Page 1

This Manual is Bookmarked
Operating Instructions and Parts Manual
Table Saw
Model: JW TS -10
WMH TOOL GROUP
2420 Vantage Drive
Elgin, Illinois 60124 Part No. M-708100
Ph.: 800-274-6848 Revision B2 9/06
www.wmhtoolgroup.com Copyright © WMH Tool Group
Page 2

WARRANTY AND SERVICE
WMH Tool Group, Inc., warrants every product it sells. If one of our tools needs service or repair, one of our
Authorized Service Centers located throughout the United States can give you quick service. In most cases, any of
these WMH Tool Group Authorized Service Centers can authorize warranty repair, assist you in obtaining parts, or
perform routine maintenance and major repair on your JET
your area call 1-800-274-6848.
MORE INFORMATION
WMH Tool Group is consistently adding new products to the line. For complete, up-to-date product information, check
with your local WMH Tool Group distributor, or visit jettools.com.
WARRANTY
JET products carry a limited warranty which varies in duration based upon the product (MW = Metalworking, WW =
Woodworking).
WHAT IS COVERED?
This warranty covers any defects in workmanship or materials subject to the exceptions stated below. Cutting tools,
abrasives and other consumables are excluded from warranty coverage.
WHO IS C OVERE D?
This warranty covers only the initial purchaser of the product.
WHAT IS THE PERIOD OF COVERAGE?
The general JET warranty lasts for the time period specified in the product literature of each product.
WHAT IS NOT COVERED?
Five Year Warranties do not cover woodworking (WW) products used for commercial, industrial or educational
purposes. Woodworking products with Five Year Warranties that are used for commercial, industrial or education
purposes revert to a One Year Warranty. This warranty does not cover defects due directly or indirectly to misuse,
abuse, negligence or accidents, normal wear-and-tear, improper repair or alterations, or lack of maintenance.
HOW TO GET SERVICE
The product or part must be returned for examination, postage prepaid, to a location designated by us. For the name
of the location nearest you, please call 1-800-274-6848.
You must provide proof of initial purchase date and an explanation of the complaint must accompany the
merchandise. If our inspection discloses a defect, we will repair or replace the product, or refund the purchase price,
at our option. We will return the repaired product or replacement at our expense unless it is determined by us that
there is no defect, or that the defect resulted from causes not within the scope of our warranty in which case we will,
at your direction, dispose of or return the product. In the event you choose to have the product returned, you will be
responsible for the shipping and handling costs of the return.
HOW STATE LAW APPLIES
This warranty gives you specific legal rights; you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
LIMITATIONS ON THIS WARRANTY
WMH TOOL GROUP LIMITS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES TO THE PERIOD OF THE LIMITED WARRANTY FOR
EACH PRODUCT. EXCEPT AS STATED HEREIN, ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS ARE EXCLUDED. SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW LONG THE IMPLIED
WARRANTY LASTS, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
WMH TOOL GROUP SHALL IN NO EVENT BE LIABLE FOR DEATH, INJURIES TO PERSONS OR PROPERTY,
OR FOR INCIDENTAL, CONTINGENT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE
OF OUR PRODUCTS. SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMI TATION OF INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
WMH Tool Group sells through distributors only. The specifications in WMH catalogs are given as ge neral information
and are not binding. Members of WMH Tool Group reserve the right to effect at any tim e, without prior notice, those
alterations to parts, fittings, and accessory equipment which they may deem necessary for any reason whatsoever.
® branded products are not sold in Canada by WMH Tool Group.
JET
® t ools. For the name of an Authorized Service Center in
2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Table of Contents....................................................................................................................................3
Warnings ....................................................................................................................... ..........................4
Assembly...............................................................................................................................................11
Unpacking and Cleanup ..................................................................................................................... 11
Stand Assembly .................................................................................................................................11
Assembling the Saw to the Stand.......................................................................................................12
Blade Tilt Point er................................................................................................................................12
Handwheels .......................................................................................................................................13
Extens io n Wing s................................................................................................................................13
Rear Guide Rail..................................................................................................................................13
Front Guide Rail.................................................................................................................................14
Support Rod.......................................................................................................................................14
Switch Bracket...................................................................................................................................15
Extens io n Wing Adjustment................................................................................................................15
Blade Guard and Splitt er ....................................................................................................................15
Install ing /R e p la cing the B lad e .............................................................................................................16
Aligning the Blade Guard and Splitter.................................................................................................16
Table Insert........................................................................................................................................17
Rip Fence..........................................................................................................................................17
Miter Gauge...........................................................................................................................................18
Grounding Instructions...........................................................................................................................19
Electrical Connections........................................................................................................................19
Extension Cord Recommendations.....................................................................................................19
Blade Raising and Tilt Mechanism......................................................................................................20
Adjusting 45º and 90º Positive Stops..................................................................................................20
Operations.............................................................................................................................................21
Table Saws........................................................................................................................................21
Kickbacks.......................................................................................................................................21
Rip Sawi ng .....................................................................................................................................22
Resawing........................................................................................................................................23
Crosscutting....................................................................................................................................23
Align-a-rip ..........................................................................................................................................24
Bevel and Miter Operat ions................................................................................................................24
Safety Devices.......................................................................................................................................25
Feather Board....................................................................................................................................25
Filler Piece.........................................................................................................................................26
Push Stick & Push Bl ock ....................................................................................................................26
Maintenance..........................................................................................................................................27
Cleaning.............................................................................................................................................27
Lubrication .........................................................................................................................................27
Miscellaneous ....................................................................................................................................27
Troubleshooting.....................................................................................................................................28
Parts......................................................................................................................................................29
Wiring Di agram ................................................................................................................. .....................37
Ordering Replacement Parts..................................................................................................................38
3
Page 4

Warnings
1. Read and understand the entire owners manual bef or e attempti ng assem bly or operation.
2. Read and understand the warnings po sted on the m achine and i n thi s manual. Failur e to comply wit h
all of these warnings m ay cause seriou s i njury.
3. Replace the warning labels if they become obscured or removed.
4. This Tabl e Saw is designed and intended f or use by properly trained and ex peri enc ed per sonnel only.
If you are not familiar with the proper and safe operation of a Table Saw, do not use until proper
training and knowledge have been obtained.
5. Do not use this Table Saw for other than its intended use. If used for other purposes, WMH Tool
Group discl aims any real or implied warranty and holds itself harmless from any injury t hat may result
from that use.
6. Always wear approved saf ety glasses/face shi elds whil e using thi s Table Saw. Ever yday eyeglasses
only have impact resi stant lenses; they are not safety glasses.
7. Bef ore operating this Tabl e Saw, remove tie, rings, watches and other j ewelry, and roll sleeves up
past the elbows. Rem ove all loose cl othing and confi ne long hair. Non-sl ip foot wear or anti-ski d floor
strips are recommended. Do not wear gloves.
8. Always use the blade guard on all '' through- sawing'' oper ati ons. A t hrough-sa wing operati on i s one in
which the blade cuts completely through the workpiece.
9. Kickback oc c ur s when the workpiece is thrown towards the operator at a high rate of speed. If you do
not have a clear understanding of kickback and how it occurs, DO NOT operate this table saw!
10. Wear ear protectors (plugs or muffs) during ext ended peri ods of oper ation.
11. Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling and other construction activities
contain chemi cals known to cause cancer , bir th defects or other r eproductiv e harm . Some examples
of these chemic als are:
• Lead from lead based paint.
• Crystalli ne sil ic a from bricks, cement and other m asonry pr oducts.
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically treated lumber.
12. Your risk of exposure varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your
exposure to these chemicals, work in a well-ventilated area and work with approved safety
equipment, such as face or dust masks that are specifically designed to filter out microscopic
particles.
13. Do not operate this machine while tired or under the influence of drugs, alcohol or any medicati on.
14. M ak e c ertain the switch is in the OFF position before connecting the machine to the power supply.
15. M ak e c ertain the machine is properly grounded.
16. M ak e all machine adjustm ents or maintenance with the machine unplugged from the power source.
17. Remove adjusting keys and wrenches. Form a habit of checking to see that keys and adjusting
wrenches are removed from the machine before turning it on.
18. Keep safety guards in place at all times when the machi ne is in use. If removed for maintenance
purposes, use extreme caution and replace the guards immediately.
19. M ak e sure the Table Saw is firmly secured to the floor or bench before use.
20. Check damaged parts. Before further use of the machine, a guard or other part that is damaged
should be carefully checked to determine that it will operate properly and perform its intended
function. Check for alignment of moving part s, binding of moving parts, br eakage of parts, mounting
and any other condi ti ons that m ay affect its operati on. A guard or ot her part that i s damaged shoul d
be properly repaired or replaced.
4
Page 5

Error! Objects canno t be created from editing field codes.
21. P r ov ide for adequate space surrounding work area and non-glare, overhead lighting.
22. K eep the floor around the m achi ne cl ean and free of scrap material, oil and grease.
23. K eep v isitors a safe distanc e from the work area. Keep children away.
24. M ak e y our workshop child proof with padlocks, master switches or by removing starter keys.
25. Giv e your work undivi ded attention. Looking ar ound, carryi ng on a conversation and “ horse-play” ar e
careless acts that can r esul t in serious injury.
26. M aintain a balanced st anc e at all times so that you do not fall into the blade or other moving par ts. Do
not overreach or use excessive force to perform any machine operation.
27. Use the ri ght t ool at the cor rect speed and feed r ate. Do not forc e a tool or attachment to do a job for
which it was not designed. T he ri ght tool will do the job better and safer.
28. Use recom mended accessories; i mproper accessories may be hazardous.
29. Maintain tools with care. Keep saw blades sharp and clean for the best and safest performance.
Follow instructions for lubricati ng and changing accessories.
30. Turn off the mac hine before cleaning. Use a brush or compressed air to remove chips or debri s — do
not use your hands.
31. Do not stand on the machine. Seri ous injury could occur if the machine ti ps over.
32. Never leave the mac hine running unattended. Turn the power off and do not leave the machine until it
comes to a complete stop.
33. Remove loose item s and unnecessary work pieces from the area before starting the machine.
Familiarize you rself with the following safety no ti ces used in this manual:
This means that if precautions are not heeded, it may result in minor injury and/or
possible machine damage.
This means that if precauti ons are not heeded, it may result in serious injury or possibly
even death.
5
Page 6

The most common accident s among table saw users, acco rding to statist ics, can
be linked to kickback, the high-speed expulsion of material from the table that can strike the
operator. Kickback can also result in operator’s hands being pull ed into the blade.
Kickback Prevention
Tips to avoid the most common causes of
kickback:
• Make sure the blade splitter is always
aligned wit h the blade. A workpiece can bind
or stop the flow of the cut if the blade spl itt er
is misaligned and resul t in kickback.
• Use the blade spli tter during every cut. The
blade splitter maintains the kerf in the
workpiece, which will reduce the chance of
kickback.
• Never attempt fr eehand cut s. The workpiece
must be f ed perf ectly parall el with t he blade,
otherwise kickback will likely occur. Always
use the rip fence or crosscut fence to
support the workpi ec e.
• Make sure that the r ip fence is parallel with
the blade. If not, the c hanc es of ki c k bac k ar e
very high. Tak e the time t o check and adjust
the rip fence.
• Feed cuts through to completion. Anytime
you stop feeding a workpiece that is in the
middle of a cut, the chance of binding,
resulting in kickback, is greatly increased.
Pro tection Ti ps from
Kickback
Kickback can happen even if precautions are
taken to prevent it. Listed below are some tips to
protect you if kickback DOES occur:
• Stand to the side of the blade when cutting.
An ejected workpiece usual ly travel s directly
in front of the blade.
• Wear safety glasses or a face shield. Your
eyes and face are the most vul nerable part
of your body.
• Never plac e your hand behind the blade. If
kickback occurs, your hand will be pulled
into the blade.
• Use a push stic k to keep your hands far ther
away from the moving blade. If a kickback
occurs, the push stick will most likely take
the damage that your hand would have
received.
6
Page 7

Features
Specifications
Model Number............................................................................................................................JWTS-10
Stock Num ber ................................................................................................................................ 708100
Blade Diameter.....................................................................................................................................10"
Arbor Diameter....................................................................................................................................5/8"
Maximum Depth of Cut.....................................................................................................................3-1/8"
Maximum Rip to Right of Blade .............................................................................................................30"
Maximum Rip to Left of Blade...............................................................................................................12"
Maximum Depth of Cut at 45° ...........................................................................................................2-1/8"
Table in Front of Blade at Maximum Cut (in) ....................................................................................10-1/2
Maximum Width of Dado..................................................................................................................13/16"
Maximum Diameter of Dado....................................................................................................................8"
Table Height...................................................................................................................................36-1/2"
Table Size (Cast Iron) with Extensions.........................................................................................27" x 44"
Table Size (Cast Ir on) without Extensions....................................................................................27" x 20"
Overall Dimensions (D x W x H)....................................................................................40" x 55-1/2" x 42"
Arbor Speed ............................................................................................................................. 3600 RPM
Motor................................................................................ 115/230V, 60Hz , 1Ph, 1-1/2HP, Prewired 115V
Net Weigh t......................................................................................................................................205 lbs
Gross Weight..................................................................................................................................214 l bs
The specifications in this manual are given as general inform ation and are not binding. WM H Tool Group
reserves the r ight to effect, at any time and without prior notice, changes or alterati ons to parts, fi ttings,
and accessory equipment deemed necessary for any reason whatsoever.
7
Page 8

Definitions And Terminology
Arbor: Metal shaft that connects the drive
mechanism to the blade.
Bevel Edge Cut: Tilt of the saw arbor and blade
between 0° and 45° to perform an angled cutting
operation.
Blade Guard: Mechanism mounted over the
saw blade to prev ent accidental c ontact with the
cutting edge.
Crosscut: Sawing oper ation in which the mi ter
gauge is used to cut across the grain of the
workpiece.
Dado Blade: Blade(s) used f or cutting grooves
and rabbets.
Dado Cut: Fl at bottomed groov e in the face of
the workpiece made wit h a dado blade.
Featherboard: Device used to keep a board
against the rip fence or table that allows the
operator to keep hands away from the saw
blade.
Kerf: The resulting cut or gap made by a saw
blade.
Kickback: An event in which the workpiece is
lifted up and thrown back toward an operator,
caused when a work piece binds on the saw
blade or between the sa w blade and rip f ence
(or other fixed object). To minimize or prevent
injury from kickbacks, see the Operating
Instructions section.
Miter Gauge: A component that controls the
workpiece movement while performing a
crosscut of vari ous angl es.
Non-Through Cut: A sawing operation that
requires the rem oval of the blade guard spl itter,
resulting in a c ut that does not protrude through
the top of the workpiece (includes Dado and
rabbet cuts).
The blade guard and split ter must be re-installed
after performing a non-through cut to avoid
accidental contact with the saw blade during
operation.
Parallel: Position of the rip fence equal in
distance at every point to the side face of the
saw blade.
Perpendicular: 90° (right angl e) intersection or
position of the vertical and horizontal planes
such as the posi tion of the saw blade (v ertical)
to the table surfac e ( hori z ontal).
Push Board/Push St ick: A n instr ument used to
safely push the workpiece through the cutting
operation.
Rabbet: A cutting operation that creates an
L-shaped channel along the edge of the board.
Rip Cut: A cut made along the grain of the
workpiece.
Splitter: Metal pl ate to which t he blade guard i s
attached that maintains the kerf opening in the
workpiece when performing a cutting operation.
Standard Kerf: 1/8" gap made with a standard
blade.
Straightedge: A tool used to check that a
surface is flat or parallel.
Through Sawing: A sawing operation in which
the workpiece thickness is completely sawn
through. Proper blade height usually allows a
1/8" of the top of the blade t o extend above the
wood stock.
Read and understand the entire contents of this manual before attempting
assembly or operat io n! Failure to comply may cause serious injury!
8
Page 9

Shipping Contents
Carton Contents
1 ea Table Saw (not shown)
1 ea Front Rail – Long (A)
1 ea Front Rail – Short (B )
1 ea Extension Wing – Left ( C)
1 ea Extension Wing – Right (D)
1 ea Support Rod with mounting screw
and washer (E)
1 ea Rear Rail – Short (F)
1 ea Rear Rail – Long (G)
1 ea Left Leg – Rear (H)
1 ea Left Leg – Front (J)
1 ea Handwheel – Large Mounting Hole (K)
1 ea Handwheel – Small Mount ing Hole (L)
2 ea Right Leg (M)
2 ea Top Plate – Short (N)
2 ea Top Plate – Long (O)
2 ea Support Plate – Short ( P)
2 ea Support Plate – Long (Q)
1 ea Saw Blade (R)
1 ea Fence (S)
1 ea Table Insert (T )
1 ea Blade Guard Assembl y ( U)
1 ea Miter (V)
Carton Contents
9
Page 10
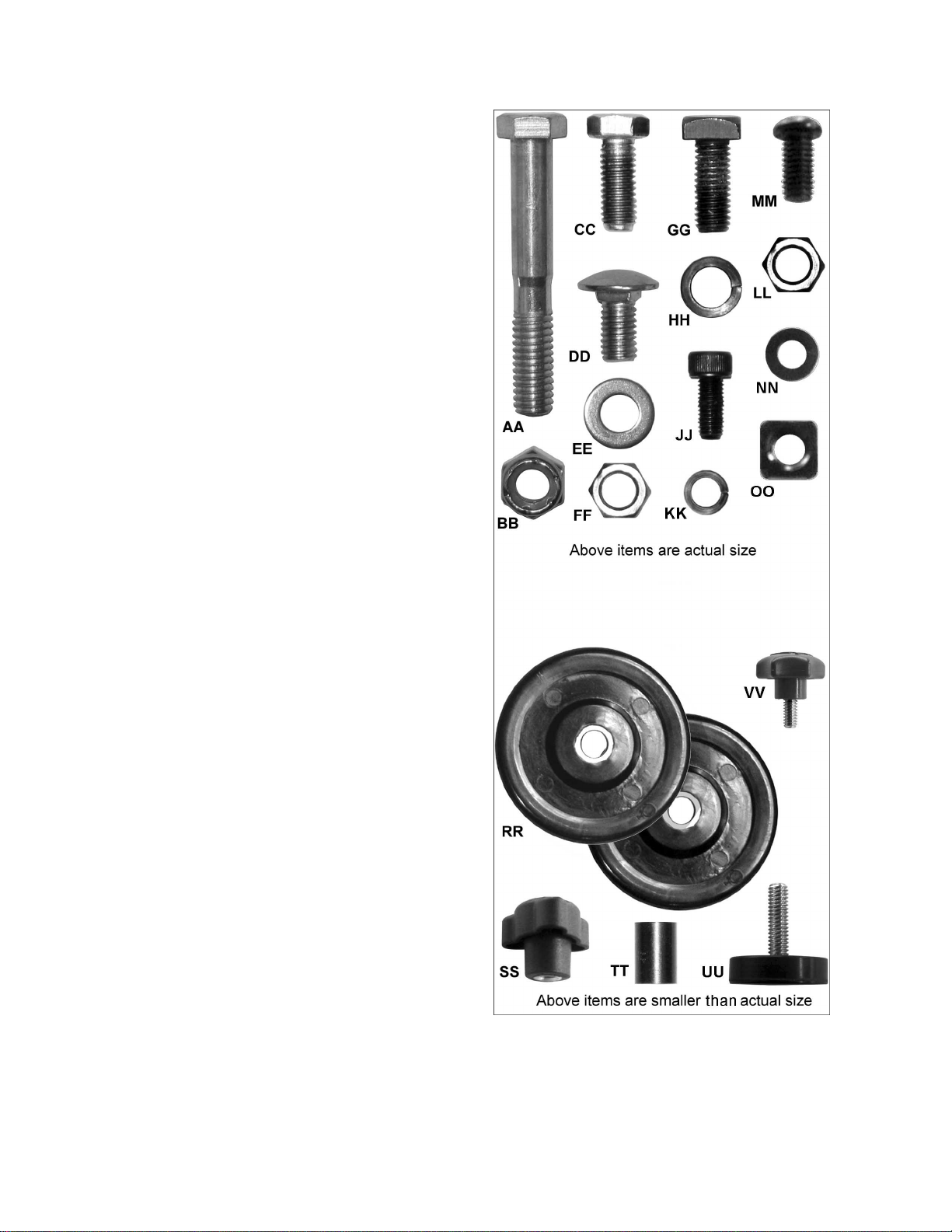
Hardware
The shipping carton includes two hardware bags
with parts f or assembli ng the JWTS-10 Tabl e Saw.
Hardware bag JWT S10-HP cont ains six packets of
parts and JWT S10-SHP contains three packets of
parts. If eit her bag is mi ssing the proper num ber of
packets, contact customer service (phone number
on cover and back pages).
Remove contents from all packets and sort.
Hardware contents can be identified by the
illustration to the right and quantities can be v erified
from the list below.
02 3/8”-16 x 2.5” Hex Cap Screw (AA)
02 3/8” Nylon Insert Lock Nut (B B )
18 M8x20 Hex Cap Screw (CC)
24 M8x12 Carriage Bolt (DD)
36 M8 Flat Washer (EE)
40 M8 Hex Nut (FF)
06 M8 Square Head Bolt (GG)
20 M8 Lock Washer (HH)
01 M5x12 Socket Head Cap Screw (JJ)
01 M5 Lock Washer ( K K)
04 5/16" Hex Nut (LL)
02 M6x10 Pan Head Screw (MM)
02 M6 Washer (NN)
02 M6 Square Nut (OO)
02 Wheel (RR)
01 Lock Knob for Front Handwheel (SS)
01 Bushing (TT)
02 Foot Pad (UU)
02 Lock Knob for Wheels (VV)
Tools Included for Assembly
2 Arbor/Blade G uar d B r acket Wrenc h
1 Hex Wrench (2.5mm)
1 12-14mm Open End Wrench
Addition al Tools Required
1 No. 1 and No. 2 Cross Point Screwdrivers
1 6"– 8" Adjustable W r enc h
1 Accurate Straight Edge (approximately 2 ft )
1 4mm Hex Wrench
1 13mm Box Wrench
Note: Use of sockets and ratchets will speed
assembly time but are not required.
Hardware Content s
10
Page 11
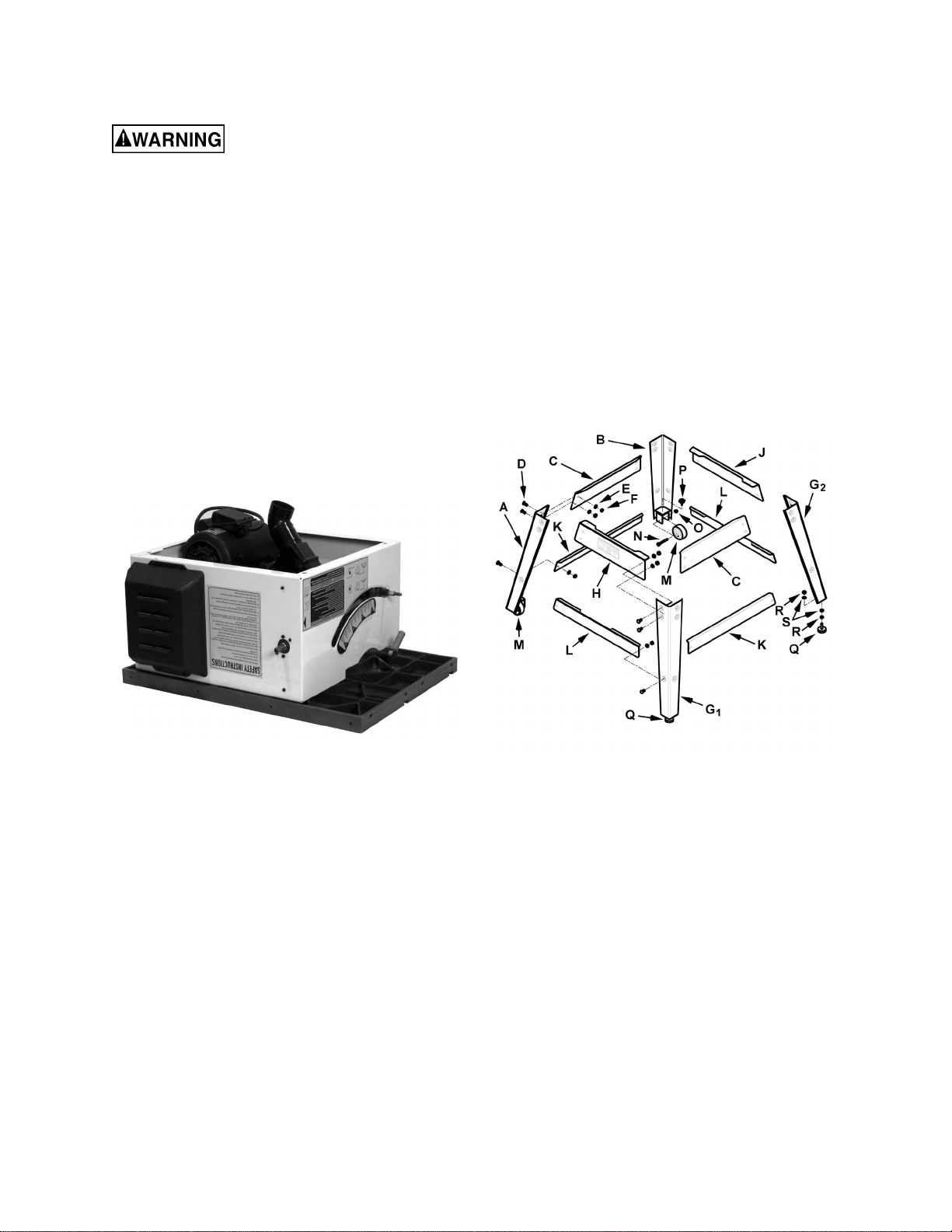
Assembly
Read and understand all
assembly instructions before attempting
assembly! Failure to comply may cause
serious injury!
Unpacking and Cleanup
1. Remove all contents from the shipping carton.
Keep the saw tabl e upside down (Figure 1) and
place on a two-by-f our or similar piec e of wood
under the rear of the saw. This will help when
picking up the t able again. Do not discard t he
carton of packing material until the saw is
assembled and is runni ng satisfactoril y.
2. Inspect the contents for shipping damage.
Report damage, if any, to your distributor.
3. Compare the contents of the shipping carton
with the contents list in this manual. Report
shortages, if any, to y our distr ibutor.
2. Assemble the right legs (G
, G2) to the
1
remaining long top plate (C) in the same
manner.
3. Assemble the short top plate wit h the JET logo
(H) to the front stand legs (A, G
) using the
1
same combination of hardware as used to
attach the long top plates. Hand-tighten the
hardware only at this time.
4. Assemble the remaining short top plate (J) to
the rear stand legs (B, G
) in the same manner.
2
5. Assemble two long support plates (K) to the
inside of the left stand legs (A, B) and right
stand legs (G
, G2) respectively with the same
1
hardware. Hand-tighten only at this time.
Note: The long support plates have no cutouts.
Figure 1
Stand Assembly
Refer to Figure 2.
Tool required – 12mm wrench
Mounting Hardware – the stand (ex cluding wheels)
is assembled usi ng 24 eac h of t he following: M8x16
carriage bolts (D), M8 flat washers (E), and M8
hex nuts (F).
The legs consi st of one lef t front leg, one l eft rear
leg and two right legs. The left legs contain the
wheel mounti ng brackets and are not inter changeable. The ri ght legs are interchangeable. Refer to
Figure 2 for identification and orientation.
1. Assemble the front l eft and rear lef t legs (A, B )
to a long top plate (C) using the mounting
hardware listed above. Hand-tighten only at
this time. The long t op plates hav e no cutouts.
Note: For entire assembly place plates inside legs.
Figure 2
6. Assemble two short support plates (L) to the
inside of the front stand legs (A, G
stand legs (B, G
) respectively with the same
2
) and rear
1
hardware. Hand-tighten only at this time.
Note: The short support pl ates have cutouts.
7. Assemble two wheels (M) t o the left legs with
two 3/8”-16 x 2.5” hex cap screws (N) and two
3/8”-16 nylon insert lock nuts (O) and tighten
with two 13mm wrenches.
8. Place two wheel loc k k nobs ( P ) on the brackets
above the wheels.
9. Attach wheel pad ass emblies to the right l egs
(no wheels), each assembly consisting of one
threaded wheel pad (Q), two 5/16" hex nuts (R)
and two M8 flat washers (S).
11
Page 12
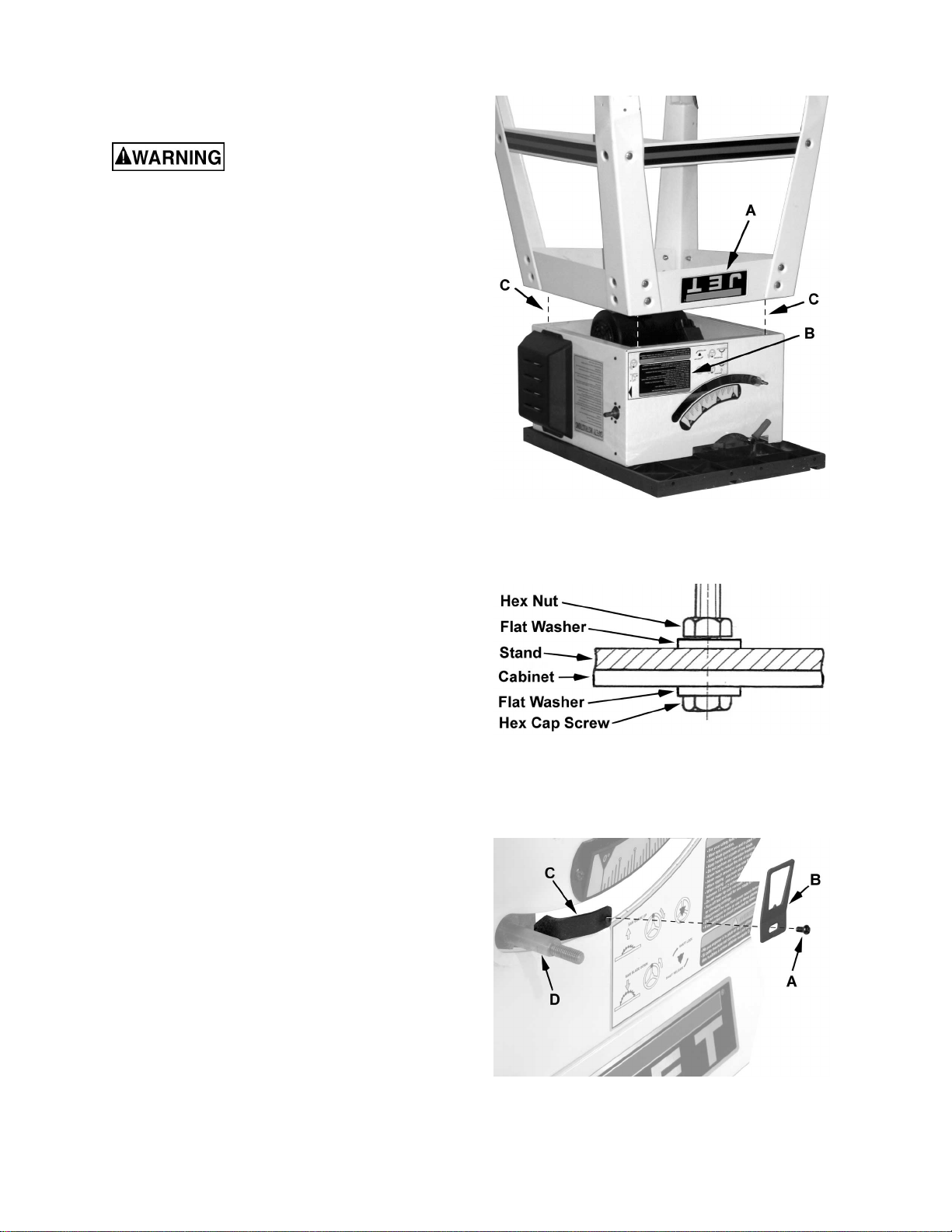
Assembling the Saw to the Stand
Do not plug the table saw into
the power source until all assembly has been
completed! Failure to comply may cause
serious injury!
1. Turn the stand upside down and place ont o the
table saw (Figure 3)
Note: The side with the JET logo (A) is the
front side of the stand and will be on the same
side as the Warning label ( B ) on the table saw.
Line up the holes i n the top pl ates of t he stand
with the holes i n the table saw (C) so t hat the
front of t he stand is f lush with the front of the
saw. The sides of the stand should also be
flush with the si des of the saw.
2. Attach the saw to the stand with four M8x20
hex cap screws, eight M8 flat washers and four
M8 hex nuts using Figure 4 as a guide. Ti ghten
the saw to the stand hardware f irmly.
3. Turn the table saw right side up. Make sure t he
saw is sitting level and with a 12mm wrench
tighten all stand har dware.
Blade Tilt Pointer
Figure 3
Figure 4
Referring to Fi gur e 5:
Secure the blade tilt pointer (B) on the front of the
saw onto the bracket (C) next to the shaft (D) with
an M4 screw (A) and tighten with a cross-point
screwdriver.
Figure 5
12
Page 13

Handwheels
Referring to Fi gur e 6:
The JWTS-10 Tabl e Saw comes equipped with t wo
handwheels which look identical except for the
mounting hol es as follows:
1. On the front of t he table saw slide the bushing
(C) onto shaft (D) followed by the handwheel
(A) with the larger mounting hole, m aking sure
to line up the fl at side in the hole wit h the flat
side on the shaft.
2. Fasten in place wit h lock knob (B).
3. Slide the remaining handwheel (D) with the
smaller mounting h ole onto the shaft (F) on the
right side of the table saw, lining up the fl at side
in the hole with the fl at side on the shaft.
4. Secure wit h an M5 lock washer (E) and M5x12
socket head cap sc r ew (F).
Extension Wings
Referring to Fi gur e 7:
1. Attach the right extension wing (A) to the table
(B) on the right side using four M8 hex cap
screws (C) and four M8 lock washers (D).
Hand-tighten only at this time.
2. Repeat for the left side.
Rear Guide Rail
Referring to Fi gur e 8:
Required Fastening Hardware:
A – 1 ea – Rear Rail (Long)
H – 1 ea – Rear Rail (Short)
E – 6 ea – Hex Cap Screws (M8x20)
F – 6 ea – Lock Washers (M8)
G – 6 ea – Hex Nuts (M8)
Required Tool s:
Two 12mm wrenches
1. Place the long rail (A) agai nst the back of the
right extension (B) and table (C). Line up the
mounting hol es.
2. Insert three hex cap screws (E) through the
rail, extension and table.
3. Place lock washers (F) and hex nuts (G ) on the
threaded ends of the scr ews and hand-t ighten
only at this time.
4. Place the short rail (H) against the back of the
table (C) and left extension (D). Line up the
mounting hol es.
Figure 6
Figure 7
Figure 8
5. Insert three socket head cap screws (E)
through the rail; extension and table.
6. Place lock washers (F) and hex nuts (G ) on the
threaded ends of the scr ews and hand-t ighten
only at this time.
13
Page 14

Front Guide Rail
Referring to Fi gur e 9:
Required Fastening Hardware (see also inset):
A – 6 ea – Square Head Bolt (M8)
B – 6 ea – Lock Washer (M8)
C – 6 ea – Hex Nuts (M8)
Required Tool s:
– 12mm wrench
1. Place six square head bolts (A) through the
mounting holes on the front of the left
extension (F), table (G) and right extension (H).
2. Place lock washers (B) and hex nuts (C) on the
threaded ends of the bolts protruding through
the extensions and table. Just start the hex
nuts but do not tighten.
3. Position all six bolts so that approximat ely 1/4"
of thread is vi sible bet ween the bolt head s and
extensions/table (J).
4. Slide the short rail (D) onto the front edge of
the extension and table from left to right (K).
The back edge of the r ail should make contact
with the f ront edge of the extension and t able
and the square head bolts shoul d slide into the
groove on the back side of t he r ail.
5. In t he same manner described i n step 4, slide
the long rail (E) onto the front edge of the
extension and t abl e from ri ght t o left ( L).
6. Slide the short and long rail sections together
so they become one pi ece. The protrudi ng pins
from the short rail should insert into the
corresponding openings in the long rail.
7. Positi on the entire rail assembl y so the left end
of the rail is about 0.75” i n from the edge of the
left extensi on.
8. Hand-tighten onl y the hex nuts (C) that secure
the front rail to the table.
Support Rod
Referring to Fi gur e 10:
1. Place the tenon end (A ) of the suppor t rod into
the slot (B) of the front rail.
2. Secure the t apped and threaded end (C) of t he
support rod to the rear rail (D) with the M6 flat
washer (E) and M6 hex cap screw (F)
provided.
Figure 9
Figure 10
14
Page 15

Switch Bracket
Referring to Fi gur e 11:
1. Insert two M6x 12 pan head screws (A) through
the back of the switch bracket m ounting holes
(B). Place M6 washers (C) and s quare nuts (D)
on the threaded ends of the screws.
2. Mount the switchbox (C) onto the rail (F) such
that the square nuts (A) slide into the
groove (E) on the lower back si de of t he r ail .
Tighten screws with a c r oss point scr ewdriver.
Extension Wing Adjustment
Referring to Fi gur e 12:
1. Level the left extension wing (B) to the saw
table (C) by using a st raight edge (A). Start by
tightening the three screws (12mm wrench
required) under the extension wing (B) that
secures it to the table (C). Tighten these just
enough to hold the wing in place but loose
enough to change the wing hei ght by tapping
on it.
2. Use the straight edge (A) to level the inside
edge of the ex tension w ing (B) to the table (C).
Tighten the three screws that hold the wings
(B) to the table (C).
Figure 11
3. Nex t bring the straight edge out t o the highest
point on the outside edge of the wing at the
front (A) of the saw. You may have to gr ab the
outside edge of t he ext ension wing and pull up
or push down to lev el. Once the highest point
at the f ront of the saw is locat ed and leveled,
tighten the hardware holding the extension
wing to the front rail.
4. Move the straight edge (D) to the rear of the
same extension wing and repeat this process.
5. Repeat steps 1 – 4 for the right extensi on wing.
Blade Guard and Splitter
Referring to Fi gur e 13:
1. Through the saw table opening on top, locate
two hex nuts (A
plates (B) and loosen with a 10mm wrench.
2. Slide the tab of the blade guard splitter (C)
between the two ret aining plates (B) and onto
the threaded mounting studs (D).
Note: The anti-kickback pawls (E) should be
held back when perf orming this step.
) that secure two retaining
1
Figure 12
3. Tighten the hex nuts (A
) enough to hold the
1
tab (C) in place but l oose enough to allow for
adjustment. You will need to install the blade
before the final adjustment.
Figure 13
15
Page 16

Installing/Replacing the Blade
When inst alling or ch anging the
saw blade, al ways di sconnect the saw f rom the
power source! Failure to comply cay cause
serious injury!
1. Using the handwheels, raise the blade arbor
fully and lock the saw at zero degrees by
tightening the lock knob in the middle of the
hand wheel.
Referring to Fi gur e 14:
2. Using the tools provided, remove the arbor
nut (A) and outer flange ( B). If replacing blade,
remove the old bl ade.
3. Place the blade (C) on the arbor shaft (E)
making sure that the teeth point down at the
front of the saw (note the blade ori entation in
Figure 14). Replace the flange (B) and arbor
nut (A).
4. Tighten the arbor nut (A ).
Aligning the Blade Guard and Splitter
Referring to Fi gur e 15:
1. Raise the blade guard ( A) away fr om the table
and hold the anti-kick pawls (B) away from the
table surface.
2. Pl ace an accurat e strai ght edge (C) against t he
saw blade (D) and splitter (E). For proper
alignment, the blade and splitter should be
perfectly in line with the straight-edge.
If alignment is required:
3. Move the straight-edge aside and through the
opening (see inset ) locate four hex nuts (F, G)
and two retaining plates (H) that secure the
splitter tab (J).
4. Slightly loosen the hex nuts (F, G).
5. To move the splitter (E) right or left, adjust all
four nuts evenly to move the retaining plate
and tab accordingly. To tilt the angle of the
splitter to achieve alignment, adjust the two
front hex nuts (F) or two rear hex nuts (G) only.
6. When adj ustment is complete, tight en the hex
nuts (F, G).
Figure 14
7. Check t he alignment by repeating steps 1 an d
two. If necessary repeat steps 3–8 until proper
alignment is achieved.
Figure 15
16
Page 17

Table Insert
Referring to Fi gur e 16:
1. Raise the blade guard assembly.
2. Lower the blade com pletely.
3. Place the table insert ( A) into the opening wit h
the notched end (B) towards the splitter (C).
A clip underneath t he notch secures the insert
to the tabl e at the rear; a n M5 flat head screw
(E) secures the insert at the front.
4. Adjust the insert (A) flush with the table by
turning f our lev eling setscrews (D) and using a
straight edge (F). A 2.5mm hex wrench is
required to adjust the setscrews.
Rip Fence
Attaching the Rip Fence
Referring to Fi gur e 17:
1. Raise the rip fence handle (A) as shown.
2. Position the rip fence ( B) over the table (C) a s
shown, holding up t he front end while engagi ng
the holding clam p (D) t o the r ear, then loweri ng
the front end (E ) onto the rail (F).
Figure 16
3. Lower the handle (A) t o clamp t he fence to t he
table.
Note: If the rip fence does not hol d onto the rail
tight enough when the handle is lowered,
adjust the hex nut (G) with a 10mm socket.
Calibrating the Rip Fence S c ale
1. Attach the rip fence to the table (as de scribed
in the previ ous section) to the right of t he saw
blade, but do not l ower the handle to cl am p the
fence to the table.
2. Slide the fence against the saw blade.
You will need to raise the blade guar d and the
anti-kick pawl to provide clearance for the
fence.
With the fenc e snug against the saw blade, cl amp
the fence in position by lowering the handle. The
hairline on t he indicator (A) should line up wit h 0"
on the rail (C). If they do not line up:
3. With a 12mm wrench, slightly loosen the six
hex nuts that secure the front rail (F) to the
table (C) and extension wings.
4. Adjust the position of the front rail so the red
hairline indicator (A, Fig. 17) on the fence scale
lines up with 0" (B, Fig. 18) on the rail.
Remember to keep t he fence snug against the
saw blade.
Figure 17
Figure 18
5. When alignment is complete, tighten the six
hex nuts securing the front rail.
17
Page 18

This fence is positioned by lifting up the lock handle
(A, Fig. 19) and sliding to the desired location.
"Fine-tuning" is accomplished by pushing the
micro-adjust k nob in (B, Fig. 19) and at the same
time turning it (C, Fig. 19) until t he ex act positi on i s
read on the scale.
Miter Gauge
Operation
Referring to Fi gur e 20:
Operate the miter gauge by loosening the lock
knob (A) and turning the miter body (B) to the
desired angle.
The pin (C) functions as an index stop. When
pushed in, the body will stop at -45º, 90º or +45º
when turned as one of three screws (D) located
underneath the mit er hits the pin.
Calibration
If a miter angle at the -45º, 90º or +45º is not
correct, the index stops can be adju sted by turni ng
one of three adjustment screws (D), then locking
the hex nut.
Note: Always make test cuts. Do not rely solely on
miter gauge indic ator marks.
Figure 19
Figure 20
18
Page 19

Grounding Instructions
1. All Grounded, Cord-c onnec ted Tools:
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown,
grounding prov i des a path of least resistanc e f or
electric current to reduce the risk of electric
shock. This tool is equipped with an electric cord
having an equipment-grounding conductor and a
grounding plug. The plug m ust be plugged into a
matching outlet that is properly installed and
grounded in accord ance wit h all l ocal codes and
ordinances.
Do not modify the plug provided - if it will not fi t
the outlet , have the proper outlet i nstalled by a
qualified elec trician.
Improper connection of the equipmentgrounding conductor can result in a risk of
electric shock. The conductor with insulation
having an outer surface that is green with or
without yellow stripes is the equipmentgrounding conductor . If repair or replacement of
the electric cord or plug is necessary, do not
connect the equi pment-grounding conductor t o a
live terminal.
3. Grounded, cor d-connected tools intended f or
use on a supply circuit having a nomi nal rati ng
between 150 - 250 volt s, incl usive:
This tool i s intended for use on a ci rcuit t hat
has an outlet t hat l ooks li ke the one i llustr ated i n
Sketch D. The tool has a grounding plug that
looks lik e the plug illustr ated in Sketc h D. Make
sure the tool is connected to an outlet having t he
same configuration as the plug. No adapter is
available or should be used with this tool. If the
tool must be rec onnected for use on a different
type of electric circuit, the reconnection should
be made by qualified service personnel; and
after reconnection, the tool should comply with
all local codes and ordinanc es.
Check with a qualified
electrician or service personnel if the
grounding instructions are not completely
understood, or if in doubt as to whether the
tool is properly grounded. Failure to comply
may cause serious injury or death!
Use only 3-wire extension cords that have 3prong grounding plugs and 3-pole receptacles
that accept the tool's plug.
Repair or replace damaged or worn cord
immediately.
2. Grounded, cor d-connected tools intended f or
use on a supply circuit having a nomi nal rati ng
less than 150 volts:
This tool i s i ntended f or use on a ci rcui t that has
an outlet that looks like the one illustrated in
Sketch A. B and C, may be used to connect thi s
plug to a 2-pol e receptacle as shown in Sketch
B if a properly grounded outl et is not available.
The tempor ary adapter should be used only unt il
a properly grounded outl et can be instal led by a
qualified electrician. (This adapter is not
permitted in Canada) The green-colored rigid
ear, lug, and the like, extending from the adapter
must be connected t o a permanent ground such
as a properly grounded outlet box.
Figure 21
Electrical Connections
The JWTS-10 table saw is rated at 115/230V
and comes from the factory prewired at 115V.
The table saw comes with a pl ug designed for
use on a cir cuit with a gr ounded outlet that looks
like the one pictured in A.
To switch the motor for 230V operation, follow
the wiring di agram found on the inside cov er of
the motor j unction box. The plug on the end of
the motor cord will have to be replaced with a
plug that is rat ed 230V.
Before hooki ng up to t he power source, be sure
the switch is in the off position.
Extension Cord Recommendations
12 Gauge Cord 0 – 25 feet
10 Gauge Cord 0 – 50 feet
8 Gauge Cord 0 – 100 feet
19
Page 20

Adjustments
Blade Raising and Tilt Mechanism
Never try to force the tilting
mechanism past the 45º or 90º stops! This may
cause the blade to go out of alignment!
Referring to Fi gur e 22:
To raise or lower the saw blade, loosen the lock
knob (A) and tur n the handwheel (B) on the front of
the saw until the desir ed height i s reached. T i ghten
the lock knob. The blade should be adjusted
between 1/8" to 1/ 4" above the top surf ace of the
material being c ut.
To tilt the saw blade, turn the lock handle (C)
countercloc kwise to l oosen, tur n the handwheel (D)
on the right si de of the saw until the desired angle
is obtained, then tighten the lock handle (C) by
turning cloc k wise.
Adjusting 45º and 90º Positive Stops
1. Disconnect the saw fr om the power source.
2. Raise the table saw blade to its maximum
height using the handwheel .
Figure 22
3. Set the blade at 90º to the tabl e by turning the
blade tilting handwheel counterclockwise
(D, Fig. 22) as far as it will go. Do not force
beyond stop.
4. Place a square (A, Fig. 23) on the table and
check to see that t he blade (B, F ig. 23) is at a
90º angle to the table. Make sure that the
square is not touchi ng a blade tooth.
If adjustment is required:
5. Back out the 90º adjust setscrew (turn
countercloc kwise) one or t wo turn s wi th a 4mm
hex wrench (C, Fig. 23) .
6. Turn the bl ade tilti ng handwheel until the blade
is exactly 90º.
7. Tighten the 90º adjust setscrew until it stops,
but do not force.
8. Set the blade at 45º to the tabl e by turning the
blade tilting handwheel clockwise (D, Fig. 22)
as far as it will go. Do not force beyond stop.
9. Place a square (D, Fig. 24) on the table and
check to see that t he blade (E, F ig. 24) is at a
45º angle to the table. Make sure that the
square is not touchi ng a blade tooth.
If adjustment is required:
10. Back out the 45º adjust setscrew (turn
counterclockwise) one or two turns with a 4mm
Figure 23
Figure 24
hex wrench (F, Fig. 24).
11. Turn t he blade tilti ng handwheel until the blade
is exactly 45º.
12. Tighten the 45º adjust setscrew until it stops,
but do not force.
Check to make sure that the point er on the fr ont of
the saw properly indicates 45º or 0º (90º). If not,
loosen screw and adj ust until the pointer indicates
properly
20
Page 21

Operations
Table Saws
Familiarize yourself with the location and
operation of all controls and adjustm ents and the
use of accessories such a s the miter gauge and
rip fence.
Kickbacks
Serious injury can result from kickbacks which
occur when a work pi ec e binds on the saw blade
or binds between the saw blade an d ri p fenc e or
other fixed object. This binding can cause the
work piece to lift up and be thrown toward the
operator.
Listed below are conditions, which can cause
kickbacks:
• Confining the cut off piece when crosscutti ng
or ripping.
• Releasing the work pi ece before compl eting
the operation or not pushing the work piece
all the way past the saw blade.
• Not using the splitter when ripping or not
maintaining alignment of the splitter with the
saw blade.
• Using a dull saw blade.
• Not maintaining alignment of the rip fence so
that it tends to angle toward rather than
away from the saw blade fr ont t o bac k.
• Applying feed force when ripping to the
cutoff (free) section of the work piece
instead of the section between the saw
blade and fence.
• Ripping wood that is twisted (not flat), or
does not have a strai ght edge, or a twisted
grain.
To minimize or prev ent injury from kickbacks:
Figure 25
Dull, badly set, improper, or improperly filed
cutting tool s and cutting tools with gum or resin
adhering to them can cause accidents. Never
use a cracked saw blade. The use of a sharp,
well maint ained, and correc t cutting tool for the
operation will help to avoid injuries.
Support the work properly and hold it firmly
against the gauge or f ence. Use a push stick or
push block when ri pping short, narrow (6" widt h
or less), or thin work. Use a push block or miter
gauge holddown when dadoing or molding.
For increased safety in crosscutting, use an
auxiliar y wood faci ng (Figur e 26) att ached t o the
miter gauge using the holes provided in the
gauge.
• Avoid conditions listed above.
• Wear a safety face shield, goggles, or
glasses.
• Do not use the m it er gauge and ri p fence i n
the same operation unless provision is made
by use of a f acing board on the f ence so a s
to allow the cutoff section of the workpiece
to come free before the next cut is started
(See Figure 33).
• As the machine rec eives use, the operation
of the anti-kickback pawls should be
checked periodically (Figure 24). If the pawls
do not stop the reverse motion of a
workpiece, resharpen al l the points.
• Where possible, keep your face and body
out of line wit h potential kickbacks includi ng
when starting or stopping the machine.
Figure 26
Never use the fence as a length stop when
crosscutti ng. Do not hold or touch the f ree end
or cutoff section of a workpiece. On throughsawing operations, t he cutoff section must NOT
be confined.
Always keep your hands out of the line of the
saw blade and never reach back of the cutti ng
blade with either hand to hold the workpiece.
Bevel rippi ng cuts should always be made with
the fence on the right si de of the saw blade so
that the blade tilts away from the fence and
minimizes the possi bili t y of the work bi ndi ng and
the resulting kickback.
21
Page 22

Rip Sawing
Ripping is where the work piece i s fed with the
grain into the saw blade using the fence as a
guide and a positioning device to ensure the
desired width of cut (Figure 27).
Figure 27
Before startin g a ripping cu t,
be sure the fence is clamped securely and
aligned properly.
• Never rip freehand or use the mi ter gauge in
combination with the fence.
• Never rip workpi ec es shorter than the saw
blade diamet er.
• Never reach behind the blade with either
hand to hold down or remove the cutoff
piece with the saw blade rotat ing.
Always use the blade guard, splitter and antikickback pawls. Make sure the splitter is
properly aligned. When wood is cut along the
grain, the kerf tends to close and bind on the
blade and kickback s can occ ur .
on the front rail, or by measuring the distance
between the blade (B ) and fence (A ). Stand out
of line with the saw blade and workpiece to
avoid sawdust and splinters coming off the blade
or a kickback, if one shoul d oc c ur .
If the work pi ece does not hav e a straight edge,
nail an auxiliary straight edged board on it to
provide one again st the fence. To c ut properly,
the board must make good contact with the
table. If it is warped, tur n the hollow side down.
In ripping, use one hand to hol d the board down
against the fence or fixture, and the other to
push it into t he bl ade between the bl ade and the
fence. If the workpiece is narrower than 6" or
shorter than 12", u se a push stick or push block
to push it through between the fence and saw
blade (Fi gure 29). Nev er push in a loc ati on such
that the pushing hand is in line with the blade.
Move the hand serving as a hold-down a safe
distance from the blade as the cut nears
completion. For very narrow ripping where a
push stick cannot be used, u se a push block or
auxiliary fence. Always push the workpiece
completely past the blade at the end of a cut to
minimize the possibility of a kickback.
Note: A caution decal is installed on the guard
and splitter assembly warning of the hazard of
misalignment.
Figure 28
The rip fence (A, Fig. 28) should be set for the
width of t he cut (C, Fig. 28) by using the scale
Figure 29
Figure 30
22
Page 23

When ripping l ong boards, use a support at the
front of the tabl e, such as a roller stand, and a
support or "tailman" at the rear as shown in
Figure 30.
Never use the rip f ence beyond the point where
the carriage i s flush with the end of the rails.
Have the blade ext end about 1/8" abov e the t op
of the workpiece. Exposi ng the blade abov e this
point can be hazardous.
Resawing
Resawing is a ripping operation in which thick
boards are cut i nto thi nner ones. Narrow board s
up to 3" can be resawed in one pass. Wider
boards up to 6" must be resawed in two passes.
In resawing wider boards, adjust the blade
height so as to overl ap the two cuts by 1/2" as
shown in Figure 31. Too deep a first cut can
result in binding and possible kickbacks on the
second cut. Always use the same side of the
board against the fence for both cuts.
Crosscutting should never be done freehand nor
should the fence be used as an end stop unless
an auxili ary block is clamped t o the front of the
blade area such that t he cut off piece comes f ree
of the block before cutting starts (Figure 33).
Figure 33
Length stops should not be used on the free end
of the workpiece in the cutoff area.
Do not crosscut workpieces shorter than 6".
Before starti ng a cut, be sure the mit er gauge is
securely cl amped at the de sired angle. Hold the
workpiece firmly against the table and back
against the miter gauge. Always use the saw
guard and spli tter and make sure the spli tter is
properly aligned.
Figure 31
Crosscutting
Crosscutting i s where the workpi ece i s f ed cross
grain into the saw blade using the miter gauge to
support and position the workpiece (Figure 31) .
For 90 degree crosscutting, most operators
prefer to use the left-hand miter gauge slot.
When using it i n this position, hold the workpiece
against the gauge wi th t he lef t hand and use the
right hand to advance the workpiece. When
using the right hand slot for miter and c ompound
crosscutting so that the blade tilt s away f rom th e
gauge, the hand positions are reversed.
When using the miter gauge, the workpiece
must be held firml y and advanced smoot hly at a
slow rate. If the workpiece is not held firmly, it
can vibrate c ausing it to bind on the blade and
dull the saw teeth.
Figure 32
Figure 34
23
Page 24

To improve t he effec tiveness of the mit er gauge
in crosscutting, some users mount an auxiliary
wooden extension f ace (with a glued-on strip of
sandpaper) to the miter gauge as shown in
Figure 34.
Provide auxiliary support for any workpiece
extending beyond t he table top with a tendency
to sag and lift up off the table.
Stop rods can be used in the hol es provided in
the miter gauge for repetitive work of equal
length. Do not use a stop rod on the f ree end of
a workpiece. It should be used on the side of the
miter gauge opposite the saw blade.
Have the blade ext end about 1/8" abov e the t op
of the workpiece. Exposi ng the blade abov e this
point can be hazardous.
Align-a-rip
same manner as ripping or crosscutting except
the fence or miter gauge shoul d be used on the
right-hand side of the saw blade to provide
added safety in avoiding a binding action
between the saw bl ade and the tabl e top. W hen
beveling with the miter gauge, the workpiece
must be held firml y to prevent creeping.
The yellow align-a-rip pad on the saw table is
used for creating a mark that lines up the
workpiece with the saw blade. After the first
workpiece is cut with the miter gauge, turn the
saw off and pull the miter gauge together with
the workpiece back. The workpiece must be
unmoved and still against the miter fence. The
cut edge of the workpiece is pul led over the pad
and the pad can be marked with a pencil
(A, Fig. 35). Now, when cutting the next marked
workpiece, the workpiece can be lined up with
the line on the pad and cut.
Figure 36
Crosscut – Crosscut s made at an angl e to the
edge of the workpiece are called miters
(Figure 37). Set the miter gauge at the required
angle, lock the miter gauge, and make the cut
the same as a normal crosscut except the
workpiece must be held extra firmly to prevent
creeping.
Note: When making compound miters (with
blade tilted) use the miter gauge in the right
hand slot to provide more hand clearance and
safety.
Have the blade extend only 1/8" above the top of
the workpiece. Exposing the blade above this
point can be hazardous.
Figure 35
Bevel and Miter Operations
Bevel Cut – A bevel cut is a special type of
operation where the saw blade is tilted at an
angle less than 90 degrees to the table top
(Figure 36). Operations are performed in the
Figure 37
24
Page 25

Dado Cutting – Dadoing is cutting a wide
groove into a workpiece or cutting a rabbet
along the edge of a workpiece. A dado insert,
shown in Figure 38, is necessary for this type of
operation.
A dado insert (stock # 708098) designed to fit
the JWTS-10 Table Saw can be ordered from
your dealer or WMH Tool Group.
Do not use the standard table
insert for dadoing operations.
Safety Devices
Feather Board
The feather board (Figure 39) should be made
of straight grain hardwood approximately 1" thick
and 4" to 8" wide depending on t he size of the
machine. The length i s developed i n ac c or danc e
with intended use. Feather boards can be
fastened to the table or rip fence by use of
C-clamps. Alt ernat iv ely, drill ed and tapped h ol es
in the tabl e top allow the use of wing nut s and
washers as a m ethod of clamping. If this method
of fasteni ng is used, provi de slots in the f eather
board for adjustment. (The illustration shows a
method of attaching and use of the feather
board as a vertical comb. The horizontal
application is essentially the same except that
the attachment is to the table top.)
Figure 38
The process of cut ting 1/8" to 13/16" groov es in
workpieces is accomplished by the use of a
stacked dado blade set or an adjustable type
blade mounted on the saw arbor. By using
various combinations of the stacked dado
blades, or properly setting the dial on an
adjustable blade, an accurate width dado can be
made. This is very useful for shelving, making
joints, tenoning, etc. The guard, splitter, and
anti-kickback pawls supplied with the saw
should be used f or all cutting operations where
they can be used. W hen performing operati ons
where the guard can not be used, as in some
dadoing operations, alternative safety
precautions should be taken. These include
push sticks, f eather boards, filler pieces, fixtures,
jigs and any other appropriate device that can
be utiliz ed to keep operator's hands away f rom
the blade. Upon completion of the operation
requiri ng removal of the guard, the entire guard
assembly m ust be placed back on the m achine
in its proper working or der .
Figure 39
Never use a dado head in a
tilted posi tion . Never operate the saw wi thou t
the blade guard, splitter and anti-kickback
pawls for operations where they can be
used.
25
Page 26

Filler Piece
Push Stick & Push Block
A filler piec e (Figure 40) is necessary for nar row
ripping and permits the blade guard to remain on
the machine. It also provides space f or the safe
use of a push stick.
Figure 40 – Filler Piec e
The use of a pus h block or push stick provides
an added level of safet y for the operator.
See the templates in Figures 41 and 42 for
construction details, or purchase one from the
JET, Performax and Powermatic Woodworking
Machinery and Acces s or ies catalog.
Figure 41 – Push Block Tem plate
Figure 42 – Push Stick Template
26
Page 27

Maintenance
Always disconnect power to the machine before performing maintenance. Failure
to do this may result in serious personal injury.
Cleaning
Clean the JWTS-10 according to the schedule
below to ensure maximum performance.
Note—The following maintenance schedule
assumes the saw is being used ever y day .
Daily:
• Wipe down the table surface and grooves
with a rust preventive.
• Clean the pitch and resin from the saw
blade.
Weekly:
• Clean the motor housing with compressed
air.
• Wipe down the fence rails with a dry silicon
lubricant.
Lubrication
Lubricate the areas indicated below every 12
months.
• Lubricate blade angling trunnions with 6 or 7
drops of light machine oil.
• Lubricate t he bl ade height trunnion with 6 or
7 drops of light mac hine oil.
• Worm gears and threads should be
lubricated with an automotive wheel bearing
grease.
Check all adjustments after lubricating.
Miscellaneous
Always be aware of the condition of your
machine. Routinely check the condition of the
following items and repair or replace as
necessary:
• Mounting bolts
• Power switch
• Saw blade
• Blade guard
27
Page 28

Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Correction
Low voltage. Check power line for proper voltage. Motor will not st art
Motor will not st art: fuses
or circuit breakers blow.
Motor stalls resulting in
blown fuses or tripped
circuit.
operating.
Loud, repetitious noise
coming from machine.
Open circuit in motor or loose
connection.
Short circuit in line cord or plug. Inspect cord or plug for damaged insulation
Short circuit in motor or loose
connections.
Incorrect fuses of circuit breakers in
power line.
Motor overloaded. Reduce load on motor. Motor overheats.
Air circulation through the motor
restricted.
Short circuit in motor or loose
connections.
Low voltage. Correct the low voltage conditions.
Incorrect fuses of circuit breakers in
power line.
Motor overloaded. Reduce load on motor.
Applying too much pressure to
workpiece.
Belts lo ose. Tighten belts.
Pulley setscrews or keys are missing
or loose.
Motor fan is hitting the cover. Tighten fan or shim cover.
Inspect all lead connections on motor for
loose or open connections.
and shorted wires.
Inspect all connections on motor for loose or
shorted terminals or worn insulation.
Install correct fuses or circuit breakers.
Clean out motor to provide normal air
circulation.
Inspect connections on motor for loose or
shorted terminals or worn insulation.
Install correct fuses or circuit breakers.
Feed workpiece slower. Machine slows when
Inspect keys and setscrews. Replace or
tighten if necessary.
Blade is not square with
the miter slot or fence is
not square to the blade.
when sliding on the table.
degrees.
V-belt is defective. Replace V-belt.
Blade is warped. Replace saw blade.
Table top is not parallel to the blade. Adjust table parallel to the blade.
Fence is not parallel to the blade. Adjust fence parallel to the blade.
Front rail is bolted too low to the table. Raise the front rail. Fence hits the table top
Rear rail is bolted too low on the table. Raise the rear rail.
90 degree stop bolt is out of
adjustment.
Pointer bracket is hitting before the
blade reaches 90 degrees.
Adjust the 90 degree stop bolt. Blade does not reach 90
File down the right side of the pointer
bracket until the blade can reach 90
degrees.
28
Page 29

Parts
JWTS-10 Table and Cabinet Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
1...............JWTS10-301........... Table................................................................. ...................................1
2...............JWTS10- 3 0 2........... Extension Wing , Left.......................................... ...................................1
3...............JWTS10- 3 0 3........... Extension Wing , R ig h t........................................ ...................................1
4...............JWTS10-304........... Guide Line Pl ate................................................ ...................................1
5...............TS-2285121............Flat Head Screw................................................M5x12........................1
6...............TS-1524051............Set Screw.......................................................... M8x20........................2
7...............TS-1522011............Set Screw.......................................................... M5x5..........................4
8...............JWTS10- 3 0 8........... Table Inse r t....................................................... ...................................1
9...............TS-1490031............Hex Cap Screw
10.............TS-2361081............ Lock Washe r *...................................................M8..............................8
11.............JWTS10-311........... Cover................................................................. ...................................1
12.............TS-1532032............ Pan Head Screw................................................ M4x10........................4
13.............JWTS10-313........... Cabinet.............................................................. ................................... 1
14.............JWTS10-172........... External Tooth Lock Washer.............................. M8..............................3
15.............TS-1490021............ Hex Cap Screw..................................................M8x16........................3
................. JWTS10-BG............ Blade G uar d Assembly (#16 thru #26)................ ...................................1
16.............JWTS10-316........... Warning Label ................................................... ...................................1
17.............JWTS10-317........... Push Nut............................................................ ...................................4
18.............JWTS10-318........... Blade G uard...................................................... ...................................1
19.............JWTS10-319........... Pin..................................................................... ...................................1
20.............JWTS10-320........... Support Arm...................................................... ...................................1
21.............JWTS10-321........... Anti-Kickback Pawl............................................ ...................................2
22.............JWTS10-322........... Bushing............................................................. ...................................2
23.............JWTS10-323........... Spring Pin.......................................................... Ø4x20.........................1
24.............JWTS10-324........... Pin..................................................................... ...................................1
25.............JWTS10-325........... Splitter............................................................... ...................................1
26.............JWTS10-326........... Spring................................................................ ...................................1
................. JWTS10-MG...........Miter Gauge Assembly (#27 thru #40)................ ...................................1
27.............JWTS10-327........... Handle............................................................... ...................................1
28.............TS-0680041............ Flat Washer....................................................... 3/8”.............................1
29.............JWTS10-329........... Miter Gauge Body.............................................. ...................................1
30.............TS-2284202............ Pan Head Screw................................................ M4x20........................3
31.............TS-1540021............ Hex Nut.............................................................M4..............................3
32.............TS-1533032............ Pan Head Screw................................................ M5x10........................1
33.............JWTS10-333........... Pointer............................................................... ...................................1
34.............JWTS10-334........... Bracket.............................................................. ...................................1
35.............JWTS10-335........... Stop Pin............................................................. ...................................1
36.............JWTS10-336........... Screw................................................................ ...................................1
37.............JWTS10-337........... Miter Bar............................................................ ...................................1
38.............JWTS10-3 38........... Guide Washe r.................................................... ...................................1
39.............JWTS10-339........... Flat Head Screw................................................M6x8..........................1
40.............JWTS10-340........... Scale................................................................. ...................................1
41.............JWL1442-118.......... Switch................................................................ ...................................1
42.............JWTS10-342........... Switch Box......................................................... ...................................1
43.............JWTS10-217........... Self Tapping Screw ............................................ M4x8..........................3
44.............JWTS10-344........... Power Cord ....................................................... ...................................1
45.............JWTS10-242........... Square Nut *...................................................... ...................................2
46.............TS-1550041............ Flat Washer *..................................................... M6..............................2
47.............JWTS10-347........... Switch Box Plate................................................ ...................................1
48.............TS-1534032............ Pan Head Screw * ............................................. M6x10........................2
49.............JWTS10-349........... Cord Strain Relief .............................................. SB8R-3.......................2
*
* ............................................... M8x20........................8
*
* Refer to Note on page 32
29
Page 30

JWTS-10 Table and Cabinet Exploded View
30
Page 31

Motor and Trunnion Assembly Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
1...............VB-A31...................Belt.................................................................... A-31 ...........................1
2...............JWTS10-102........... Belt.................................................................... 125J ...........................1
3...............TS-2342102............Nylon Insert Lock Nut......................................... M10-1.25P..................1
4...............TS-1550071............Flat Washer....................................................... M10............................1
5...............JWTS10-105........... Pulley................................................................ ...................................1
6...............JWTS10-106........... W asher.............................................................. ...................................1
7...............BB-6202VV.............Ball Bearing.......................................................6202-2NSE.................2
8...............JWTS10- 108........... Wave Washer.................................................... BWW-6202.................1
9...............JWTS10-109........... Retaining Ring, External. ................................... STW-15......................2
10.............JWTS10-110........... Pulley ................................................................ ...................................1
11.............BB-6002VV.............Ball Beari ng.......................................................6002-2NSE.................2
12.............JWTS10-112........... Retaining Ring, External .................................... STW-17 ......................1
13.............JWTS10-113........... Shaft.................................................................. ...................................1
14.............JWTS10-114........... Bearing Arm...................................................... ...................................1
15.............JWTS10-115........... Arbor ................................................................. ...................................1
16.............JWTS10-116........... Key.................................................................... 5x5x8..........................1
17.............TS-1541041............ Nylon Insert Lock Nut......................................... M10............................1
18.............TS-1550071............ Flat Washer....................................................... M10............................2
19.............TS-1503091............ Socket Head Cap Screw.................................... M6x40 ........................2
20.............TS-1491031............ Hex Cap Screw..................................................M10x25......................1
21.............TS-2361101............ Lock Washe r......................................................M10............................1
22.............JWTS10-122........... Pin..................................................................... ...................................1
23.............JWTS10-123........... Center Trunnion................................................. ...................................1
24.............JWTS10-1 2 4........... Hex Flange Bolt.................................................M6x40........................1
25.............JWTS10-125........... Spring................................................................ ...................................1
26.............TS-1550041............ Flat Washer....................................................... M6..............................2
27.............TS-1540041............ Hex Nut.............................................................M6..............................2
28.............TS-1541021............ Nylon Insert Lock Nut......................................... M6.............................. 4
29.............JWTS10-129........... Plate.................................................................. ...................................2
30.............TS-2210801............ Hex Cap Screw..................................................M10x80......................1
31.............JWTS10-131........... Blade................................................................. 10”x5/8”x28T..............1
32.............JWTS10-132........... Flange ............................................................... ...................................1
33.............JWTS10-133........... Arbor Nut........................................................... 5/8”-12........................1
34.............JWTS10-134........... Blade Dust Cover............................................... ...................................1
35.............JWTS10-135........... Wing Screw.......................................................M5x30........................ 4
36.............990805.................... Self Tapping Screw............................................ M4x10........................2
37.............JWTS10-137........... Dust Chute........................................................ ...................................1
38.............JWTS10-138........... E-Clip ................................................................ ETW-8........................1
39.............JWTS10-139........... Bolt.................................................................... ...................................1
40.............JWTS10-140........... Handle............................................................... ...................................1
41.............JWTS10-141........... Spring................................................................ ...................................1
42.............JWTS10-1 4 2........... Lock Washe r ...................................................... ...................................1
43.............JWTS10-143........... Guide Shaft....................................................... ...................................1
44.............JWTS10-144........... Knob
45.............JWTS10-145........... Handle Cap ....................................................... ...................................2
46.............JWTS10-146........... Handle............................................................... ...................................2
47.............JWTS10-147........... Shaft.................................................................. ...................................2
48.............JWTS10-148........... Hand Wheel....................................................... ................................... 1
49.............JWTS10-149........... Bushing
50.............TS-1502021............ Socket Head Cap Screw.................................... M5x10 ........................2
51.............JWTS10-151........... Plate.................................................................. ...................................1
52.............JWTS10-152........... E-Clip ................................................................ ETW-12......................2
53.............JWTS10-153........... Shaft.................................................................. ...................................1
54.............JWTS10-154........... O-Ring............................................................... P12.............................2
*
* Refer to Note on page 32
*
* ............................................................... ................................... 1
*........................................................... ...................................1
31
Page 32

Motor and Trunnion Assembly Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
55.............JWTS10-1 55........... Wave Washer....................................................WW-16.......................1
56.............TS-1532042............ Pan Head Screw................................................ M4x12........................2
57.............JWTS10-157........... Scale................................................................. ...................................1
58.............TS-1540031............ Hex Nut.............................................................M5..............................2
59.............JWTS10-159........... Collar................................................................. ...................................1
60.............JWTS10-160........... Support Bracket................................................. ...................................1
61.............TS-2284082............ Pan Head Screw................................................ M4x8..........................1
62.............JWTS10-162........... Pointer............................................................... ...................................1
63.............JWTS10-163........... Bracket.............................................................. ...................................1
64.............TS-1550031............ Flat Washer....................................................... M5..............................2
65.............TS-1533032............ Pan Head Screw................................................ M5x10........................4
66.............990805.................... Self Tapping Screw............................................ M4x10........................4
67.............JWTS10-167........... Shaft.................................................................. ...................................1
68.............JWTS10-168........... Hand Wheel....................................................... ................................... 1
69.............TS-1551031............ Lock Washe r
70.............TS-1502031............ Socket Head Cap Screw
71.............TS-1490041............ Hex Cap Screw..................................................M8x25........................6
72.............JWTS10-172........... External Tooth Lock Washer.............................. M8..............................6
73.............JWTS10-173........... Front & Rear Trunnion....................................... ...................................2
74.............JWTS10-174........... Motor………………………………………….1-1/2HP, 1Ph, 115/230V.......1
................. JWTS10-174MF...... Motor Fan (not shown)....................................... ...................................1
................. JWTS10-174MFC....Motor Fan Cover (not shown)............................. ...................................1
................. JWTS10-174CS...... Centrifugal Switch (not shown)........................... ...................................1
................. JWTS10-174SCC.... Starting Capacitor Cover (not shown)................. ................................... 1
................. JWTS10-174RCC....Running Capacitor Cover (not shown)................ ...................................1
................. JWTS10-174SC...... Starting Capacitor (not shown)........................... 200MFD, 250VAC.......1
................. JWTS10-174RC...... Running Capacit or (not shown).......................... 30uF, 350VAC............1
................. JWTS10-174JB....... Junction Box (not shown)................................... ...................................1
................. JWTS10-174JBC .... Junction Box Cover (not shown)......................... ...................................1
75.............JWTS10-175........... Pulley ................................................................ ...................................1
76.............TS-1523041............ Set Screw.......................................................... M6x12........................2
77.............JWTS10-177........... Key.................................................................... 5x5x22........................1
78.............JWTS10-1 78........... Motor Wire......................................................... ...................................1
79.............JWTS10-1 7 9........... Box Wrench
80.............JWTS10-180........... Blade Locking Wrench
81.............JWTS10-181........... Motor Cord Cl amp ............................................. ...................................1
82.............JWTS10-182........... Pan Head Screw................................................ M4x15........................1
83.............TS-1540021............ Hex Nut.............................................................M4..............................1
................. JWTS10-HP............ Hardware Package (not shown)......................... .....................................
*....................................................M5..............................1
*..................................................... ...................................1
*.................................. M5x12 ........................2
*..................................... ...................................1
* Note: Items indicated by an asterisk (*) are included in Hardware Package JWTS10-HP
32
Page 33

Motor and Trunnion Assembly Exploded View
33
Page 34

Fence and Rail Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
................. JWTS10-FA............ Fence Assembly (#1 thru #39)........................... ...................................1
1...............JWTS10-201........... Handle Cap ....................................................... ................................... 1
2...............JWTS10-202........... Micro Adjustment Handle................................... ................................... 1
3...............JWTS10-203........... Spring................................................................ ...................................1
4...............JWTS10-204........... Bushing............................................................. ...................................1
5...............JWTS10-205........... Pan Head Screw ................................................ M5x8..........................2
6...............JWTS10-206........... Bracket.............................................................. ...................................1
7...............JWTS10-207........... Push Nut............................................................ ...................................1
8...............JWTS10-208........... Rubber Wheel.................................................... ...................................1
9...............TS-1533062............Pan Head Screw................................................ M5x20........................1
10.............JWTS10-210........... Shaft.................................................................. ...................................1
11.............TS-1503051............ Socket Head Cap Screw.................................... M6x20 ........................2
12.............JWTS10-212........... Bracket.............................................................. ...................................1
13.............JWTS10-213........... Spring Pin.......................................................... Ø8x40.........................1
14.............JWTS10-214........... Handle Cap ....................................................... ...................................1
15.............JWTS10-215........... Handle............................................................... ...................................1
16.............JWTS10-2 1 6........... Cam Block......................................................... ...................................1
17.............JWTS10-217........... Self Tapping Screw ............................................ M4x8..........................4
18.............JWTS10-218........... Slide Block......................................................... ...................................2
19.............JWTS10-219........... Block ................................................................. ...................................2
20.............JWTS10-220........... Fence Body....................................................... ...................................1
21.............JWTS10-221........... Cursor ............................................................... ...................................2
22.............TS-1550031............ Flat Washer....................................................... M5..............................2
23.............JWTS10-205........... Pan Head Screw................................................ M5x8..........................2
24.............TS-1503021............ Socket Head Cap Screw.................................... M6x10 ........................2
25.............JWTS10-225........... Fence................................................................ ...................................1
26.............JWTS10-226........... Rod ................................................................... ...................................1
27.............JWTS10-227........... Plate.................................................................. ...................................1
28.............TS-0680031............ Flat Washer....................................................... 5/16”...........................1
29.............JWTS10-229........... Spring................................................................ ...................................1
30.............JWTS10-230........... Rear Lock Block................................................. ...................................1
31.............JWTS10-231........... Tightening Plate................................................. ...................................1
32.............TS-1550021............ Flat Washer....................................................... M4..............................2
33.............TS-1532032............ Pan Head Screw................................................ M4x10........................2
34.............JWTS10-234........... Fence Rear Cover............................................. ...................................1
35.............TS-1540041............ Hex Nut.............................................................M6..............................1
36.............JWTS10-236........... Mod. Screw....................................................... ...................................1
37.............JWTS10-237........... Washer.............................................................. ................................... 1
38.............JWTS10-238........... Spring Pin.......................................................... Ø6x40.........................1
39.............JWTS10-239........... Self Tapping Screw ............................................ M4x16........................4
40.............990805.................... Self Tapping Screw............................................ M4x10........................4
41.............JWTS10-241........... Rail End Cover, Left........................................... ...................................1
42.............JWTS10-242........... Square Nut ........................................................ M6..............................2
43.............TS-1534032............ Screw................................................................M6x10........................2
44.............JWTS10-244........... Front Rail, Short................................................. ...................................1
45.............JWTS10-245........... Adaptor Pin........................................................ ...................................2
46.............JWTS10-246........... Front Rail, Long................................................. ...................................1
47.............JWTS10-247........... Rail End Cover, Right........................................ ...................................1
48.............JWTS10-248........... Square Head Bolt
49.............TS-2361081............ Lock Washe r *...................................................M8............................12
50.............TS-1540061............ Hex Nut *........................................................... M8............................12
51.............TS-1490031............ Hex Cap Screw *...............................................M8x20........................6
52.............JWTS10-252........... Rear Rail, Short................................................. ...................................1
*
*............................................M8x20........................6
*
* Refer to Note on page 32
34
Page 35

Fence and Rail Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
53.............JWTS10-253........... Rear Rail, Long.................................................. ...................................1
54.............TS-1550041............ Flat Washer....................................................... M6..............................2
55.............JWTS10-255........... Support Rod ...................................................... ...................................1
56.............TS-1482021............ Hex Cap Screw..................................................M6x12........................1
57.............TS-1550041............ Flat Washer....................................................... M6..............................1
Fence and Rail Exploded View
35
Page 36

Stand Assembly Parts List and Exploded View
Index No. Part No. Description Size Qty
1...............TS-1540061............Hex Nut1**......................................................... M8............................28
2...............JWTS10-402........... Leg.................................................................... ...................................2
3...............JWTS10-403........... Top Plate, Short................................................. ...................................2
4...............JWTS10-404........... Support Plate, Short........................................... ...................................2
5...............JWTS10-405........... Support Plate, Long........................................... ...................................2
6...............JWTS10-406........... Top Plate, Long................................................. ...................................2
7...............JWTS10-407........... Pad **................................................................ ...................................2
8...............TS-1550061............Flat Washer **................................................... M8............................36
9...............JWTS10-409........... Carriage Bolt **.................................................. M8x12 ......................24
10.............TS-1490031............ Hex Cap Screw **.............................................. M8x20........................4
11.............JWBS18-140........... JET Nameplate.................................................. ...................................1
12.............JWTS10-412........... Caster Mount Leg, Rear..................................... ...................................1
13.............JWTS10-413........... Caster Mount Leg, Front.................................... ...................................1
14.............TS-0060111............ Hex Cap Screw **.............................................. 3/8"-16x2.5"................2
15.............JWTS10-415........... Lock Knob **...................................................... ...................................2
16.............JWTS10-416........... Wheel **............................................................ ...................................2
17.............TS-0640091............ Nylon Insert Lock Nut **..................................... 3/8”-16........................2
18.............TS-0561021............ Hex Nut **.......................................................... 5/16”-18......................4
................. JWTS10-SHP..........Hardware Package (not shown)......................... .....................................
1
** Included in JWTS10-SHP Stand Har dware Package
36
Page 37

Wiring Diagram
ELECTR IC AL SC HE MAT IC - 115V
200MFD 250 VAC
30MFD 350 VAC
BLACK
WHITE
GREEN
BLACK
WHITE
GREEN
ELECTR IC AL SC HE MAT IC - 230V
YELLOW
RED
BLACK
200MFD 250 VAC
30MFD 350 VAC
BLACK
WHITE
WHITE
GREEN
RED
BLACK
BLACK
YELLOW
WHITE
WHITE
GREEN
BLACK
WHITE
GREEN
BLACK
WHITE
GREEN
GROUND
37
Page 38

Ordering Replacement Parts
To order parts or reac h our servic e depar tment, call 1-800-274-6848 between 7:30am and 5:30pm (CS T),
Monday through Fr iday. Having the Model Number and Seri al Number of your machine avail able when
you call will all ow us to serve y ou quic kl y and ac c ur ately.
38
Page 39

Notes
39
Page 40

WMH Tool Gr ou p
2420 Vantage Drive
Elgin, Illinois 60124
Phone: 800-274-6848
www.wmhtoolgroup.com
40
 Loading...
Loading...