Page 1

Intel® Server Board SDS2
Technical Product Specification
Order Number: A85874-002
Revision 1.2
December 2, 2002
Enterprise Platforms and Services Marketing
Page 2
Revision History Intel® Server Board SDS2
Revision History
Date Revision
Number
9/20/2001 1.0 Initial release.
5/15/2002 1.1 Added Section 13: Errata. Corrected miscellaneous document errors.
Added Table 6.2.5.4: Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) Beep Code
Generation.
12/2/02 1.2 Added Errata 19-37 that are corrected with FAB5. Updated Table 6.2.5.4.
Added Table 25.
Modifications
Revision 1.2
ii
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 3

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Disclaimers
Disclaimers
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express
or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this
document. Except as provided in Intel's Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel
assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to
sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular
purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property
right. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions
marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
This document contains information on products in the design phase of development. Do not
finalize a design with this information. Revised information will be published when the product is
available. Verify with your local sales office that you have the latest datasheet before finalizing a
design.
The Intel® Server Board SDS2 may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may
cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are
available on request.
This document and the software described in it are furnished under license and may only be
used or copied in accordance with the terms of the license. The information in this manual is
furnished for informational use only, is subject to change without notice, and should not be
construed as a commitment by Intel Corporation. Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility or
liability for any errors or inaccu racies that may appear in this document or any software that may
be provided in association with this document.
Except as permitted by such license, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means without the express written consent
of Intel Corporation.
Intel, Pentium, Itanium, and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
*Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © Intel Corporation 2002.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
iii
Page 4

Table of Contents Intel® Server Board SDS2
iv
Table of Contents
1. Introduction .............................................................................................................................1
2. Architecture.............................................................................................................................2
3. Processor and Chipset..........................................................................................................4
3.1 Processors.........................................................................................................................4
3.1.1 Processor Voltage Regulator Module (VRM)................................................................6
3.2 Memory Subsystem............................................................................................................6
3.2.1 Memory Configuration...................................................................................................6
3.2.2 I2C Bus..........................................................................................................................8
3.3 Chipset................................................................................................................................8
3.3.1 CNB20HE-SL Champion North Bridge.........................................................................9
3.3.2 CIOB20 Champion I/O Bridge....................................................................................10
3.3.3 CSB5 South Bridge.....................................................................................................10
4. I/O Subsystem........................................................................................................................11
4.1 PCI Subsystem.................................................................................................................11
4.1.1 32-bit, 33-MHz PCI Subsystem ..................................................................................11
4.1.2 64-bit, 66-MHz PCI Subsystem ..................................................................................12
4.2 Ultra160 SCSI...................................................................................................................14
4.3 Video Controller................................................................................................................14
4.3.1 Video Modes................................................................................................................14
4.4 Network I nterface Controller (NIC)....................................................................................15
4.4.1 NIC Connector and Status LEDs................................................................................16
4.5 CSB5 South Bridge (PCI -to-LPC Bridge, IDE, USB).......................................................16
4.5.1 PCI Bus Interface........................................................................................................16
4.5.2 PCI Bus Master IDE Interface.....................................................................................16
4.5.3 USB Interface..............................................................................................................17
4.5.4 Compatibility Interrupt Control.....................................................................................17
4.5.5 APIC............................................................................................................................17
4.5.6 Power Management....................................................................................................17
4.5.7 General Purpose Input and Output Pins.....................................................................17
4.6 Chipset Support Components..........................................................................................18
4.6.1 Super I/O.....................................................................................................................18
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 5

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Table of Contents
v
4.6.2 BIOS Flash ..................................................................................................................20
4.7 Interrupt Routing...............................................................................................................20
4.7.1 Legacy Interrupt Routing.............................................................................................20
4.7.2 APIC Interrupt Routing................................................................................................21
4.7.3 Serialized IRQ Support...............................................................................................21
4.7.4 IRQ Scan for PCIIRQ..................................................................................................21
5. Server Management.............................................................................................................25
5.1 Sahalee Baseboard Management Controller...................................................................27
5.1.1 Fault Resilient Booting................................................................................................29
5.2 System Reset Control......................................................................................................30
5.2.1 Power-up Reset..........................................................................................................30
5.2.2 Hard Reset..................................................................................................................30
5.2.3 Soft Reset...................................................................................................................30
5.3 Intelligent Platform Management Buses...........................................................................30
5.4 Error Reporting.................................................................................................................32
5.4.1 Error Sources and Types ...........................................................................................32
5.4.2 PCI Bus Errors............................................................................................................32
5.4.3 Intel® Pentium® III Processor Bus Errors..................................................................32
5.4.4 Memory Bus Errors.....................................................................................................33
5.4.5 ID LED.........................................................................................................................33
5.5 ACPI..................................................................................................................................33
5.6 AC Link Mode....................................................................................................................33
6. BIOS........................................................................................................................................35
6.1 System BIOS....................................................................................................................35
6.2 BIOS Error Handling.........................................................................................................36
6.2.1 Error Sources and Types ...........................................................................................36
6.2.2 Handling and Logging System Errors.........................................................................36
6.2.3 SMI Handler.................................................................................................................38
6.2.4 Firmware (BMC).........................................................................................................39
6.2.5 Error Messages and Error Codes ..............................................................................45
6.3 Setup Utility.......................................................................................................................52
6.3.1 Configuration Utilities Overview..................................................................................52
6.3.2 Setup Utility Operation................................................................................................52
6.3.3 CMOS Memory Definition...........................................................................................67
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 6

Table of Contents Intel® Server Board SDS2
vi
6.3.4 Clearing CMOS...........................................................................................................67
6.4 Flash Update Utility...........................................................................................................67
6.4.1 Loading the System BIOS..........................................................................................67
6.4.2 User Binary Area.........................................................................................................68
6.4.3 Language Area............................................................................................................68
6.4.4 OEM Logo Screen......................................................................................................68
6.4.5 Recovery Mode...........................................................................................................68
7. Clock/Voltage Generation and Distribution ......................................................................70
7.1 Clock.................................................................................................................................70
7.2 Voltage..............................................................................................................................72
8. Connections ..........................................................................................................................74
8.1 Power Distribution Board Connector................................................................................74
8.2 Memory Module Connector...............................................................................................75
8.3 System Management Headers.........................................................................................76
8.3.1 ICMB Connector..........................................................................................................76
8.3.2 OEM IPMB Connector.................................................................................................76
8.3.3 SCSI HSBP (IPMB) Connector...................................................................................76
8.4 Front Panel Header...........................................................................................................77
8.5 PCI Slot Connector...........................................................................................................78
8.6 I/O Connectors.................................................................................................................80
8.6.1 VGA Connector...........................................................................................................80
8.6.2 SCSI Connector..........................................................................................................80
8.6.3 NIC Connectors..........................................................................................................81
8.6.4 IDE Connector............................................................................................................82
8.6.5 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Connectors.....................................................................82
8.6.6 Floppy Connector........................................................................................................83
8.6.7 Serial Port Connector.................................................................................................84
8.6.8 Parallel Port.................................................................................................................85
8.6.9 Keyboard and Mouse Connector................................................................................85
8.7 Miscellaneous Headers....................................................................................................86
8.7.1 Fan Headers...............................................................................................................86
8.7.2 Chassis Intrusion........................................................................................................86
8.7.3 External SCSI Activity LED Input Signal Connector...................................................86
8.8 Rear I/O Panel..................................................................................................................87
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 7

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Table of Contents
vii
8.9 Connector Manufacturers and Part Numbers..................................................................87
9. Jumpers..................................................................................................................................88
9.1 System Configuration Jumpers........................................................................................88
9.2 Performing CMOS Clear, BIOS Recovery, and BMC Force Update...............................92
9.2.1 Performing CMOS Clear.............................................................................................92
9.2.2 Performing BIOS Recovery Boot................................................................................92
9.2.3 Performing BMC Force Update..................................................................................93
10. Electrical and Thermal Specifications ...............................................................................94
10.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings...........................................................................................94
10.2 Power Consumption......................................................................................................94
10.3 Power Supply Specification...........................................................................................95
10.3.1 Power Timing............................................................................................................95
10.3.2 Voltage Recovery Timing Specifications...................................................................98
10.4 Estimateded Server Board MTBF...............................................................................100
11. Mechanical Specifications.................................................................................................101
12. Regulatory and Integration Information...........................................................................102
12.1 Regulatory Compliance...............................................................................................102
12.2 Installation Instructions................................................................................................103
12.2.1 Ensure EMC ............................................................................................................103
12.2.2 Ensure Host Computer and Accessory Module Certifications ...............................104
12.2.3 Prevent Power Supply Overload.............................................................................104
12.2.4 Place Battery Marking on Computer.......................................................................104
12.2.5 Use Only for Intended Applications .........................................................................105
12.2.6 Installation Precautions ...........................................................................................105
12.2.7 External ICMB Cable Information............................................................................105
13. Errata Listing.......................................................................................................................106
13.1 Summary Errata Table................................................................................................106
13.2 Errata...........................................................................................................................108
1. Intel® RAID controller SRCMR not yet supported with Intel® Server Board SDS2.......108
2. Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS update utility does not allow updates from a PXE
Server or from network drives ..................................................................................................108
3. Intel® Server Board SDS2 FRU/SDR update fails with console redirection enabled in
BIOS Setup...............................................................................................................................108
4. First characters and arrow keys not echoed with console redirection..........................109
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 8

Table of Contents Intel® Server Board SDS2
viii
5. Intel® & ICP Vortex* RAID Controllers will cause the Intel® Server Board SDS2 to halt
during POST when the BIOS Logo screen is enabled.............................................................109
6. Intel® Server Board SDS2 CD-ROM issues..................................................................110
7. NIC driver set 5.12 v.2.3.15 for UnixWare* 7.1.1 drops DPC LAN connection..............111
8. NIC driver set 5.12 v.5.41.27 for Microsoft* Windows* 2000 prevents a DPC LAN
connection when the operating system is loaded....................................................................111
9. Extended RAM Step disable option in BIOS Setup has no effect..................................112
10. High resolution video modes do not work correctly........................................................112
11. Lower performance with CAS Latency 2 memory.........................................................113
12. SDS2 reboots during POST with 4GB or more of total system memory installed........113
13. Novell NetWare* v. 6.0 does not install on SDS2...........................................................114
14. Adaptec* 2100S RAID controller causes system lockup and video blanking................114
15. SDS2 Build Your Own (BYO) Platform Confidence Test (PCT) v. 1.00 fails on the first
run 115
16. SDS2 0B71: System Temperature out of the range POST message...........................115
17. SDS2 0B75: System Voltage out of the range POST message....................................116
18. Miscellaneous numeric keys entered during POST enable PXE boot...........................116
19. SDS2 board level operating temperature and power supply voltage tolerance
modification...............................................................................................................................117
20. Recommendation for SDS2 rubber bumper installation................................................117
21. Keyboard and Mouse do not function under Microsoft* Windows* 2000 when legacy
USB is enabled in BIOS setup..................................................................................................119
22. Data miscompares when using Seagate* ATA III model ST310215A hard drives ........120
23. Boot to service partition via modem fails........................................................................120
24. Secondary IDE References Added To Documentation for FAB 5.................................120
25. Potential Mylex AcceleRAID 352 Adaptor Card Mechanical Interference at PCI Slot 6.120
26. Bootable CD will not boot if inserted during OPTION ROM scan..................................121
27. Swapping bootable for non-bootable CDROM during POST causes hang at boot.......121
28. OB P100 NICs do not show at POST but attempt PXE boot and appear in Boot Menu122
29. Dodson: Adaptec 39160 in slots 5 & 6 causes Expansion ROM error..........................122
30. Can Not Change BIOS SETUP IDE Options Using <Enter> Key..................................123
31. Minimum Wait Time Between Power Off and Power On via Front Panel Power Button Is
One Second..............................................................................................................................123
32. Unable to boot Netware 6.0 (NW6) From CD ROM With Adaptec Adaptor 2100S in Slot
6. 123
33. 3COM* 3C980C-TX NIC causes Microsoft* Windows* 2000 blue screen when greater
than 4GB of system memory is installed..................................................................................124
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 9

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Table of Contents
34. Peer-to-peer PCI transactions are not supported between the CIOB-controlled 64-bit
PCI bus and the legacy 32-bit PCI bus controlled by the HE-SL north bridge.........................125
35. SDS2 PCI slot current levels supported by the 5V rail...................................................125
36. OB P100 NICs do not show at POST but attempt PXE boot and appear in Boot Menu125
Glossary...........................................................................................................................................I
Reference Documents.................................................................................................................III
Index.............................................................................................................................................. IV
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
ix
Page 10

List of Figures Intel® Server Board SDS2
List of Figures
Figure 1. SDS2 Server Board Block Diagram.................................................................................1
Figure 2. SDS2 Memory Bank Layout..............................................................................................7
Figure 3. SDS2 Interrupt Routing Diagram (CSB5 Internal)..........................................................22
Figure 4. SDS2 Interrupt Routing Diagram....................................................................................23
Figure 5. SDS2 PCI Interrupt Mapping Diagram............................................................................24
Figure 6. SDS2 Sahalee BMC Block Diagram (View as Reference Only)....................................26
Figure 7. SDS2 Locations of ADM1026 and Sahalee....................................................................29
Figure 8. SDS2 Server Board Clock Generation/Distribution Diagram.........................................71
Figure 9. SDS2 Server Board Voltage Generation/Distribution Diagram......................................73
Figure 10. SDS2 Server Board Rear I/O Panel.............................................................................87
Figure 11. SDS2 Configuration Jumpers.......................................................................................89
Figure 12. SDS2 Configuration Jumper Locations........................................................................90
Figure 13. Output Voltage Timing..................................................................................................97
Figure 14. Turn On/Off Timing.......................................................................................................98
Figure 15. SDS2 Server Board Mechanical Drawing..................................................................101
Revision 1.2
x
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 11

Intel® Server Board SDS2 List of Tables
List of Tables
Table 1. SDS2 Intel® Pentium® III Processor Support Matrix.........................................................4
Table 2. Memory DIMM Pairs...........................................................................................................7
Table 3. I2C Addresses for DIMM Slots............................................................................................8
Table 4. PCI Bus Segment Characteristics...................................................................................11
Table 5. P32-A Configuration IDs...................................................................................................12
Table 6. P32-A Arbitration Connections.........................................................................................12
Table 7. P64-B Arbitration Connections.........................................................................................13
Table 8. P64-B Arbitration Connections.........................................................................................13
Table 9. Video Modes.....................................................................................................................15
Table 10. CSB5 GPIO Usage Table..............................................................................................17
Table 11. Super I/O GPIO Usage Table.........................................................................................18
Table 12. PCI Interrupt Routing/Sharing........................................................................................20
Table 13. Interrupt Definitions ........................................................................................................20
Table 14. ADM1026 Input Definition...............................................................................................27
Table 15. Temperature Sensors....................................................................................................28
Table 16. Sahalee Input Definition..................................................................................................28
Table 17. IPMB Bus Device s.........................................................................................................31
Table 18. Private I2C Bus 1 Devices..............................................................................................31
Table 19. Private I2C Bus 2 Devices..............................................................................................31
Table 20. Private I2C Bus 3 Devices..............................................................................................31
Table 21. Private I2C Bus 4 Devices..............................................................................................32
Table 22. BIOS Generated SEL Errors..........................................................................................37
Table 23: Event Request Message Event Data Field Contents ....................................................38
Table 24 Platform SEL Log Sensors for SDS2.............................................................................39
Table 25. Event Request Message Event Data Field Contents ....................................................45
Table 26. Port-80h Code Definition................................................................................................45
Table 27. Standard BIOS POST Codes........................................................................................46
Table 28. Recovery BIOS POST Codes .......................................................................................49
Table 29. POST Error Messages and Codes................................................................................50
Table 30. BMC Beep Codes ..........................................................................................................51
Table 31. Setup Utility Screen........................................................................................................52
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
xi
Page 12

List of Tables Intel® Server Board SDS2
Table 32. Main Menu Selections ....................................................................................................55
Table 33. Primary Master and Slave IDE Submenu Selections....................................................56
Table 34. Processor Settings Submenu Selections......................................................................57
Table 35. Advanced Menu Selections............................................................................................58
Table 36. Memory Configuration Menu Selections ........................................................................58
Table 37. PCI Configuration Menu Selections ...............................................................................59
Table 38. On-board SCSI and LAN Submenu Selections.............................................................59
Table 39. On-board VGA Submenu Selections.............................................................................59
Table 40. PCI slot Submenu Selections........................................................................................59
Table 41. I/O Device/Peripheral Configuration Submenu Selections............................................61
Table 42. Advanced Chipset Controller Submenu Selections.......................................................62
Table 43. PCI Device Submenu Selections...................................................................................62
Table 44. Security Menu Selections...............................................................................................62
Table 45. Server Menu Selections.................................................................................................63
Table 46. System Management Submenu Selections ..................................................................64
Table 47. Console Redirection Submenu Selections....................................................................65
Table 48. Boot Device Priority Selections......................................................................................65
Table 49. Hard Drive Selections ....................................................................................................66
Table 50. Removable Drive Selections..........................................................................................66
Table 51. Exit Menu Selections......................................................................................................66
Table 52. 24-Pin Main Power Connector Pin-out...........................................................................74
Table 53. 8-Pin +12 V Power Connector Pin-out...........................................................................74
Table 54. Aux Signal Connector Pin-out........................................................................................74
Table 55. DIMM Connector Pin-out................................................................................................75
Table 56. ICMB Connector Pin-out................................................................................................76
Table 57. IPMB Connector Pin-out.................................................................................................76
Table 58. HSBP-A Connector Pin-out............................................................................................76
Table 59. HSBP-B Connector Pin-out...........................................................................................77
Table 60. Front Panel 34-Pin Header Pin-out................................................................................77
Table 61. 32-bit 5 V PCI Slot Pin-out..............................................................................................78
Table 62: 64-bit 3.3V PCI Slot Pin-out............................................................................................78
Table 63. VGA Connector Pin-out..................................................................................................80
Table 64. 68-pin SCSI Connector Pin-out......................................................................................80
Table 65. RJ -45 Connector Pin-out...............................................................................................81
Revision 1.2
xii
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 13

Intel® Server Board SDS2 List of Tables
Table 66. IDE 40-pin Connector Pin-out........................................................................................82
Table 67. Stacked Three-port USB Connector Pin-out.................................................................82
Table 68. 10-pin USB Connection Header (2 x 5) Pin-out.............................................................83
Table 69. 34-pin Floppy Connector Pin-out...................................................................................84
Table 70. DB9 Serial Port Pin-out..................................................................................................84
Table 71. 10-pin Header Serial Port Pin-out..................................................................................84
Table 72. DB25 Parallel Port Pin-out.............................................................................................85
Table 73. Keyboard and Mouse PS/2 Connector Pin-out..............................................................85
Table 74. Fan Header Pin-out........................................................................................................86
Table 75. Chassis Intrusion Header Pin-out..................................................................................86
Table 76. External Drive Activity Header Pin-out...........................................................................87
Table 77. Server Board Connector Manufacturer Part Numbers..................................................87
Table 78. System Configuration Jumper Options..........................................................................91
Table 79. CPU Frequency Select Jumper Options .......................................................................91
Table 80. List of Assembled Jumpers in Production.....................................................................92
Table 81. Absolute Maximum Ratings ...........................................................................................94
Table 82. SDS2 Server Board Power Consumption.....................................................................95
Table 83: SDS2 Power Supply Specification.................................................................................95
Table 84: Voltage Timing Parameters...........................................................................................95
Table 85: Turn On/Off Timing........................................................................................................97
Table 86. Transient Load Requirements .......................................................................................99
Table 87. Estimated SDS2 Server Board MTBF.........................................................................100
Table 88. Safety Regulations.......................................................................................................102
Table 89. EMC Regulations .........................................................................................................102
Table 90. ICMB External Cable Connectors................................................................................105
Table 91. Errata Summary ...........................................................................................................106
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
xiii
Page 14

List of Tables Intel® Server Board SDS2
v
< This page intentionally left blank. >
Revision 1.2
xi
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 15
Intel® Server Board SDS2 Introduction
PCI
Slot
Slot
PCI
Slot
Slot
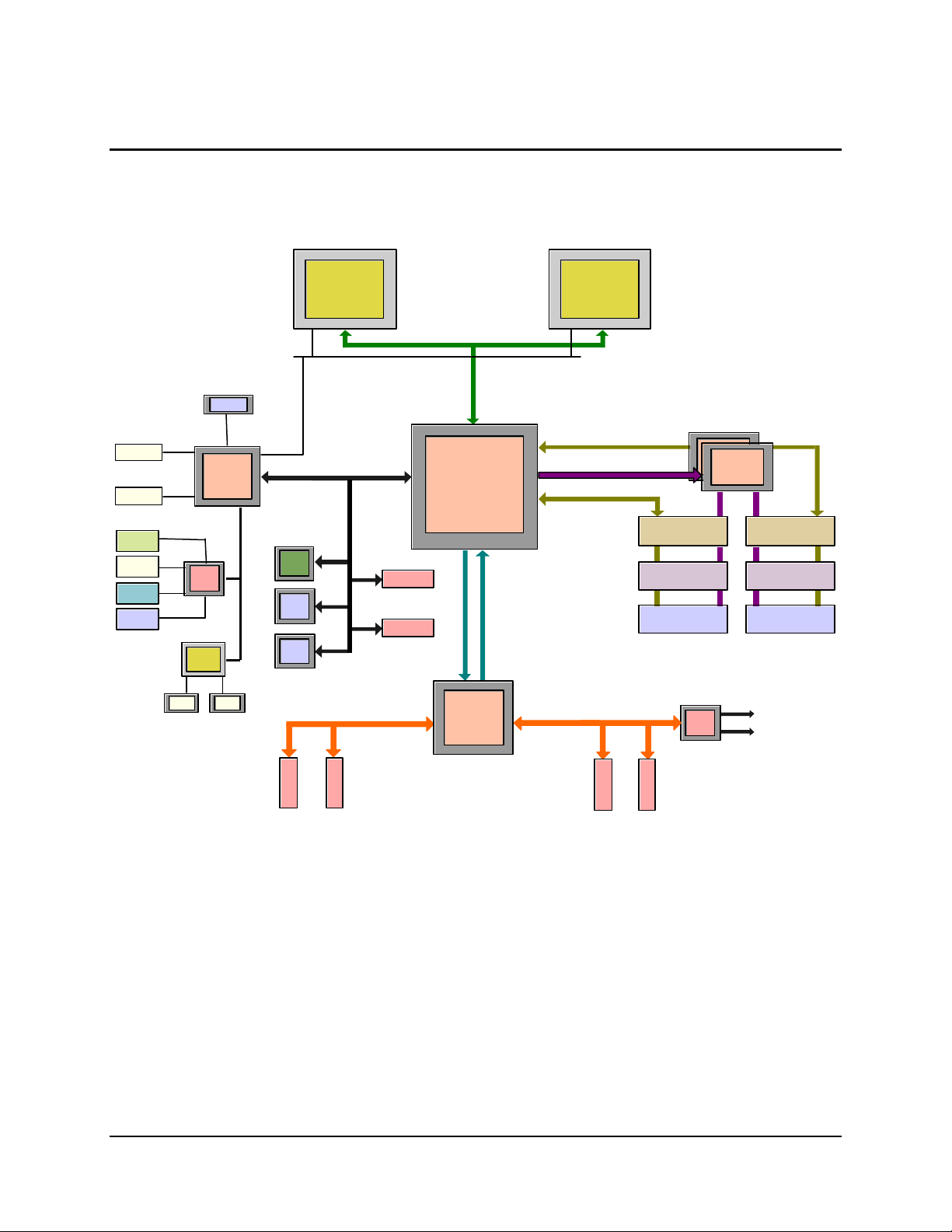
1. Introduction
This chapter provides an architectural overview of the Intel® SDS2 Server Board. It provides a
view of the functional blocks and their electrical relationships. The figure below shows the
functional blocks of the Server Board and the plug-in modules that it supports.
CPU 1
Front Side Bus (133MHz)
APIC Bus
FLASH
CPU 2
IDE Pri
USB x 4
Floppy
Keyboard
Mouse
COM1
COM2
Parallel
Port
CSB5
LPC
Bus
SIO
BMC
FLASH SRAM
DATA Bus (133MHz)
PCI 32-bit Bus (33MH z, 5V)
VIDEO
NIC 1
NIC 2
PCI 64 -bit Bus (66MHz, 3.3V)
PCI
1
2
PCI Slot 3
PCI Slot 4
HE-SL
(2 x
133MHz)
IMBus
CIOB
ADD/CTRL Bus (133MHz)
DATA Bus (133MHz)
PCI 64-bit Bus (66MHz, 3.3V)
Figure 1. SDS2 Server Board Block Diagram
BANK 1
BANK 2
BANK 3
PCI
5
Registers
Registers
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
SCSI
6
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
Channel A
Channel B
Revision 1.2
1
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 16

Architecture Intel® Server Board SDS2
2. Architecture
The SDS2 Server Board is a monolithic printed circuit board that can accept two Intel® Pentium®
III processors using the Socket 370 FCPGA2 package. The SDS2 Server Board complies with
the Entry SSI version 1.0 and ATX version 2.03 (12 inch x 13 inch) form-factor. It is designed
around the Server Works* ServerSet* III HE-SL chipset.
The chipset contains three components:
• The HE-SL CNB20 North Bridge provides an integrated memory controller
• The CIOB20 I/O Bridge provides the interface for two peer 64-bit, 66 MHz PCI busses
• The CSB5 South Bridge provides the LPC bus for legacy support.
The Server Board also contains other embedded devices such as:
• 2D/3D graphics accelerator
• Two 10/100 Network Interface Controller
• Dual channel Ultra160 SCSI
• Standard I/O
• Server management
The SDS2 Server Board provides six DIMM sockets for a maximum memory capacity of 6 GB.
Only registered PC-133 compliant Registered SDRAM memory modules are supported. The
current tested memory listing is posted on the Intel technical support web site:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SDS2/
The SDS2 Server Board provides the following features:
• Dual Intel
• Server Works ServerSet III HE-SL chipset
®
Pentium® III FCPGA2 processors (Socket370)
- HE-SL North Bridge
- CIOB20 I/O Bridge
- CSB5 South Bridge
• Support for six PC-133 compliant registered ECC SDRAM memory modules
• 32-bit, 33-MHz 5 V Full-length PCI segment A (P32-A) with three embedded devices
- 2D/3D Graphics Controller: ATI* RAGE* XL Video Controller with 4MB of SDRAM
- Two Network Interface Controller: Intel 82550 Fast Ethernet Controller
- Two 32-bit Slots: PCI Slots 3 and 4
• 64-bit, 66-MHz 3.3 V full-length PCI segment B (P64-B)
- Two 64-bit Slots: PCI slots 1 and 2
Revision 1.2
2
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 17

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Architecture
• 64-bit, 66-MHz 3.3 V full-length PCI segment C (P64-C) with one embedded device
- Dual Channel Wide Ultra160 SCSI controller: Adaptec* AIC-7899W
- Two 64-bit 3.3 V Slots: PCI slots 5 and 6
• LPC (Low Pin Count) bus segment with two embedded devices
- Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) providing monitoring, alerting, and logging
of critical system information obtained from embedded sensors on the Server Board
- Super I/O controller chip providing all PC-compatible I/O (floppy, serial, keyboard,
mouse)
• X-Bus segment from CSB5 with one embedded device
- Flash ROM device for system BIOS: Fairchild* 29LV008B 8Mbit Flash ROM
• Two IDE connectors, supporting up to two ATA -100 compatible devices each. Note: Fab
4 board PBA A58285-402 and –403 supported only one IDE connector. Fab 5 PBA
A58285-502 (and later revisions) supports two IDE connectors.
• Four Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports: Three on the rear I/O and one on the Server
Board as a 10-pin header
• Two serial ports: One out to rear I/O and one through a 10-pin header on the Server
Board
• One floppy connector
• Four multi speed system fan connectors and two single speed CPU fan connectors.
• 34-pin SSI compliant front panel connector
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
3
Page 18
Processor and Chipset Intel® Server Board SDS2
3. Processor and Chipset
The Server Works* ServerSet III HE-SL chipset provides the 36-bit address, 72-bit data (64-bit
data + 8-bit ECC) processor host bus interface , operating at 133 MHz in the AGTL signaling
environment. The HE-SL North Bridge provides an integrated memory controller, the interface to
32-bit, 33-MHz Rev 2.2 compliant PCI bus, and two Inter-Module Bus interfaces. The InterModule Bus (IMB) provides the interface to two 64-bit, 66-MHz Rev 2.2 compliant PCI buses via
the CIOB20.
The SDS2 DP Server Board direct ly supports up to 6 GB of ECC memory, using six PC-133compliant registered SDRAM DIMMs. The ECC implementation in the HE-SL can detect and
correct single-bit errors, and it can detect multiple-bit errors.
3.1 Processors
The SDS2 Server Board supports two Intel® Pentium® III processors in the Socket 370 FCPGA2
package. If two processors are installed, both processors must be of identical revisions with the
same core voltage and speed for the bus and core. If one processor is installed, an AGTL
terminator module must be installed in the other socket. The support circuitry on the Server
Board consists of the following:
• Dual Socket 370 FCPGA2 processor sockets supporting 133-MHz FSB (if using one
processor, an AGTL terminator module goes in the empty socket)
• Processor host bus AGTL support circuitry, including termination power supply
Table 1. SDS2 Intel® Pentium® III Processor Support Matrix
Processor
Family
Intel
Pentium III
Intel
Pentium III –
Tray
Intel
Pentium III –
Tray
Intel
Pentium III –
Boxed
Intel
Pentium III –
Tray
Intel
Pentium III –
Boxed
Intel FCPGA2 838253 1.4GHZ/133MHz 512KB tA1 06B1h Yes
Package
Type
FCPGA 800MHz – 1.0GHz 256KB N/A N/A No
FCPGA2 836606 1.BGHz/133MHz 256KB cD0 068Ah
FCPGA2 836716 1.13GHZ/133MHz 512KB tA1 06B1h
FCPGA2 836384 1.13GHZ/133MHz 512KB tA1 06B1h
FCPGA2 836721 1.26GHZ/133MHz 512KB tA1 06B1h
FCPGA2 836583 1.26GHZ/133MHz 512KB tA1 06B1h
MM## Speed
Core/Bus
Cache
Size
Core
Stepping
CPUID
S-Spec
SL5QJ
SL5PU
SL5LV
SL5QL
SL5LW
Supported
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Revision 1.2
4
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 19
Intel® Server Board SDS2 Processor and Chipset
Pentium III –
Tray
Intel
Pentium III –
Boxed
FCPGA2 843849 1.4GHZ/133MHz 512KB tA 1 06B1h
SL5XL
Yes
SL5XL
Notes:
• All processor sockets must be populated with either a processor or a terminator module.
The BMC will not allow DC power to be applied to the system unless both processor
sockets contain a properly seated processor or terminator module.
• Processors should be populated in the sequential order. In other words, processor
socket #1 should be populated before processor socket #2.
• BIO 50 (released on FAB 5) supports the tB1 stepping, CPUID 06B4. These processors
are being evaluated for addition to supported processor list. The current Intel support
web site has the latest supported processor list for SDS2:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SDS2/.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
5
Page 20

Processor and Chipset Intel® Server Board SDS2
3.1.1 Processor Voltage Regulator Module (VRM)
The SDS2 Server Board has dual, on board, RM circuitry to support the two processors. The
circuit is compliant with the VRM8.5 specification and provides a maximum of 60A, which will
support the currently available processors and future releases of the Pentium III processors.
The board hardware and the BMC read the processor VID (Voltage Identification) bits for each
processor before turning on the power to the processors (VRMs). If the VIDs of the two
processors are not identical, then the BMC will not turn on the VRMs and a beep code is
generated. Table 30. BMC Beep Codes lists all of the error codes.
3.2 Memory Subsystem
The SDS2 Server Board supports up to six DIMM sockets for a maximum memory capacity of 6
GB using 1 GB DIMMs. The DIMM organization is x72, which includes 8 ECC check bits. ECC
from the DIMMs is passed through to the processor front side bus.
The SDRAM interface runs at the same frequency as the processor bus. The memory controller
supports 2-way interleaved SDRAM, memory scrubbing, single-bit error correction, and multiplebit error detection. Memory can be implemented with either single-sided (one row) or doublesided (two row) DIMMs.
• Only registered PC-133 compliant memory is supported
• Support is 2-way interleaved SDRAM and requires two DIMMs to be installed per bank.
• ECC si ngle-bit error correction and multiple-bit error detection
• Maximum memory capacity of 6 GB
• Minimum memory capacity of 128 MB
Note: Memo ry interleaving is a way to increase memory performance by allowing the system to
access multiple memory modules simultaneously, rather than sequentially, in a similar fashion to
Hard Drive striping. Interleaving can only take place between identical memory modules.
3.2.1 Memory Configuration
Memory configuration requirements are as follow:
• PC-133 SDRAM Registered DIMM modules
• DIMM organization: x72 ECC
• Pin count: 168
• SDRAM Supported: 64 M b, 128 Mb, 256 Mb
• DIMM capacity: 64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB
• Serial PD: JEDEC Rev 2.0
• Voltage Options: 3.3 V (VDD/VDDQ)
• Interface : LVTTL
• DIMMs must be populated in pairs for a x144 wide memory data path
• Any or all memory banks may be populated
Revision 1.2
6
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 21
Intel® Server Board SDS2 Processor and Chipset
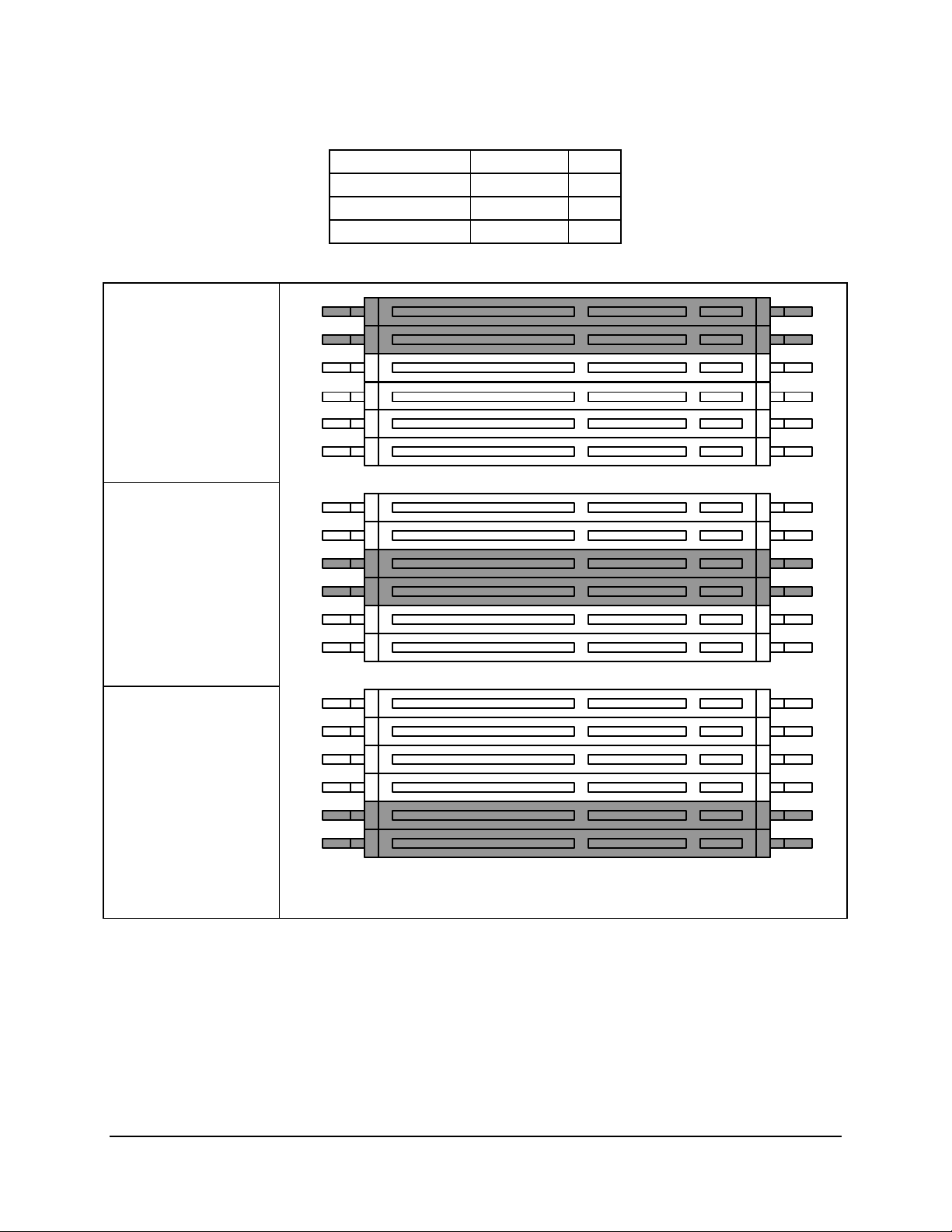
Table 2. Memory DIMM Pairs
Memory DIMM DIMM PAIR Row
DIMM1A, DIMM1B 1 1, 2
DIMM2A, DIMM2B 2 3, 4
DIMM3A, DIMM3B 3 5, 6
DIMM Pair 1
DIMM Pair 2
DIMM Pair 3
Figure 2. SDS2 Memory Bank Layout
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
7
Page 22
Processor and Chipset Intel® Server Board SDS2
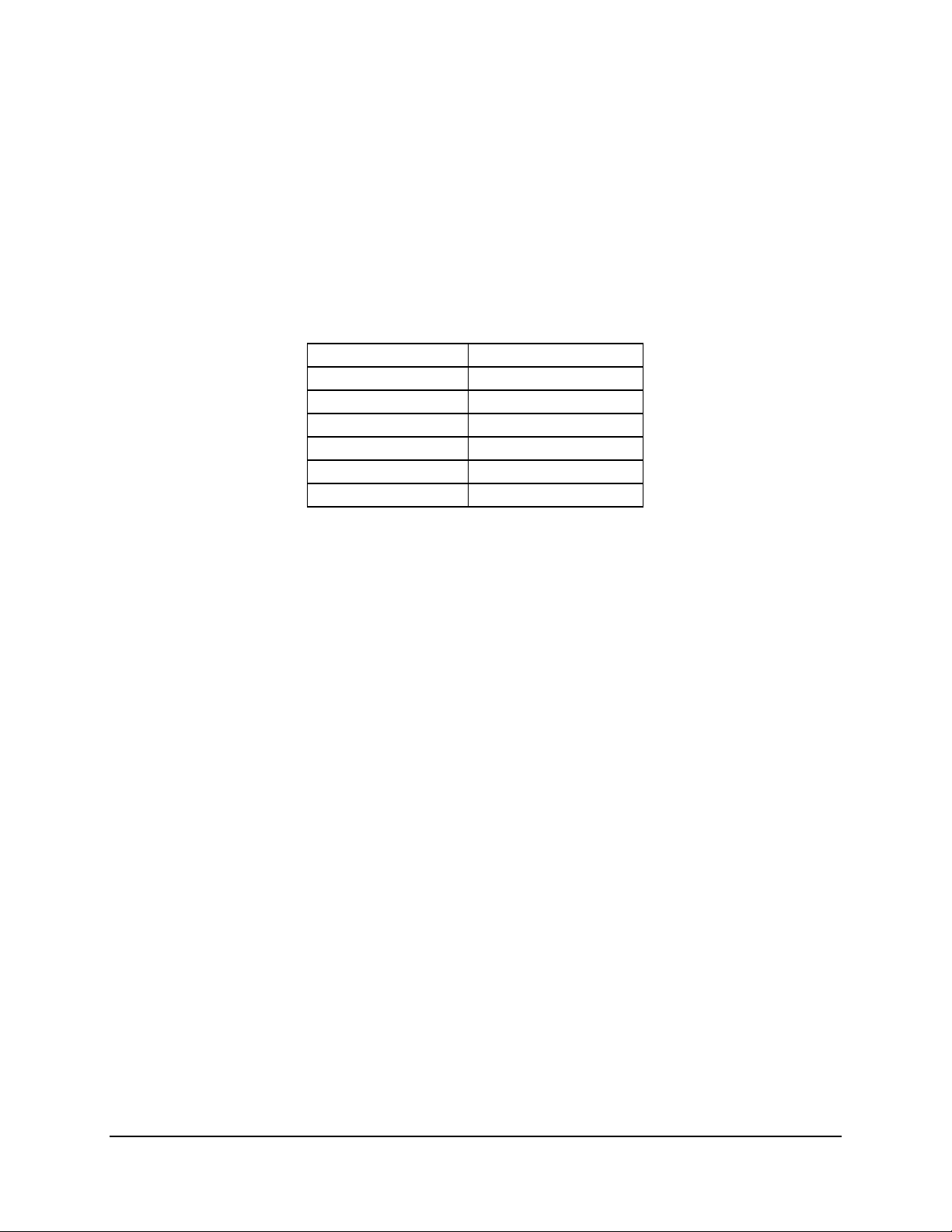
3.2.2 I2C Bus
An I2C* bus is between the BMC and the six DIMM slots. This bus is used by the system BIOS to
retrieve DIMM information needed to program the HE-SL memory registers which are required to
boot the system.
The following table provides the I2C addresses for each DIMM slot.
Table 3. I2C Addresses for DIMM Slots
Device Address
DIMM 1A 0xA0
DIMM 1B 0xA2
DIMM 2A 0xA4
DIMM 2B 0xA6
DIMM 3A 0xA8
DIMM 3B 0xAA
3.3 Chipset
The Server Works* ServerSet III HE-SL chipset provides an integrated I/O bridge and memory
controller and a flexible I/O subsystem core (PCI), targeted for multiprocessor systems and
standard high-volume servers. The Server Works* ServerSet III chipset consists of the three
components listed below:
• CNB20HE-SL: Champion North Bridge. The HE-SL North Bridge is responsible for
accepting access requests from the host (processo r) bus and for directing those
accesses to memory or to one of the PCI buses. The HE-SL monitors the host bus,
examining addresses for each request. Accesses may be directed to a memory request
queue, for subsequent forwarding to the memory subsystem, or to an outbound request
queue, for subsequent forwarding to one of the PCI buses. The HE-SL also accepts
inbound requests from the CIOB20 and the legacy PCI bus. The HE-SL is also
responsible for generating the appropriate controls to control data transfer to and from
the memory.
• CIOB20: Champion I/O Bridge. The CIOB20 provides the interface for two 64-bit, 66-
MHz Rev. 2.2 compliant PCI bus. The CIOB is both master and target on both PCI
buses.
• CSB5: South Bridge. The CSB5 controller has several components. It provides the
interface for a 32-bit, 33-MHz Rev. 2.2-compliant PCI bus. The CSB5 can be both a
master and a target on that PCI bus. The CSB5 also includes a USB controller and an
IDE controller. The CSB5 is also responsible for much of the power management
functions, with ACPI control registers built in. The CSB5 also provides a number of GPIO
pins and has the LPC bus to support low-speed legacy I/O.
Revision 1.2
8
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 23

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Processor and Chipset
3.3.1 CNB20HE-SL Champion North Bridge
The Champion North Bridge Rev 2.0 High End Super Lite (CNB20HE-SL) is the third generation
product in the Server Works Champion North Bridge Technology. The HE-SL is a 644-pin ballgrid array (BGA) device and uses the proven components of previous generations like the
Pentium Pro Bus interface unit, the PCI interface unit, and the SDRAM memory interface unit. In
addition, the HE-SL incorporates a proprietary Intra Module Bus (IMBus) Interface. The IMBus
interface enables the HE-SL to directly interface with the CIOB20 through its two unidirectional
16-bit wide data busses with parity support. The HE-SL also increases the main memory
interface bandwidth and maximum memory configuration with a 144-bit wide memory interface.
The HE-SL integrates three main functions:
• An integrated high-performance main memory subsystem
• An IMBus interface that provides a high-performance data flow path between the Pentium
Pro bus and the I/O subsystem
• A PCI interface which provides an interface to the compatibility PCI bus segment and the
CSB5 (South Bridge).
Other features provided by the HE-SL include the following:
• Full support of ECC on the processor bus
• Full support of ECC on the memory interface
• Eight deep in-order queue
• Full support of registered PC-133 ECC SDRAM DIMMs
• Support for 6 GB of 2-way interleaved SDRAM
• Memory scrubbing
3.3.1.1 PCI Bus P32-A I/O Subsystem
The HE-SL provides a legacy 32-bit PCI subsyst em and acts as the central resource on this PCI
interface.
P32-A supports the following embedded devices and connectors:
• CSB5: South Bridge
• Two Intel® 82550PM 10/100 Fast Ethernet PCI network interface controllers
• An ATI RAGE XL Video Controller with 3D/2D graphics accelerator
• Two 32-bit, 33-MHz 5V full length PCI Slots
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
9
Page 24

Processor and Chipset Intel® Server Board SDS2
3.3.2 CIOB20 Champion I/O Bridge
The Champion I/O Bridge (CIOB) is a 352-pin ball-grid array device and provides an integrated
I/O bridge that provides a high-performance data flow path between the IMBus and the 64-bit I/O
subsystem. This subsystem supports peer 64-bit PCI segments. Because it has multiple PCI
interfaces, the CIOB can provide large and efficient I/O configurations. The CIOB functions as
the bridge between the IMBus and the multiple 64-bit PCI I/O segments.
The IMBus interface can support 512 MB/s of data bandwidth in both the upstream and
downstream direction simultaneously.
The internal PCI arbiter implements the Least Recently used algorithm to grant access to
requesting masters.
3.3.2.1 PCI Bus P64-B I/O Subsystem
P64-B supports two 64-bit, 66-MHz 3.3V full-length PCI slots.
3.3.2.2 PCI Bus P64-C I/O Subsystem
P64-C supports the following embedded devices and connectors:
• Dual Channel Wide Ultra160 SCSI controller: Adaptec* AIC-7899W
• Two 64-bit, 66-MHz 3.3V full length PCI Slots
3.3.3 CSB5 South Bridge
Please refer to Section 4.5 for information on CSB5.
Revision 1.2
10
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 25
Intel® Server Board SDS2 I/O Subsystem
4. I/O Subsystem
4.1 PCI Subsystem
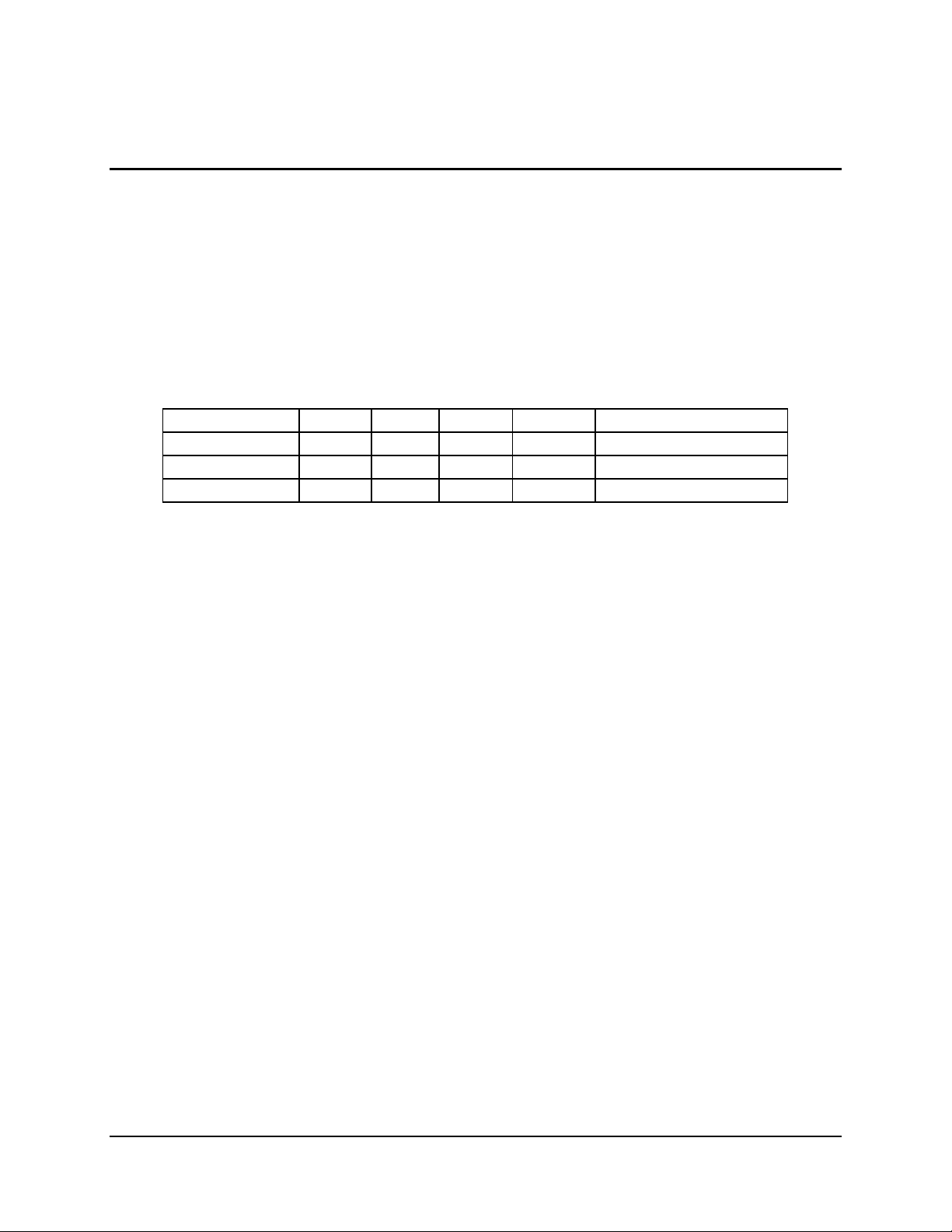
The primary I/O bus for SDS2 DP Server Board is PCI, with three PCI bus segments. The PCI
buses comply with the PCI Local Bus Specification, Rev 2.2. The P32-A bus segment is directed
through the HE-SL North Bridge while the two 64bit segments, P64-B and P64-C, are directed
through the CIOB20 I/O Bridge. The table below lists the characteristics of the three PCI bus
segments.
Table 4. PCI Bus Segment Characteristics
PCI Bus Segment Voltage Width Speed Type PCI Slots
P32-A 5 V 32-bits 33-MHz Peer Bus Slots 3 and 4 – Full Length
P64-B 3.3 V 64-bits 66-MHz Peer Bus Slots 1 and 2 – Full Length
P64-C 3.3 V 64-bits 66-MHz Peer Bus Slots 5 and 6 – Full Length
Note: When an add-in 33-MHz PCI card is plugged into a P64 bus segment, such as in the P64C slot 5, this reduces the bus speed for all devices attached to that bus segment, including the
on-board SCSI controller.
4.1.1 32-bit, 33-MHz PCI Subsystem
All 32-bit, 33-MHz PCI I/O for the SDS2 Server Board is directed through the HE-SL North
Bridge. The 32-bit, 33-MHz PCI segment created by the HE-SL is called the P32-A segment. The
P32-A segment supports full-length, full-height PCI cards and contains the following embedded
devices and connectors:
• 2D/3D Graphics Accelerator: ATI RAGE XL Video Controller
• Two Network Interface Controller: Intel 82550 Fast Ethernet Controller
• PCI Slots 3 and 4
• CSB5 South Bridge (PCI -to-LPC bridge)
Each of the embedded devices above, except for the CSB5 South Bridge, is allocated a GPIO to
disable the device.
4.1.1.1 Device IDs (IDSEL)
Each device under the PCI hub bridge has its IDSEL signal connected to one bit of AD [31:16],
which acts as a chip select on the PCI bus segment in configuration cycles. This determines a
unique PCI device ID value for use in configuration cycles. The following table shows the bit to
which each IDSEL signal is attached for P32-A devices, and corresponding device description.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
11
Page 26
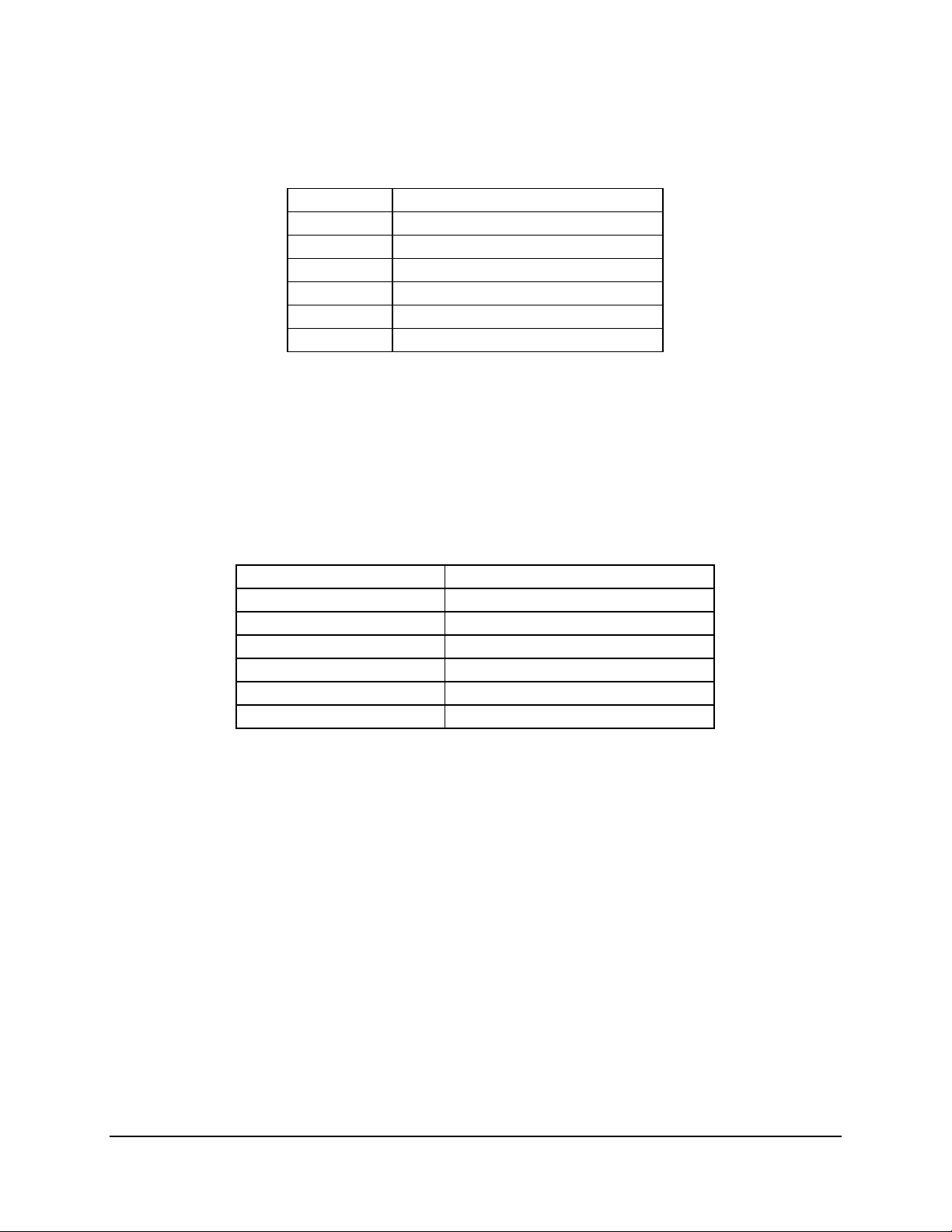
I/O Subsystem Intel® Server Board SDS2
Table 5. P32-A Configuration IDs
IDSEL Value Device
18 ATI RAGE XL Video Controller
19 Intel 82550 Fast Ethernet Controller 1
20 Intel 82550 Fast Ethernet Controller 2
24 PCI Slot 3
25 PCI Slot 4
31 CSB5 South Bridge
4.1.1.2 P32-A Arbitration
P32-A supports seven PCI masters (ATA RAGE XL, two Intel 82550s, PCI masters from slots 3
and 4, CSB5, and HE-SL). All PCI masters must arbitrate for PCI access, using resources
supplied by the HE-SL. The following table defines the arbitration connections.
Table 6. P32-A Arbitration Connections
Baseboard Signals Device
REQ_VGA / GNT_VGA ATI* RAGE XL Video Controller
D_PCIREQL1 / D_PCIGNTL1 Intel 82550 Fast Ethernet Controller 1
D_PCIREQL2 / D_PCIGNTL2 Intel 82550 Fast Ethernet Controller 2
D_PCIREQL3 / D_PCIGNTL3 PCI Slot 3
D_PCIREQL4 / D_PCIGNTL4 PCI Slot 4
D_PCIREQL5 / D_PCIGNTL5 CSB5 South Bridge
4.1.2 64-bit, 66-MHz PCI Subsystem
There are two 64-bit, 66-MHz PCI busses directed through the CIOB20 I/O Bridge. Both segments
support full-length, full-height PCI cards. The PCI cards must meet the PCI specification for height,
inclusive of cable connections and memory. The two PCI segments are peer buses.
4.1.2.1 Device IDs (IDSEL)
Each device under the PCI hub bridge has its IDSEL signal connected to one bit of AD [31:16],
which acts as a chip select on the PCI bus segment in configuration cycles. This determines a
unique PCI device ID value for use in configuration cycles. The following tables show the bit to
which each IDSEL signal is attached for P64-B and P64-C devices, and corresponding device
description.
Revision 1.2
12
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 27
Intel® Server Board SDS2 I/O Subsystem
Table 4. P64-B Configuration IDs
IDSEL Value Device
24 PCI Slot 1
25 PCI Slot 2
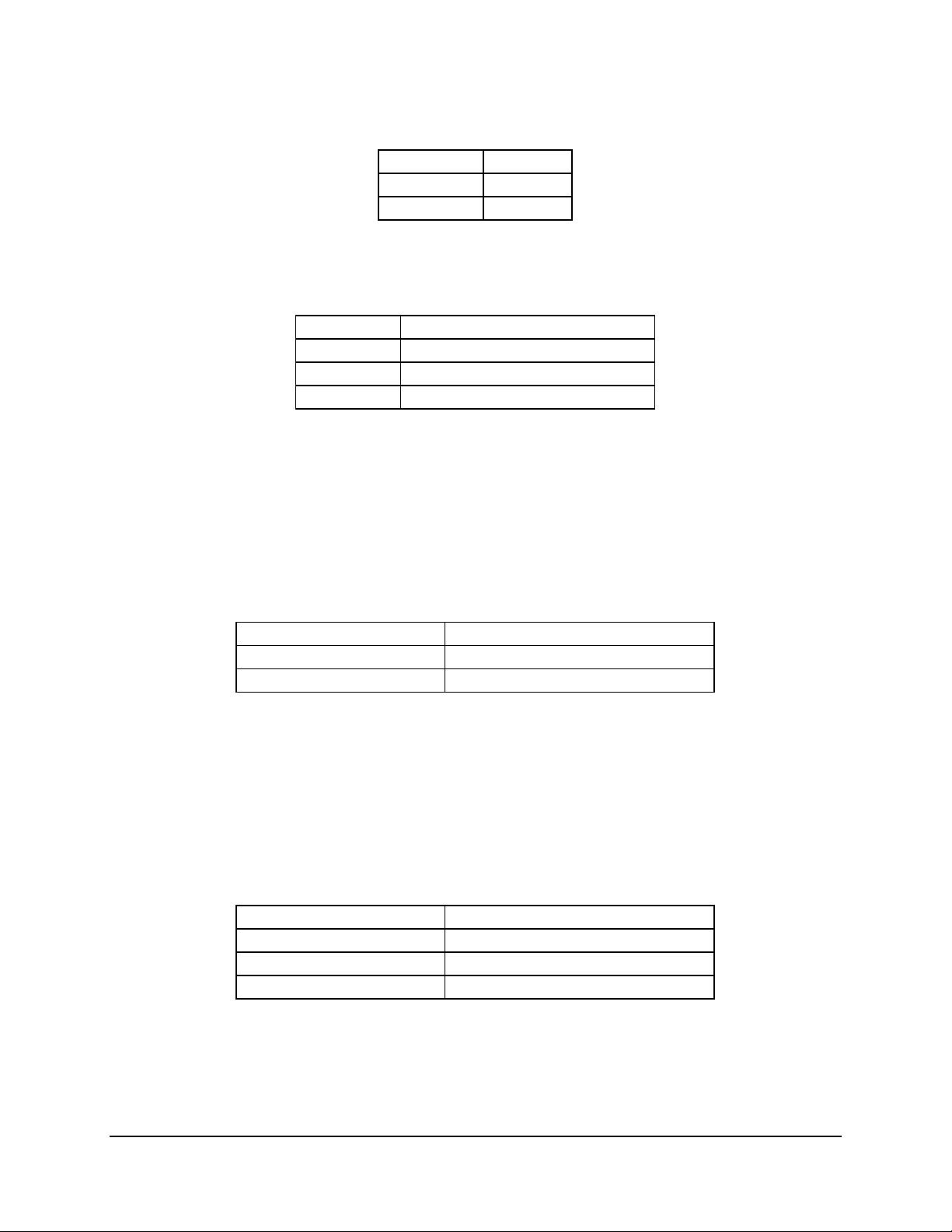
Table 5. P64-C Configuration IDs
IDSEL Value Device
20 Adaptec AIC-7899W SCSI Controller
24 PCI Slot 5
25 PCI Slot 6
4.1.2.2 P64-B Arbitration
P64-B supports three PCI masters (PCI masters from slots 1 and 2, and CIOB). All PCI
masters must arbitrate for PCI access, using resources supplied by the CIOB. The following
table defines the arbitration connections.
Table 7. P64-B Arbitration Connections
Baseboard Signals Device
FREQL1 / FGNTL1 PCI Slot 1
FREQL2 / FGNTL2 PCI Slot 2
4.1.2.3 P64-C Arbitration
P64-C supports four PCI masters (PCI masters from slots 5 and 6, onboard SCSI, and CIOB).
All PCI masters must arbitrate for PCI access, using resources supplied by the CIOB. The
following table defines the arbitration connections.
Table 8. P64-B Arbitration Connections
Baseboard Signals Device
SCSIREQL0 / SCSIGNTL0 Adaptec AIC-7899W SCSI Controller
P64REQL1 / P64GNTL1 PCI Slot 5
P64REQL2 / P64G NTL2 PCI Slot 6
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
13
Page 28

I/O Subsystem Intel® Server Board SDS2
4.1.2.4 Zero Channel RAID (ZCR) Capable PCI Slot 6
The SDS2 Server Board supports zero-channel RAID controller on PCI Slot 6. This add-in card
leverages the on-board SCSI controller along with its own built-in intelligence to provide a
complete RAID controller subsystem on-board. If a specified zero-channel RAID card is
installed, then SCSI interrupts are routed to the RAID card instead of PCI interrupt controller and
the host -based I/O device is effectively hidden from the system. The SDS2 Server Board uses
an implementation commonly referred to as “RAIDI OS” to support this feature.
Note: Zero Channel Raid Cards (ZCR) cards are only supported on PCI slot 6.
Note: Intel zero channel raid cards SRCMR and SRCMRU are not supported on SDS2.
4.2 Ultra160 SCSI
The SDS2 Server Board provides an embedded dual-channel SCSI bus through the use of the
Adaptec*’s AIC-7899W SCSI controller. The AIC-7899W controller contains two independent
SCSI controllers that share a single 64-bit, 66-MHz PCI bus master interface as a multifunction
device, packaged in a 456-pin BGA. Internally, each controller is identical, capable of operations
using either 16-bit SE or LVD SCSI providing 40 MBps (Ultra-wide SE), 80 MBps (Ultra 2), or 160
MBps (Ultra160). Each controller has its own set of PCI configuration registers and SCSI I/O
registers. The SDS2 Server Board supports disabling of the on-board SCSI controller through
the BIOS setup menu.
The SDS2 Server Board provides active terminators, termination voltage, re-settable fuse , and
protection diode for both SCSI channels. The SCSI BIOS setup menu (CNTRL -A) provides the
ability to enable or disable the on-board terminators for both channels A and B.
4.3 Video Controller
The SDS2 Server Board provides an ATI* RAGE XL PCI graphics accelerator, along with video
SDRAM and support circuitry for an embedded SVGA video subsystem. The ATI* RAGE XL chip
contains a SVGA video controller, clock generator, 2D and 3D engine, and RAMDAC in a 272-pin
PBGA. Two 2 MB SDRAM chips provide 4 MB of video memory . The SVGA subsystem supports
a variety of modes, up to 1024 x 768 resolution in 8/16/24/32 bpp modes under 2D and up to 800
x 600 resolution in 8/16/24/32 bpp modes under 3D. It also supports both CRT and LCD
monitors at up to 100 Hz vertical refresh rate. The SDS2 Server Board provides a standard 15pin VGA connector.
4.3.1 Video Modes
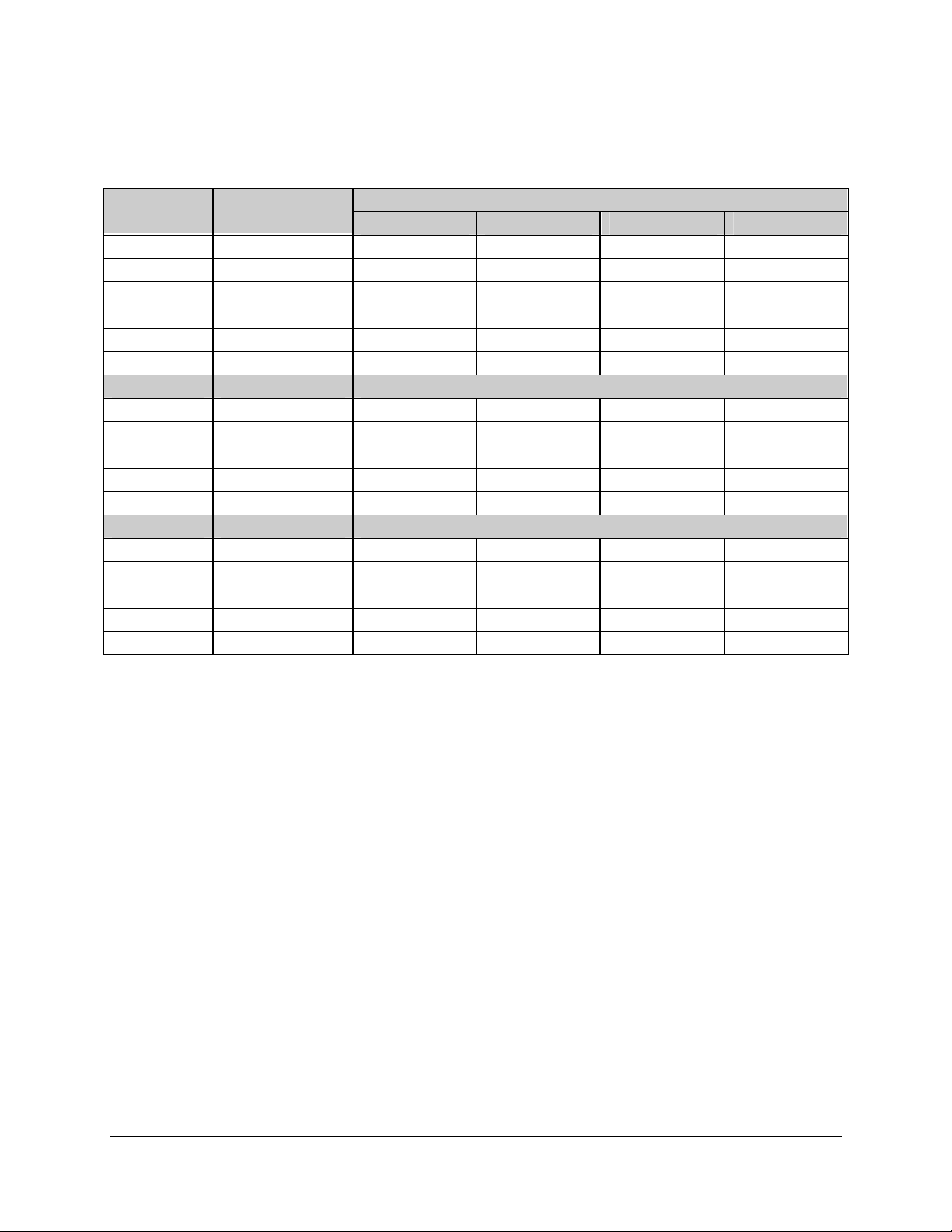
The RAGE XL chip supports all standard IBM* VGA modes. The following table shows the 2D/3D
modes supported on the CRT. The table specifies the various display resolution, refresh rates
and color depths supported.
Revision 1.2
14
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 29
Intel® Server Board SDS2 I/O Subsystem
Table 9. Video Modes
SDS2 2D Mode Video Support 2D Mode Refresh Rate (Hz)
8 bpp 16 bpp 24 bpp 32 bpp
640x480 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
800x600 60, 70, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1024x768 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1280x1024 43, 60 Supported Supported Supported –
1280x1024 70, 72 Supported – Supported –
1600x1200 60, 66, 76, 85 Supported Supported – –
3D Mode Refresh Rate (Hz) SDS2 3D Mode Video Support with Z Buffer Enabled
640x480 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
800x600 60, 70, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported –
1024x768 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported – – –
1280x1024 43, 60, 70, 72 – – – –
1600x1200 60, 66, 76, 85 – – – –
3D Mode Refresh Rate (Hz) SDS2 3D Mode Video Support with Z Buffer Disabled
640x480 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
800x600 60, 70, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1024x768 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported – –
1280x1024 43, 60, 70, 72 Supported – – –
1600x1200 60, 66, 76, 85 Supported – – –
4.4 Network Interface Controller (NIC)
The SDS2 Server Board supports two 10Base -T / 100Base-TX network subsystem using the
Intel 82550-PM NIC. The 82550 components are highly integrated PCI LAN controllers in a thin
BGA 15 mm2 package. The controller’s baseline functionality is equivalent to that of the Intel
82559 with the addition of Alert on LAN* functionality.
The SDS2 Server Board supports independent disabling of either of the two NIC controllers
under BIOS setup menu.
The 82550 supports the following features:
• 32-bit PCI/Card Bus master interface
• Integrated IEEE 802.3 10Base -T and 100Base-TX compatible PHY
• IEEE 820.3u auto-negotiation support
• Chained memory structure similar to the 82559, 82558, 82557 and 82596
• Full duplex support at both 10 and 100 Mbps operation
• Low power +3.3 V device
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
15
Page 30

I/O Subsystem Intel® Server Board SDS2
4.4.1 NIC Connector and Status LEDs
The 82550 drives LEDs on the network interface connector to indicate link/activity on the LAN and
10-Mbps or 100-Mbps operation.
• The green LED indicates a network connection when lighted solidly and TX/RX activity
when blinking.
• The amber LED indicates 100-Mbps a network connection when lighted solidly and TX/RX
activity when blinking.
4.5 CSB5 South Bridge (PCI -to-LPC Bridge, IDE, USB)
The CSB5 is a multi-function PCI device, housed in a 256-pin BGA device, providing PCI -to-LPC
bridge, PCI IDE interface, PCI USB controller, and power management controller. Each function
within the CSB5 has its own set of configuration registers. Once configured, each appears to the
system as a distinct hardware controller sharing the same PCI bus interface.
In the SDS2 Server Board implementation, the primary role of the CSB5’ is to provide the
gateway to all PC-compatible I/O devices and features. The SDS2 uses the following CSB5
features:
• PCI bus interface
• LPC bus interface
• IDE interface, with Ultra DMA 100 capability
• Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface
• PC-compatible timer/counter and DMA controllers
• APIC and 8259 interrupt controller
• Power management
• General purpose I/O
Following are descriptions of how each supported feature is implemented in SDS2.
4.5.1 PCI Bus Interface
The CSB5 fully implements a 32-bit PCI master/slave interface, in accordance with the PCI
Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.2. On the SDS2 Server Board, the PCI interface operates at
33 MHz, using the 5 V signaling environment.
4.5.2 PCI Bus Master IDE Interface
The CSB5 acts as a PCI -based Fast IDE controller that supports programmed I/O transfers and
bus master IDE transfers. The CSB5 supports two IDE channels, supporting two drives each
(drives 0 and 1). The FAB 5 (PBA A58285-502) SDS2 Server Board supports two IDE channels
through the standard 40-pin (2x20) connector. Note FAB 4 boards (PBA A58285-402 and –403)
supported only one IDE channel.
The SDS2 IDE interface supports the following features:
Revision 1.2
16
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 31

Intel® Server Board SDS2 I/O Subsystem
• The scatter / gather mechanism supports both DMA and PIO IDE drives and ATAPI
devices
• Support for ATA and ATAPI, PIO Mode 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, DMA Mode 0, 1, 2, and Ultra DMA
Mode 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
• The IDE drive transfer rate is capable of up to ATA -100 (100 MB/sec per channel)
4.5.3 USB Interface
The CSB5 contains a USB controller and four USB hubs. The USB controller moves data
between main memory and the four USB connectors.
The SDS2 Server Board provides a three external USB connector interface on the rear I/O. One
additional USB is supported internally through a 10-pin header (2 X 5) that can be cabled to a
front panel board. All four ports function identically and with the same bandwidth. The USB
Specification, Revision 1.1, defines the external connector. Table 68. 10-pin USB Connection
Header (2 x 5) Pin-out.
4.5.4 Compatibility Interrupt Control
The CSB5 provides the functionality of two 82C59 PIC devices for ISA -compatible interrupt
handling.
4.5.5 APIC
The CSB5 integrates a 32-entry I/O APIC that is used to distribute 32 PCI interrupts. It also
includes an additional 16-entry I/O APIC for the distribution of legacy ISA interrupts.
4.5.6 Power Management
One of the embedded functions of CSB5 is a power management controller. The SDS2 Server
Board uses this to implement ACPI -compliant power management features. The SDS2 supports
sleep states S0, S1, S4, and S5.
4.5.7 General Purpose Input and Output Pins
The CSB5 provides a number of general purpose input and output pins. Many of these pins have
alternate functions, and thus all are not available. The following table lists the GPI and GPO pins
used on the SDS2 Server Board and gives a brief description of their function.
Table 10. CSB5 GPIO Usage Table
Pad GPIO Name Description
V3 N_SALERTN Reporting for Fata Errors from HE-SL such as multi-bit ECC errors, Bus
protocol errors, and FSBus parity errors
W2 MIRQL Reporting for Correctable Errors from HE-SL such as single-bit errors on Front
Side Data bus and Memory Data bus
W3 N_CIOBALERTN Reporting for errors from CIOB
Y4 N_CSB5_NMI Generation of NMI from CSB5
Y1 N_BMC_IRQ_SMI_00 Input from BMC of SMI event
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
17
Page 32

I/O Subsystem Intel® Server Board SDS2
Pad GPIO Name Description
Y19 N_NVRAMCLR Input from jumper to be in BIOS Recovery mode in case of corruption
V17 N_PASSDIS_00 Input from jumper to clear password assignments
U16 N_CMOSCLR_00 Input from jumper to clear setup info in CMOS
T20 N_F3SETUPEN_00 Input from jumper to to be in special test mode (manufacturing only)
T19 N_BMC_SCIN Input from BMC of SCI event
T18 N_BMCISPMD_00 Input from jumper to to be in special test mode (manufacturing only)
U18 N_FRB3STP_00 Output signal to turn off FRB timer to stop fault conditions (this signal is wire-or
with the 2-pin jumper
Y16 N_SCSI_IDSEL_EN Output signal to disable onboard SCSI controller
V12 N_LAN2_IDSEL_EN Output signal to disable onboard NIC2
U12 N_LAN1_IDSEL_EN Output signal to disable onboard NIC1
V19 CSBPICD0 CSB5 APIC Data Bus 0
W20 CSBPICD1 CSB5 APIC Data Bus 1
Y20 N_ROM_CSN Output signal for BIOS Chip Select
U19 N_VGA_IDSEL_EN Output signal to disable onboard Video
4.6 Chipset Support Components
4.6.1 Super I/O
The National Semiconductor PC87417 Super I/O device contains all of the necessary circuitry to
control two serial ports, one parallel port, floppy disk, and PS/2-compatible keyboard and mouse .
The SDS2 Server Board supports the following features:
• GPIO
• Two serial ports
• Floppy
• Keyboard and mouse through PS/2 connectors
• Parallel port
• Real-time clock
• Wake-up control
4.6.1.1 General Purpose Input and Output - GPIO
The National Semiconductor* PC87417 Super I/O provides number of general-purpose
input/output pins that the SDS2 Server Board utilizes. The following table identifies the pin, the
signal name used in the schematic and a brief description of its usage.
Table 11. Super I/O GPIO Usage Table
Pin #
10 N_BMC_SYSIRQ_00 System Interrupt Controller interrupt from BMC
13 N_SIO_CLK_40M_BMC 40MHz clock output to BMC
Revision 1.2
18
Signal Name Description
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 33

Intel® Server Board SDS2 I/O Subsystem
Pin #
35 N_BMC_SWIN
36 N_BMCPWRN Power LED from BMC
37 N_EXTEN_00 External Event
38 N_SUPERSCI_00 System Control Interrupt used to detect wake-up events
45 N_SIO_CLK_RTC_BMC Real Time Clock output to BMC
49 N_P2_PME Power Management Event from PCI Bus (P64-B segment)
50 N_P3_PME Power Management Event from PCI Bus (P64-C segment)
51 N_FP_PWR_LED+00 Power LED indicator to Front Panel
52 N_LAN_PME Power Management Event from PCI Bus (P32-A segment)
53 N_BMC_SCIN System Management Interrupt from BMC
125 KBCLKL Keyboard Clock
126 KBDATL Keyboard Data
127 MSCLKL Mouse Clock
128 MSDATL Mouse Data
Signal Name Description
4.6.1.2 Serial Ports
Two serial ports are provided on the Server Board, a 9-pin DB9 connector is located on the rear
I/O to supply COM1 and a 10-pin header on the Server Board provides COM2.
4.6.1.3 Floppy
The FDC in the SIO is functionally compatible with floppy disk controllers in the DP8473 and
N844077. All the FDC functions are integrated into the SIO including analog data separator and
16-byte FIFO.
4.6.1.4 Keyboard and Mouse
Two PS/2 ports are provided for keyboard and mouse and are mounted within a single stacked
housing. The mouse connector is stacked over the keyboard connector.
4.6.1.5 Parallel Port
The parallel port is supported on the Server Board through the rear I/O.
4.6.1.6 Real-time Clock
The SIO contains a real-time clock with external battery backup. The device also contains 242
bytes of general purpose battery -backed CMOS RAM.
4.6.1.7 Wake-up Control
The SIO contains functionality that allows various events to control the power-on and power-off
of the system.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
19
Page 34

I/O Subsystem Intel® Server Board SDS2
4.6.2 BIOS Flash
The SDS2 Server Board incorporates a Fairchild* 29LV008B 8Mbit Flash ROM. The flash device
is connected through the X -bus of the CSB5.
4.7 Interrupt Routing
The SDS2 Server Board interrupt architecture implements both PC-compatible PIC mode and
APIC mode interrupts through the use of the integrated I/O APICs in the CSB5.
4.7.1 Legacy Interrupt Routing
For PC-compatible mode, the CSB5 provides two 82C59-compatible interrupt controllers. The
two controllers are cascaded with interrupt levels 8-15 entering on level 2 of the primary interrupt
controller (standard PC configuration). A single interrupt signal is presented to the processors, to
which only one processor will respond for servicing. The CSB5 contains configuration registers
that define which interrupt source logically maps to I/O APIC INTx pins.
Interrupts, both PCI and IRQ types, are handled by the CSB5. The CSB5 then translates these to
the APIC bus. The numbers in the table below indicate the CSB5 PCI interrupt input pin to which
the associated device interrupt (INTA, INTB, INTC, INTD) is connected. The CSB5’s I/O APIC
exists on the I/O APIC bus with the processors.
Table 12. PCI Interrupt Routing/Sharing
Interrupt Device INTA INTB INTC INTD
ATI RAGE XL 4
82550PM #1 2
82550PM #2 3
PCI Slot 1 (P64-B) 5 13 11 12
PCI Slot 2 (P64-B) 6 12 13 11
PCI Slot 3 (P32-A) 7 11 12 13
PCI Slot 4 (P32-A) 8 13 11 12
PCI Slot 5 (P64-C) 9 12 13 11
PCI Slot 6 (P64-C) 10 11 1 0
7899W-SCSI Ch A 0
7899W-SCSI Ch B 1
4.7.1.1 Legacy Interrupt Routing
The table below recommends the logical interrupt mapping of interrupt sources on the SDS2
Server Board. The actual interrupt map is defined using configuration registers in the CSB5.
Table 13. Interrupt Definitions
ISA Interrupt Description
Revision 1.2
20
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 35

Intel® Server Board SDS2 I/O Subsystem
ISA Interrupt Description
INTR Processor interrupt
NMI NMI to processor
IRQ1 Keyboard interrupt
IRQ3 Serial port 1 or 2 interrupt from SIO device
IRQ4 Serial port 1 or 2 interrupt from SIO device
IRQ5
IRQ6 Floppy Controller
IRQ7
IRQ8_L Real Time Clock interrupt
IRQ9
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ12 PS/2 Mouse interrupt
IRQ14 Primary channel IDE interrupt
SMI* System Management Interrupt. General purpose indicator sourced by
the CSB5 and BMC to the processors
SCI* System Control Interrupt. Used by system to change sleep states and
other system level type functions
4.7.2 APIC Interrupt Routing
For APIC mode, the SDS2 interrupt architecture incorporates three Intel I/O APIC devices to
manage and broadcast interrupts to local APICs in each processor. The I/O APICs monitor each
interrupt on each PCI device including PCI slots in addition to the ISA compatibility interrupts IRQ
(0-15). When an interrupt occurs, a message corresponding to the interrupt is sent across a
three-wire serial interface to the local APICs. The APIC bus minimizes interrupt latency time for
compatibility interrupt sources. The I/O APICs can also supply greater than 16 interrupt levels to
the processor(s).
4.7.3 Serialized IRQ Support
The SDS2 Server Board supports a serialized interrupt delivery mechanism. Serialized IRQs
(SERIRQ) consists of a start frame , a minimum of 17 IRQ / data channels, and a stop frame.
Any slave device in the quiet mode may initiate the start frame. While in the continuous mode,
the start frame is initiated by the host controller.
4.7.4 IRQ Scan for PCIIRQ
The IRQ / data frame structure includes the ability to handle up to 32 sampling channels with the
standard implementation using the minimum 17 sampling channels. The SDS2 Server Board
has an external PCI interrupt serializer for PCIIRQ scan mechanism of CSB5 to support 16
PCIIRQs.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
21
Page 36

I/O Subsystem Intel® Server Board SDS2
IRQ0
IRQ1
IRQ2
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ6
IRQ7
IRQ8
IRQ9
IRQ10
IRQ11
PCIIRQ0
PCIIRQ1
PCIIRQ2
PCIIRQ3
PCIIRQ4
PCIIRQ5
PCIIRQ6
PCIIRQ7
PCIIRQ8
PCIIRQ9
PCIIRQ10
PCIIRQ11
SCAN2
IRQ0-15
SCAN0
PCIIRQ0-
PCIIRQ15
INT
Mapping
IOAPIC
1
8259 PIC
MASK for
PCIIRQ0-15
PCIIRQ16
PCIIRQ17
PCIIRQ18
PCIIRQ19
PCIIRQ20
PCIIRQ21
PCIIRQ22
PCIIRQ23
PCIIRQ24
PCIIRQ25
PCIIRQ26
PCIIRQ27
PCIIRQ to
MAPPING
SCAN1
PCIIRQ16-
PCIIRQ31
IOAPIC
2
MASK for
PCIIRQ16-31
Figure 3. SDS2 Interrupt Routing Diagram (CSB5 Internal)
IRQ
Revision 1.2
22
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 37

Intel® Server Board SDS2 I/O Subsystem
PCIIRQ1
PIRQ_LATCH
PCIIRQ3
PIRQ1
PCIIRQ2
PCIIRQ4
PCIIRQ5
PCIIRQ6
PCIIRQ7
PCIIRQ8
PCIIRQ9
PCIIRQ10
PCII
RQ11
PCIIRQ12
PCIIRQ13
PCIIRQ14
PCIIRQ15
PCIIRQ0
Timer
Keyboard
Serial Port2/ISA
Serial Port1/ISA
ISA Floppy/ISA
ISA
RTC
SCI/ISA
ISA ISA Mouse/ISA
Coprocessor Error
P_IDE/ISA
S_IDE/ISA
Cascade
SE
RIRQ
SCSI Ch B
NIC 1
SCSI Ch
A
NIC 2
SCI from SIO
Video
Slot1 INTA
Slot2 INTA
Slot3 I
NTA Slot4 INTA
Slot5 INTA
Slot6 INTA
INT
BCD INTBCD
INTBCD
N/C
Serialized IRQ Interface
CSB5 Interrupt Routing
PCI Clock
33 MHz
PCI IRQ Serializer
Figure 4. SDS2 Interrupt Routing Diagram
Revision 1.2
23
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 38

I/O Subsystem Intel® Server Board SDS2
Slot 2 Slot 1Slot 4 Slot 3Slot 6 Slot 5
PCI IRQ 10
PCI IRQ 9
PCI IRQ 8
PCI IRQ 7
PCI IRQ 6
INTA
INTB
INTC
INTD
NIC 1
NIC 2
VIDEO
PCI IRQ 5
PCI IRQ 13
PCI IRQ 11
PCI IRQ 12
PCI IRQ 2
PCI IRQ 3
PCI IRQ 4
PORT A
SCSI
PORT B
ZCR Present
PCI IRQ 0
PCI IRQ 1
Figure 5. SDS2 PCI Interrupt Mapping Diagram
Revision 1.2
24
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 39

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Server Management
5. Server Management
The SDS2 server management features are implemented using the Sahalee Server Board
Management Controller chip. The Sahalee BMC is an ASIC packaged in a 156-pin BGA that
contains a 32-bit RISC processor core and associated peripherals. The following diagram
illustrates the SDS2 server management architecture. A description of the hardware architecture
follows.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
25
Page 40

Serve r Management Intel® Server Board SDS2
To Power
Distribution
Chassis Intrusion
Front Panel NMI Switch
BASEBOARD
Aux. IPMB
Connector
Hot-swap
Backplane
Header
ICMB
Transceiver
Header
RI (Wake-on-Ring)
COM 2
COMM MUX
Sleep Button
System Identify Button
Front Panel Connectors
ISOL
BBD COM2
EMP
Reset Button
Power Button
Speaker
Network Activity LEDs
PROCESSOR SOCKETS
CPU 'Core' Temp
Fault Status LED
Drive Activity/Fault LED
spkr
NIC #2
Identify LED
Power LED
DIMM SPD (6)
NIC #1
Logic 2.5V
FANs (6)
Baseboard
Temp 1
Chip Set
PCI PME
Private Management Busses
INTELLIGENT PLATFORM MANAGEMENT BUS (IPMB)
(2)
IERR (2)
Thermal Trip (2)
CPU Voltage (1)
Chassis
Intrusion
Board
3.3V Standby
LVDS-A Term. 1
LVDS-A Term. 2
LVDS-A Term. 3
LVDS-B Term. 1
LVDS-B Term. 2
LVDS-B Term. 3
5V
12V
3.3V
-12V
1.25V
Non-volatile, read-write storage
SENSOR
DATA
RECORDS
FRU INFO
& CONFIG
DEFAULTS
BASEBOARD
MANAGEMENT
SYSTEM
EVENT
LOG
CONTROLLER
System I/F
PORTS
SMM-
BIOS
I/F
SMS
I/F
(BMC)
System
Bus
Chip set NMIs
Chip set SMI
CODE
(updateable)
RAM
Platform
Management
Interrupt
Routing
- Chassis ID
- Baseboard ID
- Power State
NMI
SMI
Figure 6. SDS2 Sahalee BMC Block Diagram (View as Reference Only)
Power Connector
Revision 1.2
26
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 41

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Server Management
5.1 Sahalee Baseboard Management Controller
The Sahalee BMC contains a 32-bit RISC processor core and associated peripherals used to
monitor the system for critical events. The Sahalee BMC, packaged in a 156-pin BGA, monitors
all power supplies, including those generated by the external power supplies and those regulated
locally on the Server Board.
The Sahalee BMC also monitors SCSI termination voltage, fan tachometers for detecting a fan
failure, and system temperature. Temperature is measured on each of the processors and at
locations on the Server Board away from the fans. When any monitored parameter is outside the
defined thresholds, the Sahalee BMC logs an event in the System Event Log (SEL).
Management controllers and sensors communicate on the I2C-based Intelligent Platform
Management Bus. Attached to one of its private I2C bus is Hecetas, which is an ADM1026. The
ADM1026 is a versatile Systems Monitor ASIC. Some of its features include:
• Analog measurement channels
• Fan speed measurement channels
• General-Purpose Logic I/O pins
• Remote temperature measurement
• On-chip temperature sensor
• Chassis intrusion detection
The table below details some of the inputs on Hecetas as used in the SDS2.
Table 14. ADM1026 Input Definition
Pin Signal Name Description
3 N_ADM_DIS_CPU1_L CPU1 Stop Clock
4 N_ADM_DIS_CPU2_L CPU2 Stop Clock
5 CPU2_VID0 CPU2 VID[0]
6 CPU2_VID1 CPU2 VID[1]
9 CPU2_VID2 CPU2 VID[2]
10 CPU2_VID3 CPU2 VID[3]
11 CPU2_VID4 CPU2 VID[4]
12 CPU1_VID0 CPU1 VID[0]
2 CPU1_IERRN CPU1 IERR
1 CPU2_IERRN CPU2 IERR
48 CPU1_VID1 CPU1 VID[1]
47 CPU1_VID2 CPU1 VID[2]
46 CPU1_VID3 CPU1 VID[3]
45 CPU1_VID4 CPU1 VID[4]
44 N_CPU1_THERMTRIPN CPU1 Thermal Trip
43 N_CPU2_THERMTRIPN CPU2 Thermal Trip
16 N_FRONTOPEN+00 Chassis Intrusion
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
27
Page 42

Server Management Intel® Server Board SDS2
Pin Signal Name Description
13 N_SM2_CLK Serial Bus Clock
14 N_SM2_DATA Serial Bus Data
18 N_ADM_FAN_PWM Pulse-width modulated output for control of fan speed
19 N_RST_BMCRST_L Power-on Reset with minimum of 200ms pulse width
29 3VSB Monitors 3V Standby supply
22 5VSB Monitors 5V Standby supply
7 3V Monitors 3V supply
30 5V Monitors +5V supply
31 -12V Monitors –12V supply
32 +12v Monitors +12V supply
33 VCCORE1 Monitors CPU1 core voltage
34 +2.5V Monitors 2.5V supply
35 VTT Monitors VTT supply
36 N_SC2VREF3+00 Monitors SCSI channel 2 Terminator 3
37 N_SC2VREF2+00 Monitors SCSI channel 2 Terminator 2
38 N_SC2VREF1+00 Monitors SCSI channel 2 Terminator 1
39 N_SC1VREF3+00 Monitors SCSI channel 1 Terminator 3
40 N_SC1VREF2+00 Monitors SCSI channel 1 Terminator 2
41 N_SC1VREF1+00 Monitors SCSI channel 1 Terminator 1
An 8-bit analog readings of the following system temperatures are provided:
Table 15. Temperature Sensors
Temperature Sensor Description Resolution Accuracy
Primary Processor Primary processor socket thermal sensor 8-bit +/- 5°C or better
Secondary Processor Secondary processor socket thermal sensor 8-bit +/- 5°C or better
The table below details some of the inputs on Sahalee as used in the SDS2.
Table 16. Sahalee Input Definition
Pin Signal Name Description
D12 N_SLOT1OCC_00 CPU1 Presence Detect
D14 N_SLOT2OCC_00 CPU2 Presence Detect
B12 N_FAN1_SENSE_P CPU1 Fan Speed
A13 N_FAN2_SENSE_P CPU2 Fan Speed
B13 N_FAN3_SENSE_P Front System Fan 1 Speed
B14 N_FAN4_SENSE_P Front System Fan 2 Speed
C13 N_FAN5_SENSE_P Rear System Fan 1 Speed
Revision 1.2
28
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 43

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Server Manage ment
Pin Signal Name Description
C14 N_FAN6_SENSE_P Rear System Fan 2 Speed
L12 N_MEM_ALERT_L Memory ECC Error Detect
M12 N_BMC_SECUREMODE Secure Mode Detect
Note: For a complete listing of BMC sensors, please refer to SDS2 Baseboard Management
Controller External Product Specification.
ADM1026
Sahalee
Figure 7. SDS2 Locations of ADM1026 and Sahalee
5.1.1 Fault Resilient Booting
The Sahalee BMC implements Fault Resilient Booting (FRB) levels 1, 2, and 3. If the default
bootstrap processor (BSP) fails to complete the boot process, FRB attempts to boot using an
alternate processor.
• FRB level 1 is for recovery from a BIST failure detected during POST. This FRB recovery
is fully handled by BIOS code.
• FRB level 2 is for recovery from a Watchdog timeout during POST. The Watchdog timer
for FRB level 2 detection is implemented in the Sahalee BMC.
• FRB level 3 is for recovery from a Watchdog timeout on Hard Reset/Power-up. The
Sahalee BMC provides hardware functionality for this level of FRB.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
29
Page 44

Server Management Intel® Server Board SDS2
5.2 System Reset Control
Reset circuitry on the SDS2 Server Board looks at resets from the front panel, CSB5, ITP, and
processor subsystem to determine proper reset sequencing for all types of reset. The reset logic
is designed to accommodate a variety of ways to reset the system, which can be divided into the
following categories:
• Power-up reset
• Hard reset
• Soft (programmed) reset
The following subsections describe each category of reset.
5.2.1 Power-up Reset
When the system is disconnected from AC power, all logic on the Server Board is powered off.
When a valid input (AC) voltage level is provided to the power supply, 3.3 V standby power is
applied to the Server Board. A power monitor circuit on 3.3 V standby asserts
N_RST_BMCRST_L, causing the BMC to reset. The BMC is powered by 3.3 V standby and
monitors and controls key events in the system related to reset and power control.
After the system is turned on, the power supply asserts the N_PWRGD+00 signal after all
voltage levels in the system have reached valid levels. The BMC receives N_PWRGD+00 and
after approximately 500 ms it asserts N_RST_P6_PWRGOOD, which indicates to the
processors and CSB5 that the power is stable. Upon N_RST_P6_PWRGOOD assertion, the
CSB5 will toggle PCI reset.
5.2.2 Hard Reset
A hard reset can be initiated by resetting the system through the front panel switch. During the
reset, the Sahalee BMC de-asserts the N_RST_P6_PWRGOOD signal. After approximately 500
ms, it is reasserted, and the Power-up Reset sequence is done.
The Sahalee BMC is not reset by a hard reset. It may be reset at power-up.
5.2.3 Soft Reset
A soft reset causes the processors to begin execution in a known state without flushing the
caches or internal buffers. The keyboard controller located in the SIO or by the CSB5 can
generate soft resets. The output of the SIO (N_KBD_PINITL) is input to the CSB5.
5.3 Intelligent Platform Management Buses
Management controllers and sensors communicate on the I2C-based Intelligent Platform
Management Bus. A bit protocol defined by the I2C Bus Specification, and a byte-level protocol
defined by the Intelligent Platform Management Bus Communications Protocol Specification,
provide an independent interconnect for all devices operating on this I2C bus. The IPMB extends
throughout the Server Board and system chassis. An added layer in the protocol supports
transactions between multiple servers on inter-chassis I2C bus segments.
Revision 1.2
30
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 45

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Server Management
Table 17. IPMB Bus Devices
Function Voltage Address Notes
SCSI HSBP-A 5VSB 0xC0
SCSI HSBP-B 5VSB 0xC2
OEM Connector 5VSB N/A
In addition to the “public” IPMB, the Sahalee BMC also has five private I2C busses. Four of these
are used on the Server Board. The Sahalee BMC is the only master on the private busses. The
following table lists all Server Board connections to the Sahalee BMC private I2C busses.
Table 18. Private I2C Bus 1 Devices
Function Voltage Address Notes
PCI Slot 1 3 VSB N/A
PCI Slot 2 3 VSB N/A
PCI Slot 3 3 VSB N/A
PCI Slot 4 3 VSB N/A
PCI Slot 5 3 VSB N/A
PCI Slot 6 3 VSB N/A
Table 19. Private I2C Bus 2 Devices
Function Voltage Address Notes
PC87417 SIO 3 VSB 0x60
Front Panel Connector 3 VSB 0x9A
ADM1026 3 VSB 0x58
Power Supply #1 3 VSB 0xB0
Power Supply #1 FRU 3VSB 0xA0
Power Supply #2 3VSB 0xB2
Power Supply #2 FRU 3VSB 0xA2
Power Supply #3 3VSB 0xB6
Power Supply #3 FRU 3VSB 0xA4
Power Unit Cage 3VSB 0xBC
Power Unit FRU 3VSB 0xAC
Note: The power supply entries in Table 19 apply only to the Intel® SC5100 chassis.
Reference chassis power supplies may utilize different addresses.
Table 20. Private I2C Bus 3 Devices
Function Voltage Address Notes
HE-SL 3.3 V 0xC0 North Bridge
CIOB20 3.3 V 0xC4 I/O Bridge
Revision 1.2
31
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 46

Server Management Intel® Server Board SDS2
Function Voltage Address Notes
CSB5 3.3 V 0xC2 South Bridge
DIMM 1 3.3 V 0xA0
DIMM 2 3.3 V 0xA2
DIMM 3 3.3 V 0xA4
DIMM 4 3.3 V 0xA6
DIMM 5 3.3 V 0xA8
DIMM 6 3.3 V 0xAA
PCK2001M 3.3 V 0xD2 Clock Buffers
Table 21. Private I2C Bus 4 Devices
Function Voltage Address Notes
NIC1 3 VSB 0x84
NIC2 3VSB 0x86
5.4 Error Reporting
This section documents the types of system bus error conditions monitored by the SDS2 Server
Board.
5.4.1 Error Sources and Types
One of the major requirements of server management is to correctly and consistently handles
system errors. System errors on the SDS2, which can be disabled and enabled individually, can
be categorized as follows:
• PCI bus
• Processor bus errors
• Memory single- and multi-bit errors
• General server management sensors, managed by the Sahalee BMC
5.4.2 PCI Bus Errors
The PCI bus defines two error pins, PERR# and SERR#, for reporting PCI parity errors and
system errors, respectively. In the case of PERR#, the PCI bus master has the option to retry
the offending transaction, or to report it using SERR#. All other PCI -related errors are reported by
SERR#. SERR# is routed to NMI if enabled by BIOS.
5.4.3 Intel® Pentium® III Processor Bus Errors
The HE-SL supports all the data integrity features supported by the Pentium Pro bus including
Address, Request and Response parity. The HE-SL always generates ECC data while it is driving
the processor data bus although data bus ECC can be disabled or enabled by BIOS (enabled by
default). The HE-SL generates MIRQ# on SBEs (Single-bit errors) and generates SALERT# on
Revision 1.2
32
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 47

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Server Management
uncorrectable errors. In addition, the HE-SL can generate BERR# on unrecoverable ECC errors
detected on the processor bus. Unrecoverable errors are routed to NMI by BIOS.
5.4.4 Memory Bus Errors
The HE-SL is programmed to generate an SMI on single-bit data errors in the memory array if
ECC memory is installed. The HE-SL performs the scrubbing. The SMI handler simply records the
error and the DIMM location to the System Event Log. Double-bit errors in the memory array are
mapped to SMI because the Sahalee BMC cannot determine the location of the bad DIMM.
5.4.5 ID LED
The blue “ID LED”, located at the back edge of the Server Board near NIC2, is used to help locate
a given server platform requiring service when installed in a multi-system rack. The LED is lit when
the front panel ID button is pressed and is turned off when the button is pressed again.
5.5 ACPI
The Advance Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)-aware operating system can place the
system into a state where the hard drive spin down, the system fans stop, and all processing is
halted. In this state, the power supply is still on and the processors still dissipate some power,
such that the power supply fan and processor fans continue to run.
Note: ACPI requires an operating system that supports this feature.
The sleep states discussed below are defined as:
• S0: Normal running state
• S1: Processor sleep state. No content is lost in this state and the processor caches
maintain coherency
• S4: Hibernate or Save to Disk. The memory and machine state are saved to disk.
Pressing the power button or another wakeup event restores the system state from disk
and resumes normal operation. This assumes that no hardware changes were made to
the system while it was off
• S5: Soft off. Only the RTC section of the chip set and the BMC are running in this state
The SDS2 Server Board supports sleep states s0 , s1, s4, and s5. When the Server Board is
operating in ACPI mode, the operating system retains control of the sy stem and the operating
system policy determines the entry methods and wake up sources for each sleep state. Sleep
entry and wake-up event capabilities are provided by the hardware but are enabled by the OS.
5.6 AC Link Mode
The AC link mode allows the system to monitor its AC input power so that if AC input power is lost
and then restored, the system returns to one of the following pre-selected settings:
• Power On
• Last State (Factory Default Setting)
• Stay Off
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
33
Page 48

Serve r Management Intel® Server Board SDS2
Setup Utility (F2) can change the AC link mode settings.
Revision 1.2
34
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 49

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
6. BIOS
This section describes the BIOS-embedded software for the SDS2 server board. The BIOS
contains standard PC-compatible basic input/output (I/O) services, system-specific hardware
configuration routines and register default settings that are embedded in Flash read-only
memory (ROM). This document also describes BIOS support utilities (not ROM-resident) that
are required for system configuration and flash ROM update. The BIOS is implemented as
firmware that resides in the flash ROM.
The term BIOS, as used in the context of this document, refers to the system BIOS, the BIOS
Setup, and option ROMs for on-board peripheral devices that are contained in the system flash .
The system BIOS controls basic system functionality using stored configuration values. The
terms flash ROM, system flash , and BIOS flash may be used interchangeably in this document.
BIOS Setup is a Flash ROM-resident setup utility that provides the user with control of
configuration values stored in battery -backed CMOS configuration RAM. BIOS options can also
be set utilizing the System Setup Utility (SSU). Operation of the SSU is discussed in a separate
document. BIOS Setup is closely tied with the system BIOS and is considered a part of BIOS.
Phoenix* Phlash (PHLASH.EXE) is used to load areas of flash ROM with Setup, BIOS, and other
code/data.
The following is the breakdown of the SDS2 product ID string.
• 4-byte board ID, ‘SDS2’
• 1-byte board revision, starting from ‘0’
• 3-byte OEM ID, ‘86B’ for standard BIOS
• 4-byte build number
• 1-3 bytes describing build type (D for development, A for Alpha, B for Beta, Pxx for
production version xx)
• 6-byte build date in yymmdd format
• 4-byte time in hhmm format
6.1 System BIOS
The sy stem BIOS is the core of the flash ROM-resident portion of the BIOS. The system BIOS
provides standard PC-BIOS services and support for industry standards, such as the Advanced
Configuration and Power Interface Specification, Revision 1.0b and Wired for Management
Baseline Specification, Revision 2.0.
In addition, the system BIOS supports the following features.
• Security
• MPS support
• Server management and error handling
• CMOS configuration RAM ma nagement
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
35
Page 50

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
• OEM customization
• PCI and Plug and Play (PnP) BIOS interface
• Console redirection
• Resource allocation support
6.2 BIOS Error Handling
This section defines how errors are handled by the system BIOS on the SDS2 server board.
Also discusse d are the role of BIOS in error handling, and the interaction between the BIOS,
platform hardware, and server management firmware with regard to error handling. In addition,
error-logging techniques are described and beep codes for errors are defined.
6.2.1 Error Sources and Types
One of the major requirements of server management is to correctly and consistently handles
system errors. System errors, which can be disabled and enabled individually or as a group, can
be categorized as follows:
• PCI bus
• Memory correctable- and uncorrectable errors
• Sensors
• Processor internal error, bus/address error, thermal trip error, temperatures and
voltages, and GTL voltage levels
The BMC manages the sensors. It is capable of receiving event messages from individual
sensors and logging system events.
6.2.2 Handling and Logging System Errors
This section describes actions taken by the SMI handler with respect to the various categories of
system errors. It covers the events logged by the BIOS and the format of data bytes associated
with those events. The BIOS is responsible for monitoring and logging certain system events.
The BIOS sends a platform event message to BMC to log the event. Some of the errors, such
as processor failure, are logged during early POST and not through the SMI handler.
6.2.2.1 Logging Format Conventions
The BIOS complies with the Intelligent Platform Management Interface Specification, Revision
1.5. The BIOS always uses system software ID within the range 00h-1Fh to log errors. As a
result, the Generator ID byte is an odd number in the range 01h-3fh. OEM user binary should use
software IDs of 1. The Software ID allows external software to find the origin of the event
message.
Revision 1.2
36
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 51

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
The BIOS logs the following SEL entries.
Table 22. BIOS Generated SEL Errors
Sensor
Sensor Type
Memory 08h 0Ch 01h Uncorrectable ECC
POST Memory
Resize
POST Error 06h 0Fh – POST Error
Disabled
System Boot
Initiated
Boot Error A2h 1Eh
Sensor Failure 7Ch F6h
Critical Interrupt
Number
60h
A0h 0Eh – POST Memory Resize
09h 10h
A1h 1Dh
F4h F4h
Sensor
Type
Code
07h
Sensor-
Specific
Offset
02h FRB1/BIST Failure Processor 5Fh
03h FRB2/Hang in POST Failure
00h Correctable Memory Error Logging Disabled Event Logging
01h Event ‘Type’ Logging Disabled
00h System Reconfigured System Event 7Ah 12h
01h OEM System Boot Event (Hard Reset)
04h PCI SERR Critical Interrupt 07h 13h
05h PCI PERR
00h Initiated by power up
03h User requested PXE boot
04h Automatic boot to diagnostic
00h No bootable media
02h PXE Server not found
03h Invalid boot sector
00h
01h
02h
00h CNB2.0HE-SL function 0 errors Chipset Specific
02h CIOB20 #0 errors
I2C Bus Device Address Not Acknowledged
I2C Bus Device Error Detected
I2C Bus Timeout
Event
The Event Request Message Event Data Field Contents table below describes the various fields
in the event request message sent by the BIOS.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
37
Page 52

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Table 23: Event Request Message Event Data Field Contents
Event
Trigger
Class
Discrete 7:6 00 = Unspecified byte 2
01 = Previous state and/or severity in byte 2
10 = OEM code in byte 2
11 = Sensor specific event extension code in byte 2
5:4 00 = Unspecified byte 3
01 = Reserved
10 = OEM code in byte 3
11 = Sensor specific event extension code in byte 3
3:0 Offset from Event Trigger for discrete event state
Event Data 2
7:4 Optional offset from ‘Severity’ Event Trigger. (0Fh if unspecified).
3:0 Optional offset from Event Trigger for previous discrete event state.
0Fh if unspecified.
Event Data
6.2.3 SMI Handler
The SMI handler handles and logs system level events that are not visible to the server
management firmware. The SMI handler, even those that are normally considered to generate an
NMI, preprocesses all system errors. The SMI handler sends a command to the BMC to log the
event and provides the data to be logged, a Set NMI Source command to indicate BIOS as the
source of the NMI, and a BIOS LCD command to display the LCD and LED message(s). A
correctable memory error does not generate an SMI. Correctable and uncorrectable memory
errors are handled and logged by the BMC.
6.2.3.1 PCI Bus Error
The PCI bus defines two error pins, PERR# and SERR#, for reporting PCI parity errors and
system errors, respectively.
6.2.3.2 Intel® Pentium® III Processor Bus Error
In the case of irrecoverable errors on the host processor bus, proper execution of SMI handler
cannot be guaranteed and SMI handler cannot be relied upon to log such conditions. The BIOS
SMI handler records the error to the System Event Log only if the system has not experienced a
catastrophic failure that compromises the integrity of the SMI handler. The BIOS always enables
the error correction and detection capabilities of the processors by setting appropriate bits in
processor model specific register (MSR).
Revision 1.2
38
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 53

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
6.2.3.3 Memory Bus Error
The BMC monitors and logs memory errors. The BIOS will configure the hardware to notify the
BMC on correctable and uncorrectable memory errors. Uncorrectable errors generate an SMI to
stop the system and prevent propagation of the error. The BMC will query the hardware for error
information when notified.
6.2.3.4 System Limit Error
The BMC monitors system operational limits. It manages the A/D converter, defining voltage and
temperature limits as well as fan sensors and chassis intrusion. Any sensor values outside of
specified limits are handled by the BMC and there is no need to generate an SMI to the host
processor.
6.2.3.5 Processor Failure
The BIOS detects processor BIST failure and logs this event. The first OEM data byte field in the
log can identify the failed processor. For example, if processor 0 fails, the first OEM data byte is
0. The BIOS depends upon BMC to log the watchdog timer reset event.
6.2.3.6 Boot Event
The BIOS downloads the system date and time to the BMC during POST and logs a boot event.
This does not indicate an error, and software that parses the event log should treat it as such.
6.2.3.7 Chipset Failure
The BIOS detects the chipset (CNB2.0HE-SL and CIOB20) failure and logs this event. The
chipset error generates an SMI.
6.2.4 Firmware (BMC)
The BMC implements the logical System Event Log (SEL) device as specified in the Intelligent
Platform Management Interface Specification, Version 1.5. The SEL is accessible via all BMC
transports. This allows the System Event Log information to be accessed while the system is
down via out-of-band interfaces.
6.2.4.1 Sensor Number and Types Codes
The BIOS generates a POST error message when the System Event Log is full. This warning
will not inhibit the system from booting if halt on Post Error code is disabled in the BIOS Setup in
the Advanced menu.
Sensor Name, Sensor number and Sensor type for the SDS2 platform are listed in the following
Table 24 Platform SEL Log Sensors for SDS2.
Table 24 Platform SEL Log Sensors for SDS2
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
39
Page 54

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Sensor
Name
Power Unit
Status
Power Unit
Redundancy
Watchdog 03h
Platform
Security
Violation
Physical
Security
Violation
POST Error 06h
FP Diag
Interrupt (NMI
for IA -32, INIT
for IA -64)
Memory 08h Memory – 0Ch
Event
Logging
Disabled
BB +1.25V 0Ah Voltage – 02h
BB +2.5V 0Bh Voltage – 02h
BB +3.3V 0Ch Voltage – 02h
BB +3.3V
Standby
BB +5V 0Eh Voltage – 02h
BB +12V 0Fh Voltage – 02h
#
Sensor
Power Unit -
01h
09h
Power Unit -
02h
09h
Watchdog2 –
23h
Platform
Security
04h
Violation
Attempt - 06h
Physical
05h
Security - 05h
System
Firmware
Progress – 0Fh
Critical
07h
Interrupt - 13h
Event Logging
09h
Disabled – 10h
0Dh Voltage – 02h
Sensor Type
Event/
Reading
Type
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Generic 0Bh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Event
Offset
Triggers
Power Off,
Power Cycle,
A/C Lost,
Redundancy Regain
Redundancy lost
Timer Expired,
Hard Reset,
Power Down,
Power Cycle,
Timer Interrupt
- Secure mode
violation attempt,
- Out -of-band access
password violation
General Chassis
Intrusion,
LAN Leash Lost
POST error
Front Panel NMI
Correctable ECC,
Uncorrectable ECC
Correctable Memory
Error Logging
Disabled,
Log Area
Reset/Cleared
-
-
-
-
-
-
Revision 1.2
40
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 55

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Sensor
Name
BB -12V 10h Voltage – 02h
BB V
BAT
Proc VRM 1 12h Voltage – 02h
Proc VRM 2 13h Voltage – 02h
LVDS SCSI
channel 1
terminator 1
LVDS SCSI
channel 1
terminator 2
LVDS SCSI
channel 1
terminator 3
LVDS SCSI
channel 2
terminator 1
LVDS SCSI
channel 2
terminator 2
LVDS SCSI
channel 2
terminator 3
LVDS SCSI
channel 1
Performance
LVDS SCSI
channel 2
Performance
Baseboard
Temp
Front Panel
Temp
PDB Temp 32h Temp - 01h
Proc 1 Temp 33h Temp - 01h
Proc 2 Temp 34h Temp - 01h
Fan Boost
Baseboard
Temp
#
Sensor
11h Voltage – 02h
14h Voltage – 02h
15h Voltage – 02h
16h Voltage – 02h
17h Voltage – 02h
18h Voltage – 02h
19h Voltage – 02h
1Dh Voltage – 02h
1Eh Voltage – 02h
30h Temp - 01h
31h Temp - 01h
3Bh OEM - C7h
Sensor Type
Event/
Reading
Type
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Digital
Discrete - 06h
Digital
Discrete - 06h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Event
Offset
Triggers
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Performance Lags
Performance Lags
-
-
-
-
-
-
Revision 1.2
41
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 56

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Sensor
Name
Fan Boost
Front Panel
Temp
Fan Boost
PDB Temp
Fan Boost
Proc 1 Core
Temp
Fan Boost
Proc 2 Core
Temp
Tach Fan 1 48h Fan - 04h
Tach Fan 2 49h Fan - 04h
Tach Fan 3 4Ah Fan - 04h
Tach Fan 4 4Bh Fan - 04h
Tach Fan 5 4Ch Fan - 04h
Tach Fan 6 4Dh Fan - 04h
Digital Fan 1 50h Fan - 04h
Digital Fan 2 51h Fan - 04h
Digital Fan 3 52h Fan - 04h
Digital Fan 4 53h Fan - 04h
Digital Fan 5 54h Fan - 04h
Digital Fan 6 55h Fan - 04h
PDB Fan 1 58h Fan - 04h
PDB Fan 2 59h Fan - 04h
Power
Supply 1
#
Sensor
3Ch OEM - C7h
3Dh OEM - C7h
3Eh OEM - C7h
3Fh OEM - C7h
Power Supply -
5Ah
08h
Sensor Type
Event/
Reading
Type
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Digital
Discrete - 06h
Digital
Discrete - 06h
Digital
Discrete - 06h
Digital
Discrete - 06h
Digital
Discrete - 06h
Digital
Discrete - 06h
Threshold 01h
Threshold 01h
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Event
Offset
Triggers
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Performance Lags
Performance Lags
Performance Lags
Performance Lags
Performance Lags
Performance Lags
-
-
Presence,
Failure,
Predictive Fail,
A/C Lost
Revision 1.2
42
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 57

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Sensor
Name
Power
Supply 2
Power
Supply 3
Missing CPU
Module
Proc 1 Status 5Fh
Proc 2 Status 60h
DIMM 1 68h
DIMM 2 69h
DIMM 3 6Ah
DIMM 4 6Bh
DIMM 5 6Ch
Sensor
5Bh
5Ch
5Eh
#
Power Supply 08h
Power Supply 08h
Module/Board
– 15h
Processor 07h
Processor 07h
Slot Connector
- 21h
Slot Connector
- 21h
Slot Connector
- 21h
Slot Connector
- 21h
Slot Connector
- 21h
Sensor Type
Event/
Reading
Type
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Digital
Discrete - 03h
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Event
Offset
Triggers
Presence,
Failure,
Predictive Fail,
A/C Lost
Presence,
Failure,
Predictive Fail,
A/C Lost
State Asserted
Presence,
Thermal Trip,
IERR,
FRB1,
FRB2,
FRB3,
Disabled
Presence,
Thermal Trip,
IERR,
FRB1,
FRB2,
FRB3,
Disabled
Fault Status
Asserted,
Device Installed,
Disabled
Fault Status
Asserted,
Device Installed,
Disabled
Fault Status
Asserted,
Device Installed,
Disabled
Fault Status
Asserted,
Device Installed,
Disabled
Fault Status
Asserted,
Device Installed,
Disabled
Revision 1.2
43
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 58

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Sensor
Name
DIMM 6 6Dh
System ACPI
Power State
Button 79h Button – 14h
System
Event
SMI Timeout 7Bh
Sensor
Failure
NMI Signal
State
SMI Signal
State
#
Sensor
Slot Connector
- 21h
System ACPI
78h
Power State –
22h
System Event –
7Ah
12h
SMI Timeout –
F3h
Sensor Failure
7Ch
– F6h
7Dh OEM - C0h
7Eh OEM - C0h
Sensor Type
Event/
Reading
Type
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Sensor
Specific - 6Fh
Digital
Discrete - 03h
Digital
Discrete - 03h
Event
Offset
Triggers
Fault Status
Asserted,
Device Installed,
Disabled
S0 / G0,
S1,
S4,
S5 / G2,
G3 Mechanical Off
Power Button,
Sleep Button,
Reset Button
OEM System Boot
Event (Hard Reset)
State Asserted
I2C device not found,
I2C device error
detected,
I2C Bus Timeout
-
-
6.2.4.2 Timestamp Clock
The BMC maintains a four-byte internal timestamp clock used by the System Event Log and
Sensor Da ta Record subsystems. This clock is incremented once per second and is read and
set using the Get SEL Time and Set SEL Time commands, respectively. The Get SDR Time
command can also be used to read the timestamp clock.
The BMC has direct access the system real-time clock . This allows the BMC to automatically
synchronize the SEL/SDR timestamp clock to the real-time clock time on BMC startup. The
BMC periodically reads the real-time clock to maintain synchronization even when software
asynchronously changes the value. In addition to this, the BIOS send a timestamp to the BMC
using Set SEL Time command during POST.
Revision 1.2
44
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 59

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
6.2.5 Error Messages and Error Codes
The system BIOS displays error messages on the video screen. Before video initialization, beep
codes inform the user of errors. POST error codes are logged in the System Event Log. The
BIOS displays POST error codes on the video monitor.
6.2.5.1 ASF Progress Codes
The BIOS utilize s ASF Progress Events as described in the ASF Specification, Revision 1.0a
from the DMTF. The events that the BIOS supports are shown in the following table.
Table 25. Event Request Message Event Data Field Contents
ASF Code Description Comment
01h Memory initialization. At beginning of ECC initialization or memory test.
02h Hard-disk initialization At beginning of IDE device detection.
03h Secondary processor(s) initialization At beginning of MP Init
04h User authentication When waiting for User/Supervisor password
05h User-initiated system setup When Setup is invoked
06h USB resource configuration When USB devices scan/initialization begins
07h PCI resource configuration At beginning of configuring PCI devices in system.
08h Option ROM initialization At beginning of Option ROM scan
09h Video initialization At beginning of initialization primary video controller (if
present)
0Ah Cache initialization At beginning of setting up processor cache
0Bh SM Bus initialization At beginning of configuring SMBus to communicate
with BMC
0Ch Keyboard controller initialization At keyboard discovery scan
0Dh Embedded controller/management
controller initialization
12h Calling operating system wake-up
vector
13h Starting operating system boot
process, e.g. calling Int 19h
When first checking for functional BMC
When waking from Wake-On-LAN, Wake-On-Ring,
Magic Packet, etc.
Immediately prior to calling INT19h
6.2.5.2 POST Codes
The BIOS indicates the current testing phase to I/O location 80h and to LCD on the front panel
during POST after the video adapter has been successfully initialized. If a Port-80h card
(Postcard*) is installed, it displays this 2-digit code on a pair of hex display LEDs.
Table 26. Port-80h Code Definition
Code Meaning
CP Phoenix* check point POST code
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
45
Page 60

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
The following table contains the POST codes displayed during the boot process. A beep code is
a series of individual beeps on the PC speaker, each of equal length. The following table
describes the error conditions associated with each beep code and the corresponding POST
checks point code as seen by a ‘port 80h’ card and LCD. For example, if an error occurs at
checkpoint 22h, a beep code of 1-3-1-1 is generated. The “-“ indicates a pause within the
sequence.
Some POST codes occur before the video display is initialized. To assist in determining the
fault, a unique beep-code is derived from these checkpoints as follows:
• The 8-bit test point is broken down to four 2-bit groups.
• Each group is made one-based (1 through 4)
• One to four beeps are generated based on each group’s 2-bit pattern.
Note: Not all POST codes generate a Beep Code.
Example:
Checkpoint 4Bh is divided into: 01 00 10 11
The beep code is: 2 – 1 – 3 – 4
Table 27. Standard BIOS POST Codes
CP Beeps Reason
01 Initialize BMC
02 Verify Real Mode
03 Test BMC
04 Get Processor type
06 Initialize system hardware
08 Initialize chipset registers with initial POST values
09 Set in POST flag
0A Initialize Processor registers
0B Enable Processor cache
0C Initialize caches to initial POST values
0E Initialize I/O
0F Initialize the local bus IDE
10 Initialize Power Management
11 Load alternate registers with initial POST values
12 Restore Processor control word during warm boot
13 Initialize PCI Bus mastering devices
14 Initialize keyboard controller
16 1-2-2-3 BIOS ROM checksum
17 Initialize external cache before memory auto si ze
18 8254 timer initialization
1A 8237 DMA controller initialization
Revision 1.2
46
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 61

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
CP Beeps Reason
1C Reset Programmable Interrupt Controller
20 1-3-1-1 Test DRAM refresh
22 1-3-1-3 Test 8742 Keyboard Controller
24 Set ES segment register to 4GB
28 1-3-3-1 Auto size DRAM, system BIOS stops execution here if the BIOS does not detect any usable
memory DIMMs
29 Initializes the POST Memory Manager
2A Clear 8 MB base RAM
2C 1-3-4-1 Base RAM failure, BIOS stops execution here if entire memory is bad
2E Test the first 4MB of RAM
2F Initialize external cache before shadowing
32 Test Processor bus-clock frequency
33 Initializes the Phoenix Dispatch Manager
34 Test CMOS
35 RAM Initializ e alternate chipset registers
36 Warm start shut down
37 Reinitialize the chipset
38 Shadow system BIOS ROM
39 Reinitialize the cache
3A Auto size cache
3C Configure advanced chipset registers
3D Load alternate registers with CMOS values
41 Check unsupported processor
40 Set Initial Processor speed new
42 Initialize interrupt vectors
44 Initialize BIOS interrupts
45 POST device initialization
46 2-1-2-3 Check ROM copyright notice
47 Initialize manager for PCI Option ROMs
48 Check video configuration against CMOS
49 Initialize PCI bus and devices
4A Initialize all video adapters in system
4B Display Quiet Boot screen
4C Shadow video BIOS ROM
4E Display copyright notice
4F Allocate memory for the multiboot data
50 Display Processor type and speed
52 Test keyboard
54 Set key click if enabled
55 USB initialization
56 Enable keyboard
58 2-2-3-1 Test for unexpected interrupts
Revision 1.2
47
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 62

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
CP Beeps Reason
59 Initialize the POST display service
5A Display prompt “Press F2 to enter SETUP”
5B Disable L1 cache during POST
5C Test RAM between 512 and 640k
60 Test extended memory
62 Test extended memory address lines
64 Jump to UserPatch1
66 Configure advanced cache registers
67 Quick init of all AP's early in post
68 Enable external and processor caches
69 Initialize the SMM handler
6A Display external cache size
6B Load custom defaults if required
6C Display shadow message
6E Display non-disposable segments
70 Display error messages
72 Check for configuration errors
74 Test real-time clock
76 Check for keyboard errors
7A Test for key lock on
7C Set up hardware interrupt vectors
7D Intelligent system monitoring
7E Test coprocessor if present
81 POST device initialization routine
82 Detect and install external RS232 ports
83 Configure non-MCD IDE controllers
84 Initialize parallel ports
85 Initialize PC-compatible PnP ISA devices
86 Re-initialize on board I/O ports
87 Configure Mother Board Configurable Dev ices
88 Initialize BIOS Data Area
89 Enable Non-Maskable Interrupt s
8A Initialize Extended BIOS Data Area
8B Test and initialize PS/S mouse
8C Initialize floppy controller
90 Initialize hard disk controller
91 Initialize local bus hard disk controller
92 Jump to UserPatch2
93 Build MPTABLE for multi-processor boards
94 Disable A20 address line
95 Install CD-ROM for boot
96 Clear huge ES segment register
Revision 1.2
48
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 63

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
CP Beeps Reason
97 Fix up Multi Processor table
98 1-2 Search for option ROMs. One long, two short beeps on checksum failure
99 Check for SMART Driv e
9A Shadow option ROMs
9C Set up Power Management
9D Initialize security engine
9E Enable hardware interrupts
A0 Set time of day
A2 Check key lock
A4 Initialize spermatic rate
Table 28. Recovery BIOS POST Codes
CP Beeps Reason
E0 Initialize chip set
E1 Initialize bridge
E2 Initialize processor
E3 Initialize timer
E4 Initialize system I/O
E5 Check forced recovery boot
E6 Validate checksum
E7 Go to BIOS
E8 Initialize processors
E9 Set 4 GB segment limits
EA Perform platform initialization
EB Initialize the hardware
EC Initialize memory type
ED Initialize memory size
EE Shadow boot block
F0 Test system memory
F1 Initialize interrupt services
F2 Initialize real time clock
F3 Initialize video
F4 Initialize beeper
F5 Initialize boot
F6 Restore segment limits to 64 KB
F7 Boot mini DOS
Revision 1.2
49
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 64

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
6.2.5.3 POST Error Codes and Messages
The following table defines POST error codes and their associated messages. The BIOS
prompts the user to press a key in case of serious errors. Some error messages are preceded
by the string "Error” to indicate that the system may be malfunctioning. All POST errors and
warnings are logged in the System Event Log unless it is full.
Table 29. POST Error Messages and Codes
Code Error Message Failure Description
0200 Failure Fixed Disk Hard disk error
0210 Stuck Key Keyboard connection error
0211 Keyboard error Keyboard failure
0212 Keyboard Controller Failed Keyboard Controller Failed
0213 Keyboard locked– Unlock key switch Keyboard locked
0220 Monitor type does not mat ch CMOS– Run SETUP Monitor type does not match CMOS
0230 System RAM Failed at offset System RAM error, Offset address
0231 Shadow RAM Failed at offset Shadow RAM Failed , Offset address
0232 Extend RAM Failed at address line Extended RAM failed, Offset address
0250 System battery is dead – Replace and run SETUP NVRAM battery dead
0251 System CMOS checksum bad – Default
configuration used
0252 Password checksum bad - Passwords cleared
0260 System timer error System timer error
0270 Real time clock error RTC error
0271 Check date and time setting RTC time setting error
0280 Previous boot incomplete - Default configuration
used
0281 Memory Size found by POST differed from EISA
CMOS
02B0 Diskette drive A error Diskette drive A failure
02B1 Diskette drive B error Diskette drive B failure
02B2 Incorrect Drive A type – run SETUP Incorrect Drive A type
02B3 Incorrect Drive B type – run SETUP Incorrect Drive B type
02D0 System cache error – Cache disabled CPU cache error
02D1 System Memory exceeds the CPU's caching limit.
02F4 EISA CMOS not write able
02F5 DMA Test Failed
02F6 Software NMI Failed
02F7 Fail-safe Timer NMI Failed
0611 IDE configuration changed
0612 IDE configuration error-device disabled
0613 COM A configuration changed
CMOS checksum error
Revision 1.2
50
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 65

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Code Error Message Failure Description
0614 COM A config. error - device disabled
0615 COM B configuration changed
0616 COM B config. error - device disabled
0617 Floppy configuration changed
0618 Floppy config. error - device disabled
0619 Parallel port configuration changed
061A Parallel port config. error - device disabled
0B00 Rebooted during BIOS boot at Post Code
0B01 Rebooted during OS boot
0B02 Rebooted during OS Runtime
0B1B PCI System Error on Bus/Device/Function PCI system error in Bus/device/ Function, PCI
system error in Bus/device/Function
0B1C PCI Parity Error in Bus/Device/Function
0B22 Processors are installed out of order
0B28 Unsupported Processor detected on Processore 1 Unsupported Processor was detected
0B29 Unsupported Processor detect on Processor 2
0B30 Fan 1 Alarm occurred. Fan failed
0B31 Fan 2 Alarm occurred.
0B32 Fan 3 Alarm occurred.
0B33 Fan 4 Alarm occurred.
0B34 Fan 5 Alarm occurred.
0B35 Fan 6 Alarm occurred. Failed Processor#1 because an error was
detected., Failed Processor#2 because an error
was detected.
0B50 Processor #1 with error taken offline
0B51 Processor #2 with error taken offline
0B60 DIMM group #1 has been disabled Memory error, memory group #1 failed
0B61 DIMM group #2 has been disabled Memory error, memory group #2 failed
0B62 DIMM group #3 has been disabled Memory error, memory group #3 failed
0B70 The error occurred during temperature sensor
reading
0B71 System temperature out of the range Temperature error detected.
0B74 The error occurred during voltage sensor reading Error while detecting voltage
Error while detecting a temperature failure.
6.2.5.4 Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) Beep Code Generation
The BMC generates beep codes upon detection of the failure conditions listed in the following
table. Each digit in the code is represented by a sequence of beeps whose count is equal to the
digit.
Table 30. BMC Beep Code s
Code Reason for Beep
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
51
Page 66

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Code Reason for Beep
1-5-1-1 FRB failure (processor failure)
1-5-2-1 Empty Processor
1-5-2-2 No Processor
1-5-2-3 Processor configuration error (e.g., mismatched VIDs)
1-5-4-2 Power fault: DC power unexpectedly lost (power control failures)
1-5-4-3 Chipset control failure
1-5-4-4 Power control fault
6.3 Setup Utility
This section describes the ROM resident Setup utility that provides the means to configure the
platform. The Setup utility is part of the system BIOS and allows limited control over on-board
resources such as parallel port and mouse. The following topics are covered here:
• Setup utility operation.
• Configuration CMOS RAM definition.
• Function of CMOS clear jumper.
6.3.1 Configuration Utilities Overview
On-board devices are configured through the Setup utility that is embedded in flash ROM. Setup
provides enough configuration functionality to boot a system diskette or CD-ROM. Setup is
always provided in flash for basic system configuration.
The configuration utilities modify the CMOS and NVRAM under direction of the user. The actual
hardware configuration is accomplished by the BIOS POST routines and the BIOS Plug-N-Play
Auto-configuration Manager. The configuration utilities always update a checksum for both areas,
so that any potential data corruption is detectable by the BIOS before actual hardware
configuration takes place. If the data is corrupted, the BIOS load the default configuration and
requests that the user reconfigure the system and reboot.
6.3.2 Setup Utility Operation
The ROM-resident Setup utility configures only on-board devices.
The Setup utility screen is divided into four functional areas. Table 31 describes each area:
Table 31. Setup Utility Screen
Keyboard Command Bar Located at the bottom of the screen. This bar displays the keyboard commands
supported by the Setup utility .
Menu Selection Bar Located at the top of the screen. Displays the various major menu selections
available to the user. The server Setup utility major menus are: Main Menu, Advanced
Menu, Security Menu, System Menu, Boot Menu, and the Exit Menu.
Revision 1.2
52
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 67

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Options Menu Each Option Menu occupies the left and center sections of the screen. Each menu
contains a set of features. Selecting certain features within a major Option Menu
drops you into submenus.
Item Specific Help Screen An item-specific help screen is located at the right side of the screen.
6.3.2.1 Entering Setup Utility
During POST operation, the user is prompted to enter Setup using the F2 function key as
follows:
Press <F2> to enter Setup
Note that a few seconds might pass before Setup is entered. This is the result of POST
completing test and initialization functions that must be completed before Setup can be entered.
When Setup is entered, the Main Menu options page is displayed.
6.3.2.2 Keyboard Command Bar
The bottom portion of the Setup screen provides a list of commands that are used for navigating
the Setup utility. These commands are displayed at all times, for every menu and submenu.
Each Setup menu page contains a number of features. Except those used for informative
purposes, each feature is associated with a value field. This field contains user-selectable
parameters. Depending on the security option chosen and in effect via password, a menu
feature’s value can be changeable or not. If a value is not changeable due to insufficient security
privileges (or other reasons), the feature’s value field is inaccessible. The Keyboard Command
Bar supports the following:
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
53
Page 68

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Key Option Description
F1 Help Pressing F1 on any menu invokes the general Help window. This window describes the
Setup key legend. The up arrow, down arrow, Page Up, Page Down, Home, and End
keys scroll the text in this window.
Enter Execute Command The Enter key is used to activate sub-menus when the selected feature is a sub-menu,
or to display a pick list if a selected option has a value field, or to select a sub-field for
multi -valued features like time and date. If a pick list is displayed, the Enter key will undo
the pick list, and allow another selection in the parent menu.
ESC Exit The ESC key provides a mechanism for backing out of any field. This key will undo the
pressing of the Enter key. When the ESC key is pressed while editing any field or
selecting features of a menu, the parent menu is re-entered.
When the ESC key is pressed in any major menu, the exit confirmation window is
displayed and the user is asked whether changes can be discarded.
↑ Select Item The up arrow is used to select the previous value in a pick list, or the previous options in
a menu it em's option list. The selected item must then be activated by pressing the
Enter key.
↓ Select Item The down arrow is used to select the next value in a menu item’s option list, or a value
field’s pick list. The selected item must then be activated by pressing the Enter key.
↔ Select Menu The left and right arrow keys are used to move between the major menu pages. The
keys have no affect if a sub-menu or pick list is displayed.
F9 Setup Defaults Pressing F9 causes the following to appear:
Setup Confirmation
Load default configuration now?
[Yes] [No]
If “Yes” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, all Setup fields are set to their default
values. If “No” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, or if the ESC key is pressed, the
user is returned to where they were before F9 was pressed without affecting any
existing field values
F10 Save and Exit Pressing F10 causes the following message to appear:
Setup Confirmation
Save Configuration changes and exit now?
[Yes] [No]
If “Yes” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, all changes are saved and Setup is
exited. If “No” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, or the ESC key is pressed, the
user is returned to where they were before F10 was pressed without affecting any
existing values.
Revision 1.2
54
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 69

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
6.3.2.3 Menu Selection Bar
The Menu Selection Bar is located at the top of the screen. It displays the various major menu
selections available to the user:
• Main Menu.
• Advanced Menu.
• Security Menu.
• Server Menu.
• Boot Menu.
• Exit Menu.
These and associated submenus are described below.
6.3.2.3.1 Main Menu Selections
The following tables describe the available functions on the Main Menu, and associated
submenus. Default values are highlighted.
Table 32. Main Menu Selections
Feature Option Description
System Time HH:MM:SS Set the System Time.
System Date MM/DD/YYYY Set the System Date.
Legacy Floppy A Disabled
720 KB 3½”
1.44/1.25Mb 3½”
2.88 MB 3½”
Legacy Floppy B Disabled
720 KB 3½”
1.44/1.25 MB 3½”
2.88 MB 3½”
Hard Disk Pre-delay Disabled
3 seconds
6 seconds
9 seconds
12 seconds
15 seconds
21 seconds
30 seconds
Primary IDE Master Selects sub-menu
Primary IDE Slave Selects sub-menu
Processor Settings Selects sub-menu
Language English (US) Selects which language BIOS displays.
Hidden if not detected.
Hidden if not detected.
Allows slower spin-up drives to come ready .
Revision 1.2
55
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 70

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Feature Option Description
Spanish
Italian
French
German
Table 33. Primary Master and Slave IDE Submenu Selections
Feature Option Description
Type Auto
None
CDROM
User
ATAPI Removable
IDE Removable
Other ATAPI
CHS format
Cylinders
CHS format Heads 1 to 16 Number of read/write heads on Drive. This field is
CHS format Sectors 1 to 64 Number of Sectors per Track. This field is only
CHS format
Maximum Capacity
LBA Format
Total Sectors
LBA Format
Maximum Capacity
Multi-Sector Transfer Disabled
LBA Mode Control Disabled
32 Bit I/O Disabled
1 to 2048 Number of Cylinders on Drive. This field is only
See description Computed size of Drive from Cylinders, Heads, and
Information Only Total number of sectors on the drive that are
Information Only Capacity of the drive while using LBA addressing.
2 Sectors
4 Sectors
8 Sectors
16 Sectors
Enabled
Enabled
Select the byte of device that is attached to the IDE.
Channel.
If User is selected, the user will need to enter the
parameters of IDE device (cylinders, head and
sectors).
changeable for Type User.
This field is informational only, for Type Auto.
only available for Type User.
This field is informational only, for Type Auto.
available for Type User.
This field is informational only , for Type Auto.
Sectors entered. This field is only available for Type
User.
This field is informational only, for Type Auto.
addressable in LBA format.
This value may be higher than the ‘Maximum
Capacity’ above for drives bigger than 8.4 GB.
Specifies the number of sectors that are transferred
per block during multiple sector transfers.
This field is informational only, for Type Auto.
Enable/Disable LBA instead of cylinder, head,
sector, addressing.
This field is informational only, for Type Auto.
Enabling allows 32 bit IDE data transfers.
This field is informational only, for Type Auto.
Revision 1.2
56
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 71

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Feature Option Description
Transfer Mode Standard
FPIO 1
FPIO 2
FPIO 3
FPIO 4
FPIO 3 / DMA 1
FPIO 4 /DMA 2
Ultra DMA Mode Disabled
Mode 0
Mode 1
Mode 2
Mode 3
Mode 4
Mode 5
Select the method for moving data to/from the drive.
This field is informational only, for Type Auto.
This field is updated to display only the modes
supported by the attached device.
Selects the Ultra DMA mode used for moving data
to/from the drive.Autotype the drive toselect the
optimum transfer mode.
Table 34. Processor Settings Submenu Selections
Feature Option Description
Processor Retest No
Processor POST
speed setting
Processor 1 CPUID CPUID
Processor 1 L2
Cache Size
Processor 2 CPUID CPUID
Processor 2 L2
Cache Size
If yes, BIOS will clear historical processor status and
Yes
Information Only Displays measured processor speed.
Not Installed
Disabled
Information Only Displays L2 Cache Size for Processor 1.
Not Installed
Disabled
Information Only Displays L2 Cache Size for the next Processor.
retest all processors on the next boot.
Reports CPUID for Processor 1, if present. If empty,
reports Vacant. If disabled by BMC, reports
Disabled.
Reports CPUID for Processor 2, if present. If empty,
reports Vacant. If disabled by BMC, reports
Disabled.
Revision 1.2
57
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 72

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
6.3.2.3.2 Advanced Menu Selections
The following tables describe the menu options and associated submenus available on the
Advanced Menu. Please note that MPS 1.4/1.1 selection is no longer configurable. The BIOS
always builds MPS 1.4 tables.
Table 35. Advanced Menu Selections
Feature Option Description
Memory
Configuration
PCI Configuration Selects sub-menu.
I/O Device/peripheral
Configuration
Advanced Chipset
Control
Boot-time Diagnostic
Screen
Reset Configuration
Data
Installed O/S Other
Numlock On
Memory/Processor
Error
Select sub-menu
Selects sub-menu.
Select sub-menu
Disabled
Enabled
No
Yes
PnP O/S
Off
Boot
Halt
If enabled, the BIOS will display the OEM logo during
POST.
This option is hidden if the BIOS does not detect a
valid logo in the flash area reserved for this purpose.
Select ‘Yes’ if you want to clear the System
Configuration Data during next boot. Automatically
reset to ‘No’ in next boot.
If PnP O/S is selected, only the devices required to
boot the system are configured. If Other is selected,
all devices are configured.
Sets power on Numlock state.
Selects the behavior of the system in response to a
Memory or Processor reconfiguration. If set to Boot,
the system will attempt to boot. If set to Halt, the
system will require user intervention to complete
booting.
Table 36. Memory Configuration Menu Selections
Feature Option Description
Memory Bank #1
Memory Bank #2
Memory Bank #3
Memory Retest No
Revision 1.2
58
Normal
Not Installed
Disabled
Yes
Displays the current status of the memory bank.
Disabled indicated that a DIMM in the bank has
failed and the entire bank has been disabled.
Causes BIOS to retest all memory on next boot.
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 73

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Extended RAM Step
Disabled
1 MB
1 KB
Every - Location
Selects the size of step to use during Extended
RAM tests.
Table 37. PCI Configuration Menu Selections
Feature Option Description
Embedded SCSI Selects sub-menu
Embedded NIC 1 Selects sub-menu
Embedded NIC 2 Selects sub-menu
Embedded Video
Controller
PCI slot 1 Selects sub-menu
PCI slot 2 Selects sub-menu
PCI slot 3 Selects sub-menu
PCI slot 4 Selects sub-menu
PCI slot 5 Selects sub-menu
PCI slot 6 Selects sub-menu
Selects sub-menu
Table 38. On-board SCSI and LAN Submenu Selections
Feature Option Description
SCSI Controller
LAN Controller 1
LAN Controller 2
Option ROM Scan Enabled
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
Feature Option Description
VGA Controller Enabled
Disabled
If Disabled, the BIOS will hold the embedded chip in
reset. In this configuration, the controller HW is
completely disabled, and will be invisible to the PnP
operating systems.
If Enabled, initialize device expansion ROM.
Table 39. On-board VGA Submenu Selections
If Disabled, the BIOS will hold the embedded chip in
reset. In this configuration, the controller HW is
completely disabled, and will be invisible to the PnP
operating systems.
Table 40. PCI slot Submenu Selections
Feature Option Description
Revision 1.2
59
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 74

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Feature Option Description
Option ROM Scan Enabled
Disabled
Enable option ROM scan of the selected device.
Revision 1.2
60
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 75

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Table 41. I/O Device/Peripheral Configuration Submenu Selections
Feature Option Description
Serial Port 1 Disabled
Enabled
Auto
Base I/O Address 3F8h
2F8h
3E8h
2E8h
Interrupt 4
3
Serial Port 2 Disabled
Enabled
Auto
Base I/O Address 3F8h
2F8h
3E8h
2E8h
Interrupt 4, 3 Selects the IRQ for COM port B.
Parallel Port Disabled
Enabled
Auto
Mode Output only
Bi-Directional
EPP
ECP
Base I/O Address 378h
278h
Interrupt 5
7
DMA channel 1
3
Legacy USB support Disabled
Enabled
PS/2 Mouse Disabled
Enabled
If set to “Auto,” BIOS or OS configures the port.
Selects the base I/O address for COM port 1.
Selects the IRQ for COM port 1.
If set to “Auto”, BIOS or OS configures the port.
Selects the base I/O address for COM port B.
If set to “Auto,” BIOS or configures the port.
Selects Parallel Port Mode.
Selects the base I/O address for LPT port.
Selects the IRQ for LPT port.
Selects the DMA for LPT port.
If disabled, legacy USB support is turned off at the
end of the BIOS POST.
If disabled, PS/2 Mouse Port will not function.
Should make IRQ12 available for other devices.
Revision 1.2
61
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 76

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Table 42. Advanced Chipset Controller Submenu Selections
Feature Option Description
PCI Device Selects sub-menu
Wake On Ring Enabled
Wake On LAN Enabled
Sleep Button Present
Feature Option Description
PCI IRQ line 1
:
PCI IRQ line 16
Disable
Auto Select
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ7
IRQ9
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ14
IRQ15
Only controls legacy wake up. May not be present if
Disabled
Disabled
Absent
not supported.
Only controls legacy wake up. May not be prese nt if
not supported.
Selects the sleep button of the platform.
Table 43. PCI Device Submenu Selections
Select the IRQ for PCI IRQ
6.3.2.3.3 Security Menu Selections
Table 44. Security Menu Selections
Feature Option Description
User Password is Clear
Set
Administrator
Password is
Set User Password Press Enter When the Enter key is pressed, the user is prompted
Revision 1.2
62
Clear
Set
Order Number: A85874-002
Status only; user cannot modify. Once set, can be
disabled by setting to a null string, or clear password
jumper on board.
Status only; user cannot modify. Once set, can be
disabled by setting to a null string, or clear password
jumper on board.
for a password; press ESC key to abort. Once set,
can be disabled by setting to a null string, or clear
password jumper on board.
Page 77

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Feature Option Description
Set Administrative
Password
Password on boot Disabled
Fixed disk boot
sector
Secure Mode Timer 2 minutes
Hot Key (CTRL-ALT-) [ ], [A, B, ..L., Z], [0-9] Key assigned to invoke the secure mode feature.
Secure Mode Boot Disabled
Video Blanking Disabled
Floppy Write Protect Disabled
Power Switch Inhibit Disabled
Press Enter When the Enter key is pressed, the user is prompted
for a password; press ESC key to abort. Once set,
can be disabled by setting to a null string, or clear
password jumper on board.
If enabled, requires password entry before boot.
Enabled
Normal
Write protect
5 minutes
10 minutes
20 minutes
1 hour
2 hours
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Will write protect the boot sector of the hard drive to
prevent viruses from corrupting the drive under DOS
if set to write protect.
Period of key/PS/2 mouse inactivity specified for
Secure Mode to activate. A password is required for
Secure Mode to function. Has no effect unless at
least one password is enabled.
Cannot be enabled unless at least one password is
enabled. Can be disabled by entering a new key
followed by a backspace or by entering delete.
System boots in Secure Mode. The user must enter
a password to unlock the system. Cannot be
enabled unless at least one password is enabled.
Blank video when Secure mode is activated. A
password is required to unlock the system. This
cannot be enabled unless at least one password is
enabled. This option is only present if the system
includes an embedded video controller.
When Secure mode is activated, the floppy drive is
write protected. A password is required to re-enable
floppy writes. Cannot be enabled unless at least
one password is enabled.
Determines whether power switch function from front
panel.
6.3.2.3.4 Server Menu Selections
Table 45. Server Menu Selections
Feature Option Description
System Management Selects sub-menu.
Console Redirection Selects sub-menu.
Service Partition Type Displays the partition type of the Service
Partition; the default is 12h.
Clear Event Log Enter If selected, the System Event log will be cleared
immediately.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
63
Page 78

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Feature Option Description
Assert NMI on PERR Disabled
Enabled
Assert NMI on SERR Enabled
Disabled
FRB-2 Policy FRB2 Disable
Disable Immediately
Never Disable
Allow 3 Failures
Thermal Sensor Disabled
Enabled
BMC IRQ IRQ11
IRQ5
IRQ10
Disabled
Post Error Pause Disabled
Enabled
AC Link Power On
Last State
Stay off
If enabled, PCI bus parity error (PERR) is
enabled and is routed to NMI.
If enabled, PCI bus system error (SERR) is
enabled and is routed to NMI.
Controls the policy of the FRB-2 timeout. This
option determines when the Boot Strap
Processor (BSP) should be disabled if FRB-2
error occur. And Detemines when FRB2 stop.
Determines wheter Thermal Sensor monitoring
function
Determines BMC IRQ.
If enabled, the boot is stopped when Post error
occurs.
Selects system power state after AC loss.
Table 46. System Management Submenu Selections
Feature Option Description
BIOS Version Information field only
Board Part Number Information field only
Board Serial Number Information field only
System Part Number Information field only
System Serial Number Information field only
Chassis Part Number Information field only
Chassis Serial Number Information field only
BMC Device ID Information field only .
BMC Device Revision Information field only .
BMC Firmware Revision Information field only .
BMC Firmware BootBlock Revision Information field only .
BMC Support IPMI Version Information field only .
SDR Revision Information field only .
PIA Revision Information field only .
Primary HSBP Revision Information field only, hidden if not detected
Secondary HSBP Revision Information field only, hidden if not detected
Revision 1.2
64
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 79

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
Table 47. Console Redirection Submenu Selections
Feature Option Description
Serial Port Address Disabled
On-board COM A
On-board COM B
Baud Rate 9600
19.2k
38.4k
57.6K
115.2k
Flow Control None
CTS/RTS
XON/XOFF
CTS/RTS + CD
When enabled, Console Redirection uses the I/O port
specified. Choosing “Disabled” completely disables
Console Redirection.
When Console Redirection is enabled, use the baud
rate specified. When EMP is sharing the COM port as
console redirection, the baud rate must be set to 19.2
k to match EMP baud rate, unless auto-baud feature
is used.
None = No flow control.
CTS/RTS = Hardware based flow control.
XON/XOFF = Software flow control.
CTS/RTS +CD = Hardware based + Carrier Detect
flow control.
When EMP is sharing the COM port as console
redirection, the flow control must be set to CTS/RTS
or CTS/RTS+CD depending on whether a modem is
used.
6.3.2.3.5 Boot Menu Selections
Boot Menu options allow the user to select the boot device. The following table is an example of
a list of devices ordered in priority of the boot invocation. Items can be re-prioritized by using the
up and down arrow keys to select the device. Once the device is selected, use the plus (+) key
to move the device higher in the boot priority list. Use the minus (-) key to move the device lower
in the boot priority list.
Table 48. Boot Device Priority Selections
Boot Priority Device Description
1 Removable Devices Attempt to boot from a legacy floppy A: or removable media device
like LS-120.
2 Hard Drive Attempt to boot from a hard drive device.
3 ATAPI CD-ROM Drive Attempt to boot from an ATAPI CD-ROM drive.
4 PXE UNDI Attempt to boot from a network. This entry will appear if there is a
network device in the system that is controlled by a PXE compliant
option ROM.
Revision 1.2
65
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 80

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Table 49. Hard Drive Selections
Option Description
Drive #1 (or actual drive
string)
Other bootable cards
Additional entries for each
drive that has a PnP header
To select the boot drive, use the up and down arrows to highlight a device,
then press the plus key (+) to move it to the top of the list or the minus key (–)
to move it down.
Other bootable cards cover all the boot devices that are not reported to the
system BIOS through BIOS Boot specification mechanism. It may or may not
be bootable, and may not correspond to any device. If BIOS boot spec.
support is set to limited, this item covers all drives that are controlled by
option ROMs (like SCSI drives).
Press ESC to exit this menu.
Table 50. Removable Drive Selections
Feature Option Description
Lists Bootable Removable Devices in the
System
+
–
Use +/– keys to place the removable devices in the
boot order you want. Includes Legacy 1.44 MB floppy,
120 MB floppy etc.
6.3.2.3.6 Exit Menu Selections
The following menu options are available on the Exit menu. Use the up and down arrow keys to
select an option, and then press the Enter key to execute the option.
Table 51. Exit Menu Selections
Option Description
Exit Saving Changes Exit after writing all modified Setup item values to NVRAM.
Exit Discarding Changes Exit leaving NVRAM unmodified. User is prompted if any of the setup fields were
modified.
Load Setup Defaults Load default values for all SETUP items.
Load Custom Defaults Load values of all Setup items from previously saved Custom Default s. NOTE:
This is hidden if custom defaults are not valid or present.
Save Custom Defaults Stores Custom Defaults in NVRAM.
Discard Changes Read previous values of all Setup items from NVRAM.
Save Changes Write all Setup item values to NVRAM.
Revision 1.2
66
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 81

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
6.3.3 CMOS Memory Definition
The CMOS map is available in the NVRAM.LST file generated for every BIOS release. The
CMOS map is subject to change without notice.
6.3.4 Clearing CMOS
The BIOS detects the state of the CMOS jumper. If the jumper is set to “CMOS Clear” prior to
power-on or a hard reset, the BIOS changes the CMOS and NVRAM settings to a default state.
This guarantees the system’s ability to boot from floppy.
Password settings are unaffected through CMOS clear. The BIOS clears the ESCD parameter
block and loads a null ESCD image. The boot order information is also cleared when CMOS is
cleared via jumper. The configuration data for the on-board SCSI controllers is not cleared during
a clear CMOS event as each device controls its own default settings
If the Reset Configuration Data option is enabled in Setup, ESCD data and BIOS Boot
specification data is cleared and reinitialized in next boot.
6.4 Flash Update Utility
Note: The Phoenix* PHLASH utility must be run without the presence of a 386 protected mode
control program, such as Microsoft* Windows* NT* / 2000 or EMM386*. Phoenix* PHLASH
uses the processor’s flat addressing mode to update the flash ROM.
6.4.1 Loading the System BIOS
The BIOS update utility (PHLASH) loads a new copy of the BIOS into Flash ROM. The loaded
code and data include the following:
• On-board Video BIOS and SCSI BIOS
• BIOS Setup Utility
• Quiet Boot Logo Area
When running PHLASH in interactive mode, the user may choose to update a particular Flash
area. Updating a flash area takes a file or series of files from a hard or floppy disk, and loads it in
the specified area of Flash ROM.
To manually load a portion of the BIOS, the user must specify which data file(s) to load. The
choices include PLATCBLU.BIN, PLATCXLU.BIN, PLATCXXX.BIN, PLATCXLX.BIN or
PLATCXXU.BIN. The last three letters specify the functions to perform during the flash process:
C = Rewrite BIOS
B = Rewrite Boot block
L = Clear LOGO area
U = Clear user binary
X = place hold
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
67
Page 82

BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
This file is loaded into the PHLASH program with the /b=<bin file>.
The disk created by the BIOS.EXE program automatically runs “PHLASH /s /b=PLATCXLU.BIN
command” in non-interactive mode. For a complete list of PHLASH options, run “PHLASH /h”.
Once an update of the system BIOS is complete, the user is prompted for a reboot. The user
binary area is also updated during a system BIOS update. User binary can be updated
independently of the system BIOS. CMOS is cleared when the system BIOS is updated.
6.4.2 User Binary Area
The BIOS flash ROM includes a 16 KB area in flash for implementation-specific OEM add-ons.
The user binary area can be saved and updated. The valid extension for user files is *.ROM.
6.4.3 Language Area
The system BIOS language area can be updated only by updating the entire BIOS. The BIOS
supports English, Spanish, French, German, and Italian. These languages are selectable using
Setup.
6.4.4 OEM Logo Screen
A 128 KB region of Flash ROM is available to store the OEM logo in compressed format. The
BIOS contains the standard Intel logo. Using the Phoenix* PHLASH utility, this region can be
updated with an OEM supplied logo image. The OEM logo must fit within 640 X 384 size. If an
OEM logo is flashed into the system, it overrides the built in Intel logo.
6.4.5 Recovery Mode
The SDS2 baseboard supports a method for performing a BIOS recovery in order to restore the
system from a failed flash. This utilizes a jumper on the baseboard. The system beeps through
out the process. The recovery BIOS boots only from a 1.44 MB floppy diskette inserted into a
1.44 MB floppy drive or LS-120/240 drive. Nothing is displayed to the video screen during the
recovery process.
Note: The user must make the Recovery floppy diskette following the instructions included in the
release notes. Failure to do so will cause the process to fail.
6.4.5.1 Performing BIOS Recovery
The follow procedure boots the recovery BIOS and flashes the normal BIOS.
1. Prepare a BIOS recovery diskette by following the instructions included with the BIOS
release.
2. Turn off system power.
3. Move the BIOS recovery jumper to the recovery position.
4. Insert the BIOS recovery diskette.
Revision 1.2
68
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 83

Intel® Server Board SDS2 BIOS
5. Turn on system power.
The system boots from the recovery diskette. The BIOS will beep twice when the update
process starts. The system will continue to beep while updating the BIOS. If BIOS update
completes successfully, the system will stop beeping. If the update fails, the system will sound
an alternating pattern of a buzz and a beep.
When the flash update completes:
1. Turn off system power.
2. Remove the recovery diskette.
3. Restore the recovery jumper to its original position.
4. Turn on system power.
5. Flash any custom blocks such as user binary .
The system should now boot normally using the updated system BIOS.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
69
Page 84

Clock/Voltage Generation and Distribution Intel® Server Board SDS2
7. Clock/Voltage Generation and Distribution
7.1 Clock
All buses on the SDS2 Server Board operate using synchronous clocks. Clock
synthesizer/driver circuitry on the Server Board generates clock frequencies and voltage levels
as required, including the following:
• 133 MHz at 2.5 V logic levels: For CPU1, CPU2, HE-SL, DIMM Sockets and the ITP port
• 66 MHz at 3.3 V logic levels: For HE-SL, CIOB, P64-B and P64-C PCI slots
• 48 MHz at 3.3V logic levels: For CSB5’s USB
• 33.3 MHz at 3.3 V logic levels: For CIOB, CSB5 and on-board PCI devices and slots
• 16.67 MHz at 2.5 V logic levels: For processor and the CSB5 APIC bus clocks
• 14.318 MHz at 3.3V logic levels: For CSB5 and Video
Other clock sources on the SDS2 Server Board generates:
• 80 MHz at 3.3 V logic levels: For Ultra 360 SCSI Controller
• 32.768 MHz at 3.3 V logic levels: For SIO and BMC
• 14.318 MHz at 3.3 V logic levels: for main clock generator
For information on processor clock generation, see the CK133-WS Synthesizer/Driver
Specification.
The following figure illustrates clock generation and distribution on SDS2 Server Board.
Revision 1.2
70
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 85

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Clock/Voltage Generation and Distribution
SDRAM
SDRAM
REGISTER 1
SDRAM 1
REGISTER 2
133 MHz
133 MHz
133 MHz
SDRAM 2
133 MHz
133 MHz
SDRAM 3
SDRAM 4
133 MHz
SDRAM
CLK PLL
SDRAM 5
133 MHz
133 MHz
SDRAM 6
133 MHz
133 MHz
133 MHz
PLLCLKFB0
CNBDCLKFB
CNBRDCLK
25 MHz
25 MHz
NIC 1 NIC 2
40 MHz
PCI SLOT 5
U160 SCSI
66 MHz
66 MHz
PCI
66 MHz
66MHz CLK
PCI SLOT 6
66 MHz
BUFFER
66 MHz
PCI SLOT 1
66 MHz
PCI
66MHz CLK
66 MHz
PCI SLOT 2
66 MHz
BUFFER
66 MHz
133 MHz
133 MHz
133 MHz
CNBDCLKIN
CPU 1 CPU 2 HE-SL
16 MHz
16 MHz
16 MHz
AGPFBCLK
CSB5
48 MHz
48 MHz
14 MHz
14 MHz
32 KHz
SIO
33 MHz
VGA
40 MHz
BMC
33 MHz
33 MHz
PCI SLOT 3
PCI SLOT 4
33 MHz
33 MHz
PCI 33MHz
33 MHz
CLK
BUFFER
33 MHz
IRQ 0 IRQ 1
33 MHz
cPLD
33 MHz
CIOB
33 MHz
66 MHz
14.318 MHz
HOST CLK
APIC CLK
48 MHz
14 MHz
PCI 33MHz CLK
PCI 66MHz CLK
Figure 8. SDS2 Server Board Clock Generation/Distribution Diagram
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
71
Page 86

Clock/Voltage Generation and Distribution Intel® Server Board SDS2
7.2 Voltage
The system power supply provides +3.3V, +5V, +12V, -12V, and +5VSB and voltage regulators
on the Server Board are used to create the following voltages:
• +3.3VSB
• VCORE for the CPUs
• VTT for the CPUs
• +2.5V for the chipsets
• +1.8V for the onboard SCSI
The following figure illustrates voltage generation and distribution on the SDS2 Server Board.
Revision 1.2
72
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 87

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Clock/Voltage Generation and Distribution
HE-SLCIOB20CSB5
DIMM
Power Supply
-12V +12V +5V +3.3V +5VSB
NIC 1 NIC 2 Sahalee
5VSB --> 3.3VSB
PCI Slots
VRM
CORE
2
Processor
1
Processor
VTT
VRM
Super I/O VIDEO
Fan
KB/
MS
5V--> 2.5V
5V--> 1.8V
USB
SCSI
SCSI Term
Figure 9. SDS2 Server Board Voltage Generation/Distribution Diagram
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
73
Page 88

Connections Intel® Server Board SDS2
8. Connections
8.1 Power Distribution Board Connector
The main power supply connection is obtained using a 24-pin connector. A separate 8-pin
connector is used for the +12 V power connector dedicated to providing power to the processor.
A third 5-pin auxiliary signal connector is used to communicate with the power supply. The
following tables define the pin-outs of these connectors.
Table 52. 24-Pin Main Power Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Color Pin Signal Color
1 +3.3 V Orange 13 +3.3 V Orange
2 +3.3 V Orange 14 -12 V Blue
3 COM Black 15 COM Black
4 +5 V Red 16 PS_ON# Green
5 COM Black 17 COM Black
6 +5 V Red 18 COM Black
7 COM Black 19 COM Black
8 PWR_OK Gray 20 RSVD_(-5 V) White
9 5 VSB Purple 21 +5 V Red
10 +12 V_IO Yellow 22 +5 V Red
11 +12 V_IO Yellow 23 +5 V Red
12 +3.3 V Orange 24 COM Black
Table 53. 8-Pin +12 V Power Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Color Pin Signal Color
1 COM_CPU Black 5 +12V_CPU Yellow
2 COM_CPU Black 6 +12V_CPU Yellow
3 COM_CPU Black 7 +12V_CPU Yellow
4 COM_CPU Black 8 +12V_CPU Yellow
Note: The SDS2 server board requires a +12 V Power Connector. The board will not power on
without +12 V Power supplied to this connector.
Table 54. Aux Signal Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name
1 I2C Clock
2 I2C Data
Revision 1.2
74
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 89

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Connections
3 PS_ALERT (Not Used)
4 ReturnS
5 3.3RS
8.2 Memory Module Connector
The SDS2 Server Board has six PC-133 SDRAM DIMM connectors and supports registered
SDRAM modules. For more information on DIMM modules refer to PC SDRAM Registered
DIMM Design Support Document Rev 1.2.
Table 55. DIMM Connector Pin-out
Pin Front Pin Front Pin Front Pin Back Pin Back Pin Back
1 VSS 29 DQM1 57 DQ18 85 VSS 113 DQM5 141 DQ50
2 DQ0 30 CS0# 58 DQ19 86 DQ32 114 CS1# 142 DQ51
3 DQ1 31
4 DQ2 32 VSS 60 DQ20 88 DQ34 116 VSS 144 DQ52
5 DQ3 33 A0 61 NC 89 DQ35 117 A1 145 NC
6 VDD 34 A2 62 V
7 DQ4 35 A4 63 CKE1 91 DQ36 119 A5 147 REGE
8 DQ5 36 A6 64 VSS 92 DQ37 120 A7 148 VSS
9 DQ6 37 A8 65 DQ21 93 DQ38 121 A9 149 DQ53
10 DQ7 38 A10/AP 66 DQ22 94 DQ39 122 BA0 150 DQ54
11 DQ8 39 BA1 67 DQ23 95 DQ40 123 A11 151 DQ55
12 VSS 40 VDD 68 VSS 96 VSS 124 VDD 152 VSS
13 DQ9 41 VDD 69 DQ24 97 DQ41 125 CLK1 153 DQ56
14 DQ10 42 CLK0 70 DQ25 98 DQ42 126 A12 154 DQ57
15 DQ11 43 VSS 71 DQ26 99 DQ43 127 VSS 155 DQ58
16 DQ12 44
17 DQ13 45 CS2# 73 VDD 101 DQ45 129 CS3# 157 VDD
18 VDD 46 DQM2 74 DQ28 102 VDD 130 DQM6 158 DQ60
19 DQ14 47 DQM3 75 DQ29 103 DQ46 131 DQM7 159 DQ61
20 DQ15 48
21 CB0 49 VDD 77 DQ31 105 CB4 133 VDD 161 DQ63
22 CB1 50 NC 78 VSS 106 CB5 134 NC 162 VSS
23 VSS 51 NC 79 CLK2 107 VSS 135 NC 163 CLK3
24 NC 52 CB2 80 NC 108 NC 136 CB6 164 NC
25 NC 53 CB3 81 WP 109 NC 137 CB7 165 SA0
26 VDD 54 VSS 82 SDA 110 VDD 138 VSS 166 SA1
27 WE# 55 DQ16 83 SCL 111 CAS# 139 DQ48 167 SA2
28 DQM0 56 DQ17 84 VDD 112 DQM4 140 DQ49 168 VDD
Note:
1024 Don’t Use
DU 1
DU 1
DU 1
59 VDD 87 DQ33 115 RAS# 143 VDD
90 VDD 118 A3 146 V
REF
72 DQ27 100 DQ44 128 CKE0 156 DQ59
76 DQ30 104 DQ47 132 A13 160 DQ62
REF
Revision 1.2
75
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 90

Connections Intel® Server Board SDS2
8.3 System Management Headers
8.3.1 ICMB Connector
The Intelligent Chassis Management Bus (ICMB) allows inter-chassis communications between
intelligent chassis. This makes it possible to externally access chassis management functions,
alert logs, port-mortem data, etc. Additional information about ICMB can be found in the
Intelligent Chassis Management Bus, Version 1.0.
Table 56. ICMB Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Type Description
1 5VSB Power
2 ICMB_TX Signal Transmit signal
3 ICMB_EN Signal Enable signal
4 ICMB_RX Signal Receive signal
5 GND GND
8.3.2 OEM IPMB Connector
Table 57. IPMB Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Description
1 IPMB_SDA 5 VSB Data Line
2 GND GND
3 IPMB_SCL 5 VSB Clock Line
8.3.3 SCSI HSBP (IPMB) Connector
The Intelligent Platform Management Bus (IPMB), as used on SDS2 Server Board allows for
connections to Hot Swap Back planes (HSBP) with multiple hard drives.
Table 58. HSBP -A Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Description
1 IPMB_SDA 5 VSB Data Line
2 GND GND
3 IPMB_SCL 5 VSB Clock Line
4 I2C_ADR_CNTRL Address Control
Revision 1.2
76
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 91

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Connections
Table 59. HSBP -B Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Description
1 IPMB_SDA 5 VSB Data Line
2 GND GND
3 IPMB_SCL 5 VSB Clock Line
4 I2C_ADR_CNTRL Address Control
8.4 Front Panel Header
A 34-pin header is provided for cabling to the system front panel. The header contains reset,
NMI, power control buttons, and LED indicators. The table below details the pin-outs of the
header.
Table 60. Front Panel 34-Pin Header Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 Power LED Anode 2 5VSB
3 KEY 4 Fan Fail LED Anode
5 Power LED Cathode 6 Fan Fail LED Cathode
7 HDD Activity LED Anode 8 Power Fault LED Anode
9 HDD Activity LED Cathode 10 Power Fault LED Cathode
11 Power Switch 12 NIC#1 Activity LED A node
13 GND (Power Switch) 14 NIC#1 Activity LED Cathode
15 Reset Switch 16 I2C SDA
17 GND (Reset Switch) 18 I2C SCL
19 ACPI Sleep Switch 20 Chassis Intrusion
21 GND (ACPI Sleep Switch) 22 NIC#2 Activity LED Anode
23 NMI to CPU Switch 24 NIC#2 Activity LED Cathode
25 KEY 26 KEY
27 ID LED Anode 28 System Ready Anode
29 ID LED Cathode 30 System Ready Cathode
31 ID Switch 32 HDD Fault Anode
33 GND (ID Switch) 34 HDD Fault Cathode
Revision 1.2
77
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 92

Connections Intel® Server Board SDS2
8.5 PCI Slot Connector
The Server Board support two 32-bit, 33-MHz 5V PCI Slots and four 64-bit, 66-MHz 3.3 V PCI
Slots. The tables below define their pin-outs.
Table 61. 32-bit 5 V PCI Slot Pin-out
Pin Side B Side A Pin Side B Side A
1 -12 V TRST# 32 AD[17] AD[16]
2 TCK +12 V 33 C/BE[2]# +3.3 V
3 Ground TMS 34 Ground FRAME#
4 TDO TDI 35 IRDY# Ground
5 +5 V +5 V 36 +3.3 V TRDY#
6 +5 V INTA# 37 DEVSEL# Ground
7 INTB# INTC# 38 Ground STOP#
8 INTD# +5 V 39 LOCK# +3.3 V
9 PRSNT1# RSV 40 PERR# SMBUS CLK
10 RSV +5 V 41 +3.3 V SMBUS DAT
11 PRSNT2# RSV 42 SERR# Ground
12 Ground Ground 43 +3.3 V PAR
13 Ground Ground 44 C/BE[1]# AD[15]
14 RSV 3.3 VSB 45 AD[14] +3.3 V
15 Ground RST# 46 Ground AD[13]
16 CLK +5 V (I/O) 47 AD[12] AD[11]
17 Ground GNT# 48 AD[10] Ground
18 REQ# Ground 49 Ground AD[09]
19 +5 V PME# 50 Connector Key Connector Key
20 AD[31] AD[30] 51 Connector Key Connector Key
21 AD[29] +3.3 V 52 AD[08] C/BE[0]#
22 Ground AD[28] 53 AD[07] +3.3 V
23 AD[27] AD[26] 54 +3.3 V AD[06]
24 AD[25] Ground 55 AD[05] AD[04]
25 +3.3 V AD[24] 56 AD[03] Ground
26 C/BE[3]# IDSEL 57 Ground AD[02]
27 AD[23] +3.3 V 58 AD[01] AD[00]
28 Ground AD[22] 59 +5 V +5 V (I/O)
29 AD[21] AD[20] 60 ACK64# REQ64#
30 AD[19] Ground 61 +5 V +5 V
31 +3.3 V AD[18] 62 +5 V +5 V
Table 62: 64-bit 3.3V PCI Slot Pin-out
Pin Side B Side A Pin Side B Side A
Revision 1.2
78
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 93

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Connections
Pin Side B Side A Pin Side B Side A
1 -12 V TRST# 49 M66EN AD[09]
2 TCK +12 V 50 Ground Ground
3 Ground TMS 51 Ground Ground
4 TDO TDI 52 AD[08] C/BE[0]#
5 +5 V +5 V 53 AD[07] +3.3 V
6 +5 V INTA# 54 +3.3 V AD[06]
7 INTB# INTC# 55 AD[05] AD[04]
8 INTD# +5 V 56 AD[03] Ground
9 PRSNT1# RSV 57 Ground AD[02]
10 RSV +3.3 V 58 AD[01] AD[00]
11 PRSNT2# RSV 59 +3.3 V +3.3 V
12 Connector Key Connector Key 60 ACK64# REQ64#
13 Connector Key Connector Key 61 +5 V +5 V
14 RSV 3.3 VSB 62 +5 V +5 V
15 Ground RST#
16 CLK +3.3 V
17 Ground GNT# 63 RSV Ground
18 REQ# Ground 64 Ground C/BE[7]#
19 +3.3 V PME# 65 C/BE[6]# C/BE[5]#
20 AD[31] AD[30] 66 C/BE[4]# +3.3 V
21 AD[29] +3.3 V 67 Ground PAR64
22 Ground AD[28] 68 AD[63] AD[62]
23 AD[27] AD[26] 69 AD[61] Ground
24 AD[25] Ground 70 +3.3 V AD[60]
25 +3.3 V AD[24] 71 AD[59] AD[58]
26 C/BE[3]# IDSEL 72 AD[57] Ground
27 AD[23] +3.3 V 73 Ground AD[56]
28 Ground AD[22] 74 AD[55] AD[54]
29 AD[21] AD[20] 75 AD[53] +3.3 V
30 AD[19] Ground 76 Ground AD[52]
31 +3.3 V AD[18] 77 AD[51] AD[50]
32 AD[17] AD[16] 78 AD[49] Ground
33 C/BE[2]# +3.3 V 79 +3.3 V AD[48]
34 Ground FRAME# 80 AD[47] AD[46]
35 IRDY# Ground 81 AD[45] Ground
36 +3.3 V TRDY# 82 Ground AD[44]
37 DEVSEL# Ground 83 AD[43] AD[42]
38 Ground STOP# 84 AD[41] +3.3 V
39 LOCK# +3.3 V 85 Ground AD[40]
40 PERR# SMBUS CLK 86 AD[39] AD[38]
41 +3.3 V SMBUS DAT 87 AD[37] Ground
42 SERR# Ground 88 +3.3 V AD[36]
43 +3.3 V PAR 89 AD[35] AD[34]
44 C/BE[1]# AD[15] 90 AD[33] Ground
Revision 1.2
79
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 94

Connections Intel® Server Board SDS2
Pin Side B Side A Pin Side B Side A
45 AD[14] +3.3 V 91 Ground AD[32]
46 Ground AD[13] 92 RSV RSV
47 AD[12] AD[11] 93 RSV Ground
48 AD[10] Ground 94 Ground RSV
8.6 I/O Connectors
8.6.1 VGA Connector
The video connector interface is a standard VGA compatible 15-pin connector. An ATI RAGE XL
video controller with 4 MB of on-board video memory supplies video. The following table details
the pin-out of the VGA connector.
Table 63. VGA Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name
1 Red (analog color signal R)
2 Green (analog color signal G)
3 Blue (analog color signal B)
4 N/C
5 GND
6 GND
7 GND
8 GND
9 Fused VCC (+5V)
10 GND
11 N/C
12 DDCDAT
13 HSYNC (horizontal sync)
14 VSYNC (vertical sync)
15 DDCCLK
8.6.2 SCSI Connector
The SDS2 Server Board provides two SCSI connectors accessible internally. The following table
details the pin-out of the 68-pin SCSI connector.
Table 64. 68-pin SCSI Connector Pin-out
Connector Contact Number Signal Name Signal Name Connector Contact Number
1 +DB(12) -DB(12) 35
2 +DB(13) -DB(13) 36
Revision 1.2
80
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 95

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Connections
Connector Contact Number Signal Name Signal Name Connector Contact Number
3 +DB(14) -DB(14) 37
4 +DB(15) -DB(15) 38
5 +DB(P1) -DB(P1) 39
6 +DB(0) -DB(0) 40
7 +DB(1) -DB(1) 41
8 +DB(2) -DB(2) 42
9 +DB(3) -DB(3) 43
10 +DB(4) -DB(4) 44
11 +DB(5) -DB(5) 45
12 +DB(6) -DB(6) 46
13 +DB(7) -DB(7) 47
14 +DB(P) -DB(P) 48
15 GROUND GROUND 49
16 GROUND GROUND 50
17 RESERVED RESERVED 51
18 RESERVED RESERVED 52
19 RESERVED RESERVED 53
20 GROUND GROUND 54
21 +ATN -ATN 55
22 GROUND GROUND 56
23 +BSY -BSY 57
24 +ACK -ACK 58
25 +RST -RST 59
26 +MSG -MSG 60
27 +SEL -SEL 61
28 +C/D -C/D 62
29 +REQ -REQ 63
30 +I/O -I/O 64
31 +DB(8) -DB(8) 65
32 +DB(9) -DB(9) 66
33 +DB(10) -DB(10) 67
34 +DB(11) -DB(11) 68
8.6.3 NIC Connectors
The SDS2 Server Board supports two RJ -45 connectors. The following table details the pin-out
of these connectors.
Table 65. RJ-45 Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
81
Page 96

Connections Intel® Server Board SDS2
1 TXDP 7 RXDP
2 TXDM 8 RXDM
3 N/C 9 Activity LED Cathode
4 N/C 10 Link LED Anode
5 N/C 11 Speed LED Anode
6 N/C 12 3VSB
8.6.4 IDE Connector
There is one IDE channel on the Server Board through the use of a 40-pin connector. The
connector pin-out is detailed in the table below. Note IDE LED hard disk drive activity (Pin 39)
signal is not routed to the front panel connector. IDE hard disk activity will not cause the front
panel LED’s to turn on.
Table 66. IDE 40-pin Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 RESET_L 2 GND
3 DD7 4 IDE_DD8
5 DD6 6 IDE_DD9
7 DD5 8 IDE_DD10
9 DD4 10 IDE_DD11
11 DD3 12 IDE_DD12
13 DD2 14 IDE_DD13
15 DD1 16 IDE_DD14
17 DD0 18 IDE_DD15
19 GND 20 KEY
21 IDE_DMARQ_L 22 GND
23 IDE_IOW_L 24 GND
25 IDE_IOR_L 26 GND
27 IDE_IORDY 28 GND
29 IDE_DMAACK_L 30 GND
31 IRQ_IDE 32 N/C
33 IDE_A1 34 N/C
35 IDE_A0 36 IDE_A2
37 IDE_DCS0_L 38 IDE_DCS1_L
39 IDE_HD_ACT_L 40 GND
8.6.5 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Connectors
The Server Board provides four USB ports: three on the rear I/O and one internally through a 10pin header. The following table details the pin-out of the stacked three-port USB connector.
Table 67. Stacked Three-port USB Connector Pin-out
Revision 1.2
82
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 97

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Connections
Pin Signal Name
1 Fused 5 V
2 USB_PORT1_D3 USB_PORT1_D+
4 GND
5 Fused 5 V
6 USB_PORT2_D7 USB_PORT2_D+
8 GND
9 Fused 5 V
10 USB_PORT3_D11 USB_PORT3_D+
12 GND
A 10-pin header (2X5) located at CN18 on the Server Board provides an option to cable out the
USB to the front panel. The pin-out of the header is detailed in the following table that is
representative of the Foxconn HL07051-P9 Housing located at CN18.
Pin 6 +5Volts Pin 7
USB_PORT4_D-
Pin 8
USB_PORT4_D
Pin 9 GND Pin 10 N/C
+
Pin 1 N/C Pin 2 N/C Pin 3 N/C Pin 4 N/C Pin 5 KEY
Table 68. 10-pin USB Connection Header (2 x 5) Pin-out
Pin Signal name
1 N/C
2 N/C
3 N/C
4 N/C
5 KEY
6 Fused 5 V
7 USB_PORT4_D8 USB_PORT4_D+
9 GND
10 N/C
8.6.6 Floppy Connector
The following table details the pin-out of the 34-pin floppy connector.
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
83
Page 98

Connections Intel® Server Board SDS2
Table 69. 34-pin Floppy Connector Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 GND 2 FD_DENSEL
3 GND 4 Test Point
5 KEY 6 FD_DRATE0
7 GND 8 FD_INDEX_L
9 GND 10 FD_MTRA_L
11 GND 12 FD_DRVSELB_L
13 GND 14 FD_DRVSELA_L
15 GND 16 FD_MTRB_L
17 GND 18 FD_DIR_L
19 GND 20 FD_STEP_L
21 GND 22 FD_WDATA_L
23 GND 24 FD_WGATE_L
25 GND 26 FD_TRK0_L
27 GND 28 FD_WPT_L
29 GND 30 FD_RDATA_L
31 GND 32 FD_HDSEL_L
33 GND 34 FD_DSKCHG_L
8.6.7 Serial Port Connector
Two serial ports are provided on the Server Board, one DB9 connector is located on the rear I/O
to supply COM1 and a 10-pin header at location CN33 provides COM2. The following tables
detail their connector pin-outs.
Table 70. DB9 Serial Port Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Description
1 DCD Data Carrier Detect
2 RXD Receive Data
3 TXD Transmit Data
4 DTR Data Terminal Ready
5 GND Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request to Send
8 CTS Clear to Send
9 RI Ring Indicate
Table 71. 10-pin Header Serial Port Pin-out
Revision 1.2
84
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 99

Intel® Server Board SDS2 Connections
Pin Signal Name Description
1 DCD Data Carrier Detect
2 RXD Receive Data
3 TXD Transmit Data
4 DTR Data Terminal Ready
5 GND Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request to Send
8 CTS Clear to Send
9 RI Ring Indicate
10 KEY Key
8.6.8 Parallel Port
One DB25 parallel port connector is provided on the rear I/O. The following table details the pinout of the connector.
Table 72. DB25 Parallel Port Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 STROBE_L 14 AUTOFD_L
2 DATA0 15 ERROR_L
3 DATA1 16 INIT_L
4 DATA2 17 SLCT_INPUT_L
5 DATA3 18 GND
6 DATA4 19 GND
7 DATA5 20 GND
8 DATA6 21 GND
9 DATA7 22 GND
10 ACK_L 23 GND
11 BUSY 24 GND
12 PAPER_END 25 GND
13 SELECT
8.6.9 Keyboard and Mouse Connector
Two PS/2 ports are provided for keyboard and mouse and share a common housing. The top
one is labeled “mouse” and the bottom is labeled “keyboard,” although the board set supports
swapping these connections. The following table details the pin-out of the PS/2 connectors.
Table 73. Keyboard and Mouse PS/2 Connector Pin-out
Revision 1.2
85
Order Number: A85874-002
Page 100

Connections Intel® Server Board SDS2
Keyboard Mouse
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 KBDATA 1 MSDATA
2 N/C 2 N/C
3 GND 3 GND
4 Fused 5V 4 Fused 5V
5 KBCLK 5 MSCLK
6 N/C 6 N/C
8.7 Miscellaneous Headers
8.7.1 Fan Headers
There are two fan connectors for processors and four system fan connectors. All six fans are
monitored by the BMC and they all share the same pin-out.
Table 74. Fan Header Pin-out
Pin Signal Name Type Description
1 GND Power GROUND is the power supply ground
2 12V Power Power Supply 12 V
3 Fan Tach Out FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the FAN speed
8.7.2 Chassis Intrusion
The BMC monitors the chassis intrusion switch by polling the ADM1026 device. The cable from
the chassis cover is connected through the 2-pin header below. To disable chassis intrusion
detection, short the 2-pin header with a jumper.
Table 75. Chassis Intrusion Header Pin-out
Pin Signal name
1 CHASSIS_INTR
2 GND
8.7.3 External SCSI Activity LED Input Signal Connector
A 4-pin header (labeled HDD LED at CN44) is provided on the Server Board to track SCSI drive
activity on the Hot Swap Back -plane. The following table details the pin-out of the header. This
allows two RAID controller cards to connect their disk activity cables to the front panel hard disk
LED activity light. Note that IDE hard disk activity LED is not enabled on the SDS2 board via the
front panel connector at CN37. Pins 2 and 3 are tied together routed through an AND gate to Pin
9 of CN37 front panel connector.
Revision 1.2
86
Order Number: A85874-002
 Loading...
Loading...