
TDZ 2000 GL2/ExtremeZ GL2
System Reference
November 1998
DHA028520

Copyright
1998 Intergraph Computer Systems. All rights reserved. This document contains information protected by copyright, trade secret, and
trademark law. This document may not, in whole or in part, be reproduced in any form or by any means, or be used to make any
derivative work, without written consent from Intergraph Computer Systems.
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subdivision (c)(1)(ii) of the rights in
technical data and computer software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013. Unpublished rights are reserved under the copyright laws of the
United States.
Intergraph Computer Systems, Huntsville AL 35894-0001
Notice
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be considered a commitment by Intergraph Computer
Systems. Intergraph Computer Systems shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors in, or omissions from, this document. Intergraph
Computer Systems shall not be liable for incidental or consequential damages resulting from the furnishing or use of this document.
All warranties given by Intergraph Computer Systems about equipment or software are set forth in your purchase contract. Nothing stated
in, or implied by, this document or its contents shall be considered or deemed a modification or amendment of such warrantites.
Trademarks
Intergraph and the Intergraph logo are registered trademarks, and Ultra-Tower, TDZ, and Intense 3D are trademarks of Intergraph
Computer Systems.
Other brands and product names are trademarks of their respective owners.
FCC/DOC Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy. If the equipment is not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, it may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, try to correct the interference as follows: reorient or relocate the affected device; increase the separation between this equipment
and the affected device; connect this equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from the circuit to which the affected device is connected;
consult a dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help.
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations. Cet appareil
numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigencies du Règlement sur le materiél brouilleur du Canada.
Warnings
The service and upgrade instructions should be performed by qualified personnel only. Qualified personel do not have to be Intergraph
service personnel. Those who are familiar with servicing computers can follow instructions in a manual to service equipment, and do so
without harm to themselves or damage to the equipment.
Changes or modifications made to the system that are not approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority
to operate the equipment.
To reduce the risk of electrical shock, do not attempt to open the equipment unless instructed. Do not use a tool for purposes other than
instructed.
There is a danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type as
recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions.
There are no user serviceable parts within the power supply. In the event of failure, the power supply must be replaced by qualified service
personnel. Use Intergraph power supplies only.
To comply with FCC Class B limits, you must use shielded cables with this device.

Notes
Read all safety and operating instructions before using the equipment. Keep these instructions for future reference. Follow all warnings on
the equipment or in the operating instructions.
This device is designed and manufactured to comply with approved safety standards for information processing and business equipment.


Contents
Introduction............................................................................................................... vii
About This Document................................................................................................. vii
Document Conventions............................................................................................... vii
Customer Support...................................................................................................... viii
Hardware and Software Support Services..................................................... viii
World Wide Web......................................................................................... viii
Intergraph Bulletin Board Service ................................................................ viii
FAXLink........................................................................................................ ix
Telephone ...................................................................................................... ix
More Support Options.................................................................................... ix
1 Accessing the System................................................................................................1
Before You Begin..........................................................................................................2
Tools .............................................................................................................................2
Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge.....................................................................2
Opening and Closing the Case .......................................................................................3
System Views................................................................................................................4
v
2 Servicing the System................................................................................................7
Before You Begin..........................................................................................................8
Case Components ..........................................................................................................8
Peripheral Drives.........................................................................................................12
Floppy Disk Drive.......................................................................................... 12
CD-ROM Drive..............................................................................................13
External Bay Disk Drives............................................................................... 13
Internal Bay Disk Drives................................................................................15
Power Supply...............................................................................................................17
Processor Modules.......................................................................................................19
Heat-Sink Mounting Brackets......................................................................................20
Retention Modules.......................................................................................................21
DIMMs........................................................................................................................22
System Board...............................................................................................................23
Expansion Cards.......................................................................................................... 24
Fans.............................................................................................................................25
Lithium (CMOS/Clock) Battery...................................................................................26
LEDs, Light Pipe, and Power Switch ...........................................................................26
3 Upgrading the System............................................................................................29
Before You Begin........................................................................................................30
Adding Memory...........................................................................................................30
Precautions.....................................................................................................30
Memory Configurations .................................................................................31

vi
Adding a Processor......................................................................................................32
Single-to-Dual Upgrade..................................................................................32
Adding Expansion Cards .............................................................................................33
Slot Locations................................................................................................33
Installing Expansion Cards ............................................................................34
Assigning System Resources.......................................................................... 35
Adding Drives and Devices..........................................................................................35
Device Locations............................................................................................36
Adding External SCSI Drives ......................................................................................37
SCSI Cable Length Guidelines.......................................................................37
SCSI Cable Quality Guidelines.......................................................................38
SCSI ID Guidelines........................................................................................38
SCSI Termination Guidelines for External Devices ........................................38
Connecting the Device ...................................................................................39
Changing SCSI Adapter or Device Settings....................................................39
4 System Hardware Overview and Specifications....................................................41
Hardware Overview.....................................................................................................42
Functional Diagram .....................................................................................................43
System Board...............................................................................................................44
System Configuration Summary...................................................................................44
System Model Number.................................................................................................46
Specifications...............................................................................................................47
Hardware Monitoring ..................................................................................................48
Temperature Sensors...................................................................................... 48
Optional Hardware.......................................................................................................48
5 Peripherals..............................................................................................................49
Peripheral Cables.........................................................................................................50
EIDE Cable Connection Locations.................................................................50
Internal LVD SCSI Cable Connection Locations............................................50
Internal Ultra SCSI Cable Connection Locations............................................51
Floppy Cable Connection Locations...............................................................51
Peripheral Configuration..............................................................................................52
EIDE CD-ROM Drive....................................................................................52
SCSI CD-Recorder.........................................................................................53
Iomega JAZ 1 GB Internal SCSI Drive...........................................................54
Floppy Disk Drive.......................................................................................... 55
SCSI Disk Drives...........................................................................................55
6 Power Supply and Cooling Fans............................................................................. 57
Power Supply...............................................................................................................58
Cooling Fans ...............................................................................................................59

Introduction
This System Reference provides information necessary to service and upgrade a TDZ 2000
GL2 or ExtremeZ GL2 system.
About This Document
This document is organized as follows:
u
Chapter 1, “Accessing the System,” provides information you need to gain access to the
system.
u
Chapter 2, “Servicing the System,” describes how to replace standard parts in the
system.
u
Chapter 3, “Upgrading the System,” describes how to upgrade system components.
u
Chapter 4, “System Hardware Overview and Specifications,” provides general technical
information about the system hardware.
u
Chapter 5, “Peripherals,” provides information on cabling and configuration of common
system peripherals.
vii
u
Chapter 6, “Power Supply and Cooling Fans,” provides information on the system’s
power supply and cooling fans.
Document Conventions
Bold
Italic Variable values that you supply, or cross-references.
Monospace
SMALL CAPS Key names on the keyboard, such as D, ALT or F3. Names of files and
CTRL+D Press a key while simultaneously pressing another key; for example, press
Commands, words, or characters that you key in literally.
Output displayed on the screen.
directories. You can type filenames and directory names in the dialog boxes
or the command line in lowercase unless directed otherwise.
CTRL and D simultaneously.

viii
Customer Support
Intergraph Computer Systems offers an assortment of customer support options.
Hardware and Software Support Services
Intergraph Computer Systems provides a variety of hardware services for Intergraph and
third-party equipment. Services include warranty upgrades, repair depot service, on-site
hardware maintenance, system administration, and network consulting. Hardware
purchased from Intergraph Computer Systems includes a factory warranty ranging from 30
days to three years. A detailed warranty description is available on the World Wide Web;
see the Support pages at http://www.intergraph.com/ics.
Intergraph Computer Systems provides complimentary software support for 30 or 90 days
following shipment of a hardware or software product. This includes World Wide Web
access, Intergraph Bulletin Board Service access, FAXLink service, and telephone (Help
Desk) support. At the end of the complimentary support period, you can purchase other
levels of software support.
World Wide Web
You can visit Intergraph Computer Systems on the World Wide Web at
http://www.intergraph.com/ics. On these pages, you can get news and product
information, technical support information, software updates and fixes, and more.
Intergraph Bulletin Board Service
On the Intergraph Bulletin Board Service (IBBS), you can get technical support information,
software updates and fixes, and more.
To connect to the IBBS:
1. Set your system’s communications protocol for eight (8) data bits, no parity, one (1) stop
bit, and any baud rate up to 14,400.
2. Using a modem, call 1-256-730-8786. Outside the United States, call one of the mirror
sites listed on World Wide Web; see the Software Support pages at
http://www.intergraph.com.
3. At the login prompt, key in your user ID. If you have not connected before, type in new
to create a user ID.
4. Follow the menus to find what you need. The IBBS provides clear choices and online
help.

If you have trouble connecting to or using the IBBS, call the Customer Response Center at
1-800-633-7248 (product entry IBBS) or leave a message for the IBBS System Operator at
1-256-730-1413.
FAXLink
To use the FAXLink:
u
u
Telephone
To get customer support by telephone:
u
u
ix
Call 1-800-240-4300 for information on how to get technical support information using
the FAXLink.
Call 1-256-730-9000 to get documents (up to five per call).
In the United States, call 1-800-633-7248 between the hours of 7:00 a.m. and 7:00
p.m. Central Time, Monday through Friday (except holidays).
Outside the United States, contact your local Intergraph Computer Systems subsidiary or
distributor.
Have the following information available when you call:
u
Your service number, which identifies your site to Intergraph Computer Systems. You
use your service number for warranty or maintenance calls.
u
Your Customer Personal Identification Number (CPIN). You get a CPIN the first time
you call the Customer Response Center; it is associated with your service number for
future call logging.
u
The product’s name or model number.
u
The product’s serial number. Software product serial numbers are included in the
product packaging. Hardware product serial numbers are on a sticker affixed to the
hardware product.
u
Your name and telephone number.
u
A brief description of the question or problem.
More Support Options
To get information on more customer support options:
u
Visit the Support pages on the World Wide Web at http://www.intergraph.com/ics.
u
For hardware support questions in the United States, call 1-800-763-0242.

x
u
For software support questions in the United States, call 1-800-345-4856.
u
Outside the United States, contact your local Intergraph Computer Systems subsidiary or
distributor.

1 A ccessing the System
This chapter lists hand tools and describes servicing restrictions, methods for avoiding
electrostatic discharge, and how to remove and attach cover panels from a TDZ 2000 GL2 or
ExtremeZ GL2 workstation.
Before You Begin..........................................................................................................2
Tools .............................................................................................................................2
Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge.....................................................................2
Opening and Closing the Case .......................................................................................3
System Views................................................................................................................4
1

2
Before You Begin
WARNING Disconnect the system and peripheral devices from AC power before servicing internal
components! Failure to remove AC power may result in equipment damage or
personal injury.
CAUTION Use an antistatic wrist strap for all servicing procedures to avoid the possibility of
electrostatic discharge.
CAUTION Follow all warnings and cautions in the servicing instructions. If you fail to follow
documented, approved procedures, personal injury and damage to equipment can result.
“Right side” and “left side” are as seen from the front of the unit.
Tools
You will need the following tools to service the system:
u
Antistatic wrist strap
u
Antistatic mat connected to an earth ground
u
Quarter-inch nutdriver
u
No. 1 and No. 2 Phillips screwdrivers
u
Small or medium flat-blade standard screwdriver
You do not need any tools to open the TDZ 2000 GL2/ExtremeZ GL2 case.
Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage sensitive components inside the unit. Take the
following precautions when working with internal components:
u
Unplug the unit from AC power before servicing any electronic component inside the
chassis. Remember that the system is always on when connected to AC power.
u
Touch the bare metal of the chassis to ensure the chassis and your body are at the same
electric potential.
u
Attach the antistatic wrist strap to its connector on the antistatic mat. Ensure that the
metal conductor bead in the elastic sleeve of the antistatic strap contacts bare skin.
u
Handle all printed circuit boards as little as possible and by the edges only.
u
Leave new parts in their protective packaging until you install them.

Opening and Closing the Case
CAUTION Before you open the case, shut down the system and turn off power to the system and
external devices (including peripheral drives and display). Use caution to avoid injury when
lifting the computer or removing covers and other hardware.
Opening the system for service or upgrades consists of two simple steps. Remove the top
cover first, then remove the left side panel. No tools are needed. You need only remove the
top cover and left side panel for most routine service procedures. See Chapter 2, “Servicing
the System,” for additional details on removing and replacing case components.
CAUTION Do not use the bottom portion of the face panel or the lip at the top, rear of the unit as a hand
hold when moving the system. Equipment damage and personal injury can result.
NOTE Removing the right side panel is necessary only for servicing internal bay disk drives, the
plastic cowling on the right panel, or the face panel.
To open the case:
1. Ensure the system is shut down and that you have disconnected the system and any
attached external devices from AC power.
3
2. Grasp the lip on the top cover at the rear of the system and press up on the release. See
the following figure.
3. Keep pressing the release, slide the top cover back until it stops, remove it from the
chassis, and set it aside.
Press up on release,
located under lip
4. Grasp the cowling at the bottom of the left side panel and lift.
5. Slide the left side panel back until it stops, remove it from the chassis, and set it aside.
6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 to remove the right side panel, if necessary.

4
To close the case:
1. Place the side panel on the chassis so that all tabs on the rear of the chassis insert into
their slots.
2. Push the side panel toward the front of the chassis, then push down to seat the panel.
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 to install the remaining side panel, if necessary.
4. Place the top cover on the chassis so that all tabs are inserted into their slots.
5. Slide the top cover forward until it locks into place.
CAUTION After servicing or upgrading the system, always replace the covers that were removed. The
covers ensure the system maintains proper air flow, so internal components do not overheat
and fail. The covers also ensure that electromagnetic interference (EMI) emissions remain
below the standard requirements.
System Views
The front, left view below shows major parts of the system without covers, cables, system
board and option cards.

The back, left view below shows the chassis with all major components removed.
5

6

2 Servicing the System
This chapter describes how to replace the standard parts within a TDZ 2000 GL2 or
ExtremeZ GL2 system.
Before You Begin..........................................................................................................8
Case Components ..........................................................................................................8
Peripheral Drives.........................................................................................................12
Floppy Disk Drive.......................................................................................... 12
CD-ROM Drive..............................................................................................13
External Bay Disk Drives............................................................................... 13
Internal Bay Disk Drives................................................................................15
Power Supply...............................................................................................................17
Processor Modules.......................................................................................................19
Heat-Sink Mounting Brackets......................................................................................20
Retention Modules.......................................................................................................21
DIMMs........................................................................................................................22
System Board...............................................................................................................23
Expansion Cards.......................................................................................................... 24
Fans.............................................................................................................................25
Lithium (CMOS/Clock) Battery...................................................................................26
LEDs, Light Pipe, and Power Switch ...........................................................................26
7

8
Before You Begin
WARNING Disconnect the system and peripheral devices from AC power before servicing internal
components! Failure to remove AC power may result in equipment damage or
personal injury.
WARNING There is a danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced.
CAUTION Use an antistatic wrist strap for all servicing procedures to avoid the possibility of
electrostatic discharge.
CAUTION Do not overtighten screws and other fasteners to avoid damaging threads.
CAUTION Follow all warnings and cautions in servicing instructions. I f you fail to follow documented,
approved procedures, personal injury or damage to equipment can result.
See Chapter 1, “Accessing the System,” for instructions on opening the system, protecting
against electrostatic discharge, and closing the system. “Right side” and “left side” are as
seen from the front of the unit. Servicing procedures assume you have removed the left side
panel from the system.
Case Components
Ordinarily you will not need to replace any of the external case components unless they are
broken or cosmetically damaged. All case components are designed for durability, but the
door and hinge assembly may require replacement before other items.
To replace the hinge or door, you must first remove the top cover. To replace the face panel,
you must remove the top cover and the door.
To replace the top cover:
1. Remove the top cover.
2. Install the new cover.
To replace the door and hinge assembly:
1. Remove the top cover.
2. Lift the door and hold it at a 90-degree angle from the face panel.
3. Insert a small flat-blade screwdriver between the door and hinge, near one of the square
holes on the underside of the door.

9
r
Guide slot (1 per si de)
Doo
Locking tabs
Stop tabs
Hinge
Stop tabs
4. Pull the door toward you and pry the hinge and door apart until one side of the door
releases from its locking tab.
5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 for the other side of the door hinge.
6. Remove the door.
7. Do both of the following on the underside of the door:
−
Spread the release tabs on the large emblem and remove it
−
Squeeze the release tabs on the small emblem and remove it
8. Slide the hinge toward the front of the chassis until it stops.
9. Use a flat-blade screwdriver and pry each of the stop tabs on the hinge until the hinge
releases from the rails.
10. Orient the new hinge so that the locking tabs face down and insert the new hinge into
the track and push it forward until it stops.
11. Hold the hinge, align the beveled edges of the hinge with the guide slots on the door,
and push the door firmly onto the hinge until it snaps into place.
12. Press the two emblems onto the door until they snap into place.
13. Operate the door to test its movement.
14. Replace the top cover.
To replace the hinge rails:
1. Remove the door. See the previous procedure for details.
2. Slide the hinge toward the front of the chassis until it stops.
3. Use a flat-blade screwdriver and pry each of the stop tabs on the hinge until the hinge
releases from the rails.

10
Hinge rails
4. Remove the hinge from the rail.
5. Press a hinge rail toward the middle of the chassis until all four tabs release.
6. Lift the hinge rail off the chassis.
7. Orient the new hinge rail the same way as the one you removed, place the tabs in the
slots, and press outward until the rail snaps into place.
8. From the front of the chassis, slide the hinge into the rails.
To replace the face panel:
1. Remove the top cover and both side panels.
2. Remove the door.
3. Push the hinge back, away from the front of the chassis.
4. Use a flat-blade screwdriver to gently pry and release each of the plastic tabs on both
sides of the chassis. The tabs on the right side of the chassis are recessed. First release
the bottom tabs, release the middle tabs, and then release the top tabs.
CAUTION Release the tabs with care. Do not apply more pressure than necessary.

11
Tab
(3 per side)
Light pipe guides
Standoff posts
(4 per side)
Tab
(3 per side)
Standby switch
Power switch
5. Pull the face panel away from the chassis slightly to ensure all tabs are released.
6. Grasp the left side of the face panel and pivot it left to expose the switch and cable.
7. Spread the plastic switch mount locking tabs, grasp the switch, and pull the switch out
of its mount.
8. Turn the face panel downward until the switch button drops out.
9. Place the left side of the new face panel near the left, front of the chassis and orient the
switch so that the black and green wires are at the bottom.
10. Push the switch into the mount until it snaps into place.
11. Place the switch button into its hole and push firmly until it seats.
12. Align the new face panel with the tab notches and light pipe guides, and carefully push
the panel onto the chassis until all tabs engage.
13. Replace the door, left and right side panels, and top cover.
To replace the left or right side plastic cowling:
1. Remove the top cover, then remove the side panel that has the cowling you want to
replace.
2. Place the side panel, with the cowling side down, on a flat, padded surface.
3. Remove the screw that secures the plastic to the side panel.

12
4. Grasp one side of the panel, press the release tabs, and lift the panel off the plastic.
5. Turn the side panel over and press the new plastic onto the panel until the release tabs
engage.
6. Turn the side panel over and install the screw.
7. Replace the side panel onto the chassis.
8. Replace the top cover.
Peripheral Drives
This section explains how to replace the floppy, CD-ROM, and internal and external bay
disk drives. See Chapter 5, “Peripherals,” for details on drive configuration and cables.
Floppy Disk Drive
To replace the floppy disk drive:
1. Disconnect the power cable and data cable from the drive. Note the position of the red
stripe on the data cable.
2. Remove the two screws that secure the floppy drive to the chassis.
CD-ROM mounting
3. From inside the chassis, push the back of the floppy drive until the bezel clears the
4. Slide the new floppy drive into the chassis and align the mounting holes.
screws
Floppy drive m ounti ng
screws
chassis, and slide the device out.

5. Install the two mounting screws.
6. Connect the data cable and the power cable.
CD-ROM Drive
To replace the CD-ROM drive:
1. Disconnect the power cable, data cable, and audio cable from the CD-ROM drive.
2. Remove the screws that secure the CD-ROM drive to the chassis. See the previous
figure.
3. From inside the chassis, push the back of the CD-ROM until the bezel clears the chassis,
then slide the device out.
4. Remove the mounting guide from the right side of the CD-ROM. See the following
figure.
13
Mounting guide
5. Note the jumper settings on the rear of the CD-ROM.
6. Set the master/slave jumper to the same position as the old drive.
7. Install the mounting guide on the right side of the new CD-ROM.
8. Slide the new CD-ROM drive into the chassis and align the mounting holes.
9. Install the screws that secure the CD-ROM to the chassis.
10. Connect the audio cable, data cable, and power cable.
External Bay Disk Drives
If a Kingston or other brand of removable disk module is installed in the external bay, see
the vendor documentation for disk drive and module replacement instructions.

14
y
To replace an external bay disk drive:
1. Disconnect the data cable and power cable from the disk drive.
2. Remove the two screws that secure the external bay disk drive tray to the chassis.
External ba
mounting screws
3. From inside the chassis, push the tray out of the external bay, grasp the front of the tray,
and then slide it out of the bay.
4. Remove the screws that secure the disk drive to the tray and remove the drive.
5. Do one of the following:
−
If installing an EIDE drive, set the master/slave jumper setting on the new drive to
match that of the old drive
−
If installing a SCSI drive, set the SCSI ID on the new drive to match that of the old
drive.
See Chapter 5, “Peripherals,” for details on these tasks.
6. Place the disk drive in the tray, align the mounting holes, and install the mounting
screws that secure the disk drive to the tray. See the following figure.

Mounting guide
Drive tray
15
Access hole (2)
7. Slide the tray assembly into the chassis and align the mounting holes.
8. Install the screws that secure the tray to the chassis.
9. Connect the data cable and the power cable to the disk drive.
Internal Bay Disk Drives
To replace an internal bay disk drive:
1. Disconnect the data cable and power cable from the disk drive.
2. Remove the two screws that secure the drive bracket assembly to the left side of the
chassis.
3. Grasp the drive bracket assembly and remove the screw that secures the bracket to the
right side of the chassis.
4. Pull the drive bracket assembly out of the chassis.
5. Remove the four screws that secure the old drive to the bracket.
6. Do one of the following:
−
If installing an EIDE drive, set the master/slave jumper setting on the new drive to
match that of the old drive.

16
−
If installing a SCSI drive, set the SCSI ID on the new drive to match that of the old
drive.
See Chapter 5, “Peripherals,” for details on these tasks.
7. Install the new drive on the bracket.
Alignment tabs
Rear mounting tab
Front moun ting tabs
8. Insert the alignment tabs into the appropriate slots in the chassis.

Screw holes for front mounting tabs
9. Install the two screws that secure the drive bracket assembly front mounting tabs to the
chassis.
10. Install the screw that secures the drive bracket assembly to the right side of the chassis.
17
11. Install the right side panel.
12. Connect the data cable and the power cable to the new drive.
Power Supply
See Chapter 6, “Power Supply and Cooling Fans,” for details on the power supply.
To replace the power supply:
1. Note the location of all power cable connectors on the system board and peripheral
devices.
2. Disconnect all power cables from all internal devices and the system board.
3. Detach the air duct by removing the two screws securing it to the chassis, as shown in
the following figure, and then gently remove the air duct.

18
Power supply
Screws
Air duct
4. Remove the four outer screws from the rear of the power supply, as shown in the
following figure.
NOTE Support the power supply as you remove the screws. Do not to let the power supply fall as
you remove the fourth screw.
Inner screws
Outer screws
Outer screws
5. Remove the old power supply.
6. Remove the inner screws securing the rear plate to the power supply, as shown in the
previous figure.
7. Attach the rear plate to the new power supply using the inner screws, and then install
the new power supply using the outer screws.

8. Replace the air duct beneath the power supply, using the screws you removed previously.
9. Connect the power cables to the system board and internal devices. See Chapter 6,
“Power Supply and Cooling Fans,” for connection details.
Processor Modules
TDZ 2000 GL2 and ExtremeZ GL2 systems are compatible with 266, 300, 333, 350, 400,
and 450 MHz Pentium II processors. See the system board diagram in the System Board
Manual for connector and socket locations.
To replace a passive processor module:
1. Remove the air duct. See “Power Supply” in this chapter for details.
2. Remove the heat-sink lock from within the heat-sink fins, if necessary, by pressing the
ends of the lock inward and pulling outward.
3. Press the locking tabs on the top corners of the processor module inward, towards each
other, until they click into the release position.
4. Slide the processor module out of the retention module.
19
5. Remove the new processor from its antistatic package, and align the processor module
over the retention module. The processor module is keyed and fits only one way.
Processor
Retension module
Heat sink mounting bracket
Heat sink lock
6. Press the processor module down until it seats.

20
7. Press the processor module locking tabs outward until they click into the locked
position.
8. Install the heat-sink lock between the heat-sink fins, if necessary, by sliding the lock
between the fins and pressing it onto the heat-sink lock mounting posts.
9. Replace the air duct you removed previously.
To replace an active processor module:
1. Remove the air duct. See “Power Supply” in this chapter for details.
2. Disconnect the processor’s cooling fan power cable from the processor fan power
connector on the system board.
3. Press the locking tabs on the top corners of the processor module inward, towards each
other, until they click into the release position.
4. Slide the processor module out of the retention module.
5. Remove the new processor from its antistatic package, and align the processor module
over the retention module. The processor module is keyed and fits only one way.
6. Press the processor module down until it seats.
7. Press the processor module locking tabs outward until they click into the locked
position.
8. Connect the processor’s cooling fan power cable to the processor fan power connector on
the system board.
9. Replace the air duct you removed previously.
Heat-Sink Mounting Brackets
Pentium II processors equipped with heat-sink fins use heat-sink locks fastened to mounting
brackets to secure them to the system board, providing additional stability to the processor
module. See the system board diagram in the System Board Manual for connector and
socket locations.
To replace a heat-sink mounting bracket:
1. Remove the air duct. See “Power Supply” in this chapter for details.
2. Remove the processor module. See the “Processor Modules” in this chapter for details.
3. Two mounting locks on the rear side of the system board secure the mounting bracket.
Remove these locks, and then remove the mounting bracket from the system board.

4. The heat-sink mounting bracket has two pins on the bottom and four pins on the top.
The bottom two pins are of different sizes. The size of the pins and the holes in the
system board determine the correct orientation.
Insert the new heat-sink mounting bracket into the appropriate holes on the system
board. The bracket will click when it is correctly inserted. Ensure the four top pins are
closest to the processor slot.
5. Lock the heat-sink mounting bracket to the system board by inserting the two mounting
locks into the pins of the heat-sink mounting bracket, which are below the system board.
The locks will click when they are securely fastened.
6. Replace the air duct you removed previously.
Retention Modules
Pentium II processors are secured to the system board using retention modules. See the
system board diagram in the System Board Manual for connector and socket locations.
NOTE You do not need to replace a retention module to replace a processor module.
To replace a retention module:
21
1. Remove the air duct. See “Power Supply” in this chapter for details.
2. Remove the processor module. See “Processor Modules” in this chapter for details.
3. Remove the heat-sink locks, if necessary. See the “Heat-Sink Mounting Brackets”
section above for details.
4. Remove the screws securing the retention module to the system board, and remove the
retention module.
5. Locate the key pin on one end of the processor slot on the board. Carefully line up the
key notch on the new retention module with the key pin on the processor slot. The key
pin on the processor slot indicates the correct orientation of the CPU.
6. Lower the retention module down over the processor slot so that the retention module
seats flatly against the system board. Tighten the screws in a clockwise manner to
secure the module to the board.
WARNING Do not overtighten the screws as you may damage the module and/or the system
board.
7. Replace the heat-sink locks, if necessary. See “Heat-Sink Mounting Brackets” in this
chapter for details.
8. Replace the processor module. See “Processor Modules” in this chapter for details.
9. Replace the air duct you removed previously.

22
DIMMs
See “Adding Memory” in Chapter 3, “Upgrading the System,” for important details on
handling DIMMs. The DIMM sockets are located to the right of the processors on the
system board. See the system board diagram in the System Board Manual for socket
locations.
To replace a DIMM:
1. Remove the air duct in accordance with instructions under replacing power supply
above.
2. Press the release tabs outward, away from each other.
3. Grasp the top edge of the DIMM and pull it out of the socket.
4. Remove the new DIMM from the antistatic package.
5. Orient the DIMM so that the notches match the keys in the socket.
DIMM
Release Tab
Notch
DIMM socket
6. Push gently straight down until the release tabs snap into place.
7. Replace the air duct you removed previously.
8. When you restart the computer, the BIOS detects the new memory automatically.
9. Replace the air duct you removed previously.
NOTE Whenever you change your memory type, either from ECC to non-ECC or the reverse, you
should check that the DRAM Type BIOS parameter is set correctly. For more information,
see
System Setup
.

System Board
You must swap the DIMMs and processor module(s) from the old system board to the new
one if you replace the system board. See the system board diagram in the System Board
Manual for connector and socket locations.
Note that a number of Fastex fasteners are mounted in the right side of the chassis to secure
the system board and support for the processor retention modules. Do not overtighten the
screws to these fasteners. If overtightened, the fasteners may distort.
To remove the system board:
1. Lay the chassis down on its right side.
23
Hole in right side of chassis
Fastex fastener
2. Note the locations where all cables are connected to the system board.
3. Disconnect all cables from the system board.
4. Note the locations of the expansion cards, remove them, and place the cards on an
antistatic surface.
5. Remove the air duct covering the processor module(s). See the “Power Supply” section
above for details.
6. Remove DIMMs and processor module(s) and place them on an antistatic surface. See
the respective procedures above for details on removing these components.
7. Remove the jackscrews on all external port connectors.
WARNING Use care when removing or installing the screws to avoid damaging components on
the system board.
8. Remove the screws and the plastic rivets on the processor retention module(s), and
remove the retention module(s) from the chassis.
9. Remove the screws from the system board.
10. Lift the system board out of the chassis and place it on an antistatic surface.

24
To install a new system board:
1. Place the new system board into the chassis, align all mounting holes, and install the
jackscrews on the external port connectors.
2. Loosely install the remaining screws on the system board, except those for the processor
retention module(s). Do not tighten the screws yet.
3. Mount the retention module(s) to the system board with the plastic rivets. The retention
module(s) is keyed to the processor slots to ensure correct orientation.
4. Tighten all fasteners that secure the system board and retention module(s) to the chassis.
You may need to adjust the Fastex fasteners slightly on the right side of the chassis.
5. Install the DIMMs and processor(s) to the system board.
6. Install the air duct over the processor module(s).
7. Install the expansion cards back into their original slots.
8. Connect the internal cables to the system board. If you need help identifying cable
connections, see the System Board Manual.
Expansion Cards
See the system board diagram in the System Board Manual for connector and socket
locations.
To replace an expansion card:
1. Disconnect the external device attached to the expansion card connector on the rear of
the system.
2. Disconnect any internal cable that connects the card to another device (if installed).
3. Remove the screw that secures the card to the left card guide.
4. Pull the expansion card straight out, and place it on an antistatic surface.
5. Slide the new card into the same slot from which you removed the old card.
6. Install the screw that secures the card to the left card guide.
7. Connect any cables from other internal devices, if installed.
8. Connect the external device to the expansion card connector on the rear of the system.

Fans
See Chapter 6, “Power Supply and Cooling Fans,” for details on cooling fans.
NOTE Arrows on the fan indicate airflow direction and rotation. Ensure system fans are installed
with the airflow direction arrow pointing in the correct direction.
NOTE The entire power supply must be replaced to replace the power supply fan.
To replace the rear chassis fan:
1. Disconnect the fan power cable from the power supply cable.
2. Remove the two screws securing the air duct support to the fan, and remove the air duct
support.
25
Air duct supportScrews
3. Remove the four screws securing the grille and fan to the chassis.
4. Gently pull the fan inward and downward until the fan housing clears the chassis, and
then remove the fan.
5. Note the airflow direction of the fan and the position of the fan cable.
6. Ensure the airflow direction arrow on the new fan is pointing in the correct direction,
then place the new fan at an angle inside the chassis.

26
7. Place the grille on the outside, align the mounting holes, and install the four screws. Do
not overtighten.
8. Secure the air duct support to the new fan using the screws you removed previously.
9. Connect the fan power cable to the power supply cable.
Lithium (CMOS/Clock) Battery
The battery is located near the bottom front of the system board. See the system board
diagram in the System Board Manual for details.
After you remove the battery, the system will lose its operating parameters stored in CMOS.
As a result, the system BIOS parameters are lost. Parameters include date, time, hardware
configuration, and other data.
After you install the new battery, you must reset the date and time and reconfigure the BIOS.
See System Setup for details on updating and configuring the BIOS.
WARNING There is a danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced.
WARNING Replace the battery with the same or equivalent type only, as recommended by the
battery manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the battery
manufacturer’s instructions.
To replace the battery:
1. Remove any expansion cards that restrict access to the battery. See “Expansion Cards”
in this chapter for details.
2. Note the positive orientation of the battery. Carefully remove the discharged battery by
grasping it firmly and pulling it out of the socket.
3. Install the new battery in the same orientation as the old battery.
4. Dispose of the battery according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
5. Install the expansion cards that you removed.
LEDs, Light Pipe, and Power Switch
See the system board diagram in the System Board Manual for connector and socket
locations, and for LED and power switch cable and connector details.

To replace an LED:
1. Remove the internal bay disk drives. See “Internal Bay Disk Drives” in this chapter for
details.
2. Note the locations of each of the LEDs on the light pipe.
3. Remove the LED from its mount on the light pipe, then disconnect the LED cable from
its connector on the system board.
4. Remove the LED cable from the chassis.
5. Route the new LED cable through the chassis and connect it to the appropriate
connector on the system board.
6. Press the LED into its mount on the light pipe.
To replace the light pipe:
1. Remove the face panel. See “Case Components” in this chapter for details.
2. Remove the internal bay disk drives. See “Internal Bay Disk Drives” in this chapter for
details.
3. Disconnect the LEDs from the light pipe.
27
Power LED
Top of chassis
Disk activi ty LED
4. Squeeze the mounting tabs on the light pipe inward and push the light pipe through its
mounting hole.
5. From inside the chassis, remove the light pipe.
6. Orient the new light pipe so that the Power LED mounts face up, and press the light
pipe through its mounting hole until it snaps into place.
7. Push each of the LEDs into its respective mount on the new light pipe.
8. Install the internal bay disk drives.
9. Install the face panel.

28
To replace the power switch:
1. Remove the face panel. See “Case Components” in this chapter for details.
2. Disconnect the power switch cable connector from the system board.
3. Remove the switch cable from the chassis.
4. Insert the connector end of the switch cable through the cable access hole on the front of
the chassis and route the new switch cable through the chassis.
5. Connect the switch cable to the connector on the system board.
6. Press the switch into its mount on the face panel.
7. Install the face panel and the switch button.

3 Upgrading the System
This chapter describes upgrading memory and processors, as well as installing expansion
cards, and internal and external SCSI drives in your TDZ 2000 GL2 or ExtremeZ GL2
system.
Before You Begin........................................................................................................30
Adding Memory...........................................................................................................30
Precautions.....................................................................................................30
Memory Configurations .................................................................................31
Adding a Processor......................................................................................................32
Single-to-Dual Upgrade..................................................................................32
Adding Expansion Cards .............................................................................................33
Slot Locations................................................................................................33
Installing Expansion Cards ............................................................................34
Assigning System Resources.......................................................................... 35
Adding Drives and Devices..........................................................................................35
Device Locations............................................................................................36
Adding External SCSI Drives ......................................................................................37
SCSI Cable Length Guidelines.......................................................................37
SCSI Cable Quality Guidelines.......................................................................38
SCSI ID Guidelines........................................................................................38
SCSI Termination Guidelines for External Devices ........................................38
Connecting the Device ...................................................................................39
Changing SCSI Adapter or Device Settings....................................................39
29

30
Before You Begin
WARNING Disconnect the system and peripheral devices from AC power before servicing internal
components! Failure to remove AC power may result in equipment damage or
personal injury.
CAUTION Use an antistatic wrist strap for all servicing procedures to avoid the possibility of
electrostatic discharge.
CAUTION Do not overtighten screws and other fasteners to avoid damaging threads.
CAUTION System memory modules from Intergraph Computer Systems are certified for use with
Intergraph computers at extremes of temperature and system load to ensure reliable
performance. System memory modules available from other vendors may not function
properly or reliably in your Intergraph computer.
CAUTION Follow all warnings and cautions in servicing instructions. If you fail to follow documented,
approved procedures, personal injury and damage to equipment can result.
See Chapter 1, “Accessing the System,” for instructions on opening the system, protecting
against electrostatic discharge, and closing the system. “Right side” and “left side” are as
seen from the front of the unit. Servicing procedures assume you have removed the left side
panel from the system.
Adding Memory
You can add system memory to the computer by adding or replacing Dual Inline Memory
Modules (DIMMs).
The system board features four DIMM sockets, which combined can hold up to 1 GB of
Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (SDRAM). See the system board diagram
in the System Board Manual for socket locations.
See Chapter 2, “Servicing the System,” to install a memory upgrade.
Precautions
To avoid damaging DIMMs and voiding the warranty, take the following precautions:
u
Do not touch the gold-plated finger contacts.
u
Do not bend, twist, drop, or otherwise handle DIMMs carelessly.
u
Do not expose DIMMs to moisture or extreme temperatures.

u
Do not remove DIMMs from the antistatic bag until installation.
Before you install memory, do the following:
u
Inspect DIMM keying. The finger contacts on the DIMM must match the socket
configuration. This ensures that you have the correct voltage and type of DIMM.
u
Inspect DIMM contacts. The DIMM must have gold-plated fingers that match the goldplated socket contacts.
Follow these population rules to correctly install the DIMMs:
u
Remember that you must install DIMMs one at a time.
u
Install DIMMs one bank at a time; begin with bank 0 (nearest to the processor) or the
first open bank; end with bank 3.
u
Press the DIMM into the socket at a 90 degree angle, applying even pressure along the
top edge of the DIMM.
Memory Configurations
The following tables shows possible memory configurations. Each bank contains one socket.
31
Memory size
Configuration (ECC) Configuration (non-ECC)
32 MB 4 x 72 4 x 64
64 MB 8 x 72 8 x 64
128 MB 16 x 72 16 x 64
256 MB 32 x 72 N/A
NOTE Whenever you change your memory type, either from ECC to non-ECC or the reverse, you
should check that the DRAM Type BIOS parameter is set correctly. For more information,
see
System Setup
Memory
.
Bank 0
DIMMs
Bank 1
DIMMs
Bank 2
DIMMs
Bank 3
DIMMs
32 MB 32 MB
64 MB 64 MB
96 MB 64 MB 32 MB
128 MB 128 MB
256 MB 128 MB 128 MB
384 MB 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB
512 MB 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB 128 MB
1 GB 256 MB 256 MB 256 MB 256 MB

32
Adding a Processor
You can upgrade a single processor system to a dual processor system. You can upgrade a
processor to a faster processor.
Processors are mounted in a processor retention module which surrounds the processor slots.
See the system board diagram in the TDZ 2000 GL2/ExtremeZ GL2 System Board Manual
for the location of processor slots and related connectors.
Single-to-Dual Upgrade
You can upgrade to dual processors by purchasing a TDZ 2000 GL2 single-to-dual processor
upgrade kit from Intergraph Computer Systems. The kit contains all the hardware, software,
and documentation required to perform the upgrade.
After installing a second processor, you must reinstall Windows NT on the system to ensure
proper operation with multiple processors.
NOTE Since the second processor should be the same speed as the first, you do not have to
change any processor frequency jumper settings when installing a second processor.
To install a single-to-dual processor upgrade:
1. Remove the air duct in accordance with instructions under replacing power supply
above.
2. Install a retention module, if necessary, onto the open processor slot. See Chapter 2,
“Servicing the System,” for details.
3. Install a heat-sink mounting bracket, if necessary, into place over the open processor
slot. See Chapter 2, “Servicing the System,” for details.
4. Orient the processor module so that the heat sink fins or cooling fan points toward the
DIMM sockets, and then insert the module into the open socket of the retention module.
5. Press straight down and apply even pressure at both ends of the CPU module until it
seats. The retention module is keyed to ensure proper insertion.
6. Press the processor module locking tabs outward until they click into the locked
position.
7. If you installed a boxed processor with integral fan into the secondary processor slot,
connect the fan power cable to the processor fan power connector on the system board.
If you installed a processor with a heat-sink, secure the heat-sink fins using a heat-sink
lock. See Chapter 2, “Servicing the System,” for details.
8. Replace the air duct you removed previously.

Adding Expansion Cards
You can install Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI), non-compliant PCI, Industry
Standard Architecture (ISA), and Plug-n-Play (PnP) expansion cards in the system. See
below for a general description of the types of cards.
u
PCI cards contain configuration registers that define resource information to the system
during startup. PCI cards do not require manual system configuration when installing
the card. The system BIOS detects the board’s presence during startup and reads
information from the board’s configuration registers to assign the necessary system
resources.
33
NOTE All PCI expansion cards sold by Intergraph fully comply with the
Interconnect Specification, 2.1.
u
Non-compliant PCI cards mechanically comply with the Peripheral Component
Peripheral Component
Interconnect Specification 2.1, but do not contain configuration registers that allow the
system to automatically assign the necessary resources. These cards install in PCI slots,
but you must configure the BIOS to assign system resources before installing the card.
In this regard, they are like ISA cards, as described below.
u
Non-PnP ISA cards do not contain registers that define the resource information to the
system during startup. Therefore, you must configure the BIOS to define the card to the
system before installing the ISA card. This reserves system resources for the card.
u
PnP cards are ISA cards that contain configuration registers like PCI cards. During
startup, the system BIOS automatically detects the installed card and assigns the
necessary system resources. Since a PnP card is ISA-based, you install it in any
available ISA slot.
NOTE Assign system resources for any non-PnP ISA card and any non-compliant PCI cards before
installation. See the “Assigning System Resources” section below.
Each installed PCI card must draw less than 25 watts of power. The total allowable
maximum wattage for PCI cards is 175 watts. The PCI slots are limited to 25 watts power
dissipation per the Peripheral Component Interconnect Specification 2.1.
Slot Locations
The expansion slots are located at the bottom left section of the system board, as shown in
the following figure. The bottom PCI slot shares space with the upper ISA slot. You can
install a card in the bottom PCI slot, or in the upper ISA slot, but not in both.

34
AGP slot
PCI slot
PCI slot
PCI slot
PCI slot
PCI slot (shared)
ISA slot (shared)
ISA slot
Installing Expansion Cards
If you are installing double card sets, such as a graphics card and a geometry accelerator,
repeat the following procedure for the second card. See the documentation that came with
the card for details on connecting the two cards.
For other cards, such as internal modems or SCSI adapters, see the documentation that came
with the card for details on installation, configuration, cable connections, and operation.
To install an expansion card:
1. Locate an open slot and remove the blanking plate for the slot. Keep the retaining
screw.
NOTE If you have no open slots and/or want to replace an existing expansion card, see the
instructions in Chapter 2, “Servicing the System.”
2. Remove the expansion card from its antistatic packaging.
3. Slide the expansion card carefully into the card guides. Ensure that the connectors on
the board’s edge are aligned properly with the slot connector.
4. Push the card into the slot firmly and evenly until it is fully seated in the slot connector.
5. Inspect the connection. If it does not appear to be correct, remove and reinstall the card.

6. Install the retaining screw.
7. Attach any required cables to the internal or external connectors.
Assigning System Resources
Some expansion cards include a configuration diskette that you can use to reserve the system
resources required for the card. Other expansion cards do not include a diskette, but require
that you manually program the BIOS with the configuration information.
See System Setup for details on assigning system resources and configuring the BIOS for
expansion cards.
NOTE Treat non-compliant PCI cards and PCMCIA cards as ISA cards for assigning system
resources.
Adding Drives and Devices
The TDZ 2000 GL2/ExtremeZ GL2 features the following peripheral bays:
u
One 3.5-inch x 1.0-inch external bay for floppy disk drive.
35
u
One 5.25-inch x 1.6-inch external bay for CD-ROM.
u
Two 5.25-inch x 1.6-inch external bays for optional devices.
u
Three 3.5-inch x 1.0-inch internal bays for system or optional disks.
Note the following restrictions on adding peripheral devices:
u
The bottom 5.25-inch bay (location 4) is not designed for CD drives.
u
Other than the CD-ROM drive, only one front-accessible EIDE device can be added.
This device must be installed in the bottom 5.25-inch bay (location 4).
u
The front-accessible bays are not designed to support hard disk drives.
u
A maximum of two EIDE, three 1.0-inch SCSI, or two 1.6-inch SCSI hard disk drives
are supported internally.
u
When installing 5.25-inch peripheral devices, use the screws provided in the package
found in the Accessory Box.
See the following for related information and important details:
u
The System Board Manual for details on SCSI connector locations and pinouts.
u
Chapter 5, “Peripherals,” for details on drive locations, jumpers, and cables.

36
u
Chapter 6, “Power Supply and Cooling Fans,” for details on power supply cable
connectors and pinouts.
Remember the following when installing devices in the system’s drive bays:
u
If you are installing a SCSI drive, have the vendor’s documentation available to follow
instructions for setting the SCSI ID, enabling or disabling termination, installing device
drivers when required, and configuring other drive attributes.
u
If you are installing a drive that connects to an adapter card (such as an EIDE drive), see
the vendor’s documentation for installing the adapter card and required cables. See
“Adding Expansion Cards” in this chapter for details.
Device Locations
You can add optional mass storage devices to the internal and external drive bays. The
following table provides the drive locations and related information.
Location
Drive Peripheral Bay Max Bay Capacity
1 System disk drive Internal 3.5-inch x 1.6-inch
2 Add-on disk drive Internal 3.5-inch x 1.6-inch
3 Add-on disk drive Internal 3.5-inch x 1.6-inch
4 Add-on device External 5.25-inch x 1.6-inch
5 Add-on device External 5.25-inch x 1.6-inch
6 Floppy disk drive External 3.5-inch x 1.0-inch
7 EIDE CD-ROM External 5.25-inch x 1.6-inch
The following figure shows drive locations with devices installed in all locations. The EIDE
CD-ROM, floppy drive, and system drive are standard. Other devices are available as
options.
NOTE If you are installing an additional EIDE device, you must mount the device in location 4.
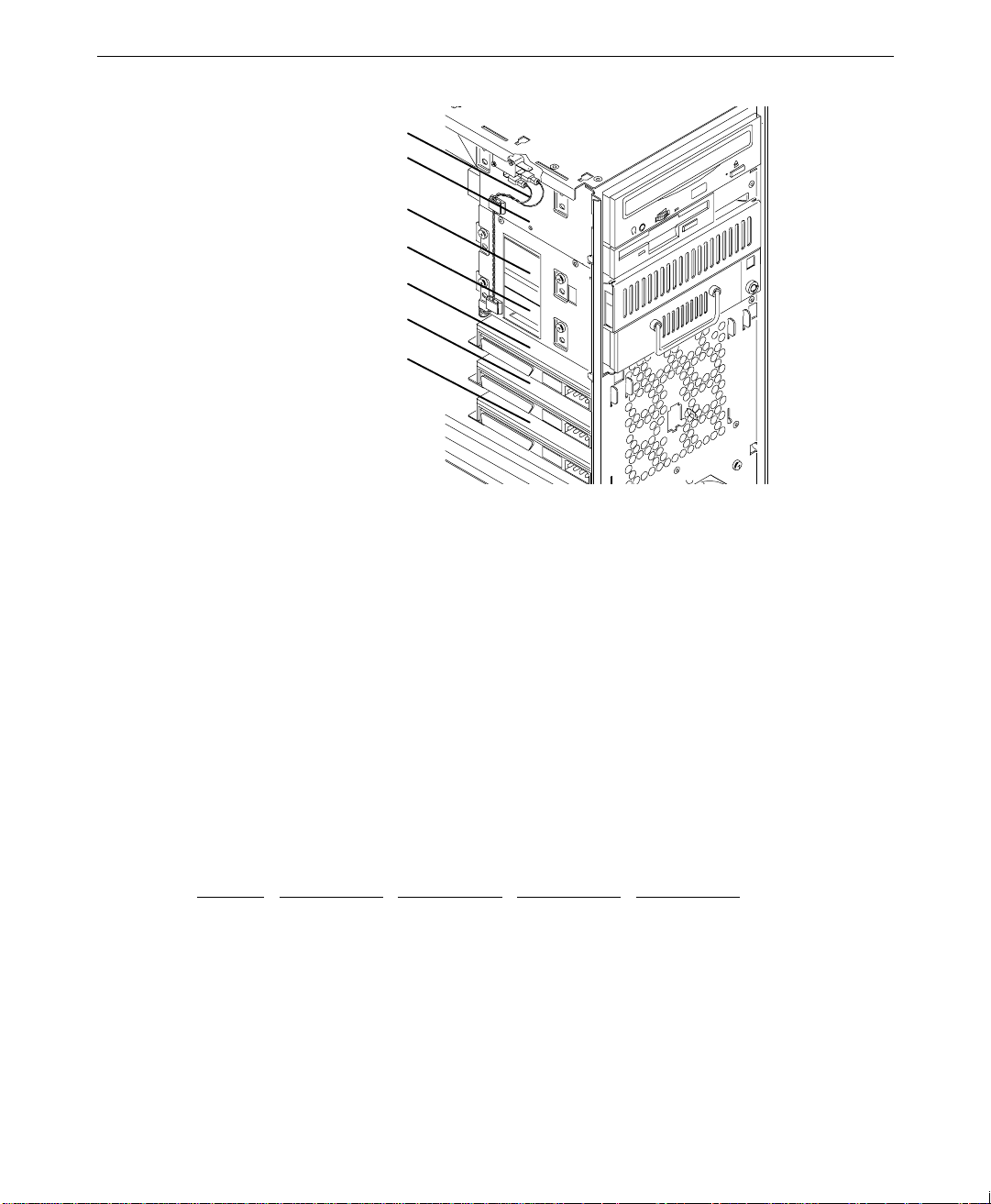
CD-ROM drive— Location 7
Floppy disk d ri ve—Locati on 6
Add-on d ri ve—Location 5
Add-on d ri ve—Location 4
Add-on d ri ve—Location 3
Add-on d ri ve—Location 2
System dr iv e—Location 1
See Chapter 2, “Servicing the System,” to install a memory upgrade.
37
Adding External SCSI Drives
You can add single-ended external SCSI drives to the system by connecting them to an
optional SCSI adapter. See “Adding Expansion Cards,” in this chapter for details on
installing an expansion card.
SCSI Cable Length Guidelines
The number of drives and length of the cables used to connect the drives is a factor when
using SCSI-1, Fast SCSI (SCSI-2), Ultra SCSI, and Wide Ultra SCSI drives. Fast SCSI,
Ultra SCSI, and Wide Ultra SCSI impose shorter cable restrictions than SCSI-1. The total
length of the SCSI cabling must not exceed the following:
Drives
1 to 4 6 meters 3 meters 3 meters 12 meters
5 to 7 6 meters 3 meters 1.5 meters 12 meters
8 to 15 N/A N/A N/A 12 meters
NOTE If longer Ultra SCSI cable lengths are required, Ultra SCSI mode can be disabled using
SYSUTIL, the Setup utility, or the on-board BIOS on the SCSI adapter. However, disabling
Ultra SCSI mode reduces the data transfer rate to 20 MB per second on Ultra Wide adapters
and to 10 MB per second on Ultra Narrow adapters.
SCSI-1 SCSI-2 Ultra LVD

38
NOTE The SCSI adapter counts as one device.
The total length of the SCSI cabling is the sum of the following:
u
SCSI cable inside each device—average 8 inches (20 cm)
u
SCSI cable between the system and the first device
u
SCSI cable between each device
SCSI Cable Quality Guidelines
To ensure data integrity and optimum performance, do the following:
u
Use only Intergraph SCSI cables. Cables from other vendors may not provide adequate
shielding.
u
Use the shortest cables possible to connect SCSI devices to the system and to each other.
NOTE Make sure the last device on a chain of external SCSI devices has an active SCSI terminator
connected to the open SCSI port. All other external SCSI devices must have SCSI
termination disabled or removed.
SCSI ID Guidelines
By default, specific devices use the following SCSI IDs:
u
SCSI adapter (optional) uses ID 7
u
Read/write CD-ROM (optional) drive uses ID 4
u
Iomega Jaz drive (optional) uses ID 6
NOTE To easily determine the ID of each SCSI device on the system, restart the system. When the
BIOS screen displays, look for the list of SCSI devices and write down the ID for each device.
Some SCSI devices have push switches to set the ID, while others have DIP switches or
jumpers. See the vendor documentation for details on setting the ID.
SCSI Termination Guidelines for External Devices
Follow the guidelines below for terminating SCSI devices:
u
Enable termination on the last external drive on the SCSI cable chain.
u
Disable termination on all other external drives on the SCSI cable chain.
u
Use only an active terminator on externally-terminated devices.

Connecting the Device
If your system has an optional SCSI adapter card installed, you can connect external SCSI
devices to the adapter’s external SCSI port.
NOTE The system BIOS will attempt to start the system using a hard disk drive connected to the
SCSI adapter in the lowest PCI slot. To start the system using an external SCSI hard disk
drive, you must ensure the drive’s SCSI adapter is installed lower in slot order than all other
bootable SCSI adapters
To add an external SCSI device:
1. Connect one end of the external SCSI cable to the external port of the SCSI adapter.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the SCSI device.
3. Set the SCSI ID of the device to an unused number.
4. If the SCSI device is:
−
the last or only device on the SCSI chain, enable SCSI termination
−
NOT the last or only device on the SCSI chain, disable SCSI termination
5. Ensure that the power switch on the device is in the off position, and then connect the
power cord to the device and then to an AC receptacle.
39
6. Turn on the power to the device and any other devices on the SCSI chain.
7. Start the system. If necessary, install the software drivers and configure the drive
according to the vendor’s instructions.
Changing SCSI Adapter or Device Settings
Depending on your system configuration or the capabilities of SCSI devices connected to
your system, you may need to change adapter or device settings. See the SCSI adapter
documentation delivered with the system for more information.

40

4 System Hardware Overview and
Specifications
This chapter contains general information about, and general specifications for, the
hardware in a TDZ 2000 GL2 or ExtremeZ GL2 system.
Hardware Overview.....................................................................................................42
Functional Diagram .....................................................................................................43
System Board...............................................................................................................44
System Configuration Summary...................................................................................44
System Model Number.................................................................................................46
Specifications...............................................................................................................47
Hardware Monitoring ..................................................................................................48
Temperature Sensors...................................................................................... 48
Optional Hardware.......................................................................................................48
41

42
(
)
Hardware Overview
The following figure shows the major parts and assemblies inside the server.
Chassis
Fan
Power Supply
with Fan
CD-ROM Drive
Floppy Disk
Drive
Disk Drives
5.25 inch
Disk Drives
System Board

Functional Diagram
The following diagram shows the power and data signals of the base unit components.
43
Power
Data
Power and Data
System Board
AC In
Speaker
Keyboard
Mouse
Monitor
AC In
Power Supply
Fan
Floppy Disk Drive
CD-ROM Drive
Serial
Ports
Parallel
Port
SCSI/EIDE
Controller
USB
Disk Drives
(Internal/External)

44
System Board
The following table lists the main components on the system board. See the System Board
Manual for more detailed information.
Component
Form Factor ATX
System BIOS
Processor(s) Intel Pentium II; 300, 350, 400, or 450 MHz, all SEC
Chipset Intel 440 BX series
Combo Controller National PC87309 Super I/O
PCI-to-ISA Bridge Intel 82371EB PCI/ISA/IDE Xcelerator (PIIX4E)
EIDE Controller Intel 82371EB
Universal Serial Bus Ports Intel 82371EB
Video Display Controller Intel 82443BX PCI/AGP
Description
AMIBIOS
(Single Edge Connector)
System Configuration Summary
The following table summarizes the main features of the system.
Feature
Processors One or two 300, 350, 400, or 450 MHz Intel Pentium II with
Bus Speed 100 MHz for 350, 400, and 450 MHz processors
Memory Four banks, one DIMM per bank
Memory Style 168 pin SDRAM DIMM, 10 ns, 3.3V, unbuffered, 64 bit (non-
Memory Type SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory)
Memory Speed 100 MHz
Minimum/Maximum
memory
Memory Expansion 32, 64, 128, or 256 MB increments
Networking 3COM 3C900 10 Mbit PCI combination NIC (optional)
Description
external 512 KB cache
66 MHz for 266, 300, and 333 MHz processors
ECC)
168 pin SDRAM DIMM, 10 ns, 3.3V, unbuffered, 72 bit (ECC)
32 MB/1 GB
3COM 3C905 10/100 Mbit PCI combination NIC (optional)

Feature Description
OLICOM PCI Token Ring NIC (optional)
SCSI Symbios dual Ultra-Wide SCSI channels, one internal and one
external (optional)
Symbios single channel LVD
EIDE Primary EIDE port for up to two hard disk drives
Secondary EIDE port for CD-ROM
Mouse Primax
Keyboard PS/2 style, standard Windows 95/98 compatible or multimedia
Audio Creative Labs Sound Blaster Pro 16 sound adapter
Graphics Intense 3D Pro 2200s, RealiZm VX113A, VX25, or ZX25 (with
optional Lynx geometry engine), Matrox Millennium II, Matrox
G200, or Accel Graphics AccelSTAR II
Disk Drive EIDE: 4.3, 10.1, or 16.8 GB 5400 RPM
SCSI: 4.3 or 9.1 GB 7200 RPM
Ultra SCSI: 4.3, 9.1, or 18.2 GB 10,000 RPM
LVD SCSI: 4.0 GB 7200 RPM, 9.1 or 18.2 GB 10,000 RPM
CD-ROM 32X EIDE CD-ROM (standard) or 4X/8X CD-Recordable drive,
with Adaptec AHA-2910 SCSI controller (optional)
I/O Slots One AGP, four PCI, one PCI/ISA (shared), one ISA
Peripheral Bays One 3.5-inch x 1.0-inch external bay for floppy drive
One 5.25-inch x 1.6-inch external bay for CD-ROM
Two 5.25-inch x 1.6-inch external bays for optional devices
Three 3.5-inch x 1.0-inch internal bays for system disk and optional
disks
I/O Ports One PS/2 Mouse Port and one PS/2 Keyboard Port
One Parallel Port, EPP- and ECP-compatible
Two Serial (COM) Ports
Two Universal Serial Bus (USB) Ports
Audio Ports: Microphone, Line In, Line Out, MIDI
Power Supply 250 Watts, manual-ranging
45

46
System Model Number
The model number on the unit identifies the system hardware and software configuration.
The following table defines the individual digits.
Digit
1: Series 5: TDZ 2000 GL2/ExtremeZ GL2
2: Processor Type 0: No processor
3. Graphics 0: No graphics
4: Chassis A: ExtremeZ GL2
5: Memory 0: No memory
Meaning
2: Single Intel Pentium II, 300 MHz, 512 KB cache
3: Dual Intel Pentium II, 300 MHz, 512 KB cache
7: Single Intel Pentium II, 400 MHz, 512 KB cache
8: Dual Intel Pentium II, 400 MHz, 512 KB cache
9: Single Intel Pentium II, 350 MHz, 512 KB cache
A: Dual Intel Pentium II, 350 MHz, 512 KB cache
B: Single Intel Pentium II, 450 MHz, 512 KB cache
C: Dual Intel Pentium II, 450 MHz, 512 KB cache
4: Intense3D Pro 2200s
7: Matrox Millennium II, 4 MB
A: RealiZm II ZX25
D: Matrox Millennium II, 8 MB
G: RealiZm II VX113A
H: DigiDesktop, 4 MB X 2
J: Accel AccelSTAR II, 8 MB
K: Millennium G200
N: RealiZm II VX25, 32 MB & Lynx
B: TDZ 2000 GL2
C: TDZ 2000 GL2 with network card
D: TDZ 2000 GL2 with network card and ZIP drive
E: ExtremeZ GL2 with network card
F: ExtremeZ GL2 with network card and JAZ drive
4: 32 MB
6: 64 MB
7: 128 MB

Digit Meaning
9: 256 MB
6: CD-ROM 0: No CD-ROM
3: CD-ROM
7: Disk Drives 0: No hard disk drive
5 4.3 GB SCSI
9 9.1 GB SCSI
P: 4.3 GB EIDE
U: 10.1 GB EIDE
V: 16.8 GB EIDE
W: 18.2 GB SCSI
8: Operating System 0: No operating system
2: Windows NT Workstation
3: Windows 95
5: Windows NT with Office Small Business Edition
6: Windows 95 with Office Small Business Edition
B: Windows 98
C: Windows 98 with Office Small Business Edition
9: Revision Variable
47
Specifications
The following specifications apply to the TDZ 2000 GL2 and ExtremeZ GL2.
Item
Dimensions
Maintenance
clearance
AC line voltage (US) 90 - 132 VAC, 47 - 63 Hz, 1 phase, 15A/125 V receptacle
AC line voltage
(International)
Recommended room
temperature
Recommended room
humidity
Heat dissipation 2,662.14 BTU/hr
Specifications
25.8 x 7.9 x 20.2 inches (65.4 x 20.0 x 50.8 cm)
36 inches (91.4 cm) front and back
180 - 264 VAC, 47 - 63 Hz, 1 phase, 15A/250 V receptacle
50° to 80° F (10° to 26° C)
20% to 80% (non-condensing)

48
Hardware Monitoring
TDZ 2000 GL2/ExtremeZ GL2 systems feature advanced hardware monitoring.
The InterSite Hardware Monitor software reports the following voltages and system states:
u
All major voltages, including processor bus voltage; +5 V; +3.3 V; +12 V; -12 V; -5 V
u
Processor voltage ID
u
Temperature at two locations (near primary processor and near expansion slots)
u
Fan speed
u
Low battery voltage alert
u
SMART Drive system compliance
Temperature Sensors
Resistive temperature sensors are located on the system board near the processors and
expansion slots. These devices provide signals for reporting temperature readout data to the
InterSite Hardware Monitor software. The temperature sensors are part of the system board
and are not field replaceable.
See the System Setup for details on InterSite Hardware Monitor, and for information about
using the Automatic Shutdown Utility.
Optional Hardware
If your system includes any of the following hardware, see the documentation delivered with
that hardware for additional information:
u
SCSI CD-Recorder (CD-R) drive
u
Internal/external SCSI disk drive
u
Removable SCSI disk drive
u
PCI SCSI adapter
u
PCI network adapter
u
SCM SwapBox PC card adapter
u
Iomega ZIP or JAZ drive
u
TR-4 tape drive

5 Peripherals
This chapter provides information on the cabling and configuration of common peripherals
in a TDZ 2000 GL2/ExtremeZ GL2 system.
Peripheral Cables.........................................................................................................50
EIDE Cable Connection Locations.................................................................50
Internal LVD SCSI Cable Connection Locations............................................50
Internal Ultra SCSI Cable Connection Locations............................................51
Floppy Cable Connection Locations...............................................................51
Peripheral Configuration..............................................................................................52
EIDE CD-ROM Drive....................................................................................52
SCSI CD-Recorder.........................................................................................53
Iomega JAZ 1 GB Internal SCSI Drive...........................................................54
Floppy Disk Drive.......................................................................................... 55
SCSI Disk Drives...........................................................................................55
49

50
Peripheral Cables
This section provides information on peripheral cables and associated connections. See the
System Board Manual for additional details. Cable illustrations are not to scale. You can
identify the cables and connectors using their spacing as reference.
CAUTION You should try to minimize cable flexing during handling. SCSI cables should not have any
creased bends. Take care when installing or replacing cables to insure that they do not
contact sharp metal surfaces or become excessively bent or twisted.
EIDE Cable Connection Locations
The following illustration and table show the cable connectors and the locations to which
they attach. This cable is approximately 10.5 in (26.7 cm) long.
1 32
Connector Connects To
1 Primary/secondary IDE controller on system board
2 Device in internal/external bay
3 Device in internal/external bay (primary IDE channel)
EIDE CD-ROM at Location 7 (secondary IDE channel)
Internal LVD SCSI Cable Connection Locations
The following illustration and table show the cable connectors and the locations to which
they attach. This cable is approximately 52 in (132 cm) long.
1 765432

Connector Connects To
1 SCSI controller
2 System Disk at Location 1 (internal bay)
3 Disk at Location 2 (internal bay)
4 Disk at Location 3 (internal bay)
5 Device at Location 4 (external bay)
6 Device at Location 5 (external bay)
7 Active terminator
See “Device Locations” in Chapter 3 for details on standard peripheral locations.
Internal Ultra SCSI Cable Connection Locations
The following illustration and table show the cable connectors and the locations to which
they attach. This cable is approximately 36 in (91 cm) long.
1 432
51
Connector Connects To
1 SCSI controller
2 Device at Location 4 (external bay)
3 Device at Location 5 (external bay)
4 External SCSI Terminator board
Floppy Cable Connection Locations
The following illustration and table show the cable connectors and the locations to which
they attach. This cable is standard and is approximately 17 in (43.1 cm) long.
1 2

52
Connector Connects To
1 Floppy disk drive controller on system board
2 Floppy disk drive
Peripheral Configuration
This section provides illustrations and information on configuring common peripherals for
the system.
See the following for related information:
u
System Board Manual for cable connector locations and pinouts.
u
Chapter 6, “Power Supply and Cooling Fans,” for power cable information and pinouts.
u
Vendor documentation provided with the peripheral device.
EIDE CD-ROM Drive
The following figure shows the back of the EIDE CD-ROM drive.
Audio connector
Mode Selec t
(Master/S lav e)
EIDE connector
Power
connector
Device Connector Connects to
Audio (analog) Audio cable connector on sound card
EIDE Secondary EIDE on system board
Power Power supply
The Mode Select header is jumpered “Master” as shown.

SCSI CD-Recorder
The following figure shows the back of the CD-recorder.
53
Audio connector
ID1
ID2
ID4
Term Power jumper
Termination jumper
Parity Enable jumper
SCSI connector
Power
connector
Device Connector Connects to
Audio (analog) Audio cable connector on sound card
Power Power supply
SCSI SCSI connector on SCSI adapter
To disable SCSI termination, remove the Termination jumper and the Term Power jumper.
Use jumpers as defined in the following table to set the SCSI ID.
SCSI ID
ID1 ID2 ID4
0 OFF OFF OFF
1 ON OFF OFF
2 OFF ON OFF
3 ONONOFF
4 OFF OFF ON
5 ON OFF ON
6 OFF ON ON

54
Iomega JAZ 1 GB Internal SCSI Drive
The following figure shows the jumpers on the bottom of the drive.
Front
Power conn ect o r
SCSI connector
ID4
ID2
ID1
Device Connector Connects to
Power Power supply
SCSI SCSI connector on SCSI adapter
The drive is not terminated and requires external termination only if installed as the last
device on the SCSI chain.
Use jumpers as defined in the following table to set the SCSI ID. The factory default address
is SCSI ID 5.
SCSI ID
ID1 ID2 ID4
0 OFF OFF OFF
1 ON OFF OFF
2 OFF ON OFF
3 ONONOFF
4 OFF OFF ON
5 ON OFF ON
6 OFF ON ON

Floppy Disk Drive
The following figure shows the cable connectors on the back of the floppy disk drive.
55
Device Connector Connects to
Power Power supply
Data Floppy disk drive controller on system board
SCSI Disk Drives
You can use any of the following Wide Ultra or LVD SCSI disk drives in the system:
Vendor
Seagate 7,200 9.1 GB
Seagate 7,200 4.3 GB
Seagate 10,000 4.3 GB
Seagate 10,000 9.1 GB
Seagate 10,000 18.2 GB
Seagate 7,200 4.3 GB LVD
Seagate 10,000 9.1 GB LVD
Seagate 10,000 18.2 GB LVD
Power
connector
RPM Capacity
Data cable
connector
The following figure shows the jumper connectors J6 and J2 on the Seagate 4.3 GB and 9.1
GB disk drives. Remove the drive from its bracket to access J2.

56
ID1
ID2
ID4
ID8
J6
J2
TE
oooooooo
oooooooo
TP
PD
SCSI
connector
Pin 1
Power
connector
Device Connector Connects to
Power Power supply
SCSI SCSI connector on SCSI adapter
To disable SCSI termination, remove the TE jumper from connector J2. To enable parity,
remove the PD jumper from connector J2. For optimum performance, remove all jumpers
from J2.
NOTE Be sure to remove the TE jumper from J2 when using a SCSI cable with an active terminator
installed.
Use jumpers as defined in the following table to set the SCSI ID.
SCSI ID
ID1 ID2 ID4 ID8
0 OFF OFF OFF OFF
1 ON OFF OFF OFF
2 OFF ON OFF OFF
3 ON ON OFF OFF
4 OFF OFF ON OFF
5 ON OFF ON OFF
6 OFF ON ON OFF

6 Power Supply and Cooling Fans
This chapter describes the system’s 250-watt power supply, power-related pinouts, cooling
fans, and hardware monitoring devices.
Power Supply...............................................................................................................58
Power Supply Cable Routing.......................................................................... 58
P1 Pinout .......................................................................................................59
P2 - P5 Pinouts...............................................................................................59
P6 Pinout .......................................................................................................59
Cooling Fans ...............................................................................................................59
57

58
Power Supply
The system’s power supply is a 250-watt manual-ranging supply. It switches between 90132 VAC or 180-264 VAC, depending on the range setting. The input frequency is 47-63
Hz, single phase. At full load, the power supply has a minimum efficiency of 65 percent.
The power supply contains no user- or field-serviceable parts.
The following table details the DC output specifications for the power supply.
Output
#1
Nominal Output
Voltages
1
Continuous
Load
(Maximum.)
Continuous
Load
(Minimum.)
+5.0 +12.0
3
26
1,2
3 0.5 0 0 0 ADC
1
The following notes apply:
1. Power supply should meet or exceed these specifications. For the noted specifications,
the “Max” values describe the smallest acceptable maximum load and the “Min” values
describe the largest acceptable minimum load.
2. The maximum combined continuous load of all outputs shall not exceed 250 Watts.
3. The maximum combined continuous load of the +5.0V and +3.3V outputs shall not
exceed 170 Watts.
Power Supply Cable Routing
The following table lists the cable connectors from the power supply that connect to the
system board and other devices.
Output#2Output#3Output#4Output
#5
−
5.0
−
12.0
9 0.5 0.8 14
+3.3 VDC
3
Unit
ADC
Connector
Device Notes
P1 J27 on System board
P2, P3, P5 Disk Drive/CD-ROM
P4 MCBL172A Chassis Fan Via cable MCBL173A
P6 Floppy Disk Drive

P1 Pinout
Pin Signal Wire Color Pin Signal Wire Color
1 +3.3V Orange 11 +3.3V Orange
2 +3.3V Orange 12 -12V Blue
3 COM Black 13 COM Black
4 +5V Red 14 Power On Green
5 COM Black 15 COM Black
6 +5V Red 16 COM Black
7 COM Black 17 COM Black
8 Powergood Gray 18 -5V White
9 +5VSB Purple 19 +5V Red
10 +12V Yellow 20 +5V Red
P2 - P5 Pinouts P6 Pinout
59
Pin Signal Wire Color Pin Signal Wire Color
1 +12V Yellow 1 +5V Red
2 COM Black 2 COM Black
3 COM Black 3 COM Black
4 +5V Red 4 +12V Yellow
Cooling Fans
The TDZ 2000 GL2/ExtremeZ GL2 has two cooling fans. One is inside the power supply;
the other is mounted in the chassis. Both fans are 12 VDC. The fans pressurize the chassis
and force warm air out from the vents. Hardware controls the dynamic speed of each fourwire fan.
See the System Board Manual for connector locations and fan cable pinouts. See also
Chapter 2, “Servicing the System,” for details on replacing the chassis fans.

60
The table below summarizes fan information.
Fan
Airflow Devices Cooled
Rear chassis Back-to-front Processors, drives
Power supply Back-to-front Power supply
The chassis fan is field replaceable.
The power supply fan is not field replaceable. If the fan requires replacement, you must
replace the power supply.
Arrows on each fan indicate airflow direction and rotation, as in the following illustration.
Rotation
Side view of fan
Airflow
Ensure that you install the chassis fan with the airflow direction arrow pointing toward the
inside of the chassis.
 Loading...
Loading...