
M3 16 5W
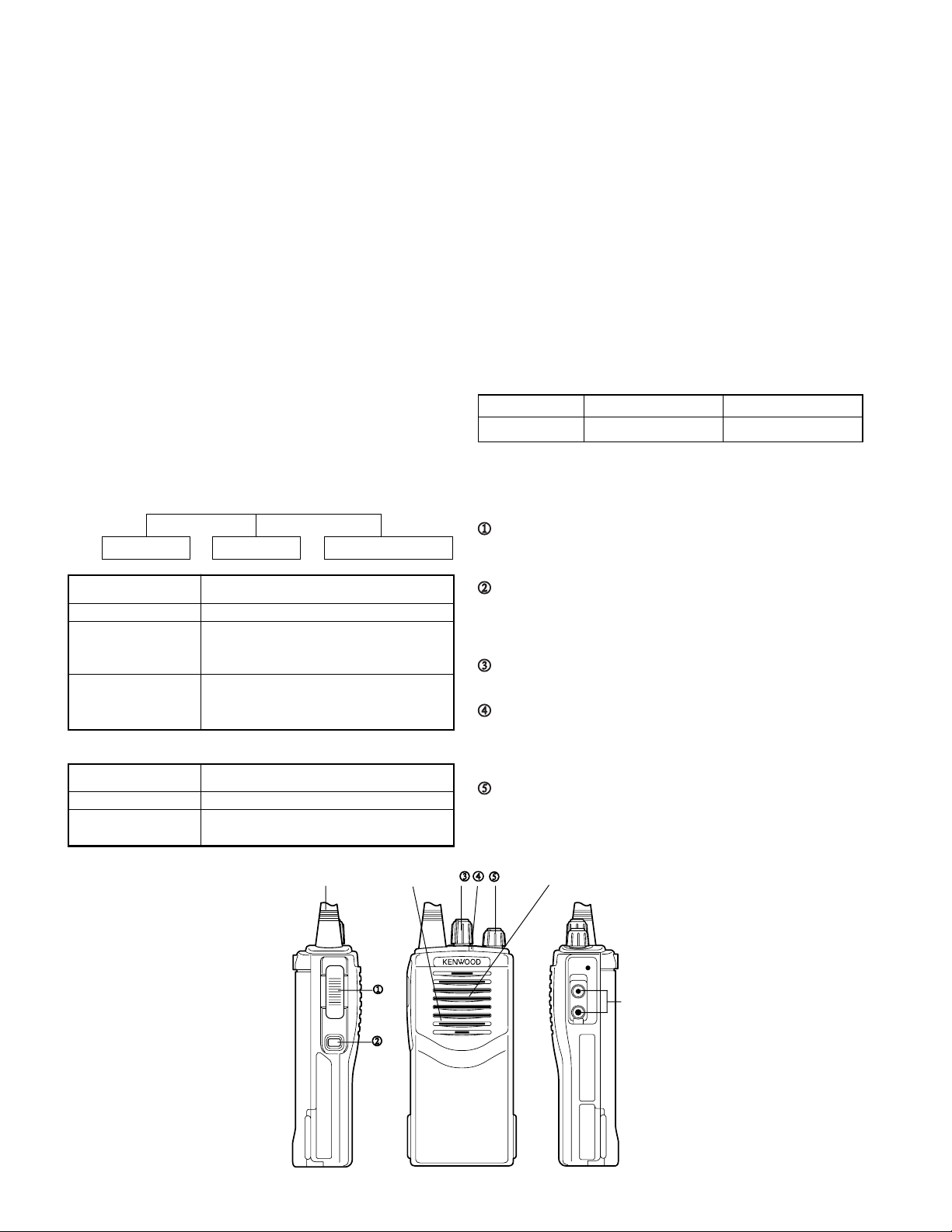
3 Getting acquainted
PTT (Push-To-Talk) switch
Press this switch, then speak into the microphone to
call a station. Release the switch to receive.
Monitor key
Press and hold to monitor how busy the current
channel is and to monitor signals being received that
do not contain the matched QT/DQT code.
Channel selector
Rotate to select channels 1 ~ 16.
LED indicator
Lights red while transmitting, green while receiving a
signal. Flashes red when the battery voltage is low
while transmitting.
Power switch/ Volume control
Turn clockwise to switch the transceiver ON. Turn
counterclockwise until a click sounds, to switch the
transceiver OFF. Rotate to adjust the volume level.
TK-260 :K, K2
2
Antenna
Microphone
Speaker
Speaker/
microphone
jacks
REALIGNMENT
PC MODE
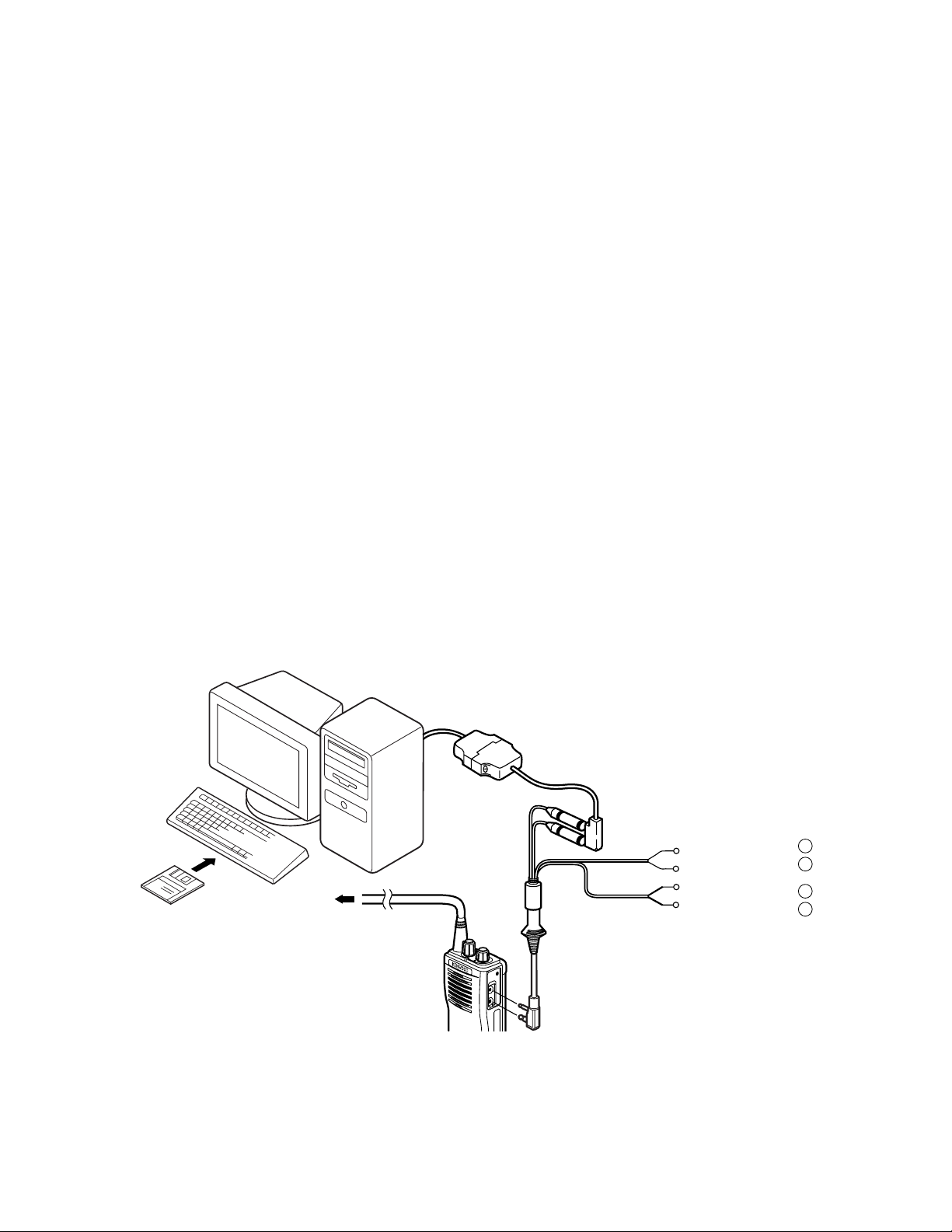
Preface
The transceiver is programmed by using a personal
computer, programming interface (KPG-22) and programming
software (KPG-55D).
The programming software can be used with an IBM PC or
compatible. Figure 1 shows the setup of an IBM PC for
programming.
TK-2107
• KPG-22 description
(PC programming interface cable: Option)
The KPG-22 is required to interface the TK-2107 with the
computer. It has a circuit in its D-subconnector (25-pin) case
that converts the RS-232C Iogic level to the TTL Ievel. The
KPG-22 connects the side panel jacks of the TK-2107 to the
computer's RS-232C serial port.
Connenction procedure
1. Connect the TK-2107 to the personal computer with the
interface cable.
2. When data is transmitting from the transceiver the red LED
lights.
When data is receiving by the transceiver the green LED
lights.
Notes:
• The data stored in the personal computer must match the
Model Name when it is written into the EEPROM.
• Do not press the [PTT] key during data transmission or
reception.
IBM-PC
• Programming software description
The KPG-55D Programming Disk is supplied in 3-1/2" the disk
format. The Software on this disk allows a user to program
TK-2107 radios via a Programming interface cable (KPG-22).
• Programming with IBM PC
If data is transferred to the transceiver from an IBM PC with
the KPG-55D, the destination data (basic radio information)
for each set can be modified. Normally, it is not necessary to
modify the destination data because their values are
determined automatically when the frequency range
(frequency type) is set.
The values should be modified only if necessary.
Data can be programmed into the EEPROM in RS-232C
format via the SP MIC plug.
In this mode the PTT Iine operates as TXD and RXD data
lines respectively.
∗ M3 type has wide mode only.
All narrow data should be not available, even thouth data would
be modified in test mode.
KPG-55D
TK-260 :K, K2
RF Power meter
or SSG
KPG-22
Fig. 1
Tuning cable
(E30-3216-05)
Gray
Gray/Black
1.5D-XV Lead wire
1.5D-XV Shield wire
+
SP
}
-
+
MIC
}
-
3
TK-2107
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
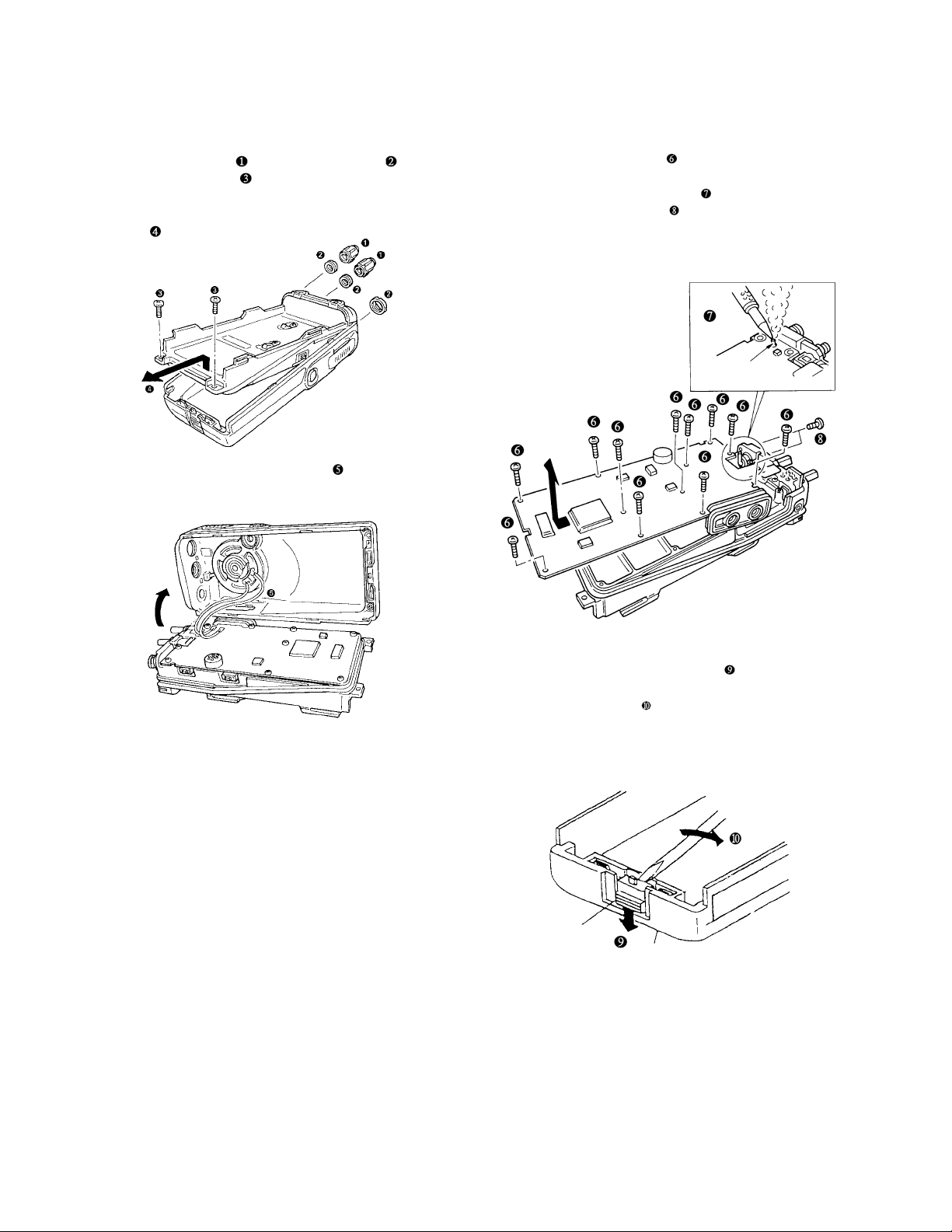
Separating the case assembly from the chassis
1. Remove the two knobs and three round nuts .
2. Remove the two screws .
3. Expand the right and left sides of the bottom of the case
assembly, Iift the chassis, and remove it from the case
assembly .
4. Taking care not to cut the speaker lead , open the chassis
and case assembly.
Separating the chassis from the unit
1. Remove the eleven screws .
2. Remove the solder from the antenna terminal using a
soldering iron then lift the unit off .
3. Remove the two screws and remove the antenna
connector.
Note : When reassembling the unit in the chassis, be sure to
solder the antenna terminal.
Antenna terminal
Removing the lever
1. Raise the lever on the lower case , insert a small flat
screwdriver into the space between the case and lever,
open the case carefully and lift the lever off.
Note : Do not force to separate the case from the lever.
Lever knob
Cace assembly
TK-260 :K, K2
4
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
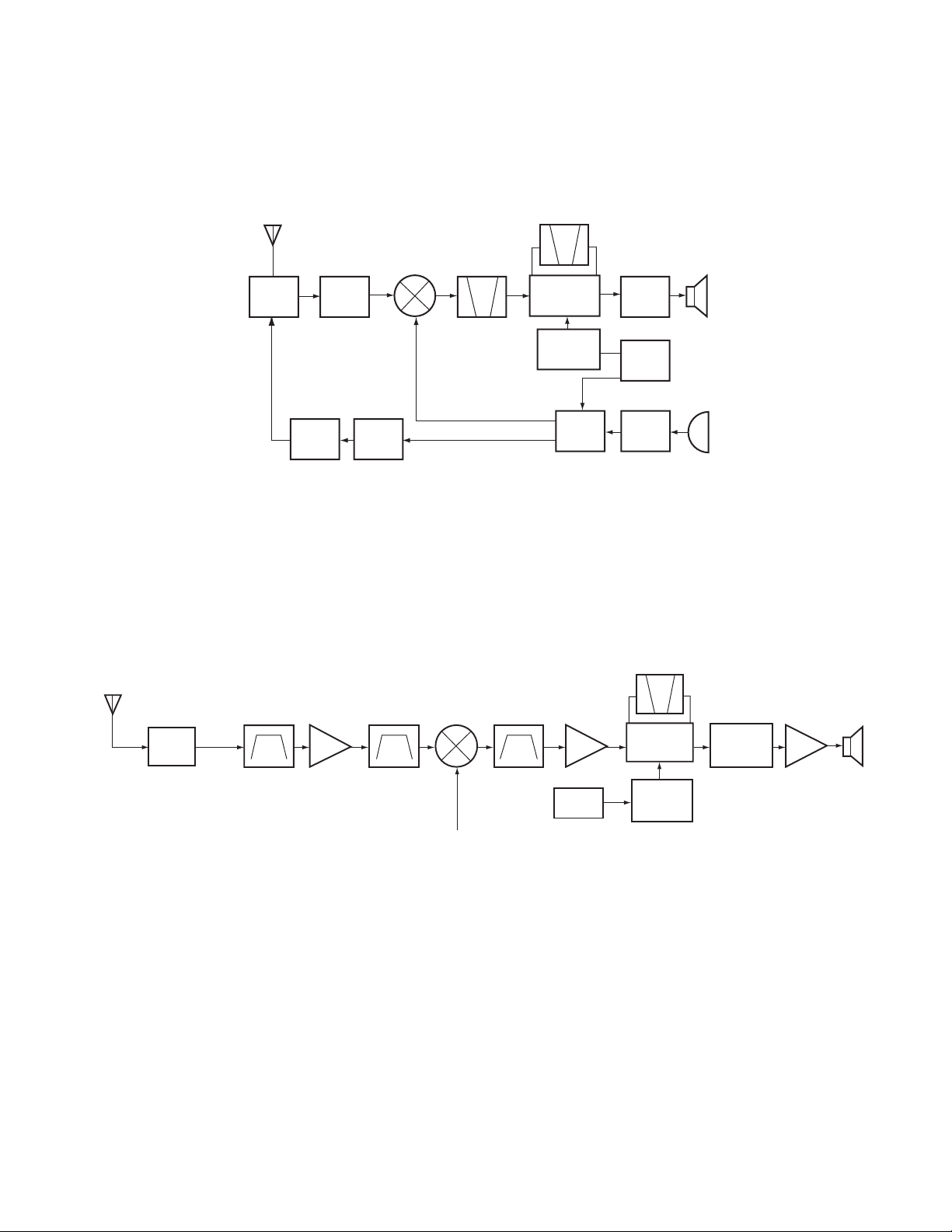
ANT
D102, D103
BPF
RF AMP
Q203
BPF
MIXER
Q202
MCF
XF200
IF AMP
Q201
CF200
IF, MIX, DET
IC200
AF AMP
LPF, HPF
IC300
AF PA AMP
IC302
SP
X3
multiply
Q1
TCXO
1st Local OSC
(PLL)
ANT SW
1.Frequency configuration
The receiver utilizes double conversion. The first IF is
38.85MHz and the second IF is 450kHz. The first local
oscillator signal is supplied from the PLL circuit.
ANT
ANT SW
RF
AMP
38.85MHz
TK-2107
The PLL circuit in the transmitter generates the necessary
frequencies. Fig. 1 shows the frequencies.
CF
450kHz
MCF
38.4MHz
IF SYSTEM
X3
multiply
AF
AMP
TCXO
SP
12.8MHz
RX
PA
AMP
TX
AMP
TX
Fig. 1 Frequency configuration
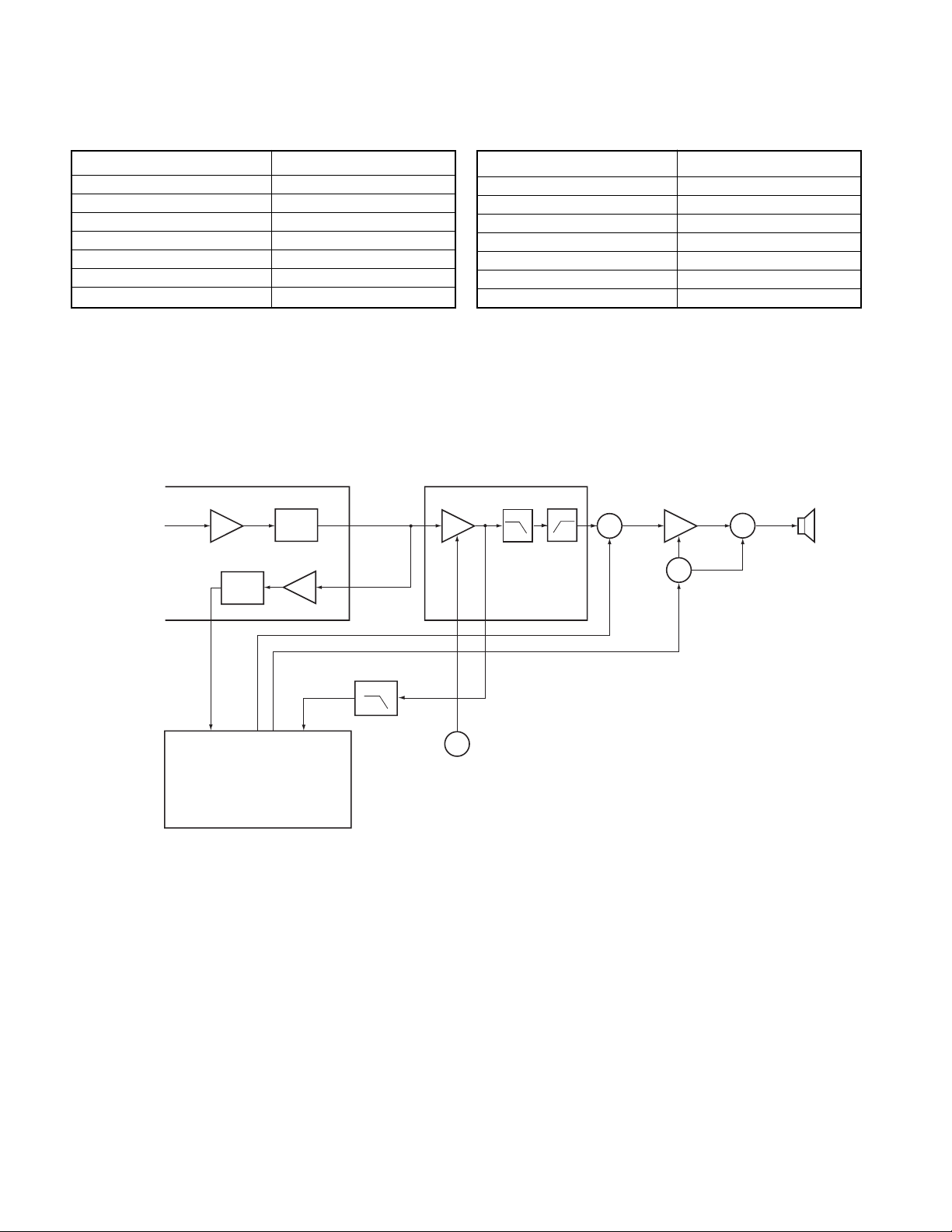
2.Receiver
The receiver is double conversion superheterodyne,
designed to operate in the frequency range of 216 to 223MHz
(M3 type).
The frequency configuration is shown in Fig. 1.
1) Front - end RF amplifier
An incoming signal from the antenna is applied to an RF
amplifier (Q203) after passing through a transmit/receive
switch circuit (D102 and D103 are off) and a band pass filter
(L208, L209 and L210). After the signal is amplified (Q203),
PLL
VCO
MIC
AMP
MIC
the signal is filtered through a band pass filter (L203 and L214)
to eliminate unwanted signals before it is passed to the first
mixer. (See Fig. 2)
Fig. 2 Receiver section configuration
2) First Mixer
The signal from the RF amplifier is heterodyned with the
first local oscillator signal from the PLL frequency synthesizer
circuit at the first mixer (Q202) to create a 38.85MHz first
intermediate frequency (1st IF) signal. The first IF signal is
then fed through two monolithic crystal filters (MCFs : XF200)
to further remove spurious signals.
3) IF amplifier
The first IF signal is amplified by Q201, and then enters
IC200 (FM processing IC). The signal is heterodyned again
with a second local oscillator signal within IC200 to create a
450kHz second IF signal. The second IF signal is then fed
through a 450kHz ceramic filter (CF200) to further eliminate
unwanted signals before it is amplified and FM detected in
TK-260 :K, K2
IC200.
4) AF amplifier
The recovered AF signal obtained from IC200 is amplified
by IC300 (1/4), filtered by the IC300 low-pass filter (2/4) and
IC300 high-pass filter (3/4) and (4/4), and de-emphasized by
R303 and C306. The processed AF signal passes through an
AF volume control and is amplified to a sufficient level to drive
a loud speaker by an AF power amplifier (IC302).
5
TK-2107
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
XF200:L71-0535-05
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency 38.850MHz
Pass band width ±7.5kHz or more at 3dB
40dB stop band width ±40.0kHz or less
Ripple 1.0dB or less
Insertion loss 3.0dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 80dB or more at fo -1000kHz
Terminal impedance 1200Ω / 1.4PF
5) Squelch
Part of the AF signal from the IC enters the FM IC again,
and the noise component is amplified and rectified by a filter
and an amplifier to produce a DC voltage corresponding to the
noise level.
The DC signal from the FM IC goes to the analog port of the
microprocessor (IC403). IC403 determines whether to output
IC200
FM IF IC
IF AMP DET
DET
HPF
AMP
AF AMP
CF200:L72-0979-05
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency 450kHz
6dB band width ±7.5kHz or more
50dB band width ±15kHz or less
Ripple 2.0dB or less at fo ±5kHz
Insertion loss 6.0dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 35.0dB or more at fo ±100kHz
Terminal impedance 1.5 kΩ
sounds from the speaker by checking whether the input
voltage is higher or lower than the preset value.
To output sounds from the speaker, IC403 sends a high
signal to the MUTE and AFCO Iines and turns IC302 on
through Q302, Q304, Q305, Q306 and Q307.(See Fig. 3)
IC300
LPF HPF
Q302
SW
IC302
AF PA AMP
Q307
SW
Q304, 305, 306
SW
SP
6
BUSY
IC403
MPU
MUTE
56762
TI
AFCO
Fig. 3 AF Amplifier and squelch
6) Receive signaling
QT/DQT
300 Hz and higher audio frequencies of the output signal
from IF IC are cut by a low-pass filter (IC301). The resulting
signal enters the microprocessor (IC403). IC403 determines
whether the QT or DQT matches the preset value, and
controls the MUTE and AFCO and the speaker output sounds
according to the squelch results.
TK-260 :K, K2
IC301
LPF
QT/DQT
Q303
W/N SW
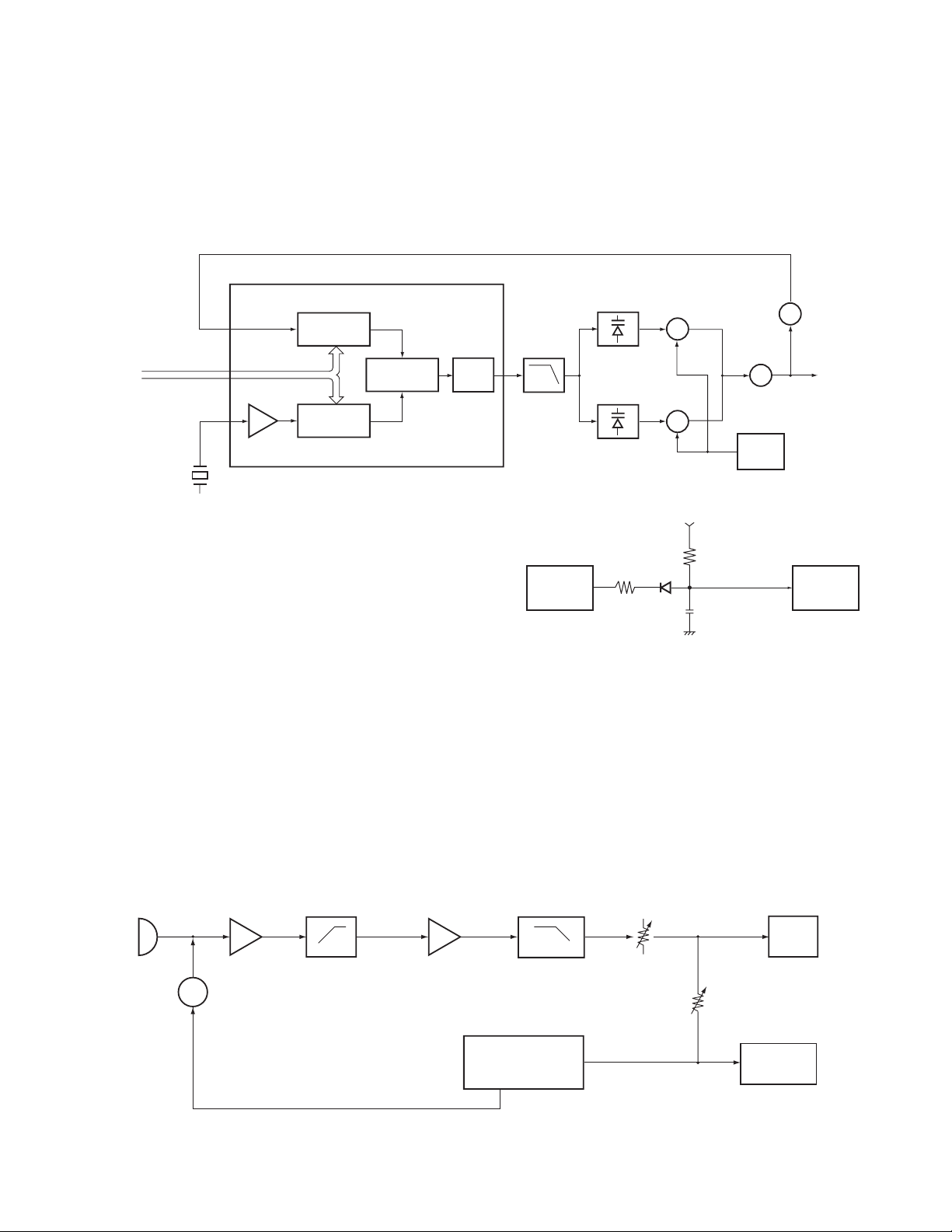
3.PLL frequency synthesizer
The PLL circuit generates the first local oscillator signal for
reception and the RF signal for transmission.
1) PLL
The frequency step of the PLL circuit is 5 or 6.25kHz.
A 12.8MHz reference oscillator signal is divided at IC1 by a fixed
counter to produce the 5 or 6.25kHz reference frequency. The
voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) output signal is buffer
amplified by Q6, then divided in IC1 by a dual-module
programmable counter . The divided signal is compared in phase
with the 5 or 6.25kHz reference signal in the phase comparator in
IC1. The output signal from the phase comparator is filtrered
through a low-pass filter and passed to the VCO to control the
oscillator frequency. (See Fig.4)
6
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
2) VCO
The operating frequency is generated by Q4 in transmit
mode and Q3 in receive mode. The oscillator frequency is
controlled by applying the VCO control voltage, obtained from
the phase comparator, to the varactor diodes (D2 and D4 in
transmit mode and D1 and D3 in receive mode). The T/R pin is
PLL IC IC1
TK-2107
set high in receive mode causing Q5 and Q7 to turn Q4 off,
and turn Q3 on . The T/R pin is set low in transmit mode. The
outputs from Q3 and Q4 are amplified by Q6 and sent to the
buffer amplifiers.
5kHz/6.25kHz
I/N
PLL DATA
REF OSC
I/M
12.8MHz
PHASE
COMPARATOR
5kHz/6.25kHz
CHARGE
PUMP
Fig. 4 PLL circuit
3) UNLOCK DETECTOR
If a pulse signal appears at the LD pin of IC1, an unlock
condition occurs, and the DC voltage obtained from D7, R6,
and C1 causes the voltage applied to the UL pin of the
microprocessor to go low. When the microprocessor detects
this condition, the transmitter is disabled, ignoring the push-totalk switch input signal. (See Fig.5)
4. Transmitter
1) Transmit audio
The modulation signal from the microphone is amplified by
IC500 (1/2), passes through a preemphasis circuit, and
amplified by the other IC500 (1/2) to perform IDC operation.
The signal then passes through a low-pass filter (splatter fiIter)
(Q501 and Q502) and cuts 3kHz and higher frequencies. The
resulting signal goes to the VCO through the VCO modulation
terminal for direct FM modulation. (See Fig. 6)
D1, 2
LPF
D3, 4
IC1
LD
PLL IC
Q4
TX VCO
Q3
RX VCO
D7
Q2
RF AMP
Q6
BUFF AMP
Q5, 7
T/R SW
5C
R6
C1
IC403
UL
MPU
Fig. 5 Unlock detector circuit
2) QT/DQT encoder
A necessary signal for QT/DQT encoding is generated by
IC403 and FM-modulated to the PLL reference signal. Since
the reference OSC does not modulate the loop characteristic
frequency or higher, modulation is performed at the VCO side
by adjusting the balance. (See Fig. 6)
MIC
TK-260 :K, K2
IC500 (1/2)
MIC
AMP
Q503
SW
PREEMPHASIS
Q501, 502
IC500 (1/2)
IDC
MUTE
LPF
(SPLATTER FILTER)
IC403
TO
Fig. 6 Transmit audio QT/DQT
QT/DQT
VR501
MAX
DEV
D5, Q4
VCO
BALANCE
X1, IC1
REFERENCE
OSC
(TCXO)
7
TK-2107
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
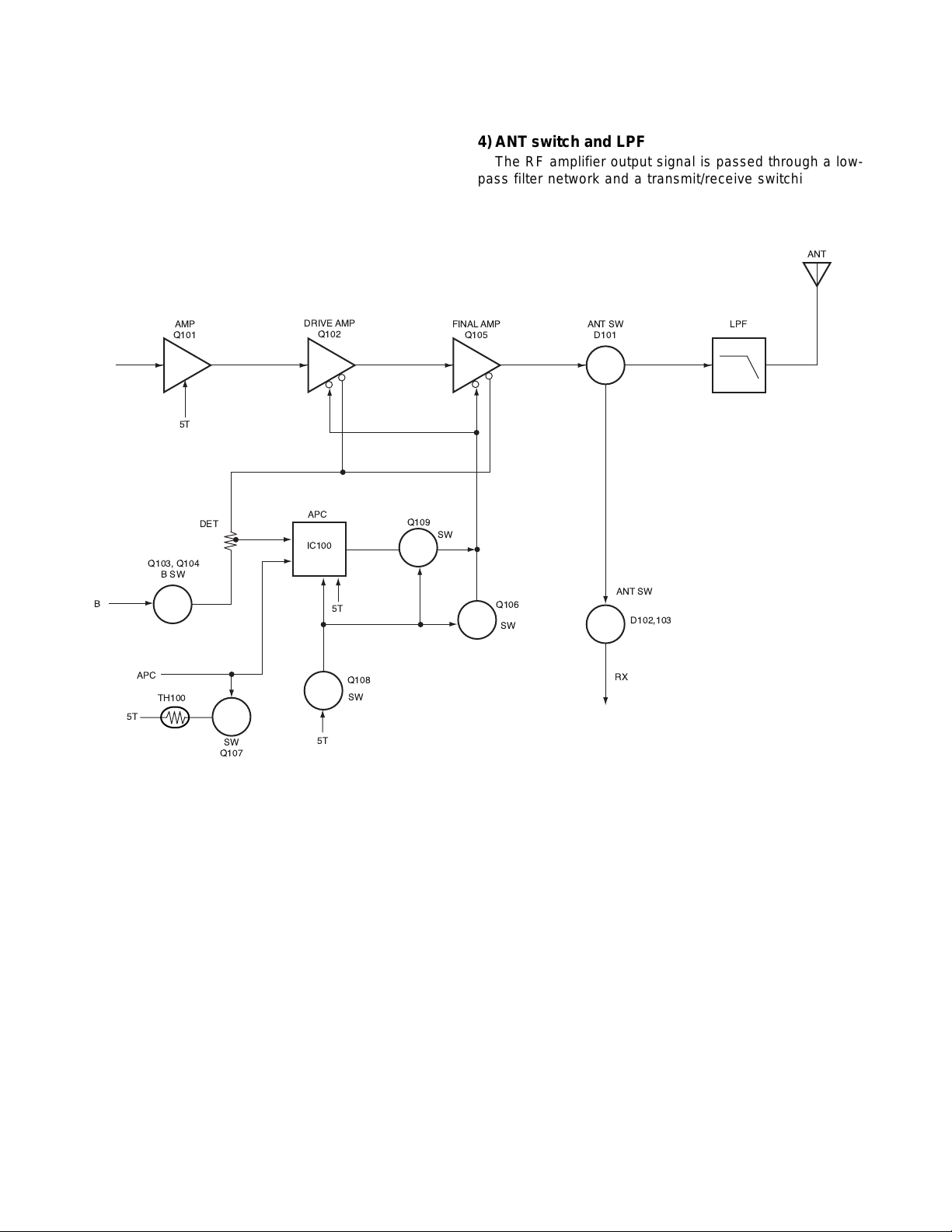
3) VCO and RF amplifier
The transmit signal obtained from the VCO buffer amplifier
Q100, is amplified by Q101. This amplified signal is passed to
the power amplifier, Q102 and Q105, which consists of a 2stage FET amplifier and is capable of producing up to 5W of
RF power. (See Fig.7)
AMP
Q101
5T
DET
Q103, Q104
BSW
B
DRIVE AMP
Q102
APC
IC100
5T
Q109
SW
4) ANT switch and LPF
The RF amplifier output signal is passed through a lowpass filter network and a transmit/receive switching circuit
before it is passed to the antenna terminal. The transmit/
receive switching circuit is comprised of D101, D102 and
D103. D102 and D103 turned on (conductive) in transmit
mode and off (isolated) in receive mode.
FINAL AMP
Q105
Q106
SW
ANT SW
D101
ANT SW
D102,103
LPF
ANT
APC
TH100
5T
SW
Q107
Q108
SW
5T
Fig. 7 APC system
5) APC
The automatic power control (APC) circuit stabilizes the
transmitter output power at a predetermined level by sensing
the drain current of the final amplifier Field Effect Transistor
(FET) . The voltage comparator, IC100 (2/2), compares the
voltage obtained from the above drain current with a reference
voltage which is set using the microprocessor. An APC
voltage proportional to the difference between the sensed
voltage and the reference voltage appears at the output of
IC100 (1/2). This output voltage controls the gate of the FET
power amplifier, which keeps the transmitter output power
constant. The transmitter output power can be varied by the
microprocessor which in turn changes the reference voltage
and hence, the output power.
6) Terminal protection circuit
When the thermistor (TH100) reaches about 80˚C, the
protection circuit turns on Q107 to protect transmitting final
amplifier (Q105) from the over heating.
RX
5. Power supply
A 5V reference power supply [5M] for the control circuit is
derived from an internal battery. This reference is used to
provide a 5V supply in transmit mode [5T], a 5V supply in
receive mode [5R], and a 5V supply common in both modes
[5C] based on the control signal sent from the microprocessor.
6. Control system
The IC403 CPU operates at 7.37MHz . This oscillator has a
circuit that shifts the frequency according to the EEPROM
data.
TK-260 :K, K2
8
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
Microprocessor: M38267M8L241GP (IC403)
Pin No.
TK-260 :K, K2
I/O Port Name Function
1 O VC1 Variable capacity tune control
2 O VC2 Variable capacity tune control
3 I NC NC
4 I TIBI
5 I TI QT/DQT signal input
6 I BUSY Busy input
7 l BATT Battery voltage detection
8 l NC NC
9 O VCCN Frequency regulation output
10 O APC
11 I NC NC
12 I NC NC
13 l NC NC
14 l NC NC
15 O BEEP Beep output
16 O TO QT/DQT output
17 l NC NC
18 I PTT [PTT] key input Connected to RXD
19 O TXD
20 I RXD
21 l NC NC
22 I SELF Self program L : disable
23 I MONl [MONl] key input
24 I NC NC
25 I NC NC
26 I NC NC
27 l NC NC
28 l ENC3 Encode input (channel select)
29 l ENC2 Encode input (channel select)
30 l ENC1 Encode input (channel select)
31 l ENC0 Encode input (channel select)
32 l INTO Power detection control
33 I RST Reset input
34 I NC NC
35 O NC NC
36 l XIN 7.3728MHz oscillator
37 O XOUT 7.3728MHz oscillator
38 I VSS GND
39 O SHIFT Beat shift H : shift on
40 O PABC Final supply H : on
41 O WNRC
42 O WNTC MAX Dev. Control Narrow: H
43 l NC NC
44 l NC NC
45 I NC NC
46 l NC NC
47 l/O SDA EEPROM data line
48 O SCL EEPROM clock line
49 I UL PLL unlock detection pin L : unlock
50 l NC NC
51 I NC NC
52 I NC NC
53 l NC NC
54 I NC NC
55 O DT Common data output
56 O CK Common clock output
57 O NC NC
58 O LE PLL IC enable H : Iatches
QT/DQT external circuit center
point input
TX : Auto power control D/A output
RX : BPF tuning D/A output
RS-232C output Connected to SP/
MIC test(REM)
RS-232C input Connected to [PTT]
line
Audio reference sensitivity
L : narrow
TK-2107
Pin No.
FET : 2SK2596(Q102)
Item V
Rating 17V ±10V 0.4A 3W 150°C -45~+150°C
FET : 2SK2595(Q105)
Item V
Rating 17V ±10V 1.1A 20W 150°C -45~+150°C
I/O Port Name Function
59 O NC NC
60 O NC NC
Control of power supply (5M) for
61 O 5MC
62 O AFCO AF amp power suppIy H : ON
63 O RX TX/RX VCO select H : RX
64 O GLED Green LED control H : Lit
65 O RLED RED LED control H : Lit
66 O SAVE Save control
67 O MUTE
68 O 5RC
69 O 5TC
70 O NC NC
71 O NC NC
72 O NC NC
73 O NC NC
74 O NC NC
75 O NC NC
76 O NC NC
77 O NC NC
78 O NC NC
79 O NC NC
80 O NC NC
81 O NC NC
82 O NC NC
83 O NC NC
84 O NC NC
85 O NC NC
86 O NC NC
87 O NC NC
88 O NC NC
89 l VCC Microcomputer power supply, 5V input
90 l VREF
91 l AVSS
92 O NC NC
93 O NC NC
94 O NC NC
95 O NC NC
96 I NC NC
97 l NC NC
98 I NC NC
99 I NC NC
100 I NC NC
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Ta=25°C)
DSS
GSS
V
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Ta=25°C)
DS
GSS
V
everything except the
microcomputer and EEPROM L
: Power supply ON
H : Save off
Mute control H : Mic mute
L : AF mute
Reception power suppIy control
Transmission power suppIy control
A/D conversion reference voltage ;
connected to Vcc
A/D converter power supply ;
connected to Vss
D
I
Pch* Tch Tstg
*Tc=25°C
D
I
Pch* Tch Tstg
*Tc=25°C
L : on
H : on
9
 Loading...
Loading...