Page 1

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System
Service Manual
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 2

WARRANTY
Keithley Instruments, Inc. warrants this product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a
period of 3 years from date of shipment.
Keithley Instruments, Inc. warrants the following items for 90 days from the date of shipment: probes, cables,
rechargeable batteries, diskettes, and documentation.
During the warranty period, we will, at our option, either repair or replace any product that proves to be defective.
To exercise this warranty, write or call your local Keithley representative, or contact Keithley headquarters in
Cleveland, Ohio. You will be given prompt assistance and return instructions. Send the product, transportation
prepaid, to the indicated service facility. Repairs will be made and the product returned, transportation prepaid.
Repaired or replaced products are warranted for the balance of the original warranty period, or at least 90 days.
LIMITATION OF WARRANTY
This warranty does not apply to defects resulting from product modification without Keithley’s express written
consent, or misuse of any product or part. This warranty also does not apply to fuses, software, non-rechargeable batteries, damage from battery leakage, or problems arising from normal wear or failure to follow instructions.
THIS WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR USE. THE
REMEDIES PROVIDED HEREIN ARE BUYER’S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES.
NEITHER KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC. NOR ANY OF ITS EMPLOYEES SHALL BE LIABLE FOR
ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT
OF THE USE OF ITS INSTRUMENTS AND SOFTWARE EVEN IF KEITHLEY INSTRUMENTS, INC., HAS
BEEN ADVISED IN ADVANCE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. SUCH EXCLUDED DAMAGES SHALL INCLUDE, BUT ARE NOT LIMITED TO: COSTS OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION,
LOSSES SUSTAINED AS THE RESULT OF INJURY TO ANY PERSON, OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY.
Keithley Instruments, Inc.
BELGIUM: Keithley Instruments B.V. Bergensesteenweg 709 • B-1600 Sint-Pieters-Leeuw • 02/363 00 40 • Fax: 02/363 00 64
CHINA: Keithley Instruments China Yuan Chen Xin Building, Room 705 • 12 Yumin Road, Dewai, Madian • Beijing 100029 • 8610-62022886 • Fax: 8610-62022892
FRANCE: Keithley Instruments Sarl 3, allée des Garays • 91127 Palaiseau Cedex • 01-64 53 20 20 • Fax: 01-60 11 77 26
GERMANY: Keithley Instruments GmbH Landsberger Strasse 65 • 82110 Germering • 089/84 93 07-40 • Fax: 089/84 93 07-34
GREAT BRITAIN: Keithley Instruments Ltd The Minster • 58 Portman Road • Reading, Berkshire RG30 1EA • 0118-9 57 56 66 • Fax: 0118-9 59 64 69
INDIA: Keithley Instruments GmbH Flat 2B, WILOCRISSA • 14, Rest House Crescent • Bangalore 560 001 • 91-80-509-1320/21 • Fax: 91-80-509-1322
ITALY: Keithley Instruments s.r.l. Viale S. Gimignano, 38 • 20146 Milano • 02-48 39 16 01 • Fax: 02-48 30 22 74
NETHERLANDS: Keithley Instruments B.V. Postbus 559 • 4200 AN Gorinchem • 0183-635333 • Fax: 0183-630821
SWITZERLAND: Keithley Instruments SA Kriesbachstrasse 4 • 8600 Dübendorf • 01-821 94 44 • Fax: 01-820 30 81
TAIWAN: Keithley Instruments Taiwan 1 Fl. 85 Po Ai Street • Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C. • 886-3572-9077 • Fax: 886-3572-903
• 28775 Aurora Road • Cleveland, OH 44139 • 440-248-0400 • Fax: 440-248-6168 • http://www.keithley.com
9/00
Page 3

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System
Service Manual
©2001, Keithley Instruments, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.A.
First Printing, March 2001
Document Number: 2750-902-01 Rev. A
Page 4

Manual Print History
The print history shown below lists the printing dates of all Revisions and Addenda created
for this manual. The Revision Level letter increases alphabetically as the manual undergoes subsequent updates. Addenda, which are released between Revisions, contain important change information that the user should incorporate immediately into the manual. Addenda are numbered
sequentially. When a new Revision is created, all Addenda associated with the previous Revision
of the manual are incorporated into the new Revision of the manual. Each new Revision includes
a revised copy of this print history page.
Revision A (Document Number 2750-902-01).............................................................. March 2001
All Keithley product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Other brand names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Page 5

Safety Precautions
The following safety precautions should be observed before using this product and any associated instrumentation. Although some instruments and accessories would normally be used with non-hazardous
voltages, there are situations where hazardous conditions may be present.
This product is intended for use by qualified personnel who recognize shock hazards and are familiar
with the safety precautions required to avoid possible injury. Read the operating information carefully
before using the product.
The types of product users are:
Responsible body
ensuring that the equipment is operated within its specifications and operating limits, and for ensuring
that operators are adequately trained.
Operators
and proper use of the instrument. They must be protected from electric shock and contact with hazardous
live circuits.
Maintenance personnel
setting the line voltage or replacing consumable materials. Maintenance procedures are described in the
manual. The procedures explicitly state if the operator may perform them. Otherwise, they should be
performed only by service personnel.
Service personnel
ucts. Only properly trained service personnel may perform installation and service procedures.
Keithley products are designed for use with electrical signals that are rated Installation Category I and
Installation Category II, as described in the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standard
IEC 60664. Most measurement, control, and data I/O signals are Installation Category I and must not
be directly connected to mains voltage or to voltage sources with high transient over-voltages. Installation Category II connections require protection for high transient over-voltages often associated with local AC mains connections. The user should assume all measurement, control, and data I/O connections
are for connection to Category I sources unless otherwise marked or described in the Manual.
Exercise extreme caution when a shock hazard is present. Lethal voltage may be present on cable connector jacks or test fixtures. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) states that a shock hazard exists when voltage levels greater than 30V RMS, 42.4V peak, or 60VDC are present.
practice is to expect that hazardous voltage is present in any unknown circuit before measuring.
Users of this product must be protected from electric shock at all times. The responsible body must ensure that users are prevented access and/or insulated from every connection point. In some cases, connections must be exposed to potential human contact. Product users in these circumstances must be
trained to protect themselves from the risk of electric shock. If the circuit is capable of operating at or
above 1000 volts,
Do not connect switching cards directly to unlimited power circuits. They are intended to be used with
impedance limited sources. NEVER connect switching cards directly to AC mains. When connecting
sources to switching cards, install protective devices to limit fault current and voltage to the card.
Before operating an instrument, make sure the line cord is connected to a properly grounded power receptacle. Inspect the connecting cables, test leads, and jumpers for possible wear, cracks, or breaks before each use.
When installing equipment where access to the main power cord is restricted, such as rack mounting, a
separate main input power disconnect device must be provided, in close proximity to the equipment and
within easy reach of the operator.
is the individual or group responsible for the use and maintenance of equipment, for
use the product for its intended function. They must be trained in electrical safety procedures
are trained to work on live circuits, and perform safe installations and repairs of prod-
no conductive part of the circuit may be exposed.
perform routine procedures on the product to keep it operating, for example,
A good safety
Page 6

For maximum safety, do not touch the product, test cables, or any other instruments while power is applied to
the circuit under test. ALWAYS remove power from the entire test system and discharge any capacitors before:
connecting or disconnecting cables or jumpers, installing or removing switching cards, or making internal
changes, such as installing or removing jumpers.
Do not touch any object that could provide a current path to the common side of the circuit under test or power
line (earth) ground. Always make measurements with dry hands while standing on a dry, insulated surface capable of withstanding the voltage being measured.
The instrument and accessories must be used in accordance with its specifications and operating instructions
or the safety of the equipment may be impaired.
Do not exceed the maximum signal levels of the instruments and accessories, as defined in the specifications
and operating information, and as shown on the instrument or test fixture panels, or switching card.
When fuses are used in a product, replace with same type and rating for continued protection against fire hazard.
Chassis connections must only be used as shield connections for measuring circuits, NOT as safety earth
ground connections.
If you are using a test fixture, keep the lid closed while power is applied to the device under test. Safe operation
requires the use of a lid interlock.
If a screw is present, connect it to safety earth ground using the wire recommended in the user documentation.
!
The symbol on an instrument indicates that the user should refer to the operating instructions located in
the manual.
The symbol on an instrument shows that it can source or measure 1000 volts or more, including the combined effect of normal and common mode voltages. Use standard safety precautions to avoid personal contact
with these voltages.
The
WARNING
read the associated information very carefully before performing the indicated procedure.
The
CAUTION
invalidate the warranty.
Instrumentation and accessories shall not be connected to humans.
Before performing any maintenance, disconnect the line cord and all test cables.
To maintain protection from electric shock and fire, replacement components in mains circuits, including the
power transformer, test leads, and input jacks, must be purchased from Keithley Instruments. Standard fuses,
with applicable national safety approvals, may be used if the rating and type are the same. Other components
that are not safety related may be purchased from other suppliers as long as they are equivalent to the original
component. (Note that selected parts should be purchased only through Keithley Instruments to maintain accuracy and functionality of the product.) If you are unsure about the applicability of a replacement component,
call a Keithley Instruments office for information.
To clean an instrument, use a damp cloth or mild, water based cleaner. Clean the exterior of the instrument
only. Do not apply cleaner directly to the instrument or allow liquids to enter or spill on the instrument. Products that consist of a circuit board with no case or chassis (e.g., data acquisition board for installation into a
computer) should never require cleaning if handled according to instructions. If the board becomes contaminated and operation is affected, the board should be returned to the factory for proper cleaning/servicing.
heading in a manual explains dangers that might result in personal injury or death. Always
heading in a manual explains hazards that could damage the instrument. Such damage may
Rev. 2/01
Page 7

Table of Contents
1 Performance Verification
Introduction ................................................................................ 1-2
Verification test requirements ..................................................... 1-3
Environmental conditions ................................................... 1-3
Warmup period .................................................................... 1-3
Line power .......................................................................... 1-3
Recommended test equipment ................................................... 1-4
Verification limits ....................................................................... 1-5
Example reading limit calculation ...................................... 1-5
Calculating resistance reading limits .................................. 1-5
Restoring factory defaults .......................................................... 1-6
Performing the verification test procedures ............................... 1-6
Verification test summary ................................................... 1-6
Test considerations .............................................................. 1-7
Model 2750 verification ............................................................. 1-8
Verifying DC voltage .......................................................... 1-8
Verifying AC voltage ......................................................... 1-10
Verifying DC current ......................................................... 1-11
Verifying AC current ......................................................... 1-13
Verifying normal resistance .............................................. 1-14
Verifying dry circuit resistance ......................................... 1-16
Verifying temperature ....................................................... 1-18
Verifying frequency .......................................................... 1-20
Model 7700 verification ........................................................... 1-20
Verifying DC voltage ........................................................ 1-21
Verifying AC voltage ......................................................... 1-22
Verifying DC current ......................................................... 1-24
Verifying AC current ......................................................... 1-25
Verifying normal resistance .............................................. 1-26
Verifying dry circuit resistance ......................................... 1-28
Verifying temperature ....................................................... 1-31
Verifying frequency .......................................................... 1-34
Verifying ratio and average ............................................... 1-35
Page 8

2 Calibration
Introduction ................................................................................ 2-2
Environmental conditions ........................................................... 2-2
Warmup period .................................................................... 2-2
Line power ........................................................................... 2-2
Calibration considerations .......................................................... 2-3
Calibration code .......................................................................... 2-4
Front panel calibration code ................................................ 2-4
Remote calibration code ...................................................... 2-4
Comprehensive calibration ......................................................... 2-5
Calibration cycle .................................................................. 2-5
Recommended equipment ................................................... 2-5
Aborting calibration ............................................................ 2-6
Front panel calibration ........................................................ 2-6
Remote calibration ............................................................ 2-14
Manufacturing calibration ........................................................ 2-20
Recommended test equipment .......................................... 2-20
Extender board preparation ............................................... 2-20
Unlocking manufacturing calibration ................................ 2-21
Measuring function generator signal amplitude ................ 2-21
Front panel manufacturing calibration .............................. 2-21
Remote manufacturing calibration .................................... 2-22
Model 7700 calibration ............................................................. 2-23
Recommended test equipment .......................................... 2-23
Extender board connections .............................................. 2-24
Model 7700 calibration ..................................................... 2-24
3 Routine Maintenance
Introduction ................................................................................ 3-2
Setting the line voltage and replacing the line fuse .................... 3-2
Replacing the AMPS fuse ........................................................... 3-4
Replacing Model 7700 plug-in module amps fuses ................... 3-5
Replacing non-volatile RAM battery ......................................... 3-6
Replace the battery as follows: ............................................ 3-7
Plug-in module relay closure count ............................................ 3-8
Closure count commands .................................................... 3-8
Reading relay closure count ................................................ 3-8
Resetting relay closure count .............................................. 3-9
Setting count update interval ............................................... 3-9
Rack mounting .......................................................................... 3-10
Rack mount kit .................................................................. 3-10
Rack mount procedure ...................................................... 3-10
Page 9

4 Troubleshooting
Introduction ................................................................................ 4-2
Repair considerations ................................................................. 4-2
Power-on self-test ....................................................................... 4-3
Front panel tests ......................................................................... 4-3
KEY test .............................................................................. 4-3
DISP test ............................................................................. 4-3
Principles of operation ............................................................... 4-4
Power supply ....................................................................... 4-4
Display board ...................................................................... 4-6
Digital circuitry ................................................................... 4-7
Analog circuitry .................................................................. 4-8
Troubleshooting ....................................................................... 4-13
Display board checks ........................................................ 4-13
Power supply checks ......................................................... 4-13
Digital circuitry checks ..................................................... 4-14
Analog signal switching states .......................................... 4-15
No comm link error .................................................................. 4-23
5 Disassembly
Introduction ................................................................................ 5-2
Handling and cleaning ............................................................... 5-2
Handling PC boards ............................................................ 5-2
Solder repairs ...................................................................... 5-2
Static sensitive devices ........................................................ 5-3
Assembly drawings .................................................................... 5-3
Disassembly procedures ............................................................. 5-4
Case cover removal ............................................................. 5-4
Motherboard removal .......................................................... 5-4
Card cage removal .............................................................. 5-5
Front panel disassembly ...................................................... 5-5
Removing power components ............................................. 5-5
Instrument reassembly ............................................................... 5-6
Input terminal wire connections .......................................... 5-6
Power module wire connections ......................................... 5-7
6 Replaceable Parts
Introduction ................................................................................ 6-2
Parts lists .................................................................................... 6-2
Ordering information ................................................................. 6-2
Factory service ........................................................................... 6-2
Component layouts .................................................................... 6-3
Page 10

A Specifications
B Calibration Reference
Introduction ............................................................................... B-2
Command summary ................................................................... B-2
Miscellaneous calibration commands ........................................ B-4
DC calibration commands ......................................................... B-8
AC calibration commands ....................................................... B-13
Manufacturing calibration commands ..................................... B-15
Model 7700 calibration commands ......................................... B-16
Remote error reporting ............................................................ B-21
Error summary .................................................................. B-21
Error queue ....................................................................... B-24
Status byte EAV (Error Available) bit .............................. B-25
Generating an SRQ on error ............................................. B-25
Detecting calibration step completion ..................................... B-25
Using the *OPC? query .................................................... B-25
Using the *OPC command ............................................... B-26
Generating an SRQ on calibration complete .................... B-26
C Calibration Program
Introduction ............................................................................... C-2
Computer hardware requirements ............................................. C-2
Software requirements ............................................................... C-2
Calibration equipment ............................................................... C-2
General program instructions .................................................... C-3
Page 11

List of Illustrations
1 Performance Verification
Figure 1-1 Connections for Model 2750 DC volts verification ............... 1-9
Figure 1-2 Connections for Model 2750 AC volts verification ............. 1-10
Figure 1-3 Connections for Model 2750 DC current verification ......... 1-12
Figure 1-4 Connections for Model 2750 AC current verification .......... 1-13
Figure 1-5 Connections for Model 2750 resistance verification
(1Ω to 10MΩ ranges) .......................................................... 1-14
Figure 1-6 Connections for Model 2750 resistance verification
(100MΩ range) .................................................................... 1-15
Figure 1-7 Connections for Model 2750 dry circuit
resistance verification .......................................................... 1-17
Figure 1-8 Connections for Model 2750 frequency verification ........... 1-20
Figure 1-9 Connections for Model 7700 DC volts verification ............. 1-21
Figure 1-10 Connections for Model 7700 AC volts verification ............. 1-22
Figure 1-11 Connections for Model 7700 DC current verification ......... 1-24
Figure 1-12 Connections for Model 7700 AC current verification .......... 1-25
Figure 1-13 Connections for Model 7700 resistance verification
(1Ω to 10MΩ ranges) .......................................................... 1-27
Figure 1-14 Connections for Model 7700 resistance verification
(100MΩ range) .................................................................... 1-27
Figure 1-15 Connections for Model 7700 dry circuit
resistance verification .......................................................... 1-29
Figure 1-16 Connections for Model 7700 thermocouple
temperature verification ....................................................... 1-31
Figure 1-17 Connections for Model 7700 frequency verification ........... 1-34
Figure 1-18 Connections for Model 7700 ratio and
average verification .............................................................. 1-35
2 Calibration
Figure 2-1 Low-thermal short connections .............................................. 2-7
Figure 2-2 Connections for DC volts and ohms calibration .................... 2-8
Figure 2-3 Connections for DC and AC amps calibration ..................... 2-11
Figure 2-4 Connections for AC volts calibration ................................... 2-12
Figure 2-5 Function generator connections
for manufacturing calibration .............................................. 2-22
3 Routine Maintenance
Figure 3-1 Power module ........................................................................ 3-3
Figure 3-2 AMPS fuse ............................................................................. 3-4
Figure 3-3 Model 7700 amps fuses ......................................................... 3-5
Figure 3-4 Rack preparation .................................................................. 3-11
Page 12

4 Troubleshooting
Figure 4-1 Power supply block diagram .................................................. 4-4
Figure 4-2 Digital circuitry block diagram .............................................. 4-6
Figure 4-3 Analog circuitry block diagram ............................................. 4-9
Figure 4-4 Simplified schematic of dry circuit ohms ............................. 4-12
C Calibration Program
Figure C-1 Model 2750 calibration program ........................................... C-3
Page 13

List of Tables
1 Performance Verification
Table 1-1 Recommended verification equipment .................................. 1-4
Table 1-2 DCV reading limits ................................................................ 1-9
Table 1-3 ACV reading limits .............................................................. 1-11
Table 1-4 DCI limits ............................................................................ 1-12
Table 1-5 ACI limits ............................................................................. 1-13
Table 1-6 Limits for normal resistance verification ............................. 1-16
Table 1-7 Limits for Model 2750 dry resistance verification ............... 1-18
Table 1-8 Thermocouple temperature verification reading limits ........ 1-19
Table 1-9 Four-wire RTD temperature verification reading limits ...... 1-19
Table 1-10 Plug-in module DCV reading limits .................................... 1-22
Table 1-11 Plug-in module ACV reading limits .................................... 1-23
Table 1-12 Plug-in module DCI limits ................................................... 1-25
Table 1-13 Plug-in module ACI limits ................................................... 1-26
Table 1-14 Limits for plug-in module normal resistance verification ... 1-28
Table 1-15 Limits for plug-in module dry circuit
Table 1-16 Model 7700 thermocouple temperature
Table 1-17 Plug-in module four-wire RTD temperature
resistance verification .......................................................... 1-30
verification reading limits .................................................... 1-32
verification reading limits .................................................... 1-33
2 Calibration
Table 2-1 Recommended equipment for comprehensive calibration ..... 2-5
Table 2-2 Comprehensive calibration procedures .................................. 2-7
Table 2-3 DC volts calibration summary ............................................... 2-9
Table 2-4 Ohms calibration summary .................................................. 2-10
Table 2-5 DC current calibration summary .......................................... 2-11
Table 2-6 AC voltage calibration summary ......................................... 2-12
Table 2-7 AC current calibration summary .......................................... 2-13
Table 2-8 DC voltage calibration programming steps ......................... 2-16
Table 2-9 Resistance calibration programming steps .......................... 2-16
Table 2-10 DC current calibration programming steps .......................... 2-17
Table 2-11 AC voltage calibration programming steps ......................... 2-18
Table 2-12 AC current calibration programming steps .......................... 2-19
Table 2-13 Recommended equipment for manufacturing calibration ... 2-20
Table 2-14 Recommended equipment for Model 7700 calibration ....... 2-23
3 Routine Maintenance
Table 3-1 Power line fuse ....................................................................... 3-3
Table 3-2 Closure count commands ....................................................... 3-8
Page 14

4 Troubleshooting
Table 4-1 Power supply components ...................................................... 4-5
Table 4-2 Display board checks ........................................................... 4-13
Table 4-3 Power supply checks ............................................................ 4-13
Table 4-4 Digital circuitry checks ........................................................ 4-14
Table 4-5 DCV signal switching .......................................................... 4-15
Table 4-6 ACV and FREQ signal switching ........................................ 4-16
Table 4-7
Table 4-8
Table 4-9
Table 4-10
Table 4-11
Table 4-12 DCA signal switching .......................................................... 4-20
Table 4-13 ACA signal switching .......................................................... 4-20
Table 4-14 DCV signal multiplexing and gain ....................................... 4-21
Table 4-15 ACV and ACA signal multiplexing and gain ....................... 4-21
Table 4-16 DCA signal multiplexing and gain ....................................... 4-21
Table 4-17
Table 4-18
Table 4-19
Table 4-20 Switching device locations ................................................... 4-23
Ω
2 signal switching .............................................................. 4-17
Ω
4 signal switching .............................................................. 4-18
Ω
4 dry circuit signal switching ............................................ 4-19
Ω2/Ω
4 reference signal switching ........................................ 4-19
Ω
4 dry circuit reference signal switching ............................ 4-20
Ω
2 signal multiplexing and gain .......................................... 4-22
Ω
4 signal multiplexing and gain .......................................... 4-22
Ω
4 dry circuit signal multiplexing and gain ......................... 4-22
5 Disassembly
Table 5-1 Input terminal wire colors ...................................................... 5-6
Table 5-2 Power module wire colors ...................................................... 5-7
6 Replaceable Parts
Table 6-1 Model 2750 motherboard parts list ........................................ 6-3
Table 6-2 Model 2750 display board parts list ..................................... 6-12
Table 6-3 Model 2750 backplane board parts list ................................ 6-13
Table 6-4 Model 2750 miscellaneous parts list .................................... 6-14
Table 6-5 Model 7700 module parts list ............................................... 6-15
B Calibration Reference
Table B-1 Remote calibration command summary ................................ B-2
Table B-2 DC calibration commands ..................................................... B-8
Table B-3 AC calibration commands ................................................... B-13
Table B-4 Model 7700 calibration commands ..................................... B-16
Table B-5 Calibration errors ................................................................ B-21
Page 15

1
Performance Verification
Page 16

1-2 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Introduction
Use the procedures in this section to verify that Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System
accuracy is within the limits stated in the instrument’s one-year accuracy specifications.
You can perform these verification procedures:
• Make sure that the instrument was not damaged during shipment, and that the unit
meets factory specifications.
• If the instrument’s accuracy is questionable.
• Following calibration.
WARNING
NOTE
There are two general verification procedures in this section:
•
Model 2750 verification
the Model 2750 using the front panel terminals.
•
Model 7700 verification —
ment made through the Model 7700 20-Channel Multiplexer. Note that the same
general procedures can be used to verify measurement accuracy of other Model
2750 plug-in modules that have similar functions. For specific information about
the individual modules, refer to the corresponding module documentation.
The information in this section is intended only for qualified service
personnel. Do not attempt these procedures unless you are qualified to
do so.
If the instrument is still under warranty and its performance is outside specified
limits, contact your Keithley representative or the factory to determine the correct course of action. If the unit is not under warranty, and it fails to meet specified limits, refer to the calibration procedures in Section 2.
— Covers procedures to verify measurement accuracy of
Discusses procedures to verify accuracy of measure-
Page 17

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-3
Verification test requirements
Be sure that you perform the verification tests:
• Under the proper environmental conditions.
• After the specified warmup period.
• Using the correct line voltage.
• Using the proper calibration equipment.
• Using the specified reading limits.
Environmental conditions
Conduct your performance verification procedures in a test environment that has:
• An ambient temperature of 18° to 28°C (65° to 82°F).
• A relative humidity of less than 80% unless otherwise noted.
Warmup period
Allow the Model 2750 to warm up for at least two hours before conducting the verification
procedures.
If the instrument has been subjected to temperature extremes (those outside the ranges
stated above), allow additional time for the instrument’s internal temperature to stabilize.
Typically, allow one extra hour to stabilize a unit that is 10°C (18°F) outside the specified
temperature range.
Also, allow the test equipment to warm up for the minimum time specified by the manufacturer.
Line power
The Model 2750 requires a line voltage of 100V/120V/220V/240V, ±10% and a line frequency of 45Hz to 66Hz or 360Hz to 440Hz. Note that the line frequency is automatically
sensed at powerup, but the line voltage must be manually set to either 100V/120V or
220V/240V as described in Section 3.
Page 18

1-4 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Recommended test equipment
Table 1-1 summarizes recommended verification equipment. You can use alternate equip-
ment as long as that equipment has specifications at least as good as those listed in
Table 1-1. In general, equipment uncertainty should be at least four times better than cor-
responding Model 2750 specifications. Keep in mind, however, that calibrator uncertainty
will add to the uncertainty of each measurement.
Table 1-1
Recommended verification equipment
Fluke 5700A Calibrator:
AC Voltage
DC Voltage
100mV:±14ppm
1.0V:±7ppm
10V:±5ppm
100V:±7ppm
1000V:±9ppm
Fluke 5725A Amplifier:
AC Voltage, 50kHz: 700V, ±375ppm
DC Current, 3A, ±500ppm
AC Current, 1kHz, 3A, ±457ppm
Stanford Research Systems DS345 Function Generator:
1V RMS 1kHz, ±5ppm
General Radio 1433-T Precision Decade Resistance Box:
10Ω to 400Ω, ±0.02%
Miscellaneous Equipment:
Double banana plug to double banana plug shielded cables (2)
BNC to double banana plug shielded cable
Note: The Fluke 5725A amplifier is necessary only if you wish to verify the 750V AC range at 50kHz and 3A AC and DC current
ranges at 3A. Verification at 220V, 50kHz, and 2.2A on the current ranges using only the 5700A calibrator is adequate for most
applications. Calibrator 1Ω uncertainty is not four times better than Model 2750 1Ω range accuracy.
(1kHz, 50kHz) DC Current
100mV:±200ppm
1.0V:±82ppm
10V:±82ppm
100V:±90ppm
700V:±85ppm
20mA:±60ppm
100mA:±70ppm
1A:±110ppm
2.2A:±94ppm
AC Current
(1kHZ) Resistance
1A:±690ppm
2.2A:±682ppm
1Ω:±95ppm
10Ω:±17ppm
100Ω:±17ppm
1kΩ:±12ppm
10kΩ:±11ppm
100kΩ:±13ppm
1MΩ:±18ppm
10MΩ:±37ppm
100MΩ:±120ppm
Page 19

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-5
Verification limits
The verification limits stated in this section have been calculated using only the Model
2750 one-year accuracy specifications, and they do not include test equipment uncertainty.
If a particular measurement falls slightly outside the allowable range, recalculate new limits based on both Model 2750 specifications and pertinent calibration equipment
specifications.
Example reading limit calculation
The following is an example of how reading limits have been calculated. Assume you are
testing the 10V DC range using a 10V input value. Using the Model 2750 one-year accuracy specification for 10V DC of ± (30ppm of reading + 5ppm of range), the calculated
limits are:
Reading limits = 10V ± [(10V × 30ppm) + (10V × 5ppm)]
Reading limits = 10V ± (0.0003 + 0.00005)
Reading limits = 10V ± 0.00035V
Reading limits = 9.99965V to 10.00035V
Calculating resistance reading limits
Resistance reading limits must be recalculated based on the actual calibration resistance
values supplied by the equipment manufacturer. Calculations are performed in the same
manner as shown in the preceding example, except, of course, that you should use the
actual calibration resistance values instead of the nominal values when performing your
calculations.
For example, assume that you are testing the 10kΩ range using an actual 10.03kΩ calibration resistance value. Using Model 2750 one-year 10kΩ range accuracy of ± (100ppm of
reading + 6ppm of range), the calculated reading limits are:
Reading limits = 10.03kΩ ± [(10.03kΩ × 100ppm) + (10kΩ × 6ppm)]
Reading limits = 10.02894kΩ to 10.03106k
Ω
Page 20

1-6 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Restoring factory defaults
Before performing the verification procedures, restore the instrument to its factory
defaults as follows:
1. Press SHIFT and then SETUP. The instrument will display the following prompt:
RESTORE: FACT.
2. Using either range key, select FACT, then restore the factory default conditions by
pressing ENTER.
Performing the verification test procedures
Verification test summary
Verification tests can be performed either through the Model 2750 front panel terminals or
through plug-in modules. This section contains the following procedures:
•
Model 2750 verification
through the front panel terminals.
•
Model 7700 verification
available plug-in modules with the same functions as the Model 7700 20-Channel
Multiplexer Card.
— Use this procedure to test Model 2750 accuracy
— Use this procedure to test accuracy through any of the
Model 2750 tests
Model 2750 verification test procedures include:
• DC volts
• AC volts
• DC current
• AC current
• Resistance
• Temperature
• Frequency
Page 21

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-7
Model 7700 tests
Model 7700 verification test procedures include:
• DC volts
• AC volts
• DC current
• AC current
• Resistance
• Temperature
• Frequency
• Ratio and average
Test considerations
When performing the verification procedures:
• Be sure to restore factory defaults as outlined above.
• Make sure the equipment is properly warmed up and connected to the correct input
terminals. Also make sure that the INPUTS switch is in the correct position.
• Do not use autoranging for any verification tests because autorange hysteresis may
cause the Model 2750 to be on an incorrect range. For each test signal, you must
manually set the correct range for the Model 2750 using the range keys.
• Make sure the calibrator is in operate before you verify each measurement.
• Always let the source signal settle before taking a reading.
Page 22

1-8 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
WARNING
Observe the following safety precautions when performing these tests:
•
Some of the procedures in this section may expose you to dangerous voltages. Use standard safety precautions when such dangerous voltages are encountered to avoid personal injury or death
caused by electric shock.
•
For the front panel terminals only, the maximum common-mode
voltage (voltage between INPUT LO and chassis ground) is 500V
peak. Exceeding this value may cause a breakdown in insulation,
creating a shock hazard.
•
For the plug-in modules, the maximum common-mode voltage
(voltage between any plug-in module terminal and chassis ground)
is listed in the module’s specifications. Exceeding this value may
cause a breakdown in insulation, creating a shock hazard.
•
When using the front panel terminals simultaneously with plug-in
modules, all cable insulation voltage ratings must equal or exceed
the maximum voltage applied to either the front panel terminals or
the plug-in module terminals.
Model 2750 verification
Perform these tests to verify accuracy using the Model 2750 front panel terminals.
Verifying DC voltage
Check DC voltage accuracy by applying accurate voltages from the DC voltage calibrator
to the Model 2750 INPUT jacks and verify that the displayed readings fall within specified
limits.
CAUTION
Follow these steps to verify DC voltage accuracy:
1. Connect the Model 2750 HI and LO INPUT jacks to the DC voltage calibrator as
shown in Figure 1-1. Make sure the INPUTS switch is set to the FRONT position.
NOTE
Do not exceed 1000V peak between front terminals INPUT HI and
INPUT LO because instrument damage may occur.
Use shielded, low-thermal connections when testing the 100mV and 1V ranges
to avoid errors caused by noise or thermal effects. Connect the shield to the calibrator’s output LO terminal.
Page 23
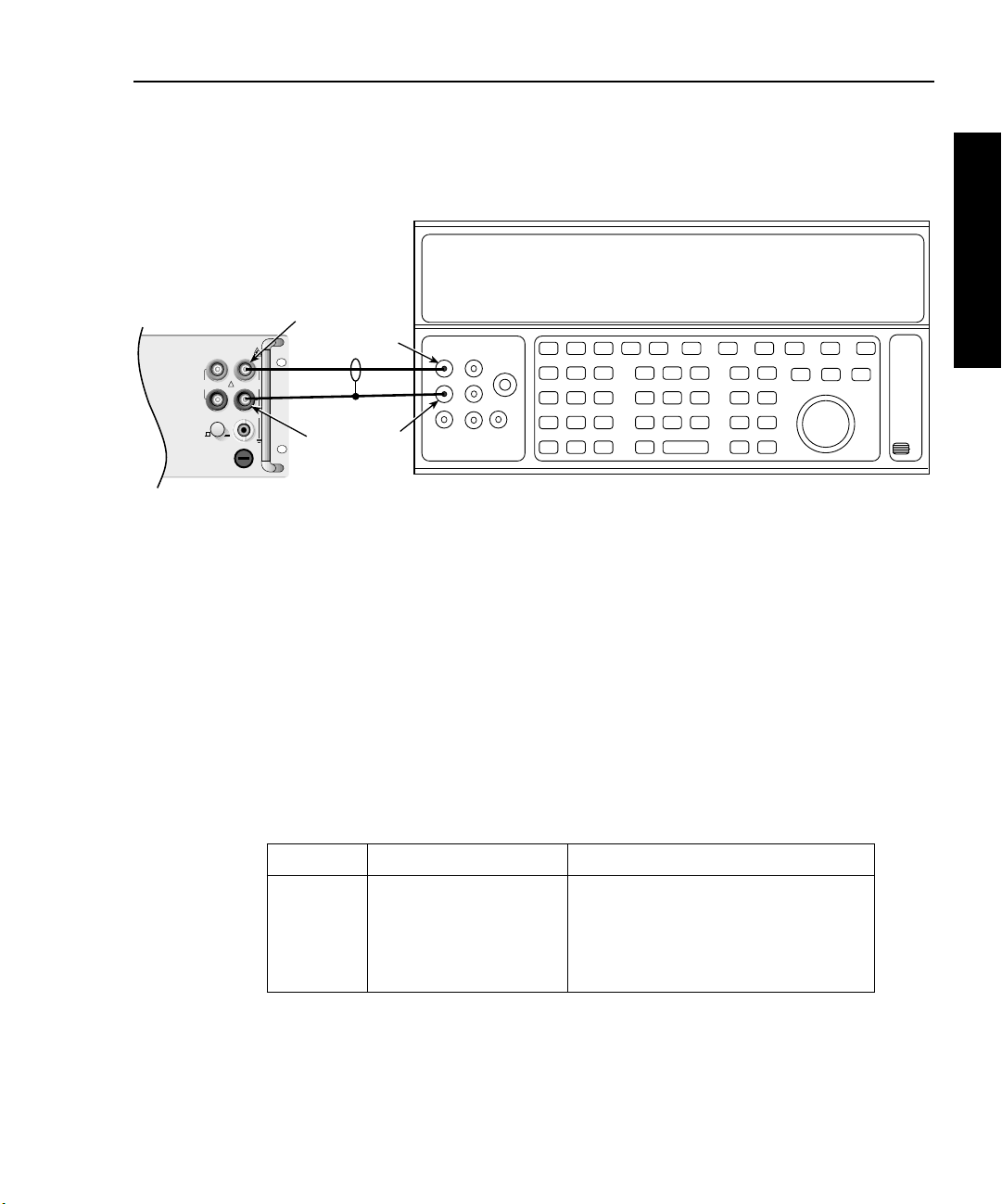
Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-9
Figure 1-1
Connections for Model 2750 DC volts verification
Calibrator (Output DC Voltage)
2750 Verification
Model 2750
Front Panel
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
!
PEAK
LO
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
AMPS
CAT I
Input
HI
Output
HI
1000V
PEAK
500V
PEAK
Input
3A, 250V
LO
Output
LO
Note: Use shielded, low-thermal cables
for 100mV and 1V ranges.
2. Select the DC volts function by pressing the
DCV
key, and set the Model 2750 to
the 100mV range.
3. Set the calibrator output to 0.00000mV DC, and allow the reading to settle.
4. Enable the Model 2750 REL mode. Leave REL enabled for the remainder of the
DC volts verification test.
5. Source positive and negative and full-scale voltages for each of the ranges listed in
Table 1-2. For each voltage setting, be sure that the reading is within stated limits.
Table 1-2
DCV reading limits
Range Applied DC Voltage* Reading Limits (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
100mV
1V
10V
100V
1000V**
*Source positive and negative values for each range.
**Refer to specifications DC note 5 for signal >500V.
100.0000mV
1.000000V
10.00000V
100.0000V
1000.000V
99.9935 to 100.0065mV
0.999963 to 1.000037V
9.99965 to 10.00035V
99.9946 to 100.0054V
999.931 to 1000.069V
Page 24
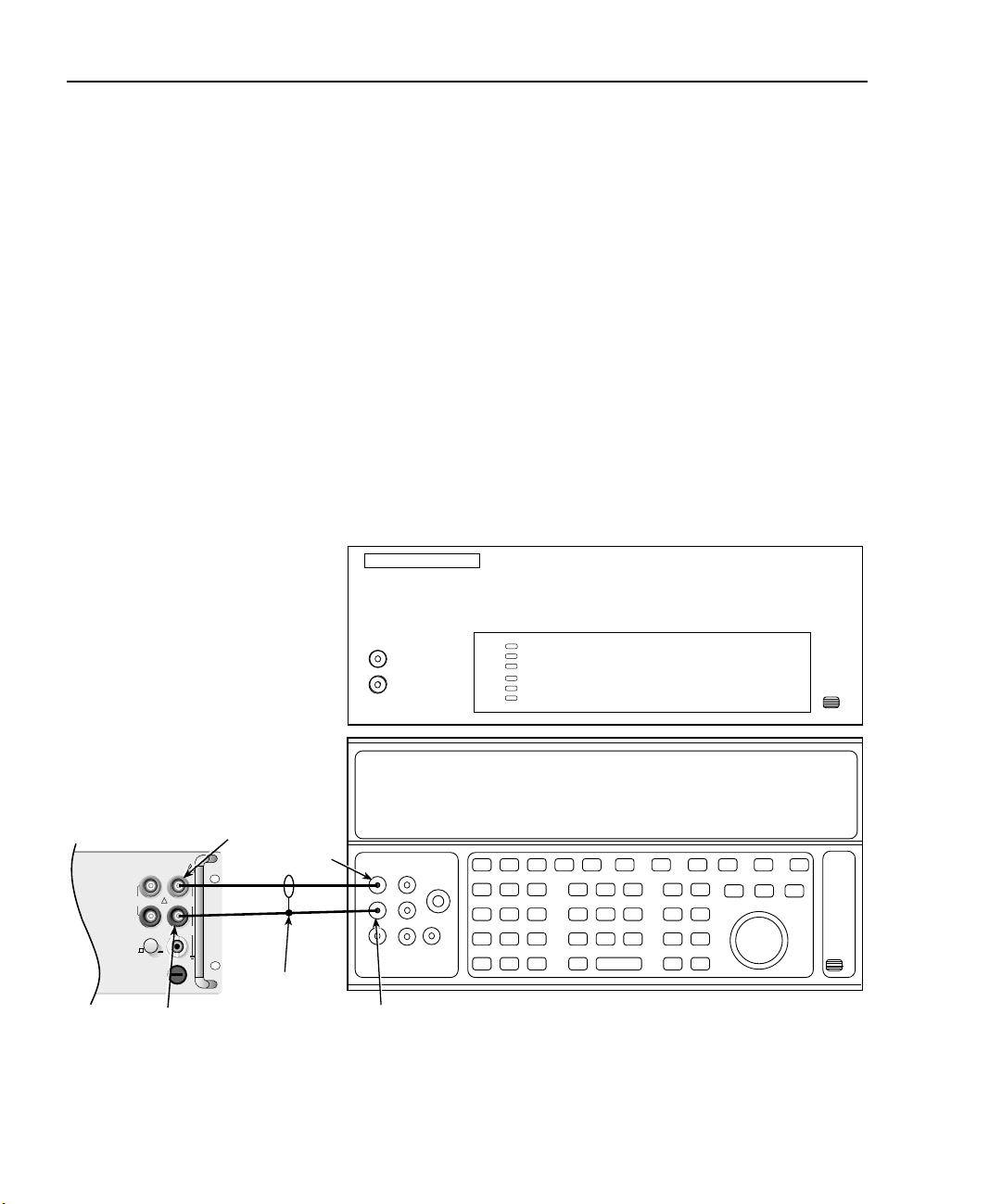
1-10 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Verifying AC voltage
Check AC voltage accuracy by applying accurate AC voltages at specific frequencies from
the AC voltage calibrator to the Model 2750 inputs and verifying that the displayed readings fall within specified ranges.
CAUTION
Do not exceed 1000V peak between front terminals INPUT HI and
INPUT LO, or 8 × 107VHz input, because instrument damage may
occur.
Follow these steps to verify AC voltage accuracy:
1. Connect the Model 2750 HI and LO INPUT jacks to the AC voltage calibrator as
shown in Figure 1-2. Be sure the INPUTS switch is in the FRONT position.
Figure 1-2
Connections for Model 2750 AC volts verification
Note: Amplifier required only for
700V, 50kHz output.
Model 2750
Front Panel
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
!
PEAK
LO
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
AMPS
CAT I
Input
LO
Input
HI
Output
HI
1000V
PEAK
500V
PEAK
3A, 250V
Shielded
Cable
Output
LO
Amplifier (Connect to Calibrator)
Calibrator (Output AC Voltage)
Page 25
Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-11
2. Select the AC volts function by pressing the ACV key.
3. Set the Model 2750 for the 100mV range; make sure that REL is disabled.
4. Source 1kHz and 50kHz AC voltages for each of the ranges summarized in
Table 1-3, and make sure the respective Model 2750 readings fall within stated
limits.
Table 1-3
ACV reading limits
2750 Verification
ACV
Range
100mV
1V
10V
100V
750V
* If the 5725A amplifier is not available, change the 700V @ 50kHz step to 220V @ 50kHz. Reading
limits for 220V @ 50kHz = 219.36 to 220.64V.
Applied AC
100.0000mV
1.000000V
10.00000V
100.0000V
700.000V*
Verifying DC current
Check DC current accuracy by applying accurate DC currents from the DC current calibrator to the AMPS input of the Model 2750 and verify that the displayed readings fall
within specified limits.
Follow these steps to verify DC current accuracy:
1. Connect the Model 2750 AMPS and INPUT LO jacks to the calibrator as shown in
Figure 1-3. Be sure the INPUTS switch is in the FRONT position.
2. Select the DC current measurement function by pressing the DCI key.
Voltage
1kHz Reading Limits
(1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
99.910 to 100.090mV
0.99910 to 1.00090V
9.9910 to 10.0090V
99.910 to 100.090V
699.36 to 700.64V
50kHz Reading Limits
(1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
99.830 to 100.170mV
0.99830 to 1.00170V
9.98300 to 10.0170V
99.830 to 100.170V
698.79 to 701.21V
Page 26
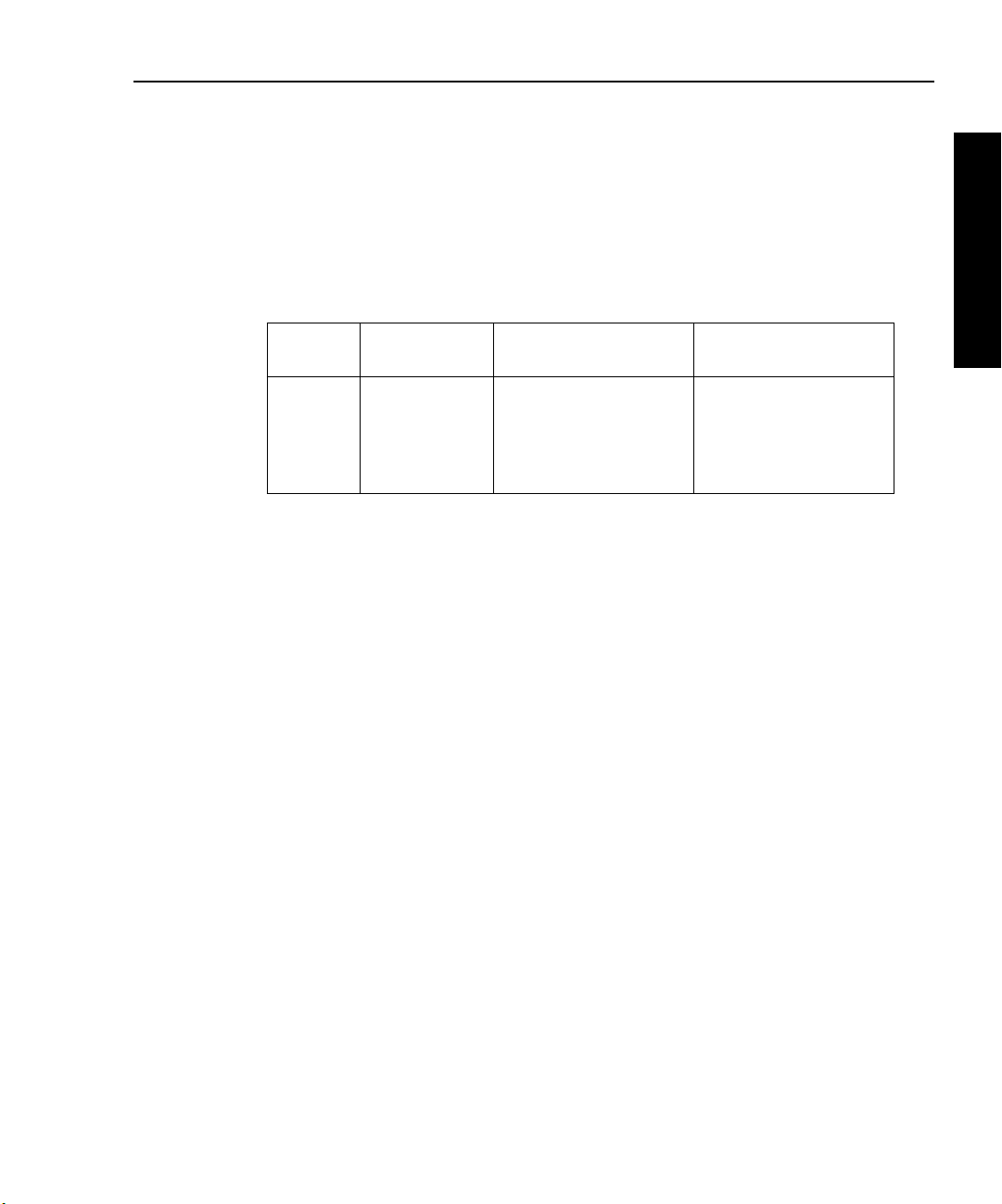
1-12 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Figure 1-3
Connections for Model 2750 DC current verification
Calibrator (Output DC Current)
Model 2750
Front Panel
Output
Input
LO
HI
Output
350V
PEAK
SENSE
Ω 4 WIRE
INPUT
F
FRONT/REAR
CAT I
INPUT
HI
1000V
!
PEAK
LO
500V
PEAK
R
AMPS
LO
Amps
Note: Be sure calibrator is set for normal current output.
3. Set the Model 2750 for the 20mA range.
4. Source positive and negative full-scale currents for each of the ranges listed in
Table 1-4, and verify that the readings for each range are within stated limits.
Table 1-4
DCI limits
DCI Range Applied DC Current* Reading Limits (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
20mA
100mA
1A
3A
* Source positive and negative currents with values shown.
** If the Fluke 5725 amplifier is not available, apply 2.2A from calibrator. Reading limits for 2.2A input
are: 2.197240 to 2.202760A.
20.0000mA
100.0000mA
1.000000A
3.000000A**
19.89960 to 20.01040mA
99.9100 to 100.0900mA
0.999160 to 1.000840A
2.99628 to 3.00372A
Page 27
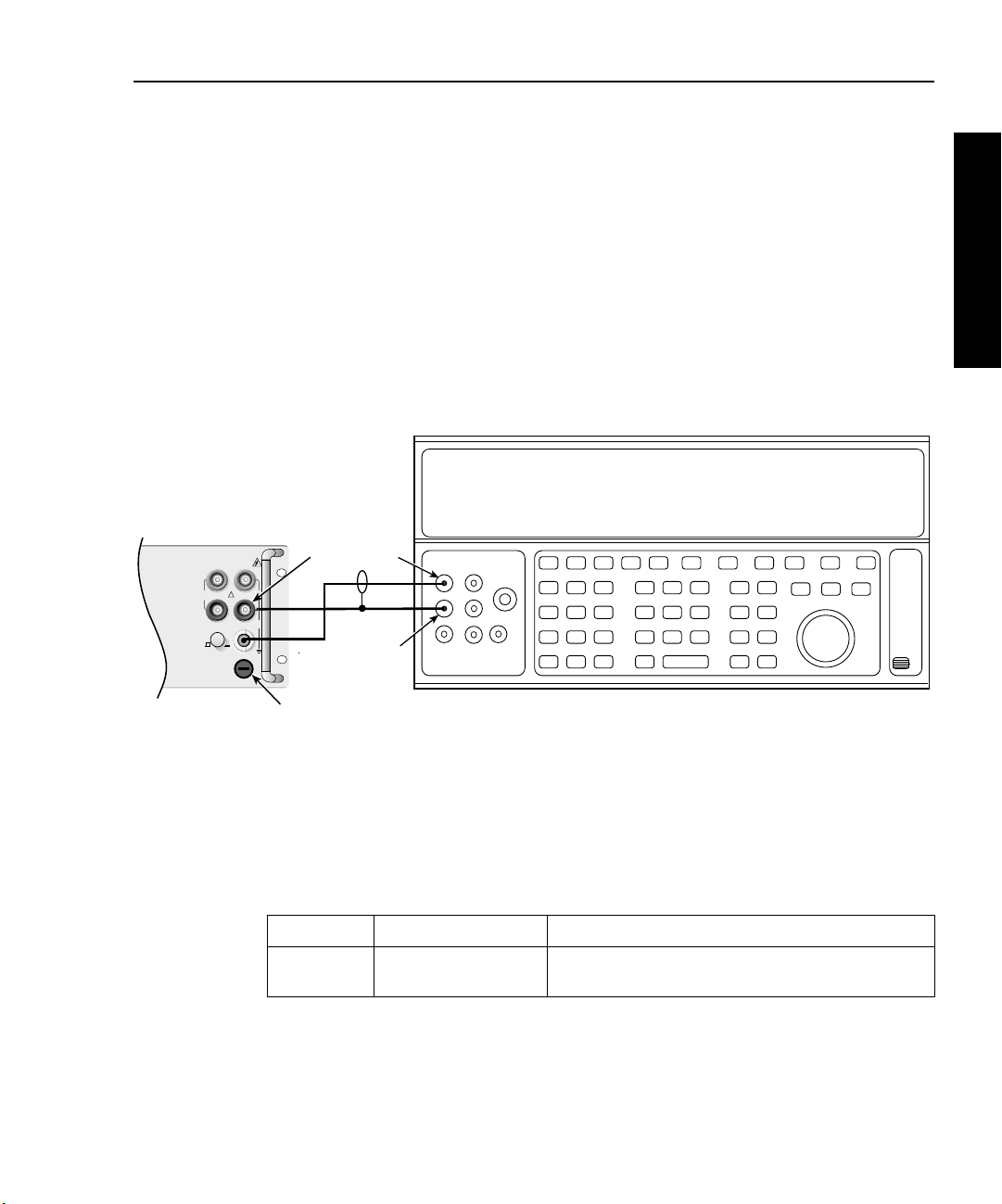
Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-13
Verifying AC current
Check AC current accuracy by applying accurate AC voltage current at specific frequencies from the AC current calibrator to the Model 2750 input, and verify that the displayed
readings fall within specified limits. Follow these steps to verify AC current:
1. Connect the Model 2750 AMPS and INPUT LO jacks to the calibrator as shown in
Figure 1-4. Be sure the INPUTS switch is in the FRONT position.
2. Select the AC current function by pressing the ACI key.
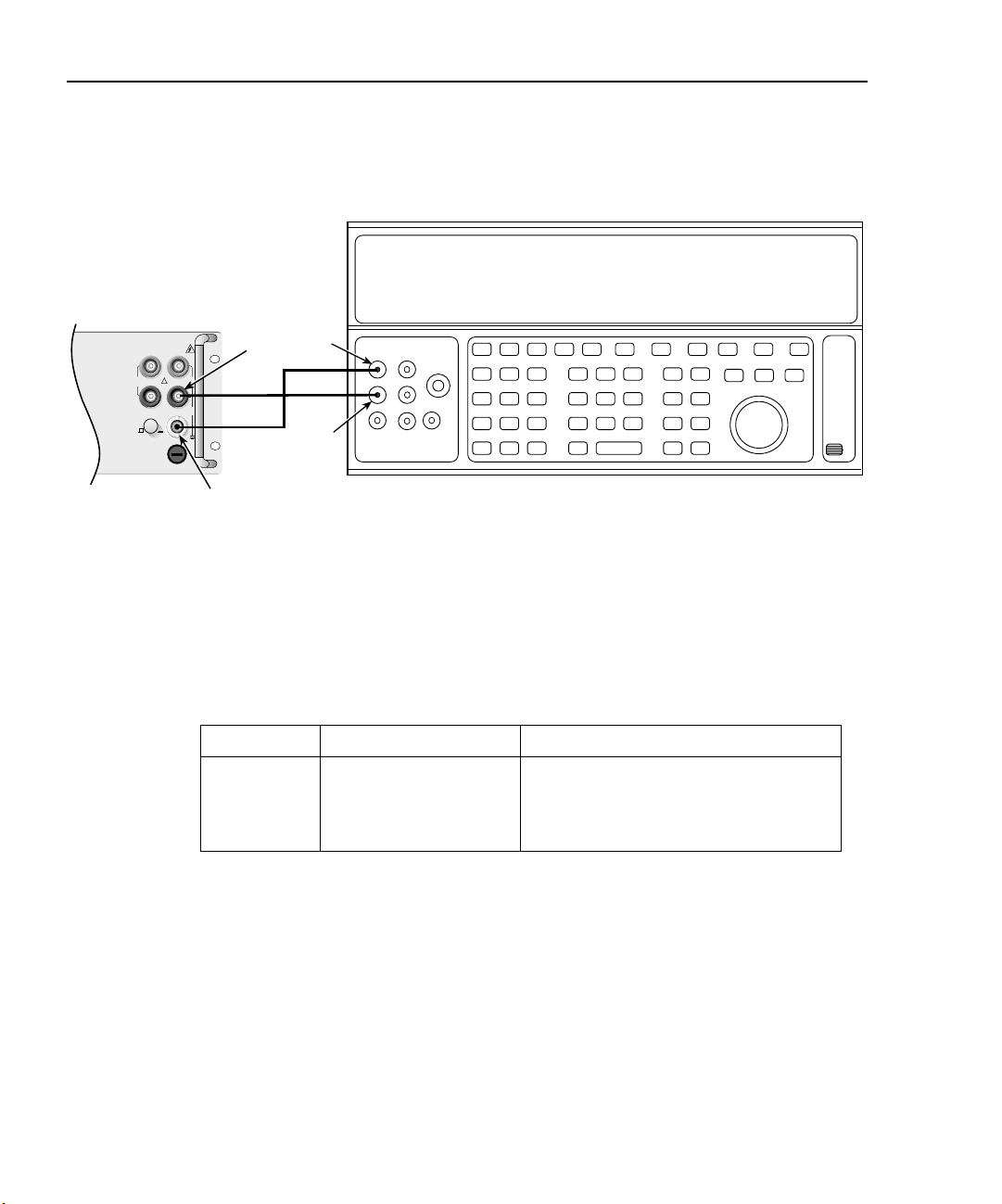
Figure 1-4
Connections for Model 2750 AC current verification
Calibrator (Output AC Current)
Model 2750
Front Panel
Output
Input
PEAK
500V
PEAK
3A, 250V
LO
HI
Output
LO
350V
PEAK
SENSE
Ω 4 WIRE
INPUT
F
FRONT/REAR
CAT I
INPUT
HI
1000V
!
LO
R
AMPS
2750 Verification
Amps
3. Set the Model 2750 for the 1A range.
4. Source 1A and 3A, 1kHz full-scale AC currents as summarized in Table 1-5, and
verify that the readings are within stated limits.
Table 1-5
ACI limits
ACV Range Applied AC Voltage Reading Limits @ 1kHz (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
1A
3A
* If the Fluke 5725A amplifier is not available, apply 2.2A from the calibrator. Reading limits for 2.2A are
2.1949 to 2.2051A.
1.000000A
3.00000A*
0.99860 to 1.00140A
2.9817 to 3.0183A
Page 28
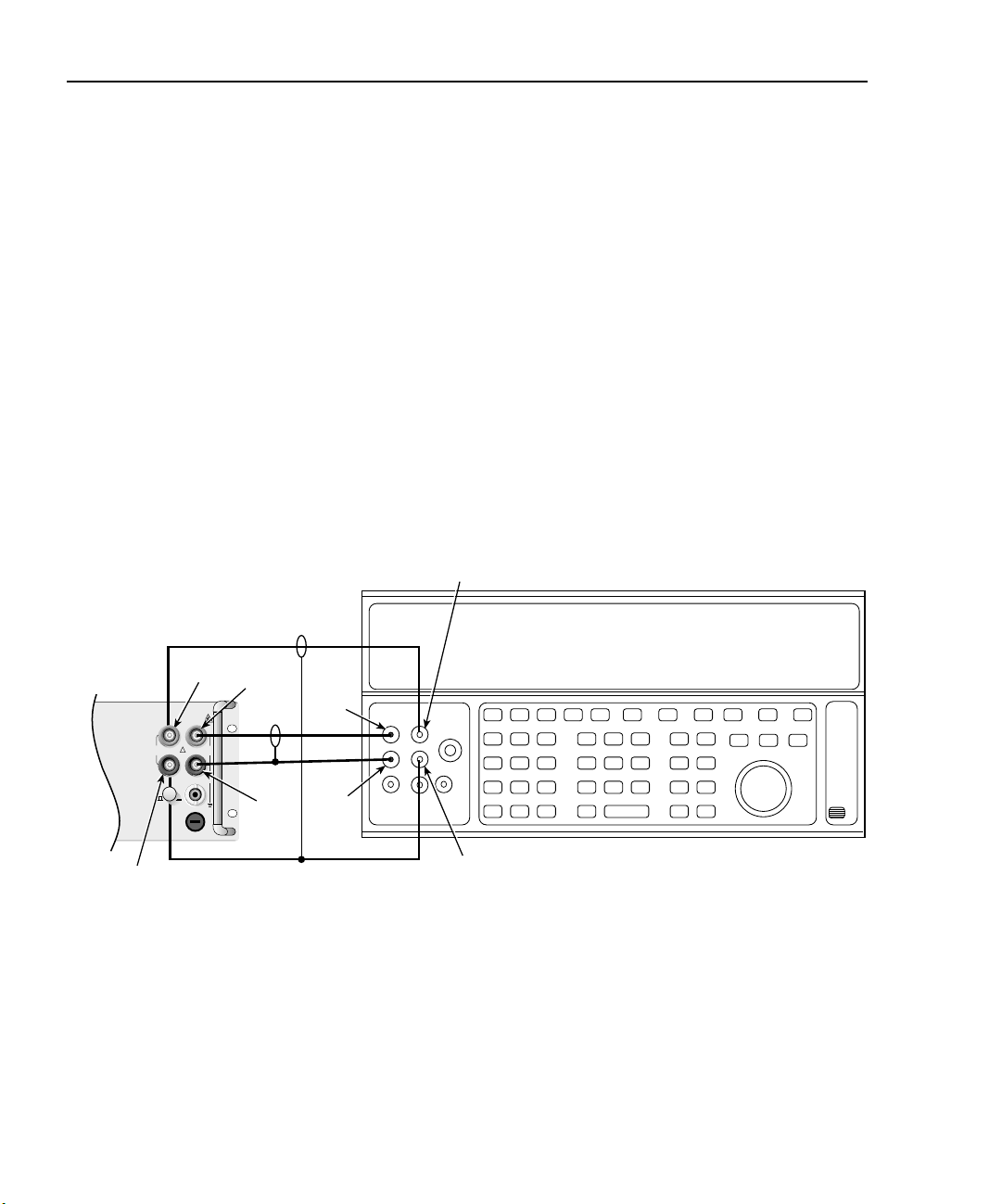
1-14 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Verifying normal resistance
Check the normal resistance function by connecting accurate resistance values to the
Model 2750 and verifying that its resistance readings are within the specified limits.
CAUTION Do not apply more than 1000V peak between front terminals INPUT
HI and LO or more than 350V peak between SENSE HI and LO, or
instrument damage could occur.
Follow these steps to verify resistance accuracy:
1. Using shielded, Teflon-insulated or equivalent cables in a 4-wire configuration,
connect the Model 2750 INPUT and SENSE jacks to the calibrator as shown in
Figure 1-5. Be sure the INPUTS switch is in the FRONT position.
2. Set the calibrator for 4-wire resistance with external sense on.
Figure 1-5
Connections for Model 2750 resistance verification (1Ω to 10MΩ ranges)
Model 2750
Front Panel
Sense
LO
Sense
HI
Sense
Input
HI
HI
Output
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
1000V
!
PEAK
PEAK
LO
500V
PEAK
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
CAT I
AMPS
Input
3A, 250V
LO
HI
Output
LO
Resistance Calibrator
Sense
LO
Note: Use shielded, low-thermal cables to minimize noise.
Enable or disable calibrator external sense as indicated
in procedure.
Page 29
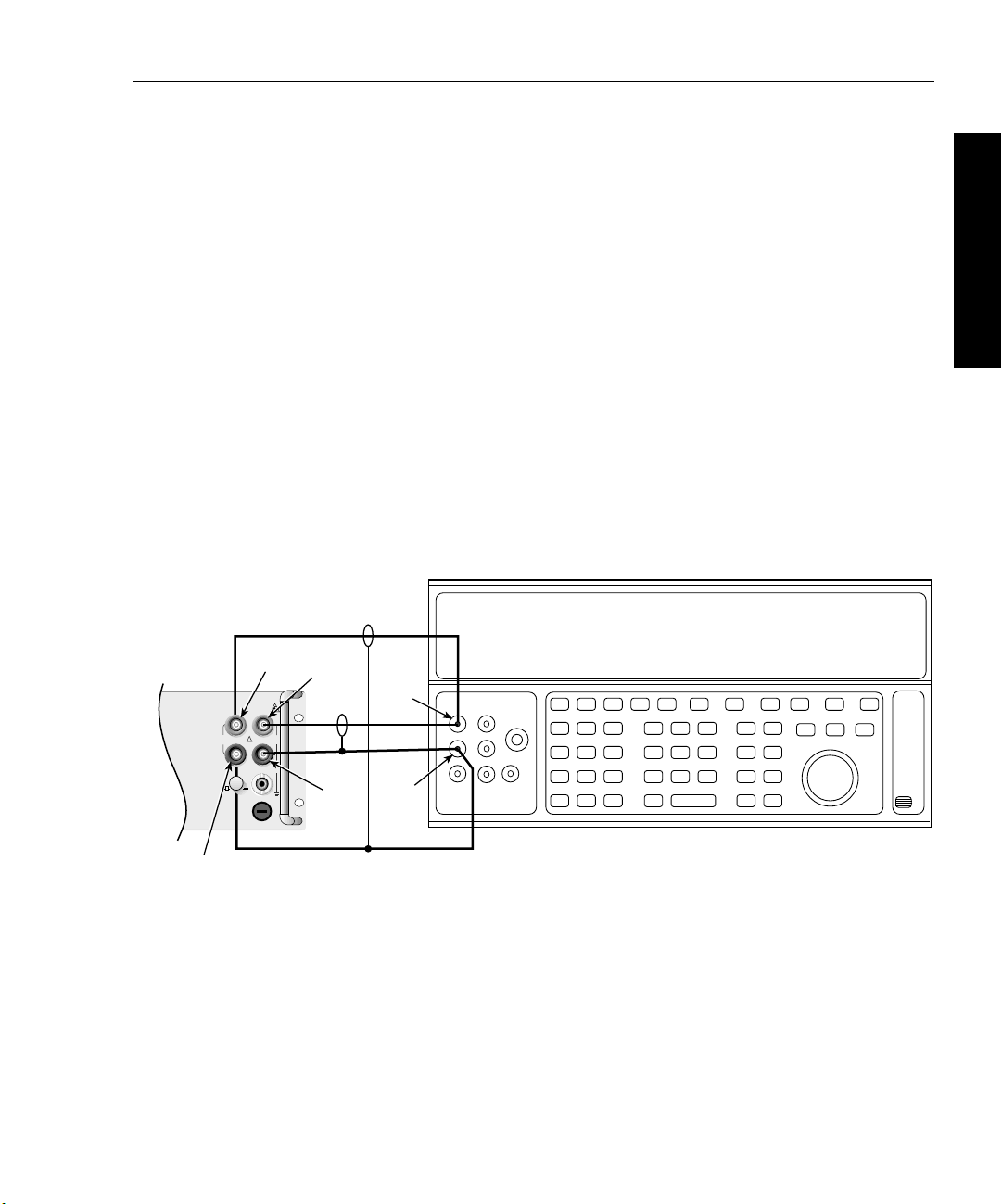
Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-15
3. Select the Model 2750 4-wire resistance function by pressing the Ω4 key, then
choose the SLOW integration rate with the RATE key.
4. Set the Model 2750 for the 1Ω range, and make sure the FILTER is on. Enable
OCOMP (offset-compensated ohms) by pressing SHIFT then OCOMP. (Use
OCOMP for 1Ω, 10Ω, and 100Ω range verification.)
5. Recalculate reading limits based on actual calibrator resistance values.
6. Source the nominal full-scale resistance values for the 1Ω-10MΩ ranges summa-
rized in Table 1-6, and verify that the readings are within calculated limits.
7. Connect the Model 2750 INPUT and SENSE jacks to the calibrator as shown in
Figure 1-6.
8. Disable external sense on the calibrator.
9. Set the Model 2750 for the 100MΩ range.
10. Source a nominal 100MΩ resistance value and verify that the reading is within calculated limits for the 100MΩ range.
Figure 1-6
Connections for Model 2750 resistance verification (100MΩ range)
Calibrator (Output 2-wire Resistance)
2750 Verification
Model 2750
Front Panel
Sense
LO
Sense
Input
HI
HI
Output
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
1000V
!
PEAK
PEAK
LO
500V
PEAK
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
CAT I
AMPS
Input
LO
HI
Output
LO
Note: Use shielded cables to minimize noise.
Disable calibrator external sense mode.
Page 30
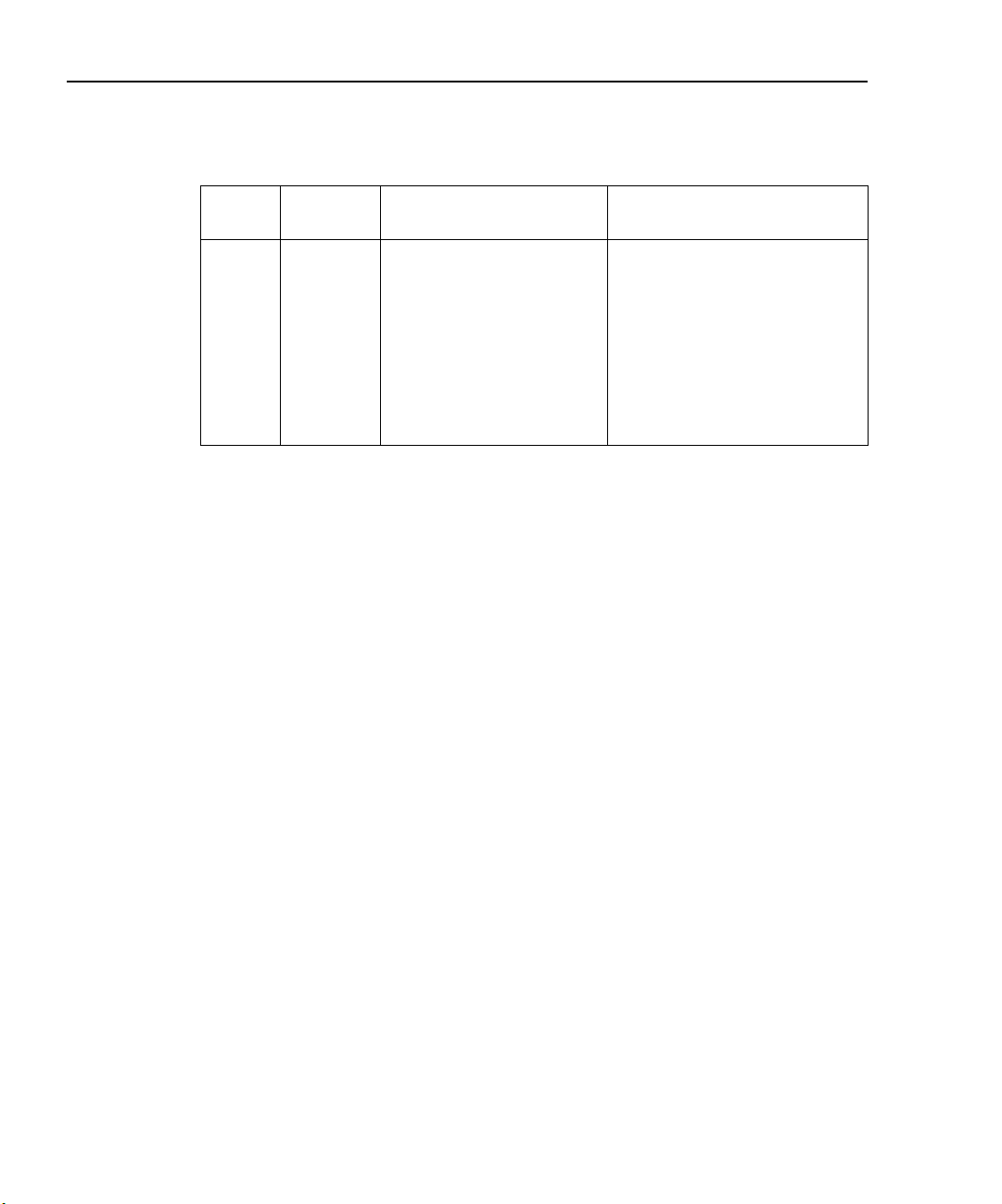
1-16 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Table 1-6
Limits for normal resistance verification
Nominal
Ω Range
10Ω∗
100Ω∗
10kΩ
100kΩ
10MΩ
100MΩ
* Enable OCOMP (offset-compensated ohms) when testing 1Ω, 10Ω, and 100Ω ranges.
** Calculate limits based on actual calibration resistance values and Model 2750 one-year resistance accuracy
specifications. See “Verification limits.”
1Ω∗
1kΩ
1MΩ
Resistance
1Ω
10Ω
100Ω
1kΩ
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
10MΩ
100MΩ
Nominal Reading Limits
(1 year, 18°C to 28°C) Recalculated Limits**
0.999820 to 1.000180Ω
9.99880 to 10.00120Ω
99.9880 to 100.0120Ω
0.999894 to 1.000106kΩ
9.99894 to 10.00106kΩ
99.9890 to 100.0110kΩ
0.999890 to 1.000110MΩ
9.99590 to 10.00410MΩ
99.7970 to 100.2030MΩ
Verifying dry circuit resistance
Check the dry circuit resistance function by connecting accurate resistance values to the
Model 2750 and verifying that its resistance readings are within the specified limits.
CAUTION Do not apply more than 1000V peak between front terminals INPUT
HI and LO or more than 350V peak between SENSE HI and LO, or
instrument damage could occur.
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ kΩ
__________ to __________ kΩ
__________ to __________ kΩ
__________ to __________ MΩ
__________ to __________ MΩ
__________ to __________ MΩ
Follow these steps to verify dry circuit resistance accuracy:
1. Using shielded, Teflon-insulated or equivalent cables in a 4-wire configuration,
connect the Model 2750 INPUT and SENSE jacks to the calibrator as shown in
Figure 1-7. Be sure the INPUTS switch is in the FRONT position.
Page 31

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-17
Figure 1-7
Connections for Model 2750 dry circuit resistance verification
2750 Verification
Model 2750
Front Panel
Sense
LO
Sense
HI
Sense
Input
HI
HI
Output
LO
HI
Output
LO
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
1000V
!
PEAK
PEAK
LO
500V
PEAK
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
CAT I
AMPS
Input
3A, 250V
Resistance Calibrator
Sense
LO
Note: Use low-thermal cables to minimize noise.
2. Set the calibrator for 4-wire resistance with external sense on.
3. Select the Model 2750 4-wire resistance function by pressing the Ω4 key, then
choose the SLOW integration rate with the RATE key.
4. Select the Model 2750 dry circuit resistance function by pressing SHIFT then
DRYCKT.
5. Set the Model 2750 for the 1Ω range, and make sure the FILTER is on. Enable
OCOMP (offset-compensated ohms) by pressing SHIFT then OCOMP. (Use
OCOMP for 1Ω, 10Ω, 100Ω, and 1kΩ range verification.) Enable line sync ON by
pressing SHIFT then LSYNC.
NOTE Maximum reading rate for the 1kΩ range is two readings per second.
6. Recalculate reading limits based on actual calibrator resistance values.
7. Source the nominal full-scale resistance values for the 1Ω-1kΩ ranges summarized
in Table 1-7, and verify that the readings are within calculated limits.
Page 32

1-18 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Table 1-7
Limits for Model 2750 dry resistance verification
Nominal
Ω Range
1Ω∗
10Ω∗
100Ω∗
1kΩ
* Enable OCOMP (offset-compensated ohms) when testing 1Ω, 10Ω, 100Ω, and 1kΩ ranges.
** Calculate limits based on actual calibration resistance values and Model 2750 one-year dry circuit resistance
accuracy specifications. See “Verification limits.”
Resistance
1Ω
10Ω
100Ω
1kΩ
Verifying temperature
Thermocouple, thermistor, and RTD temperature readings are derived from DC volts and
resistance measurements respectively. For that reason, it is not necessary to independently
verify the accuracy of temperature measurements. As long as the DC volts and resistance
functions meet or exceed specifications, temperature function accuracy is automatically
verified. However, temperature verification procedures are provided below for those who
wish to separately verify temperature accuracy.
Thermocouple temperature
1. Connect the DC voltage calibrator output terminals to the Model 2750 INPUT
jacks using low-thermal shielded connections. (Use 2-wire connections similar to
those shown in Figure 1-1.) Be sure the INPUTS switch is in the FRONT position.
2. Configure the Model 2750 for °C units, type J temperature sensor, and 0°C simulated reference junction as follows:
a. Press SHIFT then SENSOR, and note the unit displays the temperature units:
UNITS: C. (If necessary, use the cursor and range keys to select °C units.)
b. Press ENTER. The unit displays the sensor type: SENS: TCOUPLE.
c. Make sure that TCOUPLE is displayed, then press ENTER. The unit then dis-
plays the thermocouple type: TYPE: K.
d. Select a type J temperature sensor, then press ENTER. The unit then displays
the reference junction type: JUNC: SIM.
e. Make certain that the simulated reference junction type is selected, then press
ENTER. The unit then displays the current simulated reference junction tem-
perature: SIM: 023.
f. Using the cursor and range keys, set the reference junction temperature to 0°C,
then press ENTER twice to complete the temperature configuration process.
3. Select the temperature function by pressing the TEMP key.
4. Source each of the voltages summarized in Table 1-8, and verify that the temperature readings are within limits. Be sure to select the appropriate thermocouple type
for each group of readings. (See step 2 above.)
Nominal Reading Limits
(1 year, 18°C to 28°C) Recalculated Limits**
0.999860 to 1.000140Ω
9.99860 to 10.00140Ω
99.9820 to 100.0180Ω
0.999510 to 1.000490kΩ
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ kΩ
Page 33

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-19
Table 1-8
Thermocouple temperature verification reading limits
Applied DC
Thermocouple Type
J
Voltage* Reading Limits (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
-7.659mV
0mV
42.280mV
-190.2 to -189.9°C
-0.2 to +0.2°C
749.8 to 750.2°C
2750 Verification
K
* Voltages shown are based on ITS-90 standard using 0°C reference junction temperature. See text for proce-
dure to set reference junction temperature.
-5.730mV
0mV
54.138mV
-190.2 to -189.8°C
-0.2 to +0.2°C
1349.8 to 1350.2°C
RTD temperature
1. Connect the precision decade resistance box (listed in Table 1-1) to the Model
2750 INPUT and SENSE jacks using four-wire connections. (See Figure 1-5 for
similar connecting scheme.) Be sure the INPUTS switch is in the FRONT position.
2. Configure the Model 2750 temperature function for ˚C units and RTD temperature
sensor (α=0.00385) as follows:
a. Press SHIFT then SENSOR, and note the unit displays the temperature units:
UNITS: C.
b. Press ENTER, and note the unit displays the sensor type: SENS: TCOUPLE.
c. Using the cursor and range keys, set the display as follows: SENS: 4W-RTD.
d. Press ENTER, and note the unit displays: TYPE: PT100.
e. Using the cursor and range keys, set the unit for the following display: TYPE:
PT385.
f. Press ENTER to complete the temperature configuration process.
3. Select the temperature function by pressing the TEMP key.
4. Set the decade resistance box to each of the values shown in Table 1-9, and verify
that the temperature readings are within the required limits.
Table 1-9
Four-wire RTD temperature verification reading limits
Applied Resistance* Reading Limits (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
22.80Ω
100.00Ω
313.59Ω
*Based on α = 0.00385. See text.
-190.06 to -189.94°C
-0.06 to +0.06°C
599.94 to 600.06°C
Page 34

1-20 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Verifying frequency
Follow the steps below to verify the Model 2750 frequency function:
1. Connect the function generator to the Model 2750 INPUT jacks. (See Figure 1-8.)
Be sure the INPUTS switch is in the FRONT position.
2. Set the function generator to output a 1kHz, 1V RMS sine wave.
3. Select the Model 2750 frequency function by pressing the FREQ key.
4. Verify that the Model 2750 frequency reading is between 999.9Hz and 1.0001kHz.
Figure 1-8
Connections for Model 2750 frequency verification
Function Generator
Model 2750
Front Panel
SENSE
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
!
PEAK
LO
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
CAT I
INPUT
1000V
PEAK
500V
PEAK
AMPS
Banana Plug
Adapter
3A, 250V
50Ω
Coax
Cable
Function
Output
Model 7700 verification
Use these procedures to verify measurement accuracy through the Model 7700 20Channel Multiplexer Card.
NOTE Although the following tests are based on the Model 7700 20-Channel Multi-
plexer, the same general procedures can be used for other plug-in modules that
have similar capabilities. Refer to module documentation for specific information on terminals and connections for other plug-in modules.
BNC-to-Dual
Page 35

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-21
Verifying DC voltage
Check DC voltage accuracy by applying accurate voltages from the DC voltage calibrator
to the Model 7700 input terminals and verifying that the displayed readings fall within
specified limits.
CAUTION Do not exceed 300V DC between the 7700 plug-in module INPUT H
and L terminals or between any adjacent channels.
Follow these steps to verify DC voltage accuracy:
1. Connect the Model 7700 CH1 H and L INPUT terminals to the DC voltage calibrator as shown in Figure 1-9.
NOTE Use shielded, low-thermal connections when testing the 100mV and 1V ranges
to avoid errors caused by noise or thermal effects. Connect the shield to the calibrator’s output LO terminal.
Figure 1-9
Connections for Model 7700 DC volts verification
7700 Verification
CH1
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
HLHL
LO
AMPS
HLHL
CH3
CH1 CH2
Model 7700
Calibrator (Output DC Voltage)
CH5
CH6
CH4
HLHL
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Output HI
Output
LO
Note: Use shielded, low-thermal cables
for 100mV and 1V ranges.
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Select the DC volts function by pressing the DCV key, and set the Model 2750 to
the 100mV range. Close Channel 1 by pressing the CLOSE key, then ENTER for
“SINGLE” channel, and then keying in 101.
4. Set the calibrator output to 0.00000mV DC, and allow the reading to settle.
5. Enable the Model 2750 REL mode. Leave REL enabled for the remainder of the
DC volts verification test.
6. Source positive and negative and full-scale voltages for each of the ranges listed in
Table 1-10. For each voltage setting, be sure that the reading is within stated limits.
7. Press the OPEN key to open Channel 1.
Page 36

1-22 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Table 1-10
Plug-in module DCV reading limits
Range Applied DC Voltage* Reading Limits (1 year, 18° to 28°C)
100mV
1V
10V
100V
1000V
*Source positive and negative values for each range.
100.0000mV
1.000000V
10.00000V
100.0000V
300.000V
99.9935 to 100.0065mV
0.999963 to 1.000037V
9.99965 to 10.00035V
99.9946 to 100.0054V
299.976 to 300.024V
Verifying AC voltage
Check AC voltage accuracy by applying accurate AC voltages at specific frequencies from
the AC voltage calibrator to the Model 7700 inputs and verifying that the displayed readings fall within specified ranges.
CAUTION Do not exceed 300V RMS between the 7700 plug-in module INPUT H
and L terminals or between adjacent channels, or 8 × 107VHz input,
because instrument damage may occur.
Follow these steps to verify AC voltage accuracy:
1. Connect the Model 7700 CH1 H and L INPUT terminals to the AC voltage calibrator as shown in Figure 1-10.
Figure 1-10
Connections for Model 7700 AC volts verification
CH1
CH5
CH6
CH4
CH3
CH1 CH2
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
HLHL
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12 CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
LO
AMPS
HLHL
HLHL
HLHLHLHLHLHL
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
Model 7700
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Output
Shielded
Cable
HI
Amplifier (Connect to calibrator)
Output
Calibrator (Output AC Voltage)
LO
Page 37

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-23
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power, and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Select the AC volts function by pressing the ACV key. Close Channel 1 by pressing
the CLOSE key, then ENTER for “SINGLE” channel, and then keying in 101.
4. Set the Model 2750 for the 100mV range; make sure that REL is disabled.
5. Source 1kHz and 50kHz AC voltages for each of the ranges summarized in
Table 1-11, and make sure that the respective Model 2750 readings fall within
stated limits.
6. Press the OPEN key to open Channel 1.
Table 1-11
Plug-in module ACV reading limits
7700 Verification
ACV
Range
100mV
1V
10V
100V
750V
*If the 5725A amplifier is not available, change the 300V @ 50kHz step to 220V @ 50kHz. Reading limits
for 220V @ 50kHz = 219.36 to 220.64V.
Applied AC
Voltage
100.0000mV
1.000000V
10.00000V
100.0000V
300.000V*
1kHz Reading Limits
(1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
99.910 to 100.090mV
0.99910 to 1.00090V
9.9910 to 10.0090V
99.910 to 100.090V
299.60 to 300.40V
50kHz Reading Limits
(1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
99.830 to 100.170mV
0.99830 to 1.00170V
9.98300 to 10.0170V
99.830 to 100.170V
299.27 to 300.73V
Page 38

1-24 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Verifying DC current
Check DC current accuracy by applying accurate DC currents from the DC current calibrator to the input terminals of the Model 7700 and verify that the displayed readings fall
within specified limits.
Follow these steps to verify DC current accuracy:
1. Connect the Model 7700 CH21 H and L terminals to the calibrator as shown in
Figure 1-11.
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power, and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Select the DC current measurement function by pressing the DCI key.
4. Set the Model 2750 for the 20mA range. Close Channel 21 by pressing the CLOSE
key, then ENTER for “SINGLE” channel, and keying in 121.
5. Source positive and negative full-scale currents for each of the ranges listed in
Table 1-12, and verify that the readings for each range are within stated limits.
6. Press the OPEN key to open Channel 21.
Figure 1-11
Connections for Model 7700 DC current verification
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
CH21
HLHL
Model 7700
CH3
CH1 CH2
HLHL
HLHL
LO
AMPS
CH4
CH5
CH6
HLHL
HLHLHLHLHLHL
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Output HI
Output
LO
Calibrator (Output DC Current)
Note: Be sure calibrator is set for
normal current output.
Page 39

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-25
Table 1-12
Plug-in module DCI limits
DCI Range Applied DC Current* Reading Limits (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
20mA
100mA
1A
3A
* Source positive and negative currents with values shown.
** If the Fluke 5725 amplifier is not available, apply 2.2A from calibrator. Reading limits for 2.2A input are:
2.197240 to 2.202760A.
20.0000mA
100.0000mA
1.000000A
3.000000A**
19.89960 to 20.01040mA
99.9100 to 100.0900mA
0.999160 to 1.000840A
2.99628 to 3.00372A
Verifying AC current
Check AC current accuracy by applying accurate AC voltage current at specific frequencies from the AC current calibrator to the Model 7700 input terminals and verify that the
displayed readings fall within specified limits. Follow these steps to verify AC current:
1. Connect the Model 7700 CH21 H and L terminals to the calibrator as shown in
Figure 1-12.
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power, and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Select the AC current function by pressing the ACI key.
4. Set the Model 2750 for the 1A range. Close Channel 21 by pressing the CLOSE
key, then ENTER for “SINGLE” channel, and keying in 121.
7700 Verification
Figure 1-12
Connections for Model 7700 AC current verification
Model 7700
CH5
CH6
CH4
CH3
CH1 CH2
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
CH21
HLHL
HLHL
LO
AMPS
HLHL
HLHL
HLHLHLHLHLHL
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Output HI
Output
LO
Calibrator (Output AC Current)
Page 40

1-26 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
5. Source 1A and 3A, 1kHz full-scale AC currents as summarized in Table 1-13, and
verify that the readings are within stated limits.
6. Press the OPEN key to open Channel 21.
Table 1-13
Plug-in module ACI limits
ACV Range Applied AC Voltage Reading Limits @ 1kHz (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
1A
3A
*If the Fluke 5725A amplifier is not available, apply 2.2A from the calibrator. Reading limits for 2.2A are
2.1949 to 2.2051A.
1.000000A
3.00000A*
0.99860 to 1.00140A
2.9817 to 3.0183A
Verifying normal resistance
Check normal resistance by connecting accurate resistance values to the Model 7700 and
verify that its resistance readings are within the specified limits.
CAUTION Do not apply more than 300V between the 7700 plug-in module
INPUT or SENSE H and L terminal, or between any adjacent channels, or instrument damage could occur.
Follow these steps to verify normal resistance accuracy:
1. Using shielded Teflon or equivalent cables in a 4-wire configuration, connect the
Model 7700 CH1 H and L INPUT terminals, and CH11 H and L SENSE terminals
to the calibrator as shown in Figure 1-13.
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power, and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Set the calibrator for 4-wire resistance with external sense on.
4. Select the Model 2750 4-wire resistance function by pressing the Ω4 key. Close
Channel 1 by pressing the CLOSE key, then ENTER for “SINGLE” channel, and
keying in 101.
5. Set the Model 2750 for the 1Ω range, and make sure the FILTER is on. Enable
OCOMP (offset-compensated ohms) by pressing SHIFT then OCOMP. (Use
OCOMP for 1Ω, 10Ω, and 100Ω range verification.)
6. Recalculate reading limits based on actual calibrator resistance values.
Page 41

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-27
Figure 1-13
Connections for Model 7700 resistance verification (1Ω to 10MΩ ranges)
CH1
Model 7700
CH5
CH4
CH3
CH1 CH2
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
HLHL
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12 CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
LO
AMPS
HLHL
HLHL
HLHLHLHLHLHL
CH6
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Sense HI
Output
HI
Output
LO
Resistance Calibrator
7700 Verification
CH11
Sense LO
Note: Use shielded, low-thermal cables
7. Source the nominal full-scale resistance values for the 1Ω-10MΩ ranges summa-
rized in Table 1-14, and verify that the readings are within calculated limits.
8. Connect the Model 7700 CH1 and CH11 terminals to the calibrator as shown in
Figure 1-14.
9. Disable external sense on the calibrator.
10. Set the Model 2750 for the 100MΩ range.
11. Source a nominal 100MΩ resistance value, and verify that the reading is within
calculated limits for the 100MΩ range.
12. Press the OPEN key to open Channel 1.
Figure 1-14
Connections for Model 7700 resistance verification (100MΩ range)
CH1
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
Model 7700
CH4
CH3
CH1 CH2
HLHL
HLHL
CH5
CH6
HLHL
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
Output
HI
Calibrator (Output 2-wire Resistance)
to minimize noise. Enable or disable
calibrator external sense as indicated
in procedure.
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12 CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
LO
AMPS
CH11
HLHLHLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Output
LO
Note: Use shielded cables to minimize
noise. Disable calibrator external
sense mode.
Page 42

1-28 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Table 1-14
Limits for plug-in module normal resistance verification
Nominal
Ω Range
1Ω∗
10Ω∗
100Ω∗
1kΩ
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
10MΩ
100MΩ
* Enable OCOMP for 1Ω, 10Ω, and 100Ω ranges.
** Calculate limits based on actual calibration resistance values and Model 2750 one-year resistance accuracy
specifications. See “Verification limits.”
resistance
1Ω
10Ω
100Ω
1kΩ
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
10MΩ
100MΩ
Nominal reading limits
(1 year, 18°C to 28°C) Recalculated limits**
0.999820 to 1.000180Ω
9.99880 to 10.00120Ω
99.9880 to 100.0120Ω
0.999894 to 1.000106kΩ
9.99894 to 10.00106kΩ
99.9890 to 100.0110kΩ
0.999890 to 1.000110MΩ
9.99590 to 10.00410MΩ
99.5770 to 100.4230MΩ
Verifying dry circuit resistance
Check the dry circuit resistance function by connecting accurate resistance values to the
Model 2750 and verifying that its resistance readings are within the specified limits.
CAUTION Do not apply more than 300V between the 7700 plug-in module
INPUT or SENSE H and L terminal, or between any adjacent channels, or instrument damage could occur.
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ kΩ
__________ to __________ kΩ
__________ to __________ kΩ
__________ to __________ MΩ
__________ to __________ MΩ
__________ to __________ MΩ
Follow these steps to verify dry circuit resistance accuracy:
1. Using shielded Teflon or equivalent cables in a 4-wire configuration, connect the
Model 7700 CH1 H and L INPUT terminals, and CH11 H and L SENSE terminals
to the calibrator as shown in Figure 1-15.
NOTE The 1kΩ range can tolerate 80% of range (0.8Ω) lead resistance. Ensure that
relay and cable connections have ≤0.8Ω of resistance before verifying the 1Ω
range.
Page 43

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-29
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power, and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Set the calibrator for 4-wire resistance with external sense on.
4. Select the Model 2750 4-wire resistance function by pressing the Ω4 key. Close
Channel 1 by pressing the CLOSE key, then ENTER for “SINGLE” channel, and
keying in 101.
5. Set the Model 2750 for the dry circuit resistance function by pressing SHIFT then
DRYCKT.
Figure 1-15
Connections for Model 7700 dry circuit resistance verification
CH1
Model 7700
CH5
CH4
CH3
CH1 CH2
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
HLHL
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12 CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
LO
AMPS
HLHL
HLHL
HLHLHLHLHLHL
CH6
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Sense HI
Output
HI
Output
LO
Resistance Calibrator
7700 Verification
CH11
Sense LO
Note: Use shielded, low-thermal cables
to minimize noise.
Page 44

1-30 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
6. Set the Model 2750 for the 1Ω range, and make sure the FILTER is on. If previ-
ously disabled, enable OCOMP (offset-compensated ohms) by pressing SHIFT
then OCOMP. (Use OCOMP for 1Ω, 10Ω, 100Ω, and 1kΩ range verification.)
Enable line sync (press SHIFT then LSYNC).
7. Recalculate reading limits based on actual calibrator resistance values.
NOTE Maximum reading rate for 1kΩ dry circuit is two readings per second.
8. Source the nominal full-scale resistance values for the 1Ω-1kΩ ranges summarized
in Table 1-15, and verify that the readings are within calculated limits.
Table 1-15
Limits for plug-in module dry circuit resistance verification
Nominal
Ω Range
1Ω∗
10Ω∗
100Ω∗
1kΩ
* Enable OCOMP (offset-compensated ohms) when testing 1Ω, 10Ω, 100Ω, and 1kΩ ranges.
** Calculate limits based on actual calibration resistance values and Model 2750 one-year resistance accuracy
specifications. See “Verification limits.”
Resistance
1Ω
10Ω
100Ω
1kΩ
Nominal Reading Limits
(1 year, 18°C to 28°C) Recalculated Limits**
0.999860 to 1.000140Ω
9.99860 to 10.00140Ω
99.9820 to 100.0180Ω
0.999510 to 1.000490kΩ
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ Ω
__________ to __________ kΩ
Page 45

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-31
Verifying temperature
Thermocouple, thermistor, and RTD temperature readings are derived from DC volts and
resistance measurements respectively. For that reason, it is not necessary to independently
verify the accuracy of temperature measurements. As long as the DC volts and resistance
functions meet or exceed specifications, temperature function accuracy is automatically
verified. However, temperature verification procedures are provided below for those who
wish to separately verify temperature accuracy.
Thermocouple temperature
1. Connect the DC voltage calibrator output terminals and ice point reference to the
Model 7700 CH1 H and L INPUT terminals using low-thermal shielded connections, as shown in Figure 1-16.
Figure 1-16
Connections for Model 7700 thermocouple temperature verification
7700 Verification
CH1
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12 CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
HLHL
LO
AMPS
HLHL
CH4
CH3
CH1 CH2
Model 7700
CH5
CH6
HLHL
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
HLHLHLHLHLHL
Make HI and LO
Connections
in Ice Bath
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Twisted
Thermocouple Wire
Output
HI
Output
LO
Ice Bath
Calibrator (Output DC Voltage)
Low Thermal
Copper Connection
Notes: This setup and reading limits
table does not include errors
from ice point, thermocouple
wire, and connections.
HI and LO connections from
the calibrator and Model 7700
must be electrically isolated
from each other.
Page 46

1-32 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Select the temperature function by pressing the TEMP key. Close Channel 1 by
pressing the CLOSE key, then ENTER for “SINGLE” channel, and keying in 101.
4. Configure the Model 2750 for °C units, type K temperature sensor, and internal reference junction as follows:
a. Press SHIFT then SENSOR, and note the unit displays the temperature units:
UNITS: C. (If necessary, use the cursor and range keys to select °C units.)
b. Press ENTER. The unit displays the sensor type: SENS: TCOUPLE.
c. Make sure that TCOUPLE is displayed, then press ENTER. The unit displays
the thermocouple type: TYPE: J.
d. Select a type K temperature sensor, then press ENTER. The unit displays the
reference junction type: JUNC: SIM.
e. Select INT reference junction, then press ENTER.
NOTE Defaults for 7700, 7706, and 7708 modules are:
• K type.
• “C” units.
• Internal temperature sensor.
• Open Tdetect off.
• Sensor type: Tcouple.
5. Source each of the voltages summarized in Table 1-16 and verify that the temperature readings are within limits. Be sure to select the appropriate thermocouple type
for each group of readings. (See step 3 above.) Open Channel 1 after the test is
complete.
Table 1-16
Model 7700 thermocouple temperature verification reading limits
Thermocouple Type Applied DC Voltage* Reading Limits (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
J
K
*Voltages shown are based on ITS-90 standard.
-7.659mV
0mV
42.280mV
-5.730mV
0mV
54.138mV
-191.8 to -188.2°C
-1.0 to +1.0°C
749.0 to 751.0°C
-191.8 to -188.2°C
-1.0 to +1.0°C
1349.0 to 1351.0°C
Page 47

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-33
RTD temperature
1. Connect the precision decade resistance box (listed in Table 1-1) to the Model
7700 CH1 and CH11 H and L terminals using four-wire connections. (See
Figure 1-14 for similar connecting scheme.)
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Select the temperature function by pressing the TEMP key. Close Channel 1 by
pressing the CLOSE key and keying in 101.
4. Configure the Model 2750 temperature function for °C units and RTD temperature
sensor (α=0.00385) as follows:
a. Press SHIFT then SENSOR, and note the unit displays the temperature units:
UNITS: C.
b. Press ENTER, and note the unit displays the sensor type: SENS: TCOUPLE.
c. Using the cursor and range keys, set the display as follows: SENS: 4W-RTD.
d. Press ENTER, and note the unit displays: TYPE: PT100.
e. Using the cursor and range keys, set the unit for the following display: TYPE:
PT385.
f. Press ENTER to complete the temperature configuration process.
5. Set the decade resistance box to each of the values shown in Table 1-17, and verify
that the temperature readings are within the required limits. Open Channel 1 when
finished.
7700 Verification
Table 1-17
Plug-in module four-wire RTD temperature verification reading limits
Applied Resistance* Reading Limits (1 year, 18°C to 28°C)
22.80Ω
100.00Ω
313.59Ω
*Based on α = 0.00385. See text.
-190.06 to -189.94°C
-0.06 to +0.06°C
599.94 to 600.06°C
Page 48

1-34 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Verifying frequency
Follow the steps below to verify the Model 2750 frequency function:
1. Connect the function generator to the Model 7700 CH1 H and L INPUT terminals
(Figure 1-17).
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power and
allow the unit to warm up for one hour before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Set the function generator to output a 1kHz, 1V RMS sine wave.
4. Select the Model 2750 frequency function by pressing the FREQ key. Close Channel 1 by pressing the CLOSE key, then ENTER for “SINGLE” channel, and keying
in 101.
5. Verify that the Model 2750 frequency reading is between 0.9999kHz and
1.0001kHz.
Figure 1-17
Connections for Model 7700 frequency verification
CH1
CH1 CH2
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
HLHL
LO
AMPS
HLHL
CH5
CH6
CH4
CH3
HLHL
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
HLHLHLHLHLHL
Model 7700
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Function Generator
50Ω
Coax
Cable
Function
Output
Page 49

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Performance Verification 1-35
Verifying ratio and average
Follow the procedure below to verify ratio and average.
CAUTION Exceeding 300V between the 7700 plug-in module INPUT or SENSE
H and L terminals may cause instrument damage.
1. Connect the Model 7700 CH1 and CH11 H and L terminals to the DC calibrator, as
shown in Figure 1-18.
2. Install the Model 7700 in Slot 1 of the Model 2750, then turn on the power and
allow the unit to warm up for two hours before proceeding. Be sure the front panel
INPUTS switch is set to the REAR position.
3. Select the Model 2750 DCV function and the 1V range. Close Channel 1 by pressing the CLOSE key, then ENTER for “SINGLE” channel, and keying in 101.
4. Select the Model 2750 RATIO function (press SHIFT then RATIO).
5. Set the calibrator output to 1.00000V DC, and allow the reading to settle.
6. Verify that the ratio reading is between 0.9999926 and 1.000074.
7. Press OPEN to open Channel 1.
Figure 1-18
Connections for Model 7700 ratio and average verification
7700 Verification
CH1
Model 7700
INPUT SENSE
HLHL
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12 CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
HLHL
LO
AMPS
HLHL
CH4
CH3
CH1 CH2
CH11
CH5
CH6
HLHL
HLHLHLHLHLHL
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
DC Voltage Calibrator
Output
HI
Output
LO
Note: Use shielded cables to
minimize noise.
Page 50

1-36 Performance Verification Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Page 51

2
Calibration
Page 52

2-2 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Introduction
Use the procedures in this section to calibrate the Model 2750. Calibration procedures
include:
• Comprehensive calibration: Usually the only calibration required in the field.
• Manufacturing calibration: Usually only performed at the factory (unless the unit
has been repaired).
• Model 7700 calibration: Covers calibration procedures specific to Model 7700
cards.
WARNING The information in this section is intended only for qualified service
personnel. Do not attempt these procedures unless you are qualified to
do so.
All the procedures require accurate calibration equipment to supply precise DC and AC
voltages, DC and AC currents, and resistance values. Comprehensive calibration can be
performed any time by an operator either from the front panel, or by using the SCPI commands sent either over the IEEE-488 bus or the RS-232 port. DC-only and AC-only calibration may be performed individually, if desired.
Environmental conditions
Conduct the calibration procedures in a location that has:
• An ambient temperature of 18° to 28°C (65° to 82°F).
• A relative humidity of less than 80% unless otherwise noted.
Warmup period
Allow the Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System to warm up for at least two hours before
performing calibration.
If the instrument has been subjected to temperature extremes (those outside the ranges
stated above) allow extra time for the instrument’s internal temperature to stabilize. Typically, allow one extra hour to stabilize a unit that is 10°C (18°F) outside the specified temperature range.
Allow the test equipment to warm up for the minimum time specified by the manufacturer.
Line power
The Model 2750 requires a line voltage of 100V/120V/220V/240V, ±10% and a line frequency of 45Hz to 66Hz or 360Hz to 440Hz. Note that the line frequency is automatically
sensed at power-up, but the line voltage must be manually set to either 100V/120V or
220V/240V as described in Section 3.
Page 53

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-3
Calibration considerations
When performing the calibration procedures:
• Make sure that the equipment is properly warmed up and connected to the appropriate input jacks. Make sure that the correct front or rear terminals are selected
with the INPUTS switch.
• Make sure the calibrator is in OPERATE before you complete each calibration
step.
• Always let the source signal settle before calibrating each point.
• If an error occurs during calibration, the Model 2750 will generate an appropriate
error message. See Appendix B for more information.
WARNING Observe the following safety precautions when performing these tests:
• Some of the procedures in this section may expose you to danger-
ous voltages. Use standard safety precautions when such dangerous voltages are encountered to avoid personal injury or death
caused by electric shock.
• For the front panel terminals only, the maximum common-mode
voltage (voltage between INPUT LO and chassis ground) is 500V
peak. Exceeding this value may cause a breakdown in insulation,
creating a shock hazard.
Model 2750 Calibration
• For the plug-in modules, the maximum common-mode voltage
(voltage between any plug-in module terminal and chassis ground)
is listed in the module’s specifications. Exceeding this value may
cause a breakdown in insulation, creating a shock hazard.
• When using the front panel terminals simultaneously with plug-in
modules, all cable insulation voltage ratings must equal or exceed
the maximum voltage applied to either the front panel terminals or
the plug-in module terminals.
Page 54

2-4 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Calibration code
Before performing comprehensive calibration, you must first unlock calibration by entering the appropriate calibration code.
Front panel calibration code
For front panel calibration, follow these steps:
1. Access the calibration menu by pressing SHIFT then TEST, then use the up or
down range key to display TEST: CALIB. Press ENTER, and note that the instrument displays the following:
CAL: DATES
2. Use the up or down range key to scroll through the available calibration items until
the unit displays RUN, then press ENTER.
3. The Model 2750 then prompts you to enter a code:
CODE? 000000
(The factory default code is 002750.) Use the left and right arrow keys to move
among the digits; use the up range key to increment numbers and press the down
range key to specify alphabetic letters. Confirm the code by pressing ENTER.
4. The Model 2750 allows you to define a new calibration code. Use the up and down
range keys to toggle between yes and no. Choose N if you do not want to change
the code. Choose Y if you want to change the code. The unit then prompts you to
enter a new code. Enter the code, and press ENTER.
Remote calibration code
If you are performing calibration over the IEEE-488 bus or the RS-232 port, send this
command to unlock calibration:
:CAL:PROT:CODE '<8-character string>'.
The default code command is:
:CAL:PROT:CODE 'KI002750'.
To change the code via remote, simply send the :CAL:PROT:CODE command twice, first
with the present code, then with the new code.
Page 55

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-5
Comprehensive calibration
The comprehensive calibration procedure calibrates the DCV, DCI, ACV, ACI, and ohms
functions. You can also choose to calibrate only the DCV/DCI and resistance or ACV/ACI
functions.
These procedures are usually the only calibration required in the field. Manufacturing calibration is normally done only at the factory, but it should also be done in the field if the
unit has been repaired. See “Manufacturing calibration” at the end of this section for more
information.
Calibration cycle
Perform comprehensive calibration at least once a year, or every 90 days to ensure the unit
meets the corresponding specifications.
Recommended equipment
Table 2-1 lists the recommended equipment you need for comprehensive, DC-only, and
AC-only calibration procedures. You can use alternate equipment, such as a DC transfer
standard and characterized resistors, as long as the equipment has specifications at least as
good as those listed in the table. In general, equipment uncertainty should be at least four
times better than corresponding Model 2750 specifications.
Model 2750 Calibration
Table 2-1
Recommended equipment for comprehensive calibration
Fluke 5700A Calibrator:
AC Voltage
DC Voltage
10V: ±5ppm
100V: ±7ppm
Miscellaneous Equipment:
Keithley 8610 low-thermal shorting plug.
Double banana plug to double banana plug shielded cable.
BNC to double banana plug shielded cable.
*1kHz specifications. 10mV and 700V points require 1kHz only. All calibrator specifications are 90-day, 23°C ±5°C specifications
and indicate total absolute uncertainty at specified output.
(1kHz, 50kHz)* DC Current
10mV: ±710ppm
100mV: ±200ppm
1V: ±82ppm
10V: ±82ppm
100V: ±90ppm
700V: ±85ppm
10mA: ±60ppm
100mA: ±70ppm
1A: ±110ppm
AC Current
(1kHz) Resistance
100mA: ±190ppm
1A: ±690ppm
2A: ±670ppm
100kΩ: ±13ppm
100Ω: ±17ppm
10kΩ: ±11ppm
1MΩ: ±18ppm
Page 56

2-6 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Aborting calibration
You can abort the front panel calibration process at any time by pressing EXIT. The instrument will then ask you to confirm your decision to abort with the following message:
ABORT CAL?
Press EXIT to abort calibration at this point, or press any other key to return to the calibration process.
NOTE The Model 2750 will not respond to any remote programming commands while
the ABORT CAL? message is displayed.
Front panel calibration
Follow the steps in the following paragraphs in the order shown for comprehensive, DC
only, and AC only calibration procedures.
The procedures for front panel calibration include:
• Preparing the Model 2750 for calibration
• Front panel short and open calibration
• DC voltage calibration
• Resistance calibration
• DC current calibration
• AC voltage calibration
• AC current calibration
• Setting calibration dates
Preparing the Model 2750 for calibration
1. Turn on the Model 2750, and allow it to warm up for at least two hours before performing a calibration procedure.
2. Start the calibration process as follows:
a. Access the calibration menu by pressing SHIFT then TEST, then display
TEST: CALIB using the up or down range key. Press ENTER.
b. Use the up or down range key to scroll through the available calibration menu
items until the unit displays RUN, then press ENTER.
c. At the prompt, enter the calibration code. (The default code is 002750.) Use
the left and right arrow keys to move among the digits; use the up range key to
increment numbers, and press the down range key to specify alphabetic letters.
Confirm the code by pressing ENTER.
d. Choose N at the prompt to proceed without changing the code, then press
ENTER.
Page 57

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-7
3. Choose which of the calibration tests summarized in Table 2-2 you want to run at
the CAL: RUN prompt. Use the up and down range keys to scroll through the
options; select your choice by pressing ENTER.
Table 2-2
Comprehensive calibration procedures
Procedure Menu Choice Procedures
Full calibration
DCV, DCI, and ohms
ACV and ACI
Front panel short and open calibration
At the Model 2750 prompt for a front panel short, do the following:
1. Connect the Model 8610 low-thermal short to the instrument front panel INPUT
and SENSE terminals as shown in Figure 2-1. Make sure the INPUTS button is not
pressed in so that the front inputs are selected. Wait at least three minutes before
proceeding to allow for thermal equilibrium.
Figure 2-1
Low-thermal short connections
CONT
OCOMP
RATIO
CH AVG
SHIFT
LOCAL
POWER
MATH
DCV
EX TRIG
SAVE SETUP
OPEN
OUTPUT
DRYCKT
TRIG
CLOSE
DCIACV
LIMITS ON/OFFDELAY
STORE
RECALL
CONFIG HALT
STEP SCAN
PERIOD SENSOR
Ω
ACI
4
TEMP
FREQ
Ω
2
MONITOR
TYPE
CH-OFF CARD
RELFILTER
LSYNC
RS-232
TEST
GPIB
EXIT ENTER
DIGITS RATE
RANGE
AUTO
RANGE
Model 2750
SLOT 1
SLOT 2
SLOT 3
SLOT 4
SLOT 5
ALL
All comprehensive calibration steps
(DC and AC).
DC
DC voltage, DC current, and resistance
calibration.
AC
MODEL 2750 MULTIMETER/SWITCH SYSTEM
AC voltage and AC current calibration.
INTEGRA SERIES
S+
350V
PEAK
SENSE
Ω 4 WIRE
INPUT
F
FRONT/REAR
CAT I
Model 2750 Calibration
HI
INPUT
HI
!
LO
LO
R
AMPS
1000V
PEAK
500V
PEAK
3A, 250V
Model 8610
Low-thermal
short
S- LO
NOTE Be sure to connect the low-thermal short properly to the HI, LO, and SENSE ter-
minals. Keep drafts away from low-thermal connections to avoid thermal drift,
which could affect calibration accuracy.
2. Press ENTER to start short-circuit calibration. While the unit is calibrating, it will
display:
CALIBRATING
Page 58

2-8 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
3. When the unit is finished with short-circuit calibration, it will display the following
prompt:
OPEN CIRCUIT
4. Remove the calibration short, and press ENTER. During this phase, the CALIBRATING message will be displayed.
NOTE Be sure to minimize movement near front input terminals. Excessive movements
can cause capacitive coupling errors, which could affect calibration accuracy.
DC volts calibration
After the front panel short and open procedure, the unit will prompt you for the first DC
voltage: +10V. Do the following:
1. Connect the calibrator to the Model 2750 as shown in Figure 2-2. Wait three minutes to allow for thermal equilibrium before proceeding.
Figure 2-2
Connections for DC volts and ohms calibration
Model 2750
Front Panel
Sense
LO
Sense
HI
Sense
Input
HI
HI
Input
LO
Output
HI
Output
LO
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
1000V
!
PEAK
PEAK
LO
500V
PEAK
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
AMPS
CAT I
3A, 250V
DC Voltage and Resistance Calibrator
Sense
LO
Note: Use shielded, low-thermal cables to minimize noise.
Enable or disable calibrator external sense as indicated
in procedure.
Page 59

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-9
NOTE Although 4-wire connections are shown, the sense leads are connected and dis-
connected at various points in this procedure by turning calibrator external
sense on or off as appropriate. If your calibrator does not have provisions for
turning external sense on and off, disconnect the sense leads when e xternal sensing is to be turned off, and connect the sense leads when external sensing is to be
turned on.
2. Set the calibrator to output DC volts, and turn external sense off.
3. Perform the steps listed in Table 2-3 to complete DC volts calibration. For each
calibration step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated value, and make sure it is in OPERATE.
• Press the ENTER key to calibrate that step.
• Wait until the Model 2750 finishes each step. (The unit will display the CALIBRATING message while calibrating.)
NOTE If your calibrator cannot output the values recommended in Table 2-3, use the
left and right arrow keys, and the up and down range ke ys to set the Model 2750
display value to match the calibrator output voltage.
Table 2-3
DC volts calibration summary
Model 2750 Calibration
Calibration Step Calibrator Voltage Allowable Range
+10V
-10V
100V
+10.00000V
-10.00000V
+100.0000V
+9V to +11V
-9V to -11V
+90V to +110V
Page 60

2-10 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Resistance calibration
Completing the 100V DC calibration step ends the DC voltage calibration procedure. The
Model 2750 will then prompt you to connect 100Ω. Follow these steps for resistance
calibration:
1. Set the calibrator output for resistance, and turn on external sense.
NOTE Use external sense (4-wire Ω) when calibrating all resistance ranges. Be sure
that the calibrator external sense mode is turned on.
2. Perform the calibration steps summarized in Table 2-4. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated value, and place the unit in operate. (If the
calibrator cannot output the exact resistance value, use the Model 2750 left
and right arrow keys and the range keys to adjust the Model 2750 display to
agree with the actual calibrator resistance.)
• Press the ENTER key to calibrate each point.
• Wait for the Model 2750 to complete each step before continuing.
Table 2-4
Ohms calibration summary
Calibration Step Calibrator Resistance* Allowable Range
100Ω
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
*Nominal resistance. Adjust Model 2750 calibration parameter to agree with actual value.
100Ω
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
90Ω to 110Ω
9kΩ to 11kΩ
90kΩ to 110kΩ
0.9MΩ to 1.1MΩ
Page 61

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-11
DC current calibration
After the 1MΩ resistance point has been calibrated, the unit will prompt you to apply
10mA. Follow these steps for DC current calibration:
1. Connect the calibrator to the AMPS and INPUT LO terminals of the Model 2750
as shown in Figure 2-3.
Figure 2-3
Connections for DC and AC amps calibration
Model 2750
Front Panel
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
1000V
!
PEAK
LO
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
AMPS
CAT I
DC and AC Current Calibrator
Output
Input
LO
PEAK
500V
PEAK
3A, 250V
HI
Output
LO
Amps
Note: Be sure calibrator is set for normal current output.
2. Calibrate each current step summarized in Table 2-5. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated DC current, and make sure the unit is in
OPERATE.
• Make sure the Model 2750 display indicates the correct calibration current.
• Press ENTER to complete each step.
• Allow the Model 2750 to finish each step.
Model 2750 Calibration
NOTE If you are performing DC-only calibration, proceed to “Setting calibration
dates and saving calibration.”
Table 2-5
DC current calibration summary
Calibration Step Calibrator Current Allowable Range
10mA
100mA
1A
10.00000mA
100.0000mA
1.000000A
9mA to 11mA
90mA to 110mA
0.9A to 1.1A
Page 62

2-12 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
AC voltage calibration
Follow these steps for AC voltage calibration:
1. Connect the calibrator to the Model 2750 INPUT HI and LO terminals as shown in
Figure 2-4.
Figure 2-4
Connections for AC volts calibration
AC Voltage Calibrator
Model 2750
Front Panel
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
1000V
!
PEAK
PEAK
LO
500V
PEAK
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
AMPS
CAT I
3A, 250V
Input
HI
Output
HI
Output
Input
LO
LO
2. Perform the calibration steps summarized in Table 2-6. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated value, and make sure the calibrator is in
OPERATE.
• Press ENTER to complete each step.
• Wait until the Model 2750 completes each step.
Table 2-6
AC voltage calibration summary
Calibration Step Calibrator Voltage, Frequency
10mV AC at 1kHz
100mV AC at 1kHz
100mV AC at 50kHz
1V AC at 1kHz
1V AC at 50kHz
10V AC at 1kHz
10V AC at 50kHz
100V AC at 1kHz
100V AC at 50kHz
700V AC at 1kHz
10.00000mV, 1kHz
100.0000mV, 1kHz
100.0000mV, 50kHz
1.000000V, 1kHz
1.000000V, 50kHz
10.00000V, 1kHz
10.00000V, 50kHz
100.0000V, 1kHz
100.0000V, 50kHz
700.000V, 1kHz
Page 63

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-13
AC current calibration
After the 700VAC at 1kHz point has been calibrated, the unit will prompt you for 100mA
at 1kHz. Follow these steps for AC current calibration:
1. Connect the calibrator to the AMPS and INPUT LO terminals of the Model 2750
as shown in Figure 2-3.
2. Perform the calibration steps summarized in Table 2-7. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated current and frequency, and make sure the
unit is in OPERATE.
• Press ENTER to complete each calibration step.
• Allow the unit to complete each step before continuing.
Table 2-7
AC current calibration summary
Calibration Step Calibrator Current, Frequency
100mA at 1kHz
1A at 1kHz
2A at 1kHz
100.0000mA, 1kHz
1.000000A, 1kHz
2.000000A, 1kHz
Model 2750 Calibration
Setting calibration dates and saving calibration
At the end of the calibration procedure, the instrument will display the CALIBRATION
COMPLETE message. Press ENTER to continue, and the Model 2750 will prompt you to
enter the calibration date and the calibration due date. Set these dates as follows:
1. At the CAL DATE: prompt, use the left and right arrow keys and the range keys to
set the calibration date, then press ENTER.
2. The unit will then prompt you to enter the next calibration due date with this
prompt: CAL NDUE:. Use the left and right arrow keys and the range keys to set
the calibration due date, then press ENTER.
3. The unit will prompt you to save new calibration constants with this message:
SAVE CAL? YES. To save the new constants press ENTER. If you do not want to
save the new constants press the down range key to toggle to NO, then press
ENTER.
NOTE Calibration constants calculated during the present calibration procedure will
not be saved unless you choose the YES option. Previous calibration constants
will be retained if you select NO.
Page 64

2-14 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Remote calibration
Follow the steps in this section to perform comprehensive procedures via remote. See
Appendix B for a detailed list and description of remote calibration commands.
When sending calibration commands, be sure that the Model 2750 completes each step
before sending the next command. You can do so either by observing the front panel CALIBRATING message, or by detecting the completion of each step over the bus. (See
Appendix B, “Detecting calibration step completion.”)
The procedures for calibrating the Model 2750 via remote include:
• Preparing the Model 2750 for calibration
• Front panel short and open calibration
• DC volts calibration
• Resistance calibration
• DC current calibration
• AC volts calibration
• AC current calibration
• Programming calibration dates
• Saving calibration constants
• Locking out calibration
NOTE As with front panel calibration, you can choose to perform comprehensive, DC-
only, or AC-only calibration. Be sure to include a space c har acter between eac h
command and parameter.
Preparing the Model 2750 for calibration
1. Connect the Model 2750 to the IEEE-488 bus of the computer using a shielded
IEEE-488 cable, such as the Keithley Model 7007, or connect the unit to a computer through the RS-232 port using a straight-through 9-pin to 9-pin cable (use a
9-25-pin adapter if necessary).
2. Turn on the Model 2750, and allow it to warm up for at least two hours before performing calibration.
3. Make sure the primary address of the Model 2750 is the same as the address specified in the program that you will be using to send commands. (Use the GPIB key.)
4. Unlock the calibration function by sending this command:
:CAL:PROT:CODE 'KI002750'
(The above command shows the default code, KI002750. Substitute the correct
code if changed.)
5. Send the following command to initiate calibration:
:CAL:PROT:INIT
Page 65

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-15
NOTE DC calibration can be partially performed if desired. For example, to calibrate
only the 100Ω range, perform the DCU and 100Ω range steps, then save calibration using :CAL:PROT:SAVE. Uncalibrated ranges will retain previous calibration constants and can be verified as discussed in Section 1.
Short and open calibration
1. Connect the Model 8610 low-thermal short to the instrument INPUT and SENSE
terminals as shown in Figure 2-1. Make sure the INPUTS button is not pressed in
so that the front inputs are active. Wait at least three minutes before proceeding to
allow for thermal equilibrium.
NOTE Be sure to connect the low-thermal short properly to the HI, LO, and SENSE ter-
minals. Keep drafts away from low-thermal connections to avoid thermal drift,
which could affect calibration accuracy.
2. Send the following command:
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP1
3. After the Model 2750 completes this step, remove the low-thermal short, and then
send this command:
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP2
Model 2750 Calibration
NOTE Be sure to minimize movement near front input terminals. Excessive movements
can cause capacitive coupling errors, which could affect calibration accuracy.
DC volts calibration
After the front panel short and open steps, do the following:
1. Connect the calibrator to the Model 2750 as shown in Figure 2-2. Allow three minutes for thermal equilibrium.
NOTE Although 4-wire connections are shown, the sense leads are connected and dis-
connected at various points in this procedure by turning calibrator external
sense on or off as appropriate. If your calibrator does not have provisions for
turning external sense on and off, disconnect the sense leads when e xternal sensing is to be turned off, and connect the sense leads when external sensing is to be
turned on.
2. Perform the calibration steps summarized in Table 2-8. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated voltage, and make sure the unit is in operate.
(Use the recommended voltage if possible.)
• Send the indicated programming command. (Change the voltage parameter if
you are using a different calibration voltage.)
• Wait until the Model 2750 completes each step before continuing.
Page 66

2-16 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
NOTE Ensure the calibrator has settled to the final value. You can do so by verifying
that the “Settled” indicator is off, or by using the *OPC? (operation complete)
query.
Table 2-8
DC voltage calibration programming steps
Calibration
Step Calibrator Voltage Calibration Command*
+10V
-10V
100V
*Use recommended value where possible. Change parameter accordingly if using a different calibrator voltage.
+10.00000V
-10.00000V
100.0000V
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP3 10
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP4 -10
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP5 100
Parameter
Range
9 to 11
-9 to -11
90 to 110
Resistance calibration
Follow these steps for resistance calibration:
1. Set the calibrator to the resistance mode, and turn on external sensing.
NOTE Use external sense (4-wire Ω) when calibrating all resistance ranges. Be sure
that the calibrator external sense mode is turned on.
2. Perform the calibration steps summarized in Table 2-9. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated resistance, and make sure the unit is in operate. (Use the recommended resistance or the closest available value.)
• Send the indicated programming command. (Change the command parameter
if you are using a different calibration resistance than that shown.)
• Wait until the Model 2750 completes each step before continuing.
Table 2-9
Resistance calibration programming steps
Calibration
Step
100Ω
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
*Use exact calibrator resistance value for parameter.
Calibrator
Resistance Calibration Command* Parameter Range
100Ω
10kΩ
100kΩ
1MΩ
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP6 100
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP7 10E3
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP8 100E3
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP9 1E6
90 to 110
9E3 to 11E3
90E3 to 110E3
900E3 to 1.1E6
Page 67

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-17
DC current calibration
After the 1MΩ resistance point has been calibrated, follow these steps for DC current
calibration:
1. Connect the calibrator to the AMPS and INPUT LO terminals of the Model 2750
as shown in Figure 2-3.
2. Perform the calibration steps listed in Table 2-10. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated current, and make sure the unit is in operate.
(Use the recommended current if possible.)
• Send the indicated programming command. (Change the current parameter if
you are using a different calibration current.)
• Wait until the Model 2750 completes each step before continuing.
NOTE If you are performing DC-only calibration, proceed to “Programming calibra-
tion dates.”
Table 2-10
DC current calibration programming steps
Model 2750 Calibration
Calibration
Step
10mA
100mA
1A
*Change parameter if using different current.
Calibrator
Current Calibration Command* Parameter Range
10.00000mA
100.00000mA
1.000000A
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP10 10E-3
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP11 100E-3
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP12 1
9E-3 to 11E-3
90E-3 to 110E-3
0.9 to 1.1
Page 68

2-18 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
AC voltage calibration
Follow these steps for AC voltage calibration:
1. Connect the calibrator to the Model 2750 INPUT HI and LO terminals as shown in
Figure 2-4.
2. Perform the calibration steps summarized in Table 2-11. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated voltage and frequency, and make sure the
unit is in operate. (You must use the stated voltage and frequency.)
• Send the indicated programming command.
• Wait until the Model 2750 completes each step before continuing.
Table 2-11
AC voltage calibration programming steps
Calibration Step Calibrator Voltage, Frequency Calibration Command
10mV AC at 1kHz
100mV AC at 1kHz
100mV AC at 50kHz
1VAC at 1kHz
1VAC at 50kHz
10VAC at 1kHz
10VAC at 50kHz
100VAC at 1kHz
100VAC at 50kHz
700VAC at 1kHz
10.00000mV, 1kHz
100.0000mV, 1kHZ
100.0000mV, 50kHz
1.000000V, 1kHz
1.000000V, 50kHz
10.00000V, 1kHz
10.00000V, 50kHz
100.0000V, 1kHz
100.0000V, 50kHz
700.000V, 1kHz
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP1
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP2
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP3
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP4
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP5
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP6
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP7
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP8
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP9
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP10
Page 69

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-19
AC current calibration
Follow these steps for AC current calibration:
1. Connect the calibrator to the AMPS and INPUT LO terminals of the Model 2750
as shown in Figure 2-3.
2. Perform the calibration steps summarized in Table 2-12. For each step:
• Set the calibrator to the indicated current and frequency, and make sure the
unit is in operate. (You must use the stated current and frequency.)
• Send the indicated programming command.
• Wait until the Model 2750 completes each step before continuing.
Table 2-12
AC current calibration programming steps
Calibration Step Calibrator Current, Frequency Calibration Command
100mA at 1kHz
1A at 1kHz
2A at 1kHz
100.0000mA, 1kHz
1.000000A, 1kHz
2.000000A, 1kHz
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP11
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP12
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP13
Programming calibration dates
Model 2750 Calibration
Program the present calibration date and calibration due date by sending the following
commands:
:CAL:PROT:DATE <year>, <month>, <day>
:CAL:PROT:NDUE <year>, <month>, <day>
For example, the following commands assume calibration dates of 3/5/2001 and
3/5/2002 respectively:
:CAL:PROT:DATE 2001, 3, 5
:CAL:PROT:NDUE 2002, 3, 5
Saving calibration constants
After completing the calibration procedure, send the following command to save the new
calibration constants:
:CAL:PROT:SAVE
NOTE Calibration constants will not be saved unless the :CAL:PROT:SAVE command
is sent.
Locking out calibration
After saving calibration, send the following command to lock out calibration:
:CAL:PROT:LOCK
Page 70

2-20 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Manufacturing calibration
The manufacturing calibration procedure is normally performed only at the factory, but the
necessary steps are included here in case the unit is repaired, and the unit requires these
calibration procedures.
NOTE If the unit has been repaired, the entire comprehensive calibration procedure
should also be performed in addition to the manufacturing calibration
procedure.
Recommended test equipment
Table 2-13 summarizes the test equipment required for the manufacturing calibration
steps. In addition, you will need the calibrator (Table 2-1) and signal generator to com-
plete the comprehensive calibration steps.
Table 2-13
Recommended equipment for manufacturing calibration
Stanford Research Systems DS345 Function Generator:
1V RMS, 3Hz, ±5ppm
1V RMS, 1kHz, ±5ppm
Keithley Model 2001 or 2002 Digital Multimeter:
1V, 3Hz AC, ±0.13%
Keithley 7797 Calibration/Extender Board
Extender board preparation
Before performing manufacturing calibration, short the output HI, LO, SHI, and SLO terminals of the 7797 Calibration/Extender together using clean, solid copper wires. These
connections will form a low-thermal short necessary for the manufacturing calibration
procedure. The Calibration Extender Board should then be installed in scanner Slot #1.
Page 71

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-21
Unlocking manufacturing calibration
To unlock manufacturing calibration, press and hold in the OPEN key while turning on the
power.
Measuring function generator signal amplitude
The 3Hz function generator signal amplitude must be accurately measured using the digital multimeter listed in Table 2-13. Proceed as follows:
1. Connect the function generator output to the digital multimeter INPUT jacks. (See
Figure 2-5 for typical connections.)
2. Turn on the function generator and multimeter, and allow a two-hour warm-up
period before measuring.
3. Set the function generator to output a 1V RMS sine wave at 3Hz; measure and
record the signal amplitude.
Front panel manufacturing calibration
1. Install the shorted calibration extender board (see “Extender board preparation”
earlier in this section) in scanner card Slot 1, and select the rear inputs with the
INPUTS switch. Allow three minutes for thermal equilibrium.
2. Press in and hold the OPEN key while turning on the power.
3. Press SHIFT then TEST then display CALIB: TEST with the up or down range
key. Press ENTER, select RUN, then enter the appropriate calibration code
(default: 002750).
4. Select ALL at the CAL:RUN prompt.
5. Press ENTER to perform the first manufacturing calibration step.
6. Perform the entire front panel comprehensive calibration procedure discussed earlier in this section. (See “Comprehensive calibration” earlier in this section.)
7. Connect the function generator to the Model 2750 front panel INPUT jacks as
shown in Figure 2-5. Select the front input jacks with the INPUTS switch.
Model 2750 Calibration
Page 72

2-22 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Figure 2-5
Function generator connections for manufacturing calibration
Function Generator
Model 2750
Front Panel
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
!
PEAK
LO
INPUT
F
R
FRONT/REAR
AMPS
CAT I
BNC-to-Dual
Banana Plug
Adapter
1000V
PEAK
500V
PEAK
50Ω
Coax
Cable
3A, 250V
Function
Output
Note: Output voltage must be accurately
measured. (See text.)
8. After the last AC current calibration step, the instrument will prompt you to enter
3Hz at 1V RMS and 1kHz with the following prompts:
• Low-frequency cal: Set the function generator to output a 1V RMS, 3Hz sine
wave. Use the left and right arrow keys, and the range keys to adjust the display to agree with the generator amplitude you measured previously, then
press ENTER.
• Frequency cal: Set the function generator to output a 1V RMS, 1kHz sine
wave. Enter 1.000000kHz at the prompt, then press ENTER.
9. Set the calibration dates, then save calibration to complete the process.
Remote manufacturing calibration
1. Install the shorted calibration extender board (see “Extender board preparation”
earlier in this section) in scanner card Slot 1, and select the rear inputs with the
INPUTS switch. Allow three minutes for thermal equilibrium.
2. Press in and hold the OPEN key while turning on the power.
3. Enable calibration by sending the :CODE command. For example, the default command is:
:CAL:PROT:CODE 'KI002750'
4. Initiate calibration by sending the following command:
:CAL:PROT:INIT
5. Calibrate step 0 with the following command:
:CAL:PROT:DC:STEP0
Page 73

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-23
6. Perform the entire remote comprehensive calibration procedure discussed earlier in
this section. (See “Comprehensive calibration” earlier in this section.)
7. Connect the function generator to the Model 2750 INPUT jacks as shown in
Figure 2-5. Select the front input jacks with the INPUTS switch.
8. Set the generator to output a 1V RMS, 3Hz sine wave, then send the following
command:
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP14 <Cal_voltage>
Here <Cal_voltage> is the actual 3Hz generator signal amplitude you measured
previously.
9. Set the generator to output a 1V RMS, 1kHz sine wave, then send the following
command:
:CAL:PROT:AC:STEP15 1E3
10. Send the following commands to set calibration dates, save calibration, and lock
out calibration:
:CAL:PROT:DATE <year>, <month>, <day>
:CAL:PROT:NDUE <year>, <month>, <day>
:CAL:PROT:SAVE
:CAL:PROT:LOCK
Model 7700 Calibration
Model 7700 calibration
The following procedures calibrate the temperature sensors on the Model 7700 plug-in
modules.
NOTE For additional information about the Keithley modules, refer to the module
documentation.
Recommended test equipment
In order to calibrate the Model 7700, you will need equipment summarized in Table 2-14.
Table 2-14
Recommended equipment for Model 7700 calibration
Digital Thermometer:
18 to 28˚C, ±0.1˚C
Keithley 7797 Calibration/Extender Board
Page 74

2-24 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Extender board connections
The Model 7700 being calibrated should be connected to the 7797 Calibration/Extender
Board, and the extender board should then be installed in scanner Slot #1. Note that the
module being calibrated will be external to the Model 2750 to avoid card heating during
calibration.
Model 7700 calibration
NOTE Before calibrating the Model 7700, make sure that power has been removed
from the card for at least two hours to allow card circuitry to cool down. After
turning on the power during the calibration procedure, complete the procedure
as quickly as possible to minimize card heating that could affect calibration
accuracy. Allow the Model 2750 to warm up for at least two hours.
Front panel Model 7700 calibration
1. Connect the Model 7700 to the Model 7797 Calibration/Extender Board (see
“Extender board connections”).
2. With the power off, install the Model 7700/7797 combination in Slot 1, and select
the rear inputs with the INPUTS switch. Allow three minutes for thermal
equilibrium.
3. Accurately measure and record the cold temperature of the Model 7700 card surface at the center of the card with an RTD sensor.
4. Press in and hold the Model 2750 OPEN key while turning on the power.
5. Press SHIFT then TEST, then display TEST:CALIB with the up or down range
key. Press ENTER, select RUN, then enter the appropriate calibration code
(default: 002750).
6. Using the up or down range key, select CARD at the CAL:RUN prompt, then press
ENTER.
7. Set the display value to the cold calibration temperature (˚C) you measured in Step
3, then press ENTER to complete Model 7700 calibration.
Page 75

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Calibration 2-25
Remote Model 7700 calibration
1. Connect the Model 7700 to the 7797 Calibration/Extender Board (see “Extender
board connections” above).
2. With the power off, install the Model 7700/7797 combination in Slot 1, and select
the rear inputs with the INPUTS switch. Allow three minutes for thermal equilibrium.
3. Accurately measure and record the cold temperature of the Model 7700 card surface at the center of the card.
4. Press in and hold the Model 2750 OPEN key while turning on the power.
5. Enable calibration by sending the :CODE command. For example, the default command is:
:CAL:PROT:CODE 'KI002750'
6. Initiate calibration by sending the following command:
:CAL:PROT:CARD1:INIT
7. Calibrate the Model 7700 with the following command:
:CAL:PROT:CARD1:STEP0 <temp>
Here <temp> is the cold calibration temperature (˚C) measured in Step 3.
8. Send the following commands to save calibration and lock out calibration:
:CAL:PROT:CARD1:SAVE
:CAL:PROT:CARD1:LOCK
Model 7700 Calibration
Page 76

2-26 Calibration Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Page 77

3
Routine Maintenance
Routine Maintenance
Page 78

3-2 Routine Maintenance Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Introduction
The information in this section deals with routine type maintenance and includes procedures for setting the line voltage, replacing the Model 2750 line and front terminal AMPS
fuses, and replacing the amps fuses for the Models 7700 plug-in module. Replacement of
the Model 2750 non-volatile RAM battery and reading module relay card closure count is
also covered.
Setting the line voltage and replacing the line fuse
WARNING Disconnect the line cord at the rear panel, and remove all test leads
connected to the instrument (front and rear) before replacing the line
fuse.
The power line fuse is located in the power module next to the AC power receptacle
(Figure 3-1). If the line voltage must be changed, or if the line fuse requires replacement,
perform the following steps:
1. Place the tip of a flat-blade screwdriver into the power module by the fuse holder
assembly (Figure 3-1). Gently push in and to the left. Release pressure on the
assembly, and its internal spring will push it out of the power module.
CAUTION For continued protection against fire or instrument damage, replace
the fuse only with the type and rating listed. If the instrument repeatedly blows fuses, locate and correct the cause of the trouble before
replacing the fuse.
2. Remove the fuse, and replace it with the type listed in Table 3-1.
Page 79

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Routine Maintenance 3-3
Figure 3-1
Power module
Model 2750
DIGITAL I/O TRIG. LINK
!
RS-232
IEEE-488
SLT
1
MADE IN
U.S.A.
SLT
2
CAT I
Fuse
Line Voltage
Selector
220
240
0
0
120
1
Spring
Window
Fuse Holder Assembly
SLT
3
SLT
4
!
SLT
5
Routine Maintenance
CAUTION Operating the Model 2750 on the wrong line voltage may result in
instrument damage.
3. If configuring the instrument for a different line voltage, remove the line voltage
selector from the assembly, and rotate it to the proper position. When the selector is
installed into the fuse holder assembly, the correct line voltage appears inverted in
the window.
4. Install the fuse holder assembly into the power module by pushing it in until it
locks in place.
Table 3-1
Power line fuse
Line Voltage Rating Keithley Part No.
100/120V
200/240V
0.630A, 250V, 5 × 20 mm, slow-blow
0.315A, 250V, 5 × 20 mm, slow-blow
FU-106-.630
FU-106-.315
Page 80

3-4 Routine Maintenance Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Replacing the AMPS fuse
The front panel AMPS fuse protects the Model 2750 AMPS current input from an overcurrent condition. Follow the steps below to replace the AMPS fuse.
WARNING Make sure the instrument is disconnected from the power line and
other equipment before replacing the AMPS fuse.
1. Turn off the power, and disconnect the power line and test leads.
2. Using a screwdriver, rotate the fuse carrier one-quarter turn counterclockwise
(Figure 3-2). Release pressure on the jack, and its internal spring will push the fuse
carrier out of the socket.
CAUTION Do not use a fuse with a higher current rating than specified or instru-
ment damage may occur. If the instrument repeatedly blows fuses,
locate and correct the cause of the trouble before replacing the fuse.
3. Remove the fuse, and replace it with the same type: 3A, 250V, fast-blow, Keithley
part number FU-99-1.
4. Install the new fuse by reversing the above procedure.
Figure 3-2
AMPS fuse
SHIFT
LOCAL
POWER
MATH
DCV
EX TRIG
SAVE SETUP
OPEN
OUTPUT
DRYCKT
TRIG
CLOSE
RATIO
DCIACV
LIMITS ON/OFFDELAY
STORE
CONFIG HALT
STEP SCAN
CONT
CH AVG
ACIΩ2Ω4
RECALL
DIGITS RATE
Model 2750
SLOT 1
SLOT 2
SLOT 3
SLOT 4
RANGE
AUTO
RANGE
SLOT 5
MODEL 2750 MULTIMETER/SWITCH SYSTEM
INTEGRA SERIES
OCOMP
PERIOD SENSOR
TEMP
FREQ
MONITOR
TYPE
CH-OFF
CARD
RELFILTER
RS-232
LSYNC
GPIB
TEST
EXIT ENTER
SENSE
INPUT
Ω 4 WIRE
HI
350V
1000V
!
PEAK
F
FRONT/REAR
CAT I
PEAK
LO
500V
PEAK
INPUT
R
AMPS
3A, 250V
Rotate
Counterclockwise
Page 81

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Routine Maintenance 3-5
Replacing Model 7700 plug-in module amps fuses
WARNING The information in this section is intended only for qualified service
personnel. Do not perform these procedures unless you are qualified to
do so.
WARNING Make sure that all plug-in module connections are de-energized and
disconnected before replacing module amps fuses.
1. Turn off the power, and disconnect the power line and external connections from
the Model 7700.
2. Open the Model 7700 top cover.
3. Locate the amps fuses for CH21 and CH22 (Figure 3-3).
4. Remove the circuit board from the bottom plastic housing by removing the two
bottom screws.
Figure 3-3
Model 7700 amps fuses
CH22 Fuse
Model 7700
SENSE CH1
INPUT
HLHL
HLHL
CH21 CH22 CH11 CH12 CH13 CH14 CH15 CH16
CH2
HLHL
LO
AMPS
HLHL
HLHL
HLHLHLHLHLHL
CH6
CH5
CH4
CH3
CH21 Fuse
CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
HLHLHLHL
HLHLHLHL
CH17 CH18 CH19 CH20
INPUT
(V, 2 WIRE)
SENSE
(OHMS, 4 WIRE)
Routine Maintenance
Page 82

3-6 Routine Maintenance Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
5. De-solder the blown CH21 or CH22 fuse as required, taking care not to damage the
circuit board or spread solder flux around the board.
CAUTION Do not use a fuse with a higher current rating than specified or module
damage may occur.
6. Install a new 3A, 250V fast-blow fuse, Keithley part number FU-107-1.
7. Solder the new fuse in place using organic (OA based) flux solder, again taking
care not to damage the circuit board or spread solder flux around the board.
8. Carefully clean the repaired area of the circuit board with a foam tipped swab or
brush dipped in pure water, then blow dry the board with dry nitrogen gas. Allow
the board to dry for several hours in a 50˚C low-humidity environment before use.
9. Reinstall the circuit board into the plastic housing, then close the top cover.
Replacing non-volatile RAM battery
The Model 2750 has a three-year lithium battery for non-volatile RAM. Use the procedure
below to replace the battery, if required. Refer to the disassembly procedures in Section 5
and the parts list and component layout drawings at the end of Section 6 for more information.
WARNING There is a danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to federal, state, and
local laws.
The following procedure is intended only for qualified service personnel. Do not perform this procedure unless you are qualified to do so.
Disconnect the line cord and all connecting wires from the Model 2750
before removing the top cover.
Page 83

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Routine Maintenance 3-7
WARNING The precautions below must be followed to avoid personal injury.
• Wear safety glasses or goggles when working with lithium
batteries.
• Do not short the battery terminals together.
• Keep lithium batteries away from all liquids.
• Do not attempt to recharge lithium batteries.
• Observe proper polarity when installing the battery.
• Do not incinerate or otherwise expose the battery to excessive heat
(>60°C).
• Bulk quantities of lithium batteries should be disposed of as hazardous waste.
• Dispose of used batteries according to all federal, state, and local
laws.
Replace the battery as follows:
1. Before replacing the battery, refer to the troubleshooting procedures in Table 4-4 in
Section 4 to determine if the battery requires replacement
2. Remove the Model 2750 top cover using the disassembly procedures in Section 5.
3. Locate battery BT100 using the motherboard component layout drawing at the end
of Section 6.
4. De-solder the battery from the top side of the circuit board.
5. Install a new battery, Keithley part number BA-51, taking care to observe proper
polarity.
6. Solder the battery connection to the circuit board using organic (OA-based) flux
solder.
7. After soldering, remove all flux using a foam-tipped swab or brush dipped in pure
water. Blow dry the board with dry nitrogen gas, then allow the board to dry for
several hours in a 50˚C, low-humidity environment before use.
8. Reinstall the top cover by following the disassembly procedures in Section 5 in
reverse order.
Routine Maintenance
Page 84

3-8 Routine Maintenance Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Plug-in module relay closure count
The Model 2750 keeps an internal count of the number of times each module relay has
been closed. This count will help you determine if and when any relays require replacement (see module contact life specifications). The count can be read or reset only via
remote as outlined below.
Closure count commands
Table 3-2 summarizes closure count commands.
Table 3-2
Closure count commands
Command Description
:ROUTe
:CLOSe
:COUNt? (@clist)
:INTerval < NRf>
:INTerval?
:RCOunt (@clist)
* Unit must be in manufacturing calibration mode. See text below.
Route subsystem.
Path to CLOSe commands.
Query count for channels in clist (channel list).
Set count update interval in minutes (10 to 1440).
Query count update interval.
Reset count for channels in clist.*
Reading relay closure count
To determine the closure count of specific channels, send this query via remote:
:ROUTe:CLOSe:COUNt? (@clist)
Here, clist is the summary of channels. For example, to determine the closure count of
channels 1 and 4 of a module in slot 1, the following query would be sent:
:ROUT:CLOS:COUN? (@101,104)
The following query would determine the closure count of slot 1 module channels 1
through 10:
:ROUT:CLOS:COUN? (@101:110)
Page 85

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Routine Maintenance 3-9
Resetting relay closure count
NOTE The Model 2750 must be in the manufacturing calibration mode to reset the clo-
sure count. To do so, press and hold the OPEN key while turning on the power,
then send the :CAL:PROT:CODE “code” to unlock calibration (default code:
KI002750). After resetting relay counts, send :CAL:PROT:LOCK to lock out
calibration.
To reset the relay closure count of specific channels to 0, send this command via remote:
:ROUTe:CLOSe:RCOunt (@clist)
Again clist is the summary of channels to be reset. For example, the following command
resets channels 2 and 7 of a module in slot 1 to 0:
:ROUT:CLOS:RCO (@102,107)
The following command resets the count of slot 1 module channels 1 through 10:
:ROUT:CLOS:RCO (@101:110)
Setting count update interval
Relay closure counts are updated in temporary RAM every time a channel is closed
regardless of how it was closed: by an SCPI command, front panel control, or during a
scan. These counts are permanently written to the EEPROM on the card only at a user-settable time interval (which has a factory default of 15 minutes), or whenever the counts are
queried. Valid intervals (set in integer number of minutes) are between 10 and 1440 minutes (24 hrs). Relay closures are counted only when a relay cycles from open to closed
state. If you send multiple close commands to the same channel without sending an open
command, only the first closure will be counted.
The lower the interval, the less chance there is of losing relay counts due to power failures.
However, writing to the EEPROM more often may reduce scanning throughput. The
higher the interval, the less scanning throughput is reduced, but more relay counts may be
lost in the event of a power failure.
To set the count update interval, send this command:
:ROUTe:CLOSe:COUNt:INTerval <interval>
For example, to set the interval to 30 minutes, send this command:
:ROUT:CLOS:COUN:INT 30
Routine Maintenance
Page 86

3-10 Routine Maintenance Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Rack mounting
Rack mount kit
Model 4288-7 rack mount kit — Mounts a Model 2750 in a standard 19-inch rack.
Includes rear brackets to provide additional support for a mainframe that has two or more
switching modules installed.
NOTE The Model 2750 includes hardware that allows it to be mounted to the front r ails
of a standard 19-inch rack. With two or more switching modules installed, rear
support brackets may be required. The Model 4288-7 rack mount kit includes
rear support brackets.
Rack mount procedure
The Model 2750 can be mounted in a standard 19-inch rack. For a mainframe that has one
or no switching modules installed, the Model 2750 can be secured to the front rails of the
rack.
The hardware necessary to secure the mainframe to the front rails of the rack is supplied
with the Model 2750. The supplied hardware kit includes four dress screws and four
retaining clips. Each retaining clip has a captive nut.
Perform the following steps to mount the Model 2750 to the front rails of the rack:
WARNING Make sure the Model 2750 is turned off, the line cord is disconnected,
and it is not connected to any external circuitry.
1. Select a location in the rack. The mainframe takes up 3.5 inches of vertical space.
Page 87

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Routine Maintenance 3-11
2. Using Figure 3-4 as a guide, install two retaining clips on the left front rail. Slide
each retaining clip over a mounting hole such that the captive nut is positioned on
the inside of the rack cabinet. In a similar manner, install two retaining clips on the
right front rail.
Figure 3-4
Rack preparation
Left Front
Rack Rail
1.75”
Retaining Clips
with Nuts
3. Remove the four foot assemblies from the bottom of the Model 2750. The retaining
screw for an assembly is located under the rubber foot. Simply pull off the rubber
feet to gain access to the screws. Retain these foot assemblies for future use.
4. Position the Model 2750 in the rack and loosely attach the front panel to the rack
rails using the four supplied dress screws.
5. Tighten the four dress screws.
CAUTION For a Model 2750 that has two or more installed switching modules,
rear brackets may be required to support the additional weight. The
Model 4288-7 is a rack mount kit for the Model 2750 that uses rear
support brackets.
Routine Maintenance
Page 88

3-12 Routine Maintenance Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Page 89

4
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Page 90

4-2 Troubleshooting Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Introduction
This section of the manual will assist you in troubleshooting and repairing the Model
2750. Included are self-tests, test procedures, troubleshooting tables, and circuit descriptions. It is left to the discretion of the repair technician to select the appropriate tests and
documentation needed to troubleshoot the instrument. Refer to the disassembly procedures in Section 5 and the parts lists in Section 6 for further information.
WARNING The information in this section is intended only for qualified service
personnel. Do not perform these procedures unless you are qualified to
do so. Some of these procedures may expose you to hazardous voltages
that could cause personal injury or death. Use caution when working
with hazardous voltages.
The metal shield located on the motherboard is at analog LO potential
and may have hazardous voltages. To avoid a possible shock hazard,
connect the metal shield to chassis ground before servicing.
Repair considerations
Before making any repairs to the Model 2750, be sure to read the following
considerations.
CAUTION The PC boards are built using surface mount techniques and require
specialized equipment and skills for repair. If you are not equipped
and/or qualified, it is strongly recommended that you send the unit
back to the factory for repairs or limit repairs to the PC board replacement level. Without proper equipment and training, you could damage
a PC board beyond repair.
• Repairs will require various degrees of disassembly. However, it is recommended
that the Front Panel Tests be performed prior to any disassembly. The disassembly
instructions for the Model 2750 are contained in Section 5 of this manual.
• Do not make repairs to surface mount PC boards unless equipped and qualified to
do so (see previous CAUTION).
• When working inside the unit and replacing parts, be sure to adhere to the handling
precautions and cleaning procedures explained in Section 5.
• Many CMOS devices are installed in the Model 2750. These static-sensitive
devices require special handling as explained in Section 5.
• Whenever a circuit board is removed or a component is replaced, the Model 2750
must be recalibrated. See Section 2 for details on calibrating the unit.
Page 91

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Troubleshooting 4-3
Power-on self-test
During the power-on sequence, the Model 2750 will perform a checksum test on its
EPROM (U156 and U157) and test its RAM (U151, U152, U164 and U193). If one of
these tests fails, the instrument will lock up.
Front panel tests
There are two front panel tests: one to test the functionality of the front panel keys and one
to test the display. In the event of a test failure, refer to “Display board checks” for details
on troubleshooting the display board.
KEY test
The KEY test allows you to check the functionality of each front panel key. Perform the
following steps to run the KEY test:
1. Press SHIFT and then TEST to access the self-test options.
2. Use the up or down RANGE key to display “TEST: KEY.”
3. Press ENTER to start the test. When a key is pressed, the label name for that key is
displayed to indicate that it is functioning properly. When the key is released, the
message “NO KEY PRESS” is displayed.
4. Pressing EXIT tests the EXIT key. However, the second consecutive press of EXIT
aborts the test and returns the instrument to normal operation.
DISP test
The display test allows you to verify that each segment and annunciator in the vacuum fluorescent display is working properly. Perform the following steps to run the display test:
1. Press SHIFT and then TEST to access the self-test options.
2. Use the up or down RANGE key to display “TEST: DISP.”
3. Press ENTER to start the test. There are five parts to the display test. Each time
ENTER is pressed, the next part of the test sequence is selected. The five parts of
the test sequence are as follows:
a. All annunciators are displayed.
b. The segments of each digit are sequentially displayed.
c. The 12 digits (and annunciators) are sequentially displayed.
d. The annunciators located at either end of the display are sequentially
displayed.
e. The LEDs are displayed.
4. When finished, abort the display test by pressing EXIT. The instrument returns to
normal operation.
Troubleshooting
Page 92

4-4 Troubleshooting Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Principles of operation
The following information is provided to support the troubleshooting tests and procedures
covered in this section of the manual. Refer to the following block diagrams:
Figure 4-1 — Power supply block diagram.
Figure 4-2 — Digital circuitry block diagram.
Figure 4-3 — Analog circuitry block diagram.
Power supply
The following information provides some basic circuit theory that can be used as an aid to
troubleshoot the power supply. A block diagram of the power supply is shown in
Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1
Power supply block diagram
Fuse
Power
Switch
Line
Voltage
Select
Switch
Power
Transformer
CR104
C156, C175
C281, U144
C273, C274
CR116, CR117
C104, U101
CR102, CR115
C131, C148
U119, U125
CR103
C146
U124
+5VD
D Common
+37V
D Common
+18V
+15.7V
A Common
-15.7V
-18V
+5V
A Common
Page 93

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Troubleshooting 4-5
AC power is applied to the AC power module receptacle. Power is routed through the line
fuse and line voltage selection switch of the power module to the power transformer. The
power transformer has a total of four secondary windings for the various supplies.
AC voltage for the display filaments is taken from a power transformer secondary at F1
and F2, and then routed to the display board.
Each DC supply uses a rectifier and a capacitive filter, and many supplies use an IC regulator. Table 4-1 summarizes rectifier, filter, and regulator circuits for the various DC
supplies.
Table 4-1
Power supply components
Supply Rectifier Filter Regulator
+5VD
+37V
+15.7V
-15.7V
+5V, +5VRL, +5V2
+18V
-18V
CR104
CR116, CR117
CR102, CR115
CR102, CR115
CR103
CR102
CR102
C281, C156, C175, C273, C274
C104
C148
C131
C146
C148
C131
U144
U101
U125
U119
U124
-
-
Troubleshooting
Page 94

4-6 Troubleshooting Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Display board
Display board components are shown in the digital circuitry block diagram in Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2
Digital circuitry block diagram
Analog
Circuitry
(See Figure 4-3)
U122
U127
U170
U173
U174
U195
U196
XADTX
XADCLK
XADTS
XADRX
Slot
Control
O
P
T
O
I
S
O
U175
U150
U155
Trigger
U146
Trigger
Link
NVRAM
Line Sync
Control
U179
U180
U181
U182
U183
U184
U186
U136
ADTX
ADCLK
ADTS
ADRXB
TRIG IN
TRIG OUT
ROM
U156, U157
68332
µP
U135
Data OUT
Digital OUT
BAT
BT100
U151, U152
U164, U193
OUT
Data IN
RAM
IN
Battery
Back
Control/
Realtime Clock
U171
Display Board
Controller
U401
XTAL
Y101
RS-232
U159
GPIB
U158, U160,
U161
Digital Output
U188, U189
Digital Input
Y103
Keypad
Display
DS401
RS-232
Port
IEEE-488
Bus
Digital
I/O
U146, U191
U192
Page 95

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Troubleshooting 4-7
Microcontroller
U401 is the display board microcontroller that controls the display and interprets key data.
The microcontroller uses three internal peripheral I/O ports for the various control and
read functions.
Display data is serially transmitted to the microcontroller from the digital section via the
TXB line to the microcontroller RDI terminal. In a similar manner, key data is serially sent
back to the digital section through the RXB line via TDO. The 4MHz clock for the microcontroller is generated by crystal Y401.
Display
DS401 is the display module, which can display up to 12 alphanumeric characters and
includes the various annunciators and five LED annunciators.
The display uses a common multiplexing scheme with each character refreshed in
sequence. U402 and U403 are the drivers for the display characters and annunciators. Note
that data for the drivers are serially transmitted from the microcontroller (MOSI and PC1).
Filament voltage for the display is derived from the power supply transformer (F1 and F2).
The display drivers require +37VDC and +5VDC, which are supplied by U144 (+5VD)
and U101 (+37V).
Key matrix
The front panel keys (S401-S430) are organized into a row-column matrix to minimize the
number of microcontroller peripheral lines required to read the keyboard. A key is read by
strobing the columns and reading all rows for each strobed column. Key-down data is
interpreted by the display microcontroller and sent back to the main microprocessor using
proprietary encoding schemes.
Digital circuitry
Refer to Figure 4-2 for the following discussion on digital circuitry.
Microprocessor
U135 is a 68332 microprocessor that oversees all operating aspects of the instrument. The
MPU has a 16-bit data bus and provides a 21-bit address bus. It also has parallel and serial
ports for controlling various circuits. For example, the RXD and TXD lines are used for
the RS-232 interface.
The MPU clock frequency of 19.92MHz is controlled by crystal Y101. MPU RESET is
performed momentarily on power-up.
Memory circuits
ROMs U156 and U157 store the firmware code for instrument operation. U157 stores the
D0-D7 bits of each data word, and U156 stores the D8-D15 bits. RAMs U151, U152,
U164, and U193 provide battery backed operating storage.
Troubleshooting
Page 96

4-8 Troubleshooting Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Semi-permanent storage facilities include NVRAM U136. This IC stores such information
as instrument setup and calibration constants. Data transmission from this device is done
in a serial fashion.
U194, U171, Y103, and BT100 make up the battery watchdog control, along with the realtime clock. U171 automatically senses when the +5VD supply is being powered down and
then switches to BT100 for power.
RS-232 interface
Serial data transmission and reception is performed by the TXD and RXD lines of the
MPU. U159 provides the necessary voltage level conversion for the RS-232 interface port.
IEEE-488 interface
U158, U160, and U161 make up the IEEE-488 interface. U158, a 9914A GPIA, takes care
of routine bus overhead such as handshaking, while U160 and U161 provide the necessary
buffering and drive capabilities.
Trigger circuits
Buffering for Trigger Link input and output is performed by U146. Trigger input and output is controlled by the TP5 and PC2 lines of the MPU.
Digital I/O
U146, U191, and U192 make up the digital input circuitry. External triggering can occur
on J1006 or J1007. U192 allows hardware handshaking to external controllers by gating
off triggers.
U188 and U189 provide digital output. The two driver ICs, U188 and U189, provide current sink capability of 250mA each.
Module slot control
U122, U127, U170, U173, U174, U195, and U196 make up the control circuitry that
allows communication of relay data to Slot 1, Slot 2, Slot 3, Slot 4, or Slot 5.
Line sync
U179, U180, U181, U182, U183, U184, and U186 are used to control A/D triggers synchronized at the zero cross point of the power line voltage. U186 controls zero crossing
detection, while U182 and U183 preserve the trigger states until the zero crossing threshold is detected.
Analog circuitry
Refer to Figure 4-3 for the following discussion on analog circuitry.
Page 97

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Troubleshooting 4-9
Figure 4-3
Analog circuitry block diagram
A/D MUX
Front Terminals
S101
Overload
Protection
Q103, 107, 117,
CR101, 113,
U128,140, 143
VR110, 111
ADC
U165
Digital
Circuitry
(See Figure 4-2)
Front Terminals
S101
Scanner Outputs
Front Terminals
S101
Scanner Outputs
Front Terminals
S101
Scanner Outputs
Scanner Outputs
Dry Circuit
Stability
Clamp
C152, C164,
K104
INPUT
HI
SENSE
HI
SENSE
LO
AMPS
DCV
Divider
R117, Q109,
Q114, Q136
Current
Shunts
K103, R158,
R205, R338
½K102, U102, U103, U105,
U112, U118, U111, U110, U117
K101
SSP*
Q101, Q102
SSP* CR105, Q159
DCV/100
Q124, Q125, Q126,
½K102, U123, U133
SSP*
Q150, Q151
SSP*
Q122, Q135
DCA
ACA
AC Switching
&
Gain
ACV,
FREQ
Ohms I-Source
Q119, Q123,
DCV
OHMS
DCV & Ohms
Switching
K101, Q104,
Q108, Q113
X1
BUFCOM
Buffer
U113
Dry Circuit
Voltage Clamps
U162, U206
Low Ohms
Sensing
Q106
A/D
MUX &
Gain
U129, U132
U163, U166
Temp.
Sensor
(CJC)
Protection
DS101,
102
Troubleshooting
Scanner Outputs
Scanner
Inputs
Scanner
Inputs
Slot 1
Slot 5
* Solid State Protection
Slot
Control
Temp. Sensors
Page 98

4-10 Troubleshooting Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
INPUT HI
INPUT HI protection is provided by the SSP (Solid State Protection) circuit. The SSP is
primarily made up of Q101 and Q102. An overload condition opens Q101 and Q102,
which disconnects the analog input signal from the rest of the analog circuit.
Note that for the 100VDC and 1000VDC ranges, Q101 and Q102 of the SSP are open.
The DC voltage signal is routed through the DCV Divider (Q114 and Q136 on) to the
DCV switching circuit.
AMPS input
The ACA or DCA input signal is applied to the Current Shunt circuit, which is made up of
K103, R158, R205, and R338. For the 20mA DC range, 5.1Ω (R205 R338 + R158) is
shunted across the input. Relay K103 is energized (set state) to select the shunts. For all
other DCA ranges, and all ACA ranges, 0.1Ω (R158) is shunted across the input (K103
reset).
The ACA signal is then sent to the AC Switching & Gain circuit, while the DCA signal is
routed directly to the A/D MUX & Gain circuit.
Signal switching
Signal switching for DCV and OHMS is done by the DCV & Ohms Switching circuit.
FETs Q113, Q104, and Q108 connect the DCV or ohms signal to the X1 buffer (U113).
For offset-compensated ohms and all dry-circuit ohms measurements, the signal is routed
directly to the A/D mux by Q106, bypassing U113.
Note that the reference current for OHMS is generated by the Ohms I-Source circuit. For
4-wire ohms measurements, SENSE LO is connected to U163.
Signal switching and gain for ACV, FREQ and ACA is done by the AC Switching & Gain
circuit, which is primarily made up of K102, U102, U103, U105, U112, U118, U111,
U110, and U117. Note that U111 is used for frequency adjustment. The states of these
analog switches vary from unit to unit.
Page 99

Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual Troubleshooting 4-11
Multiplexer and A/D converter
All input signals, except FREQ, are routed to the A/D MUX & Gain circuit. The multiplexer (U163) switches the various signals for measurement. In addition to the input signal, the multiplexer also switches among reference and zero signals at various phases of
the measurement cycle.
When the input signal is selected by the MUX, it is amplified by U132 and U166. Gain is
controlled by switches in U129 and associated resistors.
The multiplexed signals of the measurement cycle are routed to the A/D Converter (U165)
where it converts the analog signals to digital form. The digital signals are then routed
through an opto-isolator to the MPU to calculate a reading.
The multiplexer amplifier has an overload protection circuit. The circuit reduces the multiplexer gain to unity during overload conditions. This circuit is made up of primarily
CR101, CR113, Q103, Q107, Q117, U128, U140, U143, VR110, and VR111.
Scanner card signals
Scanner card input signals are connected directly to installed scanner cards. Scanner card
output signals are routed internally to the INPUTS switch, which selects between the front
panel terminals and the scanner card outputs.
The Model 7700, 7706, and 7708 modules contain CJC (voltage) temperature sensors.
These sensors are multiplexed into U163 at various phases of the measurement cycle.
Dry circuit ohms
Figure 4-4 shows a simplified schematic of the dry circuit ohms circuitry. Dry circuit ohms
measurements are made similar to those for conventional ohms in that a 10µA to 10mA
current source (depending on ohms range) forces a current through the DUT resistance,
and the voltage across the device is measured. In the case of dry circuit ohms, however,
there are two clamps that act to limit the voltage across the DUT to 20mV. Normally the
voltage is sensed across the SENSE HI and LO terminals, and the main clamp restricts the
DUT voltage to 20mV. A secondary clamp monitors the voltage across INPUT HI and LO
and acts to restrict the voltage to 50mV if the SENSE terminals are not connected to the
DUT. When either clamp acts to limit the voltage across the DUT, the current source goes
into compliance, effectively turning the current source into a voltage source thus limiting
the DUT voltage to 20mV or 50mV as the case may be. Note that a 0.8µF capacitor and
100kΩ resistor are connected across the DUT during dry circuit ohms measurements for
stabilization.
Troubleshooting
Page 100

4-12 Troubleshooting Model 2750 Multimeter/Switch System Service Manual
Figure 4-4
Simplified schematic of dry circuit ohms
20mV Reference
(Main Clamp,
Monitors SENSE HI)
+
-
50mV Reference
(Secondary Clamp,
Monitors INPUT HI)
10µA
100µA
1mA
10mA
I Source
+
↔
ON
SSP*
SSP*
ON
-
ON
0.8µF
INPUT
DUT
INPUT
100kΩ
HI
LO
1MΩ
SSP*
SENSE
HI
SSP*
SENSE
LO
*SSP: Solid State Protection Circuit
Mux
A/D
Converter
Gain
Amp
 Loading...
Loading...