Page 1

SERVICE
MANUAL
MARINE PLOTTER/SOUNDER
DGPS BEACON RECEIVER
Page 2

6-9-16, Kamihigashi, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0002, Japan
Phone : 06 6793 5302
Fax : 06 6793 0013
Communication Equipment
Himmelgeister Str. 100, D-40225 Düsseldorf, Germany
Phone: 0211 346047 Fax : 0211 333639
URL : http://www.icomeurope.com
Unit 9, Sea St., Herne Bay, Kent, CT6 8LD, U.K.
Phone: 01227 741741 Fax : 01227 741742
URL : http://www.icomuk.co.uk
Zac de la Plaine, Rue Brindejonc des Moulinais
BP 5804, 31505 Toulouse Cedex, France
Phone: 561 36 03 03 Fax : 561 36 03 00
URL : http://www.icom-france.com
Crta. de Gracia a Manresa Km. 14,750
08190 Sant Cugat del Valles Barcelona, SPAIN
Phone: (93) 590 26 70 Fax : (93) 589 04 46
URL : http://www.icomspain.com
<
Corporate Headquarters
>
2380 116th Avenue N.E., Bellevue, WA 98004, U.S.A.
Phone: (425) 454-8155 Fax : (425) 454-1509
URL : http://www.icomamerica.com
<
Customer Service
>
Phone: (425) 454-7619
A.C.N. 006 092 575
290-294 Albert Street, Brunswick, Victoria, 3056, Australia
Phone: 03 9387 0666 Fax : 03 9387 0022
URL : http://www.icom.net.au
6F No. 68, Sec. 1 Cheng-Teh Road, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Phone: (02) 2559 1899 Fax : (02) 2559 1874
3071 #5 Road, Unit 9, Richmond, B.C., V6X 2T4, Canada
Phone: (604) 273-7400 Fax : (604) 273-1900
URL : http://www.icomcanada.com
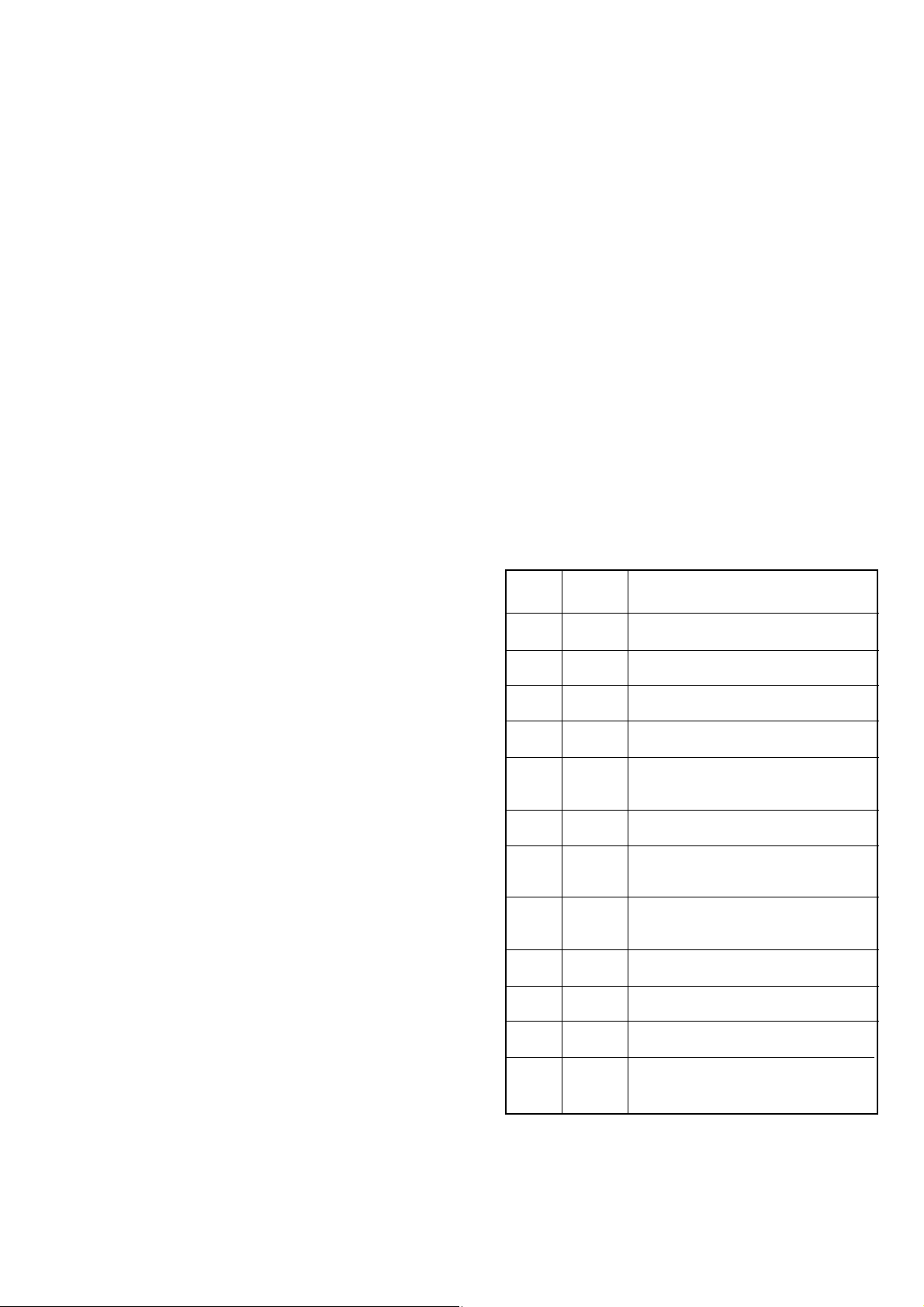
INTRODUCTION
DANGER
ORDERING PARTS
REPAIR NOTES
This service manual describes the latest service information
for the
FP-561 MARINE PLOTTER/SOUNDER and RD-200
DGPS BEACON RECEIVER
MODEL
FP-561
VERSION
General
Europe
at the time of publication.
SYMBOL
GEN
EUR
To upgrade quality, all electrical or mechanical parts and
internal circuits are subject to change without notice or
obligation.
NEVER connect the unit to an AC outlet or to a DC power
supply that uses more than 33 V (FP-561) or 16 V (RD-200).
Such a connection could cause a fire hazard and/or electric.
DO NOT expose the unit to rain, snow or any liquids.
DO NOT reverse the polarities of the power supply when
connecting the unit.
DO NOT apply an RF signal of more than 20 dBm (100mW)
to the antenna connector. This could damage the unit’s front
end.
FP-561
Be sure to include the following four points when ordering
replacement parts:
1. 10-digit order numbers
2. Component part number and name
3. Equipment model name and unit name
4. Quantity required
<SAMPLE ORDER>
0910051392 PCB B-5305 FP-561 MAIN UNIT 1 pieces
8810004540 Screw BiH 3x8 SUS FP-561 Chassis 10 pieces
Addresses are provided on the inside back cover for your
convenience.
RD-200
1. Make sure a problem is internal before disassembling
the unit.
2. DO NOT open the unit until the unit is disconnected from
its power source.
3. DO NOT force any of the variable components. Turn
them slowly and smoothly.
4. DO NOT short any circuits or electronic parts. An insulat-
ed turning tool MUST be used for all adjustments.
5. DO NOT keep power ON for a long time when the unit is
defective.
6. READ the instructions of test equipment thoroughly
before connecting equipment to the unit.
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
1-1 FP-561 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
1-2 RD-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
2-1 FP-561 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-1
2-2 RD-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
SECTION 3 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
3-1 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3-2 RECEIVER CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3-3 REGULATOR CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
3-4 INTERFACE CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
3-5 LOGIC CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
3-6 DGPS RECEIVER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-4
3-7 PORT ALLOCATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-5
SECTION 4 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
4-1 PREPARATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
4-2 FP-561 TRANSMITTER ADJUSTMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
4-3 FP-561 RECEIVER ADJUSTMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
4-4 FP-561 WATER TEMPERTUREM ADJUSTMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
4-5 RD-200 ADJUSTMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-4
SECTION 5 PARTS LIST
SECTION 6 MECHANICAL PARTS AND DISASSEMBLY
SECTION 7 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
SECTION 8 BOARD LAYOUTS
8-1 FP-561
8-1-1 SW UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-1
8-1-2 LOGIC UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-3
8-1-3 MAIN UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-5
8-2 RD-200
8-2-1 MAIN UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-7
8-2-2 ANT UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-9
SECTION 9 BLOCK DIAGRAM
9-1 FP-561 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-1
9-2 RD-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-2
SECTION 10 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
10-1 FP-561 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-1
10-2 RD-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-3
Page 4

1-1 FP-561
‘ GENERAL
• Display : 5.6 inch TFT color LCD (320×234 pixels)
• Power supply requirement : 11–30 V DC
• LCD brightness : 16 levels
• Power consumption : Less than 22 W (Less than 1.8 Aat 12 V DC)
• Dimensions (projections not included) : 186(W)×203(H)×102(D) mm; 7
5
⁄16(W)×8(H)×4(D) in
• Weight (approx.) : 2.2 kg; 4 lb 14 oz
• Usable temperature range : 0˚C to +50˚C; +32˚F to +122˚F
• Unit of water depth : m (meter), FT (feet), FM (fathom)
• Unit of water temperature : ˚C, ˚F
• Unit of speed : KT (knots), km/h, MI/h (miles/h)
• Unit of distance : NM (nautical miles), km, MI (miles)
• Input data format : NMEA0183, Water temp./speed, DGPS
• Output data format : NMEA0183 (GGA, GLL, XTE, AAM, VTG, BOD, WPL, BWC),
Start-stop serial forward; 4800 bps
‘ GPS
• Receive system : 12 parallel-channel, all-in-one view
• Receive frequency : 1575.42 MHz (±1 MHz)
• Measuring accuracy (2DRMS) : Position 100 m, 95% of the time, PDOP≤3 (Less than 100 m, S/A OFF)
Speed Less than 1 m/sec. (PDOP
≤3, S/A ON)
NOTE: All GPS receivers are subject to degradation of position and velocity accuracy under the U.S. Department of
Defence.
• Data renewed interval : 1 sec.
‘ PLOTTER
• Scale setting : 16 steps
• Plotting interval : 5 sec. to 60 min., 0.01–9.99 NM*
• No. of track memories : 5000 (selectable from 7 colors)
• No. of route memories : 20 (50 points/route)
• No. of event markers : 500
• Navigation computer : Vessel position (longitude/latitude), cursor position, distance, elapsed time,
course-out distance, direction, distance, time
• Data indication : Coastline, place name, contour line, route, lighthouse, longitude/latitude line
• Alarm : Area and Arrival alarms
1 - 1
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
Page 5

1 - 2
All stated specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation.
‘ VIDEO SOUNDER
• Transmission freq. : 50 kHz, 200 kHz
• Output power : 500 W RMS
• Water depth range : 5–640 m* in 8-color indication
• Water temp. range : 0˚C to +40˚C; +32˚F to +104˚F
• Speed range : 0.0–99.9 KT*
• Bottom lock expansion range : 5 m*, 10 m*, 20 m*, 40 m*
• Phase shift variable range : 1–640 m*
• Type of display screen : Standard, A-scope, dual frequencies, bottom and marker zoom
• Picture sweep speed : 6 levels including pause
• Alarm : Shallow, depth and fish school
*selectable in each unit
1-2 RD-200
‘ GENERAL
• Frequency coverage : 283.5 kHz to 325.0 kHz
• Type of emmision : 1K0F2B
• Antenna impedance : 50 Ω nominal
• Intermediate frequency : 455 kHz
• Usable temperature range : –20˚C to +70˚C; –4˚F to +158˚F
• Power supply requirement : 12 V DC nominal negative ground
• Current drain (at 12 V DC) : Less than 0.2 A
• Dimensions (projections not included) : 140(d)×157.2(H) mm; 5
1
⁄2(d)×63⁄16(H) in
• Weight : 1.0 kg; 2 lb 3 oz
‘ RECEIVER
• Intermediate frequency : 455 kHz
• Sensitivity : 0.2 µV at 12 dB SINAD
• Sprious response : 60 dB
• Intermodulation : 50 dB
Page 6
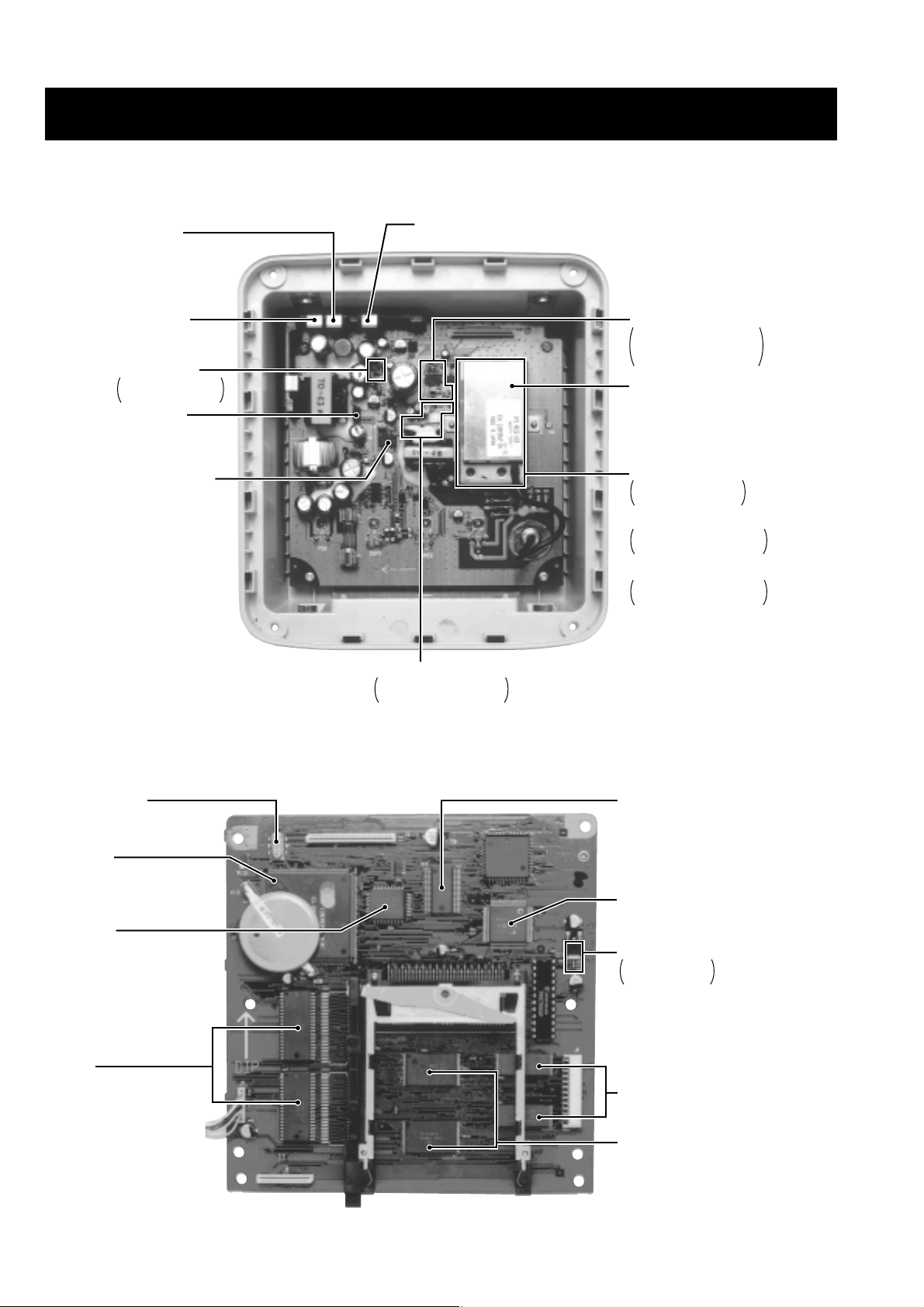
2 - 1
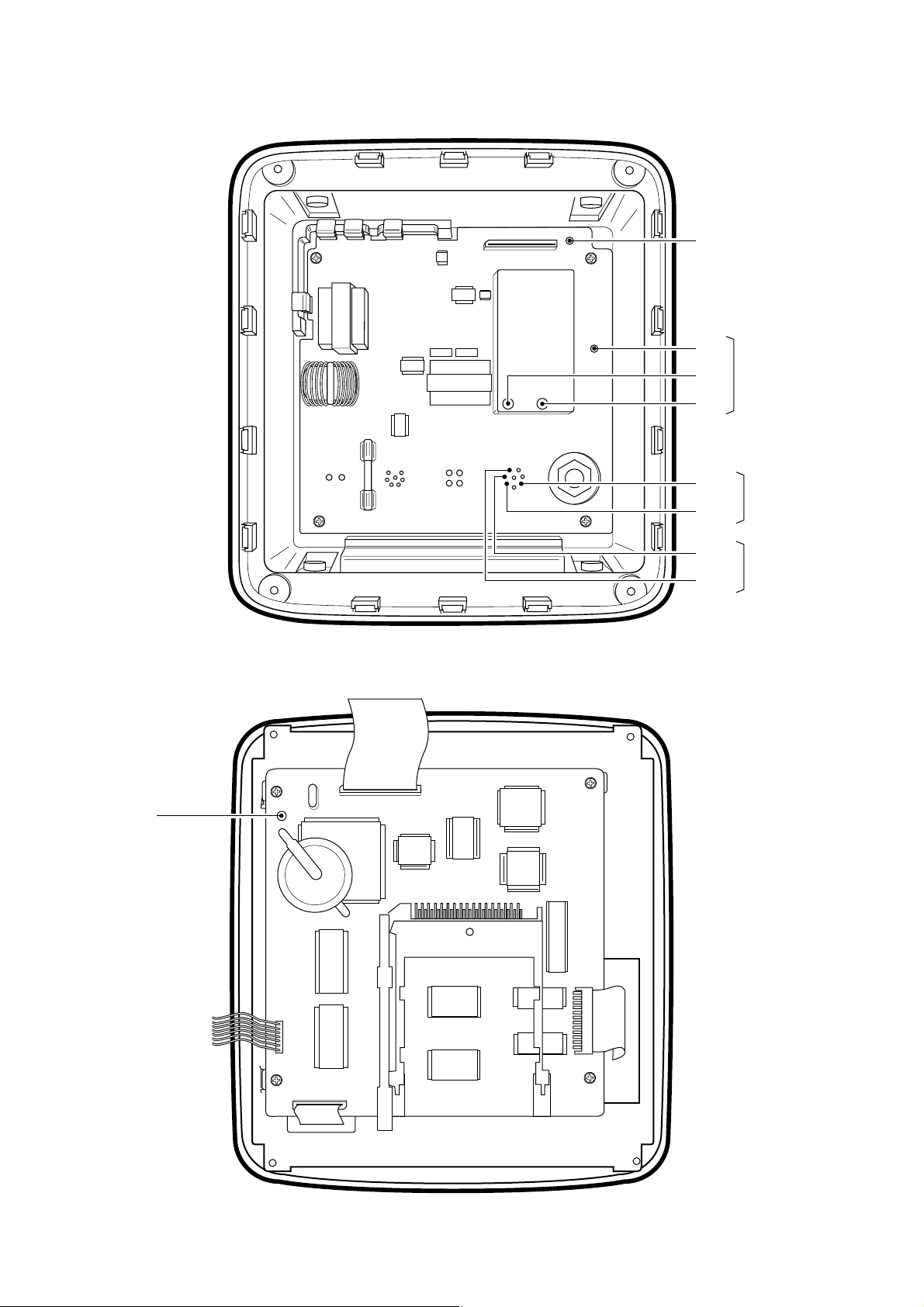
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
2-1 FP-561
• MAIN UNIT
• LOGIC UNIT
+5V regulator
(IC13: PQ05RF21)
GPS receiver
Switching control
(IC9: UPC494GS)
12V rectifier
(D13: SB30-09J)
8V rectifier
(D22: SB30-09J)
+6V regulator
Q27: 2SD1664 Q
D37: RD7.5M B1
40V rectifier
(D12: RG-2A)
Power amplifier
Q6, Q7: FS30KMJ-3
Q23, Q24: 2SC3326-B
Driver
IC2: TC4093BF
Q2, Q3: 2SC2712-GR
Q4, Q5: 2SA1162-GR
STC circuit
Q1: 2SC3326-B
Q26: 2SC2712-GR
200 kHz local oscillator circuit
IC3: TC3W03FU
X1: CR-497 (5.24MHz)
50 kHz local oscillator circuit
IC4: TC3W03FU
X2: CR-496 (4.04MHz)
Crystal oscillator
(X1: DSO-49SJ)
Main CPU
(IC1: CL-PS7500FE)
FIFO RAM
(IC20: CY7C433-40JC)
DRAM
(IC34, IC35: M5M44260CJ)
SRAM
(IC30, IC31: M5M51008BVP-70LL)
Flash ROM
(IC32, IC33: MBM29F800BA-90PFTN)
Sub CPU
(IC22: TMP90PM36F)
Mail box RAM
(IC21: M66220FP)
DC-DC converter
Q4: 2SB120IS
Q5: XP6501AB
Page 7
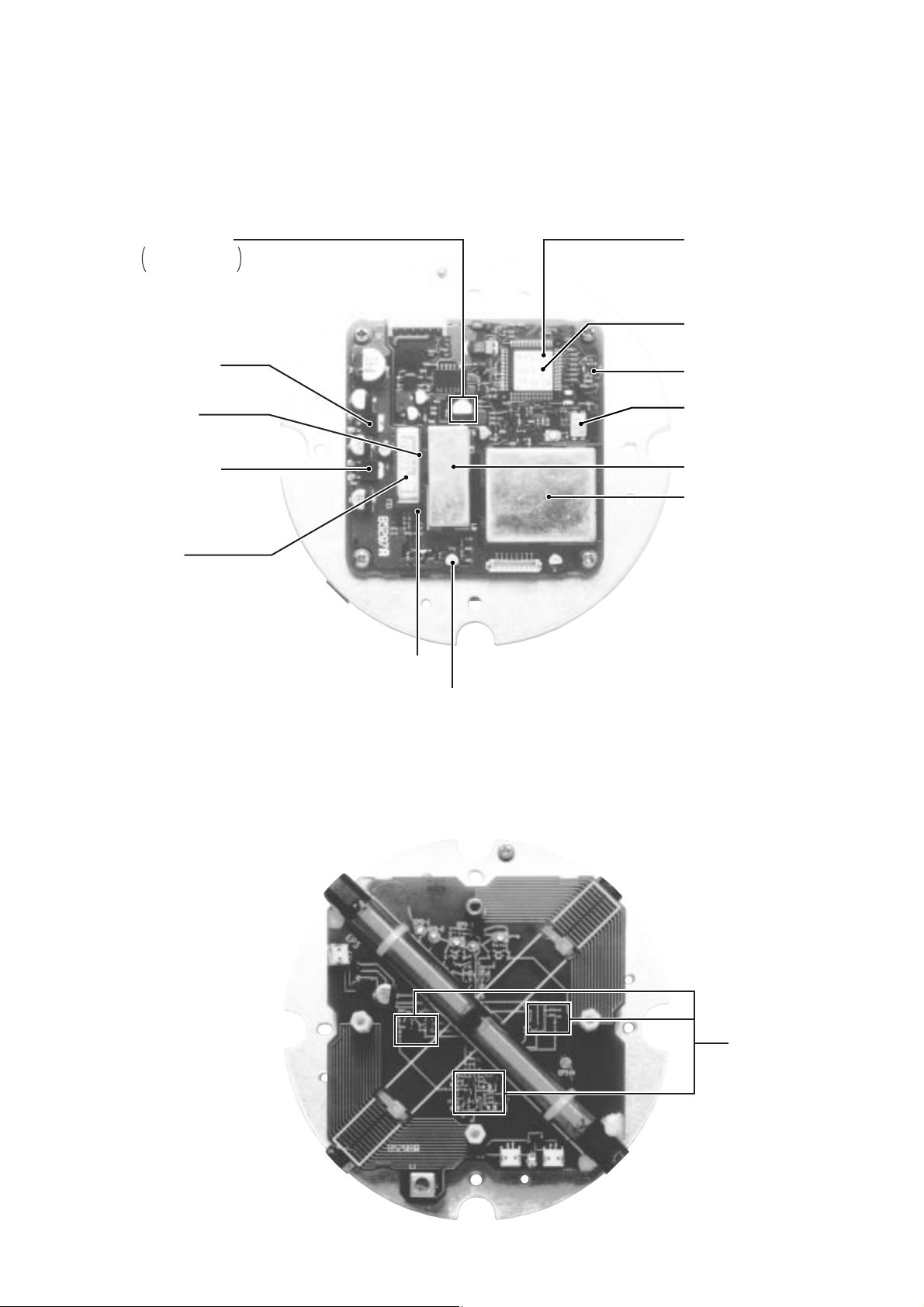
2 - 2
2-2 RD-200
• MAIN UNIT
• ANT UNIT
DDS
(IC6: SC-1287)
1st mixer
(IC2: ND487C1 3R)
CPU
(IC12: HD64F3644H)
EEPROM*
(IC13: X25320SI-2.7)
D/A converter
(IC19: TA75S01F)
Reference oscillator
(X1: DSX751S 14.5984MHz)
+5V regulator
(IC9: TA7805F)
IF filter
(FI1: CFJ455K8)
IF amplifier*
(Q1: 3SK131 K)
RF amplifier*
(IC1: µPC1676G)
* : Located under side of these point
+8V regulator
(IC8: TA7808F)
FM IF IC*
(IC3: TA31136FN (D))
+6.5V regulator*
Q3: 2SD1664 Q
D2: MA8075 L
RF amplifier
(Q1– Q8: 2SK209 GR)
Page 8
3 - 1
SECTION 3 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
3-1 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
3-1-1 TRANSMIT OUTPUT PULSE CONTROL
CIRCUIT
The 200 kHz/50 kHz pulse signals from the LOGIC unit via
J1 (pin 3) are passed through the buffer amplifier circuit (IC1,
pin 1 and pin 3), and are inverted and output from IC1 (pin 2
and pin 5) as 180˚ phase difference pulse signals.
The signals from the buffer amplifier are passed through the
integrate circuits (D1, R2, C3 and D2, R3, C4) which adjust
switching time for tuning ON Q6, Q7 separately to prevent
overlap of output pulses (200 kHz and 50 kHz). The integrate
circuits change the pulse signals which characteristics of 50
% duty-cycle to slow switching time for leading and leave
quick switching time for trailing.
The pulse signals are applied to the Schmitt NAND gates
(IC2, pins 1 and 5). Also trasmit triger signal from the LOGIC
unit is applied to IC2 (pins 2 and 6) via C86. Only when both
signals are input, IC2 outputs transmit signals from pin 11 or
pin 10.
3-1-2 TRANSMITTER OUTPUT CIRCUIT
The transmitter output circuit consists of the driver and output circuits.
The driver circuit consists of Q2–Q5. The Darlington connection, used for switching circuits, consists of a pair of transistors for Q2 and Q4, and for Q3 and Q5. This is because the
next circuit which consists of FETs requires quick switching
time for leading and trailing characteristics.
The output circuit consists of Q6, Q7 and T1. When no transmission is occurring, transmit power is charged into C28 and
energy outputs at the next moment by turning ON Q6 or Q7.
3-1-3 OUTPUT POWER CIRCUIT
This circuit consists of IC10, Q11, Q12 and Q13. A signal
from the LOGIC unit controls voltage to be applied to the primary winding of T1 through these components.
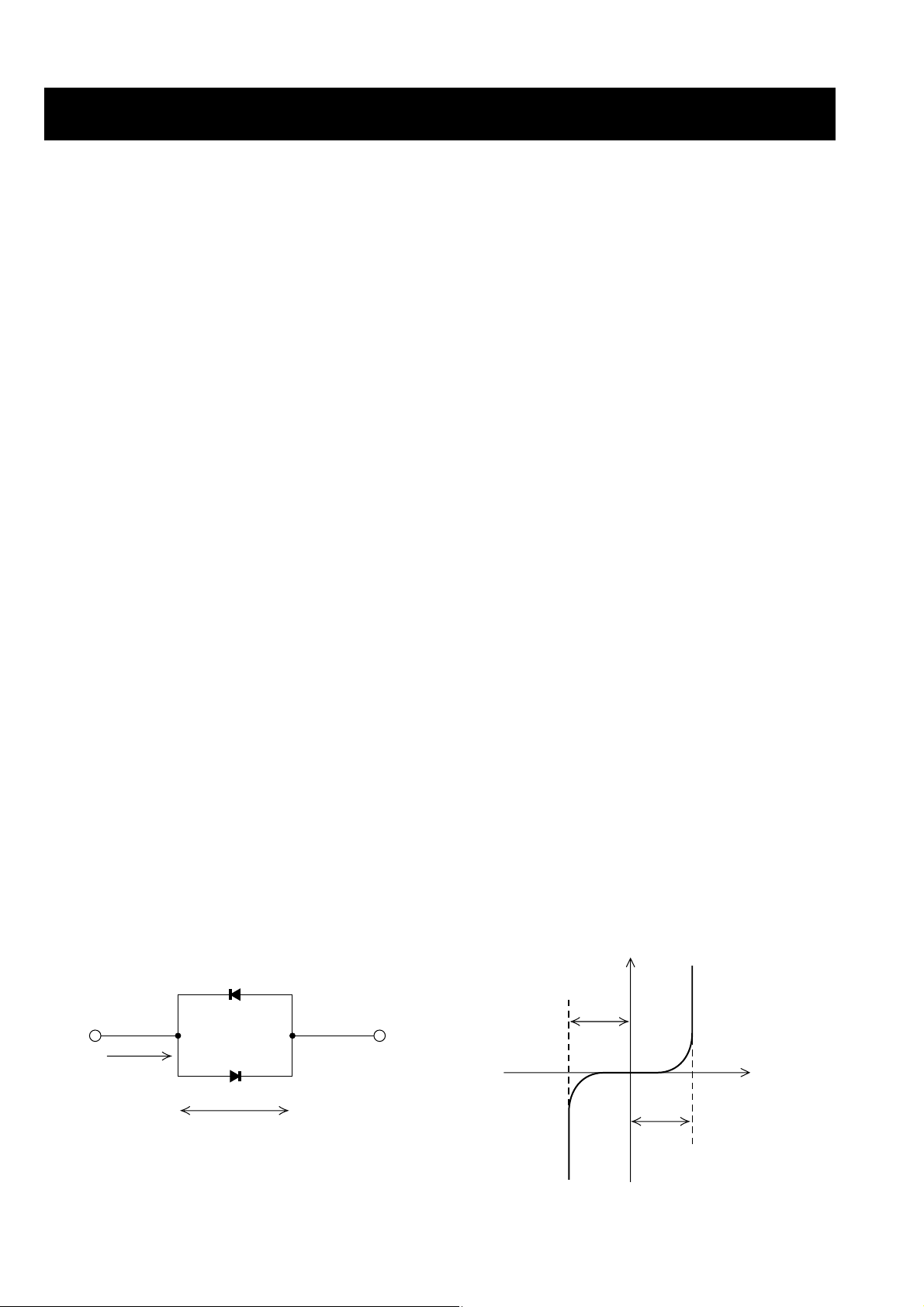
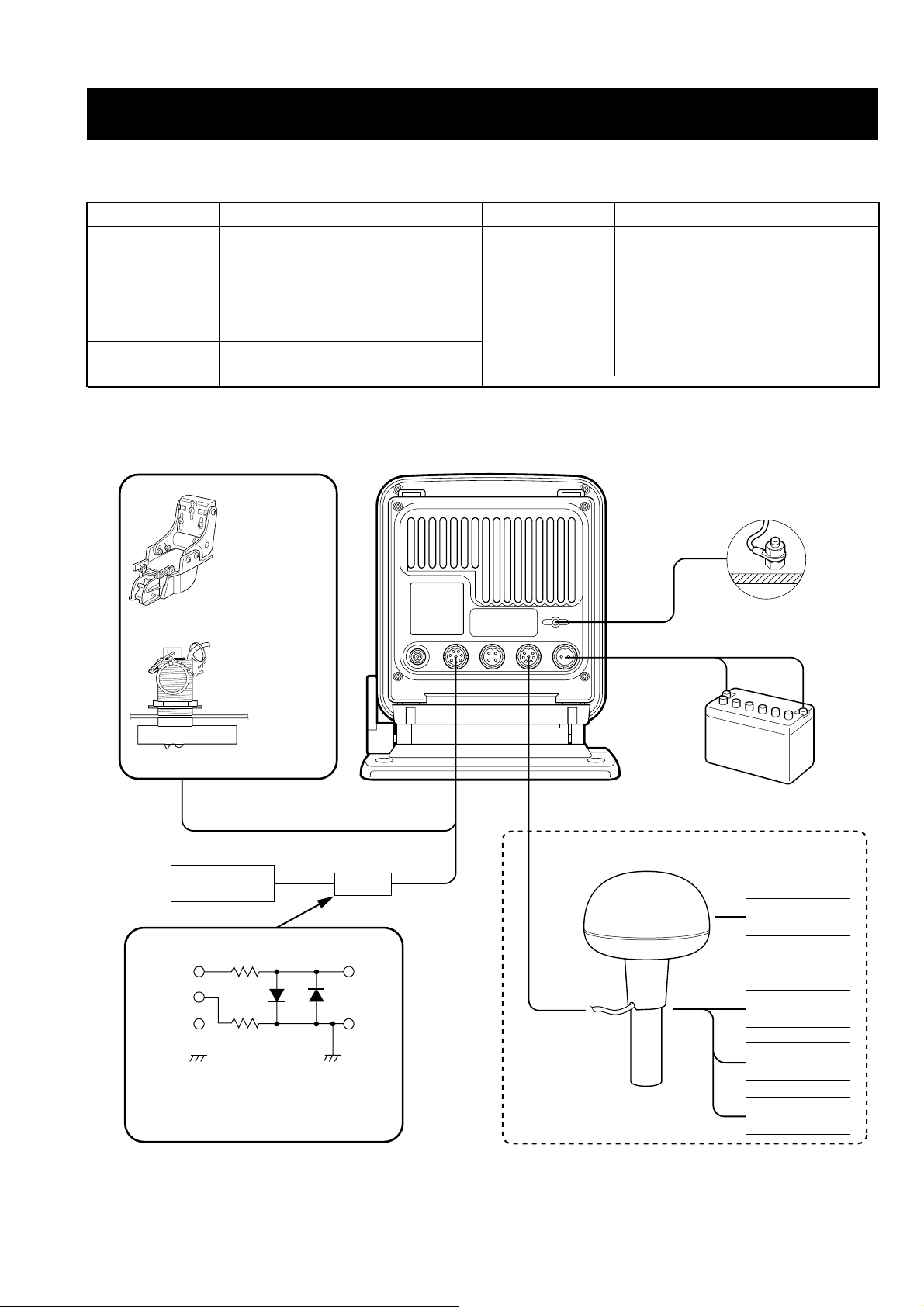
3-1-4 DIODE ISOLATION CIRCUIT
D3, D30, D4, D31, D9, D32, D35, D36 are symmetry-type sillicon-varister diodes. Interior connection is simulated as
shown in the diagram (Fig.1).
Fig.2 shows the diode’s electronic characteristics. When the
voltage is +Vd or less, internal resistance is infinitie. This
condition is the same as when a diode is OFF. when the voltage exceeds +Vd, internal resistance for each diode is at its
minimum level. This condition is the same as when a diode
is turned ON.
When transmitting, high voltage is applied to the circuit and
when receiving, no voltage is applied. Therefore, the receiver circuit is protected from high power transmit signals when
transmitting, and the receiver circuit is isolated from the
transmitter circuit when receiving.
3-2 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
3-2-1 RECEIVER MATCHING CIRCUIT
The matching circuits for the 200 kHz signal and for the 50
kHz signal consist of L1, C93 and L6, C96 respectively. The
tuned signals at each matching circuit are applied to the analog switch (IC16).
The analog switch (IC6) switches received signals by the Rx
frequency control signal (LOCONT) from LOGIC unit via J5
(pin 5), and then outputs to the next stage which is the mixer
circuit.
When transmit/receive 200 kHz signal, LOCONT is low level
and pin 7 (IC16) is ON. Therefore, IC16 (pin 1) outputs tuned
200 kHz signal.
When transmit/receive 50 kHz signal, LOCONT is high level
and pin 6 (IC16) is ON. Therefore, IC16 (pin 1) outputs tuned
50 kHz signal.
I
I
V
V
+Vd
–Vd
Fig.1 Fig.2
• DIODE ISOLATION CIRCUIT
Page 9
3 - 2
3-2-2 STC CIRCUIT
The STC circuit (Q1, R115, Q26, R116, C102) reduces the
sensitivity near-by the dispach line to set the immunity to air
bubbles in the sea surfaces so as to improve the image legibility.
When transmitting, the Tx trigger signal (TXTRG) from
LOGIC unit via J5 (pin 4) is high level, at this time Q26 is ON
and then Q1 turns ON. When switching TX to RX, the Tx trigger signal (TXTRG) becomes low level and Q26 is OFF, and
then Q1 turns to OFF slowly by connecting time constant
(R116, C102).
Thus the STC function activates.
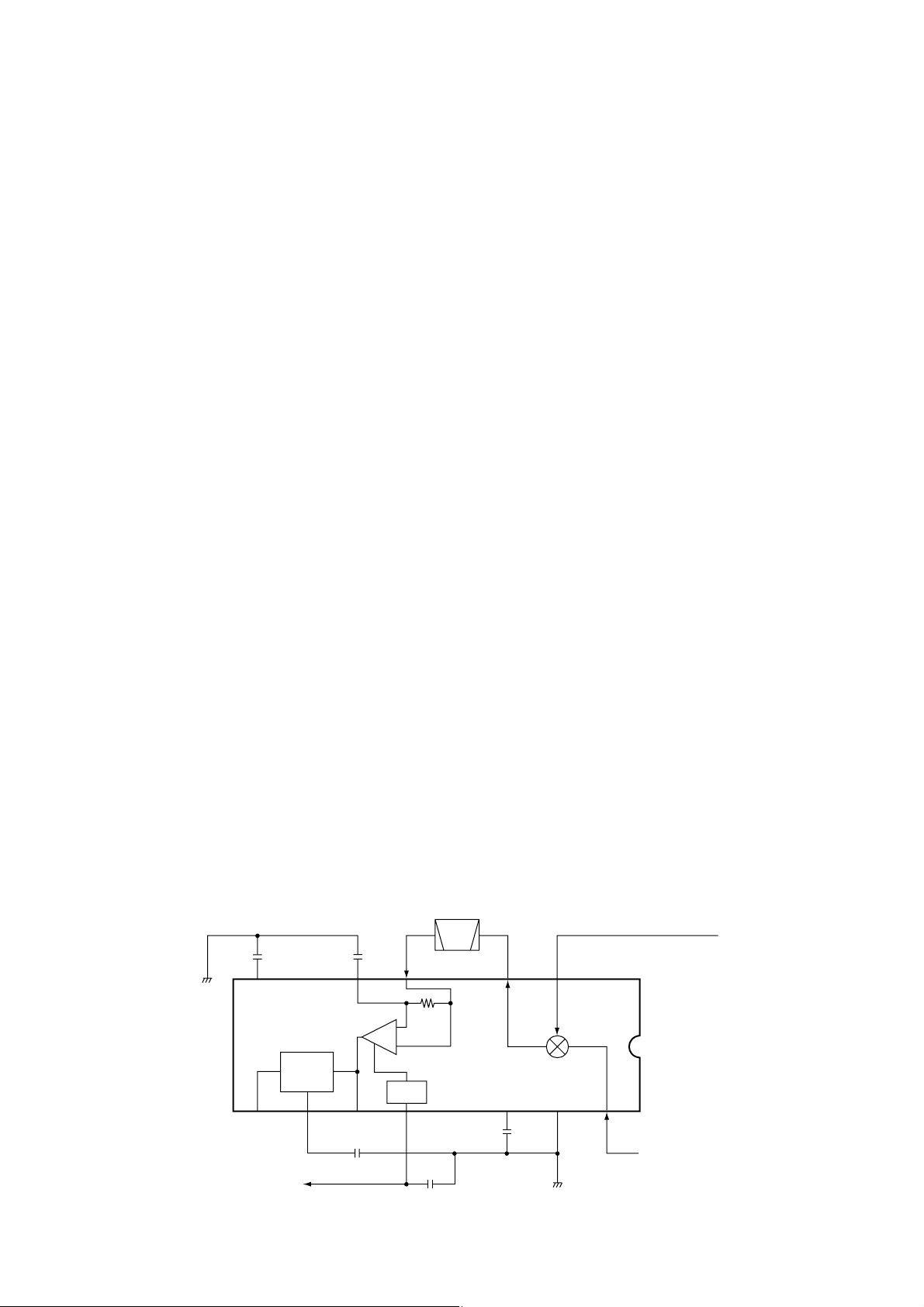
3-2-3 MIXER AND DETECTOR CIRCUITS
The mixer circuit converts the received signals into the 455
kHz IF signal.
The FM IF IC (IC5) contains the mixer, 455 kHz IF amplifier
and RSSI circuits.
The 200 kHz/50 kHz signals from the STC circuit (Q1) are
applied to the mixer section of IC5 (pin 16), and are mixed
with the 655 kHz/505 kHz LO signals generated at the 200
kHz/50 kHz local oscillator circuits to produce a 455 kHz IF
signal.
The 455 kHz IF signal from IC5 (pin 3) passes through the
ceramic filter (FI1), where unwanted signals are suppressed,
and is then applied to the IF amplifier section in IC5 (pin 5).
IC5 (pin 12) outputs RSSI voltage accoding to the input level
of IF amplifier section. The RSSI voltage is amplified at the
DC amplifier (IC6) to obtain necessary level, and is then
applied to the LOGIC unit.
The RSSI control signal from the LOGIC unit via J1 (pin 13)
becomes high level when the received signal is deeper than
80 m. Then the signal reduces noise by turning ON Q25 to
connect the by-pass capacitor (C90).
3-2-5 LOCAL OSCILLATOR CIRCUITS
200 kHz/50 kHz local oscillator circuits consist of IC3, X1 and
IC4, X2 respectively. IC3 or IC4 includes a frequency divider.
When high level signal is applied to pin 1, IC3 or IC4 oscillates and divides frequency, when low level signal is applied
to pin 1, these IC stop the oscillation.
The local oscillator circuit oscillates a local frequency according to the receive frequency. The oscillator frequency is 655
kHz when the receive frequency is 200 kHz since the equipment IF frequency is 455 kHz. In the same way, when the
receive frequency is 50 kHz, the oscillator frequency is 505
kHz.
When Rx frequency switching signal (LOCONT) is low level,
IC3 (pin 5) outputs 655 kHz signal. When the line is high
level, IC4 (pin 5) outputs 505 kHz signal.
3-3 REGULATOR CIRCUITS
3-3-1 INPUT CIRCUIT
11–30 V DC power is applied to the MAIN unit via the PWR
connector (J3) and is then passed through the line filter (L2,
C44–C47) to SW unit (via the LOGIC unit). The line filter filters RF signals to prevent their application to the swiching
circuit.
3-3-2 SWITCH CIRCUIT
SW1 and SW2 from MAIN unit are connected to the power
switch (S1) on the SW unit passing through the LOGIC unit.
When power switch (S1) is turned ON, power voltage is
applied to the regulator circuit (MAIN unit; Q12, Q13, D18)
and the circuit activates power control circuit (IC9).
3-3-3 SWITCHING CONTROL CIRCUIT
IC9 includes an oscillator circuit and a switching control. The
oscillation frequency is 138 kHz and oscillates sawtooth
waves. The time constant circuit (R75 and C77) adjusts the
oscillation frequency.
• MIXER AND DETECTOR CIRCUITS
Mixer
16
Limiter
amp.
IF filter
455 kHz
LO signal (655 kHz or 505 kHz)
RSSI
IC5 TA31136F
12 13 14 15
IF signal from Q1
"RSSI" signal to the CPU
11109
86532147
FI1
FM
detector
Page 10

3 - 3
3-3-4 SWITCHING CIRCUIT
IC9 (pins 9 and 10) controls the switch circuit (Q14, Q16),
and the primary winding of transformer (T2) is alternately
connected to and disconnected from the DC power.
3-3-5 RECTIFIER CIRCUIT
The secondary winding of T2 ( pin 6, pin 10 and pin 9) output
40 V , 12 V and 8 V (6 V) respectively. 40 V is rectified by D12,
C52 and is applied to the transmitter circuits. 12 V is rectified
by D13, C53 and is passed through the line filter (L5, C54),
and then applied to DISP unit and etc. 8 V is rectified by D22,
C69 and is applied to the 3-termianal 5 V regulator (IC13)
and 6 V regulator (Q27, D37).
3-3-6 OUTPUT VOLTAGE CONTROL CIRCUIT
8 V output is divided by R64, R65 and is applied to the comparator (IC11, pin 3). The applied voltage is compared with
other input (IC11, pin 2). When output voltage of IC11
increases due to increase of the 8 V, a base-current of the
photo-coupler (IC10) increases and a corrector–emitter’s
voltage decreases. At this time, IC9 (pin 2) reduces output
voltage and the width of output pulses from pin 9 and pin 10
becomes narrow. And also the interval which Q14 is ON, will
be short. Thus the working time of primary winding of transformer (T2) is short, and the outputs of secondary winding of
T2 decrease. This feedback circuit controls the constant output voltages even if resistance or input voltage is changed.
3-3-7 LOW VOLTAGE PROTECTION CIRCUIT
Input voltage is divided between R67, R68. The divided voltage is applied to IC9 (pin 15). When the voltage is lower than
9 V, IC9 is turned OFF.
3-4 INTERFACE CIRCUITS
3-4-1 SHIP SPEED INTERFACE CIRCUIT
Ship speed interface circuit consists of IC7, D27. Ship speed
sensor generates palse signals according to the rotation of
mill wheel in the water. The pulse signals from the ship speed
sensor via the J2 (pin 1) are shaped wave form at the Schmitt
circuit (IC7a) and applied to the LOGIC unit via J1 (pin 7).
3-4-2
WATER TEMPERATURE INTERFACE CIRCUIT
The resistance from the external thermistor accoding to the
water tempereture is input to MAIN unit via J2 (pin 7), and is
then applied to the LOGIC unit via J1 (pin 8).
3-4-3 NMEA INTERFACE CIRCUIT
• NMEA INPUT CIRCUIT
NMEA input circuit consists of IC7, IC8. The NMEA signals
from external connector (J4, pins 1, 2) are shaped wave form
at the Schmitt circuit (IC7b) via the photo-coupler (IC8), and
are then applied to the LOGIC unit via J1 (pin 9).
• NMEA OUTPUT CIRCUIT
NMEA output circuit consists of IC17, Q28–Q31. The NMEA
signals from the LOGIC unit are input to the MAIN unit via J1
(pin 10). The signals are buffer-amplified and level-shifted at
NMEA output circuit, and are then applied to the external
connector (J4, pins 3, 4).
3-4-3 DGPS INTERFACE CIRCUIT
• DGPS INPUT CIRCUIT
DGPS input circuit consists of IC7, IC15. The DGPS signals
from external connector (J5, pins 4, 5) are passed through
the photo-coupler (IC15) and shaped wave form at the
Schmitt circuit (IC7c), and are then applied to the LOGIC unit
via J1 (pin 11).
• DGPS OUTPUT CIRCUIT
DGPS output circuit consists of IC17, Q32–Q35. The DGPS
signals from the LOGIC unit are input to MAIN unit via J1 (pin
12). The signals are buffer-amplified and level-shifted at
DGPS output circuit, and are then applied to the external
connector (J5, pins 2, 3).
3-5 LOGIC CIRCUITS
3-5-1 CPU AND THE PERIPHERAL CIRCUITS
(LOGIC UNIT)
The LOGIC unit consists of ROM, RAM and 2 kind of CPU
which are 32 bit ARM RISC micro-controller and 8 bit microcontroller. CPUs and a control circuit control all functions.
The interrupt signal functions in the following way:
• MAIN CPU (IC1)
The main CPU (IC1) is a 32 bit RISC CPU and acts as a
computer circuit to control all functions and to respond to all
kind of interruptions. The main CPU uses a 32 MHz clock signal from X1.
The main CPU (IC1) generates an address signal and an
RGB signal corresponding to display coordinates and the
address of DRAM. This IC chip also generates vertical signals and synchronicity signals for the LCD
• SUB CPU (IC22)
The sub CPU controls the LCD brightness, ship speed, keyboard, sounder and serial communication from the GPS,
DGPS, NMEA. The sub CPU uses a RESET signal and 16
MHz clock signal from main CPU (IC1).
• RAM (IC20, IC21)
IC20 is a 4k×9 bit FIFO RAM which buffer strage for sending
received sounder signal from the sub CPU (IC22) to main
CPU (IC1).
IC21 is a 256×8 bit mail-box RAM which communicates GPS
data or keyboard data between the main CPU (IC1) and sub
CPU (IC22).
• ROM (IC32, IC33)
IC32 and IC33 are 8 Mbit flash ROMs. ROM contains a system operating program and data of world map.
• ADDRESS DECODER (IC28)
IC28 is a PLD (programmable logic device) which is address
decoder and controller of the card-data reader, and outputs
chip select signal to IC1 and I/O peripheral signals.
• SRAM (IC30, IC31)
IC30 and IC31 are 1 Mbit SRAMs which backuped by the
memory battery (BT1).
• DRAM (IC34, IC35)
IC34, IC35 are DRAMs and are used for video RAMs. Each
chip has a capacity of 4 Mbits.
Page 11
3 - 4
3-6 DGPS RECEIVER (RD-200)
3-6-1 ANTENNA CIRCUIT (ANT UNIT)
EP3 and EP4 consist of 2 series of antennas respectively
(total 4 series).
The received signal from the antenna (EP3) is tuned at C3,
and is amplified at the RF amplifier circuits (Q1, Q2, Q5, Q6).
On the other hand, the received signal from another antenna
(EP4) which falls at right angle with EP3, is tuned at C4. The
tuned signal is amplified at the RF amplifier circuits (Q3, Q4,
Q7, Q8).
The both amplified signals are piled up and are impedancematched to 50 Ω at L1, and are then applied to the MAIN unit
via J1.
3-6-2 RF AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The RF circuit amplifies signals within the range of frequency coverage and filters out-of-band signals.
The signals from the ANTunit via J1 (pin 2) pass through the
low-pass filter (L2, L3, C3–C7) and high-pass filter (L4,
C8–C10). The filtered signals are amplified at the RF amplifier (IC1) and are then enter another low-pass filter (L6, L7,
C15–C19) and notch filter (L24, L25, C111, C112) to suppress unwanted signals. The filtered signals are applied to
the mixer circuit.
3-6-3 MIXER CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The mixer circuit (IC2, L8, L9) is a double-balanced mixer
which converts the received signal to a fixed frequency of the
IF signal with an LO frequency.
The signals from the RF circuit are mixed with the LO signal
at the mixer circuit (IC2, L8, L9) to produce a 455 kHz IF signal.
3-6-4 IF CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
By changing the LO frequency, only the desired frequency
will pass through the IF filter at the next stage of the mixer.
The IF signal from the mixer circuit is amplified at the IF
amplifier (Q1) and is applied to a ceramic filter (FI1) to suppress out-of-band signals. The filtered signal is applied to the
FM IF IC circuit (IC3).
3-6-5 DEMODULATOR CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The FM IF IC (IC3) contains the limiter amplifier, detector circuits, etc.
The IF signal from the IF filter is applied to the limitter amplifier section of IC3 (pin 5). The amplified signal is mixed with
a 456.2 kHz signal from CPU IC (IC12) to produce a 1.2 kHz
detector signal for demodulation the IF signal into AF signals.
AF signal from FM IF IC (IC3, pin 9) passes through the lowpass filter (IC4a, IC4b). The filtered signal is amplified at the
AF amplifier (Q4) and is applied to the CPU (IC12).
3-6-6 REFERENCE OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT
(MAIN UNIT)
The reference oscillator circuit generates the reference frequency, and the signals are applied to the DDS IC and CPU.
The generated reference signal from the reference oscillator
(X1: 14.5984 MHz) is amplified and divided at the buffer
amplifier (IC7). The divided signal (7.2992 MHz) is applied to
the DDS IC (IC6) and CPU (IC12) via the amplifiers IC5, IC10
respectively.
3-6-7 LO CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The LO circuit generates the LO frequency, and the signals
are applied to the mixer circuit.
The generated LO signal is output from IC6 and passed
through the D/A converter (R26–R45), low-pass filter (L15,
L16, C55–C59) and high-pass filter (L17, C60–C62). The filtered signal is amplified at the buffer amplifier (Q2) and then
is passed through the low-pass filter (L18, L19, C65–C69).
The filtered signal is applied to the mixer circuit.
3-7 PORT ALLOCATIONS
3-7-1 FP-561
• SUB CPU (LOGIC UNIT; IC22)
Outputs Tx (50 kHz/200 kHz) pulse signals to IC1 (pins 1, 3).
Outputs control signal for LCD backlight.
Outputs control signal for the LCD contrast
A/D input port for the received signal
strength indicator voltage.
Input port for serial signal from the
GPS unit via the buffer amplifier (IC23,
pin 12).
Outputs serial signal to the buffer
amplifier (IC23, pin 3) for the GPS unit.
Input port for serial signal from the
NMEA/DGPS units via the analog
switch (IC41, pin 14).
Outputs serial signal to the analog
switch (IC41, pin 2) for the
NMEA/DGPS units.
Ship speed input port from the photo
coupler (IC7, pin 7) on the MAIN unit.
Outputs beep audio to the buzzer circuit (Q4, SP1) on the SW unit.
Outputs receive frequency switching
signal for the analog switch (IC16).
Outputs trasmit triger signal for the driver circuit (IC2, pins 2, 6) on the MAIN
unit.
1
3
4
7
16
17
18
20
72
74
77
80
TXSIG
INV
CONT
RSSI
GPSI
GPSO
NMEAI
NMO
SPD
BEEP
LOC
TXTRG
Pin Port
Description
number name
Page 12
FP-561
• MAIN CPU (LOGIC UNIT; IC1)
3-7-2 RD-200
• CPU (MAIN unit; IC12)
3 - 5
Outputs serial clock signal for the LCD.
Outputs vertical synchronizing signal
for LCD.
Outputs horizintal synchronizing signal
for LCD.
Outputs red color signal for LCD.
Outputs blue color signal for LCD.
Outputs green color signal for LCD.
Outputs RX pass-bandwidth control
signal for the RSSI controller (Q25).
High : While narrow
73
86
88
92
93
94
172
DTCK
VSYNC
HSYNC
RED
BLUE
GREEN
DEPCONT
Pin Port
Description
number name
Input port for the reset signal from the
reset circuit (IC11, Q5).
8 bit D/Aoutput ports for the bar antennas control signals.
Outputs reset signal for the DDS IC
(IC6).
Outputs serial clock signal for the DDS
IC (IC6).
Outputs serial data signals for the
DDS IC (IC6).
Outputs strobe signals for the DDS IC
(IC6).
Outputs clock signal for the EEPROM
IC (IC13).
Inputs/outputs serial signal for the
EEPROM IC (IC13).
Outputs chip select signal for the EEPROM IC (IC13).
Input port for NMEA signal or clone
signal from the NMEA connector (J3).
Outputs NMEA signal to the NMEA
connector (J3).
10
25–32
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
48
49
RESET
TUNE0–
TUNE7
DRES
CLK
DATA
STRB
ESCK
ESIO
ECS
RXDO
TXDO
Pin Port
Description
number name
Page 13
4 - 1
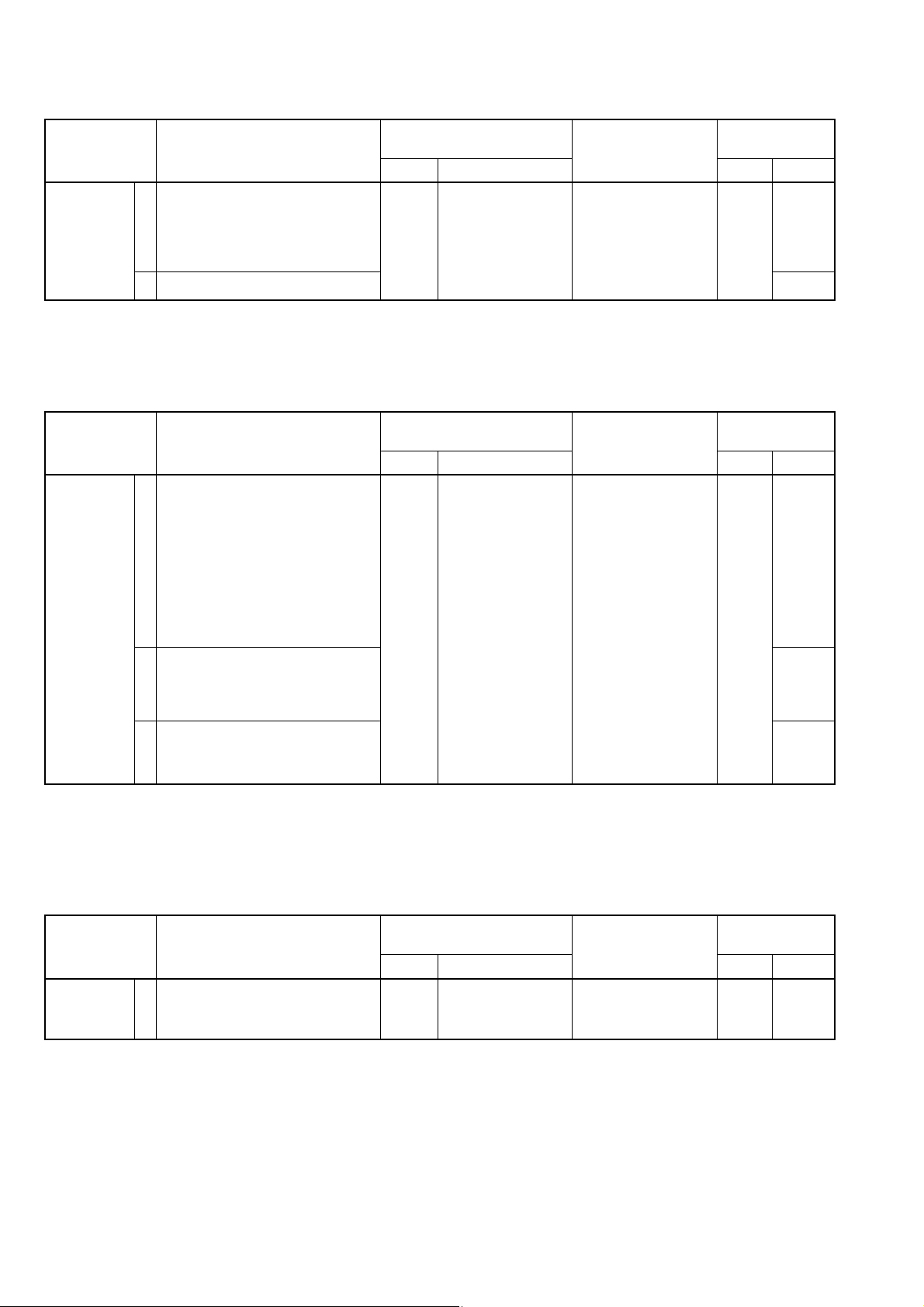
SECTION 4 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
4-1 PREPARATION
‘‘
REQUIRED TEST EQUIPMENT
‘‘
CONNECTION
EQUIPMENT
DC power supply
Frequency counter
DC voltmeter
Spectrum analyzer
GRADE AND RANGE
Output voltage : 11–30 V DC
Current capacity : 3 A or more
Frequency range : 0.1–10 MHz
Frequency accuracy: ±1 ppm or better
Sensitivity : 100 mV or better
Input impedance : 50 kΩ/V DC or better
Frequency range : At least 10 MHz
Spectrum bandwidth: ±100 kHz or more
EQUIPMENT
Oscilloscope
Tracking generator
Standard signal
generator (SSG)
GRADE AND RANGE
Frequency range : DC–20 MHz
Measuring range : 0.01–10 V
Frequency range : 100 kHz–100 MHz
Output level : 1 mV to 71 mV
(–47 dBm to –10 dBm)
Frequency range : 10 kHz–100 MHz
Output level : 0.1 µV–32 mV
(–127 to –17 dBm)
TRANSDUCER
FP-561
Marine
Ploter/Sounder
EX-1622
Transom-
type
transducer
(Option)
Coupler
Standard signal
generator
EX-1010
Through-hull type
transducer
(Option)
Coupler
R
R
D
D
FP-561 SSG
D: 1N4002
R: 100 Ω (3 W)
DGPS
RD-200
Differential
GPS receiver
Standard signal
generator
Spectrum
analyzer
Tracking
generator
Frequency
counter
A coupler should be prepared by each
user. The coupler will protect the signal
generator from transmitter power.
RD-200 adjustment
Ground
Battery
11 to 30 VDC
Red: + Black: –
PWR
GND
Page 14
4 - 2
4-2 FP-561 TRANSMITTER ADJUSTMENT
OUTPUT
POWER
ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
MEASUREMENT
VALUE
POINT
UNIT LOCATION UNIT ADJUST
12• Connect a transducer to the
[TRANSDUCER] connector.
• Mode : [SOUNDER]
• Frequency : [H]
• Depth range : 640 m
• Frequency : [L]
MAIN Connect an oscillo-
scope between pin
3 and pin 5 of J2.
880–1320 Vp-p
at maximum wave
point
Verify
Verify
4-4 FP-561 WATER TEMPERTURE ADJUSTMENT
WATER
TEMPERATURE
ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
MEASUREMENT
VALUE
POINT
UNIT LOCATION UNIT ADJUST
1 • Connect a 10 kΩ resistor
between pin 6 and pin 7 of the
[TRANSDUCER] connector J2.
Display 25.0 ˚C LOGIC R131
*This output level of the standard signal generator (SSG) is indicated as SSG’s open circuit.
4-3 FP-561 RECEIVER ADJUSTMENT
RECEIVE
SENSITIVITY
ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
MEASUREMENT
VALUE
POINT
UNIT LOCATION UNIT ADJUST
1
2
3
• Mode : [SOUNDER]
• Frequency : [H]
• Depth range : 5 m
• STC : [1]
• Connect a standard signal gener-
ator to the [TRANSDUCER] connector J2 via the coupler and set
as:
Fequency : 200 kHz
Level :
1 mV (–47 dBm)
• Frequency : [L]
• Set an SSG as:
Frequency : 50 kHz
Level :
1 mV (–47 dBm)
• Set an SSG as:
Frequency : 50 kHz
Level :
100 mV (–7 dBm)
MAIN Connect a DC volt-
meter or oscilloscope to the check
point “RSSI”.
Maximum DC voltage MAIN L1
L6
R99
Page 15
4 - 3
RSSI
Pin 3
Pin 5
R99
L1
L6
Receive sensitivity
check point
Receive sensitivity
adjustment
Output power
check point J2
Pin 6
Pin 7
Water temperature
pre-setting J2
• MAIN unit
R131
Water temperature
adjustment
• LOGIC unit
Page 16

4 - 4
*This output level of the standard signal generator (SSG) is indicated as SSG’s open circuit.
4-5 RD-200 ADJUSTMENTS
REFERENCE
FREQUENCY
RECEIVE
SENSITIVITY
DECODE
ANTENNA
(EP3)
(EP4)
ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
MEASUREMENT
VALUE
POINT
UNIT LOCATION UNIT ADJUST
1
1
1
2
1
2
3
4
• Connect the antenna connector
to the FP-561’s DGPS connector
and turn FP-561 power ON.
• Set the connected FP-561 as:
Baud rate : 200
Fequency : 300.0 kHz
• Connect a standard signal gener-
ator to J4 on the ANTunit and set
as:
Fequency : 300.0 kHz
Modulation : OFF
• Set the connected FP-561 as:
Baud rate : 200
Fequency : 300.0 kHz
• Connect a standard signal gener-
ator to J4 on the ANTunit and set
as:
Fequency : 250.0 kHz
Level :
1 mV (–47 dBm)
Modulation : OFF
• Set an SSG as:
Frequency : 350.0 kHz
• Set the connected FP-561 as:
Baud rate : 200
Fequency : 300.0 kHz
• Remove solder at CP1 on the
ANT unit.
• Conncet a traking generator (or
SSG) to the EP3 on the ANT unit
using the probe JIG and set as:
Level :
7.1 mV (–30 dBm)
Frequency : 300.0 kHz
(SSG only)
• Conncet a TG (or SSG) to the
EP4 on the ANT unit using the
probe Jig and set as:
Level :
7.1 mV (–30 dBm)
Frequency : 300.0 kHz
(SSG only)
MAIN
ANT
MAIN
ANT
Connect a frequency counter to the
check point “CP1”.
Connect a SINAD
meter to J3.
Connect a DC voltmeter or oscilloscope to the check
point “CP2”.
Connect a spectrum
analyzer to J5.
7.29920 MHz
25 % distortion
High level (5 V)
Low level (0 V)
TG
Peak point to 300 kHz
SSG
Maximum RF level
–40 dBm or more
TG
Peak point to 300 kHz
SSG
Maximum RF level
–40 dBm or more
MAIN
SSG
ANT
C71
Verify the
SSG level
less than
0.2 µV (–
121 dBm)
Verify
Verify
C3
Verify
C4
Verify
After adjustment, re-solder CP1 on the ANT unit.
+ –
10.2(d) mm
12.2(d) mm
to TG (SSG) output
ANT unit
EP4
EP3
Kind : enamelled wire
Diameter : 1.0 mm
Roll number : 2 roll
Squeeze to
PC board's edge
Wire description
• Probe JIG
Page 17

4 - 5
C71
Reference frequency
adjustment
CP2
Decode
check point
CP1
Reference frequency
check point
• MAIN unit
C3
Antenna peak
adjustment for EP3
C4
Antenna peak
adjustment for EP4
J3
Receive sensitivity
check point
CP1
Antenna peak
pre-setting
J5
Antenna peak
check point
J5
RF input
Receive sensitivity
Decode
• ANT unit
Page 18

5-1 FP-561
[MAIN UNIT]
IC1 1130005720 S.IC TC7W04F (TE12L)
IC2 1130006370 S.IC TC4093BF
IC3 1130007990 S.IC TC3W03FU (TE12L)
IC4 1130007990 S.IC TC3W03FU (TE12L)
IC5 1110003490 S.IC TA31136FN (D,EL)
IC6 1110003340 S.IC µPC358GR-T1
IC7 1130007420 S.IC TC7W14FU (TE12L)
IC8 1170000280 S.IC TLP121 (GB-TPL)
IC9 1110003070 S.IC µPC494GS
IC10 1170000280 S.IC TLP121 (GB-TPL)
IC11 1110002700 S.IC NJM2904M-T1
IC13 1180001840 IC PQ05RF21
IC14 1130003920 S.IC TC4S69F (TE85R)
IC15 1170000280 S.IC TLP121 (GB-TPL)
IC16 1130006220 S.IC TC4W53FU (TE12L)
IC17 1130009480 S.IC TC4049BF (N)
Q1 1530002550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC3326-B (TE85R)
Q2 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q3 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q4 1510000500 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1162-GR (TE85R)
Q5 1510000500 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1162-GR (TE85R)
Q6 1590002670 FET FS30KMJ-3
Q7 1590002670 FET FS30KMJ-3
Q12 1510000800 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1213-Y (TE12R,C)
Q13 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q14 1590002670 FET FS30KMJ-3
Q16 1510000500 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1162-GR (TE85R)
Q22 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q23 1530002550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC3326-B (TE85R)
Q24 1530002550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC3326-B (TE85R)
Q25 1530002550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC3326-B (TE85R)
Q26 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q27 1540000550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1664 T100Q
Q28 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q29 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R
Q30 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q31 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R
Q32 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q33 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R
Q34 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q35 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R
D1 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D2 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D3 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D4 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D9 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D10 1790000700 DIODE DSA3A1
D11 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D12 1790000760 DIODE RG-2A
D13 1790001630 DIODE SB30-09J
D14 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D17 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D18 1730000880 S.ZENER RD11M-T2B2
D21 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D22 1790001630 DIODE SB30-09J
D23 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D24 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D27 1750000130 S.DIODE DA204U T107
D28 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D30 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D31 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D32 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D33 1730000010 S.ZENER RD4.7M-T2B3
D34 1730000010 S.ZENER RD4.7M-T2B3
D35 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D36 1710000350 DIODE 1N4002
D37 1730000770 S.ZENER RD7.5M-T1B1
FI1 2020001640 CERAMIC CFWS455GY
X1 6050009190 XTAL CR-497 (5.24 MHz)
X2 6050009180 XTAL CR-496 (4.04 MHz)
L1 6150003680 COIL LS-415
L2 5920000450 COIL FK-080E-1020
L3 6200009060 S.COIL LQH 3C 101K 34
L5 6170000150 COIL LW-16
L6 6150003670 COIL LS-414
L7 6200003240 S.COIL NL 322522T-221J
L8 6200008670 S.COIL D10F-A814AY-152K
R2 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R3 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R5 7070001040 RESISTOR ERG1SJ 472 (4.7 kΩ)
R6 7070001040 RESISTOR ERG1SJ 472 (4.7 kΩ)
R7 7070000641 RESISTOR ERG2SJ 471 (470 Ω)
R8 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R9 7030003630 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 393 V (39 kΩ)
R10 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R12 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R13 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R15 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R16 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R17 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R18 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R19 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R22 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R23 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R24 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R25 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R26 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R27 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R28 7030000190 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 27 Ω (270)
R29 7030000190 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 27 Ω (270)
R35 7030000340 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 470 Ω (471)
R36 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R44 7030006520 S.RESISTOR RR0816P-561-D (560 Ω)
R45 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R46 7540000060 ABSORBER ERZ-C05DK 560
R47 7030000470 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 5.6 kΩ
R48 7030001430 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 27 kΩ
R55 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R56 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R60 7030000980 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 5.6 Ω (5R6)
R61 7030000310 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 270 Ω (271)
R62 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R63 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R64 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R65 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R66 7030000500 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 10 kΩ
R67 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R68 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R69 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ)
R70 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ)
R71 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R72 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ)
R74 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R75 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R76 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R77 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R78 7030000410 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.8 kΩ
R79 7030000170 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 18 Ω (180)
R82 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R84 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R85 7070000641 RESISTOR ERG2SJ 471 (470 Ω)
R91 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R92 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R93 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R94 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R96 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R97 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R98 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
S.=Surface mount
5 - 1
SECTION 5 PARTS LIST
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[MAIN UNIT]
Page 19

C80 4510004560 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 10 NPDW
C81 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C83 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C85 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C86 4510004910 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 10 SWN
C88 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C89 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C90 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C91 4010008470 CERAMIC DE0905 B 222K 1KV
C92 4010008470 CERAMIC DE0905 B 222K 1KV
C93 4030010240 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 391K-T-A
C94 4010008470 CERAMIC DE0905 B 222K 1KV
C95 4010008470 CERAMIC DE0905 B 222K 1KV
C96 4030008470 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 272K-T-A
C97 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C98 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C99 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C100 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C101 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C102 4550003080 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 1A 335M-8L
C103 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C104 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C105 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C106 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C107 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C108 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C109 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C110 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 1A 106M-8L
C111 4030006480 S.CERAMIC GRM42-6 B 104K 50PT
C113 4030006480 S.CERAMIC GRM42-6 B 104K 50PT
C115 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T-A
C116 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T-A
C117 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T-A
C118 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C119 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T-A
C120 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T-A
C121 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T-A
C122 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T-A
J1 6510021040 CONNECTOR 52806-3010
J2 6510021220 CONNECTOR 8S-S-E-SS
J3 6510021190 CONNECTOR 2S-S-E-SS
J4 6510021200 CONNECTOR 4S-S-E-SS
J5 6510021210 CONNECTOR 7S-S-E-SS
F1 5210000060 FUSE FGB 5A
F2 5220000020 HOLDER S-N5051
F3 5220000020 HOLDER S-N5051
T1 5920000730 TRANSFORMER TO-46
T2 5920000690 TRANSFORMER TO-43
EP1 0910051392 PCB B 5305B
EP2 0850000120 UNIT BOARD IA023-5B03S
[MAIN UNIT]
R99 7310003580 S.TRIMMER EVM-1XSX50 B15 (104)
R100 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R101 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R102 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R103 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R104 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R105 7030003390 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390 Ω)
R106 7030003390 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390 Ω)
R107 7070000641 RESISTOR ERG2SJ 471 (470 Ω)
R108 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R109 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R110 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R111 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R112 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R113 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R115 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R116 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R117 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R118 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R119 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R120 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R122 7030001090 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 47 Ω (470)
R124 7030001090 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 47 Ω (470)
R125 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R127 7030001090 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 47 Ω (470)
R128 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R130 7030001090 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 47 Ω (470)
R131 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
C1 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C3 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T-A
C4 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T-A
C5 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C7 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C8 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C10 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C11 4030009990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 200J-T-A
C12 4030009990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 200J-T-A
C13 4030009990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 200J-T-A
C14 4030009990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 200J-T-A
C16 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C17 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA1A 106M-8L
C18 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C19 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C20 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C21 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C22 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C23 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C24 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C25 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C28 4510007030 ELECTROLYTIC 63 MV 1000CZ
C40 4510005310 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA220SR
C41 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C42 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C43 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C44 4510007020 ELECTROLYTIC 35 MV 1000GX
C45 4030004740 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C46 4030004740 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C47 4510007020 ELECTROLYTIC 35 MV 1000GX
C48 4030004740 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C49 4030004740 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C50 4310000360 MYLAR 50 F2D 103J
C52 4510006880 ELECTROLYTIC 100 MV 33 CZ
C53 4510007010 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 1000GX
C54 4510006640 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 1000 CZ
C59 4510004940 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 33 NPDW
C60 4510004940 ELECTROLYTIC 50 MV 33 NPDW
C61 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C62 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C63 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
C64 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 473K-T-A
C69 4510007000 ELECTROLYTIC 10 MV 1000GX
C70 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C71 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C72 4510005940 ELECTROLYTIC 10 MV 470 HC
C73 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C74 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C75 4510005750 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1EA220SP
C76 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
C77 4310000570 MYLAR 50 F2D 222J
C79 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
5 - 2
S.=Surface mount
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 20

REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
R46 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
R47 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R48 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R49 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R51 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
R52 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
R53 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
R55 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R56 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R60 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R62 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R68 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R71 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R77 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
R78 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R81 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R82 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R83 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R85 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R86 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R87 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R88 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R89 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R90 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R91 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R92 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R93 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R94 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R95 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R96 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R97 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R98 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R99 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R100 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R101 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R102 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R104 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R105 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R106 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R107 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R108 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R109 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R110 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R111 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R112 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R126 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R127 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R128 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R129 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R130 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R131 7310003610 S.TRIMMER EVM-1XSX50 B14 (103)
R132 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
R133 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R134 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R135 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R136 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R138 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R140 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R142 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R143 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
R144 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R145 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R146 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R147 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R148 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R150 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R151 7030003220 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 150 V (15 Ω)
R155 7030006600 S.RESISTOR RR0816P-822-D (8.2 kΩ)
R156 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R162 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R163 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R164 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R165 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R167 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R168 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R169 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R170 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R171 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R172 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R173 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R174 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R177 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
S.=Surface mount
IC1 1140007500 S.IC CL-PS7500FE-QC-A
IC2 1130009170 S.IC TC74HCT245AF
IC3 1130009170 S.IC TC74HCT245AF
IC4 1130005440 S.IC TC74HC245AF
IC5 1130005440 S.IC TC74HC245AF
IC6 1130005440 S.IC TC74HC245AF
IC7 1130009390 IC TC74HCT646AP
IC13 1110003500 S.IC S-80742SL-A6-T1
IC16 1130005340 S.IC TC74HC139AF
IC18 1130005480 S.IC TC74HC573AF
IC19 1130007040 S.IC TC7W32F (TE12L)
IC20 1130009080 S.IC CY7C433-40JC
IC21 1140007540 S.IC M66220FP
IC22 1140007510 S.IC TMP90PM36F
IC23 1130005290 S.IC TC74HC14AF
IC28 1140007820 S.IC SC-1372 (MACH111-15JC)
IC30 1130009050 S.IC M5M51008BVP-70LL
IC31 1130009050 S.IC M5M51008BVP-70LL
IC32 1130009060 S.IC MBM29F800BA-90PFTN
IC33 1130009060 S.IC MBM29F800BA-90PFTN
IC34 1140007570 S.IC M5M44260CJ
IC35 1140007570 S.IC M5M44260CJ
IC41 1130007680 S.IC BU4053BCF-T1
IC42 1130005290 S.IC TC74HC14AF
IC44 1130008040 S.IC TC7SH04FU
IC45 1130005741 S.IC TC74AC74F (TP1)
IC46 1130008040 S.IC TC7SH04FU
Q1 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q3 1520000450 S.TRANSISTOR 2SB1132 T100 Q
Q4 1520000650 S.TRANSISTOR 2SB1201-S-TL
Q5 1590001190 S.TRANSISTOR XP6501-(TX) .AB
D1 1750000060 S.DIODE 1SS196 (TE85R)
D2 1750000020 S.DIODE 1SS184 (TE85R)
X1 6050010460 S.XTAL DSO-49SJ (32.000 MHz)
R1 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R2 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R3 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R4 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R5 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R6 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R7 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R8 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R9 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R10 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R11 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R12 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R13 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R14 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R15 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R16 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R17 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R18 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R19 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R20 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R21 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R22 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R23 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R24 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R25 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R26 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R27 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R28 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R29 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R30 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R31 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R32 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R36 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R37 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R38 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R39 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R40 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R41 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R42 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R43 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R44 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R45 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω)
5 - 3
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[LOGIC UNIT] [LOGIC UNIT]
Page 21

Q1 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q2 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q3 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q4 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
D1 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D2 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D3 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D4 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D5 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D6 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D7 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D8 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D9 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D10 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D11 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D12 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D13 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D14 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D15 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D16 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D17 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
R1 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R2 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R3 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R4 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R5 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R6 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R7 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R8 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R9 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R10 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R11 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R12 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R13 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R14 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R15 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ)
R16 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ)
R17 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ)
C1 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C2 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C3 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C4 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C5 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C6 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C7 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C8 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C9 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C10 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C11 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C12 4550006480 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA1C 475M-8L
C14 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
J1 6510021020 CONNECTOR 52806-1810
DS1 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
DS2 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
DS3 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
DS4 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
DS5 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
DS6 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
DS7 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
DS8 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
DS9 5040002420 S.LED SML-310MT T86
S1 2230001030 SWITCH MS-666K
S2 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S3 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S4 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S5 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S6 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S7 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S8 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S9 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
R178 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R179 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R180 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
C1 4030012600 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1A 105M-T-A
C2 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C3 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C4 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C5 4510004650 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1EA4R7SR
C6 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C7 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C10 4510005310 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA220SR
C11 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C12 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C13 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C14 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C15 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C16 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C17 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C18 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C19 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C20 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C21 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C22 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C23 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C24 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C25 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C26 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C27 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C42 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C43 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C44 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C45 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C46 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C47 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
C48 4510006650 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1EA100SR
C49 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C50 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C51 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C52 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C53 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C54 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C55 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C56 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C58 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C59 4550000460 S.TANTALUM TESVA1C 105M1-8L
C61 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C64 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C65 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C66 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C67 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C68 4510005310 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA220SR
C69 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C70 4030011810 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 224K-T-N
J1 6510021170 CONNECTOR ICME68H-L8-D1121RHA
J2 6510021040 CONNECTOR 52806-3010
J3 6510021020 CONNECTOR 52806-1810
J6 6510021510 CONNECTOR 52807-2410
BT1 3020000130 LITHIUM CR3032-1T2
W1 8900009030 CABLE OPC-902
W2 8900008740 CABLE OPC-867 [GEN]
8900009380 CABLE OPC-906 [EUR]
W3 8900008920 CABLE OPC-882
W19 7120000470 JUMPER ERDS2T0
W20 7120000470 JUMPER ERDS2T0
EP1 0910051401 PCB B 5306A
5 - 4
S.=Surface mount
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[LOGIC UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[SW UNIT]
Page 22

S.=Surface mount
S10 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S11 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S12 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S13 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S14 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S15 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S16 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S17 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
S18 2260001680 S.SWITCH SKQDPB
SP1 2520000110 PIEZO BUZZER PS1740P02
W1 8900008340 CABLE OPC-816
EP1 0910051410 PCB B 5307
DS1 5030001720 LCD LQ6AN102
5 - 5
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
FP-561
[SW UNIT]
IC1 1110001971 S.IC µPC1676G-T1
IC2 1790000050 IC ND487C1-3R
IC3 1110003490 S.IC TA31136FN (D,EL)
IC4 1110002700 S.IC NJM2904M-T1
IC5 1130003830 S.IC TC7S04F (TE85R)
IC6 1140004550 S.IC M65343FP/SC1287
IC7 1130007990 S.IC TC3W03FU (TE12L)
IC8 1180001250 S.IC TA7808F (TE16L)
IC9 1180001070 S.IC TA7805F (TE16L)
IC10 1130003830 S.IC TC7S04F (TE85R)
IC11 1110004860 S.IC S-80842ALUP-EA6-T2
IC12 1140008220 S.IC HD64F3644H
IC13 1140005880 S.IC X25320S8I-2.7T6
IC14 1130003830 S.IC TC7S04F (TE85R)
IC15 1130006370 S.IC TC4093BF
IC16 1130006680 S.IC TC7S02F (TE85R)
IC17 1130009480 S.IC TC4049BF (N)
IC18 1170000280 S.IC TLP121 (GB-TPL)
IC19 1110002750 S.IC TA75S01F (TE85R)
Q1 1580000390 S.FET 3SK131K-T1
Q2 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q3 1540000550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1664 T100Q
Q4 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q5 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q6 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q7 1510000500 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1162-GR (TE85R)
Q8 1530001950 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-GR (TE85R)
Q9 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q10 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R
Q11 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T107 R
Q12 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R
D1 1710000840 S.DIODE 1SR154-400 TE25
D2 1790001520 S.ZENER MA8075-L (TX)
D3 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D4 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
D5 1730000910 S.ZENER RD12M-T2B2
D6 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17
FI1 2020001320 CERAMIC CFJ455K8
X1 6050010760 S.XTAL DSX751S (14.5984 MHz)
L1 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L2 6200003120 S.COIL NL 322522T-8R2J
L3 6200006380 S.COIL ELJFC 150K 15U
L4 6200008610 S.COIL ELJFC 390K-F 39U
L5 6200003260 S.COIL NL 322522T-101J
L6 6200003140 S.COIL NL 322522T-150J
L7 6200006430 S.COIL ELJFC 180K-F
L8 6140001500 COIL LR-171
L9 6140001500 COIL LR-171
L10 6200008600 S.COIL ELJFC 560K-F 56U
L11 6200002090 S.COIL ELJFB 681K-F
L12 6200005550 S.COIL ELJFC 100K-F
L13 6200005550 S.COIL ELJFC 100K-F
L14 6200005550 S.COIL ELJFC 100K-F
L15 6200002970 S.COIL NL 322522T-121J
L16 6200003240 S.COIL NL 322522T-221J
L17 6200008640 S.COIL NL 322522T-391J
L18 6200003110 S.COIL NL 322522T-6R8J
L19 6200005550 S.COIL ELJFC 100K-F
L20 6200003950 S.COIL HF50ACC 322513-T
L21 6200005550 S.COIL ELJFC 100K-F
L22 6200008600 S.COIL ELJFC 560K-F 56U
L23 6200003200 S.COIL NL 322522T-560J
L24 6200000780 S.COIL LQH 3N 100K 14
L25 6200008600 S.COIL ELJFC 560K-F 56U
R1 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R2 7030003230 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 180 V (18 Ω)
R3 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R4 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
5-2 RD-200
[MAIN UNIT]
[DISP UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 23

5 - 6
S.=Surface mount
R5 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R6 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ)
R7 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R8 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R9 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R10 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R11 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R12 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R13 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R14 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R15 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R16 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω)
R17 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R18 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R19 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R20 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R21 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R22 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R23 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R24 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R25 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R26 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R27 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R28 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R29 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R30 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R31 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R32 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R33 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R34 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R35 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R36 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R37 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R38 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R39 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R40 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R41 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R42 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R43 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R44 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R45 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R46 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R47 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R48 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ)
R49 7030003490 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ)
R50 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R51 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R52 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R53 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R54 7030006080 S.RESISTOR ERJ1WYJ220H (22 Ω)
R55 7030006080 S.RESISTOR ERJ1WYJ220H (22 Ω)
R56 7030006080 S.RESISTOR ERJ1WYJ220H (22 Ω)
R57 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R58 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R59 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ)
R60 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R61 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ)
R62 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R63 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R64 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R65 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R66 7030004770 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYF 113 V (11 kΩ)
R67 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R68 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R69 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R70 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R71 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R72 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R73 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
R74 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R75 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω)
R76 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
R77 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R78 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R79 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R80 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R81 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R82 7030003220 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 150 V (15 Ω)
R83 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R84 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R85 7030000360 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 680 Ω (681)
R86 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[MAIN UNIT]
R87 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R88 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R89 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R90 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R91 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R92 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R93 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R94 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R95 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R96 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R97 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R98 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R99 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R100 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R101 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R102 7030007230 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 102V
R103 7030007220 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 202V
R104 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R106 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
R107 7030001090 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 47 Ω (470)
R108 7030001090 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 47 Ω (470)
R109 7510000790 S.THERMISTOR NTCCS2012 4AH 473KC-T
R110 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R111 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R112 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R113 7030000360 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 680 Ω (681)
C2 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C3 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C4 4030008860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 153K-T-A
C5 4030008860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 153K-T-A
C6 4030010770 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 392K-T-A
C7 4030008850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 123K-T-A
C8 4030008870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 183K-T-A
C9 4030014300 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 563K-T-A
C10 4030008870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 183K-T-A
C11 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C12 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C13 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C14 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C15 4030008850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 123K-T-A
C16 4030009970 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 182K-T-A
C17 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 223K-T-A
C18 4030009580 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 681K-T-A
C19 4030008860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 153K-T-A
C20 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C21 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T-A
C22 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C23 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C24 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C25 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T-A
C26 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C27 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C28 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C29 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C30 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C31 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C32 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C33 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C34 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C35 4030008860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 153K-T-A
C36 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C37 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C38 4030008860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 153K-T-A
C39 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C40 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 223K-T-A
C41 4030010770 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 392K-T-A
C42 4030008910 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 393K-T-A
C43 4030012600 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1A 105M-T-A
C44 4030012600 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1A 105M-T-A
C45 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C46 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C47 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C48 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C49 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C50 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C51 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C52 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C53 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C54 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C55 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T-A
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[MAIN UNIT]
Page 24

S.=Surface mount
C56 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T-A
C57 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T-A
C58 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T-A
C59 4030007160 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 181J-T-A
C60 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T-A
C61 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T-A
C62 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T-A
C63 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C64 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C65 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T-A
C66 4030008650 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 332K-T-A
C67 4030008770 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 562K-T-A
C68 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T-A
C69 4030010770 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 392K-T-A
C70 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T-A
C71 4610002150 S.TRIMMER CTZ3S-10A-W1-AF
C72 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T-A
C73 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C74 4510006670 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA471P
C75 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
C76 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C77 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C78 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
C79 4550006670 S.TANTALUM ECST1AD107R
C80 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C81 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
C82 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C83 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C84 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C85 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
C86 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C87 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C88 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C89 4030009000 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1C 224K-T-A
C90 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C91 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C92 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C93 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C94 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C95 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T-A
C96 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C97 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C98 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C99 4030008650 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 332K-T-A
C100 4030008770 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 562K-T-A
C102 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR
C103 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C104 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C105 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C106 4030008650 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 332K-T-A
C107 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C108 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C109 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C110 4550006670 S.TANTALUM ECST1AD107R
C111 4030008850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 123K-T-A
C112 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 103K-T-A
C113 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T-A
CP1 6910009670 S.CHECK P HK3-S-T
CP2 6910009670 S.CHECK P HK3-S-T
J1 6510021660 CONNECTOR IMSA-9210B-1-03Z525-T
J2 6510021670 CONNECTOR IMSA-9210B-1-05Z525-T
J3 6510003540 CONNECTOR S06B-EH-S
J4 6510019420 S.CONNECTOR B8B-ZR-SM3-TF
EP1 0910051523 PCB B 5297C
5 - 7
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[MAIN UNIT]
Q1 1560000420 S.FET 2SK209-GR (TE85R)
Q2 1560000420 S.FET 2SK209-GR (TE85R)
Q3 1560000420 S.FET 2SK209-GR (TE85R)
Q4 1560000420 S.FET 2SK209-GR (TE85R)
Q5 1560000420 S.FET 2SK209-GR (TE85R)
Q6 1560000420 S.FET 2SK209-GR (TE85R)
Q7 1560000420 S.FET 2SK209-GR (TE85R)
Q8 1560000420 S.FET 2SK209-GR (TE85R)
D1 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D2 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D3 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D4 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D5 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D6 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D7 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D8 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D9 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D10 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D11 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
D12 1750000610 S.VARICAP MA2SV0500L
L1 6150005020 COIL LS-529
R1 7030003780 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ)
R2 7030003780 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ)
R3 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R4 7030003780 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ)
R5 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R6 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R7 7030003780 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ)
R8 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R9 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R10 7030003780 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ)
R11 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R12 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R13 7030003780 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ)
R14 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R15 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R16 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R17 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R18 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R19 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R20 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R21 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R22 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R23 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R24 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R25 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R26 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R27 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R28 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
C1 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T-A
C2 4030009530 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 030B-T-A
C3 4610002150 S.TRIMMER CTZ3S-10A-W1-AF
C4 4610002150 S.TRIMMER CTZ3S-10A-W1-AF
C5 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C6 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C7 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C8 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T-A
C9 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T-A
C10 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T-A
C11 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T-A
C12 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T-A
C13 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C14 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T-A
C15 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T-A
C16 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T-A
C17 4510004640 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA470SP
C18 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T-A
C19 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C20 4550004010 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA2 1A105M-8L
C21 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C22 4030008630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JF 1C 104Z-T-A
C23 4550004010 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA2 1A105M-8L
C24 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C25 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[ANT UNIT]
Page 25

5 - 8
S.=Surface mount
C26 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
C27 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1C 104KT-N
J1 6910005280 CONNECTOR IMSA-9110S-03
J2 6910005300 CONNECTOR IMSA-9110S-05
J3 6510018300 S.CONNECTOR S2B-ZR-SM3A-TF
J4 6510018300 S.CONNECTOR S2B-ZR-SM3A-TF
J5 6510018300 S.CONNECTOR S2B-ZR-SM3A-TF
EP1 0910051533 PCB B 5298C
EP3 3310002220 ANTENNA OH-3
EP4 3310002220 ANTENNA OH-3
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
ANT UNIT]
Page 26

SECTION 6 MECHANICAL PARTS AND DISASSEMBLY
6 - 1
6-1 FP-561
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
MP1 8210016290 2142 front panel (A) assembly [GEN] 1
8210016410 2142 front panel (B) assembly [EUR] 1
MP2 8210016300 2142 rear panel assembly [GEN] 1
8210016420 2142 rear panel (A) assembly [EUR] 1
MP3 8930049451 2142 screen (A) -1 1
MP4 8410002300 2272 heatsink 1
MP5 8930049030 2142 keyboard (A) 1
MP6 8930047480 2142 F-packing 1
MP7 8930047510 2142 R-packing 1
MP8 8110006530 2142 cover 1
MP9 8010017530 2142 chassis 1
MP10 8510011851 2142 shield plate-1 1
MP11 8930042330 Sealing washer (M) 4
MP13 8930039000 1757 sheet 1
MP14 8810004540 Screw BiH M3x8 SUS 4
MP16 8810004540 Screw BiH M3x8 SUS 4
MP18 8810008200 Screw PH BT M2.6x6 NI-ZU 4
MP19 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3x8 NI-ZU 4
MP20 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3x8 NI-ZU 4
MP21 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3x8 NI-ZU 7
MP24 8830000370 Wing nut M5 SUS 1
MP25 8810008230 Bolt hex head M5x20 SUS 1
MP26 8850000500 Spring washer M5 SUS 1
MP27 8850000180 Flat washer M5 SUS 3
MP28 8830000250 Nut M5 SUS 1
MP31 8930047640 2142 handle 1
MP32 8010017500 T-bracket 1
MP33 8010017510 U-bracket 1
MP34 8930047540 2142 shaft plate 1
MP35 8930047530 2142 shaft 1
MP36 8850001740 Spring washer 8L SUS 2
MP37 8810009300 Set screw (J) 1
MP38 8850000210 Flat washer M8 SUS 2
MP39 8820001030 2142 knob bolt 2
MP40 8310025310 Label Circle seal (L) 2
[CHASSIS PARTS]
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
F1 5210000060 Fuse FGB 5A 1
EP2 0850000120 IA023-5B03S (GPS module set) 1
MP1 8510012360 2272 GPS case 1
MP3 8930018520 TR clip (A) 5
MP4 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3x8 NI-ZU 2
MP5 8810000120 Screw PH M2.6x3 2
[MAIN UNIT]
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
W1 8900009030 Cable OPC-902 1
W2 8900008740 Cable OPC-867 [GEN] 1
8900009380 Cable OPC-906 [EUR] 1
MP1 8810009830 Set screw (C) M2x12 4
MP2 8930001850 Sponge (AD) 1
[LOGIC UNIT]
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
SP1 2520000110 Piezo buzzer PS1740P02 1
W1 8900008340 Cable OPC-816 1
[SW UNIT]
6-2 RD-200
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
W1 8900008970 Cable OPC-873 1
MP1 8510012340 2273 L-Case 1
MP2 8510012350 2273 U-Case 1
MP3 8930049000 2273 L-plate 1
MP4 8930048990 2273 U-plate 1
MP5 8110006770 2273 cover 1
MP6 8930049390 2273 main seal 1
MP7 8810006050 Icom screw E7 4
MP8 8850000690 Flat washer M3 (3x7x0.5) SUS 4
MP9 8930049990 O-ring (Y) 4
MP10 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3x8 NI-ZU 4
MP11 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3x8 NI-ZU 4
MP12 8810007130 Set screw H M3x6 4
MP13 8810007130 Set screw H M3x6 4
MP15 8930000190 Stud bolt (O) 1
MP16 8930050000 Spacer BS-315 3
MP18 8930049320 2288 Vent. sheet 1
MP20 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3x8 NI-ZU 1
[CHASSIS PARTS]
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
EP3 3310002220 OH-3 1
EP4 3310002220 OH-3 1
MP1 8950000180 M.other Cable-tie-80 4
[ANT UNIT]
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
W1 8900008040 Cable OPC-786 1
MP1 8930010000 Conector cover 2
MP2 8810001500 Screw PH AO M6x3 SUS 4
MP3 8850000510 Spring washer M6 SUS 4
MP4 8850000190 Flat washer M6 (6x13x1.0) SUS 1
MP5 8930049400 2273 pipe 1
MP6 8930049740 House band HAS-40 2
[ACCESSORIES]
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
MP1 8510012330 2273 shield case 1
MP2 8510005330 Coil case 1
MP3 8510000470 Mix shield case 1
[MAIN UNIT]
Screw abbreviations A, B0, BT: Self-tapping PH: Pan head
FH: Flat head BiH: Bind head
NI: Nickel SUS: Stainless
ZK: Black
REF. NO. ODER NO. DESCRIPTION QTY .
MP1 8930049400 2273 pipe 1
MP2 8930049740 House band HAS-40 2
[ACCESSORIES]
Page 27

6 - 2
UNIT abbreviation (C): CHASSIS PARTS, (M): MAIN UNIT, (L): LOGIC UNIT, (ANT): ANTENNA UNIT
MP20 (C)
MP14 (C)
EP2 (M)
MP19 (C)
MP10 (C)
MP7 (C)
MP36 (C)
MP31 (C)
MP39 (C)
MP35 (C)
MP34 (C)
MP37 (C)
MP38 (C)
MP16 (C)
MP40 (C)
MP2 (C)
MP13 (C)
MP25 (C)
A
MP18 (C)
MP27(C)
MP27 (C)
MP24 (C)
MP26 (C)
MP3 (M)
MAIN unit
LOGIC unit
MP1 (M)
EP2 (M)
MP11 (C)
F1 (M)
W1 (L)
W1 (C)
W2 (L)
MP4 (M)
MP1 (L)
MP1 (L)
MP2 (L)
MP21 (C)
DISPLAY unit
SW unit
MP9 (C)
MP5 (C)
MP1 (C)
MP6 (C)
SP1 (S)
MP3 (C)
MAIN unit
MP7 (C)
MP8 (C)
MP9 (C)
MP1 (C)
MP5 (C)
W1 (C)
MP2 (C)
MP6 (C)
MP13 (C)
MP4 (C)
MP18 (C)
MP11 (C)
MP15 (C)
MP1 (ANT)
MP10 (C)
MP12 (C)
MP3 (C)
MP16 (C)
MP16 (C)
EP3 (ANT)
EP3 (ANT)
MP2 (M)
MP1 (M)
MP3 (M)
MP20 (C)
MP33 (C)
MP32 (C)
MP8 (C)
ACCESSORIES
ACCESSORIES
RD-200
FP-561
MP2
MP3
MP4
MP1
MP6
MP2
MP5
W1
MP1
A
Page 28

SECTION 7 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
7 - 1
2SC2712 GR
(Symbol: LG)
2SD1664 Q
(Symbol: DAQ)
2SC3326 B
(Symbol: CCB)
2SA1213 Y
(Symbol: NY)
2SA1162 GR
(Symbol: SG)
3SK131 K
(Symbol: V13)
B
C
E
C
B
C
E
C
2SA1576 R
(Symbol: FR)
B
E
C
2SC4081 R
(Symbol: BR)
E
C
B
DTC144 EU
(Symbol: 26)
B
E
C
•
TRANSISTOR AND FET’S
D
S
G2
G1
•
DIODES
RD7.5M B1
(Symbol: 751)
DA204 U
(Symbol: K)
MA8075 L
(Symbol: 7-5)
RD4.7M B3
(Symbol: 473)
1SS355
(Symbol: A)
1SR154-400
(Symbol: 14)
RD11M B2
(Symbol: 112)
RD12M B2
(Symbol: 122)
Page 29

SECTION 8 BOARD LAYOUTS
8 - 1
8-1 FP-561
8-1-1 SW UNIT
• TOP VIEW
C9
S18
D17
R6
S13
D12
C10
S7
D6
C8
S17
S6
D16
D5
C7
S16
S5
D15
D4
S4
D3
S3
D2
S2
D1
DS9 DS8
R17
R13R9R12
R8
R14
R7
R15
R16
DS7
DS5 DS4 DS3 DS2
DS1
C4
S1
C2
C3
C1
C14
DS6
R5
R10
C12
C11
R11
Q4
Q3 Q2
Q1
S12
D11
R4
S11
D10
R3
S10
D9
C6
S15
D14
R2
S9
D8
C5
S14
D13
R1
S8
D7
Page 30

8 - 2
• BOTTOM VIEW
GND
GND
SW2
SW1
12V
INV
BEEP
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
GND
GND
to LOGIC unit J3
J1
1
18
J1
SP1
Page 31

8 - 3
8-1-2 LOGIC UNIT
• TOP VIEW
GND
GND
SW1
SW2
12V
INV
BEEP
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
GND
GND
to LOGIC unit J1
NC
GPSI
GPSO
DGP
GND
VBAK
VANT
G5V
to GPS unit
118
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
SW2
SW1
NC
18V
12V
12V
12V
G5V
G5V
L5V
L5V
L5V
DEPCONT
DGPOUT
DGPIN
NMEAOUT
NMEAIN
TEMP
SPD
RSSI
LOCONT
TXTRG
TXSIG
GND
GND
to MAIN unit J1
1 30
GND
GND
VBL
VBL
GND
NC
NC
NC
GND
BLUE
GREEN
RED
CONT
NC
12V
NC
GND
VSW
GND
GND
NTP
DTCK
VSYNC
HSYNC
to LCD unit
J6
1
24
8
1
J2
J5
J3
IC13
R131
X1
IC1
BT1
J2
J5
IC28
IC34
IC35
R151
R132
C59
C21
C25
C6
R179
IC44
C47
C5
Q3
IC20
IC21
IC22
IC33
IC31
IC30
IC32
IC7
C48
Q4
C68
J1
J6
IC19
C10
J3
C7
C3
C53
C44
C43
R60
R142
R143
C50
C11
1
C24
C12
C14
C13
C56
C45
C27
C26
D2
R180
R165
C70
C46
R7
R15R6R14R5R13
R42
R20
R19
R12
R18
R11
R17
R10R9R16
R8
C49
C23
C42
C55
IC46
R147
R162
R148
C4
R56
C20
C17
R163
R178
C69
R164
R177
Q5
R135
Page 32

8 - 4
• BOTTOM VIEW
IC41 IC16 IC42
IC18
IC3
IC2 IC5
IC6 IC4
IC45
IC23
C65
C52
C58
C51
C19
C67
C61
R130
R134
R136
R128
R104
R105
R112
R155
R47
R66
C15
R101
R100
R91
R71
R102
R171
R172
R169
R170
R167
R168
R107
R110
R138
R22
R81
R48
R156
R135
R145
R144
R46
R45
R49
C64
R52
R51
R77
R53
R43
R38
R37
R146
R55
R78
R82
R83
R173
R174
R90
R44
R92
R93
R94
R39
R40
R41
R95
R96
R97
R98
R99
C2
Q1
R1
R4
D1
R3
R2
C1
R106
R108
R109
R111
R126
R127
R129
R150
C16
C18
R31
R140
R30
R29
R28
R89
R88
R87
R85
R26
R27
R25
R24
R23
R22
R21
C54
R36
R32
R62
R68
Page 33

8 - 5
8-1-3 MAIN UNIT
• TOP VIEW
GND
GND
TXSIG
TXTRG
LOCONT
RSSI
SPD
TEMP
NMI
NMO
DGPI
DGPO
DEPCONT
5V5V5V5V5V
12V
12V
12V
NC
NC
SW1
SW2
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
to LOGIC unit J2
J1
1 30
D13
D53
Q14
T2
L2
C59
D10
R46
C60
D3
D31
L1
C92
C95
L6
R6
T1
R5
D36
D35
D9
D32
C94 C91
D4
D30
J3
F2
F3
C44
J5
J4
J2
POW
DGPS NMEA T/D
C54
C80
D12
R107
R85
R7
Q7 Q6
L5
D22
D17
IC13
C72
C63
IC11
IC2
IC1
X1 X2
C86
C28
C69
Q27
C103
C75
C76
IC9
C79
C47
C77
D11
C50
C52
IC10
Q12
J1
IC17
IC15
IC7
IC8
RSSI
FI1
C70 C71
R63
R94
C4
R3
R2
C3
IC14
C5
Q5
R29
R28
R22
R101
Q4
Q2
Q23
R24
R108
R109
R26
R23
R25
R27
Q3
Q24
R104
R106
R102
R103
R105
C1
R93
C81
C83
C13
R96
R10 C7
C16
R100
R8
C14
C11
IC3
IC6
C10
C115
C24
R17
C23
C22
C12
Q25
Q26
C21
R98
R99
Q1
IC16
C98
C96
C97
C93
C90
C20
C19
C99
C25
R16
C18
C17
R15
R115
C122
C120
R19
R18
C101
C117
C116
C102
C110
C100
C119
C121
R113
R111
R112
R110
R131
IC25
L8
L7
R13R12
R97
C88
C116
C118 C117
R9
D34
IC4
C8
Q22
R84
D24
D23
D2
D1
D37
R66
Q13
C74
C73
R72
R71
R76
R74
R77
R75
R48
R68
R67
Q16
Q33
Q32
C108
C111 C113
R125
C106
C119
Q29
Q28
R92
D27
C43
R91
C62
C61
D14
R36
R56
R55
R35
C41
D33
C89
R45
R44
C42
C40
R128
R120
C109
C105
C107
R130
R127
R124
R122
R60
Q35
Q34
Q31
C85
D28
Q30
D21
R47
C45
C46
L3
C48
R79
R78
C49
R82
D18
R69
R70
C104
D118
C64
R62
R64
R61
R65
Page 34

8 - 6
• BOTTOM VIEW
J2 J4 J5 J3
Page 35

8 - 7
8-2 RD-200
8-2-1 MAIN UNIT
• TOP VIEW
MNI –
MNI +
MNO –
MNO +
+ 12
GND
J3
16
P60
CHECK
GND
F+12
REST
FCLN
TXDO
+5
J4
18
C109
J3
1
C74
C75
C79
L23
IC14
Q7
Q4
IC10
L21
IC16
L16
L18
L10
L19
L15
L17
IC5
L14
L13
L12
CP2CP1
CP1
CP2
IC7
C71
Q11Q9
IC19
L22
IC12
C37
C85
IC15
C86
C36
IC18
IC8
C81
C30
IC9
C78
B5297C
FI1
IC2
MP3
L9
L8
MP2
IC6
C13
J4
C102
C46
1
MP1
C93
R84
R91
R87
R81
R110
R109
C105
R80
R79
C90
R58
R61
R59
R62
R82
C59
C58
C60
C62
C63R47
C66
R49R50
C61
R48
C54
C52
C53
C65
C64
R51
R3
C67
C68
R1
C19
C18C16
C10
C3
C17C12
C6
C4
C23
C24
C77
C29
R10
R8
C26
C22
R12
C27
R11
C25
C5 C7
C15
R2
C69
C57
C56
C87
C88
R53
R63
C70
X1
R52
C72
C113
C73
R60
C55
R43
R41
R39
R37
R35
R33
R31
R45
R44
R42
R40
R38
R36
R34
R32
R30
R26
R28
R27
C51
C45
R46
C50
C47
C49
C48
R29
C94
R78
C39
R57
C42
R24
R23
C40
C106
C100
C99
R75 R74
C92
R99
C82
R97
R95
R93
R91
R88
R25
C2
R89
R103
R106
R101
R104
C98
R72
R76
to CHASSIS unit
Page 36

8 - 8
• BOTTOM VIEW
GND
TUNE
ANT V
AF GND
AF
J2
5
1
GNDRFGND
J1
31
R100
R102
R98
R77
R73
R71
R64
R65
C104
C107
C84
C44
C83
D2
Q3
IC4
R5
C108
D4
C95
R85
R113
R83
C41
R21
R20
R19
R17
R18
C38
R22
C35 R16
C76
C80
R13
C31
R14
R7
C34
C111
C112
C14
C11
C8
C9
C20
R9
C21
C28
Q1
L11
D5
C103
R15
C33
C32
D1
IC3
L24
L25
L5
L4
L3 L2
J1
L7
L6
IC1
R108
R107
R55
R54
R112
R111
Q10
Q12
R4
R6
R66
R69
R68
Q5
Q8
D3
R67
R86
R70
C89
Q6
IC11 L20
C110
IC17
C96
C97
R96
R94
R92
R90
C43
R50
L1
J2
IC13
D6
to ANT unit J2
to ANT unit J1
Page 37

8 - 9
8-2-2 ANT UNIT
• TOP VIEW
AF GND
AF
J3
1
2
J5
12
RF
GND
J4
12
RF
GND
R4
R7
R10
R1
R27
J3
C17
L1
C3
C4
1
C5
Q1
Q2
R5
R8
C13
Q8
Q6
Q5
Q7
R23
R24
C27
R21
R22
C26
R18
R19
C12
R15
C18
C15
C19
C14
C16
R20
C25
R16
C11
R17
C24
R25
R26
R6
C8
R3
C7
C22
C21
C23
C20
R28
R2
R11
R9
C9
C6
R14
R12
R10
Q4
Q3
R13
C2
C1
D1
D2
D9
D3
D4
D10
D5
D6
D12
D7
D8
D11
1
1
J5 J4
Page 38

8 - 10
• BOTTOM VIEW
GNDRFGND
J1
13
GND
TUNE
ANT V
AF GND
AF
J2
5
1
1
J2
J1
1
to MAIN unit J1
to MAIN unit J2
Page 39

9 - 1
SECTION 9 BLOCK DIAGRAM
BEEP
POW SW
INV
MAIN UNIT
DISP UNIT
FLASH ROM
IC32, IC33:
MBM29F800BA-90PFTN
DRAM
IC34, IC35:
M5M44260CJ
SRAM
IC30, IC31:
M5M51008BVP-70LL
PAL
IC28: SC-1372
DATA BUS
ADD BUS
DC-DC
CONVERTER
12V
VSYNC HSYNC DCLK R.G.B
INV
LCD
Q4: 2SB1201 S
Q5: XP6501 AB
VBL
CONT
GPS
BOARD
KEY
MATRIX
RL0–RL5
SL0–SL2
NMEA OUT
NMEA IN
DGPS OUT
SELECT
IC41:
BU4053BCF
LEVEL
CONVERTER
IC17: TC4049BF
Q28, Q30: 2SC4081 R
Q29, Q31: 2SA1576 R
LEVEL
CONVERTER
IC17: TC4049BF
Q32, Q34: 2SC4081 R
Q33, Q35: 2SA1576 R
PHOTO
COUPLER
IC8: TLP121 GB
IC7: TC7W14FU
SUB CPU
IC22: TMP90PM36F
TXD
RXD
TXD
RXD
SPD
INV, BEEP
SL0–SL2, RL0–RL5
ADDRES
DECODER
IC16: TC74HC139AF
IC19: TC7W32F
FIFO RAM
IC20: CY7C433-40JC
MAIL BOX
RAM
IC21: M66220FP
DATA BUS
ADD BUSADD BUS
MAIN CPU
IC1: CL-PS7500FE
DATA BUS
ADD BUS
DATA BUS
DATA BUS
ADD BUS
CONTROL
CLK (16MHz), RESET
TEMP
CARD
ADD BUS
J1:
ICME68H-L8-D1121RHA
DATA BUS
BUFFER
IC2: TC74HCT245AF
IC7: TC74HCT646AP
ADD BUS
BUFFER
IC4, IC5, IC6:
TC74HC245AF
DC IN
LOGIC UNIT
RESET
IC13: S-80742SL-A6
Q1: 2SC2712 GR
OSC
IC44: TC7SH04FU
X1:
DSO-49SJ
TRANS FORMER
T2: TO-43
SW
Q14: FS30KMJ-3
Q16: 2SA1162 GR
X2
40V RECT.
D12: RG-2A
40V
DRIVER
IC2: TC4093BF
Q2, Q3: 2SC2712 GR
Q4, Q5: 2SA1162 GR
INV GATE
IC1: TC7W04F
TXSIG
TRANSFORMER
T1: TO-46
POW AMP
Q6, Q7: FS30KMJ-3
Q23, Q24: 2SC3326 B
PHOTO
COUPLER
IC15: TLP121 GB
IC7: TC7W14FU
TRANSDUCER
DGPS IN
SPD IN
TEMP IN
TUNE
L6: LS-414
DET IC
IC5: TA31136FN
BPF
FI1: CFWS455GY
40V
TUNE
L1: LS-415
SELCT
IC16: TC4W53FU
STC
Q1: 2SC3326 B
Q26: 2SC2712 GR
TX CONT
IC14: TC4S69F
LOCAL
OSC
IC3: TC3W03FU
AMP
IC6: UPC358GR
X1: CR-497
TXTRG
RSSI
RSSI CONT
Q25: 2SC3326 B
DEPCONT
8V RECT.
D22: SB30-09J
12V RECT.
D13: SB30-09J
REG
IC13: PQ05RF21
REG
Q27: 2SD1664 Q
D37: RD7.5M B1
12V
6V
5V
REG
Q12: 2SA1213 Y
Q13: 2SC2712 GR
ERROR AMP
IC10: TLP121 GB
IC11: NJM2904M
SW UNIT
SW1 SW2
MAIN UNIT
LOCAL
OSC
IC4: TC3W03FU
X2: CR-496
LOCONT
PWM CONT
IC9: UPC494GS
TX/RX
D3, D4, D9, D30,
D31, D32, D35, D36:
1N4002
SW UNIT
DATA BUS
9-1 FP-561
Page 40

ANT UNIT
RX_f=283.5~325.0 kHz
EP3
EP4
Q1, Q2: 2SK209 GR
1Lo=738.5~780.0 kHz
Q3, Q4: 2SK209 GR
IC1: UPC1676G
NTC
IC2: ND487C1 3R
456.2 kHz
IC3: TA31136FN
IC4: NJM2904M
14.5984 MHz
IC7: TC3W03FU
Q6: 2SC4081 R
IC5: TC7S04F
IC10: TC7S04F
DDS
IC6: SC-1287
CPU
IC12: HD64F3644H
Q2: 2SC4081 R
L+5
VCC
RESET
+8
REG
+5
REG
IC11: S-80842ALUP-EA6
Q5: 2SC4081 R
IC8: TA7808F
+5
L+5
+8
+6.5
EEP
ROM
IC13: X25320SI-2.7
IC9: TA7805F
NMEA
BUFF
IC15, IC17: TC4093BF
IC18: TLP121 GB
Q9, Q11: 2SC4081 R
Q10, Q12: 2SA1576 R
FLASH
NMEA
Q4: 2SC4081 R
+6.5
REG
+6.5
Q3: 2SD1664 Q
D2: MA8075 L
TUNE
D/A
MAIN UNIT
Q5, Q6: 2SK209 GR
Q7, Q8: 2SK209 GR
FI1: CFJ455K8Q1: 3SK131K
X1: DSX751S
BPF AMP
BPF AMP
RF
AMP
AMP
AMP
LPF
BUFF D/ALPFHPF
LPF
LPF
HPF
AMP
LPF
LPF
AMP
BPF
BUFF
LIMIT
AMP
IF
AMP
AMP
IC19: TA75S01F
9-2 RD-200
9 - 2
Page 41

10 - 1
SECTION 10 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
10-1 FP-561
500 uS
5 Vp-p
200 KHz
50 KHz
5.0 V2.5 V
138 KHz
3.6 Vp-p
2.4 V
5.0 V
5.0 V
8.3 V
128 KHz
8.5 Vp-p
5.24 MHz
4.04 MHz
128 KHz
9.3 Vp-p
655 KHz
505 KHz
200 KHz 0.0 V
50 KHz 5.0 V
5.0 Vp-p
5.0 Vp-p
4.3 Vp-p
4.3 Vp-p
200 KHz, 50 KHz
1000 Vp-p
500 uS
12.5 V
42.0 V
T/D
7
4
3
6
8
2
5
1
J2
TEMPOUT
SPDOUT
SPD+
TD1
TD2
R44
560
C42
0.001
D27
DA204U
R35
470
C40
22
C41
0.01
C89
0.001
R45
100
D33
RD4.7M B3
C62
0.1
7
8
4
IC7A
TC7W14FU
C43
0.01
R36
10 k
TEMP
SPD
12V
5V
40V
R6 4.7 k
R5 4.7 k
D3 1N4002
D30 1N4002
D4 1N4002
D31 1N4002
R24
100
R2827R29
27
Q6
FS30KMJ-3
R105
390
R103
100 k
R101
22 k
Q23
2SC3326 B
R25
100
R106
390
Q24
2SC3326 B
R85 470
R7 470
Q7
FS30KMJ-3
R26
1 k
R27
1 k
3
4
8
6
5
7
T1
TO-46
R107 470
TD1
TD2
53
IC1C
TC7W04F
R22
1 k
R23
1 k
Q4
2SA1162 GR
R2
10 k
26
IC1B
TC7W04F
C3
100 P
D1
1SS355
D2 1SS355
R3
10 k
C4
100 P
C5
0.1
6
5
4
IC2B
TC4093BF
9
8
10
IC2C
TC4093BF
13
12
11
IC2D
TC4093BF
2
1
3
14
7
IC2A
TC4093BF
Q2
2SC2712 GR
Q3
2SC2712 GR
Q5
2SA1162 GR
7 1
8
4
IC1A
TC7W04F
C81
0.1
RSSI
LOCONT
TXTRG
TXSIG
2
5
3
IC14
TC4S69F
C83
0.001
R84
10 k
D23
1SS355
D24
1SS355
C1
0.1
R93
1 k
R94
10 k
5V
RSSI
LOCONT
TXTRG
TXSIG
5V
C7
0.001
C8
10
R8
47
3
2
1
4
8
IC6A
µPC358GR
R100
470
R10
15 k
R9
39 k
C86
10
R99
100 k
R98
22 k
D34
RD4.7M B3
12V
RSSI
5V
LOCONT
TXTRG
R16
1 k
C23
0.01
C22
0.01
C118
0.1
C115
18 P
L7
220 µH
C117
270 P
C116
270 P
Q22
DTC144EU
R96
100 k
1234
567
8
1234
567
8
IC3
TC3W03FU
IC4
TC3W03FU
X2
CR-496
R13
1 M
R97
56 k
C88
0.1
R17
47 k
C24
0.1
R12
1 M
X1
CR-497
C16
0.1
C10
0.1
C17
10
R15
47
C18
0.001
FI1
CFWS455GY
C28
1000
R104
100 k
L6
LS-414
L1
LS-415
C97
0.1
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
IC16 TC4W53FU
C25
0.1
R115
270
Q1
2SC3326 B
OSCIN
1
OSCOUT
2
MIXOUT
3
VCC
4
IFIN
5
DEC
6
FILOUT
7
FILIN
8
AFOUT
9
QUAD
10
IFOUT
11
RSSI
12
N-DET
13
N-REC
14
GND
15
MIXIN
16
IC5
TA31136FN
C102
3.3
R116
6.8 k
C100
0.1
C119
33 P
C121
390 P
C120
33 P
C122
390 P
L8
D10F-A814AY-152K
C101
0.1
Q26
2SC2712 GR
R117
1 k
R102
22 k
R111
100 k
C19 0.01
C20 0.001
C21 0.01
C90
0.01
R18
47 k
R19
220 k
C99
0.1
C110
10
R113
100 k
R112
100 k
R110
100 k
C98
0.1
R131
47
C94
0.0022
C95
0.0022
D35
1N4002
D36
1N4002
C96
0.0027
C91
0.0022
C92
0.0022
D32
1N4002
D9
1N4002
C93
390 P
5V
POW
1
2
3
4
J4
1 2
J3
C6033C113
0.1
C59
33
D14
1SS355
IC8
TLP121 GB
F3
F1
F2
2
IC7B
TC7W14FU
R56
1 k
R55
470
C61
0.0047
C111
0.1
HV–
5V
12V
HV+
NMI
5V
R48
27 k
Q25
2SC3326 B
R109
100 k
R108
22 k
12V
40V
R47
5.6 k
C48
0.0047
C49
0.0047
D12
RG-2A
C52
33
L5
LW-16
C53
1000
D13
SB30-09J
D11
1N4002
1
2
4
5
8
9
10
6
T2
TO-43
C50
0.01
C11
20 P
C12
20 P
C13
20 P
C14
20 P
C54
1000
D10
DSA3A1
C44
1000
R46
560
C45
0.0047
C46
0.0047
C47
1000
L2
FK-080E-1020
HV+
HV–
12V
5V
LOCONT
DEPCONT
L3
100 µH
R82
1.5 k
Q16
2SA1162 GR
R78
1.8 k
C80
10
C69
1000
SW1
SW2
C70
0.01
R79
18
Q14
FS30KMJ-3
D22
SB30-09J
D21
1SS355
C103
10
Q27
2SD1664 Q
R118
2.2 k
D37
RD7.5M B1
D17
1N4002
1
IC13
PQ05RF21
8V
R63
4.7 k
C72
470
R61
270
C63
47
3
2
1
4
8
IC11A
NJM2904M
C64
0.047
R62
2.2 k
C71
0.01
C104
0.001
R64
15 k
R65
10 k
5V
6V
3
16
8
IC17A
TC4049BF
R120
1 k
Q31
2SA1576 R
R124
47
C107
0.1
Q30
2SC4081 R
7
IC17C
TC4049BF
5
1
IC17B
TC4049BF
R119
1 k
C105
0.1
Q29
2SA1576 R
R122
47
Q28
2SC4081 R
C106
0.1
R60
5.6
NMO
12V
5V
6V
NMEA
NMIN–
NMOUT+
NMIN+
NMOUT–
DGPS
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
J5
DGPO–
DGPO+
DGPI–
DGPI+
+12
IC15
TLP121 GB
C109
0.1
14
IC17F
TC4049BF
R128
1 k
Q35
2SA1576 R
R130
47
Q34
2SC4081 R
9
IC17D
TC4049BF
11
IC17E
TC4049BF
R125
1 k
Q33
2SA1576 R
R127
47
Q32
2SC4081 R
C108
0.1
58
IC7C
TC7W14FU
R91
1 k
C85
0.0047
D28
1SS355
R92
470
DGPI
DGPO
6V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
IC9
µPC494GS
R68
22 k
R67
33 k
R69
5.6 k
R70
5.6 k
IC10
TLP121 GB
C76
47
R71
22 k
R76
10 k
C79
47
R72
5.6 k
R74
10 k
R77
22 k
C77
0.0022
R75
3.3 k
Q13
2SC2712 GR
R66
10 k
C73
0.01
D18
RD11M B2
C74
0.01
C75
22
Q12
2SA1213 Y
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
J1
LOCONT
RSSI
SPD
TEMP
SW1
SW2
12V
TXSIG
TXTRG
NMI
NMO
DGPI
DGPO
5V
DEPCONT
to LOGIC
unit J2
5
VCC
B
A
Q
CEXTXT
GND
VCC
B
A
Q
CEXTXT
GND
4
7
234
9
10
12
15
6
4
2
6
CONDITION
VCC : 12 V
RANGE : 40 M
BRIGHT : MAX
CONTRAST : CENTER
MAIN UNIT
5
6
7
IC6B
µPC358GR
5
6
7
IC11B
NJM2094M
Page 42

LOGIC UNIT
J2
GND
30
GND
29
TXSIG
28
TXTRG
27
LOCONT
26
RSSI
25
SPD
24
TEMP
23
NMEAIN
22
NMEAOUT
21
DGPIN
20
DGPOUT
19
DEPCONT
18
L5V
17
L5V
16
L5V
15
G5V
14
G5V
13
12V
12
12V
11
12V
10
18V
9
N.C
8
SW1
7
SW2
6
GND
5
GND
4
GND
3
GND
2
GND
1
12V
DEPCONT
R20
15 k
R19
15 k
R18
15 k
R17
15 k
R16
15 k
R15
15 k
R14
15 k
R13
15 k
R12
15 k
R11
15 k
R10
15 k
R9
15 k
R8
15 k
R7
15 k
R6
15 k
R5
15 k
R132
33
R151
15
NIOR
ADR12
SRAML
30
32
31
OE
A10
CS1
IC30
M5M51008BVP-70LL
A111A92A83A134WE5CS26A157VCC8NC9A1610A1411A12
ADR10
ADR11
ADR13
C59
1
12.0 V
C48
10
MDB5
MDB6
MDB7
MDB4
I/O729I/O628I/O527I/O426I/O3
NIOW
ADR15
NPOR
ADR17
Q3
2SB1132 Q
5.0 V
C47
47
MDB2
MDB3
25
24
I/O223I/O122I/O0
VSS
ADR18
MDB1
ADR16
CARD
DELAY
NIOW
MPOE
MDB3
35
MDB10
34
DQ3
FLRY
CD0B
CD1B
CD2B
CD3B
CD4B
CD5B
CD6B
CD7B
CD0B
CD1B
CD2B
CD3B
CD4B
CD5B
CD6B
CD7B
CD8B
CD9B
CD10B
CD11B
CD12B
CD13B
CD14B
CD15B
MPNE
WP
MAPCE
NAVA0
A15S
AS15
CK16M
SRAML
NIOR
MDB2
33
DQ10
ADR20
MDB9
ADR19
MDB1
ADR9
MDB8
ADR8
OEDS
CABV
SABV
NOEV
DIRE1
OEDR1
READ
NIOR
NIOW
INT5
CLK16
UARTG
UARTN
CCC2
CCS1
LNBW
MDB0
DQ029DQ830DQ131DQ932DQ2
ADR7
NIOR
NIOR
ADR6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13
IC7
TC74HCT646AP
1
DIR1
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8
A7
9
A8
10
GND
IC2
TC74HCT245AF
1
DIR1
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8
A7
9
A8
10
GND B8
IC3
TC74HCT245AF
ADR2
FLRY
ADR2
FLCE1
25CE26
27OE28
A0
VSS
24
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
24
23
22
21
20
MDB0
19
18
17
16
15
14
20
VCC
19
G
18
B1
17
B2
16
B3
15
B4
14
B5
13
B6
12
B7
11
B8
20
VCC
19
G
18
B1
17
B2
16
B3
15
B4
14
B5
13
B6
12
B7
11
ADR0
ADR1
NPOR
ADR18
BYTE
MDB15
ADR18
45
46
47
48
A16
VSS
BYTE
DQ15/A-1
A151A142A133A124A115A106A97A88N.C.9N.C.10WE11RESET12N.C.13N.C.14RY/BY15A1816A1717A718A619A520A421A322A223A1
ADR14
ADR15
ADR16
ADR17
MDB0
MDB1
MDB2
MDB1
MDB3
MDB2
MDB4
MDB5
MDB3
MDB6
MDB7
MDB4
MDB5
MDB6
MDB7
MDB8
MDB8
MDB9
MDB9
MDB10
MDB11
MDB10
MDB12
MDB13
MDB11
MDB14
MDB15
MDB12
MDB13
MDB14
C56
0.1
MDB15
MDB8
MDB9
MDB10
MDB11
MDB12
MDB13
MDB14
MDB15
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
MDB6
MDB7
MDB13
MDB14
40
41
42
43
44
DQ6
DQ7
DQ13
DQ14
IC33
MBM29F800BA-90PFTN
ADR12
ADR13
ADR11
ADR10
MDB5
DQ5
ADR5
MDB12
39
DQ12
MDB4
38
READ
ADR6
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
MDB2
MDB3
MDB10
MDB11
33
34
35
36
37
DQ3
DQ4
VCC
DQ10
DQ11
ADR20
NPOR
R21
47 k
R22
47 k
R23
47 k
R24
47 k
R25
47 k
R26
47 k
R27
47 k
R85
47 k
R86
47 k
R87
47 k
R88
47 k
R89
47 k
R28
47 k
R29
47 k
R30
47 k
R31
47 k
MDB9
ADR19
ADR10
MDB1
ADR9
MDB8
ADR8
C54
C53
0.1
0.1
5
OUT
NC
VDD
4
VSS3NC
IC13
S-80742SL-A6
INT5
ADR11
ADR12
ADR13
ADR14
ADR2 ADR2
MDB0
FLCE2
25CE26
27OE28
A0
VSS
DQ029DQ830DQ131DQ932DQ2
24
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
ADR6
ADR7
C5
4.7C40.1
J1
GND GND
135
CD15B
CD14B
CD13B
CD12B
CD11B
CD10B
CD9B
CD8B
CD7B
CD6B
CD5B
CD4B
CD3B
CD2B
CD1B
CD0B
R42
2.2 k
L5V
L5V L5V
MDB0
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5ADR6
21A020A119A218A317
A515A614A7
A4
12
13
16
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
ADR14
CD3B
CD4B
CD5B
CD6B
CD7B
/CE1
CA10
MPOE
CA11
CA9
CA8
CA13
CA14
MPWE
VccM
Vpp1
CA16
CA15
CA12
CA7
CA6
CA5
CA4
CA3
CA2
CA1
CA0
CD0B
CD1B
CD2B
WP
GND GND
CA0
CA1
CA2
CA3
CA4
CA5
CA6
CA7
INT5
CA8
CA9
CA10
CA11
CA12
CA13
CA14
CA15
CA16
CA17
CA18
CA19
CA20
CA21
CA22
CA23
SRAMH
ADR12
MDB12
MDB13
MDB14
MDB15
NIOR
SRAMH
32
30
31
OE
A10
I/O729I/O628I/O527I/O426I/O3
CS1
IC31
M5M51008BVP-70LL
A111A92A83A134WE5CS26A157VCC8NC9A1610A1411A12
NIOW
ADR10
ADR11
ADR13
ADR15
ADR17
NPOR
IC4
TC74HC245AF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
IC5
TC74HC245AF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
IC6
TC74HC245AF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MDB11
25
236
337
438
539
640
741
842
943
10 44
11 45
12 46
13 47
14 48
15 49
16 50
17 51
18 52
19 53
20 54
21 55
22 56
23 57
24 58
25 59
26 60
27 61
28 62
29 63
30 64
31
65
32
66
33
67
34 68
to Memory card
DIR1
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
GND10B8
DIR1
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
GND10B8
DIR1
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
GND10B8
MDB10
MDB8
MDB9
ADR2
24
21A020A119A218A317
I/O223I/O122I/O0
VSS
13
12
ADR9
ADR14
ADR16
ADR18
VCC
VCC
VCC
ADR3
ADR8
/CD1
CD11B
CD12B
CD13B
CD14B
CD15B
CA1
CA16
CA17
CA18
CA19
CA20
CA21
VccM
Vpp2
CA22
CA23
CA24
CA25
CD8B
CD9B
CD10B
/CD2
G
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
G
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
G
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
ADR4
A515A614A7
ADR7
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
ADR5ADR6
16
CD11B
CD12B
CD13B
CD14B
CD15B
CA1
CA16
CA17
CA18
CA19
CA20
CA21
CA22
CA23
CD8B
CD9B
CD10B
L5V
R128
MAPCE
NAVA0
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
ADR6
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
ADR10
ADR11
ADR12
ADR13
ADR14
ADR15
ADR16
ADR17
ADR18
ADR19
ADR20
ADR21
ADR22
ADR23
ADR24
A4
15 k
IC42
TC74HC14AF
141312111098
1234567
16 MHz
R140
4.7 k
ADR18
BYTE
MDB15
45
46
47
48
A16
VSS
BYTE
A151A142A133A124A115A106A97A88N.C.9N.C.10WE11RESET12N.C.13N.C.14RY/BY15A1816A1717A718A619A520A421A322A223A1
ADR14
ADR15
ADR16
ADR17
MDB4
MDB5
MDB6
MDB11
MDB12
MDB13
MDB7
MDB14
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ15/A-1
ADR13
VCC
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
IC32
MBM29F800BA-90PFTN
ADR11
ADR10
ADR12
L5V L5V
DEPCONT
C3
NPOR
R96
R99
15 k
R100
15 k
FLRY
R176
180
ID
LA15
123456789
ADR15
R179
15 k
R142
15 k
179
IOP0
LA16
ADR16
178
IOP1
LA17
ADR17
R98
15 k
177
IOP2
LA18
ADR18
176
IOP3
LA19
ADR19
175
ADR20
R39
15 k
TC
SIOCS2
OES1
CLK2
CLK16
NIOW
CCS2
CCS1
LNBW
ADR0
ADR1
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
ADR6
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
ADR10
ADR11
ADR12
ADR13
ADR14
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
IC28
SC-1372
I/O14
I/O15
VCC
C2
0.001
R40
15 k
R41
15 k
WP
CPH
R101
15 k
VCC
GDN
I/O31
GND
I/O16
I/O17
I/O18
I/O30
I/O29
I/O19
I/O28
I/O27
I/O26
I/O25
I/O24
CLK3/I5
GND
CLK2/I4
I/O23
I/O22
I/O21
I/O20
181
OD1
182
OD0
183
SETCS
184
INT9
185
NINT4
186
INT5
187
READY
188
NIOGT
189
NBLI
190
NXIPMUX16
191
NINT1
192
INT2
193
VSS
194
NEVENT1
195
NXIPLATCH
196
TC
197
NSIOCS2
198
VDD
199
NSIOCS1
200
NEASCS
201
NMSCS
202
NBLO
203
NRBE
204
NWBE
205
CLK2
206
REF8M
207
CLK8
208
CLK16
209
NIORQ
210
VSS
211
NIOR
212
VSS_CORE
213
CPUCLK
214
VDD_CORE
215
NIOW
216
VDD
217
NCCS
218
NCDACK
219
IORNW
220
NPCCS2
221
NPCCS1
222
LNBW
223
LA0
224
LA1
225
LA2
226
VSS
227
LA3
228
LA4
229
LA5
230
LA6
231
LA7
232
LA8
233
VDD
234
LA9
235
LA10
236
LA11
237
LA12
238
VSS
239
LA13
240
LA14
39
OEDR1
38
NOEV
37
LNBW
36
CHPE
35
NROM
34
33
CLK16
32
CHPC
I3
31
30
29
Q1
2SC2712 GR
R1
47 k
1
2
R2
100 k
R71
15 k
R138
47 K
ADR0
ADR1
ADR2
ADR21
ADR22
ADR23
ADR24
ADR25
C1
1
NIOR
UARTG
UARTN
D1
1SS196
R3
470 k
DIRE1
NAVA0
OEDS
SABV
MPOE
MPWE
MAPCE
CABV
NIOW
NIOR
SRAMH
SRAML
CARD
OELAT
R4
220 k
L5V
R129 15 k
R112
15 K
6543214443424140
I/O4
I/O3
7
I/O5
8
I/O6
9
I/O7
10
I0
11
CLK0/I1
12
GND
13
CLK1/I2
14
I/O8
15
I/O9
16
I/O10
17
I/O11
I/O12
I/O13
1819202122232425262728
R102 15 k
R106 15 k
R107 15 k
R108 15 k
R109 15 k
R110 15 k
R111 15 k
R126 15 k
R127 15 k
R93
15 k
15 k
R97
R95
R94
15 k
15 k
15 k
174
173
172
171
170
169
VSS
IOP4
IOP5
IOP6
IOP7
NPOR
KBDATA
LA20
LA21
VDD
LA22
VSS
LA23
LA24
101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960
ADR21
ADR22
ADR23
ADR24
R143
33
0.1
R92
R91
15 k
15 k
CD0
CD1
CD2
CD3
CD4
168
167
166
165
164
163
162
161
160
159
BD0
BD1
BD2
BD3
BD4
VDD
KBCLK
MSCLK
MSDATA
LA25
LA26
LA27
LA28
D31
D30
D29
D28
VSS
ADR25
MDB31
MDB30
MDB29
MDB28
MDB27
MDB16
MDB17
MDB18
MDB19
MDB20
MDB21
MDB22
MDB23
NRAS1
RAD0
RAD1
RAD2
RAD3 RAD4
X1
DSO-49SJ
2
V1O
G
3
CD5
CD6
CD7
CD8
CD9
158
157
156
155
154
BD5
BD6
BD7
BD8
VSS
IC1
CL-PS7500FE
D27
D26
VDD
D25
D24
D23
MDB26
MDB25
MDB24
MDN23
1
VCC
2
DQ1
3
DQ2
4
DQ3
5
DQ4
6
VCC
7
DQ5
8
DQ6
9
DQ7
10
DQ8
11
NC
12
NC
13
W
14
RAS
15
NC
16
A0
17
A1
18
A2
19
A3
20
VCC
IC34
M5M44260CJ
32 MHz
153
152
BD9
VDD_CORE
D22
MDB22
MDB21
R83
15 k
R82
15 k
R90
15 k
CD10
CD11
CD12
CD13
CD14
CD15
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
142
141
VSS
MEMCLK
VSS_CORE
D21
VSS_CORE
VSS
DQ16
DQ15
DQ14
DQ13
VSS
DQ12
DQ11
DQ10
DQ9
NC
LCAS
UCAS
OE
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
VSS
BD10
D20
MDB20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
VDD
VDD_CORE
MDB19
BD14
BD11
BD12
BD13
I_OCLK
NEVENT2
D19
D18
VSS
D17
D16
D15
D14
MDB18
MDB17
MDB16
MDB15
MDB14
MDB13
MDB31
MDB30
MDB29
MDB28
MDB27
MDB26
MDB25
MDB24
NCAS2
NCAS3NWE NWE
RAMOE
RAD8RAD9
RAD7
RAD6
RAD5
NROM
140
BD15
D13
139
138
NRESET
NROMCS
VDD
D12
MDB12
MDB11
CPS
137
RESET
D11
MDB10
R81
15 k
136
SNA
OSCDELAY
D10D9D8
MDB9
R78
15 k
135
OSCPOWER
MDB8
RESET
134
NWE
VSSD7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
R49
15 k
R162
15 k
NWE NWE
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
VSS
VDD
NCAS0
NCAS1
NCAS2
NCAS3
VSS_ATOD
MDB7
MDB6
MDB5
MDB4
MDB3
MDB2
MDB1
1
2
MDB0
3
MDB1
4
MDB2
5
MDB3
6
7
MDB4
8
MDB5
9
MDB6
10
MDB7 MDB8
11
12
13
14
NRAS1
RAD9
15
16
RAD0
17
RAD1
18
RAD2
19
RAD3
20 21
R47
15 k
R156
100
R48
15 k
126
125
124
123
122
121
ATOD0
ATOD1
ATOD2
ATOD3
ATODREF
VDD_AATOD
VSS_ANALOG
VDD_ANALOG
VDD_CORE
VSS_CORE
VSS_CORE
VDD_CORE
VDD
PCMP
VSS
VCLK1
VCLK0
MDB0
VCC
VSS
DQ1
DQ16
DQ2
DQ15
DQ3
DQ14
DQ4
DQ13
VCC
VSS
DQ5
DQ12
DQ6
DQ11
DQ7
DQ10
DQ8
DQ9
NC
NC
LCAS
W
UCAS
RAS
NC
A0
A1
A2
A3
VCC
VSS
IC35
M5M44260CJ
NC
OE
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
R53 33
R51 33
NRAS0
NRAS1
NRAS2
NRAS3
RA10
RA11
NINT6
NINT3
NINT8
NTEST
GOUT
BOUT
ROUT
VIREF
HSYNC
VSYNC
HCLK
ECLK
SYNC
SDCLK
SCLK
R155
8.2 k
R131
10 k
C64
0.1
R77 33
R52 33
C6
0.1
R46
R45
33
120
119
118
117
VDD
116
115
VSS
114
RA0
113
RA1
112
RA2
111
RA3
110
RA4
109
RA5
108
RA6
107
RA7
106
VDD
105
RA8
104
VSS
103
RA9
102
101
100
INT7
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
VSS
84
ED0
83
ED1
82
ED2
81
ED3
80
ED4
79
VDD
78
ED5
77
ED6
76
ED7
75
74
VSS
73
72
71
WS
70
69
68
SDO
67
66
VSS
65
64
VSS
63
VSS
62
VDD
61
VDD
R68
1 M
40
39
MDB15
38
MDB14
37
MDB13
36
MDB12
35
34
MDB11
33
MDB10
32
MDB9
31
30
29
NCAS0
28
NCAS1
27
RAMOE
26
RAD8
25
RAD7
24
RAD6
23
RAD5
22
RAD4
33
R44 10 k
INT6
INT8
R55
4.7 k
C7
10
R32
10 k
R62
22 k
NCAS0
NCAS1
NCAS2
NCAS3
NRAS0
NRAS1
R167
DTCK
R168
10 k
R170
10 k
R172
10 k
R174
10 k
NIOR
CCS2
AS15
AS15S
10 k
R169
10 k
R171
10 k
R173
10 k
RAD0
RAD1
RAD2
RAD3
RAD4
RAD5
RAD6
RAD7
RAD8
INT6
INT8
GREEN
BLUE
RED
R36
10 k
CK16M
UARTN
UARTG
COMPLETE VIEW
Page 43

L5V
0
2
R155
8.2 k
R131
10 k
C64
0.1
R77 33
33
R52 33
33
R46
33
120
119
1
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
R44 10 k
101
100
INT6
99
98
INT8
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
R68
1 M
MDB15
MDB14
MDB13
MDB12
MDB11
MDB10
MDB9
MDB8
NCAS0
NCAS1
RAMOE
RAD8
RAD7
RAD6
RAD5
RAD4
R32
10 k
R62
22 k
NWE
NCAS0
NCAS1
NCAS2
NCAS3
C6
0.1
R45
33
NRAS0
NRAS1
R167
10 k
NIOR
CCS2
AS15
AS15S
R169
10 k
R171
10 k
R173
10 k
CD8
CD9
CD10
CD11
CD12
CD13
CD14
CD15
DB0
DB1
DB2
5
6
7
8
9
10
CD0
11
CD1
12
13
CD2
R147
1 K
CCS1
NIOW
READ
NIOR
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
ADR6
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
CD0
CD1
CD2
CD3
CD4
CD5
CD6
CD7
R43
R38
R133
15 k
15 k
15 k
IC19
TC7W32F
DB3
DB4
4321323130
W
D3
D8
D4
NC
VCC
D2
D1
D0
XI
FL/RT
FF
Q0
Q1
XO/HF
NC
Q2
Q3Q8VSSNCRQ4Q5
14151617181920
CD3
CD4
IC20
CY7C433-40JC
1
CSA
2
WEA
3
NRDYA
4
OEA
5
A0A
6
A1A
7
A2A
8
A3A
9
A4A
10
A5A
11
A6A
12
A7A
13
I/O0A
14
I/O1A
15
I/O2A
16
I/O3A
17
I/O4A
18
I/O5A
19
I/O6A
20
I/O7A
21
GND
IC21
M66220FP
1
2
3
45
DB5
D5
NC
RS
CD5
RAD0
RAD1
RAD2
RAD3
RAD4
RAD5
RAD6
RAD7
RAD8
R55
4.7 k
C7
10
R36
10 k
CK16M
GREEN
BLUE
RED
UARTN
INT6
INT8
UARTG
DTCK
R168
10 k
R170
10 k
R172
10 k
R174
10 k
R37
15 k
R150
15 K
29
D6
28
D7
27
26
25
24
EF
23
22
Q7
21
Q6
NRDYB
IC44
TC7SH04FU
8
7
6
R148
15 k
CD6
CD7
42
VCC
41
CSB
40
WEB
39
38
OEB
37
A0B
36
A1B
35
A2B
34
A3B
33
A4B
32
A5B
31
A6B
30
A7B
29
I/O7B
28
I/O6B
27
I/O5B
26
I/O4B
25
I/O3B
24
I/O2B
23
I/O1B
22
I/O0B
IC46
TC7SH04FU
1
2
354
1
2
354
W21
DB6
DB7
CSB
WEB
NRB
OEB
AS0
AS1
AS2
AS3
AS4
AS5
AS6
AS7
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
R105
47 k
IC45
TC74AC74F
1
1CLR
2
1D
3
1CK
4
1PR
5
1Q
6
1Q
7
GND
R130
15 k
14
VCC
13
2CLR
12
2D
11
2CK
10
2PR
9
2Q
8
2Q
6.4 MHz 5Vp-p
IC16
TC74HC139AF
9
10
11
12
AS13
13
14
AS14
15
A15S
16
UARTG
UARTN
CK16M
HSYNC
W22
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
12V
SPD
12V
VSYNC
BEEP
C55
C67
0.1
0.1
15.4 kHz 5Vp-p
R134
100 k
PNL
LOCONT
TXTRG
C58
C66
C61
0.1
0.1
0.1
59 Hz 5Vp-p
L5V
R104
47 k
61
P31(WR)
62
P32(PWM0)
63
P33(PWM1)
64
P40(TPG10)
65
P41(TPG11)
66
P42(TPG12)
67
P43(TPG13)
68
P44(CAP0:AP)
69
P45(CAP1:AF)
70
P46(CAP2:BP)
71
P47(CAP3:BF)
72
P50(EXIN)
73
P51(TO4)
74
P52(TO5)
75
VCC
76
P53(INT1/T14)
77
P54(INT2/T15)
78
VSS
79
P55(WAIT/TO1)
80
P56(INT3/T12)
BRIGHT MAX 4.6 V
MIN 2.4 V
CONT MAX 4.2 V
MIN 1.9 V
C14
C15
C16
C17
C18
C12
C13
0.1
0.1
0.1
R163
1 k
C68
22
IC18
TC74HC573AF
1
OE
DB0
2
D0
DB1
3
D1
DB2
4
D2
DB3
5
D3
DB4
6
D4
DB5
7
D5
DB6
8
D6
DB7
9
D7
GND10LE
P23 (TPG03)
P22 (TPG02)
P21 (TPG01)
P26 (TPG06/TPG15)
P25 (TPG05/TPG16)
P24 (TPG04/TPG17)
IC22
TMP90PM36F
DAOUT0
DAOUT1
AVCC
AVSS
P60 (AN0)
P61 (AN1)
INV
CONT
RSSI
0.1
P20 (TPG00)
RL0
0.1
60595857565554535251504948474645444342
P30 (RD)
P27 (TPG07/TPG14)
P57 (T03)
_NMI
123456789
TXSIG
C19
0.1
0.1
0.1
Q4
2SB1201 S
Q5
XP6501 AB
R164
C69
220
0.1
20
VCC
19
AS0
Q0
18
AS1
Q1
17
AS2
Q2
16
AS3
Q3
15
AS4
Q4
14
AS5
Q5
13
AS6
Q6
12
AS7
Q7
11
AS15
AS14
AS13
VSS
P62 (AN2)
P63 (AN3)
1011121314151617181920
RL1
P17 (A15)
P16 (A14)
P64 (AN4)
P65 (AN5)
RL2
RL3
P15 (A13)
P14 (A12)
P66 (AN6)
RL4
RL5
P13 (A11)
P67 (AN7)
VCC
P11 (A9)
P12 (A10)
P70 (RXD0)
P71 (TXD0)
C20
C21
0.1
0.1
R177
3.3 k
456
321
DB7
DB6
41
P10 (A8)
P07 (AD7)
P06 (AD6)
STBY (P82)
INT0 (P81)
WDTOUT (P80)
(TXD2) P77
(SCLK2) P76
(RXD2) P75
P72 (RXD1)
P73 (SCLK1/CTS1)
P74 (TXD1)
C22
0.1
R178
1.5 k
(AD5) P05
(AD4) P04
(AD3) P03
(AD2) P02
(AD1) P01
(AD0) P00
ALE (P83)
RESET
GPSS
NMO
RESET
NMEAI
GPSO
GPSI
CONT
C50
0.1
R144
100
SW2
SW1
12V
INV
BEEP
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
NMEAIN
DGPOUT
C65
C49
0.1
0.1
R145
100
C24
C25
C46
C45
C44
C43
C52
C23
0.1
0.1
0.1
R135
100 k
SL2
SL1
SL0
CK16M
0.1
L5V
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
R56
15 K
R136
15 k
L5V
0.1
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
VCC
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
EA
25
X2
24
X1
23
VSS
22
CLK
21
C51
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.1
HSYNC
VSYNC
DTCK
12V
RED
GREEN
BLUE
VBL
INV
SL2
SL1
SL0
R146
100
C42
0.1
R180
100 k
W23
L5V
R165
100
NTP
GND
GND
VSW
C70
0.22
SW2
SW1
12V
INV
BEEP
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
IC41
BU4053BCF
1
Y1
VDD
2
Y0
3
Z1
4
Z
5
Z0
6
INH
7
VEE
VSS8C
W24
DGPIIN
141312111098
1234567
IC23
TC74HC14AF
Y
X
X1
X0
A
B
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
C1022C11
J6 to LCD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
J3
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
NMEAIN
DGPIN
R60 15 k
0.1
HSYNC
VSYNC
DTCK
NTP
GND
GND
VSW
GND
NC
12V
NC
CONT
RED
GREEN
BRUE
GND
NC
NC
NC
GND
VBL
VBL
GND
GND
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
C26
C27
0.1
0.1
SW UNIT
S2
SKQDPB
D1
1SS355
S3
SKQDPB
D2
1SS355
S4
SKQDPB
D3
1SS355
S5
SKQDPB
D4
1SS355
S6
SKQDPB
D5
1SS355
S7
SKQDPB
D6
1SS355
C4
0.001
SW2
SW1
12V
INV
BEEP
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
L5V
D2
1SS184
S8
SKQDPB
S9
SKQDPB
S10
SKQDPB
S11
SKQDPB
S12
SKQDPB
S13
SKQDPB
C3
0.001
3.0 V
D7
1SS355
D8
1SS355
D9
1SS355
D10
1SS355
D11
1SS355
D12
1SS355
C14
0.001
BT1
CR3023-1TS
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
C5
0.001
C6
0.001
C7
0.001
C8
0.001
C9
0.001
C10
0.001
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
Q1
2SC2712 GRQ22SC2712 GR
R14
4.7 k
R7
1.5 k
C12
4.7
1.95 KHz 5Vp-p
3.9 KHz 5Vp-p
C11
0.001
R11
4.7 k
S14
SKQDPB
D13
1SS355
S15
SKQDPB
R1
47 k
D14
1SS355
S16
R2
SKQDPB
47 k
D15
1SS355
S17
SKQDPB
R3
47 k
D16
1SS355
S18
SKQDPB
R4
47 k
D17
1SS355
R5
47 k
R6
47 k
C2
0.001
J5
G5V
1
VANT
2
VBAK
3
GND
4
DGP
5
GPPOUT
6
GPIN
7
NC
8
DS1
SML-310MT
DS2
SML-310MT
DS3
SML-310MT
R15
8.2 k
R10
4.7 k
12 V
R12
4.7 k
R8
1.5 k
BRIGHT MAX 4.6 V
SP1
PS1740P02
Q4
2SC2712 GR
C1
0.001
DS4
SML-310MT
DS5
SML-310MT
DS6
SML-310MT
Q3
2SC2712 GR
R16
8.2 k
MIN 1.2 V
S1
MS-666K
DS7
SML-310MT
DS8
SML-310MT
DS9
SML-310MT
R13
4.7 k
R9
R17
1.5 k
8.2 k
10 - 3
COMPLETE VIEW
Page 44

12V
DEPCONT
CARD
DELAY
NIOW
MPOE
MDB3
35
DQ3
CD0B
CD1B
CD2B
CD3B
CD4B
CD5B
CD6B
CD7B
MPNE
WP
MAPCE
NAVA0
MDB10
34
DQ10
FLRY
CD0B
CD1B
CD2B
CD3B
CD4B
CD5B
CD6B
CD7B
CD8B
CD9B
CD10B
CD11B
CD12B
CD13B
CD14B
CD15B
A15S
AS15
CK16M
SRAML
NIOR
MDB2
33
ADR20
MDB9
ADR19
MDB1
ADR9
MDB8
ADR8
OEDS
CABV
SABV
NOEV
DIRE1
OEDR1
READ
NIOR
NIOW
INT5
CLK16
UARTG
UARTN
CCC2
CCS1
LNBW
NIOR
MDB0
NIOR
DQ029DQ830DQ131DQ932DQ2
ADR6
ADR7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13
IC7
TC74HCT646AP
1
DIR1
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8
A7
9
A8
10
GND
IC2
TC74HCT245AF
1
DIR1
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8
A7
9
A8
10
GND B8
IC3
TC74HCT245AF
FLRY
ADR2
ADR2
FLCE1
26
27OE28
25
A0
CE
VSS
24
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
24
23
22
21
20
MDB0
19
18
17
16
15
14
20
VCC
19
G
18
B1
17
B2
16
B3
15
B4
14
B5
13
B6
12
B7
11
B8
20
VCC
19
G
18
B1
17
B2
16
B3
15
B4
14
B5
13
B6
12
B7
11
ADR0
ADR1
NPOR
ADR18
BYTE
MDB7
MDB15
ADR18
44
45
46
47
48
A16
VSS
BYTE
DQ15/A-1
A151A142A133A124A115A106A97A88N.C.9N.C.10WE11RESET12N.C.13N.C.14RY/BY15A1816A1717A718A619A520A421A322A223A1
ADR13
ADR14
ADR15
ADR16
ADR17
MDB0
MDB1
MDB2
MDB1
MDB3
MDB2
MDB4
MDB5
MDB3
MDB6
MDB7
MDB4
MDB5
MDB6
MDB7
MDB8
MDB8
MDB9
MDB9
MDB10
MDB11
MDB10
MDB12
MDB13
MDB11
MDB14
MDB15
MDB12
MDB13
MDB14
C56
0.1
MDB15
MDB8
MDB9
MDB10
MDB11
MDB12
MDB13
MDB14
MDB15
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
MDB6
MDB13
MDB14
41
42
43
DQ6
DQ7
DQ13
DQ14
IC33
MBM29F800BA-90PFTN
ADR12
ADR11
ADR10
MDB5
40
DQ5
ADR5
MDB12
39
DQ12
MDB4
38
READ
ADR6
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
MDB2
MDB3
MDB10
MDB11
33
34
35
36
37
DQ3
DQ4
VCC
DQ10
DQ11
ADR20
NPOR
R21
47 k
R22
47 k
R23
47 k
R24
47 k
R25
47 k
R26
47 k
R27
47 k
R85
47 k
R86
47 k
R87
47 k
R88
47 k
R89
47 k
R28
47 k
R29
47 k
R30
47 k
R31
47 k
MDB9
ADR19
ADR10
MDB1
ADR9
ADR11
MDB8
ADR8
C54
0.1
5
4
IC13
S-80742SL-A6
ADR12
MDB0
DQ029DQ830DQ131DQ932DQ2
ADR6
ADR7
C5
4.7C40.1
J1
GND GND
R20
15 k
CD15B
R19
15 k
CD14B
R18
15 k
CD13B
R17
15 k
CD12B
R16
15 k
CD11B
R15
15 k
CD10B
R14
15 k
CD9B
R13
15 k
CD8B
R12
15 k
CD7B
R11
15 k
CD6B
R10
15 k
CD5B
R9
15 k
CD4B
R8
15 k
CD3B
R7
15 k
CD2B
R6
15 k
CD1B
R5
15 k
R132
33
C59
1
MDB4
ADR17
MDB3
25
CD0B
Q3
2SB1132 Q
R42
2.2 k
5.0 V
L5V
C47
47
INT5
L5V L5V
MDB0
MDB1
MDB2
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5ADR6
NIOR
ADR12
ADR7
A515A614A7
A4
16
32
31
OE
A10
A111A92A83A134WE5CS26A157VCC8NC9A1610A1411A12
ADR11
ADR13
24
VSS
ADR18
21A020A119A218A317
I/O223I/O122I/O0
12
ADR14
ADR16
13
ADR9
ADR8
J2
GND
30
GND
29
TXSIG
28
TXTRG
27
LOCONT
26
RSSI
25
SPD
24
TEMP
23
NMEAIN
22
NMEAOUT
21
DGPIN
20
DGPOUT
19
DEPCONT
18
L5V
17
L5V
16
L5V
15
G5V
14
G5V
13
12V
12
12V
11
12V
10
18V
9
N.C
8
SW1
7
SW2
6
GND
5
GND
4
GND
3
GND
2
GND
1
R151
15
12.0 V
C48
10
MDB5
MDB6
MDB7
NIOR
ADR12
SRAML
30
32
31
OE
A10
I/O729I/O628I/O527I/O426I/O3
CS1
IC30
M5M51008BVP-70LL
A111A92A83A134WE5CS26A157VCC8NC9A1610A1411A12
ADR10
ADR11
ADR13
ADR15
NPOR
NIOW
135
CD3B
236
CD4B
337
CD5B
438
CD6B
539
CD7B
640
/CE1
741
CA10
842
MPOE
943
CA11
10 44
CA9
11 45
CA8
12 46
CA13
13 47
CA14
14 48
MPWE
15 49
16 50
VccM
17 51
Vpp1
18 52
CA16
19 53
CA15
20 54
CA12
21 55
CA7
22 56
CA6
23 57
CA5
24 58
CA4
25 59
CA3
26 60
CA2
27 61
CA1
28 62
CA0
29 63
CD0B
30 64
CD1B
31
32
33
34 68
to Memory card
IC4
TC74HC245AF
1
DIR1
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8
A7
9
A8
GND10B8
IC5
TC74HC245AF
1
DIR1
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8
A7
9
A8
GND10B8
IC6
TC74HC245AF
1
DIR1
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8
A7
9
A8
GND10B8
MDB11
MDB12
MDB13
MDB9
MDB10
25
24
I/O223I/O122I/O0
VSS
ADR16
ADR17
ADR18
NPOR
65
66
67
MDB8
ADR2
21A020A119A218A317
13
12
ADR9
ADR14
CD2B
WP
GND GND
CA0
CA1
CA2
CA3
CA4
CA5
CA6
CA7
CA8
CA9
CA10
CA11
CA12
CA13
CA14
CA15
CA16
CA17
CA18
CA19
CA20
CA21
CA22
CA23
SRAMH
MDB14
MDB15
SRAMH
30
I/O729I/O628I/O527I/O426I/O3
CS1
IC31
M5M51008BVP-70LL
ADR10
ADR15
NIOW
VCC
VCC
VCC
ADR3
ADR8
/CD1
CD11B
CD12B
CD13B
CD14B
CD15B
CA1
CA16
CA17
CA18
CA19
CA20
CA21
VccM
Vpp2
CA22
CA23
CA24
CA25
CD8B
CD9B
CD10B
/CD2
G
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
G
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
G
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
ADR4
A515A614A7
ADR7
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
ADR5ADR6
16
CD11B
CD12B
CD13B
CD14B
CD15B
CA1
CA16
CA17
CA18
CA19
CA20
CA21
CA22
CA23
CD8B
CD9B
CD10B
L5V
R128
MAPCE
NAVA0
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
ADR6
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
ADR10
ADR11
ADR12
ADR13
ADR14
ADR15
ADR16
ADR17
ADR18
ADR19
ADR20
ADR21
ADR22
ADR23
ADR24
A4
15 k
IC42
TC74HC14AF
141312111098
1234567
16 MHz
R140
4.7 k
BYTE
MDB7
MDB14
MDB15
ADR18
45
46
47
48
A16
VSS
BYTE
A151A142A133A124A115A106A97A88N.C.9N.C.10WE11RESET12N.C.13N.C.14RY/BY15A1816A1717A718A619A520A421A322A223A1
ADR14
ADR15
ADR16
ADR17
MDB4
MDB5
MDB6
MDB11
MDB12
MDB13
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ15/A-1
ADR13
VCC
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
IC32
MBM29F800BA-90PFTN
ADR12
ADR11
ADR10
L5V L5V
R156
100
R48
15 k
126
125
124
123
122
121
ATOD0
ATOD1
ATOD2
ATOD3
ATODREF
VDD_AATOD
VSS_ANALOG
VDD_ANALOG
VDD_CORE
VSS_CORE
VSS_CORE
VDD_CORE
VDD
PCMP
VSS
VCLK1
VCLK0
MDB0
VCC
VSS
DQ1
DQ16
DQ2
DQ15
DQ3
DQ14
DQ4
DQ13
VCC
VSS
DQ5
DQ12
DQ6
DQ11
DQ7
DQ10
DQ8
DQ9
NC
NC
LCAS
W
UCAS
RAS
NC
A0
A1
A2
A3
VCC
VSS
IC35
M5M44260CJ
R47
15 k
R53 33
R51 33
NRAS0
NRAS1
NRAS2
VDD
NRAS3
VSS
RA0
RA1
RA2
RA3
RA4
RA5
RA6
RA7
VDD
RA8
VSS
RA9
RA10
RA11
INT7
NINT6
NINT3
NINT8
NTEST
GOUT
BOUT
ROUT
VIREF
HSYNC
VSYNC
VSS
ED0
ED1
ED2
ED3
ED4
VDD
ED5
ED6
ED7
HCLK
VSS
ECLK
SYNC
WS
SDCLK
SCLK
SDO
VSS
VSS
VSS
VDD
VDD
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
NC
29
28
27
OE
26
A8
25
A7
24
A6
23
A5
22
A4
27OE28
ADR5
NC
INT5
VSS
ADR13
FLCE2
26
ADR4
DEPCONT
C3
NPOR
R96
R99
15 k
R100
15 k
FLRY
R176
180
ID
LA15
123456789
ADR15
R179
15 k
R142
15 k
179
IOP0
LA16
ADR16
178
ADR17
IOP1
LA17
R98
15 k
177
IOP2
LA18
ADR18
176
IOP3
LA19
ADR19
175
ADR20
R39
15 k
TC
SIOCS2
OES1
CLK2
CLK16
NIOW
CCS2
CCS1
LNBW
ADR0
ADR1
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
ADR6
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
ADR10
ADR11
ADR12
ADR13
ADR14
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
GDN
IC28
SC-1372
I/O14
I/O15
VCC
GND
R101
15 k
VCC
I/O16
R40
15 k
I/O17
I/O31
I/O18
CPH
I/O30
C2
0.001
WP
I/O29
I/O19
R41
15 k
I/O28
I/O27
I/O26
I/O25
I/O24
CLK3/I5
CLK2/I4
I/O23
I/O22
I/O21
I/O20
181
OD1
182
OD0
183
SETCS
184
INT9
185
NINT4
186
INT5
187
READY
188
NIOGT
189
NBLI
190
NXIPMUX16
191
NINT1
192
INT2
193
VSS
194
NEVENT1
195
NXIPLATCH
196
TC
197
NSIOCS2
198
VDD
199
NSIOCS1
200
NEASCS
201
NMSCS
202
NBLO
203
NRBE
204
NWBE
205
CLK2
206
REF8M
207
CLK8
208
CLK16
209
NIORQ
210
VSS
211
NIOR
212
VSS_CORE
213
CPUCLK
214
VDD_CORE
215
NIOW
216
VDD
217
NCCS
218
NCDACK
219
IORNW
220
NPCCS2
221
NPCCS1
222
LNBW
223
LA0
224
LA1
225
LA2
226
VSS
227
LA3
228
LA4
229
LA5
230
LA6
231
LA7
232
LA8
233
VDD
234
LA9
235
LA10
236
LA11
237
LA12
238
VSS
239
LA13
240
LA14
39
OEDR1
38
NOEV
37
LNBW
36
CHPE
35
NROM
34
GND
33
CLK16
32
CHPC
I3
31
30
29
Q1
2SC2712 GR
R1
C53
47 k
0.1
1
OUT
2
VDD
VSS3NC
R2
100 k
R71
15 k
R138
47 K
ADR14
ADR0
ADR1
ADR2 ADR2
ADR2
25
ADR21
ADR22
A0
CE
ADR23
ADR24
ADR25
24
ADR3
C1
1
NIOR
UARTG
UARTN
D1
1SS196
R3
470 k
DIRE1
NAVA0
OEDS
SABV
MPOE
MPWE
MAPCE
CABV
NIOW
NIOR
SRAMH
SRAML
CARD
OELAT
R4
220 k
L5V
R102 15 k
R106 15 k
R107 15 k
R108 15 k
R109 15 k
R110 15 k
R111 15 k
R126 15 k
R127 15 k
R129 15 k
R112
15 K
6543214443424140
I/O4
I/O3
7
I/O5
8
I/O6
9
I/O7
10
I0
11
CLK0/I1
12
GND
13
CLK1/I2
14
I/O8
15
I/O9
16
I/O10
17
I/O11
I/O12
I/O13
1819202122232425262728
R93
15 k
15 k
R95
R94
R97
15 k
15 k
15 k
174
173
172
171
170
169
VSS
IOP4
IOP5
IOP6
IOP7
NPOR
KBDATA
LA20
LA21
VDD
LA22
VSS
LA23
LA24
101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960
ADR21
ADR22
ADR23
ADR24
R143
33
0.1
R92
R91
15 k
15 k
CD0
CD1
CD2
CD3
CD4
168
167
166
165
164
163
162
161
160
159
BD0
BD1
BD2
BD3
BD4
VDD
KBCLK
MSCLK
MSDATA
LA25
LA26
LA27
LA28
D31
D30
D29
D28
VSS
ADR25
MDB31
MDB30
MDB29
MDB28
MDB27
MDB16
MDB17
MDB18
MDB19
MDB20
MDB21
MDB22
MDB23
NRAS1
RAD0
RAD1
RAD2
RAD3 RAD4
X1
DSO-49SJ
V1O
G
3
CD5
CD6
CD7
CD8
CD9
158
157
156
155
154
BD5
BD6
BD7
BD8
VSS
IC1
CL-PS7500FE
D27
D26
VDD
D25
D24
MDB26
MDB25
MDB24
MDN23
1
VCC
2
DQ1
3
DQ2
4
DQ3
5
DQ4
6
VCC
7
DQ5
8
DQ6
9
DQ7
10
DQ8
11
NC
12
NC
13
W
14
RAS
15
NC
16
A0
17
A1
18
A2
19
A3
20
VCC
IC34
M5M44260CJ
2
BD9
D23
153
D22
MDB22
32 MHz
R90
15 k
CD10
CD11
CD12
CD13
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
VSS
VDD
BD10
BD11
BD12
BD13
MEMCLK
VSS_CORE
VDD_CORE
D21
VSS_CORE
MDB21
MDB20
VSS
DQ16
DQ15
DQ14
DQ13
VSS
DQ12
DQ11
DQ10
DQ9
NC
LCAS
UCAS
OE
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
VSS
D20
I_OCLK
NEVENT2
VDD_CORE
D19
D18
VSS
D17
D16
D15
MDB19
MDB18
MDB17
MDB16
MDB15
40
39
MDB31
38
MDB30
37
MDB29
36
MDB28
35
34
MDB27
33
MDB26
32
MDB25
31
MDB24
30
29
NCAS2
28
NCAS3NWE NWE
RAMOE
27
26
RAD8RAD9
25
RAD7
24
RAD6
23
RAD5
22
21
CD14
142
BD14
D14
MDB14
R83
15 k
R82
15 k
CD15
141
BD15
D13
MDB13
NROM
140
139
NROMCS
VDD
MDB12
CPS
138
RESET
NRESET
D12
D11
MDB11
137
SNA
D10D9D8
MDB9
MDB10
R78
15 k
R81
15 k
RESET
136
135
134
NWE
OSCDELAY
OSCPOWER
VSSD7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
MDB8
R49
15 k
R162
15 k
NWE NWE
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
VSS
VDD
NCAS0
NCAS1
NCAS2
NCAS3
VSS_ATOD
MDB7
MDB6
MDB5
MDB4
MDB3
MDB2
MDB1
1
2
MDB0
3
MDB1
4
MDB2
5
MDB3
6
7
MDB4
8
MDB5
9
MDB6
10
MDB7
11
12
13
14
NRAS1
RAD9
15
16
RAD0
17
RAD1
18
RAD2
19
RAD3
20 21
C64
0.1
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
R68
1 M
MDB15
MDB14
MDB13
MDB12
MDB11
MDB10
MDB9
MDB8
NCAS0
NCAS1
RAMOE
RAD8
RAD7
RAD6
RAD5
RAD4
R155
8.2 k
R131
10 k
12V
CONT
C50
0.1
R144
100
SW2
SW1
12V
INV
BEEP
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
NMEAIN
DGPOUT
C65
C49
0.1
0.1
R145
100
C14
C15
C16
C17
C18
C19
C20
C21
C22
C24
C25
C46
C45
C44
C43
C52
C55
C67
0.1
0.1
HSYNC
R77 33
R52 33
R46
33
R44 10 k
INT6
INT8
R32
10 k
R62
22 k
NCAS0
NCAS1
NCAS2
NCAS3
C6
0.1
R45
33
NRAS0
NRAS1
R167
10 k
NIOR
CCS2
AS15
AS15S
R169
10 k
R171
10 k
R173
10 k
CD8
CD9
CD10
CD11
CD12
CD13
CD14
CD15
DB0
DB1
DB2
5
6
7
8
9
10
CD0
11
CD1
12
13
CD2
R147
1 K
CCS1
NIOW
READ
NIOR
ADR2
ADR3
ADR4
ADR5
ADR6
ADR7
ADR8
ADR9
CD0
CD1
CD2
CD3
CD4
CD5
CD6
CD7
R43
R38
R133
15 k
15 k
15 k
IC19
TC7W32F
DB3
DB4
4321323130
W
D3
D8
NC
VCC
D2
D1
D0
XI
FF
Q0
Q1
XO/HF
NC
Q2
Q3Q8VSSNCRQ4Q5
14151617181920
CD3
CD4
IC20
CY7C433-40JC
1
CSA
2
WEA
3
NRDYA
4
OEA
5
A0A
6
A1A
7
A2A
8
A3A
9
A4A
10
A5A
11
A6A
12
A7A
13
I/O0A
14
I/O1A
15
I/O2A
16
I/O3A
17
I/O4A
18
I/O5A
19
I/O6A
20
I/O7A
21
GND
IC21
M66220FP
1
2
3
45
DB5
D4
FL/RT
CD5
RAD0
RAD1
RAD2
RAD3
RAD4
RAD5
RAD6
RAD7
RAD8
R55
4.7 k
C7
10
R36
10 k
CK16M
GREEN
BLUE
RED
UARTN
INT6
INT8
UARTG
DTCK
R168
10 k
R170
10 k
R172
10 k
R174
10 k
R37
15 k
R150
15 K
D5
29
D6
28
D7
27
NC
26
25
RS
24
EF
23
22
Q7
21
Q6
NRDYB
IC44
TC7SH04FU
8
7
6
R148
15 k
CD6
CD7
42
VCC
41
CSB
40
WEB
39
38
OEB
37
A0B
36
A1B
35
A2B
34
A3B
33
A4B
32
A5B
31
A6B
30
A7B
29
I/O7B
28
I/O6B
27
I/O5B
26
I/O4B
25
I/O3B
24
I/O2B
23
I/O1B
22
I/O0B
IC46
TC7SH04FU
1
2
354
1
2
354
W21
DB6
DB7
CSB
WEB
NRB
OEB
AS0
AS1
AS2
AS3
AS4
AS5
AS6
AS7
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
R105
47 k
IC45
TC74AC74F
1
1CLR
2
1D
3
1CK
4
1PR
5
1Q
6
1Q
7
GND
R130
15 k
14
VCC
13
2CLR
12
2D
11
2CK
10
2PR
9
2Q
8
2Q
6.4 MHz 5Vp-p
IC16
TC74HC139AF
9
10
11
12
AS13
13
14
AS14
15
A15S
16
UARTG
UARTN
CK16M
12V
15.4 kHz 5Vp-p
W22
VSYNC
R134
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
100 k
L5V
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
BRIGHT MAX 4.6 V
PNL
LOCONT
TXTRG
CONT MAX 4.2 V
SPD
BEEP
C66
C61
0.1
0.1
59 Hz 5Vp-p
R104
47 k
P31(WR)
P32(PWM0)
P33(PWM1)
P40(TPG10)
P41(TPG11)
P42(TPG12)
P43(TPG13)
P44(CAP0:AP)
P45(CAP1:AF)
P46(CAP2:BP)
P47(CAP3:BF)
P50(EXIN)
P51(TO4)
P52(TO5)
VCC
P53(INT1/T14)
P54(INT2/T15)
VSS
P55(WAIT/TO1)
P56(INT3/T12)
MIN 1.9 V
C12
C13
C58
0.1
0.1
0.1
R163
1 k
C68
22
IC18
TC74HC573AF
1
OE
DB0
2
D0
DB1
3
D1
DB2
4
D2
DB3
5
D3
DB4
6
D4
DB5
7
D5
DB6
8
D6
DB7
9
D7
GND10LE
P23 (TPG03)
P22 (TPG02)
P21 (TPG01)
P26 (TPG06/TPG15)
P25 (TPG05/TPG16)
P24 (TPG04/TPG17)
IC22
TMP90PM36F
DAOUT0
DAOUT1
AVCC
AVSS
P60 (AN0)
P61 (AN1)
INV
CONT
RSSI
0.1
VCC
VSS
P20 (TPG00)
P62 (AN2)
P63 (AN3)
1011121314151617181920
RL0
RL1
0.1
0.1
60595857565554535251504948474645444342
P30 (RD)
P27 (TPG07/TPG14)
P57 (T03)
_NMI
123456789
TXSIG
MIN 2.4 V
0.1
0.1
Q4
2SB1201 S
Q5
XP6501 AB
R164
220
20
19
AS0
Q0
18
AS1
Q1
17
AS2
Q2
16
AS3
Q3
15
AS4
Q4
14
AS5
Q5
13
AS6
Q6
12
AS7
Q7
11
AS15
AS14
AS13
P17 (A15)
P16 (A14)
P15 (A13)
P14 (A12)
P64 (AN4)
P65 (AN5)
P66 (AN6)
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
0.1
C69
0.1
P13 (A11)
P67 (AN7)
VCC
P11 (A9)
P12 (A10)
P70 (RXD0)
P71 (TXD0)
0.1
0.1
R177
3.3 k
456
321
DB7
DB6
41
P10 (A8)
P07 (AD7)
P06 (AD6)
(AD5) P05
(AD4) P04
(AD3) P03
(AD2) P02
(AD1) P01
(AD0) P00
ALE (P83)
STBY (P82)
INT0 (P81)
WDTOUT (P80)
(TXD2) P77
(SCLK2) P76
(RXD2) P75
P72 (RXD1)
P73 (SCLK1/CTS1)
P74 (TXD1)
0.1
R178
1.5 k
RESET
GPSS
NMO
RESET
NMEAI
GPSO
GPSI
C23
0.1
0.1
0.1
R135
100 k
SL2
SL1
SL0
CK16M
0.1
L5V
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
R56
15 K
R136
15 k
L5V
0.1
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
VCC
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
EA
25
X2
24
X1
23
VSS
22
CLK
21
C51
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.1
HSYNC
VSYNC
DTCK
12V
RED
GREEN
BLUE
VBL
INV
SL2
SL1
SL0
R146
100
C42
0.1
R180
100 k
W23
L5V
R165
100
NTP
GND
GND
VSW
C70
0.22
SW2
SW1
12V
INV
BEEP
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
IC41
BU4053BCF
1
Y1
VDD
2
Y0
3
Z1
4
Z
5
Z0
6
INH
7
VEE
VSS8C
W24
DGPIIN
141312111098
1234567
IC23
TC74HC14AF
Y
X
X1
X0
A
B
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
C1022C11
J6 to LCD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
J3
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
NMEAIN
DGPIN
R60 15 k
0.1
HSYNC
VSYNC
DTCK
NTP
GND
GND
VSW
GND
NC
12V
NC
CONT
RED
GREEN
BRUE
GND
NC
NC
NC
GND
VBL
VBL
GND
GND
SW UNITLOGIC UNIT
SL0
SL1
SL2
RL0
C5
0.001
C6
0.001
C7
0.001
C8
0.001
C9
0.001
C10
0.001
RL1
RL2
RL3
RL4
RL5
Q1
2SC2712 GRQ22SC2712 GR
R14
4.7 k
C12
4.7
1.95 KHz 5Vp-p
3.9 KHz 5Vp-p
R7
1.5 k
C11
0.001
R11
4.7 k
S2
SKQDPB
S3
SKQDPB
S4
SKQDPB
S5
SKQDPB
S6
SKQDPB
S7
SKQDPB
C4
0.001
J1
1
2
SW2
3
SW1
4
12V
5
INV
6
BEEP
7
SL0
8
SL1
9
SL2
10
RL0
11
RL1
12
RL2
13
RL3
14
RL4
15
RL5
16
17
18
C26
C27
0.1
0.1
D2
1SS184
D1
1SS355
D2
1SS355
D3
1SS355
D4
1SS355
D5
1SS355
D6
1SS355
S8
SKQDPB
D7
1SS355
S9
SKQDPB
D8
1SS355
S10
SKQDPB
D9
1SS355
S11
SKQDPB
D10
1SS355
S12
SKQDPB
D11
1SS355
S13
SKQDPB
D12
1SS355
C3
0.001
L5V
3.0 V
C14
0.001
BT1
CR3023-1TS
S14
SKQDPB
D13
1SS355
S15
SKQDPB
R1
47 k
D14
1SS355
S16
R2
SKQDPB
47 k
D15
1SS355
S17
SKQDPB
R3
47 k
D16
1SS355
S18
SKQDPB
R4
47 k
D17
1SS355
R5
47 k
R6
47 k
C2
0.001
J5
G5V
1
VANT
2
VBAK
3
GND
4
DGP
5
GPPOUT
6
GPIN
7
NC
8
DS1
SML-310MT
DS2
SML-310MT
DS3
SML-310MT
R15
8.2 k
R10
4.7 k
12 V
R12
4.7 k
R8
1.5 k
BRIGHT MAX 4.6 V
SP1
PS1740P02
Q4
2SC2712 GR
C1
0.001
DS4
SML-310MT
DS5
SML-310MT
DS6
SML-310MT
Q3
2SC2712 GR
R16
8.2 k
MIN 1.2 V
S1
MS-666K
DS7
SML-310MT
DS8
SML-310MT
DS9
SML-310MT
R13
4.7 k
R9
R17
1.5 k
8.2 k
LEFT SIDE RIGHT SIDE
10 - 3
Page 45

10 - 3
GND
EP3-2
Q1
2SK209 GR
Q5
2SK209 GR
R3
3.3 k
C5
0.1
C7
0.001
R15
10 k
R28
10 k
to MAIN
unit J2
to MAIN
unit J1
C20
1
C21
0.1
C22
0.1
C23
1
L1
LS-529
C19
0.1
R27
1.2 k
1
2
3
J1
1
2
3
4
5
J2
1
2
J3
CP1
C17
47
C13
0.1
C14
47 P
C16
47 P
C18
220 P
R25
3.3 k
R26
3.3 k
C15
47 P
Q6
2SK209 GR
Q7
2SK209 GR
D2
MA2SV05
D4
MA2SV05
R1
680 k
R4
680 k
R5
1 k
R6
3.3 k
R7
680 k
R8
1 k
R9
3.3 k
C6
0.1
C8
0.001
C9
47 P
C11
47 P
C12
47 P
Q2
2SK209 GR
R16
100 k
R17
1 k
R18
10 k
R19
100 k
R20
1 k
C24
0.1
C25
0.1
GND
EP3
EP3-3
GND
C3
10 P
C1
1 P
D9
MA2SV05
D1
MA2SV05
D3
MA2SV05
D10
MA2SV05
EP4
EP4-3
EP4-2
GND
C4
10 P
C2
3 P
D5
MA2SV05
D7
MA2SV05
D11
MA2SV05
D12
MA2SV05
R23
10 k
R24
1 k
Q8
2SK209 GR
D8
MA2SV05
R2
680 k
R10
680 k
R11
1 k
R12
3.3 k
R13
680 k
R14
1 k
C10
47 P
Q3
2SK209 GR
Q4
2SK209 GR
R21
10 k
R22
1 k
C26
0.1
C27
0.1
D6
MA2SV05
1
2
J4
1
2
J5
AF
AFGND
ANTV
TUNE
GND
GND
RF
GND
RF
GND
RF
GND
7.9 V
1.65 V
300 kHz
0.3 V
0.3 V
0.3 V
0.3 V
0.3 V
0.3 V
0.3 V
0.3 V
ANT UNIT
10-2 RD-200
• ANT UNIT
Page 46

4.8 V
5.0 V
8.0 V
5.0 V
1.66 V
300 kHz
4.6 V
6.5 V
7.299200 MHz
5.0 V
0 V
MAIN UNIT
1
2
3
GND
RF
GND
1
2
3
4
5
AF
AFGND
ANTV
TUNE
GND
C41
0.0039
5
6
7
IC4B
NJM2904M
R17
47 k
R19
6.8 k
R21
6.8 k
R23
6.8 k
R24
6.8 k
C36
10
C37
10
R22
47
R16
330
3
2
1
4
8
IC4A
NJM2904M
C35
0.015
C32
0.1
R18
47 k
C38
0.015
C39
0.0047
R20
6.8 k
OSCIN
1
OSCOUT
2
MIXOUT
3
VCC
4
IFIN
5
DEC
6
FILOUT
7
FILIN
8
AFOUT
9
QUAD
10
IFOUT
11
RSSI
12
N-DET
13
N-REC
14
GND
15
MIXIN
16
IC3
TA31136FN
C28
0.1
C31
0.1
C29
0.1
C30
10
C34
0.01
R4
100
R5
56 k
R6
5.6 k
R7
2.2 k
R15
10 k
R14
2.2 k
R13
47
1 2
345
FI1
CFJ455K8
C24
0.01
C33
0.001
Q1
3SK131K
R8
10 k
C20
0.001
L8
LR-171
C22
0.1
C19
0.015
L10
56 µH
C21
0.0012
R9
33 k
C27
0.1
C26
0.1
R12
220
R10
100
C23
0.1
C25
180 P
L11
680 µH
R11
10 k
+5
C111
0.012
L24
10 µH
L6
15 µH
C9
0.056
L7
18 µH
L3
15 µH
C6
0.0039
C7
0.012
C10
0.018
C8
0.018
L4
39 µH
C5
0.015
4
1
2
3
IC1
µPC1676G
C13
10
C15
0.012
C16
0.0018
C17
0.022
C18
680 P
L5
100 µH
C11
0.1
C12
0.1
C14
0.1
C3
0.01
L2
8.2 µH
C4
0.015
J1
to ANT
unit J1
CE
1
XT
2
XT
3
GND
4
Q
5
A
6
B
7
VCC
8
IC7
TC3W03FU
C71
10 P
C72
10 P
R52
1 M
X1
DSX751S
C51
0.0047
C70
18 P
1
2
354
IC5
TC7S04F
VSS
1
FSK1
2
FSK0
3
ETC0
4
ETC1
5
VDD
6
SYS_CLK
7
NUM0
8
NUM1
9
NUM2
10
VDD
11
DA9
23
VDD
24
ROMCE
25
RESET
26
VSS
27
VDD
28
PDM0
29
PDM1
30
PDM2
31
Q
32
I
33
IC6
SC-1287
C48
0.1
C49
0.1
C73
0.1
R53
47 k
C4610C45
0.001
L14
10 µH
C47
0.1
L13
10 µH
L12
10 µH
L9
LR-171
32
41
IC2
ND487C1 3R
DRES
CLK
DATA
STRB
C53
0.1
R2
18
L19
10 µH
L18
6.8 µH
R3
270R1270
C69
0.0039
C68
0.0012
C67
0.0056
C66
0.0033
C65
0.0022
C52
0.001
R54
22
R55
22
C74
470
C40
0.022
C42
0.039
C77
0.01
C78
47
D1
1SR154-400
R56
22
C80
0.1
IC9
TA7805F
IC8
TA7808F
C81
47
C82
0.1
C75
47
C76
0.01
L20
HF50ACC322513-B
C79
100
L1
HF50ACC322513-B
+8
+8
C44
1
C110
100
NMEA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
J4
+12
GND
MNIMNI+
MNO+
MNO-
1
2
3
4
5
6
J3
D4
1SS355
C95
0.0047
IC18
TLP121 GB
R83
6.8 k
C84
0.1
C85
47
R84
100
R78
1.2 k
Q9
2SC4081 R
C108
0.1
R107
47
R113
680
R85
680
L+5
C104
0.1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
IC15
TC4093BF
C93
0.1
C83
0.1
R57
4.7 k
1
2
354
IC14
TC7S04F
Q3
2SD1664 Q
D2
MA8075 L
C54
0.1
L15
120 µH
L16
220 µH
C60
390 P
C59
180 P
C57
270 P
C61
390 P
L17
390 µH
C64
0.1
Q2
2SC4081 R
R50
100
R49
2.7
C62
390 P
R48
1.8 k
R51
47
C63
0.1
C56
180 P
C58
47 P
R47
47
C50
0.1
R46
100 k
R31
2 k
R32
1 k
R33
2 k
R34
1 k
R35
2 k
R36
1 k
R37
2 k
R38
1 k
R39
2 k
R40
1 k
R41
2 k
R42
1 k
R43
2 k
R44
1 k
CHECK
TXD0
R45
2 k
C55
100 P
R26
2 k
R27
2 k
R28
1 k
R29
2 k
R30
1 k
R63
100 k
R59
27 k
Q4
2SC4081 R
R60
15 k
R62
1.2 k
R61
1.8 k
R58
100
C86
10
C87
0.0047
MSKI
L+5
L+5
L+5
L+5
L+5
TUNE
C90
0.1
C91
0.1
L+5
PB1/AN1
1
IRQ0
16
VCC
33
P21/RXD
48
PB0/AN0
2
AVSS
3
TEST
4
X2
5
X1
6
VSS
7
OSC1
8
OSC2
9
RES
10
P90/FVPP
11
P91
12
P92
13
P93
14
P94
15
P73
34
P74/TMRIV
35
P75/TMCIV
36
P76/TMOV
37
P77
38
P80/FTCI
39
P81/FTOA
40
P82/FTOB
41
P83/FTIA
42
P84/FTIB
43
P85/FTIC
44
P86/FTID
45
P87
46
P20/SCK3
47
IC12
HD64F3644H
R86
100 k
R71
100 k
R110
47 k
R109
473KTC
CLON
TXD0
RXD0
R87
100 k
RXD0
RXD0
C105
0.1
R79
6.8 k
R80
33 k
Q7
2SA1162 GR
D6
1SS355
R77
47 k
C94
0.1
C107
0.1
R81
47 k
R112
4.7 k
Q10
2SA1576 R
Q11
2SC4081 R
Q12
2SA1576 R
R108
47
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
IC17
TC4049BF
R111
4.7 k
C109
0.1
FLASH
C103
0.1
C102
10
D5
RD12M B2
F+12
REST
FCLN
CHECK
CHECK
TXD0
F+12
REST
FCLN
TXD0
R98
1 k
R99
2 k
R100
1 k
R101
2 k
R102
1 k
R103
2 k
R106
1
R104
10 k
1
3
4
5
2
IC19
TA75S01F
1
2
354
IC16
TC7S02F
R82
15
Q8
2SC2712 GR
R88
2 k
R89
2 k
R90
1 k
R91
2 k
TV0
TV1
TV2
TV3
TV4
TV5
TV6
TV7
R92
1 k
R93
2 k
R94
1 k
R95
2 k
R96
1 k
R97
2 k
C97
0.1
C98
0.01
L22
56 µH
C99
0.0033
CS
1
SO
2
WP
3
VSS4SI
5
SCK
6
HOLD
7
VCC
8
IC13
X25320SI-2.7
R72
100
R73
1
R75
220
R76
1
L23
56 µH
C96
0.1
C100
0.0056
C106
0.0033
C92
0.1
Q6
2SC4081 R
R74
470
ECS
ESIO
ESCK
DATA
CLK
DRES
STRB
L+5
L+5
L+5
R69
220 k
CP2
R70
100 k
Q5
2SC4081 R
R64
100 k
R66
11 k
R67
470 k
R68
220 k
D3
1SS355
1
2
354
IC10
TC7S04F
IC11
S-80842ALUP-EA6
C88
0.1
C89
0.22
L21
10 µH
CP1
R65
100 k
F+12
REST
CLON
4443424140393837363534
1213141516171819202122
VSS
DA0
DA1
DA2
DA3
DA4
VSS
DA5
DA6
DA7
DA8
VDD
CON_CLK
DATA
STRB
VSS
VDD
P2
TREE
P1
UL
VSS
9
TXD0
646362616059585756555453525150
49
171819202122232425TV0
TV1
TV2
TV3
TV4
TV5
TV6
TV7
26272829303132
P60
P61
P62
P63
P65
P66
P67
P50/INT0
P51/INT1
P52/INT2
P53/INT3
P54/INT4
P55/INT5/ADTRG
P56/INT6/TMI8
PP57/INT7
P64
P82/AN2
P83/AN3
P84/AN4
P85/AN5
P86/AN6
P87/AN7
AVCC
P17/IRQ3/TRGV
P16/IRQ2
P15/IRQ1
P14/PWM
P10/TMOW
P30/SCK1
P31/SI1
P32/SO1
P22/TXD
C2
0.1
47 k
J2
to ANT
unit J2
C43
1
C112
+70
L25
56 µH
+5
+5
IO
G
IO
G
IO
G
R25
10 - 4
• MAIN UNIT
Page 47

6-9-16, Kamihigashi, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0002, Japan
Phone : 06 6793 5302
Fax : 06 6793 0013
Communication Equipment
Himmelgeister Str. 100, D-40225 Düsseldorf, Germany
Phone: 0211 346047 Fax : 0211 333639
URL : http://www.icomeurope.com
Unit 9, Sea St., Herne Bay, Kent, CT6 8LD, U.K.
Phone: 01227 741741 Fax : 01227 741742
URL : http://www.icomuk.co.uk
Zac de la Plaine, Rue Brindejonc des Moulinais
BP 5804, 31505 Toulouse Cedex, France
Phone: 561 36 03 03 Fax : 561 36 03 00
URL : http://www.icom-france.com
Crta. de Gracia a Manresa Km. 14,750
08190 Sant Cugat del Valles Barcelona, SPAIN
Phone: (93) 590 26 70 Fax : (93) 589 04 46
URL : http://www.icomspain.com
<
Corporate Headquarters
>
2380 116th Avenue N.E., Bellevue, WA 98004, U.S.A.
Phone: (425) 454-8155 Fax : (425) 454-1509
URL : http://www.icomamerica.com
<
Customer Service
>
Phone: (425) 454-7619
A.C.N. 006 092 575
290-294 Albert Street, Brunswick, Victoria, 3056, Australia
Phone: 03 9387 0666 Fax : 03 9387 0022
URL : http://www.icom.net.au
6F No. 68, Sec. 1 Cheng-Teh Road, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Phone: (02) 2559 1899 Fax : (02) 2559 1874
3071 #5 Road, Unit 9, Richmond, B.C., V6X 2T4, Canada
Phone: (604) 273-7400 Fax : (604) 273-1900
URL : http://www.icomcanada.com
Page 48

SERVICE
MANUAL
6-9-16, Kamihigashi, Hirano-ku, Osaka, 547-0002, Japan
S-13602II-CD
© 1999 Icom Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...