Page 1

DMZ Firewall Solution
Intel Express Routers 9515, 9525 an d 9535
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL
PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO
ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT.
EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTELS TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH
PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF
INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. INTEL
PRODUCTS ARE NOT INTENDED FOR USE IN MEDICAL, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE
SUSTAINING APPLICATIONS. INTEL MAY MAKE CHANGES TO SPECIFICATIONS
AND PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS AT ANY TIME, WITHOUT NOTICE.
INTEL CORPORATION ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY FOR ERRORS OR OMISSIONS
IN THIS DOCUMENT. NOR DOES INTEL MAKE ANY COMMITMENT TO UPDATE THE
INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN.
Year 2000 capable
An Intel product, when used in accordance with associated documentation, is “Year 2000
Capable” when, upon installation, it accurately stores, displays, processes, provides, and/or
receives data from, into, and between 1999 and 2000, and the twentieth and twenty-first centuries,
including leap year calculations, provided that all other technology used in combination with said
product properly exchanges date data with it. Intel makes no representation about individual
components within the product should they be used independently from the product as a whole.
Copyright
* Other product and corporate names may be trademarks of other companies and are used only
1999, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
for explanation and to owners' benefit, without intent to infringe.
Page 3

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Table of Contents
1 Introduction............................................................................................................................3
1.1 About This Document..........................................................................................................3
1.2 References............................................................................................................................3
1.3 What is a DMZ.....................................................................................................................3
1.4 IP Filters in the Express Router............................................................................................4
2 General Setup and Considerations.......................................................................................4
2.1 IP Address Selection............................................................................................................4
2.2 Routing Setup.......................................................................................................................5
2.3 DNS Setup............................................................................................................................5
2.4 E-mail (SMTP) Setup...........................................................................................................5
2.5 FTP Setup.............................................................................................................................5
2.6 HTTP Setup..........................................................................................................................5
2.7 News (NNTP) Setup ............................................................................................................5
2.8 Management Access Setup...................................................................................................5
3 DMZ Single IP Address Solution..........................................................................................6
3.1 Static Routing Setup.............................................................................................................6
3.2 Network Address Translation (NAT) Setup.........................................................................6
3.3 IP Filters Setup.....................................................................................................................7
3.3.1 LAN1 Filters ................................................................................................................7
3.3.1.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on LAN1.............................................................................7
3.3.1.2 Transmit (Tx) Filters on LAN1............................................................................8
3.3.2 LAN2 Filters ..............................................................................................................10
3.3.2.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on LAN2...........................................................................10
3.3.2.2 Transmit (Tx) filters on LAN2...........................................................................12
3.3.3 Internet Connection Filters.........................................................................................13
3.3.3.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on the connection to the Internet.......................................13
3.3.3.2 Transmit (Tx) Filters on the Connection to the Internet.....................................16
4 DMZ Multiple IP Address Solution....................................................................................17
4.1 IP Address Assignment......................................................................................................17
4.2 Static Routing Setup...........................................................................................................17
4.3 Network Address Translation (NAT).................................................................................18
4.4 IP Filters Setup...................................................................................................................18
4.4.1 LAN1 Filters ..............................................................................................................18
4.4.1.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on LAN1...........................................................................18
4.4.1.2 Transmit (Tx) Filters on LAN1..........................................................................19
4.4.2 LAN2 Filters ..............................................................................................................21
4.4.2.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on LAN2...........................................................................21
4.4.2.2 Transmit (Tx) filters on LAN2...........................................................................24
4.4.3 Internet Connection Filters.........................................................................................24
4.4.3.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on the Connection to the Internet......................................24
4.4.3.2 Transmit (Tx) Filters on the Connection to the Internet.....................................27
07-12-99 Version 1.0 2
Page 4
DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
1 Introduction
1.1 About This Document
This document explains how to configure a secure Internet solution using the second LAN
interface of the Intel
two example solutions, a Single IP Address Solution and Multiple IP Address.
It assumed that you have a solid understanding of networking concepts and experience in using
the Express Router.
1.2 References
[1] Intel Express Router User Guide
The user guide for your router explains in detail the basic configuration procedures used in
the set up of the DMZ.
[2] Brent Chapman, Elizabeth D. Zwicky, “ Building Internet Firewalls”, 1995 O’Reilly &
Associates. ISBN: 1-56592-124-0
Express router as a DMZ. The DMZ setup is explained through the use of
1.3 What is a DMZ
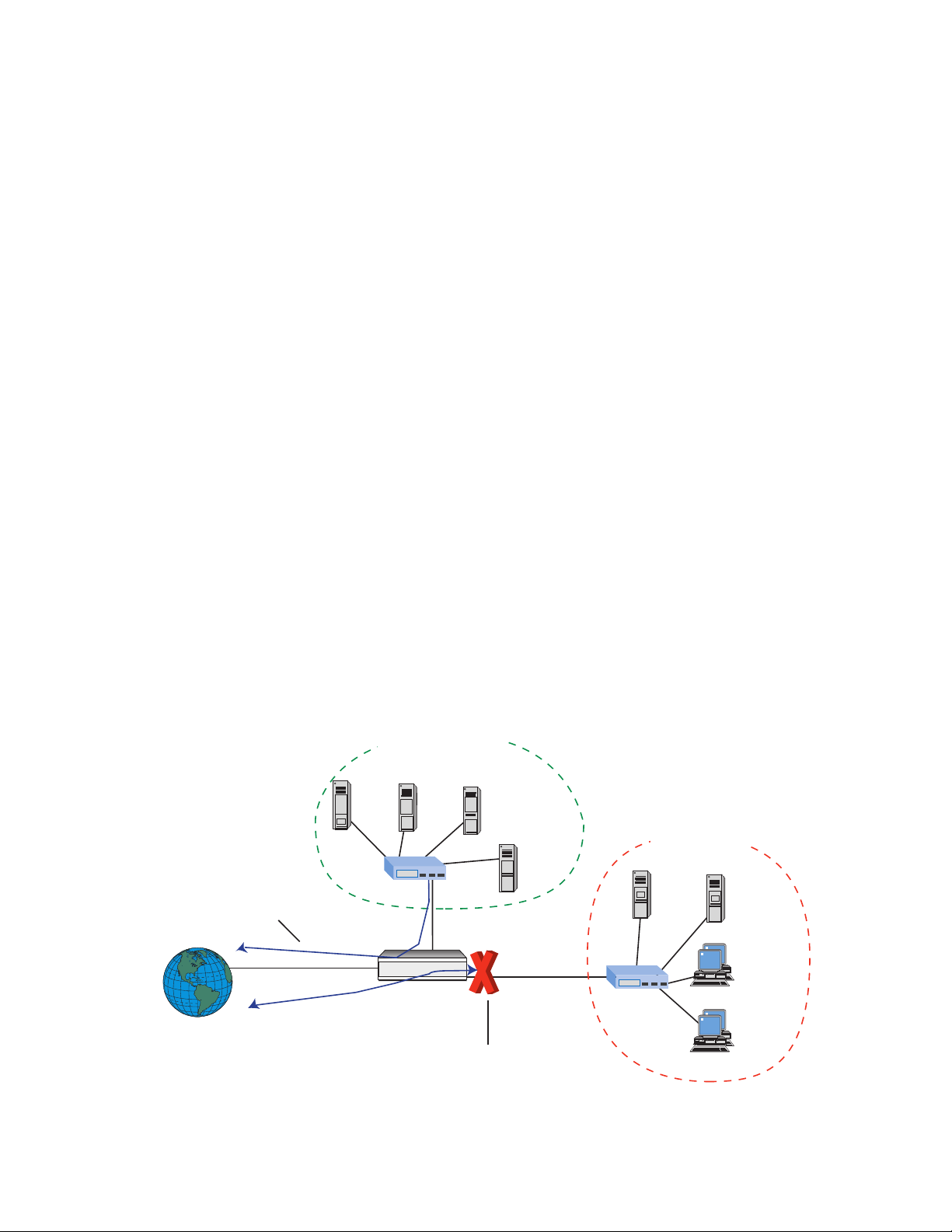
For an Intel Express Router having two LAN ports, you can setup a DMZ (DeMilitarized Zone)
to increase security on your private network. A DMZ is a network off one of the LAN ports that
acts as a kind of buffer between the external (public Internet) network and your secure network
on the other LAN interface. The DMZ gives access to services required from both the external
network and the secure network. The services are typically HTTP/FTP (Web) servers for public
access, an HTTP/FTP proxy server, an SMTP server and a News (proxy) server. Mail servers and
News servers for internal use are placed on the secure network. Through the use of IP filters, you
prohibit access from the Internet to your secure network while still providing access to services
on the DMZ.
192.168.151.0
Demilitarized Zone
Http/FTP
(Web)
server
Internet users are allowed
to access your Web
and FTP servers
Http/FTP
10/100
proxy
server
LAN2 port
News
proxy
server
SMTP
server
192.168.152.0
Main LAN
File
server
Mail
server
10/100
PC
PC
Internet
Intel Express
LAN1 port
router
IP filters on the router
block unwanted traffic
destined to the main LAN
07-12-99 Version 1.0 3
Page 5
DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
The purpose of this setup is to prohibit any direct data transmission between the Internet and the
secure network. All data must go through proxy servers on the DMZ.
We recommend that you set up the DMZ on the LAN2 (10 Mbps) port and your secure network
on the LAN1 (100/10 Mbps) port.
This document provides two DMZ solutions when connecting to the Internet, one using a single
external IP address and the other using a number of IP addresses (at least four IP addresses are
needed, including network identification and broadcast address).
Note: Solutions using dynamic address assignment by the ISP are not supported.
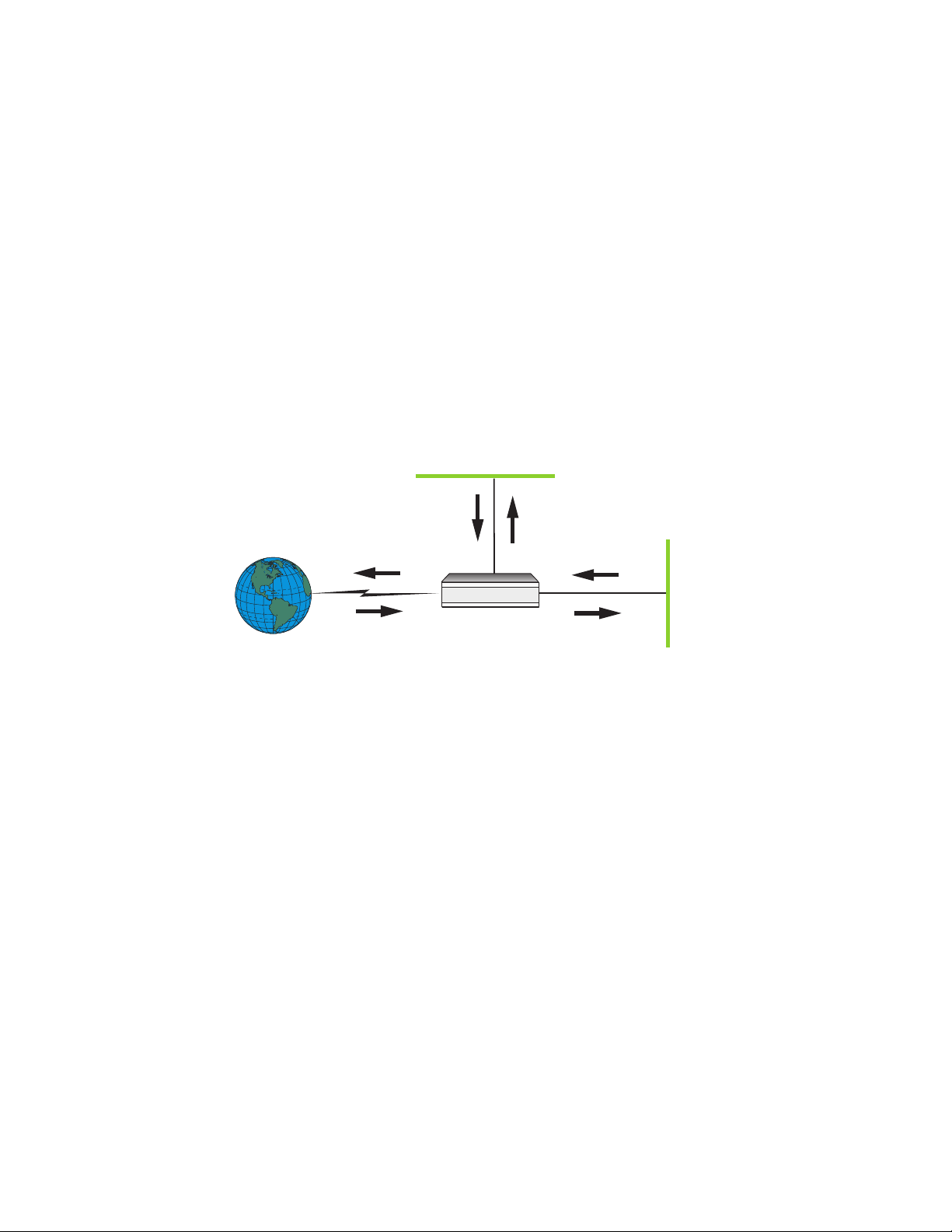
1.4 IP Filters in the Express Router
IP filters in the Express Router are defined on a link basis. Separate filters are configured for
received data (data packets from a link to the router) and transmitted data (data packets from the
router to a link). Use the diagram below to help determine the direction of data with respect to the
router and the types of filter required (Rx or Tx).
LAN2
Internet
Rx
Tx
Rx
Tx - transmitted data
Rx - received data
Intel Express
Router
Tx
Tx
Rx
LAN1
2 General Setup and Considerations
2.1 IP Address Selection
The IP addresses on the secure network and the DMZ network can be any valid IP addresses, but
we recommend that you use designated private IP addresses or registered IP addresses. Private IP
addresses are those addresses included under Class A network 10, Class B networks 172.16
through 172.31, and Class C networks 192.168.0 through 192.168.255. Registered public IP
addresses are provided by your Internet service provider (ISP). Using registered IP addresses on
the DMZ network avoids conflicts with duplicate addresses on the Internet. On the secure
network it is preferable to use designated private IP addresses. However, if you already have
unregistered public IP addresses on your private network (for example 89.20.0.0 and 90.2.0.0),
you must use Network Address Translation (NAT) to translate these addresses to private IP
addresses.
For the single IP address solution, NAT is needed to map the network services from one public IP
address to one or more private IP addresses on the DMZ network. This makes it possible to have
several public servers on DMZ using the same public IP address.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 4
Page 6

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
2.2 Routing Setup
Do not use RIP on the WAN interface or the DMZ interface. This prevents intruders from
corrupting the routing table.
If there is more than one internal network, the router must not be used as primary gateway
because the router configuration only allows the router to forward packets to the DMZ network .
2.3 DNS Setup
Some of the services on the DMZ network require external DNS queries. The most common mail
solution is to have a domain with an "MX" record and an "A" record pointing to the SMTP server
on the DMZ network. The DNS server is normally maintained and hosted by the ISP. The
solutions provided in this document do not support a DNS server on the DMZ network.
For more details about DNS please refer to [2].
2.4 E -mail (SMTP) Setup
Locate an SMTP server on the DMZ network to communicate with any host on the Internet and
an internal E-mail server on the secure network. Configure the SMTP server to use an MX record
in order to send the mail direct to the destination SMTP server.
2.5 FTP Setup
An HTTP/FTP proxy server on the DMZ network must use passive FTP for connections to the
Internet. Otherwise the filters will block the FTP data channel running on port 20. Because the
HTTP/FTP is an application proxy, support for DNS is required to resolve fully qualified domain
names into IP addresses.
2.6 HTTP Setup
An HTTP/FTP proxy normally runs on port 80 or 8080. However, the filter settings for the
following setups are based on port 80. Because the HTTP/FTP is an application proxy, support
for DNS is required to resolve fully qualified domain names into IP addresses.
2.7 News (NNTP) Setup
If you are using a News (NNTP) server on your secure network, it is required that you locate a
News (proxy) server on the DMZ. With this setup, the News server on the secure network
communicates with the News (proxy) server on the DMZ which, in turn, communicates with an
external News server on the Internet. The advantage of this setup is that all private news groups
are placed on the internal server, protected from the Internet.
2.8 Management Access Setup
To ensure security, you must disable management access (SNMP, Telnet, and TFTP)
on the WAN (Internet) link and the LAN2 (DMZ) link. For additional security, disable
management access on the LAN1 link also. With this setup, all management tasks can
only be performed from the console port.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 5
Page 7
DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
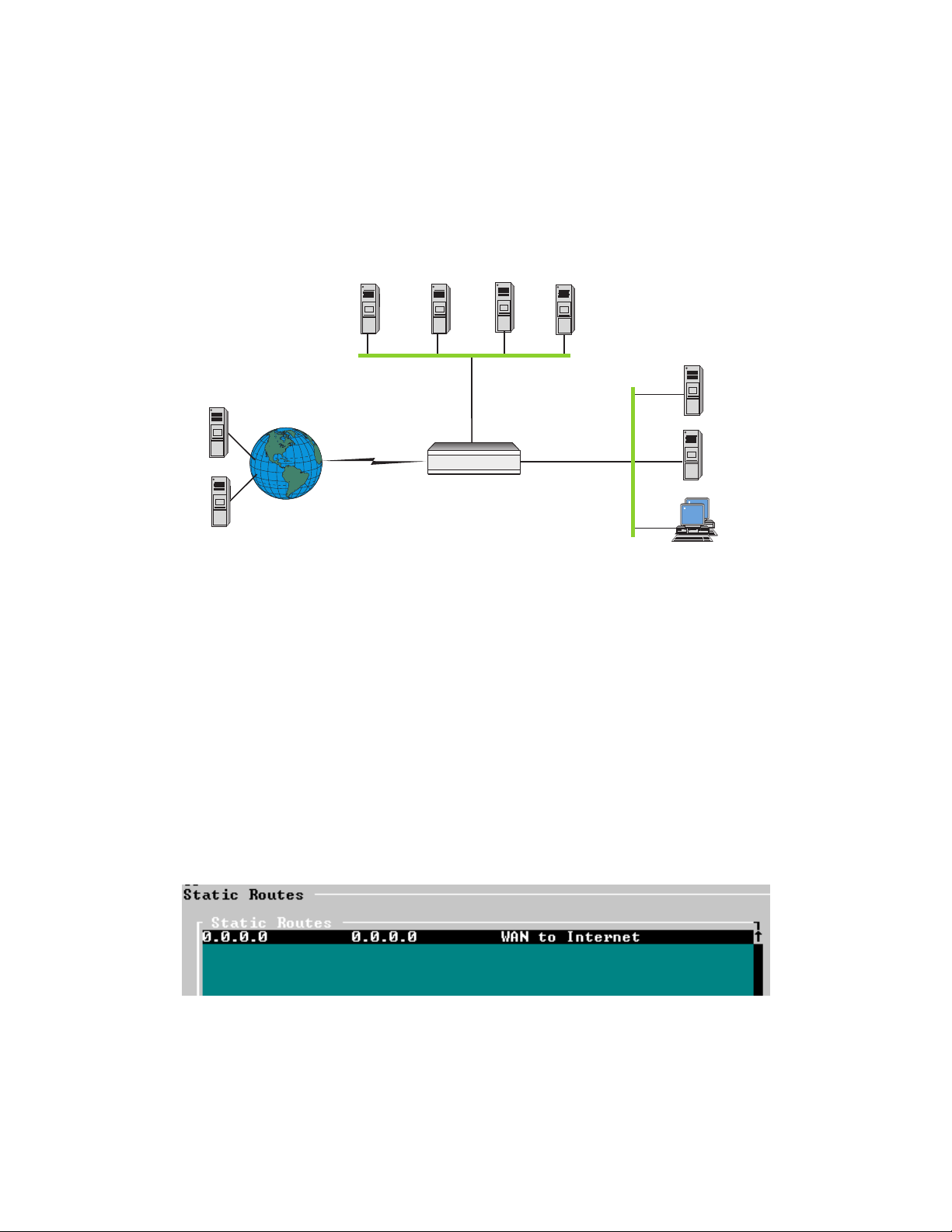
3 DMZ Single IP Address Solution
This solution explains how to set up a DMZ solution when the Internet service provider (ISP) has
assigned a single IP address to your network.
News
(proxy)
server
10.2.0.4
LAN1 port
10.5.0.10
Secure LAN
10.5.0.0
Mail
server
10.5.0.1
News
server
10.5.0.2
Users
DNS
server
194.25.6.4
News
(NNTP)
server
196.24.5.8
Internet
HTTP/FTP
DMZ
10.2.0.0
(Web)
server
10.2.0.1
HTTP/FTP
proxy
server
10.2.0.2
Intel Express
Router
SMTP
server
10.2.0.3
LAN2 port
10.2.0.10
In the example, the DMZ network connects to the LAN2 port and is on the 10.2.0.0/16 subnet.
The LAN2 port has been assigned an IP address of 10.2.0.10. The secure private network
connects to the LAN1 port and is on the 10.5.0.0/16 subnet. The LAN1 port has been assigned an
IP address of 10.5.0.10.
Note: The services available on the DMZ can be placed on a single server. If this is done, you
must configure NAT entries and filters accordingly.
3.1 Static Routing Setup
Configure static routing as follows:
• Configure static routing on the Internet connection, LAN1, and LAN2. This is done in
Advanced Setup by setting the Routing Protocol parameter to None/Static.
• Define a static route on the WAN interface to the Internet. Use the default static route setting
(network address of 0.0.0.0 and netmask 0.0.0.0) as shown in the example below.
3.2 Network Address Translation (NAT) Setup
The devices on the DMZ have been assigned private IP addresses. You must set up NAT to
translate the private IP addresses on the DMZ to the external IP address assigned by the ISP. This
will map services (i.e. port numbers) on the external IP address to servers on the DMZ.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 6
Page 8

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Note The order of the NAT entries is important.
NAT entries are defined as follows:
Entry Function Settings
1 Directs all incoming HTTP
requests to the Web server.
2 Directs all incoming FTP
requests to the Web server.
3 Directs all incoming SMTP
requests to the SMTP server
4 Directs all incoming NNTP
requests to the News server.
5 Directs all other incoming
traffic to the DMZ.
Mapping type: Static Port (Single IP)
Internal address: 10.2.0.1
Internal port: 80
External IP address: <IP address from ISP>
External port: 80
Mapping type: Static Port (Single IP)
Internal address: 10.2.0.1
Internal port: 21
External IP address: <IP address from ISP>
External port: 21
Mapping type: Static Port (Single IP)
Internal address: 10.2.0.3
Internal port: 25
External address: <IP address from ISP>
External port 25
Type: Static Port (Single IP)
Internal address: 10.2.0.4
Internal port: 119
External IP address: <IP address from ISP>
External port: 119
Type: Network to single IP
Internal address: 10.2.0.0
External IP address: <IP address from ISP>
3.3 IP Filters Setup
This section describes the required IP filters for the LAN1, LAN2 and connection to the Internet.
3.3.1 LAN1 Filters
3.3.1.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on LAN1
Configure these receive filters for the LAN1 port, shown as they appear in Advanced Setup.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 7
Page 9

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filters are defined as follows:
Filter Function Settings
— Prohibit users on the secure network
Default Action: Discard
access to the Internet
1 Allows access to the HTTP /FTP
proxy server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.2
Src. address type: All
2 Allows access to the SMTP server on
the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.3
Src. address type: All
3 Allows access to News (pr oxy ) server
on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.4
Src. address type: All
4 Allows access to the rout er from the
private LAN.
Action: Pass
Protocol: All
Dest. port address: Host
Dest. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Scr. address type: All
3.3.1.2 Transmit (Tx) Filters on LAN1
Configure these transmit filters for the LAN1 port, shown as they appear in Advanced Setup.
Filters are defined as follows:
Filter Function Settings
— Prohibit users on the secure network
Default Action: Discard
access to the Internet
1 Allows HTTP and FTP (read only using
HTTP) from secure LAN to HTTP/FTP
proxy server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: >1023
Src. address type: Host
07-12-99 Version 1.0 8
Page 10

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Src. address: 10.2.0.2
Src. port: = 80
2 Allows FTP (only passive connections)
from secure LAN to the FTP proxy
server on the DMZ (see note 1).
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: All
Two filters are required.
Dest. port: >1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 10.2.0.2
Src. port: = 21
3
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: >1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 10.2.0.2
Src. port: >1023
4 Allows incoming mail (SMTP) from
DMZ to secure LAN.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.5.0.1
Dest. port: = 25
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 10.2.0.3
Src. port: > 1023
5 Allows outgoing mail (SMTP) from
secure LAN to DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.5.0.1
Dest. port: > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 10.2.0.3
Src. port: = 25
6 Allows incoming News (NNTP) from
DMZ to secure LAN (see note 2).
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.5.0.2
Dest. port: = 119
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 10.2.0.4
Src. port: > 1023
7 Allows outgoing News (NTTP) to DMZ
from secure LAN.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
07-12-99 Version 1.0 9
Page 11

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Dest. address: 10.5.0.2
Dest. port: > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 10.2.0.4
Src. port: = 119
8 Sends all packets generated by the router
to the secure LAN (LAN1).
Note 1: Some proxy servers, such as Microsoft Proxy* 2.0, do not support FTP proxy using the
FTP protocol. For upload and download using a special FTP program like WS_FTP*, an
additional FTP proxy on DMZ is required. This proxy server normally runs on port 21 and has to
support passive FTP. If download from an Internet browser is sufficient, the two filters are not
required.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Src. port: All
Note 2: The filter is not required when using a News proxy server on DMZ.
3.3.2 LAN2 Filters
3.3.2.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on LAN2
Configure these receive filters for the LAN2 port, shown as they appear in Advanced Setup.
×
07-12-99 Version 1.0 10
Page 12

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filters are defined as follows:
Filter Function Settings
— Pass all packets destined for DMZ Default Action: Pass
1 Prevents RIP updates from entering the
DMZ network
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: RIP
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
2 Prevents tunnel packets from entering
the DMZ network
Action: Discard
Protocol: TCP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: Tunnel
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
3 Prevents RSVP packets from entering
the DMZ network/router.
Action: Discard
Protocol: RSVP
Dest. address type: All
Three separate filters are req ui red.
Dest. port : All
Src. address type: All
Src. port : All
4 Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port : = 1698
Src. address type: All
Src. port : All
5 Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port : = 1699
Src. address type: All
Src. port : All
6 Prevents BootP updates from entering
the DMZ network/router.
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: 67
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
7 Prevents Syslog updates from entering
the DMZ network/router
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: = 514
Scr. address type: All
Src. port : All
Discards all packets that spoof (or fake)
8
the IP address of the router on LAN1.
This is necessary since these packets
will pass the Tx filter on LAN1.
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: All
07-12-99 Version 1.0 11
Page 13

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Scr. address type: Host
Src. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Src. port : All
Discards all ICMP packets entering the
9
DMZ network. This prevents the router
from reporting the IP netmask.
Action: Discard
Protocol: ICMP
Dest. address type: All
Scr. address type: All
10
Discards all packets to open router
ports.
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: Host
Four filters are required.
Dest. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
11 Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: <LAN2 IP address>
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
12 Action: Discard
Protocol: TCP
Flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
13 Action: Discard
Protocol: TCP
flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: <LAN2 IP address>
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
3.3.2.2 Transmit (Tx) filters on LAN2
To pass all packets transmitted from the DMZ, set the default action to Pass.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 12
Page 14

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
3.3.3 Internet Connection Filters
3.3.3.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on the connection to the Internet
Configure these receive filters for the Internet connection, shown as they appear in Advanced
Setup.
×
Filters are defined as follows:
Filter Function Settings
— Prohibit users on the secure network
from accessing the Internet.
1 Allows HTTP from the Internet to the
HTTP/FTP server on the DMZ.
Default Action: Discard
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.1
Dest. port: = 80
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
07-12-99 Version 1.0 13
Page 15

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
2 Allows FTP (both active and passive)
from the Internet to the HTTP/FTP
server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Three filters are required.
Dest. address: 10.2.0.1
Dest. port: = 21
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
3 Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.1
Dest. port: = 20
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
4 Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.1
Dest. port: >1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: >1023
5 Allows external ping to HTTP/FTP
server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: ICMP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.1
Src. address type: All
6 Allows external HTTP from HTTP/FTP
proxy on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: = 80
7 Allows external FTP from the
HTTP/FTP proxy server on the DMZ
(see note 1).
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Two filters are required.
Dest. address: 10.2.0.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: = 21
8 Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
07-12-99 Version 1.0 14
Page 16

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Dest. address: 10.2.0.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
9 Allows DNS reply to the HTTP/FTP
proxy server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Two filters are required.
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 194.25.6.4
Src. port: = 53
10 Action: Pass
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 194.25.6.4
Src. port: = 53
11 Allows DNS reply to the SMTP server
on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Two filters are required.
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.3
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 194.25.6.4
Src. port: = 53
12 Action: Pass
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.3
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 194.25.6.4
Src. port: = 53
13 Allows incoming mail (SMTP) from
any host on the Internet to the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.3
Dest. port = 25
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
14 Allows outgoing mail (SMTP) to any
host on the Internet from the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
07-12-99 Version 1.0 15
Page 17

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.3
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: = 25
15 Allows incoming News (NNTP) from a
specified external News server to the
DMZ (see note 2).
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.4
Dest. port: = 119
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 196.24.5.8
Src. port: > 1023
16 Allows outgoing News (NNTP) to a
specified external News server from the
DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.2.0.4
Dest. port: > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 196.24.5.8
Src. port: 119
Note 1: Only passive FTP connections are supported. The HTTP/FTP proxy must be configured
to use a passive FTP connection.
Note 2: The filter is not required when using a News proxy server on DMZ.
3.3.3.2 Transmit (Tx) Filters on the Connection to the Internet
Set the default action to Pass.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 16
Page 18

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
4 DMZ Multiple IP Address Solution
This solution explains how to set up a DMZ when the ISP supplies you with multiple IP
addresses. In the example, the ISP has assigned the site a range of IP addresses: 193.84.251.0 to
193.84.251.7 (subnet mask 255.255.255.248).
HTTP/FTP
proxy
server
193.84.251.2
Intel Express
Router
SMTP
server
193.84.251.3
LAN2 port
193.84.251.5
LAN1 port
89.20.0.10
News
server
193.84.251.4
Secure LAN
89.20.0.0
Mail
server
89.20.0.1
News
server
89.20.0.2
Layer 3 switch
10/100
Users
Secure LAN
90.20.0.0
DNS
server
194.25.6.4
News
(NNTP)
server
196.24.5.8
HTTP/FTP
server
193.84.251.1
DMZ
193.84.251.0
Internet
Note: The services available on the DMZ can be placed on a single server. If this is done, you
must configure NAT accordingly.
The solution does not configure NAT on the WAN interface (connection to the Internet). This
eliminates problems with protocols that are not supported by the router’s NAT implementation.
4.1 IP Address Assignment
The servers on the DMZ network have been assigned official public IP addresses. NAT is not
required for these addresses. The secure private LAN consists of two networks, 89.20.0.0 and
90.2.0.0, which are official public IP addresses. You must use NAT to translate these addresses to
private IP addresses.
Note: The first and last IP address in the range provided by the ISP must not be used for devices.
The WAN connection to the Internet must be configured as unnumbered.
4.2 Static Routing Setup
Configure static routing as follows:
• Configure static routing on the Internet connection, LAN1, and LAN2. This is done in
Advanced Setup by setting the Routing Protocol parameter to None/Static.
• Define a static route on the WAN interface to the Internet. Use the default static route setting
(network address of 0.0.0.0 and network address of 0.0.0.0) as shown in the example below.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 17
Page 19

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
4.3 Network Address Translation (NAT)
Because the secure private networks on LAN1 use public IP addresses (89.20.0.0 and 90.20.0.0),
configure NAT to translate these addresses to private IP addresses. For example, NAT will
translate the E-mail server address from 89.20.0.1 to 10.1.0.1, the NNTP server address from
89.20.0.2 to 10.1.0.2, and the LAN1 address from 89.20.0.10 to 10.1.0.10.
Note: When adding filter entries, the internal addresses must be used.
NAT entries are defined as follows:
Entry Function Settings
1 Translate the internal IP
addresses on the network
89.20.0.0 to private IP
address on 10.1.0.0
2 Translate the internal IP
addresses on the network
90.20.0.0 to private IP
address on 10.2.0.0
Mapping type: Static
Internal address: 10.1.0.0
Internal mask: 255.255.0.0
External IP address: 89.20.0.0
External mask: 255.255.0.0
Mapping type: Static
Internal address: 10.2.0. 0
Internal mask: 255.255.0.0
External IP address: 90.20.0.0
External mask: 255.255.0.0
4.4 IP Filters Setup
This section describes the required IP filters for the LAN1, LAN2 and connection to the Internet.
4.4.1 LAN1 Filters
4.4.1.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on LAN1
Configure these receive filters for the LAN1 port, shown as they appear in Advanced Setup.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 18
Page 20

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filters are defined as follows:
Filter Function Settings
— Prohibit internal users acc ess to the
Default Action: Default
Internet
1 Allows access to the HTTP /FTP proxy
server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.2
Src. address type: All
2 Allows access to the SMTP server on
the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.3
Src. address type: all
3 Allows acce ss to News (pr oxy ) server
on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.4
Src. address type: All
4 Allows acce ss to the rout er from the
private LAN.
Action: Pass
Protocol: All
Dest. port address: Host
Dest. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Scr. address type: All
4.4.1.2 Transmit (Tx) Filters on LAN1
Configure these transmit filters for the LAN1 port, shown as they appear in Advanced Setup.
Filters are defined as follows:
Filter Function Settings
— Prohibit users on the private network
Default Action: Discard
from accessing the Internet
1 Allows HTTP and FTP (read only using
HTTP) from secure LAN to HTTP/FTP
proxy server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: All
Dest port: >1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 193.84.251.2
07-12-99 Version 1.0 19
Page 21

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Src. port: = 80
2 Allows FTP (only passive connections)
from secure LAN to the FTP proxy
server on the DMZ (see note 1).
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: All
Two filters are required.
Dest port: >1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 193.84.251.2
Src. port: = 21
3
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 193.84.251.2
Src. port: > 1023
4 Allows incoming mail (SMTP) from
DMZ to the secure LAN.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.1.0.1
Dest. port: 25
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 193.84.251.3
Src. port: > 1023
5 Allows outgoing mail (SMTP) from
secure LAN to the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.1.0.1
Dest. port: > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 193.84.251.3
Src. port: 25
6 Allows incoming News (NNTP) from
the DMZ to the secure LAN (see note
2).
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.1.0.2
Dest. port: 119
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 193.84.251.4
Src. port: > 1023
7 Allows outgoing News (NNTP) to
DMZ from secure LAN.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 10.1.0.2
07-12-99 Version 1.0 20
Page 22

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Dest. port: > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 193.84.251.4
Src. port: 119
8 Sends all packets generated by the
router to the internal LAN (LAN1).
Note 1: Some proxy servers, such as Microsoft Proxy* 2.0, do not support FTP proxy using the
FTP protocol. For uploading and downloading using a special FTP program, such as WS_FTP*,
an additional FTP proxy on DMZ is required. This proxy server normally runs on port 21, and it
has to support passive FTP. If downloading from an Internet browser is sufficient, the two filters
are not required.
Note 2: The filter is not required when using a News proxy server on DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Src. port: All
4.4.2 LAN2 Filters
4.4.2.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on LAN2
Configure these receive filters for the LAN2 port, shown as they appear in Advanced Setup.
×
Filters are defined as follows:
Filter Function Settings
— Pass all packets destined for DMZ Default Action: Pass
1 Prevents RIP updates from entering the
DMZ network
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest port: RIP
07-12-99 Version 1.0 21
Page 23

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
2 Prevents tunnel packets from entering
the DMZ network
Action: Discard
Protocol: TCP
Dest. address type: All
Dest port: Tunnel
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
3 Prevents RSVP packets from entering
the DMZ network/router. Three
separate filters are required.
Action: Discard
Protocol: RSVP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port : All
Src. address type: All
Src. port : All
4 Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port : 1698
Src. address type: All
Src. port : All
5 Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port : 1699
Src. address type: All
Src. port : All
6 Prevents BootP updates from entering
the DMZ network/router.
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: 67
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
7 Prevents Syslog updates from entering
the DMZ network/router
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: 514
Scr. address type: All
Src. port : All
Discards all packets that fake the IP
8
address of the router on LAN1 as these
packets are allowed to pass the Tx filter
on LAN1
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: All
Dest. port: All
Scr. address type: Host
Src. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Src. port : All
07-12-99 Version 1.0 22
Page 24

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Discards all ICMP packets entering the
9
DMZ network. This prevents the router
from reporting the IP netmask. These
filters must include all IP addresses on
the router, including the WAN IP
address if the router is using numbered
Action: Discard
Protocol: ICMP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: <LAN1 IP address>
Scr. address type: All
links.
10
Two filters are required.
Action: Discard
Protocol: ICMP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: <LAN2 IP address>
Scr. address type: All
11
Discards all packets to open router
ports.
Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
dest address type: Host
Four filters are required.
dest address: <LAN1 IP address>
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
12 Action: Discard
Protocol: UDP
dest address type: Host
dest address: <LAN2 IP address>
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
13 Action: Discard
Protocol: TCP
Flags: All
dest address type: Host
dest address: <LAN1 IP address>
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
14 Action: Discard
Protocol: TCP
flags: All
dest address type: Host
dest address: <LAN2 IP address>
Dest. port: All
Src. address type: All
Src. port: All
07-12-99 Version 1.0 23
Page 25

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
4.4.2.2 Transmit (Tx) filters on LAN2
Set the default action to Pass.
4.4.3 Internet Connection Filters
4.4.3.1 Receive (Rx) Filters on the Connection to the Internet
The required receive filters for the Internet connection, shown as they appear in Advanced
Setup.
×
Filters are defined as follows:
Filter Function Settings
— Prohibit users on the secure network
from accessing the Internet
1 Allows HTTP from the Internet to the
HTTP/FTP server on the DMZ.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 24
Default Action: Discard
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.1
dest port: = 80
Src. address type: All
Page 26

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Src. port: > 1023
2 Allows FTP (both active and passive)
from the Internet to the HTTP/FTP
server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Three filters are required.
Dest. address: 193.84.251.1
dest port: = 21
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
3 Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.1
dest port: = 20
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
4 Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.1
dest port: >1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: >1023
5 Allows external ping to HTTP/FTP
server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: ICMP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.1
Src. address type: All
6 Allows external HTTP from HTTP/FTP
proxy on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: = 80
7 Allow s ext erna l F TP from HTTP/FTP
proxy server on the DMZ (see note 1).
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Two filters are required.
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
8 Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
07-12-99 Version 1.0 25
Page 27

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: = 21
9 Allows DNS reply to the HTTP/FTP
proxy server on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Two filters are required.
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 194.25.6.4
Src. port: = 53
10 Action: Pass
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.2
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 194.25.6.4
Src. port: = 53
11 Allows DNS reply to the SMTP server
on the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Two filters are required.
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.3
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 194.25.6.4
Src. port: = 53
12 Action: Pass
Protocol: UDP
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.3
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 194.25.6.4
Src. port: = 53
13 Allows incoming mail (SMTP) from
any host on the Internet to the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.3
Dest. port = 25
Src. address type: All
Src. port: > 1023
07-12-99 Version 1.0 26
Page 28

DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
Filter Function Settings
14 Allows outgoing mail (SMTP) to any
host on the Internet from the DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.3
Dest. port > 1023
Src. address type: All
Src. port: = 25
15 Allows incoming News (NNTP) from a
specified external News server to the
DMZ (see note 2).
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: All
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.4
Dest. port: = 119
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 196.24.5.8
Src. port: > 1023
16 Allows outgoing News (NNTP) to a
specified external News server from the
DMZ.
Action: Pass
Protocol: TCP
TCP flags: ACK
Dest. address type: Host
Dest. address: 193.84.251.4
Dest. port: > 1023
Src. address type: Host
Src. address: 196.24.5.8
Src. port: = 119
Note 1: Only passive FTP connections are supported. The HTTP/FTP proxy must be configured
to use a passive FTP connection.
Note 2: The filter is not required when using a News proxy server on DMZ.
4.4.3.2 Transmit (Tx) Filters on the Connection to the Internet
Set the default action to Pass. No individual filters are required.
07-12-99 Version 1.0 27
 Loading...
Loading...