Page 1

Intel® Core™ i7 Processor Extreme
Edition and Intel
®
Core™ i7
Processor
Datasheet, Volume 2
November 2008
Document Number: 320835-002
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER,
AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING T O SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCT S INCLUDING
LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELA TING T O FITNES S FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANT ABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life savin g, or
life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel
reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoev er for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future
changes to them.
®
The Intel
errata which may cause the product to de viate from published spe cifications. Current char acteriz ed err ata are a vailab le on request.
Δ
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor
family, not across different processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details. Over time
processor numbers will increment based on changes in clock, speed, cache, FSB, or other features, and increments are not
intended to represent proportional or quantitative increases in any particular feature. Current roadmap processor number
progression is not necessarily representative of future roadmaps. See www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details.
Core™ i7 Processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7 Processor may contain design defects or errors known as
Hyper-Threading Technology requires a computer system with a processor supporting HT Technology and an HT Technologyenabled chipset, BIOS and operating system. Performance will va ry de pe ndi ng on the specific hardware and software y ou use. For
more information including details on which processors support HT Technology, see
http://www.intel.com/products/ht/hyperthreading_more.htm
®
64 requires a computer system with a processor, chipset, BIOS, operating system, device drivers and applications enabled
Intel
®
for Intel
depending on your hardware and software configuration s. See www .intel.com/info/em64t for more information including details on
which processors support Intel
± Intel
for some uses, certain platform software, enabled for it. Functionality, performance or other benefit will vary depending on
64. Processor will not operate (including 32-bit operation) without an Intel 64-enabled BIOS. Performance will vary
®
®
Virtualization T echnology requires a compute r system with a processor, chipset, BIOS, virtual machine monitor (VMM) and
64 or consult with your system vendor for more information.
hardware and software configurations. Intel Virtualization Technology-enabled VMM applications are currently in development.
Enabling Execute Disable Bit functionality requires a PC with a processor with Execute Disable Bit capability and a supporting
operating system. Check with your PC manufacturer on whether your system delivers Execute Disable Bit functionality.
Enhanced Intel® SpeedStep Technology. See the Processor Spec Finder
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology requires a PC with a processor with Intel Turbo Boost Technology capability. Intel Turbo Boost
Technology performance varies depending on hardware, software and overall system configuration. Check with your PC
manufacturer on whether your system delivers Intel Turbo Boost Technology. For more information, see www.intel.com
Intel, Xeon, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the United States and
other countries.
or contact your Intel representative for more information.
.
*Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright © 2008, Intel Corporation.
2 Datasheet
Page 3

Contents
1Introduction............................................................................................................11
1.1 Terminology .....................................................................................................11
1.1.1 Processor Terminology ........................ .. .. ..............................................11
1.2 References.......................................................................................................13
2 Register Description ................................................................................................15
2.1 Register Terminology.........................................................................................15
2.2 Platform Configuration Structure .........................................................................16
2.3 Device Mapping................... .. ... ......................... .. ......................... .. ...................17
2.4 Detailed Configuration Space Maps......................................................................19
2.5 PCI Standard Registers ......................................................................................37
2.5.1 VID - Vendor Identification Register ........................................................37
2.5.2 DID - Device Identification Register.........................................................37
2.5.3 RID - Revision Identification Register.......................................................38
2.5.4 CCR - Class Code Register .....................................................................38
2.5.5 HDR - Header Type Register...................................................................39
2.5.6 SID/SVID - Subsystem Identity/Subsystem Vendor
Identification Register ...........................................................................39
2.5.7 PCICMD - Command Register.................................................................40
2.5.8 PCISTS - PCI Status Register..................................................................41
2.6 SAD - System Address Decoder Registers.............................................................42
2.6.1 SAD_PAM0123 .....................................................................................42
2.6.2 SAD_PAM456.......................................................................................44
2.6.3 SAD_HEN ............................................................................................45
2.6.4 SAD_SMRAM........................................................................................45
2.6.5 SAD_PCIEXBAR....................................................................................46
2.6.6 SAD_DRAM_RULE_0, S AD_DRAM_RULE_1, SAD_DRAM_RULE_2,
2.6.7 SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_0, SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_1
2.7 Intel QPI Link Registers......................................................................................48
2.7.1 QPI_QPILCL_L0, QPI_QPILCL_L1 ............................................................48
2.8 Integrated Memory Controller Control Registers ....................................................48
2.8.1 MC_CONTROL ......................................................................................48
2.8.2 MC_STATUS.........................................................................................50
2.8.3 MC_SMI_SPARE_DIMM_ERROR_STATUS..................................................51
2.8.4 MC_SMI_SPARE_CNTRL.........................................................................52
2.8.5 MC_RESET_CONTROL............................................................................52
2.8.6 MC_CHANNEL_MAPPER..........................................................................53
2.8.7 MC_MAX_DOD......................................................................................54
2.8.8 MC_RD_CRDT_INIT...............................................................................55
2.8.9 MC_CRDT_WR_THLD.............................................................................56
2.8.10 MC_SCRUBADDR_LO.............................................................................56
2.8.11 MC_SCRUBADDR_HI.............................................................................57
2.9 TAD – Target Address Decoder Registers..............................................................58
2.9.1 TAD_DRAM_RULE_0, TAD_DRAM_RULE_1
SAD_DRAM_RULE_3
SAD_DRAM_RULE_4, SAD_DRAM_RULE_5
SAD_DRAM_RULE_6, SAD_DRAM_RULE_7 ...............................................46
SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_2, SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_3
SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_4, SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_5
SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_6, SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_7...............................47
TAD_DRAM_RULE_2, TAD_DRAM_RULE_3
TAD_DRAM_RULE_4, TAD_DRAM_RULE_5
TAD_DRAM_RULE_6, TAD_DRAM_RULE_7................................................58
Datasheet 3
Page 4

2.9.2 TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_0, TAD _INTERLEAVE_LIST_1
TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_2, TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_3
TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_4, TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_5
TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_6, TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_7................................59
2.10 Integrated Memory Controller Channel Control Registers.........................................60
2.10.1 MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_RESET_CMD
MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_RESET_CMD
MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_RESET_CMD.......................................................60
2.10.2 MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_CMD
MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_CMD
MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_CMD..........................................................61
2.10.3 MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS
MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS
MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS.....................................................62
2.10.4 MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_STATUS
MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_STATUS
MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_STATUS .....................................................63
2.10.5 MC_CHANNEL_0_DDR3CMD
MC_CHANNEL_1_DDR3CMD
MC_CHANNEL_2_DDR3CMD....................................................................64
2.10.6 MC_CHANNEL_0_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT
MC_CHANNEL_1_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT
MC_CHANNEL_2_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT......................................65
2.10.7 MC_CHANNEL_0_MRS_VALUE_0_1
MC_CHANNEL_1_MRS_VALUE_0_1
MC_CHANNEL_2_MRS_VALUE_0_1..........................................................65
2.10.8 MC_CHANNEL_0_MRS_VALUE_2
MC_CHANNEL_1_MRS_VALUE_2
MC_CHANNEL_2_MRS_VALUE_2 .............................................................66
2.10.9 MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_PRESENT
MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_PRESENT
MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_PRESENT............................................................66
2.10.10 MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_TIMING_A
MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_TIMING_A
MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_TIMING_A..........................................................67
2.10.11 MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_TIMING_B
MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_TIMING_B
MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_TIMING_B..........................................................70
2.10.12 MC_CHANNEL_0_BANK_TIMING
MC_CHANNEL_1_BANK_TIMING
MC_CHANNEL_2_BANK_TIMING..............................................................71
2.10.13 MC_CHANNEL_0_REFRESH_TIMING
MC_CHANNEL_1_REFRESH_TIMING
MC_CHANNEL_2_REFRESH_TIMING.........................................................71
2.10.14 MC_CHANNEL_0_CKE_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_1_CKE_TIMING
MC_CHANNEL_2_CKE_TIMING................................................................72
2.10.15 MC_CHANNEL_0_ZQ_TIMING
MC_CHANNEL_1_ZQ_TIMING
MC_CHANNEL_2_ZQ_TIMING .................................................................72
2.10.16 MC_CHANNEL_0_RCOMP_PARAMS
MC_CHANNEL_1_RCOMP_PARAMS
MC_CHANNEL_2_RCOMP_PARAMS...........................................................73
2.10.17 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_PARAMS1
MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_PARAMS1
MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_PARAMS1.............................................................73
2.10.18 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_PARAMS2
MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_PARAMS2
MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_PARAMS2.............................................................74
4 Datasheet
Page 5

2.10.19 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD
MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD
MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD......................................... 74
2.10.20 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD
MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD
MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD......................................... 75
2.10.21 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR
MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR
MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR........................................ 75
2.10.22 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR
MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR
MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR........................................ 75
2.10.23 MC_CHANNEL_0_WAQ_PARAMS
MC_CHANNEL_1_WAQ_PARAMS
MC_CHANNEL_2_WAQ_PARAMS .............................................................76
2.10.24 MC_CHANNEL_0_SCHEDULER_PARAMS
MC_CHANNEL_1_SCHEDULER_PARAMS
MC_CHANNEL_2_SCHEDULER_PARAMS ...................................................77
2.10.25 MC_CHANNEL_0_MAINTENANCE_OPS
MC_CHANNEL_1_MAINTENANCE_OPS
MC_CHANNEL_2_MAINTENANCE_OPS .....................................................77
2.10.26 MC_CHANNEL_0_TX_BG_SETTINGS
MC_CHANNEL_1_TX_BG_SETTINGS
MC_CHANNEL_2_TX_BG_SETTINGS........................................................78
2.10.27 MC_CHANNEL_0_RX_BGF_SETTINGS
MC_CHANNEL_1_RX_BGF_SETTINGS
MC_CHANNEL_2_RX_BGF_SETTINGS......................................................78
2.10.28 MC_CHANNEL_0_EW_BGF_SETTINGS
MC_CHANNEL_1_EW_BGF_SETTINGS
MC_CHANNEL_2_EW_BGF_SETTINGS......................................................79
2.10.29 MC_CHANNEL_0_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS
MC_CHANNEL_1_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS
MC_CHANNEL_2_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS.........................................79
2.10.30 MC_CHANNEL_0_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY
MC_CHANNEL_1_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY
MC_CHANNEL_2_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY.................................................79
2.10.31 MC_CHANNEL_0_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1
MC_CHANNEL_1_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1
MC_CHANNEL_2_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1 ..................................................80
2.10.32 MC_CHANNEL_0_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2
MC_CHANNEL_1_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2
MC_CHANNEL_2_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2 ..................................................80
2.10.33 MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTINGS_CH0
MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTINGS_CH1
MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTINGS_CH2.......................................81
2.10.34 MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH0
MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH1
MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH2...............................................81
2.10.35 MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH0
MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH1
MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH2 .............................................81
2.10.36 MC_CHANNEL_0_ADDR_MATCH
MC_CHANNEL_1_ADDR_MATCH
MC_CHANNEL_2_ADDR_MATCH..............................................................82
2.10.37 MC_CHANNEL_0_ECC_ERROR_MASK
MC_CHANNEL_1_ECC_ERROR_MASK
MC_CHANNEL_2_ECC_ERROR_MASK.......................................................83
2.10.38 MC_CHANNEL_0_ECC_ERROR_INJECT
MC_CHANNEL_1_ECC_ERROR_INJECT
MC_CHANNEL_2_ECC_ERROR_INJECT.....................................................83
Datasheet 5
Page 6

2.10.39 Error Injection Implementation...............................................................84
2.11 Integrated Memory Controller Channel Address Registers........................................85
2.11.1 MC_DOD_CH0_0, MC_DOD_CH0_1, MC_DOD_CH0_2 ................................85
2.11.2 MC_DOD_CH1_0, MC_DOD_CH1_1, MC_DOD_CH1_2 ................................86
2.11.3 MC_DOD_CH2_0, MC_DOD_CH2_1, MC_DOD_CH2_2 ................................87
2.11.4 MC_SAG_CH0_0, MC_SAG _CH0_1, MC_SAG_CH0_2
MC_SAG_CH0_3, MC_SAG_CH0_4, MC_SAG_CH0_5
MC_SAG_CH0_6, MC_SAG_CH0_7, MC_SAG_CH1_0
MC_SAG_CH1_1, MC_SAG_CH1_2, MC_SAG_CH1_3
MC_SAG_CH1_4, MC_SAG_CH1_5, MC_SAG_CH1_6
MC_SAG_CH1_7, MC_SAG_CH2_0, MC_SAG_CH2_1
MC_SAG_CH2_2, MC_SAG_CH2_3, MC_SAG_CH2_4
MC_SAG_CH2_5, MC_SAG_CH2 _ 6, MC_ S AG_ C H 2_ 7..................................88
2.12 Integrated Memory Controller Channel Rank Registers............................................89
2.12.1 MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_0, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_1
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_2, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_3
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_4, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_5
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_6, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_7
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_0, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_1
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_2, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_3
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_4, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_5
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_6, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_7
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_0, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_1
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_2, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_3
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_4, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_5
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_6, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_7 .........................................89
2.12.2 MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_0, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_1
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_2, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_3
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_4, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_5
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_6, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_7
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_8, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_9
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_10, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_11
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_12, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_13
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_14, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_15
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_16, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_17
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_18, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_19
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_20, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_21
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_22, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_23
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_24, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_25
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_26, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_27
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_28, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_29
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_30, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_31.........................................90
2.12.3 MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_0, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_1
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_2, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_3
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_4, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_5
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_6, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_7
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_8, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_9
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_10, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_11
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_12, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_13
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_14, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_15
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_16, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_17
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_18, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_19
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_20, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_21
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_22, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_23
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_24, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_25
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_26, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_27
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_28, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_29
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_30, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_31.........................................91
2.12.4 MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_0, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_1
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_2, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_3
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_4, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_5
6 Datasheet
Page 7

MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_6, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_7
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_8, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_9
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_10, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_11
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_12, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_13
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_14, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_15
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_16, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_17
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_18, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_19
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_20, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_21
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_22, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_23
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_24, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_25
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_26, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_27
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_28, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_29
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_30, MC_R IR_ W AY_ CH2_31 ........................................92
2.13 Memory Thermal Control................................................... .. .. .. ...........................93
2.13.1 MC_THERMAL_CONTROL0
MC_THERMAL_CONTROL1
MC_THERMAL_CONTROL2......................................................................93
2.13.2 MC_THERMAL_STATUS0
MC_THERMAL_STATUS1
MC_THERMAL_STATUS2........................................................................93
2.13.3 MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE0
MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE1
MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE2...................................................................94
2.13.4 MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A0
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A1
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A2....................................................................94
2.13.5 MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B0
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B1
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B2....................................................................95
2.13.6 MC_COOLING_COEF0
MC_COOLING_COEF1
MC_COOLING_COEF2............................................................................95
2.13.7 MC_CLOSED_LOOP0
MC_CLOSED_LOOP1
MC_CLOSED_LOOP2 .............................................................................96
2.13.8 MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET0
MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET1
MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET2.......................................................................96
2.13.9 MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP0
MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP1
MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP2 ...................................................................97
2.13.10 MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND0
MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND1
MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND2................................................................97
2.13.11 MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS0
MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS1
MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS2....................................................................98
2.14 Integrated Memory Controller Miscellaneous Registers............................................98
2.14.1 MC_DIMM_CLK_RATIO_STATUS .............................................................98
2.14.2 MC_DIMM_CLK_RATIO ..........................................................................99
Datasheet 7
Page 8

Tables
1-1 References........................................................................................................13
2-1 Functions Specifically Handled by the Processor.....................................................18
2-2 Device 0, Function 0: Generic Non-core Registers ..................................................19
2-3 Device 0, Function 1: System Address Decoder Registers........................................20
2-4 Device 2, Function 0: Intel QPI Link 0 Registers.....................................................21
2-5 Device 2, Function 1: Intel QPI Physical 0 Registers ...............................................22
2-6 Device 3, Function 0: Integrated Memory Controller Registers ....... ..........................23
2-7 Device 3, Function 1: Target Address Decoder Registers .........................................24
2-8 Device 4, Function 0: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0
Control Registers..................... ... ......................... .. .. ......................... .. ... ............25
2-9 Device 4, Function 1: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0
Address Registers..............................................................................................26
2-10 Device 4, Function 2: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0
Rank Registers..................................................................................................27
2-11 Device 4, Function 3: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0
Thermal Control Registers............................................. .. ............................ ........28
2-12 Device 5, Function 0: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1
Control Registers..................... ... ......................... .. .. ......................... .. ... ............29
2-13 Device 5, Function 1: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1
Address Registers..............................................................................................30
2-14 Device 5, Function 2: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1
Rank Registers..................................................................................................31
2-15 Device 5, Function 3: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1
Thermal Control Registers............................................. .. ............................ ........32
2-16 Device 6, Function 0: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2
Control Registers..................... ... ......................... .. .. ......................... .. ... ............33
2-17 Device 6, Function 1: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2
Address Registers..............................................................................................34
2-18 Device 6, Function 2: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2
Rank Registers..................................................................................................35
2-19 Device 6, Function 3: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2
Thermal Control Registers............................................. .. ............................ ........36
8 Datasheet
Page 9

Revision History
Revision
Number
-001 Initial release. November 2008
-002 Updated section 2.2 and Table 2.3. November 2008
Description Date
Datasheet 9
Page 10

10 Datasheet
Page 11

Introduction
1 Introduction
The Intel® Core™ i7 processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7 processor are
intended for high performance high-end desktop, Uni-processor (UP) server, and
workstation systems. The processor implements key new technologies:
• Integrated Memory Controller
• Point-to-point link interface based on Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI).
Reference to this interface may sometimes be abbreviated with Intel QPI
throughout this document.
®
Note: In this document the Intel
processor will be referred to as “the processor.”
This datasheet provides register descriptions for some of the registers located on the
processor.
The processor is optimized for performance with the power efficiencies of a low-power
microarchitecture to enable smaller, quieter systems.
®
The Intel
multi-core processors, based on 45 nm process technology. Processor features vary by
component and include up to two Intel QuickPath Interconnect point to point links
capable of up to 6.4 GT/s, up to 8 MB of shared cache, and an integrated memory
controller. The processors support all the existing Streaming SIMD Extensions 2
(SSE2), Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSE3) and Streaming SIMD Extensions 4
(SSE4). The processor supports several Advanced Technologies: Execute Disable Bit,
Intel
Technology (Intel® VT), Intel® Turbo Boost Technology, and Hyper-Threading
Technology.
Core™ i7 processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7 processor are
®
64 Technology, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology, Intel® Virtualization
Core™ i7 processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7
1.1 Terminology
A ‘#’ symbol after a signal name refers to an active low signal, indicating a signal is in
the active state when driven to a low level. For example, when RESET# is low, a reset
has been requested.
1.1.1 Processor Terminology
Commonly used terms are explained here for clarification:
• DDR3 — Double Data Rate 3 synchronous dynamic random access memory
(SDRAM) is the name of the new DDR memory standard that is being developed as
the successor to DDR2 SDRAM.
• Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology — Enhanced Intel SpeedStep
Technology allows trade-offs to be made between performance and power
consumption.
• Execute Disable Bit — Execute Disable allows memory to be marked as
executable or non-executable, when combined with a supporting operating system.
If code attempts to run in non-executable memory the processor raises an error to
the operating system. This feature can prevent some classes of viruses or worms
that exploit buffer over run vulnerabilities and can thus help improve the overall
security of the system. See the Intel Architecture Software Developer's Manual for
Datasheet 11
Page 12

Introduction
more detailed information. Refer to http://developer.intel.com/ for future reference
on up to date nomenclatures.
• Eye Definitions — The eye at any point along the data channel is defined to be the
creation of overlapping of a large number of Unit Interval of the data signal and
timing width measured with respect to the edges of a separate clock signal at any
other point. Each differential signal pair by combining the D+ and D- signals
produces a signal eye.
• 1366-land LGA package — The processor is available in a Flip-Chip Land Grid
Array (FC-LGA) package, consisting of the processor die mounted on a land grid
array substrate with an integrated heat spreader (IHS).
• Functional Operation — Refers to the normal operating conditions in which all
processor specifications, including DC, AC, system bus, signal quality, mechanical,
and thermal, are satisfied.
• Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) — A memory controller that is integrated
in the processor silicon.
• Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) — A component of the processor package used
to enhance the thermal performance of the package. Component thermal solutions
interface with the processor at the IHS surface.
®
• Intel
64 Architecture — An enhancement to Intel's IA-32 architec ture, allowing
the processor to execute operating systems and applications written to take
advantage of Intel 64. Further details on Intel 64 architecture and programming
model can be found at http://developer.intel.com/technology/intel64/.
®
• Intel
QuickPath Interconnect – A cache-coherent, link-based interconnect
specification for Intel processor, chipset, and I/O bridge components. Sometimes
abbreviated as Intel QPI.
• Intel® QPI — Abbreviation for Intel® QuickPath Interconnect.
• Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) — A set of hardware
enhancements to Intel server and client platforms that can improve virtualization
solutions. Intel VT provides a foundation for widely-deployed virtualization
solutions and enables more robust hardware assisted virtualization solutions. More
information can be found at: http://www.intel.com/technology/virtualization/
• Jitter — Any timing variation of a transition edge or edges from the defined Unit
Interval.
• LGA136 6 Socket — The processor (in the LGA-1366 package) mates with the
system board through this surface mount, 1366-contact socket.
• Mirror Port - Pads located on the top side of the processor package used to
provide logic analyzer probing access for Intel QPI signal analysis.
• Non-core — The portion of the processor comprising the shared cache, IMC and
Intel QPI Link interface.
• OEM — Original Equipment Manufacturer.
• Storage Conditions — Refers to a non-operational state. The processor may be
installed in a platform, in a tray , or loose. Processors ma y be sealed in packaging or
exposed to free air. Under these conditions, processor lands should not be
connected to any supply voltages, have any I/Os biased, or receive any clocks.
®
• Intel
Core™ i7 processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7 processor
— The desktop product, including processor substrate and integrated heat spreader
(IHS).
12 Datasheet
Page 13
Introduction
• Unit Interval (UI) — Signaling convention that is binary and unidirectional. In
this binary signaling, one bit is sent for every edge of the forwarded clock, whether
it be a rising edge or a falling edge. If a number of edges are collected at instances
, t2, tn,...., tk then the UI at instance “n” is defined as:
t
1
1.2 References
Material and concepts available in the following documents may be beneficial when
reading this document.
Table 1-1. References
®
Core™ i7 Processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7 Processor
Intel
Specification Update
Intel® Core™ i7 Processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7 Processor
Datasheet, Volume 1
Intel® Core™ i7 Processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7 Processor
and LGA1366 Socket Thermal and Mechanical Design Guide
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer's Manual
• Volume 1: Basic Architecture
• Volume 2A: Instruction Set Reference, A-M
• Volume 2B: Instruction Set Reference, N-Z
• Volume 3A: System Programming Guide, Part 1
• Volume 3B: Systems Programming Guide, Part 2
UI n = t n - t
Document Location
n - 1
http://download.intel.com
/design/processor/specup
dt/320836.pdf
http://download.intel.com
/design/processor/datasht
s/320834.pdf
http://download.intel.com
/design/processor/designe
x/320837.pdf
http://www.intel.com/pro
ducts/processor/manuals/
§
Datasheet 13
Page 14

Introduction
14 Datasheet
Page 15

Register Description
2 Register Description
The processor supports PCI configuration space accesses using the mechanism denoted
as Configuration Mechanism in the PCI specification as defined in the PCI Local Bus
Specification, Revision 2.3, as well as the PCI Express* enhanced configuration
mechanism as specified in the PCI Express Base Specification, Revision 1.1. All the
registers are organized by bus, device, function, etc. as defined in the PCI Express Base
Specification, Revision 1.1. All processor registers appear on the PCI bus assigned for
the processor socket. Bus number is derived by the max bus range setting and
processor socket number. All multi-byte numeric fields use “little-endian” ordering (i.e.,
lower addresses contain the least significant parts of the field).
As processor features vary by component, not all of the register descriptions in this
document apply to all processors. This document highlights registers which do not
apply to all processor components. Refer to the particular processor's Specification
Update for a list of features supported.
2.1 Register Terminology
Registers and register bits are assigned one or more of the following attributes. These
attributes define the behavior of register and the bit(s) that are contained with in. All
bits are set to default values by hard reset. Sticky bits retain their states between hard
i
resets.
Term Description
RO
WO
RW
RC
RCW
RW1C
RW0C
RW1S
RW0S
RWL
RWO
RRW
L
Read Only. If a register bit is read on ly, the hardware sets its state. The bit may be read
by software. Writes to this bit have no effect.
Write Only. The register bit is not implemented as a bit. The write causes some hardware
event to take place.
Read/Write. A register bit with this attribute can be read and written by software.
Read Clear: The bit or bits can be read by software, but the act of reading causes the
value to be cleared.
Read Clear/Write: A register bit with this attribute will get cleared after the read. The
register bit can be written.
Read/Write 1 Clear. A register bit with this attribute can be read or cleared by software.
In order to clear this bit, a one must be written to it. Writing a zero will have no effect.
Read/Write 0 Clear. A register bit with this attribute can be read or cleared by software.
In order to clear this bit, a zero must be written to it. Writing a one will have no effect.
Read/Write 1 Set: A register bit can be either read or set by software. In order to set
this bit, a one must be written to it. Writing a zero to this bit has no effect. Hardware will
clear this bit.
Read/Write 0 Set: A register bit can be either read or set by software. In order to set
this bit, a zero must be written to it. Writing a one to this bit has no effect. Hardware will
clear this bit.
Read/Write/Lock. A register bit with this attribute can be read or written by software.
Hardware or a configuration bit can lock the bit and prevent it from being updated.
Read/Write Once. A register bit with this attribute can be written to only once after
power up. After the first write, the bit becomes read only. This attribute is applied on a bit
by bit basis. For example, if the RWO attribute is applied to a 2 bit field, and only one bit
is written, then the written bit cannot be rewritten (unless reset). The unwritten bit, of the
field, may still be written once. This is special case of RWL.
Read/Restricted Write. This bit can be read and written by software. However, only
supported values will be written. Writes of non supported values will have no effect.
Lock. A register bit with this attribute becomes Read Only after a lock bit is set.
Datasheet 15
Page 16
Term Description
Reserved Bit. This bit is reserved for future expansion and must not be writte n. The PCI
RSVD
Reserved Bits
Reserved
Registers
Default Value
upon a Reset
“ST” appended
to the end of a
Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.2 requires that reserved bits must be preserved. Any
software that modifies a register that contains a reserved bit is res ponsible for reading the
register, modifying the desired bits, and writing back the result.
Some of the processor registers described in this section cont ain reserv ed bits. The se bits
are labeled “Reserved”. Software must deal correctly with fields that are reserved. On
reads, software must use appropriate masks to extract the defined bits and not rely on
reserved bits being any particular value. On writes, softw are must ens ure that the values
of reserved bit positions are preserved. That is, the values of reserved bit positions must
first be read, merged with the new values for other bit positions and then written back.
Note that software does not need to perform a read-merge-write operation for the
Configuration Address (CONFIG_ADDRESS) register.
In addition to reserved bits within a register, the processor contains address locations in
the configuration space that are marked either “Reserved” or “Intel Reserved”. The
processor responds to accesses to “Reserved” address locations by completing the host
cycle. When a “Reserved” register location is read, a zero value is returned. (“Reserved”
registers can be 8, 16, or 32 bits in size). Writes to “R eser ved” register s have no effec t on
the processor. Registers that are marked as “Intel Reserved” must not be modified by
system software. Writes to “Intel Reserved” registers may cause system failure . Reads to
“Intel Reserved” registers may return a non-zero value.
Upon a reset, the processor sets all of its internal configuration register s to predetermined
default states. Some register values at reset are determined by external strapping
options. The default state represents the minimum functionality feature set required to
successfully bring up the system. Hence, it does not represent the optimal system
configuration. It is the responsibility of the system initialization software (usually BIOS) to
properly determine the DRAM configurations, operating parameters and optional system
features that are applicable, and to program the processor registers accordingly.
The bit is “sticky” or unchanged by a hard reset. These bits can only be cleared by a
PWRGOOD reset.
bit name
Register Description
2.2 Platform Configuration Structure
The processor contains 6 PCI devices within a single physical component. The
configuration registers for these devices are mapped as devices residing on the PCI bus
assigned for the processor socket. Bus number is derived by the max bus range setting
and processor socket number.
• Device 0: Generic processor non-core. Device 0, Function 0 contains the generic
non-core configuration registers for the processor and resides at DID (Device ID) of
2C41h. Device 0, Function 1 contains the System Address Decode registers and
resides at DID of 2C01h.
• Device 2: Intel QPI. Device 2, Function 0 contains the Intel
Interconnect configuration registers for Intel QPI Link 0 and resides at DID of
2C10h. Device 2, Function 1 contains the physical layer registers for Intel QPI Link
0 and resides at DID of 2C11h.
• Device 3: Integrated Memory Controller . Device 3, Function 0 contains the general
registers for the Integrated Memory Controller and resides at DID of 2C18h. Device
3, Function 1 contains the Target Address Decode registers for the Integrated
Memory Controller and resides at DID of 2C19h. Device 3, Function 2 contains the
RAS registers for the Integrated Memory Controller and resides at DID of 2C1Ah.
Device 3, Function 4 contains the test registers for the Integrated Memory
Controller and resides at DID of 2C1Ch. Function 2 only applies to processors
supporting registered DIMMs.
• Device 4: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0. Device 4, Function 0 contains
the control registers for Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0 and resides at
DID of 2C20h. Device 4, Function 1 contains the address registers for Integrated
Memory Controller Channel 0 and resides at DID of 2C21h. Device 4, Function 2
contains the rank registers for Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0 and resides
®
QuickPath
16 Datasheet
Page 17
Register Description
at DID of 2C22h. Device 4, Function 3 contains the thermal control registers for
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0 and resides at DID of 2C23h.
• Device 5: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1. Device 5, Function 0 contains
the control registers for Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1 and resides at
DID of 2C28h. Device 5, Function 1 contains the address registers for Integrated
Memory Controller Channel 1 and resides at DID of 2C29h. Device 5, Function 2
contains the rank registers for Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1 and resides
at DID of 2C2Ah. Device 5, Function 3 contains the thermal control registers for
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1 and resides at DID of 2C2Bh.
• Device 6: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2. Device 6, Function 0 contains
the control registers for Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2 and resides at
DID of 2C30h. Device 6, Function 1 contains the address registers for Integrated
Memory Controller Channel 2 and resides at DID of 2C31h. Device 6, Function 2
contains the rank registers for Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2 and resides
at DID of 2C32h. Device 6, Function 3 contains the thermal control registers for
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2 and resides at DID of 2C33h.
2.3 Device Mapping
Each component in the processor is uniquely identified by a PCI bus address consisting
of Bus Number, Device Number , and Function Number. Device configuration is based on
the PCI T ype 0 configur ation conventions. All processor registers appear on the PCI bus
assigned for the processor socket. Bus number is derived by the max bus range setting
and processor socket number.
Table 2-1. Functions Specifically Handled by the Processor
Component Register Group DID Device Function
Intel QuickPath Architecture Generic Non-core Registers
Intel QuickPath Architect ure System Address Decoder
Intel QPI Link 0
Intel QPI Physical 0
Integrated Memory Controller Registers
Integrated Memory Controller Target Address Decoder
Integrated Memory Controller RAS Registers
Integrated Memory Controller Test Registers
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0 Control
Processor
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0 Address
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0 Rank
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0 Thermal Control
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1 Control
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1 Address
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1 Rank
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1 Thermal Control
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2 Control
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2 Address
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2 Rank
Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2 Thermal Control
2C41h
2C01h 1
2C10h
2C11 1
2C18h
2C19h 1
2C1Ah 2
2C1Ch 4
2C20h
2C21h 1
2C22h 2
2C23h 3
2C28h
2C29h 1
2C2Ah 2
2C2Bh 3
2C30h
2C31h 1
2C32h 2
2C33h 3
0
2
3
4
5
6
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
Notes:
1. Applies only to processors supporting sparing, mirroring, and scrubbing RAS features.
Datasheet 17
Page 18
2.4 Detailed Configuration Space Maps
Table 2-2. Device 0, Function 0: Generic Non-core Registers
DID VID 00h 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h
CCR RID 08h
HDR 0Ch 8Ch
10h 90h
14h 94h
18h 98h
1Ch 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
48h C8h
4Ch CCh
50h D0h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
60h E0h
64h E4h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
Register Description
84h
88h
ACh
18 Datasheet
Page 19
Register Description
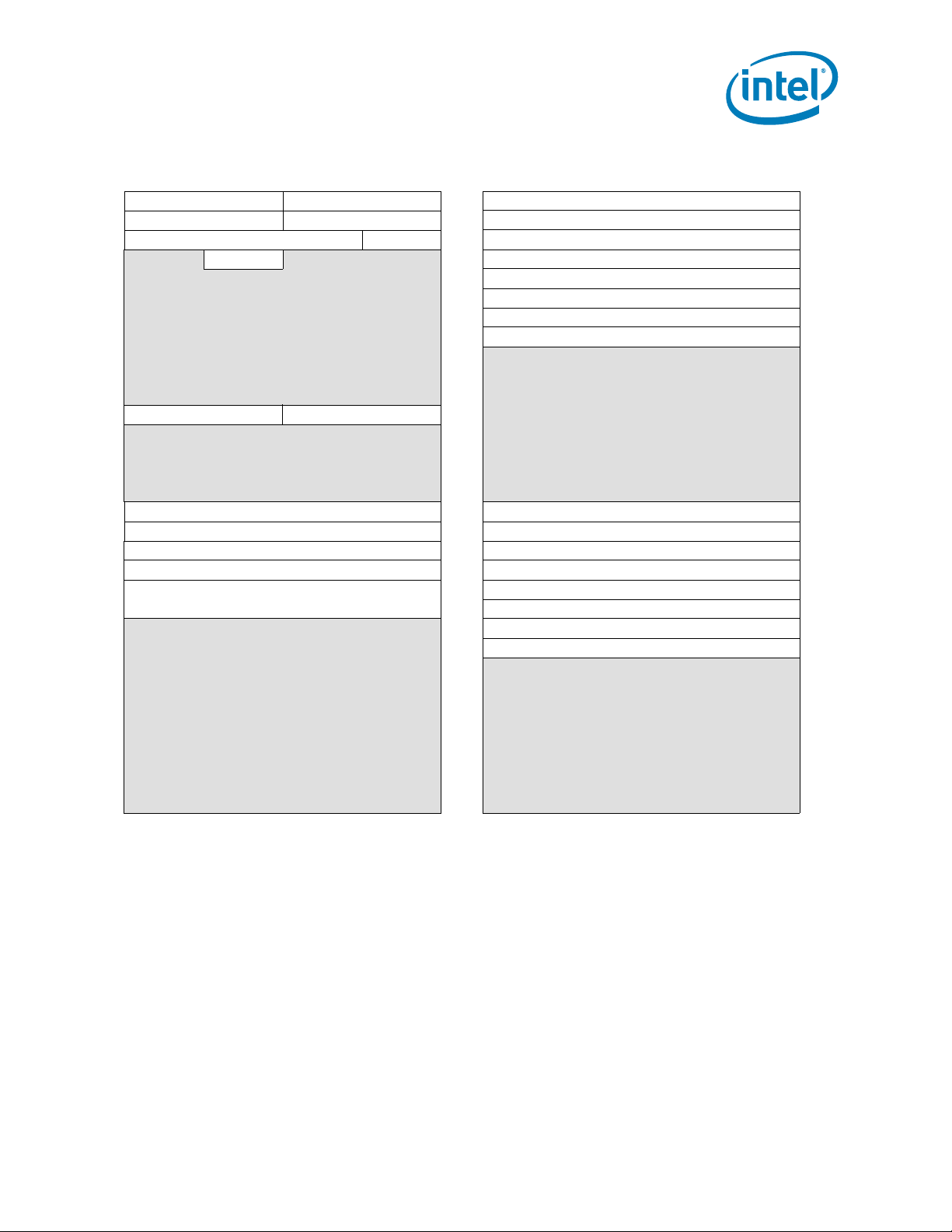
Table 2-3. Device 0, Function 1: System Address Decoder Registers
DID VID 00h SAD_DRAM_RULE_0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h SAD_DRAM_RULE_1 84h
CCR RID 08h SAD_DRAM_RULE_2 88h
HDR 0Ch SAD_DRAM_RULE_3 8Ch
10h SAD_DRAM_RULE_4 90h
14h SAD_DRAM_RULE_5 94h
18h SAD_DRAM_RULE_6 98h
1Ch SAD_DRAM_RULE_7 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
SAD_PAM0123 40h SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_0 C0h
SAD_PAM456 44h SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_1 C4h
SAD_HEN 48h SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_2 C8h
SAD_SMRAM 4Ch SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_3 CCh
SAD_PCIEXBAR 50h SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_4 D0h
54h SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_5 D4h
58h SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_6 D8h
5Ch SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_7 DCh
60h E0h
64h E4h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
ACh
Datasheet 19
Page 20
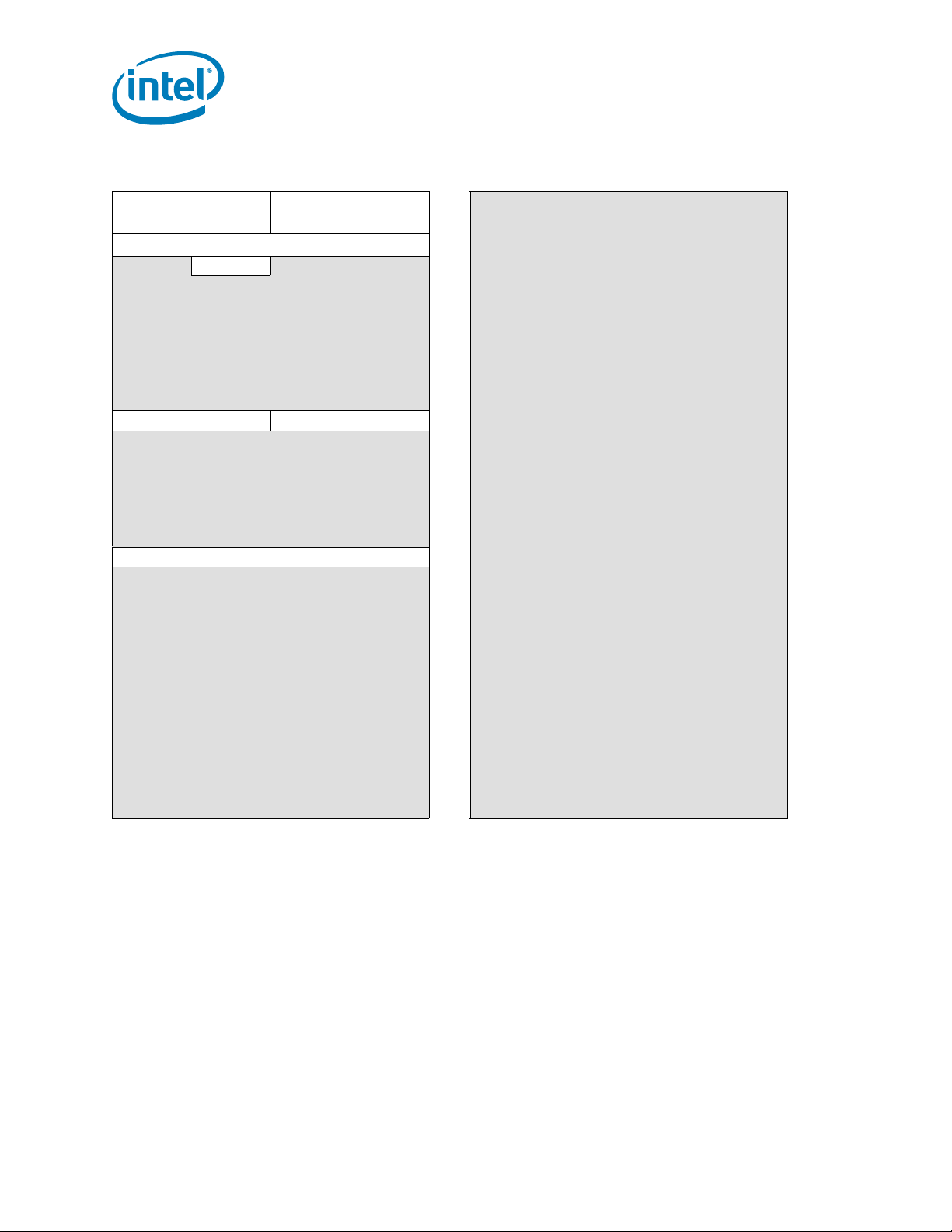
Table 2-4. Device 2, Function 0: Intel QPI Link 0 Registers
DID VID 00h 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h
CCR RID 08h
HDR 0Ch 8Ch
10h 90h
14h 94h
18h 98h
1Ch 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
QPI_QPILCL_L0 48h C8h
4Ch CCh
50h D0h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
60h E0h
64h E4h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
Register Description
84h
88h
ACh
20 Datasheet
Page 21

Register Description
Table 2-5. Device 2, Function 1: Intel QPI Physical 0 Registers
DID VID 00h 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h
CCR RID 08h
HDR 0Ch 8Ch
10h 90h
14h 94h
18h 98h
1Ch 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
48h C8h
4Ch CCh
50h D0h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
60h E0h
64h E4h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
84h
88h
ACh
Datasheet 21
Page 22
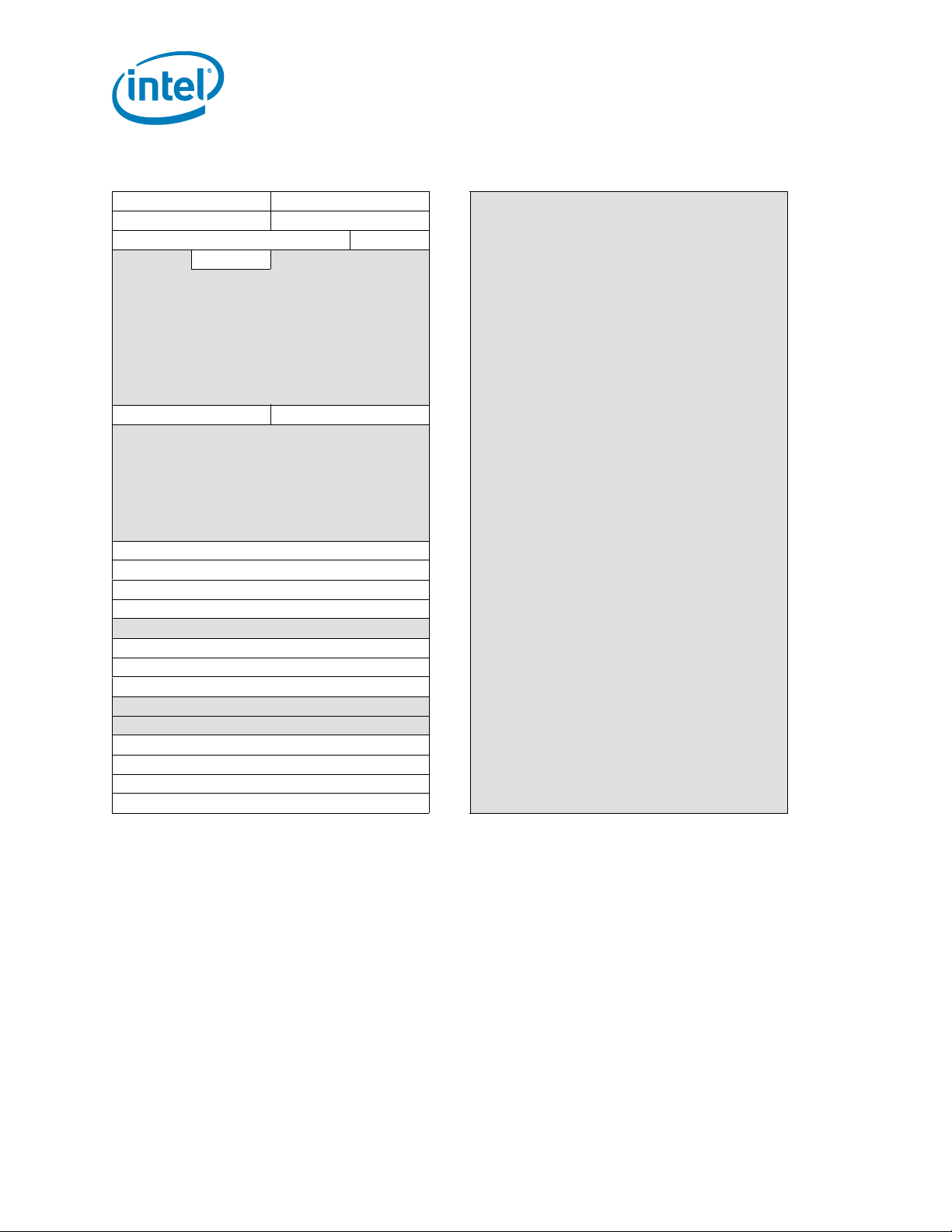
Table 2-6. Device 3, Function 0: Integrated Memory Controller Registers
DID VID 00h 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h
CCR RID 08h
HDR 0Ch 8Ch
10h 90h
14h 94h
18h 98h
1Ch 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
MC_CONTROL 48h
MC_STATUS 4Ch
MC_SMI_SPARE_DIMM_ERROR_STATUS 50h
MC_SMI_SPARE_CNTRL 54h
58h D8h
MC_RESET_CONTROL 5Ch
MC_CHANNEL_MAPPER 60h
MC_MAX_DOD 64h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
MC_RD_CRDT_INIT 70h
MC_CRDT_WR_THLD 74h
MC_SCRUBADDR_LO 78h
MC_SCRUBADDR_HI 7Ch
Register Description
84h
88h
ACh
C8h
CCh
D0h
D4h
DCh
E0h
E4h
F0h
F4h
F8h
FCh
22 Datasheet
Page 23
Register Description
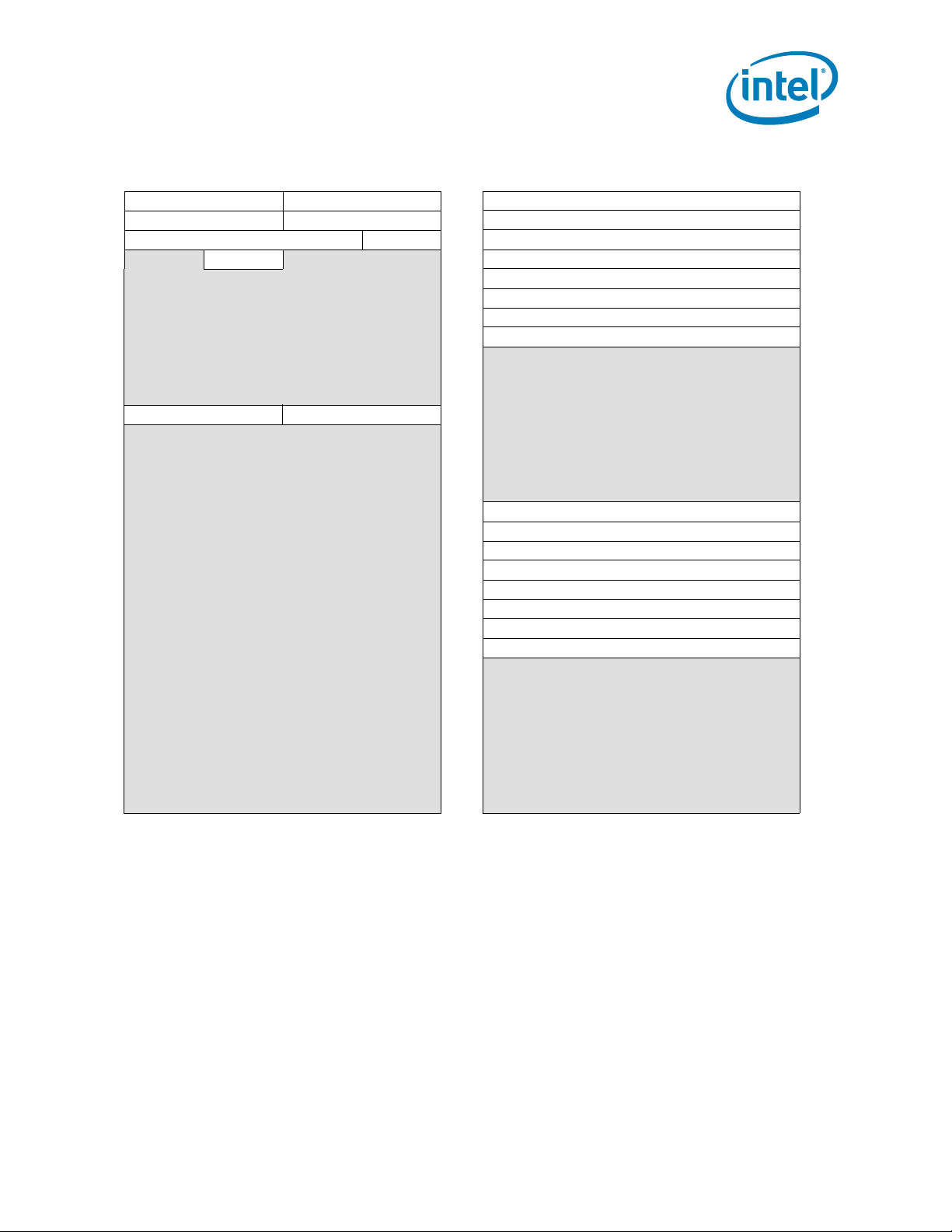
Table 2-7. Device 3, Function 1: Target Address Decoder Registers
DID VID 00h TAD_DRAM_RULE_0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h TAD_DRAM_RULE_1 84h
CCR RID 08h TAD_DRAM_RULE_2 88h
HDR 0Ch TAD_DRAM_RULE_3 8Ch
10h TAD_DRAM_RULE_4 90h
14h TAD_DRAM_RULE_5 94h
18h TAD_DRAM_RULE_6 98h
1Ch TAD_DRAM_RULE_7 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_0 C0h
44h TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_1 C4h
48h TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_2 C8h
4Ch TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_3 CCh
50h TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_4 D0h
54h TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_5 D4h
58h TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_6 D8h
5Ch TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_7 DCh
60h E0h
64h E4h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
ACh
Datasheet 23
Page 24
Register Description
Table 2-8. Device 4, Function 0: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0
Control Registers
DID VID 00h MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_TIMING_A 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_TIMING_B 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_CHANNEL_0_BANK_TIMING 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_CHANNEL_0_REFRESH_TIMING 8Ch
10h MC_CHANNEL_0_CKE_TIMING 90h
14h MC_CHANNEL_0_ZQ_TIMING 94h
18h MC_CHANNEL_0_RCOMP_PARAMS 98h
1Ch MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_PARAMS1 9Ch
20h MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_PARAMS2 A0h
24h MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD A4h
28h MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD A8h
SID SVID 2Ch MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR ACh
30h MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR B0h
34h MC_CHANNEL_0_WAQ_PARAMS B4h
38h MC_CHANNEL_0_SCHEDULER_PARAMS B8h
3Ch MC_CHANNEL_0_MAINTENANCE_OPS BCh
40h MC_CHANNEL_0_TX_BG_SETTINGS C0h
44h C4h
48h MC_CHANNEL_0_RX_BGF_SETTINGS C8h
4Ch MC_CHANNEL_0_EW_BGF_SETTINGS CCh
MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_RESET_CMD 50h MC_CHANNEL_0_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS D0h
MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_CMD 54h MC_CHANNEL_0_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY D4h
MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS 58h MC_CHANNEL_0_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1 D8h
MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_STATUS 5Ch MC_CHANNEL_0_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2 DCh
MC_CHANNEL_0_DDR3CMD 60h MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTING_CH0 E0h
64h MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH0 E4h
MC_CHANNEL_0_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT 68h MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH0 E8h
6Ch ECh
MC_CHANNEL_0_MRS_VALUE_0_1 70h MC_CHANNEL_0_ADDR_MATCH F0h
MC_CHANNEL_0_MRS_VALUE_2 74h F4h
78h MC_CHANNEL_0_ECC_ERROR_MASK F8h
MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_PRESENT 7Ch MC_CHANNEL_0_ECC_ERROR_INJECT FCh
24 Datasheet
Page 25
Register Description
Table 2-9. Devic e 4, Function 1: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0
Address Registers
DID VID 00h MC_SAG_CH0_0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_SAG_CH0_1 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_SAG_CH0_2 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_SAG_CH0_3 8Ch
10h MC_SAG_CH0_4 90h
14h MC_SAG_CH0_5 94h
18h MC_SAG_CH0_6 98h
1Ch MC_SAG_CH0_7 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
MC_DOD_CH0_0 48h
MC_DOD_CH0_1 4Ch
MC_DOD_CH0_2 50h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
60h E0h
64h E4h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
ACh
C8h
CCh
D0h
Datasheet 25
Page 26

Table 2-10. Device 4, Function 2: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0
Rank Registers
DID VID 00h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_1 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_2 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_3 8Ch
10h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_4 90h
14h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_5 94h
18h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_6 98h
1Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_7 9Ch
20h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_8 A0h
24h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_9 A4h
28h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_10 A8h
SID SVID 2Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_11 ACh
30h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_12 B0h
34h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_13 B4h
38h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_14 B8h
3Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_15 BCh
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_0 40h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_16 C0h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_1 44h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_17 C4h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_2 48h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_18 C8h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_3 4Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_19 CCh
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_4 50h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_20 D0h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_5 54h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_21 D4h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_6 58h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_22 D8h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_7 5Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_23 DCh
60h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_24 E0h
64h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_25 E4h
68h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_26 E8h
6Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_27 ECh
70h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_28 F0h
74h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_29 F4h
78h MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_30 F8h
7Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_31 FCh
Register Description
26 Datasheet
Page 27
Register Description
Table 2-11. Device 4, Function 3: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 0
Thermal Control Registers
DID VID 00h MC_COOLING_COEF0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_CLOSED_LOOP0 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET0 88h
HDR 0Ch 8Ch
10h 90h
14h 94h
18h MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP0 98h
1Ch MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND0 9Ch
20h A0h
24h MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS0 A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
MC_THERMAL_CONTROL0 48h
MC_THERMAL_STATUS0 4Ch
MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE0 50h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A0 60h
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B0 64h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
ACh
C8h
CCh
D0h
E0h
E4h
Datasheet 27
Page 28
Register Description
Table 2-12. Device 5, Function 0: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1
Control Registers
DID VID 00h MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_TIMING_A 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_TIMING_B 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_CHANNEL_1_BANK_TIMING 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_CHANNEL_1_REFRESH_TIMING 8Ch
10h MC_CHANNEL_1_CKE_TIMING 90h
14h MC_CHANNEL_1_ZQ_TIMING 94h
18h MC_CHANNEL_1_RCOMP_PARAMS 98h
1Ch MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_PARAMS1 9Ch
20h MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_PARAMS2 A0h
24h MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD A4h
28h MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD A8h
SID SVID 2Ch MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR ACh
30h MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR B0h
34h MC_CHANNEL_1_WAQ_PARAMS B4h
38h MC_CHANNEL_1_SCHEDULER_PARAMS B8h
3Ch MC_CHANNEL_1_MAINTENANCE_OPS BCh
40h MC_CHANNEL_1_TX_BG_SETTINGS C0h
44h C4h
48h MC_CHANNEL_1_RX_BGF_SETTINGS C8h
4Ch MC_CHANNEL_1_EW_BGF_SETTINGS CCh
MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_RESET_CMD 50h MC_CHANNEL_1_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS D0h
MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_CMD 54h MC_CHANNEL_1_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY D4h
MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS 58h MC_CHANNEL_1_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1 D8h
MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_STATUS 5Ch MC_CHANNEL_1_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2 DCh
MC_CHANNEL_1_DDR3CMD 60h MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTING_CH1 E0h
64h MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH1 E4h
MC_CHANNEL_1_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT 68h MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH1 E8h
6Ch ECh
MC_CHANNEL_1_MRS_VALUE_0_1 70h MC_CHANNEL_1_ADDR_MATCH F0h
MC_CHANNEL_1_MRS_VALUE_2 74h
78h MC_CHANNEL_1_ECC_ERROR_MASK F8h
MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_PRESENT 7Ch MC_CHANNEL_1_ECC_ERROR_INJECT FCh
F4h
28 Datasheet
Page 29
Register Description
Table 2-13. Device 5, Function 1: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1
Address Registers
DID VID 00h MC_SAG_CH1_0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_SAG_CH1_1 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_SAG_CH1_2 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_SAG_CH1_3 8Ch
10h MC_SAG_CH1_4 90h
14h MC_SAG_CH1_5 94h
18h MC_SAG_CH1_6 98h
1Ch MC_SAG_CH1_7 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
MC_DOD_CH1_0 48h
MC_DOD_CH1_1 4Ch
MC_DOD_CH1_2 50h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
60h E0h
64h E4h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
ACh
C8h
CCh
D0h
Datasheet 29
Page 30

Table 2-14. Device 5, Function 2: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1
Rank Registers
DID VID 00h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_1 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_2 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_3 8Ch
10h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_4 90h
14h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_5 94h
18h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_6 98h
1Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_7 9Ch
20h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_8 A0h
24h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_9 A4h
28h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_10 A8h
SID SVID 2Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_11 ACh
30h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_12 B0h
34h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_13 B4h
38h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_14 B8h
3Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_15 BCh
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_0 40h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_16 C0h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_1 44h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_17 C4h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_2 48h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_18 C8h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_3 4Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_19 CCh
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_4 50h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_20 D0h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_5 54h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_21 D4h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_6 58h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_22 D8h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_7 5Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_23 DCh
60h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_24 E0h
64h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_25 E4h
68h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_26 E8h
6Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_27 ECh
70h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_28 F0h
74h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_29 F4h
78h MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_30 F8h
7Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_31 FCh
Register Description
30 Datasheet
Page 31

Register Description
Table 2-15. Device 5, Function 3: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 1
Thermal Control Registers
DID VID 00h MC_COOLING_COEF1 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_CLOSED_LOOP1 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET1 88h
HDR 0Ch 8Ch
10h 90h
14h 94h
18h MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP1 98h
1Ch MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND1 9Ch
20h A0h
24h MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS1 A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
MC_THERMAL_CONTROL1 48h
MC_THERMAL_STATUS1 4Ch
MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE1 50h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A1 60h
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B1 64h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
ACh
C8h
CCh
D0h
E0h
E4h
Datasheet 31
Page 32

Register Description
Table 2-16. Device 6, Function 0: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2
Control Registers
DID VID 00h MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_TIMING_A 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_TIMING_B 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_CHANNEL_2_BANK_TIMING 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_CHANNEL_2_REFRESH_TIMING 8Ch
10h MC_CHANNEL_2_CKE_TIMING 90h
14h MC_CHANNEL_2_ZQ_TIMING 94h
18h MC_CHANNEL_2_RCOMP_PARAMS 98h
1Ch MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_PARAMS1 9Ch
20h MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_PARAMS2 A0h
24h MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD A4h
28h MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD A8h
SID SVID 2Ch MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR ACh
30h MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR B0h
34h MC_CHANNEL_2_WAQ_PARAMS B4h
38h MC_CHANNEL_2_SCHEDULER_PARAMS B8h
3Ch MC_CHANNEL_2_MAINTENANCE_OPS BCh
40h MC_CHANNEL_2_TX_BG_SETTINGS C0h
44h C4h
48h MC_CHANNEL_2_RX_BGF_SETTINGS C8h
4Ch MC_CHANNEL_2_EW_BGF_SETTINGS CCh
MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_RESET_CMD 50h MC_CHANNEL_2_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS D0h
MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_CMD 54h MC_CHANNEL_2_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY D4h
MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS 58h MC_CHANNEL_2_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1 D8h
MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_STATUS 5Ch MC_CHANNEL_2_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2 DCh
MC_CHANNEL_2_DDR3CMD 60h MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTING_CH2 E0h
64h MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH2 E4h
MC_CHANNEL_2_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT 68h MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH2 E8h
6Ch ECh
MC_CHANNEL_2_MRS_VALUE_0_1 70h MC_CHANNEL_2_ADDR_MATCH F0h
MC_CHANNEL_2_MRS_VALUE_2 74h
78h MC_CHANNEL_2_ECC_ERROR_MASK F8h
MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_PRESENT 7Ch MC_CHANNEL_2_ECC_ERROR_INJECT FCh
F4h
32 Datasheet
Page 33

Register Description
Table 2-17. Device 6, Function 1: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2
Address Registers
DID VID 00h MC_SAG_CH2_0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_SAG_CH2_1 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_SAG_CH2_2 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_SAG_CH2_3 8Ch
10h MC_SAG_CH2_4 90h
14h MC_SAG_CH2_5 94h
18h MC_SAG_CH2_6 98h
1Ch MC_SAG_CH2_7 9Ch
20h A0h
24h A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
MC_DOD_CH2_0 48h
MC_DOD_CH2_1 4Ch
MC_DOD_CH2_2 50h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
60h E0h
64h E4h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
ACh
C8h
CCh
D0h
Datasheet 33
Page 34

Table 2-18. Device 6, Function 2: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2
Rank Registers
DID VID 00h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_0 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_1 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_2 88h
HDR 0Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_3 8Ch
10h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_4 90h
14h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_5 94h
18h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_6 98h
1Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_7 9Ch
20h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_8 A0h
24h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_9 A4h
28h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_10 A8h
SID SVID 2Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_11 ACh
30h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_12 B0h
34h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_13 B4h
38h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_14 B8h
3Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_15 BCh
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_0 40h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_16 C0h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_1 44h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_17 C4h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_2 48h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_18 C8h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_3 4Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_19 CCh
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_4 50h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_20 D0h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_5 54h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_21 D4h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_6 58h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_22 D8h
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_7 5Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_23 DCh
60h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_24 E0h
64h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_25 E4h
68h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_26 E8h
6Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_27 ECh
70h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_28 F0h
74h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_29 F4h
78h MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_30 F8h
7Ch MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_31 FCh
Register Description
34 Datasheet
Page 35

Register Description
Table 2-19. Device 6, Function 3: Integrated Memory Controller Channel 2
Thermal Control Registers
DID VID 00h MC_COOLING_COEF2 80h
PCISTS PCICMD 04h MC_CLOSED_LOOP2 84h
CCR RID 08h MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET2 88h
HDR 0Ch 8Ch
10h 90h
14h 94h
18h MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP2 98h
1Ch MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND2 9Ch
20h A0h
24h MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS2 A4h
28h A8h
SID SVID 2Ch
30h B0h
34h B4h
38h B8h
3Ch BCh
40h C0h
44h C4h
MC_THERMAL_CONTROL2 48h
MC_THERMAL_STATUS2 4Ch
MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE2 50h
54h D4h
58h D8h
5Ch DCh
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A2 60h
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B2 64h
68h E8h
6Ch ECh
70h F0h
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch FCh
ACh
C8h
CCh
D0h
E0h
E4h
Datasheet 35
Page 36

2.5 PCI Standard Registers
These registers appear in every function for every device.
Note: Reserved bit locations are not shown in the following register tables.
2.5.1 VID - Vendor Identification Register
The VID Register contains the vendor identification number. This 16-bit register,
combined with the Device Identification Register uniquely identifies the manufacturer
of the function within the processor. Writes to this register have no effect.
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 00h
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 00h
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 00h
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 00h
Bit Type
15:0 RO 8086h
Reset
Value
Vendor Identification Number
The value assigned to Intel.
Description
Register Description
2.5.2 DID - Device Identification Register
This 16-bit register combined with the Vendor Identification register uniquely identifies
the Function within the processor. Writes to this register have no effect. See Table 2-1
for the DID of each processor function.
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 02h
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 02h
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 02h
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 02h
Bit Type
15:0 RO
Reset
Value
*See
Table 2-1
Description
Device Identification Number
Identifies each function of the processor.
36 Datasheet
Page 37

Register Description
2.5.3 RID - Revision Identification Register
This register contains the revision number of the processor. The Revision ID (RID) is a
traditional 8-bit Read Only (RO) register located at offset 08h in the standard PCI
header of every PCI/PCI Express compatible device and function.
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 08h
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 08h
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 08h
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 08h
Bit Type
7:0 RO 0h
Reset
Value
Revision Identification Number
Refer to the Intel
Processor Specification Update
®
Core™ i7 Processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Core™ i7
for the value of the Revision ID Register.
Description
2.5.4 CCR - Class Code Register
This register contains the Class Code for the device. Writes to this register have no
effect.
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 09h
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 09h
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 09h
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 09h
Bit Type
23:16 RO 06h
15:8 RO 0
7:0 RO 0
Reset
Value
Base Class
This field indicates the general device category. For the processor, this field is
hardwired to 06h, indicating it is a “Bridge Device”.
Sub-Class
This field qualifies the Base Class, providing a more detailed specification of
the device function.
For all devices the default is 00h, indicating “Host Bridge”.
Register-Level Programming Interface
This field identifies a specific programming interface (if any), that device
independent software can use to interact with the device. There are no such
interfaces defined for “Host Bridge” types, and this field is hardwired to 00h.
Description
Datasheet 37
Page 38

2.5.5 HDR - Header Type Register
This register identifies the header layout of the configuration space.
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 0Eh
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 0Eh
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 0Eh
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 0Eh
Bit Type
7RO1
6:0 RO 0
Reset
Value
Multi-function Device
Selects whether this is a multi-function device, that may have alternative
configuration layouts. This bit is hardwired to 1 for devices in the processor.
Configuration Layout
This field identifies the format of the configuration header layout for a PCI-toPCI bridge from bytes 10h through 3Fh.
For all devices the default is 00h, indicating a conventional type 00h PCI heade r.
Register Description
Description
2.5.6 SID/SVID - Subsystem Identity/Subsystem Vendor Identification Register
This register identifies the manufacturer of the system. This 32-bit register uniquely
identifies any PCI device.
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 2Ch, 2Eh
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 2Ch, 2Eh
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 2Ch, 2Eh
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 2Ch, 2Eh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
31:16 RWO 8086h
15:0 RWO 8086h
Reset
Value
Description
Subsystem Identification Number
The default value specifies Intel
Vendor Identification Number
The default value specifies Intel.
38 Datasheet
Page 39

Register Description
2.5.7 PCICMD - Command Register
This register defines the PCI 3.0 compatible command register values applicable to PCI
Express space.
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 04h
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 04h
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 04h
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 04h
Bit Type
15:11 RV 0
10 RO 0
9RO0
8RO0
7RO0
6RO0
5RO0
4RO0
3RO0
2RO1
1RO1
0RO0
Reset
Value
Reserved. (by P CI SI G)
INTxDisable: Interrupt Disable
Controls the ability of the PCI Express port to generate INTx messages.
If this device does not generate interrupts then this bit is not implemented and
is RO.
If this device generates interrupts then this bit is RW and this bit disables the
device/function from asserting INTx#. A value of 0 enables the assertion of its
INTx# signal. A value of 1 disables the assertion of its INTx# signal.
1 = Legacy Interrupt mode is disabled
0 = Legacy Interrupt mode is enabled
FB2B: Fast Back-to-Back Enable
This bit controls whether or not the master can do fast back-to-back writes.
Since this device is strictly a target this bit is not implemented. This bit is
hardwired to 0. Writes to this bit position have no effect.
SERRE: SERR Message Enable
This bit is a global enable bit for this devices SERR messaging. This host bridge
will not implement SERR messaging. This bit is hardwired to 0. If SERR is used
for error generation, then this bit must be RW and enable/disable SERR
signaling.
IDSELWCC: IDSEL Stepping/Wait Cycle Control
Per PCI 2.3 specification this bit is hardwired to 0.
PERRE: Parity Error Response Enable
Parity error is not implemented in this host bridge. This bit is hardwired to 0.
VGAPSE: VGA palette snoop Enable
This host bridge does not implement this bit. This bit is hardwired to 0.
MWIEN: Memory Write and Invalidate Enable
This host bridge will never issue memory write and invalidate commands. This
bit is therefore hardwired to 0.
SCE: Special Cycle Enable
This host bridge does not implement this bit. This bit is hardwired to a 0.
BME: Bus Master Enable
This host bridge is always enabled as a master. This bit is hardwired to a 1.
MSE: Memory Space Enable
This host bridge always allows access to main memory. This bit is not
implemented and is hardwired to 1.
IOAE: Access Enable
This bit is not implemented in this host bridge and is hardwired to 0.
Description
Datasheet 39
Page 40

2.5.8 PCISTS - PCI Status Register
The PCI Status register is a 16-bit status register that reports the occurrence of various
error events on this device's PCI interface.
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 06h
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 06h
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 06h
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 06h
Register Description
Bit Type
Reset
Value
15 RO 0
14 RO 0
13 RO 0
12 RO 0
11 RO 0
10:9 RO 0
8RO0
7RO1
6RO0
5RO0
Description
Detect Parity Error (DPE)
The host bridge does not implement this bit and is hardwired to a 0.
Signaled System Error (SSE)
This bit is set to 1 when this device generates an SERR message over the bus
for any enabled error condition. If the host bridge does not signal errors using
this bit, this bit is hardwired to a 0 and is read only.
Received Master Abort Status (RMAS)
This bit is set when this device generates request that receives an Unsupporte d
Request completion packet. Software clears the bit by writing 1 to it.
If this device does not receive Unsupported Request completion packets, the bit
is hardwired to 0 and is read only.
Received Target Abort Status (RTAS)
This bit is set when this device generates a request that receives a Completer
Abort completion packet. Software clears this bit by writing a 1 to it.
If this device does not receive Completer Abort completion packets, this bit is
hardwired to 0 and read only.
Signaled Target Abort Status (STAS)
This device will not generate a Target Abort completion or Special Cycle. This bit
is not implemented in this device and is hardwired to a 0.
DEVSEL Timing (DEVT)
These bits are hardwired to 00. This device does not physically connect to PCI
bus X. These bits are set to “00” (fast decode) so that optimum DEVSEL timing
for PCI bus X is not limited by this device.
Master Data Parity Error Detected (DPD)
PERR signaling and messaging are not implemented by this bridge, therefore
this bit is hardwired to 0.
Fast Back-to-Back (FB2B)
This bit is hardwired to 1. This device is not physically connected to a PCI bus.
This bit is set to 1 (indicating back-to-back capabilities) so that the optimum
setting for this PCI bus is not limited by this device.
Reserved
66 MHz Capable
Does not apply to PCI Express. Hardwired to 0.
40 Datasheet
Page 41

Register Description
Device: 0
Function: 0-1
Offset: 06h
Device: 2
Function: 0-1, 4-5
Offset: 06h
Device: 3
Function: 0-2, 4
Offset: 06h
Device: 4-6
Function: 0-3
Offset: 06h
Bit Type
Reset
Value
4ROTBD
3RO0
2:0 RO 0
Capability List (CLIST)
This bit is hardwired to 1 to indicate to the configuration software that this
device/function implements a list of new capabilities. A list of new capabilities is
accessed via registers CAPPTR at the configuration address offset 34h from the
start of the PCI configuration space header of this function. Register CAPPTR
contains the offset pointing to the start address with configuration space of this
device where the capability register resides. This bit must be set for a PCI
Express device or if the VSEC capability.
If no capability structures are implemented, this bit is hardwired to 0.
Interrupt Status
If this device generates an interrupt, then this read-only bit reflects the state of
the interrupt in the device/function. Only when the Interrupt Disable bit in the
command register is a 0 and this Interrupt Status bit is a 1, will the
device’s/function’s INTx# signal be asserted. Setting the Interrupt Disable bit to
a 1 has no effect on the state of this bit.
If this device does not generate interrupts, then this bit is not implemented (RO
and reads returns 0).
Reserved
Description
2.6 SAD - System Address Decoder Registers
2.6.1 SAD_PAM0123
This register is for legacy device 0, function 0 at 90h-93h address space.
Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: 40h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
29:28 RW 0
Datasheet 41
Reset
Value
Description
PAM3_HIENABLE. 0D4000h-0D7FFFh Attribute (HIENABLE).
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0D4000h to 0D7FFFh.
00 =DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
Page 42

Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: 40h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
Reset
Value
25:24 RW 0
21:20 RW 0
17:16 RW 0
13:12 RW 0
9:8 RW 0
5:4 RW 0
Description
PAM3_LOENABLE. 0D0000h-0D3FFFh Attribute (LOENABLE).
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0D0000h to 0D3FFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
PAM2_HIENABLE. 0CC000h-0CFFFFh Attribute (HIENABLE).
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0CC000h to 0CFFFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
PAM2_LOENABLE. 0C8000h-0CBFFFh Attribute (LOENABLE).
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0C8000h to 0CBFFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
PAM1_HIENABLE. 0C4000h-0C7FFFh Attribute (HIENABLE).
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0C4000h to 0C7FFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
PAM1_LOENABLE. 0C0000h-0C3FFFh Attribute (LOENABLE).
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0C0000h to 0C3FFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
PAM0_HIENABLE. 0F0000h-0FFFFFh Attribute (HIENABLE).
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0F0000h to 0FFFFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
42 Datasheet
Page 43

Register Description
2.6.2 SAD_PAM456
Register for legacy device 0, function 0 94h-97h address space.
Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: 44h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
21:20 RW 0 PAM6_HIENABLE. 0EC000h-0EFFFFh Attribute (HIENABLE).
17:16 RW 0 PAM6_LOENABLE. 0E8000-0EBFFF Attribute (LOENABLE).
13:12 RW 0 PAM5_HIENABLE. 0E4000h-0E7FFFh Attribute (HIENABLE).
9:8 RW 0 PAM5_LOENABLE. 0E0000h-0E3FFFh Attribute (LOENABLE).
5:4 RW 0 PAM4_HIENABLE. 0DC000h-0DFFFFh Attribute (HIENABLE).
1:0 RW 0 PAM4_LOENABLE. 0D8000h-0DBFFFh Attribute (LOENABLE).
Reset
Value
Description
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0EC000h to 0EFFFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0E8000 to 0EBFFF.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0E4000h to 0E7FFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0E0000h to 0E3FFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0DC000h to 0DFFFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
This field controls the steering of read and write cycles that address the BIOS
area from 0D8000h to 0DBFFFh.
00 = DRAM Disabled: All accesses are directed to ESI.
01 = Read Only: All reads are sent to DRAM. All writes are forwarded to ESI.
10 = Write Only: All writes are send to DRAM. Reads are serviced by ESI.
11 = Normal DRAM Operation: All reads and writes are serviced by DRAM.
Datasheet 43
Page 44

2.6.3 SAD_HEN
Register for legacy Hole Enable.
Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: 48h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
7RW0HEN: Hole Enable
2.6.4 SAD_SMRAM
Register for legacy 9Dh address space. Note both IOH and non-core have this now.
Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: 4Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
14 RW 0
13 RW 0
12 RW1S 0
11 RW 0
10:8 RO -
Reset
Value
Reset
Value
Description
This field enables a memory hole in DRAM space. The DRAM that lies
"behind" this space is not remapped.
0 = No Memory hole.
1 = Memory hole from 15 MB to 16 MB.
Description
SMM Space Open (D_OPEN)
When D_OPEN=1 and D_LCK=0, the SMM space DRAM is made visible even
when SMM decode is not active. This is intended to help BIOS initialize SMM
space. Software should ensure that D_OPEN=1 and D_CLS=1 are not set at
the same time.
SMM Space Closed (D_CLS)
When D_CLS = 1 SMM space DRAM is not accessible to data references, even
if SMM decode is active. Code references may still access SMM space DRAM.
This will allow SMM software to reference through SMM space to update the
display even when SMM is mapped over the VGA range. Software should
ensure that D_OPEN=1 and D_CLS=1 are not set at the same time.
SMM Space Locked (D_LCK)
When D_LCK is set to 1 then D_OPEN is reset to 0 and D_LCK, D_OPEN,
C_BASE_SEG, G_SMRAME, PCIEXBAR, (DRAM _ RULEs and
INTERLEAVE_LISTs) become read only. D_LCK can be set to 1 via a normal
configuration space write but can only be cleared by a Reset. The
combination of D_LCK and D_O P EN provide convenience with security. The
BIOS can use the D_OPEN function to initialize SMM space and th en use
D_LCK to "lock down" SMM space in the future so that no application
software (or BIOS itself) can violate the integrity of SMM space, even if the
program has knowledge of the D_OPEN function. Note that TAD does not
implement this lock.
Global SMRAM Enable (G_SMRAME)
If set to a 1, then Compatible SMRAM functions are enabled, providing 128
KB of DRAM accessible at the A0000h address while in SMM (ADSB with SMM
decode). T o enable Extended SMRAM function t his bit has to be set to 1. Once
D_LCK is set, this bit becomes read only.
Compatible SMM Space Base Segment (C_BASE_SEG)
This field indicates the location of SMM space. SMM DRAM is not remapped. It
is simply made visible if the conditions are right to access SMM space,
otherwise the access is forwarded to HI. Only SMM space between A0000h
and BFFFFh is supported so this field is hardwired to 010.
44 Datasheet
Page 45

Register Description
2.6.5 SAD_PCIEXBAR
Global register for PCIEXBAR address space.
Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: 50h
Access as a Qword
Bit Type
39:20 RW 0
3:1 RW 0
0RW0
Reset
Value
Description
ADDRESS.
Base address of PCIEXBAR. Must be naturally aligned to size; l ow order b its are
ignored.
SIZE.
Size of the PCIEXBAR address space. (MAX bus number).
000 = 256 MB.
001 = Reserved.
010 = Reserved.
011 = Reserved.
100 = Reserved.
101 = Reserved.
110 = 64 MB.
111 = 128 MB.
ENABLE.
Enable for PCIEXBAR address space. Editing size should not be done without
also enabling range.
2.6.6 SAD_DRAM_RULE_0, SAD_DRAM_RULE_1, SAD_DRAM_RULE_2, SAD_DRAM_RULE_3 SAD_DRAM_RULE_4, SAD_DRAM_RULE_5 SAD_DRAM_RULE_6, SAD_DRAM_RULE_7
This register provides SAD DRAM rules. Address Map for package determination.
Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: 80h, 84h, 88h, 8Ch, 90h, 94h, 98h, 9Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Datasheet 45
Reset
Value
Description
Page 46

Register Description
Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: 80h, 84h, 88h, 8Ch, 90h, 94h, 98h, 9Ch
Access as a Dword
LIMIT
19:6 RW -
2:1 RW -
0RW0
DRAM rule top limit address. Must be strictly greater than previous rule, even if
this rule is disabled, unless this rule and all following rules are disabled. Lower
limit is the previous rule (or 0 if it is first rule). This field is compared against
MA[39:26] in the memory address map.
MODE
DRAM rule interleave mode. If a DRAM_RULE hits a 3 bit number is used to
index into the corresponding interleave_list to determine which package the
DRAM belongs to. This mode selects how that number is computed.
00 = Address bits {8,7,6}.
01 = Address bits {8,7,6} XORed with {18,17,16}.
10 = Address bit {6}, MOD3(Address[39..6]). (Note 6 is the high order bit)
11 = Reserved.
ENABLE
Enable for DRAM rule. If Enabled Range between this rule and previous rule is
Directed to HOME channel (unless overridden by other dedicated address r ange
registers). If disabled, all accesses in this range are directed in MMIO to the
IOH.
2.6.7 SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_0, SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_1 SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_2, SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_3 SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_4, SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_5 SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_6, SAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_7
This register provides SAD DRAM package assignments. When the corresponding
DRAM_RULE hits, a 3-bit number (determined by mode) is used to index into the
interleave_list to determine which package is the HOME for this address.
00: IOH
01: Socket 0
10: Socket 1
11: Reserved
Device: 0
Function: 1
Offset: C0h, C4h, C8h, CCh, D0h, D4h, D8h, DCh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
29:28 RW - PACKAGE7. Package for index value 7 of interleaves.
25:24 RW - PACKAGE6. Package for index value 6 of interleaves.
21:20 RW - PACKAGE5. Package for index value 5 of interleaves.
17:16 RW - PACKAGE4. Package for index value 4 of interleaves.
13:12 RW - PACKAGE3. Package for index value 3 of interleaves.
9:8 RW - PACKAGE2. Package for index value 2 of interleaves.
5:4 RW - PACKAGE1. Package for index value 1 of interleaves.
1:0 RW - PACKAGE0. Package for index value 0 of interleaves.
Reset
Value
Description
46 Datasheet
Page 47

Register Description
2.7 Intel QPI Link Registers
2.7.1 QPI_QPILCL_L0, QPI_QPILCL_L1
This register provides Intel QPI Link Control.
Device: 2
Function: 0, 4
Offset: 48h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
21 RW 0
20 RW 0
18 RW 0
Reset
Value
Description
L1_MASTER
Indicates that this end of the link is the L1 master. This link transmitter bit is an
L1 power state master and can initiate an L1 power state transition. If this bit is
not set, then the link transmitter is an L1 power state slave and should respond
to L1 transitions with an ACK or NACK.
If the link power state of L1 is enabled, then there is one master and one slave
per link. The master may only issue single L1 requests, while the slave can only
issue single L1_Ack or L1_NAck responses for the corresponding request.
L1_ENABLE
Enables L1 mode at the transmitter. This bit should be ANDed with the receive
L1 capability bit received during parameter exchange to determine if a
transmitter is allowed to enter into L1. This is NOT a bit that determines the
capability of a device.
L0S_ENABLE
Enables L0s mode at the transmitter. This bit should be ANDed with the receive
L0s capability bit received during parameter exchange to determine if a
transmitter is allowed to enter into L0s. This is NOT a bit that determines the
capability of a device.
2.8 Integrated Memory Controller Control Registers
The registers in this section apply only to processors supporting registered DIMMs.
2.8.1 MC_CONTROL
This register is the Primary control register.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 48h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
10 RW 0
9RW0
Datasheet 47
Reset
Value
Description
CHANNEL2_ACTIVE
When set, indicates MC channel 2 is active. This bit is controlled (set/reset)
by software only. This bit is required to be set for any active channel when
INIT_DONE is set by software.
CHANNEL1_ACTIVE
When set, indicates MC channel 1 is active. This bit is controlled (set/reset)
by software only. This bit is required to be set for any active channel when
INIT_DONE is set by software. Channel 0 AND Channel 1 active must both be
set for a lockstep or mirrored pair.
Page 48

Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 48h
Access as a Dword
8RW0
7WO0
6RW0
5RW0
4RW0
3RW0
2RW0
1RW0
0RW0
Register Description
CHANNEL0_ACTIVE
When set, indicate MC channel 0 is active. This bit is controlled (set/reset) by
software only. This bit is required to be set for any active channel when
INIT_DONE is set by software. Channel 0 AND Channel 1 active must both be
set for a lockstep or mirrored pair.
INIT_DONE
MC initialize complete signal. Setting this bit will exit the training mode of the
Integrated Memory Controller and begin normal operation including all
enabled maintenance operations. Any CHANNNEL_ACTIVE bits not set when
writing a 1 to INIT_DONE will cause the corresponding channel to be
disabled.
DIVBY3EN
Divide By 3 enable. When set, MAD would use the longer pipeline for
transactions that are 3 or 6 way interleaved and shorter pipeline for all othe r
transactions. The SAG registers must be appropriately programmed as well.
CHANNELRESET2
Reset only the state within the channel. Equivalent to pulling warm reset for
that channel.
CHANNELRESET1
Reset only the state within the channel. Equivalent to pulling warm reset for
that channel.
CHANNELRESET0
Reset only the state within the channel. Equivalent to pulling warm reset for
that channel.
AUTOPRECHARGE.
Autoprecharge enable. This bit should be set with the closed page bit. If it is
not set with closed page, address decode will be done without setting the
autoprecharge bit.
ECCEN: ECC Enable
ECC Checking enables. When this bit is set in lockstep mode the ECC
checking is for the x8 SDDC. ECCEN without Lockstep enables the x4 SDDC
ECC checking.
CLOSED_PAGE
When set, the MC supports a Closed Page policy. The default is Open Page
but BIOS should always configure this bit.
48 Datasheet
Page 49

Register Description
2.8.2 MC_STATUS
This register is the MC primary status register.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 4Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
4RO1
2RO0
1RO0
0RO0
Description
ECC_ENABLED. ECC is enabled.
CHANNEL2_DISABLED
Channel 2 is disabled. This can be factory configured or if Init done is written
without the channel_active being set. Clocks in the channel will be disabled
when this bit is set.
CHANNEL1_DISABLED
Channel 1 is disabled. This can be factory configured or if Init done is written
without the channel_active being set. Clocks in the channel will be disabled
when this bit is set.
CHANNEL0_DISABLED
Channel 0 is disabled. This can be factory configured or if Init done is written
without the channel_active being set. Clocks in the channel will be disabled
when this bit is set.
Datasheet 49
Page 50

2.8.3 MC_SMI_SPARE_DIMM_ERROR_STATUS
SMI sparing DIMM error threshold overflow status register. This bit is set when the perDIMM error counter exceeds the specified threshold. The bit is reset by BIOS.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 50h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
13:12 RW0C
11:0 RW0C
Reset
Value
0 REDUNDANCY_LOSS_FAILING_DIMM
The ID for the failing DIMM when redundancy is lost.
0 DIMM_ERROR_OVERFLOW_STATUS
This 12-bit field is the per dimm error overflow status bits. The organization is
as follows:
If there are three or more DIMMS on the channel:
Bit 0 = DIMM 0 Channel 0
Bit 1 = DIMM 1 Channel 0
Bit 2 = DIMM 2 Channel 0
Bit 3 = DIMM 3 Channel 0
Bit 4 = DIMM 0 Channel 1
Bit 5 = DIMM 1 Channel 1
Bit 6 = DIMM 2 Channel 1
Bit 7 = DIMM 3 Channel 1
Bit 8 = DIMM 0 Channel 2
Bit 9 = DIMM 1 Channel 2
Bit 10 = DIMM 2 Channel 2
Bit 11 = DIMM 3 Channel 2
If there are one or two DIMMS on the channel:
Bit 0 = DIMM 0, Ranks 0 and 1, Channel 0
Bit 1 = DIMM 0, Ranks 2 and 3, Channel 0
Bit 2 = DIMM 1, Ranks 0 and 1, Channel 0
Bit 3 = DIMM 1, Ranks 2 and 3, Channel 0
Bit 4 = DIMM 0, Ranks 0 and 1, Channel 1
Bit 5 = DIMM 0, Ranks 2 and 3, Channel 1
Bit 6 = DIMM 1, Ranks 0 and 1, Channel 1
Bit 7 = DIMM 1, Ranks 2 and 3, Channel 1
Bit 8 = DIMM 0, Ranks 0 and 1, Channel 2
Bit 9 = DIMM 0, Ranks 2 and 3, Channel 2
Bit 10 = DIMM 1, Ranks 0 and 1, Channel 2
Bit 11 = DIMM 1, Ranks 2 and 3, Channel 2
Description
50 Datasheet
Page 51

Register Description
2.8.4 MC_SMI_SPARE_CNTRL
System Management Interrupt and Spare control register.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 54h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
16 RW 0
15 RW 0
14:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
INTERRUPT_SELECT_NMI
1 = Enable NMI signaling.
0 = Disable NMI signaling.
If both NMI and SMI enable bits are set, then only SMI is sent.
INTERRUPT_SELECT_SMI
1 = Enable SMI signaling.
0 = Disable SMI signaling.
If both NMI and SMI enable bits are set, then only SMI is sent. This bit functions
the same way in Mirror and Independent Modes.
The possible SMI events enabled by this bit are:
Any one of the error counters MC_COR_ECC_CNT_X meets the value of
SMI_ERROR_THRESHOLD field of this register.
MC_SSRSTATUS.CMPLT bit is set to 1.
MC_RAS_STATUS.REDUNDANCY_LOSS bit is set to 1.
SMI_ERROR_THRESHOLD
Defines the error threshold to compare against the per-DIMM error counters
MC_COR_ECC_CNT_X, which are also 15 bits.
2.8.5 MC_RESET_CONTROL
DIMM Reset enabling controls.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 5Ch
Access as a Dword
Description
Bit Type
0WO0
Datasheet 51
Reset
Value
BIOS_RESET_ENABLE
When set, MC takes over control of driving RESET to the DIMMs. This bit is set
on S3 exit and cold boot to take over RESET driving responsibility from the
physical layer.
Description
Page 52

2.8.6 MC_CHANNEL_MAPPER
Channel mapping register. The sequence of operations to update this register is:
Read MC_Channel_Mapper register
Compare data read to data to be written. If different, then write.
Poll MC_Channel_Mapper register until the data read matches data written.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 60h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
Reset
Value
17:15 RW 0
14:12 RW 0
11:9 RW 0
8:6 RW 0
5:3 RW 0
2:0 RW 0
Description
RDLCH2.
Mapping of Logical Channel 2 to physical channel for Reads.
001 = Maps to physical Channel 0
010 = Maps to physical Channel 1
100 = Maps to physical Channel 2
WRLCH2.
Mapping of Logical Channel 2 to physical channel for Writes.
001 = Maps to physical Channel 0
010 = Maps to physical Channel 1
100 = Maps to physical Channel 2
RDLCH1.
Mapping of Logical Channel 1 to physical channel for Reads.
001 = Maps to physical Channel 0
010 = Maps to physical Channel 1
100 = Maps to physical Channel 2
WRLCH1.
Mapping of Logical Channel 1 to physical channel for Writes.
001 = Maps to physical Channel 0
010 = Maps to physical Channel 1
100 = Maps to physical Channel 2
RDLCH0.
Mapping of Logical Channel 0 to physical channel for Read.
001 = Maps to physical Channel 0
010 = Maps to physical Channel 1
100 = Maps to physical Channel 2
WRLCH0.
Mapping of Logical Channel 0 to physical channel for Writes.
001 = Maps to physical Channel 0
010 = Maps to physical Channel 1
100 = Maps to physical Channel 2
52 Datasheet
Page 53

Register Description
2.8.7 MC_MAX_DOD
This register defines the MAX number of DIMMS, RANKS, BANKS, ROWS, COLS among
all DIMMS populating the three channels. The Memory Init logic uses this register to
cycle through all the memory addresses writing all 0's to initialize all locations. This
register is also used for scrubbing and sparing and must always be programmed if any
DODs are programmed.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 64h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
10:9 RW 0
8:6 RW 0
5:4 RW 0
3:2 RW 0
1:0 RW 0
Description
MAXNUMCOL. Maximum Number of Columns.
00 = 2^10 columns
01 = 2^11 columns
10 = 2^12 columns
11 = RSVD.
MAXNUMROW. Maximum Number of Rows.
000 = 2^12 Rows
001 = 2^13 Rows
010 = 2^14 Rows
011 = 2^15 Rows
100 = 2^16 Rows
Others = RSVD.
MAXNUMBANK. Max Number of Banks.
00 = Four-banked
01 = Eight-banked
10 = Sixteen-banked.
MAXNUMRANK. Maximum Number of Ranks.
00 = Single Ranked
01 = Double Ranked
10 = Quad Ranked.
MAXNUMDIMMS. Maximum Number of DIMMs.
00 = 1 DIMM
01 = 2 DIMMs
10 = 3 DIMMs
11 = RSVD.
Datasheet 53
Page 54

2.8.8 MC_RD_CRDT_INIT
These registers contain the initial read credits available for issuing memory reads. TAD
read credit counters are loaded with the corresponding values at reset and anytime this
register is written. BIOS must initialize this register with appropriate values depending
on the level of Isoch support in the platform. It is invalid to write this register while T AD
is active (has memory requests outstanding), as the write will break TAD's outstanding
credit count values.
Register programming rules:
• Total read credits (CRDT_RD + CRDT_RD_HIGH + CRDT_RD_CRIT) must not
exceed 31.
• CRDT_RD_HIGH value must correspond to the number of high RTIDs reserved at
the IOH.
• CRDT_RD_CRIT value must correspond to the number of critical RTIDs reserved at
the IOH.
• CRDT_RD_HIGH + CRDT_RD must be less than or equal to 13.
• CRDT_RD_HIGH + CRDT_RD_CRIT must be less than or equal to 8.
• CRDT_RD_CRIT must be less than or equal to 6. Set CRDT_RD to (16 CRDT_RD_CRIT - CRDT_RD_HIGH).
• If (Mirroring OR Sparing enabled) then Max for CRDT_RD is 14, otherwise it is 15.
• If (Isoch not enabled) then CRDT_RD_HIGH and CRDT_RD_CRIT are set to 0.
Register Description
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 70h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
20:16 RW 3 CRDT_RD_CRIT. Critical Read Credits.
12:8 RW 1 CRDT_RD_HIGH. High Read Credits.
4:0 RW 13 CRDT_RD. Normal Read Credits.
Reset
Value
Description
54 Datasheet
Page 55

Register Description
2.8.9 MC_CRDT_WR_THLD
This is the Memory Controller Write Credit Thresholds register. A Write threshold is
defined as the number of credits reserved for this priority (or higher) request. It is
required that High threshold be greater than or equal to Crit threshold, and that both
be lower than the total Write Credit init value. BIOS must initialize this register with
appropriate values depending on the level of Isoch support in the platform. The new
values take effect immediately upon being written.
Register programming rules:
• CRIT threshold value must correspond to the number of critical RTIDs reserved at
the IOH.
• HIGH threshold value must correspond to the sum of critical and high RTIDs
reserved at the IOH (which must not exceed 30).
• Set MC_Channel_*_WAQ_PARAMS.ISOCENTRYTHRESHHOLD equal to (31-CRIT).
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 74h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
12:8 RW 4 HIGH. High Credit Threshold.
4:0 RW 3 CRIT. Critical Credit Threshold.
Reset
Value
2.8.10 MC_SCRUBADDR_LO
This register contains part of the address of the last patrol scrub request issued. When
running Memtest, the failing address is logged in this register on Memtest errors.
Software can write the next address to be scrubbed into this register. Patrol scrubs
must be disabled to reliably write this register.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 78h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
29:14 RW 0 PAGE.
13:0 RW 0 COLUMN.
Reset
Value
This field contains the row of the last scrub issued. Can be written to specify the
next scrub address with STARTSCRUB in the MC_SCRUB_CONTROL register.
This field contains the column of the last scrub issued. Can be written to specify
the next scrub address with ST ARTSCRUB in the MC_SCRUB_CONTROL register.
Description
Description
Datasheet 55
Page 56

2.8.11 MC_SCRUBADDR_HI
This register pair contains part of the address of the last patrol scrub request issued.
When running memtest, the failing address is logged in this register on memtest
errors. Software can write the next address into this register. Scrubbing must be
disabled to reliably read and write this register.
Device: 3
Function: 0
Offset: 7Ch
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
Reset
Value
9:8 RW 0
7:6 RW 0
5:4 RW 0
3:0 RW 0
Description
CHNL.
This field can be written to specify the next scrub address with STARTSCRUB in
the MC_SCRUB_CONTROL register. This register is not updated with channel
address of the last scrub address issued.
DIMM.
This field contains the DIMM of the last scrub issued. Can be written to specify
the next scrub address with ST ART SCRUB in the MC_SCRUB_CONTROL register.
For writes, to the register this field always contains the Rank ID. For reads, the
following translation must be done:
If 3 DIMMs are on the channel, then the rank is RANK[0] while the dimm is the
concatenation of DIMM[0] and RANK[1].
RANK.
This field contains the rank of the last scrub issued. Can be written to specify
the next scrub address with STARTSCRUB in the MC_SCRUB_CONTROL
register.. For writes, to the register this field always contains the rank id. For
reads, the following translation must be done:
If 3 dimms are on the channel then the rank is RANK[0] while the dimm is the
concatenation of DIMM[0] and RANK[1].
BANK.
This field contains the bank of the last scrub issued. Can be written to specify
the next scrub address with STARTSCRUB in the MC_SCRUB_CONTROL
register..
56 Datasheet
Page 57

Register Description
2.9 TAD – Target Address Decoder Registers
2.9.1 TAD_DRAM_RULE_0, TAD_DRAM_RULE_1 TAD_DRAM_RULE_2, TAD_DRAM_RULE_3 TAD_DRAM_RULE_4, TAD_DRAM_RULE_5 TAD_DRAM_RULE_6, TAD_DRAM_RULE_7
TAD DRAM rules. Address map for channel determination within a package. All
addresses sent to this HOME agent must hit a valid enabled DRAM_RULE. No error will
be generated if they do not hit a valid location and memory aliasing will happen.
Device: 3
Function: 1
Offset: 80h, 84h, 88h, 8Ch, 90h, 94h, 98h, 9Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
19:6 RW -
2:1 RW -
0RW0
Reset
Value
Description
LIMIT.
DRAM rule top limit address. Must be strictly greater than previous rule, ev en
if this rule is disabled, unless this rule and all following rules are disabled.
Lower limit is the previous rule (or 0 if it is the first rule).
MODE.
DRAM rule interleave mode. If a DRAM_RULE hits, a 3-bit number is used to
index into the corresponding interleave_list to determine which channel the
DRAM belongs to. This mode selects how that number is computed.
00 = Address bits {8,7,6}.
01 = Address bits {8,7,6} XORed with {18,17,16}.
10 = Address bit {6}, MOD3(Address[39..6]). (Note 6 is the high order bit)
11 = Reserved.
ENABLE.
Enable for DRAM rule.
Datasheet 57
Page 58

Register Description
2.9.2 TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_0, TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_1 TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_2, TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_3 TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_4, TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_5 TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_6, TAD_INTERLEAVE_LIST_7
TAD DRAM package assignments. When the corresponding DRAM_RULE hits, a 3-bit
number (determined by mode) is used to index into the Interleave_List Branches to
determine which channel the DRAM request belongs to.
Device: 3
Function: 1
Offset: C0h, C4h, C8h, CCh, D0h, D4h, D8h, DCh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
29:28 RW -
25:24 RW -
21:20 RW -
17:16 RW -
13:12 RW -
Description
Logical Channel7.
Index 111 of the Interleave List. Bits determined from the matching
TAD_DRAM_RULE mode.
00 = Logical channel 0
01 = Logical channel 1
10 = Logical channel 2
11 = Reserved
Logical Channel6.
Index 110 of the Interleave List. Bits determined from the matching
TAD_DRAM_RULE mode.
00 = Logical channel 0
01 = Logical channel 1
10 = Logical channel 2
11 = Reserved
Logical Channel5.
Index 101 of the Interleave List. Bits determined from the matching
TAD_DRAM_RULE mode.
00 = Logical channel 0
01 = Logical channel 1
10 = Logical channel 2
11 = Reserved
Logical Channel4.
Index 100 of the Interleave List. Bits determined from the matching
TAD_DRAM_RULE mode.
00 = Logical channel 0
01 = Logical channel 1
10 = Logical channel 2
11 = Reserved
Logical Channel3.
Index 011 of the Interleave List. Bits determined from the matching
TAD_DRAM_RULE mode.
00 = Logical channel 0
01 = Logical channel 1
10 = Logical channel 2
11 = Reserved
58 Datasheet
Page 59

Register Description
Device: 3
Function: 1
Offset: C0h, C4h, C8h, CCh, D0h, D4h, D8h, DCh
Access as a Dword
9:8 RW -
5:4 RW -
1:0 RW -
Logical Channel2.
Index 010 of the Interleave List. Bits determined from the matching
TAD_DRAM_RULE mode.
00 = Logical channel 0
01 = Logical channel 1
10 = Logical channel 2
11 = Reserved
Logical Channel1.
Index 001 of the Interleave List. Bits determined from the matching
TAD_DRAM_RULE mode.
00 = Logical channel 0
01 = Logical channel 1
10 = Logical channel 2
11 = Reserved
Logical Channel0.
Index 000 of the Interleave List. Bits determined from the matching
TAD_DRAM_RULE mode.
00 = Logical channel 0
01 = Logical channel 1
10 = Logical channel 2
11 = Reserved
2.10 Integrated Memory Controller Channel Control Registers
2.10.1 MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_RESET_CMD MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_RESET_CMD MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_RESET_CMD
Integrated Memory Controller DIMM reset command register. This register is used to
sequence the reset signals to the DIMMs.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 50h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
2RW0
1RW0
0WO0
Reset
Value
Description
BLOCK_CKE.
When set, CKE will be forced to be deasserted.
ASSERT_RESET.
When set, Reset will be driven to the DIMMs.
RESET.
Reset the DIMMs. Setting this bit will cause the Integrated Memory Controller
DIMM Reset state machine to sequence through the reset sequence using the
parameters in MC_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS.
Datasheet 59
Page 60

2.10.2 MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_CMD MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_CMD MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_CMD
Integrated Memory Controller DIMM initialization command register. This register is
used to sequence the channel through the physical layer training required for DDR.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 54h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
17 WO 0
16 RW 0
15 RW 0
14 RW 0
13 RW 0
12 RW 0
11 RW 0
10 WO 0
9RW0
8RW0
7:5 RW 0
4:2 RW 0
1RW0
0WO0
Reset
Value
ASSERT_CKE.
When set, all CKE will be asserted. Write a 0 to this bit to stop the init block
from driving CKE. This bit has no effect once MC_CONTROL.INIT_DONE is set.
This bit must be used during INITIALIZATION only and be cleared out before
MC_CONTROL.INIT_DONE is set. This bit must not be asserted during
initialization for S3 resume.
DO_RCOMP.
When set, an RCOMP will be issued to the rank specified in the RANK field.
DO_ZQCL.
When set, a ZQCL will be issued to the rank specified in the RANK field.
WRDQDQS_MASK.
When set, the Write DQ-DQS training will be skipped.
WRLEVEL_MASK.
When set, the Write Levelization step will be skipped.
RDDQDQS_MASK.
When set, the Read DQ-DQS step will be skipped.
RCVEN_MASK.
When set, the RCVEN step will be skipped.
RESET_FIFOS.
When set, the TX and RX FIFO pointers will be reset at the next BCLK edge. The
Bubble Generators will also be reset.
IGNORE_RX.
When set, the read return datapath will ignore all data coming from the RX
FIFOS. This is done by gating the early valid bit.
STOP_ON_FAIL.
When set along with the AUTORESETDIS not being set, the phyinit FSM will stop
if a step has not completed after timing out.
RANK.
The rank currently being tested. The PhyInit FSM must be sequenced for every
rank present in the channel. The rank value is set to the rank being trained.
NXT_PHYINIT_STATE.
Set to sequence the physical layer state machine.
000 = IDLE
001 = RD DQ-DQS
010 = RcvEn Bitlock
011 = Write Level
100 = WR DQ-DQS.
AUTODIS.
Disables the automatic training where each step is automatically incremented.
When set, the physical layer state machine must be sequenced with software.
The training FSM must be sequenced using the NXT_PHYINIT_STATE field.
TRAIN.
Cycle through the training sequence for the rank specified in the RANK field.
Register Description
Description
60 Datasheet
Page 61

Register Description
2.10.3 MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_PARAMS
Initialization sequence parameters are stored in this register. Each field is 2^n count.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 58h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
26 RW 0
25 RW 0
24 RW 0
23 RW 0
22 RW 0
21:17 RW 15
16 RW 0
15 RW 0
14:10 RW 0
9:5 RW 0
4:0 RW 0
Description
DIS_3T.
When set, 3T mode will not be enabled as a part of the MRS write to the
RDIMM. The RC2 write to switch to 3T and back to 1T timing before and after an
MRS write will not be done if the bit is set. This bit should be set if the RDIMM
supports auto MRS cycles where the dimm takes care of the 3T switching on
MRS writes.
DIS_AI.
When set, address inversion will not be disabled as a part of the MRS write to
the RDIMM. The RC0 write to disable and enable address inversion will not be
done. This bit should be set if the RDIMM supports auto MRS cycles where the
dimm takes care of disabling address inversion for MRS writes.
THREE_DIMMS_PRESENT.
Set when channel contains three DIMMs. THREE_DIMMS_PRESENT=1 and
QUAD_RANK_PRESENT=1 (or SINGLE_QUAD_RANK_PRESENT=1) ar e mutually
exclusive.
SINGLE_QUAD_RANK_PRESENT.
Set when channel contains a single quad rank DIMM.
QUAD_RANK_PRESENT.
Set when channel contains 1 or 2 quad rank DIMMs.
WRDQDQS_DELAY.
Specifies the delay in DCLKs between reads and writes for WRDQDQS training.
WRLEVEL_DELAY.
Specifies the delay used between write CAS indications for write leveling
training.
0 = 16 DCLKs.
1 = 32 DCLKs.
REGISTERED_DIMM.
Set when channel contains registered DIMMs.
PHY_FSM_DELAY.
Global timer used for bounding the physical layer trainin g. If the timer exp ires ,
the FSM will go to the next step and the counter will be reloaded with
PHY_FSM_DELAY value. Units are 2^n dclk.
BLOCK_CKE_DELAY.
Delay in ns from when clocks and command are valid to the point CKE is
allowed to be asserted. Units are in 2^n uclk.
RESET_ON_TIME.
Reset will be asserted for the time specified. Units are 2^n Uclk.
Datasheet 61
Page 62

2.10.4 MC_CHANNEL_0_DIMM_INIT_STATUS MC_CHANNEL_1_DIMM_INIT_STATUS MC_CHANNEL_2_DIMM_INIT_STATUS
The initialization state is stored in this register. This register is cleared on a new
training command.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 5Ch
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
Reset
Value
9RO0
8RO0
7RO0
6RO0
5RO0
4RO0
3RO0
2:0 RO 0
Description
RCOMP_CMPLT.
When set, indicates that RCOMP command has complete. This bit is cleared by
hardware on command issuance and set once the command is complete.
INIT_CMPLT.
This bit is cleared when a new training command is issued. It is set once the
sequence is complete regardless of whether all steps passed or not.
ZQCL_CMPLT.
When set, indicates that ZQCL command has completed. This bit is cleared by
hardware on command issuance and set once the command is complete.
WR_DQ_DQS_PASS.
Set after a training command when the Write DQ-DQS training step passes.
The bit is cleared by hardware when a new training command is sent.
WR_LEVEL_PASS.
Set after a training command when the write leveling training step passes. The
bit is cleared by hardware when a new training command is sent.
RD_RCVEN_PASS.
Set after a training command when the Read Receive Enable training step
passes. The bit is cleared by hardware when a new training command is sent.
RD_DQ_DQS_PASS.
Set after a training command when the Read DQ-DQS tr aining step pa sses. The
bit is cleared by hardware when a new training command is sent.
PHYFSMSTATE.
The current state of the top level training FSM.
000 = IDLE
001 = RD DQ-DQS
010 = RcvEn Bitlock
011 = Write Level
100 = WR DQ-DQS
62 Datasheet
Page 63

Register Description
2.10.5 MC_CHANNEL_0_DDR3CMD MC_CHANNEL_1_DDR3CMD MC_CHANNEL_2_DDR3CMD
DDR3 Configuration Command. This register is used to issue commands to the DIMMs
such as MRS commands. The register is used by setting one of the *_VALID bits along
with the appropriate address and destination RANK. The command is then issued
directly to the DIMM. Care must be taken in using this register as there is no
enforcement of timing parameters related to the action taken by a DDR3CMD write.
This register has no effect after MC_CONTROL.INIT_DONE is set.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 60h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
28 RW 0
27 RW 0
26 RW 0
25 RW 0
24 RW 0
23 RW 0
22:20 RW 0
19:16 RW 0
15:0 RW 0
Description
PRECHARGE_VALID.
Indicates current command is for a precharge command.
ACTIVATE_VALID.
Indicates current command is for an activate command.
REG_VALID.
Indicates current command is for a registered DIMM config write Bit is cleared
by hardware on issuance. This bit applies only to processors supporting
registered DIMMs.
WR_VALID.
Indicates current command is for a write CAS. Bit is cleared by hardware on
issuance.
RD_VALID.
Indicates current command is for a read CAS. Bit is cleared by hardware on
issuance.
MRS_VALID.
Indicates current command is an MRS command. Bit is cleared by hardw are on
issuance.
RANK.
Destination rank for command.
MRS_BA.
Address bits driven to DDR_BA[2:0] pins for the DRAM command being issued
due to a valid bit being set in this register.
MRS_ADDR.
Address bits driven to DDR_MA pins for the DRAM command being issued due
to a valid bit being set in this register.
Datasheet 63
Page 64

Register Description
2.10.6 MC_CHANNEL_0_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT MC_CHANNEL_1_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT MC_CHANNEL_2_REFRESH_THROTTLE_SUPPORT
This register supports Self Refresh and Thermal Throttle functions.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 68h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
3:2 RW 0
1RW0
0RW0
Reset
Value
INC_ENTERPWRDWN_RATE.
Powerdown rate will be increased during thermal throttling based on the
following configurations.
00 = tRANKIDLE (Default)
01 = 16
10 = 24
11 = 32
DIS_OP_REFRESH.
When set, the refresh engine will not issue opportunistic refresh.
ASR_PRESENT.
When set, indicates DRAMs on this channel can support Automatic Self Re fresh.
If the DRAM is not supporting ASR (Auto Self Refresh), then Self Refresh entry
will be delayed until the temperature is below the 2x refresh temperature.
2.10.7 MC_CHANNEL_0_MRS_VALUE_0_1 MC_CHANNEL_1_MRS_VALUE_0_1 MC_CHANNEL_2_MRS_VALUE_0_1
The initial MRS register values for MR0, and MR1 can be specified in this register. These
values are used for the automated MRS writes used as a part of the training FSM. The
remaining values of the MRS register must be specified here.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 70h
Access as a Dword
Description
Bit Type
31:16 RW 0
15:0 RW 0
64 Datasheet
Reset
Value
Description
MR1.
The values to write to MR1 for A15:A0.
MR0.
The values to write to MR0 for A15:A0.
Page 65

Register Description
2.10.8 MC_CHANNEL_0_MRS_VALUE_2 MC_CHANNEL_1_MRS_VALUE_2 MC_CHANNEL_2_MRS_VALUE_2
The initial MRS register values for MR2. This register also contains the values used for
RC0 and RC2 writes for registered DIMMs. These values are used during the automated
training sequence when MRS writes or registered DIMM RC writes are used. The RC
fields do not need to be programmed if the address inversion and 3T/1T transitions are
disabled.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 74h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
23:20 RW 0
19:16 RW 0
15:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
RC2.
The values to write to the RC2 register on RDIMMS. This value will be written
whenever 3T or 1T timings are enabled by hardware. For this reason bit 1 of the
RC2 field (bit 21 of this register) will be controlled by hardware. [23:22] and
[20] will be driven with the RDIMM register write command for RC2.
RC0.
The values to write to the RC0 register on RDIMMS. This value will be written
whenever address inversion is enab led or disab led by hardw are. F or this re ason
bit 0 of the RC0 field (bit 16 of this register) will be controlled by hardware.
[19:17] will be driven with the RDIMM register write command for RC0.
MR2.
The values to write to MR2 for A15:A0.
2.10.9 MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_PRESENT MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_PRESENT MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_PRESENT
This register provides the rank present vector.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 7Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
7:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
RANK_PRESENT.
Vector that represents the ranks that are present. Each bit represents a logical
rank. When two or fewer DIMMs are present, [3:0] represents the four possible
ranks in DIMM0 and [7:4] represents the ranks that are possible in DIMM1.
When three DIMMs are present, then the following applies:
[1:0] represents ranks 1:0 in Slot 0
[3:2] represents ranks 3:2 in Slot 1
[5:4] represents ranks 5:4 in Slot 2
Description
Description
Datasheet 65
Page 66

2.10.10 MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_TIMING_A MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_TIMING_A MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_TIMING_A
This register contains parameters that specify the rank timing used. All parameters are
in DCLK.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 80h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
Reset
Value
28:26 RW 0
25:23 RW 0
22:19 RW 0
Description
tddWrTRd.
Minimum delay between a write followed by a read to different DIMMs.
000 = 1
001 = 2
010 = 3
011 = 4
100 = 5
101 = 6
110 = 7
111 = 8
tdrWrTRd.
Minimum delay between a write followed by a read to different ranks on the
same DIMM.
000 = 1
001 = 2
010 = 3
011 = 4
100 = 5
101 = 6
110 = 7
111 = 8
tsrWrTRd.
Minimum delay between a write followed by a read to the same rank.
0000 = 10
0001 = 11
0010 = 12
0011 = 13
0100 = 14
0101 = 15
0110 = 16
0111 = 17
1000 = 18
1001 = 19
1010 = 20
1011 = 21
1100 = 22
66 Datasheet
Page 67

Register Description
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 80h
Access as a Dword
18:15 RW 0
14:11 RW 0
10:7 RW 0
tddRdTWr.
Minimum delay between Read followed by a Write to different DIMMs.
0000 = 2
0001 = 3
0010 = 4
0011 = 5
0100 = 6
0101 = 7
0110 = 8
0111 = 9
1000 = 10
1001 = 11
1010 = 12
1011 = 13
1100 = 14
tdrRdTWr.
Minimum delay between Read followed by a write to different ranks on the
same DIMM.
0000 = 2
0001 = 3
0010 = 4
0011 = 5
0100 = 6
0101 = 7
0110 = 8
0111 = 9
1000 = 10
1001 = 11
1010 = 12
1011 = 13
1100 = 14
tsrRdTWr.
Minimum delay between Read followed by a write to the same rank.
0000 = RSVD
0001 = RSVD
0010 = RSVD
0011 = 5
0100 = 6
0101 = 7
0110 = 8
0111 = 9
1000 = 10
1001 = 11
1010 = 12
1011 = 13
1100 = 14
Datasheet 67
Page 68

Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 80h
Access as a Dword
6:4 RW 0
3:1 RW 0
0RW0
Register Description
tddRdTRd.
Minimum delay between reads to different DIMMs.
000 = 2
001 = 3
010 = 4
011 = 5
100 = 6
101 = 7
110 = 8
111 = 9
tdrRdTRd.
Minimum delay between reads to different ranks on the same DIMM.
000 = 2
001 = 3
010 = 4
011 = 5
100 = 6
101 = 7
110 = 8
111 = 9
tsrRdTRd.
Minimum delay between reads to the same rank.
0 = 4
1 = 6
68 Datasheet
Page 69

Register Description
2.10.11 MC_CHANNEL_0_RANK_TIMING_B MC_CHANNEL_1_RANK_TIMING_B MC_CHANNEL_2_RANK_TIMING_B
This register contains parameters that specify the rank timing used. All parameters are
in DCLK.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 84h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
20:16 RW 0
15:13 RW 0
12:10 RW 0
9RW0
8:6 RW 0
5:0 RW 0
Description
B2B_CAS_DELAY.
Controls the delay between CAS commands in DCLKS. The minimum spa cin g i s
4 DCLKS. Values below 3 have no effect. A value of 0 disables the logic. Setting
the value between 3-31 also spaces the read data by 0-29 DCLKS. The value
entered is one less than the spacing required, i.e. a spacing of 5 DCLKS
between CAS commands (or 1 DCLK on the read data) requires a setting of 4.
tddWrTWr.
Minimum delay between writes to different DIMMs.
000 = 2
001 = 3
010 = 4
011 = 5
100 = 6
101 = 7
110 = 8
111 = 9
tdrWrTWr.
Minimum delay between writes to different ranks on the same DIMM.
000 = 2
001 = 3
010 = 4
011 = 5
100 = 6
101 = 7
110 = 8
111 = 9
tsrWrTWr.
Minimum delay between writes to the same rank.
0 = 4
1 = 6
tRRD.
Specifies the minimum time between activate commands to the same rank.
tFAW.
Four Activate Window. Specifies the time window in which four activates are
allowed the same rank.
Datasheet 69
Page 70

2.10.12 MC_CHANNEL_0_BANK_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_1_BANK_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_2_BANK_TIMING
This register contains parameters that specify the bank timing parameters. These
values are in DCLK. The values in these registers are encoded where noted. All of these
values apply to commands to the same rank only.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 88h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
21:17 RW 0 tWTPr. Minimum Write CAS to Precharge command delay.
16:13 RW 0 tRTPr. Minimum Read CAS to Precharge command delay.
12:9 RW 0 tRCD. Minimum delay between Activate and CAS commands.
8:4 RW 0 tRAS. Minimum delay between Activate and Precharge commands.
3:0 RW 0 tRP. Minimum delay between Precharge command and Activate command.
Reset
Value
Description
2.10.13 MC_CHANNEL_0_REFRESH_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_1_REFRESH_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_2_REFRESH_TIMING
This register contains parameters that specify the refresh timings. Units are in DCLK.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 8Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
29:19 RW 0
18:9 RW 0
8:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
Description
tTHROT_OPPREF.
The minimum time between two opportunistic refreshe s. Shoul d be se t to tRFC in
DCLKS. Zero is an invalid e ncoding. A v alue of 1 should be progr ammed to disable
the throttling of opportunistic refreshes. By setting this field to tRFC, current to a
single DIMM can be limited to that required to support this scenario without
significant performance impact:
• 8 panic refreshes in tREFI to one rank
• 1 opportunistic refresh every tRFC to another rank
• full bandwidth delivered by the third and fourth ranks
Platforms that can supply peak currents to the DIMMs should disable opportunistic
refresh throttling for max performance.
tREFI_8.
Average periodic refresh interval divided by 8.
tRFC.
Delay between the refresh command and an activate or refresh command.
70 Datasheet
Page 71

Register Description
2.10.14 MC_CHANNEL_0_CKE_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_1_CKE_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_2_CKE_TIMING
This register contains parameters that specify the CKE timings. All units are in DCLK.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 90h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
31:24 RW 0
23:21 RW 0
20:11 RW 0
10:3 RW 0
2:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
tRANKIDLE.
Rank will go into powerdown after it has been idle for the specified number of
dclks. tRANKIDLE covers max(txxxPDEN). Minimum value is tWRAPDE N. If CKE
is being shared between ranks then both ranks must be idle for this amount of
time. A Power Down Entry command will be requested for a rank after this
number of DCLKs if no request to the rank is in the MC.
tXP.
Minimum delay from exit power down with DLL and any valid command. Exit
Precharge Power Down with DLL frozen to commands not requiring a locked
DLL. Slow exit precharge powerdown is not supported.
tXSDLL.
Minimum delay between the exit of self refresh and commands that require a
locked DLL.
tXS.
Minimum delay between the exit of self refresh and commands not requiring a
DLL.
tCKE.
CKE minimum pulse width.
Description
2.10.15 MC_CHANNEL_0_ZQ_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_1_ZQ_TIMING MC_CHANNEL_2_ZQ_TIMING
This register contains parameters that specify ZQ timing. All units are DCLK unless
otherwise specified. The register encodings are specified where applicable.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 94h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
30 RW 1
29 RW 1
28:8 RW 16410
7:5 RW 4
4:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
Parallel_ZQ.
Enable ZQ calibration to different ranks in parallel.
tZQenable.
Enable the issuing of periodic ZQCS calibration commands.
ZQ_Interval.
Nominal interval between periodic ZQ calibration in increments of tREFI.
tZQCS.
This field specifies ZQCS cycles in increments of 16. This is the minimum delay
between ZQCS and any other command. This register should be programmed to
at least 64/16=4='100' to conform to the DDR3 specification.
tZQInit.
This field specifies ZQInit cycles in increments of 32. This is the minimum delay
between ZQCL and any other command. This register should be progr ammed to
at least 512/32=16='10000' to conform to the DDR3 specification.
Description
Datasheet 71
Page 72

2.10.16 MC_CHANNEL_0_RCOMP_PARAMS MC_CHANNEL_1_RCOMP_PARAMS MC_CHANNEL_2_RCOMP_PARAMS
This register contains parameters that specify Rcomp timings.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 98h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
16 RW 1
15:10 RW 2
9:4 RW 9
3:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
RCOMP_EN.
Enable Rcomp. When set, the Integrated Memory Controller will do the
programmed blocking of requests and send indications.
RCOMP_CMD_DCLK.
Delay from the start of an RCOMP command blocking period in which the
command rcomp update is done. Program this field to 15 for all configurations.
RCOMP_LENGTH.
Number of Dclks during which all commands are blocked for an RCOMP update.
Data RCOMP update is done on the last DCLK of this period. Program this field
to 31 for all configurations.
RCOMP_INTERVAL.
Duration of interval between Rcomp in increments of tRefI. Register value is
tRefI-1. For example a setting of 0 will produce an interval of tRefI.
2.10.17 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_PARAMS1 MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_PARAMS1 MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_PARAMS1
This register contains parameters that specify ODT timings. All values are in DCLK.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: 9Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
26:24 RW 0
23:20 RW 6
19:16 RW 4
15:12 RW 5
11:8 RW 0
7:4 RW 5
3:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
TAOFD.
ODT turn off delay.
MCODT_DURATION.
Controls the duration of MC ODT activation. BL/2 + 2.
MCODT_DELAY.
Controls the delay from Rd CAS to MC ODT activation. This value is tCAS-1.
ODT_RD_DURATION.
Controls the duration of Rd ODT activation. This value is BL/2 + 2.
ODT_RD_DELAY.
Controls the delay from Rd CAS to ODT activation. This value is tCAS-tWL.
ODT_WR_DURATION.
Controls the duration of Wr ODT activation. value is BL/2 + 2.
ODT_WR_DELAY.
Controls the delay from Wr CAS to ODT activation. This value is always 0.
Description
Description
72 Datasheet
Page 73

Register Description
2.10.18 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_PARAMS2 MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_PARAMS2 MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_PARAMS2
This register contains parameters that specify Forcing ODT on Specific ranks. This
register is used in debug only and not during normal operation.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: A0h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
9RW0MCODT_Writes. Drive MC ODT on reads and writes.
8RW0FORCE_MCODT. Force MC ODT to always be asserted.
7RW0FORCE_ODT7. Force ODT for Rank7 to always be asserted.
6RW0FORCE_ODT6. Force ODT for Rank6 to always be asserted.
5RW0FORCE_ODT5. Force ODT for Rank5 to always be asserted.
4RW0FORCE_ODT4. Force ODT for Rank4 to always be asserted.
3RW0FORCE_ODT3. Force ODT for Rank3 to always be asserted.
2RW0FORCE_ODT2. Force ODT for Rank2 to always be asserted.
1RW0FORCE_ODT1. Force ODT for Rank1 to always be asserted.
0RW0FORCE_ODT0. Force ODT for Rank0 to always be asserted.
Reset
Value
Description
2.10.19 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_RD
This register contains the ODT activation matrix for RANKS 0 to 3 for Reads.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: A4h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
31:24 RW 1 ODT_RD3. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank3 is read.
23:16 RW 1 ODT_RD2. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank2 is read.
15:8 RW 4 ODT_RD1. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank1 is read.
7:0 RW 4 ODT_RD0. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank0 is read.
Reset
Value
Description
Datasheet 73
Page 74

2.10.20 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_RD
This register contains the ODT activation matrix for RANKS 4 to 7 for Reads.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function:)0
Offset: A8h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
31:24 RW 1 ODT_RD7. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank7 is read.
23:16 RW 1 ODT_RD6. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank6 is read.
15:8 RW 4 ODT_RD5. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank5 is read.
7:0 RW 4 ODT_RD4. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank4 is read.
Reset
Value
Description
2.10.21 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_0_3_WR
This register contains the ODT activation matrix for RANKS 0 to 3 for Writes.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: ACh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
31:24 RW 9 ODT_WR3. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank3 is written.
23:16 RW 5 ODT_WR2. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank2 is written.
15:8 RW 6 ODT_WR1. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank1 is written.
7:0 RW 5 ODT_WR0. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank0 is written.
Reset
Value
Description
2.10.22 MC_CHANNEL_0_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR MC_CHANNEL_1_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR MC_CHANNEL_2_ODT_MATRIX_RANK_4_7_WR
This register contains the ODT activation matrix for RANKS 4 to 7 for Writes.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: B0h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
31:24 RW 9 ODT_WR7. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank7 is written.
23:16 RW 5 ODT_WR6. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank6 is written.
15:8 RW 6 ODT_WR5. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank5 is written.
7:0 RW 5 ODT_WR4. Bit patterns driven out onto ODT pins when Rank4 is written
74 Datasheet
Reset
Value
Description
Page 75

Register Description
2.10.23 MC_CHANNEL_0_WAQ_PARAMS MC_CHANNEL_1_WAQ_PARAMS MC_CHANNEL_2_WAQ_PARAMS
This register contains parameters that specify settings for the Write Address Queue.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: B4h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
29:25 RW 6
24:20 RW 31
19:15 RW 31
14:10 RW 31
9:5 RW 22
4:0 RW 22
Description
PRECASWRTHRESHOLD.
Threshold above which Medium-Low Priority reads cannot PRE-CAS write
requests.
PARTWRTHRESHOLD.
Threshold used to raise the priority of underfill requests in the scheduler. Set to
31 to disable.
ISOCEXITTHRESHOLD.
Write Major Mode ISOC Exit Threshold. When the number of writes in the WAQ
drops below this threshold, the MC will exit write major mode in the presence of
a read.
ISOCENTRYTHRESHOLD.
Write Major Mode ISOC Entry Threshold. When the number of writes in the
WAQ exceeds this threshold, the MC will enter write major mode in the
presence of a read.
WMENTRYTHRESHOLD.
Write Major Mode Entry Threshold. When the number of writes in the WAQ
exceeds this threshold, the MC will enter write major mode.
WMEXITTHRESHOLD.
Write Major Mode Exit Threshold. When the number of writes in the WAQ drop
below this threshold, the MC will exit write major mode.
Datasheet 75
Page 76

2.10.24 MC_CHANNEL_0_SCHEDULER_PARAMS MC_CHANNEL_1_SCHEDULER_PARAMS MC_CHANNEL_2_SCHEDULER_PARAMS
These are the parameters used to control parameters within the scheduler.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: B8h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
12 RW 1
11 RW 0
10:6 RW 7
5RW0
3RW0
2:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
Description
CS_FOR_CKE_TRANSITION.
Specifies if chip select is to be asserted when CKE transitions with PowerDown
entry/exit and SelfRefresh exit.
FLOAT_EN.
When set, the address and command lines will float to save power when
commands are not being sent out. This setting may not work with RDIMMs.
PRECASRDTHRESHOLD.
Threshold above which Medium-Low Priority reads can PRE-CAS write requests.
DISABLE_ISOC_RBC_RESERVE.
When set this bit will prevent any RBC's from being reserved for ISOC.
ENABLE2N. Enable 2n Timing.
PRIORITYCOUNTER.
Upper 3 MSB of 8 bit priority time out counter.
2.10.25 MC_CHANNEL_0_MAINTENANCE_OPS MC_CHANNEL_1_MAINTENANCE_OPS MC_CHANNEL_2_MAINTENANCE_OPS
This register enables various maintenance operations such as Refreshes, ZQ, RCOMP,
etc..
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: BCh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
12:0 RW 0
76 Datasheet
Reset
Value
Description
MAINT_CNTR.
Value to be loaded in the maintenance counter. This counter sequences the rate
to Refreshes, ZQ, RCOMP.
Page 77

Register Description
2.10.26 MC_CHANNEL_0_TX_BG_SETTINGS MC_CHANNEL_1_TX_BG_SETTINGS MC_CHANNEL_2_TX_BG_SETTINGS
These are the parameters used to set the Start Scheduler for TX clock crossing. This is
used to send commands to the DIMMs.
The NATIVE RATIO is UCLK multiplier of BCLK = U
ALIEN RATION is DCLK multiplier of BCLK = D
PIPE DEPTH = 8 UCLK (design dependent variable)
MIN SEP DELAY = 670ps (design dependent variable, Internally this is logic delay of
FIFO + clock skew between U and D)
TOTAL EFFECTIVE DELAY = PIPE DEPTH * UCLK PERIOD in ps + MIN SEP DELAY
DELAY FRACTION = (T O TAL EFFECTIVE DELAY * D) / (UCLK PERIOD in ps * G.C.D(U,D)
Determine OFFSET MULTIPLE using the equation
FLOOR ((OFFSET MULTIPLE +1) / G.C.D (U,D)) > DELAY FRACTION
OFFSET VALUE = MOD (OFFSET MULTIPLE, U) <= Final answer for OFFSET MULTIPLE
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: C0h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
23:16 RW 2
15:8 RW 1
7:0 RW 4
Reset
Value
Description
OFFSET. TX offset setting.
ALIENRATIO. Dclk ratio to BCLK. TX Alien Ratio setting.
NATIVERATIO. Uclk ratio to BCLK. TX Native Ratio setting.
2.10.27 MC_CHANNEL_0_RX_BGF_SETTINGS MC_CHANNEL_1_RX_BGF_SETTINGS MC_CHANNEL_2_RX_BGF_SETTINGS
These are the parameters used to set the Rx clock crossing BGF.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: C8h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
26:24 RW 2
23:16 RW 0
15:8 RW 1
7:0 RW 2
Reset
Value
Description
PTRSEP.
RX FIFO pointer separation settings. THIS FIELD IS NOT USED BY HARDWARE.
RX Pointer separation can be modified via the round trip setting (larger value
causes a larger pointer separation).
OFFSET. RX offset setting.
ALIENRATIO. Qclk to BCLK ratio. RX Alien Ratio setting.
NATIVERATIO. Uclk to BCLK ratio. RX Native Ratio setting.
Datasheet 77
Page 78

2.10.28 MC_CHANNEL_0_EW_BGF_SETTINGS MC_CHANNEL_1_EW_BGF_SETTINGS MC_CHANNEL_2_EW_BGF_SETTINGS
These are the parameters used to set the early warning RX clock crossing BGF.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: CCh
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
15:8 RW 1 ALIENRATIO. Dclk to Bclk ratio. Early warning Alien Ratio setting.
Reset
Value
Description
2.10.29 MC_CHANNEL_0_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS MC_CHANNEL_1_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS MC_CHANNEL_2_EW_BGF_OFFSET_SETTINGS
These are the parameters to set the early warning RX clock crossing BGF.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: D0h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
15:8 RW 2 EVENOFFSET. Early warning even offset setting.
7:0 RW 0 ODDOFFSET. Early warning odd offset setting.
Reset
Value
Description
2.10.30 MC_CHANNEL_0_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY MC_CHANNEL_1_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY MC_CHANNEL_2_ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY
These are the parameters to set the early warning RX clock crossing the Bubble
Generator FIFO (BGF) used to go between different clocking domains. These settings
provide the gearing necessary to make that clock crossing.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: D4h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
7:0 RW 0 ROUND_TRIP_LATENCY.
78 Datasheet
Reset
Value
Description
Round trip latency for reads. Units are in UCLK. This register must be
programmed with the appropriate time for read data to be retuned from the
pads after a READ CAS is sent to the DIMMs.
Page 79

Register Description
2.10.31 MC_CHANNEL_0_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1 MC_CHANNEL_1_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1 MC_CHANNEL_2_PAGETABLE_PARAMS1
These are the parameters used to control parameters for page closing policies..
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: D8h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
15:8 RW 0 REQUESTCOUNTER.
7:0 RW 0 ADAPTIVETIMEOU TCOUNTER.
Reset
Value
Description
This field is the upper 8 MSBs of a 12-bit counter. This counter determines the
window over which the page close policy is evaluated.
This field is the upper 8 MSBs of a 12-bit counter. This counter adapts the
interval between assertions of the page close flag. For a less aggressive page
close, the length of the count interval is increased and vice versa for a more
aggressive page close policy.
2.10.32 MC_CHANNEL_0_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2 MC_CHANNEL_1_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2 MC_CHANNEL_2_PAGETABLE_PARAMS2
These are the parameters used to control parameters for page closing policies..
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: DCh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
27 RW 0 ENABLEADAPTIVEPAGECLOSE.
26:18 RW 0 MINPAGECLOSELIMIT.
17:9 RW 0 MAXPAGECLOSELIMIT.
8:0 RW 0 MISTAKECOUNTER.
Reset
Value
Description
1 = Enables Adaptive Page Closing.
This field is the upper 9 MSBs of a 13-bit threshold limit. When the mistake
counter falls below this threshold, a less aggressive page close interval (larger)
is selected.
This field is the upper 9 bits of a 13-bit threshold limit. When the mistake
counter exceeds this threshold, a more aggress ive page cl ose interv al (smaller)
is selected.
This field is the upper 8 MSBs of a 12-bit counter. This counter adapts the
interval between assertions of the page close flag. For a less aggressive page
close, the length of the count interval is increased and vice versa for a more
aggressive page close policy.
Datasheet 79
Page 80

2.10.33 MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTINGS_CH0 MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTINGS_CH1 MC_TX_BG_CMD_DATA_RATIO_SETTINGS_CH2
Channel Bubble Generator ratios for CMD and DATA .
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: E0h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
15:8 RW 1 ALIENRATIO. DCLK to BCLK ratio.
7:0 RW 4 NATIVERATIO. UCLK to BCLK ratio.
Reset
Value
Description
2.10.34 MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH0 MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH1 MC_TX_BG_CMD_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH2
Integrated Memory Controller Channel Bubble Generator Offsets for CMD FIFO. The
Data command FIFOs share the settings for channel 0 across all three channels. The
register in Channel 0 must be programmed for all configurations.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: E4h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
9:8 RW 0 PTROFFSET. FIFO pointer offset.
7:0 RW 0 BGOFFSET. BG offset.
Reset
Value
Description
2.10.35 MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH0 MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH1 MC_TX_BG_DATA_OFFSET_SETTINGS_CH2
Integrated Memory Controller Channel Bubble Generator Offsets for DATA FIFO.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: E8h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
16:14 RW 0 RDPTROFFSET. Read FIFO pointer offset.
13:10 RW 0 WRTPTROFFSET. Write FIFO pointer offset.
9:8 RW 0 PTROFFSET. FIFO pointer offset.
7:0 RW 0 BGOFFSET. BG offset.
80 Datasheet
Reset
Value
Description
Page 81

Register Description
2.10.36 MC_CHANNEL_0_ADDR_MATCH MC_CHANNEL_1_ADDR_MATCH MC_CHANNEL_2_ADDR_MATCH
This register specifies the intended address or address range where ECC errors will be
injected. It can be set to match memory address on a per channel basis. The address
fields can be masked in the Mask bits. Any mask bits set to 1 will always match. To
match all addresses, all of the mask bits can be set to 1. The
MC_CHANNEL_X_ECC_ERROR_INJECT register can be used to set the trigger for the
error injection.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: F0h
Access as a Qword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
41 RW 0
40 RW 0
39 RW 0
38 RW 0
37 RW 0
36 RW 0
35:34 RW 0
33:30 RW 0
29:14 RW 0
13:0 RW 0
Description
MASK_DIMM.
1 = If set, ignore DIMM address during address comparison.
MASK_RANK.
1 = If set, ignore RANK address during address comparison.
MASK_BANK.
1 = If set, ignore BANK address during address comparison.
MASK_PAGE.
If set, ignore PAGE address during address co mparison.
MASK_COL.
1 = If set ignore, COLUMN address during address comparison.
DIMM.
DIMM address for 1 or 2DPC. For 3DPC, bits 36 and 35 represent the DIMM
address and bit 34 represent the RANK address.
RANK.
Rank address for 1 or 2DPC. For 3DPC, bits 36 and 35 represent the DIMM
address and bit 34 represent the RANK address.
BANK. Bank address.
PAGE. Page address.
COLUMN. Column address.
Datasheet 81
Page 82

2.10.37 MC_CHANNEL_0_ECC_ERROR_MASK MC_CHANNEL_1_ECC_ERROR_MASK MC_CHANNEL_2_ECC_ERROR_MASK
This register contains mask bits for the memory controller and specifies at which ECC
bit(s) the error injection should occur. Any bits set to a 1 will flip the corresponding ECC
bit. Correctable errors can be injected by flipping 1 bit or the bits within a symbol pair
(2 consecutive aligned 8-bit pairs - i.e. 7:0 and 15:8 or 23:16 and 31:24). Flipping bits
in two symbol pairs will cause an uncorrectable error to be injected.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: F8h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
31:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
Description
ECCMASK.
This field contains the 32 bits of MC ECC mask bit for half cacheline.
2.10.38 MC_CHANNEL_0_ECC_ERROR_INJECT MC_CHANNEL_1_ECC_ERROR_INJECT MC_CHANNEL_2_ECC_ERROR_INJECT
This register contains the control bits for the actual ECC error injection. This register
needs to be written after writing into MC_CHANNEL_X_ECC_ERROR_MASK. The
INJECT_ECC bit must be set to enable error injection. Otherwise, no error injection will
take place even if the criteria programmed in the MC_CHANNEL_X_ADDR_MATCH
register is met.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 0
Offset: FCh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
4RW0
3RW0
2:1 RW 0
0RW0
Reset
Value
Description
INJECT_ADDR_PARITY.
1 = Forces Address Parity error injection. Bit will reset after the first injection
unless REPEAT_EN is set.
INJECT_ECC.
1 = Forces ECC error injection. Bit will reset after the first injection unless
REPEAT_EN is set.
MASK_HALF_CACHELINE.
11 = Inject the ECC code word for full cacheline.
10 = Inject the ECC code word for upper 32B half cacheline.
01 = Inject the ECC code word for lower 32B half cacheline.
00 = No masking will be applied.
REPEAT_EN.
1 = ECC errors will be injected on the channel until the bit is cleared.
82 Datasheet
Page 83

Register Description
2.10.39 Error Injection Implementation
The usage model is to program the MC_CHANNEL_X_ADDR_MATCH and
MC_CHANNEL_X_ECC_ERROR_MASK registers before writing the command in
MC_CHANNEL_X_ECC_ERROR_INJECT register. When writing the
MC_CHANNEL_X_ECC_ERROR_INJECT register, the REPEAT_EN and
MASK_HALF_CACHELINE bits need to be set to the desired values.
To turn off the feature, write 0 to the MC_CHANNEL_X_ECC_ERROR_INJ ECT regis t er.
Address parity error injection and ECC error injection can be done either at the same
time or independently . They will both use the same MATCH settings if both are enabled.
Note: Along with the INJECT_ECC bit set, software must generate the memory traffic that
matches the address location programmed in the MC_CHANNEL_X_ADDR_MATCH
register as described above in order for an error injection to take place. Unless the
REPEAT_EN bit is set in the MC_CHANNEL_X_ECC_ERROR_INJECT register, the
memory controller will only inject the error to the first location that matches the criteria
programmed in the MC_CHANNEL_X_ADDR_MATCH register.
Errors are injected on writes only. Reads will be required to detect the errors in the
MC_COR_ECC_CNT_X registers. Additionally, all writes used to inject errors must be
committed to memory to ensure the error is detected on subsequent reads.
Datasheet 83
Page 84

Register Description
2.11 Integrated Memory Controller Channel Address Registers
2.11.1 MC_DOD_CH0_0, MC_DOD_CH0_1, MC_DOD_CH0_2
Channel 0 DIMM Organization Descriptor Register.
Device: 4
Function: 1
Offset: 48h, 4Ch, 50h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
12:10 RW 0
9RW0
8:7 RW 0
6:5 RW 0
4:2 RW 0
1:0 RW 0
Description
RANKOFFSET.
Rank Offset for calculating RANK. This corresponds to the first logical rank on
the DIMM. The rank offset is always programmed to 0 for the DIMM 0 DOD
registers. (DIMM 0 rank offset is always 0.) DIMM 1 DOD rank offset is either 4
for two DIMMs per channel or 2 if there are three DIMMs per channel. DIMM2
DOD rank offset is always 4 as it is only used in three DIMMs per channel case.
DIMMPRESENT. DIMM slot is populated.
NUMBANK.
Defines the number of (real, not shadow) banks on these DIMMs.
00 = Four-banked
01 = Eight-banked
10 = Sixteen-banked
NUMRANK.
Number of Ranks. Defines the number of ranks on these DIMMs.
00 = Single Ranked
01 = Double Ranked
10 = Quad Ranked
NUMROW.
Number of Rows. Defines the number of rows within these DIMMs.
000 = 2^12 Rows
001 = 2^13 Rows
010 = 2^14 Rows
011 = 2^15 Rows
100 = 2^16 Rows
NUMCOL.
Number of Columns. Defines the number of columns within on these DIMMs.
00 = 2^10 columns
01 = 2^11 columns
10 = 2^12 columns
11 = RSVD.
84 Datasheet
Page 85

Register Description
2.11.2 MC_DOD_CH1_0, MC_DOD_CH1_1, MC_DOD_CH1_2
Channel 1 DIMM Organization Descriptor Register.
Device: 5
Function: 1
Offset: 48h, 4Ch, 50h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
12:10 RW 0
9RW0
8:7 RW 0
6:5 RW 0
4:2 RW 0
1:0 RW 0
Description
RANKOFFSET. Rank Offset for calculating RANK.
This field corresponds to the first logical rank on the DIMM. The rank offset is
always programmed to 0 for the DIMM 0 DOD registers. (DIMM 0 rank offset is
always 0.) DIMM 1 DOD rank offset is either 4 for two DIMMs per chan nel or 2 if
there are three DIMMs per channel. DIMM2 DOD rank offset is always 4 as it is
only used in three DIMMs per channel case.
DIMMPRESENT. DIMM slot is populated.
NUMBANK.
Defines the number of (real, not shadow) banks on these DIMMs.
00 = Four-banked
01 = Eight-banked
10 = Sixteen-banked
NUMRANK. Number of Ranks. Defines the number of ranks on these DIMMs.
00 = Single Ranked
01 = Double Ranked
10 = Quad Ranked
NUMROW. Number of Rows.
Defines the number of rows within these DIMMs.
000 = 2^12 Rows
001 = 2^13 Rows
010 = 2^14 Rows
011 = 2^15 Rows
100 = 2^16 Rows
NUMCOL. Number of Columns.
Defines the number of columns within on these DIMMs.
00 = 2^10 columns
01 = 2^11 columns
10 = 2^12 columns
11 = RSVD.
Datasheet 85
Page 86

Register Description
2.11.3 MC_DOD_CH2_0, MC_DOD_CH2_1, MC_DOD_CH2_2
Channel 2 DIMM Organization Descriptor Register.
Device: 6
Function: 1
Offset: 48h, 4Ch, 50h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
12:10 RW 0 RANKOFFSET. Rank Offset for calculating RANK.
9RW0DIMMPRESENT. DIMM slot is populated.
8:7 RW 0 NUMBANK.
6:5 RW 0 NUMRANK.
4:2 RW 0 NUMROW.
1:0 RW 0 NUMCOL.
Reset
Value
Description
This field corresponds to the first logical rank on the DIMM. The rank offset is
always programmed to 0 for the DIMM 0 DOD registers. (DIMM 0 rank offset is
always 0.) DIMM 1 DOD rank offset is either 4 for two DIMMs per channel or 2 i f
there are three DIMMs per channel. DIMM2 DOD rank offset is always 4 as it is
only used in three DIMMs per channel case.
Defines the number of (real, not shadow) banks on these DIMMs.
00 = Four-banked
01 = Eight-banked
10 = Sixteen-banked
Defines the number of ranks on these DIMMs.
00 = Single Ranked
01 = Double Ranked
10 = Quad Ranked
Defines the number of rows within these DIMMs.
000 = 2^12 Rows
001 = 2^13 Rows
010 = 2^14 Rows
011 = 2^15 Rows
100 = 2^16 Rows
Defines the number of columns within on these DIMMs.
00 = 2^10 columns
01 = 2^11 columns
10 = 2^12 columns
11 = RSVD
86 Datasheet
Page 87

Register Description
2.11.4 MC_SAG_CH0_0, MC_SAG_CH0_1, MC_SAG_CH0_2
MC_SAG_CH0_3, MC_SAG_CH0_4, MC_SAG_CH0_5
MC_SAG_CH0_6, MC_SAG_CH0_7, MC_SAG_CH1_0
MC_SAG_CH1_1, MC_SAG_CH1_2, MC_SAG_CH1_3
MC_SAG_CH1_4, MC_SAG_CH1_5, MC_SAG_CH1_6
MC_SAG_CH1_7, MC_SAG_CH2_0, MC_SAG_CH2_1
MC_SAG_CH2_2, MC_SAG_CH2_3, MC_SAG_CH2_4
MC_SAG_CH2_5, MC_SAG_CH2_6, MC_SAG_CH2_7
Channel Segment Address Registers. For each of the 8 interleave ranges, they specify
the offset between the System Address and the Memory Address and the System
Address bits used for level 1 interleave, which should not be translated to Memory
Address bits. Memory Address is calculated from System Address and the contents of
these registers by the following algorithm:
m[39:16] = SystemAddress[39:16] + (sign extend {Offset[23:0]});
m[15:6] = SystemAddress[15:6];
If (Removed[2]) {bit 8 removed};
If (Removed[1]) {bit 7 removed};
If (Removed[0]) {bit 6 removed};
MemoryAddress[36:6] = m[36: 6 ];
The following table summarizes the combinations of removed bits and divide-by-3
operations for the various supported interleave configurations. All other combinations
are not supported.
Note: If any of bits [8:6] are removed, the higher order bits are shifted down.
Removed [8:6] Divide-By-3 Interleave
000 0 None
001 0 2-Way
011 0 4-Way
000 1 3-Way
001 1 6-Way
Device: 4
Function: 1
Offset: 80h, 84h, 88h, 8Ch, 90h, 94h, 98h, 9Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
27 RW 0
26:24 RW 0
23:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
Description
DIVBY3.
This bit indicates the rule is a 3 or 6 way interleave.
REMOVED.
These are the bits to be removed after offset subtraction. These bits correspond
to System Address [8,7,6].
OFFSET.
This value should be subtracted from the current system address to create a
contiguous address space within a channel. BITS 9:0 ARE RESERVED AND
MUST ALWAYS BE SET TO 0.
Datasheet 87
Page 88

Register Description
2.12 Integrated Memory Controller Channel Rank Registers
2.12.1 MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_0, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_1
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_2, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_3
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_4, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_5
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_6, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH0_7
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_0, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_1
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_2, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_3
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_4, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_5
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_6, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH1_7
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_0, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_1
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_2, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_3
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_4, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_5
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_6, MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH2_7
Channel Rank Limit Range Registers.
Device: 4
Function: 2
Offset: 40h, 44h, 48h, 4Ch, 50h, 54h, 58h, 5Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
9:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
Description
LIMIT.
This field specifies the top of the range being mapped to the ranks specified in
the MC_RIR_WAY_CH registers. The most significant bits of the lowest address
in this range is one greater than the limit field in the RIR register with the next
lower index. This field is compared against MA[37:28].
88 Datasheet
Page 89

Register Description
2.12.2 MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_0, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_1
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_2, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_3
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_4, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_5
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_6, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_7
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_8, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_9
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_10, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_11
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_12, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_13
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_14, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_15
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_16, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_17
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_18, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_19
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_20, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_21
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_22, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_23
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_24, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_25
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_26, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_27
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_28, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_29
MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_30, MC_RIR_WAY_CH0_31
Channel Rank Interleave Way Range R egisters. Th ese registers allow the user to define
the ranks and offsets that apply to the ranges defined by the LIMIT in the
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH registers. The mappings are as follows:
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[0] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[3:0]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[1] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[7:6]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[2] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[11:10]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[3] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[15:14]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[4] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[19:18]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[5] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[23:22]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[6] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[27:26]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[7] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[31:28]
Device: 4
Function: 2
Offset: 80h, 84h, 88h, 8Ch, 90h, 94h, 98h, 9Ch, A0h, A4h, A8h, ACh, B0h, B4h, B8h, BCh, C0h,
C4h, C8h, CCh, D0h, D4h, D8h, DCh, E0h, E4h, E8h, ECh, F0h, F4h, F8h, FCh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
13:4 RW
3:0 RW
Reset
Value
0 OFFSET.
This field defines the offset used in the rank interleave. This is a 2's
complement value.
0 RANK.
This field defines which rank participates in WAY (n). If MC.CLOSEDP AGE=1, this
field defines the DRAM rank selected when MemoryAddress[7:6]=(n). If
MC.CLOSEDPAGE=0, this field defines which rank is selected when
MemoryAddress[13:12]=(n). (n) is the instantiation of the register. This field is
organized by physical rank. Bits [3:2] are the encoded DIMM ID(slot). Bits
[1:0] are the rank within that D IMM.
Description
Datasheet 89
Page 90

2.12.3 MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_0, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_1
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_2, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_3
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_4, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_5
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_6, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_7
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_8, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_9
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_10, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_11
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_12, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_13
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_14, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_15
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_16, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_17
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_18, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_19
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_20, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_21
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_22, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_23
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_24, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_25
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_26, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_27
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_28, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_29
MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_30, MC_RIR_WAY_CH1_31
Channel Rank Interleave W ay R ange Registers. These registers allow the user to define
the ranks and offsets that apply to the ranges defined by the LIMIT in the
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH registers. The mappings are as follows:
Register Description
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[0] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[3:0]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[1] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[7:6]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[2] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[11:10]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[3] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[15:14]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[4] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[19:18]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[5] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[23:22]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[6] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[27:26]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[7] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[31:28]
Device: 5
Function: 2
Offset: 80h, 84h, 88h, 8Ch, 90h, 94h, 98h, 9Ch, A0h, A4h, A8h, ACh, B0h, B4h, B8h, BCh, C0h,
C4h, C8h, CCh, D0h, D4h, D8h, DCh, E0h, E4h, E8h, ECh, F0h, F4h, F8h, FCh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
13:4 RW 0
3:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
Description
OFFSET.
This field defines the offset used in the rank interleave. This is a 2's
complement value.
RANK.
This field defines which rank participates in WAY(n). If MC.CLOSEDPAGE=1, this
field defines the DRAM rank selected when MemoryAddress[7:6]=(n). If
MC.CLOSEDPAGE=0, this field defines which rank is selected when
MemoryAddress[13:12]=(n). (n) is the instantiation of the register. This field is
organized by physical rank. Bits [3:2] are the encoded DIMM ID (slot). Bits
[1:0] are the rank within that DIMM.
90 Datasheet
Page 91

Register Description
2.12.4 MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_0, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_1
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_2, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_3
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_4, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_5
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_6, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_7
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_8, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_9
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_10, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_11
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_12, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_13
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_14, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_15
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_16, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_17
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_18, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_19
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_20, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_21
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_22, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_23
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_24, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_25
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_26, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_27
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_28, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_29
MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_30, MC_RIR_WAY_CH2_31
Channel Rank Interleave Way Range R egisters. Th ese registers allow the user to define
the ranks and offsets that apply to the ranges defined by the LIMIT in the
MC_RIR_LIMIT_CH registers. The mappings are as follows:
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[0] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[3:0]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[1] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[7:6]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[2] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[11:10]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[3] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[15:14]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[4] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[19:18]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[5] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[23:22]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[6] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[27:26]
RIR_LIMIT_CH{chan}[7] -> RIR_WAY_CH{chan}[31:28]
Device: 6
Function: 2
Offset: 80h, 84h, 88h, 8Ch, 90h, 94h, 98h, 9Ch, A0h, A4h, A8h, ACh, B0h, B4h, B8h, BCh, C0h,
C4h, C8h, CCh, D0h, D4h, D8h, DCh, E0h, E4h, E8h, ECh, F0h, F4h, F8h, FCh
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
13:4 RW 0
3:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
Description
OFFSET.
This field defines the offset used in the rank interleave. This is a 2's
complement value.
RANK.
This field defines which rank participates in WAY (n). If MC.CLOSEDP AGE=1, this
field defines the DRAM rank selected when MemoryAddress[7:6]=(n). If
MC.CLOSEDPAGE=0, this field defines which rank is selected when
MemoryAddress[13:12]=(n). (n) is the instantiation of the register. This field is
organized by physical rank. Bits [3:2] are the encoded DIMM ID(slot). Bits
[1:0] are the rank within that D IMM.
Datasheet 91
Page 92

2.13 Memory Thermal Control
2.13.1 MC_THERMAL_CONTROL0 MC_THERMAL_CONTROL1 MC_THERMAL_CONTROL2
Controls for the Integrated Memory Controller thermal throttle logic for each channel.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 48h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
2RW1
1:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
APPLY_SAFE.
Enable the application of safe values while
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B.SAFE_INTERVAL is exceeded.
THROTTLE_MODE. S
elects throttling mode.
00 = Throttle disabled
01 = Open Loop: Throttle when Virtual Temperature is greater than
MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET.
10 = Closed Loop: Throttle when MC_CLOSED_LOOP.THROTTLE_NOW is set.
11 = Closed Loop: Throttle when MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND.THROT TLE is set
and the MC_DDR_THERM pin is asserted OR OLTT will be implemented
(Condition 1).
2.13.2 MC_THERMAL_STATUS0 MC_THERMAL_STATUS1 MC_THERMAL_STATUS2
Status registers for the thermal throttling logic for each channel.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 4Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
29:4 RO 0
3:0 RO 0
Reset
Value
CYCLES_THROTTLED.
The number of throttle cycles, in increments of 256 Dclks, triggered in any r ank
in the last SAFE_INTERVAL number of ZQs.
RANK_TEMP.
The bit specifies whether the rank is above throttling threshold.
Description
Description
92 Datasheet
Page 93

Register Description
2.13.3 MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE0 MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE1 MC_THERMAL_DEFEATURE2
Thermal Throttle defeature register for each channel.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 50h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
0RW1S0
Reset
Value
THERM_REG_LOCK.
When set, no further modification of all thermal throttle registers are allowed.
This bit must be set to the same value for all channels.
2.13.4 MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A0 MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A1 MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_A2
Parameters used by Open Loop Throughput Throttling (OLTT) and Closed Loop Thermal
Throttling (CLTT).
Description
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 60h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
Reset
Value
31:24 RW 0
23:16 RW 0
15:8 RW 0
7:0 RW 0
Description
CKE_ASSERT_ENERGY.
Energy of having CKE asserted when no command is issued.
CKE_DEASSERT_ENERGY.
Energy of having CKE de-asserted when no command is issued.
WRCMD_ENERGY.
Energy of a write including data transfer.
RDCMD_ENERGY.
Energy of a read including data transfer.
Datasheet 93
Page 94

2.13.5 MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B0 MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B1 MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B2
Parameters used by the thermal throttling logic.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 64h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
31:26 RW 1
25:16 RW 255
15:8 RW 1
7:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
SAFE_INTERVAL.
Safe values for cooling coefficient and duty cycle will be applied while the
SAFE_INTERVAL is exceeded. This interval is the number of ZQ intervals since
the last time the MC_COOLING_COEF or MC_CLOSED_LOOP registers have
been written. A register to write to MC_COOLING_COEF or MC_CLOSED_LOOP
will re-apply the normal MC_COOLING_COEF and
MC_CLOSED_LOOP.MIN_THROTTLE_DUTY_CYC values. The register value
written need not be different; writing the current value will suffice. The
MC_THERMAL_STATUS.CYCLES_THROTTLED field is reloaded when the number
of ZQ intervals exceeds this value. This field must not be programmed to 0; this
value is illegal.
SAFE_DUTY_CYC. This value replaces
MC_CLOSED_LOOP.MIN_THROTTLE_DUTY_CYC while the
MC_THERMAL_PARAMS_B.SAFE_INTERVAL is exceeded.
SAFE_COOL_COEF.
This value replaces MC_COOLING_COEF while the
THERMAL_PARAMS_B.SAFE_INTERVAL is exceeded.
ACTCMD_ENERGY.
Energy of an Activate/Precharge Cycle.
2.13.6 MC_COOLING_COEF0 MC_COOLING_COEF1 MC_COOLING_COEF2
Heat removed from DRAM 8 DCLKs. This should be scaled relative to the per command
weights and the initial value of the throttling threshold. This includes idle command and
refresh energies. If 2X refresh is supported, the worst case of 2X refresh must be
assumed.
Description
When there are more than 4 ranks attached to the channel, the thermal throttle logic is
shared.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 80h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
31:24 RW 255
23:16 RW 255
15:8 RW 255
7:0 RW 255
94 Datasheet
Reset
Value
Description
RANK3. Rank 3 Cooling Coefficient.
RANK2. Rank 2 Cooling Coefficient.
RANK1. Rank 1 Cooling Coefficient.
RANK0. Rank 0 Cooling Coefficient.
Page 95

Register Description
2.13.7 MC_CLOSED_LOOP0 MC_CLOSED_LOOP1 MC_CLOSED_LOOP2
This register controls the closed loop thermal response of the DRAM thermal throttle
logic. It supports immediate thermal throttle and 2X refresh. In addition, the register is
used to configure the throttling duty cycle.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 84h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
17:8 RW 64
4RW0
3:0 RW 0
Reset
Value
MIN_THROTTLE_DUTY_CYC.
This parameter represents the minimum number of DCLKs o f oper ation allowed
after throttling. In order to provide actual command opportunities, the number
of clocks between CKE de-assertion and first command should be considered.
REF_2X_NOW.
Direct control of dynamic 2X refresh if
MC_THERMAL_CONTROL.THROTTLE_MODE = 2.
THROTTLE_NOW.
Throttler Vector to directly control throttling if
MC_THERMAL_CONTROL.THROTTLE_MODE = 2.
2.13.8 MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET0 MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET1 MC_THROTTLE_OFFSET2
Compared against bits [36:29] of virtual temperature of each rank stored in
RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP to determine the throttle point. Recommended value for each
rank is 255.
When there are more than 4 ranks attached to the channel, the therm al throttle logic is
shared.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 88h
Access as a Dword
Description
Bit Type
31:24 RW 0
23:16 RW 0
15:8 RW 0
7:0 RW 0
Datasheet 95
Reset
Value
RANK3. Rank 3 throttle offset.
RANK2. Rank 2 throttle offset.
RANK1. Rank 1 throttle offset.
RANK0. Rank 0 throttle offset.
Description
Page 96

2.13.9 MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP0 MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP1 MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP2
This register contains the 8 most significant bits [37:30] of the virtual temperature of
each rank. The difference between the virtual temperature and the sensor temperature
can be used to determine how fast fan speed should be increased. The value stored is
right shifted one bit to the right with respect to the corresponding MC_Throttle_Offset
register value. For example when When a rank throttle offset is set to 40h, the value
read from the corresponding in MC_RANK_VIRTUAL_TEMP register is 20h.
When there are more than 4 ranks attached to the channel, the thermal throttle logic is
shared.
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 98h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
31:24 RO 0
23:16 RO 0
15:8 RO 0
7:0 RO 0
Reset
Value
RANK3. Rank 3 virtual temperature.
RANK2. Rank 2 virtual temperature.
RANK1. Rank 1 virtual temperature.
RANK0. Rank 0 virtual temperature.
2.13.10 MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND0 MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND1 MC_DDR_THERM_COMMAND2
This register contains the command portion of the DDR_THERM# functionality as
described in the processor datasheet (i.e., what an assertion of the pin does).
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: 9Ch
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
3RW0
2RW0
1RW0
0RW0
Reset
Value
THROTTLE.
Force throttling when DDR_THERM# pin is asserted.
Reserved
DISABLE_EXTTS.
Response to DDR_THERM# pin is disabled. ASSERTION and DEASSERTION
fields in the register MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS are frozen.
LOCK.
When set, all bits in this register are RO and cannot be written.
Description
Description
96 Datasheet
Page 97

Register Description
2.13.11 MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS0 MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS1 MC_DDR_THERM_STATUS2
This register contains the status portion of the DDR_THERM# functionality as described
in the processor datasheet (i.e., what is ha ppening or has happened with respect to the
pin).
Device: 4, 5, 6
Function: 3
Offset: A4h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
2RO0
1RO0
0RO0
Reset
Value
Description
ASSERTION.
An assertion edge was seen on DDR_THERM#. Write-1-to-clear.
DEASSERTION.
A de-assertion edge was seen on DDR_THERM#. Write-1-to-clear.
STATE.
Present logical state of DDR_THERM# bit. This is a static indication of the pin,
and may be several clocks out of date due to the delay between the pin and the
signal.
STATE = 0 means DDR_THERM# is deasserted
STATE = 1 means DDR_THERM# is asserted
2.14 Integrated Memory Controller Miscellaneous Registers
2.14.1 MC_DIMM_CLK_RATIO_STATUS
This register contains status information about DIMM clock ratio.
Device: 3
Function: 4
Offset: 50h
Access as a Dword
Bit Type
28:24 RO 0
4:0 RO 0
Reset
Value
Description
MAX_RATIO. Maximum ratio allowed by the part.
Value = Qclk
00000 = RSVD
00110 = 800 MHz
01000 = 1066 MHz
01010 = 1333 MHz
QCLK_RATIO. Current ratio of Qclk.
Value = Qclk.
00000 = RSVD
00110 = 800 MHz
01000 = 1066 MHz
01010 = 1333 MHz
Datasheet 97
Page 98

2.14.2 MC_DIMM_CLK_RATIO
This register is for the Requested DIMM clock ratio (Qclk). This is the data r ate going to
the DIMM. The clock sent to the DIMM is 1/2 of QCLK rate.
Device: 3
Function: 4
Offset: 54h
Access as a Dword
Register Description
Bit Type
4:0 RW 6 QCLK_RATIO. Requested ratio of Qclk/Bclk.
Reset
Value
Description
00000 = RSVD
00110 = 800 MHz
01000 = 1066 MHz
01010 = 1333 MHz
§
98 Datasheet
 Loading...
Loading...