Page 1

OWNER’S MANUAL
JWP-16OS Woodworking Planer
WMH Tool Group
Consumer Woodworking Division
2420 Vantage Drive
Elgin, IL 60123
Ph: 888-594-5866 ▪ Fax: 800-626-9676 M-708531 Rev A 10/03
www.wmhtoolgroup.com Copyright © WMH Tool Group
1
Page 2
This manual has been prepared for the owner and operators of a JET Model JWP-16OS Planer. Its
purpose, aside from proper machine operation, is to promote safety through the use of accepted
operating and maintenance procedures. Completely read the safety and maintenance instructions before
operating or servicing the machine. To obtain maximum life and efficiency from your planer, and to aid in
using the machine safely, read this manual thoroughly and follow all instructions carefully.
Warranty
WMH Tool Group warrants every product it sells. If one of our tools needs service or repair, one of our
Authorized Repair Stations located throughout the United States can give you quick service.
In most cases, any one of these WMH Tool Group Repair Stations can authorize warranty repair, assist
you in obtaining parts, or perform routine maintenance and major repair on your JET, Performax,
Powermatic or Wilton tools.
For the name of an Authorized Repair Station in your area, call 1-800-274-6848.
More Information
WMH Tool Group is consistently adding new products to the line. For complete, up-to-date product
information, check with your local WMH Tool Group distributor or visit wmhtoolgroup.com.
Limited Warranty
WMH Tool Group (including JET, Performax, Powermatic and Wilton brands) makes every effort to assure
that its products meet high quality and durability standards and warrants to the original retail
consumer/purchaser of our products that each product be free from defects in materials and workmanship
as follows: 1 YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY ON ALL PRODUCTS UNLESS SPECIFIED OTHERWISE.
This warranty does not apply to defects due directly or indirectly to misuse, abuse, negligence or
accidents, normal wear-and-tear, repair or alterations outside our facilities, or to a lack of maintenance.
WMH TOOL GROUP LIMITS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES TO THE PERIOD SPECIFIED ABOVE, FROM
THE DATE THE PRODUCT WAS PURCHASED AT RETAIL. EXCEPT AS STATED HEREIN, ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR MERCHANTIBILITY AND FITNESS ARE EXCLUDED. SOME STATES DO
NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW LONG THE IMPLIED WARRANTY LASTS, SO THE ABOVE
LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. WMH TOOL GROUP SHALL IN NO EVENT BE LIABLE FOR
DEATH, INJURIES TO PERSONS OR PROPERTY, OR FOR INCIDENTAL, CONTINGENT, SPECIAL,
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OF OUR PRODUCTS. SOME STATES
DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
To take advantage of this warranty, the product or part must be returned for examination, postage prepaid,
to an Authorized Repair Station designated by our office. Proof of purchase date and an explanation of
the complaint must accompany the merchandise. If our inspection discloses a defect, WMH Tool Group
will either repair or replace the product, or refund the purchase price if we cannot readily and quickly
provide a repair or replacement, if you are willing to accept a refund. WMH Tool Group will return repaired
product or replacement at our expense, but if it is determined there is no defect, or that the defect
resulted from causes not within the scope of our warranty, then the user must bear the cost of storing and
returning the product. This warranty gives you specific legal rights; you may also have other rights, which
vary from state to state.
WMH Tool Group sells through distributors only. WMH Tool Group reserves the right to effect at any time,
without prior notice, those alterations to parts, fittings, and accessory equipment which they may deem
necessary for any reason whatsoever.
2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Warranty........................................................................................................................................................ 2
Table of Contents.......................................................................................................................................... 3
Warning......................................................................................................................................................... 5
Safety Decals ............................................................................................................................................6
Features of the JWP-16OS Planer ...............................................................................................................7
Specifications ................................................................................................................................................7
Receiving....................................................................................................................................................... 8
Parts Inventory ..........................................................................................................................................8
Assembly....................................................................................................................................................... 9
Stand Assembly......................................................................................................................................... 9
Planer Unit Placement............................................................................................................................... 9
Starter Box............................................................................................................................................... 10
Handwheel............................................................................................................................................... 10
Extension Rollers.....................................................................................................................................10
Dust Collection Hood...............................................................................................................................10
Electrical Connections................................................................................................................................. 11
Extension Cords ...................................................................................................................................... 11
Adjustments ................................................................................................................................................11
Overview.................................................................................................................................................. 11
Control and Adjustments .........................................................................................................................11
Pulleys and Belts ..................................................................................................................................... 12
Pulley Alignment......................................................................................................................................12
Belt Tension............................................................................................................................................. 12
Table Rollers ...........................................................................................................................................13
Extension Roller ......................................................................................................................................13
Depth of Cut Adjustment ......................................................................................................................... 14
Knife Adjustment .....................................................................................................................................14
Removing and Replacing Knives ............................................................................................................15
Table Adjustment.....................................................................................................................................16
Checking Work Table Parallel to Cutterhead ..........................................................................................16
Adjusting Work Table Parallel to Cutterhead (Fine Adjustment)............................................................. 17
Adjusting Work Table Parallel to Cutterhead (Major Adjustment)........................................................... 17
Transmitting Rollers.................................................................................................................................18
Infeed & Outfeed Roller Spring Tension Adjustment ..............................................................................18
Anti-Kickback........................................................................................................................................... 18
Checking and Adjusting the Feed Roller Height .....................................................................................19
Gearbox................................................................................................................................................... 20
Operation.....................................................................................................................................................20
Table Locks ............................................................................................................................................. 20
Power Feed ............................................................................................................................................. 21
Handwheel............................................................................................................................................... 21
Depth Limiter ........................................................................................................................................... 21
Initial Startup............................................................................................................................................ 21
Maintenance................................................................................................................................................ 22
General.................................................................................................................................................... 22
Sharpening Knives ..................................................................................................................................22
Lubrication................................................................................................................................................... 23
Optional Accessories ..................................................................................................................................24
Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................................................................25
Performance Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................25
Mechanical Troubleshooting ...................................................................................................................26
Parts List for the JWP-16OS Planer ...........................................................................................................27
Head Assembly .......................................................................................................................................27
Head Assembly Parts List .......................................................................................................................28
Base Assembly........................................................................................................................................ 30
Base Assembly Parts List........................................................................................................................30
Gear Box Assembly.................................................................................................................................32
Gear Box Assembly Parts List................................................................................................................. 33
3
Page 4

Stand Assembly....................................................................................................................................... 34
Stand Assembly Parts List ......................................................................................................................34
Electrical Schematic for JWP-16OS Planer ................................................................................................35
4
Page 5

Warning
1. Read the manual. Always read the owner’s manual carefully before attempting to use the machine.
Know the limitations and hazards associated with the use of this planer.
2. Installation. If mounting machine to the floor, use high quality anchor bolts through the mounting
holes on the base. If using a mobile base, be sure to lock the wheels.
3. Eye protection. Always wear approved safety goggles, glasses, or a face shield when operating this
machine. NOTE: Common eyeglasses are only impact resistant; they are not safety glasses. Also use
face or dust mask if the cutting operation is dusty.
4. Dress code. Do not wear loose clothing, neckties, jewelry, or gloves that can get caught in moving
parts. Confine long hair. Keep sleeves above the elbow.
5. Placement. Place machine so that potential kickback area is not in line with aisles, doorways, wash
stations or other work areas. Do not use machine in a damp or wet location, or expose to rain. Keep
work area well lighted.
6. Electrical grounding. Your machine must be electrically grounded. If a cord and plug are used,
make certain the grounding lug connects to a suitable ground. Follow the grounding procedure
indicated by the National Electrical Code.
7. Guards. Be sure machine guards are in place and in good working order. Do not operate while gear
cover is open. If a guard must be removed for adjustments or maintenance, it should be reinstalled
immediately upon completion of the procedure and before operating the machine.
8. Housekeeping. Before turning on machine, remove all extra equipment such as keys, wrenches,
scrap, stock, and cleaning rags from the machine. Keep the area around machine clean and free of
scrap material and sawdust to minimize the danger of slipping.
9. Power off. Make sure the machine is either unplugged or electrically disconnected and locked out
when performing maintenance or service work. Also, make sure switch is in OFF position before
plugging in power cord. Never leave the machine running unattended. Do not leave machine until it
comes to a complete stop.
10. Cutterhead. Keep knives sharp and free of all rust and pitch. Make sure gib screws are tightened
securely.
11. Work piece. Check material for loose knots, nails and other defects that can damage knives and
pose a safety hazard for the operator.
12. Keep hands away from feed rollers and cutterhead while operating.
13. Use the proper extension cord. Make sure your extension cord is in good condition. When using an
extension cord, be sure to use one heavy enough to carry the current your product will draw. An
undersize cord will cause a drop in line voltage resulting in loss of power and overheating. For runs
up to 25 feet, use an 18 AWG or larger gauge cord.
14. Do not operate this machine while under the influence of drugs, alcohol or any medication.
15. If you are not thoroughly familiar with the operation of wood planers, obtain advice from your
supervisor, instructor or other qualified person.
16. Health hazards. Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling and other
construction activities contains chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive
harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
• Lead from lead-based paint.
• Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products.
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically treated lumber.
17. Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce
your exposure to these chemicals, work in a well-ventilated area, and work with approved safety
equipment, such as those dust masks that are specifically designed to filter out microscopic particles.
5
Page 6

Familiarize yourself with the following safety notices used in this manual.
This means that if precautions are not heeded, it may result in serious injury or possibly even
death.
This means that if precautions are not heeded, it may result in minor or moderate injury and/or
possible machine damage.
Safety Decals
Familiarize yourself with the location and content of these decals on your planer.
!
1. Read instruction manua l before operating machine.
2. Do not oper ate without a ll guards properly installed.
3. Remove or fasten loose ar ticles of clothing such as neck ties, etc.
Contain long hair.
4. Remove jewelry such as fi nger rings, watches, bracel ets, etc.
5. Use approved safety glasses and/or face shield to pr otect eyes, and
use other personal safety equip ment as required. Do not wear
gloves.
DO NOT REMOVE OR OBSCURE THIS LABEL
6. Disconnect machine f rom power source before maki ng any
adjustments or cleaning chips away from mach ine.
7. Keep the floor around m achine clean and free from scra ps,
sawdust, oil and grease to minimiz e the danger of slipping.
8. Do not operate this machine while under the influence of alcohol
or dr ugs .
9. Failure to comply with these warnings may result in serio us
pe rsonal injury.
6
Page 7
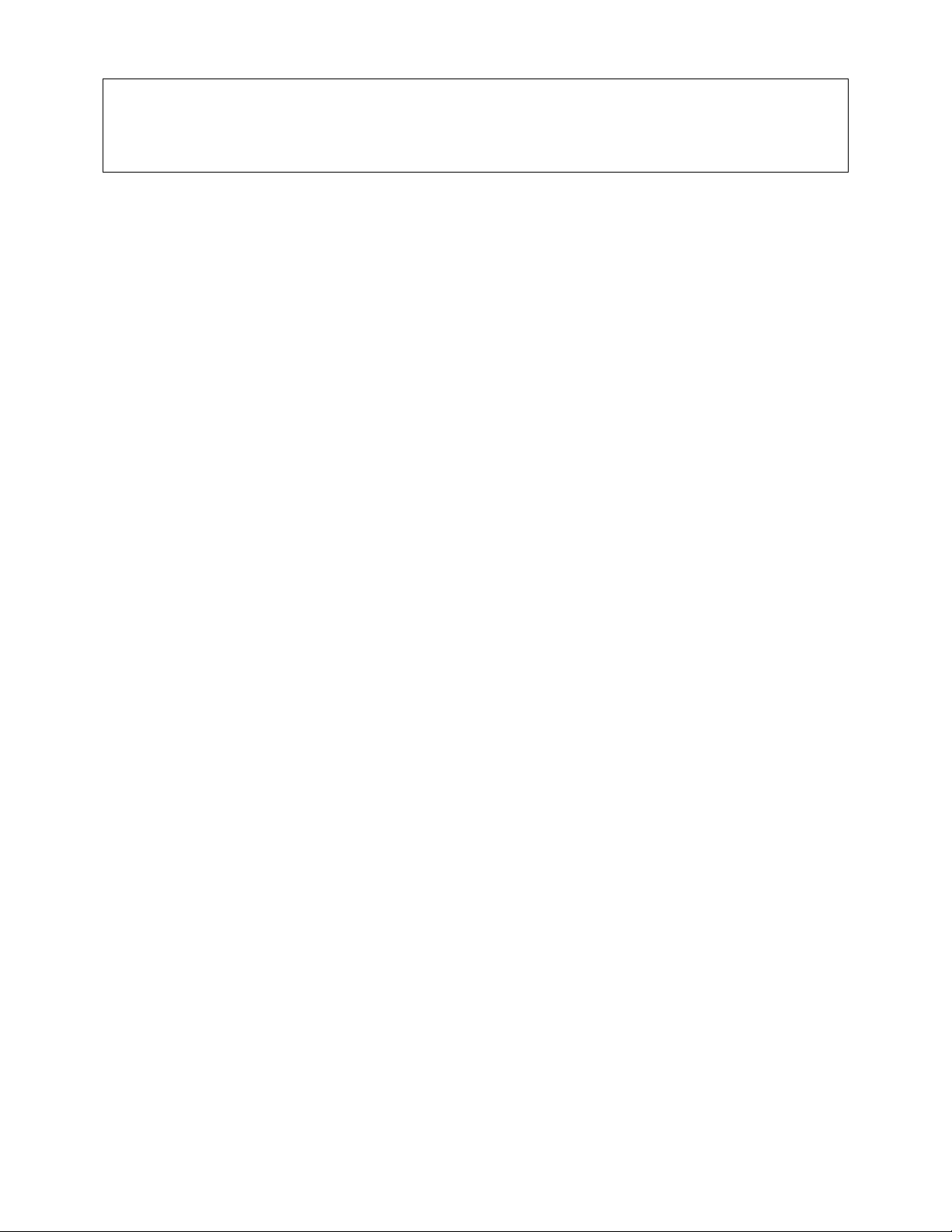
Features of the JWP-16OS Planer
Specifications
Model Number............................................................................................................................... JWP-16OS
Stock Number ..................................................................................................................................... 708531
Maximum Planing (W/in.) ............................................................................................................................ 16
Maximum Planing Thickness (T/in.).............................................................................................................. 6
Maximum Depth of Cut (in.) ..................................................................................................................... 3/16
Maximum Full Width Depth of Cut (in.) ...................................................................................................... 1/8
Maximum Opening (in.)................................................................................................................... 6-3/8 x 16
Minimum Planing Length (in.) ....................................................................................................................... 8
Knives............................................................................................................................................................ 3
Planer Blade Size (L x W x T/in.) ........................................................................................... 16-1/8 x 1 x 1/8
Cutterhead Speed (RPM)....................................................................................................................... 4,500
Cuts per Minute.................................................................................................................................... 13,500
Cutterhead Diameter (in.)........................................................................................................................2-7/8
Feed Rate (FPM) ................................................................................................................................16 & 20
Dust Port Diameter (in.) ................................................................................................................................ 4
Overall Dimensions (L x W x H/in.) ............................................................................................. 48 x 32 x 51
Motor ..................................................................................................................................... 3HP, 1Ph, 230V
Net Weight (approx. lbs.) ..........................................................................................................................430
The specifications in this manual are given as general information and are not binding. WMH Tool Group
reserves the right to effect, at any time and without prior notice, alterations to parts, fittings, and
accessory equipment deemed necessary for any reason whatsoever.
7
Page 8

Receiving
Carefully unpack the planer and any loose items
from the wood crate and inspect for damage.
Any damage should be reported immediately to
your distributor and shipping agent. Before
proceeding further, read your manual thoroughly
to familiarize yourself with proper assembly,
maintenance and safety procedures.
Remove the protective coating from the table,
bed rolls, feed rolls, cutterhead and loose items
packed with the machine, including lifting
handles and motor pulley. This coating may be
removed with a soft cloth moistened with
Kerosene. Do not use acetone, gasoline or
lacquer thinner for this purpose. Do not use
solvents on plastic parts.
Parts Inventory
Parts requiring assembly:
1 Planer Unit
1 4" Dust Hood
2 In/Outfeed Extension Roller Assembly
1 Handwheel
Cast Foot Assembly:
4 Cast Feet
1 Hardware Bag, consisting of:
8 Socket Head Flat Screws
8 Flat Washers
8 Hex Nuts
Stand Assembly:
4 Stand Legs
2 Stand Braces – long
2 Stand Braces – short
2 Stand Top – front & rear
1 Stand Top – left
1 Stand Top – right
1 Hardware Bag, consisting of:
32 Carriage Bolts
32 Flat Washers
32 Hex Nuts
Accessory Package:
1 Handle
2 Knife Gauges
1 Knife Setting Gauge Bar
4 E-Rings for Knife Setting Gauge
4 Hex Wrenches – 3, 4, 5, 6mm
2 Open Wrenches – 8/10mm, 12/14mm
Hardware Bag for Handwheel:
1 M10 Hex Nut
1 M10 Flat Washer
1 Direction Label
Hardware Bag for Infeed/Outfeed Extension
Rollers
6 M8 x 20 Hex Head Screws
6 M8 x 12 Set Screws
6 M8 Flat Washers
Hardware Bag for Dust Hood:
6 M6 x 12 Hex Head Screws
Hardware Bag for Base to Stand:
4 M8 x 30 Hex Head Screws
4 M8 Hex Nuts
8 M8 Flat Washers
8
Page 9
Assembly
Most of the JWP-16OS Planer has been
assembled at the factory. However some parts
must be assembled after delivery.
Use care when cleaning the cutterhead; the
knives are very sharp.
side of the assembly using 4 ea carriage
bolts, washers and nuts.
10. Secure the remaining short stand brace (14)
to the front and rear legs (middle mounting
holes) on the right side of the stand with (4
ea) carriage bolts, washers and nuts.
11. Make sure that the stand is symmetrical and
level. Adjust if necessary and securely
tighten all bolts.
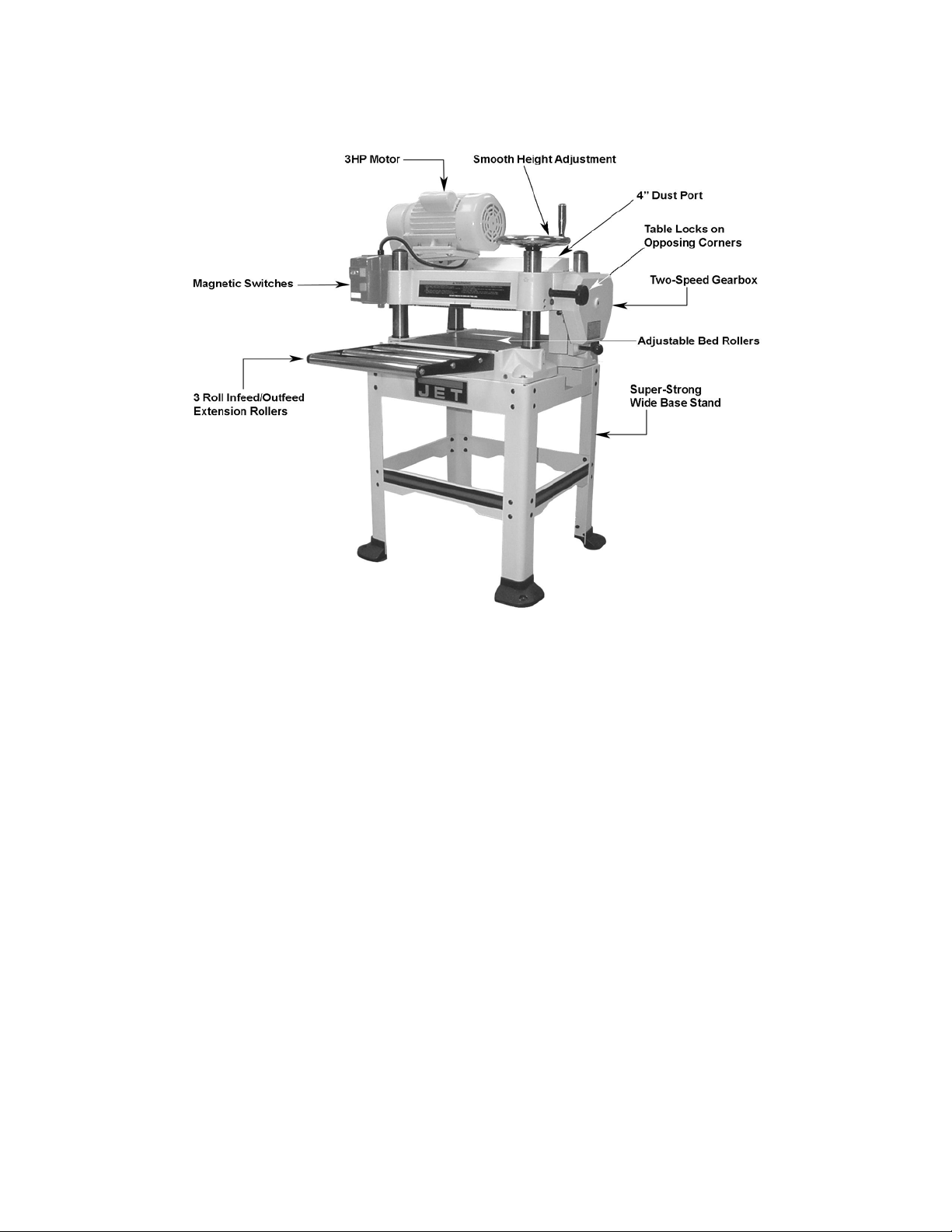
Stand Assembly
Refer to Figure 1.
1. Cast Foot Assembly – Using parts from the
cast foot assembly hardware bag, mount
casting (2) to leg (1) by inserting two socket
head flat screws (3) through the casting (2)
and leg (1). Place a flat washer (4) and hex
nut (5) on the screw and tighten.
Repeat for remaining three legs.
2. Stand Top (front) – The front and rear top
stands (braces) are identical except for the
JET logo on the front piece.
Mount one end of the stand top (6) to a leg
(1) and fasten using two each carriage bolts
(7), flat washers (8) and hex nuts (9).
Note: Do not over tighten at this time. This will
be the final step in the assembly.
3. Fasten a second leg to the other end of the
stand top, repeating the step above.
4. Take one long stand brace (10) and with
(4 ea) bolts, washers, and hex nuts fasten to
the legs of the assembly just completed in
the steps 2 and 3. Fasten to the mounting
holes in the middle of each leg.
5. Set this assembly aside for now.
6. Stand Top (rear) – Repeat steps 2–4 using
parts still remaining.
7. Take the left stand top (11)
Note: The right stand top (13) has a cutout
and will be used later.
Secure it to left side of the left legs (top
mounting holes) of the front and rear
assemblies previously constructed (the JET
logo is the front) using 4 ea carriage bolts,
flat washers and nuts.
8. Take one short stand brace (12) and secure
to the left legs of the front and rear assembly
with (4 ea) carriage bolts, washers and nuts.
12. Before mounting the planer on the stand,
locate the stand on a solid, level foundation
to ensure best planing performance and
anchor to the floor with good quality lag
screws.
Figure 1
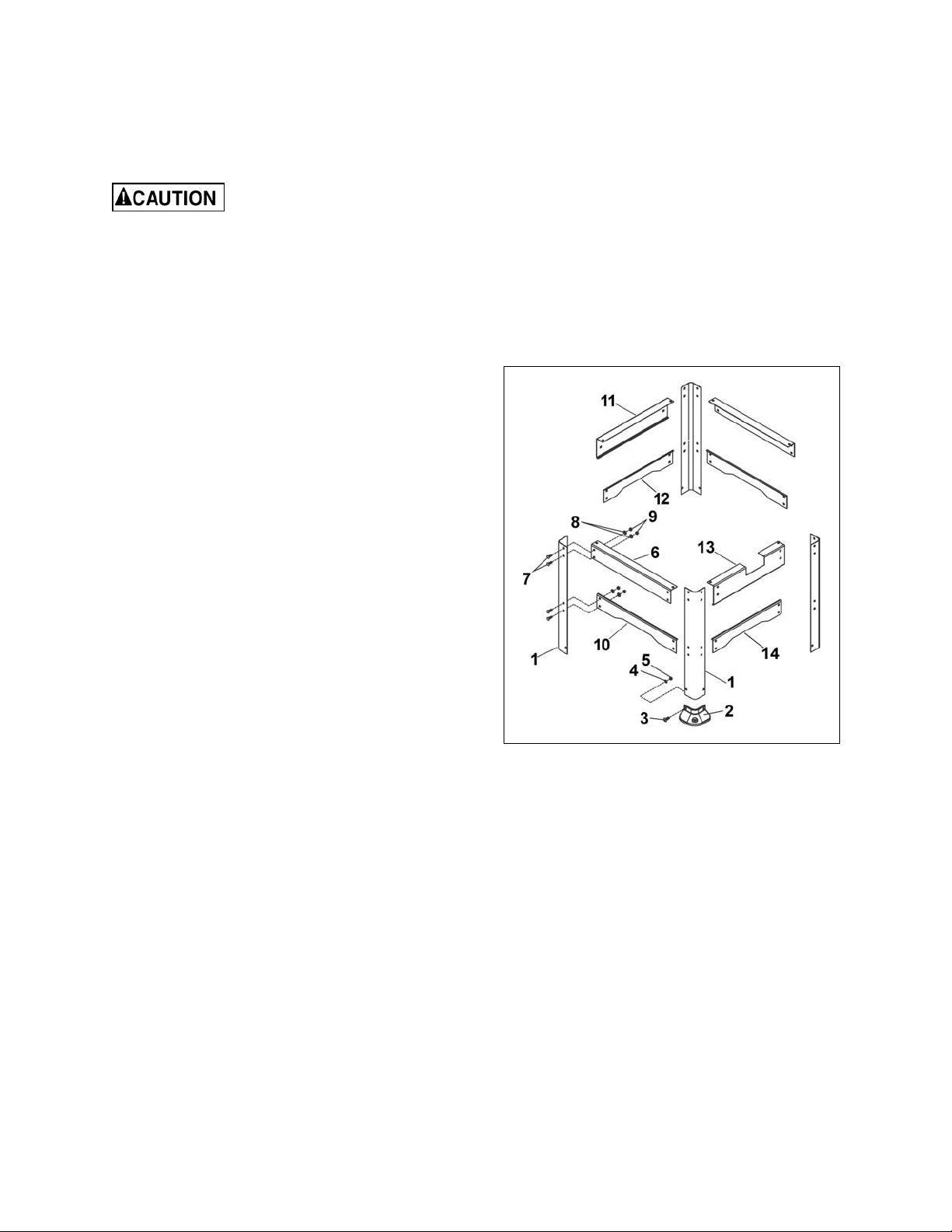
Planer Unit Placement
There are four lifting handles (Fig. 2) on the
machine. The handles can be pulled out
(A, Fig. 2) for use when the planer is to be lifted
and moved and slides into the body casting
(B, Fig. 2) when not needed.
If a sling or forklift is used to lift the machine, be
sure to lift by the handles only. Make sure
machine is kept in level position while lifting.
Set the machine on the stand that was
assembled in the previous section, then secure
the base to the stand using parts provided in the
base to stand hardware bag, consisting of 4 ea
M8 x 30 hex cap screws, 4 ea M8 hex nuts, and
8 ea M8 flat washers.
9. Take the right stand top (13) – this piece has
the cutout – and secure it to the front and
rear legs (top mounting holes) on the right
9
Page 10
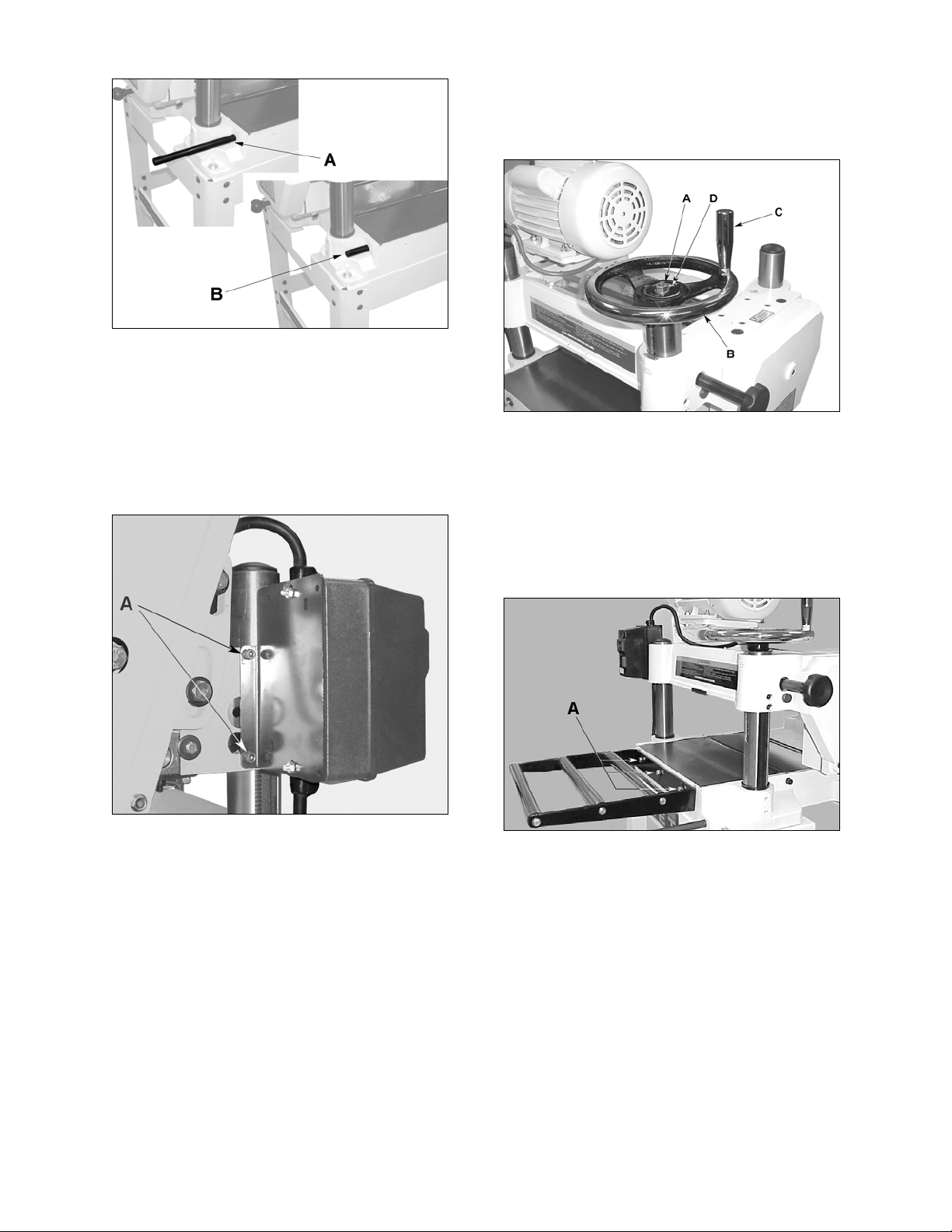
Starter Box
5. Mount the handle (C, Fig. 4) for the
handwheel in the threaded hole in the
handwheel, and tighten with a wrench
placed over the flat (12mm) on the handle.
Figure 2
The switch assembly (starter box and bracket) is
pre-assembled at the factory and simply needs
to be mounted to the head casting on the left
side of the machine with two socket head cap
screws (A, Fig. 3) already in place the head
casting.
Figure 3
Handwheel
1. Remove the tape holding the key in the
shaft.
2. Place the handwheel (B, Fig. 4) onto the
shaft; making sure it is oriented so the
handwheel slips over the key.
3. Remove the adhesive backing from the
direction label supplied with the hardware
bag for the handwheel. Place the label onto
the shaft and press it on the handwheel (D,
Fig. 4).
Figure 4
Extension Rollers
Mount two extension rollers to the table using
the provided 6 ea M8 x 20 hex cap screws
(12mm), 6 ea M8 flat washers, and 6 ea M8 x 12
set screws (A, Fig. 5). The rollers should be
adjusted before operating the planer (this will be
explained later in the Adjustment section).
Figure 5
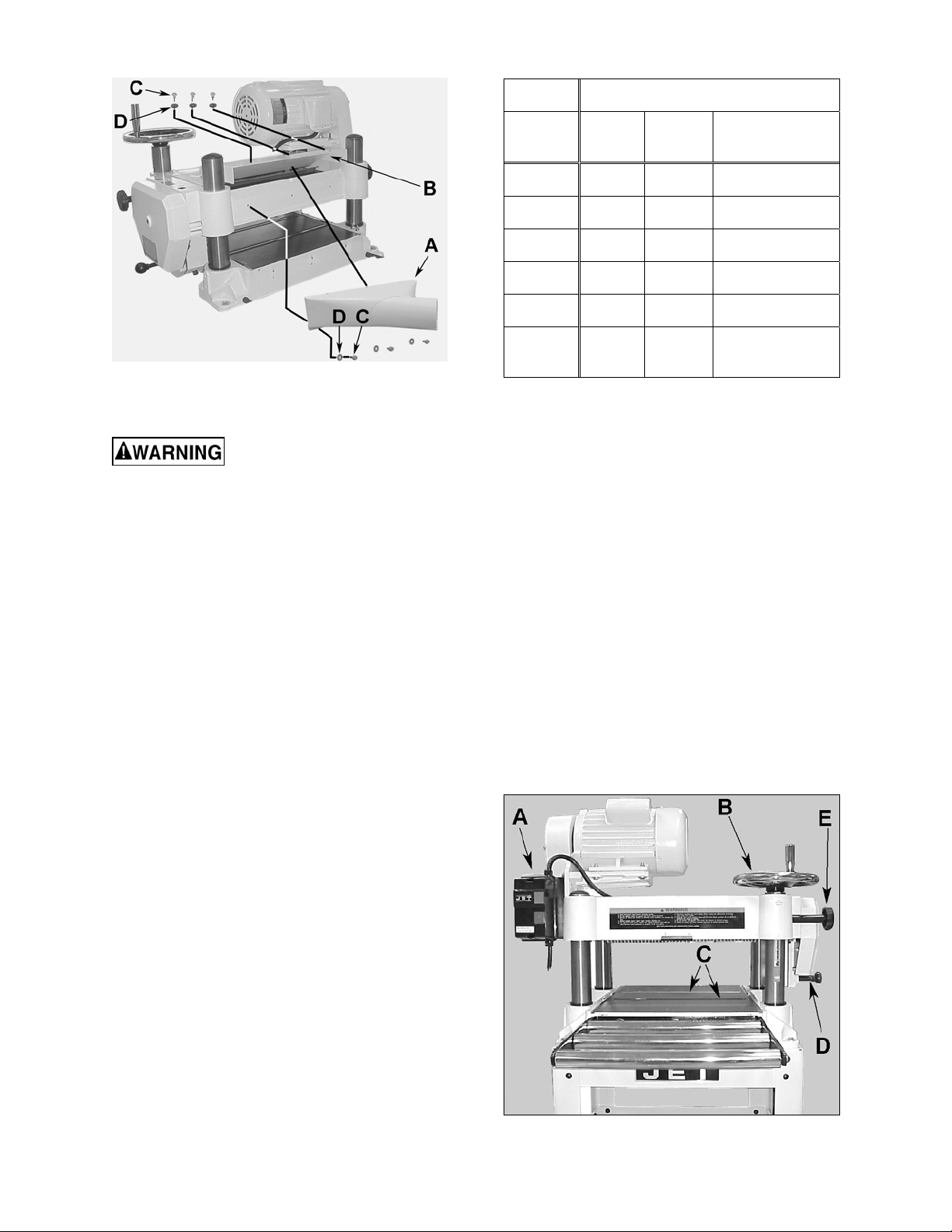
Dust Collection Hood
Referring to Figure 6:
The dust collection hood (A) comes standard
with the model JWP-16OS planer, and helps
maintain a clean and safe work area. It is
assembled to the planer (B) with six hex head
screws (C) as shown.
4. Place flat washer and hex nut on shaft and
tighten with wrench.
10
Page 11
Length of Cord
Figure 6
Electrical Connections
Electrical connections must be made by a
qualified electrician in compliance with all
relevant codes. The machine must be
properly grounded to help prevent electrical
shock and possible fatal injury.
Rated
Amps
0–6 18 16 16
7–10 18 16 14
11–12 16 16 14
13–16 14 12 12
17–20 12 12 10
21–30 10 10
25 ft 50ft 100ft
Not
recommended
Figure 7
Adjustments
Overview
Many parts are factory adjusted. The operator
should be familiar with the following procedures
to gain a better understanding of the JWP-16OS
Planer's construction and operation.
A power plug is not provided with the
JWP-16OS planer. You may either connect a
plug or "hard-wire" the machine directly to your
electrical panel provided there is a disconnect
near the machine. Consult the wiring diagrams
at the end of this manual.
This machine must be grounded. Grounding
provides a path of least resistance to help divert
current away from the operator in case of
electrical malfunction.
Make sure the voltage of your power supply
matches the specifications on the motor plate of
the machine.
Extension Cords
The use of an extension cord is not
recommended for this machine, but if one is
necessary make sure the cord rating is suitable
for the amperage listed on the machine's motor
plate. An undersized cord will cause a drop in
line voltage resulting in loss of power and
overheating.
The chart in Figure 7 shows the correct size
cord to use based on cord length and motor
plate amp rating. If in doubt, use the next
heavier gauge. The smaller the gauge numbers
the heavier the cord.
Control and Adjustments
Refer to Figure 8 for general control and
adjustment locations for the JWP-16OS Planer
and are also listed below.
A – Switch
B – Handwheel
C – Table Rollers
D – Feed Rate Change Knob
E – Two Table Lock Knobs on Opposing
Corners
Figure 8
11
Page 12

Pulleys and Belts
The belt and pulley assembly are on the left side
of the planer. To inspect for pulley alignment
and correct belt tension, remove the four hex
head screws (10mm) holding the cover in place.
Figure 9 shows the assembly with the cover
removed.
Pulley Alignment
1. Place the edge of a metal ruler so it rests
perpendicular against the flat sides of the
motor and cutterhead pulleys (Fig. 11).
If the pulleys lie in straight plane (Fig. 11)
they are aligned.
Figure 11
Belt Tension
Check the belt tension by squeezing the belts
together in the middle (between the motor and
cutterhead pulleys as shown in Fig. 12) with
moderate pressure. Proper tension is indicated
when there is approximately 1/4” deflection.
Figure 9
If the pulleys need to be aligned:
2. Loosen four bolts (12mm) on the motor
mounting base plate (Fig. 10), which will
allow the motor to move from side-to-side.
Figure 10
3. Adjust the motor until the pulleys are in the
aligned position as shown in Figure 11.
4. Re-tighten all bolts.
Figure 12
To adjust the belt tension:
1. Loosen the two 17mm bolts (A, Fig. 13) that
hold the motor/pulley assembly to the
planer.
2. Using a lever, raise the motor to increase
the belt tension.
Note: Belts will rarely be too tight. Adjustment
typically requires belt tightening.
3. Tighten the bolts and check the belt tension
again.
4. Verify that the pulleys are still in alignment.
12
Page 13

Figure 13
Table Rollers
Two table rollers (A, Fig. 14) ease stock
movement as it is fed through the planer. The
height of the rollers is dependent on the type of
wood being planed. When planing rough stock,
set the rollers slightly high to keep the lumber
from dragging along the table. Smooth lumber
should be planed with the rollers set just above
the plane of the table.
Figure 15
To adjust the rollers (refer to Figure 16):
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Select a side (left or right) and lay a steel
ruler or straightedge across both rollers (A).
3. On the side selected, loosen the screws (B)
with an Allen wrench, and turn the eccentric
shafts (C) (12mm hex head adjustment) to
raise or lower the rollers to the desired level.
Use a feeler gauge to measure the
clearance between the table and the bottom
of the straightedge.
4. When the proper height is achieved, tighten
screws (B).
Adjust the rollers from the opposite side of the
table in the same manner.
Important: Measure in several places. This
measurement must be consistent across the
entire table.
Figure 14
The two table rollers are preset at the factory at
0.004" above the table. The height adjustment
range is from 0 to 0.06" (Fig. 15).
Figure 16
Extension Roller
Referring to Figure 17:
Place a straight edge (A) over the extension
roller (B) and the table to make sure the
extension roller and table are at the same
height.
13
Page 14

Figure 17
Referring to Figure 18 – if adjustment is
required:
1. Adjust the tightness of the mounting bolts
(A) and the depth of the setscrews (B) on
the extension roller frame.
Various combinations of loosening and/or
tightening of the setscrews and bolts will be
required to level the extension rollers with
the table. Adjustment is complete when the
straightedge is level with the table and all
three rollers touch the bottom of the
straightedge.
2. Adjust both front and rear extension rollers
in the same manner.
Note: The JWP-16OS Planer has two lock
knobs; one is located by the handwheel
(C, Fig. 19). The other is located on the opposite
(left rear) corner.
Always tighten the lock knobs before
operating the planer.
Figure 19
Knife Adjustment
Figure 18
Depth of Cut Adjustment
Refer to Figure 19.
The cutting depth scale (A) is a combination
inch/metric scale with a cutting range from 0 to
6” (150mm). The distance of upward or
downward movement is controlled by the
handwheel (B). One revolution of the handwheel
is 0.158” (4mm). Before moving the head
assembly up or down, loosen the lock knobs
(C,). After obtaining the proper height for the
head assembly, tighten the lock knobs.
When checking or adjusting the cutterhead
knives, proceed as follows:
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Remove four hex cap screws (A, Fig. 20)
from the upper cover and three from the
bottom of the dust port. Remove the
cover/dust port (B, Fig 20) as a unit.
The cutterhead assembly can be seen from
the opening on top.
Motor assembly removed for clarity
Figure 20
14
Page 15

Planer knives are dangerously sharp. Use
extreme caution when inspecting, removing,
sharpening, or replacing knives into the
cutterhead. Failure to comply may cause
serious injury.
3. To check and adjust the knives, use the
provided knife gauge (Fig. 22) and check all
three knives. Press the knife gauge against
the cutterhead as shown in Figure 23.
Referring to Figure 21:
Knives (A) should just contact the bottom of
the center protrusion (B) of the knife gauge
(F).
Important: Insure that the feet of the knife
gauge sit flush against a clean surface of the
cutterhead. Make sure that no dust, pitch, or
lubrication buildup is present, which can cause
errors in the knife blade settings.
4. If an adjustment to one or more of the knives
is necessary, slightly loosen the knife gib (C)
by turning the six gib screws (D) into the gib.
Turn the screws just enough to relieve
stress in the cutterhead without disturbing
the setting of the knives. Do this for all three
knives at the same time.
6. If additional knives must be reset, repeat
steps 4 and 5 for each knife.
7. After all three knives are set with screws just
snug, back out and tighten the six gib
screws (D, Fig. 21 & Fig. 23) of the first knife
against the slot starting with the end screws,
then the center screws, until the knife is
securely held in the cutterhead. Tighten
remaining two knives in the same manner.
Important: Double check all gib screws for
tightness.
Figure 22
5. With the gauge (F) in place over a knife (A)
continue to loosen the gib screws (D) until
the springs (E) begin raising the knife.
When knife comes into contact with the
center protrusion (B) of the gauge, adjust
the jack screws higher or lower to touch the
bottom of the knife, then snug up the gib by
lightly backing out the six gib screws (D)
against the slot.
Note: At this time, only tighten the knife in the
slot just enough to hold knife in position.
Figure 23
Removing and Replacing Knives
Planer knives are dangerously sharp. Use
extreme caution when inspecting, removing,
sharpening, or replacing knives into the
cutterhead. Failure to comply may cause
serious injury.
To remove a knife:
Figure 21
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Remove four screws (A, Fig. 20) from the
upper cover and three from the bottom of
15
Page 16

the dust port. Remove the cover/dust port
(Fig. 20) as a unit.
(3 knives x 6 screws) locking screws are
tightened securely.
The cutterhead assembly can be seen from
the opening on top.
Refer to Figure 21:
3. Loosen the gib (C) by turning the six gib
screws (D) into the gib. Remove gib (C),
knife (A) and springs (E).
Note: The inner two springs may pop out
when the knife and gib are removed.
4. Remove the remaining two knives in the
same manner.
5. Thoroughly clean the knife slots, gibs,
springs and gib screws. Check the gib
screws; if the threads appear worn or
stripped or if the heads are becoming
rounded, replace them.
6. Inspect the cutting edge of the knives for
nicks or wire edge. It is recommended that
knives be replaced when they become dull
or damaged. If they are to be reused, refer
to Sharpening Knives in the Maintenance
Section.
7. Reinsert springs, knives and gib into slot of
the cutterhead. Back out gib screws just
enough to hold the knife in the cutterhead.
8. Place knife gauge (Fig. 23) over knife.
Still referring to Figure 21:
9. While holding down on the knife gauge,
loosen all six gib screws (D) by turning them
into the gib (C) until cutting edge of knife
comes into contact with the protrusion of the
gauge (B). Adjust the jack screws higher or
lower to touch the bottom of the knife. Snug
up the gib by slightly backing out the six
locking screws against the slot.
Note: At this time only, tighten the knife into
the slot just enough to hold the knife in
position.
10. Replace and reset the other two knives by
repeating steps 3 – 9.
11. After all three knives are set with the screws
just snug, back out and tighten the six
screws (D) against the slot starting with the
end screws first and then the center screws
until the knife is securely held in the
cutterhead. Tighten the remaining two
knives in the same manner.
Important: After replacing and checking knives,
CHECK AGAIN carefully. Make certain the
direction of knives is correct and all eighteen
Table Adjustment
To perform the table adjustments described in
the next two sections, you will need a straight
edge, feeler gauge, and a home made gauge
block made of hardwood. Make the gauge block
by following the dimensions shown in Fig. 24.
Precision adjustments require accuracy when
milling the gauge block.
Figure 24
Checking Work Table Parallel to Cutterhead
The worktable is set parallel to the cutterhead at
the factory and no further adjustment should be
needed. If your machine is planing a taper, first
check to see if the knives are set properly in the
cutterhead. Then check to see if the worktable is
set parallel to the cutterhead by proceeding as
follows:
1. Disconnect machine from power source.
2. Turn the handwheel clockwise; raising the
cutterhead assembly high enough to place
the gauge block (A, Fig. 25) on the work
table under one end of the head casting
(B, Fig. 25).
3. Turn the handwheel to lower the head
assembly until the head casting body barely
touches the gauge block. The blades should
not touch the block.
4. Slide the block toward the opposite side of
the head casting. Use a feeler gauge to
measure the width of the gap, if any,
between the top of the block and the bottom
of the cutterhead. Make a note of the gap, if
any.
5. If the block wedges tightly between the table
and the head casting when shifting from one
side to the other, repeat steps 2 through 4,
but start from the opposite end of the head
casting.
16
Page 17

Figure 25
If the gap difference from one side to the other is
equal to or less than 0.004", no further
adjustment is necessary
If the gap difference from one side to the other
side is grater than 0.004", but less than 0.016",
go to the Adjusting Work Table Parallel to
Cutterhead (Fine Adjustment) section.
It the gap difference from one side to the other is
grater than 0.016", the cutterhead assembly
raising chain under the planer base needs to be
adjusted – see the Adjusting Work Table Parallel
to Cutterhead (Major Adjustment) section.
Adjusting Work Table Parallel to Cutterhead (Fine Adjustment)
If the gap difference determined in the previous
section is greater than 0.004" and less than
0.016", perform the adjustment procedure as
follows:
1. Determine which side of the table must be
raised to correct the gap.
2. Locate the two socket head cap screws in
the table casting for each of the columns (A,
Fig. 26). Loosen both sets of screws for
each column on the side you wish to adjust.
3. Push down or pull up the cutterhead
assembly in the desired direction. Hold the
assembly in position and retighten the cap
screws.
4. Recheck the table to cutterhead parallelism
again as described in the previous section,
then repeat steps 1 – 3 until the deviation is
less than 0.004".
Figure 26
Adjusting Work Table Parallel to Cutterhead (Major Adjustment)
Refer to Figure 27.
1. Disconnect the machine from power source.
2. On the underside of the base, remove bolt
(A) and loosen bolt (B) which will allow you
to move the idler sprocket assembly (C) far
enough to release tension on the chain.
3. Remove chain from the particular sprocket
on the corner of the base that must be
adjusted.
4. Turn the sprocket by hand to bring that
corner into adjustment with the other three
corners.
Note: Turning sprocket clockwise will increase
the distance between the working table and
head casting; counter-clockwise will decrease
the distance. This adjustment is very sensitive –
one revolution of the lead screw equals 0.158”
(4mm) of travel. It should not be necessary to
turn the sprocket more than one or two teeth.
5. When adjustments are correct, replace
chain around the corner sprocket, slide
sprocket (C) back to re-tension chain,
tighten bolt (B) and replace and tighten
bolt (A).
Note: It may be necessary to perform the Fine
Adjustment procedure after the major to achieve
the best result.
17
Page 18

Figure 27
Transmitting Rollers
Figure 28 show the positions of the rollers that
are listed below and described in the following
sections.
A Anti Kickback Fingers
B Infeed Roller
C Chipbreaker
D Cutterhead
F Outfeed Roller
To adjust the spring tension of the infeed and
outfeed rollers, turn screws (A, Fig. 29) with a
hex wrench. A clockwise turn increases tension
on the pressure spring (Fig. 30); a
counterclockwise turn decreases tension. Adjust
the screws at the other end of the rollers with the
same number of turns.
Note: The most effective pressure settings are
dependent on the type of lumber being planed.
Experimentation will determine the best settings.
Figure 29
Figure 28
Infeed & Outfeed Roller Spring Tension Adjustment
The infeed roller (B, Fig. 28) and outfeed roller
(F, Fig. 28) feed the stock while it is being
planed. The infeed and outfeed rollers are under
spring tension and this tension must be sufficient
to feed the stock uniformly through the planer
without slipping but should not be so tight that it
causes damage to the board and/or the rubber
coating on the outfeed roller. The tension should
be equal at both ends of each roller.
Figure 30
Anti-Kickback
The JWP-16OS Planer provides an antikickback safety feature. The anti-kickback
fingers hang from a rod suspended across the
front of the cutterhead casting (A, Fig. 28) and
help prevent kickback of stock. It is necessary to
inspect them regularly to make sure they hang
freely. Check that they are free of gum and pitch
to insure independent movement and correct
operation.
18
Page 19

Figure 31
Checking and Adjusting the Feed Roller Height
The infeed and outfeed rollers propel the lumber
through the planer. The rollers also press the
lumber flat against the planer table.
The infeed and outfeed rollers are adjusted at
the factory and are set at 0.020" below the knifeedge at bottom dead center (Fig. 31).
Note: Before proceeding with this adjustment,
make sure the knives are adjusted properly as
outlined in the Knife Adjustment section.
Remove the drive chain cover to access the
roller adjustments on the drive chain side of the
planer.
To check or verify the roller height:
1. Disconnect the machine from the power
source.
2. Turn the handwheel clockwise, raising the
cutterhead assembly high enough to place
the gauge block (J, Fig. 32) on the table
directly underneath the cutterhead
(D, Fig. 32) Using a 0.02” (0.5mm) feeler
gauge (K, Fig. 32) placed on top of the
gauge block, lower the head assembly until
the knife just touches the feeler gauge when
the knife is at its lowest point. Do not move
the working table any further until the infeed
and outfeed rollers are adjusted.
Figure 32
3. Move the gauge block (J, Fig. 33) under one
end of the outfeed roller (F, Fig. 33). The
bottom of the outfeed roller should just touch
the top of the gauge block. If an adjustment
to the outfeed roller is necessary, loosen the
jam nut (L, Fig 33) and turn screw
(M, Fig. 33) until the outfeed roller just
touches the gauge block. Then tighten jam
nut (L, Fig. 33).
4. Slide the gauge block to the other end of the
outfeed roller and repeat the adjustment
described in Step 3.
5. Recheck the settings and repeat steps 1-4 if
necessary.
19
Page 20

Figure 33
Gearbox
Referring to Figure 34:
The JWP-16OS Planer is equipped with a spiral,
serrated infeed roller (F) and a solid outfeed
roller. When the feed rollers are engaged, they
turn to feed the stock. The feed rollers are driven
by chains (A) and sprockets (B) in the gearbox.
The gearbox is located on the right side of the
planer directly behind the table lock knob (A,
Fig. 35). The gearbox transfers power from the
belt-driven cutterhead to the power feed rollers.
A two-speed transmission, controlled by a
push/pull lever (D), moves the stock through the
planer at either 16 or 20 feet-per minute. The
push/pull lever is set while the machine is
running.
Because of its powerful motor and razorsharp knives, the JWP-16OS Planer is
inherently dangerous and should be
operated with considerable caution and
respect. Failure to do so could result in
damage to the machine or severe injury to
the operator or others in the work area.
Overview
There are a number of safety issues that relate
directly to the operation of the planer. Keep in
mind that these are not all-inclusive. Work
situations, wood types, and other variables that
differ from shop to shop must be considered in
order to operate this planer safely. Always
consider safety and common sense first when
operating this or other machinery.
1. Always inspect lumber for defects (warping,
cupping, twisting, etc.). Do not use lumber of
questionable quality.
2. Check lumber for nails, staples, imbedded
gravel, etc. before planing.
3. Use the full width of the planer. Alternate
between the left, the right and the middle
when feeding lumber into the planer. Your
knives will remain sharp much longer.
4. Remove glues, epoxies and other foreign
matter before planing lumber.
5. Never attempt to plane laminates,
particleboards, plastics or other man-made
materials.
6. Plane wood with the grain. Never plane
across the grain.
Figure 34
Operation
The JWP-16OS Planer is a powerful
woodworking machine, designed and
constructed for professional-quality applications.
7. Do not use boards with loose knots, splits,
cross grain or other defects. They can
damage the machine and cause injury.
8. Keep your work area clear.
9. Wood with excessive water content or wood
exposed to rain, ice, or snow will plane
poorly and cause excess wear to the knives
and motor. Excessive moisture will also
hasten rust and corrosion.
10. Learn as much as possible about planing
procedures. Alternative publications present
more wood specific planing requirements.
Table Locks
Before attempting to adjust table height, loosen
the two table lock knobs, one on the right front of
the head casting assembly (A, Fig. 35) and the
other on the left rear.
20
Page 21

Handwheel
Crank the handwheel to raise or lower the table
according to the desired workpiece thickness.
Each complete revolution of the handwheel
moves the head assembly by 0.158” (4mm).
Make sure the height scale is properly adjusted.
With the depth-limiting clip installed, you cannot
cut full width more than 1/8" in a single pass
(3/16" if lumber can fit on either side of the depth
limiting clip). While cutting this much material is
possible, it is not recommended.
Depth Limiter
Figure 35
After the head assembly height is adjusted,
tighten the two black knobs down again.
Power Feed
Referring to Figure 36:
The power feed features two feed rates, 16 FPM
and 20 FPM. When running the machine, the
operator can control the feed speed by moving
the feed control knob. Moving the knob toward
the machine produces the 20 FPM feed speed
(A), away from the machine produces 16 FPM
(C) and a center position places the gear box in
neutral (B).
The Model JWP-16OS Planer is equipped with a
depth limiter – located on the bottom of the
cutterhead casting just below the warning label
(A, Fig. 37). The depth limiter controls maximum
depth of cut to 1/8".
Figure 37
To avoid mechanical damage to the planer,
do not remove the depth limiter.
Initial Startup
After the assembly and adjustments are
complete the planer is ready to be tested.
Figure 36
Set the feed rate while the planer is running
but before feeding lumber into it. DO NOT
change speeds after the cutting operation
has begun.
If the cut is too large, the planer will slow
down considerably, possibly even stalling
the motor. Turn off the power immediately,
raise the head assembly and remove the
workpiece. Re-adjust the head assembly to
allow a lesser cut and repeat the operation.
Turn on the power supply at the main panel.
Press the Start button. Keep your finger on the
Stop button in case of a problem. The planer
should run smoothly with little or no vibration or
rubbing noises. Investigate and correct the
source of any problems before further operation.
DO NOT attempt to investigate or adjust the
planer while it is running. Wait until the
planer is turned off, unplugged and all
working parts have come to a complete
standstill.
Always wear ANSI-approved safety glasses
or goggles when operating equipment.
21
Page 22

Maintenance
General
Inspect your planer each time before using.
Check for the following conditions and repair or
replace when necessary.
1. Loose mounting bolts.
2. Worn switch.
3. Worn or damaged cords and plugs.
4. Damaged V-belts.
5. Any other condition that could hamper the
safe operation of this machine.
Buildup of sawdust and other debris can cause
your machine to plane inaccurately. Periodic
cleaning is not only recommended but also
mandatory for accurate planing.
Close-fitting parts, such as the cutterhead slot
and gibs, should be cleaned with a cloth or
brush and non-flammable solvent, and free from
clinging foreign matter.
Remove resin and other accumulations from
feed rollers and table with a soft rag and nonflammable solvent.
If knives are to be reused, it is recommended
that they be sharpened by a professional knife
sharpener. Improperly sharpened knives can
cause a number of defects to lumber and put
unnecessary load on the motor and drive
systems.
If you must sharpen the knives yourself, please
take note of the following information:
Primary Grinding Angle – 40 degrees
Secondary Grinding Angle – 42 degrees
The grinding angle has been determined by the
factory to be the best compromise for planing a
wide variety of wood types. In most cases, that
angle will produce excellent results. If you
choose to change the angle of your bevel, be
sure to consult with a trained sharpener or with a
reference book before you commit to changing
the angle of bevel.
Periodically check all the chains for proper
tension and adjust accordingly if required.
Tip: If a foreign object nicks the knives, instead
of throwing them away or trying to grind out the
deep nick, simply stagger the knives in the head,
moving one knife no more than 1/8" to the right
and another knife no more than 1/8" to the left.
The nick should no longer be noticeable.
The table should be kept clean and free of rust.
Some users prefer a paste wax on exposed
steel and cast iron surfaces. The wax provides a
layer of protection as well as reducing friction
between lumber and the table making cuts faster
and smoother. Avoid any wax that contains
silicone or other synthetic ingredients. These
materials can find their way into lumber and can
make staining and finishing difficult.
Another option is talcum powder applied with a
blackboard eraser rubbed in vigorously once a
week; this will fill casting pores and form a
moisture barrier. This method provides a
tabletop that is slick and allows rust rings to be
easily wiped from the surface. Another important
fact is that talcum powder will not stain wood or
mar finishes as wax pickup does.
Figure 38
Sharpening Knives
It is recommended that knives be replaced they
become dull or damaged.
22
Page 23

Lubrication
The bearings on the cutterhead are factory
lubricated and sealed for life – no lubrication
required.
Gearbox – The oil in the gearbox must be
drained and replaced after the first 20 hours of
operation. (See the Lubrication Table).
Inspect levels periodically and change yearly.
Replace gear oil more frequently under heavy
use. Fill until the oil reaches the top of the filler
plug port for correct oil level.
To replace the gearbox lubricant:
1. Remove the drain plug (3. Fig. 39), and filler
cap (A, Fig. 40). Drain dirty oil thoroughly.
2. Tighten the drain plug (3, Fig. 39).
3. Fill with clean lubricant through hole
(A, Fig. 40).
Tighten filler cap (A, Fig. 40).
Figure 39
No Fig Position Interval Suitable Types of Lubricant
1 39 Drive Chain Inspect and lubricate monthly Grease
2 39 Gear Box
3 41 Lead Screw Inspect and lubricate Monthly Grease
4 41 Column Inspect and lubricate weekly SAE-30
5 42 Table Chain
6 43 Feed Rollers
When operated more than
2,500 hours
Inspect monthly – lubricate
when needed
Inspect and lubricate daily
before startup
Lubrication Table
HD-100, Mobil Gear 627, Shell Omala
100, ESSO Spartan EP-100
Grease or good quality bicycle chain
lubricant
SAE-30
Figure 40
23
Page 24

Figure 41
Figure 43
Figure 42
Optional Accessories
708814 .................................................................................................................................. Knives (set of 3)
708119 .......................................................................................................................... Universal Mobil Base
24
Page 25

Troubleshooting
Performance Troubleshooting
Problem Possible Cause Solution
Snipe
Note: Snipe can
be minimized but
not eliminated
Fuzzy Grain
Torn Grain
Rough/Raised
Grain
Table rollers not set properly. Adjust rollers to proper height
Inadequate support of long
boards.
Uneven feed roller pressure front
to back.
Dull knives. Sharpen knives.
Lumber not butted properly. Butt end to end each piece of stock as they
Planing wood with a high
moisture content.
Dull knives. Sharpen or replace.
Too heavy a cut. Adjust proper depth of cut
Knives cutting against grain. Cut along the grain.
Dull knives. Sharpen knives.
Dull knives. Sharpen knives.
Too heavy a cut. Adjust proper depth.
Support long boards with extension rollers.
Adjust feed roller tension
pass through.
Remove high moisture content from wood by
drying.
Rounded, glossy
surface
Poor feeding of
lumber.
cut side to side.
Board thickness
does not match
depth of cut
scale.
Moisture content too high. Remove high moisture content from wood by
drying.
Dull knives. Sharpen or replace knives.
Feed speed too slow. Increase speed.
Cutting depth too shallow. Increase depth.
Inadequate feed roller pressure. Adjust feed roller tension. If proper tension
cannot be achieve, replace feed rollers
Planer bed rough or dirty. Clean pitch and residue, and wax planer table.
Transmission v-belt slipping. Tighten transmission v-belt.
Surface of feed rollers clogged. Clear pitch and residue out of teeth.
Knife projection. Adjust knife projection. Uneven depth of
Cutterhead not level with bed. Level bed.
Depth of cut scale incorrect. Adjust depth of cut scale.
25
Page 26

Mechanical Troubleshooting
Problem Possible Cause Solution
Chain jumping.
Machine will
not start/ restart
or repeatedly
trips circuit
breaker or
blows fuses.
Inadequate tension. Adjust chain tension.
Sprockets misaligned. Align sprockets
Sprockets worn. Replace sprockets.
No incoming power. Verify unit is connected to power
Overload automatic
reset has not reset
Planer frequently trips. One cause of overloading trips, which are not electrical in
Building circuit breaker
trips or fuse blows.
Loose electrical
connections.
When planer overloads on the circuit breaker built into
the motor starter, it takes time for the machine to cool
down before restart. Allow unit to adequately cool before
attempting restart. If problem persists, check amp setting
on the motor starter inside the electrical box.
nature, is too heavy a cut. The solution is to take a lighter
cut. If too deep a cut is not the problem, then check the
amp setting on the overload relay. Match the full load
amps on the motor as noted on the motor plate. If the
amp setting is correct then there is probably a loose
electrical lead. Check amp setting on motor starter.
Verify that planer is on a circuit of correct size. If circuit
size is correct, there is probably a loose electrical lead.
Check amp setting on motor starter.
Go through all the electrical on the planer including motor
connections, verifying the tightness of each. Look for any
signs of electrical arcing which is a sure indicator of loose
connections or circuit overload.
Motor starter failure. Examine motor starter for burned or failed components. If
damage is found, replace motor starter. If motor starter
looks okay but is still suspect, you have two options: have
a qualified electrician test the motor starter for function, or
purchase a new starter and establish if that was the
problem on changeout
Motor starter failure. If you have access to a voltmeter, you can separate a
starter failure from a motor failure by first, verifying
incoming voltage at 220+/-20 and second, checking the
voltage between starter and motor at 220+/-20. If
incoming voltage is incorrect, you have a power supply
problem. If voltage between starter and motor is
incorrect, you have a starter problem. If voltage between
starter and motor is correct, you have a motor problem.
Motor failure. If electric motor is suspect, you have two options: Have a
qualified electrician test the motor for function or remove
the motor and take it to a quality electric motor repair
shop and have it tested.
Miswiring of the unit. Double check to confirm all electrical connections are
correct and properly tight. The electrical connections
other than the motor are pre-assembled and tested at the
factory. Therefore, the motor connections should be
double checked as the highest probability for error. If
problems persist, double-check the factory wiring.
26
Page 27

Parts List for the JWP-16OS Planer
Head Assembly
27
Page 28

Head Assembly Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Quantity
1 ...............JWP16OS-101 .........Pulley Guard ............................................................................................. 1
2. ..............JWP16OS-102 ......... V-belt ....................................................................M27 ............................. 3
3 ...............TS-1491041 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M10×30L..................... 3
4 ...............TS-1550071 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M10 ............................. 4
5 ...............JWP16OS-105 .........Pulley Cover.............................................................................................. 1
6 ...............JWP16OS-106 ......... Motor Cable............................................................................................... 1
7 ...............JWP16OS-107 .........Strain Relief............................................................................................... 1
8 ...............JWP16OS-108 .........Motor ......................................................................................................... 1
9 ...............JWP16OS-109 .........Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M10×80L..................... 1
10 .............JWP16OS-110 ......... Hex Flange Screw................................................ M6×12L..................... 27
11 .............JWP16OS-111 ......... Spacer....................................................................................................... 1
12 .............TS-1490041 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M8×25L....................... 1
13 .............TS-1550061 .............Flat Washer .......................................................... M8 ............................... 9
14 .............JWP15H-014............Machine Pulley.......................................................................................... 1
15 .............TS-1540061 .............Hex Nut ................................................................M8 ............................. 12
17 .............JWP16OS-117 ......... Motor Mount......................................................... .................................... 1
18 .............TS-1490081 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M8×45L....................... 4
19 .............PA-C61 ....................Spring........................................................................................................ 1
20 .............PA-C58 .................... Bracket ...................................................................................................... 1
21 .............PA-C59 .................... Shaft .......................................................................................................... 1
22 .............PA-C57 ....................Idle Pulley.................................................................................................. 1
23 .............PA-C56 .................... Shaft .......................................................................................................... 1
24 .............PA-C60 ....................Hanger ...................................................................................................... 1
25 .............TS-1503031 .............Socket Head Cap Screw ...................................... M6×12L....................... 3
26 .............JWP16OS-126 ......... Collector Hood ..........................................................................................1
27 .............JWP16OS-127 ......... Upper Cover.............................................................................................. 1
28 .............JWP15H-040............Deflector Plate .......................................................................................... 1
29 .............JWP16OS-129 ......... Cap............................................................................................................ 3
30 .............TS-1504101 .............Socket Head Cap Screw ...................................... M8×50L....................... 4
31 .............TS-1540072 .............Hex Nut ................................................................M10-1.25M.................. 4
33 .............JWP16OS-133 .........Label, Direction ......................................................................................... 1
34 .............JWP16OS-134 .........Handwheel ................................................................................................ 1
35 .............JWP15H-060............Handle....................................................................................................... 1
36 .............JWP15H-109............Knob.......................................................................................................... 1
37 .............JWP15H-108............Lock Bushing ............................................................................................ 2
38 .............TS-1482021 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6×12L....................... 4
39 .............TS-1550041 .............Flat Washer .......................................................... M6 ............................... 6
40 .............JWP16OS-140 ......... Head Casting ............................................................................................ 1
41 .............JWP15H-036............Plate Spring............................................................................................... 3
42 .............JWP15H-021............Socket Set Screw................................................. M22-1.5P×20L ............ 4
43 .............TS-1523051 .............Socket Set Screw................................................. M6×16L....................... 4
44 .............JWP16OS-144 ......... Shaft.......................................................................................................... 2
45 .............JWP15H-106............Lock Bushing ............................................................................................ 2
46 .............PF-C22.....................Plate .......................................................................................................... 2
47 .............JWP15H-062............Spring Pin.................................................................................................. 2
48 .............JWP15H-061............Cover......................................................................................................... 1
49 .............TS-1504091 .............Socket Head Cap Screw ...................................... M8×45L....................... 1
50 .............JWP16OS-150 .........Ball Bearing.......................................................... 6205-2NSE ................. 1
51 .............JWP16OS-151 ......... Key....................................................................... 8×8×40........................ 1
52 .............JWP16OS-152 ......... Knife Bar ................................................................................................... 3
53 .............708814 .....................Knives (Set of 3) ....................................................................................... 1
54 .............JWP16OS-154......... Spring ........................................................................................................ 6
55 .............TS-1513021 .............Socket Head Flat Screw ...................................... M5×12L....................... 6
56 .............JWP16OS-156......... Cutterhead ................................................................................................ 1
28
Page 29

Head Assembly Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Quantity
57 .............JWP15H-007............Screw ...................................................................................................... 18
58 .............TS-1503041 .............Socket Head Cap Screw ...................................... M6×16L....................... 8
59 .............TS-1524031 .............Socket Set Screw................................................. M8×12L....................... 1
60 .............JWP15H-020............Spring........................................................................................................ 4
61 .............JWP208-019 ............Bushing ..................................................................................................... 4
62 .............JWP15H-022............Plate .......................................................................................................... 4
63 .............TS-1490031 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M8×20L....................... 5
64 .............TS-1540041 .............Hex Nut ................................................................M6 ............................... 6
65 .............JWP16OS-165 .........Outfeed Roller ........................................................................................... 1
66 .............JWP15H-046............Limiter Plate .............................................................................................. 1
67 .............TS-1534041 .............Machine Screw, Flat Head Phillips ......................M5-10L........................ 2
68 .............JWP15H-026............Key ....................................................................... 5×5×22........................ 2
69 .............JWP16OS-169 ......... Rivet.......................................................................................................... 2
70 .............JWP15H-031............Sprocket .................................................................................................... 4
72 .............TS-1482031 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6×16L....................... 2
73 .............JWP15H-073............Chain.................................................................... 06B×63P ..................... 1
74 .............JWP16OS-174 ......... Chip Bracket.............................................................................................. 1
75 .............JWP16OS-175 ......... Shaft.......................................................................................................... 1
76 .............JWP16OS-176 ......... Knob.......................................................................................................... 1
77 .............JWP15H-045............Retaining Ring ..................................................... ETW-15....................... 2
78 .............JWP15H-042............Collar....................................................................................................... 45
79 .............JWP15H-041............Anti-Kick Finger....................................................................................... 44
80 .............JWP16OS-180 ......... Shaft.......................................................................................................... 1
81 .............JWP16OS-181 .........Infeed Roller.............................................................................................. 1
82 .............JWP15H-027............Sprocket .................................................................................................... 1
83 .............JWP16OS-183 ......... Power Cord ............................................................................................... 1
84 .............JWP16OS-184 ......... Key....................................................................... 5×5×30........................ 1
85 .............JWP15H-017............Motor Pulley .............................................................................................. 1
87 .............JWP16OS-187 ......... Switch........................................................................................................ 1
88 .............JWP16OS-188 ......... Switch Plate .............................................................................................. 1
89 .............JWP16OS-189 ......... Tooth Washer .......................................................................................... 2
90 .............JWP16OS-190 ......... Screw ................................................................... 3/16-24 x 1-3/4............ 2
91 .............JWP16OS-191 ......... Hex Nut ................................................................ 3/16-24........................ 2
92 .............JWP16OS-192 ......... Strain Relief............................................................................................... 2
29
Page 30
Base Assembly
Base Assembly Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Quantity
1 ...............JWP16OS-201 ......... Lifting Handle ............................................................................................ 4
2 ...............JWP15H-207............Nut Fixture................................................................................................. 4
3 ...............JWP16OS-203 .........Leadscrew................................................................................................. 3
4 ...............JWP16OS-204 .........Column...................................................................................................... 4
5 ...............TS-1523041 .............Socket Set Screw................................................. M6×12L....................... 4
6 ...............JWP15H-203............Column...................................................................................................... 4
7 ...............JWP16OS-207 .........Base .......................................................................................................... 1
8 ...............TS-1525021 .............Socket Set Screw................................................. M10×12L..................... 8
9 ...............JWP16OS-209 .........Roller ......................................................................................................... 2
10 .............BB-608Z ...................Ball Bearing............................................................................................... 4
11 .............JWP15H-104............Eccentric Shaft .......................................................................................... 4
12 .............JWP15H-221............Bracket ...................................................................................................... 1
13 .............JWP15H-222............Shaft.......................................................................................................... 1
14 .............JWP15H-223............Sprocket .................................................................................................... 1
15 .............JWP15H-224............Retaining Ring ..................................................... STW-15....................... 1
16 .............JWP16OS-216 .........Chain.................................................................... 41×148P .....................1
17 .............TS-1550061 .............Flat Washer .......................................................... M8 ............................. 18
30
Page 31

Base Assembly Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Quantity
18 .............TS-1490041 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M8×25L....................... 2
19 .............BB-6202ZZ...............Ball Bearing.......................................................... 6202ZZ........................ 4
20 .............JWP15H-214............Retaining Ring ..................................................... RTW-35....................... 4
21 .............JWP15H-216............Sprocket .................................................................................................... 4
22 .............TS-0680041 .............Flat Washer .......................................................... 3/8 ............................... 4
23 .............TS-1540072 .............Nut........................................................................ M10-1.25P .................. 4
24 .............JWP15H-209............Retaining Ring ..................................................... RTW-38....................... 1
25 .............JWP15H-208............Bushing ..................................................................................................... 1
26 .............JWP16OS-226 ......... Key....................................................................... 4×4×20........................ 1
27 .............JWP16OS-227 .........Leadscrew................................................................................................. 1
28 .............JWP16OS-228 ......... Scale ......................................................................................................... 1
29 .............TS-1531012 .............Machine Screw, Pan Head Phillips ......................M3×6L ......................... 2
30 .............JWP16OS-230 ......... Column...................................................................................................... 1
31 .............TS-1490031 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M8×20L....................... 6
32 .............TS-1524031 .............Socket Set Screw................................................. M8×12L....................... 6
33 .............TS-1490051 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M8×30L....................... 4
35 .............JWP16OS-235 ......... E-ring.................................................................... ETW-10....................... 4
36 .............JWP15H-111............Roller Frame ............................................................................................. 2
37 .............TS-1482021 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6×12L..................... 12
38 .............TS-1550041 .............Flat Washer .......................................................... M6 ............................. 12
39 .............JWP15H-113............Roller Liner.............................................................................................. 12
40 .............JWP15H-114............Roller Shaft ............................................................................................... 6
41 .............JWP15H-112............Roller......................................................................................................... 6
31
Page 32

Gear Box Assembly
32
Page 33

Gear Box Assembly Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Quantity
1 ...............TS-1550041 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M6 ............................... 2
2 ...............TS-1503031 .............Socket Head Cap Screw...................................... M6×12L....................... 1
3. ..............BB-6204ZZ...............Ball Bearing.......................................................... 6204ZZ........................ 1
4 ...............JWP15H-304............Gear .......................................................................................................... 1
5 ...............TS-1503061 .............Cap Screw............................................................ M6x25L ....................... 6
6 ...............BB-6201 ...................Ball Bearing.......................................................... 6201............................ 1
7 ...............JWP15H-309............Gear .....................................................................47T.............................. 1
8 ...............JWP15H-310............Gear .....................................................................18T.............................. 1
9 ...............JWP15H-313............Key ....................................................................... 5x5x10 ........................ 2
10 .............JWP15H-337............Cover......................................................................................................... 1
11 .............JWP15H-335............Pin ............................................................................................................. 2
12 .............JWP15H-339............Oil Plug...................................................................................................... 2
13 .............OS-28408.................Oil Seal................................................................. TC28x40x8 ................. 1
14 .............JWP15H-301............Gear Box ................................................................................................... 1
15 .............JWP15H-336............Gasket....................................................................................................... 1
16 .............BB-6201Z .................Ball Bearing.......................................................... 6201Z.......................... 3
17 .............JWP15H-314............Shaft.......................................................................................................... 1
18 .............JWP15H-320............Key ....................................................................... 6x6x40 ........................ 1
19 .............JWP15H-312............Gear ..................................................................... 71T.............................. 1
20 .............JWP15H-334............Knob.......................................................................................................... 1
21 .............JWP15H-325............Sprocket ............................................................... 12T .............................. 1
22 .............TS-1482031 .............Hex Cap Screw .................................................... M6x16L ....................... 1
23 .............JWP15H-318............Gear Assembly .................................................... 96/92T......................... 1
24 .............JWP15H-323............Shaft.......................................................................................................... 1
25 .............JWP15H-322............Spring........................................................................................................ 1
26 .............JWP15H-321............Ball ............................................................................................................ 1
27 .............OS-25476.................Oil Seal...................................................................................................... 1
28 .............BB-6204Z .................Ball Bearing.......................................................... 6204Z.......................... 1
29 .............JWP16OS-329 ......... Hex Flange Screw................................................ M6x12L .......................1
30 .............JWP15H-329............Clutch ........................................................................................................ 1
31 .............JWP15H-330............Handle....................................................................................................... 1
32 .............JWP15H-333............Oil Seal...................................................................................................... 1
33
Page 34

Stand Assembly
Stand Assembly Parts List
Index No. Part No. Description Size Quantity
1 ...............JWP16OS-401 ......... Upper Side Brace (L) ................................................................................ 1
2 ...............JWP16OS-402 ......... Upper Front Brace ....................................................................................2
3 ...............JWP16OS-403 ......... Down Side Brace (R) ................................................................................ 2
4 ...............JWP16OS-404 ......... Down Front Brace..................................................................................... 2
5 ...............TS-1550061 .............Flat Washer.......................................................... M8 ............................. 48
6 ...............TS-0561021 .............Hex Nut ................................................................ 5/16”-18 .................... 32
7 ...............JWP16OS-407 ......... Carriage Bolt ........................................................ 5/16”-18×14L ............ 32
8 ...............TS-1540061 .............Hex Nut ................................................................ M8 ............................. 12
9 ...............TS-1515021 .............Socket Head Flat Screw ...................................... M8x20L .......................8
10 .............JWP16OS-410 ......... Foot........................................................................................................... 4
12 .............JWP16OS-412 ......... Leg ............................................................................................................ 4
13 .............JWP16OS-413 ......... Upper Side Brace (R)................................................................................ 1
34
Page 35

Electrical Schematic for JWP-16OS Planer
35
Page 36

WMH TOOL GROUP
2420 Vantage Drive
Elgin, IL 60123
Ph: 888-8097-7129 ▪ Fax: 800-274-6840
www.wmhtoolgroup.com
36
 Loading...
Loading...