Juniper Networks IDP250 User Manual
IDP Series Intrusion Detection and Prevention Appliances
IDP250 Installation Guide
Release 5.0
Juniper Networks, Inc.
1194 North Mathilda Avenue
Sunnyvale, California 94089
USA
408-745-2000
www.juniper.net
Part Number: 530-029729-01, Revision 01

This product includes the Envoy SNMP Engine, developed by Epilogue Technology, an Integrated Systems Company. Copyright © 1986-1997, Epilogue
Technology Corporation. All rights reserved. This program and its documentation were developed at private expense, and no part of them is in the public
domain.
This product includes memory allocation software developed by Mark Moraes, copyright © 1988, 1989, 1993, University of Toronto.
This product includes FreeBSD software developed by the University of California, Berkeley, and its contributors. All of the documentation and software
included in the 4.4BSD and 4.4BSD-Lite Releases is copyrighted by the Regents of the University of California. Copyright © 1979, 1980, 1983, 1986, 1988,
1989, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994. The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.
GateD software copyright © 1995, the Regents of the University. All rights reserved. Gate Daemon was originated and developed through release 3.0 by
Cornell University and its collaborators. Gated is based on Kirton’s EGP, UC Berkeley’s routing daemon (routed), and DCN’s HELLO routing protocol.
Development of Gated has been supported in part by the National Science Foundation. Portions of the GateD software copyright © 1988, Regents of the
University of California. All rights reserved. Portions of the GateD software copyright © 1991, D. L. S. Associates.
This product includes software developed by Maker Communications, Inc., copyright © 1996, 1997, Maker Communications, Inc.
Juniper Networks, the Juniper Networks logo, JUNOS, NetScreen, ScreenOS, and Steel-Belted Radius are registered trademarks of Juniper Networks, Inc. in
the United States and other countries. JUNOSe is a trademark of Juniper Networks, Inc. All other trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or
registered service marks are the property of their respective owners.
Juniper Networks assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies in this document. Juniper Networks reserves the right to change, modify, transfer, or
otherwise revise this publication without notice.
Products made or sold by Juniper Networks or components thereof might be covered by one or more of the following patents that are owned by or licensed
to Juniper Networks: U.S. Patent Nos. 5,473,599, 5,905,725, 5,909,440, 6,192,051, 6,333,650, 6,359,479, 6,406,312, 6,429,706, 6,459,579, 6,493,347,
6,538,518, 6,538,899, 6,552,918, 6,567,902, 6,578,186, and 6,590,785.
IDP Series Intrusion Detection and Prevention Appliances IDP250 Installation Guide
Copyright © 2009, Juniper Networks, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Revision History
May 2009—
The information in this document is current as of the date listed in the revision history.
ii ■

END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
READ THIS END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT (“AGREEMENT”) BEFORE DOWNLOADING, INSTALLING, OR USING THE SOFTWARE. BY DOWNLOADING,
INSTALLING, OR USING THE SOFTWARE OR OTHERWISE EXPRESSING YOUR AGREEMENT TO THE TERMS CONTAINED HEREIN, YOU (AS CUSTOMER
OR IF YOU ARE NOT THE CUSTOMER, AS A REPRESENTATIVE/AGENT AUTHORIZED TO BIND THE CUSTOMER) CONSENT TO BE BOUND BY THIS
AGREEMENT. IF YOU DO NOT OR CANNOT AGREE TO THE TERMS CONTAINED HEREIN, THEN (A) DO NOT DOWNLOAD, INSTALL, OR USE THE SOFTWARE,
AND (B) YOU MAY CONTACT JUNIPER NETWORKS REGARDING LICENSE TERMS.
1. The Parties. The parties to this Agreement are (i) Juniper Networks, Inc. (if the Customer’s principal office is located in the Americas) or Juniper Networks
(Cayman) Limited (if the Customer’s principal office is located outside the Americas) (such applicable entity being referred to herein as “Juniper”), and (ii)
the person or organization that originally purchased from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller the applicable license(s) for use of the Software (“Customer”)
(collectively, the “Parties”).
2. The Software. In this Agreement, “Software” means the program modules and features of the Juniper or Juniper-supplied software, for which Customer
has paid the applicable license or support fees to Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller, or which was embedded by Juniper in equipment which Customer
purchased from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller. “Software” also includes updates, upgrades and new releases of such software. “Embedded
Software” means Software which Juniper has embedded in or loaded onto the Juniper equipment and any updates, upgrades, additions or replacements
which are subsequently embedded in or loaded onto the equipment.
3. License Grant. Subject to payment of the applicable fees and the limitations and restrictions set forth herein, Juniper grants to Customer a non-exclusive
and non-transferable license, without right to sublicense, to use the Software, in executable form only, subject to the following use restrictions:
a. Customer shall use Embedded Software solely as embedded in, and for execution on, Juniper equipment originally purchased by Customer from Juniper
or an authorized Juniper reseller.
b. Customer shall use the Software on a single hardware chassis having a single processing unit, or as many chassis or processing units for which Customer
has paid the applicable license fees; provided, however, with respect to the Steel-Belted Radius or Odyssey Access Client software only, Customer shall use
such Software on a single computer containing a single physical random access memory space and containing any number of processors. Use of the
Steel-Belted Radius or IMS AAA software on multiple computers or virtual machines (e.g., Solaris zones) requires multiple licenses, regardless of whether
such computers or virtualizations are physically contained on a single chassis.
c. Product purchase documents, paper or electronic user documentation, and/or the particular licenses purchased by Customer may specify limits to
Customer’s use of the Software. Such limits may restrict use to a maximum number of seats, registered endpoints, concurrent users, sessions, calls,
connections, subscribers, clusters, nodes, realms, devices, links, ports or transactions, or require the purchase of separate licenses to use particular features,
functionalities, services, applications, operations, or capabilities, or provide throughput, performance, configuration, bandwidth, interface, processing,
temporal, or geographical limits. In addition, such limits may restrict the use of the Software to managing certain kinds of networks or require the Software
to be used only in conjunction with other specific Software. Customer’s use of the Software shall be subject to all such limitations and purchase of all applicable
licenses.
d. For any trial copy of the Software, Customer’s right to use the Software expires 30 days after download, installation or use of the Software. Customer
may operate the Software after the 30-day trial period only if Customer pays for a license to do so. Customer may not extend or create an additional trial
period by re-installing the Software after the 30-day trial period.
e. The Global Enterprise Edition of the Steel-Belted Radius software may be used by Customer only to manage access to Customer’s enterprise network.
Specifically, service provider customers are expressly prohibited from using the Global Enterprise Edition of the Steel-Belted Radius software to support any
commercial network access services.
The foregoing license is not transferable or assignable by Customer. No license is granted herein to any user who did not originally purchase the applicable
license(s) for the Software from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller.
4. Use Prohibitions. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the license provided herein does not permit the Customer to, and Customer agrees not to and shall
not: (a) modify, unbundle, reverse engineer, or create derivative works based on the Software; (b) make unauthorized copies of the Software (except as
necessary for backup purposes); (c) rent, sell, transfer, or grant any rights in and to any copy of the Software, in any form, to any third party; (d) remove
any proprietary notices, labels, or marks on or in any copy of the Software or any product in which the Software is embedded; (e) distribute any copy of
the Software to any third party, including as may be embedded in Juniper equipment sold in the secondhand market; (f) use any ‘locked’ or key-restricted
feature, function, service, application, operation, or capability without first purchasing the applicable license(s) and obtaining a valid key from Juniper, even
if such feature, function, service, application, operation, or capability is enabled without a key; (g) distribute any key for the Software provided by Juniper
to any third party; (h) use the Software in any manner that extends or is broader than the uses purchased by Customer from Juniper or an authorized Juniper
reseller; (i) use Embedded Software on non-Juniper equipment; (j) use Embedded Software (or make it available for use) on Juniper equipment that the
Customer did not originally purchase from Juniper or an authorized Juniper reseller; (k) disclose the results of testing or benchmarking of the Software to
any third party without the prior written consent of Juniper; or (l) use the Software in any manner other than as expressly provided herein.
5. Audit. Customer shall maintain accurate records as necessary to verify compliance with this Agreement. Upon request by Juniper, Customer shall furnish
such records to Juniper and certify its compliance with this Agreement.
■ iii

6. Confidentiality. The Parties agree that aspects of the Software and associated documentation are the confidential property of Juniper. As such, Customer
shall exercise all reasonable commercial efforts to maintain the Software and associated documentation in confidence, which at a minimum includes
restricting access to the Software to Customer employees and contractors having a need to use the Software for Customer’s internal business purposes.
7. Ownership. Juniper and Juniper’s licensors, respectively, retain ownership of all right, title, and interest (including copyright) in and to the Software,
associated documentation, and all copies of the Software. Nothing in this Agreement constitutes a transfer or conveyance of any right, title, or interest in
the Software or associated documentation, or a sale of the Software, associated documentation, or copies of the Software.
8. Warranty, Limitation of Liability, Disclaimer of Warranty. The warranty applicable to the Software shall be as set forth in the warranty statement that
accompanies the Software (the “Warranty Statement”). Nothing in this Agreement shall give rise to any obligation to support the Software. Support services
may be purchased separately. Any such support shall be governed by a separate, written support services agreement. TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED
BY LAW, JUNIPER SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST PROFITS, LOSS OF DATA, OR COSTS OR PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES,
OR FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THIS AGREEMENT, THE SOFTWARE, OR ANY JUNIPER OR
JUNIPER-SUPPLIED SOFTWARE. IN NO EVENT SHALL JUNIPER BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES ARISING FROM UNAUTHORIZED OR IMPROPER USE OF ANY
JUNIPER OR JUNIPER-SUPPLIED SOFTWARE. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY PROVIDED IN THE WARRANTY STATEMENT TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW,
JUNIPER DISCLAIMS ANY AND ALL WARRANTIES IN AND TO THE SOFTWARE (WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE), INCLUDING
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT DOES JUNIPER
WARRANT THAT THE SOFTWARE, OR ANY EQUIPMENT OR NETWORK RUNNING THE SOFTWARE, WILL OPERATE WITHOUT ERROR OR INTERRUPTION,
OR WILL BE FREE OF VULNERABILITY TO INTRUSION OR ATTACK. In no event shall Juniper’s or its suppliers’ or licensors’ liability to Customer, whether
in contract, tort (including negligence), breach of warranty, or otherwise, exceed the price paid by Customer for the Software that gave rise to the claim, or
if the Software is embedded in another Juniper product, the price paid by Customer for such other product. Customer acknowledges and agrees that Juniper
has set its prices and entered into this Agreement in reliance upon the disclaimers of warranty and the limitations of liability set forth herein, that the same
reflect an allocation of risk between the Parties (including the risk that a contract remedy may fail of its essential purpose and cause consequential loss),
and that the same form an essential basis of the bargain between the Parties.
9. Termination. Any breach of this Agreement or failure by Customer to pay any applicable fees due shall result in automatic termination of the license
granted herein. Upon such termination, Customer shall destroy or return to Juniper all copies of the Software and related documentation in Customer’s
possession or control.
10. Taxes. All license fees payable under this agreement are exclusive of tax. Customer shall be responsible for paying Taxes arising from the purchase of
the license, or importation or use of the Software. If applicable, valid exemption documentation for each taxing jurisdiction shall be provided to Juniper prior
to invoicing, and Customer shall promptly notify Juniper if their exemption is revoked or modified. All payments made by Customer shall be net of any
applicable withholding tax. Customer will provide reasonable assistance to Juniper in connection with such withholding taxes by promptly: providing Juniper
with valid tax receipts and other required documentation showing Customer’s payment of any withholding taxes; completing appropriate applications that
would reduce the amount of withholding tax to be paid; and notifying and assisting Juniper in any audit or tax proceeding related to transactions hereunder.
Customer shall comply with all applicable tax laws and regulations, and Customer will promptly pay or reimburse Juniper for all costs and damages related
to any liability incurred by Juniper as a result of Customer’s non-compliance or delay with its responsibilities herein. Customer’s obligations under this
Section shall survive termination or expiration of this Agreement.
11. Export. Customer agrees to comply with all applicable export laws and restrictions and regulations of any United States and any applicable foreign
agency or authority, and not to export or re-export the Software or any direct product thereof in violation of any such restrictions, laws or regulations, or
without all necessary approvals. Customer shall be liable for any such violations. The version of the Software supplied to Customer may contain encryption
or other capabilities restricting Customer’s ability to export the Software without an export license.
12. Commercial Computer Software. The Software is “commercial computer software” and is provided with restricted rights. Use, duplication, or disclosure
by the United States government is subject to restrictions set forth in this Agreement and as provided in DFARS 227.7201 through 227.7202-4, FAR 12.212,
FAR 27.405(b)(2), FAR 52.227-19, or FAR 52.227-14(ALT III) as applicable.
13. Interface Information. To the extent required by applicable law, and at Customer's written request, Juniper shall provide Customer with the interface
information needed to achieve interoperability between the Software and another independently created program, on payment of applicable fee, if any.
Customer shall observe strict obligations of confidentiality with respect to such information and shall use such information in compliance with any applicable
terms and conditions upon which Juniper makes such information available.
14. Third Party Software. Any licensor of Juniper whose software is embedded in the Software and any supplier of Juniper whose products or technology
are embedded in (or services are accessed by) the Software shall be a third party beneficiary with respect to this Agreement, and such licensor or vendor
shall have the right to enforce this Agreement in its own name as if it were Juniper. In addition, certain third party software may be provided with the
Software and is subject to the accompanying license(s), if any, of its respective owner(s). To the extent portions of the Software are distributed under and
subject to open source licenses obligating Juniper to make the source code for such portions publicly available (such as the GNU General Public License
(“GPL”) or the GNU Library General Public License (“LGPL”)), Juniper will make such source code portions (including Juniper modifications, as appropriate)
available upon request for a period of up to three years from the date of distribution. Such request can be made in writing to Juniper Networks, Inc., 1194
N. Mathilda Ave., Sunnyvale, CA 94089, ATTN: General Counsel. You may obtain a copy of the GPL at http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html, and
a copy of the LGPL at http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html.
15. Miscellaneous. This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of California without reference to its conflicts of laws principles. The provisions
of the U.N. Convention for the International Sale of Goods shall not apply to this Agreement. For any disputes arising under this Agreement, the Parties
hereby consent to the personal and exclusive jurisdiction of, and venue in, the state and federal courts within Santa Clara County, California. This Agreement
constitutes the entire and sole agreement between Juniper and the Customer with respect to the Software, and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous
iv ■

agreements relating to the Software, whether oral or written (including any inconsistent terms contained in a purchase order), except that the terms of a
separate written agreement executed by an authorized Juniper representative and Customer shall govern to the extent such terms are inconsistent or conflict
with terms contained herein. No modification to this Agreement nor any waiver of any rights hereunder shall be effective unless expressly assented to in
writing by the party to be charged. If any portion of this Agreement is held invalid, the Parties agree that such invalidity shall not affect the validity of the
remainder of this Agreement. This Agreement and associated documentation has been written in the English language, and the Parties agree that the English
version will govern. (For Canada: Les parties aux présentés confirment leur volonté que cette convention de même que tous les documents y compris tout
avis qui s'y rattaché, soient redigés en langue anglaise. (Translation: The parties confirm that this Agreement and all related documentation is and will be
in the English language)).
■ v

vi ■
Table of Contents
Preface xi
Objectives ......................................................................................................xi
Audience ........................................................................................................xi
Documentation Conventions ..........................................................................xi
Related Documentation ................................................................................xiii
Requesting Technical Support .......................................................................xiv
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources ....................................................xiv
Opening a Case with JTAC .......................................................................xv
Part 1 Hardware and Software Overview
Chapter 1 Hardware Overview 3
IDP250 Overview ............................................................................................3
Power Supply ..................................................................................................4
Hard Drive ......................................................................................................4
Fans ................................................................................................................4
System Status LEDs .........................................................................................4
USB Port ..........................................................................................................5
Serial Console Port ..........................................................................................5
Management Interface Port .............................................................................5
High Availability Interface Port ........................................................................6
Traffic Interface Ports ......................................................................................7
Copper Ports .............................................................................................7
Fiber Ports ................................................................................................8
Traffic Interface Features ..........................................................................9
Deployment Mode ............................................................................10
Internal Bypass .................................................................................10
NICs Off ...........................................................................................11
External Bypass ................................................................................12
Peer Port Modulation ..............................................................................12
Layer 2 Bypass ........................................................................................13
Chapter 2 Software Overview 15
On-Box Software Overview ...........................................................................15
Centralized Management with NSM Overview ...............................................16
J-Security Center Updates Overview ..............................................................17
Table of Contents ■ vii
IDP250 Installation Guide
Part 2 Performing the Installation
Chapter 3 Installation Overview 21
Before You Begin ...........................................................................................21
Basic Steps ....................................................................................................22
Chapter 4 Installing the Appliance to Your Equipment Rack and Connecting
Power 23
Rack Mounting Kits and Required Tools ........................................................23
Mounting to Midmount Brackets ...................................................................24
Mounting to Rack Rails ..................................................................................25
Connecting Power .........................................................................................25
Chapter 5 Performing the Initial Network Configuration and Licensing
Tasks 27
Performing the Initial Configuration ..............................................................27
Getting Started with the EasyConfig Wizard (Serial Console Port) ..................29
Getting Started with the QuickStart Wizard (Management Port) ....................30
Getting Started with the ACM Wizard (Management Port) .............................31
Installing the Product License Key .................................................................32
Chapter 6 Connecting the IDP Traffic Interfaces to Your Network and Verifying
Traffic Flow 35
Guidelines for Connecting IDP Interfaces to Your Network Devices ...............35
Choosing Cables for Traffic Interfaces (Copper Ports) ....................................36
Connecting Devices That Support Auto-MDIX .........................................36
Connecting Devices That Do Not Support Auto-MDIX .............................37
Connecting Devices to Support Internal Bypass ......................................37
Connecting and Disconnecting Fiber Cables ..................................................37
Verifying Traffic Flow ....................................................................................38
Part 3 Adding the IDP Appliance to NSM
Chapter 7 Adding the IDP Appliance to NSM 41
Reviewing Compatibility with NSM ...............................................................41
Adding a Reachable IDP Device to NSM ........................................................41
viii ■ Table of Contents

Table of Contents
Part 4 Upgrading Software and Installing Field Replaceable Units
Chapter 8 Upgrading Software 49
Updating Software (NSM Procedure) .............................................................49
Upgrading Software (CLI Procedure) ..............................................................51
Chapter 9 Installing Field Replaceable Units 53
Replacing a Power Supply .............................................................................53
Chapter 10 Reimaging the Appliance 55
Reimaging and Relicensing an Appliance ......................................................55
Part 5 Technical Specifications and Compliance Statements
Chapter 11 Technical Specifications 59
IDP250 Technical Specifications ....................................................................59
Chapter 12 Compliance Statements 61
Standards Compliance ...................................................................................61
Chapter 13 Common Criteria EAL2 Compliance 63
Common Criteria EAL2 Compliance ..............................................................63
Part 6 Index
Index .............................................................................................................67
Table of Contents ■ ix

IDP250 Installation Guide
x ■ Table of Contents
Preface
This preface includes the following topics:
■ Objectives on page xi
■ Audience on page xi
■ Documentation Conventions on page xi
■ Related Documentation on page xiii
■ Requesting Technical Support on page xiv
Objectives
This guide explains how to install, configure, update, and service an IDP Series
Intrusion Detection and Prevention appliance.
Audience
This guide is intended for experienced system and network specialists.
Documentation Conventions
Table 1: Notice Icons
This section provides all the documentation conventions that are followed in this
guide. Table 1 on page xi defines notice icons used in this guide.
DescriptionMeaningIcon
Indicates important features or instructions.Informational note
Indicates a situation that might result in loss of data or hardware damage.Caution
Alerts you to the risk of personal injury or death.Warning
Alerts you to the risk of personal injury from a laser.Laser warning
Objectives ■ xi

IDP250 Installation Guide
Table 2: Text Conventions
Table 2 on page xii defines text conventions used in this guide.
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
Bold typeface like this
Bold typeface like this
fixed-width font
Key names linked with a plus (+)
sign
Italics
The angle bracket (>)
Table 3 on page xii defines syntax conventions used in this guide.
Represents commands and keywords
■
in text.
Represents keywords
■
Represents UI elements
■
Represents text that the user must type.
Represents information as displayed on
the terminal screen.
keys simultaneously.
Emphasizes words
■
Identifies variables
■
Indicates navigation paths through the UI
by clicking menu options and links.
Issue the clock source command.
■
Specify the keyword exp-msg.
■
Click User Objects
■
user input
host1#
show ip ospf
Routing Process OSPF 2 with Router
ID 5.5.0.250
Router is an area Border Router
(ABR)
Ctrl + dIndicates that you must press two or more
The product supports two levels of
■
access, user and privileged.
clusterID, ipAddress.
■
Object Manager > User Objects > Local
Objects
Table 3: Syntax Conventions
Words separated by the pipe ( | )
symbol
Words enclosed in brackets followed
by and asterisk ( [ ]*)
xii ■ Documentation Conventions
variable to the left or right of this symbol. The
keyword or variable can be optional or
required.
can be entered more than once.
Represent required keywords or variables.Words enclosed in braces ( { } )
ExamplesDescriptionConvention
terminal lengthRepresent keywordsWords in plain text
mask, accessListNameRepresent variablesWords in italics
diagnostic | lineRepresent a choice to select one keyword or
[ internal | external ]Represent optional keywords or variables.Words enclosed in brackets ( [ ] )
[ level1 | level2 | 11 ]*Represent optional keywords or variables that
{ permit | deny } { in | out } {
clusterId | ipAddress }

Related Documentation
Table 4 on page xiii lists related IDP documentation.
Table 4: Related IDP Documentation
Preface
DescriptionDocument
Release notes
ACM Online Help
IDP Series Installation Guide: IDP200,
■
IDP600, IDP1100
IDP75 Installation Guide
■
IDP250 Installation Guide
■
IDP800 Installation Guide
■
IDP8200 Installation Guide
■
IDP Administration Guide
IDP Custom Attack Objects Reference and
Examples Guide
IDP Reporter User’s Guide
Contains information about what is included in a specific product release:
supported features, unsupported features, changed features, known problems,
and resolved problems. If the information in the release notes differs from
the information found in the documentation set, follow the release notes.
Available through the Appliance Configuration Manager (ACM). The
context-sensitive online help describes how to use the QuickStart and ACM
Wizard pages to configure network settings, network interfaces, and NIC
features.
Provides instructions for installing, configuring, updating, and servicing the
IDP Series appliances.
Explains IDP features and provides examples of how to use the system.IDP Concepts and Examples Guide
Provides procedures for implementing IDP features, monitoring performance,
and monitoring security events.
Provides in-depth examples and reference information for creating custom
attack objects.
Describes how to use IDP Reporter to view and generate security reports and
application usage reports.
Table 4 on page xiii lists related NSM documentation.
Table 5: Related NSM Documentation
Network and Security Manager release notes
Network and Security Manager Installation Guide
DescriptionDocument
Provides information about new features, changed features, fixed problems,
and known issues with the NSM release.
Describes how to install the NSM management system on a single server or
on separate servers. It also includes information on how to install and run
the NSM user interface. This guide is intended for IT administrators responsible
for the installation and/or upgrade to NSM.
Related Documentation ■ xiii
IDP250 Installation Guide
Table 5: Related NSM Documentation (continued)
DescriptionDocument
Network and Security Manager Configuring
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Devices Guide
Network and Security Manager Administration
Guide
Network and Security Manager Online Help
Requesting Technical Support
Technical product support is available through the Juniper Networks Technical
Assistance Center (JTAC). If you are a customer with an active J-Care or JNASC support
contract, or are covered under warranty, and need post-sales technical support, you
can access our tools and resources online or open a case with JTAC.
Describes how to configure and manage IDP devices using NSM. This guide
also helps in understanding of how to configure basic and advanced NSM
functionality, including adding new devices, deploying new device
configurations, updating device firmware, viewing log information, and
monitoring the status of IDP devices.
Describes how to use and configure key management features in the NSM.
It provides conceptual information, suggested workflows, and examples where
applicable. This guide is best used in conjunction with the NSM Online Help,
which provides step-by-step instructions for performing management tasks
in the NSM UI.
This guide is intended for application administrators or those individuals
responsible for owning the server and security infrastructure and configuring
the product for multi-user systems. It is also intended for device configuration
administrators, firewall and VPN administrators, and network security
operation center administrators.
Provides task-oriented procedures describing how to perform basic tasks in
the NSM user interface. It also includes a brief overview of the NSM system
and a description of the GUI elements.
■ JTAC policies—For a complete understanding of our JTAC procedures and policies,
review the JTAC User Guide located at
http://www.juniper.net/customers/support/downloads/710059.pdf.
■ Product warranties—For product warranty information, visit
http://www.juniper.net/support/warranty/.
■ JTAC Hours of Operation —The JTAC centers have resources available 24 hours
a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year.
Self-Help Online Tools and Resources
For quick and easy problem resolution, Juniper Networks has designed an online
self-service portal called the Customer Support Center (CSC) that provides you with
the following features:
■
Find CSC offerings: http://www.juniper.net/customers/support/
■
Search for known bugs: http://www2.juniper.net/kb/
■
Find product documentation: http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/
xiv ■ Requesting Technical Support

■ Find solutions and answer questions using our Knowledge Base:
http://kb.juniper.net/
■ Download the latest versions of software and review release notes:
http://www.juniper.net/customers/csc/software/
■ Search technical bulletins for relevant hardware and software notifications:
https://www.juniper.net/alerts/
■ Join and participate in the Juniper Networks Community Forum:
http://www.juniper.net/company/communities/
■
Open a case online in the CSC Case Management tool: http://www.juniper.net/cm/
To verify service entitlement by product serial number, use our Serial Number
Entitlement (SNE) Tool located at https://tools.juniper.net/SerialNumberEntitlementSearch/.
Opening a Case with JTAC
Preface
You can open a case with JTAC on the Web or by telephone.
■
Use the Case Management tool in the CSC at http://www.juniper.net/cm/ .
■ Call 1-888-314-JTAC (1-888-314-5822 toll-free in the USA, Canada, and Mexico).
For international or direct-dial options in countries without toll-free numbers, see
http://www.juniper.net/support/requesting support.html
Requesting Technical Support ■ xv

IDP250 Installation Guide
xvi ■ Requesting Technical Support

Part 1
Hardware and Software Overview
■ Hardware Overview on page 3
■ Software Overview on page 15
Hardware and Software Overview ■ 1

IDP250 Installation Guide
2 ■ Hardware and Software Overview

Chapter 1
Hardware Overview
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ IDP250 Overview on page 3
■ Power Supply on page 4
■ Hard Drive on page 4
■ Fans on page 4
■ System Status LEDs on page 4
■ USB Port on page 5
■ Serial Console Port on page 5
■ Management Interface Port on page 5
■ High Availability Interface Port on page 6
■ Traffic Interface Ports on page 7
IDP250 Overview
The IDP250 appliance is optimal for medium central sites or large branch offices.
Figure 1 on page 3 shows the location of appliance LEDs and ports.
Figure 1: IDP250 Front Panel
Related Topics ■ System Status LEDs on page 4
■ USB Port on page 5
■ Serial Console Port on page 5
■ Management Interface Port on page 5
■ High Availability Interface Port on page 6
IDP250 Overview ■ 3

IDP250 Installation Guide
Power Supply
Related Topics ■ Replacing a Power Supply on page 53
Hard Drive
Fans
■ Traffic Interface Ports on page 7
■ IDP250 Technical Specifications on page 59
The appliance has one power supply. It is a field replaceable unit (FRU).
The appliance has one 80 GB hard drive. It is not a field replaceable unit (FRU).
When the system is cool, appliance fans spin at a slower speed to reduce noise and
save energy. As the system heats up, the fans run at a faster speed. In the event of
fan failure, the appliance fault LED blinks and the remaining fan or fans run at full
speed until the failed fan is replaced.
The fans for this model are not field replaceable units (FRUs).
System Status LEDs
Table 6 on page 4 describes system status LED states.
Table 6: System Status LED States
DescriptionStatusLED
System is powered on.Solid greenPower
System is powered off.Off
Hard disk is active.Flashing amberHard Drives
Hard drive has no activity.Off
4 ■ Power Supply
Power failure.Slowly blinking redFault
Fan failure.Quickly blinking red
Overheating.Solid red
Heat and power are normal.Off
USB Port
The appliance has a USB port you can use to reimage the appliance, if necessary.
Serial Console Port
The console serial port provides access, using an RJ-45 connector, to the
command-line interface (CLI).
NOTE: Although both the console serial port and the management port use RJ-45
connectors, do not plug the network cable into the console serial port.
Management Interface Port
Chapter 1: Hardware Overview
The management interface port is a 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet port. In the
configuration and logs, the port is eth0. Use this port as a dedicated management
port, connecting the device to a switch accessible by your management subnet.
The IP address you assign the management port is the IP address you use to connect
to the Appliance Configuration Manager (ACM) when you initially configure the device.
It is also the address the Network and Security Manager (NSM) uses to connect to
the device.
Figure 2 on page 5 shows the management interface port LEDs.
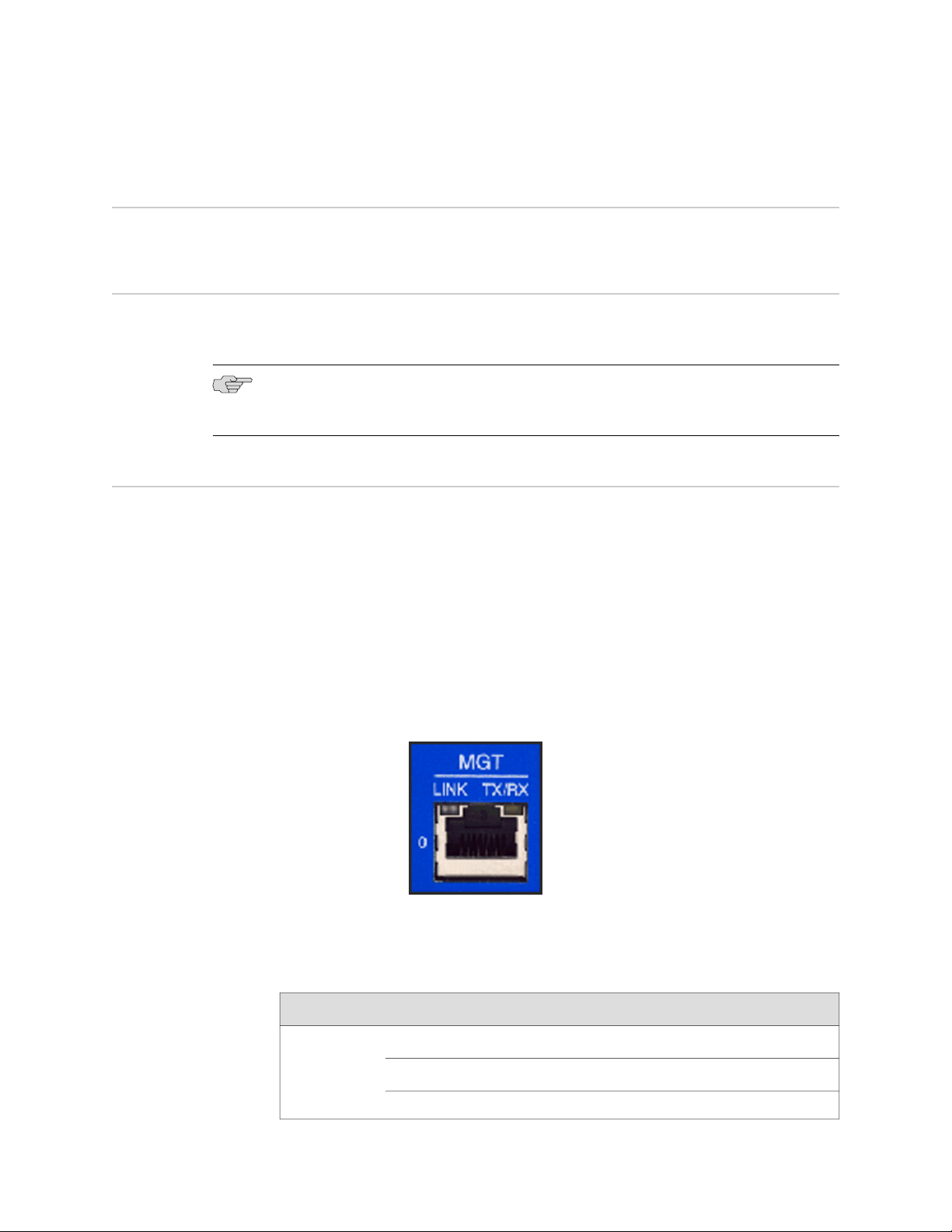
Figure 2: Management Interface Port LEDs
Table 7 on page 5 describes the management interface port LED states.
Table 7: Management Port LEDs
DescriptionStateLED
Link is present.Glows greenLINK
Activity.Blinks green
No link is present.Off
USB Port ■ 5

IDP250 Installation Guide
Table 7: Management Port LEDs (continued)
DescriptionStateLED
Connection is 1000 Mbps.OrangeTX/RX
Connection is 100 Mbps.Green
High Availability Interface Port
The high availability interface port is a 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet port. In the
configuration and logs, the port is eth1. The high availability interface is a dedicated
interface used to share state information among IDP appliances in a high availability
cluster.
NOTE: IDP 5.0 does not support high availability.
Figure 3 on page 6 shows the management interface port LEDs.
Figure 3: High Availability Interface Port LEDs
Off
If LINK indicates activity, TX/RX off indicates connection
is 10 Mbps.
If LINK indicates no activity, TX/RX off indicates no activity
as well.
Table 8 on page 6 describes the high availability interface port LED states.
Table 8: High Availability Port LEDs
6 ■ High Availability Interface Port
DescriptionStateLED
Link is present.Glows greenLINK
Activity.Blinks green
No link is present.Off

Table 8: High Availability Port LEDs (continued)
DescriptionStateLED
Connection is 1000 Mbps.OrangeTX/RX
Connection is 100 Mbps.Green
Chapter 1: Hardware Overview
Traffic Interface Ports
You use the traffic interface ports to connect the appliance to your network. The
interfaces receive and forward traffic. The type and capacity of interface ports vary
by model.
The following topics describe features of traffic interface ports:
■ Copper Ports on page 7
■ Fiber Ports on page 8
■ Traffic Interface Features on page 9
■ Peer Port Modulation on page 12
■ Layer 2 Bypass on page 13
Copper Ports
Figure 4 on page 7 shows copper port LEDs.
Off
If LINK indicates activity, TX/RX off indicates connection
is 10 Mbps.
If LINK indicates no activity, TX/RX off indicates no activity
as well.
Figure 4: Copper Port LEDs
Table 9 on page 8 describes copper port LED states.
Traffic Interface Ports ■ 7

IDP250 Installation Guide
Table 9: Copper Port LEDs
DescriptionStateLED
Link is present.Glows greenLINK ACT
Activity.Blinks green
No link present.Off
Connection is 100 Mbps.GreenLINK SPD
Connection is 1 Gbps.Yellow
Fiber Ports
Off
If LINK ACT is on, the connection is 10 Mbps. If LINK ACT
is off, LINK SPD off indicates no link is present as well.
Interface is not in bypass mode.GreenBYP
Interface is in bypass mode.Yellow
Interface is turned off (NICs off state).Off
NOTE: For copper interface ports, if failure or shutdown triggers NICs off state, LINK
ACT and LINK SPD LEDs are turned off.
Figure 5 on page 8 shows fiber port LEDs.
Figure 5: Fiber Port LEDs
8 ■ Traffic Interface Ports
Table 10 on page 9 describes fiber port LED states.

Table 10: Fiber Port LEDs
Chapter 1: Hardware Overview
DescriptionStateLED
Link is present.Glows greenLINK ACT
Activity.Flashes green
No link present.Off
Connection is 100 Mbps.GreenLINK SPD
Connection is 1 Gbps.Yellow
Connection is 10 Gbps.Orange
NOTE: For fiber interface ports, if failure or shutdown triggers NICs off state, LINK
ACT and LINK SPD LEDs remain lit.
Traffic Interface Features
In IDP deployments, pairs of traffic interfaces are implemented as virtual routers.
For example, interface ports eth2 and eth3 form a virtual router vr1. For each virtual
router, you use the Appliance Configuration Manager (ACM) to configure the
deployment mode (sniffer or transparent) and bypass options (internal, external, or
off). The following topics describe these settings:
■ Deployment Mode on page 10
■ Internal Bypass on page 10
■ NICs Off on page 11
■ External Bypass on page 12
Off
If LINK ACT is on, the connection is 10 Mbps. If LINK ACT
is off, LINK SPD off indicates no link is present as well.
Interface is not in bypass mode.GreenBYP
Interface is in bypass mode.Yellow
Interface is turned off (NICs off state).Off
For guidance on using ACM to configure virtual router settings, see the ACM online
help.
Traffic Interface Ports ■ 9

IDP250 Installation Guide
Deployment Mode
For each virtual router, you select the deployment mode:
■ Sniffer–In an out-of-path, sniffer mode deployment, the IDP appliance can detect
attacks but can take only limited action. You connect the IDP traffic interfaces
to a mirrored port of a network hub or switch.
■ Transparent–In an in-path, transparent mode deployment, traffic arrives in one
interface and is forwarded through the other. The IDP appliance detects attacks
and takes action according to your security policy rules. You connect the IDP
traffic interfaces to firewalls or switches in the network path.
You can deploy a mix of sniffer and transparent mode virtual routers on the same
IDP appliance.
For more information on deployment mode, see the IDP Concepts and Examples
Guide.
Internal Bypass
The Internal Bypass setting supports network security policies that privilege availability
over security. In the event of failure or graceful shutdown, with internal bypass
configured, the interfaces to enter an internal bypass state. In internal bypass, physical
interfaces join mechanically to form a circuit that bypasses IDP processing. For
example, if you configure internal bypass for vr0, and the IDP appliance encounters
failure or is shut down, eth2 and eth3 join to form a circuit that avoids the IDP engine
and forwards the traffic to the next network hop.
Internal bypass operates through a timing mechanism. When enabled, the timer on
traffic interfaces counts down to a bypass trigger point. When the IDP appliance is
turned on and available, it sends a reset signal to the traffic interface timer so that
it does not reach the bypass trigger point. If the IDP operating system encounters
failure, then it fails to send the reset signal, the timer counts down to the trigger
point, and the traffic interfaces enter a bypass state. If the IDP appliance is shut down
gracefully, the traffic interfaces immediately enter bypass.
Figure 6 on page 11 shows the communications path when a virtual router is in
internal bypass state.
10 ■ Traffic Interface Ports
 Loading...
Loading...