Page 1

DUAL BAND FM TRANSCEVER
S-14325XZ-C1
Mar. 2007
Page 2
INTRODUCTION CAUTION
This service manual describes the latest service information
for the IC-2820H DUAL BAND FM TRANSCEVER at the
time of publication.
MODEL VERSION
USA-01
AUS-01
IC-2820H
To upgrade quality, any electrical or mechanical parts and
internal circuits are subject to change without notice or
obligation.
KOR-01
TPE-01
EXP-01
NEVER connect the transceiver to an AC outlet or to a DC
power supply that uses more than 15 V. This will ruin the
transceiver.
DO NOT expose the transceiver to rain, snow or any liquids.
DO NOT reverse the polarities of the power supply when
connecting the transceiver.
DO NOT apply an RF signal of more than 20 dBm (100 mW)
to the antenna connector (J1). This could damage the
transceiver’s front end.
ORDERING PARTS
Be sure to include the following four points when ordering
replacement parts:
1. 10-digit order numbers
2. Component part number and name
3. Equipment model name and unit name
4. Quantity required
<SAMPLE ORDER>
1110003491 S.IC TA31136FNG IC-2820H MAIN UNIT 5 pieces
8820001210 Screw 2438 screw IC-2820H Top cover 10 pieces
Addresses are provided on the inside back cover for your
convenience.
Icom, Icom Inc. and
Kingdom, Germany, France, Spain, Russia and/or other countries.
logo are registered trademarks of Icom Incorporated (Japan) in the United States, the United
REPAIR NOTES
1. Make sure a problem is internal before disassembling
the transceiver.
2. DO NOT open the transceiver until the transceiver is
disconnected from its power source.
3. DO NOT force any of the variable components. Turn
them slowly and smoothly.
4. DO NOT short any circuits or electronic parts. An
insulated tuning tool MUST be used for all adjustments.
5. DO NOT keep power ON for a long time when the
transceiver is defective.
6. DO NOT transmit power into a signal generator or a
sweep generator.
7. ALWAYS connect a 50 dB to 60 dB attenuator between
the transceiver and a Modulation Analyzer or spectrum
analyzer when using such test equipment.
8. READ the instructions of test equipment thoroughly
before connecting equipment to the transceiver.
Page 3

CONTENTS
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
SECTION 3 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPITON
4-1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS ............................................................................................................... 4-1
4-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS ....................................................................................................... 4-4
4-3 FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER .................................................................................................. 4-6
4-4 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS ..................................................................................................... 4-8
4-5 PORT ALLOCATIONS ............................................................................................................... 4-9
SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
5-1 PREPARATION .......................................................................................................................... 5-1
5-2 FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT ................................................................................................... 5-2
5-3 TRANSMIT ADJUSTMENT ....................................................................................................... 5-3
5-4 RECEIVE ADJUSTMENT .......................................................................................................... 5-4
SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS
SECTION 8 BOARD LAYOUTS
SECTION 9 BLOCK DIAGRAM
SECTION 10 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
SECTION 11 HM-133
SECTION 12 UT-123 (Optional product)
Page 4

SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
M
,!2%.%'
s Z(-TINUEGAREVOCYCNEUQER&
E6 DNA"THGI2DNA"TFE,NOISR
!35 nX2
LARENE' nnX4
nX2
n
AILARTSU! nnX2X4
4NAWIA nnX2X4
AERO+ nnX2X4
4s-!-&NOISSIMEFOEPY YLNOEVIECE2
YLNOEGNARZ(-nDEETNARAU'
NOISREVLARENE'EHTROFZ(-n
DEETNARAUGTO.
6$
DERIUQERSI45LANOITPO
s SLLACDNASEGDENACSLCNISLENNAHCYROMEMFOREBMU.
s Z(K
NOITULOSERYCNEUQER&
s#OT#nEGNARERUTAREPMETGNITAREP/OT&&
&sMPPÒYTILIBATS
YCNEUQER
#OT#n
sÒ#$6TNEMERIUQERYLPPUSREWO0
sNIARDTNERRU#
XORPPA#$6TA
4 !7TATIMSNAR
!YBDNATSEVIECE2
EVIECERSUOENATLUMIS !OIDUAXAM
s/3ROTCENNOCANNETN!
sSNOISNEMI$
DEDULCNITONJORP
7s YTISREVI$DNAX2X4
7TIN5NIA- s ( s MM$
7 s
( s NI$
7RELLORTNOCETOME2 s ( s MM$
7sTHGIE
XORPPA
7 s
( s NI$
ZOBLGKTINUNIA-
ZOGRELLORTNOCETOME2
n
nnX4
!35EHTROFEGNARZ(-nDEETNARAU'
DNAOT
DEETNARAUGTONDNANOISREV!35ROFDETIBIHNIERASEGNARZ(-OT
NOISREVNAWIA4EHTROFYLNO7TA!
ELBACNOITARAPESLCNI
M
s NOITALUDOMYCNEUQERFECNATCAERELBAIRA6METSYSNOITALUDOs 7REWOPTUPTU/
s Z(KÒNOITAIVEDYCNEUQERFXA-
s "DnNAHTSSE,SNOISSIMESUOIRUP3
s RALUDOMNIPROTCENNOCENOHPORCI-
M
s ENYDORETEHREPUSNOISREVNOCELBUO$METSYSEVIECE2
s SEICNEUQERFETAIDEMRETN)
s YTIVITISNE3
s YTIVITISNESHCLEUQ3
sYTIVITCELE3
sNOITCEJEREGAMIDNASUOIRUP3
s
sMMDROTCUDNOCSROTCENNOCREKAEPSTX%
2%44)-3.!24
XORPPA
NOISREVNAWIA4EHTROFYLNO7
EDIW
Z(KÒ WORRAN
7
2%6)%#%2
DNABTFE,
YLNOSDNABRUETAMA
-&
6$
o
$!.)3"D
2%" 6§NAHTSSE,
o
DERIUQERSI45LANOITPO
DLOHSERHT 6§NAHTSSE,
LACIPYT
6§NAHTSSE,
"DZ(KNAHTERO-WORRA.
6$
o
REWOPTUPTUO&!
o
DERIUQERSI45LANOITPO
o
#$6TA
7NAHTERO- NAHTIWNOITROTSID
7 DAOL
"DNAHTERO-
"DNAHTERO-
"DZ(KNAHTERO-EDI7
"DZ(KNAHTSSE,
"DZ(KNAHTSSE,
TA
q 7
Z(KDNZ(-TS
Z(KDNZ(-TSDNABTHGI2
DNABTFELNO&(5ROF"DNAHTERO-
YLNOSEGNARZ(-nROnDNAZ(-nROnDEETNARAU'
ICEPSDETATSLL!l NOITAGILBOROECITONTUOHTIWEGNAHCOTTCEJBUSERASNOITAC
1 - 1
Page 5
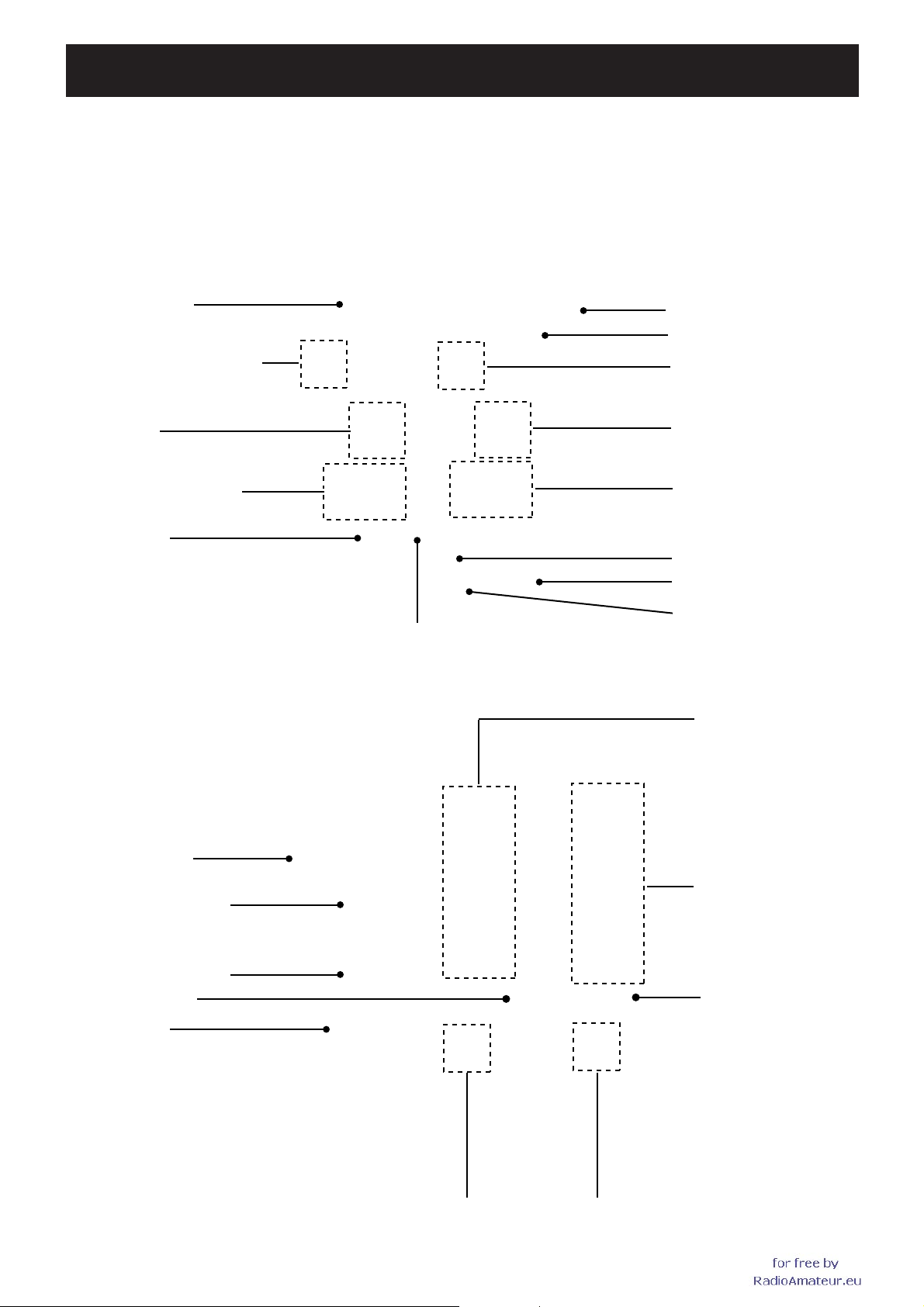
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
• TOP VIEW
D/A converter
(IC1: M62364FP)
1st IF Mixer for UHF bands
(IC20: SPM5001)
LO filter
(763.650−953.640 MHz)
Frequency synthesizer
(Right band)
AF switch
(IC30: CD4066BPWR)
• BOTTOM VIEW
D/A converter
(IC8: M62364FP)
Electric volume
(IC33: SM6451B)
D/A converter
(IC54: M62364FP)
1st IF Mixer for VHF bands
(IC19: SPM5001)
LO divider
(79.150−121.150 MHz)
Frequency synthesizer
(Left band)
AF filter
(IC48: LM2902PWR)
Level converter
(IC46: MAX3221IPWR)
AF switch
(IC31: CD4066BPWR)
VHF PA module
(IC3: S-AV32)
AF power amplifier
(IC38: LA4445)
EEPROM
(IC22: 24LC512)
CPU
(IC25: HD64F2506FC26)
IF IC (Left band RX)
(IC15: TA31136FNG)
DTMF decoder
(IC56: BU8872FS)
Reference frequency oscillator
(Left band)
2 - 1
UHF PA module
(IC2: S-AU82L)
IF IC (Right band)
(IC18: TA31136FNG)
Reference frequency oscillator
(Right band)
Page 6
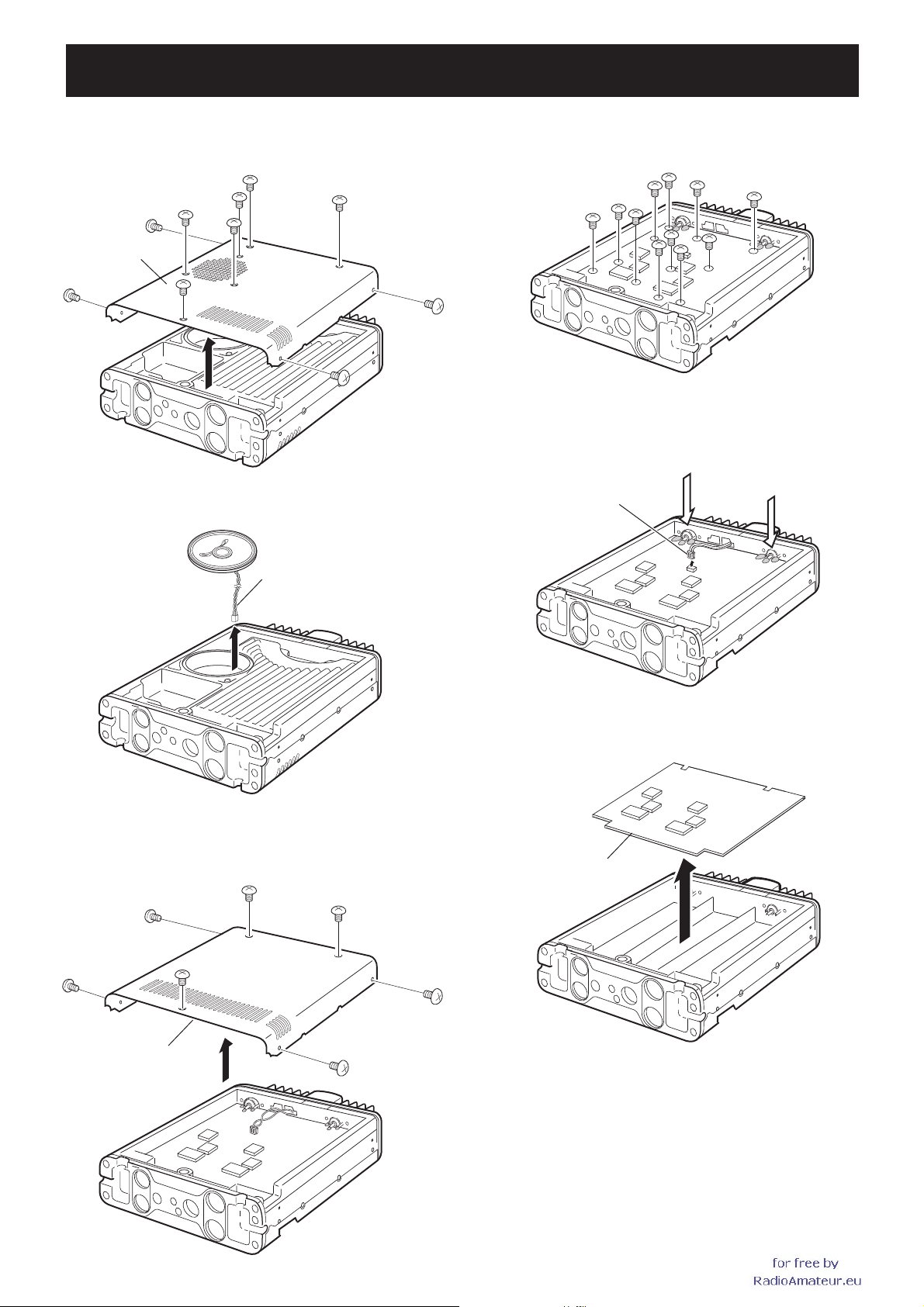
SECTION 3 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION
1. Removing the top cover
q Unscrew 10 screws, then remove the top cover.
10 screws
Top cover
w Disconnect the speaker cable.
Speaker cable
3. Removing the MAIN UNIT
q Unscrew 11 screws from the MAIN UNIT.
w Disconnect the cooling fan cable, and unsolder 6 points at
the antenna connectors (grey colored).
6 unsoldering points
Cooling fan cable
2. Removing the bottom cover
q Unscrew 7 screws, then remove the bottom cover.
7 screws
Bottom cover
e Remove the MAIN UNIT in the direction of the arrow.
MAIN UNIT
3 - 1
Page 7
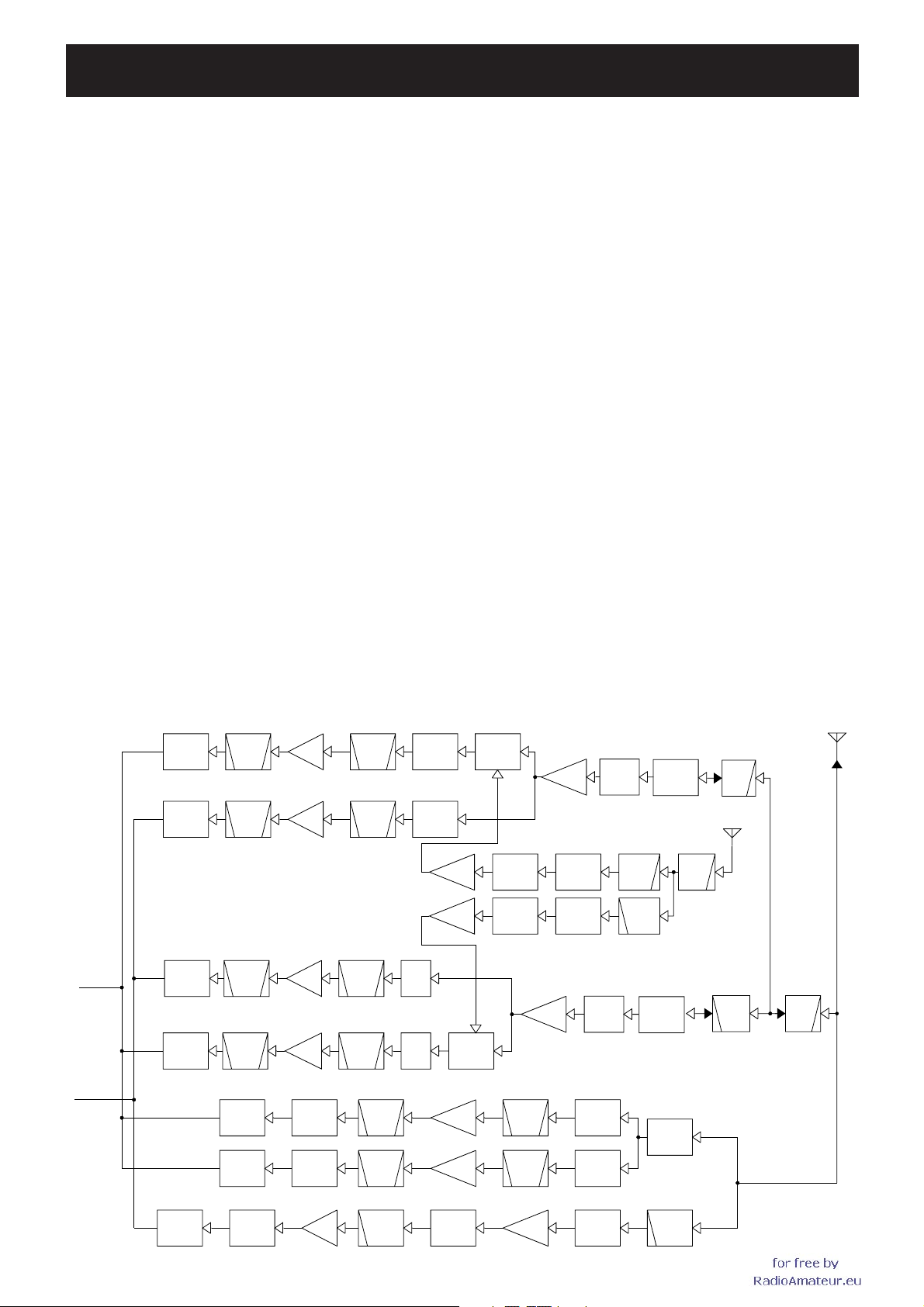
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4-1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
RF CIRCUITS
<Left band>
• 118−174 MHz
The received signals from the antenna connector ANT-1
(J1) are passed through two LPFs (L101, 104, 108, C342,
346; L88, 92, 96, C318, 326, 330), then applied to the RF
amplifi er (Q37) via TX/RX switch (D75). The amplifi ed signals
are passed through the RX switch (RL2), attenuator (D68)
and tuned BPF (D55, 66), before being applied to another
RF amplifi er (Q33). The amplifi ed signals are applied to the
1st mixer (IC19) via the another tuned BPF (D41, 44) and
RX switch (D38).
While the diversity operation is activated, the received
signals are also input from ANT-2 (J2). The received signals
are passed through two LPFs (L103, 106, 109, C344, 348;
L90, 93, 98, C319, 327, 348), antenna switch (D65, 72) and
limitter (D64, 67), then applied to the RF amplifi er (Q39).
The amplified signals are applied to the RX switch (RL2),
and gone through the same process as the received signals
from ANT-1 (J1).
• 174−260 MHz
The received signals from the antenna connector (J1) are
passed through two RX switches (RL3 and D56) and the
tuned BPF (D51), then applied to the RF amplifier (Q34).
The amplified signals are passed through the BPF (D45),
attenuator (R139, 144, 147) and RX switch (D36) before
being applied to the 1st mixer (IC19).
• 260−375 MHz
The received signals from the antenna connector (J1) are
passed through two RX switches (RL3 and D57) and the
tuned BPF (D50), then applied to the RF amplifi er (Q35).
The amplifi ed signals are passed through the BPF (D465),
attenuator (R142, 143, 150) and RX switch (D37) before
being applied to the 1st mixer (IC19).
• 375−550 MHz
The received signals from the antenna connector (J1) are
passed through the LPF (L101, 104, 108, C342, 346) and
HPF (L77, 80, C296, 297, 303, 308), then applied to the
RF amplifier (Q28) via TX/RX switch (D53, 61, 62). The
amplifi ed signals are passed through the RX switch (RL1),
attenuator (D28) and tuned BPF (D19, 21, 24, 27), before
being applied to another RF amplifi er (Q20). The amplifi ed
signals are applied to the 1st mixer (IC19) via the another
tuned BPF (D11, 13, 15, 17) and RX switch (D8).
While the diversity operation is activated, the received
signals are also input from antenna connector ANT-2 (J2).
The received signals are passed through the LPF (L103,
106, 109, C344, 348), HPF (L95, 99, C329, 333, 338),
antenna switch (D69, 73, 74) and limitter (D63, 66), then
applied to the RF amplifi er (Q29).
The amplified signals are applied to the RX switch (RL1),
and gone through the same process as the received signals
from ANT-1 (J1).
• RF CIRCUITS
Left band
ight band
D38
RX
SW
D35
RX
SW
D7
RX
SW
D8
RX
SW
D44
D41,
BPF
D40,
D43
BPF
D10,
D12,
D14,
D16
BPF
,D13,
D11
D17
D15,
BPF
D36
RX
SW
D37
RX
SW
118−174 MHz
Q33
RF
AMP
Q32
RF
AMP
118−174 MHz
375−550 MHz
Q19
RF
AMP
375−550 MHz
Q20
RF
AMP
ATT
ATT
D55,
D60
BPF
D54,
D58
BPF
D20,
D18,
D23,
D26
BPF
D21,
D19,
D24,
D27
BPF ATT
D45
BPF
D46
BPF
D68
ATT
D70
ATT
Q39
Q29
D30
ATT
RL1
Q30
D32
D28
174−260 MHz
Q34
260−375 MHz
Q35
RF
AMP
RF
AMP
RF
AMP
RF
AMP
RX
SW
RL2
Q38
D76
RX
SW
D64,D67
LIMIT
LIMIT
D63,D66
D51
BPF
D50
BPF
Q37
D65,D71,D72
D69,D73,D74
Q28
RF
AMP
RF
AMP
ANT
ANT
SW
SW
D48,D49
LIMIT
D56
D57
RX
SW
RX
SW
D78,
LIMIT
D79
LPF
HPF
TX/RX
D53
D61
D62
TX/RX
SW
RL3
Q40
D80
D59
D75
D77
SW
RX
SW
LPF
LPF
ANTENNA
HPF
ANTENNA
LPF
HPF
810−1000 MHz
ATT
Q23
RF
AMP
D9
RX
SW
ATT
Q18
RF
AMP
D22
RX
SW
HPF
4 - 1
Page 8
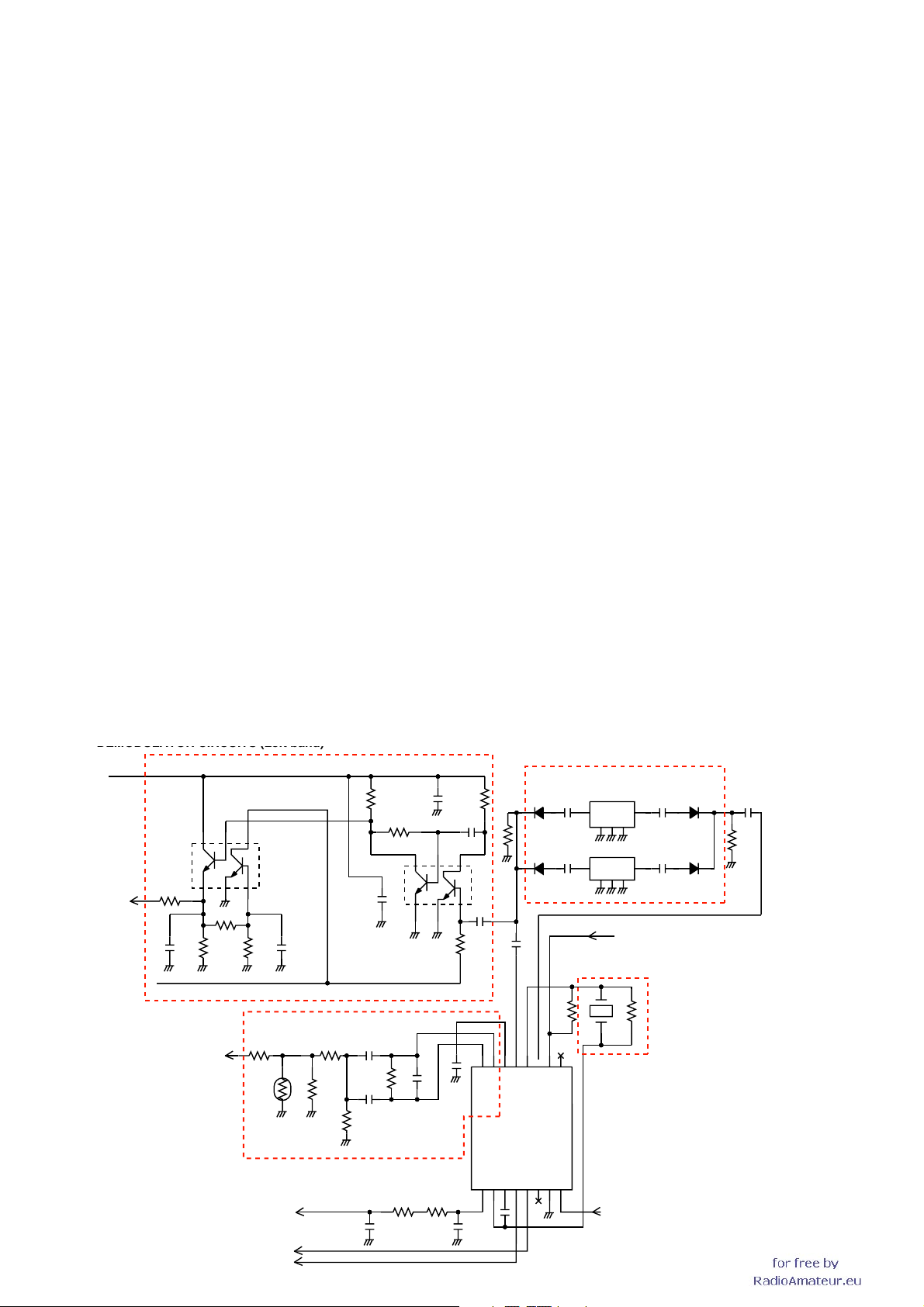
1ST IF CIRCUITS
DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS (Left band)
RX signals from the RF circuits are converted into the 38.85
MHz 1st IF signal by being mixed with LO signals from the
left band VCO (Q111, D145−147).
The converted IF signal from the 1st mixer is passed through
the IF fi lter (FI5) to be fi ltered. The fi ltered IF signal is applied
to the 1st IF amplifi er (Q66) via the limiter (D88). The amplifi ed
1st IF signal is applied to the IF IC (IC15, pin 16)
SQUELCH CIRCUITS
• NOISE SQUELCH
A portion of FM-demodulated AF signals from the IF IC
(IC15, pin 9) are level-adjusted by D/A converter (IC8), and
passed throuhgh the noise fl tier (IC15 and some R and C) to
be fi ltered noise components (30 kHz and above signals) in
the AF signals. The fi ltered noise components aree detected
in the IC15 and output from pin 13, then applied to the CPU
(IC25, pin 100) as “L_SQL” signal.
2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS (Fig. 2)
IC15 is an IF IC which contains 2nd mixer, limiter amplifi er,
noise amplifi er, quadrature detector and RSSI circuit, etc. in
its package.
The 1st IF signal from the 1st IF amplifi er (Q66) is converted
into the 450 kHz 2nd IF signal by being mixed with tripled
reference frequency signal (38.4 MHz) from the PLL IC (IC41)
via the tripler (Q105). The converted 2nd IF signal is output
from pin 3, and passed through the ceramic filter (FI1 for
narrow mode, FI2 for wide mode) to remove sideband noise,
then applied to the IF IC from pin 5 again.
• FM DEMODULATOR
The fi ltered 2nd IF signal from pin 5 is amplifi ed at the limiter
amplifier, and FM-demodulated at the quadrature detector
circuit. The demodulated AF signals are output from pin 9
and routed to the AF circuits via two AF switches (IC11 and
IC13).
• AM DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
In the AM mode, the 2nd IF signal from the FI2 is applied to
the AM-demodulator circuit (Q55, Q57). The demodulated
AF signals are routed to the AF circuits via two AF switches
(IC11 and IC13).
Then the CPU outputs “L_AF_MUTE” signal from pin 82 to the
speaker mute switch (Q102), according to the
“L_SQL” signal
level. Thus the AF line is connected to the GND to turn the AF
output OFF.
• CTCSS/DTCS
CTCSS/DTCS signals in the demodulated AF signals from
the AF switch (IC13) are passed through the tone fi lter (Q41)
. The fi ltered CTCSS/DTCS signals are applied to the CPU
IC25, pin 70) as “L_DTCSIN” signal.
The CPU (IC25) compares the applied signal and the set CTCSS/DTCS, then outputs control signal as same as “NOISE SQUELCH.”
• DTMF
DTMF signals
in the demodulated AF signals from the AF
switch (IC13) are passed through two AF switches (IC57
and IC58), then applied to the
DTMF decoder (IC56) to be
decoded.
AF CIRCUITS
The AM/FM-demodulated AF signals from the AF switch
(IC11) are passed through the AF filter (Q47). The filtered
AF signals are applied to the electric volume (IC33) to be
adjusted its level. The level-adjusted AF signals are applied
to the dual AF power amplifiier (IC38) to
power level, then applied to the internal (CHASSIS; SP1)
or an external speaker via external speaker jack (J7).
obtain AF output
• 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS (LEFT BAND)
AM DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
L_R5
R306
to the AF circuits
AM-demodulated AF signals
FM-demodulatedAF signals
from the D/A converter (IC8)
C407
AGC voltage to the 1st IF amplifier (Q66)
4
5
6
Q55
1
2
3
R310
C417
R319
R311
R884
R317
R314
C418
C419
R321
R307
NOISE FILTER
R327
R328
C423
6
1
R324
C425
5
2
C422
If an external speaker is connected to the J8, the leveladjusted AF signals from the electric volume (IC33) are
applied to the connected speaker.
2nd IF FILTERS
C427
4
3
C426
R335
Q57
C429
R332
8
FILIN
R316
C428
7
DEC
FILOUT
D82
D83
C933
I O
FI2
I O
38.4 MHz 2nd LO signal
from the PLL IC (IC41)
FI1
C932
QUADRATURE DETECTOR
X2
R341
1
2
3
4
5
6
VCC
IFIN
OSCIN
OSCOUT
MIXOUT
IF IC (IC15)
R346
C930
C931
D84
D85
C437
R334
FM-demodulated AF signals
to the AF circuits
L_SQL
L_RSSI
C404
R308
R315
4 - 2
C416
AFOUT
QUAD
9
10
C435
IFO UT
11
RSSI
12
N-REC
N-DET
14
13
GND
MIXIN
16
15
1st IF signal from
the 1st IF amplifier(Q66)
Page 9
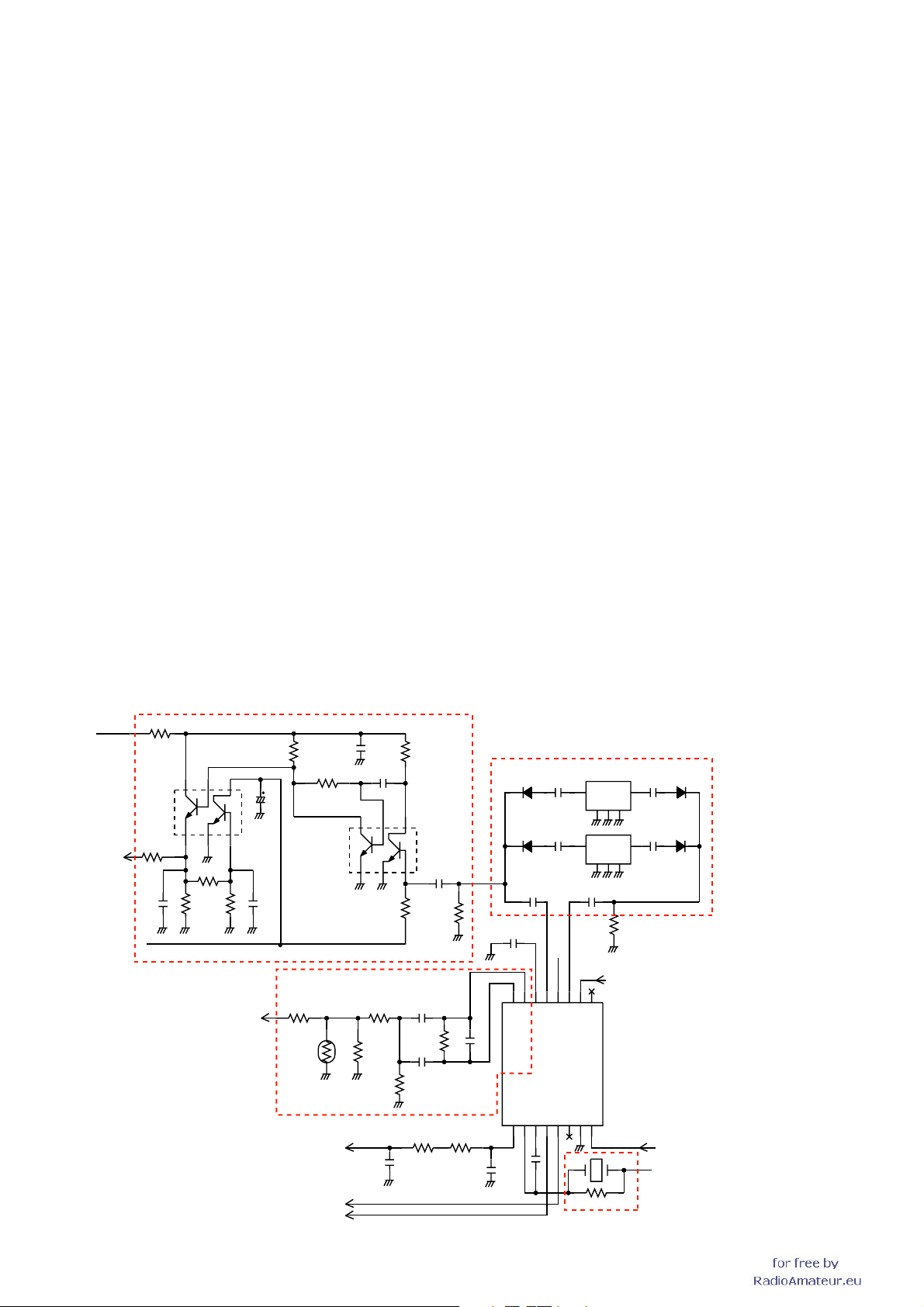
RF CIRCUITS
<Right band>
• 118−174 MHz
The received signals from the antenna connector ANT-1
(J1) are passed through two LPFs (L101, 104, 108, C342,
346; L88, 92, 96, C318, 326, 330), then applied to the
RF amplifier (Q37) via TX/RX switch (D59). The amplified
signals are passed through the attenuator (D70) and tuned
BPF (D54, 58), before being applied to another RF amplifi er
(Q32). The amplified signals are applied to the 1st mixer
(IC20) via the another tuned BPF (D40, 43) and RX switch
(D35).
• 375−550 MHz
The received signals from the antenna connector (J1) are
passed through the LPF (L101, 104, 108, C342, 346) and
HPF (L77, 80, C296, 297, 303, 308), then applied to the
RF amplifier (Q28) via TX/RX switch (D53, 61, 62). The
amplified signals are passed through the attenuator (D30)
and tuned BPF (D18, 20, 23, 26), before being applied
to another RF amplifier (Q19). The amplified signals are
applied to the 1st mixer (IC20) via the another tuned BPF
(D10, 12, 14, 16) and RX switch (D7).
• 810−1000 MHz
The received signals from the ANT-1 (J1) are passed
through the HPF (L102, 105, 107, 110, C337, 339, 340,
343, 347, 349) and RX switch (D22), then applied to the RF
amplifier (Q23). The amplified signals are passed through
the attenuator (R39, 40, 51), and applied to the another RF
amplifi er (Q18) to be amplifi ed again. The amplifi ed signals
are then passed through another attenuator (R14) and RX
switch (D9) before being applied to the 1st mixer (IC20).
1ST IF CIRCUITS
RX signals from the RF circuits are converted into the 46.35
MHz 1st IF signal by being mixed with LO signals from the
right band VCO (Q72, D89, 90; Q73, D87, 91, 92).
The converted IF signal from the 1st mixer (IC20) is passed
through the IF fi lter (IF6) to be fi ltered. The fi ltered IF signal is
applied to the 1st IF amplifi er (Q75) via the limiter (D100). The
amplifi ed 1st IF signal is applied to the IF IC (IC18, pin 16)
2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
IC15 is an IF IC which contains 2nd mixer, limiter amplifi er,
noise amplifi er, quadrature detector and RSSI circuit, etc. in
its package.
The 1st IF signal from the 1st IF amplifi er (Q75) is converted
into the 450 kHz 2nd IF signal by being mixed with tripled
reference frequency signal (45.9 MHz) from the PLL IC (IC14)
via the tripler (Q52). The converted 2nd IF signal is output
from pin 3, and passed through the ceramic filter (FI3 for
narrow mode, FI4 for wide mode) to remove sideband noise,
then applied to the IF IC from pin 5 again.
• FM DEMODULATOR
The fi ltered 2nd IF signal from pin 5 is amplifi ed at the limiter
amplifier, and FM-demodulated at the quadrature detector
circuit (X3). The demodulated AF signals are output from pin
9 and routed to the AF circuits via two AF switches (IC12
and IC16).
• AM DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
In the AM mode, the 2nd IF signal from the FI3 is applied to
the AM-demodulator circuit (Q63, Q67). The demodulated
AF signals are routed to the AF circuits via two AF switches
(IC12 and IC16).
• DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS (Right band)
R_R5
R351
4
5
6
Q63
1
2
R352
to the AF circuits
AM-demodulated AF signals
FM-demodulatedAF signals
from the D/A converter (IC8)
C450
AGC voltage to the 1st IF amplifier (Q75)
3
R358
R359
FM-demodulated AF signals
to the AF circuits
C458
R366
C454
AM DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
R374
R376
180K
Q67
R372
R885
NOISE FILTER
C471
0.01
6
1
R388
R383
R_SQL
R_RSSI
C470
5
2
C460
R374
4
3
R385
C475
C476
R397
R375
C477
R402
R389
R400
C480
2nd IF FILTERS
C486
D93
D94
C487
C478
7
8
FILIN
FILOUT
AFOUT
QUAD
9
10
C927
C929
DEC
IFOUT
11
5
6
IFIN
RSSI
12
C491
R_R5
VCC
N-DET
D95
C926
FI3
C928
FI4
C495
R414
45.9 MHz 2nd LO signal
from the PLL IC (IC14)
1
2
3
4
OSCIN
OSCOUT
MIXOUT
IF IC (IC18)
N-REC
GND
MIXIN
16
15
14
13
X3
R415
D96
1st IF signal from
the 1st IF amplifier(Q75)
R_R5
QUADRATURE DETECTOR
4 - 3
Page 10
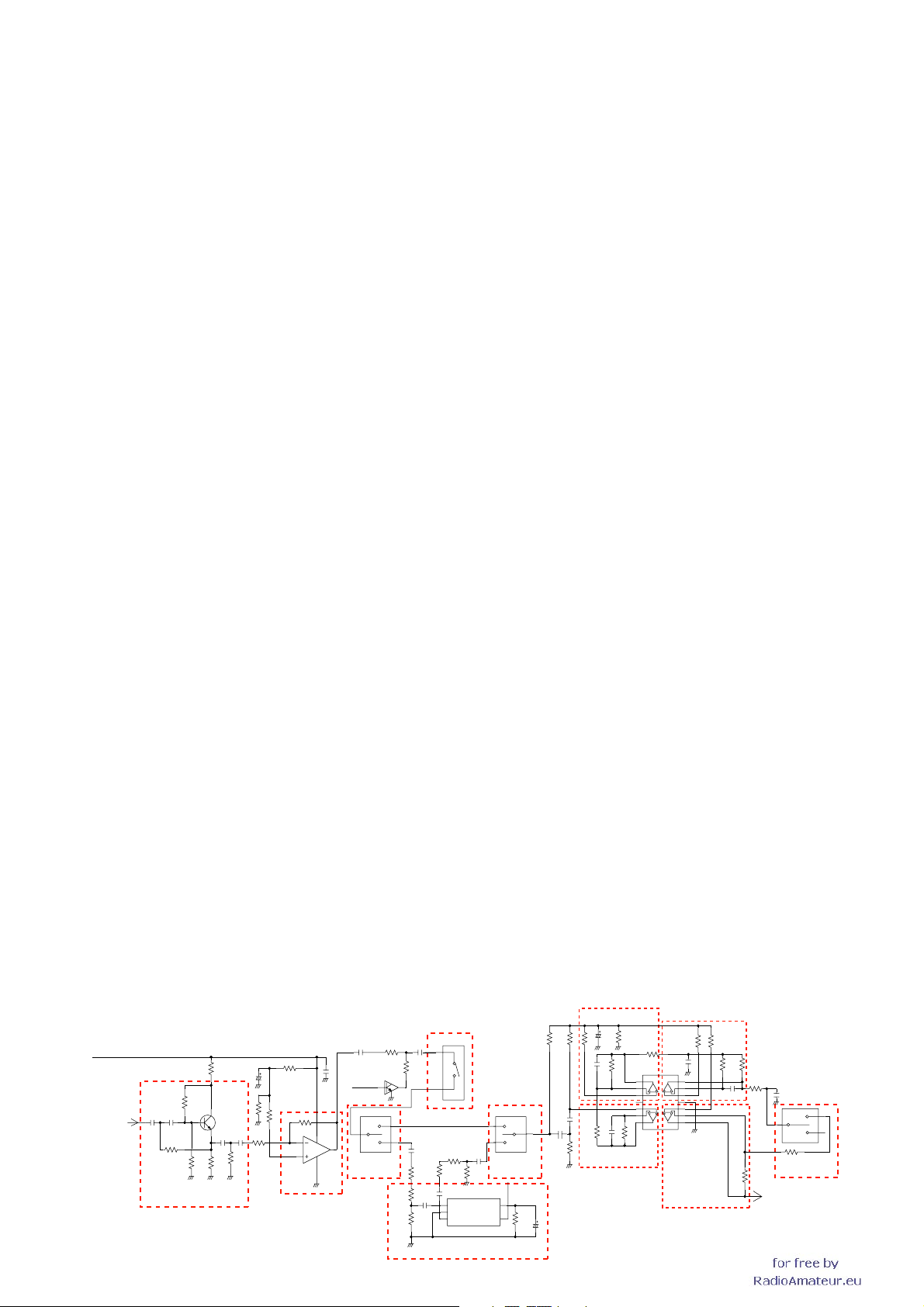
SQUELCH CIRCUITS
• NOISE SQUELCH
A portion of FM-demodulated AF signals from the IF IC
(IC18, pin 9) are level-adjusted by D/A converter (IC8), and
passed throuhgh the noise fl tier (IC18 and some R and C) to
be fi ltered noise components (30 kHz and above signals) in
the AF signals. The fi ltered noise components are detected
in the IC18 and output from pin 13, then applied to the CPU
as “R_SQL” signal.
Then the CPU outputs “R_AF_MUTE” signal from pin 51 to the
speaker mute switch (Q102), according to the
“R_SQL” signal
level. Thus the AF line is connected to the GND to turn the AF
output OFF.
• CTCSS/DTCS
CTCSS/DTCS signals in the demodulated AF signals from
the AF switch (IC16) are passed through the tone fi lter (Q42)
. The fi ltered CTCSS/DTCS signals are applied to the CPU
IC12) as “R_DTCS” signal.
The CPU (IC25) compares the applied signal and the set
CTCSS/DTCS, then outputs control signal as same as “NOISE
SQUELCH.”
• DTMF
DTMF signals
in the demodulated AF signals from the AF
switch (IC16) are passed through two AF switches (IC57
and IC58), then applied to the
DTMF decoder (IC56) to be
decoded.
AF CIRCUITS
The AM/FM-demodulated AF signals from the AF switch
(IC12) are passed through the AF filter (Q48). The filtered
AF signals are applied to the electric volume (IC33) to be
adjusted its level. The level-adjusted AF signals are applied
to the dual AF power amplifiier (IC38) to
power level, then applied to the an external speaker via
external speaker jack (J8).
obtain AF output
4-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
The audio signals from the microphone (MIC signals) are
applied to the microphone amplifi er (IC28) via J2 and HPF
(Q87). The amplified MIC signals are passed through the
microphone gain switch (Q88) and MIC mute switch (IC30),
then passed through or by-passed ALC amplifi er (IC32) via
AF switches (IC29 and IC52).
The MIC signals from the AF switch (IC52) are passed
though the HPF (IC48), LPF (IC48) and AF switch (IC51),
and then applied to the AF amplifier (IC48). The amplified
MIC signals are applied to the D/A converter (IC8) for level
(deviation) adjustment. The level adjusted MIC signals are
applied to the VCO as the modulation signals via modulation
signal selector.
<OPERATION ON THE LEFT BAND>
The modulation signals are applied to the variable capacitor
D147 of the left band VCO (Q111, D145–147) via the
modulation selector (IC9) and modulation mute switch
(Q109), and modulated. The modulated VCO output are
amplifi ed by the buffer (Q113) and LO amplifi er (IC44), and
applied to the transmit amplifi ers as the TX signal, via the LO
switches (D155, 157), LPF(L157, C818, 820) and attenuator
(R33, 37, 46).
TRANSMIT POWER AMPLIFIERS
TX signal from the attenuator (R33, 37, 46) is amplifi ed by
pre-drive (Q25) and drive (Q27) amplifi ers to obtain RF level
for power module (IC3). The amplifi ed TX signal is applied
to the power amplifier which is a VHF band PA module
composed by two power MOS-FETs. The power-amplified
TX signal is passed through the LPF, power detector,
antenna switch (D59) and LPF, before being applied to the
antenna connector (CHASSIS; J1).
• MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
5VS
MIC signals from
the microphone
C619
C620
R527
R532
R533
HPF
R537
33K
Q87
C624
C623
R541
R538
C625
R547
R545
R560
R549
Microphone
R562
5
3
1
2
IC28
amplifier
4
C635
C636
MIC_SENC
IC29
1
AF
switch
R566
APC CIRCUITS
A portion of the TX signal from IC3 is rectifi ed at the power
detector (D39, D47), and converted into the DC voltage
which is in proportion to the RF power, and applied to the
operational amplifier (IC4, pin 6). IC4 is an APC amplifier
for both of V/UHF bands. The TX power setting voltage
“PCON_V” from the D/A converter (IC1, pin 7) is applied
to the pin 5 as a reference. IC4 is rolled as a differential
amplifier which outputs voltage in inverse proportion to
rectified one. When the TX power increased, the rectified
voltage also increased, that causes the decrease of output
voltage of differential amplifier. The decrease of output
voltage of differential amplifi er causes the drop of the gate
voltage of IC3, Thus the TX power maintained to keep stable
level.
TX muting is carried out by TX mute SW (Q36) controlled
by “TX_mute” signal. Applying “TX_mute” signal to the base
terminal of Q36 to turn it ON, 8 V DC appears on the pin 6 of
IC4 and its output voltage downs to 0 V DC to inactivate IC3.
HPF
IC30
C637
1
MIC
2
R577
C649
R802
AN6123MS
INPUT
3
GND
4
OUTPUT
5
mute
switch
C648
R578
DET
VCC
IC32
7
6
switch
R550
Q88
7
6
C644
R801
C645
R574
R575
R804
IC52
C862
1
AF
2
R589
1
C656
R628
R784
C861
R774
C857
R775
C687
R766
C858
HPF
R640
R771
R765
IC48
1
2
3
5
6
7 8
Amplifier
ALC
LPF
R660
R664
C856
14
13
12
10
9
R763
C855
R764
R785
C866
IC51
7
1
6
R767
AF switch
R762
Modulation signals
to the modulation circuits
4 - 4
Page 11
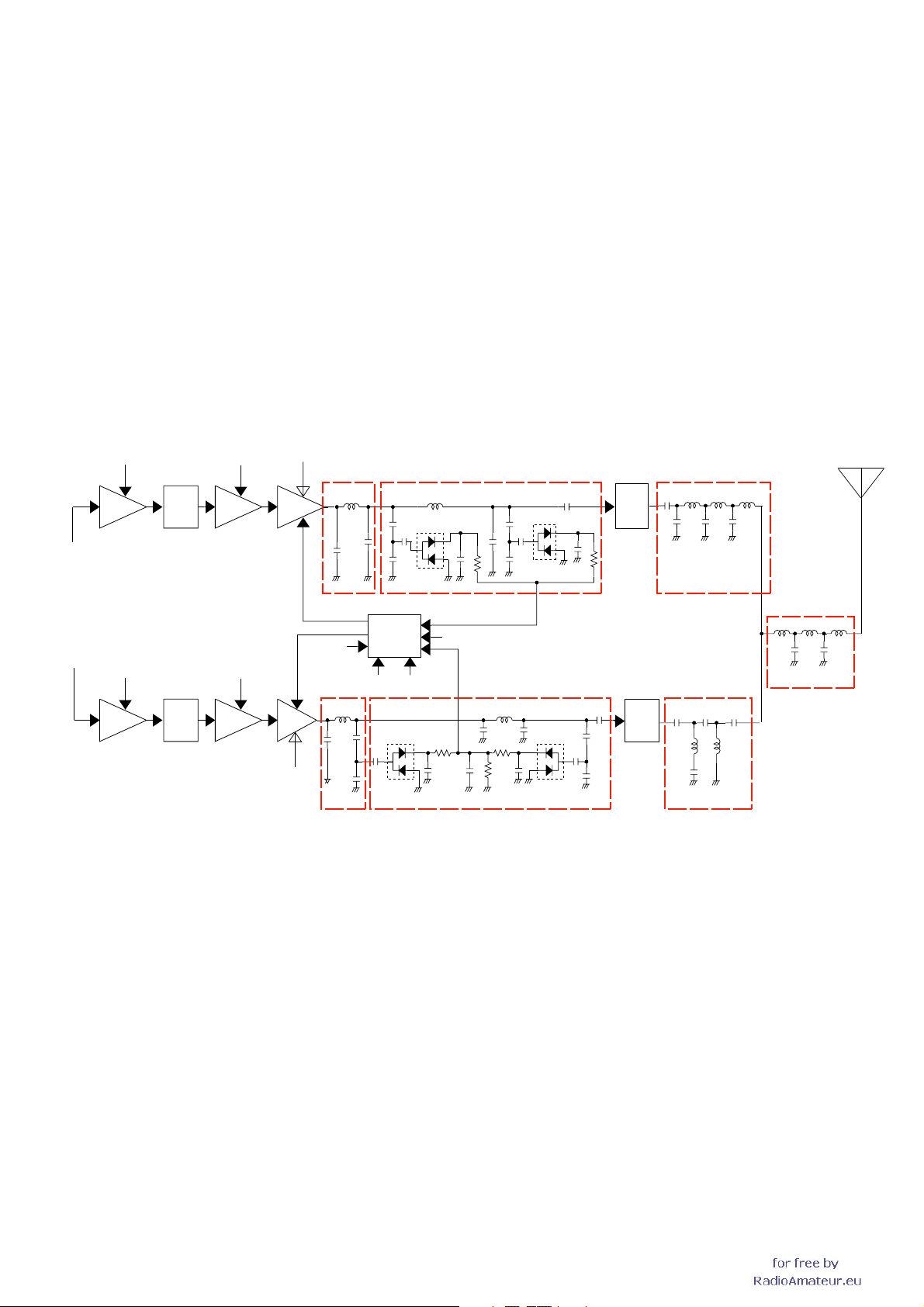
<OPERATION ON THE RIGHT BAND>
The modulation signals are applied to the variable capacitor
D87 of the left band VCO (Q73, D87, 91, 92) via the
modulation selector (IC63) and modulation mute switch
(Q64), and modulated. The modulated VCO output are
amplifi ed by the buffer (Q76) and LO amplifi er (IC45), and
applied to the transmit amplifi ers as the TX signal, via the
VCO switch (D102). The amplifi ed LO signals are applied to
the transmit amplifi ers via the LO switch (D103), two HPFs
(L124, C527, 532; L159, C533, 535) and attenuator (R43,
47, 57).
TRANSMIT POWER AMPLIFIERS
TX signal from the attenuator (R43, 47, 57) is amplifi ed by
pre-drive (Q22) and drive (Q26) amplifi ers to obtain RF level
for power module (IC2). The amplifi ed TX signal is applied
to the power amplifier which is a UHF band PA module
composed by two power MOS-FETs. The power-amplified
TX signal is passed through the LPF, power detector,
antenna switch (D62) and LPF, before being applied to the
antenna connector (CHASSIS; J1).
• APC CIRCUITS
Q25
PRE PWR
DRIVE
TX signal from
LO switch (D155, D157)
D29
LIMIT
VT8VT8
Q27
DRIVE
AMP
IC3
AMP
HV
RF POWER DETECTOR (VHF)
C155
L46
C157
C161
C162
C164
L56
D39
APC CIRCUITS
A portion of the TX signal from IC2 is rectifi ed at the power
detector (D42, 52), and converted into the DC voltage
which is in proportion to the RF power, and applied to the
operational amplifier (IC4, pin 2). IC4 is an APC amplifier
for both of V/UHF bands. The TX power setting voltage
“PCON_U” from the D/A converter (IC1, pin 6) is applied
to the pin 3 as a reference. IC4 is rolled as a differential
amplifier which outputs voltage in inverse proportion to
rectified one. When the TX power increased, the rectified
voltage also increased, that causes the decrease of output
voltage of differential amplifier. The decrease of output
voltage of differential amplifi er causes the drop of the gate
voltage of IC2, Thus the TX power maintained to keep stable
level.
TX muting is carried out by TX mute SW (Q36) controlled
by “TX_mute” signal. Applying “TX_mute” signal to the base
terminal of Q36 to turn it ON, 8 V DC appears on the pin 6 of
IC4 and its output voltage downs to 0 V DC to inactivate IC3.
C314
C318
L88
LPFLPF
C326
L92
L96
C330
C186
R154
C198
C202
C203
C212
D47
C227
C226
R201
D59,D75,D77
TX/RX
SW
TX signal from
LO switch (D103)
Q22
PRE PWR
DRIVE
D25
LIMIT
UT8UT8
Q26
DRIVE
AMP
IC2
AMP
HV
TX_MUTE
IC4,Q31,Q36
APC
CTRL
PCON_U PCON_V
L50
C173
C166
C176
C174
TX_MUTE
D53,D61,D62
D42
R166
C199
C221
C214
R176
L61
R178
C224
C231
D52
C265
C275
C273
C272
TX/RX
SW
C296
C303
L77
C297
RF POWER DETECTOR (UHF)LPF HPF
L80
C308
L101
LPF
C342
L104
L108
C346
4 - 5
Page 12
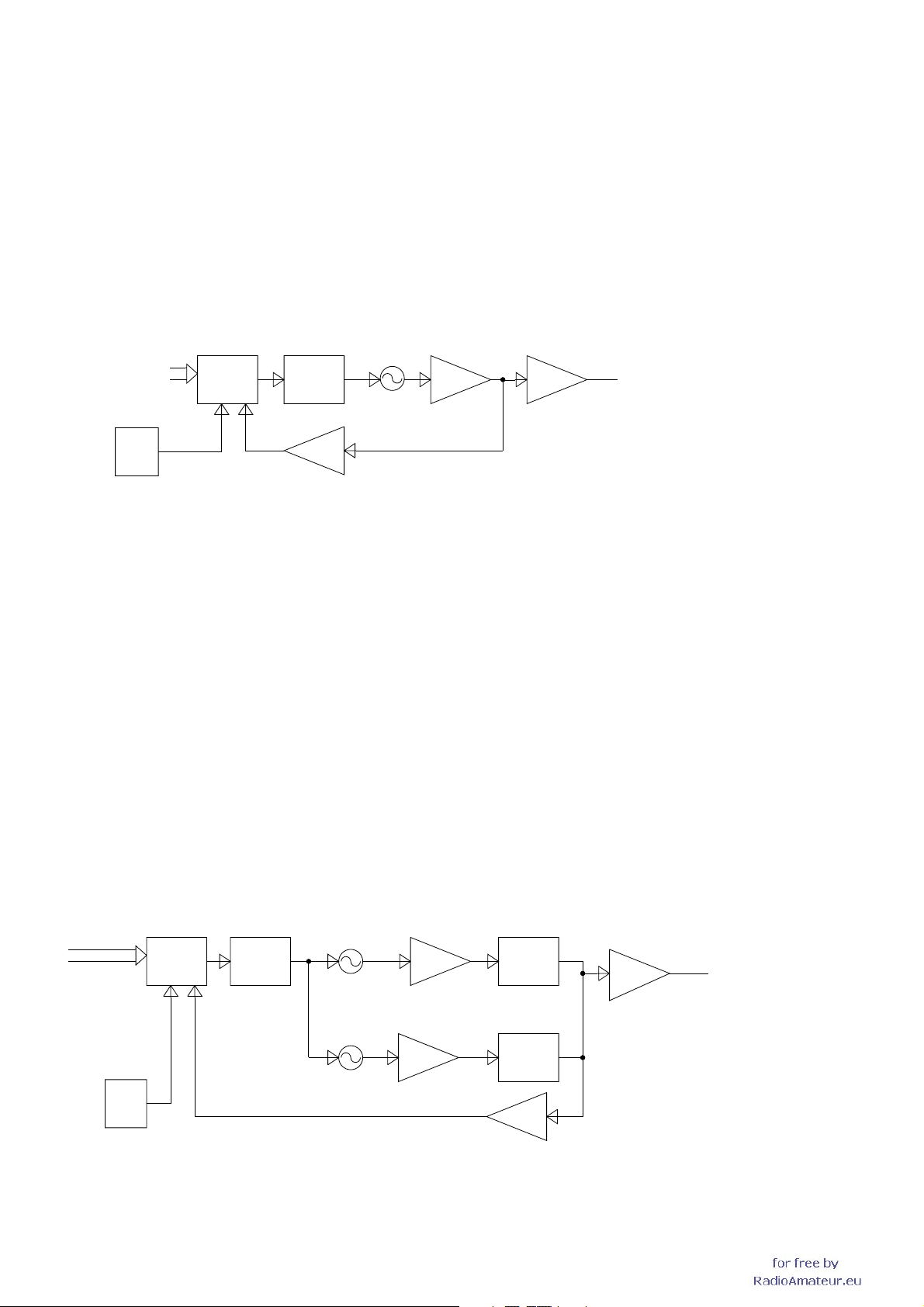
4-3 FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER
VCOs
This transceiver has 3 VCOs; Left band VCO, Right band RX
VCO and Right band TX/RX VCO.
LEFT BAND VCO (Q111, D145–147)
This VCO oscillates 1st LO signals for Left band RX and TX
signal for VHF band.
<While receiving>
The VCO output signal is amplifi ed by buffer (Q113) and LO
amplifier (IC44), and applied to the LO filters according to
the RX frequency.
• While Receiving 118–174 MHz signals
LO signals 135.575−255.575 MHz are applied to the divider
(IC43) via LO switch (D150) and attenuator (R706, 710,
711), and divided into 271.15−511.15 MHz signals. The
divided LO signals are buffer-amplified by Q116, and applied
to the left band 1st mixer (IC19) via the LPF (L115, 156,
C809, 812, 816) and another LO switch (D156).
RIGHT BAND RX VCO (Q72, D89, 90)
This VCO oscillates 1st LO signals for right band RX (118–
174 MHz and 810–1000 MHz).
The VCO output signal is amplified by buffer (Q74) and
applied to the LO amplifier (IC45) via VCO switch (D160),
and applied to the LO fi lters according to the RX frequency.
• While Receiving 118–174 MHz signals
LO signals 164.35−220.35 MHz are passed through the LPF
(L123, 125, C529, 534, 539) via LO switches (D107, 159),
and applied to the right band 1st mixer (IC20).
• While Receiving 810–1000 MHz signals
LO signals 381.825−476.82 MHz*
amplifier (IC62) via LO switch (D101). The amplified LO
signals are doubled to 763.65−953.64 MHz*
1
are applied to the LO
2
signals by
being passed through the HPF (L130, 133, C554, 558, 560),
LPF (L151, C794, 796, 799) and HPF (L135, C563, 568).
The doubled LO signals are applied to the right band 1st
mixer (IC20).
• While Receiving 174–260 MHz signals
LO signals 141.15−221.145 MHz are passed through the
LPF (L148, 152, C785, 789, 795, 804) via LO switches (D151,
153), and applied to the left band 1st mixer (IC19).
• While Receiving 375–550 MHz signals
LO signals 135.575−255.575 MHz are doubled to 271.15−
511.15 MHz signals, by being passed through the HPF (L149,
C787, 790, 791), LPF (L151, C794, 796, 799) and HPF
(L153, C800, 807) via LO switches (D152, 154). The doubled
LO signals are applied to the left band 1st mixer (IC19).
<While transmitting>
The VCO output signal is amplifi ed by buffer (Q113) and LO
amplifier (IC44), and applied to the transmit amplifiers via
the LO switches (D155, 157), LPF(L157, C818, 820) and
attenuator (R33, 37, 46).
• VCO CONFIGULATION BY FREQUENCY
LEFT BAND VCO RIGHT BAND RX VCO RIGHT BAND TX/RX VCO
(Q111, D145–147) (Q72, D89, 90) (Q73, D87, 91, 92)
136–174 MHz – 400–470 MHz
Oscillating
Frequency
VCO
Components
(118–174 MHz) 135.575−255.575 MHz 164.35−220.35 MHz –
(174–260 MHz) 141.15−221.145 MHz 381.825−476.82 MHz*
RX
(375–550 MHz) 135.575−255.575 MHz – 353.65−523.17 MHz
TX
RIGHT BAND TX/RX VCO (Q73, D87, 91, 92)
This VCO oscillates 1st LO signals for right band RX (375–
550 MHz).
<While receiving>
LO signals 353.65−523.17 MHz are passed through the
RF mute switch (Q79) and LPF (L131, 134, C562) via LO
switches (D104, 108), and applied to the right band 1st
mixer (IC20).
<While transmitting>
The VCO output signal is amplified by buffer (Q76), and
applied to the LO amplifier (IC45) via the VCO switch
(D102). The amplifi ed LO signals are applied to the transmit
amplifi ers via the LO switch (D103), two HPFs (L124, C527,
532; L159, C533, 535) and attenuator (R43, 47, 57).
1
–
4 - 6
1
*
: 810–1000 MHz for USA
2
*
: 856.35−1046.34 MHz for USA
Page 13
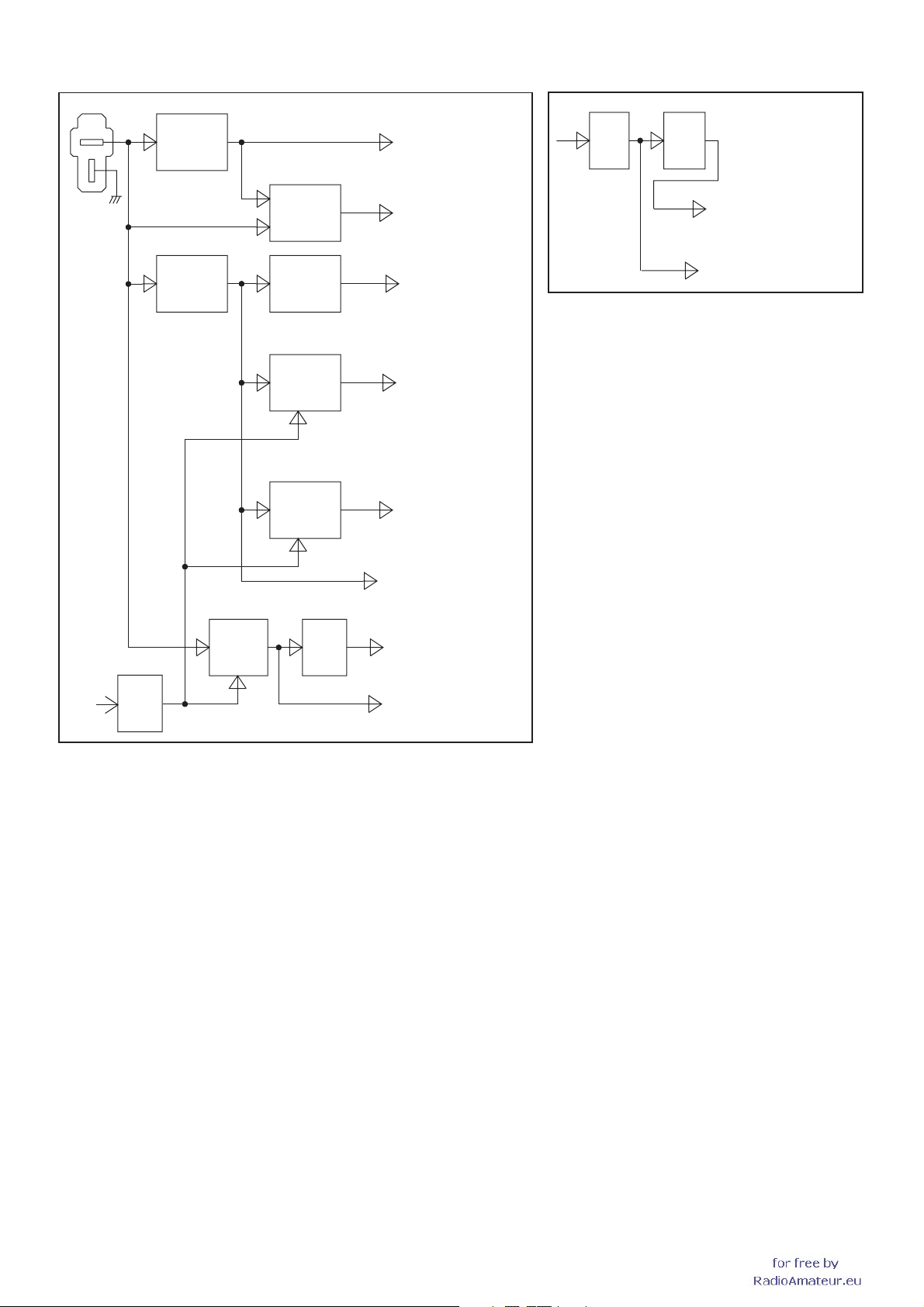
PLL CIRCUITS
The PLL circuit provides stable oscillation of the transmit
frequency and receive 1st LO frequency. The PLL output
frequency is controlled by the divided ratio (N-data) from the
CPU.
LEFT BAND VCO LOOP
A portion of VCO output signals from the buffer (Q113)
are applied to the PLL IC (IC41) via another buffer (Q112).
The applied signals are
programmable counter according to the control signals
(“L_PLLSTB,” “PLLDATA” and "PLLCK”) from the CPU.
The divided signal is phase-compared with the 12. 8 MHz
reference frequency signal from the reference frequency
oscillator (X5), at the phase detector.
LEFT BAND VCO LOOP
•
PLLCK
PLLDATA
L_PLLSTB
X5
12.8MHz
TCXO
divided at the prescaler and
IC41
PLL
IC
135.575 −255.575 MHz
LOOP
FIL
BUFF
Q112
Q111
D145
D146
D147
BUFF
The phase difference is output from pin 5 as a pulse type
signal after being passed through the internal charge pump.
The output signal is converted into the DC voltage (lock
voltage) by passing through the loop filter (R694, 696–
698, C760–762). The lock voltage is applied to the variable
capacitors (D145 and D146), and locked to keep the VCO
frequency constant.
If the oscillated signal drifts, its phase changes from that of
the reference frequency, causing a lock voltage change to
compensate for the drift in the VCO oscillating frequency.
To the TX amplifiers
Q113
AMP
IC44
or
LO filters
RIGHT BAND RX VCO LOOP
A portion of VCO output signals from the buffer (Q74) are
applied to the PLL IC (IC14) via the VCO switch (D160) and
another buffer (Q112). The applied signals are
divided at
the prescaler and programmable counter according to the
control signals (“R_PLLSTB,” “PLLDATA” and "PLLCK”) from
the CPU. The divided signal is phase-compared with the 15.3
MHz reference frequency signal from the reference frequency
oscillator (X1), at the phase detector.
The phase difference is output from pin 5 as a pulse type
signal after being passed through the internal charge pump.
The output signal is converted into the DC voltage (lock
voltage) by passing through the loop filter (Q61, 62, D86).
The lock voltage is applied to the variable capacitors (D91,
92), and locked to keep the VCO frequency constant.
RIGHT BAND RX AND TX/RX VCO LOOP
•
PLLCK
PLLDATA
R_PLLSTB
TCXO
IC14
15.3MHz
X1
PLL
IC
Q61
Q62
D86
LOOP
FIL
164.350−220.350 MHz
BUFF
−
523.170 MHz
BUFF
Q76
353.65
Q72
D89
D90
Q73
D91
D92
D87
RIGHT BAND TX/RX VCO
A portion of VCO output signals from the buffer (Q76) are
applied to the PLL IC (IC14) via the VCO switch (D102)
and another buffer (Q60). The applied signals are
at the prescaler and programmable counter according to the
control signals (“R_PLLSTB,” “PLLDATA” and "PLLCK”) from
the CPU. The divided signal is phase-compared with the 15.3
MHz reference frequency signal from the reference frequency
oscillator (X1), at the phase detector.
The phase difference is output from pin 5 as a pulse type
signal after being passed through the internal charge pump.
The output signal is converted into the DC voltage (lock
voltage) by passing through the loop filter (Q61, 62, D86).
The lock voltage is applied to the variable capacitors (D91,
92), and locked to keep the VCO frequency constant.
D160
To the TX amplifiers
or
LO filters
Q74
Q60
VCO
SW
D102
VCO
SW
BUFF
AMP
IC45
divided
4 - 7
Page 14
4-4 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS
Voltage from the power supply is routed to whole of the circuit in the transceiver via switches and regulators.
MAIN UNIT
NOISE
FILTER
IC21
5V
REG
IC55,
D164
CURRENT
DETECT
NOISE
FIL
Q83,
D119
5VS
REG
D120
Q84,
5VS
REG
HVHVTX power
amplifiers (IC2, IC3)
IDET
CPU5V
CPU (IC25)
(for current monitoring)
PLL ICs (IC14, IC41),
5VS
D/A converter (IC8),
ALC IC (IC32), etc.
DTMF decoder (IC56),
L5V
Electric volume (IC33),
AF mixer (IC59), etc.
CPU (IC25),
EEPROM (IC22),
Reset IC (IC23), etc.
IC3
+5
REG
+3
REG
+3.2V
5V
CONTROL UNIT
CPU (IC13),
Regulator (Q14, Q15),
Protector/Buffer (IC12), etc.
Reset IC (IC9),
LCD module, etc.
PWR
Q82
PWR
CTRL
Q81
VCC
REG
IC24
+8
REG
5V
Limitter (D165−D168), etc.
AF filter (Q47, Q50),
8V
MIC amplifier (IC28),
APC controller (IC4), etc.
VCC
AF power amplifier (IC38)
4 - 8
Page 15
4-5 CPU PORT ALLOCATION
PIN
PORT NAME
No.
3
4
MM_MUTE
5
6
R_WN_SEL
7
11
MIC_SENC
17
18
21
R_PLLSTB
L_PLLSTB
22
23
DTCS_SEL
24
25
L_WN_SEL
26
27
28
L_VCO_SHIFT
29
R_PLLSW
30
31
R_UNLOCK
32
33
L_UNLOCK
34
35
36
L_PLLSW
37
AN
DA_SEL
DCONT
MOD_DA
MODSEL
L_AMC
L_R5C
UMMUTE
UTX_C
PLLCK
PLLDATA
VMMUTE
VTX_C
Cut-off frequency shifting signal to the HPF
(IC48).
Cut-off frequency shifting signal to the HPF
(IC48).
MIC mute signal to the MIC mute switch (IC30).
“H”=MIC mute.
ALC amplifier control signal tot the AF
switches (IC29 and IC52).
“H”=ALC amplifi er ON.
2nd IF filter (Right band; Wide/Narrow)
toggling signal.
“H”=Narrow. "L”=Wide.
Microphone sensitivity select signal.
“H”=High sensitivity.
Modulation line switching signal to
the MOD selector (Left band; IC9).
“H”=Modulation enable.
Modulation line switching signal to
the MOD selector (Right band; IC63).
“H”=Modulation enable.
Strobe signal to the PLL IC (Right band;
IC14).
Strobe signal to the PLL IC (Left band;
IC41).
AM-demodulator circuit (Left band) control
signal.
“H”=AM mode (AM-modulator circuit is
activated).
Tone filter switching signal to the LPF
(Q100).
“H”=DTCS mode. “L"=CTCSS mode.
RX circuits (Left band) control signal.
“H”=RX circuits (Left band) is activated.
2nd IF filter (Wide/Narrow) toggling
signal.(Left band)
“H”=Narrow. “L”=Wide."
Modulation mute signal to the MOD
mute switch (Right band; Q64).
“H”=Modulation muted.
Transmitting control signal to the VT8
regulator (Q12, 15).
VCO oscillating frequency shift signal to
the Left band VCO.
Lock-up time control signal to the loop fi lter
(Right band).
“H”=Fast lock-up time.
PLL unlock signal from the PLL IC (Right
band; IC14).
Clock signal to the PLL ICs (Right band;
IC14, Left band; IC41).
(Commonly used for both of the Left and
Right bands.)
Data to the PLL ICs (Right band; IC14, Left
band; IC41).
(Commonly used for both of Left and Right
bands.)
PLL unlock signal from the PLL IC (Left
band; IC41).
Modulation mute signal to the MOD
mute switch (Left band; Q109).
“H”=Modulation muted.
Transmitting control signal to the UT8 regulator
(Q13, 17).
“H”=While transmitting.
Lock-up time control signal to the loop fi lter
(left band).
“H”=Fast lock-up time.
DESCRIPTION I/O
PIN
PORT NAME
No.
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
38
R_UVCO_SEL
R_VVCO_SEL
39
40
L_LO_SW
R_DA_SEL
42
R_AFFIL_SEL
42
R_DET_MUTE
43
L_DA_SEL
44
L_DET_MUTE
45
48
51
52
53
53
55
56
57
61
62
63
64
65
66
68
I
69
70
71
76
I
77
78
79
80
80
82
D5VC
R_AF_MUTE
L_AFFIL_SEL
DA3STB
DA2_STB
DTCS
DTMF
MIC_SEL
DTMSTB
MICUD
R_RSLV
L_RSLV
IDET
R_WXALT
R_DTCS_IN
L_WXALT
L_DTCS_IN
TEMP
SCL
AF_VOL_CK
AF_VOL_DATA
AF_VOL_STB
AF_VOL_RES
PWR
SDA
VCO power control signal to the VCO
select switch (Right band UHF; Q65, 68).
“L”=Right band TX/RX VCO is activated.
VCO power control signal to the VCO
select switch (Right band VHF; Q65, 68).
“L”=Right band RX VCO is activated.
LO filter switching signal to the LO
regulator (Q106).
AF line switching signal to the AF switch
(IC12).
Switching signal to the AF filter (Right
band; Q48).
AF line switching signal to the AF switch (IC16).
“H”=AF mute.
AF line switching signal to the AF switch
(IC11).
AF line switching signal to the AF switch (IC13).
“H”=AF mute.
Power control signal for the optional unit. O
AF mute signal to the SP mute switch (Right
band; Q101).
“H”=AF mute.
Switching signal to the AF fi lter (Left band;
Q47).
Strobe signal to the D/A converter. O
Strobe signal to the electric volume. O
DTCS signal. O
DTMF signal. O
Connected microphone detect signal. I
Strobe signal to the DTMF decoder (IC56). -
[UP]/[DWN] key input. I
While receiving; inputs RSSI
signal (IC18; Right band).
While transmitting; inputs Lock Voltage
from the PLL IC (IC14).
While receiving; inputs RSSI signal
from IF ICl (IC15; Left band).
While transmitting; inputs Lock Voltage
from the PLL IC (IC41).
Current level from the current detector
(IC55, Q164).
Demodulated Weather alert signal from the
WX fi lter (Q47). [USA] only
Demodulated DTCS signals from the
CTCSS fi lter (Q42).
Demodulated Weather alert signal from the
WX fi lter (Q48). [USA] only
Demodulated DTCS signals from the
CTCSS fi lter (Q41).
Transceiver's internal temparature from the
thermal detector circuit (R509).
I/O port for clock signal to the EEPROM
(IC22).
Serial clock signal to the electric volume
IC.
Data signal to the electric volume IC. O
Latch enable signal to the electric volume
IC.
Reset signal to the electric volume IC. O
Power control signal to the PWR controller
(Q82).
“H”=While the power is ON.
Data signal to the EEPROM (IC22). I/O
DESCRIPTION I/O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I/O
O
O
O
4 - 9
Page 16
PIN
No.
83
85
100
101
102
105
122
123
127
128
129
130
134
135
136
137
138
143
144
PORT NAME
L_AF_MUTE
MIC_PTT
RESET
L_SQL
CL_SFT2
R_SQL
R_DATA
TX_DATA
TX232
RX232
DA_CK
DA_DATA
DA_STB
R_R5C
R400_S
R_RX800
R_AMC
DTMSD
DTMCK
DESCRIPTION I/O
AF mute signal to the SP mute switch
(Q102).
Input port for [PTT] key on the connected
microphone.
Reset enable signal input. I
Noise signal from the IF IC (Left band;
IC15).
Clock frequency shifting signal. O
Noise signal from the IF IC (Right band;
IC18).
Data lines for the control unit. I
Data lines for the control unit. O
Data bus for RS-232C communication. O
Data bus for RS-232C communication. I
Serial clock signal to the D/A converter. O
Serial data to the D/A converter. O
Strobe signal to the D/A converter. O
RX circuits (Right band) control signal. O
Power line control signal to the 375−550 MHz
band RF circuit (Right band).
Power line control signal to the 810−1000
MHz band RF circuit (Right band).
AM-demodulator circuit (Right band)
control signal.
Data to the DTMF decoder (IC56). -
Clock signal to the DTMF decoder (IC56). -
O
I
I
I
O
O
O
4 - 10
Page 17
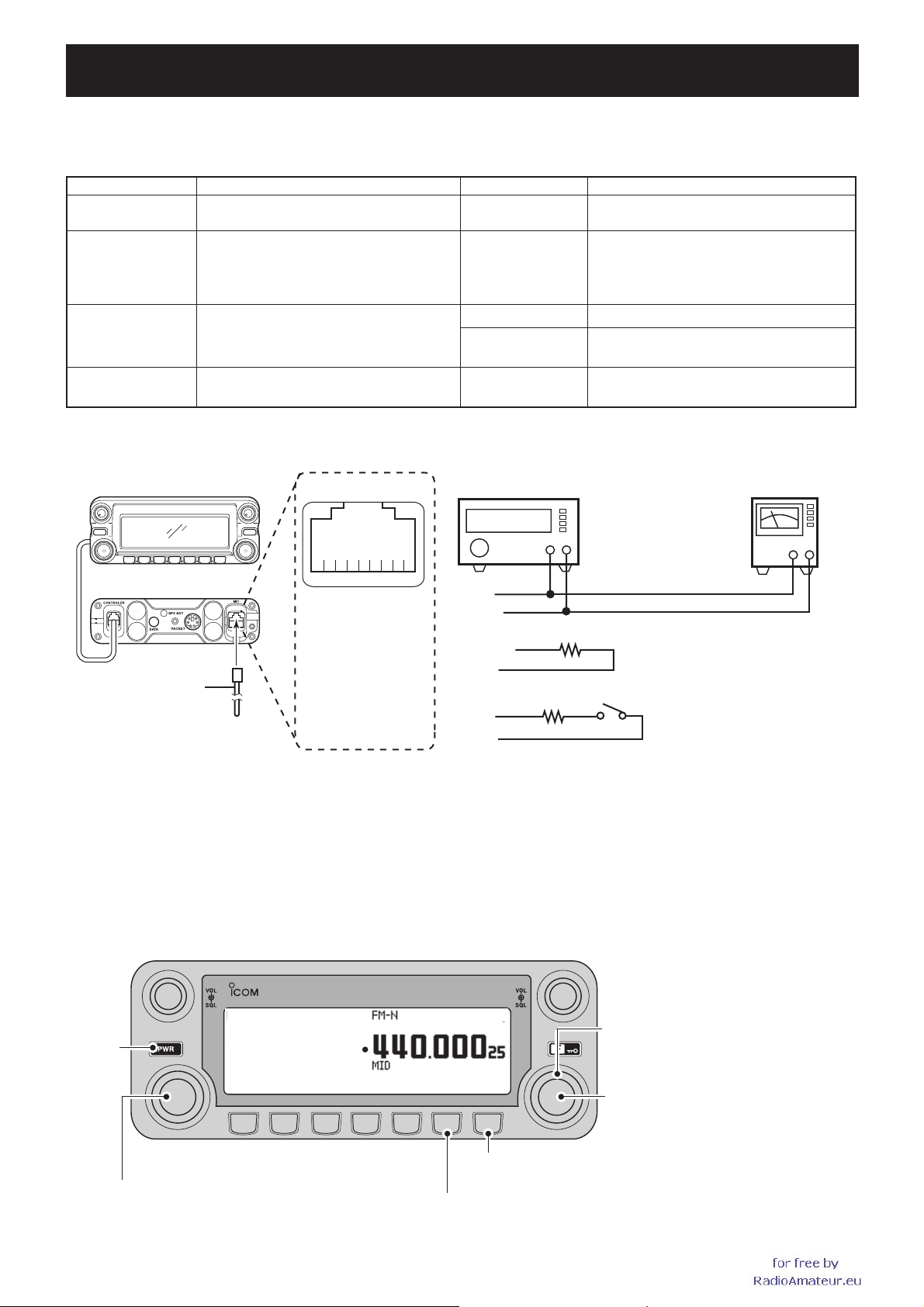
SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
5-1 PREPARATION
¤ REQUIRED TEST EQUIPMENTS
When adjusting IC-2820H, following test equipments and JIG cable (modified 8-pin modular jack; see the illust below) are required.
EQUIPMENT GRADE AND RANGE EQUIPMENT GRADE AND RANGE
DC power supply
RF power meter
(terminated type)
Frequency counter
Modulation
Analyzer
JIG CABLE
¤
Controller
Output voltage : 13.8 V DC
Current capacity : More than 20 A
Measuring range : 1–100 W
Frequency range : 100–600 MHz
Impedance : 50
Ω
SWR : Less than 1.2 : 1
Frequency range : 0.1–600 MHz
Frequency accuracy : ±1 ppm or better
Sensitivity : 100 mV or better
Frequency range : 30–600 MHz
Measuring range : DC to ±10 kHz
8-pin modular jack
ytre
i
u
q
w
Audio generator
Standard signal
generator (SSG)
AC millivoltmeter Measuring range : 10 mV to 10 V
Terminator
Attenuator
AUDIO GENERATOR
(300–3000 Hz/1–500 mV)
Frequency range : 300–3000 Hz
Output level : 1–500 mV
Frequency range : 0.1–1 GHz
Output level : 0.1 µV to 32 mV
(–127 to –17 dBm)
Impedance : 50
Ω
Capacity : More than 100 W
Power attenuation : 40 dB
Capacity : More than 100 W
AC MILLIVOLT METER
<SETTING>
Frequency
Level : 20 mV rms*
+−
80 mV rms*
: 1 kHz
1
2
(10 mV to 10 V)
+−
Main unit
JIG cable
To the MICROPHONE CONNECTOR
ENTERING ADJUSTMENT MODE
¤
q
w
e
r
t
y
u
i
8V
MICU/D
EXTMIC
PTT
MICE
MIC
GND
MICIN
y (MIC)
t (MICE)
w (MICU/D)
u (GND)
r (PTT)
u (GND)
22 kΩ
33 kΩ
[PTT]
*
*
q Connect the JIG cable to the MICROPHONE CONNECTOR (see the illust above).
w Push and hold the both of [MAIN•BAND] keys, then turn power ON.
KEY ASSIGNMENTS IN THE ADJUSTMENT MODE
¤
Entering adjustment mode, the function display shows adjustment item and conditions as below.
DUAL BAND TRANSCEIVER
REF
[PWR]
[DIAL] (Right band)
Adjusts the value
for the item manually.
D
N
A
B
N
I
A
M
V/MHz
SCAN
M/CALL
MW
DUP
MONI
NOTE: This display is example only.
TONE
DTMF
LOW
PRIO
M/CALL
MW
V/MHz
SCAN
D
N
A
[MAIN•BAND] (Right band)
B
N
I
A
M
• Stores the set value
• Adjusts the value
for the item automatically.
[V/MHz•SCAN]
[MAIN•BAND] (Left band)
Selects the next adjustment item.
[M/Call•MW]
Selects the previous adjustment item.
1
; except [USA-01]
2
; [USA-01] only
5 - 1
Page 18

5-2 FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT
• CONNECTIONS FOR FREQENCY ADJUSTMENT
FREQUENCY COUNTER
(0.1–1 GHz)
Terminator
(50 Ω/100 W)
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS OPERATION VALUE
REFERENCE
FREQUENCY
(Left Band)
[L REF]
(Right Band)
[R REF]
(Loose coupling)
IC-2820H
To J 1
DC power supply
(13.8 V/20 A)
−
⊕
−
Fuses
20 A
1•
Connect a Terminator to the
antenna connector (J1).
•
Loosely couple a Frequency Counter to the antenna connector (J1).
•
Transmitting
2 435.000 MHz
Black
Red⊕
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the reference frequency,
then push the right band’s [MAIN
•BAND] key.
146.000 MHz
[others]
445.000 MHz
[USA-01]
5 - 2
Page 19

5-3 TRANSMIT ADJUSTMENTS
¤ TRANSMIT OUTPUT POWER ADJUSTMENT
• CONNECTIONS FOR TX POWER ADJUSTMENT
To J 1
RF POWER METER
(100 W/50 Ω)
DC power supply
(13.8 V/20 A)
−
⊕
IC-2820H
ADJUSTMENT ITEM ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS OPERATION VALUE
144 MHz BAND
TRANSMIT OUTPUT
POWER
(HI POWER)
(Band
Low)
[L PHL]
(Band
High)
[L PHH]
(MID POWER) (Band
Low)
[L PML]
(Band
High)
[L PMH]
(LOW POWER) (Band
Low)
[L PLL]
(Band
High)
[L PLH]
430 MHz BAND
TRANSMIT OUTPUT
POWER
(HI POWER)
(Band
Low)
[R PHL]
(Band
High)
[R PHH]
(MID POWER) (Band
Low)
[R PML]
(Band
High)
[R PMH]
(LOW POWER) (Band
Low)
[R PLL]
(Band
High)
[R PHH]
Fuses
20 A
1••Connect an RF Power Meter to the
antenna connector (J1).
Transmitting
2
−
Black
Red⊕
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the transmit output power,
then push the right band’s [MAIN
•BAND] key during transmit.
50 W
3 15 W
[others]
22 W
4
[TPE-01]
5 5 W
6
1••Connect an RF Power Meter to the
antenna connector (J1).
Transmitting
2
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the transmit output power,
then push the right band’s [MAIN
•BAND] key during transmit.
50 W
3 15 W
[others]
22 W
4
[TPE-01]
5 5 W
6
5 - 3
Page 20

¤ DEVIATION ADJUSTMENT
• CONNECTION FOR MODULATION ADJUSTMENTS
MODULATION ANALYZER
<SETTING>
(0.1–1 GHz)
HPF : OFF
LPF : 20 kHz
De-emphasis : OFF
Detector : (P-P)/2
ATTENUATOR
(40 dB/100 W)
To J 1
DC power supply
(13.8 V/20 A)
−
⊕
IC-2820H
ADJUSTMENT ITEM ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS OPERATION VALUE
144 MHz
BAND
(Band
Low)
DEVIATION
(Left Band)
(Band
Center)
(Band
High)
144 MHz
BAND
(Band
Low)
MODULATION
BALANCE
(Left Band)
(Band
Center)
(Band
High)
144 MHz BAND
DTCS MODULATION
(Left Band)
144 MHz
CTCSS MODULATION
(Left Band)
(FM)
[L FMD]
(FM-N)
[L FMD]
(FM)
[L FMD]
(FM-N)
[L FMD]
(FM)
[L FMD]
(FM-N)
[L FMD]
(FM)
[L FMB]
(FM-N)
[L FMB]
(FM)
[L FMB]
(FM-N)
[L FMB]
(FM)
[L FMB]
(FM-N)
[L FMB]
(FM)
[L MDT]
(FM-N)
[L MDT]
(FM)
[L MCT]
(FM-N)
[L MCT]
OSCILLOSCOPE
(DC to 10 kHz)
Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
1•
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2 ±2.1 kHz
Connect an Audio Generator to the
•
JIG cable (See the page 5-1 for the
connector and setting details).
3 ±4.2 kHz
Transmitting
•
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the deviation, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key during transmit.
Fuses
20 A
−
Black
Red⊕
±4.2 kHz
4 ±2.1 kHz
5 ±4.2 kHz
6 ±2.1 kHz
Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
1•
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
Connect an oscilloscope to the de-
•
tector terminal of the Modulation
Analyzer.
3
No audio signals are applied to the
•
JIG cable (See the page 5-1).
4
Transmitting
•
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the wave form, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key during transmit.
(Square
Wave form)
5
6
Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
1•
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
No audio signals are applied to the
•
JIG cable (See the page 5-1).
Transmitting
•
Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
1•
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
No audio signals are applied to the
•
JIG cable (See the page 5-1).
Transmitting
•
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the deviation, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key.
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the deviation, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key .
±0.8 kHz
±0.75 kHz
5 - 4
Page 21

¤ DEVIATION ADJUSTMENT (continued)
ADJUSTMENT ITEM ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS OPERATION VALUE
430 MHz
DEVIATION
(Right Band)
430 MHz
MODULATION
BALANCE
(Right Band)
430 MHz
DTCS
MODULATION
(Right Band)
430 MHz
CTCSS
MODULATION
(Right Band)
DV MODE
DEVIATION*
(144 MHz Band)
DV MODE
MODULATION
BALANCE*
(144 MHz Band)
DV MODE
DEVIATION*
(430 MHz Band)
DV MODE
MODULATION
BALANCE*
(430 MHz Band)
*; Optional UT-123 is required.
(Band
Low)
(Band
Center)
(Band
High)
(Band
Low)
(Band
Center)
(Band
High)
(FM)
[R FMD]
(FM-N)
[R FMD]
(FM)
[R FMD]
(FM-N)
[R FMD]
(FM)
[R FMD]
(FM-N)
[R FMD]
(FM)
[R FMB]
(FM-N)
[R FMB]
(FM)
[R FMB]
(FM-N)
[R FMB]
(FM)
[R FMB]
(FM-N)
[R FMB]
(FM)
[R MDT]
(FM-N)
[R MDT]
(FM)
[R MCT]
(FM-N)
[R MCT]
(Band Low)
[L MDS]
(Band Center)
[L MDS]
(Band High)
[L MDS]
(Band Low)
[L MDB]
(Band Center)
[L MDB]
(Band High)
[L MDB]
(Band Low)
[R MDS]
(Band Center)
[R MDS]
(Band High)
[R MDS]
(Band Low)
[R MDB]
(Band Center)
[R MDB]
(Band High)
[R MDB]
1•
Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2 ±2.1 kHz
•
Connect an Audio Generator to the
JIG cable (See the page 5-1 for the
•
connector and setting details).
3 ±4.2 kHz
Transmitting
4 ±2.1 kHz
5 ±4.2 kHz
6 ±2.1 kHz
Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
1•
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
No audio signals are applied to the
•
JIG cable (See the page 5-1).
Transmitting
•
3
4
5
6
1•
Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
•
No audio signals are applied to the
JIG cable (See the page 5-1).
•
Transmitting
Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
1•
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
No audio signals are applied to the
•
JIG cable (See the page 5-1).
Transmitting
•
1••Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
Transmitting
3
1••Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
Transmitting
3
1••Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
Transmitting
3
1••Connect a Modulation Analyzer to
the antenna connector (J1) through
an attenuator.
2
Transmitting
3
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the deviation, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key during transmit.
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the wave form, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key during transmit.
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the deviation, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key.
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the deviation, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key.
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the deviation, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key during transmit.
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the wave form, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key during transmit.
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the wave form, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key during transmit.
Rotate the right band’s [DIAL] to
adjust the wave form, then push
the right band’s [MAIN•BAND]
key during transmit.
±4.2 kHz
(Square
Wave form)
±0.8 kHz
±0.75 kHz
±0.9 kHz
Minimum
deviation
±1 kHz
Minimum
deviation
5 - 5
Page 22

5-4 RECEIVE ADJUSTMENTS
¤ SENSITIVITY ADJUSTMENT
• CONNECTION FOR RECEIVE SENSITIVITY AND RSSI ADJUSTMENTS
To J1
<SETTING>
• For RX SENSITIVITY ADJ.
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : ±3.5 kHz
Level : 0 dBµ
STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR
(0.1–1 GHz)
DC power supply
(13.8 V/20 A)
−
⊕
IC-2820H
ADJUSTMENT ITEM ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS OPERATION VALUE
SENSITIVITY Connect a Standard Signal Generator to the antenna connector (J1).
118.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L LT1]
(Right Band)
1 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 118.020 MHz
2
[R LT1]
127.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L MT1]
(Right Band)
3 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 127.020 MHz
4
[R MT1]
135.980 MHz (Left Band)
[L HT1]
(Right Band)
5 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 135.980 MHz
6
[R HT1]
136.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L LT2]
(Right Band)
7 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 136.020 MHz
8
[R LH2]
146.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L MT2]
(Right Band)
9 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 146.020 MHz
10
[R MT2]
173.980 MHz (Left Band)
[L HT2]
(Right Band)
11 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 173.980 MHz
12
[R HT2]
174.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L LT3]
220.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L MT3]
250.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L HT3]
260.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L LT4]
310.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L MT4]
360.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L HT4]
13 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 174.020 MHz
14 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 220.020 MHz
15 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 250.020 MHz
16 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 260.020 MHz
17 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 310.020 MHz
18 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 360.020 MHz
Fuses
20 A
−
Black
Red⊕
Push the right band’s
[MAIN•BAND] key.
(Automatic
adjustment)
5 - 6
Page 23

¤ SENSITIVITY ADJUSTMENT (continued)
ADJUSTMENT ITEM ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS OPERATION VALUE
SENSITIVITY 375.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L LT5]
(Right Band)
[R LT5]
399.980 MHz (Left Band)
[L HT5]
(Right Band)
[R HT5]
400.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L LT6]
(Right Band)
[R LT6]
440.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L MT6]
(Right Band)
[R MT6]
449.980 MHz (Left Band)
[L HT6]
(Right Band)
[R HT6]
450.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L LT7]
(Right Band)
[R LT7]
500.020 MHz (Left Band)
[L MT7]
(Right Band)
[R MT7]
549.980 MHz (Left Band)
[L HT7]
(Right Band)
[R HT7]
19 • Set the SSG as;
20
21 • Set the SSG as;
22
23 • Set the SSG as;
24
25 • Set the SSG as;
26
27 • Set the SSG as;
28
29 • Set the SSG as;
30
31 • Set the SSG as;
32
33 • Set the SSG as;
34
Frequency : 375.020 MHz
Frequency : 399.980 MHz
Frequency : 400.020 MHz
Frequency : 440.020 MHz
Frequency : 449.980 MHz
Frequency : 450.020 MHz
Frequency : 500.020 MHz
Frequency : 549.980 MHz
Push the right band’s
[MAIN•BAND] key.
(Automatic
adjustment)
5 - 7
Page 24

¤ S-METER ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT ITEM ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS OPERATION VALUE
S-METER Connect a Standard Signal Generator to the antenna connector (J1).
127.020 MHz
(S3 level)
(Full scale) (Left Band)
146.020 MHz
(S3 level)
(Full scale) (Left Band)
220.020 MHz
(S3 level)
(Full scale) (Left Band)
300.020 MHz
(S3 level)
(Full scale) (Left Band)
387.020 MHz
(S3 level)
(Full scale) (Left Band)
435.020 MHz
[others]
445.020 MHz
[USA-01]
(S3 level)
(Full scale) (Left Band)
500.020 MHz
(S3 level)
(Full scale) (Left Band)
910.020 MHz
(S3 level)
(Full scale) (Right Band)
(Left Band)
[L S31]
(Right Band)
[R S31]
[L SF1]
(Right Band)
[R SF1]
(Left Band)
[L S32]
(Right Band)
[R S32]
[L SF2]
(Right Band)
[R SF2]
(Left Band)
[L S33]
[L SF3]
(Left Band)
[L S34]
[L SF4]
(Left Band)
[L S35]
(Right Band)
[R S35]
[L SF5]
(Right Band)
[R SF5]
(Left Band)
[L S36]
(Right Band)
[R S36]
[L SF6]
(Right Band)
[R SF6]
(Left Band)
[L S37]
(Right Band)
[R S37]
[L SF7]
(Right Band)
[R SF7]
(Left Band)
[R S38]
[R SF8]
1 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 127.020 MHz
Level : −1 dBµ
2
3 • Set the SSG as;
Level : +15 dBµ
4
5 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 146.020 MHz
Level : −1 dBµ
6
7 • Set the SSG as;
Level : +15 dBµ
8
9 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 220.020 MHz
Level : −1 dBµ
10 • Set the SSG as;
Level : +15 dBµ
11 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 300.020 MHz
Level : −1 dBµ
12 • Set the SSG as;
Level : +15 dBµ
13 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 387.020 MHz
Level : −1 dBµ
14
15 • Set the SSG as;
Level : +15 dBµ
16
17 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 435.020 MHz
[others]
18
445.020 MHz
[USA-01]
Level : −1 dBµ
19 • Set the SSG as;
Level : +15 dBµ
20
21 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 500.020 MHz
Level : −1 dBµ
22
23 • Set the SSG as;
Level : +15 dBµ
24
25 • Set the SSG as;
Frequency : 910.020 MHz
Level : −1 dBµ
26 • Set the SSG as;
Level : +15 dBµ
Push the right band’s
[MAIN•BAND] key.
(Automatic
adjustment)
5 - 8
Page 25

¤ SQUELCH ADJUSTMENT
• CONNECTION FOR SQUELCH ADJUSTMENT
To J 1
TERMINATOR
(50 Ω/100 W)
ADJUSTMENT ITEM OPERATION VALUE
SQUELCH Connect a Terminator (50 Ω) to the antenna connector (J1).
127.020 MHz (FM)
[L SQ1]
(FM)
[R SQ1]
(FM-N)
[L SQ1]
(FM-N)
[R SQ1]
146.020 MHz (FM)
[L SQ2]
(FM)
[R SQ2]
(FM-N)
[L SQ2]
(FM-N)
[R SQ2]
220.020 MHz (FM)
[L SQ3]
(FM-N)
[L SQ3]
300.020 MHz (FM)
[L SQ4]
(FM-N)
[L SQ4]
387.020 MHz (FM)
[L SQ5]
(FM)
[R SQ5]
(FM-N)
[L SQ5]
(FM-N)
[R SQ5]
440.020 MHz (FM)
[L SQ6]
(FM)
[R SQ6]
(FM-N)
[L SQ6]
(FM-N)
[R SQ6]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Push the right band’s [MAIN•BAND] key.
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
DC power supply
(13.8 V/20 A)
−
⊕
Fuses
20 A
IC-2820H
−
Black
Red⊕
(Automatic
adjustment)
5 - 9
Page 26

SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
[CONTROL UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
IC3 1180000421 S.IC TA78L05F (TE12R,F) B 29.7/14.1
IC6 1180002371 S.REG R1111N321B-TR-F B 42.4/18.8
IC9 1110005991 S.IC S-80945CNMC-G9F-T2G B 35.8/18.5
IC10 1110006380 S.IC LM2904PWR B 111.3/23.3
IC12 1130003831 S.IC TC7S04F (TE85R,F) B 32.2/23.2
IC13 1140014061 S.IC M30620FCPGP B 70.4/20.8
IC14 1130007111 S.IC TC7W04FU (TE12L,F) B 60.3/40.1
Q1 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 116.5/13.1
Q3 1520000201 S.TR 2SB798-T2-AZ DK B 120.6/16.8
Q14 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 98.2/9.9
Q15 1510000771 S.TR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R,F) B 98.2/14
Q16 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 43/47.5
Q17 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 39.1/47.5
Q18 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 55.4/47.5
Q19 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 51.5/47.5
Q20 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 67.8/47.5
Q21 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 63.9/47.5
Q22 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 80.2/47.5
Q23 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 76.3/47.5
Q24 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 92.6/47.5
Q25 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 88.7/47.5
Q26 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 105/47.5
Q27 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 101.1/47.5
Q28 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 117.4/47.5
Q29 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 113.5/47.5
Q31 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 35.4/21.5
D4 1790001140 S.ZEN MA8039-L (TX) B 40.2/23.6
D8 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 37/27.1
D9 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 35.6/25.4
D10 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 27.9/24.9
D11 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 27.9/21.7
D12 1790001170 S.ZEN MA8068-M (TX) B 120.5/12.5
D20 1730002670 S.ZEN MA8130-M (TX) B 98.1/23.8
D21 1790001561 S.DIO 1SS372 (TE85R,F) B 63.4/39.7
D22 1790001561 S.DIO 1SS372 (TE85R,F) B 65.9/39.7
D23 1790001561 S.DIO 1SS372 (TE85R,F) B 68.4/39.7
D24 1790001561 S.DIO 1SS372 (TE85R,F) B 67.7/35.1
X1 6050012500 S.XTL CR-839 (FTX12.288M16SM) B 54.6/12.5
L1 6200003640 S.COL MLF1608E 100K-T B 59.5/45.6
R2 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 27.5/35.1
R4 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 116.3/35.3
R6 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 25.1/35.1
R8 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 118.7/35.3
R13 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 110.5/14.3
R14 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 14.6/32.9
R21 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 k) B 113.4/14.3
R22 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) B 118.1/19.8
R24 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 25.5/24.7
R25 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 25.8/22.5
R41 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) B 58.4/8.6
R72 7410001220 S.ARY EXB28V103JX B 53.2/18.7
R76 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 96/10.6
R77 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) B 98.2/11.6
R78 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 16.1/32.4
R83 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 30.7/18.6
R122 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 64.2/10.4
R123 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 63.3/10.4
R125 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 73.6/9.4
R126 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 72.7/9.4
R127 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 71.8/9.4
R128 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 68.7/8.8
R129 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 67.8/8.8
R130 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 66.9/7.5
R131 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 66/7.5
R132 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 65.1/8.8
R133 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 43.5/45.4
R134 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 39.6/45.4
R135 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 42.3/44.9
R136 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 38.4/44.9
R137 7030003390 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390) B 114.5/8.4
R138 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680) B 76.1/6.7
R139 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680) B 48.9/8.1
R140 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 55.9/45.4
R141 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 52/45.4
R142 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 54.7/44.9
R143 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 50.8/44.9
R144 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 68.3/45.4
R145 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 64.4/45.4
R146 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 67.1/44.9
R147 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 63.2/44.9
R148 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 80.7/45.4
R149 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 76.8/45.4
R150 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 79.5/44.9
R151 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 75.6/44.9
R152 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 93.1/45.4
R153 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 89.2/45.4
R154 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 91.9/44.9
R155 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 88/44.9
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[CONTROL UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R156 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 105.5/45.4
R157 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 101.6/45.4
R158 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 104.3/44.9
R159 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 100.4/44.9
R160 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 117.9/45.4
R161 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 114/45.4
R162 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 116.7/44.9
R163 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 112.8/44.9
R168 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 34.7/23.7
R169 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) B 24/24.3
R170 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 101.5/20.6
R171 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 111.9/18.4
R172 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 111.4/16.6
R173 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) B 111.4/28.3
R174 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 111/30
R175 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 101.5/21.8
R176 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 115.7/40.6
R177 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 100/11.2
R178 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 98.2/8.1
R179 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 37.8/22
R180 7030005600 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 k) B 36.5/23.3
R187 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 63.2/13
R188 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) T 141.3/22.1
R189 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) T 9.8/30.8
R190 7410001130 S.ARY EXB28V102JX B 80.2/25.3
R191 7410001130 S.ARY EXB28V102JX B 82.2/18.5
R192 7410001130 S.ARY EXB28V102JX B 63.5/30.2
R195 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 78/27.5
R196 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 62.9/14.9
R198 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 58.1/23
R199 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 58/25
R200 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 58/25.9
R201 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 58.3/26.8
R202 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 58.3/27.7
R203 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 60.9/27.3
R204 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 60.9/25.5
R205 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 61.3/30.6
R206 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 62.8/28.4
R207 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 92.2/12.6
R208 7410001140 S.ARY EXB28V104JX B 98.6/26.8
R209 7410001140 S.ARY EXB28V104JX B 101/28.9
R210 7410001140 S.ARY EXB28V104JX B 81.7/16
R211 7410001140 S.ARY EXB28V104JX B 81.4/13.3
R212 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 59.3/29.1
R213 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 65.4/29.5
R216 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 54.9/26.7
R218 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 68.4/32.9
R219 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 59/43.4
R220 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 56.3/24.7
C1 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 27.9/36.9
C2 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 115.7/36.9
C3 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 25.6/36.9
C4 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 118.2/36.9
C5 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J B 108.3/14.3
C7 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 22.8/24.3
C8 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 111/10.7
C10 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 24.2/22
C16 4030018910 S.CER C1608 JB 0J 475K-T B 75/10.7
C24 4510008500 S.ELE EEE1CA101WP B 38.5/11.7
C25 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 28.4/10.6
C26 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K B 38.6/18
C27 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 28.4/17.6
C28 4510008800 S.ELE EEE1EA100SR B 22.3/17
C29 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 18.2/17.8
C30 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 15.6/30.1
C31 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 15.6/27.8
C34 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 76.2/29.2
C42 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 58.3/16.1
C43 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 59.8/15.7
C44 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 55.3/16.1
C45 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 56.7/15.7
C46 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 18.4/10.5
C47 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 123.9/12.3
C48 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 100.2/14.4
C50 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 40.7/25.4
C51 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 61.1/14.5
C54 4510008660 S.ELE EEE0JA220SR B 48.5/18.9
C55 4510008660 S.ELE EEE0JA220SR B 104.3/12.2
C56 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 45/12.1
C57 4550006840 S.TAN TEESVA 1E 225M8R B 90.5/25.2
C59 4550006840 S.TAN TEESVA 1E 225M8R B 95.1/25.2
C60 4550000550 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 224M8R B 83.4/25.1
C61 4550000550 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 224M8R B 72.5/32.7
C62 4550000550 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 224M8R B 72.7/34.8
C63 4550000550 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 224M8R B 72.7/36.9
C64 4550000550 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 224M8R B 72.6/39
C65 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 96.8/26.2
C66 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 49.8/30.1
C67 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 41.8/16.2
C68 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 44.8/18.5
C69 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 29.6/23.7
C70 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 17.7/31.9
C71 4510008550 S.ELE EEE1HA010SR B 104.8/18.3
C72 4510008550 S.ELE EEE1HA010SR B 104.7/23.9
C74 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 113.5/26.7
C86 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 22.1/26
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 1
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 27

[CONTROL UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C87 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 116.1/25.4
C95 4550006840 S.TAN TEESVA 1E 225M8R B 52.3/24.5
C101 4550006840 S.TAN TEESVA 1E 225M8R B 93/25.2
C102 4550006840 S.TAN TEESVA 1E 225M8R B 88.3/25.2
C104 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 118.1/21
C105 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 33.4/19
C106 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 76.2/28.3
C107 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 62/14.5
C108 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 60.9/28.5
C109 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J B 61.4/8.3
C110 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J B 61.4/9.2
C111 4550006840 S.TAN TEESVA 1E 225M8R B 85.7/25.2
C113 4030017330 S.CER ECJ0EF1C104Z B 63.4/41.5
C114 4030017330 S.CER ECJ0EF1C104Z B 65.9/41.5
C115 4030017330 S.CER ECJ0EF1C104Z B 68.4/41.5
C116 4030017330 S.CER ECJ0EF1C104Z B 69.2/37.2
C117 4030017330 S.CER ECJ0EF1C104Z B 62.5/37.8
C118 4030017330 S.CER ECJ0EF1C104Z B 64.7/37.8
C119 4030017330 S.CER ECJ0EF1C104Z B 68/37.8
C120 4030017330 S.CER ECJ0EF1C104Z B 66/36.6
C121 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 59.5/44.4
C122 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 61.3/44.1
J3 6510025760 S.CNR B5B-ZR-SM4-TF (LF) (SN) B 119.6/29.1
J4 6510025760 S.CNR B5B-ZR-SM4-TF (LF) (SN) B 24.6/29.1
J5 6510025730 CNR HJC0187-010024
J7 6510025830 S.CNR 04-6240-034-001-800/+ B 92.9/34.6
J8 6510025830 S.CNR 04-6240-034-001-800/+ B 48.1/34.6
DS1 5030003040 LCD M6-0103TRM-5
DS21 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 33/6.7
DS22 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 137.1/30
DS23 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 137.1/23.4
DS24 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 59/6.7
DS25 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 72/6.7
DS26 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 46/6.7
DS27 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 85/6.7
DS28 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 98/6.7
DS29 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 111/6.7
DS31 5040003260 S.LED FAMG1211F-TR T 34.8/48
DS32 5040003260 S.LED FAMG1211F-TR T 47.2/48
DS33 5040003260 S.LED FAMG1211F-TR T 59.6/48
DS34 5040003260 S.LED FAMG1211F-TR T 72/48
DS35 5040003260 S.LED FAMG1211F-TR T 84.4/48
DS36 5040003260 S.LED FAMG1211F-TR T 96.8/48
DS37 5040003260 S.LED FAMG1211F-TR T 109.2/48
DS38 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 6.9/23.4
DS39 5040002930 S.LED SML-512MW T86 T 6.9/30
S5 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 33/3.2
S6 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 46/3.2
S7 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 98/3.2
S8 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 111/3.2
S10 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 137.1/26.7
S11 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 59/3.2
S12 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 72/3.2
S13 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 85/3.2
S14 2260001890 S.SW SKQDPA T 6.9/26.7
S15 2250000570 ECR SW-169 (EC09E1524405)
S16 2250000570 ECR SW-169 (EC09E1524405)
EP9 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 16/17.3
EP10 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 15.3/26.6
EP11 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 15.3/29
EP12 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 15.3/31.3
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
IC1 1110004310 S.IC M62352GP 75EC T 25/108.5
IC2 1150002121 IC S-AU82L (I,Q)
IC3 1150002161 IC S-AV32 (I2 Q)
IC4 1110004050 S.IC NJM3404AV-TE1-#FMZB B 39.8/107.5
IC8 1190000350 S.IC M62363FP-650C T 52.5/24.3
IC9 1130007021 S.IC TC7S66FU (TE85L,F) B 73.8/31.2
IC11 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) T 107.5/88.7
IC12 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) T 101.2/88.9
IC13 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) B 58/39.7
IC14 1140005991 S.IC MB15A02PFV1-G-BND-ERE1 T 25.3/47.3
IC15 1110003201 S.IC TA31136FNG (EL) B 57.3/64.1
IC16 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) B 12.4/39
IC17 1130007021 S.IC TC7S66FU (TE85L,F) T 28.5/39.5
IC18 1110003201 S.IC TA31136FNG (EL) B 11.8/63.3
IC19 1190002051 S.IC SPM5001-TL-E T 64.3/90.3
IC20 1190002051 S.IC SPM5001-TL-E T 14.9/90.5
IC21 1180001071 S.IC TA7805F (TE16L,Q) B 107.1/136
IC22 1140012950 S.IC 24LC512T-I/SM B 112.6/98.2
IC23 1110005991 S.IC S-80945CNMC-G9F-T2G T 121/74.5
IC24 1180001251 S.IC TA7808F (TE16L,Q) B 100.1/136
IC25 1140013520 S.IC HD64F2506FC26DV B 114.5/73.1
IC26 1110006490 S.IC LMV321IDCKR T 116/65.9
IC28 1130007371 S.IC TA75S558F (TE85L,F) T 22.1/27
IC29 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) B 28.6/27
IC30 1130011770 S.IC CD4066BPWR T 31.8/24.7
IC31 1130011770 S.IC CD4066BPWR T 70/6.3
IC32 1110005310 S.IC AN6123MS B 34.3/21.8
IC33 1130011860 S.IC SM6451BT-G-E2 T 110.3/105.3
IC34 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) T 101.6/34.1
IC35 1130011770 S.IC CD4066BPWR B 70/8.2
IC36 1130013010 S.IC SN74AHC1G08DCK3 B 120.3/104.3
IC37 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) B 114.2/30.2
IC38 1110002541 IC LA4445-E
IC41 1140005991 S.IC MB15A02PFV1-G-BND-ERE1 T 69.9/47.3
IC42 1130007021 S.IC TC7S66FU (TE85L,F) T 74.8/37.5
IC43 1110004460 S.IC uPB1509GV-E1 T 77.6/57.8
IC44 1110006870 S.IC uPC2709TB-E3 T 90.2/57
IC45 1110006870 S.IC uPC2709TB-E3 T 42.4/56.2
IC46 1120003020 S.IC MAX3221IPWR T 94.4/9.9
IC48 1110006350 S.IC LM2902PWR T 65.8/18
IC49 1110006740 S.IC LMV358IPWR B 104.7/32.5
IC50 1110006490 S.IC LMV321IDCKR T 100.1/28.3
IC51 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) T 67.9/22.8
IC52 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) B 35.1/27
IC53 1110006490 S.IC LMV321IDCKR B 58.1/26.9
IC54 1110004310 S.IC M62352GP 75EC T 96.5/96.9
IC55 1190002500 S.IC ZXCT1022E5TA T 111.9/122.6
IC56 1130012960 S.IC BU8872FS-E2 B 119.3/53.4
IC57 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) T 108.4/54.7
IC58 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) T 115.7/54
IC59 1130004201 S.IC TC4S66F (TE85R,F) T 111.8/100.7
IC60 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) B 65/34.4
IC61 1130008511 S.IC TC7W53FU (TE12L,F) B 21.4/33.8
IC62 1110006870 S.IC uPC2709TB-E3 T 32.7/59.8
IC63 1130007021 S.IC TC7S66FU (TE85L,F) B 47.1/32.4
Q1 1590001650 S.TR XP4601 (TX) B 100.8/99.4
Q2 1590001650 S.TR XP4601 (TX) T 7.1/117
Q3 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) B 89.2/102.2
Q4 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) T 23.6/103.1
Q5 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) B 89.1/100.1
Q6 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) B 89.5/104.2
Q7 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) B 88.6/108.2
Q8 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) B 99.9/94.5
Q9 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) T 25.7/103.1
Q10 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) B 89.6/106.2
Q11 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) T 6/121.5
Q12 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 88.4/75
Q13 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 46.5/81.3
Q14 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) T 20.9/127.8
Q15 1510000581 S.TR 2SA1362-GR (TE85R,F) T 83.9/76.2
Q16 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) T 103.2/104.4
Q17 1510000581 S.TR 2SA1362-GR (TE85R,F) T 46.1/76.2
Q18 1530003581 S.TR 2SC5231C8-TL-E T 10.8/109.8
Q19 1580000800 S.FET 3SK324UG-TL-E T 15.7/112.8
Q20 1580000800 S.FET 3SK324UG-TL-E T 86/107.4
Q21 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) T 45.7/123.3
Q22 1530003231 S.TR 2SC5085-Y (TE85R,F) B 42.6/72
Q23 1530003781 S.TR 2SC5624VH-TL-E T 11.2/124.4
Q25 1530002680 S.TR 2SC3357-T1 B 87.5/74.9
Q26 1530002680 S.TR 2SC3357-T1 B 43.1/79.7
Q27 1530003291 S.TR 2SC4703-T1 SE B 87.5/80.9
Q28 1580000800 S.FET 3SK324UG-TL-E T 28/130.5
Q29 1580000800 S.FET 3SK324UG-TL-E T 101.2/115.5
Q30 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) T 26.7/127.9
Q31 1590003230 S.TR UNR9113J-(TX) B 39.2/104.4
Q32 1580000790 S.FET 3SK318YB-TL-E T 38.5/105.7
Q33 1580000790 S.FET 3SK318YB-TL-E T 70.4/109.6
Q34 1530003781 S.TR 2SC5624VH-TL-E T 54.2/105.5
Q35 1530003781 S.TR 2SC5624VH-TL-E T 60.7/105.5
Q36 1590003230 S.TR UNR9113J-(TX) B 43.3/104.3
Q37 1580000790 S.FET 3SK318YB-TL-E T 57.4/137.1
Q38 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) T 63.5/114.6
Q39 1580000790 S.FET 3SK318YB-TL-E T 82.4/120.1
Q40 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) T 35.5/144.8
Q41 1590001650 S.TR XP4601 (TX) T 112.6/83.1
Q42 1590001650 S.TR XP4601 (TX) B 101.8/90.7
Q43 1590003260 S.TR UNR911NJ-(TX) T 60.7/43.3
Q44 1590003260 S.TR UNR911NJ-(TX) T 6/90.9
Q45 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) T 6/37
Q46 1590003240 S.TR UNR9114J-(TX) T 57.2/38.9
Q47 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB T 115.4/94.5
Q48 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB T 107.9/95.9
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 2
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 28

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
Q49 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 102.9/93.5
Q50 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 113.8/89.6
Q52 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 25.4/47.8
Q53 1590003230 S.TR UNR9113J-(TX) T 57/70.6
Q54 1590003270 S.TR UNR9210J-(TX) T 59/71.2
Q55 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB B 52.3/40.5
Q56 1590003230 S.TR UNR9113J-(TX) T 54.9/70.5
Q57 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB T 53.7/43
Q58 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 82.9/46.3
Q59 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 55/68.4
Q60 1530003321 S.TR 2SC5108-Y (TE85R,F) T 37.2/48.9
Q61 1510000771 S.TR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R,F) T 25.1/41.5
Q62 1530002691 S.TR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R,F) T 23.5/39.1
Q63 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB B 6/39.8
Q64 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) B 40.6/38.1
Q65 1590001650 S.TR XP4601 (TX) B 39.3/41
Q66 1530003221 S.TR 2SC4406-4-TL-E B 63.3/66.2
Q67 1590001190 S.TR XP6501-(TX) .AB T 7.1/42.1
Q68 1590001650 S.TR XP4601 (TX) B 39.3/44.6
Q69 1590003230 S.TR UNR9113J-(TX) T 12/70
Q70 1590003270 S.TR UNR9210J-(TX) T 14.2/70
Q71 1590003230 S.TR UNR9113J-(TX) T 9.7/69.9
Q72 1530003581 S.TR 2SC5231C8-TL-E T 38.4/42.6
Q73 1530003581 S.TR 2SC5231C8-TL-E T 44.7/38.4
Q74 1530003581 S.TR 2SC5231C8-TL-E T 41.4/43.2
Q75 1530003221 S.TR 2SC4406-4-TL-E B 18.5/66.2
Q76 1530003581 S.TR 2SC5231C8-TL-E T 45.8/42.4
Q79 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 41.2/66.6
Q81 1520000460 S.TR 2SB1132 T100 R B 101.6/127
Q82 1590003450 S.TR UNR9214J-(TX) B 106.5/104.3
Q83 1510000671 S.TR 2SA1588-GR (TE85R, F) B 103.9/103
Q84 1510000671 S.TR 2SA1588-GR (TE85R, F) B 99.9/104.7
Q86 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 6.7/31.4
Q87 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) T 15.3/30.5
Q88 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 21.1/21.7
Q90 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 31.5/20.9
Q91 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 64.4/8.5
Q92 1590003230 S.TR UNR9113J-(TX) T 44.3/10.8
Q93 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 58.6/9.4
Q94 1510000581 S.TR 2SA1362-GR (TE85R,F) T 115.4/38.4
Q95 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) B 70/12
Q96 1520000201 S.TR 2SB798-T2-AZ DK T 124.5/36.5
Q97 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) T 120.9/38.6
Q98 1590003270 S.TR UNR9210J-(TX) B 117.1/99.9
Q99 1590002270 S.TR UMG9NTR T 75.5/22.3
Q100 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 113.3/71.4
Q101 1530003091 S.TR 2SC4213-B (TE85R,F) T 128/111.5
Q102 1530003091 S.TR 2SC4213-B (TE85R,F) T 123/109.1
Q103 1530003091 S.TR 2SC4213-B (TE85R,F) T 125.5/109.1
Q104 1590003260 S.TR UNR911NJ-(TX) B 74/44.4
Q105 1530003990 S.TR 2SC4738-BL (TE85L,F) B 70/47.4
Q106 1590003260 S.TR UNR911NJ-(TX) T 82.2/56.4
Q109 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 78.7/43.8
Q110 1590003300 S.TR UNR921NJ-(TX) T 89.1/35.5
Q111 1530003581 S.TR 2SC5231C8-TL-E T 88.5/42.4
Q112 1530003321 S.TR 2SC5108-Y (TE85R,F) T 82.1/49.1
Q113 1530003581 S.TR 2SC5231C8-TL-E T 90.4/46.9
Q115 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 85.8/55.7
Q116 1530003321 S.TR 2SC5108-Y (TE85R,F) T 77.4/63
Q117 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 9.7/67.7
Q118 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 116.6/42.8
Q119 1560000811 S.FET 2SK1069-4-TL-E B 71.6/36
Q120 1560000811 S.FET 2SK1069-4-TL-E B 29.3/34.4
Q121 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) T 76.8/39.4
Q122 1590003290 S.TR UNR9213J-(TX) B 30.6/41.7
Q123 1520000450 S.TR 2SB1132 T100 Q T 49.8/121.7
D1 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) T 12.7/117.1
D2 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) T 89.8/108.9
D3 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) T 70.5/113.1
D4 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) T 37/108.6
D5 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) T 57/106.8
D6 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) T 63.5/106.8
D7 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 14.1/97
D8 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 71.2/98.4
D9 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 10.4/97
D10 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 16.7/100.8
D11 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 75.7/98.4
D12 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 14.9/102.5
D13 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 76.4/101.5
D14 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 14.9/105.2
D15 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 78.4/103.3
D16 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 16.7/108.3
D17 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 82.2/104.8
D18 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 18.3/116.8
D19 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 90.8/104.5
D20 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 16.1/119.4
D21 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 94.2/106.2
D22 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 11.8/130.1
D23 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 16.1/120.6
D24 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 96.8/106.2
D25 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 38.1/77.6
D26 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 17.4/123.1
D27 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 99.6/103.7
D28 1720000241 S.DIO 1SV172 (TE85R,F) T 100.2/109.1
D29 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 82.8/78.4
D30 1720000241 S.DIO 1SV172 (TE85R,F) T 15.2/127
D31 1750000520 S.DIO DAN222TL B 41.8/88.2
D32 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 23.3/127.5
D35 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 21.2/98.8
D36 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 53.6/96.8
D37 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 60/96.8
D38 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 67.3/96.8
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
D39 1790000980 S.DIO MA742 (TX) B 76.8/133.6
D40 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 30/101.3
D41 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 67.8/103.5
D42 1790000980 S.DIO MA742 (TX) B 41/113.9
D43 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 32.7/101.3
D44 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 67.8/104.8
D45 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 56.8/102.5
D46 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 63.3/102.5
D47 1790000980 S.DIO MA742 (TX) B 74.9/139.4
D48 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 33.9/136.3
D49 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 35.1/136.3
D50 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 62.1/109
D51 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 55.6/109
D52 1790000980 S.DIO MA742 (TX) B 30.2/133.8
D53 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 40.3/137.9
D54 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 45.9/110.1
D55 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 74.1/116.8
D56 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 55.6/111.5
D57 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 58.6/111.5
D58 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 48.6/110.1
D59 1750001360 S.DIO L709CER (9401) B 78.7/150.1
D60 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 74.1/118.1
D61 1750001360 S.DIO L709CER (9401) B 32.5/143.2
D62 1750001360 S.DIO L709CER (9401) B 42.6/138.2
D63 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 106.5/119.7
D64 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 90.6/118.6
D65 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 94.8/122.3
D66 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 108.1/117.8
D67 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 91.9/118.6
D68 1720000241 S.DIO 1SV172 (TE85R,F) T 73.7/125.4
D69 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 108.4/123.2
D70 1720000241 S.DIO 1SV172 (TE85R,F) T 54.9/119.7
D71 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 93.7/125.7
D72 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 100.6/128.1
D73 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 108/128.9
D74 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 106.2/132.4
D75 1750001360 S.DIO L709CER (9401) B 69.5/145.4
D76 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 65.9/115
D77 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 66.8/140.6
D78 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 62.2/142.3
D79 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 63.4/142.3
D80 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 33.6/144.7
D81 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 29.7/49.9
D82 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 54.2/57.9
D83 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 54.2/50.4
D84 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 61.2/57.8
D85 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 61.2/50.3
D86 1750000370 S.DIO DA221 TL T 22.5/43.2
D87 1720000791 S.VCP HVC321B1TRF-E T 35.6/37
D88 1750000370 S.DIO DA221 TL B 65.5/68.4
D89 1750000831 S.VCP HVC362TRF-E T 31.5/41.8
D90 1750000831 S.VCP HVC362TRF-E T 33.1/40.1
D91 1750000721 S.VCP HVC375BTRF-E T 38.9/35.6
D92 1750000711 S.VCP HVC350BTRF-E T 38.9/34.4
D93 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 8.9/57.1
D94 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 8.1/49.5
D95 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 16.3/56.9
D96 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 16.3/49.4
D97 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 43.2/41.6
D100 1750000370 S.DIO DA221 TL B 20.7/68.4
D101 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 37.1/57.1
D102 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 44.3/48.5
D103 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 44/61.2
D104 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 40.2/57.9
D106 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 33.6/69.9
D107 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 37.3/69.9
D108 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 38.5/69.9
D109 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 41.9/63.4
D112 1750000520 S.DIO DAN222TL B 85.9/102.2
D113 1750000520 S.DIO DAN222TL B 85.9/104.2
D116 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 8.2/121.7
D117 1730000521 ZEN RD20E-AZ B2
D118 1790000700 DIO DSA3A1
D119 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 104.2/105
D120 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 105.7/106.3
D121 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 10.4/29.7
D122 1730002340 S.ZEN MA8047-M (TX) T 119.2/64
D124 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX)
[TPE-01], [EXP-01] only T 104/76.2
D125 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX)
[TPE-01], [KOR-01], [AUS-01] only T 104/77.4
D126 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 104/78.6
D127 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX)
[TPE-01], [KOR-01] only T 104/79.8
D128 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX)
[TPE-01], [KOR-01], [AUS-01] only T 106.5/76.2
D129 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX)
[TPE-01], [KOR-01], [AUS-01] only T 106.5/77.4
D133 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 104/72.6
D134 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) except [EXP-01] T 104/73.8
D135 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) except [EXP-01] T 104/75
D136 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) except [USA-01] T 106.5/71.4
D140 1750000370 S.DIO DA221 TL T 50/12.3
D141 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) T 120.9/40.3
D142 1790000980 S.DIO MA742 (TX) B 117.7/102.5
D143 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 74.6/50.8
D145 1720000791 S.VCP HVC321B1TRF-E T 83/38.9
D146 1720000791 S.VCP HVC321B1TRF-E T 83.8/37.2
D147 1720000791 S.VCP HVC321B1TRF-E T 81.8/41.4
D148 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 84.7/35.4
D150 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 86.9/58.4
D151 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 86.9/60.8
D152 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 86.9/59.6
D153 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 82.5/70.7
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 3
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 29

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
D154 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 80.7/70
D155 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 88.4/63.5
D156 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 77.1/70
D157 1790001621 S.DIO 1SV308 (TPL3,F) T 89.3/65.5
D159 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 38.9/57.9
D160 1790001260 S.DIO MA2S077-(TX) T 43/48.5
D161 1750000771 S.VCP HVC376BTRF-E B 123.3/87.8
D162 1750000771 S.VCP HVC376BTRF-E B 122.3/89.6
D164 1790001250 S.DIO MA2S111-(TX) B 114.7/88.1
D165 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 T 123.9/27.3
D166 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 T 125.1/27.3
D167 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 T 122.7/26.4
D168 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 T 120.6/26.4
D169 1790001520 S.ZEN MA8075-L (TX) T 47.3/125.2
FI1 2020002390 CER LT450HW
FI2 2020002250 CER LT450EW
FI3 2020002390 CER LT450HW
FI4 2020002250 CER LT450EW
FI5 2030000590 S.MLH FL-408 (38.850 MHz) B 71/69.6
FI6 2030000600 S.MLH FL-409 (46.350 MHz) B 26.1/68.9
X1 6050011940 S.XTL CR-783 (15.3 MHz) B 23.3/43.4
X2 6070000290 DCR JTB450C24
X3 6070000290 DCR JTB450C24
X4 6050012530 S.XTL CR-841 (SMD49/19.6608 MHz) B 126.6/88.1
X5 6050012450 S.XTL CR-833 (12.800 MHz) B 67.9/43.4
X6 6050012480 S.XTL CR-838 (SMD-49/4.194304 MHz) B 126.6/54.7
L1 6200005721 S.COL ELJRE 33NGFA T 16/97.8
L2 6200005721 S.COL ELJRE 33NGFA T 72.4/98.4
L3 6200006981 S.COL ELJRE R10GFA T 11.1/98.8
L4 6200009220 S.COL LQW18AN15NG00D T 14.9/101.3
L5 6200009220 S.COL LQW18AN15NG00D T 75.6/100.6
L6 6200003550 S.COL MLF1608A 4R7K-T T 17.4/99
L7 6200003550 S.COL MLF1608A 4R7K-T T 75.6/97.2
L8 6200010130 S.COL LQW18AN6N8C00D T 11.5/108.1
L9 6200005741 S.COL ELJRE 47NGFA B 89.4/67
L10 6200009220 S.COL LQW18AN15NG00D T 14.9/106.4
L11 6200005741 S.COL ELJRE 47NGFA B 91.3/67.8
L12 6200009220 S.COL LQW18AN15NG00D T 79.2/104.2
L13 6200003550 S.COL MLF1608A 4R7K-T T 18.5/107.6
L15 6200003550 S.COL MLF1608A 4R7K-T T 81.2/104.1
L16 6200009070 S.COL LQW18AN18NG00D T 14.9/110.1
L17 6200005671 S.COL ELJRE 12NGFA T 10.4/113.1
L18 6200009070 S.COL LQW18AN18NG00D T 82.4/107.5
L19 6200005731 S.COL ELJRE 39NGFA B 43.6/67.5
L20 6200010130 S.COL LQW18AN6N8C00D T 11.3/122.5
L21 6200003550 S.COL MLF1608A 4R7K-T T 19/115
L22 6200005721 S.COL ELJRE 33NGFA B 43.4/74.9
L23 6200012520 S.COL 0.26-1.0-5TL 12N T 16.4/117.7
L24 6200003550 S.COL MLF1608A 4R7K-T T 89.6/104.5
L25 6200005691 S.COL ELJRE 18NGFA B 85.4/71.7
L26 6200005691 S.COL ELJRE 18NGFA B 38.3/74.9
L27 6200012520 S.COL 0.26-1.0-5TL 12N T 92.5/106.1
L28 6200005741 S.COL ELJRE 47NGFA B 83.6/75.9
L29 6200005661 S.COL ELJRE 10NGFA B 39.9/77.5
L30 6200010130 S.COL LQW18AN6N8C00D T 11.8/131.4
L31 6200012520 S.COL 0.26-1.0-5TL 12N T 15.4/122.3
L32 6200003550 S.COL MLF1608A 4R7K-T T 16.9/124.9
L33 6200012520 S.COL 0.26-1.0-5TL 12N T 98.5/106.3
L34 6200003550 S.COL MLF1608A 4R7K-T T 100.8/103.7
L35 6200005701 S.COL ELJRE 22NGFA B 38.1/79.7
L36 6200005681 S.COL ELJRE 15NGFA B 40.7/82.9
L37 6200005731 S.COL ELJRE 39NGFA B 82.8/80.5
L38 6200011580 S.COL LQW18AN33NG00D T 26.1/130.4
L39 6200011580 S.COL LQW18AN33NG00D T 101.1/117.4
L40 6200011660 S.COL LQW18ANR15G00D T 31.7/134.2
L41 6200011660 S.COL LQW18ANR15G00D T 104/113.5
L42 6200011770 S.COL LQW18ANR10G00D T 30.8/137.1
L43 6200011770 S.COL LQW18ANR10G00D T 105.7/117.9
L44 6200010910 S.COL LQW18AN56NG00D T 106.9/117.9
L45 6200011580 S.COL LQW18AN33NG00D T 32.7/136.4
L46 6200010060 S.COL AS080647-56N B 88.7/128.9
L47 6200009250 S.COL LQW18ANR22G00D T 24/99.6
L48 6200005721 S.COL ELJRE 33NGFA T 55.4/97.6
L49 6200005701 S.COL ELJRE 22NGFA T 61.9/97.6
L50 6200010040 S.COL AS100340-10N B 40.3/125
L51 6200012050 S.COL LQW18AN24NG00D T 66.1/98.4
L52 6200011650 S.COL LQW18AN68NG00D T 28.2/100.5
L53 6200011590 S.COL LQW18AN39NG00D T 27.4/102.4
L54 6200011650 S.COL LQW18AN68NG00D T 66.1/101.7
L55 6200011590 S.COL LQW18AN39NG00D T 68/100.9
L56 6200010060 S.COL AS080647-56N B 86.1/137.8
L57 6200011770 S.COL LQW18ANR10G00D T 36.3/104.1
L58 6200011580 S.COL LQW18AN33NG00D T 54.3/103.6
L59 6200011770 S.COL LQW18ANR10G00D T 70.4/107.6
L60 6200009070 S.COL LQW18AN18NG00D T 60.8/103.6
L61 6200010160 S.COL AS080440-22N B 40.8/130.4
L62 6200010420 S.COL FHW1210HC 1R0JGT B 83.4/149.7
L63 6200009070 S.COL LQW18AN18NG00D T 43.8/110.2
L64 6200011670 S.COL LQW18AN82NG00D T 43.8/107.6
L65 6200009070 S.COL LQW18AN18NG00D T 73.3/115
L66 6200011670 S.COL LQW18AN82NG00D T 75.2/114.2
L67 6200009070 S.COL LQW18AN18NG00D T 62.1/110.2
L68 6200011580 S.COL LQW18AN33NG00D T 55.6/110.2
L69 6200012960 S.COL 0.45-1.4-4TL 12.1N T 35.1/139.3
L70 6200010420 S.COL FHW1210HC 1R0JGT B 45.5/133
L71 6200002390 S.COL LQW31HN64NJ03L T 74.2/120.7
L72 6200011590 S.COL LQW18AN39NG00D T 76.3/122.5
L73 6200010160 S.COL AS080440-22N B 36.4/140.3
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
L74 6200002390 S.COL LQW31HN64NJ03L T 50.6/113.7
L75 6200011590 S.COL LQW18AN39NG00D T 53.6/116.3
L76 6200011660 S.COL LQW18ANR15G00D T 88.5/119.4
L77 6200010160 S.COL AS080440-22N B 38.9/145.5
L78 6200010910 S.COL LQW18AN56NG00D T 93.7/124.4
L79 6200003960 S.COL MLF1608A 1R0K-T T 102.4/127.3
L80 6200010160 S.COL AS080440-22N B 38.9/150.6
L81 6200011670 S.COL LQW18AN82NG00D T 84.2/116.9
L82 6200012900 S.COL 0.30-2.0-7TL 57.2N T 97.5/128.1
L83 6200003960 S.COL MLF1608A 1R0K-T T 108.1/131.6
L84 6200009220 S.COL LQW18AN15NG00D T 105.7/125.8
L85 6200009250 S.COL LQW18ANR22G00D T 56/135.1
L86 6200012980 S.COL 0.40-1.4-5TR 18.3N T 105.4/130
L87 6200009250 S.COL LQW18ANR22G00D T 80.4/121.5
L88 6200010050 S.COL AS080547-47N B 65.4/152.4
L89 6200010070 S.COL AS080747-68N B 73.6/146.9
L90 6200012760 S.COL 0.35-1.6-7TL 37.5N T 99.5/133.2
L91 6200011670 S.COL LQW18AN82NG00D T 62.7/139.8
L92 6200010060 S.COL AS080647-56N B 58.9/149.2
L93 6200012910 S.COL 0.35-1.6-8TL 45.5N T 101/136.5
L94 6200012910 S.COL 0.35-1.6-8TL 45.5N T 70.3/143.9
L95 6200012960 S.COL 0.45-1.4-4TL 12.1N T 106.6/136.1
L96 6200010050 S.COL AS080547-47N B 50/153
L97 6200011660 S.COL LQW18ANR15G00D T 61/142.4
L98 6200012760 S.COL 0.35-1.6-7TL 37.5N T 102.5/139.9
L99 6200012960 S.COL 0.45-1.4-4TL 12.1N T 107.4/140
L100 6200005731 S.COL ELJRE 39NGFA T 26.8/152.3
L101 6200010040 S.COL AS100340-10N B 30.6/153.9
L102 6200010130 S.COL LQW18AN6N8C00D T 12.7/134.3
L103 6200012400 S.COL 0.30-0.91-4TL 8.6N T 100.8/143
L104 6200010160 S.COL AS080440-22N B 25.3/148.6
L105 6200010130 S.COL LQW18AN6N8C00D T 12.7/135.6
L106 6200012980 S.COL 0.40-1.4-5TR 18.3N T 100.8/147
L107 6200010130 S.COL LQW18AN6N8C00D T 12.7/136.9
L108 6200010150 S.COL AS080340-15N B 18.1/148.2
L109 6200012920 S.COL 0.20-1.0-4TL 12.1N T 99.2/149.9
L110 6200008720 S.COL 0.30-0.8-3TL 6N T 15.4/143.1
L111 6200004480 S.COL MLF1608D R82K-T B 24.8/50.8
L112 6200003540 S.COL MLF1608D R22K-T B 27.9/47.9
L113 6200005701 S.COL ELJRE 22NGFA T 30.9/49.3
L114 6200005741 S.COL ELJRE 47NGFA T 35.5/48.6
L115 6200002651 S.COL NLV25T-R18J T 32.4/37
L116 6200002651 S.COL NLV25T-R18J T 35.9/35
L117 6200010100 S.COL C2012C-33NG-A T 33.2/42.3
L118 6200010030 S.COL C2012C-15NG-A T 41.3/35.5
L119 6200004951 S.COL NLV25T-1R8J B 75.8/74.9
L120 6200010381 S.COL ELJRE R15JFA T 41.1/44.9
L121 6200005731 S.COL ELJRE 39NGFA T 45.3/44.1
L122 6130003000 S.COL #617DB-1714=P3 T 64.4/83.6
L123 6200005731 S.COL ELJRE 39NGFA T 37.4/64.4
L124 6200005691 S.COL ELJRE 18NGFA T 45.7/64.4
L125 6200005731 S.COL ELJRE 39NGFA T 36.2/65.9
L126 6130003000 S.COL #617DB-1714=P3 T 70.8/84.2
L127 6130003000 S.COL #617DB-1714=P3 T 71.1/90.4
L129 6200009220 S.COL LQW18AN15NG00D T 31.6/62.2
L130 6200005671 S.COL ELJRE 12NGFA T 32.4/64.3
L131 6200005701 S.COL ELJRE 22NGFA T 39.4/63.8
L132 6130003000 S.COL #617DB-1714=P3 T 14.9/83.9
L133 6200005671 S.COL ELJRE 12NGFA T 32.4/66.2
L134 6200005701 S.COL ELJRE 22NGFA T 39.4/67.3
L135 6200005651 S.COL ELJRE 8N2ZFA T 31.8/68.2
L136 6130003000 S.COL #617DB-1714=P3 T 21.2/84.4
L137 6130003000 S.COL #617DB-1714=P3 T 21.7/90.7
L138 6190001690 S.COL ZBFS5105-PT-01 T 119/121
L139 6190001690 S.COL ZBFS5105-PT-01 T 117.4/112
L140 6190001690 S.COL ZBFS5105-PT-01 T 115.3/121
L141 6190001690 S.COL ZBFS5105-PT-01 T 117.4/115.3
L142 6200004480 S.COL MLF1608D R82K-T B 71.9/51.3
L143 6200003540 S.COL MLF1608D R22K-T B 72.3/47.8
L144 6200002611 S.COL NLV25T-R47J T 80.8/37.2
L145 6200010310 S.COL C2012C-27NG-A T 85.2/40.4
L146 6200010310 S.COL C2012C-27NG-A T 86.5/37.7
L147 6200006671 S.COL ELJRE 68NGFA T 79.4/49.4
L148 6200005731 S.COL ELJRE 39NGFA T 84.4/65.5
L149 6200005721 S.COL ELJRE 33NGFA T 80.4/61.3
L150 6200006981 S.COL ELJRE R10GFA T 87.7/47
L151 6200005661 S.COL ELJRE 10NGFA T 81.9/63.8
L152 6200005731 S.COL ELJRE 39NGFA T 84.4/68.1
L153 6200005711 S.COL ELJRE 27NGFA T 80.2/66.3
L155 6200006671 S.COL ELJRE 68NGFA T 76.2/68.2
L156 6200006671 S.COL ELJRE 68NGFA T 78.4/68.4
L157 6200006991 S.COL ELJRE 56NGFA T 88/67.1
L158 6200009351 S.COL ELJRE R22GFA T 76.2/64.9
L159 6200005691 S.COL ELJRE 18NGFA T 45.6/68.9
L160 6200003960 S.COL MLF1608A 1R0K-T T 90.2/59
L161 6200003960 S.COL MLF1608A 1R0K-T T 42.7/58.2
L162 6200009220 S.COL LQW18AN15NG00D T 32/56.2
L163 6200003640 S.COL MLF1608E 100K-T T 93/15.2
L164 6200011660 S.COL LQW18ANR15G00D T 38.4/135.2
L165 6200011650 S.COL LQW18AN68NG00D T 62.2/144.9
L166 6200011650 S.COL LQW18AN68NG00D T 89.3/121.3
R3 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 97.8/102.8
R4 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 102.7/98.5
R5 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) B 102.7/100.1
R6 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 5.2/116.2
R7 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) T 5.2/117.8
R8 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 86.4/75
R9 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 18.9/97.8
R10 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 73.3/96.3
R11 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 11.9/100.2
R12 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 46.5/79.4
R14 7030005300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 150 X (15) T 11.1/102.6
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 4
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 30

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R15 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 103.6/101.6
R16 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 18/128.5
R17 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 85.9/76.2
R18 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 19.1/100.4
R19 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 78.5/97.2
R20 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 46.1/78.2
R22 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 87.7/67.5
R23 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 17/103.4
R24 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 78.6/100.5
R26 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 12.2/106.7
R27 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 17/104.3
R28 7030005080 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 823 X (82 k) T 12.2/109.8
R29 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 19.2/106.3
R30 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 79.2/101.2
R31 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 82.5/102.5
R33 7030010090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 180 X (18) B 90.3/69
R35 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 17/110.9
R37 7030005580 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 560 X (56) B 92.1/69.9
R38 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 84.2/105.2
R39 7030007270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150) T 10.6/116.5
R40 7030009200 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 390 X (39) T 11.1/117.7
R41 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 18.4/112.4
R43 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) B 43.9/66.4
R44 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 46.1/121.5
R45 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 14.4/115.5
R46 7030010090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 180 X (18) B 91.2/69.9
R47 7030005300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 150 X (15) B 44.3/68.8
R48 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 17.7/113.6
R49 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 85.6/104.7
R50 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 88/105.8
R51 7030007270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150) T 10.6/118.9
R52 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 13.1/114.1
R53 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 14/113.2
R54 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 86.8/105.4
R55 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 87.8/107
R56 7030007270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150) B 89.4/70.7
R57 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) B 42.2/69.3
R58 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 14.4/114.6
R59 7030009200 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 390 X (39) B 89.1/71.9
R60 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 87.8/108.6
R61 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 88.7/108.6
R63 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 44.4/72
R64 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680) B 42.2/70.2
R66 7030007270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150) B 87.9/70.7
R67 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 12.3/127.1
R68 7030007270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150) B 44.6/73.7
R70 7030005080 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 823 X (82 k) T 12.3/126.2
R72 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 19.7/113.7
R73 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 10.7/126.2
R74 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 89.6/101.6
R75 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 83.6/74.9
R76 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 83.6/74
R77 7030007250 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 220 X (22) B 41/76.3
R78 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 18.4/119.4
R79 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 19.1/120.3
R80 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 11.6/129
R81 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 94.7/104.4
R82 7030000270 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 120 (121) B 81/75.2
R83 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 95.9/104.1
R85 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 18.4/123.3
R86 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 99.9/101
R88 7030000180 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 22 (220) B 36/77.8
R89 7030005590 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 680 X (68) B 84.5/78.9
R90 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 38.4/78.7
R91 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680) B 40/79.7
R92 7030000180 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 22 (220) B 34.3/77.8
R93 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 102.6/107.4
R94 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 18.3/127.6
R95 7030000180 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 22 (220) B 80.8/78.5
R96 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 83.3/79.4
R97 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 84.5/80.5
R98 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 19.7/124.5
R100 7030000180 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 22 (220) B 79/78.5
R101 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 98.1/111.6
R102 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 98.1/117
R103 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 25/127.6
R104 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) B 39.1/84.3
R105 7030005300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 150 X (15) B 85.7/83.9
R106 7030010090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 180 X (18) B 38.6/83.1
R107 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 27.4/134.4
R108 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 30.7/130.1
R109 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 103/118
R110 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 98.5/114.4
R111 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) B 38.2/84.3
R112 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 27.4/132.8
R113 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 26.1/133
R114 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 103/116.4
R115 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 100.6/118.4
R116 7030005300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 150 X (15) B 84.1/83.9
R117 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 84.5/85.1
R118 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 28.7/133.2
R119 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 104.3/116.1
R120 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 29.6/135.1
R121 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 105.7/114.1
R122 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 28.3/127.8
R124 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 23.3/128.5
R125 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 44.5/90.1
R126 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 29.5/127.4
R128 7030007270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150) B 43.3/90.6
R129 7030008400 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 182 X (1.8 k) B 45.5/92.1
R133 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) B 40.8/103.6
R134 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 24.7/98.3
R135 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 58/98.1
R136 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 63.6/98.1
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R137 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 68.1/99.6
R138 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 85.2/87.3
R139 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 54.8/99.3
R140 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) B 87.3/86.9
R141 7030008400 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 182 X (1.8 k) B 86.4/86.9
R142 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 61.2/99.3
R143 7030005300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 150 X (15) T 60/100.5
R144 7030007250 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 220 X (22) T 53.6/100.5
R145 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 30.9/103.5
R147 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 54.8/100.9
R148 7030005060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 333 X (33 k) B 37.7/104.7
R149 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 70.6/103.7
R150 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 61.2/100.9
R152 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 34.6/105
R153 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 31.8/103.5
R154 7030005600 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 k) B 74.5/134.2
R155 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 70.6/104.6
R156 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 56.5/101.5
R157 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 33.7/105
R158 7030005080 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 823 X (82 k) B 35.1/107.9
R159 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 34.7/101.9
R160 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 62.9/101.5
R161 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 67.4/106.7
R162 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) B 34.6/106.6
R163 7030005100 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 154 X (150 k) B 33.7/109.1
R164 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) T 56.9/104.8
R165 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 36.9/101.9
R166 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 39.6/111.6
R167 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 39.1/110.3
R168 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) T 63.3/104.8
R169 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 72.5/106.7
R170 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 56.4/103.6
R171 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 62.9/103.6
R172 7030007270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150) T 39.4/103.3
R173 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 39.7/107.7
R174 7030007270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150) T 73/109.2
R175 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 40.5/104.8
R176 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) B 40.8/110.3
R177 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 41.2/108.2
R178 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) B 29.7/135.5
R179 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 73.3/111.7
R180 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 37.5/107.2
R181 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 73.3/110.8
R182 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) T 56/106.5
R183 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 53.7/107.3
R184 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 38.6/108.3
R185 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 69.7/111.8
R186 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) T 62.4/106.5
R187 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 60.1/107.3
R188 7030006070 S.RES ERJ12YJ101U (100) B 84.5/144.8
R189 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 68.5/111.2
R190 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 70.9/111.4
R191 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 65/109
R192 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 58.5/109
R193 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) B 43/111.7
R194 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) B 44.9/107.8
R195 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 61.6/111.4
R196 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) B 44.4/111.3
R197 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 45.7/106.2
R198 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 46.1/107.8
R199 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 52.9/110.7
R200 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 46.8/108.1
R201 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 72.1/139.6
R202 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 72.7/133.2
R203 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 77/117
R204 7030005530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10) T 38.2/137.9
R205 7030005060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 333 X (33 k) B 41.7/104.7
R206 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 47.7/108.1
R208 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 77/117.9
R209 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) B 74.1/133
R210 7030006070 S.RES ERJ12YJ101U (100) B 45.5/127
R211 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) B 44.8/104.3
R212 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 55.9/117.3
R213 7030005530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10) T 93.4/122.1
R215 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 103.1/106.1
R216 7030005530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10) T 106.4/123.2
R217 7030005710 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 121 X (120) T 72.4/122.5
R218 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 86.4/122.5
R219 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 103.5/126.1
R220 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 85.1/119
R221 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 86/120.6
R222 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 56.8/131.9
R223 7030005710 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 121 X (120) T 56.3/122
R224 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 109.1/130.4
R225 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 63.3/113.2
R226 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 61.9/114.7
R227 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 85.2/122.1
R228 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 84.3/122.1
R229 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 53.7/135.8
R230 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 59.4/135.3
R231 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680) T 81.6/122.1
R232 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680) T 55.4/136.2
R233 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 80.8/118.1
R234 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 56.9/138.9
R235 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 54.8/137.5
R236 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 78.4/123
R237 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 59/139.8
R238 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 59.5/137.9
R239 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 65.9/114
R240 7030005530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10) T 66.8/142.7
R241 7030005080 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 823 X (82 k) B 13.5/148.2
R242 7030005080 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 823 X (82 k) T 98.9/151.9
R243 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 35.5/146.7
R244 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 32.4/144.7
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 5
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 31

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R245 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 34.7/148.8
R246 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 112/88.6
R247 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 117/92.2
R248 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 109.6/93.6
R249 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 109/89.6
R251 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) T 115.3/82.7
R252 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 113.6/94.5
R253 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 114.4/83.6
R254 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 106.2/95.9
R255 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) T 112.3/81.3
R256 7030005290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 682 X (6.8 k) T 116.1/92.2
R257 7030005290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 682 X (6.8 k) T 108.7/93.6
R258 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 111.6/93.3
R259 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 106.2/92.7
R261 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) B 99.6/90.9
R262 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 111.9/86.8
R263 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 102.3/92.5
R264 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) B 99.6/90
R265 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 111.9/87.7
R266 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 116.9/97.4
R267 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) T 110.7/87.2
R268 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 108.7/98.1
R269 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 106.4/90.4
R270 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 107.6/90.4
R271 7030007310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 155 X (1.5 M) T 112.7/94.5
R272 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 115.8/96.3
R273 7030007310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 155 X (1.5 M) T 105.3/95.9
R274 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 107.8/98.1
R275 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) B 105.5/90
R276 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) T 111.9/85
R277 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) T 111.6/92.4
R278 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) T 110.3/85
R279 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 109.6/88.7
R280 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) T 105.3/94.2
R281 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) B 103.7/90
R282 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 108/88.7
R283 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 111.6/91.5
R284 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 105.3/91.8
R285 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) T 107.9/85
R286 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) B 103.7/88.4
R287 7030005700 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 274 X (270 k) B 21.2/46.8
R288 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 110.4/91
R290 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 103.2/92
R292 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 20/44.7
R293 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 59.9/42.1
R294 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) B 102.5/87.4
R295 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 104.1/86.3
R296 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 102.5/86.5
R298 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) B 16.5/40.5
R299 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 21.2/45.9
R301 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 55/40.9
R302 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 51.8/34
R303 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) B 55.8/37
R304 7030007060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 684X (680 k) B 27.4/46.9
R305 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 57.5/74.1
R306 7030005030 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 152 X (1.5 k) B 54.9/37.9
R307 7030005080 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 823 X (82 k) T 51.5/60.7
R308 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) B 54/65.9
R309 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 29.7/50.9
R310 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) B 52.3/38.6
R311 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 52.8/37.4
R312 7030007250 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 220 X (22) T 29.5/45.6
R313 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 26/40.9
R314 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 53.6/61.2
R315 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 54/67.5
R316 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) T 55.5/51.2
R317 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 54.8/60.7
R318 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 30.2/47.4
R319 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) B 51.9/37.4
R320 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 26.7/43.7
R321 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 56.1/61
R322 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 54.7/56.3
R323 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 54.7/48.8
R324 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) T 54.8/63.9
R325 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 31.6/47.4
R327 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 54.5/40.3
R328 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 54.5/41.2
R329 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 100.4/21.7
R330 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 62.2/59
R331 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 62.5/51.1
R332 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) T 51.9/42.8
R333 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 23.1/49.7
R334 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) T 59.3/64.3
R335 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 52.9/40.3
R336 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 22.5/48.8
R337 7030005600 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 k) T 24/43.5
R338 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 22.7/47.9
R339 7030007300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 332 X (3.3 k) B 84.3/46.1
R340 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) T 22.1/41.6
R341 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 57.3/61.9
R342 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 59.8/68.7
R343 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 23.3/41.4
R344 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 21.6/39.5
R345 7030007300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 332 X (3.3 k) T 55.1/66.8
R346 7030007300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 332 X (3.3 k) T 53/65.6
R347 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 26.8/42.5
R348 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 36.5/47.2
R349 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 37.7/47.5
R350 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 38.7/48.9
R351 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 8.6/40.3
R352 7030005030 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 152 X (1.5 k) B 7.6/38
R353 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) B 8.8/38.4
R354 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 44.5/39.1
R355 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 26.9/37.3
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R356 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 41.6/49.3
R358 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) B 6/38
R359 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 7.9/36.8
R360 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 40/36.6
R362 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 27.8/37.3
R363 7030005210 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 822 X (8.2 k) B 40.6/42.9
R364 7030005030 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 152 X (1.5 k) B 38.8/42.9
R365 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) T 27.4/36.1
R366 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) B 5.2/36.8
R367 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 11.1/42.1
R368 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) T 58.7/42.8
R369 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 27.4/34.3
R370 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 38.8/37.4
R372 7030005080 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 823 X (82 k) T 8.5/59
R373 7030005210 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 822 X (8.2 k) B 41.6/43.9
R374 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 7.3/39.4
R375 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) B 8.5/65
R376 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 7.3/40.3
R377 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) B 41.2/45.1
R378 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 29/36.1
R379 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) B 62.4/68.3
R380 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) B 61.5/66.6
R381 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) B 63.6/64.4
R382 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 36.3/38.4
R383 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 8.2/60.4
R384 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 65.6/65.9
R385 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) T 5.4/41.9
R386 7030007300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 332 X (3.3 k) B 37.3/43.3
R388 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 9.4/59.9
R389 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 8.5/66.6
R390 7030008400 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 182 X (1.8 k) T 29.9/37
R394 7030008270 S.RES RR0510R-104-D (100 k) T 37.2/37.5
R395 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 63.8/67.9
R396 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 5.6/39.4
R397 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 10.7/60.2
R398 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 16.5/69.2
R399 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) B 67.2/66.8
R400 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) T 9.4/62.2
R402 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) T 6.3/50.3
R403 7030005820 S.RES RR0510P-103-D (10 k) T 36/41.1
R404 7030005820 S.RES RR0510P-103-D (10 k) T 42.9/36.3
R405 7030005820 S.RES RR0510P-103-D (10 k) T 36/42.7
R406 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 9.4/55.4
R407 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 9.4/47.9
R408 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 37/43.8
R409 7030009270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 821 X (820) T 40.1/39.5
R411 7030005820 S.RES RR0510P-103-D (10 k) T 43.2/38.4
R412 7030005750 S.RES RR0510R-470-D (47) T 44.3/40
R413 7030008280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 271 X (270) T 46.3/34.9
R414 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) T 13.9/63.5
R415 7030007300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 332 X (3.3 k) T 7/65.5
R416 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 73.6/74.5
R417 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 16.7/59.5
R418 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 17/51.5
R419 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 12/61
R420 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 40/43.5
R421 7030008400 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 182 X (1.8 k) T 41.5/41.6
R422 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330) T 16.1/68
R423 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 40.3/46.4
R426 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 44.3/42.4
R427 7030009290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 562 X (5.6 k) T 45.9/40.9
R428 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 37.8/60.7
R429 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) B 15.8/67.5
R430 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) B 16.7/66.6
R431 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) B 18/63.5
R432 7030005590 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 680 X (68) T 44.6/45.6
R433 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 45.3/47.3
R434 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 20.4/65.5
R436 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 37.2/62.3
R438 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 19/68.9
R439 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) B 21.7/65.9
R440 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 63.1/88.3
R441 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 34.1/56.2
R443 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 68.8/81.5
R444 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) T 67.5/86.3
R445 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 44/66.7
R446 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 44.9/65.8
R447 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) T 68.6/87.4
R448 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 46/56.1
R449 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 36.3/55.6
R450 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 36.8/68.3
R452 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 28.7/73.7
R453 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 67.9/82.4
R455 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 40.2/60
R457 7030005530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10) T 30.7/59.9
R460 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 39.4/61.7
R461 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 52.2/96
R462 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 13.6/88.6
R463 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 19.3/81.7
R464 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) T 18/86.5
R465 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 31.6/70.6
R466 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 39.9/69.1
R467 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) T 19.2/87.7
R469 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 22.9/87.4
R470 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 39.9/70.7
R471 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 11.5/96.6
R472 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 7.1/122.8
R473 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 122/23.9
R475 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 121.6/91.3
R476 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 121.4/76.6
R477 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 100.4/130.4
R478 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 121.6/92.2
R479 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 117/77.1
R480 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 115.9/86.2
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 6
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 32

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R481 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) B 124.8/81.4
R482 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 116.8/86.2
R483 7030000020 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 1 (010) T 128/20.6
R484 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 118.3/77.1
R485 7030000400 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 1.5 k B 98.7/120.5
R486 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 110.1/63.1
R489 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 126.3/74
R490 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 124/24.8
R493 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 128.7/74.3
R494 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 8.4/33.2
R495 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 6.8/33.2
R497 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 123.6/23.9
R498 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 101.6/102.2
R499 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) B 103.4/101.3
R500 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 101.8/104.5
R501 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) B 102.2/105.7
R504 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 125.7/24.8
R506 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 125.2/23.9
R508 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 128.7/65.7
R509 7510001770 S.TMR NTCG10 4LH 473JT B 113.6/89.2
R510 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) B 112.4/89.6
R511 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 116.3/88.6
R512 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 117.2/88.8
R514 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 7.6/29.7
R515 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 6/29.7
R516 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 126.9/65.8
R517 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) B 9.6/31.4
R518 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 106.5/83.1
R519 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 8.4/31.9
R520 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 108.5/85.2
R521 7030005521 S.RES ERA3YKD 334V (330 k) T 116.9/68.4
R522 7030005501 S.RES ERA3YKD 124V (120 k) T 118.1/67.5
R523 7030005691 S.RES ERA3YED 123V (12 k) T 118.8/69.6
R524 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 117.8/65.4
R525 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 110.6/87.2
R527 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 15.7/28.6
R529 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 13.2/27.4
R530 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) T 114.1/65.9
R532 7030005060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 333 X (33 k) T 13.8/30.2
R533 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) T 13.8/28.6
R534 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 107.9/65.5
R536 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 112/63.4
R537 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 12.9/30.5
R538 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 16.7/28.6
R539 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 124.2/65.3
R540 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 125.1/66
R541 7030005600 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 k) T 17.6/28.6
R545 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) T 19.9/28.6
R547 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 25.5/25.9
R549 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 24.3/27.7
R550 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) T 22.5/22.8
R552 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 98.8/75.3
R553 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 119.4/66.6
R554 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 120.6/61.1
R556 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 102.8/66.7
R557 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 107.9/67.5
R558 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 99/70
R559 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 110.6/59
R560 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) T 24.3/26.1
R561 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 105.8/62.5
R562 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) T 19/27
R563 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 101/68.4
R564 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 104.6/64.9
R566 7030005210 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 822 X (8.2 k) T 21.3/23.7
R567 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 110.1/79.3
R568 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 110.5/78.1
R569 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 64.8/5.6
R570 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 30.6/28
R571 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 43.7/12.6
R572 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 112.2/98.1
R573 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 110.4/98.1
R574 7030005210 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 822 X (8.2 k) B 27.3/23.9
R575 7030008410 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 392 X (3.9 k) B 28.5/23.5
R577 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 36.5/20
R578 7030008400 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 182 X (1.8 k) B 37.3/24.1
R579 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 66.3/12.7
R581 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 58.3/7.7
R582 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 36.1/25.7
R583 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 36.1/24.1
R584 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 37/25.7
R585 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 37/24.1
R586 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 113.1/98.1
R587 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 111.3/98.1
R588 7030005210 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 822 X (8.2 k) T 50.6/10.4
R589 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) B 33.3/24
R590 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 65.7/5.6
R591 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 74.6/4.4
R592 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 114.3/101.2
R593 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680) T 115.9/103.1
R594 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 59/9.6
R598 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) B 65/8
R600 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) B 40/14.3
R608 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 108.5/101.8
R609 7030005600 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 k) T 105.3/104.2
R610 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 106.7/101.8
R611 7030005600 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 k) T 105.8/101.8
R612 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 107.6/101.8
R613 7030005600 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 k) T 105.7/103
R614 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) B 65/6.4
R615 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 99.4/32.7
R616 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 65/9.6
R617 7030007300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 332 X (3.3 k) T 120.1/41.7
R618 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 115.4/40.4
R619 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 116.6/40.9
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R620 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 121.3/41.4
R621 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) T 116.7/44.4
R623 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) B 118.5/99.4
R624 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 70.2/14.7
R625 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 125.9/114.3
R626 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 120.9/108.1
R627 7030008410 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 392 X (3.9 k) T 112.5/77.7
R628 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 70.4/17.9
R630 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) T 127.9/107.5
R631 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) T 120.9/106.3
R632 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) T 114/77.5
R635 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) B 122.6/104.9
R637 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) B 70.4/16.1
R638 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 127.5/113.4
R639 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 122.5/107.2
R640 7030009290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 562 X (5.6 k) B 59.7/17.7
R641 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 128.3/108.7
R642 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 123.2/111.8
R643 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) B 70.4/17
R644 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 114.4/76.3
R645 7030007350 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 k) T 114.9/77.5
R647 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 127.6/109.2
R649 7030005210 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 822 X (8.2 k) T 125/107.2
R653 7030009280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 391 X T 128.7/103.9
R658 7030009280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 391 X T 128.7/116.1
R659 7030000100 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 4.7 (4R7) T 124.8/142.5
R660 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 61.4/17.2
R661 7030000100 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 4.7 (4R7) T 104.7/145.9
R663 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) T 125.2/106.3
R664 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 61.4/18.8
R665 7030008010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 k) T 122.6/144.3
R677 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 75.9/47.6
R678 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 65.8/45.9
R679 7030005700 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 274 X (270 k) B 65.8/46.8
R680 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW B 64.6/44.8
R681 7030005530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10) B 73.5/46
R682 7030007060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 684X (680 k) B 71.8/46.7
R683 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 70.6/40.9
R684 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 75/47.6
R685 7030007250 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 220 X (22) T 75.1/45.7
R686 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 68.1/49.8
R688 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 67.4/48.8
R690 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 67.4/47.9
R694 7030005030 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 152 X (1.5 k) T 72/37.5
R695 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 72.8/36.6
R696 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) T 71.5/36.3
R697 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) T 74.6/35.1
R698 7030007570 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 122 X (1.2 k) T 72.4/34.7
R699 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 80.6/44.6
R700 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 79.3/41.8
R701 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 82.2/44.6
R702 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 81.8/43.4
R703 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 85.7/35
R704 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 83.6/35.8
R705 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 84/38.5
R706 7030009530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 270 X (27) T 84.9/58.4
R707 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 75.2/49.2
R708 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 88.1/39.3
R709 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 85.3/61.3
R710 7030007260 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 330 X (33) T 84.9/57.5
R711 7030009530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 270 X (27) T 83.3/58.4
R712 7030004970 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 470 X (47) T 86.9/44.2
R713 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 86.9/42.6
R714 7030009270 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 821 X (820) T 90.3/39.1
R716 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 84.5/62.9
R717 7030005710 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 121 X (120) T 90.3/42.3
R718 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 83.6/57.2
R719 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 83.7/47.6
R720 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 86.3/63.8
R721 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220) T 82.3/47.6
R722 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 82.5/60.3
R723 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 88.7/45.3
R724 7030008400 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 182 X (1.8 k) T 90.3/45.3
R725 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 85.3/49.2
R726 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 84.9/48
R727 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 88.7/44.4
R728 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680) T 87.7/49.5
R733 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 84.6/70.7
R734 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 80.7/68.3
R737 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 88.6/61.3
R738 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 78.8/70.8
R739 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 89.5/61.3
R741 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 86.2/69.8
R742 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 75.7/63.8
R743 7030005060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 333 X (33 k) T 75.9/61.4
R744 7030005590 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 680 X (68) T 75.3/60.2
R745 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 75.7/69.5
R747 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 45.3/60.4
R748 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 41.6/47.7
R750 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 36.6/58.7
R752 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 45.3/62
R754 7030007250 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 220 X (22) T 14/111.5
R755 7030007250 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 220 X (22) T 83.8/108
R756 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 68.6/108.1
R757 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 36/105.2
R758 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 90.9/11.1
R759 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 90.2/6.5
R762 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 60.5/19.8
R763 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 60.2/16.1
R764 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) T 60.2/15.2
R765 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 60.2/14.3
R766 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 70.1/15.8
R767 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 64.4/21.3
R768 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 59.3/19.3
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 7
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 33

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R769 7030005230 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 k) T 60.1/18.4
R770 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 114.4/69.1
R771 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 70/20
R772 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470) T 73.5/19.7
R773 7030009140 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 272 X (2.7 k) T 73.5/20.6
R774 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) T 72.5/18.8
R775 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) T 72.3/20
R777 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) B 103.4/36.7
R778 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) B 105/36.7
R779 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) B 104.8/28.2
R780 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 104.8/27.3
R781 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 103.2/27.3
R782 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 107/33.3
R783 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 107/31.6
R784 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 70.4/17
R785 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) T 64.4/22.2
R786 7030006610 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 k) B 74.6/11.8
R787 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) B 102.3/30
R788 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 101.9/32.1
R789 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 118.9/142.1
R790 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 66.9/91.5
R791 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 66.9/90.2
R792 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 17.5/91.7
R793 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 17.5/89.5
R794 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 12.9/67.6
R795 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 58/68.4
R796 7030007320 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 225 X (2.2 M) T 98.2/31
R797 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 101.9/28.3
R798 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 100.6/30.1
R799 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 98.4/28.3
R800 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 99.4/30.5
R801 7030005530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10) B 27.3/24.8
R802 7030007290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 k) B 36.5/21.6
R804 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) T 72.5/17
R805 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) B 60.8/27.3
R806 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 60.6/24.8
R807 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) B 56.4/27.3
R808 7030005070 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 k) B 55.9/26.1
R809 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) B 45.1/32.8
R810 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 60.1/26
R811 7030007300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 332 X (3.3 k) T 9.8/66
R812 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 101.8/78.4
R813 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 108.8/60.7
R814 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 100/76.6
R815 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 123.3/85.8
R816 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 121.9/87.9
R817 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 120.4/79.4
R818 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 120.4/78.5
R819 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 120.4/77.6
R820 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) B 123.4/53.5
R821 7030007340 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 k) T 120.7/53.1
R822 7030008410 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 392 X (3.9 k) T 120.7/54
R823 7030006610 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 k) T 105.3/53.9
R825 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 120.3/67.9
R826 7030006610 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 k) T 104.4/53.9
R827 7030006610 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 k) T 112.6/53.7
R828 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 114.7/105.4
R829 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 109.4/99.5
R830 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 128.7/69.6
R831 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 119/86.6
R832 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 120/85.1
R833 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 120.7/84.5
R835 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 127.8/73.5
R836 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 127.6/75.5
R838 7410001230 S.ARY EXB28V101JX B 118.8/59.3
R839 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) B 117.7/57.9
R840 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 71.2/37.7
R841 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 73.3/34.7
R842 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 67.2/34.9
R843 7030005060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 333 X (33 k) B 68.6/35.3
R844 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) B 30.2/31.5
R845 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 27.8/36.6
R846 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 27.4/35.2
R847 7030005060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 333 X (33 k) B 29.1/36.2
R848 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 74.8/39.3
R849 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 28.6/41.4
R850 7030008300 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 k) T 112.7/119.5
R851 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 121.4/82.5
R852 7520000250 S.POS PRF18BE471QB1RB T 78.7/149.4
R853 7520000250 S.POS PRF18BE471QB1RB T 42.6/138.9
R856 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100) T 36.5/122.7
R857 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 34.2/117.5
R858 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) T 124.8/25.7
R859 7030005170 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 474 X (470 k) T 121.7/26.1
R860 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 107.3/81.1
R861 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 104.1/70.1
R862 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) T 114.3/100.3
R863 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 108.9/79.7
R864 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 105.2/84.3
R865 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 121.1/69.9
R866 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 121.5/65.5
R867 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 121.5/63
R868 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 114.8/52.8
R869 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 70.6/43
R870 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 74.8/42.2
R871 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 111.9/118.6
R872 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 111.9/117.7
R873 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 7/119
R874 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) B 100.6/97.7
R875 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 46.1/126.9
R876 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 49.6/118.5
R877 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 37/138.3
R878 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 100.5/38.1
R879 7030005110 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 k) T 99.4/37.2
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R880 7030006610 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 k) T 107.7/57.2
R881 7030006610 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 k) T 103/55.8
R882 7030006610 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 k) T 111.6/55.4
R883 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 128.5/58.9
R884 7510001770 S.TMR NTCG10 4LH 473JT T 52.7/61.2
R885 7510001770 S.TMR NTCG10 4LH 473JT T 7.3/60.4
C1 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 97.3/104
C2 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 8/119
C3 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 99/99.7
C4 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 20.7/111.9
C5 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 87.2/107.1
C6 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 5.8/89.1
C7 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 103.6/85.8
C8 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 90/74.9
C9 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 46.6/82.9
C10 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 17.7/97.7
C11 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 72.4/96.3
C12 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 12.8/99.3
C13 4030017560 S.CER ECJ0EC1H2R5B T 14.1/99
C14 4030017560 S.CER ECJ0EC1H2R5B T 72.8/100.5
C15 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 10.4/100.2
C16 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 85.9/77.8
C17 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 104.1/102.8
C18 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 19.3/128.7
C19 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 88/88.4
C21 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 18.2/100.4
C23 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 77.3/96.8
C24 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 11/105
C25 4030017560 S.CER ECJ0EC1H2R5B T 15.3/99.3
C26 4030017560 S.CER ECJ0EC1H2R5B T 73.9/99.4
C27 4030017340 S.CER ECJ0EC1H010B T 10.6/107.1
C28 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 18.2/102.9
C29 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 14.1/103.8
C30 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 53.9/29.8
C31 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J B 88.6/65.7
C32 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 15.8/103.8
C33 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 17/102.5
C34 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 77.3/99.9
C35 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 10.6/106.2
C36 4030017520 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R3B T 76.8/102.9
C37 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J T 17/105.2
C38 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 78/101.8
C39 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 78/99.3
C40 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 18.2/104.7
C41 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J T 79.9/102.5
C43 4030017670 S.CER ECJ0EC1H390J B 90.1/65.7
C44 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 35.2/76.2
C45 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 80.4/101.7
C46 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 14.1/107.7
C47 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 18.9/108.7
C48 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 14.6/109.1
C49 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 79.6/105.7
C50 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 81.4/107
C51 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 83.3/103.4
C53 4030017340 S.CER ECJ0EC1H010B T 11.4/113.1
C54 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J B 89.4/69
C55 4030017610 S.CER ECJ0EC1H090C T 15.3/108.1
C56 4030017610 S.CER ECJ0EC1H090C T 80.7/106.3
C57 4030017340 S.CER ECJ0EC1H010B T 11.1/115.3
C58 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 17/110
C59 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 92.1/71.5
C60 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J B 45.2/68.8
C61 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 17.5/112.4
C62 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 83.3/106
C63 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 85.6/105.6
C64 4030017370 S.CER ECJ0EC1H3R5B T 11.1/120.2
C65 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 90.3/70.7
C66 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 16/114.6
C67 4030017550 S.CER ECJ0EC1H1R5B T 10.6/121.4
C68 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 42.6/73.9
C69 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 78.4/76.5
C70 4030017620 S.CER ECJ0EC1H100C B 43.4/69.7
C71 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 15.7/115.8
C72 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 12.3/128.1
C73 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 13/122.9
C74 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 12.7/115.5
C75 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 88/104.5
C76 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 86.8/109.4
C77 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 17/116.2
C78 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 89.6/107
C79 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 79.6/76.1
C80 4510008520 S.ELE EEE1CA470SP T 51.8/128.3
C81 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 87.5/71.9
C82 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 90.9/106.5
C83 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 82.4/74.4
C84 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B B 86.1/70.4
C85 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 19.7/116.4
C86 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 45.5/75.3
C87 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B B 41.3/74.9
C88 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 51.3/118.1
C89 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 81/72.8
C90 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 90.1/102.8
C91 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 18.9/118.5
C92 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 20.1/118.9
C93 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B B 40.1/75.4
C94 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 50.7/132.3
C95 4030017370 S.CER ECJ0EC1H3R5B T 11.1/127.4
C96 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 14.5/120
C97 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 17.8/120.6
C98 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 93.1/104.4
C99 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 94.7/103.5
C100 4030017520 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R3B T 95.5/107
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 8
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 34

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C101 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 95.5/105.4
C102 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 18.7/121.5
C103 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 19.6/121.5
C104 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B B 38.5/76.6
C105 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 97.4/104.4
C106 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 97.3/103.2
C107 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 19.8/123.3
C108 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 100.3/102
C109 4030017650 S.CER ECJ0EC1H270J B 84.5/77.3
C110 4030017630 S.CER ECJ0EC1H120J B 85.7/77.9
C111 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 36/79.9
C112 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 15.9/123.9
C113 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 100/105.7
C114 4030017550 S.CER ECJ0EC1H1R5B T 14.7/124.3
C115 4030017550 S.CER ECJ0EC1H1R5B T 98.1/108.4
C116 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 102.2/108.6
C117 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 15.7/129
C118 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 98.1/110
C119 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 103.1/108.6
C120 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 18.3/126.7
C121 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 79.1/80.6
C122 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 35.2/75.3
C123 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C B 42.8/82.9
C124 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B B 41.5/84.3
C125 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B B 40/84.3
C126 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B T 99/116.1
C127 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 29.8/130.1
C128 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 99.4/114.4
C129 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 78.7/75.3
C130 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 80.7/80.6
C131 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J B 87.3/83.9
C132 4030017620 S.CER ECJ0EC1H100C B 86.8/85.1
C133 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B T 25/129.2
C134 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR T 79.5/77.4
C135 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 27.4/136
C136 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 28.7/132.3
C137 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 26.1/132.1
C138 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 99.5/96.1
C139 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 103.9/114.8
C140 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 103/114.8
C141 4030017390 S.CER ECJ0EC1H180J B 85.4/85.1
C142 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 44/86.7
C143 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 40.1/86.8
C144 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 39.1/89.3
C145 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 44/87.6
C146 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 29.6/134.2
C147 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 104.8/114.8
C148 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 29.1/136.4
C149 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 105.7/115.7
C150 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 38.6/86.8
C151 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 43.6/118.5
C152 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 22.4/129.4
C153 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 49.2/116.4
C154 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 87.9/114.5
C155 4030011160 S.CER GRM31M2C2H150JV01L B 84.8/124.7
C156 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 46/103.9
C157 4030011210 S.CER GRM31M2C2H330JV01L B 87.1/133.8
C159 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 62.5/99
C160 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 22.3/99.2
C161 4030011020 S.CER GRM31M4C2H1R0CY21L B 83.6/131.4
C162 4030011140 S.CER GRM31M2C2H120JV01L B 80.2/133.9
C163 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 26.1/99.8
C164 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 78.5/132.3
C165 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 83.6/88.3
C166 4030011020 S.CER GRM31M4C2H1R0CY21L B 36.4/121.4
C167 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 53.6/98.9
C168 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 68.6/97.6
C169 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 67.2/99.6
C170 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 57.1/98.1
C171 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 60/98.9
C173 4030011020 S.CER GRM31M4C2H1R0CY21L B 40.5/118.2
C174 4030011150 S.CER GRM31M2C2H130JV01L B 37.1/116.7
C175 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 29.6/103.1
C176 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 39.2/114.9
C178 4550002980 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 225M8R B 37.6/102.3
C179 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 30.5/104.7
C181 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 69.4/102.5
C182 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 31.4/100.5
C183 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 35.5/105
C184 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 71.1/102.5
C185 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J T 31.4/102.1
C186 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 75/133
C187 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 66.1/104.1
C188 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J T 69.4/104.1
C189 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 33.2/103.9
C190 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 33.7/106.6
C191 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 33.2/103
C192 4550002980 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 225M8R B 89.7/89.9
C193 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 71.2/105.8
C194 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 56.9/100.3
C195 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 69.5/105.7
C196 4030017370 S.CER ECJ0EC1H3R5B T 53.6/102.1
C197 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 63.4/100.3
C198 4030011020 S.CER GRM31M4C2H1R0CY21L B 79.7/139.9
C199 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 40.8/112.1
C200 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 60/102.1
C202 4030011020 S.CER GRM31M4C2H1R0CY21L B 79.7/137.5
C203 4030011120 S.CER GRM31M2C2H100JV01L B 74.8/137.1
C205 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 54.8/102.5
C206 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 67.4/107.6
C207 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 35.6/102.8
C208 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 37.3/103.1
C209 4030016950 S.CER ECJ0EB1A473K B 35.5/106.6
C210 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 34.6/109.1
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C211 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 61.2/102.5
C212 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 76.8/139
C213 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 56/104.8
C214 4030011060 S.CER GRM31M2C2H4R0CY21L B 40.5/121.6
C215 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 72.5/107.6
C216 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 35.5/109.1
C217 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 62.4/104.8
C218 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 38.5/103.3
C219 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 72.1/109.2
C220 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 86.9/143.8
C221 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 40.8/111.2
C222 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 58.1/104
C223 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 64.6/104
C224 4030011060 S.CER GRM31M2C2H4R0CY21L B 37.4/131.1
C225 4510008110 S.ELE 16 CE 22 BS T 82.7/142.6
C226 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 73/139.6
C227 4030017200 S.CER GRM31BR32J102KY01L B 80.5/143.3
C228 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 43.3/102.5
C229 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 40.3/106.5
C230 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 44.2/123.3
C231 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 28.5/136
C232 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 43/110.8
C233 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 40.9/107.2
C234 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 54.9/107.7
C235 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 68.6/109.8
C236 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 42.5/108.7
C237 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 60.1/109
C238 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 43/109.9
C239 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 61.3/107.7
C240 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 86.9/146.1
C241 4030016950 S.CER ECJ0EB1A473K B 44/107.8
C242 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 73.3/112.9
C243 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 65.4/110.2
C244 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 72.1/110.8
C246 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 88.5/87.3
C247 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 63.8/109.4
C249 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 57.3/109.4
C251 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 38.2/138.8
C252 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 45.9/108.1
C253 4030017370 S.CER ECJ0EC1H3R5B T 60.4/110.9
C254 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 45.6/110.2
C255 4030017370 S.CER ECJ0EC1H3R5B T 53.9/110.7
C256 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 76.5/115.8
C257 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 46.4/106.4
C258 4030017540 S.CER ECJ0EC1HR75B T 47.3/110.9
C259 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 78.6/117
C260 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 72.5/117.5
C261 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J T 75.8/117.5
C262 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J T 47.3/109.3
C263 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 73.3/134.7
C264 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 48.2/106.9
C265 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 32.4/133.8
C266 4030011160 S.CER GRM31M2C2H150JV01L B 78.7/147.2
C267 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 78.2/118.4
C268 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 48.6/108.1
C270 4510008110 S.ELE 16 CE 22 BS T 43.8/130.3
C271 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 77/118.8
C272 4030011020 S.CER GRM31M4C2H1R0CY21L B 36.1/134.5
C273 4030011140 S.CER GRM31M2C2H120JV01L) B 32.6/136.7
C274 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 46.3/130.5
C275 4030017190 S.CER GRM31AR32J471KW01D B 41/134.5
C278 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 46/104.8
C279 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 93/119.9
C280 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 93.4/123.1
C281 4030006960 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 050C-T B 30.5/142.7
C282 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 56.4/116.1
C283 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 74.2/122.5
C284 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 104.3/106.6
C285 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 53.5/117.5
C286 4030011050 S.CER GRM31M3C2H3R0CY21L B 40.1/138.1
C287 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 87.6/122.1
C288 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 105.9/121.1
C289 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 74.2/127.5
C290 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 56.9/119.7
C291 4510008110 S.ELE 16 CE 22 BS T 99.7/123
C292 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 93.4/121.1
C293 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 106.4/122.3
C294 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 73.3/123.4
C295 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 54.4/122
C296 4030011080 S.CER GRM31M2C2H6R0DV01L B 42.6/143.2
C297 4030011730 S.CER GRM31M2C2H101JV01L B 33.6/146.8
C298 4510008110 S.ELE 16 CE 22 BS T 112.5/131.5
C299 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 82.5/122.1
C300 4030017440 S.CER ECJ0EC1H221J T 86.4/119.4
C301 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 101.1/126.6
C303 4030011060 S.CER GRM31M2C2H4R0CY21L B 42.6/148.3
C304 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 84.2/119
C305 4030017650 S.CER ECJ0EC1H270J T 94.1/126.8
C306 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 59.4/136.2
C307 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 109.1/132
C308 4030011080 S.CER GRM31M2C2H6R0DV01L B 42.6/153.2
C309 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 56.8/133.5
C310 4030011170 S.CER GRM31M2C2H180JV01L B 73.2/152.2
C311 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 83.4/122.1
C312 4030017390 S.CER ECJ0EC1H180J T 98.6/130.1
C313 4030017380 S.CER ECJ0EC1H050B T 106/127.6
C314 4030017200 S.CER GRM31BR32J102KY01L B 73.2/154.5
C315 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 52.8/135.8
C316 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 55.7/137.5
C317 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 99.8/130.4
C318 4030011170 S.CER GRM31M2C2H180JV01L B 69.4/153
C319 4030017390 S.CER ECJ0EC1H180J T 97.6/132.3
C320 4030007060 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 270J-T B 67.5/144.7
C321 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 78.8/121.8
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 9
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 35

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C322 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 81.7/118.1
C323 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B T 106.6/133.4
C324 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 59/138.9
C325 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 60.6/139.8
C326 4030011220 S.CER GRM31M2C2H360JV01L B 61.5/144
C327 4030018010 S.CER ECJ0EC1H360J T 98.4/137
C328 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 105.4/133.9
C329 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 109.1/136.1
C330 4030011190 S.CER GRM31M2C2H270JV01L B 54/149.3
C331 4030017440 S.CER ECJ0EC1H221J T 60.6/140.7
C332 4030017650 S.CER ECJ0EC1H270J T 100.3/138.8
C333 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 105.2/138.4
C334 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 67.7/142.7
C335 4030017660 S.CER ECJ0EC1H330J T 29.1/152.3
C336 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 67.9/115
C337 4030017550 S.CER ECJ0EC1H1R5B T 12.6/132.7
C338 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 104.7/140.9
C339 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 10.6/134.3
C340 4030017550 S.CER ECJ0EC1H1R5B T 14.5/134.8
C341 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 65.9/142.7
C342 4030011070 S.CER GRM31M2C2H5R0CY21L B 25/152.6
C343 4030017550 S.CER ECJ0EC1H1R5B T 14.5/136.4
C344 4030017380 S.CER ECJ0EC1H050B T 100.4/144.6
C345 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 64.7/143.1
C346 4030011090 S.CER GRM31M2C2H7R0DV01L B 21.7/148.4
C347 4030011040 S.CER GRM31M4C2H2R0CY21L T 16/139.6
C348 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 100.7/149.7
C349 4030011040 S.CER GRM31M4C2H2R0CY21L T 16/146.6
C350 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 33.6/146.9
C351 4030017760 S.CER ECJ0EB1H222K B 111.5/89.8
C352 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 117.4/93.8
C353 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 110/95.4
C354 4030017760 S.CER ECJ0EB1H222K B 109.7/90.8
C355 4030018920 S.CER ECJ0EB1H392K T 114.9/92.6
C356 4030018920 S.CER ECJ0EB1H392K T 107.5/94
C357 4030016970 S.CER ECJ0EB1C223K B 107.8/91.7
C358 4030018080 S.CER ECJ0EB1H182K T 113.2/93.3
C359 4030018080 S.CER ECJ0EB1H182K T 106.2/94.3
C360 4030016780 S.CER ECJ0EB1C153K T 113.2/92.4
C361 4030016970 S.CER ECJ0EB1C223K T 113.1/86.9
C362 4030016780 S.CER ECJ0EB1C153K T 107.5/93.1
C363 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 51/18.9
C364 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 110/83.6
C365 4030018080 S.CER ECJ0EB1H182K T 114/85.9
C366 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 74.8/28.6
C367 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K T 111.8/94.5
C368 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 110.6/90.1
C369 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 110.9/94.5
C370 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K T 111.9/85.9
C371 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K T 104.4/95.9
C372 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 104.9/88.6
C373 4030018080 S.CER ECJ0EB1H182K B 103.7/91.6
C374 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 103.5/96.3
C375 4030016780 S.CER ECJ0EB1C153K T 112.8/91
C376 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 108.8/90.8
C377 4030016780 S.CER ECJ0EB1C153K T 104.8/93
C378 4030017790 S.CER ECJ0EB1E682K T 109.1/84.5
C379 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K B 104.6/90
C380 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 111.6/90.6
C381 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 104.4/91.8
C382 4030017790 S.CER ECJ0EB1E682K B 104.1/87.2
C383 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 105.3/86.7
C384 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 108.1/91.7
C385 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 20/46.3
C386 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 103.4/85
C387 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B B 24.4/51.8
C388 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 101.2/92
C389 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 105.3/86.4
C390 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 99/87.9
C392 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 22.8/46.8
C393 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C B 26/51.8
C394 4550003220 S.TAN TEESVA 1E 105M8R B 16.5/37.1
C395 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 22.8/45.9
C396 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B B 26.5/50.1
C397 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 28.6/46.4
C398 4030017500 S.CER ECJ0EC1H560J B 25.3/49.6
C399 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 109.7/87.2
C400 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 56.6/42.5
C401 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 31.2/45.2
C402 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K T 50.5/30.1
C403 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 56.3/73.6
C404 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 54/63.8
C405 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 20.5/40.9
C406 4030017380 S.CER ECJ0EC1H050B B 26/45.9
C407 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 53.7/37.4
C408 4030017620 S.CER ECJ0EC1H100C B 24.4/40.9
C410 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 22.6/40.9
C411 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 26.7/42.1
C413 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 31.3/50.9
C414 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 29.7/48.8
C415 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K T 29.5/48
C416 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 54/69.1
C417 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 51/37.4
C418 4030017440 S.CER ECJ0EC1H221J T 56.1/62.6
C419 4030017440 S.CER ECJ0EC1H221J T 54.8/61.6
C420 4030018890 S.CER ECJ0EB0J224K T 30.4/46.5
C421 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K B 27.7/49.9
C422 4030017620 S.CER ECJ0EC1H100C T 54.8/63
C423 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 54.1/40.9
C424 4550007260 S.TAN F931C475MAABMA B 53.8/44.1
C425 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K T 52.9/39.4
C426 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 54/60.9
C427 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 52.9/41.2
C428 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 56.1/59.4
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C429 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J T 51.9/44.4
C430 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 31.2/48.3
C431 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 31.6/46.5
C432 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 55.3/65.1
C433 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K B 56.3/70.2
C434 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 32.6/49.1
C435 4030017680 S.CER ECJ0EC1H820J B 55.8/68.4
C436 4550006050 S.TAN TEESVA 0J 106M8R T 56.9/65.9
C437 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 58.8/63.1
C439 4550007080 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 106M8R B 84.7/42.7
C440 4550007080 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 106M8R B 28.5/43
C441 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 33.5/49.1
C442 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 53.5/66.8
C443 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 86.7/43.7
C444 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 35.2/46.3
C445 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 61.5/69.3
C446 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 40/49.3
C447 4030016950 S.CER ECJ0EB1A473K T 25.1/43.5
C448 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 34.4/49.1
C450 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 7/36.8
C451 4550000530 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 104M8R T 24/36.8
C452 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 28.6/42.3
C453 4550003220 S.TAN TEESVA 1E 105M8R T 59.3/38.3
C454 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 6.1/36.8
C455 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 11.1/41.2
C456 4550006250 S.TAN TEESVA 1A 106M8R T 24/34.7
C457 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 38.3/38.6
C458 4550007260 S.TAN F931C475MAABMA B 7.4/43.2
C459 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K T 10.5/42.8
C460 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 8.5/63.4
C461 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 62.7/63.5
C462 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 61/67.8
C463 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 7.7/40.3
C464 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 35.1/38.1
C466 4510009120 S.ELE EEE1VA2R2NR B 76.5/34.8
C467 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 60.6/66.6
C468 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K B 11.7/68
C469 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 80.6/42.9
C470 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K T 5.6/38.5
C471 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 5.6/40.3
C472 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 65.6/66.8
C473 4550000560 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 334M8R T 31.7/34.7
C474 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B 37.3/45.4
C475 4030017440 S.CER ECJ0EC1H221J T 10.7/61.8
C476 4030017440 S.CER ECJ0EC1H221J T 9.4/60.8
C477 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J T 5.4/43.5
C478 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 9.3/68
C479 4030017520 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R3B T 39.7/36.9
C480 4030017620 S.CER ECJ0EC1H100C T 9.4/63.1
C481 4030007080 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 390J-T T 35/42.5
C482 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 42.2/40
C483 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B B 67.2/65.9
C484 4030009350 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 3R5B-T T 41.5/37.7
C486 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 8.3/59.8
C487 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 10.7/58.6
C488 4030007010 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 100D-T T 38.4/40.9
C489 4030007060 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 270J-T T 38.4/39.7
C490 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 37/45.5
C491 4030017680 S.CER ECJ0EC1H820J B 10.5/67.6
C492 4030006990 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 080D-T T 44.6/36.7
C493 4030007030 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 150J-T T 44.6/35.4
C495 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 13.5/62.3
C496 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 37/42.2
C497 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J B 73.7/66.5
C498 4030017340 S.CER ECJ0EC1H010B T 40.6/40.7
C499 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 41.6/45.9
C500 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B B 74.4/73
C501 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 35.7/44.6
C502 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 45.9/40
C503 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 18.2/68
C504 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 40/47.7
C506 4550006050 S.TAN TEESVA 0J 106M8R T 11.6/65.1
C507 4030017630 S.CER ECJ0EC1H120J B 72.4/74.9
C508 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 42/38.8
C509 4030017530 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R5B T 46.1/38.4
C510 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 10/64.3
C511 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 43.6/44.6
C512 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J T 41.6/46.8
C513 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 17.8/68.5
C514 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 67/81.1
C515 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 18.8/64.4
C516 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 44.1/46.8
C517 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 15.5/66.2
C518 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 64/81.1
C519 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 14.9/67.5
C521 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 45.8/45.2
C522 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 45.8/46.1
C523 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 20.8/66.8
C524 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 46.2/47.3
C525 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 63.1/92
C526 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 36.3/63.2
C527 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 44/63.3
C528 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 63.1/87.4
C529 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J T 35.1/63.6
C530 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 70.1/80.7
C531 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B B 21.7/65
C532 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 44/64.9
C533 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 44.9/67.6
C534 4030017650 S.CER ECJ0EC1H270J T 34.9/65.1
C535 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 43.9/69.4
C536 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 35/57.1
C537 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 74.1/81.6
C538 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 37.3/67.1
C539 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J T 34.9/66.6
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 10
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 36

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C540 4030017390 S.CER ECJ0EC1H180J B 28.8/65.8
C541 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K T 73.2/81.6
C543 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B B 29.5/72.2
C544 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B T 32.8/57.6
C547 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 34.7/68.3
C548 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 27.5/74.2
C549 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 17.5/81.4
C550 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 73.2/90.5
C552 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 14.5/81.3
C553 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 74.1/90.5
C554 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B T 32.1/63.2
C555 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 71.2/96.3
C556 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 69.9/96.3
C557 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 30.7/63.6
C558 4030017340 S.CER ECJ0EC1H010B T 30.7/65.2
C559 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 13.2/92
C560 4030017350 S.CER ECJ0EC1H020B T 30.7/66.8
C561 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 13.6/87.7
C562 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 39.9/65.5
C563 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 33.1/67.5
C564 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 20.6/80.9
C565 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 30.7/68.9
C566 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 42/69.1
C567 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 41.5/65.1
C568 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 33.1/68.8
C569 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 24.7/81.8
C570 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K T 23.4/81.8
C572 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 23.8/90.7
C573 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 35.2/70.4
C574 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 24.7/90.7
C575 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 21.6/97.1
C576 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 21.6/96.2
C578 4030012610 S.CER C2012 JB 1C 474K-T T 120.4/134.3
C579 4510006021 ELE 16 ME 2200 HC
C580 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 110.8/137.4
C581 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 18.2/19.5
C582 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 37.8/59.1
C584 4550002980 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 225M8R T 122.2/80.9
C585 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 121.2/89.2
C586 4550007080 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 106M8R B 105.2/127.1
C588 4030017390 S.CER ECJ0EC1H180J B 123.2/91.3
C589 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 14.4/26.5
C590 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 111.2/93.1
C591 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 10.9/16.1
C592 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 7.5/24.6
C593 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 126.6/18.3
C594 4030017510 S.CER ECJ0EC1H680J B 123.4/89.9
C596 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 121.9/87
C597 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 10.3/25
C598 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 99.5/130.4
C599 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B B 125/94.6
C600 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K T 121.6/72.3
C601 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 8.9/15.1
C602 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 97.3/121
C603 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 123.6/76.2
C604 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J B 127/81
C605 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 121.7/23
C606 4030012610 S.CER C2012 JB 1C 474K-T B 99.8/123
C607 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 122/24.8
C610 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 97.3/129.4
C611 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 102.1/15.7
C612 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR T 104.5/50.1
C613 4550007080 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 106M8R B 97.9/126.5
C614 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 113.6/90.1
C616 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 126.2/67.7
C617 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 115.5/63.5
C618 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 113.1/116.3
C619 4030016940 S.CER ECJ0EB1A393K T 14.8/27.4
C620 4030016940 S.CER ECJ0EB1A393K T 14.8/28.6
C621 4550006760 S.TAN TEESVB21A336M8R T 10.4/28.9
C622 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 116.5/128.5
C623 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 17.1/29.8
C624 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T T 19.2/29.9
C625 4550002980 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 225M8R T 25.8/28.8
C626 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 111.4/124.7
C627 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 107.9/62.6
C628 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 113.1/118.3
C629 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 112.9/125.1
C630 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 112.7/120.4
C635 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 23.1/24.4
C636 4030008680 S.CER C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T T 19.7/24.5
C637 4030008680 S.CER C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T T 25.5/24.2
C638 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 109.6/78.1
C639 4030016970 S.CER ECJ0EB1C223K T 110.2/80.7
C640 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 111.7/79.5
C641 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 33/20.9
C642 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 32.2/28
C643 4030017770 S.CER ECJ0EB1E332K T 110.1/76.9
C644 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 28.9/24.8
C645 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 29.7/23.9
C646 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 30.5/24.8
C647 4030017770 S.CER ECJ0EB1E332K T 110.5/75.7
C648 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 36.1/24.6
C649 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 35.3/19.6
C650 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 62.5/12.8
C651 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T T 110.4/96.8
C652 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 34.9/24
C653 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T T 114.8/97.4
C654 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 65.3/4.4
C655 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 36.5/26.9
C656 4550006250 S.TAN TEESVA 1A 106M8R B 31.6/21.8
C657 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 114.3/102.1
C658 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR T 117.1/108
C659 4030016970 S.CER ECJ0EB1C223K T 113.5/108.8
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C660 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J T 89.9/4.9
C661 4030018910 S.CER C1608 JB 0J 475K-T T 116.5/104.5
C662 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J T 89.9/11.1
C663 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 61.9/7.5
C664 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K B 116/32.7
C665 4510008500 S.ELE EEE1CA101WP T 125.7/43
C666 4030016970 S.CER ECJ0EB1C223K T 106/107.2
C667 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR T 106.3/110.4
C668 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 116.4/37.6
C669 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K B 117.2/34
C670 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 117.3/37.6
C672 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 99.4/35.6
C673 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 119.2/98
C674 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 115.4/41.3
C675 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K B 117.2/33.1
C676 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 121/35
C677 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 72.5/5
C678 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 41.5/10.9
C679 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 125.9/113.4
C680 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 120.9/107.2
C683 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K T 113/79.2
C684 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR T 97.2/21.8
C685 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR T 103.3/21.8
C687 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 64/17.7
C688 4030018900 S.CER ECJ0EB0J474K T 128.3/109.6
C689 4030018900 S.CER ECJ0EB0J474K T 123.2/110.9
C691 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 120.6/102.5
C692 4030017920 S.CER ECJ0EB1A683K T 114/75.1
C694 4030018900 S.CER ECJ0EB0J474K T 126.1/111.3
C695 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR T 116.8/72.9
C697 4550007080 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 106M8R B 75.6/8.4
C698 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 114.4/70
C700 4510008520 S.ELE EEE1CA470SP T 124.2/102.2
C701 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 67.5/17
C703 4510008130 S.ELE 16 CE 220 BS B 123.4/98.6
C704 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K T 127.5/114.3
C705 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 69.4/20.3
C706 4510008520 S.ELE EEE1CA470SP T 125/119.2
C707 4510008500 S.ELE EEE1CA101WP B 121.7/109.1
C708 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 112.8/32.4
C709 4510008870 S.ELE EEE1AA471UP B 112.1/109.1
C710 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 127.2/142.8
C711 4510008870 S.ELE EEE1AA471UP B 104.2/117.2
C712 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 107.1/145.9
C714 4510008500 S.ELE EEE1CA101WP B 114.2/117.2
C716 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 124.2/144.3
C717 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 59.6/20.7
C718 4510008130 S.ELE 16 CE 220 BS B 123/117.2
C719 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 119.3/143.3
C722 4550007080 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 106M8R T 56.7/16.1
C723 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 75.7/43.7
C724 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 82.4/35.4
C725 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 65/48.6
C726 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 75.9/45.5
C727 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 79.7/45.5
C728 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 65/49.5
C729 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 75.7/41.3
C730 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 78.3/39.4
C731 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 65.8/47.7
C732 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 90.5/36
C733 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 68.1/50.7
C734 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 57.6/43.9
C735 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 80.2/41.2
C736 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 67.4/45.9
C737 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 67.4/46.8
C738 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B B 70.3/52
C739 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 80.7/55.5
C740 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 64.6/46.4
C741 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J B 70.3/49.6
C742 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B B 71.5/49.1
C743 4030017680 S.CER ECJ0EC1H820J B 72.7/48.8
C744 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 72.3/45.5
C746 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C B 70.5/45.8
C747 4030017620 S.CER ECJ0EC1H100C B 69/40.9
C748 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 65/40.9
C749 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 64.6/42.1
C750 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 75.5/48.8
C751 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 71.3/42.1
C752 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 74.6/49.7
C753 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K T 74.2/48
C754 4030017730 S.CER ECJ0EB1E471K T 75.1/47.3
C755 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 75.1/44.1
C759 4550000530 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 104M8R T 68.6/37.2
C760 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 71.5/34.7
C761 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 74.6/34.2
C762 4550002980 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 225M8R T 68.6/34.8
C763 4550000530 S.TAN TEESVA 1V 104M8R T 78.4/34.8
C764 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 80.2/43.4
C765 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 81.3/45.5
C766 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 90.6/36
C767 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 86.6/35
C768 4030009570 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 0R3B-T T 83/41.4
C769 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 87.5/35
C770 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 84.9/38.5
C771 4030007020 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T 85.2/42.1
C772 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T T 88.5/40.7
C773 4030007040 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 180J-T T 89.2/38.8
C774 4030017620 S.CER ECJ0EC1H100C T 76.4/49.6
C775 4030017620 S.CER ECJ0EC1H100C T 77.6/49.2
C776 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 86.5/57.4
C777 4030017340 S.CER ECJ0EC1H010B T 90.3/40.7
C779 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 85.2/44.6
C780 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 90.3/43.5
C781 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 84.4/49.2
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 11
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 37

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C782 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 79.8/57.5
C783 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 90.3/44.4
C784 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 85.4/47.1
C785 4030017670 S.CER ECJ0EC1H390J T 85.4/63.8
C786 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 75.3/55.5
C787 4030017630 S.CER ECJ0EC1H120J T 83.7/60.9
C788 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 79.8/55.5
C789 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J T 85.4/65.4
C790 4030017390 S.CER ECJ0EC1H180J T 82.5/61.3
C791 4030017600 S.CER ECJ0EC1H080C T 83/62.6
C792 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 86.3/65.9
C793 4030017340 S.CER ECJ0EC1H010B T 88.8/46.6
C794 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 79.7/63.3
C795 4030017650 S.CER ECJ0EC1H270J T 85.7/67.4
C796 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 80.9/63.8
C797 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J T 88.8/48.2
C798 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 80.4/60.3
C799 4030017580 S.CER ECJ0EC1H060C T 79.7/64.2
C800 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 81.9/65.9
C803 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 90.1/55.2
C804 4030017640 S.CER ECJ0EC1H150J T 85.7/68.9
C805 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 75.3/58.6
C806 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 83.3/69.3
C807 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 81.9/67.5
C808 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 90.7/60.1
C809 4030017650 S.CER ECJ0EC1H270J T 75.7/67
C811 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 89/60.1
C812 4030017500 S.CER ECJ0EC1H560J T 77.9/66.7
C814 4030017340 S.CER ECJ0EC1H010B T 89.8/62.5
C815 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 86.2/70.7
C816 4030017650 S.CER ECJ0EC1H270J T 79.5/68.7
C817 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 79.7/67.4
C818 4030017390 S.CER ECJ0EC1H180J T 90.6/66.3
C819 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 83.6/55.5
C820 4030017390 S.CER ECJ0EC1H180J T 89.9/67.8
C821 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 77.5/61.4
C822 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 75.7/66
C823 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 75.3/62.6
C827 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 44.5/58
C830 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 37.5/55.2
C831 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 36.2/59.9
C833 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 44.4/55.7
C835 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 42/59.5
C836 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 114.3/127.7
C837 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 75.7/70.8
C838 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 75.1/40.4
C839 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 83.1/43.7
C840 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 46.5/63.1
C841 4030017590 S.CER ECJ0EC1H070C T 31.7/55.2
C844 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 30.9/57.8
C845 4050000280 S.FED CTH30V222S15A-TM T 87.3/113.6
C846 4050000280 S.FED CTH30V222S15A-TM T 43.5/117.5
C847 4050000280 S.FED CTH30V222S15A-TM T 119.7/129.4
C848 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 19/125.4
C849 4030011810 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 224K-T T 93.3/5.5
C850 4030011810 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 224K-T T 92.6/4.3
C851 4030011810 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 224K-T T 95.2/4.3
C852 4030011810 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 224K-T T 96.8/5.5
C855 4030018140 S.CER ECJ0EB1H391K T 61.4/15.6
C856 4030018920 S.CER ECJ0EB1H392K T 58.6/14.3
C857 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 71/15.8
C858 4030017430 S.CER ECJ0EC1H101J T 70.9/20
C859 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T T 75.6/20.4
C860 4030017920 S.CER ECJ0EB1A683K T 75.1/19.4
C861 4030018240 S.CER ECJ0EB1E562K T 70.4/18.8
C862 4030016950 S.CER ECJ0EB1A473K T 72.5/17.9
C863 4030018910 S.CER C1608 JB 0J 475K-T B 107.1/36.7
C864 4030018910 S.CER C1608 JB 0J 475K-T B 101.1/27.5
C865 4030018910 S.CER C1608 JB 0J 475K-T B 104.2/37.8
C866 4030017040 S.CER ECJ0EB1A333K T 64.4/23.1
C867 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 101.7/31.2
C868 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 66.9/92.4
C869 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 66.9/89.3
C870 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 17.5/92.6
C871 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 17.5/90.4
C872 4550007080 S.TAN TEESVA 1C 106M8R T 56.7/18.2
C873 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K T 102.2/30.1
C874 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 64.2/22.5
C875 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 52.2/26.8
C876 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 64.2/27.3
C877 4510009120 S.ELE EEE1VA2R2NR B 44.1/36
C879 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 58.3/22
C882 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 105.6/101.9
C883 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 90.9/93.9
C884 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 8.2/66
C889 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 16.7/60.4
C891 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 17.3/53.2
C894 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 62.5/50.2
C895 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 29.6/111.8
C896 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 47.2/58.7
C897 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 5.6/33.6
C898 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 93.4/14.2
C899 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 128.3/77.5
C900 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 126.7/78
C901 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 123.4/55.1
C902 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J B 123.4/51.9
C903 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 119.1/53.1
C904 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 121.2/55.2
C905 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 103.2/53.9
C906 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 103.2/54.8
C907 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 114/56.2
C908 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 108/52.5
C909 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 114.6/51.8
C910 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 114.6/50.9
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C911 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 111.7/53.7
C912 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 59.9/28.2
C913 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 114.3/98.8
C914 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 121.6/93.1
C915 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 125.8/79.4
C916 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 121.3/83.4
C917 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 115.4/89.4
C918 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 69.3/25
C919 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 101.3/25.9
C920 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 69.7/37.1
C921 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 71.2/34.2
C922 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 29.8/32.7
C923 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 30.7/36.2
C924 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 23.2/36.6
C925 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 67.2/36.9
C926 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 15.8/58.6
C927 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 7.6/55.4
C928 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 15.8/51
C929 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 7.6/47.9
C930 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 61/59.5
C931 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 61.6/52
C932 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 52.9/56.3
C933 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 52.9/48.8
C934 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 122.5/71.2
C937 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 30.2/109
C938 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 33/107.9
C941 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 71.1/137.5
C942 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 54/124
C943 4030018900 S.CER ECJ0EB0J474K B 122.4/82.8
C944 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 121.7/27.7
C945 4030017520 S.CER ECJ0EC1H0R3B T 38.4/37
C946 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 51.9/124.2
C948 4510009010 S.ELE EEE1AA221P T 86.4/16.8
C949 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 46.8/30.5
C950 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J T 89.7/49.1
C951 4030018890 S.CER ECJ0EB0J224K T 76/47.7
C952 4030017570 S.CER ECJ0EC1H040B T 36.4/137.1
C953 4030017360 S.CER ECJ0EC1H030B T 37.7/136.7
C954 4510009010 S.ELE EEE1AA221P
[TPE-01], [KOR-01], [AUS-01], [EXP-01] only T 13.2/36.6
RL1 6330001560 S.RLY ATQ206SA T 27.3/119.6
RL2 6330001560 S.RLY ATQ206SA T 64.7/122.9
RL3 6330001560 S.RLY ATQ206SA T 24.7/144.8
J1 6510014961 S.CNR B2B-ZR-SM4-TF (LF) (SN) T 48.3/136.1
J2 6510023110 CNR 3008L-8P8C <KIN>
J3 6510025950 CNR PCB-606 (6P6C) BLACK
J4 6510023161 CNR DN-508B-6-L <KOU>
J5 6450001430 CNR HSJ1462-01-010
J6 6510021970 S.CNR AXN330C130P B 123.5/35.9
J7 6510014961 S.CNR B2B-ZR-SM4-TF (LF) (SN) B 101/108.4
J8 6510025940 CNR PJ-3047S <XIN>
J9 6450001440 CNR HSJ1403-01-010
J10 6510025970 S.CNR 41-002AA-R <MRF> T 94.8/112.6
J11 6510025970 S.CNR 41-002AA-R <MRF> T 39.7/123.2
J22 6510025970 S.CNR 41-002AA-R <MRF> T 94.8/117
J23 6510025970 S.CNR 41-002AA-R <MRF> T 36.5/119.6
J24 6510016381 S.CNR 52465-1071 T 126.3/67.5
W1 8900016070 CBL OPC-1669
W2 8900016070 CBL OPC-1669
W5 7120000470 JMP ERDS2T0
W6 7120000470 JMP ERDS2T0
W7 8900016020 CBL OPC-1671
EP1 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 49.3/117.4
EP2 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 51.1/133.4
EP3 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 44.3/88.7
EP4 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 39.4/88.2
EP5 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 8.9/17.2
EP6 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 8/22.9
EP7 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 10.9/17.7
EP8 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 12.4/25
EP9 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 16/25.3
EP10 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 13.9/25.3
EP11 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 15/17.2
EP12 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 18.2/21.6
EP13 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 125.9/19.6
EP14 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 120.2/21.7
EP16 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 122.9/22.5
EP18 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 121.6/94
EP19 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 123.7/81.5
EP20 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 125.7/80.6
EP23 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 12.9/28.9
EP24 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 57.1/9.6
EP25 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/32.3
EP26 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.2/41.6
EP27 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.2/40.7
EP29 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.2/39.4
EP30 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/39.5
EP31 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 89.4/9.8
EP32 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 89/4.9
EP33 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/42.2
EP34 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/41.3
EP35 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/31.4
EP36 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/40.4
EP37 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 89.5/1.7
EP38 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/38.6
EP39 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/37.7
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6 - 12
M.
S.=Surface mount
H/V
LOCATION
Page 38

[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
EP40 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/36.8
EP41 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/34.1
EP42 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/35.9
EP43 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/33.2
EP47 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 45.7/57.9
EP48 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 91/61.3
EP49 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 121.3/152.3
EP50 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 109.4/155.1
EP51 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 119.3/144.2
EP52 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 128.6/143.6
EP53 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 126.3/144.3
EP54 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 113.9/138.9
EP55 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 108.6/147.8
EP56 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.3/38.5
EP57 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.3/37.6
EP58 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.3/36.7
EP59 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T B 117.2/36.3
EP60 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T B 117.2/35.1
EP61 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.3/34.3
EP62 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.3/33.4
EP63 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.3/32.5
EP64 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 119.3/31.6
EP66 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 127.7/35
EP68 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 41.6/14.3
EP69 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 52.6/10.4
EP70 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 45/8
EP71 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT T 47.5/130.7
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[VR1 UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R1 7210003250 VAR RV-320 (RK097221005H)
W1 8900016030 CBL OPC-1666 <TJM>
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[VR2 UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R1 7210003250 VAR RV-320 (RK097221005H)
W1 8900016030 CBL OPC-1666 <TJM>
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
S.=Surface mount
M.
H/V
LOCATION
6 - 13
Page 39

SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS
[CHASSIS PARTS]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
J1 6510004880 MR-DSE-01 1
J2 6510004880 MR-DSE-01 1
P1 6510009580 ZHR-2 1
SP1 2510001160 057P0802 1
MF1 2710000820 EFB0412VHD-6P38 1
W1 9016420020 23/04/140/B09/W01 1
W2 9016420010 23/00/140/B09/W01 1
MP1 8010020640 2969 CHASSIS 1
MP2 8210023550 2969 CHASSIS PANEL 1
MP3 8310068650 2969 MAGNET PLATE 1
MP5 8110009000 2969 U-COVER 1
MP6 8110009010 2969 L-COVER 1
MP7 8110009020 2969 FAN COVER 1
MP8 8930071460 2969 SP SPONGE 1
MP9 8930071380 2969 IC CLIP 1
MP10 8810009611 Screw M2.6X6 ZK3 17
MP12 8810008661 Screw BT B0 3X8 NI-ZC3 (BT) 11
MP13 8810008661 Screw BT B0 3X8 NI-ZC3 (BT) 4
MP14 8810008661 Screw BT B0 3X8 NI-ZC3 (BT) 4
MP15 8810009991 Screw BT B0 3X8 NI-ZK3 (BT) 5
MP16 8810010141 Screw PH M3X30 ZK3 4
MP18 8930014980 59 saran net 1
MP19 8930072260 2969 NET 1
MP20 8930071590 THERMALLY SHEET (BI) 1
MP36 8930016800 Thermal sheet (U) 1
DESCRIPTION
QTY.
[CONTROL UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
J5 6510025730 HJC0187-010024 1
DS1 5030003040 M6-0103TRM-5 1
S15 2250000570 SW-169 1
S16 2250000570 SW-169 1
MP1 8210023490 2969 FRONT PANEL 1
MP2 8210023500 2969 REAR PANEL 1
MP3 8310068780 2969 WINDOW PLATE (B) 1
MP4 8310068550 2969 WINDOW LINE 1
MP5 8310068560 2969 SUB RING 2
MP6 8310068570 2969 MAIN RING 2
MP7 8610013060 KNOB K-263 1
MP8 8610013070 KNOB K-263 (A) 1
MP9 8610013030 KNOB N-353 2
MP10 8610013040 KNOB N-354 2
MP11 8610013050 KNOB N-355 2
MP12 8310068600 2969 KNOB PLATE 2
MP13 8610011310 KNOB K-229 2
MP14 8610013100 KNOB K-229 (J) 2
MP15 8610013080 KNOB K-229 (K) 1
MP16 8610013090 KNOB K-229 (L) 1
MP17 8610013110 KNOB K-229 (M) 1
MP18 8210023540 2969 REFLECTOR 1
MP19 8930071250 2969 WINDOW SHEET 1
MP20 8930071430 2969 KEY SPONGE 1
MP21 8930071410 2969 KEY SHEET 1
MP23 8930006440 Push spring (F) 2
MP25 8830003020 bit insert SB-264540-CD 2
MP26 8610007510 knob spring NO.7800 2
MP27 8610007420 knob spring NO.6601 2
MP28 8830001010 HEX NUT (A) 2
MP29 8810009221 Screw BT B0 2X8 NI-ZK3 (BT) 8
MP30 8810009611 Screw M2.6X6 ZK3 2
MP40 8930071860 2969 LCD PLATE 1
MP41 8930072030 2969 LCD FILTER 1
MP42 8930072020 2969 LCD SHEET 1
MP44 8930072050 2969 RBEF SHEET 1
DESCRIPTION
QTY.
[VR2 UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R1 7210003250 RV-320 1
W1 8900016030 OPC-1666 1
DESCRIPTION
QTY.
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
J2 6510023110 3008L-8P8C 1
J3 6510025950 PCB-606 (6P6C) 1
J4 6510023161 DN-508B-6-L 1
J5 6450001430 HSJ1462-01-010 1
J8 6510025940 PJ-3047S 1
J9 6450001440 HSJ1403-01-010 1
W1 8900016070 OPC-1669 1
W2 8900016070 OPC-1669 1
W5 7120000470 ERDS2T0 1
W6 7120000470 ERDS2T0 1
W7 8900016020 OPC-1671 1
MP2* 8510018150 2969 B-VCO CASE 1
MP3* 8510014940 2601 VCO CASE 1
MP4* 8510018150 2969 B-VCO CASE 1
MP5* 8510014940 2601 VCO CASE 1
MP6* 8510016470 2775 VCO CASE 1
MP7* 8510016470 2775 VCO CASE 1
MP8* 8510018140 2969 S-VCO CASE 1
MP9* 8510018140 2969 S-VCO CASE 1
MP10 8510018160 2969 B-VCO COVER 2
MP11 8510014950 2601 VCO COVER 2
MP12 8510016460 2775 VCO COVER 2
MP13 8510016460 2775 VCO COVER 2
MP14 8930060270 2633 M-SHEET 2
MP15 8930059770 2633 M-HOLDER 2
DESCRIPTION
*: Refer to SECTION 8 BOARD LAYOUTS.
QTY.
[ACCESSORIES]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
MC1 Optional HM-133 1
F1 5210000080 FGB 20A 1
W1 Optional OPC-1132 1
W2 8900016370 OPC-1712 1
W3 8900016050 OPC-1663 1
MP1 8010016730 150 MOBIL BRACKET (SI) 1
MP2 8930041170 452 FELT (SI) 2
MP3 8820000530 Flange bolt M4X8 NI 4
MP4 8810000951 Screw BT A0 5X16 ZC3 4
MP5 8850000180 Flat washer M5 SUS 4
MP6 8850000500 S-washer M5 SUS 4
MP7 8810000471 Screw PH (+-) M5X12 ZC3 4
MP8 8830000250 Nut M5 SUS 4
MP9 8930007300 MIC hanger 1
MP20 8310068640 2969 CHASSIS PLATE 1
MP21 8810009611 Screw M2.6X6 ZK3 1
MP22 8010020830 2969 BRACKET 1
DESCRIPTION
W1
W2
W3
MC1
QTY.
[VR1 UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
R1 7210003250 RV-320 1
W1 8900016030 OPC-1666 1
DESCRIPTION
QTY.
Screw abbreviations A, B0, BT: Self-tapping PH: Pan head ZK: Black NI-ZU: Nickel-Zinc SUS: Stainless
7 - 1
F1
MP1
MP9
MP4
MP8
MP20
MP7
MP5
MP21
MP3
MP6
MP2
Page 40

MP5(C)
MP10(C)
MP9(CON)
MP3(CON)
MP23(CON)
MP7(CON)
MP10(CON)
MP9(CON)
MP5(CON)
MP11(CON)
MP9(CON)
MP28(CON)
MP4(CON)
MP6(CON)
MP5(CON)
MP10(CON)
VR1 UNIT
VR1(VR1)
MP1(CON)
MP28(CON)
MP11(CON)
MP12(CON)
MP13(CON)
MP6(CON)
MP14(CON)
MP15(CON)
MP16(CON)
MP23(CON)
MP8(CON)
MP21(CON)
MP17(CON)
MP14(CON)
MP13(CON)
MP24(CON)×2
MP29(CON)×4
MP2(C)
MP17(C)
EP1(U)
MP1(C)
MP3(C)
MP36(C)
MP9(C)
J2(C)
MP14(C)
MF1(C)
J2(C)
IC3 (M)
MP16(C)
MP7(C)
MP18(C)
MP14(C)
SP1(C)
SP1(C)
S15(CON)
MP18(CON)
DS1(CON)
VR2 UNIT
VR2(VR2)
MP18(CON)
S16(CON)
MP29(CON)×4
CONTROL UNIT
MP15(C)
MAIN UNIT
MP12(C)
MP6(C)
MP13(M)
W7(C)
MP15(M)
MP13(C)
MP20(C)
IC2 (M)
MP14(M)
MP15(M)
MP14(M)
MP11(M)
MP12(M)
MP19(C)
MP10(M)
Unit abbreviations (C) : CHASSIS PARTS
(CON) : CONTROL UNIT
(M) : MAIN UNIT
(U) : UT-123 (Optional product)
7 - 2
Page 41

SECTION 8 BOARD LAYOUTS
• MAIN UNIT (TOP VIEW)
0V 5V 01V 51V 02V 52V03V53V04V54V05V55V06V56V07V 57V 08V 58V09V 59V 001V 501V 011V 511V 021V 521V031V531V 041V541V051V 551V
H0H5H10H15H20H25H30H35H40H45H50H55H60H65H70H75H80H85H90H95H100H105H110H115H120H125H130
1
J5
J2
EXTMIC
MICE
EP37
CTHV
RD ATA
8V
GND
NC
C850 C851
• HM-133 (TOP VIEW)
R396
C470
C471
583R
774
C
Q67
R374
R369
C761
IC34
R376
C459
459C
R340
443R
R390
L115
D87
C945
D86
3
43R
26Q
733R
744C
16Q
R347
3R
55
IC17
263R
R849
C452
98D
D90
711L
4PM
C464
84C
1
5
304R
04R
283R
694
C
493
R
C488
C489
Q72
974
C484
024R
C498
04R
9
Q74
R421
C508
C482
79D
1
14R
R412
Q73
624R
Q76
C502
R427
905C
2
33R
C425
C427
R335
Q57
R327
R328
C734
64Q
863R
354C
Q43
C456
C473
L116
C451
R365
R846
R378
D91
C
1L
81
404R
C492
C493
314R
2PM
C759
C762 C763
968R
R694
C
R
067
696
R695
896R
148R
R697
C724
R
841D
307
R
C
767
967
C
011
Q
C
C676
R870
R848
C838
C729
IC42
121Q
Q109
C
037
2PM
007R
L144
537C
467
C
7
41D
207R
541D
C839
7C
86
D146
407
R
507
L145
C771
077
C
6
41L
R
C772
Q111
807R
377C
C780
417R
717R
777C
667C
R
276
978
878R
Q94
C674
R618
Q118
9
16R
D141
716R
Q97
R620
9Q
6
566C
C592
MICU/D
PTT
MIC
MICIN
07PE
R581
Q
19
C654
965R
095R
13CI
R591
106C
C
195
8
R
175
29Q
D140
885
R
96PE
C722
42PE
C856
39Q
R763
R764
R765
558C
667R
758C
6PE
5PE
7PE
11P
E
C597
126C
EP8
R529
735R
32P
E
35R335R
2
01PE
C589
C619
Q87
026C
725R
9PE
C623
8
35R
1
21PE
1
85C
Q88
09Q
1
46C
C363
45R
C624
265R
636C
R
545
R566
IC28
0
55R
C
536
065
945R
R
C637
R547
526C
R570
C642
03CI
4PM
C655
285R385R
485R585R
IC8
D92
2
04C
C30
C872
R768
R769
717
C
R
267
466R
066R
R785
R767
C866
84CI
I
15C
R628
R784
C862
R804
C918
C861
R
177
858C
R774
577R
R772
R773
C860
C859
9
9Q
C948
EP31
3PE
2
R759
266C
066C
R
857
C849
C852
NC
GND
TX D ATA
L163
C898
IC46
486
C
586C
J3
1
6
EP14
C605
R473
61PE
R497
R506
EP13
C
395
384R
R796
997R
R
008
IC50
516
R
R798
C919
C873
7
97R
861D
C607
958R
449C
761D
R490
561D
R858
R504
D
661
804R
L121
R402
L113
06
05
C927
R372
R406
49D
69D
434C
144C
844C
C446
R356
061D
201D
C894
39D
784C
C928
814R
R316
C931
R331
C926
R417
C891
59D
448C
C841
L162
445C
R441
C536
R750
944
R
D101
C830
285C
951D
401D
IC45
L161
C833
728C
EP47
R448
C932
28D38D
R322
C930
48D58D
0
33R
L120
924C
C929
R407
CI
41
514C
21
3R
024C
C401
C430
R325
C431
444
C
411L
105C
843R
94C
0
R349
Q
3R
C504
324
R
R748
C499
C512
115C
C516
R
234
R
334
C521
C522
425C
C933
R323
14CI
C
357
457C557C
586R
707R
C
5
687
C774
1
59C
577C
L147
C727
R699
C765
R701
R721
211Q
917R
R726
187C
C779
C784
527R
217R317
R728
L
051
R727
R723 R724
797C
397C
Q113
059C
C783
08C
IC43
287C
887C
937C
Q106
R711
817R
918C
R706
R710
D152
5
11Q
C776
D150
L160
IC44
C803
514R
R
588
C884
383R
C476
C480
R388
R400
Q117
R811
17Q
015C
574
793R
C
R419
C495
C889
Q69 Q70
C
605
414R
R422
893R
C503
2CI
255C
945C
R463
C564
075
C
965C
5PM
C
754R
IC62
1
38C
554R
538C
R747
824C
447
R
C798
R722
C811
C808
065C
565C
C755
855
L129
C554
L130
C529
C
625
6
34R
L
824R
MP5
064R
131L
9
01D
301D
725C
R752
048C
R307
488R
413R
C419
C422
R324
R317
814C
123R
R341
C437
R742
328C
R743
Q116
C821
C794
C799
L149
697C
151L
C790
197
C
MP3
787C
617
R
907
R
587C
D151
027R
737R
551D
C814
937R
84PE
L124
R465
L133
531L
C568
C563
D106
C547
C534
C539
R450
521
L
C
835
321
801D
R466
C562
L
431
C567
97Q
C566
535C
544R
235C
L159
4R
335C
64
C442
643
R
Q59
R345
23
4C
634C
R342
433R
C822
C809
R745
L158
L155
C812
1L
65
C817
L153
618C
R734
08C
0
7
08C
608C
251L
841L
C804
C795
987C
R741
97C
2
751L
751D
C820
C818
44C
375C
701D
R470
Q17
R20
Q13
21R
65Q
C403
Q53
503
R
Q54
3CI
C837
651D
R738
451D
D153
R733
C815
R8
8C
8PM
815
C
C
415
R453
R443
C530
14
5C
735C
431C
51Q
61C
R
71
21Q
3PM
D124
D125
D126
D132
D133
R881
C905
C906
R
628
216C
328R
C908
088R
75CI
288R
C
119
728R
C909
C910
R621
85CI
C903
R821
R822
409C
388R
435R
684R
R536
035R
C617
425
R
221D
355R
R866
R867
D134
168R
R557
D136
D137
D138
001Q
C698
R770
62CI
596C
125R
R523
225R
528R
R865
C600
C934
42J
538R
D127
D135
068R
D128
D129
D130
D131
D139
368R
R567
C643
836C
C639
746
865R
C
C640
R255
R627
386C
R644
296C
236R
5
46R
R
974
484R
R817
R818
R819
IC23
R476
R851
C584
306C
984R
6
38R
394R
C6
44Q54Q
Q18
C35
51C
9D
L3
1
74R
11R
L132
L136
R462
C561
955C
IC20
R792
R793
C870
C871
R464
R467
MP9
L
731
R469
5C
27
475C
21C
31C
C25
7D
L1
L6
D
01C
1
2C
R9
1R
8
53D
C575
C576
C
061
L47
431R
C163
L52
9PM
C9
D5466-B
)4(,6.1=t
C525
C528
R440
L126
IC19
C868
R790
C869
R791
MP8
R444
R447
721L
055C
C
355
L122
04D
C182
R461
6
3D
761
C
R139 R142
L48 L49
491C
1C
07
531R
73D
C
171
951C
791C
R
631
15L
961C
C168
31R
7
83D
655C
555C
8D
11C
C14
2L
01R
C26
D11
L5
L7
C34
2C
3
C39
R19
R24
C883
45CI
093C
IC12
C388
R290
4Q
C7
C389
R285
873C
R278
C
463
R
C370
R262
R276
Q41
C
563C
352R
1
52R
084R
284R
9
473C
C377
173C
183C
372R
082R
482R
53C
952R
452R
9
IC11
C356
C362
Q48
C384
993C
882
R
762
C380
R283
R265
R246
573C
163
Q50
472R
862
752R
R
R829
842R
C651
353C
375R
963C
R277
R258
C358
C360
C355
652R
742R
IC59
785R
763
C
275R
172R
685R
252R
C913
R862
C653
Q47
R272
R266
253C
C27
2C
4
L8
1R
4
62R
D14
D12
92C
64C
L10
L4
01
C55
23C
R23
C33
C37
R27
61D
L13
C
82
04C
C47
92R
Q4 Q9
1CI
35L
C175
C179
C185
541R
351R
C938
C189
C191
34D
951R
R757
02C
7
L57
R180
D4
C208
5
61R
Q32
812C
481R
R173
271R
R177
R175
C229
C233
C236
C257
252C
002R
C264
602R
862C
R183
691C
441R
C205
R147
R156
D45 D46
002C
341R
R150
C211
R160
45
L
L55
C
D13
C38
R30
C41
C45
R31
47R
R86
C108
51R
1
16R
016R
216R
806R
D51
L58
Q34 Q35
432C
R170 R171
2
312C
81R
R
461
5
D
222C
R187
L60
932C
D50
7
681R
12C
861R
6D
R191R192
322C
781C
R161
C206
D41
D44
657R
181C
881C
591C
L59
R155
R149
481
391
C
C215
R169
C36
D15
C49
L12
C56
L15
C50
L18
D17
C51
C62
R755
83
R
C63
R49
02Q
45R
R50
C75
55R
06
R
16R
C78
C90
42L
28C
91D
72L
C98
12
D
B1
C99
R81
C100
C101
8R
3
42D
C105
601C
5
11C
3L
3
72D
311C
43L
R93
12R
5
61Q
C17
C284
R609
R613
666C
33CI
C657
R592
C700
6C
828R
C661
395R
C658
R626
R631
C680
R639
Q102 Q103
R649
R663
R641
036R
R 856
356
82R
C48
L16
R35
C58
C937
36L46L
45D
C262
C258
85D
R
991
5
52C
42C
9
C237
352C
R195
L67L68
742C
342
C
R189
532C
Q33
R190
912C
442
C
R181
471R
67C
2D
1C
81
R
2D
8
611C
911C
C667
95
C689
C688
Q101
7R6R
11Q
378R
274
R
2
Q
2C
61
1D
R51
R39
71L
35
C
2
5R
R58
R
35
457R
Q19
C66
R48
16C
L21
14R
27R
4C
C895
C67
L20
04R
75C
46
C
C74
1D
R45
17C
C77
58C
37C
69C
D20
L31
D23
L23
D
62
79C
R78
81D
58R
C91
201C
R79
301
C
701C
29C
1LR
758R
A2
R
658
32J
J11
C846
R44
12Q
C153
EP1
R876
L74
D56 D57
6
22R
R225
83Q
D76
R239
C336
581R
D3
R179
242
C
5
6L
L66
C845
J10
101
011R
821C
0
41C
L41
931C
741
C
121R
L139
L141
Q123
88C
C285
L75
C295
0
7D
R223
C282
212R
092C
LR
2
R217
062C
D55
R203
C
652
C259
J22
R102
C126
2Q
9
411
R
R119
C
941
6C
81
C294
D60
C283
L71
L72
162C
C271
R208
762C
C321
632R
78L
332R
132R
223
C
992C
93Q
113C
403C
822R
18L
022
R
722R
R218
C300
122R
782C
L76
661L
46D
76D
C280
C292
R213
C
972
56D
A1
C291
R115
L39
901R
4L
3
R216
C293
882C
D63
44L
D69
66D
IC55
R871
R872
C630
R850
8
26C
041L
831L
R642
496C
C706
R625
C679
C704
R638
R
D22
R73
Q23
59C
R67
R70
D30
411C
C112
L32
C120
R94
C848
R98
D32
Q
R126
B2
C339
R80
L30
C72
L102
L105
L107
733C
043C
C117
R16
C
81
41Q
C152
R124
331C
301R
03
221R
343C
743C
C137
R113
3L
8
701R
211R
531C
Q28
R118
C136
R120
C146
841C
721C
801R
L42
L40
L
54
84D
6L
9
C952
94D
778R
L164
R204
359C
C251
L110
W5
W5
(MAIN UNIT)
943C
RL3
L100
C335
R
442
053C
08D
542R
Q40
R243
D53
R853
072C
578R
D169
17PE
J1
C94
EP2
C80
C946
249C
D68
C289
513C
922R
532R
R232
L85
613C
R234
903C
222R
Q37
C324
R237
C306
R230
R238
C331
C325
79L
L91
561L
87D
97D
C345
143C
0
42R
7
7D
C
433
L94
149C
R852
C225
R661
C712
W6
(MAIN UNIT)
6W
L109
R
242
843C
601L
55PE
EP50
94PE
D71
L78
C305
L82
913C
C312
713C
D72
C301
9
7L
912R
C313
68L
48L
D73
422R
C626
926C
C622
C847
723
C
9L
0
C332
C344
L93
823C
D74
L95
C323
38L
C329
703C
892C
875C
L103
89L
C338
333C
L99
085C
45PE
C719
EP51
987R
R659
R665
C716
EP53
C710
711D
25PE
J7
GND
1
2
J1 (CHASSIS)
SP1
J2 (CHASSIS)
J9
J8
DS1 DS2
V0 V5 V10 V15 V20 V25 V30 V35 V40 V45
0H5H01H51H02H52H03H53H04
• VR1 UNIT
(TOP VIEW)
• CONTROL UNIT (TOP VIEW)
1W
1R
0V5V
H5
H0
• VR2 UNIT
(TOP VIEW)
5V
B6647A
0
V
H5
H0
H10
73SD63SD53SD43SD33SD23SD13SD
H10
22SD
981R
93SD
DS3 DS4
32SD
01S
83SD
41S
HV
11SD
DS6
MC1
01SD
H54H05H55H06H
R188
DS5
52SD42SD62SD 92SD82SD72SD
12SD
56H07H57H08H
31S21S11S
6S5S 8S7S
51S 61S
0H5H01H51H02H52H03H53H04H54H05H55H06H56H07H57H08H58H09H59H001H501H011H511H021H521H031H531H041H
V0 V5 V10 V15 V20 V25 V30 V35 V40 V45 V50
DS8
DS7
8 - 1
Page 42

• HM-133 (BOTTOM VIEW)
[PTT]
B6094B
1
S1
41C
C12
3CI
72R
4D
3D
R42
C24
R35
Q5
21R
11R
72C
9R
Q4
01R
2
1D
34R
D5
94R
15R
05R
44R
6D
R25
R24
R23
D16
4R
2
H
MC1
MIC
MICE
• CONTROL UNIT (BOTTOM VIEW)
2
1
H 031H531H041H
11H 021H 5
731R
H 5
1
H011
H50
871R
831R
R130
R131
901C
14R
55H06H 56H07H 57H 08H 58H09H59H 001
H
931R
02H 52H03H 53H 04H54H05
01H 51H
0H 5H
V0V5V10V15V20V25V30V35V40V45
• MAIN UNIT (BOTTOM VIEW)
V551V
7R
Q2
Q3
91R
R18
6CI
C15
31C
IC1
X1
R45
1C
D17
Q6 Q7
41R
62C
51R
C47
21D
Q1
12R
8C
31R
5C
C55
C48
R177
77R
41Q
51Q
R76
R207
R211
61C
R125
R126
R127
R128
R129
R132
R122
R123
R196
781R
C107
C51
011C
34C
C
54
1X
C56
C24
IC3
52C
C46
22R
84R
74R
7D
64R
11D
3R
31R
61R
Q3
22R
401C
78C
171R
R172
01CI
17C
27C
571R
071R
802R
02D
C65
C59
C101
C57
C102
C111
C60
R191
R210
091R
31CI
402R
C42
C44
76C
9PE
102R
891R
991R
002R
R220
612R
27R
C95
C54
C68
6CI
05C
4D
C26
971R
081R
IC9
D9
Q31
R168
C105
IC12
R83
C69
72C
D10 D11
52R
42R
C10
R169
C7
C28
68C
C29
01PE
R6
R8
C25
14R
R36
R37
C5
J1
L1
C22
EP1
C19
C21
3
EP2
EP3
C17
C18
9C
01C
D18
L2
C16
EP4
Q8
C11
83R
• VR1 UNIT
(BOTTOM VIEW)
B6646A
R160
R162
R161
R163
R156
R158
R157
R159
R152
R154
R153
R155
R148
R150
R149
R151
R144
R146
R145
R147
C122
1L
121C
R140
R142
R141
R143
R133
R135
R134
71Q61Q91Q81Q12Q02Q32Q22Q52Q42Q72Q62Q92Q82Q
R136
J4 (CONTROL UNIT)
5
GND
LVOL
+3.2V
LSQL
1
+3.2V
• VR2 UNIT
(BOTTOM VIEW)
1R
R5
13C
R8
R4
7J 8J
26C
16C
R218
42D
R192
R2
R6
C70
87R
21PE
R14
5J
D1
C29
C23
Q9
Q1
2R
R39 R40
C30
5
GND
RVOL
+3.2V
RSQL
1
+3.2V
J3 (CONTROL UNIT)
671R
36C
46C
C116
C120
12D22D32D
311C411C511C
711C811C911C
41CI
912R
C4466-B
1C2C 3C4C
J5
HV 1
GND
RD ATA
TD ATA 4
01D
9D
2C
3J 4J
C74
371R
R174
R209
591R
43C
601C
312R
602R
502R
C108
302R
R212
202R
66C
D8
03C
13C
11PE
2
8
J2
MICU/D
MICIN
PTT
MIC
8V
EXTMIC
MICE
GND
1
142R
7
L108
643C
401L
C342
V0V5V10V15V20V25V30V35V40V45
0H 5H 01H 51H 02H52H 03H 53H 04H54H 05H 55H 06H56H07H 57H08
L101
08L
3C
0V5V
H0 H5 H10
69L
82C
1
1
6D
C297
L77
692C
303C80
033C
L92
623C
88
C314
L
813C
C310
C
023
57D
8L
9
D59
C266
2C
72
L62
8
81R
C
042
022
C
J9
C579
J8
1W
0V5V
H0 H5 H10
31V041V541V051
132C
25D
R178
372C
C265
C272
L73
682C
C275
26D
07L
02R
1
C
622
74D
C198
202R
3
62
C
R
902
R154
681C
C203
212C
93D
2
C202
61C
L56
C157
IC24
IC21
V
V5
031
R
091C
361R
751
51R
012
2
C
261
R
R158
C
902C
612
381
C
422
16L
C274
C
461
C161
661C
C174
3
L50
012R
C
71C
C214
C151
03
2
C
551
64L
C610
895C
774R
C836
206C
316C
584R
C606
Q81
685C
C711C714C718
D118
C
841R
671C
R167R176
661R
C199
C221
D42
C232
C238
R193
691R
C254
C154
J7
C709
C707
R647
C178
1
3Q
4CI
331R
502R
822
C
Q
63
142C
1
12R
491
R
791
R
C156
C278
R198
211D311D
5C
7Q
D120
5Q
Q
3
6Q
01Q
1C
R3
3C
C138
Q8
1Q
R874
R498
4R5R
R499
C882
R501
D119
48Q
005R
38Q
Q82
IC22
Q98
D142
326R
376C
63CI
C691
R635
EP18
307C
C599
051C
C144
EP4
341
C
13D
R128
C142
C145
521
R
EP3
R
921
561C
R138
141R
041R
C19
C246
C192
R261
R264
24
Q
R263
R294
R296
373C
182R
682R
C382
973C
C372
383C
572R
962R
753C
R270
R282
C
673
R249
453C
R525
R279
863C
153C
C590
015R
C614
R509
D164
719C
1
15R
215R
R831
585C
261D
C914
R475
R478
C596
R816
495C
C588
161D
4X
08V58V09V59V001V501V011V511V021V521
9R
2
88R
C111
D25
111R
L35
R90
C104
R106
R
401
5
21C
421C
711R
141C
231C
683C
R295
468R
R520
R832
518R
92L
19R
R
L36
C123
R116
R105
C131
77
62Q
C69
00
1R
C121
59R
C130
D29
L37
R96
C
R
901
98
79R
C110
72Q
R814
R812
R518
R833
C916
C943
91PE
184R
02PE
C915
C900
C604
998C
07
V
V57V
983
R
874
C
C491
C
64
8
R794
915C
924R
4R
03
3
15C
R438
C523
D100
FI6
C548
254
R
2
21C
L26
C
39
C87
C68
L22
R68
68C
C507
614R
C500
L119
C
921
97C
C
8
9
2
8R
38C
R75
R76
L28
52Q
R552
C
C543
R57
R64
Q22
07C
L19
R43
74R
36R
C
06
3R
614C
51
R
C435
3
34C
R795
C
64
7
C462
R
544C
83
0
973
R
R395
C472
D88
R399
FI5
794
C
L25
48C
22R
C81
66R
R59
45C
65R
L9
33R
56C
64R
11L
73R
95C
R558
R563
IC25
C616
038
R
83CI
06
V56
05V55V
3IF
3X
5
064
7
C
3R
C486
IC18
C517
R431
57Q
C515
434R
C531
R439
045
R336
R333
C387
L111
C398
C393
693C
C421
R309
C414
D81
C413
MP6
C896
FI1
2X
C
8
24
404C
03
6
IC15
C461
66Q
R381
R384
C483
C725
C728
R688
C733
R686
C738
C741
47C
2
1L
24
C743
C752
R
D143
C750
MP7
13C
34C
R556
R564
R561
C627
R813
R559
C907
R
868
R839
R838
R554
935R
045R
R516
805R
65CI
209C109C
028R
6X
V
4V
5
4IF
C458
583
C
292R
R287
R299
R338
C395
C392
X1
Q52
MP6
C406
023
R
R304
L112
793C
8
13R
R
83
6
4
74
C
86Q
R
773
R373
FI2
C424
047
086
C
R
C731
R678
R679
C736
C737
R690
X5
7PM
Q105
C746
R682
447C
L143
R681
Q104
486
776R
627C
C723
Q58
R
933
34C
C443
V04
V53
03
663R
C
798
454C
R358
Q63
054C
364C
R352
153
R
R
353
R367
C455
I
61C
892R
C405
C408 C410
R313
1
14C
044C
1Q
22
C457
Q65
46Q
R363 R364
R354
R310
Q55
324C
103
R
R306
004C
31CI
R293
947C
C747 C748
R683
C
157
R840
Q86
R
953
R514 R515
R519
R494 R495
7
15R
D121
493C
IC61
429
C
R801
R
548
R847
021Q
C922
448
R
C923
073R
R360
C877
908
R
C949
36CI
7
14C
913R
R302
113R
704C
R303
IC60
248R
529C
R843
0
29C
C921
9
11Q
9CI
R574
R
575
92CI
C644
C645
C646
R589
I
C652
25C
846
C
R578
C875
R808
708
R
IC53
219
C
R810
R
608
508R
C876
C366
C466
C469
9
237C
V0
2V52V
01V51
0V5
V
H0 H5 H10 H15 H20 H25 H30 H35 H40 H45 H50 H55 H60 H65 H70 H75 H80 H85 H90 H95 H100 H105 H110 H115 H120 H125 H130
J2
C
656
IC32
C649
208
775
R
R
R600
76C
8
C874
EP68
978C
R640
C687
7C
10
507C
R637
R643
495
R
C
C650
R
895R
R579
5
53CI
9Q
4
26R
R
687
79
6C
J4
366
416R616
C677
J5
923R
C864
C867
R788
16 15
GPSRXD0
GPSTXD0
GND
GPSRESET
GPSBOOT
GPSOPT
EP26
EP27
EP33
EP34
EP36
AMBECLK
CPU5V
C865
866C
076C
EP29
EP56
EP57
EP30
EP38
EP39
AMBEEPR
AMBERES
AMBESTB
RXCK
RXDT
DCEL
R777R778
C863
EP59
EP58
6J
EP40
EP42
OP+5V
TXDT
EP60
EP61
EP66
C5V
TXCK
C669
C675
EP62
EP41
EP43
DMOD
ACQ
IC49
387R287R
C708
466C
EP63
EP64
EP25
EP35
DAFOUT
AF
AMBETXD
DVC
787R
R779
R780 R781
73CI
30 1
BTONE
GND
NC
AMBERXD
NC
NC
J6
C611
3J
S-14325XH-P2
Printed in Japan
© 2007 Icom Inc.
8 - 2
Page 43

SECTION 9 BLOCK DIAGRAM
• BLOCK DIAGRAM (Left side)
W50
CONTROL UNIT
to VR1 UNIT
to VR2 UNIT
VR1 UNIT
LVOL
/LSQL
VR2 UNIT
RVOL
/RSQL
S15
A
B
COM
S16
A
B
COM
Q14:2SC4738
Q15:2SA1586
NOISE
FIL
IC21;TA7805F
5V
REG
Q82:
UNR9214J
PWR
CTRL
PWR
LSQL,LVOL
RSQL,RVOL
LDIAL_A
LDIAL_B
RDIAL_A
RDIAL_B
J4
1
2
3
4
5
J3
1
2
3
4
5
+3.2V
LCD_3V
REG
LCD_3V
LCD
MODULE
IC55:ZXCT1022
D164:MA2S111
CURRENT
DETECT
NOISE
FIL
Q83;2SA1588
D119;MA2S111
5VS
REG
Q84;2SA1588
D120;MA2S111
5VS
REG
Q81:2SB1132
VCC
REG
to CONTROL UNIT J4
1
2
3
4
5
to CONTROL UNIT J3
1
2
3
4
5
KEY
S5-8,S10-14
L_DIAL_SW
R_DIAL_SW
LSQL,LVOL
RSQL,RVOL
(12.288MHz)
X1
CR-839
PWR
IC14:TC7W04FU
VOLTAGE
D20:MA8130
UP CON-
D21:1SS372
VERTER
D22:1SS372
D23:1SS372
D24:1SS372
A_CS1,B_CS1
A0,D0-D5,D6(SCL)
D7(SI),/RES,WR(R/W),RD(E)
IC24;TA7808F
W1
W1
L_V/MHz
L_M/CALL
R_M/CALL
R_V/MHz
SET
DUP
TONE
LOW
PWR_SW
HV
IDET
CPU5V
5VS
L5V
5V
+8
REG
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
IC13:
M30620FCPGP
LPF
LPF
L5V
MUTE
DADJMUTE
L5V
IC37:
TC7W53FU
L5V
RSSI/LV
SELECT
VTX_C
5VS
RSSI/LVR_RSLV
SELECT
UTX_C
5VS
DA_SEL
DTCS
AMP
L5V
BUFF
IC49:
LMV358IPW
DDETMUTE
DDETSEL
L5V
OP+5V
VCC
IC60:
TC7W53FU
IC61:
TC7W53FU
IC51:
TC7W53FU
AF
SW
IC50:
LMV321IDCK
VAFO
UAFO
Q94:2SA1362BTONE
Q118:UNR9213J
REG
Q96:2SB798
Q97:2SC4738
D141:MA2S111
C5V
REG
DAFOUT
L_RSSI
L_LV
R_RSSI
R_LV
VDET
UDET
D5VC
D5VC
AMP
IC48 3/4:
LM2902PWR
AMOD
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J2
RX line
TX line
Common line
5VS
FANC
IC1:M62352GP
J5
to CONTROL UNITto MAIN UNIT
UATTC
5VS
D/A
L5V
D/A
IC54:M62352GP
J3
1
2
3
4
5
TXDATA
RDATA
CTHV
CTRL
Q14:2SC4738
R_RX140DA_CK
R_RX400
L_RX140
L_RX220
L_RX300
L_RX400
VD5C
UD5C
L5V
ATT
CTRL
Q16:2SC4738
CPU5V
LEVEL
CONV
IC46:
MAX3221IPWR
5V
LIMIT
D165,D166,
D167,D168:
1SS400
MATRIX
D124 - D139:
MA2S111
CPU5V
D161:HVC376B
D162:HVC376B
L140_R5
CPU5V
RESET
CPU5V
EEPROM
1/2
L5V
CL_SFT1/
L220_R5
L300_R5
L400_R5
5VS
REG
R_RX800
VATTVATTC
TX232
RX232
TX_DATA
R_DATA
RESET
SCL/SDA
CL_SFT2
X4
CR-841
19.6608MHz
R_BPF1
R_BPF2
R_BPF3
R_BPF4
PCON_U
PCON_V
PL_U
TX_MUTE
L_BPF1
L_BPF2
L_BPF3
L_BPF4
L400_S
IC23:S-80945CNMC
IC22:24LC512
R1,R2
R_UVCO_SEL,R_VVCO_SEL
L_LO_SW,R_DA_SEL
R_AFFILSEL,R_DET_MUTE
L_DA_SEL,L_DET_MUTE
CLOCK
SHIFT
CHASSIS UNIT
MF1
8V
VCC
5V
+3.2V
Q31:2SC4738
IC12:TC7S04F
D8 - D11:1SS400
PROTECT
AND
BUFF
CPU
1D_NEERG
1D_DER
VOLTAGE
TRANS-
DUCER
IC10:
LM2904PWR
CPU_TXD
CPU_RXD
DS31-DS37:
FAMG1211F
TDATA
RDATA
HV
RESET
5V
+3.2V
+3.2V
PWR
LCD
BACK
LIGHT
CURRENT
CONTROL
Q16-Q29:
2SC4738
IC9:S-80945CNMC
HV
HV
FUN
CTRL
Q21:2SC4738
Q123:2SB1132
D169:MA8075
DA_STB
DA_DATA
DA3_STB
DA_CK
DA_DATA
RS-232C
J5
1
2
3
4
5
66
RESET
5V
+5
REG
IC3;TA78L05F
+3
REG
IC6:R1111N321B
D4:MA8039
DRIVER
KEY
BACK
LIGHT
DS21-29,
DS38,39:
SML-512MW
HV
Q1:2SC4738
Q3:2SB798
D12:MA8068
To the microphone
UATTATT
D112:DAN222
REG
SEL
D113:DAN222
REG
SEL
Q3 - Q11
UNR9114J
L140_R5
R140_R5
L220_R5
L300_R5
VD5
UD5
R400_R5
L400_R5
R800_R5
L_VR5
L_UR5
CPU5V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
J8
J9
SP1
R_RX800IDET
CPU
IC25:HD64F2506FC26
MICIN
J4
CLONE_IN
CLONE_OUT
MIC
PTT
Q87:
2SC4738
56
34
12
L5V
8V
IC28: IC30:
TA75S558F
HPF
5VS
D121:MA2S111
PTT
MIC_PTT
DETECT
L5V
98_DATA
LEVEL
CONV
IC26:LMV321IDCK
D122:MA8047
VCC
IC38:
LA4445
AF
AMP
Q98:UNR9210J
D142:MA742
CLONE
MIC
AMP
DATAIN
AFOUT
DATAOUT
L5V
AND
SP
MUTE
MIC_PTT
98_DATA
DTCS
DTMF
P_PTT
P_SQL
AF_VOL_RES
AF_VOL_DATA
AF_VOL_CK
AF_VOL_STB
Q88:UNR9213J
IC36:
SN74AHC1G08
DTMSTB
DTMSD
5VS
CD4066BPWR
MIC SENS
SELECT SW
MIC_SENS
5VS
PACKET
SQL
CONTROL
Q93:
UNR9213J
D140:DA221
LIMIT
5VS
PACKET
DATA
SELECT
P_LR_SEL
L_R5C
R_R5C
R_AMC
L_AMC
PLLCK
PLLDATA
L_PLLSTB
R_PLLSTB
DA_CK
DA_DATA
DA2_STB
L_WXALT
L_DTCS_IN
R_WXALT
R_DTCS_IN
L_RSLV
R_RSLV
L_SQL
R_SQL
MIC
MUTE
MM_MUTE
5VS
Q92:
UNR9113J
5VS
P_LR_SEL
Q95:UNR9213J
IC35:CD4066BPWR
Q102:2SC4213
SP
MUTE
L_AF_MUTE
R_AF_MUTE
SP
MUTE
Q101:2SC4213Q103:2SC4213
L5V L5V
IC56:
BU8872FSDTMCK
DTMF
DEC
X6
CR-838
4.194304MHz
PACKET
PTT
DETECT
PACKET
AF
SELECT
Q95:UNR9213J
IC35:CD4066BPWR
L5V
ELEC.
DVDTMFSEL
Q43,Q44:UNR911NJ
Q45,Q46:UNR9114J
P_SQL
P_MOD_MUTE
IC33:
SM6451B
VR
IC58:
DET
SELECT
5VSL5V
REG
IC29:
TC7W53FU
AF
DCONT
5VS
PACKET
MODE
MUTE
IC31
CD4066BPWR
AF_VOL_RES
AF_VOL_DATA
AF_VOL_CK
AF_VOL_STB
ALC
AMP
1200_9600SEL
VAFO
UAFO
L5V
AF
MIXER
IC59
TC4S66F
ANALOGSW
DAFOUT
L5V
DET
SELECT
DTMFSEL
AN6123MS
5VS
Q90:UNR9213J
IC30:CD4066BPWR
PACKET
MOD
SELECT
IC57:
TC7W53FUTC7W53FU
L_R5
R_R5
R_AM
L_AM
IC32:
P_PTT
VDET
UDET
GPSBOOT
GPSRESET C5V
GPSOPT
GPSRXD0
GPSTXD0
AMBECLK
AMBERES
AMBESTB
AMBEEPR
AMBETXD
AMBERXD
DCEL
RXDT/RXCK
TXDT/TXCK
ACQ/DVC
IC52:
TC7W53FU
AF
SW
8V
Q99:
UMG9N
DA_SEL
DTCS
DTMF
CUTOFF
SHIFT
IC48 1/4,2/4:
LM2902PWR
HPF
AN
DMOD
CPU5V
OPTION
UT-123 UNIT
IC48 4/4:
LM2902PWR
Q100:Q86:2SC4738
UNR9213J
DTCS_SEL
IC34:
TC7W53FU
DADJSEL
DIGITAL
MOD SEL
DET
SELECT
L_RSLV
9 - 1
Page 44

• BLOCK DIAGRAM (Right side)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
5VS
MOD_DA MODSEL
AMP
IC53:
LMV321IDCK
DA_CK
DA_DATA
DA2_STB
VDET
UDET
VAFO
UAFO
IC9:
TC7S66FU
MOD
SELECT
L_LV
PLLCK
PLLDATA
L_PLLSTB
R_LV
PLLCK
PLLDATA
R_PLLSTB
D/A
L5V
IC63:
TC7S66FU
MOD
SELECT
IC8:
M62363FP
DAFOUT
Q119:
2SK1069
X5:CR-833
TCXO
DOM_FER_L
NOCFERL
DOM_OCV_L
8V
BUFF
D143
MA2S111
IC41: Q111:2SC5231
MB15A02PFV
12.8MHz
Q105:
2SC4738
X3
R_VCO_MOD
DOM_FER_R
NOCFERR
VAFO
UAFO
PLL
IC
Q104:
UNR911NJ
X3
REG
L_R5C
8V
Q120:
2SK1069
BUFF
D81:
MA2S111
IC14:
MB15A02PFV
15.3MHz
X1:CR-783
TCXO
5VS
R_R5
X3
Q52:2SC4738
8V
L_AFFILSEL
AF
FIL
8V
R_AFFILSEL
AF
FIL
L5V
Q47:XP6501
Q50:UNR9213J
Q48:XP6501
Q49:UNR9213J
IC42:TC7S66FU
Q121:UNR9213J
FILTER
SW
LOOP
FIL
135.575
–
255.575 MHz
8V
BUFF
Q112:
2SC5108
L5V
IC17:TC7S66FU Q65:XP4601
Q122:UNR9213J
R_PLLSW
5VS
PLL
IC
UMMUTE
MUTE
Q64:
UNR9213J
L_PLLSW
Q109:
UNR9213J
MUTE
FILTER
SW
LOOP
FIL
Q61:2SA1586
Q62:2SC4116
D86:DA221
L_WXALT
L_DTCS_IN
L_DET_MUTE
L_DA_SEL
VDET
R_WXALT
R_DTCS_IN
UDET
R_DET_MUTE
R_DA_SEL
L_VCO8
D145:HVC321B
D146:HVC321B
D147:HVC321B
VMMUTE
Q68:XP4601
VCO
SELECT
164.350–
220.350 MHz
Q72:2SC5231
D89:HVC362
D90:HVC362
353.65
523.170 MHz
Q73:2SC5231
D91:HVC375B
D92:HVC350B
D87:HVC321B
WXALT
FIL
5VS
Q41:
XP4601
CTCSS
FIL
5VS
IC11:
TC7W53FU
DIGI/AN
SELECT
WXALT
FIL
5VS
Q42:
XP4601
CTCSS
FIL
5VS
IC12:
TC7W53FU
DIGI/AN
SELECT
L_VCO8
REG
BUFF
L_VCO_SHIFT
Q58:
2SC4738
Q113:
2SC5231
Q110:UNR921NJ
D148:MA2S077
SHIFT
R_VVCO_SEL
R_UVCO_SEL
BUFF
–
BUFF
L5V
DET OUT
5VS
DET OUT
TC7W53FU
IC44:
UPC2709TB
Q74:
2SC5231
Q76:
2SC5231
D97:
MA2S111
IC13:
TC7W53FU
SELECT
IC16:
SELECT
AMP
L_VR5
L5V
L_VCO8
Q115:
UNR9213J
VT8
D155:1SV308
D157:1SV308
LO SW
D151:MA2S077
LO SW
D152:MA2S077
LO SW
D150:
L_UR5 L_UR5
MA2S077
LO SW
REG
D160:MA2S077
D102:MA2S077
8V
Q60:
2SC5108
L_AM
VCO
SW
VCO
SW
BUFF
L_WN_SEL
Q55,57:
XP6501
AM
DET
R_AM
L_LO_SW
L_R5
R_WN_SEL
Q63,67:
XP6501
AM
DET
REG
Q106:
UNR911NJ
AMP
UPC2709TB
R800_R5
D109:MA2S111
450kHz
FI2:
LT450EW
CERAMIC
BPF
WIDE/NARROW
L_SQL
L_RSSI
L_2ndLO 38.4MHz
450kHz
FI4:
LT450EW
CERAMIC
BPF
WIDE/NARROW
R_R5
R_2ndLO
ATT
L5V
5VS
IC45:
SW
FI1:
LT450HW
CERAMIC
SELECTOR
SELECTOR
45.9MHz
R_SQL
R_RSSI
HPF
BPF
FI3:
LT450HW
CERAMIC
BPF
IF IC
136.000–174.000MHz
141.150–221.145MHz
LPF
271.150–511.150MHz
LPF
79.150–121.150MHz
IC43:UPB1509GV
Pre
SCALER
R140_R5
Q59:UNR9213J
Q53:UNR9113J
Q54:UNR9210J
Q56:UNR9113J
D82:MA2S111
D83:MA2S111
D84:MA2S111
D85:MA2S111
IF IC
D93:MA2S11
D94:MA2S11
D95:MA2S11
D96:MA2S11
Q69:UNR9113J
Q70:UNR9210J
Q71:UNR9113J
Q117:UNR9213J
UAGC
VAGC
BUFF
D103:UT8
1SV308
LO SW
D159:
MA2S077
LO SW
D101:
MA2S077
LO SW
D104:MA2S077
LO SW
R400_R5
X2
JTB450C24
X3
JTB450C24
Q116:
2SC5108
IC18:
TA31136FN
IC62:
UPC2709TB
AMP
L_R5
R_R5
LPF LPF
HPF
LPF
400.000–469.995MHz
164.350–220.350MHz
856.350–1046.340MHz
763.650–953.640MHz
HPF
353.650–503.650MHz
RF
MUTE
Q79:UNR9213J
IF
AMP
Q66:
2SC4406
IC15:
TA31136FN
IF
AMP
Q75:
2SC4406
D153:MA2S077
LO SW
D154:MA2S077
LO SW
LO SW
D156:
MA2S077
D88:
DA221
LIMIT
D100:
DA221
LIMIT
AGC
D1–D
6:
MA2S728
HPFHPF
LPF
LPF
LPF
ATT
38.85MHz
FI5:
FL-408
Q15:2SA1362
Q12:UNR9213J
8V
VTX_C
8V
UTX_C UT8
ATT
UHFYGR
R140_R5 D107:
[USA]
[others]
D108:MA2S077
R400_R5
XTAL
BPF
46.35MHz
XTAL
BPF
FI6:
FL-409
VU1
UU1
VU2
VV
UV
V220
VT8
REG
Q17:2SA1362
Q13:UNR9213J
L_RXLO
MA2S077
LO SW
D106:MA2S077
LO SW
VT8
Q25 D75:L709CE
2SC3357
PRE
DRIVE
UT8
Q22REG
2SC5085
PRE
DRIVE
R_Lo
D29
MA2S111
LIMITER
D25
MA2S111
LIMITER
VVIF
Q27
2SC4703
Q26
2SC3357
UUIF
DRIVE
AMP
DRIVE
AMP
L140_R5
D38:MA2S077
R140_R5
D35:MA2S077
HV
LPF
IC4:NJM3404AV
Q31:UNR9113J
Q36:UNR9113J
APC
CTRL
PCON_V
D55:HVC350B
D60:HVC350B
RF
AMP
L_BPF2
D54:HVC350B
D58:HVC350B
RF
AMP
D47:MA742
D39:MA742
SWR
DET
D42:MA742
D52:MA742
SWR
DET
TX_MUTE
118–174MHz
D68:1SV172
BPF
L_BPF1L_BPF4
D70:1SV172
BPF
R_BPF1
IC3
S-AV32
PWR
AMP
D41:HVC350B
D44:HVC350B
RX
SW
D40:HVC350B
D43:HVC350B
RX
SW
R_BPF4
LPF
HV
IC2
S-AU82L
PWR
AMP
8V
TX_MUTE
PCON_U
VV
BPF
Q33:3SK318
L_BPF3
UV
BPF
Q32:3SK318
R_BPF3 R_BPF2 UATT
118–174MHz
Q39:3SK318
RF
LO SW
IC19:
SPM5001
L_RXLO
IC20:
SPM5001
VVIF
R_Lo
UUIF
D10:1SV308
D16:1SV308
D12:HVC375B
D14:HVC375B
RX
UUIF
SW
D7:MA2S077 Q19:3SK324
Q2:XP4601
5V
SHIFT
CTRL
R400_S
RX
VVIF
SW
D8:MA2S077
Q1:XP4601
5V
SHIFT
CTRL
L400_S
UUIF
R_BPF3
R_BPF4
D11:1SV308
D17:1SV308
D13:HVC375B
D15:HVC375B
L_BPF3
L_BPF4
VVIF
VVIF
R800_R5
RX
SW
BPF
BPF
D36:MA2S077
D37:MA2S077
R400_R5
RF
AMP
RF
AMP
Q18:2SC5231
D18:1SV308
D26:1SV308
D20:HVC375B
D23:HVC375B
R_BPF1
R_BPF2
D19:1SV308
D27:1SV308
D21:HVC375B
D24:HVC375B
L_BPF1
L_BPF2
ATT
ATT
RF
AMP
BPF
BPF
D45:HVC350B
D46:HVC375B
UU1
SHIFT D48,D49:
L400_R5
VU2
Q20:3SK324
SHIFT
RX
SW
RX
SW
ATT
AMP
VD5
Q29:3SK324
RF
AMP
UD5
D30:1SV172
ATT
UATT
375–550 MHz
D28:1SV172
ATT
VATT
375–550 MHz
BPF
L_BPF4 L_BPF3
BPF
HPF
TX/RX
ATT
VATT
ATT
V220
Q34:2SC5624
VU1
Q35:2SC5624
ATT
D59:L709CE
D77:MA2S077
SW
D64,D67:
MA2S111
LIMITER
D63,D66:
MA2S111
LIMITER
5VS
RX
SW
UD5
L220_R5
RF
AMP
L300_R5
RF
AMP
D53:MA2S077
D61:L709CE
D62:L709CE
TX/RX
SW
L5V
VD5
D65,D71:MA2S077
D72:1SV308
UD5
D69,D73:MA2S077
D74:1SV308
VD5
RL1:ATQ206SA
Q30:2SC4738
D32:MA2S111
D51:HVC350B
D50:HVC375B
L_BPF3L_BPF4
Q23:2SC5624
HPF
RL2:ATQ206SA
Q38:2SC4738
D76:MA2S111
RX
SW
Q37:3SK318
ANT
SW
ANT
SW
Q28:3SK324
174–260 MHz
BPF
BPF
RF
AMP
R_R5
RF
AMP
D56:MA2S077
D22:1SV308D9:MA2S077
LPF
HPF
L220_R5L220_R5
L300_R5L300_R5
LPF
L_R5
MA2S111
LIMITER
RX
SW
RX
SW
D78:MA2S111
D79:MA2S111
RF
LIMITER
AMP
(CHASSIS; J2)
LPF
5VS
RX
SW
RL3:ATQ206SAD57:MA2S077
Q40:2SC4738
D80:MA2S111
260–375 MHz
810–1000 MHz
RX
SW
HPF
ANT-2
ANT-1
(CHASSIS; J1)
9 - 2
Page 45

SECTION 10 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
10-1 CONTROL UNIT
2SC4738
R146
10K
680
R145
10K
1M
R41
CR-839
X1
33P
P71/RXD2/SCL
P70/TXD2/SD A
P67/TXD1
P66/RXD 1
P65/CLK1
P64/CTS1/RTS1
P63/TXD0
P62/RXD 0
P61/CLK0
P60/CTS0/RTS0
P57/RDY/CLKOUT
P56/AL E
P55/HOL D
P54/HLDA
P53/BCLK
P52/RD
P51/WRH/BHE
P50/WRL/WR
P47/CS3
P46/CS2
P45/CS1
P44/CS0
P43/A19
P42/A18
R14
DS33
FAMG1211F
GO
Q20
2SC4738
Q21
R147
680
R187
33P
C110
P72/clk2/TA1OUT
100K
2SC4738
10K
R148
R149
10K
R_DIAL_SW
10K
R122
0
P73/CTS2/RTS2
P41/A17
Q22
R150
680
L_DIAL_SW
24
25
P74/TA2OUT/W
P40/A16
52
51
G REEN_D1
RED_D1
R170
47K
R175
47K
C46
SW-169
Left
C47
COM
SW-169
Right
2SC473 8
R134
10K
LDIAL_A
LDIAL_B
RDIAL_A
RDIAL_B
PWR_SW
RESET
CPU_TXD
Q16
680
R135
R207
R220
CPU_RXD
CPU_TXD
2SC4738
Q17
R136
680
47K
F_CE
C70
GO
DS31
FAMG1211F
10k
3.2V
1k
R78
10K
0.001
R140
R72
C108
R212
R171
R172
4.7K
10K
1
C7 1
4
567
LM2904PWR
1
C72
R173
R174
12K
10K
S5
SKQDPA
S6
SKQDPA
S11
SKQDPA
S12
SKQDPA
S13
SKQDPA
S7
SKQDPA
S8
SKQDPA
S10
SKQDPA
0.01
S15
A
B
COM
0.01
S16
A
B
123
IC10
8
C74
L_V/MHz
L_M/CALL
DUP
TONE
LOW
R_M/CALL
R_V/MHz
LDIAL_A
LDIAL_B
L_DIAL_SW
RDIAL_A
RDIAL_B
R_DIAL_SW
R176
100
R133
10K
0.01
SET
C44
0.01
47K
R205
47K
2SC4738
R142
10K
680
R141
10K
0.001
C45
R202
R203
47K
R206
R213
R192
1k
Q18
R201
47K
47K
0
0.001
47K
R200
R204
47K
RD(E)
DS32
FAMG1211F
GO
2SC4738
Q19
R143
680
0.001
C42
47K
R199
47K
R198
WR(R/W)
B_CS1
S14
SKQDPA
C43
47K
A_CS1
0.001
C109
R144
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
GO
2SC473 8
Q23
R151
680
10K
R123
/RES
PWR
22
23
P76/TA3OUT
P75/TA2IN/ W
P36/A14
P37/A15
54
53
C106
DS34
FAMG1211F
19
20
21
P82/INT0
P77/TA3I N
P81/TA4IN/U
P80/TA4OUT/U
P32/A10
P33/A11
P34/A12
P35/A13
57
56
55
0.1
0.01
10K
PWR_SW
17
18
P84/INT2
P83/INT1
P31/A 9
VCC
59
58
C34
2SC473 8
R154
R152
680
R153
10K
R196
47K
15
16
P85/NMI
P30/A8(/-/D7)
VSS
62
61
60
DS35
FAMG1211F
GO
Q24
2SC4738
Q25
R155
680
RESET
L_V/MHz
0.01
C51
10KR132
0.1
C107
10
11
12
13
XIN14VCC
VSS
XOUT
RESET
P86/XCOUT
P26/A6(/D6/D5)
P23/A3(/D3/D2)
P24/A4(/D4/D3)
P27/A7(/D7/D6)
P25/A5(/D/D4)
66
65
64
63
CPU_RXD
10K
L_M/CALL
10KR131
7
8
9
CNVSS
P87/XCIN
P22/A2(/D2/D1)
P21/A1(/D1/D0)
67
69
68
1k
R195
A0
R83
2SC4738
R156
R157
10K
DUP
TONE
10KR130
10KR129
6
BYTE
P91/TB1IN/SIN 35P90/TB0IN/CLK3
P20/A0(/D0/-)
P16/D14/INT4
P17/D15/INT5
71
70
+3.2V
10K
Q26
R158
680
LOW
10KR128
4
P92/TB2IN/SOUT 3
P15/D13/INT3
72
R159
GREEN_D1
3
P14/D12
73
C105
DS36
FAMG1211F
GO
2SC4738
Q27
680
RED_D1
1
P94/DA1/TB4I N2P93/DA0/TB3I N
P95/ANEX0/CLK4
P96/ANEX1/SOUT4
P97/ADTRG/SIN4
P104/AN4/KI0
P105/AN5/KI1
P106/AN6/KI2
P107/AN7/KI3
P13/D11
75
74
1
2
3
0.001
2SC4738
10K
R160
R161
10K
P100/AN 0
P101/AN 1
P102/AN 2
P103/AN 3
P00/D 0
P01/D 1
P02/D 2
P03/D 3
P04/D 4
P05/D 5
P06/D 6
P07/D 7
P10/D 8
P11/D 9
P12/D10
M 30620FCPGP
IC9
OUT
VDD
VSS
S-80945CNMC
Q28
R162
680
AVCC
VREF
AVSS
IC13
MA8039
CD
NC
2SC4738
Q29
R163
680
D4
5
4
DS37
FAMG1211F
GO
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
C50
C26
SET
R_V/MHz
R_M/CALL
10K R126
10K R127
10K R125
1k
R190
0.01
D8
0.033
D9
R210
100k
R191
+3.2V
1SS400
LVOL
LSQL
RVOL
RSQL
1k
1SS400
R216
100kR211
D6(SCL)
D7(SI)
C54
SML-512MW
SML-512MW
SML-512M W
/RES
47K
C16
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
22
HV
SML-512MW
SML-512MW
RSQL
RVOL
C4
VOUT
NC
R1111N321B
R179
47K
RSQL
RVOL
R138
LSQL
1
0.
7.5mA
680
LVOL
IC6
GND
VDD
DS24
DS25
CE
R180
PWR
C1
C2
SML-512M W
SML-512MW
C5
0.1
C3
R4
10K
R8
10K
0.1
1
2
3
2SC4738
Q31
27K
R13
10K
100P
DS21
DS26
7.5mA
680
R139
2SC473 8
Q1
10
+3.2V
R76
100K
J4
B5B-ZR-SM4-TF
1
R6
2
10K
3
R2
4
10K
5
0.1
0.01
C86
1
2
3
4
5
J3
C87
0.01
B5B-ZR-SM4-TF
0.01
C67
SML-512M W
SML-512MW
7.5mA
1.2K
R188
HV
R22
C8
R21
67
67
W1
10
C56
DS22
DS23
R77
R178
W1
1
2
3
4
5
R168
DS38
SML-512M W
SET S10
470K
D1 2
MA8068
2.2K
2SA1586
Q15
470K
100K
SML-512MW
7.5mA
1.2K
R189
2SB798
Q3
+9.3V
R177
PWR S14
DS39
10K
Q14
2SC4738
LCD_3V
C48
C104
0.1
C55
VR1 UNIT
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
R1
VR2 UNIT
1
2
3
4
5
5V HV
100
47K
1
2
3
C24
C25
IC12
TC7S04F
R1
TA78L05FIC 3
G
0.01
5
4
0.01
LCD_3V
R208
100k
1SS372
C118
0.1
1SS400
1SS400
D22
R24
D20
C114
R25
MASTER
LCD_3V
2.2 MSVAC59
2.2 MSVAC101
2.2 MSVAC57
2.2 MSVAC102
MA8130
0.1
10K
10K
SLAVE
C119
0.1
D23
1SS372
C115
R169
2.2 MSVAC111
0.22 SV AC60
0.22 SV AC61
0.22 SV AC62
0.22 SV AC63
0.22 SV AC64
2.2 MSVAC95
1
C66
R209
100k
LCD_3V
1k
R218
C116
0.1
0.1
D24
1SS372
C120
0.1
18K
C7
1SS372
MMZ1608Y102B T
EP12
MMZ1608Y102BT
EP11
MMZ1608Y102BT
EP10
MMZ1608Y102BT
EP9
C30
C31
C29
47P
47P
0.001
47P
47P
C10
A_CS1
1
C65
22
L1
10U
1
1
C121
C122
R219
47K
IC14
8
1
7
2
6
3
5
4
TC7W04FU
IO
C_10_25V_EEE-S_C
C28
0.001
C27
10
C69
0.01
C117
0.1
D21
5V
C113
0.1
D10
D11
B_CS1
/RES
A0
W R(R/W)
RD(E)
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6(SCL)
D7(SI)
DS27
DS28
7.7mA
DS29
390
R137
4.7
5
4
0.01
C68
NC
FR
NC
CL
/DO F
04-6240-034-001-800
J7
34
36
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
VDD(3.18V)
16
15
A_VOUT(11.1V)
14
A_CAP5+
13
A_CAP3+
12
A_CAP1-
11
A_CAP1+
10
A_CAP2+
9
A_CAP28
A_CAP4+
7
A_V4 (1.01V)
6
A_V3 (1.98)
5
A_V2 (6.84V)
4
A_V1 (7.82V)
3
A_V0 (8.78V)
2
C86
35
1
P/S
04-6240-034-001-800
J8
34
36
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
VDD(3.18V)
16
15
B_VOUT(8.34V)
14
B_CAP5+
13
B_CAP3+
12
B_CAP1-
11
B_CAP1+
10
B_CAP2+
9
B_CAP28
B_CAP4+
7
B_V4 (1.01V)
6
B_V3 (1.98)
5
B_V2 (6.84V)
4
B_V1 (7.82V)
3
B_V0 (8.78V)
2
C86
35
1
P/S
J5
TDAT A
4
RDAT A
3
GND
2
HV
1
HJC0187-010024
*; Refer to “PARTS LIST.”
10 - 1
Page 46

10-2 MAIN UNIT (1)
OPC-465
MICU/D
EXTMIC
MICIN
HSJ1462-01-010
J5
CTH30V222S15A
C847
HV
W50
8V
PTT
MICE
MIC
GND
3008L-8P8C
PCB-606
IC21
TA7805F
I O
0.47
C578
HVC376B
R476
J2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
MMZ1005Y102CT
6
5
4
3
2
1
J3
G
IC22
1
A0
2
A1
3
A2
4
VSS5SDA
24LC512T
22K
R475
C588
18P
D162
R816
100K
0.01
C900
C585
4.7K
C603
C584
2.2 MSVA
4.7K
R494
MMZ1608Y102BT X8
EP5
EP6
EP7
EP8
EP9
EP10
EP11
EP12
C581
MMZ1005Y102CT
EP32
EP31
EP37
C660
22P
C662
6
TXDATA
5
RDATA
4
GND
3
CTHV
2
1
RD20E
D118
D117
C;4.95V
C5800.1
VCC
WP
SCL
C914
22K
R478
68P
C594
D161
HVC376B
C596
0.001
1
0.001
2
3
S-80945CNMC
C589
47P
0.001
R759
100
22P
MMZ1608Y102BT
C579
2200
DSA3A1
C58610
EP18
CPU5V
8
C590
7
6
0.1
X4
CR-841
R481
1M
4P
C599
R815
100K
C899
0.01
RESET
IC23
CD
OUT
VDD
VSS
NC
R484
R479
1k
R495
1k
MICU/D
0.001
C592
C591
0.001
0.22
1
C849
2
3
C850
4
0.22
5
C851
6
0.22
7
C852
8
0.22
MMZ1005Y102CTEP16
1kR473
MMZ1608Y102BTEP14
EP13
To the CONTROL UNIT
0.001
C836
MMZ1005Y102CT
47K
0.1
R482
R480
22P
C604
CL_SFT1
CL_SFT2
0.001
5
4
0.033
C600
100K
MIC_SEL
MICUD
C897
0.001
C597
0.001
IC46
EN
FORCEOFF
C1+
V+
C1C2+
FORCEON
C2V-
INVALID
RIN9ROUT
MAX3221IPWR
100
R758
C593
R477
47K
10K
CLONE_OUT
CLONE_IN
AF_VOL_CK
AF_VOL_DATA
AF_VOL_STB
AF_VOL_RES
L_AF_MUTE
MIC_PTT
NMI
MD2
MIC_PTT
RESET
L_SQL
CL_SFT2
CL_SFT1
GPSRESET
R_SQL
DCEL
ACQ
98_DATA
NMI
MD2
RESET
0.001
C601
VCC
GND
COUT
DIN
47P
2SB1132
UNR9214J
C934
220
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
C898
Q81
0.001
0.1
L163
C948
VCC
C598
0.1
Q82
R819
R836
100
ICU and Flash
CF20OPEN
CP1
*R883
TX232
10U
R483
0.1
C602
R485
SCL
SDA
PWR
R831
100
R833
100
47K
R818
RX232
1
R490 10K
47P
C605
0.47
1.5K
MA2S111
D119
4.7K
MA2S111
D120
100
R511
R512
47K
R817
100
R489
R835
100
J24
12
34
56
78
91 0
52465-1071
C944
47P
IC24
TA7808F
I O
C606
100
100R832
47K
R851
EP19
EP20
R858
470K
1SS400
D165
R859
470K
1SS400
D167
0.01
R497 4.7K
C607
C622
0.001
G
Q83
2SA1588
4.7K
R498
470
R499
R500
470
R501
R509
R510
C917
XIN
0.1
C916
C915
47K
MMZ1005Y102CT
MMZ1005Y102CT
XOUT
10K
R865
TX_DATA
100
2SA1588
Q84
NTCG10
39K
0.1
C943
10K
R866
R_DATA
R506
R504
0.1
10
10
C614
0.1
0.47
R867
10K
1SS400
1SS400
C610
0.1
10K
D166
D168
ZBFS5105
L138
ZBFS5105
10
C611
C612
TEMP
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
ZBFS5105
L140
L139
ZBFS5105
C613
0.001
C629
D164
MA2S111
AVcc
P50/TxD2
P51/RxD2
P52/SCK2
PF0/BREQ/IRQ2
PF1/BACK/BUZZ
PF2/WAIT
PF3/LWR/ADTRG/IRQ3
PF4/HWR
PF5/RD
PF6/AS
P1Vcc
PF7/FAI
Vss
TEST
VCL*
OSC2
OSC1
NMI
MD2
XTAL
Vss
EXTAL
Vcc
MD0
MD1
STBY
RES
P20/TIOCA3
P21/TIOCB3
P22/TIOCC3
P23/TIOCD3
P24/TIOCA4
P25/TIOCB4
P26/TIOCA5
P27/TIOCB5
C616
0.1
ICURX
ICUSCK
ICUTX
L141
100
R830
100
R508
TXDT
TXCK
MA2S111
22K
10K
C618
0.001
C626
L_DTCS_IN
R525
100
D121
R514
R515
L_WXALT
72
109
R517
2.2K
LOAD
5
0.001
R_WXALT
R_DTCS_IN
68
Vref
P43/AN369P42/AN270P41/AN171P40/AN0
P17/TIOCB2/TCLKD
P16/TIOCA2/IRQ1
P15/TIOCB1/TCLKC
P14/TIOCA1/IRQ0
P13/TIOCD0/TCLKB
110
111
112
113
100 R516
RXDT
RXCK
AMBERES
100K
R519
Q86
2SC4738
ZXCT1022
L_RSLV
R520100
67
AVss
P12/TIOCC0/TCLKA
114
115
AMBECLK
VOUT4VIN
GND
NC
IC55
MICUD
R_RSLV
DTMSTB
ID ET
P11/TIOCB0
P10/TIOCA0
Vss
116
117
118
AMBEEPR
AMBESTB
3
2
1
P2Vcc
P37/TxD4
119
GPSTXD0
61
120
GPSOPT
R518
100
P91/AN962P90/AN863P47/AN764P46/AN665P45/AN566P44/AN4
P36/RxD4
P35/SCK1/SCK4/SCL0/IRQ5
P34/RxD1/SDA0
121
122
R540
100
GPSRXD0
R_DATA
R521
120K
R522
12K
R523
330K
0.001
C628
C630
DTCS
DTMF
M IC_SEL
DA3_STB
54
55
56
57
Vss
P95/AN1358P94/AN1259P93/AN1160P92/AN10
P97/AN15/DA1
P96/AN14/DA0
IC25
HD64F2506FC26
P33/TxD1/SCL1
P32/SCK0/SDA1/IRQ4
P31/RxD0
P30/TxD0
P77/TxD3
123
124
125
126
127
128
R539
100
TX_DATA
RX232
ICUTX
ICURX
ICUSCK
TX232
C;7.88V
R529
1k
33 MSVB2
C619
0.039
0.1
C617
1
3
10K
R524
D122
MA8047
R850
180K
0.1
DA_STB
GPSBOOT
L_AFFILSEL
R_AF_MUTE
P76/RxD3
P75/TMO3/SCK3
P74/TMO2/MRES
P73/TMO1/CS7
129
130
131
132
R553
100 R825
100
AMBERXD
AMBETXD
DA_CK
DA_DATA
MMZ1005Y102CT
EP23
C621
C620
0.039
R527
4.7K
IC26
5
4
2
LMV321IDCK
P72/TMO0/CS6
R871
100K
R872
R2
R1
D5VC
L_DA_SEL
R_AFFILSEL
L_DET_MUTE
R_DET_MUTE
46
PJ747PJ648PJ549PJ450PJ351PJ252PJ153PJ0
P71/TMRI23/TMCI23/CS5
P70/TMRI01/TMCI01/CS4
PG4/CS0
PG3/CS1
PG2/CS2
PG1/CS3/IRQ7
PG0/IRQ6
PE0/D0
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
100
R493
R554
100
DVC
DA2_STB
R_R5C
R400_S
R_RX800
100
33K
R532
68K
R538
R533
470K
R530
22K
100 R812
PE1/D1
141
142
R838
R_AMC
R537
2SC4738
Q87
C623
0.1
4.7K
R_DA_SEL
38
PH739PH640PH541PH442PH343PH244PH145PH0
PE2/D2
PE3/D3
143
RPT_MUTE
27K
L_LO_SW
R_VVCO_SEL
37
PA7/A23
PE4/D4
144
P_LR_SEL
SUB_SEL
C624
R_UVCO_SEL
100
R541
R814
100
100 R839
P_MOD_MUTE
1
2.2 MSVA
22K
R545
L_PLLSW
R552
PA6/A22
PA5/A21
PA4/A20
PA3/A19
PA2/A18
PA1/A17
PA0/A16
PB7/A15
PB6/A14
PB5/A13
PB4/A12
PB3/A11
PB2/A10
PD7/D15
PD6/D14
PD5/D13
PD4/D12
PD3/D11
PD2/D10
DTMSD
15K
100
PB1/A9
PB0/A8
PC7/A7
PC6/A6
PC5/A5
PC4/A4
PC3/A3
PC2/A2
PC1/A1
PC0/A0
PD1/D9
PD0/D8
PE7/D7
PE6/D6
PE5/D5
DTMCK
C625
R547
P1Vcc
HV
C661
0.1
14
13
12
11
10
9
C651
1
C647
0.0033
R579
10
DATAIN
C653
0.0033
8V
15K
R623
100K
0.0056
15K
220K
220K
R627
3.9K
R784
R772
C860
1
3
C678
UNR9213J
100K
470
0.068
UMG9N
DTMSD
DTMCK
DTMSTB
R868
0.033
Q100
15K
R773
C859
5
2
R799
220K
10
D142
MA742
1
2
3
SN74AHC1G08DCK3
C679
0.1
C680
0.1
R632
39K
C683
R637
15K
10
R640
C687
5.6K
C857
2.7K
R775
1
5
Q99
IC50
4
100K
UNR9210J
Q98
AF_VOL_CK
AF_VOL_STB
AF_VOL_DATA
C673
10K
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
100K
DCEL
RXDT
EP39
EP30
EP38
11
12
13
AXN330C130P
20
19
18
EP29
EP57
EP56
AMBERES
AMBESTB
AMBECLK
220K
R878
C666
RXCK
TXDT
EP42
EP40
10
9
22
21
EP59
EP58
AMBEEPR
M PZ1608S221A
C669
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10
C667
0.022
DVC
ACQ
TXCK
EP41
EP66
EP43
6
7
8
25
24
23
EP61
EP62
EP60
C5V
DMOD
470P
IC35
I/ O1
O/I1
O/I2
I/ O2
CONT2
CONT3
VSS8I/ O3
CD4066BPWR
10K
R608
R609
27K
AMBETXD
AMBERXD
EP25
EP35
4
5
27
26
EP63
EP64
BTONE
DAFOUT
VDD
CONT1
CONT4
I/ O4
O/I4
O/I3
R610
R611
3
28
C672
R593
680
R828
0
10
C658
4.7
R590
MRIPT
R591
1
0
C650
2.2M
R600
2.2M
2.2M
C659
0.022
RPT_MUTE
R614
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
C913
2.2M
Q95
UNR9213J
IC33
SM6451B
0.001
GPSRXD0
GPSTXD0
RSTN
ADRS1
MLEN
ADRS2
DVDD
ROUT
LOUT
LIN
AVDD
VRL9VRR
4
5
IC59
123
47K
R864
MMZ1005Y102CT
EP26
EP27
R616
10K
MDT
MCK
DVSS
RIN
AVSS
R829
TC4S66F
GPSOPT
GPSRESET
GPSBOOT
EP34
EP36
EP33
14
1516
17
MMZ1005Y102CT
D5VC
1200_9600SEL
R879
220K
0.001
10K
R612
R613
27K
27K
CLONE_IN
CLONE_OUT
1
2
2SA1362
Q94
J6
30
29
OP+5V
M PZ1608S221A
470
R619
Q118
UNR9213J
0.01
0.1
C668
C670
2SB798
Q96
D141
C5V
MA2S111
100
C665
470P
C664
C675
0.001
14
13
12
11
10
9
5
6
7
8
470P
TC7W53FU
A
CH1
CH0
VCC
3.3K
R617
GND
4
VEE
3
INH
2
COM
1
IC34
R615
2.2M
0.1
C677
R618
C674
Q97
2SC4738
L_AF_MUTE
R_AF_MUTE
DTCS
DTCS_SEL
R624
100
47K
0.001
18K
R804
R628
0.001
C676
R620
10K
1M
R621
C861
C862
0.047
R774
LMV321IDCK
R797
R796
2.2M
R798
1
C873
R800
220K
C;4.87V
IC36
5
4
R630
330K
R625
47K
R631
330K
R626
47K
10K
C692
0.068
R643
100P
220K
R766
470K
100P
C858
1
2
34
0.001
C919
SD
9
NC
10
ACK
11
NC
12
NC
13
EST
14
NC
15
VDD
16
R635
330K
R644
R771
1
2
3
4
C684 10
C685 10
BU8872FS
0.001
C688
0.47
R639
1k
C689
0.47
L_RSLV
R765
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 8
220K
IC37
COM
INH
VEE
GND
TC7W53FU
OSCI
OSC0
INPUT
IC56
C691
C694
0.47
R638
10K
100K
100K
IC60
1
COM
2
INH
3
VEE
4
GND5A
C695
10
R645
220K
IC48
LM2902PWR
VCC
CH0
CH1
GND
NC
NC
NC
NC
2SC4213
100K
R641
R642
TC7W53FU
39K
9600bps
8
7
6
5
A
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Q103
R647
Q101
2SC4213
R649
8.2K
Q102
2SC4213
0.001
C925
VCC
CH0
CH1
CTCSS/DTCS
0.01
C698
0.1
C856
14
13
12
11
10
9
1M
R820
X6
CR-838
R660
0.0039
R769
10
VAFO
UAFO
8
7
6
C902
47P
C901
47P
390
R653
47
C700
C701
R664
100K
330K
C722
C708
IC38
11223344556677889
390
220
R658
47
C703
C706
C704
470P
L_LV
L_RSSI
10
C705
R770
220K
100K
22K
R764
R763
390P
C855
220K
R768
R762
10
C872
R779
220K
8
IC49
0.001
123
R777
220K
C903
0.1
R821
15K
C904
R822
3.9K
0.1
0.1
R659
220K
R778
C863
100
C709
330K
R663
R_RSLV
68K
R785
2.2K
390K
10
LA4445
9101011111212
C707
470
C710
4.7
IC61
1
COM
2
INH
3
VEE
4
GND5A
R786
C697
mini RIP
567
4
220K
4.7
470
C711
0.1
C712
4.7
R661
TC7W53FU
D-star
LMV358IPW
1
2
3
4
100
C714
0.1
C716
R665
12K
C924
C866
1
COM
2
INH
3
VEE
4
GND5A
R780
100K
R783
R782
COM
INH
VEE
GND
IC57
1
2
3
4
220
47P
0.001
VCC
CH0
CH1
0.033
IC51
TC7W53FU
R767
220K
100K
1/2 VCC
C867
100K
IC58
TC7W53FU
COM
INH
VEE
GND
TC7W53FU
C718
R789
C719
EP51
8
7
6
VCC
CH0
CH1
R781
10K
1
VCC
CH0
CH1
C907
MPZ1608S221A
EP55
1k
EP53
M PZ1608S221A
MMZ1005Y102CT
8
7
6
C864
4.7
15K
R787
10K
R788
C865
4.7
8
7
C909
6
5
A
0.01
C908
0.001
8
VCC
7
CH0
6
CH1
5
A
E
R880
5VS
R2
R1
*D1 32
R_UVCO_SELR_UVCO_SEL
R_VVCO_SELR_VVCO_SEL
L_LO_SWL_LO_SW
R_DA_SELR_DA_SEL
R_AFFILSEL
R_DET_MUTE
L_DA_SEL
L_DET_MUTE
100
R558
R563
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
R486
13
Vss
0
100
12
R536
0.01
5
2
C627
R562
470K
IC28
TA75S558F
100
C635
0.001
4
98_DATA
MIC_PTT
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
18K
R560
R549
3
1
R813
R559
C636
1
M IC_SENC
DCONT
P_PTT
P_SQL
P_LR_SEL
R556
R561
Q88
UNR9213J
47K
R571
100
R564
R534
R566
8.2K
1
2
3
4
100
100
COM
INH
VEE
GND5A
UNR9213J
Q93
*D1 33
*D1 34
*D1 35
*D1 24
*D1 25
*D1 26
*D1 27
100
R557
100
100
100
100
1.2K
IC29
TC7W53FU
Q92
VMMUTE
L_UNLOC
PLLDATA
R_UNLOCK
R_PLLSW
L_VCO_SHIFT
UTX_C
UMMUTE
L_WN_SEL
L_R5C
TCS_SEL
D
L_AMC
_PLLSTB
L
R_PLLSTB
ANALOGSW
DDETSEL
MODSEL
MOD_DA
DADJSEL
DADJMUTE
DDETMUTE
MIC_SENC
1200_9600SEL
R_WN_SEL
DCONT
MM_MUTE
DA_SEL
DTMFSEL
DVDTMFSEL
C637
1
R550
8
VCC
7
CH0
6
CH1
UNR9113J
*D136
*D137
*D138
*D139
*D128
*D129
*D130
*D131
VTX_C
K
PLLCK
P_SQL
P_PTT
AN
1
R801
8.2K
C645
0.1
5.6K
R581
MMZ1005Y102CT
EP70
MMZ1005Y102CT
P_MOD_MUTE
SUB_SEL
DTMF
R863
MM_MUTE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Q90
C646
C644
10
R574
R575
100K
EP24
R860
UNR9213J
R567
4.7K
47K
0.01
C638
IC30
I/O1
O/I1
CONT1
O/I2
CONT4
I/O2
CONT2
CONT3
VSS8I/ O3
CD4066BPWR
R570
100K
UNR9213J
0.1
R802
2.2K
10K
R577
0.1
C649
3
4
OUTPUT
5
DATAOUT
EP69
MMZ1005Y102CT
47K
R861
Q91
C640
14
VDD
13
12
11
I/ O4
10
O/I4
9
O/I3
0.001
C641
1.8K
INPUT
GND
J4
DN-508B-6-L
47K
R569
R572
100K
R573
100K
0.1
0.001
0.1
C648
R578
AN6123MS
R594
4.7K
100K
C642
IC32
56
34
12
5V
ANALOGSW
AF_VOL_RES
100K
R592
1M
R862
C657
0.001
C654
IC31
1
VDD
I/O1
2
CONT1
O/I1
3
CONT4
O/I2
4
I/O4
I/O2
5
O/I4
CONT2
6
O/I3
CONT3
7
VSS8I/O3
CD4066BPWR
22K
R586
22K
R587
R568
100K
C643
C639
0.022
CPU DTMF
R584
2.2M
R582
0.1
C655
2.2M
R583
2.2M
R585
2.2M
C;4.86V
IC52
8
7
6
5
DET
VCC
10
C663
2
1
R598
AFOUT
VCC
CH0
CH1
A
C652
TC7W53FU
0.1
2.2M
COM
INH
VEE
GND
1M
R589
EP68
MMZ1005Y102CT
R588
8.2K
1
2
3
4
C656
10 MSVA
DA221
D140
B2B-ZR-SM4-TF
J7
1
2
P50
M PZ1608S221A
EP52
EP49
MPZ1608S221A
C918
DADJMUTE
DDETMUTE
DDETSEL
VDET
390K
R882
UDET
0.01
C910
0.001
DVDTMFSEL
R827
390K
390K
R823
R826
DTMFSEL
390K
390K
R881
HV
8V
5VS
L5V
34
EP54
M PZ1608S221A
HSJ1403-01-010
M PZ1608S221A
R_RSSI
R_LV
0.1
C717
100P
AN
DA_SEL
DADJSEL
0.1
C911
0.1
C905
390K
0.1
C906
5V
SP1
1
2
J9
J8
PJ-3047S
MOD_DA
MODSEL
UTX_CUTX_C
VTX_C
DA3_STB
DA2_STB
DA_STB
DA_CK
DA_DATA
L_LV
R_LV
L_LO_SW
R_VVCO_SEL
R_UVCO_SEL
VMMUTE
UMMUTE
L_VCO_SHIFT
PLLDATA
PLLCK
L_PLLSTB
R_PLLSTB
L_PLLSW
R_PLLSW
L_UNLOCK
R_UNLOCK
L_R5C
R_R5C
R_AMC
L_AMC
R400_S
AMOD
R_RX800
L_WN_SEL
L_DET_MUTE
L_DA_SEL
L_AFFILSEL
R_AFFILSEL
L_DTCS_IN
L_WXALT
DAFOUT
R_WN_SEL
R_DET_MUTE
R_DA_SEL
R_WXALT
R_DTCS_IN
L_SQ L
L_RSSI
R_SQL
R_RSSI
VDET
UDET
VAFO
UAFO
*; Refer to “PARTS LIST.”
10 - 2
Page 47

MAIN UNIT (2)
HV
8V
5V
5VS
L5V
MOD_DA
MODSEL
R_LV
L_LV
VTX_C
UTX_C
AMOD
DA_STB
DA_CK
DA_DATA
DA2_STB
DA3_STB
L_LV
R_LV
L_LO_SW
R_VVCO_SEL
R_UVCO_SEL
VMMUTE
UMMUTE
To VCO
C;4.9V
C366
R805
10 EEE-S
HV
8V
L5V
R339
10 MSVA
2
SC4738
Q58
3.3K
47P
C443
C439
L_REF_MOD
0.001
C896
L_VCO_MOD
R_VCO_MOD
R_REF_MOD
R_VVCO_SEL
R_UVCO_SEL
C453
1 MSVA
2.2
C877
1 MSVA
C394
C466
2
2.
R298
18K
R368
C469
18K
L_VCO_SHIFT
47P
R_UVCO_SEL
R_VVCO_SEL
L_VCO8
VMMUTE
LREFCON
L_2ndLo
L_LO_SW
REF_MOD
L_PLLSW
L_UNLOCK
UMMUTE
R_REFMOD
RREFCON
R_2ndLo
R_UNLOCK
PLLCK
PLLDATA
R_PLLSTB
R_PLLSW
L_R5C
R_MOD
R_R5
R_LV
GND
MOD
L_LV
5VS
R_2ndLo
L_LV
L_R5C
VMMUTE
L_VCO_SHIFT
LREFCON
_PLLSW
L_LO_SW
L
L_UNLOCK
PLLCK
PLLDATA
L_PLLSTB
PLLCK
PLLDATA
L_PLLSTB
MAIN UNIT (4)
8V
8V
UMMUTE
(PLL circuit for Left band)
VHFYGR
L_RXLO
GND
L_VR5
L_UR5
R140_R5
R800_R5
R400_R5
R_Lo
5VS
UT8
UHFYGR
L5V
DAN222
D112
DAN222
D113
L_RXLO
L220_R5
L140_R5
L300_R5
L400_R5
R140_R5
R800_R5
R400_R5
5VS
MAIN UNIT (5)
(PLL circuit for Right band)
R_UNLOCK
PLLCK
PLLDATA
R_PLLSTB
R_PLLSW
R_LV
L_RXLO
MOD_DA
4
5
0.001
IC9
TC7S66FU
123
0.1
C912
C879
R_SQL
1
3
68K
R808
C875
10 EEE-S
10
11
12
LMV321IDCK
5
IC53
4
2
R807
220K
IC8
1
VIN1
2
VOUT1
3
VOUT2
4
VIN2
5
VDD
6
LD
7
CLK
8
DI
9
VIN3
VOUT3
VOUT4
VIN413VIN5
M62363FP
C876
10 EEE-S
VDAREF
R810
18K
100K
C874
22K
R806
10 EEE-S
VOUT8
VOUT7
RESET
VOUT6
VOUT5
LREFCON
C363
0.001
24
VIN8
23
22
21
VIN7
20
GND
19
18
17
DO
16
VIN6
15
14
L_SQL
MODSEL
C949
0.001
4
5
IC63
TC7S66FU
123
220K
R809
L5V
5V
VHFYGR
VTX_C
UTX_C
UT8
UHFYGR
L_VCO_SHIFT
PLLDATA
PLLCK
L_PLLSTB
R_PLLSTB
L_PLLSW
R_PLLSW
L_UNLOCK
R_UNLOCK
L_R5C
R_R5C
R_AMC
L_AMC
R400_S
R_RX800
L_WN_SEL
L_DET_MUTE
L_DA_SEL
L_AFFILSEL
R_AFFILSEL
L_DTCS_IN
L_WXALT
DAFOUT
VDET
UDET
R_WN_SEL
R_DET_MUTE
R_DA_SEL
VAFO
UAFO
L_SQL
L_RSSI
R_SQL
R_RSSI
R_WXALT
R_DTCS_I
I
L_R5C
R_R5C
R_AMC
_AMC
L
C351
R_DET_MUTE
R_AFFILSEL
R_DA_SEL
0.001
0.001
0.0022
C;7.9V
L_DA_SEL
VCC
CH0
CH1
IC13
TC7W53FU
IC12
TC7W53FU
0.001
R296
C386
0.01
L_AFFILSEL
8
7
6
0.001
C389
8
VCC
7
CH0
6
CH1
8
VCC
7
CH0
6
CH1
C390
0.001
10K
L_DET_MUTE
C;4.9V
Q43
UNR911NJ
Q44
UNR911NJ
Q45
UNR9114J
Q46
UNR9114J
R256
6.8K
C352
1.5M
R247
C355
0.0039
0.0018
R252
47K
R253
100K
R246
1.2K
68K
R251
R257
6.8K
C353
1.5M
R248
C356
C359
0.0039
0.0018
R254
47K
100K
R249
C354
C357
0.0022
C358
3
2
1
100K
R255
0.022
R258
C361
R259
68K
Q41
XP4601
C360
22K
R262
0.022
C362
22K
R261
0.015
0.015
1.2K
R;3.7V
Q47
XP6501
4
5
6
4.7K
R266
R267
15K
10K
4
5
6
C365
R265
10K
Q48
XP6501
4
5
6
4.7K
R268
R269
100K
Q42
R263
XP4601
3
2
1
R270
10K
R264
R;1.2V
0.0018
0.001
10K
4
5
6
L_R5
R_R5
R_AM
L_AM
1.5M
R271
R;0.8V
R283
R277
C367
3
39K
R272
R;1.9V
0.033
C373
22K
C375
C380
C369
0.015
0.01
0.001
330
C370
0.033
0.01
1.5M
C371
C374
330
R274
15K
R281
68K
0.0018
Q50
UNR9213J
R278
R285
68K
68K
C378
0.0068
R282
10K
C376
R280
R284
39K
22K
C381
C377
0.001
0.015
Q49
0.01
C372
C379
R286
0.033
68K
68K
C382
0.033
2
1
C364
0.01
R276
68K
100K
R279
C368
R273
3
2
1
R275
R288
12K
R290
12K
0.01
UNR9213J
R294
0.0068
R293
C384
UDET
0.001
0
0.001
1
COM
2
INH
3
VEE
4
GND5A
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
100K
R295
C383
IC11
TC7W53FU
COM
INH
VEE
GND5A
COM
INH
VEE
GND5A
C388
L_WN_SEL
R305
10K
Q53
UNR9113J
Q54
UNR9210J
C400
L_R5
R_R5
0.1
Q57
XP6501
C429
22P
R332
C433
15K
470
8
FILINAFOUT
9
C432
C436
10 MSVA
0.1
C437
R334
R335
C428
0.1
VCC
DEC
IFIN
FILOUT
MIXOUT
N-REC
N-DET
RSSI
IFOUT
QUAD
10111213141516
82P
C435
0.033
L_2ndLo
OSCOUT
GND
R_AM
1K
R341
X2
JTB450C24
1234567
OSCIN
MIXIN
R795
22K
330
R342
Q56
UNR9113J
0.01
C403
C894
0.01
R301
100
0.1
R303
R306
18K
1.5K
0.01
R307
82K
470P
C402
R302
R308
0
0.001
C404
15K
C407
470
R316
123
R310
22K
R884
L_SQL
R_SQL
R_RSSI
470K
R311
R315
0
MA2S111
D82
MA2S111
D83
NTCG10
12K
456
Q55
XP6501
R319
180K
4.7K
R314
0.001
R;3.5V
R322
12K
FI1
LT450HW
C932
I O
0.1
C933
I O
0.1
FI2
R323
LT450EW
R;4.4V(MODE:AM)
C417
0.001
R317
C418
220P
10K
C419
220P
2.2K
R321
C416
R329
0
12K
R330
D84
C930
0.1
MA2S111
D85
C931
0.1
MA2S111
12K
R331
1
C425
1K
R327
R328
C427
0.01
180K
456
C423
123
0.1
330K
C424
4.7 F93
0.1
C426
C422
R324
68K
10P
TA31136FNG
IC15
L_RSSI
M
L_A
C399
0.01
R345
C442
R346
UNR9213J
3.3K
0.1
1
COM
2
INH
3
VEE
4
GND5A
3.3K
Q59
IC16
TC7W53FU
L_R5
C445
0.001
R;4.4V(MODE:AM)
R351
100
Q63
XP6501
123
R352
1.5K
R358
18K
470K
C450
R353
0.01
22K
R359
8
VCC
7
CH0
6
CH1
0.1
C455
R_WN_SEL
DA_STB
A_CK
D
DA_DATA
DA3_STB
VT;0V
UT;4.6V
R;4.7V
470P
0.001
C541
C537
L_R5
47
R379
R440
0.01
C518
0.001
0.001
C525
617DB
0.01
L122
C528
R_R5
47
R429
470
R430
0.001
C519
0.01
C523
D100
100K
470
R434
R431
R438
10K
0.001
C462
470
R380
0.001
C467
Q66
2SC4406
0.001
C461
R374
1K
R376
456
180K
R366
180K
C463
0.1
C454
0.001
R372
82K
470P
C459
R367
0
C458
4.7 F93
10K
R388
NTCG10
R885
4.7K
R383
R375
470
C460
0.001
R381
1
C471
0.01
123
C468
470
C470
0.033
0.01
R399
C472
330
D88
10K
10K
Q69
UNR9210J
22P
Q117
UNR9213J
Q70
2.2K
UNR9113J
C475
220P
C476
220P
R397
R811
3.3K
DA221
C483
UNR9113J
Q71
0.1
15K
R402
R400
68K
10P
R389
0
C884
0.1
100K
R384
R395
R398
470
R396
456
Q67
XP6501
C477
330K
R385
C889
C480
3P
0.001
C891
0.001
2
4
D93
M A2S111
D94
M A2S111
C487
0.1
C486
0.1
FILIN
TA31136FNG
AFOUT
82P
C478
OUT3GND
GND
R;3.4V
R406
C927
0.1
R407
C929
0.1
7
8
6
DEC
FILOUT
IFOUT
QUAD
9
10
11
C491
FL-408
IN
56
FI5
12K
LT450HW
12K
LT450EW
C495
0.1
4
5
VCC
IFIN
N-REC
N-DET
RSSI
12
13
14
R416
C507
0
3P
330
12K
D95
12K
D96
MA2S111
C514
0.001
12P
1.8U
L119
C513
0.001
C517
Q75
2SC4406
C515
C510
0.1
C506
1
15P
C500
C497
0.1
C503
R422
FI3
R417
C926
I O
0.1
MA2S111
FI4
R418
C928
I O
0.1
15K
R414
1
2
IC18
OSCIN
1K
R419
OSCOUT3MIXOUT
GND
MIXIN
R794
15
16
22K
JTB450C24
X3
R415
3.3K
10 MSVA
47
0.01
VT;4.7V
UT;0V
R;4.6V
R439
220
DA221
0
0.01
C530
617DB
L126
R443
R444
220
1
2
3
2
4
3P
C531
IC19
G1
D1
D24S2
SPM5001
FL-409
OUT3GND
GND
C540
R447
220
G2
S1
IN
5 6
FI6
18P
100K
C868
R453
0.01
R790
6
5
R452
1
C543
L127
100
R791
100
617DB
C869
0.01
R463
0.01
C564
47
R462
0.01
C559
0.01
C561
617DB
C548
C549
0.01
0
0.001
C552
0.01
3P
0
R464
220
1
2
3
L132
617DB
IC20
G1
D1
D24S2
SPM5001
0.01
C553
C550
L136
R467
220
6
G2
5
S1
R_Lo
L_R5
C555
0.1
C556
0.001
4.7K
R461
0.01
470P
0.001
C570
C569
R471
4.7K
0.1
C575
C576
100K
R469
0.01
0.01
C572
C574
L137
100
100
R793
R792
C870
C871
0.01
120K
R472
D116
MA2S111
VAGC
UAGC
VVIF
UUIF
5VS
R_R5
R400_S
5V
UAGC
VAGC
L140_R5
R140_R5
L220_R5
0.001
L300_R5
L_R5
R_R5
617DB
R400_R5
L400_R5
R_RX80
0
0.01
R800_R5
10 - 3
Page 48

MAIN UNIT (3)
R_RX400
R_RX140
R400_S
L400_S
L_RX140
R_RX140
L_RX220
L_RX300
VD5C
UD5C
R_RX400
L_RX400
R400_R5
L400_R5
R_RX800
R800_R5
L5V
DA_DATA
10K
R873
C2
5V
R874
10K
C1
C3
UAGC
VAGC
L140_R5
UNR9114
R140_R5
UNR9114J
L220_R5
UNR9114J
L300_R5
UNR9114J
UNR9114J
UNR9114J
L5V
VHFYGR
UT8
UHFYGR
DA3_STB
DA_STB
DA_CK
0.1
0.1
L_R5
R_R5
Q8
UNR9114J
8V
HV
VTX_C
UTX_C
UUI
F
VVI
F
5VS
1
2
3
1
2
3
R3
0
0.001
MA2S728
MA2S728
MA2S728
MA2S728
MA2S728
MA2S728 D6
Q3
UNR9114J
J
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
Q9
Q10
Q11
VTX_C
UTX_C
R_BPF3
R_BPF4
PL_U
TX_MUTE
PCON_
PCON_V
UATTC
XP4601
Q1
XP4601
UNR9114
6
5
4
4.7K
C7
C5
6
5
4
Q2
470K
L140_R5
C6
U
0.1
R4
D1
D2
0.001
L220_R5
L300_R5
0.001
0.001
DA_DATA
C4
R5
D3
D4
D5
R140_R5
R400_R5
L400_R5
R800_R5
J
J21
3008L-8P8C
5P
C341
L104
C350
L106
18.3N
100P
M A2S111
MA2S111
5P
AS080340
C346
C345
D79
D80
R244
4.7K
2SC4738
R243
47K
3008L-8P8C
C348
Q40
L108
R242
L109
12.1N
7P
J20
7P
R245
2
1
2
R241
RL3
ATQ206SA
10K
1
W6
82K
W5
82K
ERDS2T0
ERDS2T0
0.001
UHFLPF
5VS
R_R5
VT8
AS080647
L46
C161
1P
C164
0.001
33P
C157
15P
C155
0.001
R128
R129
VVIF
150
1.8K
L_R5
R140_R5
L220_R5
L300_R5
UD5
VD5
12P
C162
UT8
R138
0.001
C165
AS100340
L50
1P
C166
UNR9113J
R133
330K
C156
0.001
TX_MUTE
PCON_U
L140_R5
2.2K
R137
C169
8P
L51
D38
LQW18AN24NG00D
MA2S077
3P
C168
2.2K
R134
L52
C163
8P
LQW18AN68NG00D
L47
D35
0.22U
MA2S077
V220
MA2S077
D36
D37
MA2S077
39N
L53
C160
3P
2.2K
R135
C170
33N
L48
0.001
C167
330
2.2K
R136
0.001
C159
22N
L49
C171
L56
AS080647
MA742
C186
0.001
D39
0
220
R140
1.8K
R141
1P
C173
C176
0.001
13P
C174
2.2 MSVA
R148
33K
Q31
0.001
C937
L54
HVC350B
LQW18AN68NG00D
100P
C181
39N
L55
D40
100P
C175
C179
R_BPF4
(174–260 MHz)
0.001
22
R144
R139
R147
C178
0.001
L_BPF4
C182
HVC350B
C185
100KR145
0.001
C183
D41
C184
0.5P
33P
R_BPF3
330
MA742
C190
R853
PRF18
C187
0.5P
33P
C188
100KR153
D42
R152
100
0.001
T;0V
R;4.76V
100K
R149
0.001
C189
L_BPF4
L_BPF3
HVC350B
100P
0.001
R154
2.2 MSVA
R157
100K
R155
C193
D43
C191
R;4.73V
C194
R;4.72V
27K
C192
1K
HVC350B
0.001
C196
3.5P
0.001
(260–375 MHz)
15
R143
0.001
R150
R142
330
330
L_BPF4
C;7.85V
Q12
UNR9213J
R8
1K
C8
0.001
VHFYGR
DA_CK
IC1
1
VSS
2
AO3
3
AO4
4
AO5
5
AO6
6
AO7
7
AO8
8
AO9
9
AO10
10
VDD11VCC
M62352GP
4.7K
R6
470K
R7
V220
L_R5
R_R5
VD5
UD5
R400_R5
L400_R5
UU1
VU2
VV
UV
VU1
UUIF
20
GND
19
AO2
18
AO1
17
DI
16
CLK
15
LD
14
DO
13
AO12
12
AO11
R_BPF1
0.001
C895
UU1
2.2K
R9
L1
0.001
C10
33N
MA2S077
C13
2.5P
D7
VU2
R10
L2
0.001
C11
C14
2.5P
D8
MA2S077
R800_R5
R11
L3
100P
C12
VATTC
UATTC
MA2S077
C15
4P
D9
UUIF
33N
0.1U
C16
0.001
R_BPF2
L4
2.2K
2.2K
Q15
0.001
47K
R17
2SA1362
1K
R22
L9
47N
33P
C31
C19
47K
0.001
R20
R12
Q13
1K
UNR9213J
C9
IC54
L_RX300
L_RX400
L_BPF3
C25
D10
470
L_BPF4
L7
4.7U
C24
VD5C
2.5P
1SV308
C23
4P
T;0V
R;4.73V
0.001
1
2
UD5C
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
D12
HVC375B
100KR23
C33
R_BPF4
C28
2.5P
C26
D11
1SV308
LQW18AN6N8C00
L8
1P
C27
C35
VSS
AO3
AO4
AO5
AO6
AO7
AO8
AO9
AO10
VDD
M62352GP
C29
0.5P
C32
0.5P
7P
0.001
HVC375B
C34
L_BPF4
0.001
7P
R26
C36
0.3P
D13
R24
C39
C37
R_BPF3
T;0V
R;4.05V
C38
0.5P
HVC375B
D14
15P
100K
0.001
100
R28
82K
L_RX220
L_RX140
0.001
C883
L6
4.7U
C21
0.001
15N
R18
470
15N
L5
R19
R14
15
R33
L11
18
47N
33P
39P
C54
C43
Q17
2SA1362
L400_S
20
GND
19
AO2
18
AO1
17
DI
16
CLK
15
LD
14
DO
13
AO12
12
AO11
11
VCC
8P
C46
15N
L10
C48
L13
100K
4.7U
R27
C47
0.001
R29
470
0.001
C40
47
R38
C49
8P
15N
D15
L12
HVC375B
R30
100K
L15
15P
C41
4.7U
470
0.001
C51
L_BPF3
R31
C45
C53
1P
Q18
2SC5231
L17
0.1
R35
47
4P
1SV308
C57
1P
FANC
C55
C50
0.001
L_BPF2
12N
C44
C60
L_BPF1
9P
D16
4P
C56
D17
R37
C59
15P
VATTC
L16
22
0.001
C61
9P
R;3.59V
R39
56
0.001
L19
R44
10K
18N
3SK324
22
1SV308
150
18
R46
R47
15
39N
330
R43
Q21
2SC4738
0.001
C58
180K
R45
R754
Q19
120K
100
R41
R48
0.001
18N
L18
C62
R50
R755
Q20
3SK324
100
C63
R49
0.001
R40
39
R51
C65
0.001
R876
R875
0
R52
R53
180K
R55
R54
C64
3.5P
150
0.001
R59
39
150
R56
0.001
C68
C70
10P
330
R57
M PZ1608S221A
EP1
C88
100K
Q123
2SB1132
D169
MA8075
1k
47K
R58
8P
220K
0.001
C66
47K
R61
220K
120K
R60
C72
LQW18AN6N8C00
L20
1.5P
C67
C73
C69
0.001
C79
C83
0.001
C89
L25
0.001
C81
18N
150
R66
2P
C84
150
R68
0.001
C86
L22
33N
4.7K
R63
R64
0.001
680
Q22
2SC5085
MMZ1608Y102BT
47
C80
C87
3P
C946
C93
18N
EP71
EP2
0.001
M PZ1608S221A
(375–550 MHz)
0.001
C74
C71
12.0N
L23
3P
C77
L21
470
4.7U
R72
D18
1SV308
C85
0.001
(375–550 MHz)
0.001
C75
0
8P
C78
3P
C82
L24
4.7U
D19
1SV308
C90
C76
0.001
100
0.001
R67
R70
82K
0.001
Q23
2SC5624
0.001
3P
L26
C94
D20
7P
C91
0.001
C92
12.0N
L27
R74
0.001
C95
3.5P
R73
R82
47N
R75
4.7K
1K
R76
R77
22
B2B-ZR-SM4-TF
1
2
0.001
C96
0.5P
HVC375B
HVC375B
C97
0.5P
100K
R79
R78
100K
R_BPF1
R_BPF2
C100
0.3P
D21
HVC375B
0.5P
C101
470
7P
C98
C99
0.001
L_BPF2
4.7K
R80
D22
1SV308
2.2M
C103
C104
34
100KR81
120
L28
Q25
2SC3357
J1
D23
C102
7P
0.001
L_BPF1
L30
L29
10N
2P
CHASSIS unit
470
R85
D24
HVC375B
100K
R83
C105 7P
0.001
C106
LQW18AN6N8C00
R95
C121
0.001
R89
27P
C109
68
12P
C110
22
R88
0.001
C111
R90
M A2S111
D25
R91
1
2
1.5P
C114
12.0N
L31
3P
C112
L32
4.7U
0.001
C107
D26
1SV308
C115
1.5P
12.0N
L33
3P
C113
D28
L34
4.7U
470
0.001
C108
D27
1SV308
R86
R96
MA2S111
D29
R97
22
R92
0.001
C122
L35
22N
4.7K
7P
C123
C124
680
Q26
2SC3357
MF1
FAN
0.001
100
C848
R98
D30
1SV172F
1K
R94
0.001
C117
0.001
C120
C118
0.001
1SV172F
1K
0.001
C116
R93
0.001
C119
(810–1000 MHz)
47K
R15
C17
Q14
2SC4738
47K
R16
C18
Q16
2SC4738
0.1
0.001
0.001
C30
C882
0.1
22
4.7K
1K
L36
15N
2P
R100
39N
Q27
2SC4703
C125
0
R103
0
R101
41-002AA-R
J22
41-002AA-R
R102
C126
UD5
22
L37
33P
C131
3SK324
C127
J11
3SK324
C128
C129
C130
2P
C133
2P
0.001
0.001
10P
C132
220
R104
D31
DAN222
R107
2P
L38
Q28
R108
0.001
J10
41-002AA-R
0
R109
L39
Q29
R110
0.001
C134
10 EEE-S
R105
15
R106
18
MMZ1608Y102BT
PL_U
47
C135
33N
C136
100
C137
2SC4738
47
C138
33N
C139
100
C140
18P
C141
R111
220
0.001
C142
0.001
0.001
R112
0.001
220K
0.001
R113
M A2S111
Q30
0.001
0.001
R114
220KR115
0.001
LQW18ANR15G00D
R116
15
100
R117
C144
0.001
EP4
C143
C150
MMZ1608Y102BT
EP3
C145
0.001
VT;4.20V
UT;0V
R;4.18V
180K
47K
R118
0.001
C148
3P
C146
L40
LQW18ANR15G00D
4.7K
R124
D32
R856
100
47K
R122
47K
180K
R119
C149
0.001
3P
C147
R121
L41
IC2
S-AU82L
VGG3VDD4OUT
1IN2
CTH30V222S15A
C846
0.001
L42
0.1U
180K
R120
R126
VT;0V
UT;4.45V
R;4.41V
L43
0.1U
120K
R125
0
ATQ206SA
41-002AA-R
10K
C151
0.001
L45
0.001
0
R857
J23
L44
LQW18AN56NG00
IC 3
S-AV32
1IN2
C845
33N
C152
RL1
VGG3VDD4OUT
CTH30V222S15A
C154
C153
VV
UV
V220
UUIF
VU1
VT;7.81V
UT;0V
R;0V
1P
0.001
C202
C212
1P
C198
10P
C203
C214
22K
R166
C199
0.001
R162
C209
0.047
220K
82K
R158
R163
150K
C210
C938
MA2S111
C206
0.001
D44
100K
R161
100P
C195
T;0V
R;4.75V
C207
0.001
R165
100K
0.1U
L57
R159
0.001
C208
(118–174 MHz)
R164
R156
100P
C205
L58
100K
HVC350B
D45
C213
C200
3P
R160
100P
C211
100K
HVC375B
D46
0.001
C197
10K
0.1
0.001
0.001
0.001
MA742
D48
L59
39K
33N
R168
L60
4P
C216
47
R757
0
R170
D47
L61
AS080440
R167
M A2S111
47
R169
C215
0.1U
R756
0
R174
C218
100
R171
39K
18N
0.001
C217
C220
C221
D49
0.001
150
C219
Q32
0.001
C222
2SC5624
100
0.001
C224
2.2K
0.001
IC4
1
2
3
4
NJM3404AV
C952
4P
3SK318
Q33
0.001
R173
3SK318
R172
0.001
Q34
C223
2SC5624
22 CV
0.001
0.001
0.001
Q35
C227
4P
15K
R178
R176
R179
47K
R175
150
R182
R183
R188
C225
1U
C226
C230
0.001
0.01
C228
8
7
6
5
C232
L164
LQW18ANR15G00D
180K
R185
120K
R189
R181
180K
R177
R184
120K
220K
R180
39K
2.2M
L_BPF3
39K
R186
2.2M
R187
100
L62
0.001
C231
C238
0.1
3P
0
R190
0.001
220K
LQW18AN82NG00D
C233
0
C236
8P
C229
0.001
3PC234
C237
C239
3P
R191
100K
L_BPF3
0.001
C240
100
R197
0.001
C246
MA742
D52
C241
220K
0.047
R198
R194
1K
68K
R193
39K
R196
0.001
0.001
C941
R877
0
D53
C953
C251
MA2S077
(118–174 MHz)
0.001
C244
47K
18N
L65
C242
8P
C235
L66
0.001
18N
L63
HVC350B
100P
L64
C252
R_BPF2
LQW18AN82NG00D
R199
2.2K
C255
3.5P
D51
HVC350B
R192
100K
L68
0.001
100P
C249
R195
2.2K
C253
3.5P
D50
HVC375B
18N
L67
100P
C247
0.001
C243
R201
8V
10K
R852
0.001
HVC350B
100P
C256
L_BPF2
C258
0.75P
D54
C262
100K
R200
C257
33N
PRF18
R204
10
D55
R203
C259
33P
0.001
22K
R202
C254
C260
0.5P
C261
33P
R_BPF1
C263
100K
0.001
L_BPF1
100K
R206
C264
D56
M A2S077
D57
M A2S077
VATT
UATT
C265
0.001
R205
0.001
C266
0.001
33K
100KR208
C267
HVC350B
C268
0.001
15P
C270
2.2K
C942
HVC350B
C271
0.001
D58
100P
D59
L709CE
22 CV
C274
C275
470P
C272
C273
R209
UNR9113J
0.001
L69
12.1N
D60
100P
1P
12P
0.001
Q36
VT;0V
UT;7.73V
R;0V
R210
1U
PCON_V
D61
L71
L72
C284
UATT
D63
MA2S111
100
L70
0.001
L709CE
C283
8P
100P
C280
D62
L709CE
C278
C281
64N
39N
R215
1K
0.001
C279
C291
0.001
MA2S111
R211
TX_MUTE
L73
AS080440
5P
C294
1SV172F
L74
64N
C282
MA2S111
22 CV
R213
D65
C288
D66
330K
3P
C286
0.001
120
D68
0.001
C289
C285
8P
39N
L75
R212
0.001
0.001
C287
LQW18ANR15G00D
D64
L166
D67
MA2S111
1k
R219
0.001
C301
LQW18AN56NG00
L78
10
0.5P
C292
MA2S077
MA2S077
C298
4P
R216
0.001
C293
D69
MA2S077
C303
C296
6P
L77
C297
100P
0
R217
C295
0.001
D70
1K
0.001
C290
10K
L76
LQW18AN68NG00D
L79
1U
C305
D71
R224
22 CV
L84
15N
10
MA2S077
4P
AS080440
1.5P
C337
C309
R222
3SK318
C306
1SV172F
R225
R218
100
D72
1SV308
L82
57.2N
27P
1k
C307
D73
C308
6P
L80
AS080440
1.5P
C340
L102
100P
C339
LQW18AN6N8C00
R229
L85
6P
Q37
R230
0.001
120
R223
47K
R226
0.001
C299
C300
220P
120K
C312
L83
1U
0.001
L86
18.3N
5P
C313
AS080547
C314
0.001
C318
AS080747
L89
C310
18P
1.5P
C343
L105
LQW18AN6N8C00
0.001
C315
100
0.22U
R232
100
0.001
C316
4.7K
M A2S111
D76
Q38
2SC4738
180K
R221
C304
R220
L81
LQW18AN82NG00D
C317
0.001
18P
C319
D74
1SV308
AS080647
L88
L92
18P
C326
D75
C320
27P
2P
C347
L107
L110
LQW18AN6N8C00
VT;0V
UT;3.90V
R;3.85V
680
47K
R234
C324
C325
L91
220K
R235
LQW18AN82NG00D
R239
R227
47K
R231
3P
220K
R228
0.001
L90
37.5N
18P
C327
6P
C328
2P
C323
C349
36P
L93
45.5N
12.1N
C329
L94
45.5N
L709CE
0.001
3P
680
C311
36P
AS080547
C330
2P
6N
R237
R238
0.22U
100
C333
L95
100P
C331
220P
C332
L96
27P
C334
120K
120K
L87
Q39
3SK318
R233
L98
37.5N
4P
12.1N
AS100340
L101
10
6P
D77
M A2S111
L165
LQW18ANR15G00D
L97
0
R236
6P
C321
0.001
C322
L103
8.6N
27P
6P
C338
L99
AS080440
C342
R240
0.001
MA2S077
D78
0.001
LQW18AN68NG00D
39N
L100
33P
C335
0.001
C336
RL2
ATQ206SA
C344
10 - 4
Page 49

MAIN UNIT (4)
L_VCO8
C724
47P
LREFCON
C731
L_R5C
VMMUTE
L_VCO_SHIFT
C732
C727
47P
0.001
C723
47P
47P
270K
R679
C735
MOD
47P
10K
C736
R678
C740
1
Q104
UNR911NJ
C737
C738
3P
0.001
1
C741
R680
0
15P
R681
L142
10
C742
4P
1
2
0.82U
C743
X5
VCON
GND3OUT
CR-833
C744
L143
0.01
82P
VCC
0.22U
Q105
2SC4738
L5V
10P
D145
R701
HVC321B
C765
1K
2.2M
R702
100K
0.001
Q110
UNR921NJ
C;7.88V
L147
68N
C767
C768
D147
2SC5108
0.001
0.3P
HVC321B
1K
0.001
Q11 2
47K
R703
R719
C781
M A2S077
C769
0.001
R721
R704
D148
C784
220
1K
0.001
C770
4.7K
R705
0.001
22K
10K
C839
MA2S077
D151
R725
0.001
L145
L146
R726
R728
68 0
T;7.08V
R;7.11V
C771
12P
C2012C
C2012C
R709
R708
0
C772
10K
C773
10K
R713
R716
22P
18P
0.001
C819
D157
L157
1SV308
56N
47
820
4.7K
0
C777
1P
C785
39P
C779
R712
C780
Q 111
2SC5231
R714
R720
C789
0.001
R717
39N
15P
0.001
C783
120
C792
L148
0.001
R723
R724
0.001
27P
10K
1.8K
L152
39N
C795
R727
L150
0.1U
Q113
2SC5231
C806
0.001
C804
1K
1P
R;3.51V
15P
C793
22P
C797
4.7K
C950
22P
R733
D153
MA2S077
C815
C803
0.001
0.001
3
GND
2
GND
1
IN
IC44
OUT
GND
VCC
UPC2709TB
D155
EP48
MMZ1005Y102CT
L160
1U
4
5
6
0.001
C808
1SV308
C818
0.001
C811
18P
R;3.87V
R739
C820
R737
0
2.2K
C814
18P
VHFYGR
L5V
VHFYG
R
L_RXLO
L_VR5
L_UR5
1P
1K
R741
Q115
UNR9213J
8V
C;4.78V
2.2M
L144
0.47U
C763
100K
R707
C766
C774
10P
C775
HVC321B
D146
R699
0.001
4
C748
R683
10P
C747
R682
680K
C746
R684
MA2S111
C750
6P
C752
22K
D143
0.001
0.1
C749
10K
0.001
100
R696
1.2K
R841
Q119
2SK1069
0.001
IC42
C760
C761
5
123
0.1
0.001
10K
UNR9213J
R848
4
R698
Q109
UNR9213J
Q121
TC7S66FU
R697
1.2K
1.2K
2.2 MSVA
C762
C764
0.1 SVA
0.1
R700
MOD
C751
0.001
10K
R870
0
R694
1.5K
33K
47K
C920
R843
C759
0.001
C838
R695
0.1 SVA
C921
R685
22
0.22
470P
FOUT
DATA
0.1
C755
16
B
15
P
14
13
NC
12
FC
11
LE
10
R840
1k
10K
10K
10K
L_LV
R686
R688
R690
R842
C951
C754
IC41
1
OSCIN
2
OSCOUT
3
VP
4
VCC
5
DO
6
GND
7
LD
8
470P
FIN9CLOCK
R869
0
B15A02PFV1
M
8V
47P
0.1
C753
PLLCK
PLLDATA
L_PLLSTB
C725
L_2ndLo
L_LO_SW
8V
REF_MOD
L_PLLSW
L_UNLOCK
L_LV
C726
C728
0.001
C729
C730
0.001
C733
0.001
0.001
C734
0.001
0.001
0.001
PLLCK
C739
R677
Q106
UNR911NJ
0.001
10K
L_LV
10 - 5
PLLDATA
L_PLLSTB
2969
MP 2
123
MA2S077
D152
R722
C798
MP 3
4
123
2601
MP 7
123
4
2775
MP 8
4
123
4
2969
MA2S077
D150
R706
27
C787
12P
2.2K
0.001
R710
C776
C791
8P
C790
L149
R711
27
33
0.001
18P
33N
R718
C794
1K
C782
0.001
L151
10N
C796
6P
6P
R;4.15V
C786
0.001
C788
C799
C800
7P
0.001
6P
1
2
3
4
C807
7P
L153
IC43
VCC1
IN
IN
GND5SW1
UPB1509GV
D154
MA2S077
2.2K
27N
R734
8
VCC2
C821
7
OUT
6
47P
SW2
0.001
C805
R738
R743
Q116
2SC5108
4.7K
33K
R744
0.22U
68
L158
R742
C822
47P
C823
2.2K
C809
0.01
L155
68N
27P
C837
C812
L156
0.001
68N
56P
2.2K
R745
D156
C816
MA2S077
C817
27P
0.001
Page 50

MAIN UNIT (5)
8V
R_REFMOD
RREFCON
R_2ndLo
R_UNLOCK
PLLDATA
R_PLLSTB
R_PLLSW
R_LV
R_R5
PLLCK
UMMUTE
C392
R287
270K
1
5VS
R_MOD
C395
1
C385
R_R5
R299
C387
3P
0.001
10K
R292
0
L111
R354
47K
0.82U
C396
C393
C;7.88V
R457
0.001
C844
10
IC62
3
GND4OU T
2
8P
15N
7P
0.001
0.001
C835
R428
R455
0
GND
1
IN
UPC2709TB
R436
0
L161
1U
4.7K
R747
C544
2P
L162
C841
C831
R750
4.7K
C582
5
GND
6
VCC
0
R460
0
EP47
C827
GND
VCC
100P
C557
5
6
C526
0.001
C529
L131
22N
0.001
C840
MMZ1005Y102CT
1SV308
D103
0.001
L123
39N
15P
C562
R752
15N
R140_R5
C527
7P
L129
C554
2P
UNR9213J
8P
4.7K
C534
L134
22N
C566
L124
C830
12N
L125
39N
27P
Q79
0.001
0.001
C532
18N
C558
1P
L130
1K
C567
7P
12N
C538
0.001
C539
R466
D108
MA2S077
0.001
R446
0
15P
C560
2P
L133
R400_R5
T;7.74V
R;0V
R450
C563
5VS
R470
R445
0
L135
8.2N
6P
2.2K
C547
D107
MA2S077
4.7K
0.001
UT8
C565
C568
C533
7P
0.001
6P
4.7K
MA2S077
0.001
L159
R465
D106
C573
C535
7P
18N
R140_R5
R800_R5
D109
MA2S111
R400_R5
R_Lo
UHFYGR
5VS
UT8
R426
R427
4
4
4
10K
1.8K
22K
5.6K
R432
L121
MP 9
123
2969
R423
L120
Q74
2SC5231
68
C516
39N
Q76
2SC5231
1K
0.15U
0.001
C521
3P
4
C524
C522
R449
4.7K
R441
C536
47P
0
D101
MA2S077
MA2S077
D159
R748
4.7K
D160
C512
22P
MA2S077
R433
4.7K
47P
D102
4P
MA2S077
4.7K
C833
0.001
R448
MA2S077
IC45
3
GND4OUT
2
GND
1
IN
UPC2709TB
D104
MP 4
C501
C496
0.001
47
270
2969
2601
2775
47P
0.001
MP 5
MP 6
T;6.98V
R;7.01V
C504
C499
C498
1P
D97
MA2S111
R412
C511
Q73
2SC5231
C509
R413
123
123
123
0.001
0.001
R420
R421
0.001
0.5P
C444
0.001
470
R348
47N
FOUT
DATA
CLOCK
C441
R364
1.5K
L114
4P
Q60
2SC510
27K
R337
16
B
15
P
14
13
NC
12
FC
11
LE
10
9
10K
R333
PLLCK
47P
22N
3P
C430
3P
C431
8.2K
R363
D86
DA221
IC14
OSCI N
OSCOUT
VP
VCC
DO
GND
LD
FIN
MB15A02PFV1
C434
L113
R_UVCO_SEL
R_VVCO_SEL
10K
R360
Q64
UNR9213J
X1
1
VCON
2
GND
CR-783
C397
4P
56P
7P
0.01
C398
4
VCC
3
OUT
C401
L112
0.22U
R304
8
Q52
2SC473
0. 1
680K
C;4.86V
C405
C408
C406
R370
0.001
5P
C457
0. 1
100K
C410
R313
10P
10K
R309
R_UNLOCK
R312
22
0. 1
C411
0.001
C413
C464
10K
R318
0.001
22K
C414
MA2S111
0. 1
C415
47P
R320
0
D81
470P
C420
470P
0.22
C421
2.2M
R325
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
8
R340
R336
22K
R350
R373
6
5
4
10K
PLLDATA
R349
C446
Q65
2SC4116
18K
R845
C440
0.01
100P
10K
XP4601
R343
4.7K
2SA1586
Q62
R344
10K
R338
R_PLLSTB
R847
33K
47K
10 MSVA
C448
R377
8.2K
Q61
10K
C922
R356
1
2
3
330
1.2K
R347
0.001
C923
100
C447
0
0.1 SVA
Q120
0.001
Q68
6
5
4
XP4601
0.047
R846
2SK1069
R355
R365
1.2K
C451
C452
R386
3.3K
100R362
10K
0.001
IC17
1
2
3
R369
R844
1k
C474
5
123
R849
10K
330
C456
4
1
UNR9213J
Q122
TC7S66FU
R378
0
10 MSVA
R_PLLSW
L115
R390
0.18U
100K
D87
HVC321B
1.8K
0 .33 SV A
C945
0.3P
HVC362
R394
0.18U
C473
D90
R382
L116
D89
HVC362
2.2M
0.3P
C479
L117
C481
39P
C2012C
HVC375B
D92
R403
D91
L118
HVC350B
C502
C484
3.5P
C488
10K
C489
0.001
C2012C
C490
10K
R405
10P
27P
T;6.60V
R;6.65V
C508
R404
0.001
47P
10K
R408
820
10K
C492
C493
47
Q72
2SC5231
R409
C482
R411
8P
15P
10 - 6
Page 51

SECTION 11 HM-133
• EXPLODED VIEW
MP3 (C)
MP2 (C)
• ELECTRICAL PARTS
[MAIN-A UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
IC1 1140011491 S.IC uPD789071MC-041-5A4-E1-A B 51.1/24.5
IC3 1110006310 S.IC BD5245G-TR B 67.3/34.8
IC6 1130012030 S.IC BR24L02FV-WE2 B 39.4/30.1
Q1 1530001941 S.TR 2SC2712-BL (TE85L,F) B 26.1/11
Q2 1590000680 S.TR DTC114EUA T106 B 21.6/34.8
Q3 1590001330 S.TR DTA114EUA T106 B 24.7/34.8
Q4 1510000771 S.TR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R,F) B 54.7/34.9
Q5 1510000771 S.TR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R,F) B 54.5/37.5
Q6 1510000771 S.TR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R,F) B 48.5/5.8
Q7 1510000771 S.TR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R,F) B 48.5/3.3
Q8 1530001941 S.TR 2SC2712-BL (TE85L,F) B 19.5/9.9
Q9 1590001010 S.TR DTB113ZK T146 B 22.8/11
D1 1790000950 S.ZEN MA8056-M (TX) B 23.1/17
D3 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 64.7/23.2
D4 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 64.7/29.2
D5 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 59.6/25.5
D6 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 58.7/20.8
D7 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 42.8/16.7
D9 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 34.1/16.3
D10 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 34.9/17.8
D11 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 38.8/14.5
D12 1750000940 S.DIO ISS400 TE61 B 57.2/29
D16 1730002280 S.ZEN MA8091-M (TX) B 55.2/14.5
D17 1730002280 S.ZEN MA8091-M (TX) B 48.8/14.5
D18 1730002280 S.ZEN MA8091-M (TX) B 12.5/13.9
X1 6060000610 S.CER EFOS4914E3 B 42.6/22.3
L1 6200001520 S.COL MLF2012D R82K-T B 12/28.9
L2 6200001520 S.COL MLF2012D R82K-T B 10.7/13.9
R2 7030000400 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 1.5 k B 24.2/8.3
R3 7030000400 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 1.5 k B 41.9/8.3
R4 7030000400 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 1.5 k B 57.3/8.2
R5 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470) B 28.6/11.2
R6 7030003620 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 k) B 26.8/34.7
R7 7030003620 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 k) B 23.3/36.8
R8 7030003570 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 k) B 19.1/33.7
R9 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 k) B 57.6/35.6
R10 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 57.6/34.3
R11 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 k) B 57.6/36.9
R12 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 k) B 60.4/37.2
R13 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 k) B 45.7/5.5
R14 7030003420 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680) B 51.5/5.9
R14 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 51.5/5.9
R15 7030003400 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470) B 51.5/3.3
R15 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 k) B 51.5/3.3
R16 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 k) B 45.7/4.2
R18 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 k) B 41.6/33.6
R19 7030003640 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 k) B 38.4/34.5
R22 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 k) B 37.9/18.7
R23 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 k) B 56.1/18.1
R24 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 k) B 58/18.6
R25 7030003520 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 k) B 59.8/18.9
R27 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 k) B 68.1/32.5
R35 7030000400 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 1.5 k B 69.1/11.9
R36 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 k) B 20.5/30.6
R37 7030003460 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 k) B 19.1/30.6
R38 7030003720 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 k) B 17.5/7.7
R39 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 k) B 24.4/5.7
R40 7030003480 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 k) B 24.4/3
R41 7030003560 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 k) B 17/32.7
R42 7030003860 S.RES ERJ3GE JPW V B 68.4/21.6
R43 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 57.4/27.5
R44 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 57.3/22.1
R45 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 53.9/18
R46 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 37.8/15.8
R47 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 37.6/17.1
R48 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 45.3/17.6
R49 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 57.3/26.2
R50 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 58.1/23.4
R51 7030003440 S.RES ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 k) B 57.4/24.7
C1 4030006850 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 471K-T B 52/16.9
C2 4510008500 S.ELE EEE1CA101WP B 35.5/5.8
C5 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B 14.9/30.4
C9 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B 16.3/16.9
C10 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B 15.6/15.5
C11 4030007050 S.CER C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B 15.6/7.2
C12 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 64.9/34.4
C13 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 44.3/27.6
C14 4030006900 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B 67.5/37.2
C15 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 41.9/29.7
C16 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 14.1/13.6
C17 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 11.7/17.4
C18 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 10.4/17.4
C19 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 13/25.8
C21 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 11.7/25.8
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C22 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 10.4/28.5
C23 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 23.1/14
C24 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 67.2/12.1
C25 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 25.6/32.2
C26 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 53/4.6
C27 4030006860 S.CER C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B 60.9/35.9
C29 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 26.4/16
C30 4030011600 S.CER C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B 23/3
C31 4510008540 S.ELE EEE1CA100SR B 28.3/4.9
J1 6510023110 CNR 3008L-8P8C <KIN>
DS1 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T 21.9/11
DS2 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T 21.9/32
DS3 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T 39.3/11
DS4 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T 39.3/32
DS5 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T 55.9/2.5
DS6 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T 56.2/26.8
DS7 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T 71.7/14.8
DS8 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T 72.2/33.8
DS10 5010000150 S.LED LT1EP53A T 51.6/5
DS10 5040003160 S.LED BRPY1211C-TR T 51.6/5
DS11 5010000150 S.LED LT1EP53A T 51.6/38
DS11 5040003160 S.LED BRPY1211C-TR T 51.6/38
MC1 7700002310 MIC EM-140
S1 2260000980 SW SKHHLP014A
EP1 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 10.4/25.8
EP2 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 14.3/17.4
EP3 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 13/17.4
EP4 6910012350 S.BEA MMZ1608Y 102BT B 14.5/11
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
S.=Surface mount
M.
H/V
LOCATION
• MECHANICAL PARTS
[CHASSIS PARTS]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
DESCRIPTION
W1 8900011271 OPC-1153A 1
MP1 8210018830 2539 FRONT PANEL 1
MP2 8210018840 2539 REAR PANEL 1
MP3 8930057380 2539 PTT BUTTON 1
MP4 8930057390 2539 LED LENS 2
MP5 8930057570 2539 SW RUBBER 1
MP6 8930057520 2539 KEYBOARD 1
MP8 8810009371 Screw BT B0 3X12NI-ZK3 (BT) 2
MP9 8810009561 Screw BT B0 2X6 NI-ZK3 (BT) 3
QTY.
[MAIN-A UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
DESCRIPTION
J1 6510023110 3008L-8P8C 1
MC1 7700002310 EM-140 1
S1 2260000980 SKHHLP014A 1
QTY.
• DIMENTIONS
(2
61.0
(2
54.3
1
/8)
104.0
(4 3/32)
13
/32)
Unit: mm (inch)
(1
31.5
1
/4)
Unit abbreviations
(C): CHASSIS PARTS
(M): MAIN-A UNIT
MP5 (C)
MP1 (C)
MP4 (C)
• VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
C:7.6
J1
M8V
1
MU/D
2
M8VSW
3
PTT
4
MICE
5
MIC
6
E
7
MDATA
8
C19
L2
C21
C22
EP1
MC1
F: [FUNC] is pushed
D: DTMF is activated
C: Common
R: Receiving
T: Transmitting
84R
94R
05R
15R
3D
BANDUP
S7
MR
S3S4S5
VFO
S2
4D
7D
ABCD
S9
3
S6
S13 S14
2
S17
1
S21
5D
F-2
PTT
F-1
1S
MAIN-A UNIT
MP9 (C)
S1 (M)
MP6 (C)
MP8 (C)
MC1 (M)
J1 (M)
W1 (C)
Q1
R5
32C
L1
EP2
EP3
EP4
C16
C18
C17
D18
71D
74R
01D
S10
6
5
S18
4
S22
1C
64R
9D
S11
9
S15 S16
8
S19
7
S23
D16
R:6.8
T:6.8
C11
C10
C30
S12
0
S20
S24
2C
92C
D1
C9
C5
R39R40
C31
MKEY-08
MKEY-07
MKEY-06
MKEY-05
MKEY-04
MKEY-03
MKEY-02
MKEY-01
MKEY-00
34R
44R
54
R
11D
DTMF
FUNC
21D
6D
DN
S8
S25
S26
C:5.0
53R
4R
R:7.5
T:7.5
Q9
Q8
R38
F:1.9
R22
MKEY-I0
R23
MKEY-I1
R24
MKEY-I2
R25
MKEY-I3
42C
R37
51R
Q7
61R
R
DS10
24
0
R
C:3.8 C:3.8 C:3.8
7SD8SD
63R
R8
14R
41R
62C
Q6
31R
F:1.9
D:1.9
G
T:1.9 P:1.9
01P
1CI
1
R27
C:5.0
Q2
21R
72
41P8231P9221P0311P
09OZB/13P
TESER
PPV
2
3
4
52X6
HR30
IC3
1
OUT
2
VDD
3
VSS
3R
5SD6SD
3SD
4SD
C12
Q3
72C
01R
11R
Q4
Q5
9R
R
G
DS11
LED-S2
SEND
LED-M2
LED-M1
61
81
91
12
70P
02DXT7102KCSA
60P0250P
40P2230P3220P4210P5200P6251P
021IS/22P
2PTNI/62P211PTNI/52P310PTNI/42P
09OT/03P0108IT/72P
02SS/3
SSV8DDV
1X
X1
2P
7
51
9
11
41
R18
R19
C13
51C
5
CD
41C
4
NC
52C
2R
1SD2SD
C:3.8
R6R7
)1M-DEL(R-EDOM
)2MDEL(G-EDOM
5
6
7PW8
ADS
CCV
LCS
SSV
6CI
0A
21A32A4
1
11 - 1
Page 52

SECTION 12 UT-123 (Optional product)
• VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
863C
763C
RXDT
R390
J1
R391
GND
3A
83Y9
103G114Y124A134G14
TXCK
1
2345678
AGND
R392
AMB_TXD
AMB_RXD
BTONE
DAFOUT
RXCK
11G21A31Y42G52A62Y7
VCC
ACQ
DVC
DMOD
AMODIN
C304
IC354
D_TXDT
D_TXCK
9
222324252627282930
C5V
TOOBSPG
0DXTSPG
IC359
0DXRSPG
R393
D_RXCK
D_RXDT
1011121314
AMB_EPR
AMB_STB
873C
Q222
VCC
NC
2A3
1
783R
AMBERXD
DCEL
CPU5V
13PIN OPT1
17
18
192021
AMB_RES
AMB_CLK
V5
GPSRESET
663C
583R
4Y5
GND
R386
GPSBOOT
GPSRESET
15
16
GPSRXD0
GPSTXD0
0DXRG
D102
0DXTG
463C
563R
1
2
3
4
1
2
43
12
13
14
15
AD1
EPORT9
EPORT12
VDD_BACKUP
TX018RX0
EPORT11/RX1
EPORT10/TX1
17
19
16
R362
R363
103CI
473C
673C
773C
573C
5
9
10
11
GND
XRESET
BOOT2/EXROMI
GND
GND23GND
ADREFT
20
21
22
J2
C303
8
7
6
5
R307
C212
Q219
AD0
AMBEEPR
1NC2A3
GND
IC357
VCC
4Y5
383R
AMB_EPR
553R
073C
C213
C206
R212
4
2
3
C207
13
DOC214DOC1
VSS
RX_SIG_IN
12
R209
5
1
11
EP203
R211
RXFB
163C
CE
263C
EP353
RX
C:3.3V
C103
IC203
TXDT
RXDT
RXCK
R210
SIGN201
15BT16
TXO17TXE18TXP19TXD20RXD21RXC22TXC23S/N24VDD
VBIAS
PLLACQ
CLKDIVB5RX_HOLD6RXDCACQ
CLKDIVA
RX_PSAVE
4
7
8
9
10
C209
R208
1
3
VDD2GND
IC352
VOUT
4NC5
C:3.2V
C102
C104
TXCK
XTAL
IC202
XTAL/CLK_RX
1
2
3
R203
R204
R205
R206
RX
001
99
89
79
69
59
49
39
29
19
09
98
88
78
68
58
48
38
28
18
08
97
87
77
67
CP201
CP202
CP203
C205
DXT_BMA
TDXT_D
493R
R396
1
3
CE
VDD2GND
IC361
VOUT
4NC5
EP355
Q218
753R
Q221
763R
1
2
3
5
6
8
GND
EPORT4
EPORT54EPORT7
EPORT67EPORT3
IC353
BOOT1/EPORT2
GND26GND
VDD
1PPS
EPORT8
EPORT1
363C
R306
27
C211
Q200
Q223
173C
28
29
30
273C
Q201
C214
DCEL
ACQ
R217
C208
C210
24RF25
R305
RX
C:4.8V
CN
CN
CN
CN
CN
CN
CN
CN
CN
CN
DDV
DNG
DNG
DDV
NE_D
1LES_CED
0ELS_CEDOC
NE_PEELS
NE_PILS
1LES_DUAB
0LES_DUAB
NE_TFOS
CN
1LES_NNAHC
DDV
EP202
R207
AV
CP2
C204
R202
12 - 1
DVC
C51
C52
C53
1
2NC3NC4NC5NC6NC7NC8
GND
OC
CHANN_SEL0
RATE_SEL4
75
74
RXp-p
3.3V
5Q6
CLR7PRE8VCC
GND
C202
R216
R100
GND3OUT
GND
73
2D3Q4
Q202
2
1
RATE_SEL3
CLK
VCC
C203
AMBERES
873R
R373
AMB_RES
C50
R50
1
2
Q51
5
34
Q50
C54
C101
VDD9GND10GND11VDD12VDD
RATE_SEL2
RATE_SEL1
RATE_SEL0
X2/CLKIN
RESETN
X1
NC
70
69
68
67
66
65
72
71
AMBERES
EP201
C201
IC201
1
R215
FM:0V
C216
DV:1.4V
C200
X200
4
EP200
C302
TXDTAMB_STB
AMBESTB
GND
3A
IC360
83Y9
D_TXDT
AMB_TXD
RX
FM:0V
DV:3.3V
R2
C100
14NC15NC16NC17
13
NC
IC101
GND
VDD
GND
NC
62
64
63
D100
C110
R104
R213
R214
RX
C360
AGND
R303
23
24
25
20
21
NC18NC19NC
NC22NC
EPR
VDD
GND
ENCODER_EN
KLC_XR_CEDOC
KLC_XR_NAHC
BRTS_XR_CEDOC
BRTS_XR_NAHC
ATAD_XR_CEDOC
ATAD_XR_NAHC
KLC_XT_CE
KLC_XT_NAHC
BRTS_XT_CEDOC
BRTS_XT_NAHC
ATAD_XT_CEDOC
ATAD_XT_NAHC
CLOCK_MODE
VDD
GND
VDD
GND
NC
NC
59
C357
C356
11
DGND12DVDD
AVDD210AGND2
C354
NC
58
C109
RESET
9
C352
57
56
AMBERES
SCLKSCLK
13
14
SCLK15MCLK
REFOUT8REFCAP
7
C353
R304
EP352
R353
55
NC
54
R105
SO
16
SDO
SDOFS18SDIFS
VINP6VINN
5
GND
53
52
51
CP1
SI
SENSEN
17
19
20
SE
SDI
AVDD14AGND1
VOUTP2VOUTN
1
3
R352
1
2
3
4
NC
61
60
AMBETXD
103G114Y124A134G14
AMB_CLK
C358
R354
EP351
IC350
R351
IC300
R302
963C
AMBECLK
11G21A31Y42G52A62Y7
VCC
AMBE2020
VIH=Vdd+0.3V
RX
C:4.5V
C1
1
3
CE
VDD2GND
VOUT
4NC5
C2
C3
DNG
DOC
DNG
DDV
DDV
DNG
CN
D
DV
DDV
DDV
DDV
DDV
DDV
DNG
C116
EP350
R350
8
7
6
5
• PARTS LIST
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
IC1 1180002371 S.REG R1111N321B-TR-F T 13/6.8
IC101 1130010920 S.IC AMBE-2020 B 9.8/9.5
IC102 1130011930 S.IC SN74LVC1G04DCKR T 4.7/5.1
IC201 1130013440 S.IC SN74LVC2G74DCTR T 30.3/12.3
IC202 1110005430 S.IC CMX589AD5 B 37/7.5
IC203 1130007021 S.IC TC7S66FU (TE85L,F) T 39.6/5.2
IC300 1110005290 S.IC NJM2115V-TE1-#ZZZB T 28.6/6.3
IC301 1130006921 S.IC TA75W01FU (TE12L,F) T 35.7/9.1
IC350 1130011631 S.IC AD73311ARSZ B 24.3/6.4
IC352 1180002371 S.REG R1111N321B-TR-F B 12.9/26.7
IC353 1190002470 S.IC ITRAX130 <MRF> B 52.2/36.7
IC354 1130013640 S.IC TC74VHCT125AFK (E,K) T 2.5/27.2
IC357 1130013570 S.IC SN74LVC1G07DCK T 18.4/22.7
IC359 1130013570 S.IC SN74LVC1G07DCK T 18.9/18.2
IC360 1130013650 S.IC TC74VHC125FK (EL,K) T 17.8/28.8
IC361 1180002371 S.REG R1111N321B-TR-F T 23.8/20.7
Q1 1510000581 S.TR 2SA1362-GR (TE85R,F) T 12/15.7
Q2 1590003390 S.TR UNR9215J-(TX) T 8.4/13.2
Q224
Q1
R1
IC1
EP1
62
72
82
92
03
13
23
33
43
53
63
73
83
93
04
14
24
34
44
54
64
74
84
94
05
C108
4Y5
GND
2
GND3OUT
GND
1
DNGA
C351
C350
R3
Q2
RPEEBMA
KLCEBMA
RX
FM:0V
DV:3.2V
BTSEBMA
OS
DXTEBMA
KLCS
NES
IS
C106
DXREBMA
C107
C113
R109
C310
DV:4.7V
FM:0.5V
RX
FM:0V
DV:0.4V
Q100
R108
C117
R106
R310
RX
C112
R107
FM:0V
RX
DV:1.3V
VCC
IC102
1NC2A3
111C
X100
VCC
4
C114
EP100
C300
EP300
R300
R301
C301
Q50 1510000581 S.TR 2SA1362-GR (TE85R,F) B 3.3/30.7
Q51 1590001170 S.TR XP1501-(TX) .AB B 7.8/30.1
Q100 1530002280 S.TR 2SC4081 T106 S T 2.2/7.3
Q200 1590003390 S.TR UNR9215J-(TX) T 39/11.8
Q201 1590003390 S.TR UNR9215J-(TX) T 35.5/3.9
Q202 1530002280 S.TR 2SC4081 T106 S T 26.2/12.8
Q218 1520000561 S.TR 2SB1123 T-TD-E B 8.6/22.5
Q219 1590001170 S.TR XP1501-(TX) .AB B 8.1/26.4
Q221 1590003390 S.TR UNR9215J-(TX) T 6/14.4
Q222 1590003390 S.TR UNR9215J-(TX) T 5.9/17.4
Q223 1590003390 S.TR UNR9215J-(TX) T 40.9/10.8
Q224 1590003250 S.TR UNR9115J-(TX) B 5.2/24.5
D100 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) T 8.1/2.1
D102 1790001240 S.DIO MA2S728-(TX) T 27.9/20.1
X100 6050012290 S.XTL CR-820 (16.384 MHz) T 7.9/8.4
X200 6050012300 S.XTL CR-821 (9.8304 MHz) T 21.5/11.8
R1 7030000180 S.RES MCR10EZHJ 22 (220) T 10.3/12.5
R2 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 10/5.3
R3 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 9.9/15.7
R50 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) B 7.3/28.3
R100 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 6.3/2.2
R104 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 7/4.1
R105 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330 ) T 17.1/6.5
R106 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 ) T 2.6/3.5
R107 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 2.6/5.1
R108 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 4/7.7
R109 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220 ) T 1.7/10.3
R202 7030010040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ-JPW T 32.8/13.6
R203 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 34.7/12.8
R204 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 35.6/13
R205 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 36.5/13.3
R206 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 37.4/13.8
R207 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 39.3/13.3
R208 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 41.1/13.9
R209 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) B 39.9/13.6
R210 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 31.5/4.1
R211 7030006610 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 k) T 38.7/3.3
R212 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 40.1/7.6
R213 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 ) T 28.1/12.7
R214 7030005120 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 k) T 27.8/11.1
R215 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 26.3/14.6
R216 7030004990 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 221 X (220 ) T 25.6/10.8
R217 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 39.3/14.2
R300 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 22.4/5.9
R301 7030005310 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 k) T 23.9/6.4
R302 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 23.9/7.6
R303 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 29.5/2.9
R304 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 30.3/3.8
R305 7310004610 S.TRI EVM-2WSX80 B15 (104) B 31.3/6.7
R306 7030005060 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 333 X (33 k) T 35.7/5.8
R307 7030005090 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 k) T 33.6/6.4
R310 7030005530 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10 ) T 22.9/3
R350 7030005010 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680 ) T 25.3/8.8
R351 7030008400 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 182 X (1.8 k) T 27.5/8.8
R352 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) T 27.9/3.8
R353 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 ) B 29.4/5.8
R354 7030005240 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 k) B 20.6/11.1
R355 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) B 15.5/26.3
R357 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 7.5/15.4
R362 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330 ) T 20.2/20.4
R363 7030007280 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330 ) T 21.5/18.1
R365 7030005000 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 471 X (470 ) B 10.4/27.3
R367 7030005040 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 k) T 7.5/17
R373 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 16.1/24.1
R378 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) T 19/24.9
R383 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 17.5/24.8
R385 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 17.1/18.3
R386 7030005050 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 k) T 16.1/20.8
R387 7030008290 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 k) T 18/20.1
R390 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) T 4.1/30.6
R391 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) T 4.4/23.8
R392 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) T 1.6/22.4
R393 7030005160 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 M) T 3/32
R394 7030005220 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 k) T 22.9/23.7
R396 7030004980 S.RES ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 ) T 24.6/22.8
C1 4550007680 S.TAN TEESVP 0J 226M8R T 11.9/9.7
C2 4550007600 S.TAN F920J106MPABMA T 12.7/11.4
C3 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 13.4/12.8
C50 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 13.1/29
DESCRIPTION
M.
H/V
LOCATION
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
NO. NO.
C51 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 4.2/26.4
C52 4550006930 S.TAN TEESVP 0J 225M8R B 1.8/27.8
C53 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 3.2/28.3
C54 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 4.3/27.6
C100 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 14.8/19.2
C101 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 5.9/19
C102 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 5/8.8
C103 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 4/11.8
C104 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 3.4/2.2
C106 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 16.7/10.2
C107 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 17.6/10.2
C108 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 16.8/5
C109 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 12.1/2.8
C110 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 10.1/2
C111 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 5.6/10
C112 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 1.7/5.1
C113 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 1.7/9.4
C114 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 8.5/5.8
C116 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 5.1/2.7
C117 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 2.9/9.6
C200 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 22/14.1
C201 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 26.5/10.8
C202 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 24.7/10.8
C203 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 18.5/13.8
C204 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 32.5/12.4
C205 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 38.2/1.5
C206 4030017030 S.CER ECJ0EB1A273K B 39.1/1.5
C207 4030017030 S.CER ECJ0EB1A273K B 40/1.5
C208 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 33.1/2.1
C209 4030017400 S.CER ECJ0EC1H220J B 40.1/12.7
C210 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K B 38.7/12.8
C211 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 40.5/14.6
C212 4030017760 S.CER ECJ0EB1H222K B 31.1/2.9
C213 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 39.5/8.5
C214 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 33.9/3.9
C216 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 24.7/14.6
C300 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 25.2/4.4
C301 4030018860 S.CER ECJ0EB0J105K T 22.4/4.3
C302 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 27.9/2.9
C303 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 38.2/9.8
C304 4030017490 S.CER C1608 JB 1A 105K-T T 32.7/9.6
C310 4550007730 S.TAN TEESVJ 0J 106M8R T 24.9/2.1
C350 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K T 23.5/8.8
C351 4030016970 S.CER ECJ0EB1C223K T 24.4/8.8
C352 4030016950 S.CER ECJ0EB1A473K B 29.4/7.4
C353 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 30.2/3.1
C354 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 29.3/3.1
C355 4030017420 S.CER ECJ0EC1H470J T 18.2/8.8
C356 4550006930 S.TAN TEESVP 0J 225M8R B 23.9/11.1
C357 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 22/12.8
C358 4030016930 S.CER ECJ0EB1A104K B 20.6/12
C360 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K B 27.8/2.2
C361 4550007090 S.TAN TEESVA 1A 226M8R B 15.8/29.3
C362 4550007600 S.TAN F920J106MPABMA B 10.1/30.3
C363 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 59.8/46.7
C364 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 10.4/25.6
C366 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 20.5/23.7
C367 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 1.3/32.1
C368 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 17.4/21
C369 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 20.6/27.4
C370 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K B 13.7/30
C371 4550006930 S.TAN TEESVP 0J 225M8R B 56.9/16.2
C372 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 18.8/14.8
C374 4550007600 S.TAN F920J106MPABMA T 27.1/22.8
C375 4550007600 S.TAN F920J106MPABMA T 26.4/20.3
C376 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 24.8/24
C377 4030016790 S.CER ECJ0EB1C103K T 24.5/18.5
C378 4030017460 S.CER ECJ0EB1E102K T 29.7/17.3
J1 6510018440 S.CNR AXN430C330P T 10.5/25.7
J1 6510025790 S.CNR AXN430C030S T 10.5/25.7
EP1 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 14.6/9.7
EP100 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 8.5/4.9
EP200 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 20.1/13.8
EP201 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 27.9/14.6
EP202 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 37.1/4.4
EP203 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 38.5/7.6
EP300 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 24.1/3.4
EP350 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 28.9/1.9
EP351 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T B 21.8/11.6
EP352 6910018460 S.BEA MMZ1005Y102C-T T 17.1/7.7
EP353 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T T 20.9/15.5
EP355 6910014690 S.BEA MPZ1608S221A-T B 12.5/23
DESCRIPTION
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
S.=Surface mount
M.
H/V
LOCATION
Page 53

• BOARD LAYOUTS
• MAIN UNIT (TOP VIEW)
• MAIN UNIT (BOTTOM VIEW)
C363
173C
353CI
2J
R208
902C
902R
C210
R206
R205
R204
R203
653C
EP351
753C
453R
853C
IC352
C361
073C
05C
C100
553R
553PE
C362
15Q
05R
C54
Q50
C53
C101
463C
563R
812Q
Q219
422Q
15C
C52
702R
202R
C200
002PE
302C
2Q
Q221
3C
002Q
C204
102CI
R213
Q202
002X
R1
301C
322Q
212R
302CI
312C
302PE
C303
103CI
C304
412R
153R
C201
R216
R350
C202
C351
203R
C350
603R
R307
IC300
R301
R300
112R
DT
EP202
Q201
C214
403R
253R
003C
EP300
013R
C301
3H04H54H05H55H06H
KC
DNG
303R
053PE
203C
013C
02H52H03H5
553C
C107
501R
EP352
X100
R108
001Q
IC1
C108
C109
011C
R2
001PE
411C
401R
IC102
R106 R107
C112
C116
001D
C104
R100
01H51H
1PC
0H5H
V0 V5 V10 V15 V20 V25 V30 V35 V40 V45 V50 V55 V60
C106
1PE
2C
1C
C111
201C
C117
901R
311C
C211
712R
B9466B
D102
473C
C375
C376
693R
163CI
493R
C369
063CI
C366
IC357
863C
R362
783R
R386
873R
R383
R373
KCM
C378
102PE
512R
953CI
R385
R363
612C
EP353
273C
773C
Q1
J1
R367
R3
R357
Q222
R390
393R
C367
193R
453CI
R392
C207
C206
C205
DT
C208
C212
C353
DNGKC
C354
C360
202CI
012R
503R
C352
R353
IC350
101CI
1PC
0H 5H 01H51H02H52H03H53H04H 54H05H55H 06H
V0V5V10V15V20V25V30V35V40V45V50V55V60
12 - 2
Page 54

+AMIMINAMI(IRANOKU/SAKA*APAN
0HONE
&AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMCOJPWORLDINDEXHTML
#ORPORATE(EADQUARTERS
TH!VENUE.%"ELLEVUE7!53!
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMAMERICACOM
%MAILSALES ICOMAMERICACOM
#USTOMER3ERVICE
0HONE
'LENWOOD#ENTRE
(IGHWAY$ELTA"#6+"#ANADA
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMCANADACOM
%MAILINFO ICOMCANADACOM
5NIT'ARDEN2OAD#LAYTON6)#!USTRALIA
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMNETAU
%MAILSALES ICOMNETAU
!(ARRIS2OAD%AST4AMAKI
!UCKLAND.EW:EALAND
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMCONZ
%MAILINQUIRIES ICOMCONZ
2OOM#TH&LOOR,ONG3ILVER-ANSION.O
9ONG$ING2OAD(AIDIAN$ISTRICT"EIJING#HINA
0HONE&AX
52, HTTPWWWBJICOMCOM
%MAILBJICOM BJICOMCOM
#OMMUNICATION%QUIPMENT
(IMMELGEISTER3TR$$USSELDORF'ERMANY
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMEUROPECOM
%MAILINFO ICOMEUROPECOM
#TRA2UBI3ANT#UGATDEL6ALLES"ARCELONA30!).
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMSPAINCOM
%MAILICOM ICOMSPAINCOM
5NIT3EA3T(ERNE"AY+ENT#4,$5+
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMUKCOUK
%MAILINFO ICOMUKCOUK
:ACDELA0LAINE
2UE"RINDEJONCDES-OULINAIS"0
4OULOUSE#EDEX&RANCE
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWICOMFRANCECOM
%MAILICOM ICOMFRANCECOM
&.O3EC#HENG4EH2OAD4AIPEI4AIWAN2/#
0HONE &AX
52, HTTPWWWASIAICOMCOM
%MAILSALES ASIAICOMCOM
3OPOT-AJA0OLAND
0HONE &AX
%MAILICOMPOLSKA ICOMPOLSKACOMPL
Page 55

1-1-32, Kamiminami, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0003, Japan
S-14310XZ-C1
© 2007 Icom Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...