Page 1
5310 S
Tractor
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
5310 S Tractor
OMRE247111 Issue G6 (ENGLISH)
CALIFORNIA
Proposition 65 Warning
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are
known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth
defects, and other reproductive harm.
If this product contains a gasoline engine:
WARNING
The engine exhaust from this product contains chemicals
known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth
defects or other reproductive harm.
The State of California requires the above two warnings.
John Deere Equipment Private Limited
Printed in India.
Page 2

Foreword
Introduction
READ THIS MANUAL carefully to learn how to operate
and service your machine correctly. Failure to do so
could result in personal injury or equipment damage.
This manual and safety signs on your machine may
also be available in other languages (see your John
Deere dealer to order).
THIS MANUAL SHOULD BE CONSIDERED a
permanent part of your machine and should remain
with the machine.
MEASUREMENTS in this manual are given in both
metric and customary U.S. unit equivalents. Use only
correct replacement parts and fasteners. Metric and
inch fasteners may require a specific metric or inch
wrench.
RIGHT-HAND AND LEFT-HAND sides are determined
by facing the direction of forward travel.
WRITE TRACTOR SERIAL (CHASSIS) NUMBER in
the Specification or Identification Numbers section.
Accurately record all the numbers to help in tracing the
machine should it be stolen. Your dealer also needs
these numbers when you order parts. File the
identification numbers in a secure place off the
machine.
BEFORE DELIVERING THIS MACHINE, your dealer
performed a predelivery inspection. After operating for
the first 100 hours, schedule an after-sale inspection
with your dealer to ensure best performance.
THIS TRACTOR IS DESIGNED SOLELY for use in
customary agricultural or similar operations
("INTENDED USE"). Use in any other way is
considered as contrary to the intended use. The
manufacturer accepts no liability for damage or injury
resulting from this misuse, and these risks must be
borne solely by the user. Compliance with and strict
adherence to the conditions of operation, service and
repair as specified by the manufacturer also constitute
essential elements for the intended use.
THIS TRACTOR SHOULD BE OPERATED, serviced
and repaired only by persons familiar with all its
particular characteristics and acquainted with the
relevant safety rules (accident prevention). The
accident prevention regulations, all other generally
recognized regulations on safety and occupational
medicine and the road traffic regulations must be
observed at all times. Any arbitrary modifications
carried out on this tractor will relieve the manufacturer
of all liability for any resulting damage or injury.
SETTING FUEL DELIVERY BEYOND PUBLISHED
factory specifications or otherwise overpowering will
result in loss of warranty protection for this machine.
AG,OUO6075,97 –19–21FEB06–1/2
082206
PN=2
Page 3

Introduction
John Deere 5310 S tractor
NOTE: Tractors shown may have optional equipment.
PY5155 –UN–21AUG05
AG,OUO6075,97 –19–21FEB06–2/2
082206
PN=3
Page 4

Introduction
082206
PN=4
Page 5

Contents
Page Page
Safety ................................05-1
Working With Speed/Hour Meter ............45-7
Stopping the Engine......................45-8
Safety Signs ...........................10-1
Controls and Instruments
Tractor Controls .........................15-1
Instrument Panel ........................15-3
Using Booster Battery.....................45-8
Driving the Tractor
Operator Training Required ................50-1
Driving on Public Roads...................50-1
Operating Transmission ...................50-3
Lights
Light Switch Positions.....................20-1
Using Headlights ........................20-2
Using High Beam Indicator.................20-2
Using Tail Lights.........................20-3
Shifting Transmission .....................50-3
Selecting a Gear ........................50-4
Using Brakes ...........................50-4
Using Differential Lock ....................50-5
Stopping Tractor.........................50-6
Using Turn Signals.......................20-4
Using Hazard Lights......................20-5
Using Flood Lamp .......................20-6
Seven-Terminal Outlet—If Equipped..........20-6
Operator’s Platform
Selecting Seat Position....................25-1
Adjusting Ride Comfort....................25-1
Break-In Period
Observe Engine Operation Closely...........35-1
Break-In Service.........................35-1
Prestarting Checks
Service Daily Before Start-Up...............40-1
Operating the Engine
Before Starting the Engine .................45-1
Starting the Engine.......................45-2
Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Match Tractor Power to Implement...........55-1
3-Point Hitch Components .................55-1
Rockshaft Control Levers ..................55-2
Setting Position Control Lever Stop ..........55-2
Using Rockshaft Position Control ............55-3
Using Draft Control.......................55-4
Adjusting Rockshaft Rate-of-Drop/
Implement lock ........................55-5
Preparing Implement .....................55-5
Positioning Center Link....................55-6
Attaching Implements to 3-Point Hitch ........55-7
Adjusting Hitch Side Sway .................55-8
Leveling the Hitch........................55-9
Adjusting Lateral Float ...................55-10
Adjusting Rockshaft Control Lever Friction ....55-10
Warming Hydraulic System Oil.............55-11
Check Instruments After Starting ............45-3
Oil Pressure Indicator.....................45-3
Charging System Indicator .................45-3
Air Restriction Indicator ...................45-4
Coolant Temperature Gauge ...............45-4
Watch Fuel Level ........................45-4
Changing Engine Speeds..................45-5
Warming Up the Engine ...................45-5
Remote Hydraulic Cylinders
Use Correct Hose Tips....................60-1
Control Lever and Coupler Identification—If
Equipped ............................60-1
Connecting Hoses .......................60-2
Connecting Single-Acting Cylinder ...........60-3
Correcting Reversed Cylinder Response ......60-3
Restart Stalled Engine ....................45-6 Neutral Lever Position ....................60-3
Avoid Idling the Engine....................45-6
Observe Engine Work and Idle Speeds .......45-7
Continued on next page
All information, illustrations and specifications in this manual are based on
the latest information available at the time of publication. The right is
reserved to make changes at any time without notice.
COPYRIGHT2003
DEERE & COMPANY
Moline, Illinois
A John Deere ILLUSTRUCTIONManual
All rights reserved
i
082206
PN=1
Page 6

Contents
Page Page
Extending/Retracting Cylinder...............60-4 Fill Fuel Tank ...........................85-3
Lubricant Storage........................85-3Disconnecting Hoses .....................60-5
Diesel Engine Coolant ....................85-4
Drawbar and PTO
Observe Drawbar / Wagon Hitch Load
Limitations............................65-1
Stay Clear of Rotating Drivelines ............65-1
Use Correct Transmission-Hydraulic Filter
Element .............................85-5
Transmission and Hydraulic Oil .............85-5
Grease................................85-6
Attaching PTO-Driven Implement ............65-2
Operating Tractor PTO (Standard) ...........65-3
Operating Tractor Dual PTO (Optional) .......65-4
Adjusting PTO Clutch Operating Rod .........65-5
Service and Maintenance
Observe Service Intervals..................90-1
Break-In Service.........................90-1
Service Intervals.........................90-2
Ballast
Planning for Maximum Productivity...........70-1
Selecting Ballast Carefully .................70-1
Matching Ballast to Load Work..............70-1
Measuring Wheel Slip—Manually ............70-2
Ballast Limitations........................70-3
Ballasting Front End for Transport ...........70-4
Ballasting Tractor ........................70-5
Service—Every 10 Hours
Check Engine Oil Level ...................95-1
Check Coolant Level .....................95-1
Drain Water and Sediment From Fuel
Tank and Fuel Filter ....................95-2
Water Separator Bowl ....................95-3
Lubricate as Necessary ...................95-3
Determining Maximum Rear Ballast ..........70-5
Determining Maximum Front Ballast..........70-5
Using Cast Iron Weights...................70-6
Installing Rear Cast Iron Weights ............70-6
Using Liquid Weight ......................70-7
Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Service Tyres Safely .....................75-1
Check Implement-to-Tyre Clearance .........75-1
Service—Every 50 Hours
Check Transmission-Hydraulic System
Oil Level ............................100-1
Clean and Check Battery .................100-1
Lubricate Front Axle Pivot Pin .............100-1
Lubricate Steering Spindles ...............100-2
Inspect Tyres and Loose Hardwares ........100-2
Check Tyre Inflation Pressure ..............75-2
Tyre Inflation Pressure Chart ...............75-3
Tighten Wheel/Axle Hardware Correctly .......75-3
Tighten Bolts—Adjustable Front Axle .........75-4
Tighten Bolts—Rear Axle ..................75-5
Observe Rear Wheel Tread Width Limitations . . 75-5
Tread Settings—Multi-Position Rear Wheels . . . 75-6
Tread Settings—Adjustable Front Axle........75-7
Service—Every 250 Hours
Change Engine Oil and Filter ..............110-1
Service Air Cleaner .....................110-2
Inspect and Adjust Alternator/Fan Belt .......110-2
Lubricate 3-Point Hitch...................110-3
Check Neutral Start System ...............110-3
Check and Adjust Clutch Pedal Free Play ....110-4
Adjust Front Axle Tread Width ..............75-9
Checking Toe-In........................75-10
Adjusting Toe-In........................75-11
Service—Every 500 Hours
Replace Fuel Filter......................115-1
Replace Transmission-Hydraulic Filter .......115-1
Transporting
Use Safety Lights and Devices..............80-1
Driving Tractor on Roads ..................80-1
Transport on Carrier......................80-4
Towing Tractor ..........................80-4
Service—Every 600 Hours
Clean Engine Crankcase Vent Tube.........115-1
Pack Front Wheel Bearings ...............115-1
Check Hoses and Hose Clamps for
Tightness ...........................115-2
Lubricate Rear Axle Bearings..............115-2Fuels, Lubricants and Coolant
Handle Fuel Safely—Avoid Fires ............85-1 Check Engine Idle Speeds ................115-3
Check Front Axle Pivot Pin................115-3Handle Fluids Safely—Avoid Fires ...........85-1
Diesel Engine Oil ........................85-2 Adjust Engine Valve Clearance ............115-3
Fuel Storage............................85-2
Diesel Fuel.............................85-2
Continued on next page
ii
082206
PN=2
Page 7

Contents
Page Page
Service—Every 1250 Hours Aiming Headlights......................140-19
Adjusting Headlights....................140-20Change Transmission-Hydraulic Oil and
Filter ...............................120-1 Replace Headlight Bulb .................140-20
Replace Tail Light and Warning LightClean Transmission-Hydraulic Pickup
Screen .............................120-2 Bulbs .............................140-21
Replace Flood Lamp Bulb ...............140-22
Service—Annually
Checking Tyres .......................140-22
Replace Air Cleaner Elements .............125-1
Troubleshooting
Service—2 Years/2000 Hours
Flush Cooling System....................130-1
Engine Troubleshooting ..................145-1
Transmission Troubleshooting .............145-5
Hydraulic System Troubleshooting ..........145-6
Service—As Required
Service Air Cleaner .....................135-1
Adjust Throttle Friction ...................135-1
Brakes Troubleshooting ..................145-6
Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Troubleshooting ......................145-7
Electrical System Troubleshooting ..........145-9
Service
Additional Service Information .............140-1
Service Tractor Safely ...................140-1
Engine Break-In Oil .....................140-1
Work In Ventilated Area ..................140-2
Using High-Pressure Washers .............140-2
Opening Hood .........................140-2
Removing Side Screens..................140-3
Removing Hood ........................140-3
Air Intake System Components ............140-3
Service Air Cleaner at Regular Intervals......140-4
Checking Air Intake System ...............140-4
Removing Primary Air Cleaner Element ......140-5
Cleaning Primary Element ................140-5
Washing Primary Element ................140-6
Inspecting Element......................140-6
Storing Element ........................140-7
Replacing Alternator/Fan Belt..............140-7
Fuel System Components ................140-7
Bleeding Fuel System....................140-8
Do Not Modify Fuel System ...............140-8
Engine Cooling System Components ........140-9
Cleaning Grille, Screens, Radiator and
Oil Cooler ..........................140-10
Prevent Battery Explosions...............140-10
Observe Electrical Service Precautions .....140-11
Battery Access ........................140-11
Removing Battery......................140-12
Checking Battery Condition ..............140-12
Servicing Battery ......................140-13
Charging Battery ......................140-15
Battery Replacement Specifications ........140-15
Connecting Starter Wiring................140-16
Connecting Alternator Wiring .............140-16
Tractor Storage
Storing Tractor .........................150-1
Removing Tractor From Storage ...........150-3
Specifications
John Deere 5310 S Tractor ...............155-1
Ground Speed at Rated Engine Speed
(2400 RPM) .........................155-2
Metric Bolt and Cap Screw Torque Values....155-3
Unified Inch Bolt and Cap Screw Torque
Values..............................155-4
Identification Numbers
Identification Plates .....................160-1
Record Tractor Serial (Chassis) Number .....160-1
Record Front Axle Serial Number...........160-1
Record Engine Serial Number .............160-2
Record Transmission Serial Number ........160-2
Lubrication Maintenance Record Charts
50, 250 Hour Service Chart ...............165-1
500 Hour Service Chart ..................165-2
600 Hour Service Chart ..................165-3
1000,1250 Hour Service Chart .............165-4
Annual Service Chart ...................165-5
2000 Hour Service Chart .................165-6
As Required Service Chart................165-7
John Deere Service
John Deere Parts .......................170-1
The Right Tools ........................170-1
Well Trained Technician..................170-1
Prompt Service.........................170-1
Locating Fusible Link ...................140-17
Locating Fuses........................140-17
Fuse Size and Function .................140-18
iii
082206
PN=3
Page 8

Contents
iv
082206
PN=4
Page 9

Safety
Recognize Safety Information
This is a safety-alert symbol. When you see this symbol
on your machine or in this manual, be alert to the
potential for personal injury.
Follow recommended precautions and safe operating
practices.
Understand Signal Words
A signal word—DANGER, WARNING, or CAUTION—is
used with the safety-alert symbol. DANGER identifies the
most serious hazards.
DANGER or WARNING safety signs are located near
specific hazards. General precautions are listed on
CAUTION safety signs. CAUTION also calls attention to
safety messages in this manual.
Follow Safety Instructions
Carefully read all safety messages in this manual and on
your machine safety signs. Keep safety signs in good
condition. Replace missing or damaged safety signs. Be
sure new equipment components and repair parts include
the current safety signs. Replacement safety signs are
available from your John Deere dealer.
DX,ALERT –19–29SEP98–1/1
T81389 –UN–07DEC88
TS187 –19–30SEP88
DX,SIGNAL –19–03MAR93–1/1
Learn how to operate the machine and how to use
controls properly. Do not let anyone operate without
instruction.
Keep your machine in proper working condition.
Unauthorized modifications to the machine may impair the
function and/or safety and affect machine life.
If you do not understand any part of this manual and need
assistance, contact your John Deere dealer.
05-1
TS201 –UN–23AUG88
DX,READ –19–03MAR93–1/1
082206
PN=7
Page 10

Prevent Machine Runaway
Avoid possible injury or death from machinery runaway.
Do not start engine by shorting across starter terminals.
Machine will start in gear if normal circuitry is bypassed.
NEVER start engine while standing on ground. Start
engine only from operator’s seat, with transmission in
neutral.
Safety
Operate Tractor Safely
Features designed into your tractor make operation safer
and let it perform a wide variety of jobs. Use your tractor
only for specified jobs it was designed to perform:
implement carrier, load mover, remote power source, or
transport unit—not a recreational vehicle.
Careless use or misuse can result in unnecessary
accidents. Be alert to hazards of tractor operation.
Understand causes of accidents and take every
precaution to avoid them. Most common accidents are
caused from:
• Tractor upsets
• Improper starting procedures
• Crushing and pinching during hitching
• Collisions with other motor vehicles
• Getting entangled in PTO shafts
• Falls from tractors
CED,OUO1032,2778 –19–15OCT99–1/1
TS177 –UN–11JAN89
M47224A –19–02JUN97
Avoid accidents by taking the following precautions:
• Put the gear lever in Park position. Leaving
transmission in gear with engine stopped will NOT
prevent the tractor from moving.
• Be sure everyone is clear of tractor and attached
equipment before starting engine.
• Never try to get on or off a moving tractor.
• When tractor is left unattended, put the gear lever in
Park position , stop the engine , remove the key, lower
implements to the ground.
05-2
TS276 –UN–23AUG88
AG,OUO6035,84 –19–18MAY00–1/1
082206
PN=8
Page 11

Safety
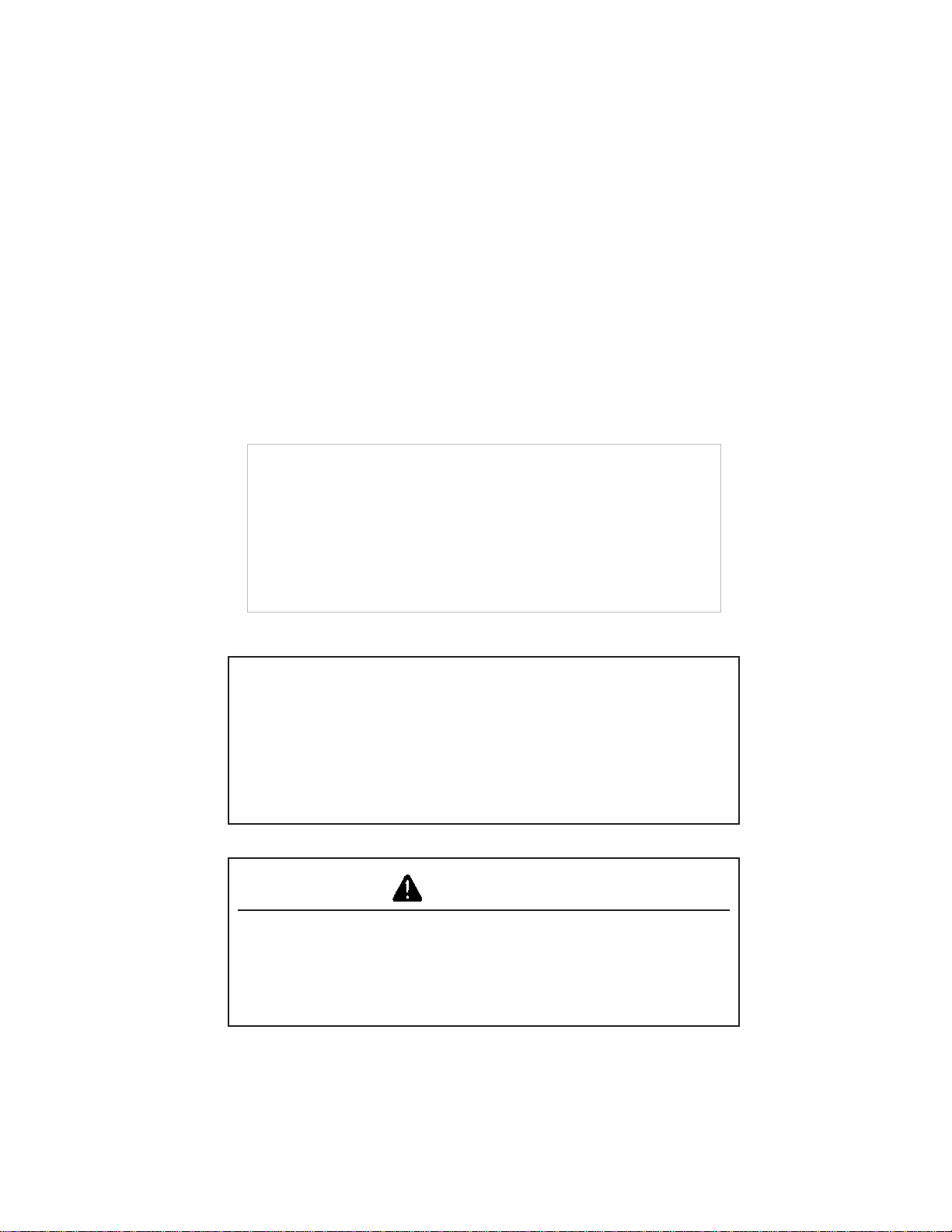
Use Caution on Hillsides
Avoid holes, ditches, and obstructions which cause the
tractor to tip, especially on hillsides. Avoid sharp, uphill
turns.
Never drive near the edge of a gully or steep
embankment -- it might cave in.
Driving forward out of a ditch or mired condition or up a
steep slope could cause tractor to tip over rearward. Back
out of these situations if possible.
Danger of overturn increases greatly with narrow tread
setting, at high speed.
Hitch towed loads only to drawbar. When using a chain,
take up the slack slowly.
TS205 –UN–23AUG88
Shift to Low Gear on Hills
Shift to a low gear before descending a steep hill to
improve your control of the tractor with little or no braking.
Use engine braking to reduce speed before applying
tractor brakes. Run-away tractors often tip over. Never
coast downhill.
When driving on icy, wet or oily surfaces, reduce speed
and be sure tractor is properly ballasted (specially front
tyres)to avoid skidding and loss of steering control.
Additional ballast may be needed for transporting heavy
hitch mounted implements. When implement is raised,
drive slowly over rough ground, regardless of how much
ballast is used.
AG,OUO6035,65 –19–17MAY00–1/1
LV4042 –UN–09JUL99
AG,OUO6035,83 –19–17MAY00–1/1
05-3
082206
PN=9
Page 12

Avoid Tipping
Do not drive where machine could slip or tip.
Stay alert for holes, rocks, and roots in the terrain, and
other hidden hazards. Keep away from drop-offs.
Slow down before you make a sharp turn.
Take care when pulling loads or using heavy equipment:
Safety
• Use only approved drawbar hitch points.
• Limit loads to those you can safely control.
• Use counterweights or wheel weights when suggested
in this operator’s manual.
Reduce speed and exercise extreme caution on slopes
and in sharp turns to prevent tipping or loss of control. Be
especially cautious when changing direction on slopes.
Do not stop or start suddenly when going uphill or
downhill.
If machine stops going up hill:
• STOP the PTO.
• Back down slowly.
TS205 –UN–23AUG88
MX,AVOIDTIP1A1 –19–22JUL94–1/1
05-4
082206
PN=10
Page 13
Safety
Freeing a Mired Machine
Attempting to free a mired machine can involve safety
hazards such as the mired tractor tipping rearward, the
towing tractor overturning, and the tow chain or tow bar (a
cable is not recommended) failing and recoiling from its
stretched condition.
Back your tractor out if it gets mired down in mud. Unhitch
any towed implements. Dig mud from behind the rear
wheels. Place boards behind the wheels to provide a solid
base and try to back out slowly. If necessary, dig mud
from the front of all wheels and drive slowly ahead.
If necessary to tow with another unit, use a tow bar or a
long chain (a cable is not recommended). Inspect the
chain for flaws. Make sure all parts of towing devices are
of adequate size and strong enough to handle the load.
Always hitch to the drawbar of the towing unit. Do not
hitch to the front pushbar attachment point. Before
moving, clear the area of people. Apply power smoothly to
take up the slack: a sudden pull could snap any towing
device causing it to whip or recoil dangerously.
TS1645 –UN–15SEP95TS263 –UN–23AUG88
Park Tractor Safely
To park tractor safely:
• Disengage PTO.
• Lower equipment to the ground.
• Put gear shift lever in PARK.
• STOP the engine.
• Remove key.
Before you leave the operator’s seat, wait for engine and
attachment parts to stop moving.
05-5
DX,MIRED –19–07JUL99–1/1
M35691 –UN–26APR89
MX,SAIP,AAA1 –19–21AUG99–1/1
082206
PN=11
Page 14
Safety
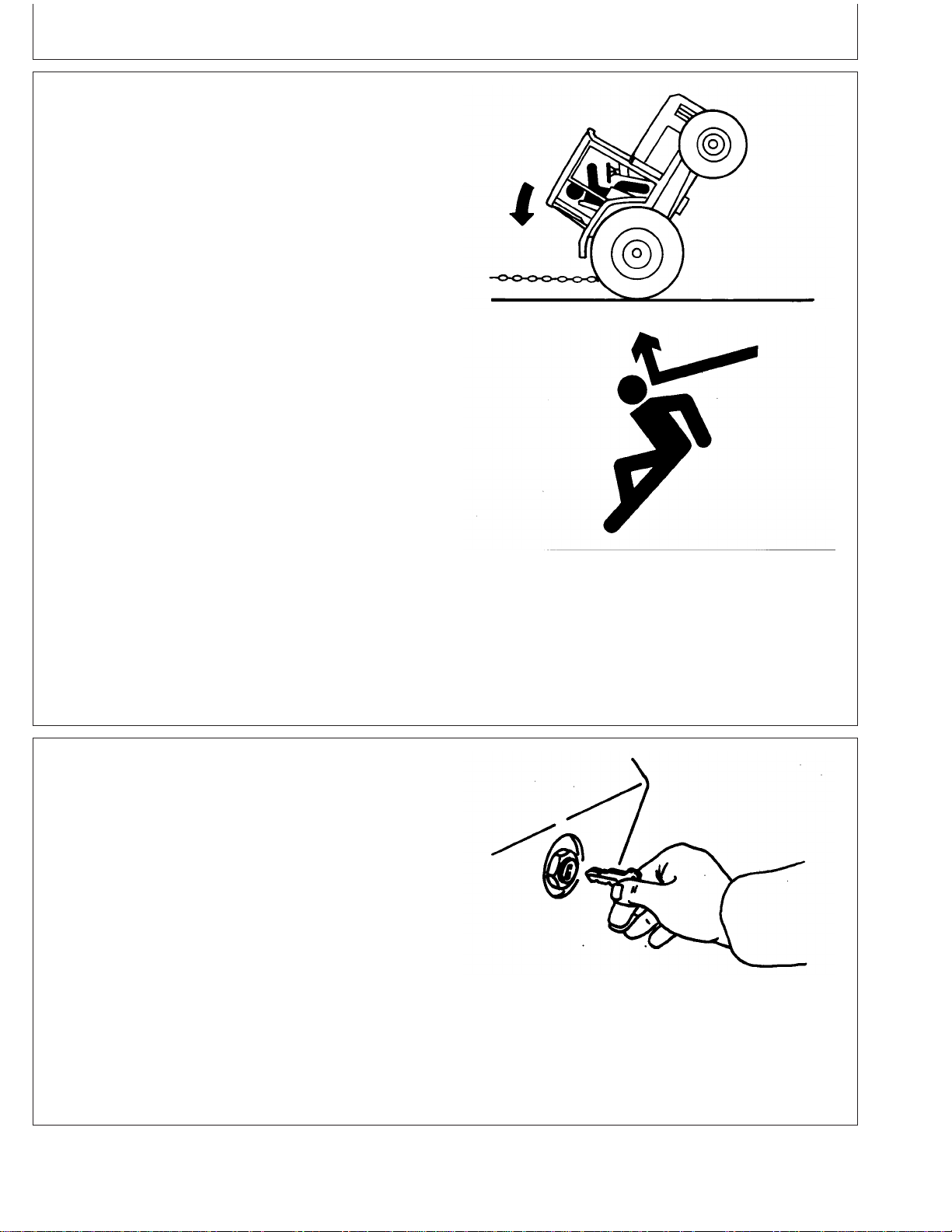
Handle Fuel Safely—Avoid Fires
Handle fuel with care: it is highly flammable. Do not refuel
the machine while smoking or when near open flame or
sparks.
Always stop engine before refueling machine. Fill fuel tank
outdoors.
Prevent fires by keeping machine clean of accumulated
trash, grease, and debris. Always clean up spilled fuel.
Prepare for Emergencies
TS202 –UN–23AUG88
DX,FIRE1 –19–03MAR93–1/1
Be prepared if a fire starts.
Keep a first aid kit and fire extinguisher handy.
Keep emergency numbers for doctors, ambulance service,
hospital, and fire department near your telephone.
Wear Protective Clothing
Wear close fitting clothing and safety equipment
appropriate to the job.
Prolonged exposure to loud noise can cause impairment
or loss of hearing.
Wear a suitable hearing protective device such as
earmuffs or earplugs to protect against objectionable or
uncomfortable loud noises.
Operating equipment safely requires the full attention of
the operator. Do not wear radio or music headphones
while operating machine.
DX,FIRE2 –19–03MAR93–1/1
TS291 –UN–23AUG88
TS206 –UN–23AUG88
05-6
DX,WEAR –19–10SEP90–1/1
082206
PN=12
Page 15

Protect Against Noise
Prolonged exposure to loud noise can cause impairment
or loss of hearing.
Wear a suitable hearing protective device such as
earmuffs or earplugs to protect against objectionable or
uncomfortable loud noises.
Safety
Stay Clear of Rotating Drivelines
Entanglement in rotating driveline can cause serious injury
or death.
Keep tractor master shield and driveline shields in place
at all times. Make sure rotating shields turn freely.
Wear close fitting clothing. Stop the engine and be sure
PTO driveline is stopped before making adjustments,
connections, or cleaning out PTO driven equipment.
DX,NOISE –19–03MAR93–1/1
TS207 –UN–23AUG88
TS1644 –UN–22AUG95
DX,PTO –19–12SEP95–1/1
Use Safety Lights and Devices
Prevent collisions between other road users, slow moving
tractors with attachments or towed equipment, and
self-propelled machines on public roads. Frequently check
for traffic from the rear, especially in turns, and use turn
signal lights.
Use headlights, flashing warning lights, and turn signals
day and night. Follow local regulations for equipment
lighting and marking. Keep lighting and marking visible,
clean, and in good working order. Replace or repair
lighting and marking that has been damaged or lost. An
implement safety lighting kit is available from your John
Deere dealer.
05-7
TS951 –UN–12APR90
DX,FLASH –19–07JUL99–1/1
082206
PN=13
Page 16
Safety
Safely Transporting the Tractor
A disabled tractor is best transported on a flatbed carrier.
Use chains to secure the tractor to the carrier.
Never tow a tractor at a speed greater than 16 km/h (10
mph). An operator must steer and brake the tractor under
tow.
Tow Loads Safely
Stopping distance increases with speed and weight of
towed loads, and on slopes. Towed loads with or without
brakes that are too heavy for the tractor or are towed too
fast can cause loss of control. Consider the total weight of
the equipment and its load.
Observe these recommended maximum road speeds, or
local speed limits which may be lower:
• If towed equipment does not have brakes, do not travel
more than 32 km/h (20 mph) and do not tow loads more
than 1.5 times the tractor weight.
• If towed equipment has brakes, do not travel more than
40 km/h (25 mph) and do not tow loads more than 4.5
times the tractor weight.
Ensure the load does not exceed the recommended
weight ratio. Add ballast to recommended maximum for
tractor, lighten the load, or get a heavier towing unit. The
tractor must be heavy and powerful enough with adequate
braking power for the towed load. Use additional caution
when towing loads under adverse surface conditions,
when turning, and on inclines.
MX,SAIP,LA1 –19–29JUL94–1/1
LV610 –UN–22APR94
TS216 –UN–23AUG88
05-8
DX,TOW –19–02OCT95–1/1
082206
PN=14
Page 17
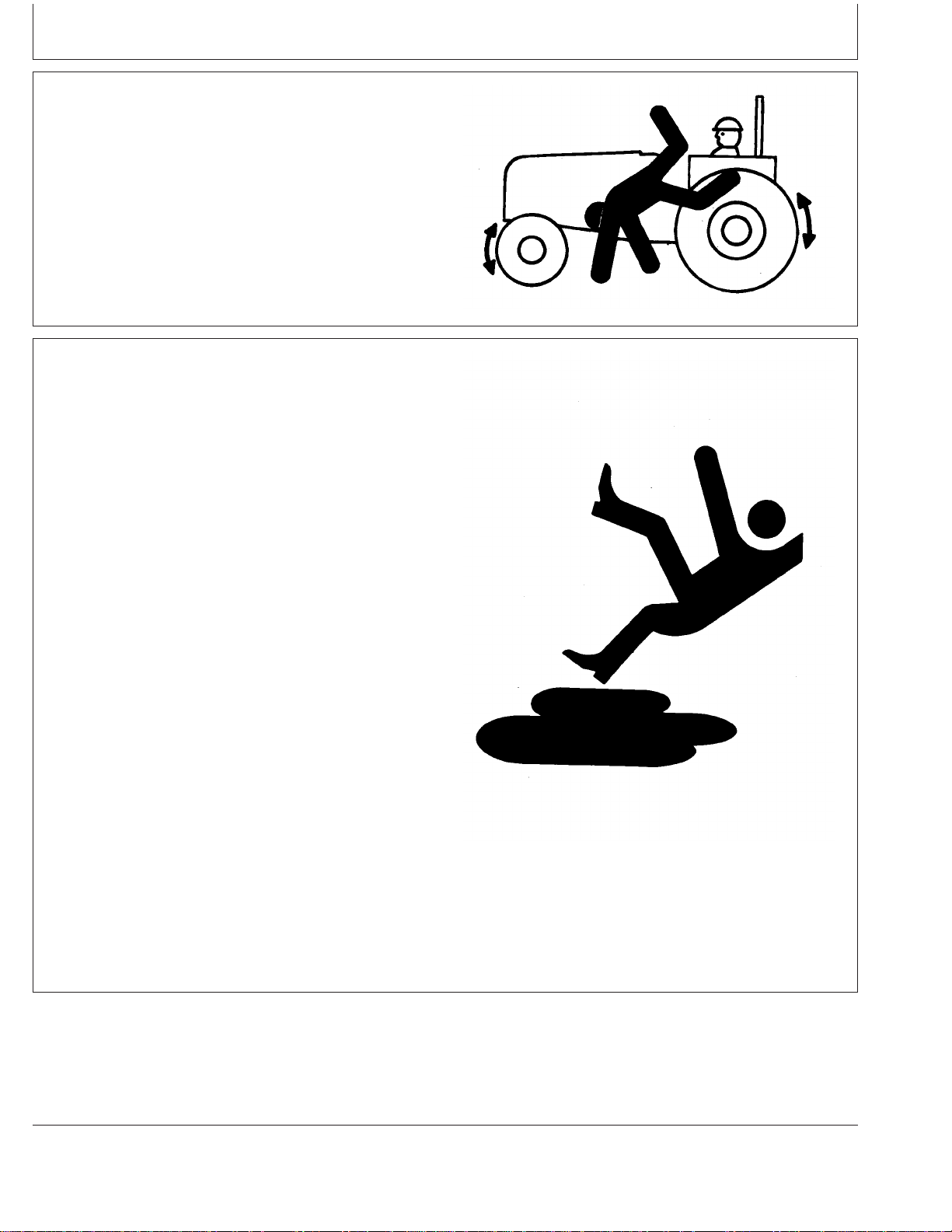
Safety
Keep Riders Off Machine
Only allow the operator on the machine. Keep riders off.
Riders on machine are subject to injury such as being
struck by foreign objects and being thrown off of the
machine. Riders also obstruct the operator’s view resulting
in the machine being operated in an unsafe manner.
Practice Safe Maintenance
Understand service procedure before doing work. Keep
area clean and dry.
Never lubricate, service, or adjust machine while it is
moving. Keep hands, feet , and clothing from
power-driven parts. Disengage all power and operate
controls to relieve pressure. Lower equipment to the
ground. Stop the engine. Remove the key. Allow machine
to cool.
Securely support any machine elements that must be
raised for service work.
Keep all parts in good condition and properly installed. Fix
damage immediately. Replace worn or broken parts.
Remove any buildup of grease, oil, or debris.
On self-propelled equipment, disconnect battery ground
cable (-) before making adjustments on electrical systems
or welding on machine.
DX,RIDER –19–03MAR93–1/1
TS290 –UN–23AUG88
On towed implements, disconnect wiring harnesses from
tractor before servicing electrical system components or
welding on machine.
05-9
TS218 –UN–23AUG88
DX,SERV –19–17FEB99–1/1
082206
PN=15
Page 18
Safety
Service Tractor Safely
Do not service the tractor while it is in motion or while the
engine is running.
Tighten wheel hardware to correct torque as specified in
Wheels, Tyres and Tread section. Torque at intervals
shown in Break-In Period and Lubrication and
Maintenance sections, to ensure that wheel hardware
does not loosen.
Reinstall shields removed during service.
Work In Ventilated Area
Engine exhaust fumes can cause sickness or death. If it is
necessary to run an engine in an enclosed area, remove
the exhaust fumes from the area with an exhaust pipe
extension.
If you do not have an exhaust pipe extension, open the
doors and get outside air into the area
LV828 –UN–08AUG94
AG,OUO6035,70 –19–17MAY00–1/1
TS220 –UN–23AUG88
DX,AIR –19–17FEB99–1/1
Support Machine Properly
Always lower the attachment or implement to the ground
before you work on the machine. If the work requires that
the machine or attachment be lifted, provide secure
support for them. If left in a raised position, hydraulically
supported devices can settle or leak down.
Do not support the machine on cinder blocks, hollow tiles,
or props that may crumble under continuous load. Do not
work under a machine that is supported solely by a jack.
Follow recommended procedures in this manual.
When implements or attachments are used with a
machine, always follow safety precautions listed in the
implement or attachment operator’s manual.
05-10
TS229 –UN–23AUG88
DX,LOWER –19–24FEB00–1/1
082206
PN=16
Page 19

Safety
Avoid Heating Near Pressurized Fluid Lines
Flammable spray can be generated by heating near
pressurized fluid lines, resulting in severe burns to
yourself and bystanders. Do not heat by welding,
soldering, or using a torch near pressurized fluid lines or
other flammable materials. Pressurized lines can
accidentally burst when heat goes beyond the immediate
flame area.
Avoid High-Pressure Fluids
Escaping fluid under pressure can penetrate the skin
causing serious injury.
Avoid the hazard by relieving pressure before
disconnecting hydraulic or other lines. Tighten all
connections before applying pressure.
Search for leaks with a piece of cardboard. Protect hands
and body from high pressure fluids.
If an accident occurs, see a doctor immediately. Any fluid
injected into the skin must be surgically removed within a
few hours or gangrene may result. Doctors unfamiliar with
this type of injury should reference a knowledgeable
medical source. Such information is available from Deere
& Company Medical Department in Moline, Illinois, U.S.A.
DX,TORCH –19–10DEC04–1/1
TS953 –UN–15MAY90
X9811 –UN–23AUG88
Service Cooling System Safely
Explosive release of fluids from pressurized cooling
system can cause serious burns.
If radiator cap must be removed, do not remove when
engine is hot. Shut engine off and wait until cap is cool
enough to touch with bare hands. Slowly loosen cap to
first stop to relieve pressure before removing completely.
05-11
DX,FLUID –19–03MAR93–1/1
TS281 –UN–23AUG88
AG,OUO1032,2682 –19–30SEP99–1/1
082206
PN=17
Page 20
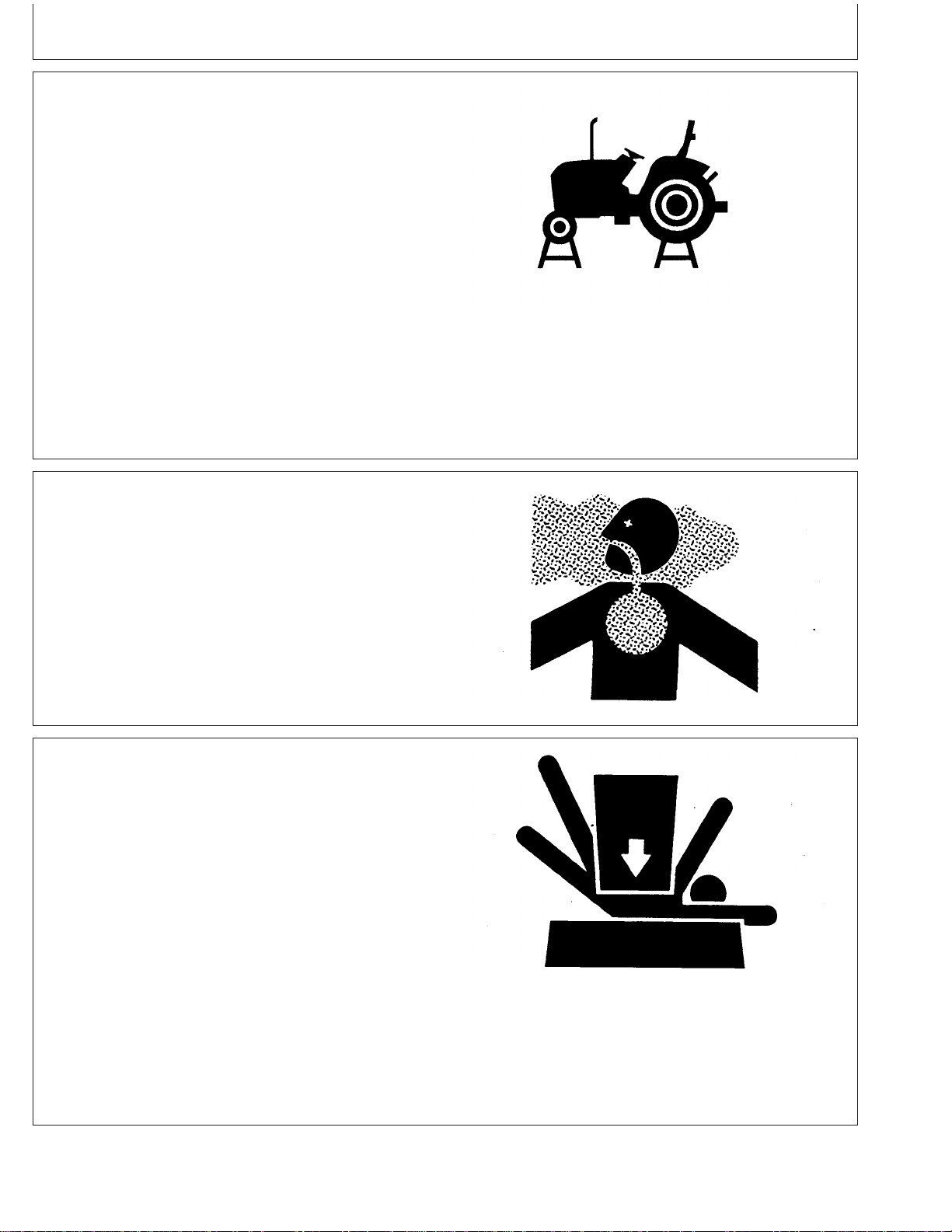
Store Attachments Safely
Stored attachments such as dual wheels, cage wheels,
and loaders can fall and cause serious injury or death.
Securely store attachments and implements to prevent
falling. Keep playing children and bystanders away from
storage area.
Safety
Prevent Acid Burns
Sulfuric acid in battery electrolyte is poisonous. It is strong
enough to burn skin, eat holes in clothing, and cause
blindness if splashed into eyes.
Avoid the hazard by:
1. Filling batteries in a well-ventilated area.
2. Wearing eye protection and rubber gloves.
3. Avoiding breathing fumes when electrolyte is added.
4. Avoiding spilling or dripping electrolyte.
5. Use proper jump start procedure.
If you spill acid on yourself:
1. Flush your skin with water.
2. Apply baking soda or lime to help neutralize the acid.
3. Flush your eyes with water for 15—30 minutes. Get
medical attention immediately.
DX,STORE –19–03MAR93–1/1
TS219 –UN–23AUG88
If acid is swallowed:
1. Do not induce vomiting.
2. Drink large amounts of water or milk, but do not
exceed2L(2quarts).
3. Get medical attention immediately.
05-12
TS203 –UN–23AUG88
DX,POISON –19–21APR93–1/1
082206
PN=18
Page 21
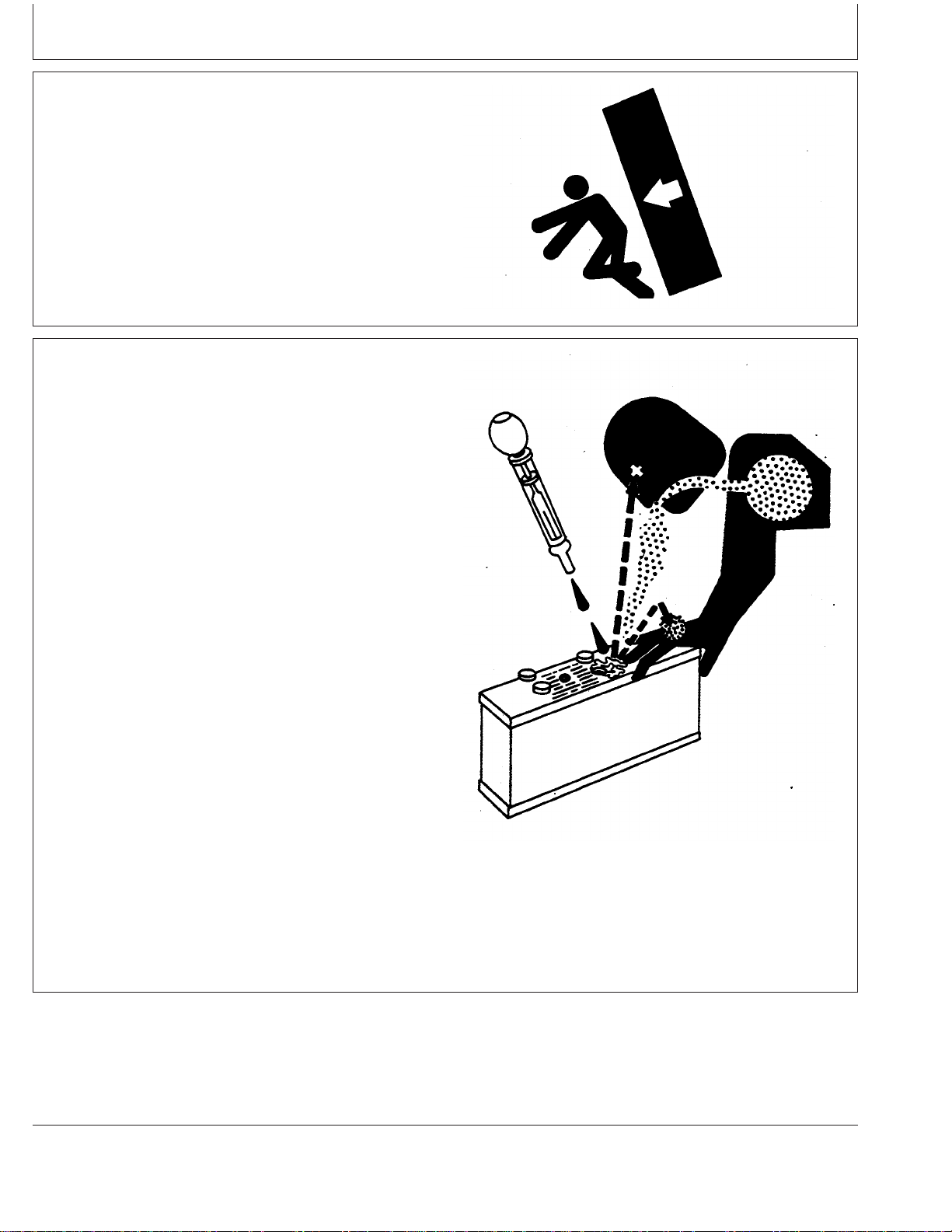
Safety
Service Tires Safely
Explosive separation of a tire and rim parts can cause
serious injury or death.
Do not attempt to mount a tire unless you have the proper
equipment and experience to perform the job.
Always maintain the correct tire pressure. Do not inflate
the tires above the recommended pressure. Never weld or
heat a wheel and tire assembly. The heat can cause an
increase in air pressure resulting in a tire explosion.
Welding can structurally weaken or deform the wheel.
When inflating tires, use a clip-on chuck and extension
hose long enough to allow you to stand to one side and
NOT in front of or over the tire assembly. Use a safety
cage if available.
Check wheels for low pressure, cuts, bubbles, damaged
rims or missing lug bolts and nuts.
Dispose of Waste Properly
Improperly disposing of waste can threaten the
environment and ecology. Potentially harmful waste used
with John Deere equipment include such items as oil, fuel,
coolant, brake fluid, filters, and batteries.
Use leakproof containers when draining fluids. Do not use
food or beverage containers that may mislead someone
into drinking from them.
Do not pour waste onto the ground, down a drain, or into
any water source.
Inquire on the proper way to recycle or dispose of waste
from your local environmental or recycling center, or from
your John Deere dealer.
DX,RIM –19–24AUG90–1/1
TS211 –UN–23AUG88
TS1133 –UN–26NOV90
05-13
AG,OUO1032,2683 –19–30SEP99–1/1
082206
PN=19
Page 22

Safety Signs
Warning Labels
Keep warning labels in good condition, replace if not in
readable condition.
GENERIC,0000038 –19–28JUN06–1/4
Top surface of PTO shield
Just below starter body
PY5800 –UN–11JUL06
PY5801 –UN–11JUL06
M71026 –19–02JUL90
LV1932 –19–02JUN97
LV4307 –19–04NOV05
Left fender
PY1057 –UN–25JUN01
Continued on next page
10-1
GENERIC,0000038 –19–28JUN06–2/4
082206
PN=20
Page 23

Safety Signs
PY2280 –UN–18NOV04
Top of Battery
Right Fender
PY1965 –UN–24FEB04
GENERIC,0000038 –19–28JUN06–3/4
PY4879 –UN–06DEC05
PY4342 –UN–29DEC04
Right Fender
10-2
GENERIC,0000038 –19–28JUN06–4/4
082206
PN=21
Page 24

Tractor Controls
Controls and Instruments
A—Steering Wheel D—Light Switch G—Clutch Pedal I—Foot Throttle
B—Hand Throttle E—Hazard Switch H—Key Switch J—Brake Pedal
C—Horn Button F—Turn Signal Switch
Continued on next page
PY80265,05I0102 –19–17FEB06–1/2
PY5158 –UN–17FEB06
15-1
082206
PN=22
Page 25

Controls and Instruments
PY5501 –UN–16FEB06
PY4077 –UN–19JAN06
PY5544 –UN–06MAR06
.
A—Selective Control Lever C—Rockshaft Draft Control E—PTO Shift Lever H—Differential Lock Pedals
B—Rockshaft Position Control Lever F—Range Shift Lever
Lever D—Gear Shift Lever G—Rockshaft Rate-of- drop
Knob
PY4542 –UN–26JAN05
15-2
PY80265,05I0102 –19–17FEB06–2/2
082206
PN=23
Page 26

Instrument Panel
Controls and Instruments
A—Air Restriction Indicator D—Charging System Indicator F—Coolant Temperature H—Tachometer
B—High Beam Indicator E—Engine Oil Pressure Gauge I—Fuel Gauge
C—Hour Meter Indicator G—Turn Signal Direction
Indicators
PY80265,05I0105 –19–12SEP05–1/1
PY5766 –UN–02JUN06
15-3
082206
PN=24
Page 27

Lights
Light Switch Positions
Tractor light switch has five positions:
A—Turns off all lights.
B—Turns on warning lights only. Use for parking the
vehicle
C—Turns on dim headlights, tail lights and warning lights.
Turn switch to this position before meeting other vehicles.
D—Turns on bright headlights, tail lights and warning
lights. For highway driving during night time
E—Turns on high beamlight.
F— Switch on flood light (plough lamp). for field use only.
Do not use on roads. Flood light might blind or confuse
other drivers.
A—Lights Off
B—Warning Lights Position
C—Dim Headlights,Tail Lights and Warning Light
Position
D—Bright Headlights, Tail Lights and Warning Lights
Position
E—High Beamlights
F—Flood Light Switch
PY4481 –UN–11JAN05PY4107 –UN–21AUG04
20-1
GENERIC,000003A –19–11JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=25
Page 28

Lights
Using Headlights
Dual-beam headlights (F) are switched on by either “High
Beamlight” (E), “Bright Headlight” (D), or “Dim Headlight”
(C) light switch positions.
Always dim lights before meeting another vehicle.
Keep headlights adjusted properly, (see Adjusting
Headlights in Service section).
A—Lights Off
B—Warning Lights Position
C—Dim Headlights, Tail Lights, and Warning Light
Position
D—Bright Headlights, Tail Lights and Warning Lights
Position
E—High Beamlight
F—Headlights
PY4481 –UN–11JAN05
Using High Beam Indicator
High beam indicator (A) should glow when light switch is
turned to “Bright Headlight” position or “Flood Light”
position. Bright headlights, tail lights, flood light and
warning lights should be on.
A—High Beam Indicator
PY5148 –UN–23FEB06
GENERIC,000003B –19–11JUL06–1/1
PY5768 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0108 –19–02JUN06–1/1
20-2
082206
PN=26
Page 29

Using Tail Lights
Red tail lights (A) are switched on by either bright
headlight or dim headlight light switch position.
Be sure tail light lenses are clean before driving on a
road, so other drivers can see it easily.
CAUTION: Prevent collisions between other
road users, slow moving tractors with
attachments or towed equipment, and
self-propelled machines on public roads.
Frequently check for traffic from the rear,
especially in turns, and use hand signals or
turn signal lights.
Use headlights, flashing warning lights, and
turn signals day and night. Follow local
regulations for equipment lighting and marking.
Keep lighting and marking visible and in good
working order. Replace or repair lighting and
marking that has been damaged or lost. An
implement safety lighting kit is available from
your John Deere dealer.
Lights
PY4883 –UN–22APR05
A—Tail Lights
B—ReflexReflector
C—TurnSignalLights
20-3
PY80265,05I0109 –19–11JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=27
Page 30

Using Turn Signals
Lights
PY4114 –UN–23FEB06
Move turn signal lever (A) down to indicate left-hand turn
or up for right-hand turn. Indicator lights (D) will flash to
signal turn direction.
When lever is up, front and rear turn lights on right-hand
side (C) will flash . When lever is down, front and rear turn
lights on left-hand side (B) will flash.
NOTE: Be sure to manually return lever to center position
after turning.
PY5510 –UN–17FEB06PY5767 –UN–02JUN06
A—Turn Signal Lever
B—Left-Hand Lights
C—Right-Hand Lights
D—Dash Indicator Lights
GENERIC,000003D –19–11JUL06–1/1
20-4
082206
PN=28
Page 31

Using Hazard Lights
Lights
Rear lights
All 4 turn signal lights ( 2 front and 2 rear) start to blink
when hazard light switch (C) is pulled out. Use harzard
lights to warn approaching vehicles when tractor is
stopped on the road
A—Turn Signal Light on Rear Side
B— Turn Signal Light on Front Side
C— Hazard Light Switch
PY4338 –UN–28DEC04
Front light
PY4339 –UN–28DEC04
PY4896 –UN–20FEB06
Hazard Light Switch
GENERIC,000003E –19–21FEB06–1/1
20-5
082206
PN=29
Page 32

Lights
Using Flood Lamp
Flood lamp (G) is switched on by “Flood Light (H)” switch
. Horn (F) is located just right-hand side of light switch
CAUTION: When operating on a road, move
light switch to either “Bright or Dim Head
Lamp” positions Never use flood lamp when
transporting. A clear, bright light at the rear of
the tractor could confuse drivers of other
vehicles as they approach from the rear.
A—Lights Off
B—Warning Lights Position
C—Dim Headlights, Tail Lights and Warning Light
Position
D—Bright Headlights, Tail Lights and Warning Lights
Position
E—High Beamlight
F—Horn
G—Flood Lamp
H—Flood Light Switch
PY4106 –UN–23FEB06PY4150 –UN–20FEB06
Seven-Terminal Outlet—If Equipped
Outlet (A) is used to connect lights, turn signals, and
remote electrical equipment on trailers or implements.
Always use auxiliary light on towed implement when
tractor rear signals and other lights are obscured.
NOTE: Matching plug is available through your John
Deere dealer.
Terminal Function Wire Color
1 Ground Black
2 Flood Lamp Purple
3 Left Turn Dark Green
4 Accessory Red
5 Right Turn Dark Green
6 Tail Lamp Gray
7 Accessory Red
PY80265,05I0112 –19–11JUL06–1/1
PY5525 –UN–21FEB06PY5606 –UN–23FEB06
A—Seven-Terminal Outlet
20-6
GENERIC,0000053 –19–11JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=30
Page 33

Operator’sPlatform
Selecting Seat Position
Deluxe Seat
Seat can be moved forward or backward depending on
operator’s requirement. To move seat on either side, just
lift lever (A) and push the seat.
A—Seat Adjustment Lever
Adjusting Ride Comfort
Adjustment knob is located behind seat.
Weight markings are given on the rear of seat.Turn
adjustment knob (A) for a firm or soft ride. Seat
suspension will function properly relative to operator’s
weight.
PY1032 –UN–24JUN01
PY80265,05I0114 –19–12SEP05–1/1
A—Weight Adjustment Knob
PY1033 –UN–24JUN01
PY80265,05I0115 –19–12SEP05–1/1
25-1
082206
PN=31
Page 34

Break-In Period
Observe Engine Operation Closely
IMPORTANT: The engine is ready for normal
operation. Be extra cautious during the
first 100 hours, until you become
thoroughly familiar with the sound and
feel of your new tractor. Stay extra
attentive and alert.
Warm up tractor carefully. Check charging (A) and oil
pressure (B) warning indicator lights and coolant
temperature gauge (C).
PY5769 –UN–02JUN06
Avoid unnecessary engine idling.
Check engine oil, coolant, and transmission/hydraulic fluid
levels frequently. Watch for fluid leaks.
NOTE: If engine oil must be added, use seasonal
viscosity grade oil. Use only lubricants meeting
specifications given in the Fuels, Lubricants, and
Coolant section.
Break-In Service
IMPORTANT: Keep wheel hardware tight to avoid
tractor damage. Check wheel
hardware torque before operating,
twice during first ten hours of
operation, after fifty hours of
operation, and periodically
thereafter.
A—Charging Indicator
B—Oil Pressure Indicator
C—Coolant Temperature Indicator
PY80265,05I0116 –19–02JUN06–1/1
Tighten wheel hardware. (See Wheels, Tyres, and
Treads section)
Check alternator/fan belt tension and tighten air intake
and cooling system hose clamps
Perform 50 Hours Service
During the First 10 Hours of Operation:
Perform daily or 10 hours service. (See Service
Intervals in Lubrication and Maintenance section)
Tighten wheel hardware. (See Wheels, Tyres, and
Treads section)
After the First 50 Hours of Operation:
1
See Engine Break-In Oil in Service section for additional
information.
After the First 100 Hours of Operation:
Replace transmission-hydraulic filter element
Change engine oil and filter
1
After the First 1100 Hours of Operation:
Change transmission-hydraulic oil
PY80265,05I0117 –19–12SEP05–1/1
35-1
082206
PN=32
Page 35

Prestarting Checks
Service Daily Before Start-Up
1. Check the engine oil level. Wipe dipstick (A) off and
reinsert it fully. Remove and locate oil level.
Safe operating range is between two marks on
dipstick. Do not operate engine when oil level is below
lower mark on dipstick. Add recommended engine oil
through filler hole (B). (See Fuel, Lubricants, and
Coolant section for oil specifications.)
CAUTION: DO NOT remove radiator cap or drain
coolant until coolant is cold. Always loosen
radiator cap slowly to relieve any excess
pressure.
2. Check coolant level in recovery tank (C). If engine is
COOL and level is below “LOW” mark, add coolant to
recovery tank to bring level to “LOW” mark.
NOTE: Coolant level with a cold engine should be at the
“LOW” mark. A tractor at operating temperature
should have a coolant level at the “HOT FULL”
mark.
3. Lubricate the following items at 10 hour intervals if
operating in extremely wet or muddy conditions.
• Front axle pivot pin(s)
• Steering spindles
• Tie rod ends
Use multipurpose grease. For detailed information see
Lubrication and Maintenance section.
PY4036 –UN–19JUN06PY5511 –UN–17FEB06
A—Engine Oil Dipstick
B—Engine Oil Filler Cap
C—Recovery Tank
D—Radiator Cap
40-1
GENERIC,000003F –19–17FEB06–1/1
082206
PN=33
Page 36

Operating the Engine
Before Starting the Engine
TS220 –UN–23AUG88
CAUTION: Prevent asphyxiation. Engine
exhaust fumes can cause sickness or death to
you or someone else.
If you must operate engine in a building, be
positive there is adequate ventilation. Either use
an exhaust pipe extension to remove the
exhaust fumes or open doors and windows to
bring enough outside air into the area.
1. Check fuel gauge to be sure tractor has plenty of fuel.
2. Place Gear shift lever (A) in neutral (N) or Park and
Range shift lever (B) in Neutral position. Starter will not
operate if gear shift lever is not in these positions.
3. Place rockshaft control levers (D and E) in lower
position.
4. Check indicator lights. Indicators should illuminate
when key switch is turned to the “ON” position.
PY5512 –UN–17FEB06PY5527 –UN–21FEB06PY4316 –UN–14DEC04
If any indicator does not function properly, see your
John Deere dealer.
A—Gear Shift Lever
B—Range Shift Lever
C—PTO Lever
D—Rockshaft Draft Control Lever
E—Rockshaft Position Control Lever
45-1
GENERIC,0000054 –19–11JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=34
Page 37

Operating the Engine
Starting the Engine
1. Push hand throttle (A) forward off idle position
(approximately 1/3 of full throttle). Engine may not start
with throttle pulled completely down.
CAUTION: Avoid possible injury or death from a
machine runaway.
Do not start engine by shorting across starter
terminals. Machine will start in gear and move if
normal circuitry is bypassed.
Start engine only from operator’s seat with
transmission in NEUTRAL.
NEVER start engine while standing on ground.
IMPORTANT: DO NOT run a cold engine at full
throttle. Engine should be kept at idling
for 30 sec before the RPM is increased,
this should be strictly followed
otherwise sudden acceleration may
damage the Turbocharger.
TS177 –UN–11JAN89PY4497 –UN–13JAN05
2. Depress clutch pedal and turn key switch fully
clockwise (B) to engage starter. Release key when
engine starts. If key is released before engine starts,
wait until starter and engine stop turning before trying
again.
IMPORTANT: DO NOT operate starter more than 20
seconds at a time. If engine does not
start, wait at least two minutes for the
starter motor to cool before trying
again. If engine does not start in four
attempts, refer to “Troubleshooting”
section.
A—Hand Throttle
B—Key Switch On
PY80265,05I0120 –19–12SEP05–1/1
45-2
082206
PN=35
Page 38

Operating the Engine
Check Instruments After Starting
IMPORTANT: If charging system (A) or oil pressure
(B) indicators fail to go out, or
temperature gauge (C) indicates hot,
stop engine and determine the cause.
A—Charging System Indicator
B—Oil Pressure Indicator
C—Temperature Gauge
Oil Pressure Indicator
Oil pressure indicator (A) will light if engine oil pressure is
low. Indicator should light when key is turned to engage
starter and go out when engine starts.
IMPORTANT: NEVER operate engine without
sufficient oil pressure. If indicator stays
lit for longer than five seconds under
normal operating conditions, stop
engine and check for cause.
If low oil level is not the problem, see your John Deere
dealer.
PY80265,05I0121 –19–02JUN06–1/1
PY5769 –UN–02JUN06
PY5770 –UN–02JUN06
A—Oil Pressure Indicator
PY80265,05I0122 –19–02JUN06–1/1
Charging System Indicator
Charging system indicator (A) will light when alternator
output is low. Indicator should light when key is turned to
engage starter, and go out when engine starts.
If indicator stays lit for longer than five seconds in normal
operation, stop engine and check for cause. If loose or
broken fan belt is not the cause, see your John Deere
dealer.
A—Charging System Indicator
45-3
PY5771 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0123 –19–02JUN06–1/1
082206
PN=36
Page 39

Operating the Engine
Air Restriction Indicator
Air restriction indicator (A) will light if air cleaner becomes
plugged. Service air cleaner as soon as possible.
Indicator should light momentarily when key is turned
slowly to starter engagement position.
A—Air Restriction Indicator
Coolant Temperature Gauge
The needle on the temperature gauge (A) rises as engine
warms up. If needle reaches red zone, stop engine and
determine the cause.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove radiator cap or drain
coolant until coolant is cold. Always loosen
radiator cap slowly to relieve any excess
pressure.
Check coolant level in radiator when engine cools. Also
check grille, radiator and radiator side screens for
plugging. Check fan belt tension. If problem is not
corrected, see your John Deere dealer.
PY80265,05I0124 –19–02JUN06–1/1
PY5731 –UN–31MAY06
PY5773 –UN–02JUN06
A—Coolant Temperature Gauge
PY80265,05I0125 –19–02JUN06–1/1
Watch Fuel Level
Stop to refuel before gauge (A) reaches empty mark.
IMPORTANT: Use diesel fuel only. See Fuel and
Lubricants section for fuel
specifications.
Should tractor run out of fuel and not start in several tries,
air must be bled from fuel system. (See Bleeding Fuel
System in Service section).
A—Fuel Gauge
45-4
PY5774 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0126 –19–02JUN06–1/1
082206
PN=37
Page 40

Operating the Engine
Changing Engine Speeds
To increase speed, push hand throttle (A) forward.
To temporarily increase engine speed above hand throttle
setting, depress foot throttle (B).
CAUTION: Engine should be kept at idling for
30 sec before the RPM is increased, this should
be strictly followed otherwise sudden
acceleration may damage the Turbocharger.
A—Hand Throttle
B—Foot Throttle
PY4485 –UN–16FEB06PY4937 –UN–01JUN06
Warming Up the Engine
Do not place tractor under full load until it is properly
warmed up.
1. Idle engine at about 1200 rpm for 1 to 2 minutes (2 to
4 minutes in cold weather) .
2. Run engine at about 1900 rpm and under light load
until engine reaches normal operation condition.
NOTE: If hydraulic functions are slow, see Warming
Hydraulic Oil in Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
section.
PY80265,05I0127 –19–12SEP05–1/1
PY5775 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0128 –19–02JUN06–1/1
45-5
082206
PN=38
Page 41

Operating the Engine
Restart Stalled Engine
CAUTION: DO NOT run a cold engine at full
throttle. Engine should be kept at idling for 30
sec before the RPM is increased, this should be
strictly followed otherwise sudden acceleration
may damage the Turbocharger.
Should the engine stall when operating under load,
depress clutch (A) and restart it immediately to prevent
abnormal heat build up and continue with normal
operation or operate at slow idle for one or two minutes
before stopping.
CAUTION: Engine should not be shut off at high
RPM, deacceleration should be done slowly &
engine should be kept at idling for 15-30 sec
when the engine is stopped.
PY4001 –UN–06JUN06
A—Clutch Pedal
Avoid Idling the Engine
Allowing engine to idle at low RPM uses fuel inefficiently,
and can cause a build-up of carbon in the engine.
If tractor must be left with the engine running more than
three or four minutes, minimum engine speed should be
1200 RPM.
GENERIC,0000055 –19–11JUL06–1/1
PY5775 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0130 –19–02JUN06–1/1
45-6
082206
PN=39
Page 42

Operating the Engine
Observe Engine Work and Idle Speeds
Slow idle speed should be 800-875 RPM. At light or no
load, full throttle speed will increase to 2500 RPM.
Normal working speed is 1600—2400 RPM rated speed.
Within these limits engine can be put under full load.
For correct PTO speed, run engine at 2376 RPM for
standard 540 RPM operation (load requiring full engine
power).
Working With Speed/Hour Meter
PY5775 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0131 –19–02JUN06–1/1
Tachometer (A) shows engine RPM, read in hundreds.
For 540 RPM PTO speed, increase engine speed until
tachometer needle is aligned with 2376 RPM mark (B).
Hour meter (C) shows hours of operation in full hours and
tenths.
A—Hourmeter
B—2376 RPM Mark (540)
C—Tachometer
PY5776 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0132 –19–02JUN06–1/1
45-7
082206
PN=40
Page 43

Operating the Engine
Stopping the Engine
1. Pull hand throttle (A) down to slow idle position. Allow
engine to idle for one to two minutes.
2. Put gear shift lever in Park position (B).
IMPORTANT: Cooling of certain engine parts is
provided by engine oil. Stopping a hot
engine suddenly could cause damage
to these parts by overheating or lack of
lubrication.
3. Turn key switch to the OFF position.
CAUTION: Engine should not be shut off at high
RPM, deacceleration should be done slowly &
engine should be kept at idling for 15-30 sec
when the engine is stopped for a gap of 1 hr.
Remove key from key switch to prevent
operation by untrained personnel.
Using Booster Battery
Battery gas is explosive:
• DO NOT smoke while charging battery.
• Keep all flames and sparks away.
• DO NOT charge frozen battery.
• DO NOT connect booster battery negative (—) cable to
starting vehicle negative (—) terminal.
1. Access battery. (See procedure in Service section.)
2. Connect positive (+) booster cable to booster battery
positive (+) post (D).
3. Connect the other end of positive (+) booster cable to
tractor battery positive (+) post (A).
PY4501 –UN–13JAN05
A—Hand Throttle
B—Key Switch OFF
PY80265,05I0133 –19–12SEP05–1/1
PY5821 –UN–12JUL06
A—Tractor Battery Positive (+) Post
B—Engine Ground
C—Booster Battery Negative (—) Post
D—Booster Battery Positive (+) Post
4. Connect negative (—) booster cable to booster battery
negative (—) post (C).
5. Connect the other end of negative (—) booster cable to
engine ground (B), away from battery and starter.
45-8
PY80265,05I0134 –19–12JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=41
Page 44

Operator Training Required
Driving the Tractor
• Study the Operation section of this manual before
operating tractor.
• Operate tractor in an open, unobstructed area under
direction of an experienced operator.
Driving on Public Roads
CAUTION: When transporting on a public road
or highway, use accessory lights and devices
for adequate warning to operators of other
vehicles. Check local governmental regulations.
Various safety devices are available from your
John Deere dealer. Keep safety items in good
condition. Replace missing or damaged items.
Observe the following precautions when operating the
tractor on the road:
CAUTION: Before operating tractor on a road,
lock brake pedals together. Use brake lightly
and cautiously at transport speeds.
• Learn use of all controls.
• Operator experience is required to learn moving,
stopping, turning and other operating characteristics
of tractor.
PY80265,05I0135 –19–12SEP05–1/1
PY4938 –UN–21FEB06
A—Brake Pedals Locking Plate
1. Couple brake pedals together using brake locking bar
(A). Avoid hard applications of brakes. Reduce speed if
towed load weighs more than the tractor and is not
equipped with brakes.
Use additional caution when transporting towed loads
under adverse surface conditions and when turning or
braking on inclines. Be sure wheel tread is adjusted
wide to provide maximum stability.
IMPORTANT: To prevent unnecessary wear, never
ride the brakes by resting a foot on the
pedals.
Continued on next page
50-1
PY80265,05I0136 –19–11JUL06–1/2
082206
PN=42
Page 45

Driving the Tractor
2. Check local laws and regulations for lighting
requirements. Be sure turn signal lights (C) and tail
lights (A) are clean and visible.
3. Turn light switch to position (E).
Always turn light switch to dim lights position (E) when
meeting another vehicle. Never use flood lamps or any
other lights which could blind or confuse other drivers.
4. Use turn signal when turning. Be sure to return lever
(F) to center position after turning.
5. Drive slowly enough to maintain safe control at all
times. Before descending a hill, shift to a gear low
enough to control speed without using brakes. Slow
down for rough ground, and sharp turns, especially
when transporting heavy, rear mounted equipment.
PY4883 –UN–22APR05
PY4400 –UN–15JUN06PY4469 –UN–10JAN06
A—Tail Light
B—Reflex Reflector
C—Turn Signal Light
D—Bright Headlight Switch Position
E—Dim Headlight Switch Position
F—Tail Signal Lever
50-2
PY80265,05I0136 –19–11JUL06–2/2
082206
PN=43
Page 46

Operating Transmission
Driving the Tractor
Left Side
PY4000 –UN–10JAN06
A—Range Shift Lever B—Speed Shift Lever
Range shift lever (A) provides three forward speed
ranges, (A,B&C).
Using range and speed shift levers in different
combinations, nine forward speeds and three reverse
speeds can be obtained.
Shifting Transmission
IMPORTANT: To prevent transmission damage, do
not use speed shift on-the-go. To
prevent unnecessary wear, never “ride”
the clutch by resting a foot on the
pedal.
Depress clutch pedal (A) and stop tractor before shifting
either range shift lever or gear shift lever. Release clutch
pedal gradually to take up load smoothly.
A—Clutch Pedal
Right Side
PY3099 –UN–23FEB06
Range shift must be in neutral for the engine to be
started.
PY80265,05I0137 –19–11JUL06–1/1
PY4001 –UN–06JUN06
50-3
PY80265,05I0138 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=44
Page 47

Driving the Tractor
Selecting a Gear
IMPORTANT: To extend drive train life and avoid
excessive soil compaction and rolling
resistance when using ballast, operate
one gear lower than normal.
The tractor may be operated in any gear with engine
speeds between 1400 RPM and 2400 rated engine RPM.
Within these limits the engine can be put under full load.
For light load operation, use a higher gear and lower
engine speed. This saves fuel and reduces wear.
Ground Speed Estimates for different tyre sizes are
located in Specifications section.
Using Brakes
PY5775 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0139 –19–02JUN06–1/1
CAUTION: Before operating tractor on a road,
lock pedals together. Use brake lightly and
cautiously at transport speeds.
Use individual brakes to assist in making sharp turns.
Disengage brake pedal locking bar (A) and depress only
one brake pedal.
To stop tractor, depress both brake pedals.
IMPORTANT: To prevent unnecessary wear, never
ride the brakes by resting a foot on the
pedals.
Reduce speed if towed load is not equipped with brakes
and weighs more than the tractor. Avoid hard braking
applications.Use additional caution when transporting
towed loads under adverse conditions, when turning or
stopping on inclines.
PY4938 –UN–21FEB06
A—Brake Pedals Locking Plate
PY80265,05I0140 –19–12SEP05–1/1
50-4
082206
PN=45
Page 48

Driving the Tractor
Using Differential Lock
CAUTION: DO NOT operate tractor at high
speed or attempt to turn with differential lock
engaged.
IMPORTANT: To prevent damage to drive train, DO
NOT engage differential lock when one
wheel is spinning and the other is
completely stopped by the respective
brake.
When one wheel starts to lose traction, engage differential
lock by depressing pedal (A) down.
Keep the pedal pressed till the traction at both the tyres
equalizes & tractor comes out of the diych. If lock does
not disengage, depress one brake pedal and then the
other.
If tyres repeatedly slip, then get to traction, then slip
again, hold pedal in the engaged position.
PY1202 –UN–11JUN02
A—Differential Lock Pedal
PY80265,05I0141 –19–12SEP05–1/1
50-5
082206
PN=46
Page 49

Driving the Tractor
Stopping Tractor
CAUTION: Always place the range shift lever in
neutral (N) and set brakes before dismounting.
Leaving transmission in gear with engine off
MAY NOT prevent tractor from moving.
1. Stop the tractor and place gear shift lever (A) in Park
position.
2. Apply brakes.
3. Lower all equipment to ground using rockshaft control
levers (C & D).,
4. Pull hand throttle (B) down to slow idle position. Allow
engine to idle for one to two minutes.
IMPORTANT: Cooling of certain engine parts is
provided by engine oil. Stopping a hot
engine suddenly could cause damage
to these parts by overheating or lack of
lubrication.
CAUTION: Remove the key from key switch to
prevent operation by untrained personnel.
5. Turn key switch to OFF position.
A—Gear Shift Lever
B—Hand Throttle
C—Rockshaft Draft Control Lever
D—Rockshaft Position Control Lever
PY1205 –UN–11JUN02
PY1215 –UN–11JUN02PY1469 –UN–28AUG03
50-6
PY80265,05I0142 –19–11JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=47
Page 50

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Match Tractor Power to Implement
IMPORTANT: Tractor power should be matched to the
size of certain implements. Excessive
power can damage an implement, and
too large an implement can damage the
tractor. (Refer to your implement
operators manual for minimum and
maximum power requirements before
attaching an implement.)
3-Point Hitch Components
A—Lift Arms
B—Lift Links
C—Sway Chains
D—Center Link
E—Draft Links
PY80265,05I0143 –19–12SEP05–1/1
55-1
PY4279 –UN–17FEB06
PY80265,05I0144 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=48
Page 51

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Rockshaft Control Levers
The rockshaft position is controlled by two levers, the
rockshaft position control lever (A) and the rockshaft draft
control lever (B)
The rockshaft position control lever (A) raises the hitch
when pulled rearward, and lowers the hitch when moved
forward. See Using Rockshaft Position Control in this
section for more information.
The rockshaft draft control lever (B) controls hitch position
relative to draft loads. See Using Draft Control in this
section for more information.
Setting Position Control Lever Stop
NOTE: Position control lever stop is used when operating
depth or height needs to be repeated.
1. Operate implement for a few minutes to determine
proper depth or height.
2. Loosen lever stop (A), and slide against position
control lever. Lock stop in position by turning in a
clockwise direction. Rockshaft will now lower to same
position each time control lever is pushed forward to
the stop.
PY1470 –UN–28AUG03
A—Rockshaft Position Control Lever
B—Rockshaft Draft Control Lever
PY80265,05I0145 –19–11JUL06–1/1
PY1471 –UN–28AUG03
A—Lever Stop
55-2
PY80265,05I0146 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=49
Page 52

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Using Rockshaft Position Control
CAUTION: To prevent unexpected movement of
rockshaft, place draft control lever (B) in a full
forward position before attaching an implement.
Put draft control lever (B) forward when you DO NOT
want rockshaft to adjust automatically to draft load, such
as attaching implement to tractor.
Use position control lever (A) to control hitch movement
and depth. Position control should be used for the
following applications:
TRANSPORT of implements and end of field turn-around.
Position control lever should be moved fully rearward (C)
for transport for both load and non-load sensing usage.
CONSTANT DEPTH of implements on level terrain and
for non- ground engaging implements such as spreaders
or sprayers. Place position control lever at depth desired
(D).
FLOAT operation for implements with skids or depth
gauge wheels designed to carry full implement weight.
Push both levers all the way forward (E) so implement
can follow the ground contour.
NOTE: Lift links can be adjusted for lateral float. (See
Lateral Float in this section.)
A—Rockshaft Position Control Lever
B—Rockshaft Draft Control Lever
C—Position Control Lever in rearward position
D—Position Control Lever in desired depth position
E—Position Control Lever and Draft Control Lever in
float position
PY1470 –UN–28AUG03M47168 –UN–31JAN92
55-3
PY80265,05I0147 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=50
Page 53

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Using Draft Control
The rockshaft is equipped with variable draft control
system.
Use draft load sensing when:
• Operating with a fully mounted implement in hill and
swale terrain. The implement will raise and lower to
follow the ground contours while maintaining a nearly
constant depth.
• Operating in varying soil conditions. The implement is
raised slightly to get through tough spots so you do not
have to shift to a lower gear.
Draft control lever (B) controls amount of load required
before hitch responds. With lever placed fully forward to
the position marked “off” (C), there is no draft sensing.
Placing the lever toward the rear position reduces the
amount of draft load required to override the position
setting set by the position control lever (A) and raise the
rockshaft.
PY1472 –UN–28AUG03M47169 –19–29JAN92
Draft sensitivity ranges can be changed by repositioning
the center link. (See Positioning Center Link in this section
for additional information.)
For draft load sensing operation:
• Initially place position control lever (A) in its fully
rearward position and the draft control lever (B) in the
fully forward (least draft) position.
• With tractor moving, push position control lever (A)
forward to set implement operating depth. Set position
control lever stop (D) so control lever can be brought
back to the same position. The operating depth set-up
will prevent the rockshaft from lowering all the way
when the tractor begins to slip. Then pull draft sensing
lever (B) rearward until desired draft sensing sensitivity
is obtained.
• The position control lever (A) can also be raised slightly
to override the draft control setting to help get through
slippery spots without getting stuck.
• The position control lever (A) can be moved fully
rearward to raise the hitch at the end of the field.
A—Rockshaft Position Control Lever
B—Rockshaft Draft Control Lever
C—Draft Sensing Off Position
D—Position Control Lever Stop
55-4
PY80265,05I0148 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=51
Page 54

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Adjusting Rockshaft Rate-of-Drop/ Implement lock
CAUTION: Excessive rate-of-drop may cause
damage or injury. Fully lowering implement
should require at least two seconds.
Rockshaft drops faster when a heavy implement is
attached. Adjust rate-of-drop knob so that it is slow
enough to be safe and prevent implement damage.
Turn rockshaft rate-of-drop knob (A), located under the
seat, clockwise to slow rockshaft drop.
Turn knob counterclockwise to increase rate-of-drop.
Rate-of-drop knob is also called implement lock. When
knob is fully screw in, implement will not lower down even
if position control lever is fully down. Use implement lock
while transporting implement.
PY4543 –UN–23JAN05
A—Rockshaft Rate-Of-Drop Knob cum Implement
Lock
Preparing Implement
Category II implements should have the top hole of the
implement mast located 610 mm (24 in.) above the lower
pins. Drill another hole in top mast or extend top mast if
necessary.
Category Mast Width Pin Size
Height Between
Lower Pins
Lower Upper
II 610 mm 824 mm 28.7 mm 25.5 mm
(24 in.) (32-7/16 in.) (1-1/8 in.) (1 in.)
PY80265,05I0149 –19–12SEP05–1/1
PY2274 –UN–07JUN06
PY80265,05I0150 –19–12SEP05–1/1
55-5
082206
PN=52
Page 55

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Positioning Center Link
The draft sensing rockshaft center link attaching bracket
has holes which allow three different positions for
attaching the center link. The position effects the draft
sensing sensitivity.
Standard position is (C).
Move the center link attachment to holes (B) if:
• Excessive hitch activity or hunting occurs in draft control
operation.
• The rear of the implement raises too much when lifted.
The implement weight which can be lifted is reduced
slightly with the center link attachment in the lower
holes.
• The draft control lever range is too small.
Move the center link attachment to holes (C) if:
• The hitch seems unresponsive in draft control operation
and allows the engine speed to drop too far before
raising the rockshaft.
• The rear of the implement droops and drags the ground
as the implement is lifted.
PY4005 –UN–14JUL04
A—Upper Hole
B—Middle Hole
C—Lower Hole
Upper hole (A) eliminates nearly all draft sensing.
NOTE: Implement with Category II mast height 610 mm
(24 in.) will use the upper two holes.
PY80265,05I0151 –19–12SEP05–1/1
55-6
082206
PN=53
Page 56

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Attaching Implements to 3-Point Hitch
1. Be sure drawbar will not interfere. If necessary, move
drawbar ahead, or remove it. Check for any other
potential interference.
CAUTION: Prevent unexpected movement of
rockshaft by placing draft sensing lever in the
forward or OFF position before attaching
implement to hitch.
2. Back tractor up to implement (A) so hitch points align.
Place transmission in neutral (N), stop the engine and
engage brakes BEFORE leaving the tractor seat.
3. Slip draft links over implement hitch pins (B) and retain
with quick-lock pins.
NOTE: Locking pins can be stored on draft links (through
holes in sway chain ears) when not in use.
Align Hitch Point
PY5374 –UN–09DEC05
4. To remove center-link from transport hook, lift center
link locking clip (C) and rotate tab (D) to rear of center
link clip.
5. Attach center link to implement top mast.
6. Adjust center link and lift links as necessary. (See
Leveling the Hitch in this section.)
CAUTION: To avoid bodily injury or machine
damage whenever an implement, implement
quick coupler, or other attachment is connected
to the tractor 3-Point Hitch, check full range of
operation for interference, binding or PTO
separation.
7. Using Rockshaft Position Control Lever (E), lower and
raise implement slowly and check for any point of
interference.
Central Link Locking Clip
PY5375 –UN–09DEC05
PY5530 –UN–22FEB06
Rockshaft Control Lever
A—Implement
B—Implement Hitch Pins
C—Center Link Locking Clip
D—Tab
E—Rockshaft Position Control Lever
F—Rockshaft Draft Control Lever
55-7
GENERIC,000004D –19–11JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=54
Page 57

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Adjusting Hitch Side Sway
NOTE: Check implement operator’s manual for instruction
on whether to allow side sway.
IMPORTANT: DO NOT shorten chains so short that
they do not allow hitch to be raised
completely. If chain prevents hitch from
raising, hydraulic relief valve will open,
causing excessive oil heating, pump
damage or equipment damage.
NOTE: Use spring or rubber strap to keep draft links out
of rear tyres when draft links are not attached to
implement.
Implement side sway should be adjusted when the
rockshaft is raised for transport by loosening the jam nut
on the threaded link (A) and turning the center rod to
increase or decrease the length of chain. Tighten jam nut
again when adjusted.
PY4892 –UN–14APR05
A—Threaded Link
PY80265,05I0153 –19–12SEP05–1/1
55-8
082206
PN=55
Page 58

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Leveling the Hitch
1. Lower implement to take weight off hitch.
IMPORTANT: DO NOT attempt to overextend center
link beyond limits of locking clip or lift
links past the stops. Link body threads
could be damaged.
NOTE: Maximum adjustment range of the center link can
only be obtained if the ends are positioned equally
within the body when attached to an implement.
2. Adjust center link to level implement front-to-rear.
Unlatch locking clip (A). Rotate center link body (B)
clockwise to lengthen center link or counterclockwise to
shorten it. Be sure to latch the locking clip.
3. Adjust right-hand link to level implement side-to-side.
Lift locking handle (C and turn 1/4 turn to engage slot
(D) onto roll-pin in the center portion of the lift link.
PY5285 –UN–24NOV05PY5459 –UN–09JAN06
Turn crank handle clockwise to raise draft link.
Turn crank handle counterclockwise to lower draft link.
After adjustment, lift handle (C) and turn to engage slot
(D) onto the lower body to prevent change of
adjustment during operation.
4. The left-hand lift link is also adjustable in length to
accommodate different tyre sizes.
To change the left-hand lift link length, remove the
upper lift link pin and rotate the upper end assembly
clockwise to shorten or counterclockwise to lengthen,
and then reinstall the upper pin and locking pin.
Adjust left and right lift links to accommodate various
tyre sizes. Set the lift links to have fully-lowered draft
link balls approximately seven inches off the ground for
greatest range of usable hitch motion.
A—Locking Clip
B—Center Link Body
C—Locking Handle
D—Slot
55-9
GENERIC,0000064 –19–08MAR06–1/1
082206
PN=56
Page 59

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Adjusting Lateral Float
To allow the draft link to raise slightly as implement
follows ground contour, place head of float pin and the
rectangular washer on the inside end of the pin in a
vertical position (A).
To hold implement rigid, place head of float pin and the
rectangular washer in the horizontal position (B).
Use lift link pins in the float position for hitch-mounted
implements such as a cultivator or mower, which have
ground gauging skids or wheels which may cause the
implement to twist relative to the tractor.
Use the rigid position for implements such as plows and
ground engaging implements that should not twist relative
to the tractor.
PY5381 –UN–10DEC05
A—Pin In Vertical Position
B—Pin In Horizontal Position
PY5380 –UN–10DEC05
Adjusting Rockshaft Control Lever Friction
A—Adjustment Set Screws
If the rockshaft position control lever or rockshaft draft
control lever do not stay in set position, increase lever
GENERIC,0000042 –19–22FEB06–1/1
PY4406 –UN–10DEC05
friction by tightening the set screws (A) for the
appropriate lever until the proper friction is obtained.
PY4385 –UN–10DEC05
55-10
PY80265,05I0156 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=57
Page 60

Rockshaft and 3-Point Hitch
Warming Hydraulic System Oil
Hydraulic system may be slow to function when tractor is
started in cold weather. This is because cold oil will not
flow as easily through the hydraulic system filter (A).
Steering may be slow until system warms up.
Hydraulic system will function normally when oil warms
up.
IMPORTANT: To prevent damaging hydraulic pump or
relief valve, DO NOT exceed two to
three minutes warm-up time with
steering wheel held in full left or full
right turn position.
1. Depress clutch pedal, start engine and idle at about
1000 RPM.
2. Turn and hold steering wheel in full left or right turn.
A—Hydraulic Oil Filter
PY4407 –UN–22FEB06PY5775 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0157 –19–02JUN06–1/1
55-11
082206
PN=58
Page 61

Remote Hydraulic Cylinders
Use Correct Hose Tips
If your tractor is equipped with a selective control valve
(SCV), the couplers receptacles accept a standard hose
tip as recommended by ISO1and SAE2. Adapters are
available to allow connecting the older John Deere hose
tips to the ISO couplers on your tractor.
1
International Standards Organization
2
Society of Automotive Engineers
Control Lever and Coupler Identification—If Equipped
PY80265,05I0158 –19–12SEP05–1/1
Movement of SCV lever (A) fore and aft operates coupler
receptacles (B).
Coupler has a detented float position when lever (A) is
moved in the fully forward direction.
A— SCV Lever
B—SCV Receptacles
PY5789 –UN–08JUN06PY5792 –UN–08JUN06
PY80265,05I0159 –19–08JUN06–1/1
60-1
082206
PN=59
Page 62

Remote Hydraulic Cylinders
Connecting Hoses
CAUTION: Escaping fluid under pressure can
penetrate the skin causing serious injury. Avoid
the hazard by relieving pressure before
disconnecting hydraulic or other lines. Tighten
all connections before applying pressure.
Search for leaks with a piece of cardboard.
Protect hands and body from high pressure
fluids.
If an accident occurs, see a doctor immediately.
Any fluid injected into the skin must be
surgically removed within a few hours or
gangrene may result. Doctors unfamiliar with
this type of injury should reference a
knowledgeable medical source. Such
information is available from Deere & Company
Medical Department in Moline, Illinois, U.S.A.
1. Remove dust caps (if equipped) from hose end.
X9811 –UN–23AUG88
2. Pull dust plug (A) from couplers.
3. Make sure hose end and coupler receptacles are
clean.
4. Check hoses to see which is used for extending
cylinder. This hose must be connected to a coupler
receptacle (B) in order for cylinder to extend when
SCV levers are moved rearward or inward.
CAUTION: Hydraulic hoses can fail due to
physical damage, kinks, age and exposure.
Check hoses regularly. Replace damaged
hoses. See your John Deere dealer.
5. To connect each hose, push hose tip firmly into
coupler receptacle. Pull lightly on hose to make sure
positive connection was made.
A—Dust Plug
B— Receptacle
PY5796 –UN–08JUN06PY5792 –UN–08JUN06PY5795 –UN–08JUN06
60-2
GENERIC,000004F –19–08JUN06–1/1
082206
PN=60
Page 63

Remote Hydraulic Cylinders
Connecting Single-Acting Cylinder
In order for lever (A) to work properly, a single-acting
cylinder should be connected only to SCV outlet in the
extend position (top coupler) (B).
IMPORTANT: Volume of oil required to extend
cylinder must not lower
transmission-hydraulic oil level below
lower sight glass. Check oil level with
cylinder fully extended. (See Check
Transmission-Hydraulic Oil Level in
Service—50 Hours chapter.)
Push SCV No. 1 control lever full forward to use “float”
position to lower single-acting cylinder.
“Float” position allows a cylinder to extend and retract
freely and uses no engine power.
A—SCV Outlet Lever
B—SCV Outlet
PY5789 –UN–08JUN06PY5797 –UN–08JUN06
Correcting Reversed Cylinder Response
CAUTION: If cylinder response is reversed,
extending when it should retract, reverse
cylinder hose connections at coupler.
Neutral Lever Position
Spring pressure returns lever (A) to a centered position
(except when lever is fully forward in the “Float” position).
When the control levers are in the centered position, the
remote cylinder is hydraulically locked in position.
A—SCV Lever
GENERIC,0000050 –19–20FEB06–1/1
PY80265,05I0162 –19–12SEP05–1/1
60-3
GENERIC,0000051 –19–20FEB06–1/1
PY2245 –UN–20FEB06
082206
PN=61
Page 64

Remote Hydraulic Cylinders
Extending/Retracting Cylinder
Extending Cylinder
Pull lever (A) to the rear of neutral and hold it against
spring pressure. This extends cylinder (B) (up arrow)
connected to couplers and in most cases raises
implement. Lever returns to neutral when released.
Retracting Cylinder
Push lever (A) forward and hold it against spring pressure.
This retracts cylinder (B) connected to SCV couplers and
in most cases lowers implement. Lever returns to neutral
when released.
Float Position
Push lever full forward into detent to operate Float feature.
Float operation allows cylinder to extend and retract
freely, such as when an implement follows ground
contour.
IMPORTANT: When “Float” is not needed, manually
move lever back to neutral position to
prevent accidental use of “Float”.
PY5789 –UN–08JUN06
M47174 –UN–31JAN92
A—Control Lever
B—Extend and Retract Cylinder
GENERIC,0000052 –19–20FEB06–1/1
60-4
082206
PN=62
Page 65

Remote Hydraulic Cylinders
Disconnecting Hoses
1. If possible, retract remote cylinder as much as possible
to protect cylinder rod from damage.
CAUTION: Escaping fluid under pressure can
penetrate the skin causing serious injury. Avoid
the hazard by relieving pressure before
disconnecting hydraulic or other lines. Tighten
all connections before applying pressure.
Search for leaks with a piece of cardboard.
Protect hands and body from high pressure
fluids.
If an accident occurs, see a doctor immediately.
Any fluid injected into the skin must be
surgically removed within a few hours or
gangrene may result. Doctors unfamiliar with
this type of injury should reference a
knowledgeable medical source. Such
information is available from Deere & Company
Medical Department in Moline, Illinois, U.S.A.
X9811 –UN–23AUG88
2. With as much hydraulic pressure relieved as possible
from hoses, pull hoses from couplers.
3. Make sure dust plugs (A) for receptacles and dust
caps for hoses are clean, then install dust plugs.
PY5796 –UN–08JUN06
A—Dust Plug
PY80265,05I0156 –19–08JUN06–1/1
60-5
082206
PN=63
Page 66

Drawbar and PTO
Observe Drawbar / Wagon Hitch Load Limitations
IMPORTANT: Certain heavy equipment, such as a
loaded single-axle trailer, can place
excessive strain on drawbar. Strain is
greatly increased by speed and rough
ground.
Static vertical load on drawbar/wagon
hitch should not exceed 556 kg (1225
lb).
Drive slowly with heavy loads.
Stay Clear of Rotating Drivelines
PY80265,05I0157 –19–12SEP05–1/1
Entanglement in rotating driveline can cause serious injury
or death.
Keep tractor master shield and driveline shields in place
at all times. Make sure rotating shields turn freely.
Wear close fitting clothing. Stop the engine and be sure
PTO driveline is stopped before making adjustments,
connections, or cleaning out PTO driven equipment.
TS1644 –UN–22AUG95
PY80265,05I0158 –19–12SEP05–1/1
65-1
082206
PN=64
Page 67

Drawbar and PTO
Attaching PTO-Driven Implement
CAUTION: Stop engine before attaching
implement or working in area of implement
hitch.
1. Attach implement to tractor before connecting PTO
drive line. Raise hitch to upward position if it is not to
be used.
2. Range shift lever in neutral (N), turn key to OFF
position, pull fuel shut-off knob to stop engine and set
brakes.
3. Attach implement to 3-Point Hitch, be sure drawbar will
not interfere. Remove it if necessary.
4. Rotate PTO shield upward for clearance. With engine
off, turn shaft slightly by hand if necessary to line up
splines. Connect drive line to PTO shaft. Pull out on
shaft to be sure drive line is locked to PTO shaft. Place
PTO shield in downward position.
5. Be sure all shields are in place and in good condition.
Never operate PTO unless master shield is properly
installed. WITH ENGINE STOPPED, check integral
shields on drive line by making sure they rotate freely
on shaft. Lubricate or repair as necessary.
6. Check carefully for any interference, make sure hitch is
raised to the upper position if it is not used.
PY1094 –UN–10APR05
65-2
PY80265,05I0159 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=65
Page 68

Drawbar and PTO
Operating Tractor PTO (Standard)
1. Start engine and push hand throttle lever (A) forward
until tachometer indicates PTO rated speed 2400 RPM
(C) for standard 540 operation.
2. Move control lever (B) forward to engage PTO.
CAUTION: Turn key OFF to stop engine, put
tractor in park position and make sure all
mechanisms have stopped before cleaning out
machine or making any adjustments to PTO
driven implement.
3. Pull control lever back to disengage PTO.
A—Hand Throttle Lever
B—PTO Shift Lever
C—540 Operation Speed
PY4485 –UN–16FEB06PY5534 –UN–22FEB06PY5531 –UN–22FEB06
65-3
GENERIC,000005B –19–11JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=66
Page 69

Drawbar and PTO
Operating Tractor Dual PTO (Optional)
1. Start engine and push hand throttle lever (A) forward
until tachometer indicates PTO rated speed 1782 RPM
(D) for 540E operation or 2400 RPM (E) for standard
540 operation.
2. Move control lever (B) forward to engage PTO.
3. Move control lever (C) forward for economical 540
operation and backward for 540 standard operation.
CAUTION: Turn key OFF to stop engine, put
tractor in park position and make sure all
mechanisms have stopped before cleaning out
machine or making any adjustments to PTO
driven implement.
4. Pull control lever back to disengage PTO.
A—Hand Throttle Lever
B—PTO Lever
C—Economy PTO Lever
D—540E Operation Speed
E—540 Standard Operation Speed
PY4485 –UN–16FEB06PY5535 –UN–22FEB06PY5765 –UN–02JUN06
65-4
GENERIC,000005C –19–02JUN06–1/1
082206
PN=67
Page 70

Drawbar and PTO
Adjusting PTO Clutch Operating Rod
PY4487 –UN–17FEB06
1. Move PTO lever (A) to rearward (disengaged) position.
2. Remove clip pin (B) from rear end of clevis (E).
3. Remove clip pin (H) from forward end of clevis (G).
4. Check for equal thread engagement at clevis (G).
Loosen jam nuts (F) and (C). Turn rod (D) until threads
on each side of clevis are equal. Tighten jam nut (F).
PY5016 –UN–21MAY05PY5019 –UN–21MAY05
5. Loosen jam nut (C) from rear of front clevis (E).
6. Adjust length of arm (D) so the clip pin (B) can be
inserted with the rod pulled forward and the arm pulled
rearward to eliminate free play. Lengthen rod by turn of
the clevis to provide PTO clutch lever free play and
PTO clutch rod travel in fully engaged position to
specification.
Specification
PTO Clutch Lever—Free Play 15 mm........................................................
PTO Clutch Rod (In Fully
Engaged Position)—Travel 14 mm -16 mm................................................
NOTE: Adjust clevis (G) if you cannot make proper
adjustment with clevis (E).
7. Reinstall clip pin (B & H) in clevis (E & G) respectively
and arm (D).
8. Tighten jam nut (C) at clevis.
PTO Clutch Rod (In Fully Engaged Position)
A—PTO Clutch Lever
B—Clip Pin
C—Jam Nut
D—Arm
E—Clevis
F—Jam Nut
G—Clevis
H—Clip Pin
65-5
PY80265,05I0162 –19–20FEB06–1/1
082206
PN=68
Page 71

Planning for Maximum Productivity
Ballast
Proper ballasting is an important factor in tractor
performance. maximum productivity can be achieved
only if tractor weight is appropriate for the job.
John Deere FMO (Fundamentals of Machine
Operations) Tractors, discusses methods of
determining correct tractor weight and ballast selection.
Selecting Ballast Carefully
Match amount of ballast needed for each job. What is
right for one job may be wrong for another job. Ballast
for traction and stability.
Factors determining amount of ballast:
FMO-Machinery Management includes information on
tractor and implement matching and increasing
productivity. .
Your John Deere dealer can assist you with
information on these subjects.
PY80265,05I0163 –19–12SEP05–1/1
• Soil surface-loose or firm.
• Type of implement-integral/semi-integral or towed.
• Travel speed-slow or fast.
• Tractor power output-partial or full load.
• Tyres-single, oversize, or dual.
PY80265,05I0164 –19–12SEP05–1/1
Matching Ballast to Load Work
Use no more ballast than necessary, and remove
ballast when it is no longer needed.
Rather than weighing tractor down to pull heavy loads,
try to reduce load. Pulling a lighter load at a higher
speed is more economical and more efficient.
The best way to check for correct ballast is to measure
amount of travel reduction (% slip) of the drive wheels.
Under normal field conditions, travel reduction should
be 10—15 percent.
Add more weight to drive wheels if slip is excessive. If
there is less than 10 percent slip, weight should be
removed.
Too Little Ballast Too Much Ballast
1. Excessive wheel slip 1. Increased load
2. Power loss due to 2. Power loss due to
churning soil carrying extra weight
3. tyre wear 3. tyre strain
4. Fuel waste 4. Soil compaction
5. Lower productivity 5. Fuel waste
6. Lower productivity
70-1
PY80265,05I0165 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=69
Page 72

Ballast
Measuring Wheel Slip—Manually
1. Place a mark (A) on a rear tyre which is easily
observed (a chalk mark is recommended).
2. With tractor working and implement lowered, mark a
starting point (B) on the ground at the place where the
tyre mark (A) meets the ground.
3. Mark the ground again where the tyre mark (A)
completes 10 full revolutions (C).
4. With implement raised return in the opposite direction.
At the second mark on the ground (C) remark the tyre
(D).
5. While driving the tractor along the same path
(implement raised), count the tyre revolutions required
to reach the starting point (B).
6. Use the return tyre revolutions count and “Wheel
Slippage Chart” to determine slippage. 10—15 percent
is ideal.
PY5516 –UN–17FEB06
7. Adjust ballast or load to give correct slippage.
NOTE: Available horsepower is greatly reduced when
wheel slip drops below 10 percent.
WHEEL SLIPPAGE CHART
Non-Loaded Wheel Estimated % Recommended Action
Revolutions (Step 5) Slip
10 0 Remove Ballast
9-1/2 5 Remove Ballast
9 10 Proper Ballast
8-1/2 15 Proper Ballast
8 20 Add Ballast
7-1/2 25 Add Ballast
7 30 Add Ballast
PY80265,05I0166 –19–21FEB06–1/1
70-2
082206
PN=70
Page 73

Ballast Limitations
Ballast
Ballast should be limited by either tyre capacity or
tractor capacity. Each tyre has a recommended
carrying capacity which should not be exceeded (see
Wheels, Tyres and Treads section). If a greater
amount of weight is needed for traction, a larger tyre
should be considered.
Ballast can be added as either liquid or cast iron.
PY80265,05I0167 –19–12SEP05–1/1
70-3
082206
PN=71
Page 74

Ballasting Front End for Transport
CAUTION: Additional front ballast may be
needed for transporting rear-mounted
implements. When implement is raised, drive
slowly over rough ground, regardless of how
much ballast is used.
CAUTION: Weights are heavy. Use proper lifting
equipment. Up to 6 additional weights, 50
Kg(110 lb)each, can be installed on the basic
weight. Approximate weight of starter weight
(A) is : 65 kg (143 lb). Approximate weight of
QUIK-TATCHa¨weights (D) are 50 kg (110 lb).
Specification
Starter Weight (Ballast)—Weight 65 kg (143 lb) Each...............................
QUIK-TATCH Weight
(Ballast)—Weight 50 kg (110 lb) Each........................................................
IMPORTANT: Tighten the basic weight attaching
screws (A) to 550 N•m (405 lb-ft) and
the screws (C) on front weights (D) to
230 N•m (170 lb-ft).
Ballast
PY2246 –UN–21FEB06
A—Attaching Bolts
B—Starter Weight
C—Nuts
D—Additional Weights
Installing QUIK-TATCH Weights: QUIK-TATCH
weights can be installed on the front of the tractor.
One starter weight and up to 6 QUIK-TATCH weights
can be installed.
1. Install the basic weight (B) with bolts (A).
2. Place additional weights (D) as required. Secure them
with nuts (C).
QUIK-TATCH is a trademark of Deere & Company
PY80265,05I0168 –19–11JUL06–1/1
70-4
082206
PN=72
Page 75

Ballasting Tractor
Ballast
Add weight to front end if needed for stability. Heavy
pulling and heavy rear-mounted implements tend to lift
front wheels. Add enough ballast to maintain steering
control and prevent tip-over.
Determining Maximum Rear Ballast
IMPORTANT: DO NOT overload tyres. If maximum
weight shown in chart is not enough
for safety, reduce load or install
heavier ply tyres.
To extend drive train life, avoid
excessive soil compaction and
rolling resistance, avoid adding too
much ballast. Ballast should never
exceed the weight required to
provide traction for continuous full
Refer to the implement operator’s manual, along with
“Using Implement Codes” in this section, to determine
the minimum number of front weights that are required
for your tractor model.
PY80265,05I0169 –19–12SEP05–1/1
power loads in 3rd gear. Remove
ballast if tractor engine labors when
pulling heavy loads in the third
gears.
Chart shows carrying capacity per tyre.
MAXIMUM LOAD PER WHEEL (Aat 19 psi)
Tyre Size Capacity
Bias Ply Tyres Ply Rating kg (lb)
18.4-30 14 2550 (5628)
Determining Maximum Front Ballast
Use appropriate front ballast for a particular operating
condition. Two-wheel drive tractors should only have
enough ballast to maintain safe steering control.
Remove ballast when it is no longer needed.
Chart shows carrying capacity per tyre.
IMPORTANT: DO NOT overload tyres. If maximum
weight shown in chart is not enough
70-5
PY80265,05I0170 –19–12SEP05–1/1
for safety, reduce load or install
tyres with a higher load rating.
MAXIMUM LOAD PER WHEEL
2-WD
Capacity
Tyre Size Ply Rating kg (lb)
6.5-20 8 550 (1213)
PY80265,05I0171 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=73
Page 76

Ballast
Using Cast Iron Weights
Cast iron weights are available in a 48 kg (106 lb) size.
Weights can be installed on the inside or outside of wheel.
See your John Deere dealer for more information and
recommendations on weight use and placement.
Cast Iron Weights—Weight 48 kg (106 lb)..................................................
Specification
Installing Rear Cast Iron Weights
CAUTION: Optional cast iron weight weighs 48
kg (106 lb). Handle with care! Use appropriate
equipment or have the job done by your John
Deere dealer.
1. Attach first weight to wheel disks.
2. To install additional weights (A), install bolts in previous
weight (B). Rotate the added weight to align bolts with
weight holes (C).
3. Tighten attaching bolts securely. Tighten again after a
few hours service. Check tightness regularly.
M47215 –UN–29JAN92
PY80265,05I0172 –19–12SEP05–1/1
PY1635 –UN–17FEB06
A—Additional Weight
B—Weight
C—Weight Holes
70-6
PY80265,05I0173 –19–17FEB06–1/1
082206
PN=74
Page 77

Using Liquid Weight
Ballast
CAUTION: Installing liquid ballast requires
special equipment and training. Have the job
done by your John Deere dealer or a tyre
service store.
IMPORTANT: NEVER fill tyre to more than 75%
full. More solution would leave too
little air space to absorb shocks.
Damage to tyre could occur.
A solution of water and calcium chloride provides safe,
economical ballast. Used properly, it will not damage
Tyres, tubes, or rims.
Use calcium chloride to prevent water from freezing. A
mixture of 0.6 kg per liter (5.0 lb of calcium chloride
per gal) will not freeze solid above —45°C (—53°F).
Charts on this page show how much each tyre size
holds if filled to 75 % full.
LIQUID WEIGHT FOR FRONT Tyres
With 0.6 kg/L (5 lb/gal) Calcium Chloride Solution
Liquid Weight per tyre
Tyre Size kg (lb)—75% Full
6.5-20 34 (74)
LIQUID WEIGHT FOR REAR TYRES
With 0.6 kg/L (5 lb/gal) Calcium Chloride Solution
Liquid weight per Tyre
Tyre Size kg (lb)—75% Full
18.4-30 414 (912)
PY80265,05I0174 –19–12SEP05–1/1
70-7
082206
PN=75
Page 78

Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Service Tyres Safely
Explosive separation of at tyre and rim parts can cause
serious injury or death.
Do not attempt to mount a tyre unless you have the
proper equipment and experience to perform the job.
Always maintain the correct tyre pressure. Do not inflate
the tyres above the recommended pressure. Never weld
or heat a wheel and tyre assembly. The heat can cause
an increase in air pressure resulting in a tyre explosion.
Welding can structurally weaken or deform the wheel.
When inflating tyres, use a clip-on chuck and extension
hose long enough to allow you to stand to one side and
NOT in front of or over the tyre assembly. Use a safety
cage if available.
Check wheels for low pressure, cuts, bubbles, damaged
rims or missing lug bolts and nuts.
Check Implement-to-Tyre Clearance
IMPORTANT: Check for adequate clearance (A)
between outside diameter of the tyre
and implement with hitch in raised
position.
When large diameter rear tyres are
installed on a tractor with a 3-Point
Hitch, a quick coupler or similar device
may be required to provide adequate
implement-to-tyre clearance.
A—Clearance
PY80265,05I0175 –19–12SEP05–1/1
TS211 –UN–23AUG88
M47177 –UN–31JAN92
PY80265,05I0176 –19–12SEP05–1/1
75-1
082206
PN=76
Page 79

Check Tyre Inflation Pressure
Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Check tyres daily for damage or noticeably low
pressure.
At least every 100 hours of operation, check inflation
pressure with a gauge. Use an accurate gauge having
10 kPa (0.1 bar) (1 psi) graduations.
If tyres contain liquid ballast, use a special air-water
gauge and measure with valve stem at bottom.
NOTE: When furrow plowing or during hillside
operation, tyre pressure can be increased 28
kPa (0.28 bar) (4 psi) ABOVE maximum to
prevent tyre wrinkling or buckling.
IMPORTANT: Always check inflation pressure with
an accurate tyre gauge to prevent
over-inflation. Over-inflation reduces
performance and increases strain of
both tyre and rim.
NOTE: Following inflation information applies to both
front and rear tyres and Tyre Inflation Pressure
Chart.
2. Operation of tyres at the inflation pressures listed
on chart will result in optimum tractive performance
of the tyre/vehicle system. Correctly inflated radial
tyres will show a large deflection of the sidewall or
“cheeks”. This is normal and will not hurt the tyre if
the inflation pressure is maintained.
3. Inflation pressures less than 80 kPa (12 psi) should
be monitored regularly because of the increased
risk of low pressure air leaks (especially due to
leaking valve cores).
4. Tractors operating on steep side slopes should
increase inflation pressures 28 kPa (4 psi) above
the values listed to compensate for lateral weight
transfer.
5. Tyres run as singles in high traction conditions
sometimes experience bead slip if the bead was not
fully seated or if too much lubricant was used to
mount the tyre. Increasing the inflation pressure will
compensate for this condition but will not cause
reduced traction. Consult your tyre dealer if this
problem occurs.
1. All inflation pressures are calculated for 29 km/h
(18 mph) travel speeds for both diagonal (bias) ply
and radial ply tyres.
6. If higher load capacities are needed, contact your
John Deere dealer for tyre manufacturers load and
inflation table information.
PY80265,05I0177 –19–12SEP05–1/1
75-2
082206
PN=77
Page 80

Tyre Inflation Pressure Chart
Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Tyre Inflation Pressure Chart 5310 S
Front Tyres With Little or No Added Weight Mounted Implement
Tyre Size Ply Rating Tread kPa (bar) (psi) kPa (bar) (psi)
6.5-20 8 F2 140 (1.4) (20) 200 (1.9) (29)
Rear Tyres With Little or No Added Weight Mounted Implement
Tyre Size Ply Rating Tread kPa (bar) (psi) kPa (bar) (psi)
18.4-30 14 R1 97 (0.97) (14) 131 (1.31) (19)
With Maximum Ballast or Heavy
With Maximum Ballast or Heavy
PY80265,05I0178 –19–12SEP05–1/1
Tighten Wheel/Axle Hardware Correctly
CAUTION: NEVER operate tractor with a
loose rim, wheel, hub, or axle.
1. After driving tractor about 100 m (109 yd), and
before placing it under load, tighten hardware to
specified torque.
Any time hardware is loosened, tighten to specified
torque.
NOTE: Follow checking procedure when a new tractor
is first used, or wheels have been off.
2. Check hardware after working three hours and
again after 10 hours.
3. Check all hardware frequently and keep it tight.
PY80265,05I0179 –19–12SEP05–1/1
75-3
082206
PN=78
Page 81

Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Tighten Bolts—Adjustable Front Axle
Tighten bolts in the following locations to specifications:
Adjustable Front Axle—
Specification
Axle-to-Knee Bolts—Torque 480 N•m (350 lb-ft)........................................
Adjustable Front Axle—
Disk-to-Flange Bolts—Torque 210 N•m (155 lb-ft).....................................
A—Axle-to-knee
B—Disk-to-flange
PY5528 –UN–21FEB06PY1487 –UN–18JAN06
GENERIC,0000056 –19–21FEB06–1/1
75-4
082206
PN=79
Page 82

Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Tighten Bolts—Rear Axle
Tighten bolts in the following locations to specifications:
Rear Axle Rim-to-Disk—Torque 245 N•m (180 lb-ft)..................................
Specification
Rear Axle Disk-to-Flange—
Torque 550 N•m (406 lb-ft).........................................................................
A—Rim-to-disk bolts
B—Disk-to-flange bolts
C—Stud
D—Nut
PY4282 –UN–06DEC04PY1956 –UN–12JAN04
Observe Rear Wheel Tread Width Limitations
IMPORTANT: Tyres must have at least 25 mm (1 in.)
clearance with fenders (A) and fuel
tank. When large diameter rear tyres are
installed, check clearance between tyre
and fenders .
75-5
PY80265,05I0181 –19–12SEP05–1/1
M47179 –UN–31JAN92
PY80265,05I0182 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=80
Page 83

Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Tread Settings—Multi-Position Rear Wheels
Wheel tread on rear axle with multi-position wheels
can be adjusted by repositioning or exchanging the
rims or by reversing the wheel disks.
Wheel tread can also be adjusted by exchanging the
complete wheel to the opposite side of the tractor (This
maneuver permits the change from disk-dished-in to
disk-dished-out operations without disassembling the
wheel). When changing rear wheels from one side to
the other, the arrow on side wall of tyre points in the
direction of forward rotation.
The relationship of the wheel disk and rim in obtaining
the different tread settings is shown in the diagrams on
the facing page.
A study of these diagrams, before attempting to
change tread settings, will save unnecessary labor.
IMPORTANT: After setting wheel spacing, tighten
rim-to-disk and disk-to-flange bolts.
Drive tractor 100 m (109 yd) and
tighten again.
Specification
Multi-Position Rear Wheels
Rim-to-Disk—Torque 245 N•m (180 lb-ft)............................................
Multi-Position Rear Wheels
Disk-to-Flange—Torque 550 N•m (406 lb-ft)........................................
NOTE: Tread settings are measured at bottom of
centerline.
STEEL DISKS
REAR TREAD WIDTH
Centerline-to-Centerline
Diagram Tyre Sizes
18.4-30
A 1379 mm (54.3 in.)
B 1475 mm (58.1 in.)
C 1579 mm (62.2 in.)
D 1678 mm (66.1 in.)
E 1782 mm (70.2 in.)
75-6
PY80265,05I0183 –19–12SEP05–1/2
IN227 –UN–24MAY00
PY80265,05I0183 –19–12SEP05–2/2
082206
PN=81
Page 84

Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Tread Settings—Adjustable Front Axle
PY5528 –UN–21FEB06
LV1515 –UN–05MAR96
A—Adjustment Holes
Front rims are offset. With some tires, this provides
two tread spacings at each axle setting.
ADJUSTABLE FRONT AXLE TREAD SETTINGS
Tire 123456
1449 mm 1549 mm 1649 mm 1749 mm 1849 mm 1949 mm
6.50-20 (57.0 in.) (61.0 in.) (64.9 in.) (68.9 in.) (72.8 in.) (76.7 in.)
1449 mm 1549 mm 1649 mm 1749 mm 1849 mm 1949 mm
7.50-16 (57.0 in.) (61.0 in.) (64.9 in.) (68.9 in.) (72.8 in.) (76.7 in.)
1468 mm 1568 mm 1668 mm 1768 mm 1868 mm 1968 mm
9.5L-15 (57.8 in.) (61.7 in.) (65.7 in.) (69.6 in.) (73.5 in.) (77.5 in.)
1468 mm 1568 mm 1668 mm 1768 mm 1868 mm 1918 mm
10.0-15 (57.8 in.) (61.7 in.) (65.7 in.) (69.6 in.) (73.5 in.) (75.5 in.)
1473 mm 1573 mm 1673 mm 1773 mm 1873 mm 1973 mm
11L-15 (58.0 in.) (61.9 in.) (65.9 in.) (69.8 in.) (73.7 in.) (77.7 in.)
b
INT
1546 mm 1646 mm 1746 mm 1846 mm 1946 mm
27/9.5-15 (60.9 in.) (64.8 in.) (68.7 in.) (72.7 in.) (76.6 in.)
1477 mm 1577 mm 1677 mm 1777 mm 1877 mm 1977 mm
27/12LL-15 (58.1 in.) (62.1 in.) (66.0 in.) (70.0 in.) (73.9 in.) (77.8 in.)
a
Tread position 1 is with axle adjustment at its most inward location. See Adjust Front Axle Tread Width in this section.
b
Interference (Do not use)
Diagram C
Centerline-to-Centerline
Tread Position
a
Continued on next page
75-7
GENERIC,0000057 –19–21FEB06–1/2
082206
PN=82
Page 85

Wheels, Tyres and Treads
ADJUSTABLE FRONT AXLE TREAD SETTINGS
Diagram D
Centerline-to-Centerline
Tread Position
a
Tire 123456
1583 mm 1683 mm 1783 mm 1883 mm 1983 mm 2083 mm
6.50-16 (62.3 in.) (66.3 in.) (70.2 in.) (74.1 in.) (78.1 in.) (82.0 in.)
1583 mm 1683 mm 1783 mm 1883 mm 1983 mm 2083 mm
7.50-16 (62.3 in.) (66.3 in.) (70.2 in.) (74.1 in.) (78.1 in.) (82.0 in.)
1549 mm 1649 mm 1749 mm 1849 mm 1949 mm 2049 mm
9.5L-15 (61.0 in.) (64.9 in.) (68.9 in.) (72.8 in.) (76.7 in.) (80.7 in.)
1549 mm 1649 mm 1749 mm 1849 mm 1949 mm 2049 mm
10.0-15 (61.0 in.) (64.9 in.) (68.9 in.) (72.8 in.) (76.7 in.) (80.7 in.)
1554 mm 1654 mm 1754 mm 1854 mm 1954 mm 2054 mm
11L-15 (61.2 in.) (65.1 in.) (69.1 in.) (73.0 in.) (76.9 in.) (80.9 in.)
1527 mm 1627 mm 1727 mm 1827 mm 1927 mm 2027 mm
27/9.5-15 (60.1 in.) (64.1 in.) (68.0 in.) (71.9 in.) (75.9 in.) (79.8 in.)
1559 mm 1659 mm 1759 mm 1859 mm 1959 mm 2059 mm
27/12LL-15 (61.4 in.) (65.3 in.) (69.3 in.) (73.2 in.) (77.1 in.) (81.1 in.)
a
Number 1 position is with axle adjustment at its most inward location. See Adjust Front Axle Tread Width in this section.
GENERIC,0000057 –19–21FEB06–2/2
75-8
082206
PN=83
Page 86

Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Adjust Front Axle Tread Width
IMPORTANT: DO NOT place jack under engine oil
pan.
1. Jack up front end of tractor.
2. When making large tread adjustments, loosen cap
screws (E) and adjust the tie rod (A) length with axle
length.
3. Remove two nuts (B), sleeves (D), and cap screws (C)
from front axle (2 on each side).
4. Slide axle knees to desired position. Both sides should
be adjusted to same spacing.
5. Install sleeves (if equipped), cap screws and nuts on
each side. Tighten cap screws to specification.
Specification
Adjustable Front Axle-to-Knee
Bolts—Torque 400 N•m (295 lb-ft)..............................................................
6. Set toe-in. See Check and Adjust Toe-In for your axle
type.
PY5529 –UN–21FEB06
A—Tie Rod
B—Axle Nuts (4 used)
C—Cap Screws (4 used)
D—Sleeve (4 used)
E—Tie Rod Cap Screw
GENERIC,0000058 –19–22FEB06–1/1
75-9
082206
PN=84
Page 87

Checking Toe-In
Wheels, Tyres and Treads
PY4033 –UN–22JUL04
A—Front Axle Toe-In Distance
1. Park machine on level surface.
2. Turn steering wheel so front wheels are in the
straight-ahead position. Stop engine.
3. Measure distance (A) between tyres at hub level in
front of axle. Record measurement and mark the
tyres.
4. Move tractor back about1m(3ft), so mark is at
hub level behind the axle. Again, measure distance
between tyres at same point on tyre. Record
measurement.
5. Determine the difference between front and rear
measurements. If the front measurement is smaller,
toe is “in”. If the rear is smaller, toe is “out”.
6. Distance (A) at front of tyres should be 3—6 mm
less than distance measured for at rear of tyres.
Adjust toe-in if necessary. (See procedure in this
section.)
PY80265,05I0186 –19–12SEP05–1/1
75-10
082206
PN=85
Page 88

Wheels, Tyres and Treads
Adjusting Toe-In
1. Loosen lock nuts (A) and back out the bolts (B) on tie
rod tubes several turns.
2. Adjust tie rods on both sides of the tractor equally by
rotating the inner tube (C) to lengthen or shorten tie
rod. Adjust toe-in to 3 to 6 mm (1/8 to 1/4 in.)
Tie Rod Rotation Approximate Change in Toe-in
1/2 turn 8 mm (5/16 in.)
1 turn 16 mm (5/8 in.)
3. Tighten bolts (B) to specification. Do not overtighten as
damage to the tube may occur.
Specification
Tie Rod Bolts—Torque 85 N•m (62 lb-ft)....................................................
4. Tighten the lock nuts (A) to specification.
Specification
Tie Rod Lock Nuts—Torque 90 N•m (66 lb-ft)...........................................
PY4009 –UN–14JUL04
A—Lock Nuts
B—Tie Rod Bolts
C—Inner Tube
PY80265,05I0187 –19–11JUL06–1/1
75-11
082206
PN=86
Page 89

Transporting
Use Safety Lights and Devices
Prevent collisions between other road users, slow moving
tractors with attachments or towed equipment, and
self-propelled machines on public roads. Frequently check
for traffic from the rear, especially in turns, and use hand
signals or turn signal lights.
Use headlights, flashing warning lights, and turn signals
day and night. Follow local regulations for equipment
lighting and marking. Keep lighting and marking visible
and in good working order. Replace or repair lighting and
marking that has been damaged or lost.
Driving Tractor on Roads
TS951 –UN–12APR90
PY80265,05I0188 –19–12SEP05–1/1
CAUTION: Observe the following precautions
when operating on a road.
1. Before operating tractor on highway be sure tail lights
(A) and flashing turning lights (C) work properly. Install
and use Slow Moving Vehicle (SMV) emblem and
equipment as required for safety and by local
regulations.
A—Tail Light
B—Reflex Reflector
C—Turning Lights
Continued on next page
PY4883 –UN–22APR05
PY80265,05I0189 –19–11JUL06–1/5
80-1
082206
PN=87
Page 90

Transporting
CAUTION: NEVER operate flood lampwhen
transporting tractor. Clear bright light at the
rear of the tractor could confuse drivers of
other vehicles as they approach from the rear.
IMPORTANT: Refer to Lights section for detailed
descriptions of lighting operations and
functions.
2. Turn light switch to high beam headlights or low beam
headlights position. Never use bright lights which are
visible from the rear. Always dim headlights before
meeting another vehicle. Keep headlights properly
adjusted.
PY4106 –UN–23FEB06
A—Lights OFF
B—Parking Lights
C—Dim Headlights
D—Bright Headlights
E—High Beamlight
PY80265,05I0189 –19–11JUL06–2/5
3. Use turn signals when turning. Be sure to return
control lever (A) to center position after turning.
A—Turn Signal Lever
4. Couple brake pedals (A) together before driving on a
road. Avoid hard applications of brakes.
5. Drive slowly enough to maintain safe control at all
times. Slow down for hillsides, rough ground, and
sharp turns, especially when transporting heavy,
rear-mounted equipment.
6. Before going down a hill, shift to a gear low enough to
control speed without using brakes. Never coast down
hill.
PY80265,05I0189 –19–11JUL06–3/5
PY4114 –UN–23FEB06
7. When transporting downhill on icy or graveled grades,
be alert for skids which could result in loss of steering
control. To decrease chance of skids, reduce speed
and be sure tractor has proper ballast.
80-2
A—Brake Pedals
Continued on next page
PY4941 –UN–01JUN06
PY80265,05I0189 –19–11JUL06–4/5
082206
PN=88
Page 91

Transporting
CAUTION: Stopping distance increases with
speed and weight of towed loads, and on
slopes. Towed loads with or without brakes that
are too heavy for the tractor or are towed too
fast can cause loss of control. Consider the
total weight of the equipment and its load.
Observe these recommended maximum road
speeds, or local speed limits which may be
lower:
If towed equipment does not have brakes, do
not travel more than 32 km/h (20 mph) and do
not tow loads more than 1.5 times the tractor
weight.
If towed equipment has brakes, do not travel
more than 40 km/h (25 mph) and do not tow
loads more than 4.5 times the tractor weight.
Ensure the load does not exceed the
recommended weight ratio. Add ballast to
recommended maximum for tractor, lighten the
load, or get a heavier towing unit. The tractor
must be heavy and powerful enough with
adequate braking power for the towed load. Use
additional caution when towing loads under
adverse surface conditions, when turning, and
on inclines.
8. Use caution when operating tractor at transport
speeds. Reduce speed if towed load weighs more than
tractor and is not equipped with brakes. (See Towed
Equipment operator’s manual for recommended
transport speeds.)
LV4042 –UN–09JUL99
9. Use additional caution when transporting towed loads
under adverse surface conditions, when turning and on
inclines.
10. Heavy towed or rear mounted implements may start
swaying in transport. Excessive swaying will result in
loss of steering control. Drive slowly and avoid quick
turns of steering wheel. Refer to your implement
operator’s manual regarding maximum travel speed
limitations.
80-3
PY80265,05I0189 –19–11JUL06–5/5
082206
PN=89
Page 92

Transporting
Transport on Carrier
CAUTION: Chain tractor to carrier securely.
Drive carrier slowly.
The best method of transporting a disabled tractor is to
haul it on a flatbed carrier.
IMPORTANT: Seal exhaust to prevent dirt from
entering and damaging engine.
Towing Tractor
CAUTION: NEVER tow tractor faster than 16
km/h (10 mph). Have an operator steer and
brake tractor.
IMPORTANT: To avoid damaging
transmission-hydraulic system, observe
the following precautions:
1. Be sure transmission-hydraulic system oil is to the full
level line on dipstick (A). If the tractor is to be towed
with the front wheels raised, add 1 liter of oil to
hydraulic fill port for each 90 mm (3-1/2 in.) the wheels
are raised. DO NOT raise front wheels more than 305
mm (12 in.) above ground.
NOTE: After transporting tractor, drain oil that was added
for towing.
2. Make sure the differential lock is disengaged.
PY80265,05I0190 –19–12SEP05–1/1
LV610 –UN–22APR94
PY4942 –UN–21APR05
A—Dipstick
3. Make sure range lever is in neutral and gear lever is in
4th gear.
80-4
PY80265,05I0191 –19–11JUL06–1/1
082206
PN=90
Page 93

Fuels,LubricantsandCoolant
Handle Fuel Safely—Avoid Fires
Use only diesel fuel.
Handle fuel with care, it is highly flammable.
DO NOT refuel machine:
• While you smoke.
• When machine is near open flame or sparks.
• When engine is running. STOP engine.
Fill fuel tank outdoors.
Help prevent fires:
• Clean oil, grease and dirt from machine.
• Clean up spilled fuel immediately.
Do not store machine with fuel in tank in a building where
fumes may reach an open flame or spark.
M73115 –UN–09MAR90
Handle Fluids Safely—Avoid Fires
When you work around fuel, do not smoke or work near
heaters or other fire hazards.
Store flammable fluids away from fire hazards. Do not
incinerate or puncture pressurized containers.
Make sure machine is clean of trash, grease, and debris.
Do not store oily rags; they can ignite and burn
spontaneously.
PY80265,05I0192 –19–12SEP05–1/1
TS227 –UN–23AUG88
PY80265,05I0193 –19–12SEP05–1/1
85-1
082206
PN=91
Page 94

Fuels, Lubricants and Coolant
Diesel Engine Oil
Use genuine engine oil. This oil is available in pack of
1litre and 8.5 litre at John Deere Dealership only
Fuel Storage
PY5149 –UN–21AUG05
GENERIC,000005D –19–22FEB06–1/1
Buy good quality, clean fuel from a reputable supplier.
Proper fuel storage is critically important. Use clean
storage and transfer tanks. Periodically drain water
and sediment from bottom.
Diesel Fuel
Fuel sulphur content should be less than 1.0 percent
preferably less than 0.5 percent. Diesel fuel having
sulphur content higher than 1.0 percent may cause
increase wear on metal engine parts because of acids
produced by sulphur during combustion.
IMPORTANT: If fuel sulphur content exceeds 0.7
percent, the engine oil drain interval
must be reduced by 50 percent to
125 hours.
Avoid storing fuel over long periods of time.
Store fuel in a convenient place away from buildings.
PY80265,05I0194 –19–12SEP05–1/1
Cetane number should be no less than 40 to assure
satisfactory starting and overall performance.
Fitleration of fuel is critical for proper operation of
engine. Use genuine MICO fuel filters. Always change
fuel filter inserts at given interval
85-2
PY80265,05I0195 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=92
Page 95

Fuels, Lubricants and Coolant
Fill Fuel Tank
CAUTION: Handle fuel with care: It is highly
flammable. DO NOT refuel the machine while
smoking or when near open flame or sparks.
Always stop engine before refueling machine.
Fill fuel tank outdoors.
Prevent fires by keeping machine clean of
accumulated trash, grease and debris. Always
clean up spilled fuel.
Fuel tank can be filled through fill cap (A). Fill fuel tank at
end of each day’s operation. This prevents condensation
in tank as moist air cools.
TS202 –UN–23AUG88PY4101 –UN–20AUG04
Fuel Tank—Capacity 68 L..........................................................................
Specification
A—Fuel Tank Filler Cap
Lubricant Storage
Your equipment can operate at top efficiency only
when clean lubricants are used.
Use clean containers to handle all lubricants.
Whenever possible, store lubricants and containers in
an area protected from dust, moisture, and other
contamination. Store containers on their side to avoid
water and dirt accumulation.
PY80265,05I0196 –19–12SEP05–1/1
Make certain that all containers are properly marked to
identify their contents.
Properly dispose of all old containers and any residual
lubricant they may contain.
85-3
PY80265,05I0197 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=93
Page 96

Diesel Engine Coolant
Fuels, Lubricants and Coolant
The engine cooling system is filled to provide
year-round protection against corrosion and cylinder
liner pitting, and winter freeze protection to -37°C
(-34°F). If protection at lower temperatures is required,
consult your John Deere dealer for recommendations.
John Deere COOL-GARD Prediluted Coolant is
preferred for service.
John Deere COOL-GARD Prediluted Coolant is
available in a concentration of either 50% ethylene
glycol or 55% propylene glycol.
Additional recommended coolants
The following engine coolant is also recommended:
• John Deere COOL-GARD Coolant Concentrate in a
40% to 60% mixture of concentrate with quality
water.
John Deere COOL-GARD coolants do not require use
of supplemental coolant additives, except for periodic
replenishment of additives during the drain interval.
Other fully formulated coolants
Other fully formulated low silicate ethylene or
propylene glycol base coolants for heavy-duty engines
may be used if they meet one of the following
specifications:
Other low silicate ethylene glycol base coolants for
heavy-duty engines may also be used if they meet one
of the following specifications:
• ASTM D4985 ethylene glycol base prediluted (50%)
coolant
• ASTM D4985 ethylene glycol base coolant
concentrate in a 40% to 60% mixture of concentrate
with quality water
Coolants meeting ASTM D4985 require an initial
charge of supplemental coolant additives, formulated
for protection of heavy duty diesel engines against
corrosion and cylinder liner erosion and pitting. They
also require periodic replenishment of additives during
the drain interval.
Other coolants
It is possible that neither John Deere COOL-GARD nor
coolants meeting one of the coolant standards listed
above is available in the geographical area where
service is performed. If these coolants are unavailable,
use a coolant concentrate or prediluted coolant with a
quality additive package that provides cylinder liner
cavitation protection and protects the cooling system
metals (cast iron, aluminum alloys, and copper alloys
such as brass) from corrosion.
The additive package must be part of one of the
following coolant mixtures:
• ASTM D6210 prediluted (50%) coolant
• ASTM D6210 coolant concentrate in a 40% to 60%
mixture of concentrate with quality water
Coolants meeting ASTM D6210 do not require use of
supplemental coolant additives, except for periodic
replenishment of additives during the drain interval.
Coolants requiring supplemental coolant additives
COOL-GARD is a trademark of Deere & Company
• ethylene glycol or propylene glycol base prediluted
(40% to 60%) coolant
• ethylene glycol or propylene glycol base coolant
concentrate in a 40% to 60% mixture of concentrate
with quality water
Water quality
Continued on next page
DX,COOL3 –19–27OCT05–1/2
85-4
082206
PN=94
Page 97

Fuels, Lubricants and Coolant
Water quality is important to the performance of the
cooling system. Distilled, deionized, or demineralized
water is recommended for mixing with ethylene glycol
and propylene glycol base engine coolant concentrate.
IMPORTANT: Do not use cooling system sealing
additives or antifreeze that contains
sealing additives.
Use Correct Transmission-Hydraulic Filter Element
To protect systems, replace transmission-hydraulic oil filter
with a John Deere service filter element. Minimum and
maximum performance specifications are printed on John
Deere filters. Other filters may be used if they meet these
performance specifications.
See Lubrication and Maintenance section for
recommended filter change intervals.
IMPORTANT: Do not mix ethylene glycol and
propylene glycol base coolants.
DX,COOL3 –19–27OCT05–2/2
Transmission and Hydraulic Oil
Same oil is used for transmission and hydraulic. Use
HY-GARDtransmission-hydraulic oil. This oil is available
in pack of 1litre and 20 litre at John Deere Dealership only
HY-GARD is a trademark of Deere & Company
85-5
PY80265,05I0201 –19–12SEP05–1/1
PY5149 –UN–21AUG05
PY80265,05I0202 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=95
Page 98

Grease
Fuels, Lubricants and Coolant
Depending upon the expected air temperature range
during the service interval, use grease as shown on
the adjoining table.
John Deere
High-Temperature/Extreme-Pressure/Non-Clay Grease
is recommended.
If other greases are used, they must be greases
meeting SAE Multipurpose High Temperature Grease
with Extreme Pressure (EP) Performance and capable
of operating at compartment temperatures above
150°C (302°F)
At temperatures below —30°C (—22°F), use arctic
greases such as those meeting Military Specification
MIL-G-10942C.
Grease Type Temperature Limits
Arctic Grease Below —10°C (14°F)
SAE(NLGI)#0or#1 0°Cto—30°C (32°Fto—22°F)
SAE (NLGI) #2 50°Cto0°C (122°Fto32°F)
JD High Temperature 50°Cto—10°C (122°Fto14°F)
PY80265,05I0203 –19–12SEP05–1/1
85-6
082206
PN=96
Page 99

ServiceandMaintenance
Observe Service Intervals
Using hour meter (A) as a guide, perform all services at
the hourly intervals indicated on the following pages. Keep
a service record on charts provided in the Lubrication and
Maintenance Record Charts section.
IMPORTANT: Recommended service intervals are for
average conditions. Service MORE
OFTEN if tractor is operated under
adverse conditions.
A—Hourmeter
Break-In Service
PY5777 –UN–02JUN06
PY80265,05I0204 –19–02JUN06–1/1
IMPORTANT: Keep wheel hardware tight to avoid
tractor damage. Check wheel
hardware torque before operating,
twice during first ten hours of
operation, after fifty hours of
operation, and periodically
thereafter.
During the First 10 Hours of Operation:
Perform daily or 10 hours service. (See Service
Intervals in Lubrication and Maintenance section.)
Tighten wheel hardware. (See Wheels, Tyres, and
Treads section.)
After the First 50 Hours of Operation:
1
See Engine Break-In Oil in Service section for additional
information.
Tighten wheel hardware. (See Wheels, Tyres, and
Treads section.)
Check alternator/fan belt tension and tighten air intake
and cooling system hose clamps
Perform 50 Hours Service
After the First 100 Hours of Operation:
Replace transmission-hydraulic filter element
Change engine oil and filter
1
After the First 1100 Hours of Operation:
Replace transmission-hydraulic oil
PY80265,05I0205 –19–12SEP05–1/1
90-1
082206
PN=97
Page 100

Service Intervals
Service and Maintenance
Every 10 Hours
• Check engine oil level
• Check coolant level
• Drain water and sediment from fuel filters
• Lubricate tie rod ends
• Lubricate steering spindles
• Lubricate front axle pivot pin
• Lubricate rear axle bearings
1
1
1
1
Every 50 Hours
• Check transmission-hydraulic system oil level
• Clean and check battery
• Inspect all tyres
• Lubricate front axle pivot pin
• Lubricate steering spindles
• Inspect tractor for loose nuts and bolts
First 100 Hours
• Change engine oil and filter
• Replace transmission-hydraulic filter
Every 250 Hours
• Service air cleaner
• Change engine oil and filter
• Clean and check battery
• Inspect and adjust alternator/fan belt
• Lubricate 3-point hitch
• Check neutral start system
• Check clutch pedal free travel
• Check brake pedal adjustment
Every 500 Hours
• Replace fuel filter
• Replace transmission-hydraulic filter
Every 600 Hours
• Clean engine crankcase vent tube
• Repack front wheel bearings
• Check and tighten all hoses and hose clamps
• Check cooling system for leaks
• Lubricate rear axle bearings
• Check engine idle speeds
• Have your John Deere dealer:
-Check front axle pivot pin
-Adjust engine valve clearance
Inspect fuel injectors
First 1100 Hours
• Change transmission-hydraulic oil and filter
Every 1250 Hours
• Change transmission-hydraulic oil and filter
• Clean transmission-hydraulic pickup screen
Annually
• Change engine oil and filter
• Replace air cleaner elements
Every 2 Years or 2000 Hours (Whichever Comes
First)
• Flush cooling system
Service As Required
• Service air cleaner
• Adjust throttle friction
• Drain water and sediment from fuel tank and fuel
filters
1
Only necessary when operating in extremely wet and muddy
conditions.
90-2
PY80265,05I0206 –19–12SEP05–1/1
082206
PN=98
 Loading...
Loading...