Intel BX80569Q9550 - Core 2 Quad 2.83 GHz Processor, Itanium 9300 Series, Itanium 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 1

Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
Series and 9500 Series
Intel® Itanium® Processor Quad-Core 1.86-1.73 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9350
®
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Datasheet
November 2012
Itanium® Processor Quad-Core 1.73-1.60 GHz with 20 MB L3 Cache 9340
®
Itanium® Processor Quad-Core 1.60-1.46 GHz with 20 MB L3 Cache 9330
®
Itanium® Processor Quad-Core 1.46-1.33 GHz with 16 MB L3 Cache 9320
®
Itanium® Processor Dual-Core 1.60 GHz Fixed Frequency with 10 MB L3 Cache 9310
®
Itanium® Processor Eight-Core 2.53 GHz with 32 MB LLC Cache 9560
®
Itanium® Processor Four-Core 2.40 GHz with 32 MB LLC Cache 9550
®
Itanium® Processor Eight-Core 2.13 GHz with 24 MB LLC Cache 9540
®
Itanium® Processor Four-Core 1.73 GHz with 20 MB LLC Cache 9520
Reference Number: 322821-002
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER
AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING T O S ALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCT S INCLUDING
LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELA TING T O FITNES S FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANT ABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
A “Mission Critical Application” is any application in which failure of the Intel Product could result, directly or indirectly, in personal
injury or death. SHOULD YOU PURCHASE OR USE INTEL'S PRODUCTS FOR ANY SUCH MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, YOU
SHALL INDEMNIFY AND HOLD INTEL AND ITS SUBSIDIARIES, SUBCONTRACTORS AND AFFILIATES, AND THE DIRECTORS,
OFFICERS, AND EMPLOYEES OF EACH, HARM LESS AGAINST ALL CLAIMS COSTS, DAMAGES, AND EXPENSES AND REASONABLE
AT TORNEY S' FEES ARISING O UT OF, DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY, ANY CLAIM OF PRODUCT LIABILITY, PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH
ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF SUCH MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, WHETHER OR NOT INTEL OR ITS SUBCONTRACTOR WAS
NEGLIGENT IN THE DESIGN, MANUFACTURE, OR WARNING OF THE INTEL PRODUCT OR ANY OF ITS PARTS.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Designers must not rely on the
absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined”. Intel reserves these for future
definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them. The
information here is subject to change without notice. Do not finalize a design with this information.
The products described in this document may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to
deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained
by calling 1-800-548-4725, or go to: http://www.intel.com/design/literature.htm%20
2
C is a two-wire communication bus /protocol developed by Phillips. SMBus is a subset of the I2C bus/protocol developed by Intel.
I
Implementation of the I
Electronics, N.V. and North American Phillips Corporation.
Intel® Virtualization Technology requires a computer system with an enabled Intel® processor, BIOS, virtual machine monitor
(VMM) and, for some uses, certain computer system software enabled for it. Functionality, performance or other benefits will vary
depending on hardware and software configur ations and may re quire a BIOS update. S oftware applicatio ns may not be compatible
2
C bus/protocol or the SMBus bus/protocol may require licenses from various entities, including Phillips
with all operating systems. Please check with your application vendor.
Intel, Itanium, and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U. S. and\or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2012, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
2 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 3

Contents
1Introduction..............................................................................................................9
1.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................9
1.2 Architectural Overview.......................................................................................15
1.2.1 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Overview .......................................15
1.2.2 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Overview .......................................16
1.3 Processor Feature Comparison ............................................................................19
1.4 Processor Abstraction Layer................................................................................20
1.5 Mixing Processors of Different Frequencies and Cache Sizes ....................................20
1.6 Terminology .....................................................................................................20
1.7 State of Data............................................. ............................ ...........................21
1.8 Reference Documents..................... .. .. ...............................................................21
2 Electrical Specifications...........................................................................................23
2.1 Intel
2.2 Signal Groups.......................... ........................... ........................... ...................24
2.3 Reference Clocking Specifications ........................................................................26
2.4 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® SMI Signaling Specifications..................... 28
2.5 Processor Absolute Maximum Ratings...................................................................38
2.6 Processor DC Specifications ................................................................................39
2.7 Core and Uncore Voltage Identification.................................................................57
2.8 Cache Voltage Identification (Intel
2.9 RSVD, Unused, and DEBUG Pins..........................................................................63
2.10 Mixing Processors..............................................................................................64
2.11 Supported Power-up Voltage Sequence................................................................64
2.12 Supported Power-down Voltage Sequence ............................................................68
2.13 Timing Relationship Between RESET_N and SKTID.................................................69
®
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® Scalable Memory Interconnect
Differential Signaling .........................................................................................23
2.4.1 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
2.4.2 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Requirements for
2.4.3 Intel
2.5.1 Intel
®
Intel
QuickPath Interconnect and
®
SMI Specifications for 4.8 GT/s.......................................................28
Intel
®
QuickPath Interconnect for 4.8 and 6.4 GT/s ....................................32
Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Processor Requirements for
®
Intel
SMI Specifications for 6.4 GT/s.......................................................37
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Absolute Maximum Ratings...............39
2.5.2 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Absolute Maximum Ratings...............39
®
2.6.1 Flexible Motherboard Guidelines for the Intel
Processor 9300 Series.............................................................................40
2.6.2 Flexible Motherboard Guidelines for the Intel
Processor 9500 Series.............................................................................43
2.6.3 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Uncore, Core, and Cache Tolerances.. 44
Itanium®
®
Itanium®
2.6.4 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Uncore and Core Tolerances ............. 49
2.6.5 Overshoot and Undershoot Guidelines.......................................................52
2.6.6 Signal DC Specifications............................................. .. .. .. .. .....................53
2.6.7 Motherboard-Socket Specification for VR Sense Point ..................................57
2.7.1 Core and Uncore Voltage Identification for the
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series....................................................58
2.7.2 Core and Uncore Voltage Identification for the
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series.....................................................59
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series only)...............62
2.11.1 Supported Power-up Voltage Sequence for the
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series....................................................66
2.11.2 Supported Power-up Voltage Sequence for the
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series.....................................................67
Intel
2.11.3 Power-up Voltage Sequence Timing Requirements......................................68
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 3
Page 4

2.14 Test Access Port (TAP) Connection..................................... ... .. .............................71
3 Pin Listing................................................................................................................73
3.1 Processor Package Bottom Pin Assignments...........................................................73
3.1.1 Package Bottom Pin Listing by Pin Name....................................................73
3.1.2 Pin Listing by Pin Number........................................................................89
3.2 Processor Package Top Pin Assignments..............................................................105
3.2.1 Top-Side J1 Connector Two-Dimensional Table .........................................105
3.2.2 Top-Side J2 Connector Two-Dimensional Table .........................................108
3.2.3 Top-Side J3 Connector Two-Dimensional Table .........................................111
3.2.4 Top-Side J4 Connector Two-Dimensional Table .........................................114
4 Mechanical Specifications ...................................................................................... 119
4.1 Package Mechanical Drawing.............................................................................120
4.2 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series...............................................................121
4.3 Processor Component Keepout Zones.................................................................129
4.4 Package Loading Specifications..........................................................................129
4.5 Package Handling Guidelines.............................................................................129
4.6 Processor Mass Specifications............................................................................130
4.7 Processor Materials..........................................................................................130
4.8 Package Markings............................................................................................130
5 Thermal Specifications...........................................................................................133
5.1 Thermal Features..................... ............................ ........................... .................133
5.1.1 Digital Thermometer............................. ........................... .....................134
5.1.2 Thermal Management....................... ............................ .. .. .....................135
5.1.3 Thermal Alert.................................... ... ........................... .....................136
5.1.4 TCONTROL...........................................................................................137
5.1.5 Thermal Warning.......................................... .. .. ............................ .. ......137
5.1.6 Thermal Trip.................................................................................... ....137
5.1.7 PROCHOT............................................................................................138
5.1.8 FORCEPR_N Signal Pin... ... .....................................................................138
5.1.9 Ararat Voltage Regulator Thermal Signals ................................................138
5.2 Package Thermal Specifications and Considerations..............................................139
5.3 Storage Conditions Specifications.......................................................................140
6 System Management Bus Interface........................................................................143
6.1 Introduction....................................................................................................143
6.2 SMBus Memory Component...............................................................................144
6.2.1 Processor Information ROM (PIROM).......................................................144
6.2.2 Scratch EEPROM...................................................................................149
6.2.3 PIROM and Scratch EEPROM Supported SMBus Transactions.......................150
6.3 Memory Component Addressing.........................................................................150
6.4 PIROM Field Definitions.....................................................................................152
6.4.1 General...............................................................................................152
6.4.2 Processor Data.....................................................................................152
6.4.3 Processor Core Data..............................................................................152
6.4.4 Processor Uncore Data ..........................................................................153
6.4.5 Cache Data..........................................................................................154
6.4.6 Package Data.......................................................................................155
6.4.7 Part Number Data.................................................................................155
6.4.8 Thermal Reference Data...................................... .. ... ........................... ..155
6.4.9 Feature Data........................................................................................ 156
6.4.10 Other Data ................................. ..................................................... ....157
6.4.11 Checksums..........................................................................................157
7Signal Definitions...................................................................................................159
4 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 5

Figures
1-1 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Processor Block Diagram............................. 16
1-2 Intel
1-3 Intel
2-1 Active ODT for a Differential Link Example............................................................23
2-2 Single-ended Maximum and Minimum Levels and Vcross Levels...............................27
2-3 Vcross-delta Definition.......................................................................................27
2-4 Differential Edge Rate Definition..........................................................................28
2-5 VRB and TStable Definitions................................................................................28
2-6 TX Equalization Diagram ............................. ... .. .. .. ..............................................31
2-7 TX Return Loss ............................................................. ............................ ........32
2-8 RX Return Loss ................................................. .. ........................... ...................32
2-9 Processor I
2-10 VCCUNCORE Static and Transient Tolerance for
2-11 VCCCORE Static and Transient Tolerance for
2-12 VCCCACHE Static and Transient Tolerance for
2-13 VCCUNCORE Static and Transient Tolerance for the
2-14 VCCUNCORE Load Line for the Intel
2-15 VCCCORE Load Line for the Intel
2-16 VR Sense Point (Representation).........................................................................57
2-17 Supported Power-up Voltage Sequence Timing Requirements for the
2-18 Supported Power-up Sequence Timing Requirements for
2-19 Supported Power-down Voltage Sequence Timing Requirements.............................. 69
2-20 RESET_N and SKITID Timing for Warm and Cold Resets.........................................70
4-1 Processor Package Assembly Sketch.................................................................. 119
4-2 Intel
4-3 Intel
4-4 Intel
4-5 Intel
4-6 Intel
4-7 Intel
4-8 Intel
4-9 Intel
4-10 Processor Marking Zones.................................................................................. 131
5-1 Intel
5-2 Intel
6-1 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Processor Block Diagram............................. 17
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Firmware Diagram......................................18
CC_CORE
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series................................................................45
Load Current versus Time........................................................42
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series................................................................47
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series................................................................48
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series................................................................50
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series .....................50
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series ......................... 51
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series...............................................................66
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series...............................................................67
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Package Drawing (Sheet 1 of 4)................. 121
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 2 of 4)... 122
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Package Drawing (Sheet 3 of 4)................. 123
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Package Drawing (Sheet 4 of 4)................. 124
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Package Drawing (Sheet 1 of 4)................ 125
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Package Drawing (Sheet 2 of 4)................. 126
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Package Drawing (Sheet 3 of 4)................. 127
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Package Drawing (Sheet 4 of 4)................. 128
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series’ Thermal States ....................................... 134
Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Package Thermocouple Location................. 140
Intel
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Package................................................. 151
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 5
Page 6

Tables
1-1 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Feature Comparison....................................19
2-1 Signals with RTT................................................................................................24
2-2 Signal Groups ...................................................................................................24
2-3 Intel
2-4 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Clock Frequency Table.................................29
2-5 Intel
2-6 Intel
2-7 Intel
2-8 Intel
2-9 Intel
2-10 Intel
2-11 Intel
2-12 PLL Specification for TX and RX ...........................................................................38
2-13 Intel
2-14 Intel
2-15 FMB Voltage Specifications for the Intel
2-16 FMB 130W Current Specifications for the Intel
2-17 FMB 155W/185W Current Specifications for the
2-18 FMB Voltage Specifications for the Intel
2-19 FMB 170W and 130W Current Specifications for the
2-20 VCCUNCORE Static and Transient Tolerance for
2-21 VCCCORE Static and Transient Tolerance for
2-22 VCCCACHE Static and Transient Tolerance for
2-23 VCCUNCORE Static and Transient Tolerance for the
2-24 VCCCORE Static and Transient Tolerance for the
2-25 Overshoot and Undershoot Specifications For Differential
2-26 Overshoot and Undershoot Specifications For Differential
2-27 Voltage Regulator Signal Group DC Specifications ..................................................53
2-28 Voltage Regulator Control Group DC Specification ..................................................54
2-29 TAP and System Management Group DC Specifications...........................................54
2-30 Error, FLASHROM, Power-Up, Setup, and Thermal Group DC Specifications................54
2-31 VID_VCCCORE[6:0], VID_VCCUNCORE[6:0] and VID_VCCCACHE[5:0] DC
2-32 SVID Group DC Specifications for the Intel
®
QuickPath Interconnect/Intel® Scalable Memory
‘Interconnect Reference Clock Specifications26
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Transmitter Parameter Values for Intel®
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel SMI Channels @ 4.8 GT/s ....................................29
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Receiver Parameter
Values for Intel® QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® SMI Channels @ 4.8 GT.. ........... 30
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Clock Frequency Table.................................33
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Link Speed Independent Specifications ..........33
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and
Receiver Parameter Values for Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and
®
QPI Channel at 4.8 GT/s.................................34
Receiver Parameter Values for Intel® QPI at 6.4 GT/s.............................................35
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and
Receiver Parameter Values for Intel® SMI at 6.4 GT/s and lower..............................37
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Absolute Maximum Ratings..........................39
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Processor Absolute Maximum Ratings............39
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series ................40
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series ...... .41
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series.................................................................42
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series ................43
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series.................................................................44
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series.................................................................45
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series.................................................................46
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series.................................................................48
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series.................................................................49
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series.................................................................51
®
Intel
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® SMI and Single-Ended Signals
®
for the Intel
Intel® QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® SMI and Single-Ended
Signals for the Intel
Specifications for the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series ......................................................52
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series ...........................................53
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series...................................55
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series............55
6 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 7

2-33 SMBus and Serial Presence Detect (SPD) Bus Signal Group DC Specifications............ 55
2-34 Debug Signal Group DC Specifications..................................................................56
2-35 PIROM Signal Group DC Specifications .................................................................56
2-36 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series VCCCORE (VID_VCCCORE) and
VCCUNCORE and (VID_VCCUNCORE) Voltage Identification Definition for Ararat........58
2-37 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series VCCCORE (VID_VCCCORE)
and VCCUNCORE and (VID_VCCUNCORE) Voltage Identification
Definition for Ararat II .......................................................................................59
2-38 Cache (VID_VCCCACHE) Voltage Identification Definition for Ararat .........................63
2-39 Power-up Voltage Sequence Timing Requirements .................................................68
2-40 RESET_N and SKTID Timing ...............................................................................70
3-1 Pin List by Pin Name..........................................................................................73
3-2 Pin List by Pin Number.......................................................................................89
3-3 Top-Side J1 Connector Two-Dimensional Table
3-4 Top-Side J1 Connector Two-Dimensional Table
3-5 Top-Side J2 Connector Two-Dimensional Table
(Intel
(Intel
(Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series)............................................................ 105
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series)............................................................ 106
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series)............................................................ 108
3-6 Top-Side J2 Connector Two-Dimensional Table
(Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series)............................................................ 110
3-7 Top-Side J3 Connector Two-Dimensional Table
3-8 Top-Side J3 Connector Two-Dimensional Table
(Intel
(Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series)............................................................ 111
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series)............................................................ 113
3-9 Top-Side J4 Connector Two-Dimensional Table
(Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series)............................................................ 114
3-10 Top-Side J4 Connector Two-Dimensional Table
(Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series)............................................................ 116
4-1 Processor Loading Specifications ....................................................................... 129
4-2 Package Handling Guidelines........................ ... ........................... .. .. ................... 129
4-3 Processor Package Insertion Specification........................................................... 130
4-4 Package Materials..................... .. .. ........................... .. ............................ .. .. ...... 130
4-5 1248 FCLGA Package Marking Zones.................................................................. 130
5-1 Thermal Sensor Accuracy Distribution for the
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series.............................................................. 134
5-2 Thermal Sensor Accuracy Distribution for the
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series............................................................. 135
5-3 Thermal Specification for the Intel
5-4 Thermal Specification for the Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series ..................... 139
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Processor ....... 139
5-5 Storage Condition Ratings ................................................................................ 141
6-1 Processor Information ROM Data....................................................................... 144
6-2 Read Byte SMBus Packet.................................................................................. 150
6-3 Write Byte SMBus Packet ................................................................................. 150
6-4 Offset 78h/79h Definitions............................................ ............................ .. ...... 156
6-5 128 Byte PIROM Checksum Values ..................................................... ............... 157
7-1 Signal Definitions for the Intel
Series and Intel
®
Itanium® 9500 Series............................................................. 159
®
Itanium® Processor 9300
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 7
Page 8

Revision History
Document
Number
322821 -002 • Initial release of the 9300/9500 document. November 2012
322821 -001 • Initial release of the document. February 2010
Revision
Number
Description Date
§
8 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 9

Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
employ Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing (EPIC) design concepts for a tighter
coupling between hardware and software. In this design style, the interface between
hardware and software is designed to enable the software to exploit all available
compile-time information, and efficiently deliver this information to the hardware. It
addresses several fundamental performance bottlenecks in modern computers, such as
memory latency, memory address disambiguation, and control flow dependencies. The
EPIC constructs provide powerful architectural semantics, and enable the software to
make global optimizations across a large scheduling scope, thereby exposing available
Instruction Level Parallelism (ILP) to the hardware. The hardware takes advantage of
this enhanced ILP, and provides abundant execution resources. Additionally, it focuses
on dynamic run-time optimizations to enable the compiled code schedule to flow at
high throughput. This strategy increases the synergy between hardware and software,
and leads to greater overall performance.
®
The Intel
system interface, with its 4 full width and 2 half width Intel® QuickPath Interconnects,
enables each processor to directly connect to other system components, thus can be
used as an effective building block for very large systems. The balanced core and
memory subsystem provide high performance for a wide range of applications ranging
from commercial workloads to high performance technical computing.
The Intel
are pin compatible and support a range of computing needs and configurations from a
2-way to large SMP servers (although OEM field upgrade methodologies vary). This
document provides the electrical, mechanical and thermal specifications that must be
met when using the Intel
Processor 9500 Series in your systems.
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium®
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 9
Page 10

Introduction
10 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 11

Introduction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 SeriesIntel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
Intel® Itanium® Processor Quad-Core 1.86-1.73 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9350
®
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Itanium® Processor Quad-Core 1.73-1.60 GHz with 20 MB L3 Cache 9340
®
Itanium® Processor Quad-Core 1.60-1.46 GHz with 20 MB L3 Cache 9330
®
Itanium® Processor Quad-Core 1.46-1.33 GHz with 16 MB L3 Cache 9320
®
Itanium® Processor Dual-Core 1.60 GHz Fixed Frequency with 10 MB L3 Cache 9310
Product Features
Quad Core
— Four complete 64-bit processing cores on one
processor.
— Includes Dynamic Domain Partitioning.
Advanced EPIC (Explicitly Parallel Instruction
Computing) Architecture for current and future
requirements of high-end enterprise and technical
workloads.
— Provide a variety of advanced implementations of
parallelism, predication, and speculation,
resulting in superior Instruction-Level Parallelism
(ILP).
®
Intel
Hyper-Threading Technology
— Two times the number of OS threads per core.
Wide, parallel hardware based on Intel
®
Itanium®
architecture for high performance:
— Integrated on-die L3 cache of up to 24 MB; cache
hints for L1, L2, and L3 caches for reduced
memory latency.
— 128 general and 128 floating-point registers
supporting register rotation.
— Register stack engine for effective management
of processor resources.
— Support for predication and speculation.
Extensive RAS features for business-critical
applications, for example:
— Machine check architecture with extensive ECC
and parity protection.
— On-chip thermal management.
— Built-in processor information ROM (PIROM).
— Built-in programmable EEPROM.
—Hot-Plug Socket
— Hot-add and hot removal.
— Double Device Data Correction (DDDC) for x4
DRAMs, plus correction of a single bit error.
— Single Device Data Correction (SDDC) for x8
DRAMs, plus correction of a single bit error.
®
—Intel
—Intel
— Intel QuickPath Interconnect (Intel
— DIMM Sparing, Memory Scrubbing, Memory
QuickPath Interconnect Dynamic Link
Width Reduction.
®
QuickPath Interconnect Clock Fail-Safe
Feature.
Add and Removal.
Mirroring, and Memory Migration.
®
QPI) Hot-
— Architected firmware stack, including PAL and
SAL support.
— Directory-based and source-based coherency
protocol.
— Intel QPI poisoning, viral containment and
cleanup.
On-die Memory Controller
— Each memory controller supports two Intel
Scalable Memory Interconnects.
— Support for one Scalable Memory Buffer per Intel
Scalable Memory Interconnect; four Scalable
®
Memory Buffers per processor.
— High memory bandwidth, thus improved
performance.
— 4.8 GT/s for the Intel
Buffer.
Intel
®
Virtualization T echnology for virtualization for
®
7500 Scalable Memory
data-intensive applications.
— Reduce virtualization complexity.
— Improve virtualization performance.
— Increase operating system compatibility.
Intel
®
Cache Safe Technology ensures mainframecaliber availability.
— Minimize L3 cache errors.
— Disable cache entries that have become hard
errors.
— Improve availability.
High bandwidth Intel
multiprocessor scalability:
®
QuickPath Interconnect for
— 4 full and 2 half width Intel QPI Links
— 4.8GT/s transfer rate.
— Systems are easily scaled without sacrificing
performance.
Features to support flexible platform environments:
— IA-32 Execution Layer supports IA-32 application
binaries.
— Bi-endian support.
— Processor abstraction layer eliminates processor
dependencies.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 11
Page 12

Introduction
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series delivers new levels of flexibility, reliability,
performance, and cost-effective scalability for your most data-intensive business and
technical applications. It provides 24 megabytes L3 cache accessed at core speed,
Hyper-Threading Technology for increased performance, Intel
Technology for improved virtualization, Intel
®
Cache Safe Technology for increased
®
Virtualization
availability.
®
The Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series consists of up to 4 core processors and a
system interface unit. Each processor core provides a 6-wide, 8-stage deep execution
pipeline. The resources consist of six integer units, six multimedia units, two load and
two store units, three branch units and two floating-point units each capable of
extended, double and single precision arithmetic. The hardware employs dynamic
prefetch, branch prediction, a register scoreboard, and non-blocking caches to optimize
for compile-time non-determinism. Each core provides duplication of all architectural
state to support hardware multithreading, thus enabling greater throughput. Three
levels of on-die cache minimize overall memory latency. It interfaces with the Ararat
“1” Voltage Regulator Module, which used exclusively with the Intel
®
Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series.
12 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 13

Introduction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
Intel® Itanium® Processor Eight-Core 2.53 GHz with 32 MB LLC Cache 9560
®
Intel
Intel
Itanium® Processor Four-Core 2.40 GHz with 32 MB LLC Cache 9550
®
Itanium® Processor Eight-Core 2.13 GHz with 24 MB LLC Cache 9540
Intel® Itanium® Processor Four-Core 1.73 GHz with 20 MB LLC Cache 9520
Product Features
Eight Core
— Eight complete 64-bit processing cores on one
processor, with two threads per core.
— Each core provides in-order issue and execution
of up to twelve instructions per cycle.
— Includes dynamic domain partitioning and static
hard partitioning.
Advanced EPIC (Explicitly Parallel Instruction
Computing) Architecture for current and future
requirements of high-end enterprise and technical
workloads.
— Provide a variety of advanced implementations of
parallelism, predication, and speculation,
resulting in superior Instruction-Level Parallelism
(ILP).
®
Intel
Wide, parallel hardware based on Intel
Hyper-Threading Technology
— Dual Domain Multithreading with independent
front end and back end thread domains providing
hardware support for 2 threads per core.
— Support for Intel
Instructions.
architecture for high performance:
— Integrated on-die LLC cache of up to 32MB;
cache hints for FLC, MLC, and LLC caches for
®
Itanium® Processor New-
®
Itanium®
reduced memory latency.
— 160 general and 128 floating-point registers
supporting register rotation.
— Register stack engine for effective management
of processor resources.
— Support for predication and speculation.
Extensive RAS features for business-critical
applications, for example:
— Machine check architecture with extensive ECC
and parity protection with firmware first error
handling.
— End-to-end error detection.
— On-chip thermal management and power
management.
— Built-in processor information ROM (PIROM).
— Built-in programmable EEPROM.
—Hot Plug Socket.
— Hot-add and hot removal support.
— Double Device Data Correction (DDDC) for x4
DRAMs, plus correction support of a single bit
error.
— Single Device Data Correction (SDDC) for x8 and
x4 DRAMs, plus correction of a single bit error.
—Intel
—Intel
—Intel
®
QuickPath Interconnect Dynamic Link
Width Reduction.
®
QuickPath Interconnect Clock Fail-Safe
Feature.
®
QuickPath Interconnect Hot-Add and
Removal.
— Memory DIMM and Rank Sparing, Memory
Scrubbing, Memory Mirroring, and Memory
Migration.
—Intel
®
Turbo Boost Technology, featuring
sustained boost.
— Architected firmware stack, including PAL and
SAL support.
— Directory-based and source-based coherency
protocol.
— Intel QPI poisoning, viral containment and
cleanup.
Two On-die Memory Controllers
— Each memory controller supports two Intel
Scalable Memory Interconnects that operate in
lockstep.
®
— Support for one Scalable Memory Buffer per Intel
Scalable Memory Interconnect; four Scalable
Memory Buffers per processor.
— High memory bandwidth, thus improved
performance.
— 4.8 GT/s for the Intel
Buffer.
— 6.4 GT/s for the Intel
Buffer.
Intel
Intel
®
Instruction Replay Technology to replay core
pipeline for pipeline management and core RAS.
®
Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) for
Intel® 64 or Itanium ®architecture (Intel ® Vt-i) 3 Virtualization Support Extensions for Intel
®
7500 Scalable Memory
®
7510 Scalable Memory
®
Virtualization Technology.
— Reduce virtualization complexity.
— Improve virtualization performance via hardware
optimization.
— Increase operating system compatibility.
Intel
®
Cache Safe Technology ensure mainframecaliber availability.
— Minimize LLC cache errors.
— Disable cache entries that have become hard
errors.
— Directory Cache covers 33% more cache lines.
— Improve availability.
High bandwidth Intel
®
QuickPath Interconnect for
multiprocessor scalability:
— 4 full and 2 half width Intel QPI Links
— 6.4GT/s transfer rate with aggregate data
bandwidth of 28.8 GB/s.
— Systems are easily scaled without sacrificing
performance.
Features to support flexible platform environments:
— Fully compatible with binaries for the Intel
Itanium processor family with Instruction level
advancements.
— LGA1248 Socket Level compatible wit h the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series.
— Bi-endian support.
— Processor abstraction layer eliminates processor
dependencies.
®
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 13
Page 14
Introduction
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series delivers increased levels of flexibility,
reliability, performance, and cost-effective scalability for your most data-intensive
business and technical applications.
®
The Intel
cache, Hyper-Threading Technology for increased performance, Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series processor provides up to 32 megabytes LLC
®
Virtualization
Technology for improved virtualization, Intel® Cache Safe Technology for increased
availability. Intel® Turbo Boost Technology, featuring sustained boost. The Intel®
Itanium
®
Processor 9500 Series employs advanced power monitoring and control to
deliver a higher processor frequency at all times, for maximum performance on all
workloads. The result is a higher thermal envelope utilization for more overall
performance. The Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series offers large cache arrays
covered by ECC including the large LLC utilizing double correct/triple detect (DECTED)
and protecting the MLI/MLD with in-line single correct/double detect (SECDED). In
addition, the processor provides extensive parity protection and parity interleaving on
nearly all RFs, end-to-end parity protection with recovery-support on all critical internal
buses and data paths including the ring. Residue protection on Floating Point unit,
along with the adoption of radiation-hardened (RAD) sequential latching elements for
vulnerable architectural and state. The Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
processor interfaces exclusively with the Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module.
®
The Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series consists of up to 8 core processors and a
system interface unit. Each processor core provides a 12-wide, 11-stage deep
execution pipeline. The resources consist of six integer units, one integer multiply unit,
four multimedia units, two load/store units, three branch units and two floating-point
units each capable of extended, double and single precision arithmetic. The hardware
employs dynamic prefetch, branch prediction, a register scoreboard, and non-blocking
caches to optimize for compile-time non-determinism. 32 additional stacked general
registers are provided over the Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series, and hardware
support is provided for denormal, unnormal, and pseudo-normal operands for floating
point software assist offloading.
®
New instructions on the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series simplify common tasks.
They include: clz (count leading zeros), mpy4 and mpyshl4(unsigned integer multiply/
shift and multiply), mov-to-DAHR/mv-from-DAHR (for improved MLD/FLD prefetcher
hinting and performance), and hint@priority (used by the processor to temporarily
allocate more resources to a thread). Advanced Explicitly Parallel Instruction
Computing (EPIC) is enhanced on the Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series by
increasing the capacity of retiring instructions per cycle from 6 to a maximum of 12
instructions per cycle per core.
®
Hyper-threading Technology is enhanced in the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500
Intel
Series with dual domain multithreading, which enables independent front-end and
back-end pipeline execution to improve multi-thread efficiency and performance for
both new and legacy applications. It provides hardware support for two threads per
core, with a threaded 96 entry per thread Instruction Buffer and threaded MLDTLB and
FLDTLB, and a dedicated load return path from the MLD to the integer register file.
Three levels of on-die cache minimize overall memory latency, with 16 KB instruction
cache FLI/16 KB write-through data cache FLD that comprise the FLC and 512 KB MLI/
256 KB writeback data cache MLD that comprise the MLC.
®
The Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series offers a new RAS feature: Intel®
Instruction Replay Technology. Pipeline replay resolves stall conditions that occur when
the microprocessor pipeline encounters a resource hazard that prevents immediate
execution. In a replay , the instruction that encountered the resource hazard is removed
from the pipeline, along with all the instructions that come after it. The instruction is
then read again out of the instruction buffer for replay and re-executed. To ensure a
14 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 15
Introduction
replay can be initiated for any instruction in the pipeline that encounters a resource
hazard, a copy of each instruction is maintained in the instruction buffer until the
instruction has successfully traversed the pipeline and is no longer needed. If
necessary, an instruction can replay multiple times. As a result, Intel
®
Instruction
Replay Technology automatically detects and many corrects soft errors in the
instruction pipeline. With this technology, soft errors can be identified and corrected in
as few as seven clock cycles, which is fast enough to be invisible to the software
running on the platform.
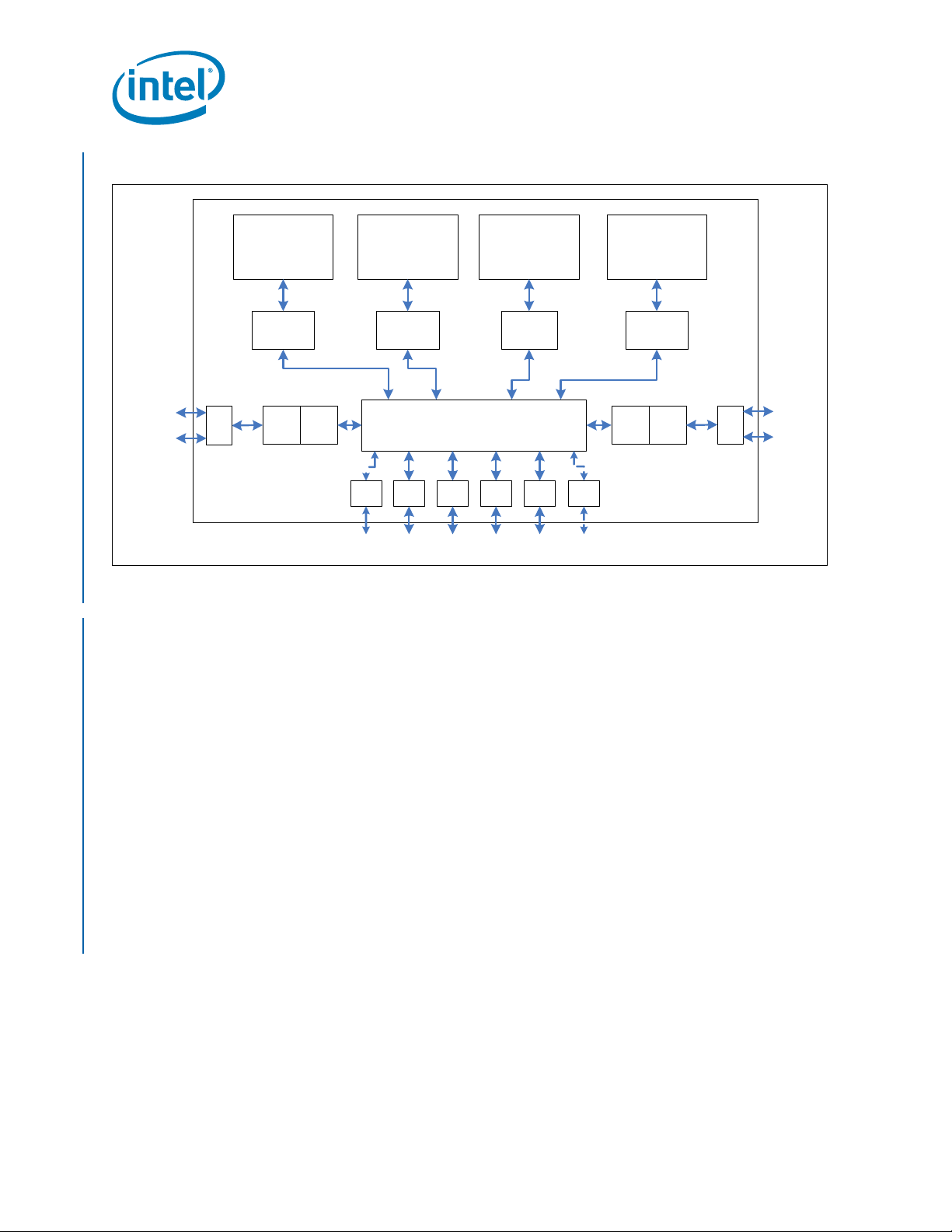
1.2 Architectural Overview
The sections below give an overview of the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series.
1.2.1 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Overview
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series processor is a quad-core architecture. It
supports up to four processor cores, each with its own L3, L2, and L1 level cache. Also
supported are the following page sizes for purges or inserts: 4K, 8K, 16K, 64K, 256K,
1M, 4M, 16M, 64M, 256M, 1G, 4G.
The architecture interfacing the cores to the system is referred to as the System
Interface. Each processor core has it own Caching Agent (CPE). The CPE interfaces
between the processor core and the Intel QuickPath Interconnect. The Intel
Processor 9300 Series processor has two Home Agents (Bbox). The Bbox interfaces
between the memory controller and the Intel
directory cache. Each Bbox interfaces with a memory controllers (Zbox). Each memory
controller supports two Intel SMI in lockstep. The Intel SMI are the interconnects to
®
7500 Scalable Memory Buffer. The processor supports six Intel QuickPath
Intel
Interconnects at the socket, four full width and two half width. The Caching Agent,
Home Agent, and Intel QuickPath Interconnects are connected via a 12-port Crossbar
Router, each port supporting the Intel QuickPath Interconnect protocol. Figure 1-1
shows the Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series block diagram.
®
QuickPath Interconnect and supports a
®
Itanium®
The Intel QPI viral and poison fields are used to flag corrupted system state and bad
data accordingly. Once it has “gone viral”, an Intel QPI agent will set the viral field
within all packet headers. Viral mode is entered in three ways: receiving a viral packet,
upon a detecting fatal/panic error, or when a global viral signal (from Cboxes) is
asserted. Viral is cleared on Reset. Poisoning is used to indicate bad data on a per-flit
basis. Poison does not indicate corrupted system coherency, but rather that a particular
block of data is not reliable.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 15
Page 16
Introduction
Core0 Core3Core2Core1
CPE0 CPE3CPE2CPE1
RboxBbox0Zbox0 Zbox1Bbox1
Pbox
PZ1
Pbo x
PR1
Pbo x
PR 0
Pbo x
PH4
Pbo x
PH5
Pbo x
PR 3
Pbo x
PR 2
Intel® SM I
Intel® SM I
Intel®
QPI
Intel®
QPI
Intel®
QPI
Intel®
QPI
Intel®
QPI
Intel®
QPI
Pbox
PZ0
Intel® SM I
Intel® SM I
0xA 0
87 3
16 9 5240xB
Figure 1-1. Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Processor Block Diagram
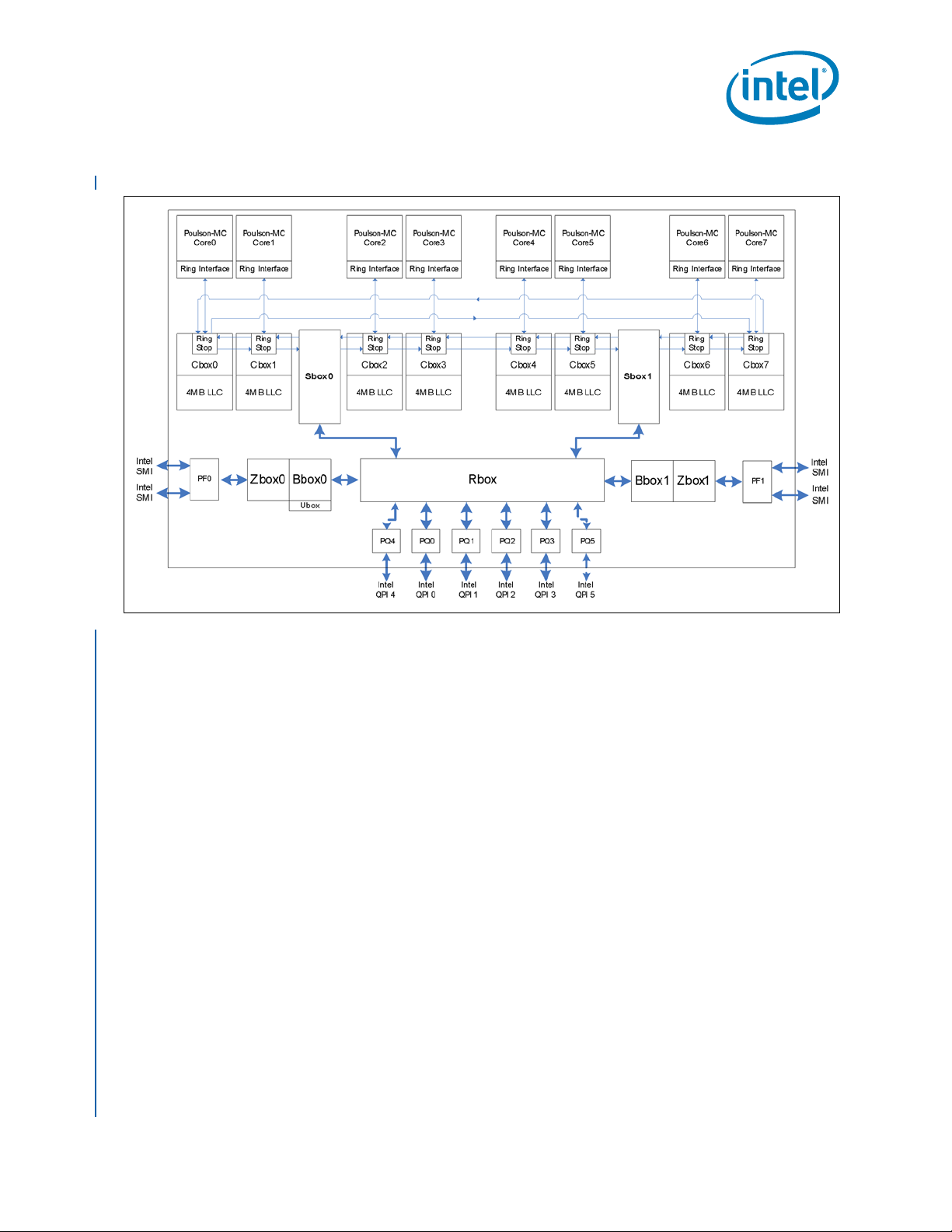
1.2.2 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Overview
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series is an eight core architecture. It supports up
to eight cores, each with its own First Level Cache (FLC) and Mid Level Cache (MLC),
both of which are split into instruction and data caches (FLI/FLD and MLI/MLD,
respectively). The Last Level Cache (LLC) is shared among the cores and supports up to
32 MB. Also supported are the following page sizes for purges or inserts: 4K, 8K, 16K,
64K, 256K, 1M, 4M, 16M, 64M, 256M, 1G, 4G.
The architecture interfacing the cores to the system is referred to as the uncore. Each
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series core interfaces to the Ring. The Ring provides
Intel
connectivity to the Last Level Cache via the Cache Controllers (Cboxes). The Ring also
provides connectivity to Intel QPI via Ring/Sbox. The Sbox and Cbox provide the
supports for the two Intel QPI Caching Agents. The processor has two Home Agents
(Bbox). The Bbox interfaces between the memory controller and the Intel
Interconnect and supports a directory cache. Each memory controller supports two
®
Scalable Memory Interconnects (Intel® SMI) in lockstep. The Intel SMI are the
Intel
interconnects to Scalable Memory Buffer. The Intel
processor supports six Intel® QuickPath Interconnects at the socket, four full width and
two half width. The Caching Agent, Home Agent, and Intel
are connected via a 10-port Crossbar Router, each port supporting the Intel
Interconnect protocol. Figure 1-2 shows the processor block diagram.
®
QuickPath
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
®
QuickPath Interconnects
®
QuickPath
16 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 17
Introduction
Figure 1-2. Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Processor Block Diagram
The Intel QPI viral and poison fields are used to flag corrupted system state and bad
data accordingly. Once it has “gone viral”, an Intel QPI agent will set the viral field
within all packet headers. Viral mode is entered in three ways: receiving a viral packet,
upon a detecting fatal/panic error, or when a global viral signal (from Cboxes) is
asserted. Viral is cleared on Reset. Poisoning is used to indicate bad data on a per-flit
basis. Poison does not indicate corrupted system coherency, but rather that a particular
block of data is not reliable.
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series PAL's Demand Based Switching (DBS) support
Intel
includes implementations of Power/Performance states (P-states) and Halt states (Cstates). For the PAL Halt state interface and architected specifications of the PAL Pstate interface, see the Intel
Volume 2, Section 11.6. PAL controls the Intel
®
Itanium® Architecture Software Developer's Manual,
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
processor power through a special built-in microcontroller that manipulates voltage and
frequency. PAL communicates requested P-states to this controller through internal
registers.
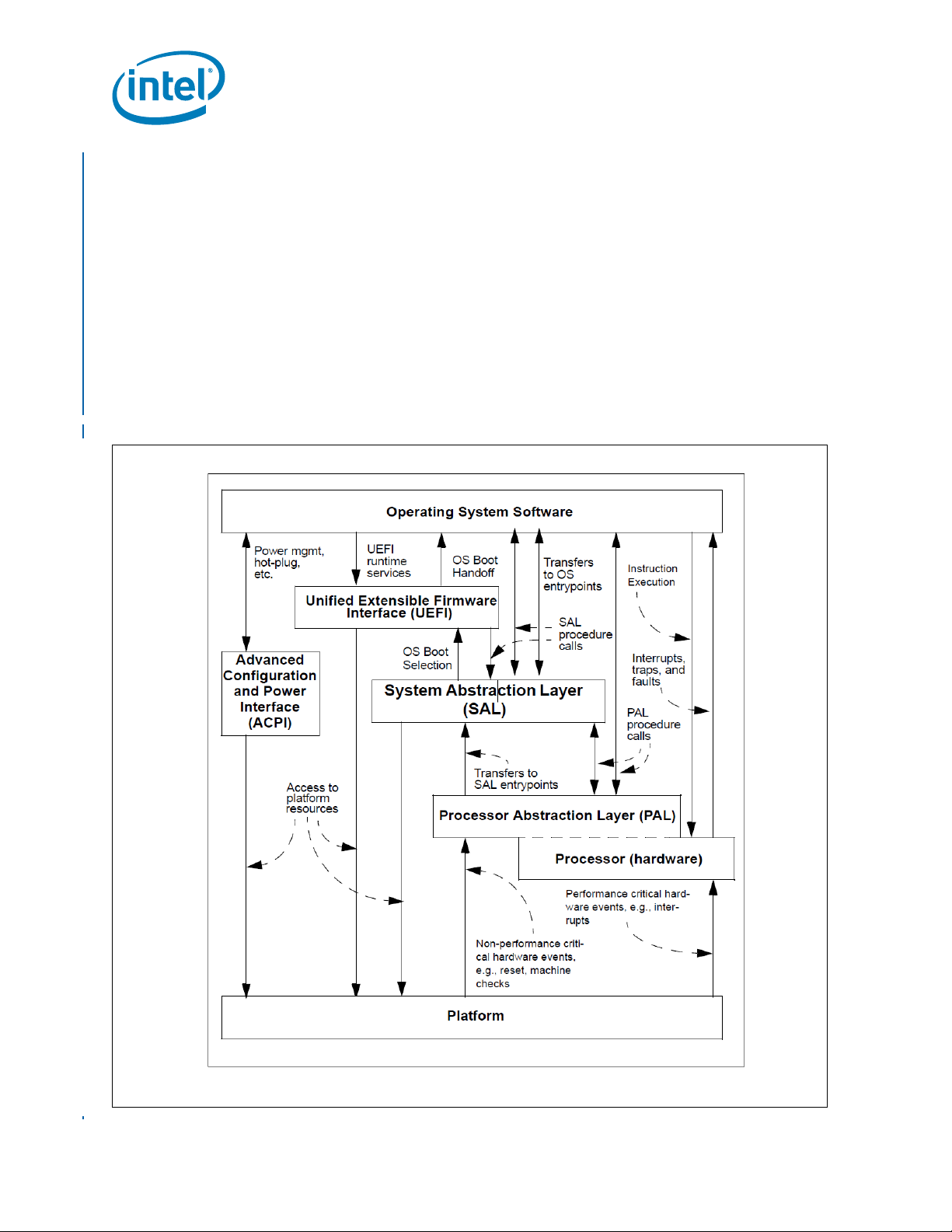
As shown in Figure 1-3, Itanium architecture-based firmware consists of several major
components: Processor Abstraction Layer (PAL), System Abstraction Layer (SAL),
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and Advanced Configuration and Power
Interface (ACPI). PAL, SAL, UEFI and ACPI together provide processor and system
initialization for an operating system boot. PAL and SAL provide machine check abort
handling. PAL, SAL, UEFI and ACPI provide various run-time services for system
functions which may vary across implementations. The interactions of the various
services that PAL, SAL, UEFI and ACPI provide are illustrated in Figure 1-3. In the
context of this model and throughout the rest of this chapter, the System Abstraction
Layer (SAL) is a firmware layer which isolates operating system and other higher level
software from implementation differences in the platform, while PAL is the firmware
layer that abstracts the processor implementation.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 17
Page 18
Protection Keys provide a method to restrict permission by tagging each virtual page
with a unique protection domain identifier. The Protection Key Registers (PKR)
represent a register cache of all protection keys required by a process. The operating
system is responsible for management and replacement polices of the protection key
cache. Before a memory access (including IA-32) is permitted, the processor compares
a translation’s key v alue against all keys contained in the PKRs. If a matching key is not
found, the processor raises a Key Miss fault. If a matching Key is found, access to the
page is qualified by additional read, write and execute protection checks specified by
the matching protection key register. If these checks fail, a Key Permission fault is
raised. Upon receipt of a Key Miss or Key P e rmission fault, software can implement the
desired security policy for the protection domain. Some processor models may
implement additional protection key registers and protection key bits. Unimplemented
bits and registers are reserved. Please see the processor-specific documentation for
further information on the number of protection key registers and protection key bits
implemented on the processor.
Figure 1-3. Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Firmware Diagram
Introduction
18 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 19
Introduction
1.3 Processor Feature Comparison
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series processor and Intel® Itanium® Processor
9500 Series processor features are compared below in Table 1-1.
®
Table 1-1. Intel
Intel
Description
Socket LG1248 LG1248
Transistors 2 billion 3.1 billion
Cores/Threads up to 4/8 up to 8/16
Clock speeds up to 1.86 GHz via Intel
Integrated on-die cache L1 (L1I 16K/L1D 16K),
Ararat Voltage Regulator Module Support Ararat “I” Ararat II
Supported speeds DDR3-800 DDR3-800 and DDR3-1067
Intel QPI links 6
Intel QPI Hot-plug Supported Supported
Intel QPI Link self-healing Supported Supported
Intel QPI Clock fail-safe Supported Supported
Intel QPI Data scrambling Supported Required
Intel QPI Periodic retraining Not Supported Required
Integrated memory controllers 2 2
®
Intel
SMI Interface Intel® 7500 Scalable Memory Buffer
®
Intel
SMI Hot-plug Supported Supported
Physical address space/virtual address
space
Caching agent architecture four caching agents per socket where
Home agents per socket 2 2
Directory Cache Supported Supported
®
Intel
Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) Intel® Vt-i 2 Intel® Vt-i 3
Hot add/hot removal at Intel QPI link and
DIMM memory interface
Hot add CPU Supported
Hot add memory Supported
Hot remove/hot replace memory Supported
Memory sparing technique DIMM DIMM and Rank
Memory scrubbing Supported Supported
Memory mirroring Supported Supported
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Feature Comparison
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300
Series
®
with sustained boost
L2 (L2I 512K, L2D 256K),
inclusive L3 (6 MB per core,
up to 24 MB)
(4 full/2 half width at up to 4.8 GT/s)6 (4 full/2 half width at up to 6.4 GT/s)
(4.8 GT/s)
50 physical/64 virtual 50 physical/64 virtual
each agent is responsible for all of the
address space and dedicated to a core
Supported Supported
T urbo Boost
2,3
2,3
2,3
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500
FLC (FLI 16K/FLD 16K),
MLC (MLI 512K, MLD 256K),
LLC (shared, up to 32 MB)
Intel® 7500 Scalable Memory Buffer
®
7510 Scalable Memory Buffer
Intel
two caching agents per socket are
responsible for half the address space
and shared among the cores
Series
1.73 - 2.53 GHz
1
(4.8 GT/s)
(6.4 GT/s)
Supported
Supported
Supported
2,3
2,3
2,3
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 19
Page 20

Notes:
®
Itanium® Processor 9300
Description
Memory patrolling Supported Supported
Memory migration Supported Supported
Support for mixing of x4 and x8 on the
same DDR channel
Online/Offline CPU (OS assisted) Supported Supported
Online/Offline Memory (OS assisted) Supported Supported
Online/Offline I/O Hub Supported Supported
Thermal Design Power (TDP) SKUs 130W, 155W, 185W 130W and 170W
1. OEM responsible for specifying platform-specific retraining interval.
2. Electrical isolation only, no physical add/remove supported.
3. Assume spare is installed.
Intel
Series
Not Supported Supported
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500
Series
1.4 Processor Abstraction Layer
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
require implementation-specific Processor Abstraction Layer (PAL) firmware. PAL
firmware supports processor initialization, error recovery, and other functionality. It
provides a consistent interface to system firmware and operating systems across
processor hardware implementations. The Intel
Developer’s Manual, Volume 2: System Architecture, describes PAL. Platforms must
provide access to the firmware address space and PAL at reset to allow the processors
to initialize.
®
Itanium® Architecture Software
Introduction
The System Abstraction Layer (SAL) firmware contains platform-specific firmware to
initialize the platform, boot to an operating system, and provide runtime functionality.
Further information about SAL is available in the Intel
®
Itanium® Processor Family
System Abstraction Layer Specification.
1.5 Mixing Processors of Different Frequencies and Cache Sizes
All Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series processors and Intel® Itanium® Processor
9500 Series in the same system partition are required to have the same last level
cache size and identical core frequency . Mixing processors of different core frequencies,
cache sizes, and mixing Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series with Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9500 Series is not supported and has not been validated by Intel. Operating
system support for multiprocessing with mixed components should also be considered.
1.6 Terminology
In this document, “the processor” refers to the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
and/or Intel
An ‘_N’ notation after a signal name refers to an active low signal. This means that a
signal is in the active state (based on the name of the signal) when driven to a low
level. For example, when RESET_N is low, a processor reset has been requested. When
NMI is high, a non-maskable interrupt has occurred. In the case of lines where the
name does not imply an active state but describes part of a binary sequence (such as
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series, unless otherwise indicated.
20 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 21

Introduction
address or data), the ‘_N’ notation implies that the signal is inverted. For example,
D[3:0] = ‘HLHL’ refers to a Hex ‘A’, and D [3:0] _N = ‘LHLH’ also refers to a Hex ‘A’ (H
= High logic level, L = Low logic level).
A signal name has all capitalized letters, for example, VCTERM.
A symbol referring to a voltage level, current level, or a time value carries a plain
subscript, for example, Vccio, or a capitalized abbreviated subscript, for example, TCO.
1.7 State of Data
The data contained in this document is subject to change. It is the best information
that Intel is able to provide at the publication date of this document.
1.8 Reference Documents
The reader of this specification should also be familiar with material and concepts
presented in the following documents:
Document Name
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Specification Update
®
Intel
Itanium® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1:
Application Architecture
®
Itanium® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2: System
Intel
Architecture
®
Itanium® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3: Instruction Set Reference
®
Itanium® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 4: IA-32 Instruction Set Reference
®
Itanium® 9300 Series Processor Reference Manual for Software
Intel
Development and Optimization
®
Itanium® 9500 Series Processor Reference Manual for Software
Intel
Development and Optimization
®
Itanium® Processor Family System Abstraction Layer Specification
Intel
®
Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500
Series Platform Design Guide
System Management Bus (SMBus) Specification
Note: Contact your Intel representative or check http://developer.intel.com for the latest
revision of the reference documents.
§
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 21
Page 22

Introduction
22 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 23

Electrical Specifications
T
X
R
X
R
TT
R
TT
R
TT
R
TT
Signal
Signal
2 Electrical Specifications
This chapter describes the electrical specifications of the Intel® Itanium® Processor
9300 Series and 9500 Series processors.
2.1 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® Scalable Memory Interconnect Differential Signaling
The links for Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI) and Intel® Scalable Memory
Interconnect (Intel® SMI) signals use differential signaling. The Intel® SMI bus pins are
referred to as FB-DIMM pins on the package. The termination voltage level for the
processor for uni-directional serial differential links, each link consisting of a pair of
opposite-polarity (D+, D-) signals, is V
SS
.
Termination resistors are provided on the processor silicon and are terminated to V
thus eliminating the need to terminate the links on the system board for the Intel®
QuickPath Interconnect and FB-DIMM signals.
When designing a system, Intel strongly recommends that design teams perform
analog simulations of the Intel
refer to the latest available revision of the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Platform Design Guide.
Figure 2-1 illustrates the active on-die termination (ODT) of these differential signals.
All the differential signals listed in Table 2-1 have ODT resistors. Also included in the
table are the debug signals.
Figure 2-1. Active ODT for a Differential Link Example
®
QuickPath Interconnect and FB-DIMM pins. Please
SS,
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 23
Page 24
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-1. Signals with R
CSI[3:0]R[P/N]Dat[19:0]
CSI[5:4]R[P/N]Dat[9:0]
CSI[3:0]T[P/N]Dat[19:0]
CSI[5:4]T[P/N]Dat[9:0]
CSI[5:0]R[P/N]Clk
CSI[5:0]T[P/N]Clk
FBD0NBICLK[A/B][P/N]0
FBD1NBICLK[C/D][P/N]0
FBD0SBOCLK[A/B][P/N]0
FBD1SBOCLK[C/D][P/N]0
FBD0NBI[A/B][P/N][13:0]
FBD1NBI[C/D][P/N][13:0]
FBD0SBO[A/B][P/N][10:0]
FBD1SBO[C/D][P/N][10:0]
XDPOCPD_N[7:0]
TRIGGER_N[1:0]
XDPOCPFRAME_N
XDPOCP_STRB_IN_N
PRBMODE_REQST_N
XDPOCP_STRB_OUT_N
PRBMODE_RDY_N
TT
Signal Termination
2.2 Signal Groups
VSS
VSS
VCCIO
The signals are grouped by buffer type and similar characteristics as listed in Table 2-2.
The buffer type indicates which signaling technology and specifications apply to the
signals.
Table 2-2. Signal Groups (Sheet 1 of 3)
Signal Group Buffer Type Signals 1, 2, 3
Differential System Reference Clock
Differential CMOS In Differential Pair SYSCLK, SYSCLK_N;
®
QuickPath Interconnect Signal Groups
Intel
Differential Input CSI[3:0]R[P/N]Dat[19:0], CSI[5:4]R[P/N][9:0]
Differential Output CSI[3:0]T[P/N]Dat[19:0], CSI[5:4]T[P/N][9:0],
FB-DIMM Signals
Differential Input FBD0NBICLK[A/B][P/N]0
Differential Output FBD0SBOCLK[A/B][P/N]0
Differential Input FBD0NBI[A/B][P/N][13:0]
Differential Output FBD0SBO[A/B][P/N][10:0]
TAP
SYSUTST_REFCLK_N, SYSUTST_REFCLK
CSI[5:0]R[P/N]CLK
CSI[5:0]T[P/N]CLK
FBD1NBICLK[C/D][P/N]0
FBD1SBOCLK[C/D][P/N]0
FBD1NBI[C/D][P/N][13:0]
FBD1SBO[C/D][P/N][10:0]
24 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 25
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-2. Signal Groups (Sheet 2 of 3)
Signal Group Buffer Type Signals 1, 2, 3
Single-ended CMOS Inputs TCK, TDI, TMS, TRST_N
GTL Open Drain Output TDO
SMBus
Single-ended GTL I/O SMBCLK,
SPD Bus
Single-ended GTL I/O SPDCLK
Setup
Single-ended GTL Input BOOTMODE[1:0], SKTID[2:0]
System Management
Single-ended CMOS Input LRGSCLSYS
Flash ROM Port
Single-ended GTL-open Drain Input FLASHROM_CFG[2:0],
GTL-open Drain Output FLASHROM_CS[3:0]_N, FLASHROM_C LK,
ERROR Bus
Single-ended GTL Open Drain Output
Power-up
Single-ended GTL Input PWRGOOD, RESET_N
Thermal
Single-ended GTL-Open Drain Output
VID Port
4
Single-ended CMOS Output VID_VCCCORE[6:0], VID_VCCCACHE[5:0],
SVID Port
Single-ended GTL Output SVID_CLK
GTL Input
GTL Input
(Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series)
4
(Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series)
GTL I/O SVD_DATIO
GTL Input SVID_ALERT_N
SMBDAT
SPDDAT
FLASHROM_DATI
FLASHROM_DATO, FLASHROM_WP_N
ERROR[0]_N, ERROR[1]_N
MEM_THROTTLE_L
PROCHOT_N, THERMTRIP_N, THERMALERT_N
FORCEPR_N
VID_VCCUNCORE[6:0]
Voltage Regulator
Single-ended Open Collector/Drain Output VR_THERMTRIP_N, VRPWRGD (Intel® Itanium®
Voltage Regulator Control
Single-ended CMOS Input
4
4
GTL Input
Open Collector/Drain Output
Processor 9300 Series processor), VR_READY (Intel
®
Itanium
Processor 9500 Series processor), VR_FAN_N
VROUTPUT_ENABLE0
VR_THERMALERT_N
VR_THERMTRIP_N, VRPWRGD, VR_FAN_N
®
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 25
Page 26
Notes:
Table 2-2. Signal Groups (Sheet 3 of 3)
Signal Group Buffer Type Si gna l s 1, 2, 3
Debug
GTL I/O XDPOCPD_N[7:0],TRIGGER_N[1:0]
Single-ended
Power Supplies
V
CC33_SM
PIROM
GTL Input XDPOCP_STRB_IN_N, PRBMODE_REQST_N
GTL Output XDPOCP_STRB_OUT_N, PRBMODE_RDY_N
Core V
Uncore V
Cache (Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series)
Analog V
I/O V
Stand-by V
Pins
Input PIR_SCL
I/O PIR_SDA
Input PIR_A0
Input PIR_A1
Input SM_WP
XDPOCPFRAME_N
4
CCCORE
CCUNCORE
V
CCCACHE
CCA
CCIO
CC33_SM
4
4
Electrical Specifications
1. CMOS signals have a reference voltage (Vref) equal to VCCIO/2.
2. GTL signals have a reference voltage (Vref) equal to VCCIO*(2/3).
3. All single-ended buffer types, including inputs, outputs and input/outputs, include an on-die pull up resistor
between 4 kOhms and 8.7 kOhms. Recommended values for external pull-downs on the inputs and input/
output signals must meet the V
specification for that buffer.
il
2.3 Reference Clocking Specifications
The processor has one input reference clock, SYSCLK/SYSCLK_N for the Intel® QPI
interface. The processor timing specified in this section is defined at the processor pins
unless otherwise noted.
Table 2-3. Intel® QuickPath Interconnect/Intel® Scalable Memory Interconnect
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Units Notes
fsysclk (ssc-off) System clock frequency
Fsyclk (scc-on) System clock frequency 132.62 132.99 133.37 MHz
ER
sysclk-diff-Rise,
ER
sysclk-diff-Fall
T
sysclk_dutycycle
C
i-CK
VH Differential High Input Voltage 0.15 V 3
VL Differential Low Input Voltage -0.15 V 3
V
Cross
V
Cross_delta
V
RB-Diff
Reference Clock Specifications (Sheet 1 of 2)
133.31 133.33 133.34 MHz
Differential Rising and Falling Edge
Rates
Duty cycle of Reference clock 40 60 % period 3
Clock Input Capacitance 0.5 2.0 pf
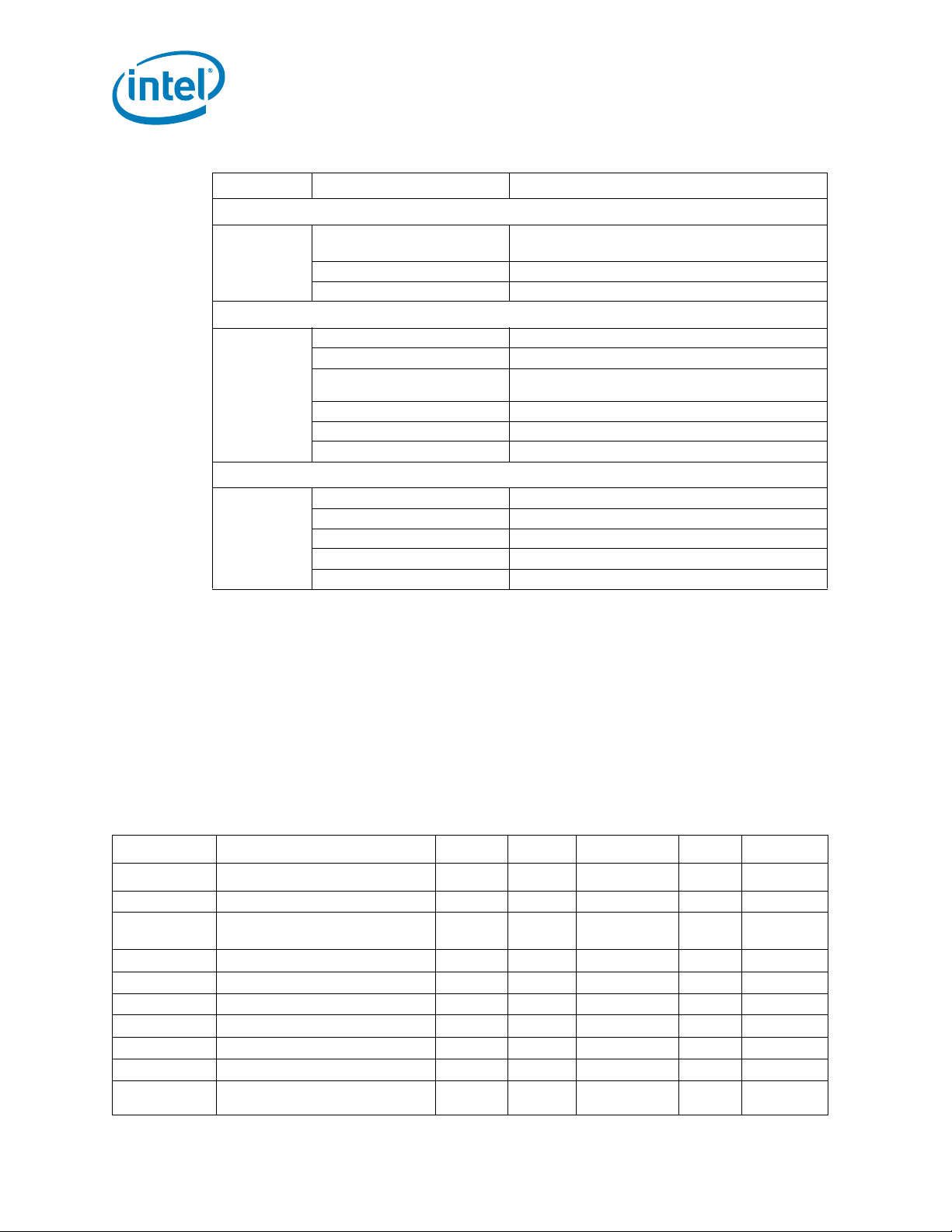
Absolute crossing point 0.25 0.35 0.55 V 1, 5, 6
Peak-peak variation 140 mv 1, 5, 7
Differential Ringback voltage
threshold
1.0 4.0 V/ns 3,4
-100 100 mV 3, 10
26 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 27
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-3. Intel® QuickPath Interconnect/Intel® Scalable Memory Interconnect
Reference Clock Specifications (Sheet 2 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Units Notes
T
Stable
T
REFCLK-JITTER-RMS-
ONEPLL
Note:
1. Measurement taken from single-ended waveform.
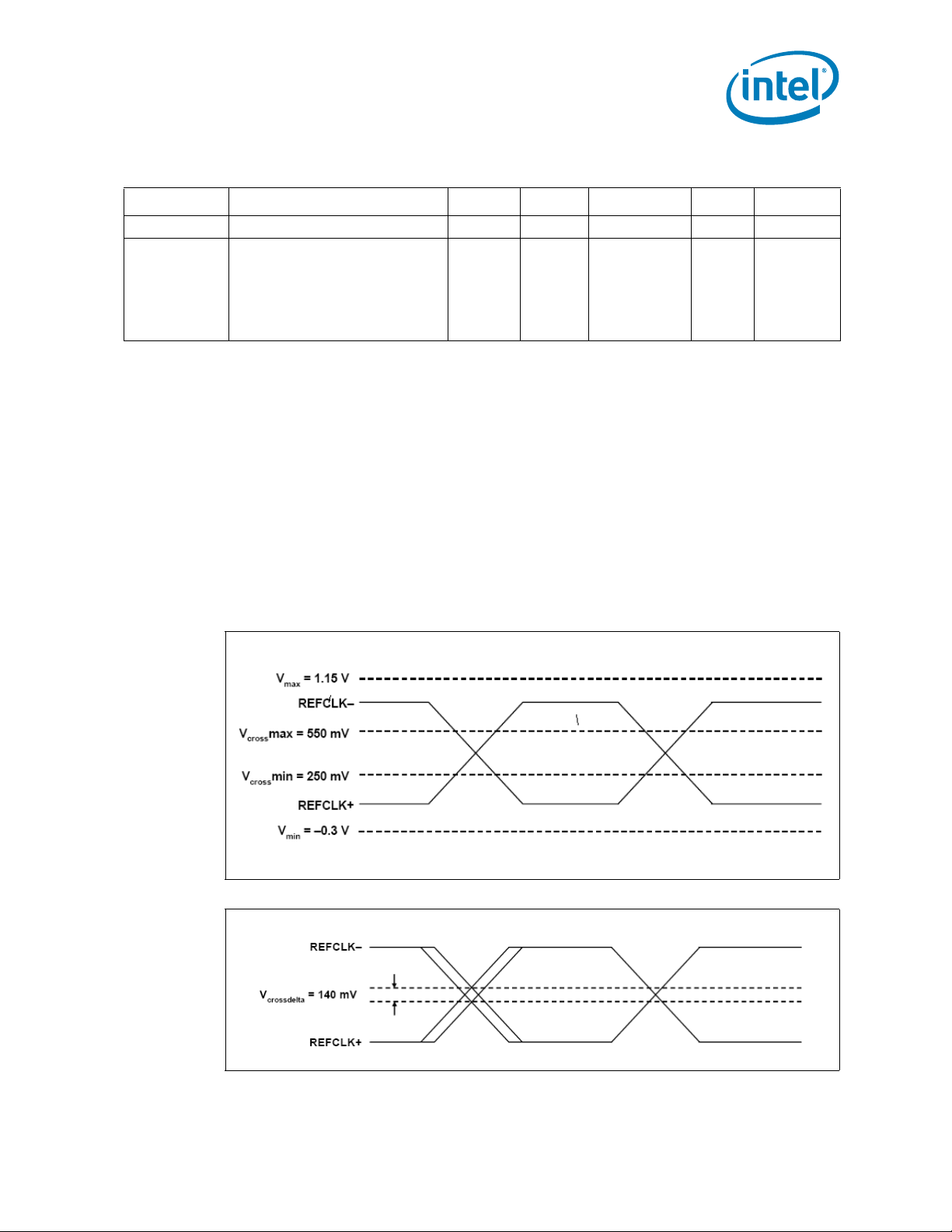
2. The given PLL parameters are: Underdamping (z) = 0.8 an d natural frequency = fn = 7.86E6 Hz; wn = 2 *fn. N_minUI = 12
for Intel
3. Measurement taken from differential waveform.
4. Measured from -150 mV to +150 mV on the differential waveform (derived from SYSCLK minus SYSCLK_N). The signal must
be monotonic through the measurement region for rise and fall time. The 300 mV measurement window is centered on the
differential zero crossing. See Figure 2-4.
5. Measured at crossing point where the instantaneous voltage value of the rising edge SYSCLK equals the falling edge
SYSCLK_N. See Figure 2-2.
6. Refers to the total variation from the lowest crossing point to the highest, regardless of which edge is crossing. Refers to all
crossing points for this measurement. See Figure 2-3.
7. Defined as the total variation of all crossing voltages of Rising SYSCLK and falling SYSCLK_N. This is the maximum allowed
variance in Vcross for any particular system. See Figure 2-2.
8. Defined as the maximum instantaneous voltage including overshoot. See Figure 2-2.
9. Defined as the minimum instantaneous voltage including undershoot. See Figure 2-2.
10. T
is the time the differential clock must maintain a minimum ±150 mV differential voltage after rising/falling edges
Stable
before it is allowed to droop back into the VRB ±100 mV range. See Figure 2-5.
Allowed time before ringback 500 ps 3, 10
Accumulated rms jitter over n UI of a
given PLL model output in response to
the jittery reference clock input. The
PLL output is generated by conv olving
the measured reference clock phase
jitter with a given PLL transfer
function. Here n=12.
®
QuickPath Interconnect 4.8 Gt/s channel.
0.5 ps 2
Figure 2-2. Single-ended Maximum and Minimum Levels and V
Figure 2-3. V
cross-delta
Definition
cross
Levels
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 27
Page 28
Figure 2-4. Differential Edge Rate Definition
REFCLK
diff
ER
Refclk-diff-Fall
ER
Refclk-diff-Rise
V
Refclk-diff-ih
= 150 mV
V
Refclk-diff-il
= –150 mV
0.0 V
REFCLK
di ff
V
RB- di ff max
100 mV
0.0 V
V
RB-diff min
= – 100 mV
V
Ref cl k-diff-ih
= 150 mV
V
Ref cl k-diff-ih
= – 150 mV
T
Sta bl e
T
Stab le
Electrical Specifications
Figure 2-5. VRB and T
Stable
Definitions
2.4 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® SMI Signaling Specifications
.
2.4.1 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Intel® QuickPath
Interconnect and Intel
The applicability of this section applies to Intel® QPI for the Intel® Itanium® Processor
9300 Series. This section contains information for Intel
(1/4 frequency of the reference clock) and processor’s normal operating frequency, 4.8
GT/s, for Intel
®
QPI and Intel® SMI.
®
SMI Specifications for 4.8 GT/s
®
QPI slow boot up speed
28 Intel
®
For Intel
QPI slow boot up speed, the signaling rate is defined as 1/4 the rate of the
system reference clock. For example, a 133 MHz system reference clock would have a
forwarded clock frequency of 33.33 MHz and the signaling rate would be 66.67 MT/s.
The transfer rates available for the processor are shown in Table 2-4. Transmitter and
receiver parameters for Intel
®
QPI slow mode, Intel® QPI and Intel® SMI are shown in
Table 2-5 and Table 2-6 respectively.
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 29
Electrical Specifications
Notes:
Table 2-4. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Clock Frequency Table
Intel® QuickPath Interconnect
Forwarded Clock Frequency
33.33 MHz 66.66 MT/s (see note 1
2.40 GHz 4.8 GT/s
1. This speed is the 1/4 SysClk Frequency.
Intel® QuickPath Interconnect Data
Transfer Rate
)
Table 2-5. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Transmitter Parameter Values for
Intel
®
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel SMI Channels @ 4.8 GT/s (Sheet 1 of
2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Units Notes
UI
avg
N
MIN-UI-Validation
T
slew-rise-fall-pin
V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
R
TX
Z
TX_LINK_DETECT
V
TX_LINK_DETECT
T
DATA_TERM_SKEW
Intel® QPI
T
DATA_TERM_SKEW
Intel® SMI
T
INBAND_RESET_SENSE
T
CLK_DET
T
SYSCLK-TX-VARIABILITY
TX
EQ-BOOST
V
TX-CM-PIN
V
TX-CM-RIPPLE-PIN
Average UI size at 4.8 GT/s 208.33 ps
# of UI over which the eye mask voltage and
timing spec needs to be validated
Defined as the slope of the rising or falling
waveform as measured between ±100 mV of
the differential transmitter output, data or
clock
1E6
612V/ns
Transmitter differential swing 900 1300 mV
Transmitter termination resistance 37.4 47.6 Ω 4
Link Detection Resistor 500 2000 Ω
Link Detection Resistor Pull-up Voltage max VCCIO V
Skew between first to last data termination
meeting Z
Skew between first to last data termination
meeting Z
Time taken by inband reset detector to sense
Inband Reset
Time taken by clock detector to observe clock
stability
RX_LOW_CM_DC
RX_LOW_CM_DC
Phase variability between re ference Clk (at Tx
600 UI 2
780 UI 2
8k 256k UI
8k 256k UI
500 ps
input) and Tx output.
Voltage ratio between the cursor and the
post-cursor when transmitting successive
ones
025dB3
T ransmitte r data or clock co mmon mode level 23 27 %
Transmitter data or clock common mode
ripple
014%8,9
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 29
Page 30
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-5. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Transmitter Parameter Values for
Intel
®
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel SMI Channels @ 4.8 GT/s (Sheet 2 of
2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Units Notes
TX
DUTY-CYCLE-PIN
Transmitter clock or data duty cycle at the
pin. T rans mit duty cy cle at the pin, defined as
UI to UI jitter as specified by the Intel
®
QPI
Electrical Specification, Rev 1.0.
T
TX-DATA-CLK-SKEW-PIN
TX
ACC-JIT-N_UI-1E-9
TX
JITUI-UI-1E-9PIN
RL
TX-DIFF
RL
TX-DIFF
Delay of any data lane relative to clock lane,
as measured at Tx output
Peak-to-peak accumulated jitter out of an y TX
data or clock over 0<= n <= N UI where
N=12, measured with 1E-9 probability.
Transmitter clock or data UI-UI jitter at 1E-9
probability.
Transmitter Differential return loss from
50MHz to 2GHz
Transmitter Differential return loss from
2GHz to 4GHz
Notes:
1. Parameter value at full Intel
2. Stagger offset = 0xF.
3. See Figure 2-6.
4. The termination small signal resistance; tolerance over the entire signalling voltage range shall not exceed ±5 ohms.
5. Requires Matlab script.
6. Refer to Intel
definition is used herein, where the value of UI-UI DCD = 2*UI DCD.
7. See Figure 2-7.
8. Applies to Vtx-diff-pp-pin.
9. Peak-to-peak value of the ripple.
®
QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI) - Electrical Specifications for calculation of this value. Note that UI to UI.
®
QPI Refclk.
-0.076 0.076 UI-UI 6
-0.5 0.5 UI 1,2
00.18UI5
00.17UI5
-10 dB 7
-6 dB 7
Table 2-6. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Receiver Parameter Values for Intel®
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel
®
SMI Channels @ 4.8 GT (Sheet 1 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Units Notes
R
RX
T
Rx-data-clk-skew-pin
T
Rx-data-clk-skew-pin
RL
RX-DIFF
RL
RX-DIFF
V
Rx-data-cm-pin
V
Rx-data-cm-ripple-
pin
V
Rx-clk-cm-pin
V
Rx-clk-cm-ripple-pin
V
RX-eye-data-pin
V
RX-eye-clk-pin
RX termination resistance 37.4 47.6 Ω 3
Delay of any data lane relative to the clock lane, as
measured at the end of Tx+ channel. This parameter is
a collective sum of effects of data clock mismatches in
Tx and on the medium connecting Tx and Rx.
Delay of any data lane relative to the clock lane, as
measured at the end of Tx+ channel. This parameter is
a collective sum of effects of data clock mismatches in
Tx and on the medium connecting Tx and Rx.
-0.5 3.5 UI 2
0.48 0.52 UI 1
Receiver differential return loss from 50 MHz to 2 GHz -10 dB 6
Receiver differential return loss from 2GHz to 4GHz -6 dB 6
Receiver data common mode level 125 350 mV 2
Receiver data common mode ripple 0 100 mV
p-p
Receiver clock common mode level 175 350 mV
Receiver clock common mode ripple 0 100 mV
p-p
Minimum eye height at pin for data 200 mV 4
Minimum eye height at pin for clk 225 mV 5
30 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 31

Electrical Specifications
C
-1
C
2
C
0
C
1
Vsust
Vpre
Vpost
Vpre = A(C
-1 -C0-C1-C2
)
Vsust = A(C
-1
+ C0+ C1+ C2 )
Vpost = A(C
-1
+ C0-C1-C2)
A
-A
Vpost- Vpre – Vsust = |C
-1
| + |C0|+ |C1|+ |C2| = 1
Example: A=500mV, C
-1
= -0.035, C0= 0.685, C1= -0.28, C2= 0
Vpre = 0.500(-0.035 – 0.685 + 0.28) = 0.5(-0.44) = -220mV
Vpost = 0.500(-0.035 + 0.685 + 0.28) = 0.5(0.93) = 465mV
Vsust
= 0.500(-0.035 + 0.685 – 0.28) = 0.5(0.37) = 185m V
Peaking = 465/185 = 251
%
C
-1
C
0
C
1
C
2
0
%Peaking = V post/Vsust
C
0
= 1 – sum of abs value of other coeficents
TXEQ-BOOST = 20log(Vpost/Vsust) = 20log(465/185) = 8dB
C
-1
C
2
C
0
C
1
Vsust
Vpre
Vpost
Vpre = A(C
-1 -C0-C1-C2
)
Vsust = A(C
-1
+ C0+ C1+ C2 )
Vpost = A(C
-1
+ C0-C1-C2)
A
-A
Vpost- Vpre – Vsust = |C
-1
| + |C0|+ |C1|+ |C2| = 1
Example: A=500mV, C
-1
= -0.035, C0= 0.685, C1= -0.28, C2= 0
Vpre = 0.500(-0.035 – 0.685 + 0.28) = 0.5(-0.44) = -220mV
Vpost = 0.500(-0.035 + 0.685 + 0.28) = 0.5(0.93) = 465mV
Vsust
= 0.500(-0.035 + 0.685 – 0.28) = 0.5(0.37) = 185m V
Peaking = 465/185 = 251
%
C
-1
C
0
C
1
C
2
0
%Peaking = V post/Vsust
C
0
= 1 – sum of abs value of other coeficents
TXEQ-BOOST = 20log(Vpost/Vsust) = 20log(465/185) = 8dB
Table 2-6. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Receiver Parameter Values for Intel®
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel
®
SMI Channels @ 4.8 GT (Sheet 2 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Units Notes
T
RX-eye-pin
QPI BER
SMI BER
Notes:
1. Parameter value at 1/4 Intel
2. Parameter value at full Intel
3. The termination small signal resistance; tolerance over the entire signalling voltage range shall not exceed ±5 ohms with
4. HVM guaranteed error free value for stressed PRBS signaling across PVT. Link BER is the dominant spec of which eye
5. HVM guaranteed error free value for stressed ‘1010 signaling across PVT. Link BER is the dominant spec of which eye
Lane
Lane
regard to the average of the values measured in the high output voltage state and the low output voltage state for that pin.
dimensions are only one factor, and improving another factor could compensate for eye height or width.
dimensions are only one factor, and improving another factor could compensate for eye height or width.
Minimum eye width at pin for clk and data 0.6 UI 4
Bit Error Rate per lane valid for 4.8 and 6.4 GT/s 1.0E-14 Events
Bit Error Rate per lane valid for 4.8 and 6.4 GT/s 1.0E-12 Events
®
QPI Refclk.
®
QPI Refclk.
6. See Figure 2-8.
Figure 2-6. TX Equalization Diagram
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 31
Page 32

Figure 2-7. TX Return Loss
Figure 2-8. RX Return Loss
Electrical Specifications
2.4.2 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Requirements for Intel® QuickPath Interconnect for 4.8 and 6.4 GT/s
The applicability of this section applies to Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series. This
section contains information for slow boot up speed (1/4 frequency of the reference
clock), 4.8 GT/s, and 6.4 GT/s, for Intel
For Intel® QPI slow boot up speed, the signaling rate is defined as 1/4 the rate of the
system reference clock. For example, a 133 MHz system reference clock would have a
forwarded clock frequency of 33.33 MHz and the signaling rate would be 66.67 MT/s.
32 Intel
®
QPI and Intel® SMI.
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 33

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
The transfer rates available for the processor are shown in Table 2-7. Transmitter and
receiver parameters for Intel® QPI slow mode, Intel® QPI and Intel® SMI are shown in
Table 2-8 and Table 2-9 respectively.
Table 2-7. Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Clock Frequency Table
Intel® QuickPath Interconnect
Forwarded Clock Frequency
33.33 MHz 66.66 MT/s (see note 1)
2.40 GHz 4.8 GT/s
3.2 GHz 6.4 GT/s
1. This speed is the 1/4 SysClk Frequency.
The applicability of this section applies to Intel
Intel® QuickPath Interconnect Data
Transfer Rate
®
QPI for the Intel® Itanium® Processor
9500 Series. This section contains information for slow boot up speed (1/4 frequency of
the reference clock), 4.8 GT/s, and 6.4 GT/s.
Specifications for link speed independent specifications are called out in Table 2-8.
Electrical specifications for Transmit and Receive for 4.8 GT/s are captured in Table 2-9
and for 6.4 GT/s are captured in Table 2-10.
Table 2-8. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Link Speed Independent Specifications
(Sheet 1 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Unit Notes
UIavg Average UI size at “G”
T
slew-rise-fall-pin
ΔZ
TX_LOW_CM_DC
ΔZ
RX_LOW_CM_DC
N
MIN-UI-Validation
Z
TX_HIGH_CM_DC
Z
RX_HIGH_CM_DC
GT/s (Where G = 4.8,
6.4, and so on)
Defined as the slope of
the rising or falling
waveform as measured
between ±100mV of the
differential transmitter
output, for any data or
clock
Defined as:
(max(Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC
min(Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC))
Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC
in %, over full range of Tx
single ended voltage
Defined as:
(max(Z
min(Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC))
Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC
in %, over full range of Tx
single ended voltage
# of UI over which the
eye mask voltage and
timing spec needs to be
validated
Single ended DC
impedance to GND for
either D+ or D- of any
data bit at Tx
Single ended DC
impedance to GND for
either D+ or D- of any
data bit at Rx
expressed
TX_LOW_CM_DC
expressed
0.999 *
nominal
920V/nsec
-6 6 % of
) -
/
-6 0 6 % of
) -
/
1,000,000
4k
4k
1000/G 1.001 *
nominal
psec
Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC
Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC
Ω
Ω
1
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 33
Page 34
Electrical Specifications
Notes:
Table 2-8. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Link Speed Independent Specifications
(Sheet 2 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Unit Notes
Z
TX_LINK_DETECT
V
TX_LINK_DETECT
T
DATA_TERM_SKEW
T
INBAND_RESET_
SENSE
Tclk
_DET
T
CLK_FREQ_DET
T
Refclk-Tx-Variability
T
Refclk-Rx-Variability
L
D+/D-RX-Skew
BER
Lane
Link Detection Resistor 500 2000
Link Detection Resistor
Pull-up Voltage
Skew between first to last
data termination meeting
Z
RX_LOW_CM_DC
Time taken by inband
reset detector to sense
Inband Reset
Time taken by clock
detector to observe clock
stability
Time taken by clock
frequency detector to
decide slow vs.
operational clock after
stable clock
Phase variability between
reference Clk (at Tx
input) and Tx output.
Phase variability between
reference Clk (at Rx
input) and Rx output.
Phase skew between D+
and D- lines for any data
bit at Rx
Bit Error Rate per lane
1000 psec
max VCCIO V
128 UI
1.5 μs
20K UI
32 Reference
500 psec
0.03 UI
1.0E-14 Events
valid for 4.8 and 6.4 GT/s
Ω
Clock Cycles
1. Used during initialization. It is the state of “OFF” condition for the receiver when o nly the minimum termination
is connected.
Table 2-9. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and Receiver Pa rameter
Values for Intel
®
QPI Channel at 4.8 GT/s (Sheet 1 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Unit Notes
V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC
Z
RX_LOW_CM_DC
V
Tx-cm-dc-pin
V
Tx-cm-ac-pin
TX
duty-pin
TX
jitUI-UI-1E-7-pin
TX
jitUI-UI-1E-9-pin
Transmitter differential swing 900 1400 mV 1
DC resistance of Tx terminations
at half the single ended swing
(which is usually 0.25*V
) bias point
pin
DC resistance of Rx terminations
at half the single ended swing
(which is usually 0.25*V
) bias point
pin
Transmitter output DC common
mode, defined as average of V
and V
D-
Transmitter output AC common
mode, defined as ((V
V
Tx-cm-dc-pin
)
Tx-diff-pp-
Tx-diff-pp-
+ VD-)/2 -
D+
37.4 50 Ω
37.4 50 Ω
0.23 0.27 Fraction of
D+
-0.0375 0.0375 Fraction of
V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
Average of UI-UI jitter -0.055 0.055 UI
UI-UI jitter measured at Tx output
pins with 1E-7 probability
UI-UI jitter measured at Tx output
pins with 1E-9 probability.
-0.075 0.075 UI
-0.085 0.085 UI
2
34 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 35

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-9. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and Receiver Parameter
Values for Intel
®
QPI Channel at 4.8 GT/s (Sheet 2 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Unit Notes
TX
clk-acc-jit-N_UI-1E-7
p-p accumulated jitter out of
transmitter over 0 <= n <= N UI
where N=12, measured with 1E-7
00.15UI
probability.
TX
clk-acc-jit-N_UI-1E-9
T
Tx-data-clk-skew-pin
p-p accumulated jitter out of
transmitter over 0 <= n <= N UI
where N=12, measured with 1E-9
probability.
Delay of any data lane relative to
clock lane, as measured at Tx
00.17UI
-0.5 0.5 UI
output
V
Rx-diff-pp-pin
Voltage eye opening at the end of
Tx+ channel for any data or clock
channel measured with a
cumulative probability of 1E-9
225 1200 mV
(UI).
T
Rx-diff-pp-pin
T
Rx-data-clk-skew-pin
Forward CLK Rx input voltage
V
Rx-CLK
V
Rx-cm-dc-pin
V
Rx-cm-ac-pin
Timing eye opening at the end of
Tx+ channel for any data or clock
channel measured with a
cumulative probability of 1E-9 (UI)
Delay of any data lane relative to
the clock lane, as measured at the
end of Tx+ channel. This
parameter is a collective sum of
effects of data clock mismatches
in Tx and on the medium
connecting Tx and Rx.
sensitivity (differential pp)
DC common mode ranges at the
Rx input for any data or clock
channel
AC common mode ranges at the
Rx input for any data or clock
0.63 1 UI
-1 3 UI
180 mV
125 350 mV
-50 50 mV 2
channel, defined as:
((V
D+
+ VD-/2 - V
RX-cm-dc-pin
)
Notes:
1. 1300 mVpp swing is recommended when CPU to CPU or CPU to IOH length is within 2” of PDG max trace
length. Note that default value is 1100 mVpp.
2. Measure AC CM noise at the TX and decimate to its spectral components. For all spectral components above
3.2 GHz, apply the attenuation of the channel at the appropriate frequency. If the resultant AC CM at the
receiver is met after taking out the appropriate spectral components meets the RX AC CM spec then we can
allow the transmitter AC CM noise to pass.
Table 2-10. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and Receiver Parameter
Values for Intel
®
QPI at 6.4 GT/s (Sheet 1 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Unit Notes
V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC
Z
RX_LOW_CM_DC
V
Tx-cm-dc-pin
Transmitter differential swing 900 1400 mV 1
DC resistance of Tx terminations
at half the single ended swing
(which is usually 0.25*V
) bias point
pin
DC resistance of Rx terminations
at half the single ended swing
(which is usually 0.25*V
) bias point
pin
Tx-diff-pp-
Tx-diff-pp-
Transmitter output DC common
mode, defined as average of V
and V
D-
37.4 50 Ω
37.4 50 Ω
0.23 0.27 Fraction of
D+
V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
4
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 35
Page 36
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-10. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and Receiver Pa rameter
Values for Intel
®
QPI at 6.4 GT/s (Sheet 2 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Unit Notes
V
Tx-cm-ac-pin
TX
duty-pin
TX
jitUI-UI-1E-7-pin
TX
jitUI-UI-1E-9-pin
TX
clk-acc-jit-N_UI-1E-7
Transmitter output AC common
mode, defined as ((V
V
Tx-cm-dc-pin
)
+ VD-)/2 -
D+
-0.0375 0.0375 Fraction of
Average of absolute UI-UI jitter -0.06 0.06 UI
UI-UI jitter measured at Tx output
-0.085 0.085 UI 3
pins with 1E-7 probability.
UI-UI jitter measured at Tx output
pins with 1E-9 probability.
p-p accumulated jitter out of
transmitter over 0 <= n <= N UI
where N=12, measured with 1E-7
-0.09 0.09 UI
00.15UI
V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
2
probability.
TX
clk-acc-jit-N_UI-1E-9
T
Tx-data-clk-skew-pin
V
Rx-diff-pp-pin
p-p accumulated jitter out of
transmitter over 0 <= n <= N UI
where N=12, measured with 1E-9
probability.
Delay of any data lane relative to
clock lane, as measured at Tx
output
Voltage eye opening at the end of
Tx+ channel for any data or clock
channel measured with a
cumulative probability of 1E-9
00.17UI
-0.5 0.5 UI
155 1400 mV 2, 5
(UI).
T
Rx-diff-pp-pin
T
Rx-data-clk-skew-pin
Forward CLK Rx input voltage
V
Rx-CLK
V
Rx-cm-dc-pin
V
Rx-cm-ac-pin
Timing eye opening at the end of
Tx+ channel for any data or clock
channel measured with a
cumulative probability of 1E-9 (UI)
Delay of any data lane relative to
the clock lane, as measured at the
end of Tx+ channel. This
parameter is a collective sum of
effects of data clock mismatches
in Tx and on the medium
connecting Tx and Rx.
sensitivity (differential pp)
DC common mode ranges at the
Rx input for any data or clock
channel
AC common mode ranges at the
Rx input for any data or clock
channel, defined as:
+ VD-/2 - V
((V
D+
RX-cm-dc-pin
0.61 1 UI
-1 4 UI
150 mV
90 350 mV
-50 50 mV
)
Notes:
1. 1300 mVpp swing is recommended when CPU to CPU or CPU to IOH length is within 2” of PDG max trace
length. Note that default value is 1200 mVpp.
2. Measure AC CM noise at the TX and decimate to its spectral components. For all spectral components above
3.2 GHz, apply the attenuation of the channel at the appropriate frequency. If the resultant AC CM at the
receiver is met after taking out the appropriate spectral co mponents meets the RX AC CM spec t hen we can
allow the transmitter AC CM noise to pass.
3. Measured with neighboring lines being quiet and the remaining lines toggling PRBS patterns.
4. DC CM can be relaxed to 0.20 and 0.30 Vdiffp-p swing if RX has wide DC common mode range.
5. Based on transmitting a PRBS pattern.
36 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 37

Electrical Specifications
2.4.3 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Processor Requirements for Intel® SMI Specifications for 6.4 GT/s
This section defines the high-speed differential point-to-point signaling link for Intel®
®
SMI for the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series. The link consists of a transmitter
and a receiver and the interconnect between them. The specifications described in this
®
section covers 6.4 Gb/s operation. The parameters for Intel
SMI at 6.4 GT/s and
lower are captured in Table 2-11 and the PLL specification for transmit and receive are
captured in Table 2-12.
Table 2-11. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and Receiver Parameter
Values for Intel
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Unit Not es
V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
Z
TX_LOW_CM_DC
Z
RX_LOW_CM_DC
V
Tx-diff-pp-CLK-pin
V
Tx-cm-dc-pin
V
Tx-cm-ac-pin
TX
duty-UI-pin
TX1UI-Rj-NoXtalk-pin
TX1UI-Dj-NoXtalk--pin
TXN-UI-Rj-NoXtalkpin
TXN-UI-Dj-NoXtalkpin
T
Tx-data-clk-skew-pin
T
Rx-data-clk-skew-pin
Forward CLK Rx input voltage sensitivity
V
Rx-CLK
Transmitter differential swing 800 1200 mV
DC resistance of Tx terminations at half
the single ended swing (which is usually
0.25*V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
DC resistance of Rx terminations at half
the single ended swing (which is usually
0.25*V
Tx-diff-pp-pin
Transmitter differential swing using a CLK
like pattern
Transmitter output DC common mode,
defined as average of V
Transmitter output AC common mode,
defined as ((V
This is computed as absolute difference
between average value of all UI with that
of average of odd UI, which in magnitude
would equal absolute difference between
average of all UI and average of all even
UI.
Rj value of 1-UI jitter. With X-talk off, but
on-die system like noise present. This
extraction is to be done after software
correction of DCD
pp Dj value of 1-UI jitter. With X-talk off,
but on-die system like noise present.
Rj value of N-UI jitter. With X-talk off, but
on-die system like noise present. Here 1
< N < 9.This extraction is to be done
after software correction of DCD
pp Dj value of N-UI jitter. With X-talk off,
but on-die system like noise present.
Here 1 < N < 9.Dj here indicated Djdd of
dual-dirac fitting, after software
correction of DCD
Delay of any data lane relative to clock
lane, as measured at Tx output
Delay of any data lane relative to the
clock lane, as measured at the end of Tx+
channel. This parameter is a collective
sum of effects of data clock mismatches
in Tx and on the medium connecting Tx
and Rx.
(differential pp)
®
SMI at 6.4 GT/s and lower (Sheet 1 of 2)
37.4 50 Ω
) bias point
37.4 50 Ω
) bias point
0.9*min(VTxdiff-pp-pin)
0.23 0.27 Fraction of
-0.0375 0.0375 Fraction of
)
0 0.018 UI
0 0.008 UI 2
-0.01 0.01 UI 2
0 0.012 UI 2
-0.04 0.04 0.2 UI 2
-0.5 0.5 UI
-1 3.5 UI
+ VD-)/2 - V
D+
D+
and V
Tx-cm-dc-pin
D-
max(VTxdiff
-pp-pin)
150 mV
mV 1
V
pin
V
pin
Tx-diff-pp-
3
Tx-diff-pp-
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 37
Page 38

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-11. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Transmitter and Receiver Pa rameter
Values for Intel
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Unit Notes
VRx-Vmargin
TRx-Tmargin
V
Rx-cm-dc-pin
V
Rx-cm-ac-pin
Notes:
1. This is the swing specification for the forwarded CLK output. Note that this specification will also have to be suitably deembedded for package/PCB loss to translate the value to the pad, since there is a significant variation between traces in a
setup.
2. While the X-talk is off, on-die noise similar to that occurring with all the transmitter and receiver lanes toggling will still need
to be present. When a socket is not present in the transmitter measurement setup, in many cases the contribution of the
cross-talk is not significant or can be estimated within tolerable error even with all the transmitter lanes sending patterns.
Therefore for all Tx measurements, use of a socket should be avoided. The contribution of cross-talk may be significant and
should be done using the same setup at Tx and compared against the expectations of full link si gnaling. Note that there may
be cases when one of Dj and Rj specs is met and another violated in which case the signaling analysis should be ran to
determine link feasibility.
3. DC CM can be relaxed to 0.20 and 0.30 Vdiffp-p swing if RX has wide DC common mode range.
Any data lane Rx input voltage
(differential pp) measured at BER=1E-9
Timing width for any data lane using
repetitive patterns and clean forwarded
CLK, measured at BER=1E-9
DC common mode ranges at the Rx input
for any data or clock channel, defined as
average of VD+ and VD-.
AC common mode ranges at the Rx input
for any data or clock channel, defined as:
+ VD-/2 - V
((V
D+
®
SMI at 6.4 GT/s and lower (Sheet 2 of 2)
100 mV
0.8 UI
125 350 mV
-50 50 mV
RX-cm-dc-pin
)
Table 2-12. PLL Specification for TX and RX
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Notes
F
PLL-BW_TX-RX
JitPk
TX-RX
-3dB bandwidth 4 16 MHz
Jitter Peaking 3 dB
2.5 Processor Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 2-13 specifies absolute maximum and minimum ratings for the Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series. Within operational maximum and minimum limits, the
processor functionality and long-term reliability can be expected. The processor
maximum ratings listed in Table 2-13 are applicable for the 130 W, 155 W, and 185 W
parts.
Table 2-14 specifies absolute maximum and minimum ratings for the Intel
Processor 9500 Series. Within operational maximum and minimum limits, the
processor functionality and long-term reliability can be expected. The processor
maximum ratings listed in Table 2-14 are applicable for the 130 W and 170 W parts.
At conditions outside operational maximum ratings, but within absolute maximum and
minimum ratings, neither functionality nor long-term reliability can be expected. If a
device is returned to conditions within operational maximum and minimum ratings
after having been subjected to conditions outside these limits, but within the absolute
maximum and minimum ratings, the device may be functional, but with its lifetime
degraded depending on exposure to conditions exceeding the functional operation
condition limits.
®
Itanium®
38 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 39
Electrical Specifications
At conditions exceeding absolute maximum and minimum ratings, neither functionality
nor long-term reliability can be expected. Moreover, if a device is subjected to these
conditions for any length of time, then, when returned to conditions within the
functional operating condition limits, it will either not function, or its reliability will be
severely degraded.
Although the processor contains protective circuitry to resist damage from static
electric discharge, precautions should always be taken to avoid high static voltages or
electric fields.
2.5.1 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Absolute Maximum Ratings
®
Table 2-13. Intel
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Notes
V
CCCORE
V
CCUNCORE
V
CCA
V
CCIO
V
CC33_SM
Notes:
1. For functional operation, all processor electrical, signal quality, mechanical, and thermal specifications must be satisfied.
2. Overshoot and undershoot voltage guidelines for input, output, and I/O signals are outlined in Section 2.6.3. Excessive
overshoot or undershoot on any signal will likely result in permanent damage to the processor.
Processor core supply voltage with respect to VSS –0.3 1.55 V 1,2
Processor uncore suppl y voltage with respect to VSS –0.3 1.55 V 1,2
Processor Analog Supply Voltage with respect to VSS –0.3 1.89 V 1,2
Processor I/O Supply Voltage with respect to VSS –0.3 1.55 V 1,2
Processor 3.3 V Supply Voltage with respect to VSS -0.3 3.465 V 1,2
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Absolute Maximum Ratings
2.5.2 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 2-14. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Processor Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units
V
CCCORE
V
CCUNCORE
V
CCA
V
CCIO
V
CC33_SM
Notes:
1. For functional operation, all processor electrical, signal quality, mechanical, and thermal specifications must be satisfied.
2. Overshoot and undershoot voltage guidelines for input, output, and I/O signals are outlined in Section 2.6.4. Excessive
overshoot or undershoot on any signal will likely result in permanent damage to the processor.
Processor core supply voltage with respect to VSS -0.3 1.42 V 1,2
Processor uncore supply voltage with respect to VSS -0.3 1.42 V 1,2
Processor Analog Supply Voltage with respect to VSS -0.3 1.89 V 1,2
Processor I/O Supply Voltage with respect to VSS -0.3 1.55 V 1,2
Processor 3.3 V Supply Voltage with respect to VSS -0.3 3.465 V 1,2
Notes
2.6 Processor DC Specifications
Table 2-15 through Table 2-35 list the DC specifications for the Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series and are valid only while meeting specifications
for case temperature, clock frequency, and input voltages.
The following notes apply:
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 39
Page 40
Electrical Specifications
Notes:
• Unless otherwise noted, all specifications in the tables apply to all frequencies
• For the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor
9500 Series, these specifications are based on characterized data from silicon
measurements.
2.6.1 Flexible Motherboard Guidelines for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
The Flexible Motherboard (FMB) guidelines are estimates of the maximum ratings that
the processor will have over certain time periods. The ratings are only estimates as
actual specifications for future processors may differ. The processor may or may not
have specifications equal to the FMB value in the foreseeable future.
Table 2-15 defines the FMB voltage specification values applied to the 130W, and
®
155W/185W Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series stock-keeping units (SKUs).
Current specifications are identified for each processor SKU separately in Table 2-16
through Table 2-17.
Table 2-18 defines the FMB voltage specification values applied to the 130 W and
®
170 W SKUs for the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series. Current specifications are
identified for each processor SKU separately in Table 2-19.
Table 2-15. FMB Voltage Specifications for the Intel
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Notes
VID
Range
UVID
Range
VCCUNCORE Processor uncore supply voltage See Table 2-20 and Figure 2-10 V2,1
VCCCORE Processor core supply voltage See Table 2-21 and Figure 2-11 V2,3,4
VCCCACHE Processor cache supply voltage See Tab le 2-22 and Figure 2-12 V5
VID Transition VID step size during transition ± 12.5 mV
VID_DCshift Total allowable DC load line shift from VID
VCCIO Processor I/O supply voltage at die
VCCIO Processo r I/O supply voltage (high
VCCIO Processor I/O supply voltage at package
VCCA Processor analog supply voltage (DC spec) 1.764 1.8 1.836 V
VCCA Processor analog supply voltage (AC
VCCA Processor analog supply voltage (AC
VCCA Processor analog supply voltage (Total =
VCC33_SM 3.3 V supply voltage 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
VCCCORE VID Range 0.8 1.1 1.35 V
VCCUNCORE VID Range 0.8 1.1 1.35 V
steps.
including all AC and DC
frequency AC p-p noise at die)
pin including all AC and DC
tolerance for noise at scope full
bandwidth)
tolerance for noise > 1MHz)
DC spec + AC tolerance)
1.147 1.175 1.203 V 8
1.739 1.8 1.861 V
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
-450 mV 6
1.08 1.15 1.22 V 7
050mV
1.8 ±25 mV 9, 10
1.8 ±15 mV 9, 11
1. The voltage specification requirements are measured across the VCC UNCORESENSE and VSSUNCORESENSE pins using an
oscilloscope set to a 100 MHz bandwidth and probes that are 1.5 pF maximum capacitance and 1 mOhms minimum impedance
at the processor socket. The maximum length of gr ound wire on the probe should be le ss than 5 mm. Ensure external noise from
the system is not coupled into the scope probe.
40 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 41

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
2. These voltages are target only. A variable voltage source should exist on systems in the event that a different voltage is required.
See Ararat Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for more information.
3. Uncore, Core, and Cache voltage and Current Rating are at the Package Pad.
4. The voltage specification requirements are measured across the VCCCORESENSE and VSSCORESENSE pins using an oscilloscope
set to a 100 MHz bandwidth and probes that are 1.5 pF maximum capacitance and 1 MOhm minimum impedance at the processor
socket. The maximum length of ground wire on the probe sh ould be less th an 5 mm. Ens ure exte rnal no ise from the sys t em is
not coupled into the scope probe.
5. The voltage specification requirements are measured across the VCCCACHESENSE and VSSCACHESENSE pins using an
oscilloscope set to a 100 MHz bandwidth and probes that are 1.5 pF maximum capacitance and 1 mOhms minimum impedanc e
at the processor socket. The maximum length of g round wire on the probe should be less than 5 mm. Ensure exter nal noise from
the system is not coupled into the scope probe.
6. Warm boot reset, only in downward direction.
7. Min and Max range is spec at the die for both VCCIO. This range includes 50 mV p-p AC noise. It also includes any DC and AC
tolerances at package pin.
8. The FMB remote sense tolerance is ±2.5% for DC to 20 MHz at the package, whe re ±1.5% is allotted for a DC to 1 MHz range
and an additional ±1% for 1 MHz to 20 MHz. Similarly , ±6.4% is allotted for DC to 20 MHz at the die. It is expected that VCCIO
regulators meet ±1.5% at the remote sense location based on the general remote sense termination po int location as described
in Figure 2-16, VR Sense Point (Representation). F or future processor compatibility, it is strongly recommended that the platform
query the PIROM to assure VCCIO is set to the appropriate level prior to powering up the VCCIO supply.
9. All voltage regulation measurements taken at remote sense termination points.
10.For peak-to-peak Ripple and Noise (R&N) measured with full bandwidth (BW) of the scope (Min 1 GHz BW scope is required):
set scope diff probe and the scope at full BW (capture waveform A, channel 1).
11.For peak-to-peak Ripple and Noise (R&N) measured above 1 MHz:
Step 1 = set both: scope diff probe and/or the scope at 1 MHz BW limit (capture waveform B, channel 2).
Step 2 = calculate A-B (use scope Math function: subtract channel 1 - channel 2).
Table 2-16. FMB 130W Current Specifications for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
Series
Symbol Parameter Max Units Notes
I
CC_CORE
I
CC_CORE_TDC
I
CC_CORE_STEP
d
ICC_CORE/dt
I
CC_UNCORE
I
CC_UNCORE_TDC
I
CC_UNCORE_STEP
dI
CC_UNCORE/dt
I
CC_IO
I
CC_Analog
I
CC33_SM
I
for core 151 A
CC
Thermal Design Current for Core 100 A 1
Max Load step for core 95 A 2
Slew rate for core at Ararat output 154 A/us
ICC for uncore 50 A
Thermal Design Current for Uncore 43 A 3
Max Load step for uncore 22 A 4
Slew rate for uncore at Ararat output 75 A/us
ICC for processor I/O 22 A 5
ICC for processor Analog 4 A
ICC33 for main supply 200 mA
1. ICC_CORE_TDC is the sustained (DC equivalent) current that the processor core is capable of drawing indefinitely and should be
used for the Ararat voltage regulator temperature assessment. The Ararat voltage regulator is responsible for monitoring its
temperature and asserting the VR_FAN_N, VR_THERMALERT_N, VR_THERMTRIP_N signals sequentially to inform the processor
and platform of a thermal excursion. Of the three signals, only VR_THERMALTERT_N is monitored by the processor. Please see
the Ararat Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for further details. The processor is capable of drawing ICC_CORE_TDC
indefinitely. Refer to Figure 2-9 for further details on the average processor current draw over various time durations. This
parameter is based on design characterization and is not tested.
2. During system power on, the pulse inrush (ICC_CORE_STEP) can be as high as 130A peak-to-peak.
3. ICC_UNCORE_TDC is the sustained (DC equivalent) current that the processor uncore is capable of drawing indefinitely and
should be used for the Ararat voltage regulator temperature assessment. The Ararat voltage regulator is responsible for
monitoring its temperature and asserting the VR_FAN_N, VR_THERMALERT_N, VR_THERMTRIP_N si gnals sequentially to inform
the processor and platform of a thermal excursion. Of the three signals, only VR_THERMAL TER T_N is monitored by the processor.
Please see the Ararat Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for further details. The processor is capable of drawing
ICC_UNCORE_TDC indefinitely. This parameter is based on design characterization and is not tested.
4. During system power on, the pulse inrush (ICC_UNCORE_STEP) can be as high as 40A peak-to-peak.
5. The ICC_IO current specification applies to the total current from VCCIO pins.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 41
Page 42

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
0.01 100 10001010.1
ITDC
IMax
Time Duration (us)
Sustained Current (A)
Table 2-17. FMB 155W/185W Current Specifications for the Intel® Itanium® Processor
9300 Series
Symbol Parameter Max Units Notes
I
CC_CORE
I
CC_CORE_TDC
I
CC_CORE_STEP
d
ICC_CORE/dt
I
CC_UNCORE
I
CC_UNCORE_TDC
I
CC_UNCORE_STEP
dI
CC_UNCORE/dt
I
CC_IO
I
CC_Analog
I
CC33_SM
1. ICC_CORE_TDC is the sustained (DC equivalent) current that the processor core is capable of drawing indefinitely and should be
used for the Ararat voltage regulator temperature assessment. The Ararat voltage regulator is responsible for monitoring its
temperature and asserting the VR_FAN_N, VR_THE RMALERT_N, VR_THERMTRIP_N signals sequentially to inform the processor
and platform of a thermal excursion. Of the three signals, only VR_THERMALTERT_N is monitored by the processor. Please see
the Ararat Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for further details. The processor is capable of drawing ICC_CORE_TDC
indefinitely. Refer to Figure 2-9 for further details on the average processor current draw over various time durations. This
parameter is based on design characterization and is not tested.
2. During system power on, the pulse inrush (ICC_CORE_STEP) can be as high as 130A peak-to-peak.
3. ICC_UNCORE_TDC is the sustained (DC equivalent) current that the processor uncore is capable of drawing indefinitely and
should be used for the Ararat voltage regulator temperature assessment. The Ararat voltage regulator is responsible for
monitoring its temperature and asserting the VR_FA N_N, VR_THERMALER T_N, VR_THERMTRIP_N signals sequentially to inform
the processor and platform of a thermal excursion. Of the three signals, only VR_THERMAL TER T_N is monitored by the processor.
Please see the Ararat Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for further details. The processor is capable of drawing
ICC_UNCORE_TDC indefinitely. This parameter is based on design characterization and is not tested.
4. During system power on, the pulse inrush (ICC_UNCORE_STEP) can be as high as 40A peak-to-peak.
5. The ICC_IO current specification applies to the total current from VCCIO pins.
I
for core 180 A
CC
Thermal Design Current for Core 131 A 1
Max Load step for core 95 A 2
Slew rate for core at Ararat output 154 A/us
I
for uncore 50 A
CC
Thermal Design Current for Uncore 43 A 3
Max Load step for uncore 22 A 4
Slew rate for uncore at Ararat output 75 A/us
I
for processor I/O 22 A 5
CC
ICC for processor Analog 4 A
I
for main supply 200 mA
CC33
Figure 2-9. Processor I
CC_CORE
Load Current versus Time
42 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 43
Electrical Specifications
Notes:
2.6.2 Flexible Motherboard Guidelines for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
The Flexible Motherboard (FMB) guidelines are estimates of the maximum ratings that
the processor will have over certain time periods. The ratings are only estimates as
actual specifications for future processors may differ. The processor may or may not
have specifications equal to the FMB value in the foreseeable future.
Table 2-18 defines the FMB voltage specification values applied to the 130 W and
®
170 W SKUs for the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series. Current specifications are
identified for each processor SKU separately in Table 2-19.
Table 2-18. FMB Voltage Specifications for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Notes
CVID
Range
CVID
Boot
UVID
Range
UVID
Boot
VCCUNCORE Processor uncore supply voltage See Table 2-23 and Figure 2-15 V2, 1
VCCCORE Processor core supply voltage See Ta ble 2-24 and Figure 2-14 V2, 3, 4
VID Transition VID step size during transition ± 5mV
VID_DCshift Total allowable DC load line shift from VID
VCCIO Processor I/O supply voltage at die
VCCIO Processor I/O supply voltage (high
VCCIO Processor I/O supply voltage at package
VCCA Processor analog supply voltage (DC spec) 1.764 1.8 1.836 V
VCCA Processor analog supply voltage (AC
VCCA Processor analog supply voltage (AC
VCCA Processor analog supply voltage (Total =
VCCA Ramp Min time allowed to ramp VCCA from 10%
VCC33_SM 3.3 V supply voltage 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
VCCCORE VID Range 0.800 1.105 1.22 V
VCCCORE VID default value 0 V
VCCUNCORE VID Range 0.800 0.975 1.19 V
VCCUNCORE VID default value 1.0 V
steps.
including all AC and DC
frequency AC p-p noise at die)
pin including all AC and DC
tolerance for noise at scope full
bandwidth)
tolerance for noise > 1MHz)
DC spec + AC tolerance)
to 90% typical value
1.011 1.050 1.094 V 6
1.026 1.075 1.088 V 7
1.8 ±25 mV 8, 9
1.8 ±15 mV 9, 10
1.739 1.8 1.861 V
110ms
-420 mV 5
35 mV
1
1
1
1
8
1. The voltage specification requirements are measured across the VCCUNCORESENSE and VSSUNCORESENSE pins using an
oscilloscope set to a 100 MHz bandwidth and probes that are 1.5 pF maximum capacitance and 1 mOhms minimum impedanc e
at the processor socket. The maximum length of g round wire on the probe should be less than 5 mm. Ensure exter nal noise from
the system is not coupled into the scope probe.
2. These voltages are target only. A variable voltage source should exist on systems in th e event that a different voltage is required.
See the Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for more information.
3. Uncore and Core voltage and Current Rating are at the Package Pad.
4. The voltage specification requirements are measured across the VCCCORESENSE and VSSCORESENSE pins using an oscilloscope
set to a 100 MHz bandwidth and probes that are 1.5 pF maximum capacitance and 1 mOhms minimum impedance at the
processor socket. The maximum length of ground wire on the pr obe should be less than 5 mm. Ensure external noise fro m the
system is not coupled into the scope probe.
5. Warm boot reset, only in downward direction.
6. Min and Max range is spec at the die for VCCIO. This range includes 35 mV p-p AC noise. It also includes any DC and AC
tolerances at package pin.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 43
Page 44
Electrical Specifications
Notes:
7. The FMB remote sense tolerance is ±2.5% for DC to 20 MHz at the package, where ±1.5% is allotted for a DC to 1 MHz range
and an additional ±1.0% for 1 MHz to 20 MHz. Similarly , ±6.4% is allotted for DC to 20 MHz at the die. It is expected that VCCIO
regulators meet ±1.5% at the remote sense location based on the general remote sense termination point location as described
in Figure 2-16 VR Sense Point (Representation). For future processor compatibility , it is strongly recommended that the platform
query the PIROM to assure VCCIO is set to the appropriate level prior to powering up the VCCIO supply.
8. All voltage regulation measurements taken at remote sense termination points.
9. For peak-to-peak Ripple and Noise (R&N) measured with full band width (BW) of the sc ope (Min 1 GHz BW scope is requir ed):
set scope diff probe an d the scope at full BW (capture waveform A, channel 1).
10.For peak-to-peak Ripple and Noise (R&N) measured above 1 MHz:
Step 1 = set both: scope diff probe and/or the scope at 1 MHz BW limit (capture waveform B, channel 2)
Step 2 = calculate A-B (use scope Math function: subtract channel 1 - channel 2).
Table 2-19. FMB 170W and 130W Current Specifications for the Intel® Itanium® Processor
9500 Series
Symbol Parameter Max Min Units Notes
I
CC_CORE
I
CC_CORE_TDC
I
CC_CORE_STEP
d
ICC_CORE/dt
I
CC_UNCORE
I
CC_UNCORE_TDC
I
CC_UNCORE_STEP
dI
CC_UNCORE/dt
I
CC_IO
d
ICC_IO/dt
I
CC_IO_STEP
T
CC_IO_STEP
I
CC_Analog
I
CC33_SM
1. Values per core pair.
2. ICC_CORE_TDC is the sustained (DC equivalent) current that the processor core is capable of drawing indefinitely and should be
used for the Ararat voltage regulator temperature assessment. The Ararat voltage regulator is responsible for monitoring its
temperature and asserting the VR_FAN_N, VR_THERMALERT_N, VR_T HERMTRIP_N signals sequentially to inform the processor
and platform of a thermal excursion. Of the three signals, only VR_THERMALTERT_N is monitored by the processor. Please see
the Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for further details. The processor is capable of drawing ICC_CORE_TDC
indefinitely.
3. During system power on, the pulse inrush (ICC_CORE_STEP) can be as high as 35A peak-to-peak.
4. ICC_UNCORE_TDC is the sustained (DC equivalent) current that the processor uncore is capable of drawing indefinitely and
should be used for the Ararat voltage regulator temperature assessment. The Ararat voltage regulator is responsible for
monitoring its temperature and asserting the VR_FAN_N, VR_THERMALERT_N, VR_THERMTRIP_N signals sequentially to inform
the processor and platform of a thermal excursion. Of the three signals, only VR_THERMAL TERT_N is monitored by the processor.
Please see the Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for further details. The processor is capable of drawing
ICC_UNCORE_TDC indefinitely. This parameter is based on design characterization and is not tested.
5. During system power on, the pulse inrush (ICC_UNCORE_STEP) can be as high as 40A peak-to-peak.
6. The ICC_IO current specification applies to the total current from VCCIO pins.
7. The max load step represents the maximum current required during Intel
between steps represents the time between Intel
I
for core 3 5.0 A 1
CC
Thermal Design Current for Core 30.0 A 1, 2
Max Load step for core 14.62 A 1, 3
Slew rate for core at Ararat output 34.4 A/us
1
ICC for uncore 80.0 A
Thermal Design Current for Uncore 75.0 A 4
Max Load step for uncore 30.4 A 5
Slew rate for uncore at Ararat output 168.0 A/us
I
for processor I/O 17.2 A 6
CC
Slew rate for IO at the package pin 54.0 A/us
Max Load step for max slew rate 5.1 A 7
Time between steps 4.7 us
7
ICC for processor Analog 4 A
I
for main supply 200 mA
CC33
®
®
QPI and Intel® SMI initialization.
QPI and Intel® SMI port initialization. The min time
2.6.3 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series Uncore, Core, and
Cache Tolerances
2.6.3.1 Uncore Static and Transient Tolerances
Table 2-20 and Figure 2-10 specify static and transient tolerances for the uncore
outputs.
44 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 45

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
VccUNCORE Tolerance Bands
-0.24
-0.22
-0.20
-0.18
-0.16
-0.14
-0.12
-0.10
-0.08
-0.06
-0.04
-0.02
0.00
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Icc (A)
Normal iz ed Vcc (V )
AC max (V)
DC max (V)
Typical Vcc (V)
DC min (V)
AC min (V)
Table 2-20. V
CC
UNCORE
Series
Uncore
Current (A)
I
CC_UNCORE
Static and Transient Tolerance for Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
Voltage Deviation from VID Setting (V)1,2,3,4
V
CC_Max
V
CC_Typ
0 VID - 0 VID - 0.02 VID - 0.04
5 VID - 0.02 VID - 0.04 VID - 0.06
10 VID - 0.04 VID - 0.06 VID - 0.08
15 VID - 0.06 VID - 0.08 VID - 0.1
20 VID - 0.08 VID - 0.1 VID - 0.12
25 VID - 0.1 VID - 0.12 VID - 0.14
30 VID - 0.12 VID - 0.14 VID - 0.16
35 VID - 0.14 VID - 0.16 VID - 0.18
40 VID - 0.16 VID - 0.18 VID - 0.2
45 VID - 0.18 VID - 0.2 VID - 0.22
50 VID - 0.2 VID - 0.22 VID - 0.24
1. The V
2. This table is intended to aid in reading discrete points on Figure 2-10.
3. The load lines specify voltage limits at the die measured at the V
Voltage regulation feedback for voltage regulator circuits must be taken from processor V
Refer to the Ararat Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for socket load line guidelines and VR
implementation.
4. V
DC
CC_MIN
and V
load lines represent static and transient limits.
CC_MAX
CCUNCORESENSE
(max)=VID-Rll*ICC-5 mV; VDC(min)=VID-Rll*ICC-35mV; Rll=4 mW.
and V
V
CC_Min
SSUNCORESENSE
and VSS pins.
CC
pins.
Figure 2-10. V
CC
UNCORE
Series
Static and Transient Tolerance for Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 45
Page 46

2.6.3.2 Core Static and Transient Tolerances
Table 2-21 and Figure 2-11 specify static and transient tolerances for the core outputs.
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-21. V
CC
Series (Sheet 1 of 2)
Static and Transient Tolerance for Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
CORE
Core Current (A) Voltage Deviation from VID Setting (V)1,2,3,4
I
CC_CORE
0 VID - 0 VID - 0.02 VID - 0.04
5 VID - 0.004 VID - 0.024 VID - 0.044
10 VID - 0.009 VID - 0.029 VID - 0.049
15 VID - 0.013 VID - 0.033 VID - 0.053
20 VID - 0.017 VID - 0.037 VID - 0.057
25 VID - 0.021 VID - 0.041 VID - 0.061
30 VID - 0.026 VID - 0.046 VID - 0.066
35 VID - 0.03 VID - 0.05 VID - 0.07
40 VID - 0.034 VID - 0.054 VID - 0.074
45 VID - 0.038 VID - 0.058 VID - 0.078
50 VID - 0.043 VID - 0.063 VID - 0.083
55 VID - 0.047 VID - 0.067 VID - 0.087
60 VID - 0.051 VID - 0.071 VID - 0.091
65 VID - 0.055 VID - 0.075 VID - 0.095
70 VID - 0.06 VID - 0.08 VID - 0.1
75 VID - 0.064 VID - 0.084 VID - 0.104
80 VID - 0.068 VID - 0.088 VID - 0.108
85 VID - 0.072 VID - 0.092 VID - 0.112
90 VID - 0.077 VID - 0.097 VID - 0.117
95 VID - 0.081 VID - 0.101 VID - 0.121
100 VID - 0.085 VID - 0.105 VID - 0.125
105 VID - 0.089 VID - 0.109 VID - 0.129
110 VID - 0.094 VID - 0.114 VID - 0.134
115 VID - 0.098 VID - 0.118 VID - 0.138
120 VID - 0.102 VID - 0.122 VID - 0.142
125 VID - 0.106 VID - 0.126 VID - 0.146
130 VID - 0.111 VID - 0.131 VID - 0.151
135 VID - 0.115 VID - 0.135 VID - 0.155
140 VID - 0.119 VID - 0.139 VID - 0.159
145 VID - 0.123 VID - 0.143 VID - 0.163
150 VID - 0.128 VID - 0.148 VID - 0.168
155 VID - 0.132 VID - 0.152 VID - 0.172
160 VID - 0.136 VID - 0.156 VID - 0.176
165 VID - 0.14 VID - 0.16 VID - 0.18
V
CC_Max
V
CC_Typ
V
CC_Min
46 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 47

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
VccCORE Tolerance Bands
-0.20
-0.18
-0.16
-0.14
-0.12
-0.10
-0.08
-0.06
-0.04
-0.02
0.00
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180
Icc (A)
Normalized Vcc (V)
AC max (V)
DC max (V)
Typical Vcc (V)
DC min (V)
AC min (V)
Table 2-21. V
Figure 2-11. V
CC
Series (Sheet 2 of 2)
1. The V
2. This table is intended to aid in reading discrete points on
3. The load lines specify voltage limits at the die measured at the V
4. V
CC
Series
Static and Transient Tolerance for Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
CORE
Core Current (A) Voltage Deviation from VID Setting (V)1,2,3,4
I
CC_CORE
170 VID - 0.145 VID - 0.165 VID - 0.185
175 VID - 0.149 VID - 0.169 VID - 0.189
180
and V
CC_MIN
Voltage regulation feedback for voltage regulator circuits must be taken from processor V
Refer to the Ararat Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for socket load line guidelines and VR
implementation.
(max)=VID-Rll*ICC-4 mV;VDC(nom)=VID-Rll*ICC-19 mV;VDC(min)=VID-Rll*ICC-34mV; Rll=0.85 mΩ.
DC
Static and Transient Tolerance for Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
CORE
CC_MAX
V
CC_Max
load lines represent static and transient limits.
V
CC_Typ
Figure 2-11.
CCCORESENSE
and V
SSCORESENSE
V
CC_Min
pins.
and VSS pins.
CC
2.6.3.3 Cache Static and Transient Tolerances
Table 2-22 and Figure 2-12 specify static and transient tolerances for the cache
outputs.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 47
Page 48

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
VccCACHE Tolerance Bands
-0.2 2
-0.2 0
-0.1 8
-0.1 6
-0.1 4
-0.1 2
-0.1 0
-0.0 8
-0.0 6
-0.0 4
-0.0 2
0.00
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 5 0
Icc (A)
Normalized Vcc (V)
AC max (V)
DC max (V)
Typical Vcc (V)
DC min (V)
AC min (V)
Table 2-22. V
Figure 2-12. V
CC
Series
Static and Transient Tolerance for Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
CACHE
Cache Current (A) Voltage Deviation from VID Setting (V)1,2,3,4
I
CC_CACHE
V
CC_Max
V
CC_Typ
0 VID - 0 VID - 0.02 VID - 0.04
5 VID - 0.017 VID - 0.037 VID - 0.057
10 VID - 0.035 VID - 0.055 VID - 0.075
15 VID - 0.052 VID - 0.072 VID - 0.092
20 VID - 0.069 VID - 0.089 VID - 0.109
25 VID - 0l.086 VID - 0.106 VID - 0.126
30 VID - 0.104 VID - 0.124 VID - 0.144
35 VID - 0.121 VID - 0.141 VID - 0.161
40 VID - 0.138 VID - 0.158 VID - 0.178
45 VID - 0.155 VID - 0.175 VID - 0.195
50 VID - 0.173 VID - 0.193 VID - 0.213
55 VID - 0.19 VID - 0.21 VID - 0.23
1. The V
2. This table is intended to aid in reading discrete points o
3. The load lines specify voltage limits at the die measured at the V
Voltage regulation feedback for voltage regulator circuits must be taken from processor V
Refer to the Ararat Vo ltage Regulator Module Design Guide for socket load line guidelines and VR
implementation.
4. V
DC
CC
CACHE
Series
CC_MIN
and V
load lines represent static and transient limits.
CC_MAX
n Figure 2-12.
CCCACHESENSE
and V
SSCACHESENSE
(max)=VID-Rll*ICC-5 mV; VDC(min)=VID-Rll*ICC-35 mV; Rll=3.45 mW.
Static and Transient Tolerance for Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
V
CC_Min
pins.
and VSS pins.
CC
48 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 49
Electrical Specifications
Notes:
2.6.4 Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Uncore and Core Tolerances
2.6.4.1 Uncore Static and Transient Tolerances
Table 2-23 and Figure 2-13 specify static and transient tolerances for the uncore
outputs.
Table 2-23. V
CC
UNCORE
9500 Series
Uncore
Current (A)
I
CC_UNCORE
Static and Transient Tolerance for the Intel® Itanium® Processor
Voltage Deviation from VID Setting (V)1,2,3,4
V
CC_Max
0 VID + 0.015 VID VID - 0.015
5 VID + 0.00875 VID - 0.00625 VID - 0.02125
10 VID + 0.0025 VID - 0.0125 VID - 0.0275
15 VID - 0.00375 VID - 0.01875 VID - 0.03375
20 VID - 0.01 VID - 0.025 VID - 0.04
25 VID - 0.01625 VID - 0.03125 VID - 0.04625
30 VID - 0.0225 VID - 0.0375 VID - 0.0525
35 VID - 0.02875 VID - 0.04375 VID - 0.05875
40 VID - 0.035 VID - 0.05 VID - 0.065
45 VID - 0.04125 VID - 0.05625 VID - 0.07125
50 VID - 0.0475 VID - 0.0625 VID - 0.0775
55 VID - 0.05375 VID - 0.06875 VID - 0.08375
60 VID - 0.06 VID - 0.075 VID - 0.09
65 VID - 0.06625 VID - 0.08125 VID - 0.09625
70 VID - 0.0725 VID - 0.0875 VID - 0.1025
V
CC_Typ
V
CC_Min
1. The V
2. This table is intended to aid in reading discrete points on Figure 2-14.
3. The load lines specify voltage limits at the die measured at the VCCUNCORESENSE and VSSUNCORESENSE
pins. Voltage regulation feedback for voltage regulator circuits must be taken from processor VCC and VSS
pins. Refer to the Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for socket load line guidelines and VR
implementation.
4. V
DC
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 49
and V
CC_MIN
(max)=VID-Rll*ICC+15 mV; VDC(min)=VID-Rll*ICC-15 mV; Rll=1.25 mOhm.
load lines represent static and transient limits.
CC_MAX
Page 50
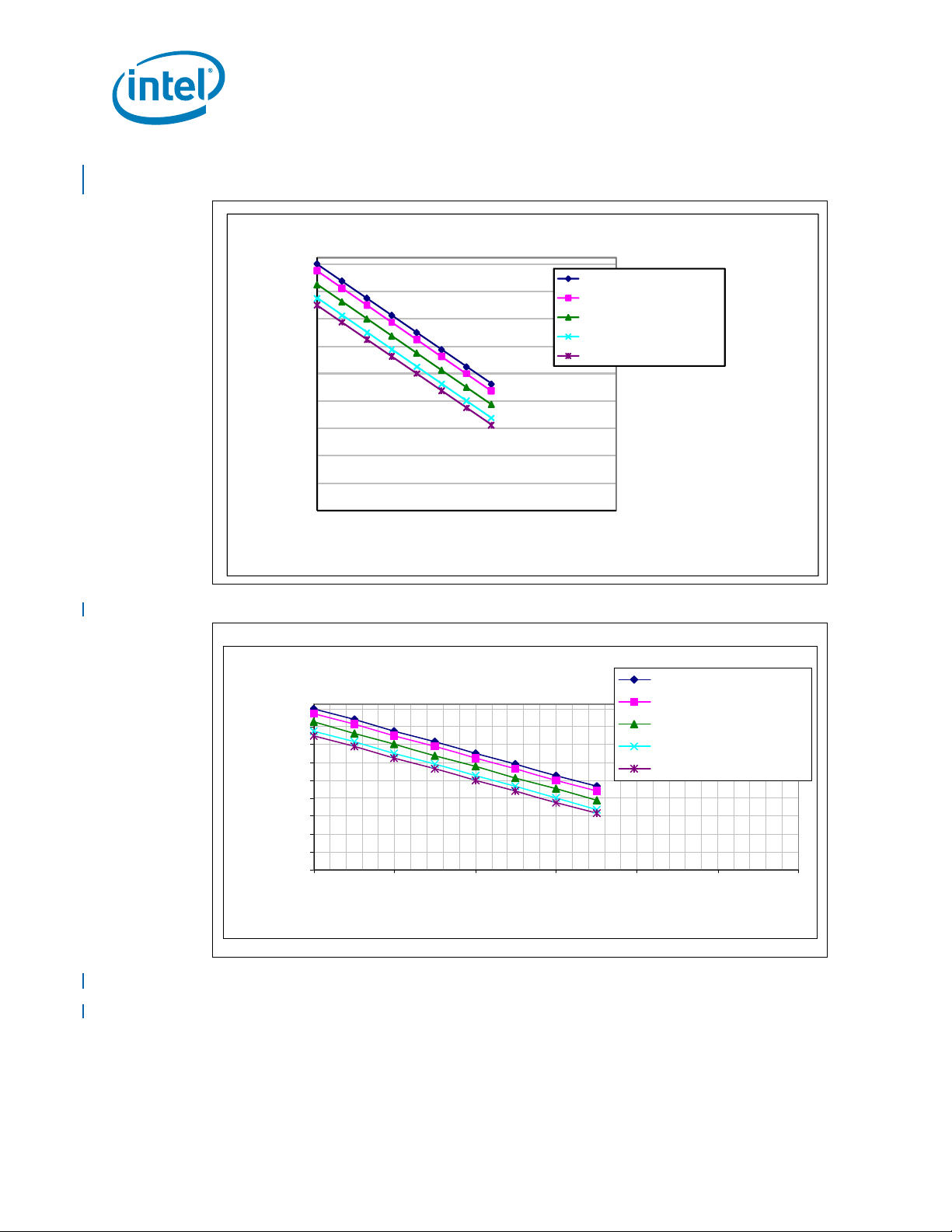
Electrical Specifications
-0.1650
-0.1450
-0.1250
-0.1050
-0.0850
-0.0650
-0.0450
-0.0250
-0.0050
0.0150
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Normalized VccUnCore (V)
IccUnCore (A)
VccUnCore Tolerance Band
VccUnCore ACM ax (V)
VccUnCore DCMax (V)
Normalized Vcc UnCore (V)
VccUnCore DCMin (V)
VccUnCore ACM in (V)
VccUnCore Tolerance Band
-0.1650
-0.1450
-0.1250
-0.1050
-0.0850
-0.0650
-0.0450
-0.0250
-0.0050
0.0150
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
IccUnCore (A)
Normalized VccUnCore (V)
Vc cUnCore ACMax (V)
Vc cUnCore DCMax (V )
Normalized V ccUnCore (V)
Vc cUnCore DCMin (V)
Vc cUnCore ACMin (V)
Figure 2-13. V
Figure 2-14. V
CC
UNCORE
9500 Series
CC
UNCORE
Static and Transient Tolerance for the Intel® Itanium® Processor
Load Line for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
2.6.4.2 Core Static and Transient Tolerances
Table 2-24 and Figure 2-15 specify static and transient tolerances for the core outputs.
50 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 51

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
VccCore[1-4] Toler ance Band
-0.11
-0.1
-0.09
-0.08
-0.07
-0.06
-0.05
-0.04
-0.03
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45
IccCor e (A)
Normalized VccCore (V)
VccCore ACMax (V)
VccCore DCMax (V)
Nor malized VccCore (V)
VccCore DCMin (V)
VccCore ACMin (V)
Table 2-24. V
Figure 2-15. V
CC
9500 Series
1. The V
2. This table is intended to aid in reading discrete points on Figure 2-15.
3. The load lines specify voltage limits at the die measured at the VCCCORESENSE and VSSCOR ESENSE pins.
Voltage regulation feedback for voltage regulator circuits must be taken from processor VCC and VSS pins.
Refer to the Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for socket load line guidelines and VR
implementation.
4. V
CC
Static and Transient Tolerance for the Intel® Itanium® Processor
CORE
Core Current (A) Voltage Deviation from VID Setting (V)1,2,3,4
I
CC_CORE
0 VID + 0.015 VID VID - 0.015
5 VID + 0.005 VID - 0.010 VID - 0.025
10 VID - 0.005 VID - 0.020 VID - 0.035
15 VID - 0.015 VID - 0.030 VID - 0.045
20 VID - 0.025 VID - 0.040 VID - 0.055
25 VID - 0.035 VID - 0.050 VID - 0.065
30 VID - 0.045 VID - 0.060 VID - 0.075
and V
CC_MIN
(max)=VID-Rll*ICC+15 mV; VDC(nom)=VID-Rll*ICC; VDC(min)=VID-Rll*ICC-15 mV; Rll= 2 mOhms.
DC
Load Line for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
CORE
load lines represent static and transient limits.
CC_MAX
V
CC_Max
V
CC_Typ
V
CC_Min
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 51
Page 52

Electrical Specifications
2.6.5 Overshoot and Undershoot Guidelines
Overshoot (or undershoot) is the value of the maximum voltage above or below VSS.
The overshoot and undershoot specifications limit transitions beyond VCCIO or VSS due
to the fast signal edge rates. The processor can be damaged by single and/or repeated
overshoot or undershoot events on any input, output, or I/O buffer if the charge is
large enough (that is, if the overshoot or undershoot is great enough). Determining the
impact of an overshoot or undershoot condition requires knowledge of the magnitude,
the pulse duration, and the activity factor (AF). Permanent damage to the processor is
the likely result of excessive overshoot or undershoot.
2.6.5.1 Overshoot/Undershoot Ma gnitude, Pulse Duration and Activity Factor
Magnitude describes the maximum potential difference between a signal and its voltage
reference level. For the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9500 Series, both are referenced to VSS. It is important to note that
overshoot and undershoot conditions are separate and their impact must be
determined independently.
Pulse duration describes the total amount of time that an overshoot or undershoot
event exceeds the overshoot or undershoot reference voltage. Activity factor (AF)
describes the frequency of overshoot or undershoot occurrence relative to a clock.
Since the highest frequency of assertion of a single-ended signal is every other clock,
an AF = 1 indicates that the specific overshoot or undershoot waveform occurs every
other clock cycle. Thus, an AF = 0.01 indicates that the specific overshoot or
undershoot waveform occurs one time in every 200 clock cycles. The highest frequency
of assertion of any differential signal is every active edge of its associated clock (not
the reference clock). So, an AF = 1 indicates that the specific overshoot or undershoot
waveform occurs every cycle.
2.6.5.2 Overshoot/Undershoot Specifications
The overshoot and undershoot specifications listed in the following table specify the
allowable overshoot or undershoot for a single overshoot or undershoot event.
Table 2-25 specifies the maximum overshoot and undershoot for the Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series, while Table 2-26 specifies the maximum overshoot and undershoot for the Intel
single ended and the differential signalling pins. The overshoot and undershoot values
assume an activity factor of 100% and a pulse width of 25% over the signal pulse
width. The tables also include the absolute maximum and minimum values beyond
which the processor is not guaranteed to operate properly. These values assume a
pulse width of 1% and an activity factor of 100%.
2.6.5.2.1 Overs hoot and Un de rshoot Specifications for the Intel
9300 Series
Table 2-25. Overshoot and Undershoot Specifications For Differential
Intel
®
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® SMI and Single-Ended Signals
for the Intel
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
V
MAX-OS-SE
V
MIN-US-SE
V
ABSMAX-OS-SE
V
ABSMIN-US-SE
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series, respectively, identifying both the
®
Itanium® Processor
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series (Sheet 1 of 2)
Overshoot for single-ended signals 1.45 V
Undershoot for single-ended signals -0.247 V
Absolute Max for single-ended signals 1.6 V
Absolute Min for single-ended signals -0.425 V
52 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 53

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
Table 2-25. Overshoot and Undershoot Specifications For Differential
®
Intel
for the Intel
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® SMI and Single-Ended Signals
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
V
MAX-OS-DIFF
V
MAX-US-DIFF
V
ABSMAX-OS-DIFF
V
ABSMAX-US-DIFF
V
MAX_OS_SYSCLK
V
MIN_US_SYSCLK
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series (Sheet 2 of 2)
Overshoot for Intel® QPI and Intel® SMI
signals
Undershoot for Intel® QPI and Intel® SMI
signals
Absolute Max for Intel® QPI and Intel®
SMI signals
Absolute Min for Intel® QPI and Intel® SMI
signals
Sysclk single-ended maximum voltage 1.54 V
Sysclk single-ended minimum voltage -0.337 V
-0.337 V
-0.525 V
1.54 V
1.7 V
2.6.5.2.2 Overshoot and Undershoot Specifications for the Intel® Itanium® Processor
9500 Series
Table 2-26. Overshoot and Undershoot Specifications For Differential
®
Intel
Signals for the Intel
QuickPath Interconnect and Intel® SMI and Single-Ended
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
V
MAX-OS-SE
V
MIN-US-SE
V
ABSMAX-OS-SE
V
ABSMIN-US-SE
V
MAX-OS-DIFF
V
MAX-US-DIFF
V
ABSMAX-OS-DIFF
V
ABSMAX-US-DIFF
V
MAX_OS_SYSCLK
V
MIN_US_SYSCLK
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
Overshoot for single-ended signals 1.36 V
Undershoot for single-ended signals -0.22 V
Absolute Max for single-ended signals 1.46 V
Absolute Min for single-ended signals -0.32 V
Overshoot for Intel® QPI and Intel® SMI
signals
Undershoot for Intel® QPI and Intel®
SMI signals
Absolute Max for Intel® QPI and Intel®
SMI signals
Absolute Min for Intel® QPI and Intel®
SMI signals
Sysclk single-ended maximum voltage 1.3 V
Sysclk single-ended minimum voltage -0.3 V
-0.3 V
-0.4 V
1.3 V
1.4 V
2.6.6 Signal DC Specifications
Table 2-27 through Table 2-35 state the DC specifications for the single-ended signal
groups defined in Table 2-2.
Table 2-27. Voltage Regulator Signal Group DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OH
V
OL
1. Open collector and drain outputs need pull-up resistors on the motherboard.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 53
Input Low Voltage 0 0.4 V
Input High Voltage 0.8 3.6 V
Output High Voltage 0.8 3.6 V 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Output Low Voltage 0 0.4 V 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Page 54

2. These outputs can be pulled up to VCCIO or VCC_STDBY on the platform.
Notes:
Notes:
Notes:
3. Pull-up resistance should limit current to 2 mA.
4. Actual V
5. These values are based on 2.2 KΩ pull-up to 3 .3 V supply.
and VOL levels are determined by pull-up resistance and supply voltage values.
OH
Table 2-28. Voltage Regulator Control Group DC Specification
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OH
V
OL
1. Open collector and drain outputs need pull-up resistors on the motherboard.
2. Actual V
Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide or the Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for I
3. See Intel
resistor values.
4. VR_THERMALERT_N is an input to the top of the package and an output from the bottom of the package. V
and V
output levels on the package pins at the bottom of the package.
Input Low Voltage 0 (VCCIO*0.67) - 0.2 V
Input High Voltage (VCCIO*0.67) + 0.2 VCCIO V
Output High Voltage V 1, 2, 3, 4
Output Low Voltage V
and VOL levels determined by pull-up resistance and supply voltage value. Refer to the Ararat
OH
®
Itanium® 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® 9500 Series Platform Design Guide for recommended
levels are for the input at the top of the package, sensed by the processor; VOH and VOL are for the
IL
Table 2-29. TAP and System Management Group DC Specifications
Electrical Specifications
1, 2, 3, 4
max.
OL
IH
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OH
V
OL
I
OL
I
ILeak
I
OLeak
1. With 50 W termination to VCCIO at the far end.
2. With V at the pin at 1.1 V and 0 V. System designers are advised to check the tolerance of their voltage
regulator solutions to ensure V at the pin is 1.1 V.
3. Internal weak pull-up included for TCLK.
4. Internal weak pull-up included for TRST_N, TMS and TDI.
Input Low Voltage 0 (VCCIO*0.5) - 0.2 V
Input High Voltage (VCCIO*0.5) + 0.2 VCCIO V
Output High Voltage VCCIO-0.2 VCCIO V
Output Low Voltage 0 0.25 V
Output Low Current 16 23 mA 1
Input Leakage Current –200 200 µA 2, 3, 4
Output Leakage Current –1000 200 µA
Table 2-30. Error, FLASHROM, Power-Up, Setup, and Thermal Group DC Specifications
Symbol P arameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OH
V
OL
I
OL
I
ILeak
I
OLeak
Input Low Voltage 0 (VCCIO*0.67) - 0.2 V
Input High Voltage (VCCIO*0.67) + 0.2 VCCIO V
Output High Voltage VCCIO-0.2 VCCIO V
Output Low Voltage 0 0.25 V
Output Low Current 16 23 mA 1
Input Leakage Current –1000 200 µA 2
Output Leakage Current –1000 200 µA
1
1
1. With 50W termination to VCCIO at the far end.
54 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 55

Electrical Specifications
Notes:
Notes:
2. With input leakage current measured at the pin with 0V and with 1.1 V supplied to the pin. System designer s
are advised to check the tolerance of their voltage regulator solutions to ensure a voltage of 1.1 V at the pin.
2.6.6.1 VID_VCCCORE, VID_VCCUNCORE, and VID_VCCCACHE DC
Specifications for the Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series processor supplies top side VID signal pins
to the Arafat Voltage Regulator Module, as shown in Table 2-31.
Table 2-31. VID_VCCCORE[6:0], VID_VC CUNCORE[6:0] and VID_VCCCACHE[5 :0] DC
Specifications for the Intel
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
OH
V
OL
I
OLeak
1. These parameters are not tested and are based on design simulations.
2. Leakage to VSS with pin held at 1.1 V and leakage to 1.1 V with pin held at VSS.
Output High Voltage V CCIO-0.1 VCCIO V
Output Low Voltage 0 0.1 V
Output Leakage Current –200 200 µA 1, 2
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
1
1
2.6.6.2 SVID Group DC Specifications for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500
Series
The Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series implements a Serial VID BUS that is used
to transfer power management information between the microprocessor and the five
output voltages. Voltage levels are compliant to the VR12.0 1V TTL signaling
requirements and are shown in Table 2-32.
Table 2-32. SVID Group DC Specifications for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OH
V
OL
I
OL
I
ILeak
I
OLeak
1. With 50W termination to VCCIO at the far end.
2. With input leakage current measured at the pin with 0V and with 1.075V supplied to the pin. System designers
are advised to check the tolerance of their voltage regulator solutions to ensure Vpin of 1.1 V.
Input Low Voltage 0 (VCCIO*0.5) - 0.2 V
Input High Voltage (VCCIO*0.5) + 0.2 VCCIO V
Output High Voltage VCCIO-0.2 VCCIO V
Output Low Voltage 0 0.25 V
Output Low Current 16 23 mA 1
Input Leakage Current –200 200 µA 2
Output Leakage Current –200 200 µA
1
Table 2-33. SMBus and Serial Presence Detect (SPD) Bus Signal Group DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
I
OL
I
LEAK
I
LO
Input Low Voltage 0 (VCCIO*0.67) -0.2 V 1
Input High Voltage (VCCIO*0.67) + 0.2 VCCIO V 1
Output Low Voltage 0 0.25 V 1
Output Low Current 16 23 mA 1,2
Input Leakage Current –1000 200 µA 1
Output Leakage Current –1000 200 µA 1
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 55
Page 56

Notes:
Notes:
Notes:
1. These parameters are based on design characterization and are not tested.
2. With 50Ω termination to VCCIO at the far end.
Table 2-34. Debug Signal Group DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OH
V
OL
I
OL
I
ILeak
I
OLeak
1. With 2 parallel 50Ω termination to VCCIO at the far end.
2. With input leakage current measured at the pin with 0V and with 1.1V supplied to the pin. System designers
Input Low Voltage 0 (VCCIO*0.67) - 0.2 V
Input High Voltage (VCCIO*0.67) + 0.2 VCCIO V
Output High Voltage VCCIO-0.2 VCCIO V
Output Low Voltage 0 0.35 V 1
Output Low Current 13 23 mA 1
Input Leakage Current –1000 200 µA 2
Output Leakage Current –1000 200 µA
are advised to check the tolerance of their voltage regulator solutions to ensure Vpin of 1.1 V.
Table 2-35. PIROM Signal Group DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min TYP Max Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL2
V
OL1
I
ILeak
I
OLeak
Input Low Voltage -0.6 Vcc*0.3 2,1
Input High Voltage Vcc*0.7 Vcc +0.5 2,1
Output Low Voltage (IOL
= 2.1 mA)
Output Low Voltage (IOL
= 0.15 mA)
Input Leakage Current 0.1 3.0 2
Output Leakage Current 0.05 3.0 2
Electrical Specifications
0.4 2
0.2
2
1. VIL(min) and VIH(max) are reference only and are not tested.
2. Applicable over recommended operating range T = -40 °C to +88 °C; Vcc = +1.7 V to +3.6 V.
56 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 57

Electrical Specifications
FBD pins
VR Sense point
FBD pins
VR Sense point
2.6.7 Motherboard-Socket Specification for VR Sense Point
Figure 2-16. VR Sense Point (Representation)
Note: ±1.5% DC (DC to 1 MHz) and ±1% AC (1 MHz to 20 MHz) specified at MB/socket.
2.7 Core and Uncore Voltage Identification
The VID_VCCCORE[6:0] and VID_VCCUNCORE[6:0] lands supply the encoding that
determine the voltage to be supplied by the VCCCORE and VCCUNCORE voltage
regulators. The VID_VCCCORE and VID_VCCUNCORE specifications for the Intel®
Itanium
Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide and Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module
Design Guide, respectively. The voltage set by the VID_VCCCORE and
VID_VCCUNCORE lands are the maximum VCCCORE and VCCUNCORE voltage allowed
by the processor.
Individual processor VID_VCCCORE and VID_VCCUNCORE values may be calibrated
during manufacturing such that two devices at the same core speed may have different
default VID_VCCCORE and VID_VCCUNCORE settings. Furthermore, any Intel
Itanium
different VID_VCCCORE and VID_VCCUNCORE settings during normal operation.
Table 2-36 and Table 2-37 specify the voltage levels corresponding to the state of
VID_VCCCORE and VID_VCCUNCORE for the Intel
and Intel
high voltage level and a ‘0’ refers to a low voltage level.
The Intel
provide the ability to operate while transitioning to an adjacent VID and its associated
processor core voltage (VCCCORE). This will represent a DC shift in the load line. It
should be noted that a low-to-high or high-to-low voltage state change may result in
many VID transitions as necessary to reach the target core voltage. Transitions above
the specified VID are not permitted.
®
Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series are defined in the Ararat 170 Watt
®
Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series can drive
®
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series respectively. A ‘1’ in this table refers to a
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
®
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 57
The Ararat voltage regulator must be capable of regulating its output to the value
defined by the new VID. Please refer to the Ararat 170 Watt Voltage Regulator Module
®
Design Guide for the Intel
Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series processor or the Ararat II
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series.
Page 58
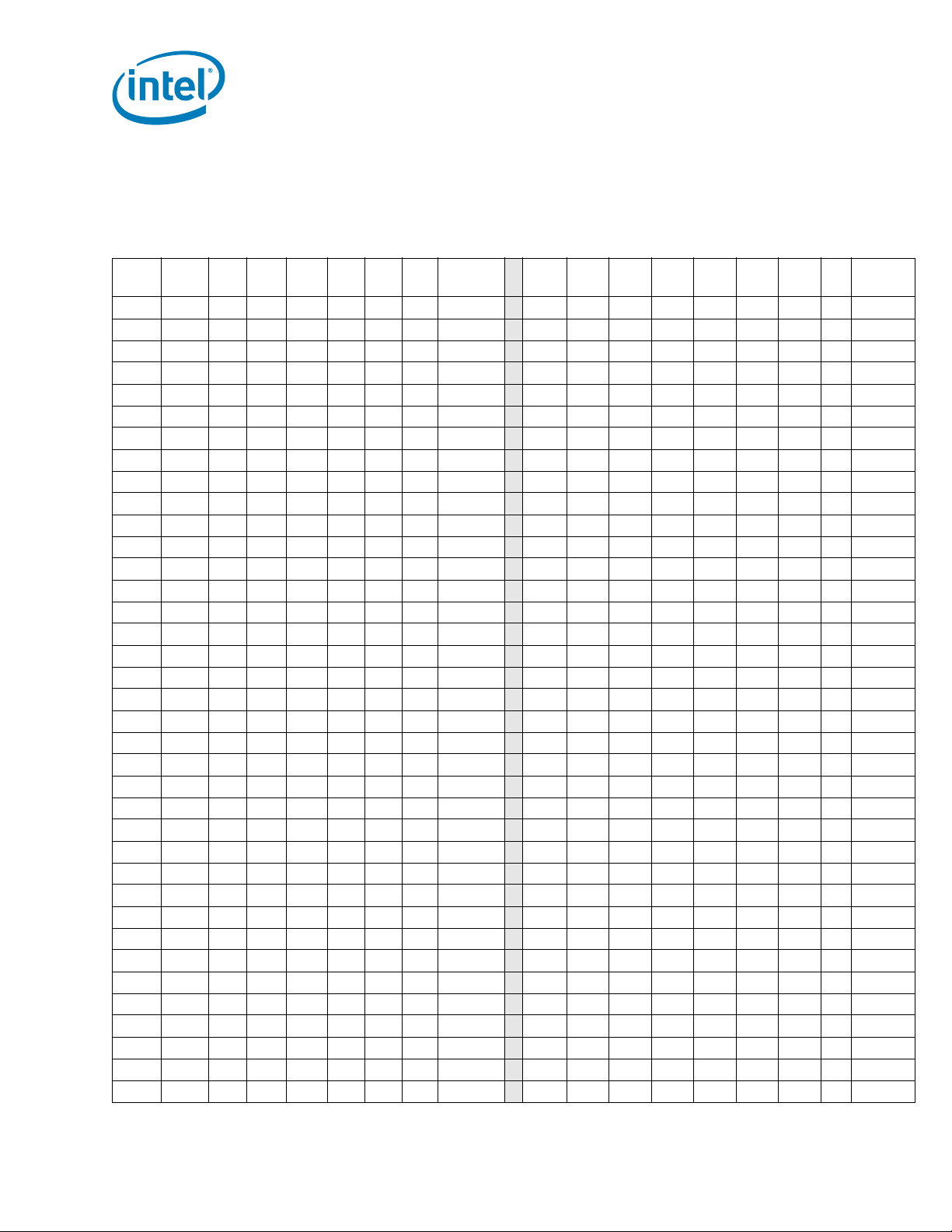
Electrical Specifications
2.7.1 Core and Uncore Voltage Identification for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
Table 2-36. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series VCCCORE (VID_VCCCORE) and
VCCUNCORE and (VID_VCCUNCORE) Voltage Identification Definition for
Ararat (Sheet 1 of 2)
Hex VID6
00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 OFF
01 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1.6000
02 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1.5875
03 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1.5750
04 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1.5625
05 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1.5500
06 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1.5375
07 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1.5250
08 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1.5125
09 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1.5000
0A 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1.4875
0B 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1.4750
0C 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1.4625
0D 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1.4500
0E 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1.4375
0F 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1.4250
10 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1.4125
11 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1.4000
12 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1.3875
13 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1.3750
14 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1.3625
15 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1.3500
16 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1.3375
17 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1.3250
18 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1.3125
19 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1.3000
1A 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1.2870
1B 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1.2750
1C 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1.2625
1D 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1.2500
1E 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1.2375
1F 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1.2250
20 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1.2125
21 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1.2000
22 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1.1875
23 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1.1750
24 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1.1625
VID5VID
4
VID3
VID2VID1VID
0
VID (V) Hex VID6VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1
VI
VID (V)
D0
2E 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1.0375
2F 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1.0250
30 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1.0125
31 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1.000
32 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0.9875
33 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0.9750
34 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0.9625
35 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0.9500
36 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0.9375
37 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0.9250
38 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0.9125
39 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0.9000
3A 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0.8875
3B 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0.8750
3C 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0.8625
3D 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0.8500
3E 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0.8375
3F 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0.8250
40 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0.8125
41 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0.8000
42 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0.7875
43 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0.7750
44 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0.7625
45 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0.7500
46 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0.7375
47 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0.7250
48 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0.7125
49 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0.7000
4A 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0.6875
4B 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0.6750
4C 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0.6625
4D 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0.6500
4E 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0.6375
4F 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0.6250
50 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.6125
51 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0.6000
52 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0.5875
58 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 59
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-36. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series VCCCORE (VID_VCCCORE) and
VCCUNCORE and (VID_VCCUNCORE) Voltage Identification Definition for
Ararat (Sheet 2 of 2)
Hex VID6
25 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1.1500 53 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0.5750
26 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1.1375
27 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1.1250
28 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1.1125
29 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1.1000
2A 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1.0875
2B 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1.0750
2C 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1.0625
2D 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1.0500
VID5VID
4
VID3
VID2VID1VID
0
VID (V) Hex VID6VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1
54 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0.5625
55 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0.5500
56 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0.5375
57 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0.5250
58 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0.5125
59 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0.5000
7F1111111OFF
VI
D0
2.7.2 Core and Uncore Voltage Identification for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
Table 2-37. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series VCCCORE (VID_VCCCORE) and
Hex
00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 OFF
01 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0.250
02 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0.255
03 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0.260
04 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0.265
05 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0.270
06 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0.275
07 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0.280
08 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0.285
09 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0.290
0A 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0.295
0B 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0.300
0C 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0.305
0D 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0.310
0E 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0.315
0F 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0.320
10 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0.325
11 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0.330
12 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0.335
13 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0.340
14 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0.345
15 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0.350
VCCUNCORE and (VID_VCCUNCORE) Voltage Identification Definition for
Ararat II (Sheet 1 of 4)
VID
7
VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID
VID6
VID (V) Hex
0
VID7VID6VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID0VID
27001001110.440
28001010000.445
29001010010.450
2A001010100.455
2B001010110.460
2C001011000.465
2D001011010.470
2E001011100.475
2F001011110.480
30001100000.485
31001100010.490
32001100100.495
33001100110.500
34001101000.505
35001101010.510
36001101100.515
37001101110.520
38001110000.525
39001110010.530
3A001110100.535
3B001110110.540
3C001111000.545
(V)
VID (V)
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 59
Page 60

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-37. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series VCCCORE (VID_VCCCORE) and
VCCUNCORE and (VID_VCCUNCORE) Voltage Identification Definition for
Ararat II (Sheet 2 of 4)
VID
Hex
7
16 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0.355
17 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0.360
18 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0.365
19 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0.370
1A 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0.375
1B 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0.380
1C 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0.385
1D 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0.390
1E 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0.395
1F 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0.400
20 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0.405
21 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0.410
22 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0.415
23 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0.420
24 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0.425
25 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0.430
26 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0.435
4E 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0.635
4F 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0.640
50 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.645
51 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0.650
52 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0.655
53 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0.660
54 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0.665
55 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0.670
56 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0.675
57 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0.680
58 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0.685
59 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0.690
5A 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0.695
5B 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0.700
5C 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0.705
5D 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0.710
5E 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0.715
5F 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0.720
60 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0.725
61 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0.730
62 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0.735
63 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0.740
64 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0.745
VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID
VID6
VID (V) Hex
0
VID7VID6VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID0VID
3D001111010.550
3E001111100.555
3F001111110.560
40011100000.565
41011100010.570
42011100100.575
43010100110.580
44010001000.585
45010001010.590
46010001100.595
47010001110.600
48010010000.605
49010010010.610
4A010010100.615
4B010010110.620
4C010011000.625
4D010011010.630
76011101100.835
77011101110.840
78011110000.845
79011110010.850
7A011110100.855
7B011110110.860
7C011111000.865
7D011111010.870
7E011111100.875
7F011111110.880
80100000000.885
81100000010.890
82100000100.895
83100000110.900
84100001000.905
85100001010.910
86100001100.915
87100001110.920
88100010000.925
89100010010.930
8A100010100.935
8B100010110.940
8C100011000.945
(V)
60 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 61

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-37. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series VCCCORE (VID_VCCCORE) and
VCCUNCORE and (VID_VCCUNCORE) Voltage Identification Definition for
Ararat II (Sheet 3 of 4)
VID
Hex
65 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0.750
66 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0.755
67 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0.760
68 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0.765
69 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0.770
6A 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0.775
6B 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0.780
6C 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0.785
6D 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0.790
6E 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0.795
6F 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0.800
70 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0.805
71 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0.810
72 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0.815
73 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0.820
74 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0.825
75 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0.830
9E 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1.035
9F 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1.040
A0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1.045
A1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1.050
A2 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1.055
A3 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1.060
A4 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1.065
A5 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1.070
A6 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1.075
A7 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1.080
A8 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1.085
A9 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1.090
AA 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1.095
AB 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1.100
AC 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1.105
AD 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1.110
AE 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1.115
AF 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1.120
B0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1.125
B1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1.130
B2 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1.135
B3 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1.140
B4 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1.145
7
VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID
VID6
VID (V) Hex
0
VID7VID6VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID0VID
8D100011010.950
8E100011100.955
8F100011110.960
90100100000.965
91100100010.970
92100100100.975
93100100110.980
94100101000.985
95100101010.990
96100101100.995
97100101111.000
98100110001.005
99100110011.010
9A100110101.015
9B100110111.020
9C100111001.025
9D100111011.030
C6110001101.235
C7110001111.240
C8110010001.245
C9110010011.250
CA110010101.255
CB110010111.260
CC110011001.265
CD110011011.270
CE110011101.275
CF110011111.280
D0110100001.285
D1110100011.290
D2110100101.295
D3110100111.300
D4110101001.305
D5110101011.310
D6110101101.315
D7110101111.320
D8110110001.325
D9110110011.330
DA110110101.335
DB110110111.340
DC110111001.345
(V)
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 61
Page 62
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-37. Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series VCCCORE (VID_VCCCORE) and
VCCUNCORE and (VID_VCCUNCORE) Voltage Identification Definition for
Ararat II (Sheet 4 of 4)
VID
Hex
7
B5 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1.150 DD110111011.350
B6 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1.155
B7 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1.160
B8 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1.165
B9 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1.170
BA 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1.175
BB 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1.180
BC 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1.185
BD 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1.190
BE 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1.195
BF 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1.200
C0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1.205
C1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1.210
C2 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1.215
C3 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1.220
C4 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1.225
C5 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1.230
EE 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1.435
EF 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1.440
F0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1.445
F1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1.450
F2 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1.455
F3 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1.460
F4 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1.465
F5 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1.470
F6 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1.475
VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID
VID6
VID (V) Hex
0
VID7VID6VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID0VID
DE110111101.355
DF110111111.360
E0111000001.365
E1111000011.370
E2111000101.375
E3111000111.380
E4111001001.385
E5111001011.390
E6111001101.395
E7111001111.400
E8111010001.405
E9111010011.410
EA111010101.415
EB111010111.420
EC111011001.425
ED111011011.430
F7111101111.480
F8111110001.485
F9111110011.490
FA111110101.495
FB111110111.500
FC111111001.505
FD111111011.510
FE111111101.515
FF111111111.520
(V)
2.8 Cache Voltage Identification (Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series only)
The Cache Voltage Identification (CVID) value supplies the voltage for VCCCACHE, the
L3 cache voltage for the Intel
specification for the processor is supported by the Ararat I Regulator Module Design
Guide. The voltage set by the VID_VCCCACHE value is the maximum VCCCACHE
voltage allowed by the processor.
Individual processor CVID values may be calibrated during manufacturing such that
two devices at the same core speed may have different default VID_VCCCACHE
settings.
62 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series. The VID_VCCCACHE
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 63

Electrical Specifications
The processor uses the VID_VCCCACHE value to support automatic selection of the
power supply voltages. Table 2-38 specifies the voltage level corresponding to the state
of VID_VCCCACHE. A ‘1’ in this table refers to a high voltage level and a ‘0’ refers to a
low voltage level. See the Ararat I Regulator Module Design Guide for more details.
Table 2-38. Cache (VID_VCCCACHE) Voltage Identification Definition for Ararat
VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID0VID
Hex
00000000OFF
010000011.6000
020000101.5875
030000111.5750
040001001.5625
050001011.5500
060001101.5375
070001111.5250
080010001.5125
090010011.5000
0A0010101.4875
0B0010111.4750
0C0011001.4625
0D0011011.4500
0E0011101.4375
0F0011111.4250
100100001.4125
110100011.4000
120100101.3875
130100111.3750
140101001.3625
150101011.3500
160101101.3375
170101111.3250
180110001.3125
190110011.3000
1A0110101.2870
1B0110111.2750
1C0111001.2625
1D0111011.2500
1E0111101.2375
1F0111111.2250
(V)
HexVID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID0
20 1 0 0 0 0 0 1.2125
21 1 0 0 0 0 1 1.2000
22 1 0 0 0 1 0 1.1875
23 1 0 0 0 1 1 1.1750
24 1 0 0 1 0 0 1.1625
25 1 0 0 1 0 1 1.1500
26 1 0 0 1 1 0 1.1375
27 1 0 0 1 1 1 1.1250
28 1 0 1 0 0 0 1.1125
29 1 0 1 0 0 1 1.1000
2A 1 0 1 0 1 0 1.0875
2B 1 0 1 0 1 1 1.0750
2C 1 0 1 1 0 0 1.0625
2D 1 0 1 1 0 1 1.0500
2E 1 0 1 1 1 0 1.0375
2F 1 0 1 1 1 1 1.0250
30 1 1 0 0 0 0 1.0125
31 1 1 0 0 0 1 1.000
32 1 1 0 0 1 0 0.9875
33 1 1 0 0 1 1 0.9750
34 1 1 0 1 0 0 0.9625
35 1 1 0 1 0 1 0.9500
36 1 1 0 1 1 0 0.9375
37 1 1 0 1 1 1 0.9250
38 1 1 1 0 0 0 0.9125
39 1 1 1 0 0 1 0.9000
3A 1 1 1 0 1 0 0.8875
3B 1 1 1 0 1 1 0.8750
3C 1 1 1 1 0 0 0.8625
3D 1 1 1 1 0 1 0.8500
3E 1 1 1 1 1 0 0.8375
3F 1 1 1 1 1 1 0.8250
VID
(V)
2.9 RSVD, Unused, and DEBUG Pins
All RSVD (RESERVED) pins must be left unconnected. Connection of these pins to
power, VSS, or to any other signal (including each other) can result in component
malfunction or incompatibility with future processors.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 63
Page 64

Electrical Specifications
For reliable operation, always terminate unused inputs or bi-directional signals to their
respective deasserted states. A resistor must be used when tying bi-directional signals
®
to power or ground, also allowing for system testability. Unused pins of Intel
QuickPath Interconnect and FB-DIMM ports may be left as no-connects since
termination is provided on the processor silicon.
Unused outputs may be terminated on the system board or left connected. Note that
leaving unused outputs unterminated may interfere with some Test Access Port (TAP)
functions, complicate debug probing, and prevent boundary scan testing. Signal
®
termination for these signal types is discussed in latest revisions of Intel
Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series Platform Design
Guide.
Debug pins have ODT and can be left as no-connects. Their routing guidelines are
®
provided in the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and Intel® Itanium® Processor
9500 Series Platform Design Guide.
2.10 Mixing Processors
Intel will support mixing CPUs in the same system or hard partition as defined below. A
hard partition is a smaller system capable of booting an OS, consisting of one or more
processors, memory and I/O controller hubs that are formed by domain partitioning.
1. CPUs from adjacent steppings. For example if one cpu is from stepping N, and
another cpu is from the next stepping, N+1, then CPU
Similarly CPU
is not compatible with CPU
N
N+2
.
and CPU
N
2. All CPUs in the system or hard partition must have the same core clock speed or
speed range and the same cache size.
®
3. All Intel
QPI links must have the same data rate, except for Intel® QPI links which
are disabled or in slow mode.
®
Additionally, for the Intel
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series:
4. If variable frequency mode (VFM) is enabled in one CPU it must be enabled in all
CPUs. If VFM mode is disabled in one CPU it must be disabled in all CPUs.
5. Mixing an enabled VFM part with an fixed frequency mode (FFM) part within the
same system or hard partition.
2.11 Supported Power-up Voltage Sequence
are compatible.
N+1
The supported order of voltage sequencing for the processor, detailed in Figure 2-17
and Figure 2-18 and Table 2-39, is VCC33_SM, VccArarat(12V), VCCA, VCCIO,
VCCUNCORE and VCCCORE for the Intel
and followed by VCCCACHE for the Intel
customers need to apply VccArarat(12V) before VCC33_SM, the processor will not
sustain damage. The application of VCC33_SM before VccArarat(12V) allows the PIROM
to be read before the processor is powered.
Once started, the power up sequence must complete within 1000 ms, as defined by the
time limit for PWRGOOD to be asserted. VCC33_SM is brought up first to allow
platforms to read the socket Processor Information data and the PROCTYPE pin.
VccArarat (12V) is the input voltage to the Arar at regulator. The VCCA supply is used to
power the processor’s analog circuits. VCCIO is used to power the I/O circuits. Once
VCCIO is up and stable the external environment can generate the SYSINT clock
signals. Once the SYSINT clocks are valid, the external environment can assert the
64 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series processor
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series processor . If
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 65

Electrical Specifications
VROUTPUT_ENABLE0 signal. After VROUTPUT_ENABLE0 is asserted the sequence of
powering up the VCCUNCORE and VCCCORE supplies and the VCCCACHE (Inte l®
Itanium
For the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series, the VCCUNCORE, VCCCORE and
VCCCACHE supplies power the sysint, cores and large cache arrays respectively.
For the Intel
supplies power the sysint, the cores and the large cache arrays respectively.
When all supplies are up and stable, Ararat asserts VRPWRGD which signals the
external environment that it can assert the PWRGOOD signal. PWRGOOD assertion
initiates the processor internal cold reset sequence.
With reference to the power sequencing timing requirements imposed by the Ararat VR
as shown in Figure 2-17 and Figure 2-18, timing specifications for the elapsed time
taken for an Ararat regulator to bring up each of its output voltages can be found in the
Ararat 170 Watt Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for the Intel
Processor 9300 Series and the Ararat II Voltage Regulator Module Design Guide for the
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series.
When the platform asserts PWRGOOD to the processor, the Intel® Itanium® Processor
9300 Series requires a minimum of 10 ms to complete its internal reset sequence
before deasserting RESET_N, while the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
requires a minimum of 15 ms. For platforms that use both processors, a minimum of
15 ms is needed to meet the requirements of both processors.
®
Processor 9300 Series) begins.
®
Itanium® Processor 9500 Series, the VCCUNCORE and VCCCORE
®
Itanium®
During platform initialization, the RESET_N pin to any component in the platform can
be removed ONLY after all other components have had sufficient time to sample their
respective reset pins. This is needed to prevent unknown behavior that may result if
any one system component comes out of reset before other components have received
the reset signal.
With the exception of standby miscellaneous pins, all input pins, bi-directional pins, and
terminated output pins must not be allowed to exceed the processor's actual VCCIO
voltage prior to and during ramp up of the VCCIO supply.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 65
Page 66

Electrical Specifications
VCC33_SM (3.3v)
PROCTYPE
VCCIO
VCCA (1.8V)
VccArarat (12V)
>= 0us
VROUTPUT_ENABLE0
RESET_N
PWRGOOD
VCCCORE
VCCCACHE
VCCUNCORE
VCCUNCORE VID Value
VCCCORE VID Value
VCCCACHE VID Value
VRPWRGD
>0us
SYSCLK (133MHz)
<= 1000mS
>=10ms
Core and Cache Vids
may change to vfus e values
Core Vi d may
change in response
to power manager
>0us
>0us
>0us
>0us
>0us
>0us
>100ms *
>1uS
>1us *
>0us
>0us
>0us
Uncore Vid may
change to on-di e
fuse based value
> 200 ms*
>1
us *
pulled to VSS on package f or Intel® Itanium® processor 9300 series (VCC33_SM for other products)
>0uS
>0us
pulled to VSS on package for Intel® Itanium® processor 9300 series (VCC33_S M for other products)
* Nominal value; refer to Ararat Spec for actual number
VR_PROCTYPE[1:0]
>=0us
uncore fuse value vfuse valueVids = 0x29 (1. 1V)
> 0us
2.11.1 Supported Power-up Voltage Sequence for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
Figure 2-17. Supported Power-up Voltage Sequence Timing Requirements for the
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series
66 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 67

VCCSTBY33
(3.3V)
PROCTYPE
VCCIO
VCCA
(1.8V)
VCC (12V)
>= 0us
VROUTPUT_ENABLE0
RESET_N
PWRGOOD
VCCCORE[1- 4]
VCCUNCORE
SVID
VR_READY
1V
Vstr ap
V=hfuse
>0us
SYSCLK
(133MHz)
> 0us
VR_PROCTYPE
Pulled to 3.3VSM pin on platform
Pulled to Ararat’ s internal 3.3V rai l on Ararat it self
≥15ms
>= 0us
svid changes
to vfuse
values
svid_vcccore
may change in
response to
power
manager
VCCVUNCOREREADY
svids change
to hfuse val ues
Vhfu se
0.9V
Pwrgd reset can change core VR set
V=vf use
<=1000ms
>0us
> 0us
> 100ms
> 1 ms
All i nputs low prior to VCCIO
<200ms
Electrical Specifications
2.11.2 Supported Power-up Voltage Sequence for the Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series
Figure 2-18. Supported Power-up Sequence Timing Requirements for Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9500 Series
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 67
Page 68
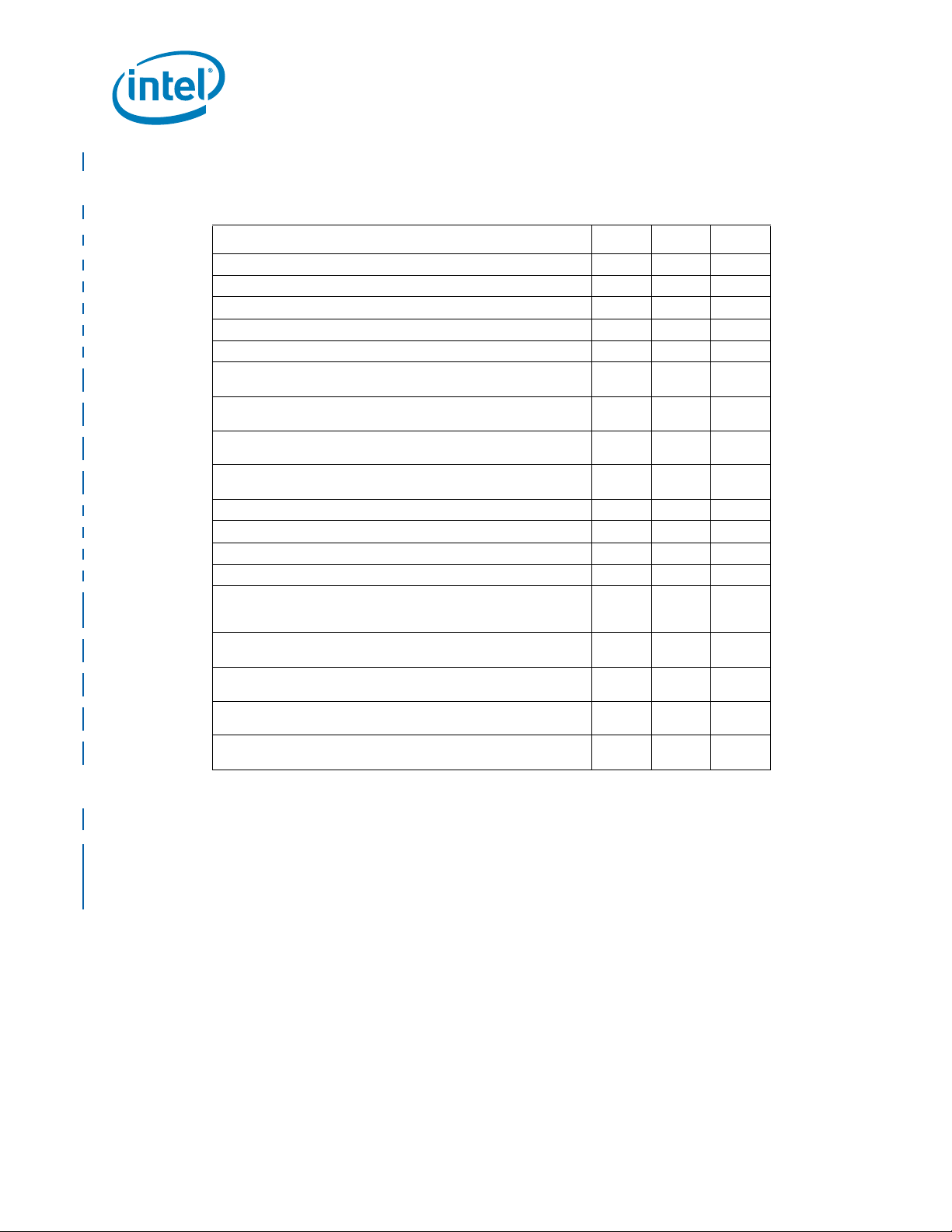
Electrical Specifications
2.11.3 Power-up Voltage Sequence Timing Requirements
Table 2-39. Power-up Voltage Sequence Timing Requirements
Parameter Min Max Unit
VCC33_SM stable high to VCCA delay >0
VCCA to VCCIO delay time 0 μs
VCCIO to PWRGOOD high delay time 1000 ms
VCCIO stable high to SYSCLK >0 μs
SYSCLK valid before VROUTPUTENABLE0 high >0 μs
VCCIO stable before VROUTPUT_ENABLE0 high for Intel
®
Itanium
VCCIO stable before VROUTPUT_ENABLE0 high for Intel
Itanium
VROUTPUT_ENABLE0 high to VRPWRGOOD high for Intel
Itanium
VROUTPUT_ENABLE0 high to VR_READY for Intel
Processor 9500 Series
Processor 9300 Series
®
Processor 9500 Series
®
Processor 9300 Series
2
VCCUNCORE time to stabilize
1
2
1
1
Delay from VCCUNCORE at programmed VID value to VCCCORE
VCCCORE steady at safe VID value
1
VCCCORE transition time from safe VID to programmed VID
Delay from VCCCORE/VCCUNCORE/VCCCACHE at programmed
values to VRPWRGOOD high for Intel
1
Series
VRPWRGD high to PWRGOOD high for Intel® Intel
Processor 9300 Series
VR_READY high to PWRGOOD high for Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300
®
Itanium® Processor
9500 Series
PWRGOOD high to RESET_N high (t
Processor 9300 Series
PWRGOOD high to RESET_N high (t
Processor 9500 Series
) Intel® Itanium®
RESET_N
) Intel® Itanium®
RESET_N
®
®
®
Itanium®
®
Itanium®
®
>1 μs
>1 ms
200 ms
200 ms
15ms
1
0.05 8 ms
0.05 3 ms
1
2.5
0.05 3
>0 ms
>0 ms
10 ms
15 ms
2.12 Supported Power-down Voltage Sequence
The supported power down sequence of voltage for the processor is detailed in
Figure 2-19. It should be noted that when the processor is required to be physically
removed from its socket, power rails VCC33_SM and Vcc(12V) must also be powered
down before removal of the processor.
68 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 69

Electrical Specifications
RESET_N
PWGOOD
VR_OUTPUT_EN
(133 MHz)
VIDs
VCCCORE
VCCUNCORE
VCCA
VCCCACHE
REFCLK
VCCIO
t
RESET_N
A s fast as p o s s ib le
All supplies to power down as fast as
Possible after PW RGO O D deassertion
> 1us
> 0us
VCCA MUST UNPOWER ALONG WITH VCCIO
t
RESET_N
= 10ms for Intel Itanium 9300 Series Processor
= 15m s fo r P oulso n -M C P ro c e s sor
> =0us
All signal inputs on VCCIO plane can power down with VCCIO
change to safe VID
Figure 2-19. Supported Power-down Voltage Sequence Timing Requirements
2.13 Timing Relationship Between RESET_N and SKTID
In the processor, the SKTID pins are time-shared:
SKTID[0] is interpreted as a NodeID bit during cold reset and pwrgood reset. It is
interpreted as the error reset modifier during warm-logic reset if SKTID[0] is asserted.
SKTID[2] is interpreted as a NodeID bit during cold reset and pwrgood reset, and it is
interpreted as an error input being signaled by the system at all other times (except
during non-cold resets when it is ignored). Figure 2-20 and Table 2-40 show the timing
relationship between RESET_N and SKTID pins for different reset cases.
The LRGSCLSYS pin is sampled only during the PWRGOOD and cold reset period.
The BOOTMODE[2:0] and FLASHROM_CFG[1:0] pins are sampled during the assertion
of all resets except warm-logic resets.
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 69
Page 70

Figure 2-20. RESET_N and SKITID Timing for Warm and Cold Resets
BOOTMODE[2:0]
FLASHROM
_CFG
[1:0]
PWRGOOD
RESET_N
SKTID[1:0 ]
T2
T
5
T4
SKTID[2]
LRGSCLSYS
socket id
Error Reset
(Warm-Logic) if
SKTID [0]==1
socket id
error_in
strap value
T9
T7
T8
T 11
T 13
T 13
T10
(PWR CYCLE OR PWRGOOD)
COLD RESET
WARM-
STATE OR WARM-
LOGIC RESETS
T12
T 14
strap values strap values
T1
T6
T3 T3
SYSCLK
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-40. RESET_N and SKTID Timing (Sheet 1 of 2)
Parameter Description MIN MAX UNIT
T1
T2
T2
T3
T4
T5
T5
T6
T7
T8
T9
T10
70 Intel
PWRGOOD deasserted delay to RESET_N
asserted
PWRGOOD asserted delay to RESET_N
deasserted (Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300
Series)
PWRGOOD asserted delay to RESET_N
deasserted (Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500
Series)
RESET_N setup and hold relative to SYSCLK
asserted
RESET_N deasserted pulse width
RESET_N asserted pulse width (Intel ® Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series)
RESET_N asserted pulse width (Intel ® Itanium®
Processor 9500 Series)
SKTID[2:0] (as rst modifier, error) hold after
PWRGOOD deasserted
SKTID[2:0] (as socket id), LRGSCLSYS,
BOOTMODE[2:0], FLASHROM_CFG[1:0] setup to
PWRGOOD deasserted
SKTID[2:0] (as socket id), LRGSCLSYS hold
after RESET_N deasserted
SKTID[1:0] (as rst modifier) setup to RESET_N
asserted
SKTID[1:0] (as rst modifier) hold after RESET_N
asserted
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
0 200 ns
10 ms
15 ms
500 ps
8
10 ms
15 ms
0ns
0ns
0ns
200 ns
200 ns
SYSCLK
cycles
Page 71

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-40. RESET_N and SKTID Timing (Sheet 2 of 2)
Parameter Description MIN MAX UNIT
T11
T12
T13
T14
RESET_N deasserted delay to SKTID[2]
deasserted (as error in)
SKTID[2] (as error in) asserted pulse width
BOOTMODE[2:0], FLASHROM_CFG[1:0] hold
after RESET_N deasserted
BOOTMODE[2:)], FLASHROM_CFG[1:0] setup to
RESET_N asserted
3
1us
0ns
2.14 Test Access Port (TAP) Connection
The recommended TAP connectivity is detailed in the Intel® Itanium® Platform Debug
Port Design Guide (DPDG).
§
100 ns
SYSCLK
cycles
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 71
Page 72

Electrical Specifications
72 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 73

Pin Listing
3 Pin Listing
3.1 Processor Package Bottom Pin Assignments
This section provides a sorted package bottom pin list in Table 3-1 and Table 3-2.
Table 3-1 is a listing of all processor package bottom side pins ordered alphabetically
by pin name. Table 3-2 is a listing of all processor package bottom side pins ordered by
pin number. All pins are defined for both Intel
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9500 Series except where noted.
3.1.1 Package Bottom Pin Listing by Pin Name
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 1
of 33)
Pin
Number
G10 BOOTMODE[0] I
G9 BOOTMODE[1] I
C3 CPU_PRES1_N I/O
D37 CPU_PRES2_N I/O
AT36 CPU_PRES3_N I/O
AT3 CPU_PRES4_N I/O
J37 CSI0RNCLK Differential I
B33 CSI0RNDAT[0] Differential I
D34 CSI0RNDAT[1] Differential I
B34 CSI0RNDAT[2] Differential I
D35 CSI0RNDAT[3] Differential I
C36 CSI0RNDAT[4] Differential I
E37 CSI0RNDAT[5] Differential I
F36 CSI0RNDAT[6] Differential I
G35 CSI0RNDAT[7] Differential I
H36 CSI0RNDAT[8] Differential I
J35 CSI0RNDAT[9] Differential I
L36 CSI0RNDAT[10] Differential I
L38 CSI0RNDAT[11] Differential I
N37 CSI0RNDAT[12] Differential I
P36 CSI0RNDAT[13] Differential I
R37 CSI0RNDAT[14] Differential I
T36 CSI0RNDAT[15] Differential I
T38 CSI0RNDAT[16] Differential I
U36 CSI0RNDAT[17] Differential I
V38 CSI0RNDAT[18] Differential I
W37 CSI0RNDAT[19] Differential I
K37 CSI0RPCLK Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 2
of 33)
Pin
Number
A33 CSI0RPDAT[0] Differential I
C34 CSI0RPDAT[1] Differential I
B35 CSI0RPDAT[2] Differential I
E35 CSI0RPDAT[3] Differential I
D36 CSI0RPDAT[4] Differential I
E38 CSI0RPDAT[5] Differential I
F37 CSI0RPDAT[6] Differential I
G36 CSI0RPDAT[7] Differential I
H37 CSI0RPDAT[8] Differential I
J36 CSI0RPDAT[9] Differential I
L37 CSI0RPDAT[10] Differential I
M38 CSI0RPDAT[11] Differential I
N38 CSI0RPDAT[12] Differential I
P37 CSI0RPDAT[13] Differential I
R38 CSI0RPDAT[14] Differential I
T37 CSI0RPDAT[15] Differential I
U38 CSI0RPDAT[16] Differential I
V36 CSI0RPDAT[17] Differential I
V37 CSI0RPDAT[18] Differential I
W36 CSI0RPDAT[19] Differential I
K33 CSI0TNCLK Differential O
K30 CSI0TNDAT[0] Differential O
J31 CSI0TNDAT[1] Differential O
G31 CSI0TNDAT [2] Differential O
F30 CSI0TNDAT[3] Differential O
K32 CSI0TNDAT[4] Differential O
F31 CSI0TNDAT[5] Differential O
E32 CSI0TNDAT[6] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 73
Page 74

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 3
of 33)
Pin
Number
F33 CSI0TNDAT[7] Differential O
H33 CSI0TNDAT[8] Differential O
L31 CSI0TNDAT[9] Differential O
L33 CSI0TNDAT[10] Differential O
M34 CSI0TNDAT[11] Differential O
N32 CSI0TNDAT[12] Differential O
N34 CSI0TNDAT[13] Differential O
R34 CSI0TNDAT[14] Differential O
R33 CSI0TNDAT[15] Differential O
U33 CSI0TNDAT[16] Differential O
V32 CSI0TNDAT[17] Differential O
V34 CSI0TNDAT[18] Differential O
W32 CSI0TNDAT[19] Differential O
K34 CSI0TPCLK Differential O
J30 CSI0TPDAT[0] Differential O
H31 CSI0TPDAT[1] Differential O
G30 CSI0TPDAT[2] Differential O
E30 CSI0TPDAT[3] Differential O
J32 CSI0TPDAT[4] Differential O
F32 CSI0TPDAT[5] Differential O
E33 CSI0TPDAT[6] Differential O
G33 CSI0TPDAT[7] Differential O
H34 CSI0TPDAT[8] Differential O
L32 CSI0TPDAT[9] Differential O
M33 CSI0TPDAT[10] Differential O
M35 CSI0TPDAT[11] Differential O
N33 CSI0TPDAT[12] Differential O
P34 CSI0TPDAT[13] Differential O
R35 CSI0TPDAT[14] Differential O
T33 CSI0TPDAT[15] Differential O
U34 CSI0TPDAT[16] Differential O
V33 CSI0TPDAT[17] Differential O
W34 CSI0TPDAT[18] Differential O
Y32 CSI0TPDAT[19] Differential O
AK38 CSI1RNCLK Differential I
AU33 CSI1RNDAT[0] Differential I
AV33 CSI1RNDAT[1] Differential I
AV34 CSI1RNDAT[2] Differential I
AR34 CSI1RNDAT[3] Differential I
AT35 CSI1RNDAT[4] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 4
of 33)
Pin
Number
AP36 CSI1RNDAT[5] Differential I
AP37 CSI1RNDAT[6] Differential I
AN37 CSI1RNDAT[7] Differential I
AM36 CSI1RNDAT[8] Differential I
AL37 CSI1RNDAT[9] Differential I
AJ37 CSI1RNDAT[10] Differential I
AH38 CSI1RNDAT[11] Differential I
AG36 CSI1RNDAT[12] Differential I
AF38 CSI1RNDAT[13] Differential I
AF36 CSI1RNDAT[14] Differential I
AE37 CSI1RNDAT[15] Differential I
AD36 CSI1RNDAT[16] Differential I
AC37 CSI1RNDAT[17] Differential I
AA38 CSI1RNDAT[18] Differential I
Y38 CSI1RNDAT[19] Differential I
AK37 CSI1RPCLK Differential I
AT33 CSI1RPDAT[0] Differential I
AV32 CSI1RPDAT[1] Differential I
AU34 CSI1RPDAT[2] Differential I
AR33 CSI1RPDAT[3] Differential I
AU35 CSI1RPDAT[4] Differential I
AP35 CSI1RPDAT[5] Differential I
AR37 CSI1RPDAT[6] Differential I
AN36 CSI1RPDAT[7] Differential I
AM35 CSI1RPDAT[8] Differential I
AL36 CSI1RPDAT[9] Differential I
AJ36 CSI1RPDAT[10] Differential I
AH37 CSI1RPDAT[11] Differential I
AH36 CSI1RPDAT[12] Differential I
AG38 CSI1RPDAT[13] Differential I
AF37 CSI1RPDAT[14] Differential I
AE38 CSI1RPDAT[15] Differential I
AD37 CSI1RPDAT[16] Differential I
AC38 CSI1RPDAT[17] Differential I
AB38 CSI1RPDAT[18] Differential I
Y37 CSI1RPDAT[19] Differential I
AJ32 CSI1TNCLK Differential O
AL27 CSI1TNDAT[0] Differential O
AN28 CSI1TNDAT[1] Differential O
AL28 CSI1TNDAT[2] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
74 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 75
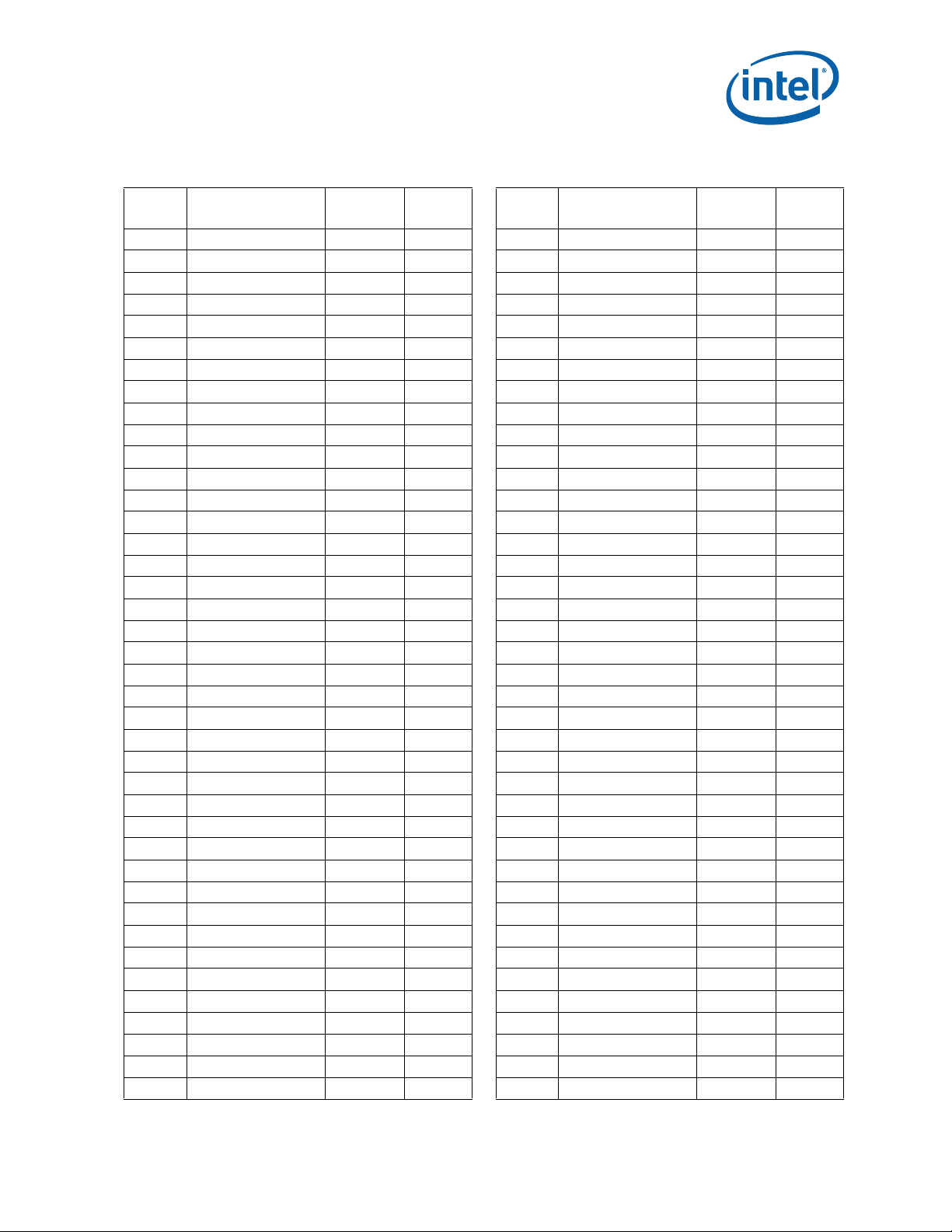
Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 5
of 33)
Pin
Number
AN29 CSI1TNDAT[3] Differential O
AP31 CSI1TNDAT[4] Differential O
AL30 CSI1TNDAT[5] Differential O
AN32 CSI1TNDAT[6] Differential O
AN34 CSI1TNDAT[7] Differential O
AM31 CSI1TNDAT[8] Differential O
AL33 CSI1TNDAT[9] Differential O
AK33 CSI1TNDAT[10] Differential O
AH34 CSI1TNDAT[11] Differential O
AH32 CSI1TNDAT[12] Differential O
AG33 CSI1TNDAT[13] Differential O
AE33 CSI1TNDAT[14] Differential O
AE34 CSI1TNDAT[15] Differential O
AC34 CSI1TNDAT[16] Differential O
AB34 CSI1TNDAT[17] Differential O
AA35 CSI1TNDAT[18] Differential O
Y34 CSI1TNDAT[19] Differential O
AK32 CSI1TPCLK Differential O
AL26 CSI1TPDAT[0] Differential O
AN27 CSI1TPDAT[1] Differential O
AM28 CSI1TPDAT[2] Differential O
AP29 CSI1TPDAT[3] Differential O
AP30 CSI1TPDAT[4] Differential O
AM30 CSI1TPDAT[5] Differential O
AP32 CSI1TPDAT[6] Differential O
AN33 CSI1TPDAT[7] Differential O
AN31 CSI1TPDAT[8] Differential O
AL32 CSI1TPDAT[9] Differential O
AK34 CSI1TPDAT[10] Differential O
AJ34 CSI1TPDAT[11] Differential O
AH33 CSI1TPDAT[12] Differential O
AG34 CSI1TPDAT[13] Differential O
AF33 CSI1TPDAT[14] Differential O
AE35 CSI1TPDAT[15] Differential O
AD34 CSI1TPDAT[16] Differential O
AB35 CSI1TPDAT[17] Differential O
AA36 CSI1TPDAT[18] Differential O
Y35 CSI1TPDAT[19] Differential O
A21 CSI2RNCLK Differential I
J22 CSI2RNDAT[0] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 6
of 33)
Pin
Number
H21 CSI2RNDAT[1] Differential I
G20 CSI2RNDAT[2] Differential I
F21 CSI2RNDAT[3] Differential I
E23 CSI2RNDAT[4] Differential I
E20 CSI2RNDAT[5] Differential I
D21 CSI2RNDAT[6] Differential I
C21 CSI2RNDAT [7] Differential I
B20 CSI2RNDAT[8] Differential I
C22 CSI2RNDAT [9] Differential I
B23 CSI2RNDAT[10] Differential I
B25 CSI2RNDAT[11] Differential I
C26 CSI2RNDAT[12] Differential I
A25 CSI2RNDAT[13] Differential I
D26 CSI2RNDAT[14] Differential I
C27 CSI2RNDAT[15] Differential I
B28 CSI2RNDAT[16] Differential I
B30 CSI2RNDAT[17] Differential I
C31 CSI2RNDAT[18] Differential I
C33 CSI2RNDAT[19] Differential I
A22 CSI2RPCLK Differential I
J21 CSI2RPDAT[0] Differential I
G21 CSI2RPDAT[1] Differential I
G19 CSI2RPDAT[2] Differential I
F20 CSI2RPDAT[3] Differential I
E22 CSI2RPDAT[4] Differential I
D20 CSI2RPDAT[5] Differential I
D22 CSI2RPDAT[6] Differential I
B21 CSI2RPDAT[7] Differential I
A20 CSI2RPDAT[8] Differential I
C23 CSI2RPDAT[9] Differential I
A23 CSI2RPDAT[10] Differential I
B24 CSI2RPDAT[11] Differential I
B26 CSI2RPDAT[12] Differential I
A26 CSI2RPDAT[13] Differential I
D27 CSI2RPDAT[14] Differential I
C28 CSI2RPDAT[15] Differential I
B29 CSI2RPDAT[16] Differential I
A30 CSI2RPDAT[17] Differential I
B31 CSI2RPDAT[18] Differential I
C32 CSI2RPDAT[19] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 75
Page 76

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 7
of 33)
Pin
Number
H29 CSI2TNCLK Differential O
H23 CSI2TNDAT[0] Differential O
G24 CSI2TNDAT[1] Differential O
F25 CSI2TNDAT[2] Differential O
D24 CSI2TNDAT[3] Differential O
H26 CSI2TNDAT[4] Differential O
F26 CSI2TNDAT[5] Differential O
E29 CSI2TNDAT[6] Differential O
J26 CSI2TNDAT[7] Differential O
F28 CSI2TNDAT[8] Differential O
H27 CSI2TNDAT[9] Differential O
K28 CSI2TNDAT[10] Differential O
M29 CSI2TNDAT[11] Differential O
P30 CSI2TNDAT[12] Differential O
M31 CSI2TNDAT[13] Differential O
R30 CSI2TNDAT[14] Differential O
P32 CSI2TNDAT[15] Differential O
T31 CSI2TNDAT[16] Differential O
U29 CSI2TNDAT[17] Differential O
U31 CSI2TNDAT[18] Differential O
W30 CSI2TNDAT[19] Differential O
J29 CSI2TPCLK Differential O
G23 CSI2TPDAT[0] Differential O
G25 CSI2TPDAT[1] Differential O
E25 CSI2TPDAT[2] Differential O
E24 CSI2TPDAT[3] Differential O
G26 CSI2TPDAT[4] Differential O
F27 CSI2TPDAT[5] Differential O
D29 CSI2TPDAT[6] Differential O
J27 CSI2TPDAT[7] Differential O
G28 CSI2TPDAT[8] Differential O
H28 CSI2TPDAT[9] Differential O
K29 CSI2TPDAT[10] Differential O
M30 CSI2TPDAT[11] Differential O
P31 CSI2TPDAT[12] Differential O
N31 CSI2TPDAT[13] Differential O
T30 CSI2TPDAT[14] Differential O
R32 CSI2TPDAT[15] Differential O
T32 CSI2TPDAT[16] Differential O
U30 CSI2TPDAT[17] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 8
of 33)
Pin
Number
V31 CSI2TPDAT[18] Differential O
W31 CSI2TPDAT[19] Differential O
AU21 CSI3RNCLK Differential I
AN18 CSI3RNDAT[0] Differential I
AL17 CSI3RNDAT[1] Differential I
AM16 CSI3RNDAT[2] Differential I
AN17 CSI3RNDAT[3] Differential I
AP19 CSI3RNDAT[4] Differential I
AR19 CSI3RNDAT[5] Differential I
AV17 CSI3RNDAT[6] Differential I
AU18 CSI3RNDAT[7] Differential I
AV19 CSI3RNDAT[8] Differential I
AT20 CSI3RNDAT[9] Differential I
AT22 CSI3RNDAT[10] Differential I
AU23 CSI3RNDAT[11] Differential I
AV24 CSI3RNDAT[12] Differential I
AU25 CSI3RNDAT[13] Differential I
AU26 CSI3RNDAT[14] Differential I
AT27 CSI3RNDAT[15] Differential I
AU28 CSI3RNDAT[16] Differential I
AV29 CSI3RNDAT[17] Differential I
AU30 CSI3RNDAT[18] Differential I
AV31 CSI3RNDAT[19] Differential I
AT21 CSI3RPCLK Differential I
AM18 CSI3RPDAT[0] Differential I
AL16 CSI3RPDAT[1] Differential I
AM15 CSI3RPDAT[2] Differential I
AN16 CSI3RPDAT[3] Differential I
AN19 CSI3RPDAT[4] Differential I
AR18 CSI3RPDAT[5] Differential I
AV16 CSI3RPDAT[6] Differential I
AT18 CSI3RPDAT[7] Differential I
AU19 CSI3RPDAT[8] Differential I
AR20 CSI3RPDAT[9] Differential I
AR22 CSI3RPDAT[10] Differential I
AT23 CSI3RPDAT[11] Differential I
AV23 CSI3RPDAT[12] Differential I
AU24 CSI3RPDAT[13] Differential I
AT26 CSI3RPDAT[14] Differential I
AR27 CSI3RPDAT[15] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
76 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 77

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 9
of 33)
Pin
Number
AT28 CSI3RPDAT[16] Differential I
AV28 CSI3RPDAT[17] Differential I
AU29 CSI3RPDAT[18] Differential I
AU31 CSI3RPDAT[19] Differential I
AK29 CSI3TNCLK Differential O
AL20 CSI3TNDAT[0] Differential O
AM20 CSI3TNDAT[1] Differential O
AM23 CSI3TNDAT[2] Differential O
AN21 CSI3TNDAT[3] Differential O
AN23 CSI3TNDAT[4] Differential O
AM24 CSI3TNDAT[5] Differential O
AP25 CSI3TNDAT[6] Differential O
AN26 CSI3TNDAT[7] Differential O
AM26 CSI3TNDAT[8] Differential O
AJ27 CSI3TNDAT[9] Differential O
AH29 CSI3TNDAT[10] Differential O
AJ30 CSI3TNDAT[11] Differential O
AG31 CSI3TNDAT[12] Differential O
AF30 CSI3TNDAT[13] Differential O
AF31 CSI3TNDAT[14] Differential O
AD32 CSI3TNDAT[15] Differential O
AC31 CSI3TNDAT[16] Differential O
AB33 CSI3TNDAT[17] Differential O
AA31 CSI3TNDAT[18] Differential O
AA32 CSI3TNDAT[19] Differential O
AK28 CSI3TPCLK Differential O
AK20 CSI3TPDAT[0] Differential O
AM21 CSI3TPDAT[1] Differential O
AL23 CSI3TPDAT[2] Differential O
AP21 CSI3TPDAT[3] Differential O
AN22 CSI3TPDAT[4] Differential O
AN24 CSI3TPDAT[5] Differential O
AR25 CSI3TPDAT[6] Differential O
AP26 CSI3TPDAT[7] Differential O
AM25 CSI3TPDAT[8] Differential O
AK27 CSI3TPDAT[9] Differential O
AJ29 CSI3TPDAT[10] Differential O
AJ31 CSI3TPDAT[11] Differential O
AH31 CSI3TPDAT[12] Differential O
AG30 CSI3TPDAT[13] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 10
of 33)
Pin
Number
AF32 CSI3TPDAT[14] Differential O
AE32 CSI3TPDAT[15] Differential O
AC32 CSI3TPDAT[16] Differential O
AC33 CSI3TPDAT[17] Differential O
AB31 CSI3TPDAT[18] Differential O
AA33 CSI3TPDAT[19] Differential O
H18 CSI4RNCLK Differential I
B15 CSI4RNDAT[0] Differential I
D15 CSI4RNDAT[1] Differential I
C16 CSI4RNDAT [2] Differential I
A17 CSI4RNDAT[3] Differential I
B18 CSI4RNDAT[4] Differential I
C17 CSI4RNDAT [5] Differential I
D19 CSI4RNDAT[6] Differential I
E17 CSI4RNDAT[7] Differential I
E18 CSI4RNDAT[8] Differential I
F17 CSI4RNDAT[9] Differential I
G18 CSI4RPCLK Differential I
A15 CSI4RPDAT[0] Differential I
D16 CSI4RPDAT[1] Differential I
B16 CSI4RPDAT[2] Differential I
A18 CSI4RPDAT[3] Differential I
B19 CSI4RPDAT[4] Differential I
C18 CSI4RPDAT[5] Differential I
C19 CSI4RPDAT[6] Differential I
D17 CSI4RPDAT[7] Differential I
E19 CSI4RPDAT[8] Differential I
F18 CSI4RPDAT[9] Differential I
L21 CSI4TNCLK Differential O
M14 CSI4TNDAT[0] Differential O
K13 CSI4TNDAT[1] Differential O
K15 CSI4TNDAT[2] Differential O
J14 CSI4TNDAT[3] Differential O
G15 CSI4TNDAT [4] Differential O
J16 CSI4TNDAT[5] Differential O
K17 CSI4TNDAT[6] Differential O
L18 CSI4TNDAT[7] Differential O
K19 CSI4TNDAT[8] Differential O
L20 CSI4TNDAT[9] Differential O
L22 CSI4TPCLK Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 77
Page 78

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 11
of 33)
Pin
Number
M15 CSI4TPDAT[0] Differential O
K14 CSI4TPDAT[1] Differential O
J15 CSI4TPDAT[2] Differential O
H14 CSI4TPDAT[3] Differential O
G16 CSI4TPDAT[4] Differential O
H16 CSI4TPDAT[5] Differential O
J17 CSI4TPDAT[6] Differential O
K18 CSI4TPDAT[7] Differential O
J19 CSI4TPDAT[8] Differential O
K20 CSI4TPDAT[9] Differential O
AP17 CSI5RNCLK Differential I
AL12 CSI5RNDAT[0] Differential I
AM13 CSI5RNDAT[1] Differential I
AN14 CSI5RNDAT[2] Differential I
AP15 CSI5RNDAT[3] Differential I
AR13 CSI5RNDAT[4] Differential I
AT13 CSI5RNDAT[5] Differential I
AU14 CSI5RNDAT[6] Differential I
AR15 CSI5RNDAT[7] Differential I
AU15 CSI5RNDAT[8] Differential I
AT16 CSI5RNDAT[9] Differential I
AR17 CSI5RPCLK Differential I
AL13 CSI5RPDAT[0] Differential I
AN13 CSI5RPDAT[1] Differential I
AP14 CSI5RPDAT[2] Differential I
AP16 CSI5RPDAT[3] Differential I
AR14 CSI5RPDAT[4] Differential I
AU13 CSI5RPDAT[5] Differential I
AV14 CSI5RPDAT[6] Differential I
AT15 CSI5RPDAT[7] Differential I
AU16 CSI5RPDAT[8] Differential I
AT17 CSI5RPDAT[9] Differential I
AJ22 CSI5TNCLK Differential O
AG13 CSI5TNDAT[0] Differential O
AH14 CSI5TNDAT[1] Differential O
AJ15 CSI5TNDAT[2] Differential O
AG16 CSI5TNDAT[3] Differential O
AH17 CSI5TNDAT[4] Differential O
AH19 CSI5TNDAT[5] Differential O
AK18 CSI5TNDAT[6] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 12
of 33)
Pin
Number
AG19 CSI5TNDAT[7] Differential O
AJ20 CSI5TNDAT[8] Differential O
AL21 CSI5TNDAT[9] Differential O
AK22 CSI5TPCLK Differential O
AH13 CSI5TPDAT[0] Differential O
AJ14 CSI5TPDAT[1] Differential O
AK15 CSI5TPDAT[2] Differential O
AH16 CSI5TPDAT[3] Differential O
AJ17 CSI5TPDAT[4] Differential O
AJ19 CSI5TPDAT[5] Differential O
AK19 CSI5TPDAT[6] Differential O
AG20 CSI5TPDAT[7] Differential O
AJ21 CSI5TPDAT[8] Differential O
AL22 CSI5TPDAT[9] Differential O
H12 ERROR[0]_N O
J12 ERROR[1]_N O
AT11 FBD0NBIAN[0] Differential I
AU9 FBD0NBIAN[1] Differential I
AV8 FBD0NBIAN[2] Differential I
AR10 FBD0NBIAN[3] Differential I
AT8 FBD0NBIAN[4] Differential I
AT6 FBD0NBIAN[5] Differential I
AP4 FBD0NBIAN[6] Differential I
AN2 FBD0NBIAN[7] Differential I
AN3 FBD0NBIAN[8] Differential I
AL3 FBD0NBIAN[9] Differential I
AL1 FBD0NBIAN[10] Differential I
AK2 FBD0NBIAN[11] Differential I
AR2 FBD0NBIAN[12] Differential I
AU4 FBD0NBIAN[13] Differential I
AV11 FBD0NBIAN[14] Differential I
AU11 FBD0NBIAP[0] Differential I
AU10 FBD0NBIAP[1] Differential I
AV9 FBD0NBIAP[2] Differential I
AT10 FBD0NBIAP[3] Differential I
AU8 FBD0NBIAP[4] Differential I
AU6 FBD0NBIAP[5] Differential I
AR4 FBD0NBIAP[6] Differential I
AP2 FBD0NBIAP[7] Differential I
AN4 FBD0NBIAP[8] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
78 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 79

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 13
of 33)
Pin
Number
AM3 FBD0NBIAP[9] Differential I
AL2 FBD0NBIAP[10] Differential I
AK3 FBD0NBIAP[11] Differential I
AR3 FBD0NBIAP[12] Differential I
AU5 FBD0NBIAP[13] Differential I
AV12 FBD0NBIAP[14] Differential I
AN9 FBD0NBIBN[0] Differential I
AM9 FBD0NBIBN[1] Differential I
AP7 FBD0NBIBN[2] Differential I
AP6 FBD0NBIBN[3] Differential I
AM5 FBD0NBIBN[4] Differential I
AK5 FBD0NBIBN[5] Differential I
AG1 FBD0NBIBN[6] Differential I
AF3 FBD0NBIBN[7] Differential I
AF2 FBD0NBIBN[8] Differential I
AE3 FBD0NBIBN[9] Differential I
AD1 FBD0NBIBN[10] Differential I
AB1 FBD0NBIBN[11] Differential I
AH2 FBD0NBIBN[12] Differential I
AJ4 FBD0NBIBN[13] Differential I
AM10 FBD0NBIBN[14] Differential I
AP9 FBD0NBIBP[0] Differential I
AM8 FBD0NBIBP[1] Differential I
AR7 FBD0NBIBP[2] Differential I
AN6 FBD0NBIBP[3] Differential I
AM6 FBD0NBIBP[4] Differential I
AL5 FBD0NBIBP[5] Differential I
AH1 FBD0NBIBP[6] Differential I
AG3 FBD0NBIBP[7] Differential I
AF1 FBD0NBIBP[8] Differential I
AE2 FBD0NBIBP[9] Differential I
AD2 FBD0NBIBP[10] Differential I
AC1 FBD0NBIBP[11] Differential I
AJ2 FBD0NBIBP[12] Differential I
AK4 FBD0NBIBP[13] Differential I
AL10 FBD0NBIBP[14] Differential I
AR5 FBD0NBICLKAN0 Differential I
AT5 FBD0NBICLKAP0 Differential I
AH3 FBD0NBICLKBN0 Differential I
AH4 FBD0NBICLKBP0 Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 14
of 33)
Pin
Number
AL6 FBD0REFSYSCLKN Differential I
AL7 FBD0REFSYSCLKP Differential I
V4 FBD0SBOAN[0] Differential O
W1 FBD0SBOAN[1] Differential O
V2 FBD0SBOAN[2] Differential O
U1 FBD0SBOAN[3] Differential O
T1 FBD0SBOAN[4] Differential O
N3 FBD0SBOAN[5] Differential O
M1 FBD0SBOAN[6] Differential O
L3 FBD0SBOAN[7] Differential O
L1 FBD0SBOAN[8] Differential O
P1 FBD0SBOAN[9] Differential O
J2 FBD0SBOAN[10] Differential O
W4 FBD0SBOAP[0] Differential O
W2 FBD0SBOAP[1] Differential O
V3 FBD0SBOAP[2] Differential O
V1 FBD0SBOAP[3] Differential O
T2 FBD0SBOAP[4] Differential O
N2 FBD0SBOAP[5] Differential O
N1 FBD0SBOAP[6] Differential O
M3 FBD0SBOAP[7] Differential O
L2 FBD0SBOAP[8] Differential O
P2 FBD0SBOAP[9] Differential O
K2 FBD0SBOAP[10] Differential O
AK8 FBD0SBOBN[0] Differential O
AJ7 FBD0SBOBN[1] Differential O
AH6 FBD0SBOBN[2] Differential O
AF7 FBD0SBOBN[3] Differential O
AF6 FBD0SBOBN[4] Differential O
AC4 FBD0SBOBN[5] Differential O
AB3 FBD0SBOBN[6] Differential O
AD6 FBD0SBOBN[7] Differential O
AA2 FBD0SBOBN[8] Differential O
AD7 FBD0SBOBN[9] Differential O
Y3 FBD0SBOBN[10] Differential O
AK9 FBD0SBOBP[0] Differential O
AK7 FBD0SBOBP[1] Differential O
AH7 FBD0SBOBP[2] Differential O
AF8 FBD0SBOBP[3] Differential O
AG6 FBD0SBOBP[4] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 79
Page 80

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 15
of 33)
Pin
Number
AD4 FBD0SBOBP[5] Differential O
AC3 FBD0SBOBP[6] Differential O
AD5 FBD0SBOBP[7] Differential O
AA3 FBD0SBOBP[8] Differential O
AE7 FBD0SBOBP[9] Differential O
Y4 FBD0SBOBP[10] Differential O
R2 FBD0SBOCLKAN0 Differential O
R3 FBD0SBOCLKAP0 Differential O
AE5 FBD0SBOCLKBN0 Differential O
AF5 FBD0SBOCLKBP0 Differential O
L8 FBD1NBICLKCN0 Differential I
M8 FBD1NBICLKCP0 Differential I
R7 FBD1NBICLKDN0 Differential I
P7 FBD1NBICLKDP0 Differential I
V9 FBD1NBICN[0] Differential I
V7 FBD1NBICN[1] Differential I
T8 FBD1NBICN[2] Differential I
U10 FBD1NBICN[3] Differential I
R9 FBD1NBICN[4] Differential I
P9 FBD1NBICN[5] Differential I
K9 FBD1NBICN[6] Differential I
J11 FBD1NBICN[7] Differential I
G11 FBD1NBICN[8] Differential I
G8 FBD1NBICN[9] Differential I
H9 FBD1NBICN[10] Differential I
F11 FBD1NBICN[11] Differential I
L12 FBD1NBICN[12] Differential I
M9 FBD1NBICN[13] Differential I
Y8 FBD1NBICN[14] Differential I
W9 FBD1NBICP[0] Differential I
V8 FBD1NBICP[1] Differential I
U8 FBD1NBICP[2] Differential I
U9 FBD1NBICP[3] Differential I
R8 FBD1NBICP[4] Differential I
N9 FBD1NBICP[5] Differential I
K8 FBD1NBICP[6] Differential I
J10 FBD1NBICP[7] Differential I
H11 FBD1NBICP[8] Differential I
H8 FBD1NBICP[9] Differential I
J9 FBD1NBICP[10] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 16
of 33)
Pin
Number
F10 FBD1NBICP[11] Differential I
L11 FBD1NBICP[12] Differential I
M10 FBD1NBICP[13] Differential I
Y9 FBD1NBICP[14] Differential I
AB6 FBD1NBIDN[0] Differential I
AA6 FBD1NBIDN[1] Differential I
W7 FBD1NBIDN[2] Differential I
W6 FBD1NBIDN[3] Differential I
U5 FBD1NBIDN[4] Differential I
T7 FBD1NBIDN[5] Differential I
M6 FBD1NBIDN[6] Differential I
M5 FBD1NBIDN[7] Differential I
N8 FBD1NBIDN[8] Differential I
K4 FBD1NBIDN[9] Differential I
L7 FBD1NBIDN[10] Differential I
J7 FBD1NBIDN[11] Differential I
P5 FBD1NBIDN[12] Differential I
R5 FBD1NBIDN[13] Differential I
AC8 FBD1NBIDN[14] Differential I
AB5 FBD1NBIDP[0] Differential I
AA7 FBD1NBIDP[1] Differential I
Y7 FBD1NBIDP[2] Differential I
V6 FBD1NBIDP[3] Differential I
U6 FBD1NBIDP[4] Differential I
T6 FBD1NBIDP[5] Differential I
N6 FBD1NBIDP[6] Differential I
L5 FBD1NBIDP[7] Differential I
N7 FBD1NBIDP[8] Differential I
K5 FBD1NBIDP[9] Differential I
L6 FBD1NBIDP[10] Differential I
K7 FBD1NBIDP[11] Differential I
P6 FBD1NBIDP[12] Differential I
T5 FBD1NBIDP[13] Differential I
AB8 FBD1NBIDP[14] Differential I
AD9 FBD1REFSYSCLKN Differential I
AC9 FBD1REFSYSCLKP Differential I
A8 FBD1SBOCLKCN0 Differential O
A7 FBD1SBOCLKCP0 Differential O
E4 FBD1SBOCLKDN0 Differential O
E3 FBD1SBOCLKDP0 Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
80 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 81

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 17
of 33)
Pin
Number
D12 FBD1SBOCN[0] Differential O
E8 FBD1SBOCN[1] Differential O
E7 FBD1SBOCN[2] Differential O
C9 FBD1SBOCN[3] Differential O
C8 FBD1SBOCN[4] Differential O
B10 FBD1SBOCN[5] Differential O
C11 FBD1SBOCN[6] Differential O
A12 FBD1SBOCN[7] Differential O
C13 FBD1SBOCN[8] Differential O
B9 FBD1SBOCN[9] Differential O
B13 FBD1SBOCN[10] Differential O
D11 FBD1SBOCP[0] Differential O
E9 FBD1SBOCP[1] Differential O
D7 FBD1SBOCP[2] Differential O
D9 FBD1SBOCP[3] Differential O
C7 FBD1SBOCP[4] Differential O
A10 FBD1SBOCP[5] Differential O
B11 FBD1SBOCP[6] Differential O
A11 FBD1SBOCP[7] Differential O
C12 FBD1SBOCP[8] Differential O
B8 FBD1SBOCP[9] Differential O
A13 FBD1SBOCP[10] Differential O
H1 FBD1SBODN[0] Differential O
G3 FBD1SBODN[1] Differential O
G4 FBD1SBODN[2] Differential O
F2 FBD1SBODN[3] Differential O
D2 FBD1SBODN[4] Differential O
C4 FBD1SBODN[5] Differential O
B6 FBD1SBODN[6] Differential O
D5 FBD1SBODN[7] Differential O
F7 FBD1SBODN[8] Differential O
B4 FBD1SBODN[9] Differential O
G6 FBD1SBODN[10] Differential O
H2 FBD1SBODP[0] Differential O
H3 FBD1SBODP[1] Differential O
G5 FBD1SBODP[2] Differential O
F3 FBD1SBODP[3] Differential O
E2 FBD1SBODP[4] Differential O
D4 FBD1SBODP[5] Differential O
C6 FBD1SBODP[6] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 18
of 33)
Pin
Number
D6 FBD1SBODP[7] Differential O
F6 FBD1SBODP[8] Differential O
B5 FBD1SBODP[9] Differential O
H6 FBD1SBODP[10] Differential O
N28 FLASHROM_CFG[0] I
M28 FLASHROM_CFG[1] I
L28 FLASHROM_CFG[2] I
N27 FLASHROM_CLK O
L30 FLASHROM_CS[0]_N O
P29 FLASHROM_CS[1]_N O
R29 FLASHROM_CS[2]_N O
N29 FLASHROM_CS[3]_N O
T28 FLASHROM_DATI I
R28 FLASHROM_DATO O
L27 FLASHROM_WP_N I
K10 FORCEPR_N I
M11 LRGSCLSYS I
K12 MEM_THROTTLE_L I
AJ25 PIR_A0 Power/Other I
AJ24 PIR_A1 Power/Other I
AG24 PIR_SCL Power/Other I
AH24 PIR_SDA Power/Other I/O
AF11 PRBMODE_RDY_N O
AF12 PRBMODE_REQST_N I
L10 PROCHOT_N O
AP1 PROCTYPE I
AR9 PWRGOOD I
V12 RESET_N Power/Other I
AD12 RSVD I
A1 RSVD
A2 RSVD
A35 RSVD
A37 RSVD
A38 RSVD
A4 RSVD
AA11 RSVD
AA27 RSVD
AC12 RSVD
AC27 RSVD
AC28 RSVD
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 81
Page 82

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 19
of 33)
Pin
Number
Pin Name
AC29 RSVD
AD27 RSVD
AD29 RSVD
AD30 RSVD
AE12 RSVD
AE27 RSVD
AE30 RSVD
AG21 RSVD
AH21 RSVD
AK12 RSVD
AL31 RSVD
AL8 RSVD
AM11 RSVD
AM38 RSVD
AN11 RSVD
AN38 RSVD
AP27 RSVD
AR1 RSVD
AR38 RSVD
AT2 RSVD
AT37 RSVD
AT38 RSVD
AU1 RSVD
AU2 RSVD
AU3 RSVD
AU36 RSVD
AU37 RSVD
AV1 RSVD
AV2 RSVD
AV35 RSVD
AV37 RSVD
AV38 RSVD
AV4 RSVD
B2 RSVD
B3 RSVD
B36 RSVD
B37 RSVD
B38 RSVD
C1 RSVD
C2 RSVD
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 20
of 33)
Pin
Number
Pin Name
C37 RSVD
D1 RSVD
D38 RSVD
F1 RSVD
F38 RSVD
G1 RSVD
G38 RSVD
H13 RSVD
J20 RSVD
L13 RSVD
M13 RSVD
M20 RSVD
M21 RSVD
M36 RSVD
M4 RSVD
P10 RSVD (Intel
®
Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series)
SVID_CLK2 (Intel
®
Itanium
Processor
9500 Series)
P27 RSVD
R10 RSVD
(Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series)
SVID_DATIO
Itanium
9500 Series)
(Intel®
®
Processor
R27 RSVD
T11 RSVD
(Intel® Itanium®
Processor 9300 Series)
2
SVID_ALERT_N
Itanium
9500 Series)
(Intel®
®
Processor
U4 RSVD
V27 RSVD
V29 RSVD
W10 RSVD
W12 RSVD
W27 RSVD
Y10 RSVD
AG29 SKTID[0] I
AH28 SKTID[1] I
AG28 SKTID[2] I
AE28 SM_WP I
AT32 SMBCLK SMBus I/O
AR32 SMBDAT SMBus I/O
®
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
82 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 83
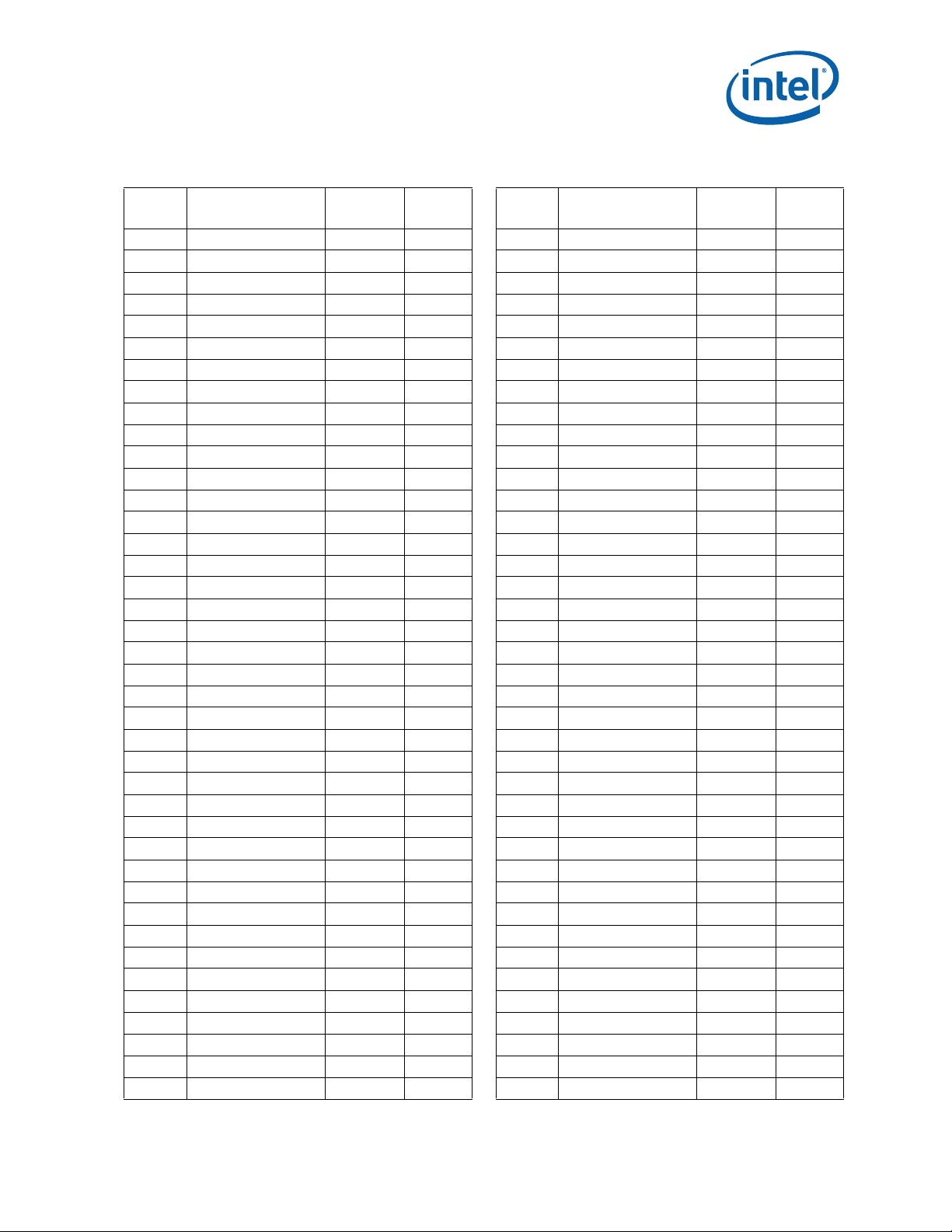
Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 21
of 33)
Pin
Number
AT30 SPDCLK I/O
AT31 SPDDAT I/O
Y12 SYSCLK Differential I
AA12 SYSCLK_N Differential I
V11 SYSUTST_REFCLK Differential I
U11 SYSUTST_REFCLK_N Differential I
P11 TCK I
P12 TDI I
N12 TDO O
Y28 TESTHI[1] I
W29 TESTHI[2] I
V28 TESTHI[4] I
A5 THERMALERT_N O
A6 THERMTRIP_N O
R12 TMS I
AL11 TRIGGER[0]_N I/O
AP11 TRIGGER[1]_N I/O
N11 TRST_N I
AV6 VCC33_SM Power/Other
AV7 VCC33_SM Power/Other
A27 VCCA Power/Other
A28 VCCA Power/Other
A31 VCCA Power/Other
A32 VCCA Power/Other
AV21 VCCA Power/Other
AV22 VCCA Power/Other
AV26 VCCA Power/Other
AV27 VCCA Power/Other
AA37 VCCIO Power/Other
AB28 VCCIO Power/Other
AB30 VCCIO Power/Other
AB36 VCCIO Power/Other
AD11 VCCIO Power/Other
AD31 VCCIO Power/Other
AE29 VCCIO Power/Other
AF10 VCCIO Power/Other
AF27 VCCIO Power/Other
AG14 VCCIO Power/Other
AG18 VCCIO Power/Other
AG25 VCCIO Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 22
of 33)
Pin
Number
AG35 VCCIO Power/Other
AH12 VCCIO Power/Other
AH22 VCCIO Power/Other
AH27 VCCIO Power/Other
AK13 VCCIO Power/Other
AK17 VCCIO Power/Other
AK23 VCCIO Power/Other
AL15 VCCIO Power/Other
AL25 VCCIO Power/Other
AL35 VCCIO Power/Other
AM14 VCCIO Power/Other
AM19 VCCIO Power/Other
AM29 VCCIO Power/Other
AM33 VCCIO Power/Other
AN12 VCCIO Power/Other
AP20 VCCIO Power/Other
AP24 VCCIO Power/Other
AP34 VCCIO Power/Other
AR12 VCCIO Power/Other
AR23 VCCIO Power/Other
AR28 VCCIO Power/Other
AR30 VCCIO Power/Other
AR35 VCCIO Power/Other
AT25 VCCIO Power/Other
AU20 VCCIO Power/Other
C14 VCCIO Power/Other
C24 VCCIO Power/Other
C29 VCCIO Power/Other
D32 VCCIO Power/Other
E14 VCCIO Power/Other
E27 VCCIO Power/Other
E34 VCCIO Power/Other
F16 VCCIO Power/Other
F23 VCCIO Power/Other
F35 VCCIO Power/Other
G13 VCCIO Power/Other
G29 VCCIO Power/Other
G34 VCCIO Power/Other
H17 VCCIO Power/Other
H19 VCCIO Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 83
Page 84

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 23
of 33)
Pin
Number
H22 VCCIO Power/Other
H24 VCCIO Power/Other
H32 VCCIO Power/Other
J34 VCCIO Power/Other
K24 VCCIO Power/Other
K27 VCCIO Power/Other
K35 VCCIO Power/Other
L15 VCCIO Power/Other
M18 VCCIO Power/Other
M23 VCCIO Power/Other
M26 VCCIO Power/Other
N36 VCCIO Power/Other
T27 VCCIO Power/Other
T35 VCCIO Power/Other
U28 VCCIO Power/Other
W35 VCCIO Power/Other
Y27 VCCIO Power/Other
Y30 VCCIO Power/Other
Y33 VCCIO Power/Other
AA1 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AA8 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AB4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AB9 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AC2 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AC6 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AE4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AE8 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AG4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AJ1 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AJ5 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AM4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AN7 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AP10 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AP5 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AR8 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AT7 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
E10 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
E12 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
E5 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
F8 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 24
of 33)
Pin
Number
H7 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
J1 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
J4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
N4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
T10 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
T3 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
W5 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
Y2 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
T12 VFUSERM I
AN1 VR_FAN_N O
K38 VR_THERMALERT_N O
H38 VR_THERMTRIP_N O
AL38 VROUTPUT_ENABLE0 I
AM1 VRPWRGD (Intel
A14 VSS Power/Other
A16 VSS Power/Other
A19 VSS Power/Other
A24 VSS Power/Other
A29 VSS Power/Other
A3 VSS Power/Other
A34 VSS Power/Other
A36 VSS Power/Other
A9 VSS Power/Other
AA10 VSS Power/Other
AA28 VSS Power/Other
AA29 VSS Power/Other
AA30 VSS Power/Other
AA34 VSS Power/Other
AA4 VSS Power/Other
AA5 VSS Power/Other
AA9 VSS Power/Other
AB10 VSS Power/Other
AB11 VSS Power/Other
AB12 VSS Power/Other
AB2 VSS Power/Other
AB27 VSS Power/Other
AB29 VSS Power/Other
AB32 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
®
Itanium
9300 Series)
VR_READY
®
Itanium
9500 Series)
®
Processor
2
(Intel®
Processor
Buffer Type
Signal
Direction
O
84 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 85

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 25
of 33)
Pin
Number
AB37 VSS Power/Other
AB7 VSS Power/Other
AC10 VSS Power/Other
AC11 VSS Power/Other
AC30 VSS Power/Other
AC35 VSS Power/Other
AC36 VSS Power/Other
AC5 VSS Power/Other
AC7 VSS Power/Other
AD10 VSS Power/Other
AD28 VSS Power/Other
AD3 VSS Power/Other
AD33 VSS Power/Other
AD35 VSS Power/Other
AD38 VSS Power/Other
AD8 VSS Power/Other
AE1 VSS Power/Other
AE10 VSS Power/Other
AE11 VSS Power/Other
AE31 VSS Power/Other
AE36 VSS Power/Other
AE6 VSS Power/Other
AE9 VSS Power/Other
AF28 VSS Power/Other
AF29 VSS Power/Other
AF34 VSS Power/Other
AF35 VSS Power/Other
AF4 VSS Power/Other
AF9 VSS Power/Other
AG12 VSS Power/Other
AG15 VSS Power/Other
AG17 VSS Power/Other
AG2 VSS Power/Other
AG22 VSS Power/Other
AG23 VSS Power/Other
AG26 VSS Power/Other
AG27 VSS Power/Other
AG32 VSS Power/Other
AG37 VSS Power/Other
AG5 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 26
of 33)
Pin
Number
AG7 VSS Power/Other
AH10 VSS Power/Other
AH15 VSS Power/Other
AH18 VSS Power/Other
AH20 VSS Power/Other
AH23 VSS Power/Other
AH25 VSS Power/Other
AH26 VSS Power/Other
AH30 VSS Power/Other
AH35 VSS Power/Other
AH5 VSS Power/Other
AJ12 VSS Power/Other
AJ13 VSS Power/Other
AJ16 VSS Power/Other
AJ18 VSS Power/Other
AJ23 VSS Power/Other
AJ26 VSS Power/Other
AJ28 VSS Power/Other
AJ3 VSS Power/Other
AJ33 VSS Power/Other
AJ35 VSS Power/Other
AJ38 VSS Power/Other
AJ6 VSS Power/Other
AJ8 VSS Power/Other
AK1 VSS Power/Other
AK11 VSS Power/Other
AK14 VSS Power/Other
AK16 VSS Power/Other
AK21 VSS Power/Other
AK24 VSS Power/Other
AK25 VSS Power/Other
AK26 VSS Power/Other
AK30 VSS Power/Other
AK31 VSS Power/Other
AK35 VSS Power/Other
AK36 VSS Power/Other
AK6 VSS Power/Other
AL14 VSS Power/Other
AL18 VSS Power/Other
AL19 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 85
Page 86

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 27
of 33)
Pin
Number
AL24 VSS Power/Other
AL29 VSS Power/Other
AL34 VSS Power/Other
AL4 VSS Power/Other
AL9 VSS Power/Other
AM12 VSS Power/Other
AM17 VSS Power/Other
AM2 VSS Power/Other
AM22 VSS Power/Other
AM27 VSS Power/Other
AM32 VSS Power/Other
AM34 VSS Power/Other
AM37 VSS Power/Other
AM7 VSS Power/Other
AN10 VSS Power/Other
AN15 VSS Power/Other
AN20 VSS Power/Other
AN25 VSS Power/Other
AN30 VSS Power/Other
AN35 VSS Power/Other
AN5 VSS Power/Other
AN8 VSS Power/Other
AP12 VSS Power/Other
AP13 VSS Power/Other
AP18 VSS Power/Other
AP22 VSS Power/Other
AP23 VSS Power/Other
AP28 VSS Power/Other
AP3 VSS Power/Other
AP33 VSS Power/Other
AP38 VSS Power/Other
AP8 VSS Power/Other
AR11 VSS Power/Other
AR16 VSS Power/Other
AR21 VSS Power/Other
AR24 VSS Power/Other
AR26 VSS Power/Other
AR29 VSS Power/Other
AR31 VSS Power/Other
AR36 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 28
of 33)
Pin
Number
AR6 VSS Power/Other
AT1 VSS Power/Other
AT12 VSS Power/Other
AT14 VSS Power/Other
AT19 VSS Power/Other
AT24 VSS Power/Other
AT29 VSS Power/Other
AT34 VSS Power/Other
AT4 VSS Power/Other
AT9 VSS Power/Other
AU12 VSS Power/Other
AU17 VSS Power/Other
AU22 VSS Power/Other
AU27 VSS Power/Other
AU32 VSS Power/Other
AU38 VSS Power/Other
AU7 VSS Power/Other
AV10 VSS Power/Other
AV13 VSS Power/Other
AV15 VSS Power/Other
AV18 VSS Power/Other
AV20 VSS Power/Other
AV25 VSS Power/Other
AV3 VSS Power/Other
AV30 VSS Power/Other
AV36 VSS Power/Other
AV5 VSS Power/Other
B1 VSS Power/Other
B12 VSS Power/Other
B14 VSS Power/Other
B17 VSS Power/Other
B22 VSS Power/Other
B27 VSS Power/Other
B32 VSS Power/Other
B7 VSS Power/Other
C10 VSS Power/Other
C15 VSS Power/Other
C20 VSS Power/Other
C25 VSS Power/Other
C30 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
86 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 87

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 29
of 33)
Pin
Number
C35 VSS Power/Other
C38 VSS Power/Other
C5 VSS Power/Other
D10 VSS Power/Other
D13 VSS Power/Other
D14 VSS Power/Other
D18 VSS Power/Other
D23 VSS Power/Other
D25 VSS Power/Other
D28 VSS Power/Other
D3 VSS Power/Other
D30 VSS Power/Other
D31 VSS Power/Other
D33 VSS Power/Other
D8 VSS Power/Other
E1 VSS Power/Other
E11 VSS Power/Other
E13 VSS Power/Other
E15 VSS Power/Other
E16 VSS Power/Other
E21 VSS Power/Other
E26 VSS Power/Other
E28 VSS Power/Other
E31 VSS Power/Other
E36 VSS Power/Other
E6 VSS Power/Other
F12 VSS Power/Other
F13 VSS Power/Other
F14 VSS Power/Other
F15 VSS Power/Other
F19 VSS Power/Other
F22 VSS Power/Other
F24 VSS Power/Other
F29 VSS Power/Other
F34 VSS Power/Other
F4 VSS Power/Other
F5 VSS Power/Other
F9 VSS Power/Other
G12 VSS Power/Other
G14 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 30
of 33)
Pin
Number
G17 VSS Power/Other
G2 VSS Power/Other
G22 VSS Power/Other
G27 VSS Power/Other
G32 VSS Power/Other
G37 VSS Power/Other
G7 VSS Power/Other
H10 VSS Power/Other
H15 VSS Power/Other
H20 VSS Power/Other
H25 VSS Power/Other
H30 VSS Power/Other
H35 VSS Power/Other
H4 VSS Power/Other
H5 VSS Power/Other
J13 V SS Power/Other
J18 V SS Power/Other
J23 V SS Power/Other
J24 V SS Power/Other
J25 V SS Power/Other
J28 V SS Power/Other
J3 VSS Power/Other
J33 V SS Power/Other
J38 V SS Power/Other
J5 VSS Power/Other
J6 VSS Power/Other
J8 VSS Power/Other
K1 VSS Power/Other
K11 VSS Power/Other
K16 VSS Power/Other
K21 VSS Power/Other
K22 VSS Power/Other
K23 VSS Power/Other
K25 VSS Power/Other
K26 VSS Power/Other
K3 VSS Power/Other
K31 VSS Power/Other
K36 VSS Power/Other
K6 VSS Power/Other
L14 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 87
Page 88

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 31
of 33)
Pin
Number
L16 VSS Power/Other
L17 VSS Power/Other
L19 VSS Power/Other
L23 VSS Power/Other
L24 VSS Power/Other
L25 VSS Power/Other
L26 VSS Power/Other
L29 VSS Power/Other
L34 VSS Power/Other
L35 VSS Power/Other
L4 VSS Power/Other
L9 VSS Power/Other
M12 VSS Power/Other
M16 VSS Power/Other
M17 VSS Power/Other
M19 VSS Power/Other
M2 VSS Power/Other
M22 VSS Power/Other
M24 VSS Power/Other
M25 VSS Power/Other
M27 VSS Power/Other
M32 VSS Power/Other
M37 VSS Power/Other
M7 VSS Power/Other
N10 VSS Power/Other
N30 VSS Power/Other
N35 VSS Power/Other
N5 VSS Power/Other
P28 VSS Power/Other
P3 VSS Power/Other
P33 VSS Power/Other
P35 VSS Power/Other
P38 VSS Power/Other
P4 VSS Power/Other
P8 VSS Power/Other
R1 VSS Power/Other
R11 VSS Power/Other
R31 VSS Power/Other
R36 VSS Power/Other
R4 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 32
of 33)
Pin
Number
R6 VSS Power/Other
T29 VSS Power/Other
T34 VSS Power/Other
T4 VSS Power/Other
T9 VSS Power/Other
U12 VSS Power/Other
U2 VSS Power/Other
U27 VSS Power/Other
U3 VSS Power/Other
U32 VSS Power/Other
U35 VSS Power/Other
U37 VSS Power/Other
U7 VSS Power/Other
V10 VSS Power/Other
V30 VSS Power/Other
V35 VSS Power/Other
V5 VSS Power/Other
W11 VSS Power/Other
W28 VSS Power/Other
W3 VSS Power/Other
W33 VSS Power/Other
W38 VSS Power/Other
W8 VSS Power/Other
Y1 VSS Power/Other
Y11 VSS Power/Other
Y29 VSS Power/Other
Y31 VSS Power/Other
Y36 VSS Power/Other
Y5 VSS Power/Other
Y6 VSS Power/Other
AJ11 XDPOCP_STRB_IN_N I
AH11 XDPOCP_STRB_OUT_N O
AH8 XDPOCPD[0]_N I/O
AG8 XDPOCPD[1]_N I/O
AJ9 XDPOCPD[2]_N I/O
AG9 XDPOCPD[3]_N I/O
AH9 XDPOCPD[4]_N I/O
AG10 XDPOCPD[5]_N I/O
AJ10 XDPOCPD[6]_N I/O
AK10 XDPOCPD[7]_N I/O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
88 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 89

Pin Listing
Table 3-1. Pin List by Pin Name (Sheet 33
of 33)
Pin
Number
AG11 XDPOCPFRAME_N I/O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
3.1.2 Pin Listing by Pin Number
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 1
of 32)
Pin
Number
A1 RSVD
A2 RSVD
A3 VSS Power/Other
A4 RSVD
A5 THERMALERT_N O
A6 THERMTRIP_N O
A7 FBD1SBOCLKCP0 Differential O
A8 FBD1SBOCLKCN0 Differential O
A9 VSS Power/Other
A10 FBD1SBOCP[5] Differential O
A11 FBD1SBOCP[7] Differential O
A12 FBD1SBOCN[7] Differential O
A13 FBD1SBOCP[10] Differential O
A14 VSS Power/Other
A15 CSI4RPDAT[0] Differential I
A16 VSS Power/Other
A17 CSI4RNDAT[3] Differential I
A18 CSI4RPDAT[3] Differential I
A19 VSS Power/Other
A20 CSI2RPDAT[8] Differential I
A21 CSI2RNCLK Differential I
A22 CSI2RPCLK Differential I
A23 CSI2RPDAT[10] Differential I
A24 VSS Power/Other
A25 CSI2RNDAT[13] Differential I
A26 CSI2RPDAT[13] Differential I
A27 VCCA Power/Other
A28 VCCA Power/Other
A29 VSS Power/Other
A30 CSI2RPDAT[17] Differential I
A31 VCCA Power/Other
A32 VCCA Power/Other
A33 CSI0RPDAT[0] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 2
of 32)
Pin
Number
A34 VSS Power/Other
A35 RSVD
A36 VSS Power/Other
A37 RSVD
A38 RSVD
AA1 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AA2 FBD0SBOBN[8] Differential O
AA3 FBD0SBOBP[8] Differential O
AA4 VSS Power/Other
AA5 VSS Power/Other
AA6 FBD1NBIDN[1] Differential I
AA7 FBD1NBIDP[1] Differential I
AA8 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AA9 VSS Power/Other
AA10 VSS Power/Other
AA11 RSVD
AA12 SYSCLK_N Differential I
AA27 RSVD
AA28 VSS Power/Other
AA29 VSS Power/Other
AA30 VSS Power/Other
AA31 CSI3TNDAT[18] Differential O
AA32 CSI3TNDAT[19] Differential O
AA33 CSI3TPDAT[19] Differential O
AA34 VSS Power/Other
AA35 CSI1TNDAT[18] Differential O
AA36 CSI1TPDAT[18] Differential O
AA37 VCCIO Power/Other
AA38 CSI1RNDAT[18] Differential I
AB1 FBD0NBIBN[11] Differential I
AB2 VSS Power/Other
AB3 FBD0SBOBN[6] Differential O
AB4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 89
Page 90

Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 3
of 32)
Pin
Number
AB5 FBD1NBIDP[0] Differential I
AB6 FBD1NBIDN[0] Differential I
AB7 VSS Power/Other
AB8 FBD1NBIDP[14] Differential I
AB9 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AB10 VSS Power/Other
AB11 VSS Power/Other
AB12 VSS Power/Other
AB27 VSS Power/Other
AB28 VCCIO Power/Other
AB29 VSS Power/Other
AB30 VCCIO Power/Other
AB31 CSI3TPDAT[18] Differential O
AB32 VSS Power/Other
AB33 CSI3TNDAT[17] Differential O
AB34 CSI1TNDAT[17] Differential O
AB35 CSI1TPDAT[17] Differential O
AB36 VCCIO Power/Other
AB37 VSS Power/Other
AB38 CSI1RPDAT[18] Differential I
AC1 FBD0NBIBP[11] Differential I
AC2 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AC3 FBD0SBOBP[6] Differential O
AC4 FBD0SBOBN[5] Differential O
AC5 VSS Power/Other
AC6 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AC7 VSS Power/Other
AC8 FBD1NBIDN[14] Differential I
AC9 FBD1REFSYSCLKP Differential I
AC10 VSS Power/Other
AC11 VSS Power/Other
AC12 RSVD
AC27 RSVD
AC28 RSVD
AC29 RSVD
AC30 VSS Power/Other
AC31 CSI3TNDAT[16] Differential O
AC32 CSI3TPDAT[16] Differential O
AC33 CSI3TPDAT[17] Differential O
AC34 CSI1TNDAT[16] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 4
of 32)
Pin
Number
AC35 VSS Power/Other
AC36 VSS Power/Other
AC37 CSI1RNDAT[17] Differential I
AC38 CSI1RPDAT[17] Differential I
AD1 FBD0NBIBN[10] Differential I
AD2 FBD0NBIBP[10] Differential I
AD3 VSS Power/Other
AD4 FBD0SBOBP[5] Differential O
AD5 FBD0SBOBP[7] Differential O
AD6 FBD0SBOBN[7] Differential O
AD7 FBD0SBOBN[9] Differential O
AD8 VSS Power/Other
AD9 FBD1REFSYSCLKN Differential I
AD10 VSS Power/Other
AD11 VCCIO Power/Other
AD12 RSVD
AD27 RSVD
AD28 VSS Power/Other
AD29 RSVD
AD30 RSVD
AD31 VCCIO Power/Other
AD32 CSI3TNDAT[15] Differential O
AD33 VSS Power/Other
AD34 CSI1TPDAT[16] Differential O
AD35 VSS Power/Other
AD36 CSI1RNDAT[16] Differential I
AD37 CSI1RPDAT[16] Differential I
AD38 VSS Power/Other
AE1 VSS Power/Other
AE2 FBD0NBIBP[9] Differential I
AE3 FBD0NBIBN[9] Differential I
AE4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AE5 FBD0SBOCLKBN0 Differential O
AE6 VSS Power/Other
AE7 FBD0SBOBP[9] Differential O
AE8 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AE9 VSS Power/Other
AE10 VSS Power/Other
AE11 VSS Power/Other
AE12 RSVD
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
90 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 91

Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 5
of 32)
Pin
Number
AE27 RSVD
AE28 SM_WP I
AE29 VCCIO Power/Other
AE30 RSVD
AE31 VSS Power/Other
AE32 CSI3TPDAT[15] Differential O
AE33 CSI1TNDAT[14] Differential O
AE34 CSI1TNDAT[15] Differential O
AE35 CSI1TPDAT[15] Differential O
AE36 VSS Power/Other
AE37 CSI1RNDAT[15] Differential I
AE38 CSI1RPDAT[15] Differential I
AF1 FBD0NBIBP[8] Differential I
AF2 FBD0NBIBN[8] Differential I
AF3 FBD0NBIBN[7] Differential I
AF4 VSS Power/Other
AF5 FBD0SBOCLKBP0 Differential O
AF6 FBD0SBOBN[4] Differential O
AF7 FBD0SBOBN[3] Differential O
AF8 FBD0SBOBP[3] Differential O
AF9 VSS Power/Other
AF10 VCCIO Power/Other
AF11 PRBMODE_RDY_N O
AF12 PRBMODE_REQST_N I
AF27 VCCIO Power/Other
AF28 VSS Power/Other
AF29 VSS Power/Other
AF30 CSI3TNDAT[13] Differential O
AF31 CSI3TNDAT[14] Differential O
AF32 CSI 3 TPDAT[14] Differential O
AF33 CSI 1 TPDAT[14] Differential O
AF34 VSS Power/Other
AF35 VSS Power/Other
AF36 CSI1RNDAT[14] Differential I
AF37 CSI1RPDAT[14] Differential I
AF38 CSI1RNDAT[13] Differential I
AG1 FBD0NBIBN[6] Differential I
AG2 VSS Power/Other
AG3 FBD0NBIBP[7] Differential I
AG4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 6
of 32)
Pin
Number
AG5 VSS Power/Other
AG6 FBD0SBOBP[4] Differential O
AG7 VSS Power/Other
AG8 XDPOCPD[1]_N I/O
AG9 XDPOCPD[3]_N I/O
AG10 XDPOCPD[5]_N I/O
AG11 XDPOCPFRAME_N I/O
AG12 VSS Power/Other
AG13 CSI5TNDAT[0] Differential O
AG14 VCCIO Power/Other
AG15 VSS Power/Other
AG16 CSI5TNDAT[3] Differential O
AG17 VSS Power/Other
AG18 VCCIO Power/Other
AG19 CSI5TNDAT[7] Differential O
AG20 CSI5TPDAT[7] Differential O
AG21 RSVD
AG22 VSS Power/Other
AG23 VSS Power/Other
AG24 PIR_SCL Power/Other I
AG25 VCCIO Power/Other
AG26 VSS Power/Other
AG27 VSS Power/Other
AG28 SKTID[2] I
AG29 SKTID[0] I
AG30 CSI3TPDAT[13] D ifferential O
AG31 CSI3TNDAT[12] Differential O
AG32 VSS Power/Other
AG33 CSI1TNDAT[13] Differential O
AG34 CSI1TPDAT[13] D ifferential O
AG35 VCCIO Power/Other
AG36 CSI1RNDAT[12] Differential I
AG37 VSS Power/Other
AG38 CSI1RPDAT[13] Differential I
AH1 FBD0NBIBP[6] Differential I
AH2 FBD0NBIBN[12] Differential I
AH3 FBD0NBICLKBN0 Differential I
AH4 FBD0NBICLKBP0 Differential I
AH5 VSS Power/Other
AH6 FBD0SBOBN[2] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 91
Page 92

Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 7
of 32)
Pin
Number
AH7 FBD0SBOBP[2] Differential O
AH8 XDPOCPD[0]_N I/O
AH9 XDPOCPD[4]_N I/O
AH10 VSS Power/Other
AH11 XDPOCP_STRB_OUT_N O
AH12 VCCIO Power/Other
AH13 CSI5TPDAT[0] Differential O
AH14 CSI5TNDAT[1] Differential O
AH15 VSS Power/Other
AH16 CSI5TPDAT[3] Differential O
AH17 CSI5TNDAT[4] Differential O
AH18 VSS Power/Other
AH19 CSI5TNDAT[5] Differential O
AH20 VSS Power/Other
AH21 RSVD
AH22 VCCIO Power/Other
AH23 VSS Power/Other
AH24 PIR_SDA Power/Other I/O
AH25 VSS Power/Other
AH26 VSS Power/Other
AH27 VCCIO Power/Other
AH28 SKTID[1] I
AH29 CSI3TNDAT[10] Differential O
AH30 VSS Power/Other
AH31 CSI3TPDAT[12] Differential O
AH32 CSI1TNDAT[12] Differential O
AH33 CSI1TPDAT[12] Differential O
AH34 CSI1TNDAT[11] Differential O
AH35 VSS Power/Other
AH36 CSI1RPDAT[12] Differential I
AH37 CSI1RPDAT[11] Differential I
AH38 CSI1RNDAT[11] Differential I
AJ1 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AJ2 FBD0NBIBP[12] Differential I
AJ3 VSS Power/Other
AJ4 FBD0NBIBN[13] Differential I
AJ5 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AJ6 VSS Power/Other
AJ7 FBD0SBOBN[1] Differential O
AJ8 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 8
of 32)
Pin
Number
AJ9 XDPOCPD[2]_N I/O
AJ10 XDPOCPD[6]_N I/O
AJ11 XDPOCP_STRB_IN_N I
AJ12 VSS Power/Other
AJ13 VSS Power/Other
AJ14 CSI5TPDAT[1] Differential O
AJ15 CSI5TNDAT[2] Differential O
AJ16 VSS Power/Other
AJ17 CSI5TPDAT[4] Differential O
AJ18 VSS Power/Other
AJ19 CSI5TPDAT[5] Differential O
AJ20 CSI5TNDAT[8] Differential O
AJ21 CSI5TPDAT[8] Differential O
AJ22 CSI5TNCLK Differential O
AJ23 VSS Power/Other
AJ24 PIR_A1 Power/Other I
AJ25 PIR_A0 Power/Other I
AJ26 VSS Power/Other
AJ27 CSI3TNDAT[9] Differential O
AJ28 VSS Power/Other
AJ29 CSI3TPDAT[10] Differential O
AJ30 CSI3TNDAT[11] Differential O
AJ31 CSI3TPDAT[11] Differential O
AJ32 CSI1TNCLK Differential O
AJ33 VSS Power/Other
AJ34 CSI1TPDAT[11] Differential O
AJ35 VSS Power/Other
AJ36 CSI1RPDAT[10] Differential I
AJ37 CSI1RNDAT[10] Differential I
AJ38 VSS Power/Other
AK1 VSS Power/Other
AK2 FBD0NBIAN[11] Differential I
AK3 FBD0NBIAP[11] Differential I
AK4 FBD0NBIBP[13] Differential I
AK5 FBD0NBIBN[5] Differential I
AK6 VSS Power/Other
AK7 FBD0SBOBP[1] Differential O
AK8 FBD0SBOBN[0] Differential O
AK9 FBD0SBOBP[0] Differential O
AK10 XDPOCPD[7]_N I/O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
92 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 93

Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet 9
of 32)
Pin
Number
AK11 VSS Power/Other
AK12 RSVD
AK13 VCCIO Power/Other
AK14 VSS Power/Other
AK15 CSI5TPDAT[2] Differential O
AK16 VSS Power/Other
AK17 VCCIO Power/Other
AK18 CSI5TNDAT[6] Differential O
AK19 CSI5TPDAT[6] Differential O
AK20 CSI3TPDAT[0] Differential O
AK21 VSS Power/Other
AK22 CSI5TPCLK Differential O
AK23 VCCIO Power/Other
AK24 VSS Power/Other
AK25 VSS Power/Other
AK26 VSS Power/Other
AK27 CSI3TPDAT[9] Differential O
AK28 CSI3TPCLK Differential O
AK29 CSI3TNCLK Differential O
AK30 VSS Power/Other
AK31 VSS Power/Other
AK32 CSI1TPCLK Differential O
AK33 CSI1TNDAT[10] Differential O
AK34 CSI1TPDAT[10] Differential O
AK35 VSS Power/Other
AK36 VSS Power/Other
AK37 CSI1RPCLK Differential I
AK38 CSI1RNCLK I
AL1 FBD0NBIAN[10] Differential I
AL2 FBD0NBIAP[10] Differential I
AL3 FBD0NBIAN[9] Differential I
AL4 VSS Power/Other
AL5 FBD0NBIBP[5] Differential I
AL6 FBD0REFSYSCLKN Differential I
AL7 FBD0REFSYSCLKP Differential I
AL8 RSVD
AL9 VSS Power/Other
AL10 FBD0NBIBP[14] Differential I
AL11 TRIGGER[0]_N I/O
AL12 CSI5RNDAT[0] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
10 of 32)
Pin
Number
AL13 CSI5RPDAT[0] Differential I
AL14 VSS Power/Other
AL15 VCCIO Power/Other
AL16 CSI3RPDAT[1] Differential I
AL17 CSI3RNDAT[1] Differential I
AL18 VSS Power/Other
AL19 VSS Power/Other
AL20 CSI3TNDAT[0] Differential O
AL21 CSI5TNDAT[9] Differential O
AL22 CSI5TPDAT[9] Differential O
AL23 CSI3TPDAT[2] Differential O
AL24 VSS Power/Other
AL25 VCCIO Power/Other
AL26 CSI1TPDAT[0] Differential O
AL27 CSI1TNDAT[0] Differential O
AL28 CSI1TNDAT[2] Differential O
AL29 VSS Power/Other
AL30 CSI1TNDAT[5] Differential O
AL31 RSVD
AL32 CSI1TPDAT[9] Differential O
AL33 CSI1TNDAT[9] Differential O
AL34 VSS Power/Other
AL35 VCCIO Power/Other
AL36 CSI1RPDAT[9] Differential I
AL37 CSI1RNDAT[9] Differential I
AL38 VROUTPUT_ENABLE0 I
AM1 VRPWRGD (Intel
AM2 VSS Power/Other
AM3 FBD0NBIAP[9] Differential I
AM4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AM5 FBD0NBIBN[4] Differential I
AM6 FBD0NBIBP[4] Differential I
AM7 VSS Power/Other
AM8 FBD0NBIBP[1] Differential I
AM9 FBD0NBIBN[1] Differential I
AM10 FBD0NBIBN[14] Differential I
AM11 RSVD
AM12 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
9300 Series) VR_READY
Processor 9500 Series)
(Intel
®
Itanium®
®
Itanium
®
Processor
Buffer Type
Signal
Direction
O
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 93
Page 94
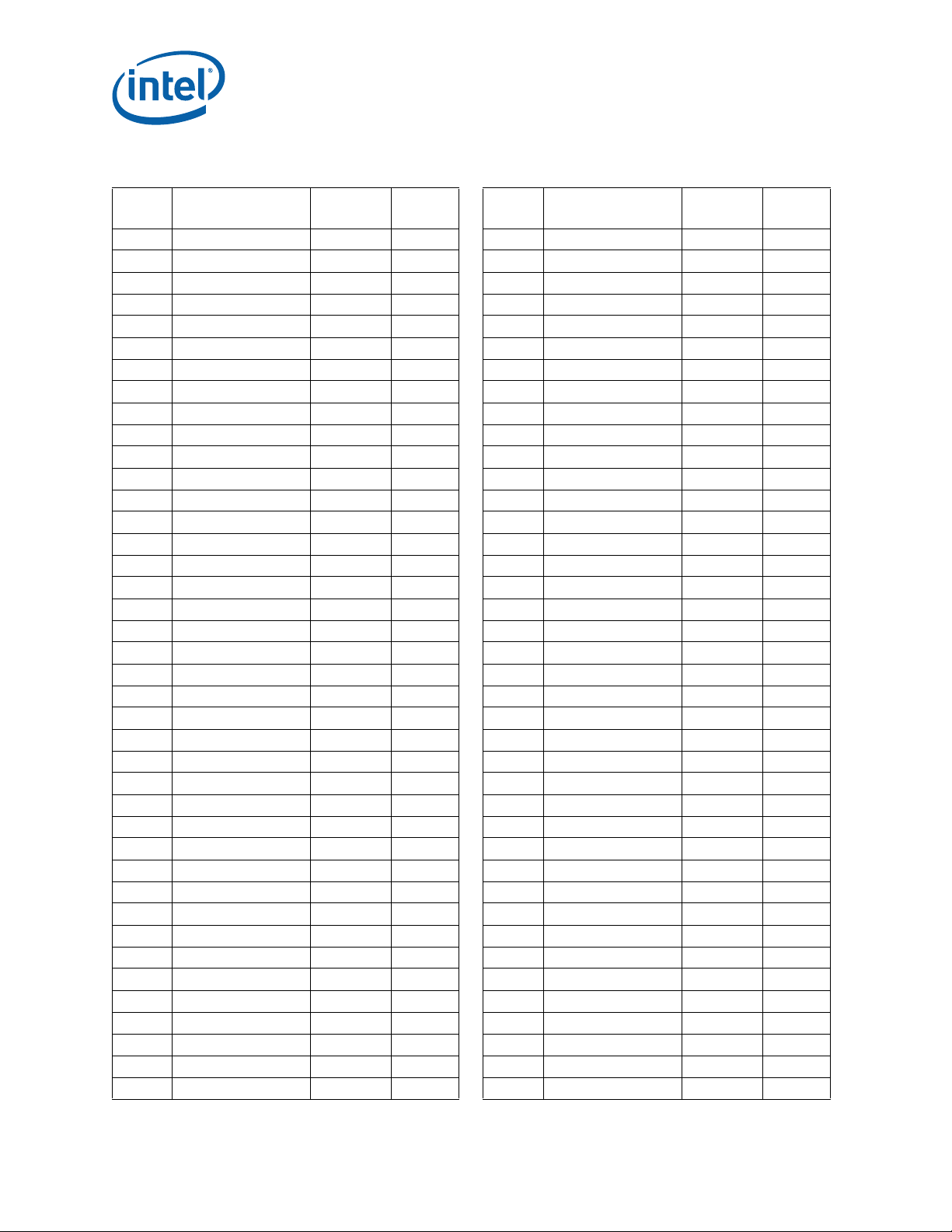
Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
11 of 32)
Pin
Number
AM13 CSI5RNDAT[1] Differential I
AM14 VCCIO Power/Other
AM15 CSI3RPDAT[2] Differential I
AM16 CSI3RNDAT[2] Differential I
AM17 VSS Power/Other
AM18 CSI3RPDAT[0] Differential I
AM19 VCCIO Power/Other
AM20 CSI3TNDAT[1] Differential O
AM21 CSI3TPDAT[1] Differential O
AM22 VSS Power/Other
AM23 CSI3TNDAT[2] Differential O
AM24 CSI3TNDAT[5] Differential O
AM25 CSI3TPDAT[8] Differential O
AM26 CSI3TNDAT[8] Differential O
AM27 VSS Power/Other
AM28 CSI1TPDAT[2] Differential O
AM29 VCCIO Power/Other
AM30 CSI1TPDAT[5] Differential O
AM31 CSI1TNDAT[8] Differential O
AM32 VSS Power/Other
AM33 VCCIO Power/Other
AM34 VSS Power/Other
AM35 CSI1RPDAT[8] Differential I
AM36 CSI1RNDAT[8] Differential I
AM37 VSS Power/Other
AM38 RSVD
AN1 VR_FAN_N O
AN2 FBD0NBIAN[7] Differential I
AN3 FBD0NBIAN[8] Differential I
AN4 FBD0NBIAP[8] D ifferential I
AN5 VSS Power/Other
AN6 FBD0NBIBP[3] D ifferential I
AN7 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AN8 VSS Power/Other
AN9 FBD0NBIBN[0] Differential I
AN10 VSS Power/Other
AN11 RSVD
AN12 VCCIO Power/Other
AN13 CSI5RPDAT[1] Differential I
AN14 CSI5RNDAT[2] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
12 of 32)
Pin
Number
AN15 VSS Power/Other
AN16 CSI3RPDAT[3] Differential I
AN17 CSI3RNDAT[3] Differential I
AN18 CSI3RNDAT[0] Differential I
AN19 CSI3RPDAT[4] Differential I
AN20 VSS Power/Other
AN21 CSI3TNDAT[3] Differential O
AN22 CSI3TPDAT[4] Differential O
AN23 CSI3TNDAT[4] Differential O
AN24 CSI3TPDAT[5] Differential O
AN25 VSS Power/Other
AN26 CSI3TNDAT[7] Differential O
AN27 CSI1TPDAT[1] Differential O
AN28 CSI1TNDAT[1] Differential O
AN29 CSI1TNDAT[3] Differential O
AN30 VSS Power/Other
AN31 CSI1TPDAT[8] Differential O
AN32 CSI1TNDAT[6] Differential O
AN33 CSI1TPDAT[7] Differential O
AN34 CSI1TNDAT[7] Differential O
AN35 VSS Power/Other
AN36 CSI1RPDAT[7] Differential I
AN37 CSI1RNDAT[7] Differential I
AN38 RSVD
AP1 PROCTYPE I
AP2 FBD0NBIAP[7] Differential I
AP3 VSS Power/Other
AP4 FBD0NBIAN[6] Differential I
AP5 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AP6 FBD0NBIBN[3] Differential I
AP7 FBD0NBIBN[2] Differential I
AP8 VSS Power/Other
AP9 FBD0NBIBP[0] Differential I
AP10 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AP11 TRIGGER[1]_N I/O
AP12 VSS Power/Other
AP13 VSS Power/Other
AP14 CSI5RPDAT[2] Differential I
AP15 CSI5RNDAT[3] Differential I
AP16 CSI5RPDAT[3] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
94 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 95
Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
13 of 32)
Pin
Number
AP17 CSI5RNCLK Differential I
AP18 VSS Power/Other
AP19 CSI3RNDAT[4] Differential I
AP20 VCCIO Power/Other
AP21 CSI3TPDAT[3] Differential O
AP22 VSS Power/Other
AP23 VSS Power/Other
AP24 VCCIO Power/Other
AP25 CSI3TNDAT[6] Differential O
AP26 CSI3TPDAT[7] Differential O
AP27 RSVD
AP28 VSS Power/Other
AP29 CSI1TPDAT[3] Differential O
AP30 CSI1TPDAT[4] Differential O
AP31 CSI1TNDAT[4] Differential O
AP32 CSI1TPDAT[6] Differential O
AP33 VSS Power/Other
AP34 VCCIO Power/Other
AP35 CSI1RPDAT[5] Differential I
AP36 CSI1RNDAT[5] Differential I
AP37 CSI1RNDAT[6] Differential I
AP38 VSS Power/Other
AR1 RSVD
AR2 FBD0NBIAN[12] Differential I
AR3 FBD0NBIAP[12] Differential I
AR4 FBD0NBIAP[6] Differential I
AR5 FBD0NBICLKAN0 Differential I
AR6 VSS Power/Other
AR7 FBD0NBIBP[2] Differential I
AR8 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AR9 PWRGOOD I
AR10 FBD0NBIAN[3] Differential I
AR11 VSS Power/Other
AR12 VCCIO Power/Other
AR13 CSI5RNDAT[4] Differential I
AR14 CSI5RPDAT[4] Differential I
AR15 CSI5RNDAT[7] Differential I
AR16 VSS Power/Other
AR17 CSI5RPCLK Differential I
AR18 CSI3RPDAT[5] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
14 of 32)
Pin
Number
AR19 CSI3RNDAT[5] Differential I
AR20 CSI3RPDAT[9] Differential I
AR21 VSS Power/Other
AR22 CSI3RPDAT[10] Differential I
AR23 VCCIO Power/Other
AR24 VSS Power/Other
AR25 CSI3TPDAT[6] Differential O
AR26 VSS Power/Other
AR27 CSI3RPDAT[15] Differential I
AR28 VCCIO Power/Other
AR29 VSS Power/Other
AR30 VCCIO Power/Other
AR31 VSS Power/Other
AR32 SMBDAT SMBus I/O
AR33 CSI1RPDAT[3] Differential I
AR34 CSI1RNDAT[3] Differential I
AR35 VCCIO Power/Other
AR36 VSS Power/Other
AR37 CSI1RPDAT[6] Differential I
AR38 RSVD
AT1 VSS Power/Other
AT2 RSVD
AT3 CPU_PRES4_N I/O
AT4 VSS Power/Other
AT5 FBD0NBICLKAP0 Differential I
AT6 FBD0NBIAN[5] Differential I
AT7 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
AT8 FBD0NBIAN[4] Differential I
AT9 VSS Power/Other
AT10 FBD0NBIAP[3] Differential I
AT11 FBD0NBIAN[0] Differential I
AT12 VSS Power/Other
AT13 CSI5RNDAT[5] Differential I
AT14 VSS Power/Other
AT15 CSI5RPDAT[7] Differential I
AT16 CSI5RNDAT[9] Differential I
AT17 CSI5RPDAT[9] Differential I
AT18 CSI3RPDAT[7] Differential I
AT19 VSS Power/Other
AT20 CSI3RNDAT[9] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 95
Page 96
Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
15 of 32)
Pin
Number
AT21 CSI3RPCLK Differential I
AT22 CSI3RNDAT[10] Differential I
AT23 CSI3RPDAT[11] Differential I
AT24 VSS Power/Other
AT25 VCCIO Power/Other
AT26 CSI3RPDAT[14] Differential I
AT27 CSI3RNDAT[15] Differential I
AT28 CSI3RPDAT[16] Differential I
AT29 VSS Power/Other
AT30 SPDCLK I/O
AT31 SPDDAT I/O
AT32 SMBCLK SMBus I/O
AT33 CSI1RPDAT[0] Differential I
AT34 VSS Power/Other
AT35 CSI1RNDAT[4] Differential I
AT36 CP U_PRES3_N I/O
AT37 RSVD
AT38 RSVD
AU1 RSVD
AU2 RSVD
AU3 RSVD
AU4 FBD0NBIAN[13] Differential I
AU5 FBD0NBIAP[13] Differential I
AU6 FBD0NBIAP[5] Differential I
AU7 VSS Power/Other
AU8 FBD0NBIAP[4] Differential I
AU9 FBD0NBIAN[1] Differential I
AU10 FBD0NBIAP[1] Differential I
AU11 FBD0NBIAP[0] Differential I
AU12 VSS Power/Other
AU13 CSI5RPDAT[5] Differential I
AU14 CSI5RNDAT[6] Differential I
AU15 CSI5RNDAT[8] Differential I
AU16 CSI5RPDAT[8] Differential I
AU17 VSS Power/Other
AU18 CSI3RNDAT[7] Differential I
AU19 CSI3RPDAT[8] Differential I
AU20 VCCIO Power/Other
AU21 CSI3RNCLK Differential I
AU22 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
16 of 32)
Pin
Number
AU23 CSI3RNDAT[11] Differential I
AU24 CSI3RPDAT[13] Differential I
AU25 CSI3RNDAT[13] Differential I
AU26 CSI3RNDAT[14] Differential I
AU27 VSS Power/Other
AU28 CSI3RNDAT[16] Differential I
AU29 CSI3RPDAT[18] Differential I
AU30 CSI3RNDAT[18] Differential I
AU31 CSI3RPDAT[19] Differential I
AU32 VSS Power/Other
AU33 CSI1RNDAT[0] Differential I
AU34 CSI1RPDAT[2] Differential I
AU35 CSI1RPDAT[4] Differential I
AU36 RSVD
AU37 RSVD
AU38 VSS Power/Other
AV1 RSVD
AV2 RSVD
AV3 VSS Power/Other
AV4 RSVD
AV5 VSS Power/Other
AV6 VCC33_SM Power/Other
AV7 VCC33_SM Power/Other
AV8 FBD0NBIAN[2] D ifferential I
AV9 FBD0NBIAP[2] Differential I
AV10 VSS Power/Other
AV11 FBD0NBIAN[14] Differential I
AV12 FBD0NBIAP[14] Differential I
AV13 VSS Power/Other
AV14 CSI5RPDAT[6] Differential I
AV15 VSS Power/Other
AV16 CSI3RPDAT[6] Differential I
AV17 CSI3RNDAT[6] Differential I
AV18 VSS Power/Other
AV19 CSI3RNDAT[8] Differential I
AV20 VSS Power/Other
AV21 VCCA Power/Other
AV22 VCCA Power/Other
AV23 CSI3RPDAT[12] Differential I
AV24 CSI3RNDAT[12] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
96 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 97

Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
17 of 32)
Pin
Number
AV25 VSS Power/Other
AV26 VCCA Power/Other
AV27 VCCA Power/Other
AV28 CSI3RPDAT[17] Differential I
AV29 CSI3RNDAT[17] Differential I
AV30 VSS Power/Other
AV31 CSI3RNDAT[19] Differential I
AV32 CSI1RPDAT[1] Differential I
AV33 CSI1RNDAT[1] Differential I
AV34 CSI1RNDAT[2] Differential I
AV35 RSVD
AV36 VSS Power/Other
AV37 RSVD
AV38 RSVD
B1 VSS Power/Other
B2 RSVD
B3 RSVD
B4 FBD1SBODN[9] Differential O
B5 FBD1SBODP[9] Differential O
B6 FBD1SBODN[6] Differential O
B7 VSS Power/Other
B8 FBD1SBOCP[9] Differential O
B9 FBD1SBOCN[9] Differential O
B10 FBD1SBOCN[5] Differential O
B11 FBD1SBOCP[6] Differential O
B12 VSS Power/Other
B13 FBD1SBOCN[10] Differential O
B14 VSS Power/Other
B15 CSI4RNDAT[0] Differential I
B16 CSI4RPDAT[2] Differential I
B17 VSS Power/Other
B18 CSI4RNDAT[4] Differential I
B19 CSI4RPDAT[4] Differential I
B20 CSI2RNDAT[8] Differential I
B21 CSI2RPDAT[7] Differential I
B22 VSS Power/Other
B23 CSI2RNDAT[10] Differential I
B24 CSI2RPDAT[11] Differential I
B25 CSI2RNDAT[11] Differential I
B26 CSI2RPDAT[12] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
18 of 32)
Pin
Number
B27 VSS Power/Other
B28 CSI2RNDAT[16] Differential I
B29 CSI2RPDAT[16] Differential I
B30 CSI2RNDAT[17] Differential I
B31 CSI2RPDAT[18] Differential I
B32 VSS Power/Other
B33 CSI0RNDAT[0] Differential I
B34 CSI0RNDAT[2] Differential I
B35 CSI0 R PDAT[2] Differential I
B36 RSVD
B37 RSVD
B38 RSVD
C1 RSVD
C2 RSVD
C3 CPU_PRES1_N I/O
C4 FBD1 SBODN[5] Differential O
C5 VSS Power/Other
C6 FBD1SBODP[6] Differential O
C7 FBD1SBOCP[4] Differential O
C8 FBD1SBOCN[4] Differential O
C9 FBD1SBOCN[3] Differential O
C10 VSS Power/Other
C11 FBD1SBOCN[6] D ifferential O
C12 FBD1SBOCP[8] Differential O
C13 FBD1SBOCN[8] D ifferential O
C14 VCCIO Power/Other
C15 VSS Power/Other
C16 CSI4RNDAT[2] Differential I
C17 CSI4RNDAT[5] Differential I
C18 CSI4RPDAT[5] Differential I
C19 CSI4RPDAT[6] Differential I
C20 VSS Power/Other
C21 CSI2RNDAT[7] Differential I
C22 CSI2RNDAT[9] Differential I
C23 CSI2RPDAT[9] Differential I
C24 VCCIO Power/Other
C25 VSS Power/Other
C26 CSI2RNDAT[12] Differential I
C27 CSI2RNDAT[15] Differential I
C28 CSI2RPDAT[15] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 97
Page 98

Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
19 of 32)
Pin
Number
C29 VCCIO Power/Other
C30 VSS Power/Other
C31 CSI2RNDAT[18] Differential I
C32 CSI2RPDAT[19] Differential I
C33 CSI2RNDAT[19] Differential I
C34 CSI0RPDAT[1] Differential I
C35 VSS Power/Other
C36 CSI0RNDAT[4] Differential I
C37 RSVD
C38 VSS Power/Other
D1 RSVD
D2 FBD1SBODN[4] Differential O
D3 VSS Power/Other
D4 FBD1SBODP[5] Differential O
D5 FBD1SBODN[7] Differential O
D6 FBD1SBODP[7] Differential O
D7 FBD1SBOCP[2] Differential O
D8 VSS Power/Other
D9 FBD1SBOCP[3] Differential O
D10 VSS Power/Other
D11 FBD1SBOCP[0] Differential O
D12 FBD1SBOCN[0] Differential O
D13 VSS Power/Other
D14 VSS Power/Other
D15 CSI4RNDAT[1] Differential I
D16 CSI4RPDAT[1] Differential I
D17 CSI4RPDAT[7] Differential I
D18 VSS Power/Other
D19 CSI4RNDAT[6] Differential I
D20 CSI2RPDAT[5] Differential I
D21 CSI2RNDAT[6] Differential I
D22 CSI2RPDAT[6] Differential I
D23 VSS Power/Other
D24 CSI2TNDAT[3] Differential O
D25 VSS Power/Other
D26 CSI2RNDAT[14] Differential I
D27 CSI2RPDAT[14] Differential I
D28 VSS Power/Other
D29 CSI2TPDAT[6] Differential O
D30 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
20 of 32)
Pin
Number
D31 VSS Power/Other
D32 VCCIO Power/Other
D33 VSS Power/Other
D34 CSI0RNDAT[1] Differential I
D35 CSI0RNDAT[3] Differential I
D36 CSI0RPDAT[4] Differential I
D37 CPU_PRES2_N I/O
D38 RSVD
E1 VSS Power/Other
E2 FBD1SBODP[4] Differential O
E3 FBD1SBOCLKDP0 Differential O
E4 FBD1SBOCLKDN0 Differential O
E5 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
E6 VSS Power/Other
E7 FBD1SBOCN[2] Differential O
E8 FBD1SBOCN[1] Differential O
E10 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
E11 VSS Power/Other
E12 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
E13 VSS Power/Other
E14 VCCIO Power/Other
E15 VSS Power/Other
E16 VSS Power/Other
E17 CSI4RNDAT[7] Differential I
E18 CSI4RNDAT[8] Differential I
E19 CSI4RPDAT[8] Differential I
E20 CSI2RNDAT[5] Differential I
E21 VSS Power/Other
E22 CSI2RPDAT[4] Differential I
E23 CSI2RNDAT[4] Differential I
E24 CSI2TPDAT[3] Differential O
E25 CSI2TPDAT[2] Differential O
E26 VSS Power/Other
E27 VCCIO Power/Other
E28 VSS Power/Other
E29 CSI2TNDAT[6] Differential O
E30 CSI0TPDAT[3] Differential O
E31 VSS Power/Other
E32 CSI0TNDAT[6] Differential O
E33 CSI0TPDAT[6] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
98 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
Page 99
Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
21 of 32)
Pin
Number
E34 VCCIO Power/Other
E35 CSI0RPDAT[3] Differential I
E36 VSS Power/Other
E37 CSI0RNDAT[5] Differential I
E38 CSI0RPDAT[5] Differential I
E9 FBD1SBOCP[1] Differential O
F1 RSVD
F2 FBD1SBODN[3] Differential O
F3 FBD1SBODP[3] Differential O
F4 VSS Power/Other
F5 VSS Power/Other
F6 FBD1SBODP[8] Differential O
F7 FBD1SBODN[8] Differential O
F8 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
F9 VSS Power/Other
F10 FBD1NBICP[11] Differential I
F11 FBD1NBICN[11] Differential I
F12 VSS Power/Other
F13 VSS Power/Other
F14 VSS Power/Other
F15 VSS Power/Other
F16 VCCIO Power/Other
F17 CSI4RNDAT[9] Differential I
F18 CSI4RPDAT[9] Differential I
F19 VSS Power/Other
F20 CSI2RPDAT[3] Differential I
F21 CSI2RNDAT[3] Differential I
F22 VSS Power/Other
F23 VCCIO Power/Other
F24 VSS Power/Other
F25 CSI2TNDAT[2] Differential O
F26 CSI2TNDAT[5] Differential O
F27 CSI2TPDAT[5] Differential O
F28 CSI2TNDAT[8] Differential O
F29 VSS Power/Other
F30 CSI0TNDAT[3] Differential O
F31 CSI0TNDAT[5] Differential O
F32 CSI0TPDAT[5] Differential O
F33 CSI0TNDAT[7] Differential O
F34 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
22 of 32)
Pin
Number
F35 VCCIO Power/Other
F36 CSI0RNDAT[6] Differential I
F37 CSI0RPDAT[6] Differential I
F38 RSVD
G1 RSVD
G2 VSS Power/Other
G3 FBD1SBODN[1] Differential O
G4 FBD1SBODN[2] Differential O
G5 FBD1SBODP[2] Differential O
G6 FBD1SBODN[10] Differential O
G7 VSS Power/Other
G8 FBD1NBICN[9] Differential I
G9 BOOTMODE[1] I
G10 BOOTMODE[0] I
G11 FBD1NBICN[8] Differential I
G12 VSS Power/Other
G13 VCCIO Power/Other
G14 VSS Power/Other
G15 CSI4TNDAT[4] Differential O
G16 CSI4TPDAT[4] Differential O
G17 VSS Power/Other
G18 CSI4RPCLK Differential I
G19 CSI2RPDAT[2] Differential I
G20 CSI2RNDAT[2] Differential I
G21 CSI2RPDAT[1] Differential I
G22 VSS Power/Other
G23 CSI2TPDAT[0] Differential O
G24 CSI2TNDAT[1] Differential O
G25 CSI2TPDAT[1] Differential O
G26 CSI2TPDAT[4] Differential O
G27 VSS Power/Other
G28 CSI2TPDAT[8] Differential O
G29 VCCIO Power/Other
G30 CSI0TPDAT[2] Differential O
G31 CSI0TNDAT[2] Differential O
G32 VSS Power/Other
G33 CSI0TPDAT[7] Differential O
G34 VCCIO Power/Other
G35 CSI0RNDAT[7] Differential I
G36 CSI0RPDAT[7] Differential I
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Intel® Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet 99
Page 100

Pin Listing
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
23 of 32)
Pin
Number
G37 VSS Power/Other
G38 RSVD
H1 FBD1SBODN[0] Differential O
H2 FBD1SBODP[0] Differential O
H3 FBD1SBODP[1] Differential O
H4 VSS Power/Other
H5 VSS Power/Other
H6 FBD1SBODP[10] Differential O
H7 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
H8 FBD1NBICP[9] Differential I
H9 FBD1NBICN[10] Differential I
H10 VSS Power/Other
H11 FBD1NBICP[8] Differential I
H12 ERROR[0]_N O
H13 RSVD
H14 CSI4TPDAT[3] Differential O
H15 VSS Power/Other
H16 CSI4TPDAT[5] Differential O
H17 VCCIO Power/Other
H18 CSI4RNCLK Differential I
H19 VCCIO Power/Other
H20 VSS Power/Other
H21 CSI2RNDAT[1] Differential I
H22 VCCIO Power/Other
H23 CSI2TNDAT[0] Differential O
H24 VCCIO Power/Other
H25 VSS Power/Other
H26 CSI2TNDAT[4] Differential O
H27 CSI2TNDAT[9] Differential O
H28 CSI2TPDAT[9] Differential O
H29 CSI2TNCLK Differential O
H30 VSS Power/Other
H31 CSI0TPDAT[1] Differential O
H32 VCCIO Power/Other
H33 CSI0TNDAT[8] Differential O
H34 CSI0TPDAT[8] Differential O
H35 VSS Power/Other
H36 CSI0RNDAT[8] Differential I
H37 CSI0RPDAT[8] Differential I
H38 VR_THERMTRIP_N O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 3-2. Pin List by Pin Number (Sheet
24 of 32)
Pin
Number
J1 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
J2 FBD0SBOAN[10] Differential O
J3 VSS Power/Other
J4 VCCIO_FBD Power/Other
J5 VSS Power/Other
J6 VSS Power/Other
J7 FBD1NBIDN[11] Differential I
J8 VSS Power/Other
J9 FBD1NBICP[10] Differential I
J10 FBD1NBICP[7] Differential I
J11 FBD1NBICN[7] Differential I
J12 ERROR[1]_N O
J13 V SS Power/Other
J14 CSI4TNDAT[3] Differential O
J15 CSI4TPDAT[2] Differential O
J16 CSI4TNDAT[5] Differential O
J17 CSI4TPDAT[6] Differential O
J18 V SS Power/Other
J19 CSI4TPDAT[8] Differential O
J20 RSVD
J21 CSI2RPDAT[0] Differential I
J22 CSI2RNDAT[0] Differential I
J23 V SS Power/Other
J24 V SS Power/Other
J25 V SS Power/Other
J26 CSI2TNDAT[7] Differential O
J27 CSI2TPDAT[7] Differential O
J28 V SS Power/Other
J29 CSI2TPCLK Differential O
J30 CSI0TPDAT[0] Differential O
J31 CSI0TNDAT[1] Differential O
J32 CSI0TPDAT[4] Differential O
J33 V SS Power/Other
J34 VCCIO Power/Other
J35 CSI0RNDAT[9] Differential I
J36 CSI0RPDAT[9] Differential I
J37 CSI0RNCLK Differential I
J38 V SS Power/Other
K1 VSS Power/Other
K2 FBD0SBOAP[10] Differential O
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
100 Intel
®
Itanium® Processor 9300 Series and 9500 Series Datasheet
 Loading...
Loading...