Page 1

Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600
v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet - Volume One of Two
September 2013
Reference Number: 329187-001
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH Intel® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, Express* OR IMPL IED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY Expres s* OR IMPL IE D WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED IN WRITING BY INTEL, THE INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED NOR INTENDED FOR ANY APPLICATION IN WHICH THE FAILURE OF THE INTEL PRODUCT COULD CREATE A SITUATION WHERE PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY OCCUR.
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER
AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING T O S ALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCT S INCLUDING
LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELA TING T O FITNES S FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANT ABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED IN WRITING BY INTEL, THE INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED NOR INTENDED FOR ANY
APPLICATION IN WHICH THE FAILURE OF THE INTEL PRODUCT COULD CR EA TE A SITUA TION WHERE PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH
MAY OCCUR.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Designers must not rely on the
absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for future
definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them. The
information here is subject to change without notice. Do not finalize a design with this information.
The Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families, Intel® C600 Series chipset, and the Intel® Xeon®
Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families-based platform described in this document may contain design defects or
errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are
available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained
by calling 1-800-548-4725, or go to: http://www.intel.com/#/en_US_01
Hyper-Threading Technology requires a computer system with a processor supporting HT Technology and an HT Technology
enabled chipset, BIOS and operating system. Performance will vary depending on the specific hardware and so ftware you use. For
more information including details on which processors support HT Technology, see
http://www.intel.com/products/ht/hyperthreading_more.htm.
Enabling Execute Disable Bit functionality requires a PC with a processor with Execute Disable Bit capability and a supporting
operating system. Check with your PC manufacturer on whether your system delivers Execute Disable Bit functionality.
Intel® Virtualization Technology requires a computer system with an enabled Intel® processor, BIOS, virtual machine monitor
(VMM) and, for some uses, certain computer system software enabled for it. Functionality, performance or other benefits will vary
depending on hardware and software configur ations and may re quire a BIOS update. S oftware applicatio ns may not be compatible
with all operating systems. Please check with your application vendor.
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology requires a PC with a processor with Intel Turbo Boost Technology capability. Intel Turbo Boost
Technology performance varies depending on hardware, software and overall system configuration. Check with your PC
manufacturer on whether your system delivers Intel Turbo Boost Technology. For more information, see
http://www.intel.com/technology/turboboost/.
64-bit computing on Intel architecture requires a computer system with a processor, chipset, BIOS, operating system, device
drivers and applications enabled for Intel® 64 architecture. Performance will vary depending on your hardware and software
configurations. Consult with your system vendor for more information.
Δ Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor
family, not across different processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor%5Fnumber/ for details.
2
C is a two-wire communications bus/protocol developed by Philips. SMBus is a subset of the I2C bus/protocol and was developed
I
by Intel. Implementations of the I
North American Philips Corporation.
2
C bus/protocol may require licenses from various entities, including Philips Electronics N.V. and
Intel, Xeon, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology, and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U. S. and/or
other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2009-2013, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
2 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 3

Table of Contents
1Overview.................................................................................................................11
1.1 Introduction .....................................................................................................11
1.1.1 Processor Feature Details ........................................................................14
1.1.2 Supported Technologies..........................................................................14
1.2 Interfaces ........................................................................................................14
1.2.1 System Memory Support.........................................................................14
1.2.2 PCI Express*.........................................................................................16
1.2.3 Direct Media Interface Gen 2 (DMI2).........................................................17
1.2.4 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI) ..............................................18
1.2.5 Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI)...........................................18
1.3 Power Management Support...............................................................................19
1.3.1 Processor Package and Core States...........................................................19
1.3.2 System States Support ...........................................................................19
1.3.3 Memory Controller.................................................................... .. ............19
1.3.4 PCI Express*.........................................................................................19
1.3.5 Intel® QPI ............................................................................................19
1.4 Thermal Management Support ............................................................................19
1.5 Package Summary.............................................................................................19
1.6 Terminology .....................................................................................................20
1.7 Related Documents ...........................................................................................22
1.8 Statement of Volatility (SOV)..............................................................................23
1.9 State of Data....................................................................................................23
2Interfaces................................................................................................................25
2.1 System Memory Interface ..................................................................................25
2.1.1 System Memory Technology Support ................ .. .. ... .. ...............................25
2.1.2 System Memory Timing Support...................................... .. .......................25
2.2 PCI Express* Interface.......................................................................................26
2.2.1 PCI Express* Architecture .......................................................................26
2.2.2 PCI Express* Configuration Mechanism .....................................................27
2.3 DMI2/PCI Express* Interface..............................................................................28
2.3.1 DMI2 Error Flow.....................................................................................28
2.3.2 Processor/PCH Compatibility Assumptions..................................................28
2.3.3 DMI2 Link Down.....................................................................................28
2.4 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI) .........................................................28
2.5 Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI)......................................................29
2.5.1 PECI Client Capabilities ...........................................................................30
2.5.2 Client Command Suite ................... .. ... ........................... .........................31
2.5.3 Client Management............................................................................. ....68
2.5.4 Multi-Domain Commands ........................................................................73
2.5.5 Client Responses............................................................. .. .....................74
2.5.6 Originator Responses..............................................................................75
2.5.7 DTS Temperature Data ...........................................................................75
3 Technologies ...........................................................................................................77
3.1 Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) ........................................................77
3.1.1 Intel® VT-x Objectives ...........................................................................77
3.1.2 Intel® VT-x Features..............................................................................78
3.1.3 Intel® VT-d Objectives ...........................................................................78
3.1.4 Intel® Virtualization Technology Processor Extensions ................................79
3.2 Security Technologies........................................................................................79
3.2.1 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology........................................................79
3.2.2 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology – Server Extensions...........................80
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 3
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 4

3.2.3 AES Instructions.....................................................................................80
3.2.4 Execute Disable Bit.................................................................................81
3.3 Intel® Secure Key............................ .. ...............................................................81
3.4 Intel® OS Guard ........... .. ........................... .......................................................81
3.5 Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology................................................................... ..81
3.6 Intel® Turbo Boost Technology .................. .. ............................ .. .. .......................82
3.6.1 Intel® Turbo Boost Operating Frequency....................................... .. .. .. .. ....82
3.7 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology...............................................................82
3.8 Intel® Intelligent Power Technology.....................................................................83
3.9 Intel® Advanced Vector Extensions (Intel® AVX) ................... ........................... ....83
3.10 Intel® Dynamic Power Technology.......................................................................84
4 Power Management .................................................................................................85
4.1 ACPI States Supported.......................................................................................85
4.1.1 System States........................................ .. .. ............................................85
4.1.2 Processor Package and Core States...........................................................85
4.1.3 Integrated Memory Controller States..................................................... .. ..86
4.1.4 DMI2/PCI Express* Link States......................... ............................ .. ..........87
4.1.5 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect States........................................................87
4.1.6 G, S, and C State Combinations................................................................87
4.2 Processor Core/Package Power Management .........................................................88
4.2.1 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology....................................................88
4.2.2 Low-Power Idle States.............................................................................88
4.2.3 Requesting Low-Power Idle States .................. .. .. .. ............................ .. .. ....89
4.2.4 Core C-states.........................................................................................90
4.2.5 Package C-States ...................................................................................91
4.2.6 Package C-State Power Specifications........................................................95
4.2.7 Processor Package Power Specifications.....................................................95
4.3 System Memory Power Management....................................................................96
4.3.1 CKE Power-Down........................... .......................... .. .. ...........................96
4.3.2 Self Refresh...........................................................................................97
4.3.3 DRAM I/O Power Management..................................................................97
4.4 DMI2/PCI Express* Power Management............................................. .. .. ... ............98
5 Thermal Management Specifications........................................................................99
5.1 Package Thermal Specifications ...........................................................................99
5.1.1 Thermal Specifications........................... .. ........................... .. .. .................99
5.1.2 TCASE and DTS Based Thermal Specifications...........................................101
5.1.3 Processor Operational Thermal Specifications ...........................................102
5.1.4 Embedded Server Thermal Profiles..........................................................106
5.1.5 Thermal Metrology................................ .. .. ........................... .. ...............109
5.2 Processor Core Thermal Features.......................................................................110
5.2.1 Processor Temperature..........................................................................110
5.2.2 Adaptive Thermal Monitor...................... ........................... .....................110
5.2.3 On-Demand Mode.................................................................................112
5.2.4 PROCHOT_N Signal...............................................................................113
5.2.5 THERMTRIP_N Signal ............................................................................113
5.2.6 Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) Thermal Features...............................114
6 Signal Descriptions ................................................................................................117
6.1 System Memory Interface Signals......................................................................117
6.2 PCI Express* Based Interface Signals.................................................................118
6.3 DMI2/PCI Express* Port 0 Signals................................................... .. .................120
6.4 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect Signals ...............................................................120
6.5 PECI Signal.....................................................................................................121
6.6 System Reference Clock Signals ........................................................................121
6.7 JTAG and TAP Signals.......................................................................................121
6.8 Serial VID Interface (SVID) Signals....................................................................122
4 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 5

6.9 Processor Asynchronous Sideband and Miscellaneous Signals................................ 122
6.10 Processor Power and Ground Supplies................................................................ 125
7 Electrical Specifications......................................................................................... 127
7.1 Processor Signaling ......................................................................................... 127
7.1.1 System Memory Interface Signal Groups ................................................. 127
7.1.2 PCI Express Signals.............................................................................. 127
7.1.3 DMI2/PCI Express Signals ..................................................................... 127
7.1.4 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect............................................................... 127
7.1.5 Platform Environmental Control Interface (PECI) ...................................... 128
7.1.6 System Reference Clocks (BCLK{0/1}_DP, BCLK{0/1}_DN)....................... 128
7.1.7 JTAG and Test Access Port (TAP) Signals ............................................. .. .. 129
7.1.8 Processor Sideband Signals ................................................................... 129
7.1.9 Power, Ground and Sense Signals........................................................... 129
7.1.10 Reserved or Unused Signals................................................................... 134
7.2 Signal Group Summary............................... ............................ .. ....................... 134
7.3 Power-On Configuration (POC) Options............................................................... 138
7.4 Fault Resilient Booting (FRB)............................................................................. 138
7.5 Mixing Processors............................................................................................ 139
7.6 Flexible Motherboard Guidelines (FMB)............................. ... ............................... 140
7.7 Absolute Maximum and Minimum Ratings ........................................................... 140
7.7.1 Storage Condition Specifications............................................................. 140
7.8 DC Specifications ............................................................................................ 141
7.8.1 Voltage and Current Specifications.......................................................... 141
7.8.2 Die Voltage Validation................................... .. .. .. ............................ .. .. .. 146
7.8.3 Signal DC Specifications................................................... .. .. .. ............... 147
7.9 Signal Quality...................................... ............................ ........................... .... 154
7.9.1 DDR3 Signal Quality Specifications ......................................................... 154
7.9.2 I/O Signal Quality Specifications............................................................. 154
7.9.3 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect Signal Quality Specifications....................... 154
7.9.4 Input Reference Clock Signal Quality Specifications................................... 154
7.9.5 Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance............................................................ 155
8 Processor Land Listing........................................................................................... 159
8.1 Listing by Land Name ............................... ............................ ........................... 159
8.2 Listing by Land Number .............................. ... .................................................. 183
9 Package Mechanical Specifications ........................................................................ 209
9.1 Package Size and SKUs....................... ..................................................... ........ 209
9.2 Package Mechanical Drawing (PMD)............................................ .. .. .. ................. 210
9.3 Processor Component Keep-Out Zones........................... .................................... 215
9.4 Package Loading Specifications .................... ... .. .. ........................... .. .. ... ............ 215
9.5 Package Handling Guidelines............................. .. ........................... .. .. ............... 215
9.6 Package Insertion Specifications................................................... .. .. .. ............... 215
9.7 Processor Mass Specification............................................................................. 216
9.8 Processor Materials.......................................................................................... 216
9.9 Processor Markings.......................................................................................... 216
10 Boxed Processor Specifications ............................................................................. 217
10.1 Introduction ................................................................................................... 217
10.1.1 Available Boxed Thermal Solution Configurations...................................... 217
10.1.2 Intel Thermal Solution STS200C
(Passive/Active Combination Heat Sink Solution)...................................... 217
10.1.3 Intel Thermal Solution STS200P and STS200PNRW
(Boxed 25.5 mm Tall Passive Heat Sink Solutions).................................... 218
10.2 Mechanical Specifications ................................................................................. 219
10.2.1 Boxed Processor Heat Sink Dimensions and Baseboard Keepout Zones ........ 219
10.2.2 Boxed Processor Retention Mechanism and Heat Sink Support (ILM-RS) ...... 228
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 5
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 6

10.3 Fan Power Supply [STS200C]................ ............................................................228
10.3.1 Boxed Processor Cooling Requirements....................................................229
10.4 Boxed Processor Contents.................................................................................232
Figures
1-1 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2 Product Family on the 1 Socket
Platform ...........................................................................................................13
1-2 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-2600 v2 Product Family on the 2 Socket
Platform ............................................. .. ................................................... .. .. ....13
1-3 PCI Express* Lane Partitioning and Direct Media Interface Gen 2 (DMI2)...................17
2-1 PCI Express* Layering Diagram...........................................................................26
2-2 Packet Flow through the Layers...........................................................................27
2-3 Ping() ..............................................................................................................31
2-4 Ping() Example..................................................................................................31
2-5 GetDIB() ..........................................................................................................32
2-6 Device Info Field Definition .................................................................................32
2-7 Revision Number Definition.................................................................................33
2-8 GetTemp()........................................................................................................34
2-9 GetTemp() Example.................................... .. ... ..................................................34
2-10 RdPkgConfig()...................................................................................................35
2-11 WrPkgConfig()...................................................................................................37
2-12 DRAM Thermal Estimation Configuration Data........................................................40
2-13 DRAM Rank Temperature Write Data....................................................................41
2-14 The Processor DIMM Temperature Read / Write .....................................................41
2-15 Ambient Temperature Reference Data ..................................................................42
2-16 Processor DRAM Channel Temperature .................................................................42
2-17 Accumulated DRAM Energy Data..........................................................................43
2-18 DRAM Power Info Read Data ...............................................................................44
2-19 DRAM Power Limit Data.............................................. ............................ ............45
2-20 DRAM Power Limit Performance Data................................................... .. ... .. ..........45
2-21 CPUID Data ......................................................................................................49
2-22 Platform ID Data ...............................................................................................49
2-23 PCU Device ID...................................................................................................49
2-24 Maximum Thread ID...........................................................................................49
2-25 Processor Microcode Revision ..............................................................................50
2-26 Machine Check Status ........................................................................................50
2-27 Package Power SKU Unit Data .............................................................................50
2-28 Package Power SKU Data....................................................................................51
2-29 Package Temperature Read Data .........................................................................52
2-30 Temperature Target Read...................................................................................53
2-31 Thermal Status Word ............................ .. .. ............................ .. ...........................53
2-32 Thermal Averaging Constant Write / Read.............................................................54
2-33 Current Config Limit Read Data ...........................................................................54
2-34 Accumulated Energy Read Data...........................................................................55
2-35 Power Limit Data for VCC Power Plane......................................... .. .......................56
2-36 Package Turbo Power Limit Data..........................................................................57
2-37 Package Power Limit Performance Data ................................................................57
2-38 Efficient Performance Indicator Read ....................................................................58
2-39 ACPI P-T Notify Data..........................................................................................58
2-40 Caching Agent TOR Read Data.............................................................................59
2-41 DTS Thermal Margin Read.............................. ............................ .. .. .....................59
6 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 7

2-42 Processor ID Construction Example......................................................................60
2-43 RdIAMSR().......................................................................................................61
2-44 PCI Configuration Address..................................................................................63
2-45 RdPCIConfig()...................................................................................................64
2-46 PCI Configuration Address for local accesses.........................................................65
2-47 RdPCIConfigLocal()............................................................................................65
2-48 WrPCIConfigLocal() ...........................................................................................67
2-49 The Processor PECI Power-up Timeline() ..............................................................69
2-50 Temperature Sensor Data Format........................................................................75
4-1 Idle Power Management Breakdown of the Processor Cores.....................................89
4-2 Thread and Core C-State Entry and Exit ...............................................................89
4-3 Package C-State Entry and Exit.......................................... ........................... .. .. ..93
5-1 TCase Temperature Thermal Profile .......... .. .. ..................................................... 104
5-2 Digital Thermal Sensor DTS Thermal Profile ........................................................ 106
5-3 Embedded Case Temperature Thermal Profile...................................................... 108
5-4 Embedded DTS Thermal Profile ......................................................................... 109
5-5 Case Temperature (TCASE) Measurement Location.................................. .. .. .. ...... 110
5-6 Frequency and Voltage Ordering........................................................................ 112
7-1 Input Device Hysteresis ................................................................................... 128
7-2 VR Power-State Transitions............................................................................... 132
7-3 Processor VCC Static and Transient Tolerance Loadlines ....................................... 145
7-4 Load Current Versus Time ................. .. ........................... ... ........................... .. .. 146
7-5 VCC Overshoot Example Waveform.................................................................... 147
7-6 BCLK{0/1} Differential Clock Crosspoint Specification .......................................... 153
7-7 BCLK{0/1} Differential Clock Measurement Point for Ringback .............................. 153
7-8 BCLK{0/1} Single Ended Clock Measurement Points for Absolute Cross Point
and Swing...................................................................................................... 153
7-9 Maximum Acceptable Overshoot/Undershoot Waveform........................................ 157
9-1 Processor Package Assembly Sketch .................................................................. 209
9-2 Processor PMD Package A (52.5 x 45 mm) Sheet 1 of 2........................................ 211
9-3 Processor PMD Package A (52.5 x 45 mm) Sheet 2 of 2........................................ 212
9-4 Processor PMD Package B (52.5 x 51 mm) Sheet 1 of 2........................................ 213
9-5 Processor PMD Package B (52.5 x 51 mm) Sheet 2 of 2........................................ 214
9-6 Processor Top-Side Markings ........................................................................... 216
10-1 STS200C Passive/Active Combination Heat Sink (with Removable Fan)................... 218
10-2 STS200C Passive/Active Combination Heat Sink (with Fan Removed) ..................... 218
10-3 STS200P and STS200PNRW 25.5 mm Tall Passive Heat Sinks................................ 219
10-4 Boxed Processor Motherboard Keepout Zones (1 of 4).......................................... 220
10-5 Boxed Processor Motherboard Keepout Zones (2 of 4).......................................... 221
10-6 Boxed Processor Motherboard Keepout Zones (3 of 4).......................................... 222
10-7 Boxed Processor Motherboard Keepout Zones (4 of 4).......................................... 223
10-8 Boxed Processor Heat Sink Volumetric (1 of 2).................................................... 224
10-9 Boxed Processor Heat Sink Volumetric (2 of 2).................................................... 225
10-10 4-Pin Fan Cable Connector (For Active Heat Sink)................................................ 226
10-11 4-Pin Base Baseboard Fan Header (For Active Heat Sink)...................................... 227
10-12 Fan Cable Connector Pin Out For 4-Pin Active Thermal Solution ............................. 229
Tables
1-1 HCC, MCC, and LCC SKU Table Summary .............................................................11
1-2 Volume Structure and Scope...............................................................................12
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 7
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 8

1-3 Referenced Documents.......................................................................................22
2-1 Summary of Processor-specific PECI Commands ....................................................30
2-2 Minor Revision Number Meaning..........................................................................33
2-3 GetTemp() Response Definition .................. ............................ .. .. .. .......................34
2-4 RdPkgConfig() Response Definition............ .. .. ............................ .. .. .......................35
2-5 WrPkgConfig() Response Definition ......................................................................37
2-6 RdPkgConfig() & WrPkgConfig() DRAM Thermal and Power Optimization
Services Summary.............................................................................................38
2-7 Channel & DIMM Index Decoding.........................................................................40
2-8 RdPkgConfig() & WrPkgConfig() CPU Thermal and Power Optimization
Services Summary.............................................................................................46
2-9 Power Control Register Unit Calculations...............................................................50
2-10 RdIAMSR() Response Definition ...........................................................................61
2-11 RdIAMSR() Services Summary12.........................................................................62
2-12 RdPCIConfig() Response Definition.......................................................................64
2-13 RdPCIConfigLocal() Response Definition................................................................66
2-14 WrPCIConfigLocal() Response Definition................................................................67
2-15 WrPCIConfigLocal() Memory Controller and IIO Device/Function Support...................68
2-16 PECI Client Response During Power-Up.................................................................69
2-17 SOCKET ID Strapping.........................................................................................70
2-18 Power Impact of PECI Commands vs. C-states.......................................................70
2-19 Domain ID Definition........................................................................... ... ............73
2-20 Multi-Domain Command Code Reference...............................................................73
2-21 Completion Code Pass/Fail Mask..........................................................................74
2-22 Device Specific Completion Code (CC) Definition....................................................74
2-23 Originator Response Guidelines................... .. .......................................................75
2-24 Error Codes and Descriptions...............................................................................76
4-1 System States........................................................................................... ........85
4-2 Package C-State Support....................................................................................85
4-3 Core C-State Support.........................................................................................86
4-4 System Memory Power States .............................................................................86
4-5 DMI2/PCI Express* Link States................... .. .. ... ........................... .......................87
4-6 Intel® QPI States..............................................................................................87
4-7 G, S and C State Combinations............................................................................87
4-8 P_LVLx to MWAIT Conversion..............................................................................90
4-9 Coordination of Core Power States at the Package Level..........................................92
4-10 Package C-State Power Specifications...................................................................95
4-11 Processor Package Power Pmax ...........................................................................95
5-1 TCase Temperature Thermal Specifications..........................................................103
5-2 Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) Specification Summary...........................................104
5-3 Embedded TCase Temperature Thermal Specifications..........................................107
5-4 Embedded DTS Thermal Specifications ........................................ .. .....................109
6-1 Memory Channel DDR0, DDR1, DDR2, DDR3.......................................................117
6-2 Memory Channel Miscellaneous..........................................................................118
6-3 PCI Express* Port 1 Signals ..............................................................................118
6-4 PCI Express* Port 2 Signals ..............................................................................118
6-5 PCI Express* Port 3 Signals ..............................................................................119
6-6 PCI Express* Miscellaneous Signals....................................................................119
6-7 DMI2 and PCI Express Port 0 Signals..................................................................120
6-8 Intel QPI Port 0 and 1 Signals................. .. .........................................................120
6-9 Intel QPI Miscellaneous Signals..........................................................................120
6-10 PECI Signals ...................................................................................................121
8 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 9

6-11 System Reference Clock (BCLK{0/1}) Signals ..................................................... 121
6-12 JTAG and TAP Signals ................................................ .. ............................ ........ 121
6-13 SVID Signals .................................................................................................. 122
6-14 Processor Asynchronous Sideband Signals.......................................................... 122
6-15 Miscellaneous Signals ................................. ............................ ......................... 125
6-16 Power and Ground Signals................................................................................ 125
7-1 Power and Ground Lands.................................................................................. 129
7-2 SVID Address Usage........................................................................................ 132
7-3 VR12.0 Reference Code Voltage Identification (VID)............................................. 133
7-4 Signal Description Buffer Types......................................................................... 134
7-5 Signal Groups..................... .. ... ....................................................................... 135
7-6 Signals with On-Die Termination ................................... .. ... .. .. ........................... 137
7-7 Power-On Configuration Option Lands................................................................ 138
7-8 Fault Resilient Booting (Output Tri-State) Signals ................................................ 139
7-9 Processor Absolute Minimum and Maximum Ratings............................................. 140
7-10 Storage Condition Ratings ................................................................................ 141
7-11 Voltage Specification........................................................................................ 141
7-12 Processor Current Specifications........................................................................ 143
7-13 Processor VCC Static and Transient Tolerance ..................................................... 144
7-14 VCC Overshoot Specifications............................................................................ 146
7-15 DDR3 and DDR3L Signal DC Specifications.......................................................... 147
7-16 PECI DC Specifications..................................................................................... 149
7-17 System Reference Clock (BCLK{0/1}) DC Specifications ....................................... 149
7-18 SMBus DC Specifications .................................................................................. 150
7-19 JTAG and TAP Signals DC Specifications ............................................................. 150
7-20 Serial VID Interface (SVID) DC Specifications...................................................... 150
7-21 Processor Asynchronous Sideband DC Specifications ............................................ 151
7-22 Miscellaneous Signals DC Specifications.............................................................. 152
7-23 Processor I/O Overshoot/Undershoot Specifications ............................................. 155
7-24 Processor Sideband Signal Group Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance........................ 157
8-1 Land Name..................................................................................................... 159
8-2 Land Number.................................................................................................. 183
9-1 Processor Package Sizes................................................................................... 210
9-2 Processor Loading Specifications ....................................................................... 215
9-3 Package Handling Guidelines........................ ... .. ........................... .. .. ................. 215
9-4 Processor Materials.......................................................................................... 216
10-1 PWM Fan Frequency Specifications For 4-Pin Active Thermal Solution..................... 228
10-2 PWM Fan Characteristics for Active Thermal Solution............................................ 228
10-3 PWM Fan Connector Pin and Wire Description...................................................... 229
10-4 Server Thermal Solution Boundary Conditions ..................................................... 230
§
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 9
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 10

Revision History
Revision
Number
001 • Initial Release September 2013
Description Revision Date
§
10 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 11
Overview
1 Overview
1.1 Introduction
The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families datasheetVolume One provides DC electrical specifications, signal integrity, differential signaling
specifications, land and signal definitions, and an overview of additional processor
feature interfaces.
This document is intended to be distributed as a part of the complete document which
consists of two volumes. The structure and scope of the two volumes are provided in
Table 1-2.
The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families are the next
generation of 64-bit, multi-core enterprise processors built on 22-nanometer process
technology. Throughout this document, the Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E52600 v2 product families may be referred to as simply the processor. Where
information differs between the EP SKUs, this document uses specific Intel® Xeon®
processor E5-1600 v2 product family and Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600 v2 product
family notation. Based on the low-power/high performance 3rd Generation Intel®
Core™ Processor Family microarchitecture, the processor is designed for a two-chip
platform as opposed to the traditional three-chip platforms (processor, MCH, and ICH).
The two-chip platform consists of a processor and the Platform Controller Hub (PCH)
and enables higher performance, easier validation, and improved x-y footprint.
This generation of processor introduces the High-Core count (HCC), Mid-Core count
(MCC), and Low-Core count (LCC) die size terminology to the SKU models. The table
below summarizes the die size associated with the processor TDP, Model Number, and
Core Count.
Table 1-1. HCC, MCC, and LCC SKU Table Summary
Die Size TDP (W) Model Number Core Count
High-Core Count 130W 1U E5-2697 v2 12
115W 1U E5-2695 v2 12
Mid-Core Count 150W WS E5-2687W v2 8
130W 1U E5-2690 v2 10
130W 2U E5-2687W v2
130W 2U E5-2643 v2 6
115W 1U E5-2680 v2
95W 1U E5-2660 v2 10
95W 1U E5-2650 v2
70W 1U E5-2650L v2 10
8
E5-2667 v2
10
E5-2670 v2
8
E5-2640 v2
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 11
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 12
Table 1-1. HCC, MCC, and LCC SKU Table Summary
Die Size TDP (W) Model Number Core Count
Low-Core Count 130W 2U E5-2637 v2 4
130W 1S E5-1660 v2
130W 1S E5-1620 v2 4
95W 1U E5-2630 v2 6
80W 1U E5-2630 v2
80W 1U E5-2609 v2
60W 1U E5-2630L v2 6
Some processor features are not available on all platforms. Refer to the Intel® Xeon®
Processor E5 v2 Product Family Specification Update for details of each processor SKU.
The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families support these
segments.
• The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2 product family is designed for single
processor Workstation platforms only.
• The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600 v2 product family is designed for dual
processor Workstation, Efficient Performance server and HPC platforms.
Overview
6
E5-1650 v2
6
E5-2620 v2
4
E5-2603 v2
These processors feature per socket, two Intel® QuickPath Interconnect point-to-point
links capable of up to 8.0 GT/s, up to 40 lanes of PCI Express* 3.0 links capable of
8.0 GT/s, and 4 lanes of DMI2/PCI Express* 2.0 interface with a peak transfer rate of
5.0 GT/s. The processor supports up to 46 bits of physical address space and 48-bit of
virtual address space.
Included in this family of processors is an integrated memory controller (IMC) and
integrated I/O (IIO) (such as PCI Express* and DMI2) on a single silicon die. This single
die solution is known as a monolithic processor.
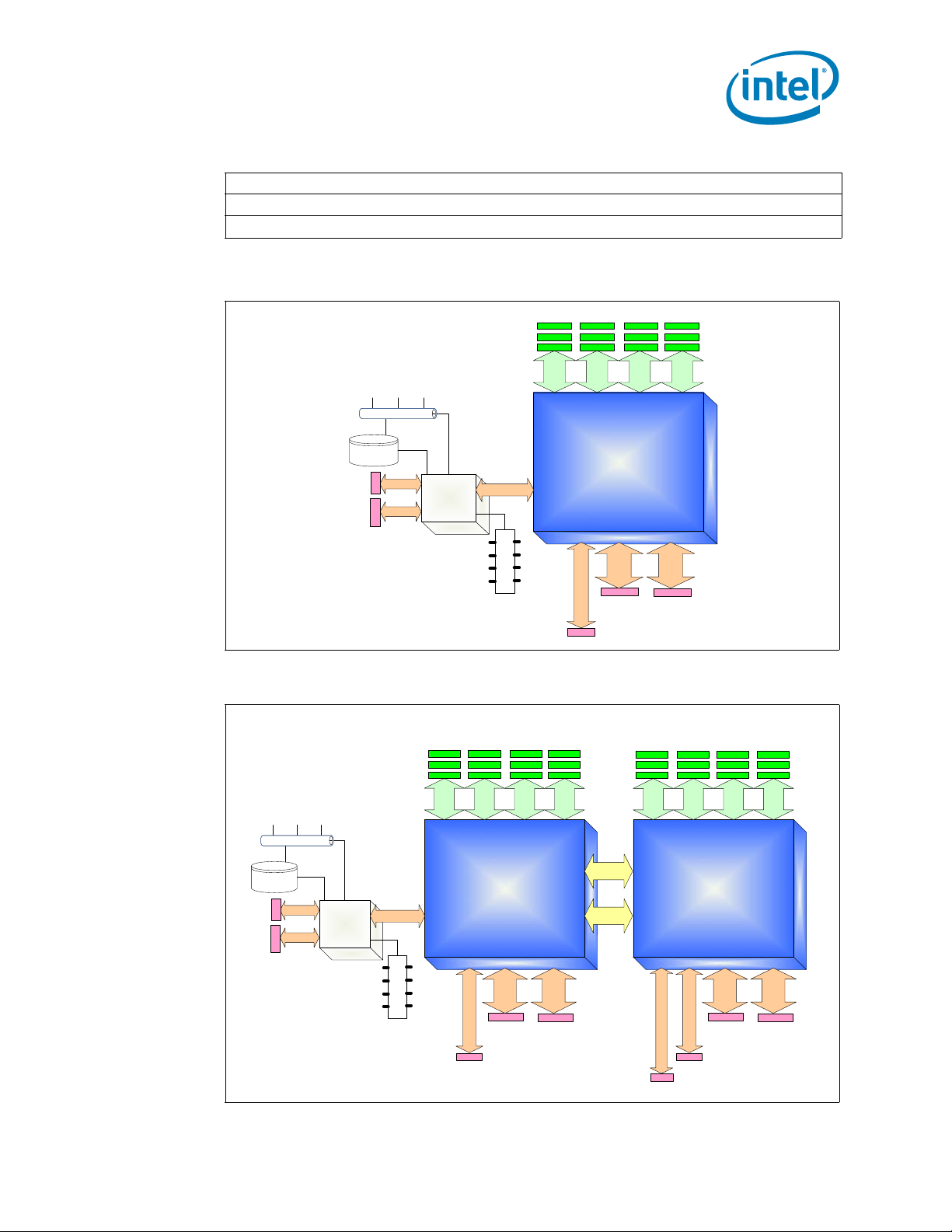
Figure 1-1 shows the processor 2-socket platform configuration. The “Legacy CPU” is
the boot processor that is connected to the PCH component, this socket is set to
NodeID[0].
Table 1-2. Volume Structure and Scope (Sheet 1 of 2)
Volume 1: Electrical, Mechanical and Thermal Specification
•Overview
•Interfaces
• Technologies
• Power Management
• Thermal Management Specifications
• Signal Descriptions
• Electrical Specifications
• Processor Land L isting
• Package Mechanical Specifications
• Boxed Processor Specifications
Volume 2: Register Information
12 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 13
x8
Processor
“Legacy”
DDR3
DDR3
DDR3
DDR3
PCH
DMI2
PCIe
PCIe
.
.
.
SATA
ethernet
B
I
O
S
x4
x1
PCIe
x16
PCIe
x16
PCIe
x8
Processor
“Legacy”
DDR3
DDR3
DDR3
DDR3
QPI
QPI
PCH
DMI2
PCIe
PCIe
...
SATA
ethernet
B
I
O
S
x4
x1
Processor
“Peer”
DDR3
DDR3
DDR3
DDR3
PCIe
x16
PCIe
x16
PCIe
x16
DMI2/PCIe
x4
PCIe
x8
PCIe
x16
PCIe
Overview
Table 1-2. Volume Structure and Scope (Sheet 2 of 2)
• Configuration Process and Registers
• Processor Integrated I/O (IIO) Configuration Registers
• Processor Uncore Configuration Registers
Figure 1-1. Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2 Product Family on the 1 Socket
Platform
Figure 1-2. Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-2600 v2 Product Family on the 2 Socket
Platform
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 13
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 14

1.1.1 Processor Feature Details
• Up to 12 execution cores
• Each core supports two threads (Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology), up to 24
threads per socket
• 46-bit physical addressing and 48-bit virtual addressing
• 1 GB large page support for server applications
• A 32-KB instruction and 32-KB data first-level cache (L1) for each core
• A 256-KB shared instruction/data mid-level (L2) cache for each core
•Up to 30 MB last level cache (LLC): up to 2.5 MB per core instruction/data last level
cache (LLC), shared among all cores
1.1.2 Supported Technologies
• Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT)
• Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)
• APIC Virtualization (APICv)
• Intel® Virtualization Technology Processor Extensions
• Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT)
• Intel® 64 Architecture
•Intel® Streaming SIMD Extensions 4.1 (Intel® SSE4.1)
•Intel® Streaming SIMD Extensions 4.2 (Intel® SSE4.2)
• Intel® Advanced Vector Extensions (Intel® AVX)
• Intel® AVX Floating Point Bit Depth Conversion (Float 16)
• Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology
• Execute Disable Bit
• Intel® Turbo Boost Technology
• Intel® Intelligent Power Technology
• Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
• Intel® Dynamic Power Technology (Memory Power Management)
• Intel® Secure Key, formerly known as Digital Random Number Generator (DRNG)
• Intel® OS Guard, formerly known as Supervisor Mode Execution Protection Bit
(SMEP)
Overview
1.2 Interfaces
1.2.1 System Memory Support
• Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families supports 4 DDR3
channels
• Unbuffered DDR3 and registered DDR3 DIMMs
• LR DIMM (Load Reduced DIMM) for buffered memory solutions demanding higher
capacity memory subsystems
14 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 15

Overview
• Independent channel mode or lockstep mode
• Data burst length of eight cycles for all memory organization modes
• Memory DDR3 data transfer rates of 800, 1066, 1333, 1600, and 1866 MT/s
• 64-bit wide channels plus 8-bits of ECC support for each channel
• DDR3 standard I/O Voltage of 1.5 V and DDR3 Low Voltage of 1.35 V
• 1-GB, 2-GB, and 4-GB DDR3 DRAM technologies supported for these devices:
— UDIMMs x8, x16
— RDIMMs x4, x8
— LRDIMM x4, x8 (2-Gb and 4-Gb only) LR-DIMMs are supported only on server
specific SKUs (Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product
families). LR-DIMMs are not supported in workstation specific SKUs such as the
Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2 product family.
• Up to 8 ranks supported per memory channel: 1, 2 or 4 ranks per DIMM
• Open with adaptive idle page close timer or closed page policy
• Per channel memory test and initialization engine can initialize DRAM to all logical
zeros with valid ECC (with or without data scrambler) or a predefined test pattern
• Isochronous access support is not available on any CPU model containing two home
agents.
• Minimum memory configuration: independent channel support with 1 DIMM
populated
• Integrated dual SMBus master controllers
• Command launch modes of 1n/2n
• RAS Support (including and not limited to):
Note: RAS support depends on processor SKU. For example, Workstation SKUs do
not support sparing or tagging, lockstep mode, mirroring mode, channel
mirroring mode within a socket, error containment.
— Rank Level Sparing and Device Tagging
— Demand and Patrol Scrubbing
— DRAM Single Device Data Correction (SDDC) for any single x4 or x8 DRAM
device failure. Independent channel mode supports x4 SDDC. x8 SDDC
requires lockstep mode
— Lockstep mode where channels 0 & 1 and channels 2 & 3 are operated in
lockstep mode
— The combination of memory channel pair lockstep and memory mirroring is not
supported
— Data scrambling with address to ease detection of write errors to an incorrect
address.
— Error reporting via Machine Check Architecture
— Read Retry during CRC error handling checks by iMC
— Channel mirroring within a socket
— Channel Mirroring mode is supported on memory channels 0 & 1 and channels
2 & 3
— Error Containment Recovery
• Improved Thermal Throttling with dynamic Closed Loop Thermal Throttling (CLTT)
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 15
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 16

• Memory thermal monitoring support for DIMM temperature via two memory
signals, MEM_HOT_C{01/23}_N
1.2.2 PCI Express*
• The PCI Express* port(s) are fully-compliant to the PCI Express* Base
Specification, Revision 3.0 (PCIe 3.0)
• Support for PCI Express* 3.0 (8.0 GT/s), 2.0 (5.0 GT/s), and 1.0 (2.5 GT/s)
• Up to 40 lanes of PCI Express* interconnect for general purpose PCI Express*
devices at PCIe* 3.0 speeds that are configurable for up to 10 independent ports
• 4 lanes of PCI Express* at PCIe* 2.0 speeds when not using DMI2 port (Port 0),
also can be downgraded to x2 or x1
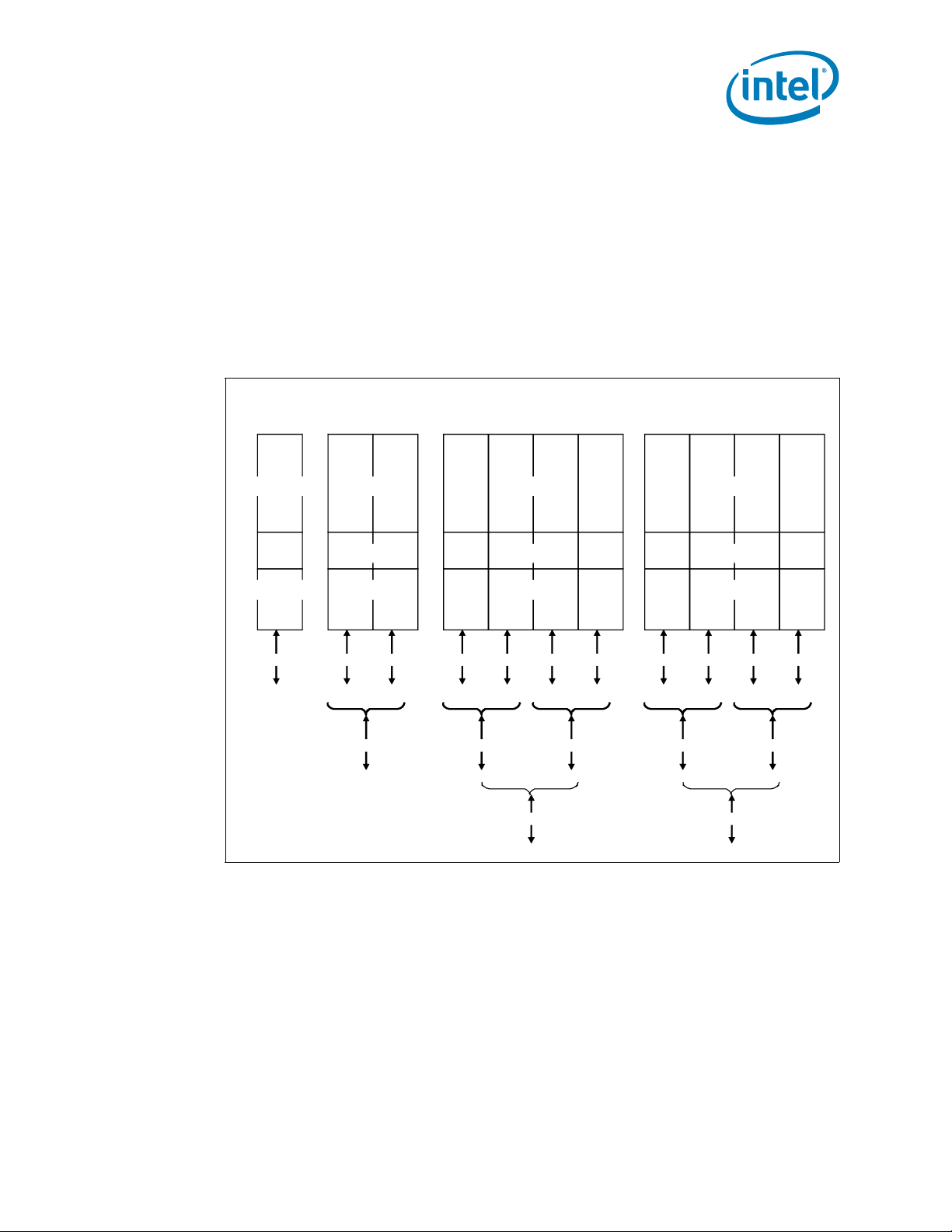
• Negotiating down to narrower widths is supported, see Figure 1-3:
— x16 port (Port 2 & Port 3) may negotiate down to x8, x4, x2, or x1.
— x8 port (Port 1) may negotiate down to x4, x2, or x1.
— x4 port (Port 0) may negotiate down to x2, or x1.
— When negotiating down to narrower widths, there are caveats as to how lane
reversal is supported.
• Non-Transparent Bridge (NTB) is supported by PCIe Port3a/IOU1. For more details
on NTB mode operation refer to PCI Express Base Specification - Revision 3.0:
— x4, x8 or x16 widths and at PCIe* 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 speeds
— Two usage models; NTB attached to a Root Port or NTB attached to another
NTB
— Supports three 64-bit BARs
— Supports posted writes and non-posted memory read transactions across the
NTB
— Supports INTx, MSI and MSI-X mechanisms for interrupts on both side of NTB
in upstream direction only
• Address Translation Services (ATS) 1.0 support
• Hierarchical PCI-compliant configuration mechanism for downstream devices.
• Traditional PCI style traffic (asynchronous snooped, PCI ordering).
• PCI Express* extended configuration space. The first 256 bytes of configuration
space aliases directly to the PCI compatibility configuration space. The remaining
portion of the fixed 4-KB block of memory-mapped space above that (starting at
100h) is known as extended configuration space.
• PCI Express* Enhanced Access Mechanism. Accessing the device configuration
space in a flat memory mapped fashion.
• Automatic discovery, negotiation, and training of link out of reset.
• Supports receiving and decoding 64 bits of address from PCI Express*.
— Memory transactions received from PCI Express* that go above the top of
physical address space (when Intel VT -d is enabled, the check would be against
the translated HPA (Host Physical Address) address) are reported as errors by
the processor.
— Outbound access to PCI Express* will always have address bits 63 to 46
cleared.
• Re-issues Configuration cycles that have been previously completed with the
Configuration Retry status.
Overview
16 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 17
Transaction
Link
Physical
0…3
X4
DMI
Port 0
DM I / PCIe
4…7
X4
Port 1b
Transaction
Link
Physical
0…3
X4
Port 1a
Port 1
(IOU2)
PCIe
X8
Port 1a
8…11
Transaction
Link
Physical
0…3
Port 2
(IOU0)
PCIe
X4
Port 2b
X4
Port 2a
X8
Port 2a
X4
Port 2d
X4
Port 2c
X8
Port 2c
X16
Port 2a
12..154…7 8…11
Transaction
Link
Physical
0…3
Port 3
(IOU1)
PCIe
X4
Port 3b
X4
Port 3a
X8
Port 3a
X4
Port 3d
X4
Port 3c
X8
Port 3c
X16
Port 3a
12..154…7
Overview
• Power Management Event (PME) functions.
• Message Signaled Interrupt (MSI and MSI-X) messages
• Degraded Mode support and Lane Reversal support
• Static lane numbering reversal and polarity inversion support
• Support for PCIe* 3.0 atomic operation, PCIe 3.0 optional extension on atomic
read-modify-write mechanism
• Additional read buffers for point-point transfers. This increases the number of
outstanding transactions in point-point transfers across same processor sockets,
from previous generation of 16 to 64 in this generation.
Figure 1-3. PCI Express* Lane Partitioning and Direct Media Interface Gen 2 (DMI2)
1.2.3 Direct Media Interface Gen 2 (DMI2)
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 17
Datasheet Volume One of Two
• Serves as the chip-to-chip interface to the Intel® C600 Chipset
• The DMI2 port supports x4 link width and only operates in a x4 mode when in DMI2
• Operates at PCI Express* 1.0 or 2.0 speeds
• Transparent to software
• Processor and peer-to-peer writes and reads with 64-bit address support
• APIC and Message Signaled Interrupt (MSI) support. Will send Intel-defined “End of
Interrupt” broadcast message when initiated by the processor.
• Downstream System Management Interrupt (SMI), SCI, and SERR error indication
Page 18

• Static lane numbering reversal support
• Supports DMI2 virtual channels VC0, VC1, VCm, and VCp
1.2.4 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI)
• Compliant with Intel QuickPath Interconnect v1.1 standard packet formats
• Implements two full width Intel QPI ports
• Full width port includes 20 data lanes and 1 clock lane
• 64 byte cache-lines
• Isochronous access support is not available on any CPU model containing two home
agents.
Note: RAS support depends on processor SKU. For example, Workstation SKUs do
not support sparing or tagging, lockstep mode, mirroring mode, channel
mirroring mode within a socket, error containment.
• Home snoop based coherency
•4-bit Node ID
• 46-bit physical addressing support
• No Intel QuickPath Interconnect bifurcation support
• Differential signaling
• Forwarded clocking
• Up to 8.0 GT/s data rate (up to 16 GB/s direction peak bandwidth per port)
— All ports run at same operational frequency
— Reference Clock is 100 MHz
— Slow boot speed initialization at 50 MT/s
• Common reference clocking (same clock generator for both sender and receiver)
• Intel® Interconnect Built-In-Self-Test (Intel® IBIST) for high-speed testability
• Polarity Inversion and Lane reversal (Rx side only)
Overview
1.2.5 Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI)
The PECI is a one-wire interface that provides a communication channel between a
PECI client (the processor) and a PECI master (the PCH).
• Supports operation at up to 2 Mbps data transfers
• Link layer improvements to support additional services and higher efficiency over
PECI 2.0 generation
• Services include CPU thermal and estimated power information, control functions
for power limiting, P-state and T-state control, and access for Machine Check
Architecture registers and PCI configuration space (both within the processor
package and downstream devices)
• PECI address determined by SOCKET_ID configuration
• Single domain (Domain 0) is supported
18 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 19

Overview
1.3 Power Management Support
1.3.1 Processor Package and Core States
• ACPI C-states as implemented by the following processor C-states:
— Package: PC0, PC1/PC1e, PC2, PC3, PC6 (Package C7 is not supported)
— Core: CC0, CC1, CC1E, CC3, CC6 (Processor Core C7 is not supported)
• Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
1.3.2 System States Support
• S0, S1, S3, S4, S5
1.3.3 Memory Controller
• Multiple CKE power down modes
• Multiple self-refresh modes
• Memory thermal monitoring via MEM_HOT_C01_N and MEM_HOT_C23_N Signals
1.3.4 PCI Express*
• L0s is not supported
• L1 ASPM power management capability
1.3.5 Intel® QPI
• L0s is not supported
• L0p and L1 power management capabilities
1.4 Thermal Management Support
• Digital Thermal Sensor with multiple on-die temperature zones
• Adaptive Thermal Monitor
• THERMTRIP_N and PROCHOT_N signal support
• On-Demand mode clock modulation
• Open and Closed Loop Thermal Throttling (OL T T/CLTT) support for system memory
in addition to Hybrid OLTT/CLTT mode
• Fan speed control with DTS
• Two integrated SMBus masters for accessing thermal data from DIMMs
• New Memory Thermal Throttling features via MEM_HOT_C{01/23}_N signals
• Running Average Power Limit (RAPL), Processor and DRAM Thermal and Power
Optimization Capabilities
1.5 Package Summary
The processor socket type is 52.5 x 45 mm or 52.5 x 51 mm FCLGA12 package
(LGA2011-0).
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 19
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 20
1.6 Terminology
Term Description
ASPM Active State Power Management
BMC Baseboard Management Controllers
Cbo Cache and Core Box. It is a term used for internal logic providing ring interface to
DDR3 Third generation Double Data Rate SDRAM memory technology that is the
DMA Direct Memory Access
DMI Direct Media Interface
DMI2 Direct Media Interface Gen 2
DTS Digital Thermal Sensor
ECC Error Correction Code
Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep® Technology
(EIST)
Execute Disable Bit The Execute Disable bit allows memory to be marked as executable or non-
Flit Flow Control Unit. The Intel QPI Link layer’s unit of transfer; 1 Flit = 80-bits.
Functional Operation Refers to the normal operating conditions in which all processor specifications,
IMC
IIO The Integrated I/O Controller. An I/O controller that is integrated in the
Intel® ME Intel® Management Engine (Intel® ME)
Intel® QuickData
Technology
Intel® QuickPath
Interconnect (Intel® QPI)
Intel® 64 Technology 64-bit memory extensions to the IA-32 architecture. Further details on Intel 64
Intel® Turbo Boost
Technology
Intel® TXT Intel® Trusted Execution Technology
Intel® Virtualization
Technology (Intel® VT)
Intel® VT-d Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) for Directed I/O. Intel VT-d is a
Overview
LLC and Core.
successor to DDR2 SDRAM
Allows the operating system to reduce power consumption when performance is
not needed.
executable, when combined with a supporting operating system. If code
attempts to run in non-executable memory the processor raises an error to the
operating system. This feature can prevent some classes of viruses or worms
that exploit buffer overrun vulnerabilities and can thus help improve the overall
security of the system. See the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software
Developer's Manuals for more detailed information.
including DC, system bus, signal quality, mechanical, and thermal, are satisfied.
The Integrated Memory Controller. A Memory Controller that is integrated in the
processor die.
processor die.
Intel QuickData Technology is a platform solution designed to maximize the
throughput of server data traffic across a broader range of configurations and
server environments to achieve faster, scalable, and more reliable I/O.
A cache-coherent, link-based Interconnect specification for Intel processors,
chipsets, and I/O bridge components.
architecture and programming model can be found at
http://developer.intel.com/technology/intel64/.
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology is a way to automatically run the processor core
faster than the marked frequency if the part is operating under power,
temperature, and current specifications limits of the Thermal Design Power
(TDP). This results in increased performance of both single and multi-threaded
applications.
Processor virtualization which when used in conjunction with Virtual Machine
Monitor software enables multiple, robust independent software environments
inside a single platform.
hardware assist, under system software (Virtual Machine Manager or OS)
control, for enabling I/O device virtualization. Intel VT-d also brings robust
security by providing protection from errant DMAs by using DMA remapping, a
key feature of Intel VT-d.
20 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 21

Overview
Term Description
Intel® Xeon® processor
E5-1600 v2 product family
Intel® Xeon® processor
E5-2600 v2 product family
Integrated Heat Spreader
(IHS)
Jitter Any timing variation of a transition edge or edges from the defined Unit Interval
IOV I/O Virtualization
LGA2011-0 Socket The LGA2011-0 land FCLGA12 package mates with the system board through
LLC Last Level Cache
LRDIMM Load Reduced Dual In-line Memory Module
NCTF Non-Critical to Function: NCTF locations are typically redundant ground or non-
NEBS Network Equipment Building System. NEBS is the most common set of
PCH Platform Controller Hub. The next generation chipset with centralized platform
PCU Power Control Unit
PCI Express* 3.0 The third generation PCI Express* specification that operates at twice the speed
PCI Express 3 PCI Express* Generation 3.0
PCI Express 2 PCI Express* Generation 2.0
PCI Express PCI Express* Generation 2.0/3.0
PECI Platform Environment Control Interface
Phit
Processor The 64-bit, single-core or multi-core component (package)
Processor Core The term “processor core” refers to silicon die itself which can contain multiple
RDIMM Registered Dual In-line Module
Rank A unit of DRAM corresponding four to eight devices in parallel, ignoring ECC.
SCI System Control Interrupt. Used in ACPI protocol.
SSE Intel® Streaming SIMD Extensions (Intel® SSE)
Intel’s 22-nm processor design, is the follow-on to the 3rd Generation Intel®
Core™ Processor Family design. It is the next generation processor for use in
Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families-based
platforms. Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2 product family supports
workstation platforms only.
Intel’s 22-nm processor design, is the follow-on to the 3rd Generation Intel®
Core™ Processor Family design. It is the next generation processor for use in
Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families-based
platforms. Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600 v2 product family supports
workstation, Efficient Performance server, and HPC platforms.
A component of the processor package used to enhance the thermal
performance of the package. Component thermal solutions interface with the
processor at the IHS surface.
(UI).
this surface mount, LGA2011-0 contact socket.
critical reserved, so the loss of the solder joint continuity at end of li fe condition s
will not affect the overall product functionality.
environmental design guidelines applied to telecommunications equipment in the
United States.
capabilities including the main I/O interfaces along with display connectivity,
audio features, power management, manageability, security and storage
features.
of PCI Express* 2.0 (8 Gb/s); however, PCI Express* 3.0 is completely backward
compatible with PCI Express* 1.0 and 2.0.
Physical Unit. An Intel® QPI terminology defining units of transfer at the physical
layer. 1 Phit is equal to 20 bits in ‘full width mode’ and 10 bits in ‘half width
mode’
execution cores. Each execution core has an instruction cache, data cache, and
256-KB L2 cache. All execution cores share the L3 cache. All DC and signal
integrity specifications are measured at the processor die (pads), unless
otherwise noted.
These devices are usually, but not always, mounted on a single side of a DDR3
DIMM.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 21
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 22
Overview
Term Description
SKU A processor Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) to be installed in either server or
workstation platforms. Electrical, power and thermal specifications for these
SKU’s are based on specific use condition assumptions. Server processors may
be further categorized as Efficient Performance server, workstation and HPC
SKUs. For further details on use condition assumptions, please refer to the latest
Product Release Qualification (PRQ) Report available via your Customer Quality
Engineer (CQE) contact.
SMBus System Management Bus. A two-wire interface through which simpl e system and
power management related devices can communicate with the rest of the
system. It is based on the principals of the operation of the I2C* two-wire serial
bus from Philips Semiconductor.
Storage Conditions A non-operational state. The processor may be installed in a platform, in a tray,
or loose. Processors may be sealed in packaging or exposed to free air. Under
these conditions, processor landings should not be connected to any supply
voltages, have any I/Os biased or receive any clocks. Upon exposure to “free air”
(that is, unsealed packaging or a device removed from packaging material) the
processor must be handled in accordance with moisture sensitivity labeling
(MSL) as indicated on the packaging material.
TAC Thermal Averaging Constant
TDP Thermal Design Power
TSOD Thermal Sensor on DIMM
UDIMM Unbuffered Dual In-line Module
Uncore The portion of the processor comprising the shared cache, IMC, HA, PCU, UBox,
Unit Interval Signaling convention that is binary and unidirectional. In this binary signaling,
V
CC
V
SS
V
_01, VCCD_23 Variable power supply for the processor system memory interface. VCCD is the
CCD
and Intel QPI link interface.
one bit is sent for every edge of the forwarded clock, whether it be a rising edge
or a falling edge. If a number of edges are collected at instances t
then the UI at instance “n” is defined as:
UI
= t n - t n - 1
n
, t2, tn,...., t
1
k
Processor core power supply
Processor ground
generic term for VCCD_01, VCCD_23.
x1 Refers to a Link or Port with one Physical Lane
x4 Refers to a Link or Port with four Physical Lanes
x8 Refers to a Link or Port with eight Physical Lanes
x16 Refers to a Link or Port with sixteen Physical Lanes
1.7 Related Documents
Refer to the following documents for additional information.
Table 1-3. Referenced Documents (Sheet 1 of 2)
Document Document Number/ Location
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family Processor Datasheet,
Volume Two: Registers
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600/2600/4600 v1 and v2 Product
Families Thermal / Mechanical Design Guide
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families –
Boundary Scan Description Language (BSDL) File
Intel® C600 Series Chipset Datasheet http://www.intel.com
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface Specification 3.0 http://www.acpi.info
PCI Local Bus Specification 3.0 http://www.pcisig.com/specifications
22 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
http://www.intel.com
http://www.intel.com
http://www.intel.com
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 23

Overview
Table 1-3. Referenced Documents (Sheet 2 of 2)
Document Document Number/ Location
PCI Express Base Specification - Revision 2.1 and 1.1
PCI Express Base Specification - Revision 3.0
System Management Bus (SMBus) Specification http://smbus.org/
DDR3 SDRAM Specification http://www.jedec.org
Low (JESD22-A119) and High (JESD-A103) Temperature Storage
Life Specifications
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer's Manuals
• Volume 1: Basic Architecture
• Volume 2A: Instruction Set Reference, A-M
• Volume 2B: Instruction Set Reference, N-Z
• Volume 3A: System Programming Guide
• Volume 3B: System Programming Guide
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Optimization Reference Manual
Intel® Virtualization Technology Specification for Directed I/O
Architecture Specification
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology Software Development Guide http://www.intel.com/technology/security/
National Institute of Standards and Technology NIST SP800-90 http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/PubsSPs.html
http://www.pcisig.com
http://www.jedec.org
http://www.intel.com/products/processor/manu
als/index.htm
http://download.intel.com/technology/computin
g/vptech/Intel(r)_VT_for_Direct_IO.pdf
1.8 Statement of Volatility (SOV)
Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families do not retain any
end-user data when powered down and/or the processor is physically removed from
the socket.
1.9 State of Data
The data contained within this document is the most accurate information available by
the publication date of this document.
§
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 23
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 24

Overview
24 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 25

Interfaces
2 Interfaces
This chapter describes the interfaces supported by the processor.
2.1 System Memory Interface
2.1.1 System Memory Technology Support
The Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) supports DDR3 protocols with four
independent 64-bit memory channels with 8 bits of ECC for each channel (total of
72-bits) and supports 1 to 3 DIMMs per channel depending on the type of memory
installed. The type of memory supported by the processor is dependent on the target
platform:
• Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families platforms
support:
— ECC registered DIMMs: with a maximum of three DIMMs per channel allowing
up to eight device ranks per channel.
— ECC and non-ECC unbuffered DIMMs: with a maximum of two DIMMs per
channel thus allowing up to four device ranks per channel. Support for mixed
non-ECC with ECC un-buffered DIMM configurations.
2.1.2 System Memory Timing Support
The IMC supports the following DDR3 Speed Bin, CAS Write Latency (CWL), and
command signal mode timings on the main memory interface:
• tCL = CAS Latency
• tRCD = Activate Command to READ or WRITE Command delay
• tRP = PRECHARGE Command Period
• CWL = CAS Write Latency
• Command Signal modes = 1n indicates a new command may be issued every clock
and 2n indicates a new command may be issued every 2 clocks. Command launch
mode programming depends on the transfer rate and memory configuration.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 25
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 26
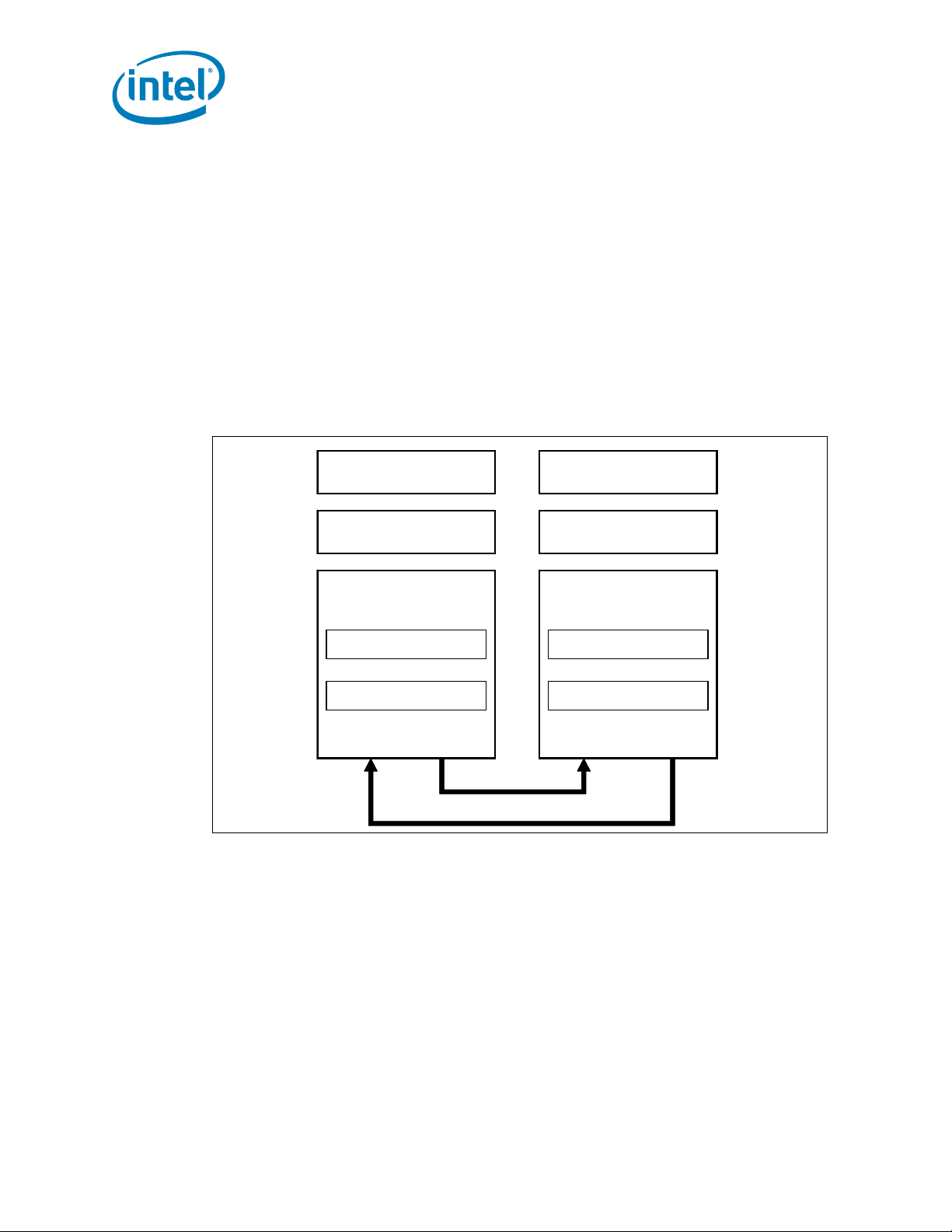
Transaction
Data Link
Physical
Logical Sub-Block
Electrical Sub-Block
RX TX
Transaction
Data Link
Physical
Logical Sub-Block
Electrical Sub-Block
RX TX
Transaction
Data Link
Physical
Logical Sub-Block
Electrical Sub-Block
RX TX
Transaction
Data Link
Physical
Logical Sub-Block
Electrical Sub-Block
RX TX
2.2 PCI Express* Interface
Interfaces
This section describes the PCI Express* 3.0 interface capabilities of the processor. See
the PCI Express* Base Specification for details of PCI Express*
2.2.1 PCI Express* Architecture
Compatibility with the PCI addressing model is maintained to ensure that all existing
applications and drivers operate unchanged. The PCI Express* configuration uses
standard mechanisms as defined in the PCI Plug-and-Play specification.
The PCI Express* architecture is specified in three layers: T ransaction Layer, Data Link
Layer, and Physical Layer. The partitionin g in the component is not necessarily along
these same boundaries. Refer to Figure 2-1 for the PCI Express* Layering Diagram.
Figure 2-1. PCI Express* Layering Diagram
3.0.
26 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
PCI Express* uses packets to communicate information between components. Packets
are formed in the Transaction and Data Link Layers to carry the information from the
transmitting component to the receiving component. As the transmitted packets flow
through the other layers, they are extended with additional information necessary to
handle packets at those layers. At the receiving side, the reverse process occurs and
packets get transformed from their Physical Layer representation to the Data Link
Layer representation and finally (for Transaction Layer Packets) to the form that can be
processed by the Transaction Layer of the receiving device.
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 27
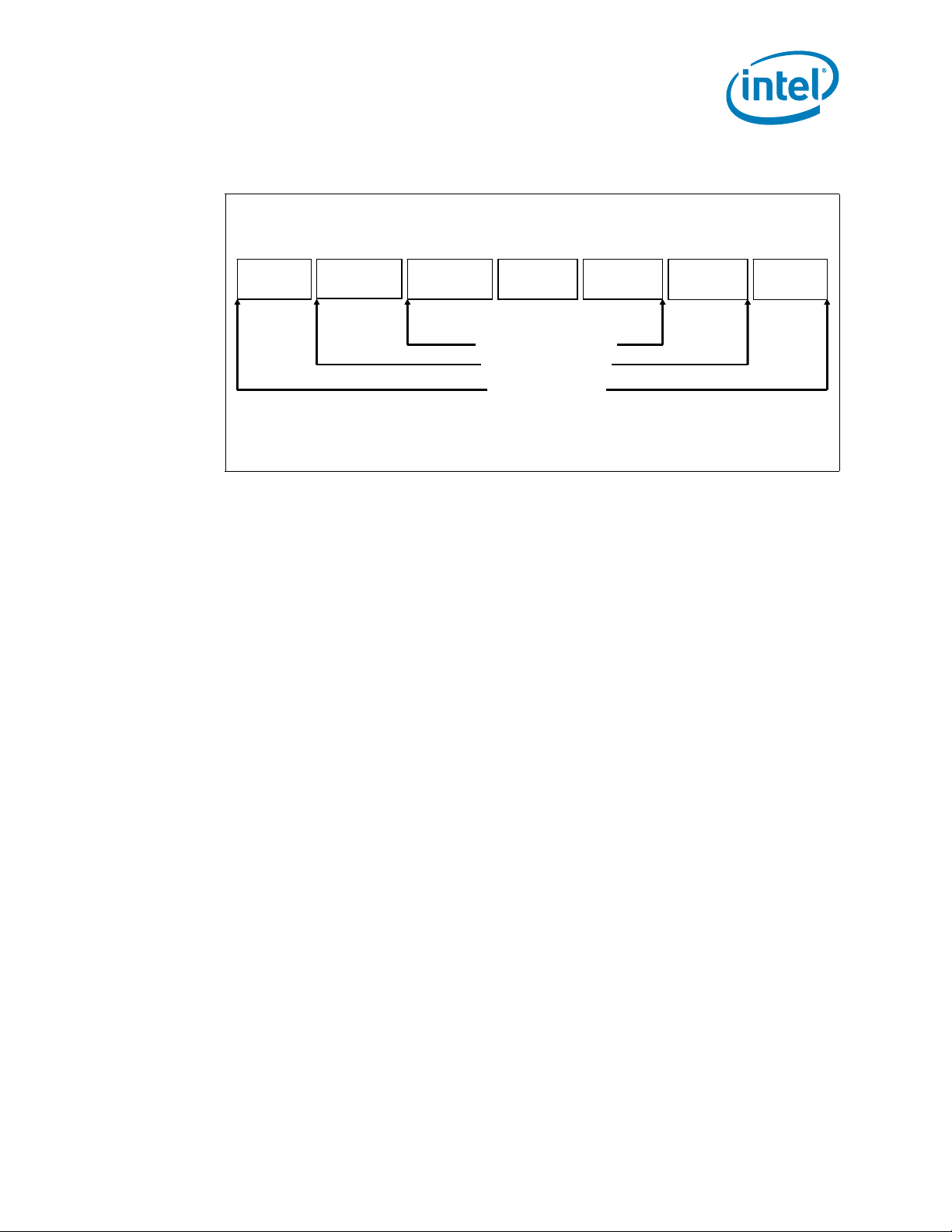
Framing
Sequence
Number
Header Date LCRCECRC Framing
Data Link Layer
Transaction Layer
Physical Layer
Framing
Sequence
Number
Header Date LCRCECRC Framing
Data Link Layer
Transaction Layer
Physical Layer
Interfaces
Figure 2-2. Packet Flow through the Layers
2.2.1.1 Transaction Layer
The upper layer of the PCI Express* architecture is the Transaction Layer. The
Transaction Layer's primary responsibility is the assembly and disassembly of
Transaction Layer Packets (TLPs). TLPs are used to communicate transactions, such as
read and write, as well as certain types of events. The Transaction Layer also manages
flow control of TLPs.
2.2.1.2 Data Link Layer
The middle layer in the PCI Express* stack, the Data Link Layer, serves as an
intermediate stage between the Transaction Layer and the Physical Layer.
Responsibilities of Data Link Layer include link management, error detection, and
error correction.
The transmission side of the Data Link Layer accepts TLPs assembled by the
Transaction Layer, calculates and applies data protection code and TLP sequence
number, and submits them to Physical Layer for transmission across the Link. The
receiving Data Link Layer is responsible for checking the integrity of received TLPs and
for submitting them to the T ransaction Layer for further processing. On detection of TLP
error(s), this layer is responsible for requesting retransm ission of TLPs until information
is correctly received, or the Link is determined to have failed. The Data Link Layer also
generates and consumes packets which are used for Link management functions.
2.2.1.3 Physical Layer
The Physical Layer includes all circuitry for interface operation, including driver and
input buffers, parallel-to-serial and serial-to-parallel conversion, PLL(s), and impedance
matching circuitry . It also includes logical functions related to interface initialization and
maintenance. The Physical Layer exchanges data with the Data Link Layer in an
implementation-specific format, and is responsible for converting this to an appropriate
serialized format and transmitting it across the PCI Express* Link at a frequency and
width compatible with the remote device.
2.2.2 PCI Express* Configuration Mechanism
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 27
Datasheet Volume One of Two
The PCI Express* link is mapped through a PCI-to-PCI bridge structure.
Page 28

PCI Express* extends the configuration space to 4096 bytes per-device/function, as
compared to 256 bytes allowed by the Conventional PCI Specification. PCI Express*
configuration space is divided into a PCI-compatible region (which consists of the first
256 bytes of a logical device's configuration space) and an extended PCI Express*
region (which consists of the remaining configuration space). The PCI-compatible
region can be accessed using either the mechanisms defined in the PCI specification or
using the enhanced PCI Express* configuration access mechanism described in the PCI
Express* Enhanced Configuration Mechanism section.
The PCI Express* Host Bridge is required to translate the memory-mapped PCI
Express* configuration space accesses from the host processor to PCI Express*
configuration cycles. To maintain compatibility with PCI configuration addressing
mechanisms, it is recommended that system software access the enhanced
configuration space using 32-bit operations (32-bit aligned) only.
See the PCI Express* Base Specification for details of both the PCI-compatible and PCI
Express* Enhanced configuration mechanisms and transaction rules.
2.3 DMI2/PCI Express* Interface
Direct Media Interface 2 (DMI2) connects the processor to the Platform Controller Hub
(PCH). DMI2 is similar to a four-lane PCI Express* supporting a speed of 5 GT/s per
lane. This interface can be configured at power-on to serve as a x4 PCI Express* link
based on the setting of the SOCKET_ID[1:0] and FRMAGENT signal for processors not
connected to a PCH.
Interfaces
Note: Only DMI2 x4 configuration is supported.
2.3.1 DMI2 Error Flow
DMI2 can only generate SERR in response to errors, never SCI, SMI, MSI, PCI INT, or
GPE. Any DMI2 related SERR activity is associated with Device 0.
2.3.2 Processor/PCH Compatibility Assumptions
The processor is compatible with the PCH and is not compatible with any previous MCH
or ICH products.
2.3.3 DMI2 Link Down
The DMI2 link going down is a fatal, unrecoverable error. If the DMI2 data link goes to
data link down, after the link was up, then the DMI2 link hangs the system by not
allowing the link to retrain to prevent data corruption. This is controlled by the PCH.
Downstream transactions that had been successfully transmitted across the link
prior to the link going down may be processed as normal. No completions from
downstream, non-posted transactions are returned upstream over the DMI2 link after a
link down event.
2.4 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI)
The Intel® QuickPath Interconnect is a high speed, packetized, point-to-point
interconnect used in the 3rd Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family. The narrow
high-speed links stitch together processors in distributed shared memory and
integrated I/O platform architecture. It offers much higher bandwidth with low latency.
28 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 29

Interfaces
The Intel® QuickPath Interconnect has an efficient architecture allowing more
interconnect performance to be achieved in real systems. It has a snoop protocol
optimized for low latency and high scalability, as well as packet and lane structures
enabling quick completions of transactions. Reliability, availability, and serviceability
features (RAS) are built into the architecture.
The physical connectivity of each interconnect link is made up of twenty differential
signal pairs plus a differential forwarded clock. Each port supports a link pair consisting
of two uni-directional links to complete the connection between two components. This
supports traffic in both directions simultaneously. To facilitate flexibility and longevity,
the interconnect is defined as having five layers: Physical, Link, Routing, Transport,
and Protocol.
• The Physical layer consists of the actual wires carrying the signals, as well as
circuitry and logic to support ancillary features required in the transmission and
receipt of the 1s and 0s. The unit of transfer at the Physical layer is 20-bits, which
is called a Phit (for Physical unit).
• The Link layer is responsible for reliable transmission and flow control. The Link
layer’s unit of transfer is 80-bits, which is called a Flit (for Flow control unit).
• The Routing layer provides the framework for directing packets through
the fabric.
• The Transport layer is an architecturally defined layer (not implemented in
the initial products) providing advanced routing capability for reliable
end-to-end transmission.
• The Protocol layer is the high-level set of rules for exchanging packets of data
between devices. A packet is comprised of an integral number of Flits.
The Intel® QuickPath Interconnect includes a cache coherency protocol to keep the
distributed memory and caching structures coherent during system operation. It
supports both low-latency source snooping and a scalable home snoop behavior. The
coherency protocol provides for direct cache-to-cache transfers for optimal latency.
2.5 Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI)
The Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) uses a single wire for self-clocking
and data transfer. The bus requires no additional control lines. The physical layer is a
self-clocked one-wire bus that begins each bit with a driven, rising edge from an idle
level near zero volts. The duration of the signal driven high depends on whether the
bit value is a logic ‘0’ or logic ‘1’. PECI also includes variable data transfer rate
established with every message. In this way , it is highly flexible even though underlying
logic is simple.
The interface design was optimized for interfacing to Intel processor and chipset
components in both single processor and multiple processor environments. The single
wire interface provides low board routing overhead for the multiple load connections in
the congested routing area near the processor and chipset components. Bus speed,
error checking, and low protocol overhead provides adequate link bandwidth and
reliability to transfer critical device operating conditions and configuration information.
The PECI bus offers:
• A wide speed range from 2 Kbps to 2 Mbps
• CRC check byte used to efficiently and atomically confirm accurate data delivery
• Synchronization at the beginning of every message minimizes device timing
accuracy requirements
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 29
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 30

Interfaces
Generic PECI specification details are out of the scope of this document. What follows is
a processor-specific PECI client definition, and is largely an addendum to the PECI
Network Layer and Design Recommendations sections for the PECI specification.
Note: The PECI commands described in this document apply primarily to the Intel® Xeon®
processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 product families. The processors utilizes the
capabilities described in this document to indicate support for four memory channels.
Refer to
Table 2-1 for the list of PECI commands supported by the processors.
Table 2-1. Summary of Processor-specific PECI Commands
Command Supported on the Processor
Ping() Yes
GetDIB() Yes
GetTemp() Yes
RdPkgConfig() Yes
WrPkgConfig() Yes
RdIAMSR() Yes
WrIAMSR() No
RdPCIConfig() Yes
WrPCIConfig() No
RdPCIConfigLocal() Yes
WrPCIConfigLocal() Yes
2.5.1 PECI Client Capabilities
The processor PECI client is designed to support the following sideband functions:
• Processor and DRAM thermal management
• Platform manageability functions including thermal, power, and error monitoring
— The platform ‘power’ management includes monitoring and control for both the
processor and DRAM subsystem to assist with data center power limiting.
2.5.1.1 Thermal Management
Processor fan speed control is managed by comparing Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS)
thermal readings acquired via PECI against the processor-specific fan speed control
reference point, or T
CONTROL
via the processor PECI client. These variables are referenced to a common
temperature, the TCC activation point, and are both defined as negative offsets from
that reference.
PECI-based access to the processor package configuration space provides a means for
Baseboard Management Controllers (BMCs) or other platform management devices to
actively manage the processor and memory power and thermal features. Details on the
list of available power and thermal optimization services can be found in
Section 2.5.2.6.
2.5.1.2 Platform Manageability
PECI allows read access to certain error registers in the processor MSR space and
status monitoring registers in the PCI configuration space within the processor and
downstream devices. Details are covered in subsequent sections.
. Both T
CONTROL
and DTS thermal readings are accessible
30 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 31

Byte #
Byte
Definition
0
Client Address
1
Write Length
0x00
2
Read Length
0x00
3
FCS
Byte #
Byte
Definition
0
0x30
1
0x00
2
0x00
3
0xe1
Interfaces
PECI permits writes to certain Memory Controller RAS-related registers in the processor
PCI configuration space. Details are covered in Section 2.5.2.10.
2.5.2 Client Command Suite
PECI command requires at least one frame check sequence (FCS) byte to ensure
reliable data exchange between originator and client. The PECI message protocol
defines two FCS bytes that are returned by the client to the message originator. The
first FCS byte covers the client address byte, the Read and Write Length bytes, and all
bytes in the write data block. The second FCS byte covers the read response data
returned by the PECI client. The FCS byte is the result of a cyclic redundancy check
(CRC) of each data block.
2.5.2.1 Ping()
Ping() is a required message for all PECI devices. This message is used to enumerate
devices or determine if a device has been removed, been powered-off, and so forth. A
Ping() sent to a device address always returns a non-zero W rite FCS if the device at the
targeted address is able to respond.
2.5.2.1.1 Command Format
The Ping() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x00
Read Length: 0x00
Figure 2-3. Ping()
An example Ping() command to PECI device address 0x30 is shown below.
Figure 2-4. Ping() Example
2.5.2.2 GetDIB()
The processor PECI client implementation of GetDIB() includes an 8-byte response and
provides information regarding client revision number and the number of supported
domains. All processor PECI clients support the GetDIB() command.
2.5.2.2.1 Command Format
The GetDIB() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x01
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 31
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 32

Byte #
Byte
Definition
0
Client Address
1
Write Length
0x01
2
Read Length
0x08
4
FCS
3
Cmd Code
0xf7
5
Device Info
6
Revision
Number
7
Reserved
8
Reserved
9
Reserved
10
Reserved
11
Reserved
12
Reserved
13
FCS
Reserved
# of Domains
Reserved
76543210
Byte# 5
Read Length: 0x08
Command: 0xf7
Figure 2-5. GetDIB()
Interfaces
2.5.2.2.2 Device Info
The Device Info byte gives details regarding the PECI client configuration. At a
minimum, all clients supporting GetDIB will return the number of domains inside the
package via this field. With any client, at least one domain (Domain 0) must exist.
Therefore, the Number of Domains reported is defined as the number of domains in
addition to Domain 0. For example, if bit 2 of the Device Info byte returns a ‘1’, that
would indicate that the PECI client supports two domains.
Figure 2-6. Device Info Field Definition
2.5.2.2.3 Revision Number
All clients that support the GetDIB command also support Revision Number reporting.
The revision number may be used by a host or originator to manage different command
suites or response codes from the client. Revision Number is always reported in the
second byte of the GetDIB() response. The ‘Major Revision’ number in Figure 2-7
always maps to the revision number of the PECI specification that the PECI client
processor is designed to. The ‘Minor Revision’ number value depends on the exact
command suite supported by the PECI client as defined in Table 2-2.
32 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 33

0
3
4
7
Major Revision#
Minor Revision#
Byte# 6
Interfaces
Figure 2-7. Revision Number Definition
Table 2-2. Minor Revision Number Meaning
Minor Revision Supported Command Suite
0 Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp()
1 Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp(), WrPkgConfig(), RdPkgConfig()
2 Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp(), WrPkgConfig(), RdPkgConfig(), RdIAMSR()
3 Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp(), WrPkgConfig(), RdPkgConfig(), RdIAMSR(),
4 Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp(), WrPkgConfig(), RdPkgConfig(), RdIAMSR(),
5 Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp(), WrPkgConfig(), RdPkgConfig(), RdIAMSR(),
6 Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp(), WrPkgConfig(), RdPkgConfig(), RdIAMSR(),
RdPCIConfigLocal(), WrPCIConfigLocal(), RdPCIConfig(), WrPCIConfig(), WrIAMSR()
RdPCIConfigLocal(), WrPCIConfigLocal(), RdPCIConfig()
RdPCIConfigLocal(), WrPCIConfigLocal(), RdPCIConfig(), WrPCIConfig()
RdPCIConfigLocal(), WrPCIConfigLocal()
For the processor PECI client, the Revision Number it returns will be ‘0011 0100b’.
2.5.2.3 GetTemp()
The GetTemp() command is used to retrieve the die temperature from a target PECI
address. The temperature is used by the external thermal management system to
regulate the temperature on the die. The data is returned as a negative value
representing the number of degrees Celsius below the processor DTS temperature
(T
corresponds to T
) at which PROCHOT_N asserts. The PECI temperature value of zero
Prochot
Prochot
processor Thermal Control Circuit activates. The actual value that the thermal
management system uses as a control set point (T
negative number below T
issuing a PECI RdPkgConfig() command as described in Section 2.5.2.4 or using a
RDMSR instruction. T
the Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600/2600/4600 v1 and v2 Product Families Thermal /
Mechanical Design Guide.
Please refer to Section 2.5.7 for details regarding PECI temperature data formatting.
2.5.2.3.1 Command Format
The GetTemp() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x01
Read Length: 0x02
. This also represents the minimum temperature at which the
) is also defined as a
Prochot
CONTROL
. T
CONTROL
may be extracted from the processor by
CONTROL
application to fan speed control management is defined in
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 33
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 34

Byte #
Byte
Definition
0
Client Address
1
Write Length
0x01
2
Read Length
0x02
4
FCS
5
Temp[7:0]
6
Temp[15:8]
7
FCS
3
Cmd Code
0x01
Byte #
Byte
Definition
0
0x30
1
0x01
2
0x02
4
0xef
5
0x80
6
0xfd
7
0x4b
3
0x01
Command: 0x01
Description: Returns the highest die temperature for addressed processor PECI client.
Figure 2-8. GetTemp()
Example bus transaction for a thermal sensor device located at address 0x30 returning
a value of negative 10 counts is show in Figure 2-9.
Figure 2-9. GetTemp() Example
Interfaces
2.5.2.3.2 Supported Responses
The typical client response is a passing FCS and valid thermal data. Under some
conditions, the client’s response will indicate a failure. GetTemp() response definiti ons
are listed in Table 2-3. Refer to Section 2.5.7.4 for more details on sensor errors.
Table 2-3. GetTemp() Response Definition
Response Meaning
General Sensor Error (GSE)
Bad Write FCS Electrical error
Abort FCS Illegal command formatting (mismatched RL/WL/Command Code)
1
0x0000
All other data Valid temperature reading, reported as a negative offset from T
Notes:
1. This response will be reflected in Bytes 5 & 6 in Figure 2-9.
1
Thermal scan did not complete in time. Retry is appropriate.
Processor is running at its maximum temperature or is currently being reset.
Prochot
.
2.5.2.4 RdPkgConfig()
The RdPkgConfig() command provides read access to the package configuration space
(PCS) within the processor, including various power and thermal management
functions. Typical PCS read services supported by the processor may include access to
temperature data, energy status, run time information, DIMM temperatures and so on.
34 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Refer to Section 2.5.2.6 for more details on processor-specific services supported
through this command.
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 35
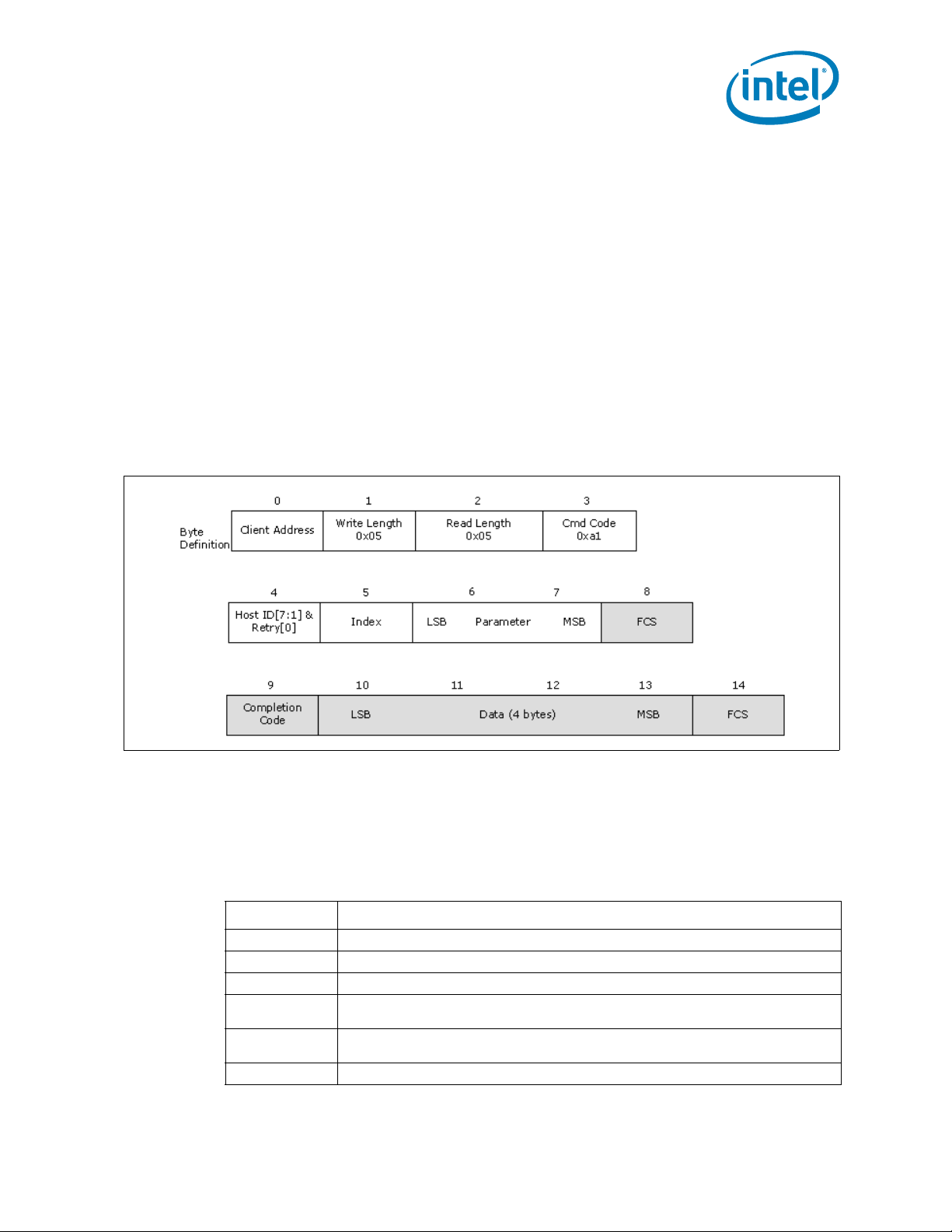
Interfaces
2.5.2.4.1 Command Format
The RdPkgConfig() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x05
Read Length: 0x05 (dword)
Command: 0xa1
Description: Returns the data maintained in the processor package configuration
space for the PCS entry as specified by the ‘index’ and ‘parameter’ fields. The ‘index’
field contains the encoding for the requested service and is used in conjunction with the
‘parameter’ field to specify the exact data being requested. The Read Length dictates
the desired data return size. This command supports only dword responses on the
processor PECI clients. All command responses are prepended with a completion code
that contains additional pass/fail status information. Refer to Section 2.5.5.2 for details
regarding completion codes.
Figure 2-10. RdPkgConfig()
Note: The 2-byte parameter field and 4-byte read data field defined in Figure 2-10 are sent in standard PECI ordering with LSB
first and MSB last.
2.5.2.4.2 Supported Responses
The typical client response is a passing FCS, a passing Completion Code and valid data.
Under some conditions, the client’s response will indicate a failure.
Table 2-4. RdPkgConfig() Response Definition
Response Meaning
Bad Write FCS Electrical error
Abort FCS Illegal command formatting (mismatched RL/WL/Command Code)
CC: 0x40 Command passed, data is valid.
CC: 0x80 Response timeout. The processor is not able to gener ate the re quired resp onse in a timel y
CC: 0x81 Response timeout. The processor is not able to allocate resources for servicing this
CC: 0x90 Unknown/Invalid/Illegal Request
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 35
Datasheet Volume One of Two
fashion. Retry is appropriate.
command at this time. Retry is appropriate.
Page 36

Table 2-4. RdPkgConfig() Response Definition
Response Meaning
CC: 0x91 PECI control hardware, firmware or associated logic error. The processor is unable to
process the request.
CC: 0x93 Pcode MCA - PECI access allowed, but PECI access cannot be completed.
CC: 0x94 Pcode MCA - PECI access allowed and access completes. Will respond with the data along
with the response code.
2.5.2.5 WrPkgConfig()
The WrPkgConfig() command provides write access to the package configuration space
(PCS) within the processor, including various power and thermal management
functions. Typical PCS write services supported by the processor may include power
limiting, thermal averaging constant programming and so on. Refer to Section 2.5.2.6
for more details on processor-specific services supported through this command.
2.5.2.5.1 Command Format
The WrPkgConfig() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x0a(dword)
Interfaces
Read Length: 0x01
Command: 0xa5
AW FCS Support: Yes
Description: Writes data to the processor PCS entry as specified by the ‘index’ and
‘parameter’ fields. This command supports only dword data writes on the processor
PECI clients. All command responses include a completion code that provides
additional pass/fail status information. Refer to Section 2.5.2.2 for details regarding
completion codes.
The Assured Write FCS (AW FCS) support provides the processor client a high degree
of confidence that the data it received from the host is correct. This is especially
critical where the consumption of bad data might result in improper or non-recoverable
operation.
36 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 37
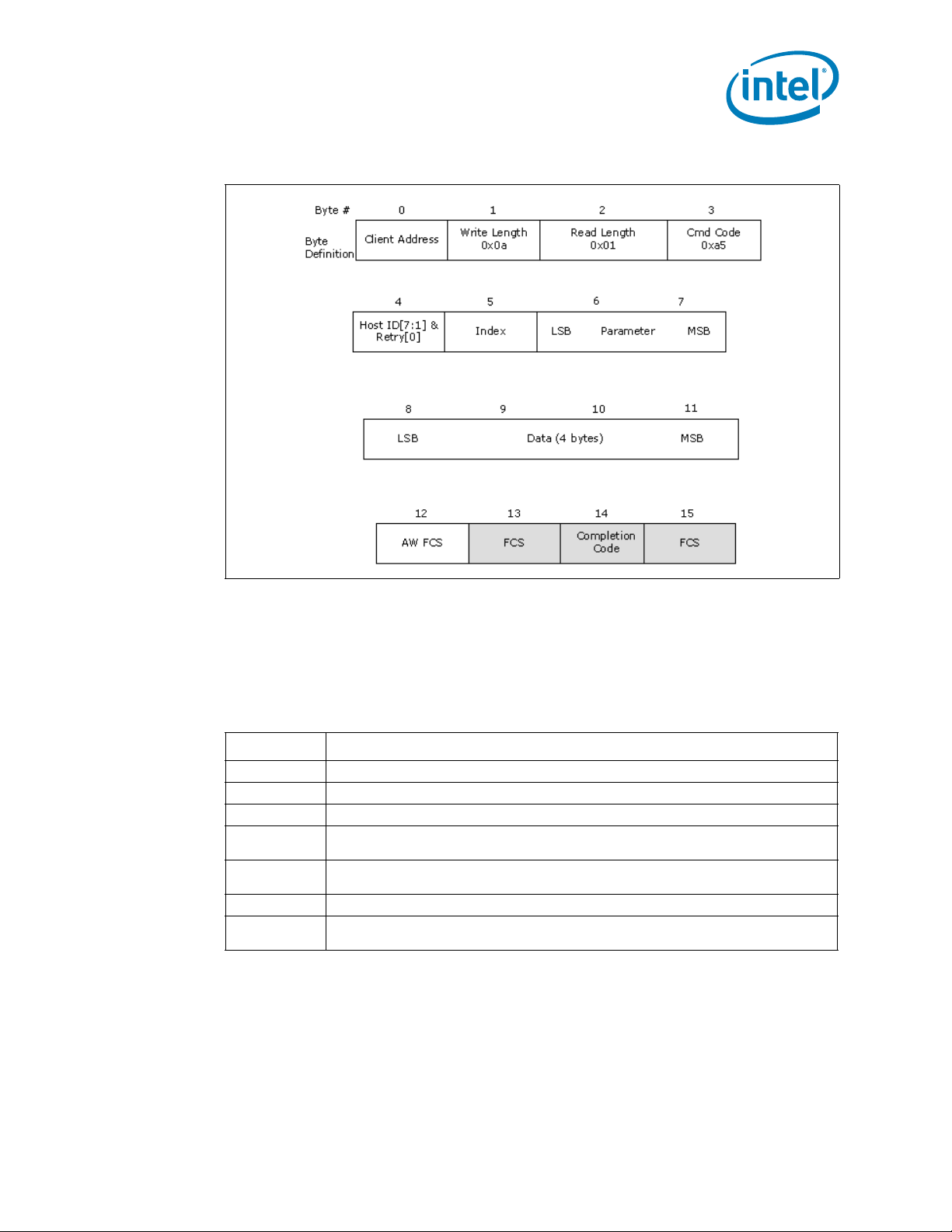
Interfaces
Figure 2-11. WrPkgConfig()
Note: The 2-byte parameter field and 4-byte write data field defined in Figure 2-11 are sent in standard PECI
ordering with LSB fir st and MSB last.
2.5.2.5.2 Supported Responses
The typical client response is a passing FCS, a passing Completion Code and valid data.
Under some conditions, the client’s response will indicate a failure.
Table 2-5. WrPkgConfig() Response Definition
Response Meaning
Bad Write FCS Electrical error or AW FCS failure
Abort FCS Illegal command formatting (mismatched RL/WL/Command Code)
CC: 0x40 Command passed, data is valid.
CC: 0x80 Response timeout. The processor was not able to generate the required response in a
CC: 0x81 Response timeout. The processor is not able to allocate resources for servicing this
CC: 0x90 Unknown/Invalid/Illegal Request
CC: 0x91 PECI control hardware, firmware or associated logic error. The processor is unable to
timely fashion. Retry is appropriate.
command at this time. Retry is appropriate.
process the request.
2.5.2.6 Package Configuration Capabilities
Table 2-6 combines both read and write servi ces. Any service listed as a “read” would
use the RdPkgConfig() command and a service listed as a “write” would use the
WrPkgConfig() command. PECI requests for memory temperature or other data
generated outside the processor package do not trigger special polling cycles on the
processor memory or SMBus interfaces to procure the required information.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 37
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 38
2.5.2.6.1 DRAM Thermal and Power Optimization Capabilities
DRAM thermal and power optimization (also known as RAPL or “Running Average P ower
Limit”) services provide a way for platform thermal management solutions to program
and access DRAM power, energy and temperature parameters. Memory temperature
information is typically used to regulate fan speeds, tune refresh rates and throttle the
memory subsystem as appropriate. Memory temperature data may be derived from a
variety of sources including on-die or on-board DIMM sensors, DRAM activity
information or a combination of the two. Though memory temperature data is a byte
long, range of actual temperature values are determined by the DIMM specifications
and operating range.
Note: DRAM related PECI services described in this section apply only to the memory
connected to the specific processor PECI client in question and not the overall platform
memory in general. For estimating DRAM thermal information in closed loop throttling
mode, a dedicated SMBus is required between the CPU and the DIMMs. The processor
PCU requires access to the VR12 voltage regulator for reading average output current
information through the SVID bus for initial DRAM RAPL related power tuning.
Table 2-6 provides a summary of the DRAM power and thermal optimization capabilities
that can be accessed over PECI on the processor. The Index values referenced in
Table 2-6 are in decimal format.
Interfaces
Table 2-6 also provides information on alternate inband mechanisms to access similar
or equivalent information through register reads and writes where applicable. The user
should consult the Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family Processor Datasheet,
Volume Two: Registers for exact details on MSR or CSR register content.
Table 2-6. RdPkgConfig() & WrPkgConfig() DRAM Thermal and Power Optimization
Services Summary (Sheet 1 of 2)
Service
DRAM
Thermal
Estimation
Configuration
Data
Read/Write
DRAM
Thermal
Estimation
Configuration
Data
Read/Write
DRAM Rank
Temperature
Write
DIMM
Temperature
Read
Index
Value
(decimal)
15
15
18
14
Parameter
Value
(word)
0x0000
0x0000
Channel
Index &
DIMM Index
Channel
Index
RdPkgConfig()
Data
(dword)
DRAM Thermal
Estimation
Configuration Data
N/A DRAM Thermal
N/A Absolute
Absolute
temperature in
Degrees Celsius for
DIMMs 0, 1, & 2
WrPkgConfig()
Data
(dword)
N/A Read the DRAM
Estimation
Configuration
Data
temperature in
Degrees Celsius
for ranks 0, 1, 2
& 3
N/A Read
DRAM Thermal
temperature of
Description
Thermal
Estimation
configuration
parameters.
Configure the
Estimation
parameters.
Write
temperature
for each rank
within a single
DIMM.
each DIMM
within a
channel.
Alternate
Inband
MSR or CSR
Access
MEM_TRML_ESTIMATION_
MEM_TRML_ESTIMATION_
CSR: DIMMTEMPSTAT_[0:2]
CSR:
CONFIG
CSR:
CONFIG
N/A
38 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 39

Interfaces
Table 2-6. RdPkgConfig() & WrPkgConfig() DRAM Thermal and Power Optimization
Services Summary (Sheet 2 of 2)
Service
DIMM
Ambient
Temperature
Write/Read
DIMM
Ambient
Temperature
Write/Read
DRAM
Channel
Temperature
Read
Accumulated
DRAM Energy
Read
DRAM Power
Info Read
DRAM Power
Info Read
DRAM Power
Limit Data
Write/Read
DRAM Power
Limit Data
Write/Read
DRAM Power
Limit
Performance
Status Read
Index
Value
(decimal)
19
19
22
04
35
36
34
34
38
Parameter
Value
(word)
0x0000
0x0000
0x0000
Channel
Index
0x00FF - All
Channels
0x0000
0x0000
0x0000
0x0000
0x0000
RdPkgConfig()
Data
(dword)
N/A Absolute
Absolute
temperature in
Degrees C to be
used as ambient
temperature
reference
Maximum of all
rank temperatures
for each channel in
Degrees Celsius
DRAM energy
consumed by the
DIMMs
Typical and
minimum DRAM
power settings
Maximum DRAM
power settings &
maximum time
window
N/A DRAM Plane
DRAM Plane Power
Limit Data
Accumulated DRAM
throttle time
WrPkgConfig()
Data
(dword)
temperature in
Degrees C to be
used as ambient
temperature
reference
N/A Read ambient
N/A Read the
N/A Read the DR AM
N/A Read DRAM
N/A Read DRAM
Power Limit Data
N/A Read DRAM
N/A Read sum of al l
DIMM has been
Description
Write ambient
temperature
reference for
activity-based
rank
temperature
estimation.
temperature
reference for
activity-based
rank
temperature
estimation.
maximum
DRAM channel
temperature.
energy
consumed by
all the DIMMs
in all the
channels or all
the DIMMs
within a
specified
channel.
power settings
info to be used
by power
limiting entity.
power settings
info to be used
by power
limiting entity
Write DRAM
Power L imit
Data
Power L imit
Data
time durations
for which each
throttled
Alternate
Inband
MSR or CSR
Access
N/A
N/A
N/A
MSR 619h:
DRAM_ENERGY_STATUS
CSR: DRAM_ENERGY_STATUS
DRAM_ENERGY_STATUS_CH[
CSR: DRAM_POWER_INFO
CSR: DRAM_POWER_INFO
DRAM_PLANE_POWER_LIMIT
DRAM_PLANE_POWER_LIMIT
DRAM_RAPL_PERF_STATUS
CSR:
0:3]
MSR 61Ch:
DRAM_POWER_INFO
MSR 61Ch:
DRAM_POWER_INFO
MSR 618h:
DRAM_POWER_LIMIT
CSR:
MSR 618h:
DRAM_POWER_LIMIT
CSR:
CSR:
1
Notes:
1. Time, energy and power units should be assumed, where applicable, to be based on values returned by a read of the
PACKAGE_POWER_SKU_UNIT MSR or through the Package Power SKU Unit PCS read service.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 39
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 40

Memory Thermal Estimation Configuration Data
RESERVED
1031
BETA VARIABLE
9 0
THETA VARIABLE
1920
2.5.2.6.2 DRAM Thermal Estimation Configuration Data Read/Write
This feature is relevant only when activity-based DRAM temperature estimation
methods are being utilized and would apply to all the DIMMs on all the memory
channels. The write allows the PECI host to configure the ‘β’ and ‘θ’ variables in
Figure 2-12 for DRAM channel temperature filtering as per the equation below:
= β ∗ TN-1 + θ ∗ ΔEnergy
T
N
Interfaces
T
N
and T
are the current and previous DRAM temperature estimates respectively in
N-1
degrees Celsius, ‘β’ is the DRAM temperature decay factor, ‘ΔEnergy’ is the energy
difference between the current and previous memory transactions as determined by
the processor power control unit and ‘θ’ is the DRAM energy-to-temperature translation
coefficient. The default value of ‘β’ is 0x3FF. ‘θ’ is defined by the equation:
θ = (1 - β) ∗ (Thermal Resistance) ∗ (Scaling Factor)
The ‘Thermal Resistance’ serves as a multiplier for translation of DRAM energy changes
to corresponding temperature changes and may be derived from actual platform
characterization data. The ‘Scaling Factor’ is used to convert memory transaction
information to energy units in Joules and can be derived from system/memory
configuration information. Refer to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software
Developer’s Manual for methods to program and access ‘Scaling Factor’ information.
Figure 2-12. DRAM Thermal Estimation Configuration Data
2.5.2.6.3 DRAM Rank Temperature Write
This feature allows the PECI host to program into the processor, the temperature for all
the ranks within a DIMM up to a maximum of four ranks as shown in Figure 2-13. The
DIMM index and Channel index are specified through the parameter field as shown in
Table 2-7. This write is relevant in platforms that do not have on-die or on-board DIMM
thermal sensors to provide memory temperature information or if the processor does
not have direct access to the DIMM thermal sensors. This temperature information is
used by the processor in conjunction with the activity-based DRAM temperature
estimations.
Table 2-7. Channel & DIMM Index Decoding
Index Encoding Physical Channel# Physical DIMM#
000 0 0
001 1 1
010 2 2
011 3 Reserved
40 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 41
15 7 0
Rank Temperature Data
Rank# 3
Absolute Temp
(in Degrees C)
Rank# 2
Absolute Temp
(in Degrees C)
Rank# 1
Absolute Temp
(in Degrees C)
Rank# 0
Absolute Temp
(in Degrees C)
816232431
15
2
Parameter format
Reserved DIMM Index
6
Channel Index
5 3 0
15 7 0
DIMM Temperature Data
Reserved
DIMM# 2
Absolute Temp
(in Degrees C)
DIMM# 1
Absolute Temp
(in Degrees C)
DIMM# 0
Absolute Temp
(in Degrees C)
816232431
15
2
Parameter format
Reserved Channel Index
3 0
Interfaces
Figure 2-13. DRAM Rank Temperature Write Data
2.5.2.6.4 DIMM Temperature Read
This feature allows the PECI host to read the temperature of all the DIMMs within a
channel up to a maximum of three DIMMs. This read is not limited to platforms using a
particular memory temperature source or temperature estimation method. For
platforms using DRAM thermal estimation, the PCU will provide the estimated
temperatures. Otherwise, the data represents the latest DIMM temperature provided
by the TSOD or on-board DIMM sensor and requires that CLTT (closed loop throttling
mode) be enabled and OLT T (open loop throttling mode) be disabled. Refer to Table 2-7
for channel index encodings.
Figure 2-14. The Processor DIMM Temperature Read / Write
2.5.2.6.5 DIMM Ambient Temperature Write/Read
This feature allows the PECI host to provide an ambient temperature reference to be
used by the processor for activity-based DRAM temperature estimation. This write is
used only when no DIMM temperature information is available from on-board or on-die
DIMM thermal sensors. It is also possible for the PECI host controller to read back the
DIMM ambient reference temperature.
Since the ambient temperature may vary over time within a system, it is recommended
that systems monitoring and updating the ambient temperature at a fast rate use the
‘maximum’ temperature value while those updating the ambient temperature at a slow
rate use an ‘average’ value. The ambient temperature assumes a single value for all
memory channel/DIMM locations and does not account for possible temperature
variations based on DIMM location.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 41
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 42

7 0
Ambient Temperature Reference Data
Reserved
Ambient
Temperature
(in Degrees C)
831
15 7 0
Channel Temperature Data
Channel 3
Maximum
Temperature
(in Degrees C)
Channel 2
Maximum
Temperature
(in Degrees C)
Channel 1
Maximum
Temperature
(in Degrees C)
Channel 0
Maximum
Temperature
(in Degrees C)
816232431
Figure 2-15. Ambient Temperature Reference Data
2.5.2.6.6 DRAM Channel Temperature Read
This feature enables a PECI host read of the maximum temperature of each channel.
This would include all the DIMMs within the channel and all the ranks within each of the
DIMMs. Channels that are not populated will return the ‘ambient temperature’ on
systems using activity-based temperature estimations or alternatively return a ‘zero’
for systems using sensor-based temperatures.
Figure 2-16. Processor DRAM Channel Temperature
Interfaces
2.5.2.6.7 Accumulated DRAM Energy Read
This feature allows the PECI host to read the DRAM energy consumed by all the DIMMs
within all the channels or all the DIMMs within just a specified channel. The parameter
field is used to specify the channel index. Units used are defined as per the Package
Power SKU Unit read described in Section 2.5.2.6.11. This information is tracked by a
32-bit counter that wraps around. The channel index in Figure 2-17 is specified as per
the index encoding described in Table 2-7. A channel index of 0x00FF is used to specify
the “all channels” case. While Intel requires reading the accumulated energy data at
least once every 16 seconds to ensure functional correctness, a more realistic polling
rate recommendation is once every 100 mS for better accuracy. This feature assumes a
200W memory capacity. In general, as the power capability decreases, so will the
minimum polling rate requirement.
When determining energy changes by subtracting energy values between successive
reads, Intel advocates using the 2’s complement method to account for counter
wraparounds. Alternatively, adding all ‘F’s (‘0xFFFFFFFF’) to a negative result from the
subtraction will accomplish the same goal.
42 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 43

0
Accumulated DRAM Energy Data
Accumulated DRAM Energy
31
15
2
Parameter format
Reserved Channel Index
3 0
Interfaces
Figure 2-17. Accumulated DRAM Energy Data
2.5.2.6.8 DRAM Power Info Read
This read returns the minimum, typical and maximum DRAM power settings and the
maximum time window over which the power can be sustained for the entire DRAM
domain and is inclusive of all the DIMMs within all the memory channels. Any power
values specified by the power limiting entity that is outside of the range specified
through these settings cannot be guaranteed. Since this data is 64 bits wide, PECI
facilitates access to this register by allowing two requests to read the lower 32 bits and
upper 32 bits separately as shown in Table 2-6. Power and time units for this read are
defined as per the Package Power SKU Unit settings described in Section 2.5.2.6.11.
The minimum DRAM power in Figure 2-18 corresponds to a minimum bandwidth
setting of the memory interface. It does ‘not’ correspond to a processor IDLE or
memory self-refresh state. The ‘time window’ in Figure 2-18 is representative of the
rate at which the power control unit (PCU) samples the DRAM energy consumption
information and reactively takes the necessary measures to meet the imposed power
limits. Programming too small a time window may not give the PCU enough time to
sample energy information and enforce the limit while too large a time window runs the
risk of the PCU not being able to monitor and take timely action on energy excursions.
While the DRAM power setting in Figure 2-18 provides a maximum value for the ‘time
window’ (typically a few seconds), the minimum value may be assumed to be
~100 mS.
The PCU programs the DRAM power settings described in Figure 2-18 when DRAM
characterization has been completed by the memory reference code (MRC) during boot
as indicated by the setting of the RST_CPL bit of the BIOS_RESET_CPL register. The
DRAM power settings will be programmed during boot independent of the ‘DRAM Power
Limit Enable’ bit setting. Please refer to the Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product
Family Processor Datasheet, Volume Two: Registers for information on memory energy
estimation methods and energy tuning options used by BIOS and other utilities for
determining the range specified in the DRAM power settings. In general, any tuning of
the power settings is done by polling the voltage regulators supplying the DIMMs.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 43
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 44
DRAM_POWER_INFO (lower bits)
Reserved
14
Minimum DRAM Power
16
TDP DRAM Powe r
(Typical Value)
30 015
Reserved
31
DRAM_POWER_INFO (upper bits)
Maximum DRAM Power
3246
Reserved
47
Maximum Time
Window
4854
Reserved
5563
Figure 2-18. DRAM Power Info Read Data
2.5.2.6.9 DRAM Power Limit Data Write/Read
This feature allows the PECI host to program the power limit over a specified time or
control window for the entire DRAM domain covering all the DIMMs within all the
memory channels. Actual values are chosen based on DRAM power consumption
characteristics. The units for the DRAM Power Limit and Control Time Window are
determined as per the Package Power SKU Unit settings described in
Section 2.5.2.6.11. The DRAM Power Limit Enable bit in Figure 2-19 should be set to
activate this feature. Exact DRAM power limit values are largely determined by platform
memory configuration. As such, this feature is disabled by default and there are no
defaults associated with the DRAM power limit values. The PECI host may be used to
enable and initialize the power limit fields for the purposes of DRAM power budgeting.
Alternatively, this can also be accomplished through inband writes to the appropriate
registers. Both power limit enabling and initialization of power limit values can be done
in the same command cycle. All RAPL parameter values including the power limit value,
control time window, and enable bit will have to be specified correctly even if the intent
is to change just one parameter value when programming over PECI.
Interfaces
The following conversion formula should be used for encoding or programming the
‘Control Time Window’ in bits [23:17].
‘y’
Control Time Window (in seconds) = ([1 + 0.25 * ‘x’] * 2
) * ‘z’ where
‘x’ = integer value of bits[23:22]
‘y’ = integer value of bits[21:17]
‘z’ = Package Power SKU Time Unit[19:16] (see Section 2.5.2.6.13 for details on
Package Power SKU Unit)
For example, using this formula, a control time value of 0x0A will correspond to a
‘1-second’ time window. A valid range for the value of the ‘Control Time Window’ in
Figure 2-19 that can be programmed into bits [23:17] is 250 mS - 40 seconds.
From a DRAM power management standpoint, all post-boot DRAM power management
activities (also referred to as ‘DRAM RAPL’ or ‘DRAM Running Average Power Limit’)
should be managed exclusively through a single interface like PECI or alternatively an
inband mechanism. If PECI is being used to manage DRAM power budgeting activities,
BIOS should lock out all subsequent inband DRAM power limiting accesses by setting
bit 31 of the DRAM_POWER_LIMIT MSR or DRAM_PLANE_POWER_LIMIT CSR to ‘1’.
44 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 45
DRAM_POW ER_LIMIT Data
DRAM
Power Limit
Enable
1523
DRAM Power Limit
14 0
RESERVED
16
Control Time
Window
1731
RESERVED
24
DRAM Power Limit Performance
Accumulated DRAM Throttle Time
0
31
Interfaces
Figure 2-19. DRAM Power Limit Data
2.5.2.6.10 DRAM Power Limit Performance Status Read
This service allows the PECI host to assess the performance impact of the currently
active DRAM power limiting modes. The read return data contains the sum of all the
time durations for which each of the DIMMs has been operating in a low power state.
This information is tracked by a 32-bit counter that wraps around. The unit for time is
determined as per the Package Power SKU Unit settings described in
Section 2.5.2.6.11. The DRAM performance data does not account for stalls on the
memory interface.
In general, for the purposes of DRAM RAPL, the DRAM power management entity
should use PECI accesses to DRAM energy and performance status in conjunction with
the power limiting feature to budget power between the various memory sub-systems
in the server system.
Figure 2-20. DRAM Power Limit Performance Data
2.5.2.6.11 CPU Thermal and Power Optimization Capabilities
Table 2-8 provides a summary of the processor power and thermal optimization
capabilities that can be accessed over PECI.
Note: The Index values referenced in Table 2-8 are in decimal format.
Table 2-8 also provides information on alternate inband mechanisms to access similar
or equivalent information for register reads and writes where applicable. The user
should consult the appropriate Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family Processor
Datasheet, Volume Two: Registers for exact details on MSR or CSR register content.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 45
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 46

Table 2-8. RdPkgConfig() & WrPkgConfig() CPU Thermal and Power Optimization
Services Summary (Sheet 1 of 3)
Service
Package
Identifier
Read
Package
Power SKU
Unit Read
Package
Power SKU
Read
Package
Power SKU
Read
“Wake on
PECI” Mode
bit Write /
Read
“Wake on
PECI” Mode
bit Write /
Read
Accumulated
Run Time
Read
Package
Temperature
Read
Index
Value
(decimal)
00 0x0000 CPUID
30 0x0000 Time, Energy
28 0x0000 Package Power
29 0x0000 Package Power
05 0x0001 -
05 0x0000 “Wake on
31 0x0000 T otal reference
02 0x00FF Processor
Parameter
Value
(word)
0x0001 Platform ID Used to ensure
0x0002 PCU Device ID Returns the Device
0x0003 Max Thread ID Returns the
0x0004 CPU Microcode
0x0005 MCA Error
Set
0x0000 -
Reset
RdPkgConfig
()
Data
(dword)
Information
Update
Revision
Source Log
and Power
Units
SKU[31:0]
SKU[64:32]
N/A “Wake on
PECI” mode
bit
time
package
Temperature
WrPkgConfig
()
Data
(dword)
N/A Read units for power,
N/A Returns Thermal
N/A Returns the
PECI” mode bit
N/A Read status of
N/A Returns the total run
N/A Returns the
Description
Returns processorspecific information
including CPU family,
model and stepping
information.
microcode update
compatibility with
processor.
ID information for
the processor Power
Control Unit.
maximum ‘Thread
ID’ value supported
by the processor.
Returns processor
microcode and PCU
firmware revision
information.
Returns the MCA
Error Source Log
energy and time
used in power
control registers.
Design Power and
minimum package
power values for the
processor SKU.
maximum package
power value for the
processor SKU and
the maximum time
interval for which it
can be sustained.
Enables package
pop-up to C2 to
service PECI
PCIConfig() accesses
if appropriate.
“Wake on PECI”
mode bit
time.
maximum processor
die temperature in
PECI format.
Alternate
Inband
MSR or CSR
Access
Execute CPUID instruction to get
processor signature
MSR 17h: IA32_PLATFORM_ID
CSR: DID
MSR: RESOLVED_CORES_MASK
CSR: RESOLVED_CORES_MASK
MSR 8Bh: IA32_BIOS_SIGN_ID
CSR: MCA_ERR_SRC_LOG
PACKAGE_POWER_SKU_UNIT
PACKAGE_POWER_SKU_UNIT
CSR: PACKAGE_POWER_SKU
CSR: PACKAGE_POWER_SKU
IA32_TIME_STAMP_COUNTER
IA32_PACKAGE_THERM_STATUS
MSR 606h:
CSR:
MSR 614h:
PACKAGE_POWER_SKU
MSR 614h:
PACKAGE_POWER_SKU
MSR 10h:
MSR 1B1h:
Interfaces
N/A
N/A
46 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 47
Interfaces
Table 2-8. RdPkgConfig() & WrPkgConfig() CPU Thermal and Power Optimization
Services Summary (Sheet 2 of 3)
Service
Per Core DTS
Temperature
Read
Temperature
Target Read
Package
Thermal
Status Read /
Clear
Thermal
Averaging
Constant
Write/Read
Thermal
Averaging
Constant
Write/Read
Thermally
Constrained
Time Read
Current Limit
Read
Accumulated
Energy Status
Read
Power Limit
for the VCC
Power Plane
Write / Read
Power Limit
for the VCC
Power Plane
Write / Read
Package
Power Limits
for Multiple
Turbo Modes
Index
Value
(decimal)
09 0x0000-
Parameter
Value
(word)
0x0007
(cores 0-7)
0x00FF -
System
Agent
16 0x0000 Processor
20 0x0000 Thermal
21 0x0000 Thermal
21 0x0000 N/A Thermal
32 0x0000 Thermally
17 0x0000 Current Limit
03 0x0000 -
VCC
0x00FF -
CPU
package
25 0x0000 N/A Power Limit
25 0x0000 Power Limit
26 0x0000 N/A Power Limit 1
RdPkgConfig
()
Data
(dword)
Per core DTS
maximum
temperature
and
T
Prochot
T
CONTROL
Status
Register
Averaging
Constant
Constrained
Time
per power
plane
Accumulated
CPU energy
Data
WrPkgConfig
()
Data
Description
(dword)
N/A Read the maximum
DTS temperature of
a particular core or
the System Agent
within the processor
die in relative PECI
temperature format
N/A Returns the
PROCHOT_N
assertion
temperature and
processor T
N/A Read the thermal
status register and
optionally clear any
log bits. The register
includes status and
log bits for TCC
activation,
PROCHOT_N
assertion and Critical
Temperature.
N/A Reads the Thermal
Averaging Constant
Averaging
Constant
N/A Read the time for
Writes the Thermal
Averaging Constant
which the processor
has been operating
in a lowered power
state due to internal
TCC activation.
N/A Reads the current
limit on the VCC
power plane
N/A Returns the value of
Data
N/A Read power limit
the energy
consumed by just
the VCC power plane
or entire CPU
package.
Program power limit
for VCC power plane
data for VCC power
plane
Write power limit
Data
data 1 in multiple
turbo mode.
CONTROL
Alternate
Inband
MSR or CSR
Access
MSR 19Ch:
IA32_THERM_STATUS
MSR 1A2h:
TEMPERATURE_TA RGET
CSR: TEMPERATURE_TARGET
.
IA32_PACKAGE_THERM_STATUS
MSR 1B1h:
PRIMARY_PLANE_CURRENT_
CONFIG_CONTROL
MSR 639h: PP0_ENERGY_
STATUS
CSR: PP0_ENERGY_STATUS
MSR 611h:
PACKAGE_ENERGY_STATUS
CSR: PACKAG_ENERGY_STATUS
MSR 638h: PP0_POWER_LIMIT
CSR: PP0_POWER_LIMIT
MSR 638h: PP0_POWER_LIMIT
CSR: PP0_POWER_LIMIT
MSR 610h:
PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT
CSR: PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT
N/A
N/A
N/A
CSR:
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 47
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 48
Table 2-8. RdPkgConfig() & WrPkgConfig() CPU Thermal and Power Optimization
Services Summary (Sheet 3 of 3)
Service
Package
Power L imits
for Multiple
Turbo Modes
Package
Power L imits
for Multiple
Turbo Modes
Package
Power L imits
for Multiple
Turbo Modes
Package
Power L imit
Performance
Status Read
Efficient
Performance
Indicator Read
ACPI P-T
Notify Write &
Read
ACPI P-T
Notify Write &
Read
Caching Agent
TOR Read
Thermal
Margin Read
Index
Value
(decimal)
27 0x0000 N/A Power Limit 2
26 0x0000 Power Limit 1
27 0x0000 Power Limit 2
08 0x00FF -
06 0x0000 Number of
33 0x0000 N/A New p-state
33 0x0000 New p-state
39 Cbo Index,
10 0x0000 Thermal
Parameter
Value
(word)
CPU
package
TOR Index,
Bank#;
Read Mode
RdPkgConfig
()
Data
(dword)
Data
Data
Accumulated
CPU throttle
time
productive
processor
cycles
equivalent of
P1 used in
conjunction
with package
power limiting
Caching Agent
(Cbo) T able o f
Requests
(TOR) data;
Core ID &
associated
valid bit
margin to
processor
thermal profile
or load line
WrPkgConfig
()
Data
(dword)
Data
N/A Read power limit 1
N/A Read power limit 2
N/A Read the total time
N/A Read number of
equivalent of
P1 used in
conjunction
with package
power limiting
N/A Read the processor
N/A Read the Cbo TOR
N/A Read margin to
Description
Write power limit
data 2 in multiple
turbo mode.
data in multiple
turbo mode.
data in multiple
turbo mode.
for which the
processor package
was throttled due to
power limiting.
productive cycles for
power budgeting
purposes.
Notify the processor
PCU of the new p-
state that is one
state below the
turbo frequency as
specified through the
last ACPI Notify
PCU to determine
the p-state that is
one state below the
turbo frequency as
specified through the
last ACPI Notify
data for all enabled
cores in the event of
a 3-strike timeout.
Can alternatively be
used to read ‘Core
ID’ data to confirm
that IERR was
caused by a core
timeout
processor thermal
load line
Alternate
Inband
MSR or CSR
Access
MSR 610h:
PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT
CSR: PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT
MSR 610h:
PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT
CSR: PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT
MSR 610h:
PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT
CSR: PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT
PACKAGE_RAPL_PERF_STATUS
CSR:
Interfaces
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
2.5.2.6.12 Package Identifier Read
This feature enables the PECI host to uniquely identify the PECI client processor. The
parameter field encodings shown in Table 2-8 allow the PECI host to access the
relevant processor information as described below.
48 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 49

CPU ID Data
Model
4
20
Stepping ID
3 0
Family ID
16
Processor
Type
1931
RESERVED
27
Extended
Model
Extended
Family ID
78111228
RESERVED
1315 14
Platform ID Data
Processor
Flag
Reserved
2
31
0
3
PCU Device ID Data
RESERVED
031
PCU Device ID
1516
Maximum Thread ID Data
Max Thread
ID
Reserved
3
31
0
4
Interfaces
• CPUID data: This is the equivalent of data that can be accessed through the
CPUID instruction execution. It contains processor type, stepping, model and
family ID information as shown in
Figure 2-21. CPUID Data
• Platform ID data: The Platform ID data can be used to ensure processor
microcode updates are compatible with the processor. The value of the Platform ID
or Processor Flag[2:0] as shown in
type and processor stepping. Refer to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures
Software Developer’s Manual for more information.
Figure 2-22. Platform ID Data
Figure 2-21.
Figure 2-22 is typically unique to the platform
• PCU Device ID: This information can be used to uniquely identify the processor
power control unit (PCU) device when combined with the Vendor Identification
register content and remains constant across all SKUs. Refer to the appropriate
register description for the exact processor PCU Device ID value.
Figure 2-23. PCU Device ID
• Max Thread ID: The maximum Thread ID data provides the number of supported
processor threads. This value is dependent on the number of cores within the
processor as determined by the processor SKU and is independent of whether
certain cores or corresponding threads are enabled or disabled.
Figure 2-24. Maximum Thread ID
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 49
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 50

CPU microcode and PCU firmware revision
31
0
CPU code patch revision
MCA Error Source Log
Reserved
28
0
MCERRIERRCATERR
293031
Reserved
2031
Time Unit19Reserved
16 15
Energy Unit
12 8
Reserved Power U n it
13 7 4 3 0
• CPU Microcode Update Revision: Reflects the revision number for the microcode
update and power control unit firmware updates on the processor sample. The
revision data is a unique 32-bit identifier that reflects a combination of specific
versions of the processor microcode and PCU control firmware.
Figure 2-25. Processor Microcode Revision
• Machine Check Status: Returns error information as logged by the MCA Error
Source Log register. See Figure 2-26 for details. The power control unit will assert
the relevant bit when the error condition represented by the bit occurs. For
example, bit 29 will be set if the package asserted MCERR, bit 30 is set if the
package asserted IERR and bit 31 is set if the package asserted CAT_ERR_N. The
CAT_ERR_N may be used to signal the occurrence of a MCERR or IERR.
Figure 2-26. Machine Check Status
Interfaces
2.5.2.6.13 Package Power SKU Unit Read
This feature enables the PECI host to read the units of time, energy and power used in
the processor and DRAM power control registers for calculating power and timing
parameters. In Figure 2-27, the default value of the power unit field [3:0] is 0011b,
energy unit [12:8] is 10000b and the time unit [19:16] is 1010b. Actual unit values are
calculated as shown in Table 2-9.
Figure 2-27. Package Power SKU Unit Data
Table 2-9. Power Control Register Unit Calc ulat ions
Unit Field Value Calculation Default Value
Time 1s / 2
Energy 1J / 2
Power 1W / 2
TIME UNIT
ENERGY UNIT
POWER UNIT
1s / 210 = 976 µs
1J / 216 = 15.3 µJ
1W / 23 = 1/8 W
50 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 51

Package Power SKU (lower bits)
Reserved
14
Minimum Package Power
16
TDP Package Power
30 015
Reserved
31
Package Power SKU (upper bits)
Maximum Package Power
3246
Reserved
47
Maximum Time
Window
4854
Reserved
5563
Interfaces
2.5.2.6.14 Package Power SKU Read
This read allows the PECI host to access the minimum, Thermal Design Power and
maximum power settings for the processor package SKU. It also returns the maximum
time interval or window over which the power can be sustained. If the power limiting
entity specifies a power limit value outside of the range specified through these
settings, power regulation cannot be guaranteed. Since this data is 64 bits wide, PECI
facilitates access to this register by allowing two requests to read the lower 32 bits and
upper 32 bits separately as shown in Table 2-8. Power units for this read are
determined as per the Package Power SKU Unit settings described in
Section 2.5.2.6.13.
‘Package Powe r SKU data’ is programmed by the PCU firmw are during boot time b ased
on SKU dependent power-on default values set during manufacturing. The TDP
package power specified through bits [14:0] in Figure 2-28 is the maximum value of
the ‘Power Limit1’ field i n Section 2.5.2.6.26 while the maximum package power in bits
[46:32] is the maximum value of the ‘Power Limit2’ field.
The minimum package power in bits [30:16] is applicable to both the ‘Power Limit1’ &
‘Power Limit2’ fields and corresponds to a mode when all the cores are operational and
in their lowest frequency mode. Attempts to program the power limit below the
minimum power value may not be effective since BIOS/OS, and not the PCU, controls
disabling of cores and core activity.
The ‘maximum time window’ in bits [54:48] is representative of the maximum rate at
which the power control unit (PCU) can sample the package energy consumption and
reactively take the necessary measures to meet the imposed power limits.
Programming too large a time window runs the risk of the PCU not being able to
monitor and take timely action on package energy excursions. On the other hand,
programming too small a time window may not give the PCU enough time to sample
energy information and enforce the limit. The minimum value of the ‘time window’ can
be obtained by reading bits [21:15] of the PWR_LIMIT_MISC_INFO CSR using the PECI
RdPCIConfigLocal() command.
Figure 2-28. Package Power SKU Data
2.5.2.6.15 “Wake on PECI” Mode bit Write / Read
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 51
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Setting the “Wake on PECI” mode bit enables successful completion of the
WrPCIConfigLocal(), RdPCIConfigLocal(), WrPCIConfig() and RdPCIConfig() PECI
commands by forcing a package ‘pop-up’ to the C2 state to service these commands if
the processor is in a low-power state. The exact power impact of such a ‘pop-up’ is
determined by the product SKU, the C-state from which the pop-up is initiated an d the
Page 52

T
n
T
n1–
255
256
------
t
n
256
------
+
×=
Sign
Bit
14
RESERVED
16
PECI Temperature
(Integer Value)
61531
PECI Temperature
(Frac tio na l V alu e)
5 0
negotiated PECI bit rate. A ‘reset’ or ‘clear’ of this bit or simply not setting the “Wake
on PECI” mode bit could result in a “timeout” response (completion code of 0x82) from
the processor indicating that the resources required to service the command are in a
low power state.
Alternatively, this mode bit can also be read to determine PECI behavior in package
states C3 or deeper.
2.5.2.6.16 Accumulated Run Time Read
This read returns the total time for which the processor has been executing with a
resolution of 1mS per count. This is tracked by a 32-bit counter that rolls over on
reaching the maximum value. This counter activates and starts counting for the first
time at RESET_N de-assertion.
2.5.2.6.17 Package Temperature Read
This read returns the maximum processor die temperature in 16-bit PECI format. The
upper 16 bits of the response data are reserved. The PECI temperature data returned
by this read is an exponential moving average of the maximum sensor temperature
(max [core and uncore sensors]), updated once every ms. The equation for the update
is:
Interfaces
Where: Tn is the current average value
T
is the last average value
n-1
is the current maximum sensor temperature
t
n
Figure 2-29. Package Temperature Read Data
Note: This value is not the value as returned by the PECI GetTemp() described in
Section 2.5.2.3.
2.5.2.6.18 Per Core DTS Temperature Read
This feature enables the PECI host to read the maximum value of the DTS temperature
for any specific core within the processor . Alternativ ely, this service can be used to read
the System Agent temperature. Temperature is returned in the same format as the
Package Temperature Read described in Section 2.5.2.6.17. Data is returned in relative
PECI temperature format.
Reads to a parameter value outside the supported range will return an error as
indicated by a completion code of 0x90. The supported range of parameter values can
vary depending on the number of cores within the processor. The temperature data
returned through this feature is the instantaneous value and not an averaged value. It
is updated once every 1 mS.
52 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 53

Critical Temperature Log
Critical Temperature Status
Bidirectional PROCHOT# Log
Bidirectional PROCHOT#
Status
TCC Activation Log
TCC Activation Status
31
6543210
Reserved
Interfaces
2.5.2.6.19 Temperature Target Read
The Temperature Target Read allows the PECI host to obtain the target DTS
temperature (T
) for PROCHOT_N assertion in degrees Celsius. This is the
Prochot
minimum temperature at which the processor thermal control circuit (TCC) activates.
The actual temperature of TCC activation may vary slightly between processor units
due to manufacturing process variations. The Temperature T arget read also returns the
processor T
CONTROL
value. T
CONTROL
is returned in standard PECI temperature format
and represents the threshold temperature used by the thermal management system
for fan speed control.
Figure 2-30. Temperature Target Read
2.5.2.6.20 Package Thermal Status Read / Clear
The Thermal Status Read provides information on package level thermal status. Data
includes:
• Thermal Control Circuit (TCC) activation
• Bidirectional PROCHOT_N signal assertion
•Critical Temperature
Both status and sticky log bits are managed in this status word. All sticky log bits are
set upon a rising edge of the associated status bit and the log bits are cleared only by
Thermal Status reads or a processor reset. A read of the Thermal Status word always
includes a log bit clear mask that allows the host to clear any or all of the log bits that
it is interested in tracking.
A bit set to ‘0’ in the log bit clear mask will result in clearing the associated log bit. If a
mask bit is set to ‘0’ and that bit is not a legal mask, a failing completion code will be
returned. A bit set to ‘1’ is ignored and results in no change to any sticky log bits. For
example, to clear the TCC Activation Log bit and retain all other log bits, the Thermal
Status Read should send a mask of 0xFFFFFFFD.
Figure 2-31. Thermal Status Word
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 53
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 54

Thermal Averaging Constant
RESERVED
431
PECI Temperature
Averaging Constant
3 0
Current Config Limit Data
RESERVED
1331
Current Limit for processor VCC
12 0
2.5.2.6.21 Thermal Averaging Constant Write/Read
This feature allows the PECI host to control the window over which the estimated
processor PECI temperature is filtered. The host may configure this window as a power
of two. For example, programming a value of 5 results in a filtering window of 25 or 32
samples. The maximum programmable value is 8 or 256 samples. Programming a
value of zero would disable the PECI temperature averaging feature. The default value
of the thermal averaging constant is 4 which translates to an aver aging window size of
4
or 16 samples. More details on the PECI temperature filtering function can be found
2
in Section 2.5.7.3.
Figure 2-32. Thermal Averaging Constant Write / Read
2.5.2.6.22 Thermally Constraine d Time Read
This features allows the PECI host to access the total time for which the processor has
been operating in a lowered power state due to TCC activation. The returned data
includes the time required to ramp back up to the original P-state target after TCC
activation expires. This timer does not include TCC activation as a result of an external
assertion of PROCHOT_N. This is tracked by a 32-bit counter with a resolution of 1mS
per count that rolls over or wraps around. On the processor PECI clients, the only logic
that can be thermally constrained is that supplied by VCC.
Interfaces
2.5.2.6.23 Current Limit Read
This read returns the current limit for the processor VCC power plane in 1/8A
increments. Actual current limit data is contained only in the lower 13 bits of the
response data. The default return value of 0x438 corresponds to a current limit value of
135A.
Figure 2-33. Current Config Limit Read Data
2.5.2.6.24 Accumulated Energy Status Read
This service can return the value of the total energy consumed by the entire processor
package or just the logic supplied by the VCC power plane as specified through the
parameter field in Table 2-8. This information is tracked by a 32-bit counter that wraps
around and continues counting on reaching its limit. Energy units for this read are
determined as per the Package Power SKU Unit settings described in
Section 2.5.2.6.13.
54 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 55

Accumulated Energy Status
Accumulated CPU Energy
0
31
Interfaces
While Intel requires reading the accumulated energy data at least once every 16
seconds to ensure functional correctness, a more realistic polling rate recommendation
is once every 100mS for better accuracy. This feature assumes a 150W processor. In
general, as the power capability decreases, so will the minimum polling rate
requirement.
When determining energy changes by subtracting energy values between successive
reads, Intel advocates using the 2’s complement method to account for counter
wraparounds. Alternatively, adding all ‘F’s (‘0xFFFFFFFF’) to a negative result from the
subtraction will accomplish the same goal.
Figure 2-34. Accumulated Energy Read Data
2.5.2.6.25 Power Limit for the VCC Power Plane Write / Read
This feature allows the PECI host to program the power limit over a specified time or
control window for the processor logic supplied by the VCC power plane. This typically
includes all the cores, home agent and last level cache. The processor does not support
power limiting on a per-core basis. Actual power limit values are chosen based on the
external VR (voltage regulator) capabilities. The units for the Power Limit and Control
Time Window are determined as per the Package Power SKU Unit settings described in
Section 2.5.2.6.13.
Since the exact VCC plane power limit value is a function of the platform VR, this
feature is not enabled by default and there are no default values associated with the
power limit value or the control time window. The Power Limit Enable bit in Figure 2-35
should be set to activate this feature. The Clamp Mode bit is also required to be set to
allow the cores to go into power states below what the operating system originally
requested. In general, this feature provides an improved mechanism for VR protection
compared to the input PROCHOT_N signal assertion method. Both power limit enabling
and initialization of power limit values can be done in the same command cycle. Setting
a power limit for the VCC plane enables turbo modes for associated logic. External VR
protection is guaranteed during boot through operation at safe voltage and frequency.
All RAPL parameter values including the power limit value, control time window, clamp
mode and enable bit will have to be specified correctly even if the intent is to change
just one parameter value when programming over PECI.
The usefulness of the VCC power plane RAPL may be somewhat limited if the platform
has a fully compliant external voltage regulator. However, platforms using lower cost
voltage regulators may find this feature useful. The VCC RAPL value is generally
expected to be a static value after initialization and there may not be any use cases for
dynamic control of VCC plane power limit values during run time. BIOS may be ideally
used to read the VR (and associated heat sink) capabilities and program the PCU with
the power limit information during boot. No matter what the method is, Intel
recommends exclusive use of just one entity or interface, PECI for instance, to manage
VCC plane power limiting needs. If PECI is being used to manage VCC plane power
limiting activities, BIOS should lock out all subsequent inband VCC plane power limiting
accesses by setting bit 31 of the PP0_POWER_LIMIT MSR and CSR to ‘1’.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 55
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 56

VCC Power Plane Power Limit Data
Power Limit
Enable
1523
VCC Plane Power Limit
14 0
Clamp
Mode
16
Control Time
Window
1731
RESERVED
24
The same conversion formula used for DRAM Power Limiting (see Section 2.5.2.6.9)
should be applied for encoding or programming the ‘Control Time Window’ in bits
[23:17].
Figure 2-35. Power Limit Data for VCC Power Plane
2.5.2.6.26 Package Power Limits for Multiple Turbo Modes
This feature allows the PECI host to program two power limit values to support multiple
turbo modes. The operating systems and drivers can balance the power budget using
these two limits. Two separate PECI requests are available to program the lower and
upper 32 bits of the power limit data shown in Figure 2-36. The units for the Power
Limit and Control Time Window are determined as per the Package Power SKU Unit
settings described in Section 2.5.2.6.13 while the valid range for power limit values are
determined by the Package Power SKU settings described in w are determined as per
the Package Power SKU Unit settings described in Section 2.5.2.6.14. Setting the
Clamp Mode bits is required to allow the cores to go into power states below what the
operating system originally requested. The Power Limit Enable bits should be set to
enable the power limiting function. Power limit values, enable and clamp mode bits can
all be set in the same command cycle. All RAPL parameter values including the power
limit value, control time window, clamp mode and enable bit will have to be specified
correctly even if the intent is to change just one parameter value when programming
over PECI.
Interfaces
Intel recommends exclusive use of just one entity or interface, PECI for instance, to
manage all processor package power limiting and budgeting needs. If PECI is being
used to manage package power limiting activities, BIOS should lock out all subsequent
inband package power limiting accesses by setting bit 31 of the
PACKAGE_POWER_LIMIT MSR and CSR to ‘1’. The ‘power limit 1’ is intended to limit
processor power consumption to any reasonable value below TDP and defaults to TDP.
‘Power Limit 1’ values may be impacted by the processor heat sinks and system air
flow. Processor ‘power limit 2’ can be used as appropriate to limit the current drawn by
the processor to prevent any external power supply unit issues. The ‘Power Limit 2’
should always be programmed to a value (typically 20%) higher than ‘Power Limit 1’
and has no default value associated with it.
Though this feature is disabled by default and external programming is required to
enable, initialize and control package power limit values and time windows, the
processor package will still turbo to TDP if ‘Power Limit 1’ is not enabled or initialized.
‘Control Time Window#1’ (Power_Limit_1_Time also known as Tau) values may be
programmed to be within a range of 250 mS-40 seconds. ‘Control Time Window#2’
(Power_Limit_2_Time) values should be in the range 3 mS-10 mS.
The same conversion formula used for the DRAM Power Limiting feature (see
Section 2.5.2.6.9) should be applied when programming the ‘Control Time Window’ bits
[23:17] for ‘power limit 1’ in Figure 2-36. The ‘Control Time Window’ for ‘power limit 2’
can be directly programmed into bits [55:49] in units of mS without the aid of any
conversion formulas.
56 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 57

Package Power Limit 1
Power Limit
Enable #1
1523
Power Limit # 1
14 0
Clamp
Mode #1
16
Control Time
Window #1
1731
RESERVED
24
Package Power Limit 2
Power Limit
Enable #2
4755
Power Limit # 2
46 32
Clamp
Mode #2
48
Control Time
Window #2
4963
RESERVED
56
Accumulated CPU Throttle Time
Accumulated CPU Throttle Time
0
31
Interfaces
Figure 2-36. Package Turbo Power Limit Data
2.5.2.6.27 Package Power Limit Performance Status Read
This service allows the PECI host to assess the performance impact of the currently
active power limiting modes. The read return data contains the total amount of time for
which the entire processor package has been operating in a power state that is lower
than what the operating system originally requested. This information is tracked by a
32-bit counter that wraps around. The unit for time is determined as per the Package
Power SKU Unit settings described in w are determined as per the Package Power SKU
Unit settings described in Section 2.5.2.6.13.
Figure 2-37. Package Power Limit Performance Data
2.5.2.6.28 Efficient Performance Indicator Read
The Efficient Performance Indicator (EPI) Read provides an indication of the total
number of productive cycles. Specifically, these are the cycles when the processor is
engaged in any activity to retire instructions and as a result, consuming energy. Any
power management entity monitoring this indicator should sample it at least once
every 4 seconds to enable detection of wraparounds. Refer to the Intel® 64 and IA-32
Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, for details on programming the
IA32_ENERGY_PERFORMANCE_BIAS register to set the ‘Energy Efficiency’ policy of
the processor.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 57
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 58

Efficien t Pe rfo r m a nc e Ind ica to r D a ta
Efficient Performance Cycles
0
31
ACPI P-T Notify Data
New P1 stateReserved
7
31
0
8
Figure 2-38. Efficient Performance Indicator Read
2.5.2.6.29 ACPI P-T Notify Write & Read
This feature enables the processor turbo capability when used in conjunction with the
PECI package RAPL or power limit. When the BMC sets the package power limit to a
value below TDP, it also determines a new corresponding turbo frequency and notifies
the OS using the ‘ACPI Notify’ mechanism as supported by the _PPC or performance
present capabilities object. The BMC then notifies the processor PCU using the PECI
‘ACPI P-T Notify’ service by programming a new state that is one p-state below the
turbo frequency sent to the OS via the _PPC method.
When the OS requests a p-state higher than what is specified in bits [7:0] of the PECI
ACPI P-T Notify data field, the CPU will treat it as request for P0 or turbo. The PCU will
use the IA32_ENERGY_PERFORMANCE_BIAS register settings to determine the exact
extent of turbo. Any OS p-state request that is equal to or below what is specified in
the PECI ACPI P-T Notify will be granted as long as the RAPL power limit does not
impose a lower p-state. However, turbo will not be enabled in this instance even if there
is headroom between the processor energy consumption and the RAPL power limit.
Interfaces
This feature does not affect the Thermal Monitor behavior of the processor nor is it
impacted by the setting of the power limit clamp mode bit.
Figure 2-39. ACPI P-T Notify Data
2.5.2.6.30 Caching Agent TOR Read
This feature allows the PECI host to read the Caching Agent (Cbo) Table of Requests
(TOR). This information is useful for debug in the event of a 3-strike timeout that
results in a processor IERR assertion. The 16-bit parameter field is used to specify the
Cbo index, TOR array index and bank number according to the following bit
assignments.
• Bits [1:0] - Bank Number - legal values from 0 to 2
• Bits [6:2] - TOR Array Index - legal values from 0 to 19
• Bits [10:7] - Cbo Index - legal values from 0 to 7
• Bit [11] - Read Mode - should be set to ‘0’ for TOR reads, ‘1’ for Core ID reads
• Bits [15:12] - Reserved
58 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 59

Read Mode (bit 11) = ‘0’ (within the Paramenter)
031
Cbo TOR Data
Read Mode (bit 11) = ‘1’ (within the Parameter)
RESERVED
031
Core ID
35
Valid
4
Sign
Bit
14
RESERVED
16
Thermal Margin
(Integer Value)
61531
The rmal Marg in
(Fra c t io nal Value)
5 0
Interfaces
Bit[11] is the Read Mode bit and should be set to ‘0’ for TOR reads. The Read Mode bit
can alternatively be set to ‘1’ to read the ‘Core ID’ (with associated valid bit as shown in
Figure 2-40) that points to the first core that asserted the IERR. In this case bits [10:0]
of the parameter field are ignored. The ‘Core ID’ read may not return valid data until at
least 1 mS after the IERR assertion.
Figure 2-40. Caching Agent TOR Read Data
Note: Reads to caching agents that are not enabled will return all zeroes. Refer to the debug handbook for
details on methods to interpret the crash dump results using the Cbo TOR data shown in Figure 2-40.
2.5.2.6.31 Thermal Margin Read
This service allows the PECI host to read the margin to the processor thermal profile or
load line. Thermal margin data is returned in the format shown in Figure 2-41 with a
sign bit, an integer part and a fractional part. A negative thermal margin value implies
that the processor is operating in violation of its thermal load line and may be indicative
of a need for more aggressive cooling mechanisms through a fan speed increase or
other means. This PECI service will continue to return valid margin values even when
the processor die temperature exceeds T
Figure 2-41. DTS Thermal Margin Read
2.5.2.7 RdIAMSR()
The RdIAMSR() PECI command provides read access to Model Specific Registers
(MSRs) defined in the processor’s Intel® Architecture (IA). MSR definitions may be
found in the Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family Processor Datasheet,
Volume Two: Registers. Refer to Table 2-11 for the exact listing of processor registers
accessible through this command.
Prochot
.
2.5.2.7.1 Command Format
The RdIAMSR() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x05
Read Length: 0x09 (qword)
Command: 0xb1
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 59
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 60
T0T1T0T1T0T1T0T1T0T1T0T1T0T1T0T1
C0C1C2C3…………………C10C11C12
0123456………………181920212223
Processor
ID (0...23)
Cores 0,1,2...12
Thread (0,1) Mask for Core10
7
Description: Returns the data maintained in the processor IA MSR space as specified
by the ‘Processor ID’ and ‘MSR Address’ fields. The Read Length dictates the desired
data return size. This command supports only qword responses. All command
responses are prepended with a completion code that contains additional pass/fail
status information. Refer to Section 2.5.5.2 for details regarding completion codes.
2.5.2.7.2 Processor ID Enumeration
The ‘Processor ID’ field that is used to address the IA MSR space refers to a specific
logical processor within the CPU. The ‘Processor ID’ always refers to the same physical
location in the processor silicon regardless of configuration as shown in the example in
Figure 2-42. For example, if certain logical processors are disabled by BIOS, the
Processor ID mapping will not change. The total number of Processor IDs on a CPU is
product-specific.
‘Processor ID’ enumeration involves discovering the logical processors enabled within
the CPU package. This can be accomplished by reading the ‘Max Thread ID’ value
through the RdPkgConfig() command (Index 0, Parameter 3) described in
Section 2.5.2.6.12 and subsequently querying each of the supported processor
threads. Unavailable processor threads will return a completion code of 0x90.
Alternatively, this information may be obtained from the RESOLVED_CORES_MASK
register readable through the RdPCIConfigLocal() PECI command described in
Section 2.5.2.9 or other means. Bits [7:0] and [9:8] of this register contain the ‘Core
Mask’ and ‘Thread Mask’ information respectively. The ‘Thread Mask’ applies to all the
enabled cores within the processor package as indicated by the ‘Core Mask’. For
the processor PECI clients, the ‘Processor ID’ may take on values in the range 0
through 23.
Interfaces
Figure 2-42. Processor ID Construction Example
60 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 61

Interfaces
Figure 2-43. RdIAMSR()
Note: The 2-byte MSR Address field and read data field defined in Figure 2-43 are sent in standard PECI
ordering with LSB fir st and MSB last.
2.5.2.7.3 Supported Responses
The typical client response is a passing FCS, a passing Completion Code and valid data.
Under some conditions, the client’s response will indicate a failure.
Table 2-10. RdIAMSR() Response Definition
Response Meaning
Bad FCS Electrical error
Abort FCS Illegal command formatting (mismatched RL/WL/Command Code)
CC: 0x40 Command passed, data is valid.
CC: 0x80 Response timeout. The processor was not able to generate the required response in a timely
CC: 0x81 Response timeout. The processor is not able to allocate resources for servicing this command
CC: 0x82 The processor hardware resources required to service this command are in a low power state.
CC: 0x90 Unknown/Invalid/Illegal Request
CC: 0x91 PECI control hardware, firmware or associated logic error. The processor is unable to process
fashion. Retry is appropriate.
at this time. Retry is appropriate.
Retry may be appropriate after modification of PECI wake mode behavior if appropriate.
the request.
2.5.2.7.4 RdIAMSR() Capabilities
The processor PECI client allows PECI RdIAMSR() access to the registers listed in
Table 2-11. These registers pertai n to the processor core and uncore error banks
(machine check banks 0 through 19). Information on the exact number of accessible
banks for the processor device may be obtained by reading the IA32_MCG_CAP[7:0]
MSR (0x0179). This register may be alternatively read using a RDMSR RBIOS
instruction. Please consult the Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Prodcut Family
Specification Update for more information on the exact number of cores supported by a
particular processor SKU. Any attempt to read processor MSRs that are not accessible
over PECI or simply not implemented will result in a completion code of 0x90.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 61
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 62

PECI access to these registers is expected only when in-band access mechanisms are
not available.
Table 2-11. RdIAMSR() Services Summary12
Interfaces
Processor
ID (byte)
0x0-0xF 0x0400 IA32_MC0_CTL
MSR
Address
(dword)
Meaning
Processor
ID (byte)
0x0-0xF 0x041B IA32_MC6_MISC 0x0-0xF 0x0436 IA32_MC13_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x0280 IA32_MC0_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x041C IA32_MC7_CTL
0x0-0xF 0x0401 IA32_MC0_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x0287 IA32_MC7_CTL2
0x0-0xF 0x0402 IA32_MC0_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x041D IA32_MC7_STATUS
1
0x0-0xF 0x0403 IA32_MC0_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x041E IA32_MC7_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x0439 IA32_MC14_STATUS
0x0-0xF 0x0404 IA32_MC1_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x041F IA32_MC7_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x0281 IA32_MC1_CTL2
0x0-0xF 0x0420 IA32_MC8_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x043B IA32_MC14_MISC
MSR
Address
(dword)
Meaning
Processor
ID (byte)
MSR
Address
(dword)
Meaning
0x0-0xF 0x0437 IA32_MC13_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x0438 IA32_MC14_CTL
0x0-0xF 0x028E IA32_MC14_CTL2
0x0-0xF 0x043A IA32_MC14_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x0405 IA32_MC1_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x0288 IA32_MC8_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x043C IA32_MC15_CTL
0x0-0xF 0x0406 IA32_MC1_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x0407 IA32_MC1_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x0408 IA32_MC2_CTL
0x0-0xF 0x0282 IA32_MC2_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x0424 IA32_MC9_CTL
0x0-0xF 0x0409 IA32_MC2_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x0289 IA32_MC9_CTL2
0x0-0xF 0x040A IA32_MC2_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x040B IA32_MC2_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x040C IA32_MC3_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x0427 IA32_MC9_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x0283 IA32_MC3_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x0428 IA32_MC10_CTL
0x0-0xF 0x0421 IA32_MC8_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x028F IA32_MC15_CTL2
0x0-0xF 0x0422 IA32_MC8_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x043D IA32_MC15_STATUS
2
0x0-0xF 0x0423 IA32_MC8_MISC 0x0-0xF 0x043E IA32_MC15_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x043F IA32_MC15_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x0440 IA32_MC16_CTL
2
0x0-0xF 0x0425 IA32_MC9_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x0290 IA32_MC16_CTL2
2
0x0-0xF 0x0426 IA32_MC9_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x0441 IA32_MC 16_STATUS
0x0-0xF 0x0442 IA32_MC16_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x0443 IA32_MC16_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x040D IA32_MC3_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x028A IA32_MC10_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x0444 IA32_MC17_CTL
0x0-0xF 0x040E IA32_MC3_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x0429 IA32_MC10_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x0291 IA32_MC17_CTL2
0x0-0xF 0x040F IA32_MC3_MISC 0x0-0xF 0x042A IA32_MC10_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x0445 IA32_MC17_STATUS
0x0-0xF 0x0410 IA32_MC4_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x042B IA32_MC10_MISC 0x0-0xF 0x0446 IA32_MC17_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x0284 IA32_MC4_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x042 C IA32_MC11_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x0447 IA32_MC17_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x0411 IA32_MC4_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x028B IA32_MC11_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x0448 IA32_MC18_CTL
2
0x0-0xF 0x0412 IA32_MC4_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x0413 IA32_MC4_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x042D IA32_MC11_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x0292 IA32_MC18_CTL2
2
0x0-0xF 0x042E IA32_MC11_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x0449 IA32_MC18_STATUS
0x0-0xF 0x0414 IA32_MC5_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x042F IA32_MC11_MISC 0x0-0xF 0x044A IA32_MC18_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x0285 IA32_MC5_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x043 0 IA32_MC12_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x044B IA32_MC18_MISC
0x0-0xF 0x0415 IA32_MC5_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x028C IA32_MC12_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x044C IA32_MC19_CTL
0x0-0xF 0x0416 IA32_MC5_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x0431 IA32_MC12_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x0293 IA32_MC19_CTL2
0x0-0xF 0x0417 IA32_MC5_MISC 0x0-0xF 0x0432 IA32_MC12_ ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x044D IA32_MC19_STATUS
0x0-0xF 0x0418 IA32_MC6_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x0433 IA32_MC12_MISC 0x0-0xF 0x044E IA32_MC19_ADDR
0x0-0xF 0x0286 IA32_MC6_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x0434 IA32_MC13_CTL 0x0-0xF 0x0179 IA32_MCG_CAP
0x0-0xF 0x0419 IA32_MC6_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x028D IA32_MC13_CTL2 0x0-0xF 0x017A IA32_MCG_STATUS
0x0-0xF 0x041A IA32_MC6_ADDR 0x0-0xF 0x0435 IA32_MC13_STATUS 0x0-0xF 0x0178 IA32_MCG_CONTAIN
Notes:
1. The MCi_ADDR and MCi_MISC registers for machine check banks 2 & 4 are not implemented on the processors. The MCi_CTL
register for machine check bank 2 is also not implemented.
62 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 63

31
Reserved
2728 20 19 15 1114 12 0
FunctionDevice
Bus
Register
Interfaces
2. The PECI host must determine the total number of machine check banks and the validity of the MCi_ADDR and MCi_MISC
register contents prior to issuing a read to the machine check bank similar to standard machine check architecture
enumeration and accesses.
3. The information presented in Table 2-11 is applicable to th e processor only. No association between bank numbers and logical
functions should be assumed for any other proces sor devices (past, present or future) based on the information presented in
Table 2-11.
4. The processor machine check banks 4 through 19 reside in the processor uncore and hence will return the same value
independent of the processor ID used to access these banks.
5. The IA32_MCG_STATUS, IA32_MCG_CONTAIN and IA32_MCG_CAP are located in the uncore and will return the same value
independent of the processor ID used to access them.
6. The processor machine check banks 0 through 3 are core-specific. Since the processor ID is thread-specific and not corespecific, machine check banks 0 through 3 will return the same value for a particular core independent of the thread
referenced by the processor ID.
7. PECI accesses to the machine check banks may not be possible in the event of a core hang. A warm reset of the processor
may be required to read any sticky machine check banks.
8. Valid processor ID values may be obtained by using the enumeration methods described in Section 2.5.2.7.2.
9. Reads to a machine check bank within a core or thread that is disabled will return all zeroes with a completion code of 0x90.
10. For SKUs where Intel QPI is disabled or absent, reads to the corresponding machine check banks will return all zeros with a
completion code of 0x40.
11. Greyed out services are reserved: MC6, MC8, MC13, MC14, MC15, MC16
2.5.2.8 RdPCIConfig()
The RdPCIConfig() command provides sideband read access to the PCI configuration
space maintained in downstream devices external to the processor. PECI originators
may conduct a device/function/register enumeration sweep of this space by issuing
reads in the same manner that the BIOS would. A response of all 1’s may indicate that
the device/function/register is unimplemented even with a ‘passing’ completion code.
Alternatively, reads to unimplemented registers may return a completion code of 0x90
indicating an invalid request. Responses will follow normal PCI protocol.
PCI configuration addresses are constructed as shown in Figure 2-44. Under normal inband procedures, the Bus number would be used to direct a read or write to the proper
device. Actual PCI bus numbers for all PCI devices including the PCH are programmable
by BIOS. The bus number for PCH devices may be obtained by reading the CPUBUSNO
CSR. Refer to the Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family Processor Datasheet,
Volume Two: Registers document for details on this register.
Figure 2-44. PCI Configuration Address
PCI configuration reads may be issued in byte, word or dword granularities.
2.5.2.8.1 Command Format
The RdPCIConfig() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x06
Read Length: 0x05 (dword)
Command: 0x61
Description: Returns the data maintained in the PCI configuration space at the
requested PCI configuration address. The Read Length dictates the desired data return
size. This command supports only dword responses with a completion code on the
processor PECI clients. All command responses are prepended with a completion code
that includes additional pass/fail status information. Refer to Section 2.5.5.2 for details
regarding completion codes.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 63
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 64

Interfaces
Figure 2-45. RdPCIConfig()
Note: The 4-byte PCI configuration address and read data field defined in Figure 2-45 are sent in standard PECI ordering with
LSB first and MSB last.
2.5.2.8.2 Supported Responses
The typical client response is a passing FCS, a passing Completion Code and valid data.
Under some conditions, the client’s response will indicate a failure.
The PECI client response can also vary depending on the address and data. It will
respond with a passing completion code if it successfully submits the request to the
appropriate location and gets a response. Exactly what the receiving agent does with
the data or how it responds is up to that agent and is outside the scope of PECI 3.0.
Table 2-12. RdPCIConfig() Response Definition
Response Meaning
Bad FCS Electrical error
Abort FCS Illegal command formatting (mismatched RL/WL/Command Code)
CC: 0x40 Command passed, data is valid.
CC: 0x80 Response timeout. The processor was not able to generate the required response in a
CC: 0x81 Response timeout. The processor is not able to allocate resources for servicing this
CC: 0x82 The processor hardware resources required to service this command are in a low power
CC: 0x90 Unknown/Invalid/Illegal Request
CC: 0x91 PECI control hardware, firmware or associated logic error. The processor is unable to
timely fashion. Retry is appropriate.
command at this time. Retry is appropriate.
state. Retry may be appropriate after modification of PECI wake mode behavior if
appropriate.
process the request.
2.5.2.9 RdPCIConfigLocal()
The RdPCIConfigLocal() command provides sideband read access to the PCI
configuration space that resides within the processor. This includes all processor IIO
and uncore registers within the PCI configuration space as described in the Intel®
Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family Processor Datasheet, Volume Two: Registers
document.
PECI originators may conduct a device/function enumeration sweep of this space by
issuing reads in the same manner that the BIOS would. A response of all 1’s may
indicate that the device/function/register is unimplemented even with a ‘passing’
64 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 65

20 19 15 1114 12 0
23
DeviceBus Function Register
01 2 3
Byte #
FCS
12
7
9
Completion
Code
LSB PCI Configuration Address MSB
10
Write Length
0x05
LSB Data (1, 2 or 4 bytes) MSB
5
Cmd Code
0xe1
14
Read Length
{0x02,0x03,0x05}
68
Host ID[7:1] &
Retry[0]
Client Address
13
4
11
FCS
Byte
Definition
Interfaces
completion code. Alternatively, reads to unimplemented or hidden registers may return
a completion code of 0x90 indicating an invalid request. It is also possible that reads to
function 0 of non-existent IIO devices issued prior to BIOS POST may return all ‘0’s
with a passing completion code. PECI originators can access this space even prior to
BIOS enumeration of the system buses. There is no read restriction on accesses to
locked registers.
PCI configuration addresses are constructed as shown in Figure 2-46. Under normal inband procedures, the Bus number would be used to direct a read or write to the proper
device. PECI reads to the processor IIO devices should specify a bus number of ‘0000’
and reads to the rest of the processor uncore should specify a bus number of ‘0001’ for
bits [23:20] in Figure 2-46. Any request made with a bad Bus number is ignored and
the client will respond with all ‘0’s and a ‘passing’ completion code.
Figure 2-46. PCI Configuration Address for local accesses
2.5.2.9.1 Command Format
The RdPCIConfigLocal() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x05
Read Length: 0x02 (byte), 0x03 (word), 0x05 (dword)
Command: 0xe1
Description: Returns the data maintained in the PCI configuration space within the
processor at the requested PCI configuration address. The Read Length dictates the
desired data return size. This command supports byte, word and dword responses as
well as a completion code. All command responses are prepended with a completion
code that includes additional pass/fail status information. Refer to Section 2. 5. 5 .2 for
details regarding completion codes.
Figure 2-47. RdPCIConfigLocal()
Note: The 3-byte PCI configuration address and read data field defined in Figure 2-47 are sent in standard PECI ordering with
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 65
Datasheet Volume One of Two
LSB first and MSB last.
Page 66

2.5.2.9.2 Supported Responses
The typical client response is a passing FCS, a passing Completion Code and valid data.
Under some conditions, the client’s response will indicate a failure.
The PECI client response can also vary depending on the address and data. It will
respond with a passing completion code if it successfully submits the request to the
appropriate location and gets a response. Exactly what the receiving agent does with
the data or how it responds is up to that agent and is outside the scope of PECI 3.0.
Table 2-13. RdPCIConfigLocal() Response Definition
Response Meaning
Bad FCS Electrical error
Abort FCS Illegal command formatting (mismatched RL/WL/Command Code)
CC: 0x40 Command passed, data is valid.
CC: 0x80 Response timeout. The processor was not able to generate the required response in a
CC: 0x81 Response timeout. The processor is not able to allocate resources for servicing this
CC: 0x82 The processor hardware resources required to service this command are in a low power
CC: 0x90 Unknown/Invalid/Illegal Request
CC: 0x91 PECI control hardware, firmware or associated logic error. The processor is unable to
timely fashion. Retry is appropriate.
command at this time. Retry is appropriate.
state. Retry may be appropriate after modification of PECI wake mode behavior if
appropriate.
process the request.
Interfaces
2.5.2.10 WrPCIConfigLocal()
The WrPCIConfigLocal() command provides sideband write access to the PCI
configuration space that resides within the processor. PECI originators can access this
space even before BIOS enumeration of the system buses. The exact listing of
supported devices and functions for writes using this command on the processor is
defined in Table 2-19. The write accesses to registers that are locked will not take effect
but will still return a completion code of 0x40. However , write accesses to registers that
are hidden will return a completion code of 0x90.
Because a WrPCIConfigLocal() command results in an update to potentially critical
registers inside the processor, it includes an Assured Write FCS (AW FCS) byte as
part of the write data payload. In the event that the AW FCS mismatches with the
client-calculated FCS, the client will abort the write and will always respond with a bad
write FCS.
PCI Configuration addresses are constructed as shown in Figure 2-46. The write
command is subject to the same address configuration rules as defined in
Section 2.5.2.9. PCI configuration writes may be issued in byte, word or dword
granularity.
2.5.2.10.1 Command Format
The WrPCIConfigLocal() format is as follows:
Write Length: 0x07 (byte), 0x08 (word), 0x0a (dword)
Read Length: 0x01
Command: 0xe5
66 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 67
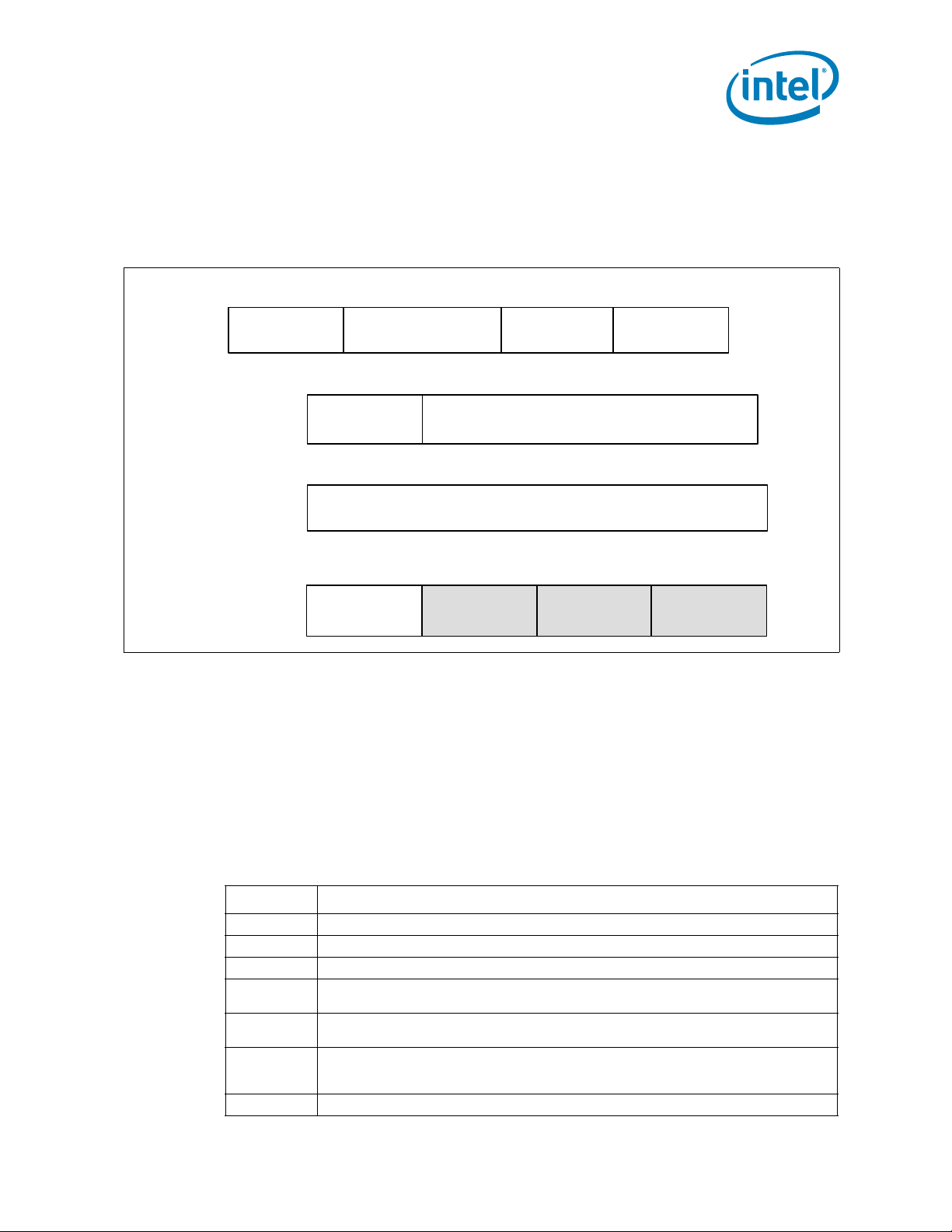
Byte
Definition
01 2
FCS
3
Completion
Code
AW FCS
12
Byte #
FCS
13 14 15
Write Length
{0x07, 0x08, 0x0a}
Host ID[7:1] &
Retry[0]
4
8
Read Length
0x01
56
Cmd Code
0xe5
10
11
Client Address
9
LSB PCI Configuration Address MSB
LSB Data (1, 2 or 4 bytes) MSB
7
Interfaces
AW FCS Support: Yes
Description: Writes the data sent to the requested register address. Write Length
dictates the desired write granularity. The command always returns a completion code
indicating pass/fail status. Refer to Section 2.5.5.2 for details on completion codes.
Figure 2-48. WrPCIConfigLocal()
Note: The 3-byte PCI configuration address and write data field defined in Figure 2-48 are sent in standard PECI ordering with
LSB first and MSB last.
2.5.2.10.2 Supported Responses
The typical client response is a passing FCS, a passing Completion Code and valid data.
Under some conditions, the client’s response will indicate a failure.
The PECI client response can also vary depending on the address and data. It will
respond with a passing completion code if it successfully submits the request to the
appropriate location and gets a response. Exactly what the receiving agent does with
the data or how it responds is up to that agent and is outside the scope of PECI 3.0.
Table 2-14. WrPCIConfigLocal() Response Definition (Sheet 1 of 2)
Response Meaning
Bad FCS Electrical error or AW FCS failure
Abort FCS Illegal command formatting (mismatched RL/WL/Command Code)
CC: 0x40 Command passed, data is valid.
CC: 0x80 Response timeout. The processor was not able to generate the r equired response in a timely
CC: 0x81 Response timeout. The processor is not able to allocate resources for servicing this command
CC: 0x82 The processor hardware resources required to service this command are in a low power
CC: 0x90 Unknown/Invalid/Illegal Request
fashion. Retry is appropriate.
at this time. Retry is appropriate.
state. Retry may be appropriate after modification of PECI wake mode behavior if
appropriate.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 67
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 68

Interfaces
Table 2-14. Wr PC IConfigLocal() Response Definition (Sheet 2 of 2)
Response Meaning
CC: 0x91 PECI control hardware, firmware or associated logic error. The processor is unable to process
the request.
2.5.2.10.3 WrPCIConfigLocal() Capabilities
On the processor PECI clients, the PECI WrPCIConfigLocal() command provides a
method for programming certain integrated memory controller and IIO functions as
described in Table 2-15. Refer to the Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family
Processor Datasheet, Volume Two: Registers for more details on specific register
definitions. It also enables writing to processor REUT (Robust Electrical Unified Test)
registers associated with the Intel® QPI, PCIe* and DDR3 functions.
Table 2-15. WrPCIConfigLocal() Memory Controller and IIO Device/Function Support
Bus Device Function Offset Range Description
0000 0-5 0-7 000-FFFh Integrated I/O (IIO) Configuration Registers
0001 15 0 104h-127h Integrated Memory Controller 0 MEM_HOT_N Registers
0001 15 0 180h-1AFh Integrated Memory Controller 0 SMBus Registers
0001 15 1 080h-0CFh Integrated Memory Controller 0 RAS Registers
0001 16 0, 1, 4, 5 104h-18Bh
1F4h-1FFh
0001 16 2, 3, 6, 7 104h-147h Integrated Memory Controller 0 Error Registers
0001 29 0 104h-127h Integrated Memory Controller 1 MEM_HOT_N Registers
0001 29 0 180h-1AFh Integrated Memory Controller 1 SMBus Registers
0001 29 1 080h-0CFh Integrated Memory Controller 1 RAS Registers
0001 30 0, 1, 4, 5 104h-18Bh
1F4h-1FFh
0001 30 2, 3, 6, 7 104h-147h Integrated Memory Controller 1 Error Registers
(Scrub/Spare)
Integrated Memory Controller 0 Thermal Control Registers
(Scrub/Spare)
Integrated Memory Controller 1 Thermal Control Registers
2.5.3 Client Management
2.5.3.1 Power-up Sequencing
The PECI client will not be available when the PWRGOOD signal is de-asserted. Any
transactions on the bus during this time will be completely ignored, and the host will
read the response from the client as all zeroes. PECI client initialization is completed
approximately 100 µS after the PWRGOOD assertion. This is represented by the start of
the PECI Client “Data Not Ready” (DNR) phase in Figure 2-49. While in this phase, the
PECI client will respond normally to the Ping() and GetDIB() commands and return the
highest processor die temperature of 0x0000 to the GetTemp() command. All other
commands will get a ‘Response Timeout’ completion in the DNR phase as shown in
Table 2-16. All PECI services with the exception of core MSR space accesses become
available ~500 µS after RESET_N de-assertion as shown in Figure 2-49. PECI will be
fully functional with all services including core accesses being available when the core
comes out of reset upon completion of the RESET microcode execution.
In the event of the occurrence of a fatal or catastrophic error, all PECI services with the
exception of core MSR space accesses will be available during the DNR phase to
facilitate debug through configuration space accesses.
68 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 69

PWRGOOD
RESET_N
Core executio n
idle running
Reset uCode Boot BIOS
PECI Client
Status
Data Not Ready
Available except core
services
SOCKET_ID[1:0]
XSOCKET ID Valid
In Reset
Fully Opera t io n al
In Reset
Interfaces
Table 2-16. PECI Client Response During Power-Up
Command
Ping() Fully functional Fully functional
GetDIB() Fully functional Fully functional
GetT emp() Client responds with a ‘hot’ reading or 0x0000 Fully functional
RdPkgConfig() Client responds with a time out completion
WrPkgConfig() Client responds with a timeout completion
RdIAMSR() Client responds with a timeout com pletion
RdPCIConfigLocal() Client responds w ith a timeout completion
WrPCIConfigLocal() Client responds with a timeout completion
RdPCIConfig() Client responds with a timeout completion
code of 0x81
code of 0x81
code of 0x81
code of 0x81
code of 0x81
code of 0x81
Response During
‘Data Not Ready’
In the event that the processor is tri-stated using power-on-configuration controls, the
PECI client will also be tri-stated. Processor tri-state controls are described in
Section 7.3, “Power-On Configuration (POC) Options”.
Figure 2-49. The Processor PECI Power-up Timeline()
Response During
‘Available Except Core Services’
Fully functional
Fully functional
Client responds with a timeout
completion code of 0x81
Fully functional
Fully functional
Fully functional
2.5.3.2 Device Discovery
2.5.3.3 Client Addressing
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 69
Datasheet Volume One of Two
The PECI client is available on all processors. The presence of a PECI enabled processor
in a CPU socket can be confirmed by using the Ping() command described in
Section 2.5.2.1. Positive identification of the PECI revision number can be achieved by
issuing the GetDIB() command. The revision number acts as a reference to the PECI
specification document applicable to the processor client definition. Please refer to
Section 2.5.2.2 for details on GetDIB response formatting.
The PECI client assumes a default address of 0x30. The PECI client address for the
processor is configured through the settings of the SOCKET_ID[1:0] signals. Each
processor socket in the system requires that the two SOCKET_ID signals be configured
Page 70

to a different PECI addresses. Strapping the SOCKET_ID[1:0] pins results in
the client addresses shown in Table 2-17. These package strap(s) are evaluated
at the assertion of PWRGOOD (as depicted in Figure 2-49). Refer to the appropriate
Platform Design Guide for recommended resistor values for establishing non-default
SOCKET_ID settings.
The client address may not be changed after PWRGOOD assertion, until the next power
cycle on the processor. Removal of a processor from its socket or tri-stating a processor
will have no impact to the remaining non-tri-stated PECI client addresses. Since each
socket in the system should have a unique PECI address, the SOCKET_ID strapping is
required to be unique for each socket.
Table 2-17. SOCKET ID Strapping
SOCKET_ID[1] Strap SOCKET_ID[0] Strap PECI Client Address
Ground Ground 0x30
Ground V
V
TT
V
TT
2.5.3.4 C-states
TT
Ground 0x32
V
TT
0x31
0x33
Interfaces
The processor PECI client may be fully functional in most core and package C-states.
• The Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp(), RdPkgConfig() and WrPkgConfig() commands
have no measurable impact on CPU power in any of the core or package C-states.
• The RdIAMSR() command will complete normally unless the targeted core is in a Cstate that is C3 or deeper. The PECI client will respond with a completion code of
0x82 (see
Table 2-22 for definition) for RdIAMSR() accesses in core C-states that
are C3 or deeper.
• The RdPCIConfigLocal(), WrPCIConfigLocal(), and RdPCIConfig() commands will
not impact the core C-states but may have a measurable impact on the package C state. The PECI client will successfully return data without impacting package Cstate if the resources needed to service the command are not in a low power state.
— If the resources required to service the command are in a low power state, the
PECI client will respond with a completion code of 0x82 (see
definition). If this is the case, setting the “Wake on PECI” mode bit as described
Section 2.5.2.6 can cause a package ‘pop-up’ to the C2 state and enable
in
successful completion of the command. The exact power impact of a pop-up to
C2 will vary by product SKU, the C -state from which the pop-up is initiated and
the negotiated PECI bit rate.
Table 2-18. Power Impact of PECI Commands vs. C-states (Sheet 1 of 2)
Command Power Impact
Ping() Not measurable
GetDIB() Not measurable
GetTemp() Not measurable
RdPkgConfig() Not measurable
WrPkgConfig() Not measurable
RdIAMSR() Not measurable. PECI client will not return valid data in core C-state that is C3 or
RdPCIConfigLocal() May require package ‘pop-up’ to C2 state
deeper
Table 2-22 for
70 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 71

Interfaces
Table 2-18. Power Impact of PECI Commands vs. C-states (Sheet 2 of 2)
Command Power Impact
WrPCIConfigLocal() May require package ‘pop-up’ to C2 state
RdPCIConfig() May require package ‘pop-up’ to C2 state
2.5.3.5 S-states
The processor PECI client is always guaranteed to be operational in the S0 sleep state.
• The Ping(), GetDIB(), GetTemp(), RdPkgConfig(), WrPkgConfig(),
RdPCIConfigLocal() and WrPCIConfigLocal() will be fully operational in S0 and S1.
Responses in S3 or deeper states are dependent on POWERGOOD assertion status.
• The RdPCIConfig() and RdIAMSR() responses are guaranteed in S0 only. Behavior
in S1 or deeper states is indeterminate.
• PECI behavior is indeterminate in the S3, S4 and S5 states and responses to PECI
originator requests when the PECI client is in these states cannot be guaranteed.
2.5.3.6 Processor Reset
The processor PECI client is fully reset on all RESET_N assertions. Upon deassertion of
RESET_N where power is maintained to the processor (otherwise known as a ‘warm
reset’), the following are true:
• The PECI client assumes a bus Idle state.
• The Thermal Filtering Constant is retained.
• PECI SOCKET_ID is retained.
• GetTemp() reading resets to 0x0000.
• Any transaction in progress is aborted by the client (as measured by the client no
longer participating in the response).
• The processor client is otherwise reset to a default configuration.
PECI commands that utilize processor resources being reset will receive a ‘resource
unavailable’ response till the reset sequence is completed.
2.5.3.7 System Service Processor (SSP) Mode Support
Sockets in SSP mode have limited PECI command support. Only the following PEC I
commands will be supported while in SSP mode. Other PECI commands are not
guaranteed to complete in this mode.
•Ping
• RdPCIConfigLocal
• WrPCIConfigLocal (all uncore and IIO CSRs within the processor PCI configuration
space will be accessible)
• RdPkgConfig (Index 0 only)
Sockets remain in SSP mode until the “Go” handshake is received. This is applicable to
the following SSP modes.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 71
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 72

2.5.3.7.1 BMC INIT Mode
The BMC INIT boot mode is used to provide a quick and efficient means to transfer
responsibility for uncore configuration to a service processor like the BMC. In this
mode, the socket performs a minimal amount of internal configuration and then waits
for the BMC or service processor to complete the initialization.
2.5.3.7.2 Link Init Mode
In cases where the socket is not one QPI hop away from the Firmware Agent socket, or
a working link to the Firmware Agent socket cannot be resolved, the socket is placed in
Link Init mode. The socket performs a minimal amount of internal configuration and
waits for complete configuration by BIOS.
2.5.3.8 Processor Error Handling
Availability of PECI services may be affected by the processor PECI client error status.
Server manageability requirements place a strong emphasis on continued av ailability of
PECI services to facilitate logging and debug of the error condition.
• Most processor PECI client services are available in the event of a CAT_ERR_N
assertion though they cannot be guaranteed.
• The Ping(), GetDIB(), GetT emp(), RdPkgConfig() and WrPkgConfig() commands will
be serviced if the source of the CAT_ERR_N assertion is not in the processor power
control unit hardware, firmware or associated register logic. Additionally, the
RdPCIConfigLocal() and WrPCIConfigLocal() commands may also be serviced in this
case.
• It is recommended that the PECI originator read Index 0/Parameter 5 using the
RdPkgConfig() command to debug the CAT_ERR_N assertion.
— The PECI client will return the 0x91 completion code if the CAT_ERR_N
assertion is caused by the PCU hardware, firmware or associated logic errors.
In such an event, only the Ping(), GetTemp() and GetDIB() PECI commands
may be serviced. All other processor PECI services will be unavailable and
further debug of the processor error status will not be possible.
— If the PECI client returns a passing completion code, the originator should use
the response data to determine the cause of the CA T_ERR_N assertion. In such
an event, it is also recommended that the PECI originator determine the exact
suite of available PECI client services by issuing each of the PECI commands.
The processor will issue ‘timeout’ responses for those services that may not be
available.
— If the PECI client continues to return the 0x81 completion code in response to
multiple retries of the RdPkgConfig() command, no PECI services, with the
exception of the Ping(), GetTemp() and GetDIB(), will be guaranteed.
• The RdIAMSR() command may be serviced during a CAT_ERR_N assertion though it
cannot be guaranteed.
Interfaces
2.5.3.9 Originator Retry and Timeout Policy
The PECI originator may need to retry a command if the processor PECI client responds
with a ‘response timeout’ completion code or a bad Read FCS. In each instance, the
processor PECI client may have started the operation but not completed it yet. When
the 'retry' bit is set, the PECI client will ignore a new request if it exactly matches a
previous valid request.
72 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 73

Interfaces
The processor PECI client will not clear the semaphore that was acquired to service the
request until the originator sends the ‘retry’ request in a timely fashion to successfully
retrieve the response data. In the absence of any automatic timeouts, this could tie up
shared resources and result in artificial bandwidth conflicts.
2.5.3.10 Enumerating PECI Client Capabilities
The PECI host originator should be designed to support all optional but desirable
features from all processors of interest. Each feature has a discovery method and
response code that indicates availability on the destination PECI client.
The first step in the enumeration process would be for the PECI host to confirm the
Revision Number through the use of the GetDIB() command. The revision number
returned by the PECI client processor always maps to the revision number of the PECI
specification that it is designed to. The Minor Revision Number as described in Table 2-2
may be used to identify the subset of PECI commands that the processor in question
supports for any major PECI revision.
The next step in the enumeration process is to utilize the desired command suite in a
real execution context. If the Write FCS response is an Abort FCS or if the data
returned includes an “Unknown/Invalid/Illegal Request” completion code (0x90), then
the command is unsupported.
Enumerating known commands without real, execution context data, or attempting
undefined commands, is dangerous because a write command could result in
unexpected behavior if the data is not properly formatted. Methods for enumerating
write commands using carefully constructed and innocuous data are possible, but are
not guaranteed by the PECI client definition.
This enumeration procedure is not robust enough to detect differences in bit definitions
or data interpretation in the message payload or client response. Instead, it is only
designed to enumerate discrete features.
2.5.4 Multi-Domain Commands
The processor does not support multiple domains, but it is possible that future products
will, and the following tables are included as a reference for domain-specific definitions.
Table 2-19. Domain ID Definition
Domain ID Domain Number
0b01 0
0b10 1
Table 2-20. Multi-Domain Command Code Reference (Sheet 1 of 2)
Command Name
GetTemp() 0x01 0x02
RdPkgConfig() 0xa1 0xa2
WrPkgConfig() 0xa5 0xa6
RdIAMSR() 0xb1 0xb2
RdPCIConfig() 0x61 0x62
RdPCIConfigLocal() 0xe1 0xe2
Domain 0
Code
Domain 1
Code
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 73
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 74

Table 2-20. Multi-Domain Command Code Reference (Sheet 2 of 2)
Interfaces
Command Name
WrPCIConfigLocal() 0xe5 0xe6
2.5.5 Client Responses
2.5.5.1 Abort FCS
The Client responds with an Abort FCS under the following conditions:
• The decoded command is not understood or not supported on this processor (this
includes good command codes with bad Read Length or Write Length bytes).
• Assured Write FCS (AW FCS) failure. Under most circumstances, an Assured Write
failure will appear as a bad FCS. However, when an originator issues a poorly
formatted command with a miscalculated AW FCS, the client will intentionally abort
the FCS in order to guarantee originator notification.
2.5.5.2 Completion Codes
Some PECI commands respond with a completion code byte. These codes are designed
to communicate the pass/fail status of the command and may also provide more
detailed information regarding the class of pass or fail. For all commands listed in
Section 2.5.2 that support completion codes, the definition in the following table
applies. Throughout this document, a completion code reference may be abbreviated
with ‘CC’.
An originator that is decoding these commands can apply a simple mask as shown in
Table 2-21 to determine a pass or fail. Bit 7 is always set on a command that did not
complete successfully and is cleared on a passing command.
Domain 0
Code
Domain 1
Code
Table 2-21. Completion Code Pass/Fail Mask
0xxx xxxxb Command passed
1xxx xxxxb Command failed
Table 2-22. Device Specific Completion Code (CC) Def i n i ti on
Completion
Code
0x40 Command Passed
CC: 0x80 Response timeout. The processor was not able to generate the required response in a timely
CC: 0x81 Response timeout. The processor was not able to allocate resources for servicing this
CC: 0x82 The processor hardware resources required to service this command are in a low power
CC: 0x83-8F Reserved
CC: 0x90 Unknown/Invalid/Illegal Request
CC: 0x91 PECI control hardware, firmware or associated logic error. The processor is unable to process
CC: 0x92-9F Reserved
fashion. Retry is appropriate.
command. Retry is appropriate.
state. Retry may be appropriate after modification of PECI wake mode behavior if
appropriate.
the request.
Description
74 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 75

Interfaces
Note: The codes explicitly defined in Table 2-22 may be useful in PECI originator response
algorithms. Reserved or undefined codes may also be generated by a PECI client
device, and the originating agent must be capable of tolerating any code. The Pass/Fail
mask defined in
Table 2-21 applies to all codes, and general response policies may be
based on this information. Refer to Section 2.5.6 for originator response policies and
recommendations.
2.5.6 Originator Responses
The simplest policy that an originator may employ in response to receipt of a failing
completion code is to retry the request. However, certain completion codes or FCS
responses are indicative of an error in command encoding and a retry will not result in
a different response from the client. Furthermore, the message originator must have a
response policy in the event of successive failure responses. Refer to Table 2-22 for
originator response guidelines.
Refer to the definition of each command in Section 2.5.2 for a specific definition of
possible command codes or FCS responses for a given command. The following
response policy definition is generic, and more advanced response policies may be
employed at the discretion of the originator developer.
Table 2-23. Originator Response Guidelines
Response After 1 Attempt After 3 Attempts
Bad FCS Retry Fail with PECI client device error.
Abort FCS Retry Fail with PECI client device error if command was not illegal or
CC: 0x8x Retry The PECI client has failed in its attempts to generate a response.
CC: 0x9x Abandon any further
None (all 0’s) Force bus idle (drive
CC: 0x4x Pass n/a
Good FCS Pass n/a
attempts and notify
application layer
low) for 1 mS and retry
malformed.
Notify application layer.
n/a
Fail with PECI client device error. Client may not be alive or may be
otherwise unresponsive (for example, it could be in RESET).
2.5.7 DTS Temperature Data
2.5.7.1 Format
The temperature is formatted in a 16-bit, 2’s complement value representing a number
of 1/64 degrees Celsius. This format allows temperatures in a range of ±512°C to be
reported to approximately a 0.016°C resolution.
Figure 2-50. Temperature Sensor Data Format
MSB
Upper nibble
S x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Sign Integer Value (0-511) Fractional Value (~0.016)
MSB
Lower nibble
LSB
Upper nibble
LSB
Lower nibble
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 75
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 76

2.5.7.2 Interpretation
The resolution of the processor’s Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) is approximately 1°C,
which can be confirmed by a RDMSR from the IA32_THERM_STATUS MSR where it is
architecturally defined. The MSR read will return only bits [13:6] of the PECI
temperature sensor data defined in Figure 2-50. PECI temperatures are sent through a
configurable low-pass filter prior to delivery in the GetTemp() response data. The
output of this filter produces temperatures at the full 1/64°C resolution even though
the DTS itself is not this accurate.
Temperature readings from the processor are always negative in a 2’s complement
format, and imply an offset from the processor T
processor T
running at approximately 10°C below T
not reliable at temperatures above T
range and hence, PECI temperature readings are never positive.
The changes in PECI data counts are approximately linear in relation to changes in
temperature in degrees Celsius. A change of ‘1’ in the PECI count represents roughly a
temperature change of 1 degree Celsius. This linearity is approximate and cannot be
guaranteed over the entire range of PECI temperatures, especially as the offset from
the maximum PECI temperature (zero) increases.
Prochot
Interfaces
(PECI = 0). For example, if the
Prochot
is 100°C, a PECI thermal reading of -10 implies that the processor is
or 90°C. PECI temperature readings are
Prochot
since the processor is outside its operating
Prochot
2.5.7.3 Temperature Filtering
The processor digital thermal sensor (DTS) provides an improved capability to monitor
device hot spots, which inherently leads to more varying temperature readings over
short time intervals. Coupled with the fact that typical fan speed controllers may only
read temperatures at 4Hz, it is necessary for the thermal readings to reflect thermal
trends and not instantaneous readings. Therefore, PECI supports a configurable lowpass temperature filtering function that is expressed by the equation:
TN = (1-α) * T
where T
respectively,
‘α’ = 1/2
and T
N
T
X
, where ‘X’ is the ‘Thermal Averaging Constant’ that is programmable as
+ α * T
N-1
are the current and previous averaged PECI temperature values
N-1
SAMPLE
is the current PECI temperature sample value and the variable
SAMPLE
described in Section 2.5.2.6.21.
2.5.7.4 Reserved Values
Several values well out of the operational range are reserved to signal temperature
sensor errors. These are summarized in Table 2-24.
Table 2-24. Error Codes and Descriptions
Error Code Description
0x8000 General Sensor Error (GSE)
0x8001 Reserved
0x8002 Sensor is operational, but has detected a temperature below its operational range
0x8003-0x81ff Reserved
(underflow)
§
76 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 77

Technologies
3 Technologies
3.1 Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT)
Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) makes a single system appear as multiple
independent systems to software. This allows multiple, independent operating systems
to run simultaneously on a single system. Intel VT comprises technology components
to support virtualization of platforms based on Intel architecture microprocessors and
chipsets.
• Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) for Intel® 64 and IA-32
Intel® Architecture (Intel® VT-x)
improve the virtualization performance and robustness. Intel VT-x specifications
and functional descriptions are included in the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures
Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B and is available at
http://www.intel.com/products/processor/manuals/index.htm
• Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) for Directed I/O
(Intel®
improve I/O virtualization performance and robustness. The Intel VT-d spec and
other Intel VT documents can be referenced at
http://www.intel.com/technology/virtualiz ation/index.htm
VT-d) adds processor and uncore implementations to support and
adds hardware support in the processor to
3.1.1 Intel® VT-x Objectives
Intel VT-x provides hardware acceleration for virtualization of IA platforms. Virtual
Machine Monitor (VMM) can use Intel VT-x features to provide improved reliable
virtualized platform. By using Intel VT-x, a VMM is:
• Robust: VMMs no longer need to use para-virtualization or binary translation. This
means that they will be able to run off-the-shelf OS’s and applications without any
special steps.
• Enhanced: Intel VT enables VMMs to run 64-bit guest operating systems on IA x86
processors.
• More reliable: Due to the hardware support, VMMs can now be smaller, less
complex, and more efficient. This improves reliability and availability and reduces
the potential for software conflicts.
• More secure: The use of hardware transitions in the VMM strengthens the isolation
of VMs and further prevents corruption of one VM from affecting others on the
same system.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 77
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 78

3.1.2 Intel® VT-x Features
The processor core supports the following Intel VT-x features:
• Extended Page Tables (EPT)
— hardware assisted page table virtualization
— eliminates VM exits from guest OS to the VMM for shadow page-table
maintenance
• Virtual Processor IDs (VPID)
— Ability to assign a VM ID to tag processor core hardware structures (for
example, TLBs)
— This avoids flushes on VM transitions to give a lower-cost VM transition time
and an overall reduction in virtualization overhead.
• Guest Preemption Timer
— Mechanism for a VMM to preempt the execution of a guest OS after an amount
of time specified by the VMM. The VMM sets a timer value before entering a
guest
— The feature aids VMM developers in flexibility and Quality of Service (QoS)
guarantees
• Descriptor-Table Exiting
— Descriptor-table exiting allows a VMM to protect a guest OS from internal
(malicious software based) attack by preventing relocation of key system data
structures like IDT (interrupt descriptor table), GDT (global descriptor table),
LDT (local descriptor table), and TSS (task segment selector).
— A VMM using this feature can intercept (by a VM exit) attempts to
relocate these data structures and prevent them from being tampered by
malicious software.
• Pause Loop Exiting (PLE)
— PLE aims to improve virtualization performance and enhance the scaling of
virtual machines with multiple virtual processors
— PLE attempts to detect lock-holder preemption in a VM and helps the VMM to
make better scheduling decisions
• APIC Virtualization (APICv)
— APICv adds hardware support in the processor to reduce the overhead of virtual
interrupt processing (APIC accesses and interrupt delivery). This benefits
mostly interrupt intensive workloads.
— In a virtualized environment the virtual machine manager (VMM) must emulate
nearly all guest OS accesses to the advanced programmable interrupt
controller (APIC) registers which requires “VM exits” (time-consuming
transitions to the VMM for emulation and back). These exits are a major source
of overhead in a virtual environment. Intel's Advanced Programmable Interrupt
Controller virtualization (APICv) reduces the number of exits by redirecting
most guest OS APIC reads/writes to a virtual-APIC page to allow most reads to
occur without VM exits.
Technologies
3.1.3 Intel® VT-d Objectives
The key Intel VT-d objectives are domain-based isolation and hardware-based
virtualization. A domain can be abstractly defined as an isolated environment in a
platform to which a subset of host physical memory is allocated. Virtualization allows
for the creation of one or more partitions on a single system. This could be multiple
78 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 79

Technologies
partitions in the same operating system, or there can be multiple operating system
instances running on the same system – offering benefits such as system
consolidation, legacy migration, activity partitioning or security.
3.1.3.1 Intel VT-d Features Supported
The processor supports the following Intel VT-d features:
• Root entry, context entry, and default context
• Support for 4-K page sizes only
• Support for register-based fault recording only (for single entry only) and support
for MSI interrupts for faults
— Support for fault collapsing based on Requester ID
• Support for both leaf and non-leaf caching
• Support for boot protection of default page table
— Support for non-caching of invalid page table entries
• Support for hardware based flushing of translated but pending writes and pending
reads upon IOTLB invalidation.
• Support for page-selective IOTLB invalidation.
• Support for ARI (Alternative Requester ID - a PCI SIG ECR for increasing the
function number count in a PCIe device) to support IOV devices.
• Improved invalidation architecture
• End point caching support (ATS)
• Interrupt remapping
3.1.4 Intel® Virtualization Technology Processor Extensions
The processor supports the following Intel VT Processor Extensions features:
• Large Intel VT-d Pages
— Adds 2 MB and 1 GB page sizes to Intel VT-d implementations
— Matches current support for Extended Page Tables (EPT)
— Ability to share CPU's EPT page-table (with super-pages) with Intel VT-d
— Benefits:
• Less memory foot-print for I/O page-tables when using super-pages
• Potential for improved performance - Due to shorter page-walks, allows
hardware optimization for IOTLB
• Transition latency reductions expected to improve virtualization performance
without the need for VMM enabling. This reduces the VMM overheads further and
increase virtualization performance.
3.2 Security Technologies
3.2.1 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology
Intel TXT defines platform-level enhancements that provide the building blocks for
creating trusted platforms.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 79
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 80

Technologies
The Intel TXT platform helps to provide the authenticity of the controlling environment
such that those wishing to rely on the platform can make an appropriate trust decision.
The Intel TXT platform determines the identity of the controlling environment by
accurately measuring and verifying the controlling software.
Another aspect of the trust decision is the ability of the platform to resist attempts to
change the controlling environment. The Intel TXT platform will resist attempts by
software processes to change the controlling environment or bypass the bounds set by
the controlling environment.
Intel TXT is a set of extensions designed to provide a measured and controlled launch
of system software that will then establish a protected environment for itself and any
additional software that it may execute.
These extensions enhance two areas:
• The launching of the Measured Launched Environment (MLE).
• The protection of the MLE from potential corruption.
The enhanced platform provides these launch and control interfaces using Safer Mode
Extensions (SMX).
The SMX interface includes the following functions:
• Measured/Verified launch of the MLE.
• Mechanisms to ensure the above measurement is protected and stored in a secure
location.
• Protection mechanisms that allow the MLE to control attempts to modify itself.
For more information refer to the Intel® Trusted Execution Technology Software
Development Guide. For more information on Intel Trusted Execution Technology, see
http://www.intel.com/technology/security/
3.2.2 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology – Server Extensions
• Software binary compatible with Intel® Trusted Execution Technology –
Server Extensions
• Provides measurement of runtime firmware, including SMM
• Enables run-time firmware in trusted session: BIOS and SSP
• Covers support for existing and expected future Server RAS features
• Only requires portions of BIOS to be trusted, for example, Option ROMs need not
be trusted
• Supports S3 State without teardown: Since BIOS is part of the trust chain
3.2.3 AES Instructions
These instructions enable fast and secure data encryption and decryption, using the
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) wh ich is defined by FIPS Publication number 197.
Since AES is the dominant block cipher, and it is deployed in various protocols, the new
instructions will be valuable for a wide range of applications.
80 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 81

Technologies
The architecture consists of six instructions that offer full hardware support for AES.
Four instructions support the AES encryption and decryption, and the other two
instructions support the AES key expansion. Together, they offer a significant increase
in performance compared to pure software implementations.
The AES instructions have the flexibility to support all three standard AES key lengths,
all standard modes of operation, and even some nonstandard or future variants.
Beyond improving performance , the AES instructions provide important security
benefits. Since the instructions run in data-independent time and do not use lookup
tables, they help in eliminating the major timing and cache-based attacks that threaten
table-based software implementations of AES. In addition, these instructions make AES
simple to implement, with reduced code size. This helps reducing the risk of
inadvertent introduction of security flaws, such as difficult-to-detect side channel leaks.
3.2.4 Execute Disable Bit
Intel's Execute Disable Bit functionality can help prevent certain classes of malicious
buffer overflow attacks when combined with a supporting operating system.
• Allows the processor to classify areas in memory by where application code can
execute and where it cannot.
• When a malicious worm attempts to insert code in the buffer, the processor
disables code execution, preventing damage and worm propagation.
3.3 Intel® Secure Key
This was formerly known as Digital Random Number Generator (DRNG).
The processor supports an on-die digital random number generator (DRNG). This
implementation is based on the ANSI X9.82 2007 draft and the NIST SP800-90
specification.
The X9.82 standard describes two components necessary to generate high quality
random numbers: an Entropy Source and a Deterministic Random Bit Generator
(DRBG). The Entropy Source is also referred to as a Non-Deterministic Random Bit
Generator (NRBG).
3.4 Intel® OS Guard
This was formerly known as Supervisor Mode Execution Protection (SMEP)
Supervisor Mode Execution Protection Bit (SMEP) prevents execution and calls to the
operating system by compromised application in the user mode or code pages. This
also allows additional malware protection over existing Intel XD bit technology.
3.5 Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology
The processor supports Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel® HT Technology),
which allows an execution core to function as two logical processors. While some
execution resources such as caches, execution units, and buses are shared, each
logical processor has its own architectural state with its own set of general-purpose
registers and control registers. This feature must be enabled via the BIOS and requires
operating system support.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 81
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 82

For more information on Intel Hyper-Threading Technology, see
http://www.intel.com/products/ht/hyperthreading_more.htm.
3.6 Intel® Turbo Boost Technology
Intel Turbo Boost Technology is a feature that allows the processor to opportunistically
and automatically run faster than its rated operating frequency if it is operating below
power, temperature, and current limits. The result is increased performance in multithreaded and single threaded workloads. It should be enabled in the BIOS for the
processor to operate with maximum performance.
3.6.1 Intel® Turbo Boost Operating Frequency
The processor’s rated frequency assumes that all execution cores are running an
application at the thermal design power (TDP). However, under typical operation, not
all cores are active. Therefore most applications are consuming less than the TDP at the
rated frequency . To take advantage of the available TDP headroom, the active cores can
increase their operating frequency.
To determine the highest performance frequency amongst active cores, the processor
takes the following into consideration:
• The number of cores operating in the C0 state.
• The estimated current consumption.
• The estimated power consumption.
• The die temperature.
Technologies
Any of these factors can affect the maximum frequency for a given workload. If the
power, current, or thermal limit is reached, the processor will automatically reduce the
frequency to stay with its TDP limit.
Note: Intel Turbo Boost Technology is only active if the operating system is requesting the P0
state. For more information on P-states and C-states refer to
Management”.
Section 4, “Power
3.7 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
The processor supports Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® T echnology as an advanced means
of enabling very high performance while also meeting the power-conservation needs of
the platform.
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology builds upon that architecture using design
strategies that include the following:
• Separation between Voltage and Frequency Changes. By stepping voltage up
and down in small increments separately from frequency changes, the processor is
able to reduce periods of system unavailability (which occur during frequency
change). Thus, the system is able to transition between voltage and frequency
states more often, providing improved power/performance balance.
• Clock Partitioning and Recovery. The bus clock continues running during state
transition, even when the core clock and Phase-Locked Loop are stopped, which
allows logic to remain active. The core clock is also able to restart more quickly
under Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology.
For additional information on Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology see Section 4.2.1.
82 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 83

Technologies
3.8 Intel® Intelligent Power Technology
Intel® Intelligent Power Technology conserves power while delivering advanced powermanagement capabilities at the rack, group, and data center level. Providing the
highest system-level performance per watt with “Automated Low Power States” and
“Integrated Power Gates”. Improvements to this processor generation are:
• Intel Network Power Management Technology
• Intel Power Tuning Technology
For more information on Intel Intelligent Power Technology, see this link
http://www.intel.com/technology/intelligentpower/.
3.9 Intel® Advanced Vector Extensions (Intel® AVX)
Intel® Advanced V ector Extensions (Intel® A VX) is a 256-bit v ector SIMD extension of
Intel Architecture that continues with the 3rd Generation Intel® Core™ Processor
Family. Intel AVX accelerates the trend of parallel computation in general purpose
applications like image, video, and audio processing, engineering applications such as
3D modeling and analysis, scientific simulation, and financial analysts.
Intel AVX is a comprehensive ISA extension of the Intel 64 Architecture. The main
elements of Intel AVX are:
• Support for wider vector data (up to 256-bit) for floating-point computation.
• Efficient instruction encoding scheme that supports 3 operand syntax and
headroom for future extensions.
• Flexibility in programming environment, ranging from br anch handling to relax ed
memory alignment requirements.
• New data manipulation and arithmetic compute primitives, including broadcast,
permute, fused-multiply-add, and so forth.
• Floating point bit depth conversion (Float 16)
• A group of 4 instructions that accelerate data conversion between 16-bit
floating point format to 32-bit and vice versa.
• This benefits image processing and graphical applications allowing
compression of data so less memory and bandwidth is required.
The key advantages of Intel AVX are:
• Performance - Intel AVX can accelerate application performance via data
parallelism and scalable hardware infrastructure across existing and new
application domains:
— 256-bit vector data sets can be processed up to twice the throughput of 128-bit
data sets.
— Application performance can scale up with number of hardware threads and
number of cores.
— Application domain can scale out with advanced platform interconnect fabrics,
such as Intel QPI.
• Power Efficiency - Intel AVX is extremely power efficient. Incremental power is
insignificant when the instructions are unused or scarcely used. Combined with the
high performance that it can deliver, applications that lend themselves heavily to
using Intel AVX can be much more energy efficient and realize a higher
performance-per-watt.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 83
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 84

• Extensibility - Intel AVX has built-in extensibility for the future vector extensions:
— OS context management for vector-widths beyond 256 bits is streamlined.
— Efficient instruction encoding allows unlimited functional enhancements:
• Vector width support beyond 256 bits
• 256-bit Vector Integer processing
• Additional computational and/or data manipulation primitives.
• Compatibility - Intel AVX is backward compatible with previous ISA extensions
including Intel SSE4:
— Existing Intel® SSE applications/library can:
• Run unmodified and benefit from processor enhancements
• Recompile existing Intel® SSE intrinsic using compilers that generate
Intel AVX code
• Inter-operate with library ported to Intel AVX
— Applications compiled with Intel AVX can inter-operate with existing Intel SSE
libraries.
3.10 Intel® Dynamic Power Technology
Intel® Dynamic Power technology (Memory Power Management) is a platform feature
with the ability to transition memory components into various low power states based
on workload requirements. The Intel® Xeon® processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2
product families platform supports Dynamic CKE (hardware assisted) and Memory Self
Refresh (software assisted). For further details refer to the
Memory Power Management document.
Technologies
ACPI Specifications for
§
84 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 85

Power Management
4 Power Management
This chapter provides information on the following power management topics:
•ACPI States
•System States
• Processor Core/Package States
• Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) and System Memory States
• Direct Media Interface Gen 2 (DMI2)/PCI Express* Link States
• Intel QuickPath Interconnect States
4.1 ACPI States Supported
The ACPI states supported by the processor are described in this section.
4.1.1 System States
Table 4-1. System States
State Description
G0/S0 Full On
G1/S3-Cold Suspend-to-RAM (STR). Context saved to memory.
G1/S4 Suspend-to-Disk (STD). All power lost (except wakeup on PCH).
G2/S5 Soft off. All power lost (except wakeup on PCH). Total reboot.
G3 Mechanical off. All power removed from system.
4.1.2 Processor Package and Core States
Table 4-2 lists the package C-state support as: 1) the shallowest core C-state that
allows entry into the package C-state, 2) the additional factors that will restrict the
state from going any deeper, and 3) the actions taken with respect to the Ring Vcc, PLL
state and LLC.
Table 4-3 lists the processor core C-states support.
Table 4-2. Package C-State Support (Sheet 1 of 2)
Package
C-State
PC0 Active
PC2 Snoopable
Idle
Core
States
CC0 N/A No No 2
CC3-CC6 • PCIe/PCH and Remote Socket
• PCIe/PCH and Remote Socket
• Interrupt response time
• DMI Sidebands
• Configuration Constraints
Limiting Factors
Snoops
Accesses
requirement
Retention and
PLL-Off
VccMin
Freq = MinFreq
PLL = ON
LLC
Fully
Flushed
No 2
Notes
1
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 85
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 86

Table 4-2. Package C-State Support (Sheet 2 of 2)
Power Management
Package
C-State
PC3 - Light
Retention
PC6 Deeper
Retention
Notes:
1. Processor Core and Package C7 is not supported.
2. All package states are defined to be “E” states - such that they always exit back into the LFM point upon
execution resume
3. The mapping of actions for PC3, and PC6 are suggestions - microcode will dynamically determine which
actions should be taken based on the desired exit latency parameters.
4. CC3/CC6 will all use a voltage below the VccMin operational point; The exact voltage selected will be a
function of the snoop and interrupt response ti me require ments mad e by the device s (PC Ie* and DMI) and
the operating system.
5. The processor supports retention voltage during package C3 and package C6.
Core
States
at least
one Core
in C3
CC6- • LLC ways open
•Core C-state
• Snoop Response Time
• Interrupt Response Time
• Non Snoop Response Time
• Snoop Response Time
• Non Snoop Response Time
• Interrupt Response Time
Table 4-3. Core C-State Support
Core C-State Global Clock PLL L1/L2 Cache Core VCC Context
CC0 Running On Coherent Active Maintained
CC1 Stopped On Coherent Active Maintained
CC1E Stopped On Coherent Request LFM Maintained
CC3 Stopped On Flushed to LLC Request Retention Maintained
CC6 Stopped Off Flushed to LLC Power Gate Flushed to LLC
Limiting Factors
Retention and
PLL-Off
Vcc = retention
PLL = OFF
Vcc = retention
PLL = OFF
LLC
Fully
Flushed
No 2,3,4, 5
No 2,3,4, 5
Notes
1
4.1.3 Integrated Memory Controller States
Table 4-4. System Memory Power States (Sheet 1 of 2)
State Description
Power Up/Normal Operation CKE asserted. Active Mode, highest power consumption.
CKE Power Down Opportunistic, per rank control after idle time:
• Active Power Down (APD) (default mode)
— CKE de-asserted. Power savings in this mode, relative to active idle
state is about 55% of the memory power. Exiting this mode takes 3
• Pre-charge Power Down Fast Exit (PPDF)
• Pre-charge Power Down Slow Exit (PPDS)
• Register CKE Power Down:
– 5 DCLK cycles.
— CKE de-asserted. DLL -On. Also known as Fast CKE. Power savings in
this mode, relative to active idle state is about 60% of the memory
power. Exiting this mode takes 3 – 5 DCLK cycles.
— CKE de-asserted. DLL -Off . Also known as Slow CKE. P ower savings in
this mode, relative to active idle state is about 87% of the memory
power. Exiting this mode takes 3 – 5 DCLK cycles until the first
command is allowed and 16 cycles until first data is allowed.
— IBT-ON mode: Both CKE’s are de-asserted, the Input Buffer
Terminators (IBTs) are left “on”.
— IBT-OFF mode: Both CKE’s are de-asserted, the Input Buffer
Terminators (IBTs) are turned “off”.
86 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 87

Power Management
Table 4-4. System Memory Power States (Sheet 2 of 2)
State Description
Self-Refresh CKE de-asserted. In this mode, no transactions are executed and the system
memory consumes the minimum possible power. Self refresh modes apply to
all memory channels for the processor.
• IO-MDLL Off: Option that sets the IO master DLL off when self refresh
occurs.
• P LL Off: Option that sets the PLL off when self refresh occurs.
In addition, the register component found on registered DIMMs (RDIMMs) is
complemented with the following power down states:
— Clock Stopped Power Down with IBT-On
— Clock Stopped Power Down with IBT-Off
4.1.4 DMI2/PCI Express* Link States
Table 4-5. DMI2/PCI Express* Link States
State Description
L0 Full on – Active transfer state.
L1 Lowest Active State Power Management (ASPM) - Longer exit latency.
Note: L1 is only supported when the DMI2/PCI Express* port is operating as a PCI Express* port.
4.1.5 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect States
Table 4-6. Intel® QPI States
State Description
L0 Link on. This is the power on active working state,
L0p A lower power state from L0 that reduces the link from full width to half width
L1 A low power state with longer latency and lower power than L0s and is
activated in conjunction with package C-states below C0.
4.1.6 G, S, and C State Combinations
Table 4-7. G, S and C State Combinations
Global (G)
State
G0 S0 C0 Full On On Full On
G0 S0 C1/C1E Auto-Halt On Auto-Halt
G0 S0 C3 Deep Sleep On Deep Sleep
G0 S0 C6 Deep Power
G1 S3 Power off Off, except RTC Suspend to RAM
G1 S4 Power off Off, except RTC Suspend to Disk
G2 S5 Power off Off, except RTC Soft Off
G3 N/A Power off Power off Hard off
Sleep
(S) State
Processor
Core
(C) State
Processor
State
Down
System
On Deep Power Down
Clocks
Description
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 87
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 88

Power Management
4.2 Processor Core/Package Power Management
While executing code, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology optimizes the
processor’s frequency and core voltage based on workload. Each frequency and voltage
operating point is defined by ACPI as a P-state. When the processor is not executing
code, it is idle. A low-power idle state is defined by ACPI as a C-state. In general, lower
power C-states have longer entry and exit latencies.
4.2.1 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
The following are the key features of Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology:
• Multiple frequency and voltage points for optimal performance and power
efficiency. These operating points are known as P-states.
• Frequency selection is software controlled by writing to processor MSRs. The
voltage is optimized based on temperature, leakage, power delivery loadline and
dynamic capacitance.
— If the target frequency is higher than the current frequency, VCC is ramped up
to an optimized voltage. This voltage is signaled by the SVID Bus to the voltage
regulator. Once the voltage is established, the PLL locks on to the target
frequency.
— If the target frequency is lower than the current frequency, the PLL locks to the
target frequency, then transitions to a lower voltage by signaling the target
voltage on the SVID Bus.
— All active processor cores share the same frequency and voltage. In a multi-
core processor, the highest frequency P-state requested amongst all active
cores is selected.
— Software-requested transitions are accepted at any time. The processor has a
new capability from the previous processor generation, it can preempt the
previous transition and complete the new request without waiting for this
request to complete.
• The processor controls voltage ramp rates internally to ensure glitch-free
transitions.
• Because there is low transition latency between P-states, a significant number of
transitions per second are possible.
4.2.2 Low-Power Idle States
When the processor is idle, low-power idle states (C-states) are used to save power.
More power savings actions are taken for numerically higher C-states. Howev er, higher
C-states have longer exit and entry latencies. Resolution of C-states occurs at the
thread, processor core, and processor package level. Thread level C-states are
available if Intel Hyper-Threading Technology is enabled. Entry and exit of the C - States
at the thread and core level are shown in Figure 4-2.
88 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 89

Processor P ackage State
Core N State
Thread 1Thread 0
Core 0 State
Thread 1T hread 0
C1 C1E C6C3
MWAIT(C1), HLT
C0
MWAIT(C6),
P_LVL3 I/O Read
MWAIT(C3),
P_LVL2 I/O Read
MWAIT(C1), HLT
(C1E Enabled)
Power Management
Figure 4-1. Idle Power Management Breakdown of the Processor Cores
Figure 4-2. Thread and Core C-State Entry and Exit
While individual threads can request low power C-states, power saving actions only
take place once the core C-state is resolved. Core C-states are automatically resolved
by the processor. For thread and core C-states, a transition to and from C0 is required
before entering any other C-state.
4.2.3 Requesting Low-Power Idle States
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 89
Datasheet Volume One of Two
The core C-state will be C1E if all actives cores have also resolved a core C1 state or
higher.
The primary software interfaces for requesting low power idle states are through the
MWAIT instruction with sub-state hints and the HLT instruction (for C1 and C1E).
However, software may make C-state requests using the legacy method of I/O reads
Page 90

Power Management
from the ACPI-defined processor clock control registers, referred to as P_LVLx. This
method of requesting C-states provides legacy support for operating systems that
initiate C-state transitions via I/O reads.
For legacy operating systems, P_LVLx I/O reads are converted within the processor to
the equivalent MWAIT C-state request. Therefore, P_L VLx reads do not directly result in
I/O reads to the system. The feature, known as I/O MWAIT redirection, must be
enabled in the BIOS.
Note: The P_LVLx I/O Monitor address needs to be set up before using the P_LVLx I/O read
interface. Each P-LVLx is mapped to the supported MWAIT(Cx) instruction as follows.
Table 4-8. P_LVLx to MWAIT Conversion
P_LVLx MWAIT(Cx) Notes
P_LVL2 MWAIT(C3) The P_LVL2 base address is defined in the PMG_IO_CAPTURE MSR,
P_LVL3 MWAIT(C6) C6. No sub-states allowed.
described in the Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family
Processor Datasheet, Volume Two: Registers.
The BIOS can write to the C-state range field of the PMG_IO_CAPTURE MSR to restrict
the range of I/O addresses that are trapped and emulate MWAIT like function ality. Any
P_LVLx reads outside of this range does not cause an I/O redirection to MW AIT(Cx) like
request. They fall through like a normal I/O instruction.
Note: When P_LVLx I/O instructions are used, MWAIT substates cannot be defined. The
MWAIT substate is always zero if I/O MWAIT redirection is used. By default, P_LVLx I/O
redirections enable the MWAIT 'break on EFLAGS.IF’ feature which triggers a wakeup
on an interrupt even if interrupts are masked by EFLAGS.IF.
4.2.4 Core C-states
The following are general rules for all core C-states, unless specified otherwise:
• A core C-State is determined by the lowest numerical thread state (e.g., Thread 0
requests C1E while Thread 1 requests C3, resulting in a core C1E state). See
Table 4-7.
• A core transitions to C0 state when:
— an interrupt occurs.
— there is an access to the monitored address if the state was entered via an
MWAIT instruction.
• For core C1/C1E, and core C3, an interrupt directed toward a single thread wakes
only that thread. However, since both threads are no longer at the same core
C-state, the core resolves to C0.
• An interrupt only wakes the target thread for both C3 and C6 states. Any interrupt
coming into the processor package may wake any core.
4.2.4.1 Core C0 State
The normal operating state of a core where code is being executed.
4.2.4.2 Core C1/C1E State
C1/C1E is a low power state entered when all threads within a core execute a HLT or
MWAIT(C1/C1E) instruction.
90 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 91

Power Management
A System Management Interrupt (SMI) handler returns execution to either Normal
state or the C1/C1E state. See the
Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A/3B: System Programmer’s Guide
While a core is in C1/C1E state, it processes bus snoops and snoops from other
threads. For more information on C1E, see Section 4.2.5.2, “Package C1/C1E”.
To operate within specification, BIOS must enable the C1E feature for all installed
processors. Please refer to the
Datasheet, Volume Two: Registers
4.2.4.3 Core C3 State
Individual threads of a core can enter the C3 state by initiating a P_LVL2 I/O read to
the P_BLK or an MWAIT(C3) instruction. A core in C3 state flushes the contents of its
L1 instruction cache, L1 data cache, and L2 cache to the shared L3 cache, while
maintaining its architectural state. All core clocks are stopped at this point. Because the
core’s caches are flushed, the processor does not wake any core that is in the C3 state
when either a snoop is detected or when another core accesses cacheable memory.
4.2.4.4 Core C6 State
Individual threads of a core can enter the C6 state by initiating a P_LVL3 I/O read or an
MWAIT(C6) instruction. Before entering core C6, the core will save its architectural
state to a dedicated SRAM. Once complete, a core will have its voltage reduced to zero
volts. In addition to flushing core caches core architecture state is saved to the uncore.
Once the core state save is completed, core voltage is reduced to zero. During exit, the
core is powered on and its architectural state is restored.
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software
for more information.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5 v2 Product Family Processor
for more details.
4.2.4.5 Delayed Deep C-States
The Delayed Deep C-states (DDCst) feature on this processor replaces the “C-state
auto-demotion” scheme used in the previous processor generation. Deep C-states are
defined as CC3 through CC6 (refer to Table 4-3 for supported deep c-states).
The Delayed Deep C-states are intended to allow a staged entry into deeper C-states
whereby the processor enters a lighter, short exit-latency C-state (core C1) for a period
of time before committing to a long exit-latency deep C-state (core C3 and core C6).
This is intended to allow the processor to get past the cluster of short-duration idles,
providing each of those with a very fast wake-up time, but to still get the power benefit
of the deep C-states on the longer idles.
4.2.5 Package C-States
The processor supports C0, C1/C1E, C2, C3, and C6 power states. The following is a
summary of the general rules for package C-state entry. These apply to all package
C-states unless specified otherwise:
• A package C-state request is determined by the lowest numerical core C-state
amongst all cores.
• A package C-state is automatically resolved by the processor depending on the
core idle power states and the status of the platform components.
— Each core can be at a lower idle power state than the package if the platform
does not grant the processor permission to enter a requested package C-state.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 91
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 92
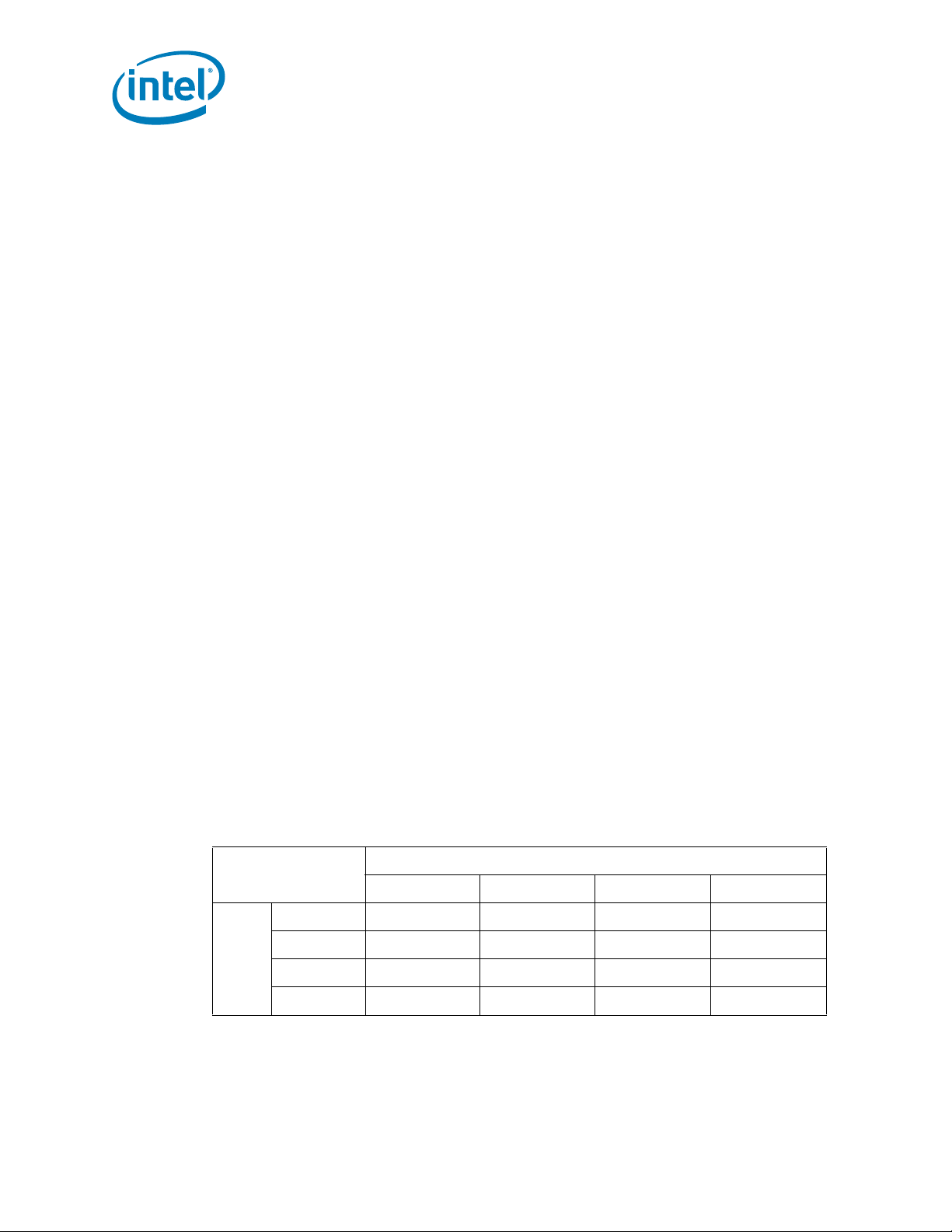
Power Management
— The platform may allow additional power savings to be realized in the
processor.
• For package C-states, the processor is not required to enter C0 before entering any
other C-state.
The processor exits a package C-state when a break event is detected. Depending on
the type of break event, the processor does the following:
• If a core break event is received, the target core is activated and the break event
message is forwarded to the target core.
— If the break event is not masked, the target core enters the core C0 state and
the processor enters package C0.
— If the break event is masked, the processor attempts to re-enter its previous
package state.
• If the break event was due to a memory access or snoop request.
— But the platform did not request to keep the processor in a higher package
C-state, the package returns to its previous C-state.
— And the platform requests a higher power C-state, the memory access or snoop
request is serviced and the package remains in the higher power C-state.
The package C-states fall into two categories: independent and coordinated.
C0/C1/C1E are independent, while C2/C3/C6 are coordinated.
Package C-states are based on exit latency requirements which are accumulated from
the PCIe* devices, PCH, and software sources. The level of power savings that can be
achieved is a function of the exit latency requirement from the platform. As a result,
there is no fixed relationship between the coordinated C-state of a package, and the
power savings that will be obtained from the state. Coordinated package C-states offer
a range of power savings which is a function of the guaranteed exit latency requirement
from the platform.
There is also a concept of Execution Allowed (EA), when EA status is 0, the cores in a
socket are in C3 or a deeper state, a socket initiates a request to enter a coordinated
package C-state. The coordination is across all sockets and the PCH.
Table 4-9 shows an example of a dual-core processor package C-state resolution.
Figure 4-3 summarizes package C-state transitions with package C2 as the interim
between PC0 and PC1 prior to PC3 and PC6.
Table 4-9. Coordination of Core Power States at the Package Level
Package C-State
C0
C1
Core 0
C3
C6
C0 C1 C3 C6
C0 C0 C0 C0
C0 C1
C0 C1
C0 C1
Core 1
1
1
1
C1
1
C3 C3
C3 C6
C1
1
1. The package C-state will be C1E if all actives cores have resolved a core C1 state or higher.
92 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 93

C2
C0
C1
C6C3
Power Management
Figure 4-3. Package C-State Entry and Exit
4.2.5.1 Package C0
The normal operating state for the processor. The processor remains in the normal
state when at least one of its cores is in the C0 or C1 state or when the platform has
not granted permission to the processor to go into a low power state. Individual cores
may be in lower power idle states while the package is in C0.
4.2.5.2 Package C1/C1E
No additional power reduction actions are taken in the package C1 state. However, if
the C1E substate is enabled, the processor automatically transitions to the lowest
supported core clock frequency, followed by a reduction in voltage. Autonomous power
reduction actions which are based on idle timers, can trigger depending on the activity
in the system.
The package enters the C1 low power state when:
• At least one core is in the C1 state.
• The other cores are in a C1 or lower power state.
The package enters the C1E state when:
• All cores have directly requested C1E via MWAIT(C1) with a C1E sub-state hint.
• All cores are in a power state lower that C1/C1E but the package low power state is
limited to C1/C1E via the PMG_CST_CONFIG_CONTROL MSR.
• All cores have requested C1 using HLT or MWAIT(C1) and C1E auto-promotion is
enabled in POWER_CTL.
No notification to the system occurs upon entry to C1/C1E.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 93
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 94

4.2.5.3 Package C2 State
Package C2 state is an intermediate state which represents the point at which the
system level coordination is in progress. The package cannot reach this state unless all
cores are in at least C3.
The package will remain in C2 when:
• it is awaiting for a coordinated response
• the coordinated exit latency requirements are too stringent for the package to take
any power saving actions
If the exit latency requirements are high enough the package will transition to C3 or C6
depending on the state of the cores.
4.2.5.4 Package C3 State
A processor enters the package C3 low power state when:
• At least one core is in the C3 state.
• The other cores are in a C3 or lower power state, and the processor has been
granted permission by the platform.
• L3 shared cache retains context and becomes inaccessible in this state.
• Additional power savings actions, as allowed by the exit latency requirements,
include putting Intel QPI and PCIe* links in L1, the uncore is not available, further
voltage reduction can be taken.
Power Management
In package C3, the ring will be off and as a result no accesses to the LLC are possible.
The content of the LLC is preserved.
4.2.5.5 Package C6 State
A processor enters the package C6 low power state when:
• At least one core is in the C6 state.
• The other cores are in a C6 or lower power state, and the processor has been
granted permission by the platform.
• L3 shared cache retains context and becomes inaccessible in this state.
• Additional power savings actions, as allowed by the exit latency requirements,
include putting Intel QPI and PCIe* links in L1, the uncore is not available, further
voltage reduction can be taken.
In package C6 state, all cores have saved their architectural state and have had their
core voltages reduced to zero volts. The LLC retains context, but no accesses can be
made to the LLC in this state, the cores must break out to the internal state package C2
for snoops to occur.
94 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 95

Power Management
4.2.6 Package C-State Power Specifications
The table below lists the processor package C-state power specifications for various
processor SKUs. For details on processor SKU information, see Table 1-1, “HCC, MCC,
and LCC SKU Table Summary.”.
Table 4-10. Package C-State Power Specifications
TDP SKUs
150W WS (8cores) 58 27 14
130W 1U (12-cores) 47 22 15
130W 1U (10-cores) 47 22 14
130W 1U and 2U (8cores) 53 35 14
130W 2U (6-cores) 53 28 14
130W 2U (4-cores) 53 28 13
130W 1S WS (6/4-cores) 53 28 13
115W (12-cores) 47 22 15
115W (10-cores) 47 22 14
95W (10cores) 47 22 14
95W (8cores) 48 22 14
95W (6/4-cores) 47 22 13
80W (6/4-cores) 42 30 13
70W (10cores) 39 20 13
60W (6cores) 38 20 12
LV95W (10cores) 47 22 14
LV70W (10/8-cores) 39 20 13
LV50W (6cores) 21 13 12
1
C1E (W)
2
C3 (W)
3
3
C6 (W)
18 (E5-2640 v2)
21 (E5-2620 v2)
21 (E5-2603 v2)
Notes:
1. SKU’s are subject to change. Please contact your Intel Field Representative to obtain the latest SKU
information.
2. Package C1E power specified at Tcase=60
3. Package C3/C6 power specified at Tcase = 50
o
C
o
C
4.2.7 Processor Package Power Specifications
Processor package power, P
socket and is reported by the PACKAGE_POWER_SKU MSR/CSR Registers. For details
on processor SKU information, see Table 1-1, “HCC, MCC, and LCC SKU Table
Summary.”.
Table 4-11. Processor Package Power P
150W WS (8cores) 230
130W 1U (12/10/8-cores) 200
130W 2U (8-cores) 200
130W 2U (6/4-cores) 175
130W 1S WS (6-cores) 190
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 95
Datasheet Volume One of Two
, is defined by the maximum instantaneous power at the
max
max
TDP SKUs P
max
(W)
Page 96

Power Management
Table 4-11. Processor Package Power P
130W 1S WS (4-cores) 175
115W (12/10-cores) 180
95W (10/8-cores) 150
95W (6/4-cores) 130
80W (6/4-cores) 110
70W (10-cores) 120
60W (6-cores) 100
LV95W (10-cores) 150
LV70W (10/8-cores) 120
LV50W (6-cores) 75
max
TDP SKUs P
4.3 System Memory Power Management
The DDR3 power states can be summarized as the following:
• Normal operation (highest power consumption).
• CKE Power-Down: Opportunistic, per rank control after idle time. There may be
different levels.
—Active Power-Down.
— Precharge Power-Down with Fast Exit.
— Precharge power Down with Slow Exit.
• Self Refresh: In this mode no transaction is executed. The DDR consumes the
minimum possible power.
max
(W)
4.3.1 CKE Power-Down
The CKE input land is used to enter and exit different power-down modes. The memory
controller has a configurable activity timeout for each rank. Whenever no reads are
present to a given rank for the configured interval, the memory controller will transition
the rank to power-down mode.
The memory controller transitions the DRAM to power-down by de-asserting CKE and
driving a NOP command. The memory controller will tri-state all DDR interface lands
except CKE (de-asserted) and ODT while in power-down. The memory controller will
transition the DRAM out of power-down state by synchronously asserting CKE and
driving a NOP command.
When CKE is off the internal DDR clock is disabled and the DDR power is significantly
reduced.
The DDR defines three levels of power-down:
• Active power-down: This mode is entered if there are open pages when CKE is deasserted. In this mode the open pages are retained. Existing this mode is 3 - 5
DCLK cycles.
• Precharge power-down fast exit: This mode is entered if all banks in DDR are
precharged when de-asserting CKE. Existing this mode is 3 - 5 DCLK cycles.
Difference from the active power-down mode is that when waking up all pagebuffers are empty.
96 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 97

Power Management
• Precharge power-down slow exit: In this mode the data-in DLL’s on DDR are off.
Existing this mode is 3 - 5 DCLK cycles until the first command is allowed, but
about 16 cycles until first data is allowed.
4.3.2 Self Refresh
The Power Control Unit (PCU) may request the memory controller to place the DRAMs
in self refresh state. Self refresh per channel is supported. The BIOS can put the
channel in self-refresh if software remaps memory to use a subset of all channels. Also
processor channels can enter self refresh autonomously without PCU instruction when
the package is in a package C0 state.
4.3.2.1 Self Refresh Entry
Self refresh entrance can be either disabled or triggered by an idle counter. Idle counter
always clears with any access to the memory controller and remains clear as long as
the memory controller is not drained. As soon as the memory controller is drained, the
counter starts counting, and when it reaches the idle-count, the memory controller will
place the DRAMs in self refresh state.
Power may be removed from th e memory controller core at this point. But V
(1.5 V or 1.35 V) to the DDR IO must be maintained.
4.3.2.2 Self Refresh Exit
Self refresh exit can be either a message from an external unit (PCU in most cases, but
also possibly from any message-channel master) or as reaction for an incoming
transaction.
Here are the proper actions on self refresh exit:
• CK is enabled, and four CK cycles driven.
• When proper skew between Address/Command and CK are established, assert
CKE.
• Issue NOPs for tXSRD cycles.
• Issue ZQCL to each rank.
• The global scheduler will be enabled to issue commands.
4.3.2.3 DLL and PLL Shutdown
Self refresh, according to configuration, may be a trigger for master DLL shut-down
and PLL shut-down. The master DLL shut-down is issued by the memory controller
after the DRAMs have entered self refresh.
The PLL shut-down and wake-up is issued by the PCU. The memory controller gets a
signal from PLL indicating that the memory controller can start working again.
CCD
supply
4.3.3 DRAM I/O Power Management
Unused signals are tristated to save power. This includes all signals associated with an
unused memory channel.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 97
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 98

The I/O buffer for an unused signal should be tristated (output driver disabled), the
input receiver (differential sense-amp) should be disabled. The input path must be
gated to prevent spurious results due to noise on the unused signals (typically handled
automatically when input receiver is disabled).
4.4 DMI2/PCI Express* Power Management
Active State Power Management (ASPM) support using L1 state, L0s is not supported.
§
Power Management
98 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 99

Thermal Management Specifications
5 Thermal Management
Specifications
5.1 Package Thermal Specifications
The processor requires a thermal solution to maintain temperatures within operating
limits. Any attempt to operate the processor outside these limits may result in
permanent damage to the processor and potentially other components within the
system, see Section 7.7.1, “Storage Condition Specifications.” Maintaining the proper
thermal environment is key to reliable, long-term system operation.
A complete solution includes both component and system level thermal management
features. Component level thermal solutions can include active or passive heatsinks
attached to the processor integrated heat spreader (IHS). Typical system level thermal
solutions may consist of system fans combined with ducting and venting.
This section provides data necessary for developing a complete thermal solution. For
more information on designing a component level thermal solution, refer to the
Xeon® Processor E5-1600/2600/4600 v1 and v2 Product Families Thermal /
Mechanical Design Guide.
Intel®
5.1.1 Thermal Specifications
To allow optimal operation and long-term reliability of Intel processor-based systems,
the processor must remain within the minimum and maximum case temperature
) specifications as defined by the applicable thermal profile. Thermal solutions
(T
CASE
not designed to provide sufficient thermal capability may affect the long-term reliability
of the processor and system. For more details on thermal solution design, please refer
to the
Thermal / Mechanical Design Guide.
The processors implement a methodology for managing processor temperatures which
is intended to support acoustic noise reduction through fan speed control and to assure
processor reliability. Selection of the appropriate fan speed is based on the relative
temperature data reported by the processor’s Platform Environment Control Interface
(PECI) as described in Section 2.5, “Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI).”
If the DTS value is less than T
exceed the Thermal Profile, but the DTS value must remain at or below TCONTROL.
For T
temperature must meet the T
For DTS implementations:
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600/2600/4600 v1 and v2 Product Families
CONTROL
implementations, if DTS is greater than TCONTROL, then the case
CASE
CASE
•T
• If DTS is greater than Tcontrol then follow DTS thermal profile specifications for fan
thermal profile can be ignored during processor run time.
CASE
speed optimization.
, then the case temperature is permitted to
based Thermal Profiles.
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 99
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Page 100

Thermal Management Specifications
The temperature reported over PECI is always a negative value and represents a delta
below the onset of thermal control circuit (TCC) activation, as indicated by PROCHO T_N
(see Chapter 7, “Electrical Specifications”). Systems that implement fan speed control
must be designed to use this data. Systems that do not alter the fan speed need to
guarantee the case temperature meets the thermal profile specifications.
The processor thermal profiles for planned SKUs are summarized in Section 5.1.3,
“Processor Operational Thermal Specifications.” Thermal profiles ensure adherence to
Intel reliability requirements.
Thermal Profile 2U is representative of a volumetrically unconstrained thermal solution
(that is, industry enabled 2U heatsink). With adherence to the thermal profile, it is
expected that the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC) would be activated for very brief
periods of time when running the most power intensive applications.
Thermal Profile 1U is indicative of a constrained thermal environment (that is, 1U form
factor). Because of the reduced cooling capability represented by this thermal solution,
the probability of TCC activation and performance loss is increased. Additionally,
utilization of a thermal solution that does not meet Thermal Profile 1U will violate the
thermal specifications and may result in permanent damage to the processor. Refer to
Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600/2600/4600 v1 and v2 Product Families Thermal /
the
Mechanical Design Guide for details on system thermal solution design, thermal profiles
and environmental considerations.
The upper point of the thermal profile consists of the Thermal Design Power (TDP) and
the associated T
value. It should be noted that the upper point associated with
CASE
Thermal Profile 1U.
(x = TDP and y = T
CASE_MAX_B
@ TDP) represents a thermal solution design point. In
actuality the processor case temperature will not reach this value due to TCC
activation.
For Embedded Servers, Communications and storage mar kets Intel has plan SKU’ s that
support Thermal Profiles with nominal and short-term conditions for products intended
for NEBS level 3 thermal excursions. For these SKU’ s oper ation at either the nominal or
short-term thermal profiles should result in virtually no TCC activation. Thermal Profiles
for these SKU’s are found in Section 5.1.4, “Embedded Server Therm al Profiles.”
Intel recommends that complete thermal solution designs target the Thermal Design
Power (TDP). The Adaptive Thermal Monitor feature is intended to help protect the
processor in the event that an application exceeds the TDP recommendation for a
sustained time period. To ensure maximum flexibility for future requirements, systems
should be designed to the Flexible Motherboard (FMB) guidelines, even if a processor
with lower power dissipation is currently planned. The Adaptive Thermal Monitor
feature must be enabled for the processor to remain within its specifications.
100 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
 Loading...
Loading...