Page 1

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil)
Issue 16
Date 2021-03-22
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2021. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specied in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every eort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
Page 3

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) Contents
Contents
1 Introduction to obsutil........................................................................................................... 1
2 Download and Installation....................................................................................................4
3 Getting Started........................................................................................................................ 6
3.1 Preparing the Environment..................................................................................................................................................6
3.2 Performing Initial
3.3 Quick Start.................................................................................................................................................................................9
Conguration........................................................................................................................................ 8
4 Bucket Commands................................................................................................................ 12
4.1 Creating a Bucket..................................................................................................................................................................12
4.2 Listing Buckets....................................................................................................................................................................... 14
4.3 Querying Bucket Properties...............................................................................................................................................16
4.4 Setting Bucket Properties...................................................................................................................................................18
4.5 Deleting a Bucket..................................................................................................................................................................21
4.6 Conguring a Bucket Policy.............................................................................................................................................. 22
4.7 Obtaining a Bucket Policy..................................................................................................................................................23
4.8 Deleting a Bucket Policy.....................................................................................................................................................24
5 Object Commands................................................................................................................. 26
5.1 Creating a Folder...................................................................................................................................................................26
5.2 Uploading an Object............................................................................................................................................................28
5.3 Querying Object Properties............................................................................................................................................... 40
5.4 Setting Object Properties................................................................................................................................................... 42
5.5 Listing Objects........................................................................................................................................................................46
5.6 Copying an Object................................................................................................................................................................ 49
5.7 Moving an Object................................................................................................................................................................. 59
5.8 Downloading an Object......................................................................................................................................................68
5.9 Generating the Download Link of an Object..............................................................................................................79
5.10 Deleting an Object............................................................................................................................................................. 83
5.11 Synchronously Uploading Incremental Objects....................................................................................................... 86
5.12 Synchronously Copying Incremental Objects............................................................................................................94
5.13 Synchronously Downloading Incremental Objects...............................................................................................104
5.14 Restoring Objects from OBS Archive.........................................................................................................................112
5.15 Resuming a Failed Upload Task.................................................................................................................................. 115
5.16 Resuming a Failed Copy Task...................................................................................................................................... 123
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
Page 4

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) Contents
5.17 Resuming a Failed Download Task............................................................................................................................ 132
5.18 Listing Multipart Upload Tasks................................................................................................................................... 139
5.19 Deleting a Multipart Upload Task..............................................................................................................................141
5.20 Creating an Authorization Code for Directory Sharing.......................................................................................144
5.21 Listing Objects by Using an Authorization Code.................................................................................................. 146
5.22 Downloading Objects by Using an Authorization Code..................................................................................... 149
6 Auxiliary Commands.......................................................................................................... 159
6.1 Updating a
6.2 Deleting Part Records....................................................................................................................................................... 160
6.3 Viewing Command Help Information......................................................................................................................... 162
6.4 Querying the Version Number.......................................................................................................................................164
6.5 Archiving Log Files............................................................................................................................................................. 164
6.6 Checking and Updating the Version............................................................................................................................ 166
6.7 Listing Failure Result Files............................................................................................................................................... 167
Conguration File....................................................................................................................................... 159
7 Common Examples............................................................................................................. 169
7.1 Upload.................................................................................................................................................................................... 169
7.2 Synchronous Upload..........................................................................................................................................................171
7.3 Download.............................................................................................................................................................................. 172
7.4 Synchronous Download....................................................................................................................................................174
7.5 Copy........................................................................................................................................................................................ 174
7.6 Synchronous Copy.............................................................................................................................................................. 175
7.7 Listing..................................................................................................................................................................................... 176
7.8 Listing Multipart Upload Tasks......................................................................................................................................177
7.9 Deleting All Multipart Upload Tasks in a Bucket.................................................................................................... 177
8 Fault Locating...................................................................................................................... 178
8.1 Overview................................................................................................................................................................................178
8.2 Log Files.................................................................................................................................................................................178
8.3 Result Lists............................................................................................................................................................................ 179
8.4 Return Codes........................................................................................................................................................................180
9 Best Practices....................................................................................................................... 182
9.1 Using the obsutil help Command to Search for Functions..................................................................................182
Conguring Scheduled Tasks Using the Crontab Command...............................................................................183
9.2
9.3 Setting obsutil Commands as Built-in Commands................................................................................................. 184
9.4 Conguring Auto Obtaining of Access Keys for obsutil........................................................................................187
9.5 Fine-Tuning obsutil Performance..................................................................................................................................188
9.6 Using obsutil for Resumable Data Transfer...............................................................................................................189
9.7 Using obsutil to Upload a Symbolic Link................................................................................................................... 190
Conguring an HTTP Proxy for obsutil.......................................................................................................................190
9.8
9.9 Using obsutil to Share Directories................................................................................................................................ 191
9.10 Using obsutil to Replicate Data Across Regions on the Client Side............................................................... 192
A Parameter Description.......................................................................................................193
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii
Page 5

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) Contents
B Change History.................................................................................................................... 204
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iv
Page 6
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 1 Introduction to obsutil
1 Introduction to obsutil
obsutil is a command line tool for accessing and managing OBS on HUAWEI
CLOUD. You can use this tool to perform common
creating buckets, uploading and downloading les/folders, and deleting les/
folders. If you are familiar with command line interface (CLI), obsutil is
recommended for batch processing and automated tasks.
congurations on OBS, such as
obsutil is compatible with the Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems
(OSs). Table 1-1 lists the recommended OS versions. To obtain the obsutil
download links and methods for
Table 1-1 Recommended OS versions for using obsutil
OS
Windows ● Windows 7
Linux ● SUSE 11
macOS macOS 10.13.4
Tool Advantages
dierent OSs, refer to Downloading obsutil.
Recommended Version
● Windows 8
● Windows 10
● Windows Server 2016
● EulerOS 2
● CentOS 7
obsutil features the following advantages:
1. Simple and easy to use
2. Lightweight and installation-free
3. Compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems
Diversied congurations and excellent performance
4.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
Page 7
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 1 Introduction to obsutil
Application Scenarios
● Automated backup and archiving, for example, periodically uploading local
data to OBS.
● Scenarios that cannot be implemented using other tools such as OBS Browser
+, for example, synchronously uploading, downloading, and copying objects.
Functions
Table 1-2 lists obsutil functions.
Table 1-2 obsutil functions
Function Description
Basic operations on
buckets
Basic operations on
objects
Logging Allows you to congure logging on the client side to
Create buckets of dierent storage classes in specic
regions, delete buckets, and obtain the bucket list and
conguration information.
Manage objects, including uploading, downloading,
deleting, and listing objects. Supported operations are
detailed as follows:
● Upload one or more les or folders.
● Upload large les in multiple parts.
● Synchronously upload, download, and copy
incremental objects.
● Copy a single object or copy multiple objects in
batches by object name
● Move a single object or move objects in batches by
object name
● Resume failed upload, download, or copy tasks.
record operations on buckets and objects for statistics
analysis later.
prex.
prex.
Advanced bucket and object management operations are being developed
continuously, and will be available in later versions of obsutil. You can also go to
OBS Console and explore more. For details, see OBS Console Operation Guide.
Command Line Structure
The obsutil command line structures are as follows:
● In Windows
obsutil
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
command [parameters...] [options...]
command [parameters...] [options...]
Page 8
NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 1 Introduction to obsutil
● command indicates the command to be executed, for example, ls or cp.
● parameters indicates the basic parameters (mandatory) of the command, for example,
bucket name when creating a bucket.
● options indicates the additional parameters (optional) of the command. Additional
parameters must be preceded with a hyphen (-) when you run the command.
● The square brackets ([]) are not part of the command. Do not enclose parameter values
with them when entering a command.
● If the command contains special characters including ampersands (&), angle brackets
(<) and (>), and spaces, they need to be escaped using quotation marks. Use single
quotation marks for Linux or macOS and quotation marks for Windows.
● Additional parameters can be input in the -
-acl=private, or -acl private. There is no dierence between the two formats. Select
either one as you like.
● In Windows, you can directly execute obsutil.exe to enter an interactive command
mode. In this mode, you can input
command [parameters...] [options...]
to run a command. An example is provided as follows:
Enter "exit" or "quit" to logout
Enter "help" or "help command" to show help docs
Input your command:
-->ls -limit=3 -s
obs://bucket-001
obs://bucket-002
obs://bucket-003
Bucket number is: 3
key=value
or -
key value
format, for example,
without obsutil
Input your command:
-->
● If you use SSH to remotely log in to the Linux or macOS for running obsutil commands,
you are advised to set TMOUT=0 to prevent the program from exiting due to the
expiration of the SSH session.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
Page 9
NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 2 Download and Installation
2 Download and Installation
Download Links
Table 2-1 lists the download links of obsutil for
Table 2-1 Download links of obsutil
Operatin
g System
Windows
(64-bit)
Linux
AMD
(64-bit)
Linux
ARM
(64-bit)
macOS
(64-bit)
Download Link How to Use View Help
obsutil_windows64
obsutil_windows64_sha256
obsutil_linux_amd64
obsutil_linux_amd64_sha256
obsutil_linux_arm64
obsutil_linux_arm64_sha256
obsutil_mac64
obsutil_mac64_sha256
dierent operating systems.
After the download
is complete, click
here to see how to
quickly get started
with obsutil.
Basic functions
● Listing Buckets
● Uploading an
Object
● Listing Objects
You can also
click here to
learn how
to use the
help
command
to get
familiar
with more
functions of
obsutil.
For details about the version revision records of obsutil, see ChangeLog.
Quick Installation
Methods of downloading obsutil vary according to dierent operating systems.
obsutil is an installation-free tool and can be used after the package is
downloaded and decompressed.
● In Windows
a. Directly download the obsutil package to your local PC using the
corresponding download link.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
Page 10

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 2 Download and Installation
b. After the download completes, decompress the package to a specied
folder.
c. Double-click obsutil.exe in the decompressed folder and then you can
use the tool.
Alternatively, you can open the CLI to go to the upper-level directory of
obsutil.exe and run obsutil commands. The command line structures of the two
modes are dierent. For details, see Command Line Structure.
● In Linux
a. Open the CLI and run the wget command to download the obsutil tool
package.
wget https://obs-community-intl.obs.ap-southeast-1.myhuaweicloud.com/obsutil/current/
obsutil_linux_amd64.tar.gz
You can also download the obsutil package from a PC running the Windows
operating system and then use a cross-platform transfer tool (such as WinSCP) to
transfer the package to your host running the Linux operating system.
b. Run the following command in the directory where the tool package
resides:
tar -xzvf obsutil_linux_amd64.tar.gz
c. Go to the directory where obsutil resides and run the following command
to grant the execute permission to obsutil:
chmod 755 obsutil
● macOS
a. Directly download the obsutil package to your local PC using the
corresponding download link.
b. After the download completes, decompress the package to a
specied
folder.
c. Open the CLI, go to the directory where obsutil resides, and run the
following command to grant the execute permission to obsutil:
chmod 755 obsutil
If you need to use obsutil on a HUAWEI CLOUD ECS, see the reference section below to
congure access to OBS over intranet to save trac costs.
● Accessing OBS over Intranet by Using obsutil on a Linux ECS
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
Page 11

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 3 Getting Started
3 Getting Started
3.1 Preparing the Environment
To use obsutil, you need to register a cloud service account, enable OBS, and
obtain the access keys (AK and SK)
rst.
Step 1 Register a cloud service account.
Before using OBS, ensure that you have a cloud service account.
1. Open a browser.
2. Log in to the HUAWEI CLOUD website at huaweicloud.com/intl/en-us/.
3. In the upper right corner of the page, click Register.
4. Enter the registration information and click Register.
Step 2 Enable OBS.
Ensure that your account balance is
1. Log in to OBS Console.
2. Click Fees in the upper right corner of the page. The Billing Center page is
displayed.
3. Then click Top Up.
4. Top up the account as prompted.
5. Go back to the management console page after the recharging is successful.
6. Click Service List on the top menu bar. Choose Storage > Object Storage
Service to log in to OBS Console.
Step 3 (Optional) Create an IAM user.
sucient before using OBS.
For data security, it is recommended that you do not use the account directly to
access OBS. Through the Identity and Access Management (IAM) service, you can
create a user who has the permission to access OBS resources and manage
buckets and objects on obsutil. If you do not need to use any IAM user, skip this
step.
1. On the top navigation bar of the console, choose Service List > Management
& Deployment > Identity and Access Management.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
Page 12

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 3 Getting Started
2. On the displayed IAM console page, create a user group with OBS permissions
congured.
For details, see Creating a User Group. After the user group is created, locate
the row that displays Global service > OBS in the User Group Permissions,
and click Congure Policy in the row to set OBS permissions for the user
group.
For details about OBS policies, see Permissions Management
3. Create a user.
For details, see Creating a User. When creating a user, set the User Group to
the one created in Step 3.2 with OBS permissions congured.
If the user group is not congured with OBS permissions, you can congure ne-grain
permissions on OBS Console through bucket policies or object policies. For details, see
Permission Control.
Step 4 Obtain access keys.
OBS uses AKs and SKs in user accounts for signature verication to ensure that
only authorized accounts can access
specied OBS resources. Detailed
explanations about AK and SK are as follows:
● Access key ID (AK): indicates the ID of the access key, which is a unique
identier used together with a secret access key to sign requests
cryptographically.
● Secret access key (SK): indicates the private key used together with its
associated AK to cryptographically sign requests. The AK and SK are used
together to identify a request sender to prevent the request from being
modied.
A user can create a maximum of two valid access keys.
Create access keys as follows:
1. In the upper right corner of the console page, select My Credential under the
username.
2. On the My Credentials page, select Access Keys in the navigation pane on
the left.
3. On the Access Keys page, click Add Access Key.
A user can create a maximum of two valid access keys.
4. In the Add Access Key dialog box that is displayed, enter the password and
verication code.
its
– If you have not bound an email address or mobile number, enter only the
password.
– If you have bound an email address and a mobile number, you can select the
verication by email or mobile phone.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
Page 13

NO TE
NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 3 Getting Started
5. Click OK.
6. In the Download Access Key dialog box that is displayed, click OK to save the
access keys to your browser's default download path.
Keep the access keys properly to prevent information leakage. If you click Cancel in
the dialog box, the access keys will not be downloaded, and you cannot download
them later. Re-create access keys if required.
7. Open the downloaded credentials.csv le to obtain the access keys (AK and
SK).
In the access key le, the value in the Access Key ID column is the AK, and the value
in the Secret Access Key column is the SK.
----End
3.2 Performing Initial Conguration
Before using obsutil, you need to congure the interconnection between obsutil
and OBS, including the endpoint and access keys (AK and SK) of OBS. You can use
obsutil to perform operations on OBS buckets and objects only after obtaining the
OBS authentication.
Prerequisites
● You have downloaded the software package of obsutil. For details, see
Download and Installation.
● You have obtained the enabled regions and endpoints of OBS. For details, see
Regions and Endpoints. If you want to access OBS in the AP-Hong Kong
region, the actual OBS service address is: https://obs.apsoutheast-3.myhuaweicloud.com.
● You have obtained the access keys (AK and SK). For details about how to
obtain access keys, see Preparing the Environment. Click here to open the
access key management page.
Conguration Method
Method 1: Run the
cong command, see Updating a Conguration File. The following is an
example:
cong command to initialize obsutil. For details about the
● In Windows
obsutil cong -i=ak -k=sk -e=
endpoint
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil cong -i=ak -k=sk -e=
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
endpoint
Page 14

NO TE
NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 3 Getting Started
● After running the preceding commands, a conguration le .obsutilcong is
automatically generated in the same home directory of the user who executes obsutil
commands (the ~ directory in Linux or macOS, and the C:\Users\
in Windows).
● For details about the parameters in the .obsutilcong le, see Parameter Description.
● The .obsutilcong le contains the AK and SK information of a user. Therefore, it is
hidden by default to prevent key disclosure. To query the le, run the following
command in the home directory of the user who executes obsutil commands.
● In Windows
dir
● In Linux or macOS
ls -a
or
ls -al
● obsutil encrypts the AK and SK in the
● Note: You can use the -i, -k, and -e options to
authentication. You can run the history command in the Linux OS to query the
parameter values. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
.obsutilcong contains all the conguration information of obsutil.
.obsutilcong le to ensure key security.
congure user information for
<Username>
directory
Method 2: You can use Conguring Auto Obtaining of Access Keys for obsutil
to implement initial
Checking the Connectivity
After the
the following commands:
● In Windows
● In Linux or macOS
Check the conguration result based on the command output:
● If the command output contains Bucket number is:, the conguration is
● If the command output contains Http status [403], the access keys are
● If the command output contains A connection attempt failed, then OBS
conguration is complete, you can check whether it is correct by running
obsutil ls -s
./obsutil ls -s
correct.
incorrectly congured.
cannot be accessed. In this case, check the network condition.
conguration.
If the command output contains Http status [403], you may not have the required
permissions for obtaining the bucket list. In this case, further locate the root cause based on
the specic situation.
3.3 Quick Start
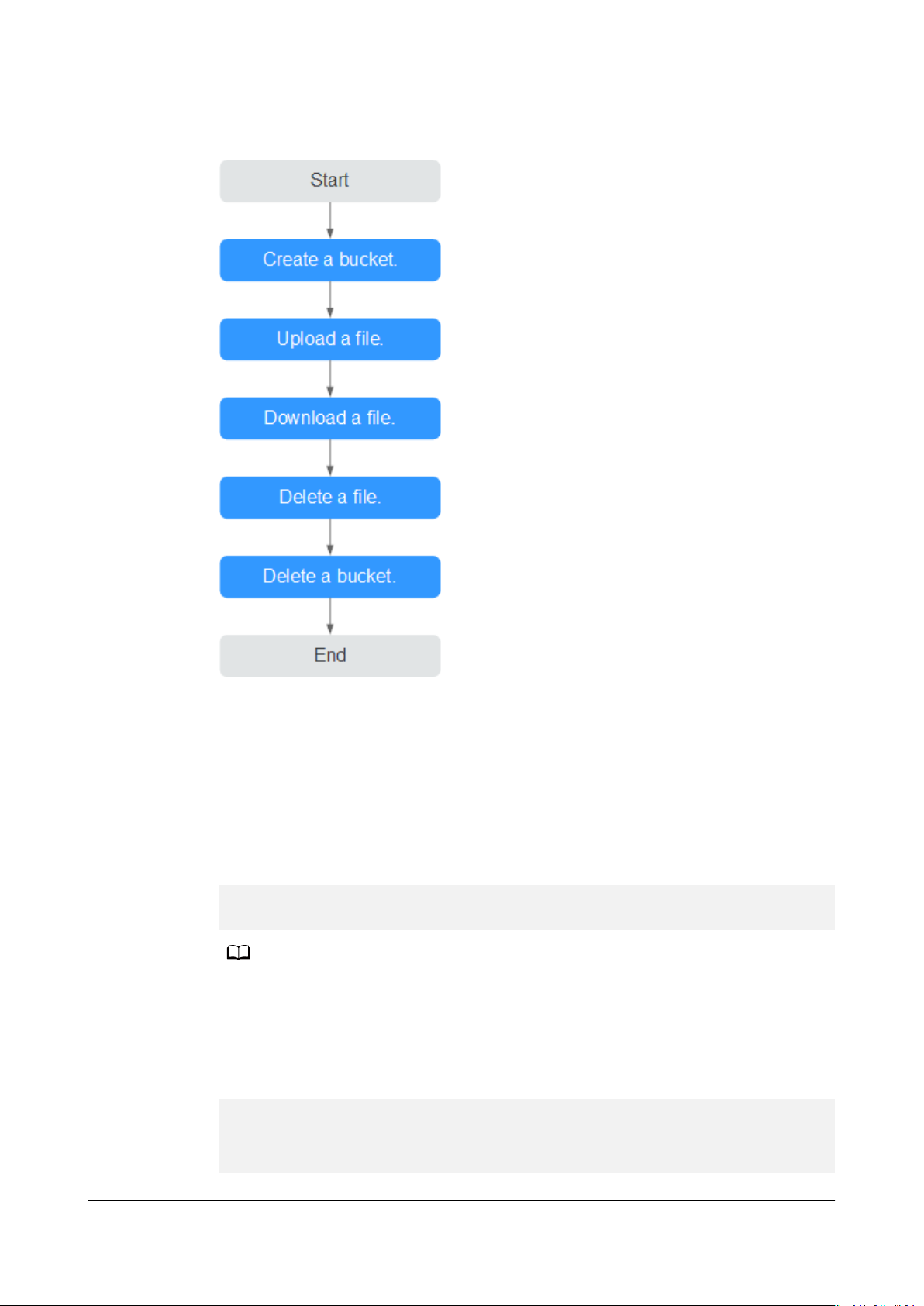
This section uses the Linux OS as an example to describe how to use obsutil to
perform basic data operations in OBS. For details, see Figure 3-1.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
Page 15
NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 3 Getting Started
Figure 3-1 obsutil ow for a quick start
Prerequisites
Procedure
Step 1 Run the ./obsutil mb obs://bucket-test -location=cn-south-1 command to create
Step 2 Run the ./obsutil cp /temp/test.txt obs://bucket-test/test.txt command to
● You have obtained obsutil and completed initial conguration.
● The directory saving the tool is accessed.
a new bucket named bucket-test in the CN South-Guangzhou region.
./obsutil mb obs://bucket-test -location=cn-south-1
Create bucket [bucket-test] successfully!
In the preceding command, parameter location indicates the region where a bucket is
created. It is mandatory only when the endpoint set during initial conguration belongs to
any other regions than the default one CN North-Beijing1 (cn-north-1). Click here to query
currently valid regions.
upload the test.txt le to bucket bucket-test.
./obsutil cp /temp/test.txt obs://bucket-test/test.txt
Parallel: 5 Jobs: 5
Threshold: 52428800 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
Page 16

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 3 Getting Started
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: /temp/.obsutil_checkpoint
test.txt:[==============================================] 100.00% 48.47 KB/s 0s
Upload successfully, 4.44KB, /temp/test.txt --> obs://bucket-test1/test.txt
Step 3 Run the ./obsutil cp obs://bucket-test/test.txt /temp/test1.txt command to
download test.txt from bucket bucket-test to a local PC.
./obsutil cp obs://bucket-test/test.txt /temp/test1.txt
Parallel: 5 Jobs: 5
Threshold: 52428800 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: /temp/.obsutil_checkpoint
test.txt:[=============================================] 100.00% 775.52 KB/s 0s
Download successfully, 4.44KB, obs://bucket-test1/test.txt --> /temp/test1.txt
Step 4 Run the ./obsutil rm obs://bucket-test/test.txt -f command to delete object
test.txt from bucket bucket-test.
./obsutil rm obs://bucket-test/test.txt -f
Delete object [test.txt] in the bucket [bucket-test] successfully!
Step 5 Run the ./obsutil rm obs://bucket-test -f command to delete bucket bucket-test.
./obsutil rm obs://bucket-test -f
Delete bucket [bucket-test] successfully!
----End
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
Page 17

NO TE
NO TICE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
4 Bucket Commands
4.1 Creating a Bucket
Function
You can use this command to create a bucket. A bucket name must be unique in
OBS. One account can create a maximum of 100 buckets.
If you create a bucket and name it the same as an existing one in the same account and
region, no error will be reported and status code 200 is returned. The bucket properties
comply with those set in the rst creation request. In other cases, creating a bucket with
the same name as an existing one will receive the status code 409, indicating that the
bucket already exists.
If the congured endpoint is a global domain name, you may need to wait several
minutes before uploading objects to the created bucket. Therefore, set the
endpoint to a regional domain name according to Performing Initial
Conguration if you want to upload objects instantly to the bucket.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil mb obs://bucket [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-location=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil mb obs://bucket [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-location=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx]
[-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil mb obs://bucket-test
command to create a bucket. The creation is successful.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
Page 18
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
obsutil mb obs://bucket-test
Create bucket [bucket-test] successfully, request id [0000016979E1D2EA860BB5E80A6B8FCC]
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil mb obs://bucket001
command to create a namesake bucket. The creation fails.
obsutil mb obs://bucket001
Create bucket [bucket001] failed, http status [409], error code [BucketAlreadyExists], error message
[The requested bucket name is not available. The bucket namespace is shared by all users of the
system. Please select a
[04030000016757F31A0333281A6B1E92]
dierent name andtry again.], request id
Parameter Description
Parame
ter
Optional or
Mandatory
Description
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
NOTE
A bucket name must comply with the following rules:
● Contains 3 to 63 characters, including lowercase
letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.), and starts
with a digit or letter.
● Cannot be an IP address.
● Cannot start or end with a hyphen (-) or period (.).
● Cannot contain two consecutive periods (.), for
example, my..bucket.
● Cannot contain periods (.) and hyphens (-) adjacent
to each other, for example, my-.bucket or my.-
bucket.
acl Optional
(additional
parameter)
Access control policies that can be specied when
creating a bucket. Possible values are:
● private
● public-read
● public-read-write
NOTE
The preceding three values indicate private read and
write, public read, and public read and write.
sc Optional
(additional
parameter)
Default bucket storage class that can be specied
when creating a bucket. Possible values are:
● standard: OBS Standard, which features low
access latency and high throughput, and is
applicable to storing frequently accessed data
(multiple accesses per month) or data that is
smaller than 1 MB
● warm: OBS Infrequent Access. It is applicable to
storing infrequently accessed (less than 12 times
a year) data that requires quick response.
● cold: OBS Archive. It is secure, durable, and
inexpensive, and applicable to archiving rarelyaccessed (once a year) data.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
Page 19

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Parame
ter
Optional or
Mandatory
location Mandatory
unless the
region where
the OBS service
resides is not
the default
region
(additional
parameter)
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Region where the bucket resides.
NOTE
This parameter indicates the region where a bucket will
be created. It is mandatory only when the endpoint
belongs to any other regions than the default one CN
North-Beijing1 (cn-north-1). Click here to query currently
valid regions.
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can
be congured, see Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
4.2 Listing Buckets
Function
You can use this command to obtain the bucket list. In the list, bucket names are
displayed in lexicographical order.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil ls [-s] [-sc] [-j=1] [-limit=1] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil ls [-s] [-sc] [-j=1] [-limit=1] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil ls -limit=5 command
to obtain the bucket list.
obsutil ls -limit=5
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
Page 20
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Bucket CreationDate Location BucketType
obs://bucket001 2018-09-03T01:53:02Z example OBJECT
obs://bucket002 2018-11-01T01:40:01Z example OBJECT
obs://bucket003 2018-10-25T11:45:45Z example OBJECT
obs://bucket004 2018-10-26T02:33:09Z example OBJECT
obs://bucket005 2018-10-26T02:34:50Z example OBJECT
Bucket number is: 5
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or Mandatory Description
s Optional (additional
parameter)
sc Optional (additional
parameter)
j Optional (additional
parameter). It must be
used together with sc.
limit Optional (additional
parameter)
cong Optional (additional
parameter)
Displays simplied query result.
NOTE
In the simplied format, the returned
result contains only the bucket name.
Queries the storage classes of the
buckets when listing buckets.
Indicates the maximum number of
concurrent tasks for querying the
bucket storage class. The default
value is the value of defaultJobs in
the conguration le.
NOTE
The value is ensured to be greater than or
equal to 1.
Maximum number of buckets that
can be queried. If the value is less
than 0, all buckets are listed. If it is
left blank, a maximum of 1000
buckets can be listed by default.
User-dened conguration le for
executing a command. For details
about parameters that can be
congured, see Parameter
Description.
e Optional (additional
Species the endpoint.
parameter)
i Optional (additional
Species the user's AK.
parameter)
k Optional (additional
Species the user's SK.
parameter)
t Optional (additional
Species the user's security token.
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
Page 21

NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
In the bucket listing result, the BucketType eld indicates the bucket type; OBJECT
indicates the bucket for object storage.
4.3 Querying Bucket Properties
Function
You can use this command to query the basic properties of a bucket, including its
default storage class, region, version ID, storage usage, bucket quota, and the
number of objects in the bucket.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil stat obs://bucket [-acl] [-bf=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil stat obs://bucket [-acl] [-bf=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil stat obs://bucket-test
command to query the basic properties of bucket bucket-test.
obsutil stat obs://bucket-test
Bucket:
obs://bucket-test
StorageClass:
standard
ObsVersion:
3.0
ObjectNumber:
8005
Size:
320076506
Quota:
0
Parameter Description
Parameter
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
acl Optional Queries the access control policies of the
Optional or
Mandatory
Description
bucket while querying bucket properties.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
Page 22
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
bf Optional
(additional
parameter)
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Display format of the used bucket capacity
(in bytes) Value options:
● human-readable
● raw
NOTE
If this parameter is not congured, the display
format of the used bucket capacity (in bytes) is
determined by the humanReadableFormat
parameter in the
conguration le.
User-dened conguration le for executing
a command. For details about parameters
that can be congured, see Parameter
Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Response
k Optional
Species the user's SK.
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
Species the user's security token.
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
parameter)
Field
Description
Bucket Bucket name
StorageClass Default storage class of the bucket
Location Region where the bucket resides
ObsVersion Version of the bucket
BucketType Type of a bucket. OBJECT indicates a bucket for object
storage.
ObjectNumber Number of objects in the bucket
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
Page 23

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Field Description
Size Storage usage of the bucket, in bytes
Quota Bucket quota. Value 0 indicates that no upper limit is set for
the bucket quota.
Acl Access control policy of the bucket
4.4 Setting Bucket Properties
Function
You can use this command to set the properties of a bucket, such as storage
classes and access policies.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil chattri obs://bucket [-sc=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-aclXml=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx]
[-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil chattri obs://bucket [-sc=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-aclXml=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil chattri obs://buckettest -acl=private command to change the access control policy of the bucket
to private read and write.
obsutil chattri obs://bucket-test -acl=private
Set the acl of bucket [bucket-test] to [private] successfully, request id
[04050000016836C5DA6FB21F14A2A0C0]
Parameter Description
Parameter
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
Optional or
Mandatory
Description
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
Page 24
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
sc Optional
(additional
parameter)
acl Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Default storage class of the bucket. Possible
values are:
● standard: OBS Standard, which features
low access latency and high throughput,
and is applicable to storing frequently
accessed data (multiple accesses per
month) or data that is smaller than 1
MB
● warm: OBS Infrequent Access. It is
applicable to storing infrequently
accessed (less than 12 times a year) data
that requires quick response.
● cold: OBS Archive. It is secure, durable,
and inexpensive, and applicable to
archiving rarely-accessed (once a year)
data.
Access control policies that can be specied
for buckets. Possible values are:
● private
● public-read
● public-read-write
NOTE
The preceding three values indicate private read
and write, public read, and public read and write.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
Page 25
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
aclXml Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Access control policy of the bucket, in XML
format.
<AccessControlPolicy>
<Owner>
<ID>
</Owner>
<AccessControlList>
<Grant>
<Grantee>
<ID>
</Grantee>
<Permission>
READ_ACP|FULL_CONTROL]
</Grant>
<Grant>
<Grantee>
<Canned>Everyone</Canned>
</Grantee>
<Permission>
READ_ACP|FULL_CONTROL]
</Grant>
</AccessControlList>
</AccessControlPolicy>
NOTE
NOTICE
ownerid
</ID>
userid
</ID>
[WRITE|WRITE_ACP|READ|
</Permission>
[WRITE|WRITE_ACP|READ|
</Permission>
● Owner: Optional. Specify the bucket owner's
ID.
● In AccessControlList, the Grant
the authorized users. Grantee
IDs of authorized users. Canned species the
authorized user group (currently, only
Everyone is supported).
● The following permissions can be granted:
WRITE (write), WRITE_ACP (write ACL), READ
(read), READ_ACP (read ACL), and
FULL_CONTROL (full control).
Because angle brackets (<) and (>) are
unavoidably included in the parameter value, you
must use quotation marks to enclose them for
escaping when running the command. Use single
quotation marks for Linux or macOS and
quotation marks for Windows.
eld contains
species the
cong
Optional
(additional
parameter)
User-dened conguration le for executing
a command. For details about parameters
that can be congured, see Parameter
Description.
e Optional
Species the endpoint.
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
Species the user's AK.
(additional
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
Page 26

NO TE
NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
Only one from sc, acl, or aclXml can be set for each command.
4.5 Deleting a Bucket
Description
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
Function
You can use this command to delete a bucket. The bucket to be deleted must be
empty (containing no objects, historical versions, or fragments).
To delete a non-empty bucket, run the commands in Deleting a Multipart Upload Task
and Deleting an Object to clear the bucket, and then run the following command to
delete the bucket.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil rm obs://bucket [-f] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil rm obs://bucket [-f] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil rm obs://bucket-test
command to delete bucket bucket-test.
obsutil rm obs://bucket-test
Do you want delete bucket [bucket-test] ? Please input (y/n) to conrm:
y
Delete bucket [bucket-test] successfully!
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
Page 27
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
f Optional (additional
parameter)
cong Optional (additional
parameter)
e Optional (additional
parameter)
i Optional (additional
parameter)
k Optional (additional
parameter)
t Optional (additional
parameter)
payer Optional (additional
parameter)
Description
Runs in force mode.
User-dened conguration le for
executing a command. For details about
parameters that can be congured, see
Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on
a bucket.
4.6 Conguring a Bucket Policy
Function
You can use this command to congure a bucket policy.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=put -localle=xxx [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx]
[-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=put -localle=xxx [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx]
[-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil bucketpolicy obs://
bucket -method=put
bucket policy based on le policy.json.
obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=put -localle=d:\temp\policy.json
-localle=d:\temp\policy.json command to set a
Put bucketPolicy succeed, requestId is [04050000016836C5DA6FB21F14A2A0C0]
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 22
Page 28
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
method Mandatory Species the method. Set this parameter to put
localle Mandatory Path of the local policy le to import
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
when conguring a bucket policy.
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can
be congured, see Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
4.7 Obtaining a Bucket Policy
Function
You can use this command to obtain a bucket policy.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=get [-localle=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx]
[-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=get [-localle=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 23
Page 29
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil bucketpolicy obs://
bucket -method=get -localle=d:\temp\policy.json command to export the
bucket policy to local le policy.json.
obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=get -localle=d:\temp\policy.json
Export bucketPolicy to [d:\temp\policy.json] succeed, requestId is
[04050000016836C5DA6FB21F14A2A0C0]
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
method Mandatory Species the method. Set this parameter to gut
localle Optional
(additional
parameter)
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
when obtaining a bucket policy.
If this parameter is set, the policy is exported to a
local le. If not set, the policy is exported in a
standard manner by default.
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can
be congured, see Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
4.8 Deleting a Bucket Policy
Function
You can use this command to delete a bucket policy.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 24
Page 30
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 4 Bucket Commands
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=delete [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=delete [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil bucketpolicy obs://
bucket -method=delete command to delete a bucket policy.
obsutil bucketpolicy obs://bucket -method=delete
Delete bucketPolicy succeed, requestId is [04050000016836C5DA6FB21F14A2A0C0]
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or
Description
Mandatory
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
method Mandatory Species the method. Set this parameter to delete
when deleting a bucket policy.
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can
be congured, see Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
Species the user's AK.
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
Species the user's SK.
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
Species the user's security token.
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 25
Page 31

NO TICE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
5 Object Commands
5.1 Creating a Folder
Function
You can use this command to create a folder in a specied bucket or local le
system.
No error is returned if a folder with the same name as an existing one is created,
and the content of the existing folder remain unchanged.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
– Creating a folder in a
obsutil mkdir obs://bucket/folder[/subfolder1/subfolder2] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Creating a folder in the local le system
obsutil mkdir folder_url [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
– Creating a folder in a
./obsutil mkdir obs://bucket/folder[/subfolder1/subfolder2] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Creating a folder in the local le system
./obsutil mkdir folder_url [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
specied bucket
specied bucket
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil mkdir obs://buckettest/folder1/folder2 command to create a folder in a bucket.
obsutil mkdir obs://bucket-test/folder1/folder2
Create folder [obs://bucket-test/folder1/] successfully, request id
[0000016979E1D23C860BB3D8E4577C5E]
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 26
Page 32

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Create folder [obs://bucket-test/folder1/folder2] successfully, request id
[0000016979E1D2B2860BB5181229C72C]
Parameter Description
Parame
ter
Optional or
Mandatory
bucket Mandatory
when
creating a
folder in a
specied
bucket
folder Mandatory
when
creating a
folder in a
specied
bucket
folder_urlMandatory
when
creating a
folder in the
local le
system
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Bucket name
Folder path in the bucket. This value can contain
multi-level folders. Separate each level with a slash
(/).
Folder path in the local le system. The value can be
an absolute path or a relative path.
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can be
congured, see Parameter Description.
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a bucket.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 27
Page 33

NO TICE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
5.2 Uploading an Object
Function
You can use this command to upload one or more local les or folders to a
specied path in OBS. These les can be texts, images, videos, or any other type of
les.
Do not change the local le or folder when uploading it. Otherwise, the upload
may fail or data may be inconsistent.
Restrictions
obsutil has restrictions on the size of les or folders to be uploaded. You can
upload an empty le or folder of 0 bytes. You can also upload a single le or
folder with a maximum size of 5 GB in normal mode or a single le with a
maximum size of 48.8 TB in multipart mode.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
– Uploading a le
obsutil cp le_url obs://bucket[/key] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [p=1] [-threshold=5248800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-o=xxx] [cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx]
– Uploading a folder
obsutil cp folder_url obs://bucket[/key] -r [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-f] [-at] [-u] [vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2]
[-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
– Uploading multiple les/folders
obsutil cp le1_url,folder1_url|lelist_url obs://bucket[/prex] -msm=1 [-r] [-arcDir=xxx] [dryRun] [-link] [-f] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5]
acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx][timeRange=time1-time2] [-at] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
– Uploading a
./obsutil cp le_url obs://bucket[/key] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [p=1] [-threshold=5248800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-o=xxx] [cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx]
– Uploading a folder
./obsutil cp folder_url obs://bucket[/key] -r [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-f] [-at] [-u] [vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2]
[-at] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
– Uploading multiple les/folders
./obsutil cp le1_url,folder1_url|lelist_url obs://bucket[/prex] -msm=1 [-r] [-arcDir=xxx] [dryRun] [-link] [-f] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5]
acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx][-
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-at] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-
le
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-at] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 28
Page 34

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil cp d:\temp\test.txt
obs://bucket-test/key command to upload the test.txt le in the temp
directory in the D: drive to bucket bucket-test and rename the
obsutil cp d:\temp\test.txt obs://bucket-test/key
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
[====================================================] 100.00% 1.68 MB/s 5s
Upload successfully, 8.46MB, d:\temp\test.txt --> obs://bucket-test/key
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil cp d:\temp obs://
bucket-test -f -r command to recursively upload all
les and subfolders in
the temp directory in the D: drive to the temp folder in bucket bucket-test.
obsutil cp d:\temp obs://bucket-test -f -r
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
OutputDir: xxxx
le as key.
[========================================================] 100.00% 2.02 KB/s 0s
Succeed count is: 5 Failed count is: 0
Metrics [max cost:90 ms, min cost:45 ms, average cost:63.80 ms, average tps:35.71]
Task id is: 104786c8-27c2-48fc-bc6a-5886596fb0ed
● For more examples, see Upload.
Parameter Description
Parameter
le_url Optional for
Optional or
Mandatory
uploading
multiple les/
folders
Mandatory for
uploading a
le
Description
Local le path
NOTE
● Do not nest paths when uploading multiple
les/folders. For example, you cannot
specify /a/b/c and /a/b/ at the same time.
● If this parameter is congured when uploading
multiple les/folders, msm must be set to 1. In
this case, use commas (,) to separate multiple
le paths, for example, le_url1,le_url2.
● Files and folders can both be included when
uploading multiple les/folders. For example,
le_url1,folder_url1,le_url2,folder_url2.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 29
Page 35

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
folder_url Optional for
uploading
multiple les/
folders
Mandatory for
uploading a folder
lelist_url Optional for
uploading
multiple les/
folders
Description
Local folder path
NOTE
● If at is not congured when uploading a
folder, the entire folder is uploaded. If
congured, all les in the folder are uploaded.
● Do not nest paths when uploading multiple
les/folders. For example, you cannot
specify /a/b/c and /a/b/ at the same time.
● If this parameter is
multiple les/folders, msm must be set to 1. In
this case, use commas (,) to separate multiple
folder paths, for example,
folder_url1,folder_url2.
● Files and folders can be included when
uploading multiple
le_url1,folder_url1,le_url2,folder_url2.
congured when uploading
les/folders. For example,
at is
Indicates the path of the le that contains the
list of les/folders to be uploaded. If this
parameter is congured, msm must be set to
2.
NOTE
● The list
as TXT and CSV. Each line in the le indicates a
le or folder to be uploaded. For example:
le_url1
le_url2
folder_url1
folder_url2
● Do not nest paths in the list
you cannot specify /a/b/c and /a/b/ at the
same time.
le is in common text le formats, such
le. For example,
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 30
Page 36

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Description
Mandatory
key Optional Indicates the object name or object name
prex specied when uploading a le, or the
object name prex specied when uploading
a folder.
The rules are as follows:
● If this parameter is left blank when
uploading a
le, the le is uploaded to the
root directory of the bucket and the object
name is the
le name. If the value ends
with a slash (/), the value is used as the
object name
prex when the le is
uploaded, and the object name is the value
plus the le name. If the value does not
end with a slash (/), the
le is uploaded
with the value as the object name.
● If this parameter is left blank when
uploading a folder, the folder is uploaded
to the root directory of the bucket. If the
value ends with a slash (/), the value is
used as the object name
prex of the
folder to be uploaded. If the value does
not end with a slash (/), the folder to be
uploaded is
prexed with the value plus a
slash (/).
NOTE
For details about how to use this parameter, see
Upload.
fr
Optional for
uploading a le
(additional
parameter)
at Optional for
uploading a folder
or multiple les/
folders (additional
parameter)
arcDir Optional
(additional
parameter)
dryRun Optional
(additional
parameter)
Generates an operation result list when
uploading a le.
Uploads all les in a folder but not the folder
itself.
Path to which the uploaded les are archived
Conducts a dry run.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 31
Page 37

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
link Optional
(additional
parameter)
u Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Uploads the actual path of the symbolic-link
le/folder
NOTICE
● If this parameter is not specied and the le to
be uploaded is a symbolic-link le whose target
le does not exist, the exception message "The
system cannot
displayed in Windows OS, while the exception
message "No such le or directory" will be
displayed in macOS or Linux OS.
● Avoid the symbolic link loop of a folder,
otherwise, the upload will exit due to panic. If
you do not want the system to panic, set
panicForSymbolicLinkCircle to false in the
conguration le.
nd the le specied" will be
Indicates incremental upload. If this
parameter is set, each le can be uploaded
only when it does not exist in the bucket, its
size is dierent from the namesake one in the
bucket, or it has the latest modication time.
vlength Optional
(additional
parameter)
vmd5 Optional
(additional
parameter)
p Optional
(additional
parameter)
After the upload is complete, check whether
the sizes of the objects in the bucket are the
same as those of the local les.
After the upload completes, check whether
the MD5 values of the objects in the bucket
are the same as those of the local les.
NOTE
● If the size of the le or folder to be uploaded is
too large, using this parameter will degrade the
overall performance due to MD5 calculation.
● After the MD5 value
the parameter value is set to the object
metadata x-obs-md5chksum, which is used for
later MD5 verication during download or copy.
verication is successful,
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
multipart upload tasks when uploading a le.
The default value is the value of
defaultParallels in the conguration le.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 32
Page 38

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
threshold Optional
(additional
parameter)
acl Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the threshold for enabling multipart
upload, in bytes. The default value is the
value of defaultBigleThreshold in the
conguration le.
NOTE
● If the size of the
smaller than the threshold, upload it directly.
Otherwise, a multipart upload is required.
● If you upload a le or folder directly, no part
record is generated, and resumable transmission
is not supported.
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For
example, 1 MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
le or folder to be uploaded is
Access control policies that can be specied
when uploading les. Possible values are:
● private
● public-read
● public-read-write
● bucket-owner-full-control
NOTE
The preceding four values indicate private read and
write, public read, public read and write, and
bucket owner full control.
sc Optional
(additional
parameter)
meta Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the storage classes of objects that
can be specied when uploading les.
Possible values are:
● standard: OBS Standard, which features
low access latency and high throughput,
and is applicable to storing frequently
accessed data (multiple accesses per
month) or data that is smaller than 1 MB
● warm: OBS Infrequent Access. It is
applicable to storing infrequently accessed
(less than 12 times a year) data that
requires quick response.
● cold: OBS Archive. It is secure, durable, and
inexpensive, and applicable to archiving
rarely-accessed (once a year) data.
Indicates the customized metadata that can
be specied when uploading les. The format
is key1:value1#key2:value2#key3:value3.
NOTE
The preceding value indicates that the objects in
the bucket contain three groups of customized
metadata after the
key2:value2, and key3:value3.
le is uploaded: key1:value1,
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 33
Page 39

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
ps Optional
(additional
parameter)
cpd Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the size of each part in a multipart
upload task, in bytes. The value ranges from
100 KB to 5 GB. The default value is the value
of defaultPartSize in the conguration le.
NOTE
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For
example, 1 MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
● The parameter can be set to auto. In this case,
obsutil automatically sets the part size for each
multipart task based on the source
le size.
Indicates the folder where the part records
reside. The default value
is .obsutil_checkpoint, the subfolder in the
home directory of the user who executes
obsutil commands.
NOTE
A part record is generated during a multipart
upload and saved to the upload subfolder. After
the upload succeeds, its part record is deleted
automatically. If the upload fails or is suspended,
the system attempts to resume the task according
to its part record when you perform the upload the
next time.
r Mandatory for
uploading a folder
(additional
parameter)
Optional for
uploading
multiple
les/
folders
f Optional for
uploading a folder
or multiple les/
folders (additional
parameter)
j Optional for
uploading a folder
or multiple les/
folders (additional
parameter)
Indicates les and subfolders within the folder
when uploading a folder recursively.
Runs in force mode.
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
tasks for uploading a folder. The default value
is the value of defaultJobs in the
conguration le.
NOTE
The value is ensured to be greater than or equal to
1.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 34
Page 40
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
msm Mandatory for
uploading
multiple les/
folders (additional
parameter)
exclude Optional for
uploading a folder
or multiple les/
folders (additional
parameter)
Description
Enables the mode for uploading multiple
les/folders. Possible values are 1 and 2.
NOTE
● If msm is set to 1, the source URL indicates a
list of le/folder names separated by commas.
● If msm is set to 2, the source URL indicates a
le containing a list of le/folder names.
● If the le or folder name already contains
commas (,), do not set msm to 1.
● If parameter r is not set, the folders in the list
will not be uploaded.
Indicates the le matching patterns that are
excluded, for example: *.txt.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of
characters, and the question mark (?)
represents any single character. For instance,
abc*.txt indicates any
with abc and ends with .txt.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to
represent ?.
● If the name of the
the value of this parameter, the le is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the
matching pattern to prevent special characters
from being escaped by the OS and leading to
unexpected results. Use single quotation marks
for Linux or macOS and quotation marks for
Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute
le path (including the le name and le
directory).
● The matching pattern takes
in the folder.
● Multiple exclude parameters can be specied,
for example, -exclude=*.xxx -exclude=*.xxx.
le whose name starts
le to be uploaded matches
eect only for les
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 35
Page 41

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
include Optional for
uploading a folder
or multiple les/
folders (additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the le matching patterns that are
included, for example: *.jpg.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of
characters, and the question mark (?)
represents any single character.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to
represent ?.
● Only after identifying that the name of the
to be uploaded does not match the value of
exclude, the system checks whether the
name matches the value of this parameter. If
yes, the le is uploaded. If not, the le is
skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the
matching pattern to prevent special characters
from being escaped by the OS and leading to
unexpected results. Use single quotation marks
for Linux or macOS and quotation marks for
Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute
le path (including the le name and le
directory).
● The matching pattern takes eect only for les
in the folder.
● Multiple include parameters can be
for example, -include=*.xxx -include=*.xxx.
le
le
specied,
at
disableDir
Object
Optional for
uploading a folder
or multiple les/
folders (additional
parameter)
Optional for
uploading
multiple folders
(additional
parameter)
Indicates that only the les whose latest
access time is within the value of timeRange
are uploaded.
NOTE
● This parameter must be used together with
timeRange.
Indicates the folders themselves are not
uploaded as an object. Conguring this
parameter can avoid uploading empty folders
to a bucket. If a folder contains les, the les
will be uploaded and the original path format
is retained.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 36
Page 42
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
timeRange Optional for
uploading a folder
or multiple les/
folders (additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the time range matching pattern
when uploading les. Only les whose latest
modication time is within the congured
time range are uploaded.
This pattern has a lower priority than the le
matching patterns (exclude/include). That is,
the time range matching pattern is executed
after the congured le matching patterns.
NOTE
● The matching time range is represented in
time1-time2
or the same as
yyyyMMddHHmmss
● Automatic formatting is supported. For
example, yyyyMMdd is equivalent to
yyyyMMdd000000, and yyyyMM is equivalent to
yyyyMM01000000.
● If this parameter is set to *-
whose latest modication time is earlier than
time2
les whose latest modication time is later than
time1
NOTICE
Time in the matching pattern is the UTC time.
, where
are matched. If it is set to
are matched.
time1
must be earlier than
time2
. The time format is
.
time2
, all les
time1
-*, all
mf
Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates that the name matching pattern
(include or exclude) and the time matching
pattern (timeRange) also take eect on
folders.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 37
Page 43
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
o Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the folder where operation result
lists reside. After the command is executed,
result lists (possibly including success, failure,
and warning les) are generated in the folder.
The default value is .obsutil_output, the
subfolder in the home directory of the user
who executes obsutil commands.
NOTE
● The naming rule for result lists is as follows:
cp_{succeed | failed |
time
warning}_report_
● By default, the maximum size of a single result
list is 30 MB and the maximum number of
result lists that can be retained is 1024. You can
set the maximum size and number by
conguring recordMaxLogSize and
recordBackups in the conguration le.
● If there are multiple folders and les and you
need to conrm the detailed error information
about a failed task, refer to the failure list
cp_failed_report_
list folder and the log les in the log path.
_TaskId.txt
time
_TaskId.txt in the result
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that
can be congured, see Parameter
Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 38
Page 44
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Response
Field Description
Parallel Parameter -p in the request
Jobs Parameter -j in the request
Threshold Parameter -threshold in the request
PartSize Parameter -ps in the request
Exclude Parameter -exclude in the request
Include Parameter -include in the request
TimeRange Parameter -timeRange in the request
VerifyLength Parameter -vlength in the request
VerifyMd5 Parameter -vmd5 in the request
CheckpointDir Parameter -cpd in the request
OutputDir Parameter -o in the request
ArcDir Parameter -arcDir in the request
Succeed count Number of successful tasks
Failed count Number of failed tasks
Skip count Number of tasks that are skipped during incremental upload,
download, or copy, and synchronous upload, download, or
copy.
NOTE
Skipped tasks are recorded into successful tasks.
Warning count Number of tasks that are executed successfully but contain
warnings.
NOTE
● The task for which a warning is generated may be a failure or a
success, which needs to be further determined according to the
corresponding result list.
● The number of tasks that generate warnings is independent of the
number of successful or failed tasks. The total number of tasks is
the number of successful tasks plus the number of failed tasks.
Succeed bytes Number of bytes that are successfully uploaded or
downloaded.
max cost Maximum duration of all tasks, in ms
min cost Minimum duration of all tasks, in ms
average cost Average duration of all tasks, in ms
average tps The average number of tasks completed per second
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 39
Page 45

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Field Description
Task id Unique ID of an operation, which is used to search for the
result list generated in a batch task
5.3 Querying Object Properties
Function
You can use this command to query the basic properties of an object.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil stat obs://bucket/key [-acl][-bf=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil stat obs://bucket/key [-acl][-bf=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil stat obs://buckettest/key command to query the basic properties of an object.
obsutil stat obs://bucket-test/key
Key:
obs://bucket-test/key
LastModied:
2018-11-16T02:15:49Z
Size:
7
ETag:
43d93b553855b0e1fc67e31c28c07b65
ContentType:
text/plain
Parameter Description
Parameter
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
key Mandatory Object name
acl Optional Queries the access control policies of the
Optional or
Mandatory
Description
object at the same time.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 40
Page 46

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
bf Optional
(additional
parameter)
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Display format of the object size (in bytes)
Value options:
● human-readable
● raw
NOTE
If this parameter is not congured, the display
format of the object size (in bytes) is determined
by the humanReadableFormat parameter in the
conguration le.
User-dened conguration le for
executing a command. For details about
parameters that can be congured, see
Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Response
k Optional
Species the user's SK.
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
Species the user's security token.
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
Species that requester-pays is enabled on
a bucket.
parameter)
Field
Description
Key Object name
LastModied Latest modication time of the object
Size Object size, in bytes
StorageClass Storage class of the object
MD5 Real MD5 of the object
NOTE
You can query this value only after running the cp command and
conguring the -vmd5 parameter.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 41
Page 47

NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Field Description
ETag ETag value of an object calculated on the server
ContentType Content-Type of the object
Metadata Customized metadata of the object
Acl Access control policy of the object
5.4 Setting Object Properties
Function
You can use this command to set properties of an object or set properties of
objects in batches by a specied object name prex.
You can set storage classes only for buckets whose version is 3.0.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
– Setting properties of a single object
obsutil chattri obs://bucket/key [-sc=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-aclXml=xxx] [-versionId=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Setting properties of objects in batches
obsutil chattri obs://bucket[/key] -r [-f] [-v] [-sc=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-aclXml=xxx] [-o=xxx] [-j=1] [-
cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
– Setting properties of a single object
./obsutil chattri obs://bucket/key [-sc=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-aclXml=xxx] [-versionId=xxx] [-fr] [o=xxx]
– Setting properties of objects in batches
./obsutil chattri obs://bucket[/key] -r [-f] [-v] [-sc=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-aclXml=xxx] [-o=xxx] [-j=1]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example, run the obsutil chattri obs://buckettest/key -acl=public-read command to set the access permission to an object
to public read.
obsutil chattri obs://bucket-test/key -acl=public-read
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Set the acl of object [key] in the bucket [bucket-test] to [public-read] successfully, request id
[04050000016836DDFA73B2B5320E2651]
● Take the Windows OS as an example, run the obsutil chattri obs://bucket-
test -r -f -acl=public-read command to set the access permission to all
objects in the bucket to public read.
obsutil chattri obs://bucket-test -r -f -acl=public-read
[------------------------------------------------] 100.00% tps:155.15 5/5 233ms
Succeed count is: 5 Failed count is: 0
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 42
Page 48

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Metrics [max cost:177 ms, min cost:53 ms, average cost:102.40 ms, average tps:20.41]
Task id is: 9d7f73-f747-4fdd-9b2a-815ba2dc3b07
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or
Description
Mandatory
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
key Mandatory for
setting properties
of an object.
Optional for
setting properties
of objects in
batches.
sc Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the name of the object whose
properties are to be set, or the name prex of
objects whose properties are to be set in
batches.
NOTE
If this parameter is left blank during batch
operation, properties of all objects in the bucket are
set.
Storage classes of objects. Possible values are:
● standard: Standard storage class, which
features low access latency and high
throughput, and is applicable to storing
frequently accessed data (multiple accesses
per month) or data that is smaller than 1
MB
● warm: Infrequent Access or Warm storage
class. It is applicable to storing infrequently
accessed (less than 12 times a year) data
that requires quick response.
● cold: Archive or Cold storage class. It is
secure, durable, and inexpensive, and
applicable to archiving rarely-accessed
(once a year) data.
NOTE
For an object whose storage class is cold, restore the
rst and then set its storage class. To restore
object
an object, see Restoring Objects from OBS Archive.
acl Optional
(additional
parameter)
Access control policies that can be specied for
objects. Possible values are:
● private
● public-read
● public-read-write
● bucket-owner-full-control
NOTE
The preceding four values indicate private read and
write, public read, public read and write, and bucket
owner full control.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 43
Page 49

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
aclXml Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Access control policy of the bucket, in XML
format.
<AccessControlPolicy>
<Owner>
<ID>
</Owner>
<AccessControlList>
<Grant>
<Grantee>
<ID>
</Grantee>
<Permission>
FULL_CONTROL]
</Grant>
<Grant>
<Grantee>
<Canned>Everyone</Canned>
</Grantee>
<Permission>
FULL_CONTROL]
</Grant>
</AccessControlList>
</AccessControlPolicy>
NOTE
NOTICE
ownerid
</ID>
userid
</ID>
[WRITE|WRITE_ACP|READ|READ_ACP|
</Permission>
[WRITE|WRITE_ACP|READ|READ_ACP|
</Permission>
● Owner: Optional. Specify the object owner's ID.
● In AccessControlList, the Grant
the authorized users. Grantee species the IDs of
authorized users. Canned
authorized user group (currently, only Everyone
is supported).
● The following permissions can be granted: WRITE
(write), WRITE_ACP (write ACL), READ (read),
READ_ACP (read ACL), and FULL_CONTROL (full
control).
Because angle brackets (<) and (>) are unavoidably
included in the parameter value, you must use
quotation marks to enclose them for escaping when
running the command. Use single quotation marks
for Linux or macOS and quotation marks for
Windows.
eld contains
species the
versionId
Optional for
setting properties
Version ID of the object whose properties are
to be set
of an object
(additional
parameter)
fr Optional for
setting properties
Generates an operation result list when setting
properties of an object.
of an object
(additional
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 44
Page 50

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
f Optional when
setting properties
of objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
r Mandatory when
setting properties
of objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
v Optional when
setting properties
of objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
o Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Runs in force mode.
Sets properties of objects in batches based on
a specied object name prex.
Sets properties of versions of objects in batches
based on a specied object name prex.
Indicates the folder where operation result lists
reside. After the command is executed, result
lists (including success and failure les) are
generated in the folder. The default value
is .obsutil_output, the subfolder in the home
directory of the user who executes obsutil
commands.
NOTE
● The naming rule for result lists is as follows:
chattri_{succeed |
time
failed}_report_
By default, the maximum size of a single result
list is 30 MB and the maximum number of result
lists that can be retained is 1024. You can set the
maximum size and number by
recordMaxLogSize and recordBackups in the
conguration le.
● If there are multiple folders and les and you
need to conrm the detailed error information
about a failed task, refer to the failure list
chattri_failed_report_
result list folder and the log les in the log path.
_TaskId.txt
time
_TaskId.txt in the
conguring
j Optional when
setting properties
of objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 45
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
tasks for setting object properties in batches.
The default value is the value of defaultJobs in
the conguration le.
NOTE
The value is ensured to be greater than or equal to
1.
Page 51

NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that
can be congured, see Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
Only one from acl, sc, or aclXml can be set for each command.
Response
Refer to Response for uploading an object.
5.5 Listing Objects
Function
You can use this command to query objects or object versions in a bucket. All
objects are listed in lexicographical order by object name and version ID.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil ls obs://bucket[/prex] [-s] [-d] [-v] [-marker=xxx] [-versionIdMarker=xxx] [-bf=xxx] [limit=1]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil ls obs://bucket[/prex] [-s] [-d] [-v] [-marker=xxx] [-versionIdMarker=xxx] [-bf=xxx] [limit=1] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 46
Page 52

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil ls obs://bucket-test limit=10 command to list objects in the bucket.
obsutil ls obs://bucket-test -limit=10
Folder list:
obs://bucket-test/api/
Object list:
key
obs://bucket-test/AUTHORS 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 33243 standard
"796393c1eaf502ef56a85c2ceb640aea"
obs://bucket-test/CONTRIBUTING.md 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 1366
standard "12d93325ba6131f852daecd18dd65edc"
obs://bucket-test/CONTRIBUTORS 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 45710
standard "b486b5003e6215c9199e86ab3ccec9fa"
obs://bucket-test/LICENSE 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 1479 standard
"5d4950ecb7b26d2c5e4e7b4e0dd74707"
obs://bucket-test/PATENTS 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 1303 standard
"3a55d95595a6f9e37dee53826b4da2"
obs://bucket-test/README.md 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 1399 standard
"97351fd7946b9ea021a31a86ba2a10ab"
obs://bucket-test/VERSION 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 7 standard
"43d93b553855b0e1fc67e31c28c07b65"
obs://bucket-test/api/README 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 521 standard
"4e9e63a87075df60cdf65c8ce9e92117"
obs://bucket-test/api/except.txt 2018-11-16T02:15:49Z 20194 standard
"8eb96de3f60447e2f09a7531c99fb3ee"
Next marker is: api/except.txt
Folder number is: 1
File number is: 9
LastModied Size StorageClass ETag
● For more examples, see Listing.
Parameter Description
Parameter
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
prex Optional Prex of an object name for listing objects
s Optional
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 47
Optional or
Mandatory
(additional
parameter)
Description
NOTE
If this parameter is left blank, all objects in the
bucket are listed.
Displays simplied query result.
NOTE
In the simplied format, the returned result
contains only the object name.
Page 53

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
d Optional
(additional
parameter)
v Optional
(additional
parameter)
marker Optional
(additional
parameter)
versionIdMa
rker
Optional
(additional
parameter). It
must be used
together with the v
and marker
parameters.
Description
Lists only objects and subdirectories in the
current directory, instead of recursively
listing all objects and subdirectories.
NOTE
According to the naming conventions in OBS, a
slash (/) is used as the directory separator.
Lists versions of an object in a bucket. The
result contains the latest version and
historical versions (if any) of the object.
Object name to start with when listing
objects in a bucket. All objects are listed in
lexicographical order by object name.
NOTE
For details about how to use this parameter, see
Listing.
Version ID to start with when listing
versions of objects in a bucket. All versions
and objects are listed in lexicographical
order by object name and version ID.
NOTE
If the value of versionIdMarker is not a version
ID
specied by marker, versionIdMarker is
invalid.
bf Optional
(additional
parameter)
limit Optional
(additional
parameter)
Display formats of bytes in the listing
result. Possible values are:
● human-readable
● raw
NOTE
If this parameter is not congured, the display
format of bytes in the result is determined by
the humanReadableFormat parameter in the
conguration le.
Maximum number of objects that can be
listed. If the value is less than or equal to 0,
all objects are listed. If it is left blank, 1000
objects are listed by default.
NOTE
If there are a large number of objects in a
bucket, you are advised to set this parameter to
limit the number of objects to be listed each
time. If not all objects are listed, marker and
versionIdMarker of the next request will be
returned in the result, which you can use to list
the remaining objects.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 48
Page 54

NO TICE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
User-dened conguration le for
executing a command. For details about
parameters that can be congured, see
Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on
a bucket.
5.6 Copying an Object
Function
You can use this command to copy a single object or copy objects in batches by a
specied object name prex.
● Do not change the source objects in the OBS bucket when copying a single
object or objects in batches. Otherwise, the operation may fail or data may be
inconsistent.
● If the storage class of the object to be copied is cold, you must restore the
object to be copied
● To copy objects, you must have the read permission on the objects to be copied
and the write permission on the destination bucket.
● If the client-side cross-region replication function is not enabled, ensure that
the source bucket and destination bucket are in the same region.
rst. Otherwise, the copy fails.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 49
Page 55

NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
– Copying a single object
obsutil cp obs://srcbucket/key obs://dstbucket/[dest] [-dryRun][-u] [-crr] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-versionId=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [ps=auto] [-cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Copying objects in batches
obsutil cp obs://srcbucket[/key] obs://dstbucket[/dest] -r [-dryRun][-f] [-at] [-u] [-crr] [vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2]
[-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
– Copying a single object
./obsutil cp obs://srcbucket/key obs://dstbucket/[dest] [-dryRun] [-u] [-crr] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-versionId=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [ps=auto] [-cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx]
– Copying objects in batches
./obsutil cp obs://srcbucket[/key] obs://dstbucket[/dest] -r [-dryRun] [-f] [-at] [-u] [-crr] [vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2]
[-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● The source path and destination path cannot be the same.
● The source path and destination path cannot be partly overlapped either. If the source
path overlaps with the prex of the destination path, recursive replication applies. If the
destination path overlaps with the prex of the source path, the replication may
overwrite objects in the source path.
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil cp obs://bucket-
test/key obs://bucket-test2 command to copy a single object.
obsutil cp obs://bucket-test/key obs://bucket-test2
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
[=====================================================] 100.00% 6/s 0s
Copy successfully, 19B, obs://bucket-test/key --> obs://bucket-test2/key
ext.txt
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil cp obs://bucket-test/
temp/ obs://bucket-test2 -f -r command to copy objects in batches.
obsutil cp obs://bucket-test/temp/ obs://bucket-test2 -r -f
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
OutputDir: xxxx
[=============================================================] 100.00% 10/s 0s
Succeed count is: 5 Failed count is: 0
Metrics [max cost:298 ms, min cost:192 ms, average cost:238.00 ms, average tps:9.71]
Task id is: 0476929d-9d23-4dc5-b2f8-0a0493f027c5
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 50
Page 56

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
● For more examples, see Copy.
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or
Description
Mandatory
srcbucket Mandatory Source bucket name
dstbucket Mandatory Destination bucket name
dest Optional Indicates the destination object name when
copying an object, or the name prex of
destination objects when copying objects in
batches.
key Mandatory
for copying
an object.
Optional for
copying
objects in
batches.
Indicates the source object name when copying an
object, or the name prex of source objects when
copying objects in batches.
The rules are as follows:
● This parameter cannot be left blank when
copying an object. If dest is left blank, the
source object is copied to the root directory of
the destination bucket. If the value of dest
ends with a slash (/), the destination object
name is the value of dest plus the source
object name. Otherwise, the destination object
name is the value of dest.
● If this parameter is left blank when copying
objects in batches, all objects in the source
bucket are copied. If not, objects whose name
prex is the set value in the source bucket are
copied. The rules for
conrming the name of
the destination object are as follows:
– If the value of dest ends with a slash (/),
the destination object name is the value of
dest plus the source object name.
– If the value of dest does not end with a
slash (/), the destination object name is
value of dest/source object name
NOTE
● If this parameter is
parameter is not when copying objects in batches,
the name of the source object contains the name
prex of the parent object. If at is congured, then
the name of the source object does not contain the
prex of the parent object.
name
● For details about how to use this parameter, see
Copy.
congured but the at
.
the
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 51
Page 57

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
fr Optional for
copying an
object
(additional
parameter)
at Optional for
copying
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
dryRun Optional
(additional
parameter)
crr Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Generates an operation result list when copying
an object.
The name prex of the parent object is excluded
when copying objects in batches.
Conducts a dry run.
Enables the client-side cross-region replication
function. In this mode, data is directly copied to
the destination bucket from the source bucket
through data stream. The buckets can by any two
OBS buckets.
NOTE
● If this parameter is congured, ensure that the
conguration of client-side cross-region replication is
updated in the conguration le. For details, see
Updating a Conguration File.
● The congurations of the source bucket and
destination bucket are respectively akCrr/skCrr/
tokenCrr/endpointCrr and ak/sk/token/endpoint in
the conguration le.
NOTICE
After this function is enabled, both upload and
download bandwidth are occupied.
vlength Optional
(additional
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 52
Veries whether the object size in the destination
bucket is the same as that in the source bucket
after the copy task completes.
NOTE
This parameter must be used together with crr.
Page 58

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
vmd5 Optional
(additional
parameter)
u Optional
(additional
parameter)
p Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Veries whether the MD5 value of the destination
bucket is the same as that of the source bucket
after the copy task completes.
NOTE
● This parameter must be used together with crr.
● Objects in the source bucket must contain metadata
x-obs-md5chksum. Otherwise, MD5
be skipped.
After the MD5 value verication is successful, the
parameter value is set to the destination object
metadata x-obs-md5chksum, which is used for later
MD5 verication during download or copy.
verication will
Indicates incremental copy. If this parameter is set,
each object can be copied only when it does not
exist in the destination bucket, its size is dierent
from the namesake one in the destination bucket,
or it has the latest modication time.
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
multipart copy tasks when copying an object. The
default value is the value of defaultParallels in
the conguration le.
threshold Optional
(additional
parameter)
versionId Optional for
copying an
object
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the threshold for enabling multipart
copy, in bytes. The default value is the value of
defaultBigleThreshold in the conguration le.
NOTE
● If the size of the object to be copied is smaller than
the threshold, copy the object directly. If not, a
multipart copy is required.
● If you copy an object directly, no part record is
generated, and resumable transmission is not
supported.
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For example,
1 MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
Source object version ID that can be specied
when copying an object
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 53
Page 59

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
acl Optional
(additional
parameter)
sc Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Access control policies for destination objects that
can be specied when copying objects. Possible
values are:
● private
● public-read
● public-read-write
● bucket-owner-full-control
NOTE
The preceding four values indicate private read and
write, public read, public read and write, and bucket
owner full control.
Storage classes of the destination objects that can
be specied when copying objects. Possible values
are:
● standard: OBS Standard, which features low
access latency and high throughput, and is
applicable to storing frequently accessed data
(multiple accesses per month) or data that is
smaller than 1 MB
● warm: OBS Infrequent Access. It is applicable
to storing infrequently accessed (less than 12
times a year) data that requires quick response.
● cold: OBS Archive. It is secure, durable, and
inexpensive, and applicable to archiving rarelyaccessed (once a year) data.
meta Optional
(additional
parameter)
ps Optional
(additional
parameter)
Metadata of destination objects that can be
specied when copying objects. The format is
key1:value1#key2:value2#key3:value3
NOTE
The preceding value indicates that the destination
objects in the bucket contain three groups of customized
metadata after objects are copied: key1:value1,
key2:value2, and key3:value3.
.
Indicates the size of each part in a multipart copy
task, in bytes. The value ranges from 100 KB to 5
GB. The default value is the value of
defaultPartSize in the conguration le.
NOTE
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For example,
1 MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
● The parameter can be set to auto. In this case,
obsutil automatically sets the part size for each
multipart task based on the source object size.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 54
Page 60

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
cpd Optional
(additional
parameter)
r Mandatory
for copying
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
f Optional for
copying
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the folder where the part records reside.
The default value is .obsutil_checkpoint, the
subfolder in the home directory of the user who
executes obsutil commands.
NOTE
A part record is generated during a multipart copy and
saved to the copy subfolder. After the copy succeeds, its
part record is deleted automatically. If the copy fails or is
suspended, the system attempts to resume the task
according to its part record when you perform the copy
the next time.
Copies objects in batches based on a specied
name prex of objects in the source bucket.
Runs in force mode.
j Optional for
copying
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
tasks for copying objects in batches. The default
value is the value of defaultJobs in the
conguration le.
NOTE
The value is ensured to be greater than or equal to 1.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 55
Page 61

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
exclude Optional for
copying
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the matching patterns of source objects
that are excluded, for example: *.txt.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of characters,
and the question mark (?) represents any single
character. For instance, abc*.txt indicates any le
whose name starts with abc and ends with .txt.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to represent ?.
● If the name of the object to be copied matches the
value of this parameter, the object is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the
matching pattern to prevent special characters from
being escaped by the OS and leading to unexpected
results. Use single quotation marks for Linux or
macOS and quotation marks for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute path of
an object, including the object name
object name starting from the root directory. For
example, if the path of an object in the bucket is
obs://bucket/src1/src2/test.txt, then the absolute
path of the object is src1/src2/test.txt.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
● Multiple exclude parameters can be
example, -exclude=*.xxx -exclude=*.xxx.
prex and
specied, for
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 56
Page 62

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
include Optional for
copying
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the matching patterns of source objects
that are included, for example: *.jpg.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of characters,
and the question mark (?) represents any single
character.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to represent ?.
● Only after identifying that the name of the
copied does not match the value of exclude, the
system checks whether the
value of this parameter. If yes, the
not, the le is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the
matching pattern to prevent special characters from
being escaped by the OS and leading to unexpected
results. Use single quotation marks for Linux or
macOS and quotation marks for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute path of
an object, including the object name
object name starting from the root directory. For
example, if the path of an object in the bucket is
obs://bucket/src1/src2/test.txt, then the absolute
path of the object is src1/src2/test.txt.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
● Multiple include parameters can be
example, -include=*.xxx -include=*.xxx.
le name matches the
le is copied. If
le to be
prex and
specied, for
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 57
Page 63

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
timeRange Optional for
copying
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the time range matching pattern when
copying objects. Only objects whose latest
modication time is within the congured time
range are copied.
This pattern has a lower priority than the object
matching patterns (exclude/include). That is, the
time range matching pattern is executed after the
congured object matching patterns.
NOTE
time1
● The matching time range is represented in
time2
, where
as
time2
● Automatic formatting is supported. For example,
yyyyMMdd is equivalent to yyyyMMdd000000, and
yyyyMM is equivalent to yyyyMM01000000.
● If this parameter is set to *-
latest modication time is earlier than
matched. If it is set to
modication time is later than
NOTICE
● Time in the matching pattern is the UTC time.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
time1
must be earlier than or the same
. The time format is
time1
yyyyMMddHHmmss
time2
, all les whose
time2
-*, all les whose latest
time1
are matched.
-
.
are
mf
Optional
(additional
parameter)
o Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates that the name matching pattern
(include or exclude) and the time matching
pattern (timeRange) also take eect on objects
whose names end with a slash (/).
Indicates the folder where operation result lists
reside. After the command is executed, result lists
(possibly including success, failure, and warning
les) are generated in the folder. The default
value is .obsutil_output, the subfolder in the
home directory of the user who executes obsutil
commands.
NOTE
● The naming rule for result lists is as follows:
cp_{succeed | failed |
time
warning}_report_
● By default, the maximum size of a single result list is
30 MB and the maximum number of result lists that
can be retained is 1024. You can set the maximum
size and number by
and recordBackups in the conguration le.
● If there are multiple folders and les and you need
conrm the detailed error information about a
to
failed task, refer to the failure list
cp_failed_report_
folder and the log les in the log path.
_TaskId.txt
conguring recordMaxLogSize
time
_TaskId.txt in the result list
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 58
Page 64

NO TICE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can
be congured, see Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
Response
Refer to Response for uploading an object.
5.7 Moving an Object
Function
You can use this command to move a single object or move objects in batches by
a
specied object name prex.
● Do not change the source objects in the OBS bucket when moving objects.
Otherwise, the operation may fail or data may be inconsistent.
● If the storage class of the object to be moved is cold, you must restore the
object
● The source objects are deleted after the move operation succeeds.
rst. Otherwise, the moving fails.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 59
Page 65

NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
– Moving a single object
obsutil mv obs://srcbucket/key obs://dstbucket/[dest] [-dryRun] [-u] [-p=1] [threshold=52428800] [-versionId=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto]
[-cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Moving objects in batches
obsutil mv obs://srcbucket[/key] obs://dstbucket[/dest] -r [-dryRun] [-f] [-at] [-u] [-j=1] [p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-
● In Linux OS or macOS
– Moving a single object
./obsutil mv obs://srcbucket/key obs://dstbucket/[dest] [-dryRun] [-u] [-p=1] [threshold=52428800] [-versionId=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto]
[-cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Moving objects in batches
./obsutil mv obs://srcbucket[/key] obs://dstbucket[/dest] -r [-dryRun] [-f] [-at] [-u] [-j=1] [p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● The source path and destination path cannot be the same.
● The source and destination paths cannot be nested when moving objects in batches.
[-
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil mv obs://bucket-
test/key obs://bucket-test2 command to move a single object.
obsutil mv obs://bucket-test/key obs://bucket-test2
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
[=====================================================] 100.00% 6/s 0s
Move successfully, 19B, obs://bucket-test/key --> obs://bucket-test2/key
ext.txt
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil mv obs://bucket-test/
temp/ obs://bucket-test2 -f -r command to move objects in batches.
obsutil mv obs://bucket-test/temp/ obs://bucket-test2 -f -r
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
OutputDir: xxxx
[=============================================================] 100.00% 10/s 0s
Succeed count is: 5 Failed count is: 0
Metrics [max cost:298 ms, min cost:192 ms, average cost:238.00 ms, average tps:9.71]
Task id is: 0476929d-9d23-4dc5-b2f8-0a0493f027c5
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 60
Page 66

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or
Description
Mandatory
srcbucket Mandatory Source bucket name
dstbucket Mandatory Destination bucket name
dest Optional Indicates the destination object name when
moving a single object, or the name prex of
destination objects when moving objects in
batches.
key Mandatory
for moving a
single object
Optional for
moving
objects in
batches
Indicates the source object name when moving a
single object, or the name prex of source objects
when moving objects in batches.
The rules are as follows:
● This parameter cannot be left blank when
moving a single object. If dest is left blank, the
source object is moved to the root directory of
the destination bucket. If the value of dest
ends with a slash (/), the destination object
name is the value of dest plus the source
object name. Otherwise, the destination object
name is the value of dest.
● If this parameter is left blank when moving
objects in batches, all objects in the source
bucket are moved. If not, objects whose name
prex is the set value in the source bucket are
moved. The rules for
conrming the name of
the destination object are as follows:
– If the value of dest ends with a slash (/),
the destination object name is the value of
dest plus the source object name.
– If the value of dest does not end with a
slash (/), the destination object name is
value of dest/source object name
NOTE
● If this parameter is
not when moving objects in batches, the name of the
source object contains the name prex of the parent
object. If at is congured, then the name of the
source object does not contain the name prex of
the parent object.
● For details about how to use this parameter, see
Command Line Structure.
congured but parameter at is
.
the
fr
Optional for
moving an
Generates an operation result list when moving an
object.
object
(additional
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 61
Page 67

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
at Optional for
moving
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
dryRun Optional
(additional
parameter)
u Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
The name prex of the parent object is excluded
when moving objects in batches.
Conducts a dry run.
Indicates incremental move. If this parameter is
set, each object can be moved only when it does
not exist in the destination bucket, its size is
dierent from the namesake one in the
destination bucket, or it has the latest
modication time.
NOTE
If the size and
object are the same as those of the source object, the
source object is directly deleted instead of being moved.
modication time of the destination
p Optional
(additional
parameter)
threshold Optional
(additional
parameter)
versionId Optional for
moving an
object
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
multipart move tasks when moving an object. The
default value is the value of defaultParallels in
the conguration le.
Indicates the threshold for enabling multipart
move, in bytes. The default value is the value of
defaultBigleThreshold in the conguration le.
NOTE
● If the size of the object to be moved is smaller than
the threshold, move the object directly. If not, a
multipart move is required.
● If you move an object directly, no part record is
generated, and resumable transmission is not
supported.
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For example,
1 MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
Source object version ID that can be specied
when moving a single object
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 62
Page 68

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
acl Optional
(additional
parameter)
sc Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Access control policies for destination objects that
can be specied when moving objects. Possible
values are:
● private
● public-read
● public-read-write
● bucket-owner-full-control
NOTE
The preceding four values indicate private read and
write, public read, public read and write, and bucket
owner full control.
Storage classes of the destination objects that can
be specied when moving objects. Possible values
are:
● standard: OBS Standard, which features low
access latency and high throughput, and is
applicable to storing frequently accessed data
(multiple accesses per month) or data that is
smaller than 1 MB
● warm: OBS Infrequent Access. It is applicable
to storing infrequently accessed (less than 12
times a year) data that requires quick response.
● cold: OBS Archive. It is secure, durable, and
inexpensive, and applicable to archiving rarelyaccessed (once a year) data.
meta Optional
(additional
parameter)
ps Optional
(additional
parameter)
Metadata of destination objects that can be
specied when copying objects. The format is
key1:value1#key2:value2#key3:value3
NOTE
The preceding value indicates that the destination
objects in the bucket contain three groups of customized
metadata after objects are copied: key1:value1,
key2:value2, and key3:value3.
.
Indicates the size of each part in a multipart move
task, in bytes. The value ranges from 100 KB to 5
GB. The default value is the value of
defaultPartSize in the conguration le.
NOTE
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For example,
1 MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
● The parameter can be set to auto. In this case,
obsutil automatically sets the part size for each
multipart task based on the source object size.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 63
Page 69

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
cpd Optional
(additional
parameter)
r Mandatory
for moving
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
f Optional for
moving
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the folder where the part records reside.
The default value is .obsutil_checkpoint, the
subfolder in the home directory of the user who
executes obsutil commands.
NOTE
A part record is generated during a multipart move and
saved to the copy subfolder. After the move succeeds, its
part record is deleted automatically. If the move fails or
is suspended, the system attempts to resume the task
according to its part record when you perform the move
the next time.
Moves objects in batches based on a specied
name prex of objects in the source bucket.
Runs in force mode.
j Optional for
moving
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
tasks for moving objects in batches. The default
value is the value of defaultJobs in the
conguration le.
NOTE
The value is ensured to be greater than or equal to 1.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 64
Page 70

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
exclude Optional for
moving
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the matching patterns of source objects
that are excluded, for example: *.txt.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of characters,
and the question mark (?) represents any single
character. For instance, abc*.txt indicates any le
whose name starts with abc and ends with .txt.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to represent ?.
● If the name of the object to be moved matches the
value of this parameter, the object is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the
matching pattern to prevent special characters from
being escaped by the OS and leading to unexpected
results. Use single quotation marks for Linux or
macOS and quotation marks for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute path of
an object, including the object name
object name starting from the root directory. For
example, if the path of an object in the bucket is
obs://bucket/src1/src2/test.txt, then the absolute
path of the object is src1/src2/test.txt.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
● Multiple exclude parameters can be
example, -exclude=*.xxx -exclude=*.xxx.
prex and
specied, for
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 65
Page 71

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
include Optional for
moving
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the matching patterns of source objects
that are included, for example: *.jpg.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of characters,
and the question mark (?) represents any single
character.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to represent ?.
● Only after identifying that the name of the
moved does not match the value of exclude, the
system checks whether the
value of this parameter. If yes, the
not, the le is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the
matching pattern to prevent special characters from
being escaped by the OS and leading to unexpected
results. Use single quotation marks for Linux or
macOS and quotation marks for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute path of
an object, including the object name
object name starting from the root directory. For
example, if the path of an object in the bucket is
obs://bucket/src1/src2/test.txt, then the absolute
path of the object is src1/src2/test.txt.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
● Multiple include parameters can be
example, -include=*.xxx -include=*.xxx.
le name matches the
le is moved. If
le to be
prex and
specied, for
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 66
Page 72

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
timeRange Optional for
moving
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the time range matching pattern when
moving objects. Only objects whose latest
modication time is within the congured time
range are moved.
This pattern has a lower priority than the object
matching patterns (exclude/include). That is, the
time range matching pattern is executed after the
congured object matching patterns.
NOTE
time1
● The matching time range is represented in
time2
, where
as
time2
● Automatic formatting is supported. For example,
yyyyMMdd is equivalent to yyyyMMdd000000, and
yyyyMM is equivalent to yyyyMM01000000.
● If this parameter is set to *-
latest modication time is earlier than
matched. If it is set to
modication time is later than
NOTICE
● Time in the matching pattern is the UTC time.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
time1
must be earlier than or the same
. The time format is
time1
yyyyMMddHHmmss
time2
, all les whose
time2
-*, all les whose latest
time1
are matched.
-
.
are
mf
Optional
(additional
parameter)
o Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates that the name matching pattern
(include or exclude) and the time matching
pattern (timeRange) also take eect on objects
whose names end with a slash (/).
Indicates the folder where operation result lists
reside. After the command is executed, result lists
(possibly including success, failure, and warning
les) are generated in the folder. The default
value is .obsutil_output, the subfolder in the
home directory of the user who executes obsutil
commands.
NOTE
● The naming rule for result lists is as follows:
mv_{succeed | failed |
time
warning}_report_
● By default, the maximum size of a single result list is
30 MB and the maximum number of result lists that
can be retained is 1024. You can set the maximum
size and number by
and recordBackups in the conguration le.
● If there are multiple folders and les and you need
conrm the detailed error information about a
to
failed task, refer to the failure list
mv_failed_report_
folder and the log les in the log path.
_TaskId.txt
conguring recordMaxLogSize
time
_TaskId.txt in the result list
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 67
Page 73

NO TICE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can
be congured, see Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
Response
Refer to Response for uploading an object.
5.8 Downloading an Object
Function
You can use this command to download an object or download objects in batches
by object name prex to your local PC.
● Do not change the source objects in the OBS bucket when downloading a
single object or objects in batches. Otherwise, the download may fail or data
may be inconsistent.
● If the storage class of the object to be copied is cold, you must restore the
object to be downloaded
rst. Otherwise, the download fails.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 68
Page 74

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
– Downloading a single object
obsutil cp obs://bucket/key le_or_folder_url [-tempFileDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-u] [-vlength] [vmd5] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-versionId=xxx] [-ps=auto] [-cpd=xxx][-fr] [-o=xxx] [-
cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Downloading objects in batches
obsutil cp obs://bucket[/key] folder_url -r [-tempFileDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-f] [-at] [-u] [vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-
● In Linux or macOS
– Downloading a single object
./obsutil cp obs://bucket/key le_or_folder_url [-tempFileDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-u] [-vlength] [vmd5] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-versionId=xxx] [-ps=auto] [-cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx]
cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-
– Downloading objects in batches
./obsutil cp obs://bucket[/key] folder_url -r [-tempFileDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-f] [-at] [-u] [vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil cp obs://bucket-
test/key d:\temp\test.txt command to download a single object.
obsutil cp obs://bucket-test/key d:\temp\test.txt
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
[==========================================] 100.00% 4.86 KB/s 0s
Download successfully, 19B, obs://bucket-test/key --> d:\temp\test.txt
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil cp obs://bucket-test/
temp d:\ -f -r command to download objects in batches.
obsutil cp obs://bucket-test/temp d:\ -f -r
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
OutputDir: xxxx
[======================================================] 100.00% 155.59 KB/s 0s
Succeed count is: 6 Failed count is: 0
Metrics [max cost:153 ms, min cost:129 ms, average cost:92.00 ms, average tps:17.86]
Task id is: 3066a4b0-4d21-4929-bb84-4829c32cbd0f
● For more examples, see Download.
Parameter Description
Parameter
le_or_fold
er_url
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 69
Optional or
Mandatory
Mandatory for
downloading an
object
Description
Local le/folder path
Page 75

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Description
Mandatory
folder_url Mandatory for
Local folder path
downloading
objects in batches
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 70
Page 76

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
key Mandatory for
downloading an
object
Optional for
downloading
objects in a batch
Description
Indicates the name of the object to be
downloaded, or the name prex of the
objects to be downloaded in batches.
This parameter cannot be left blank when
downloading an object. The saving and
naming rules are as follows:
● If this parameter
species a le or folder
path that does not exist, the tool checks
whether the value ends with a slash (/)
or backslash (\). If yes, a folder is created
based on the path, and the object is
downloaded to this newly created
directory.
● If this parameter
species a le or folder
path that does not exist and the value
does not end with a slash (/) or
backslash (\), the object is downloaded
to your local PC with the value of key as
le name.
the
● If this parameter species an existing le,
the object is downloaded to your local PC
overwriting the existing le, with the
value of key as the
le name.
● If this parameter species an existing
folder, the object is downloaded to the
directory
specied by le_or_folder_url
with the object name as the le name.
The saving rules when downloading objects
in batches are as follows:
● If this parameter is left blank, all objects
in the bucket are downloaded to the
directory
specied by folder_url.
● If this parameter is congured, objects
whose name
prex is the congured
value in the bucket are downloaded to
the directory
NOTE
● If this parameter is congured but the at
parameter is not congured when
downloading objects in a batch, the name of
the downloaded le contains the name prex
of the parent object. If at is congured, then
the name of the downloaded le does not
contain the name prex of the parent object.
● For details about how to use this parameter,
see Download.
specied by folder_url.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 71
Page 77

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
fr Optional for
downloading an
object (additional
parameter)
at Optional for
downloading
objects in batches
(additional
parameter)
tempFileDir Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Generates an operation result list when
downloading an object.
The name prex of the parent object is
excluded when downloading objects in
batches.
Indicates the directory for storing temporary
les during multipart download. The default
value is the value of defaultTempFileDir in
the conguration le.
NOTE
● If this parameter is left blank and the
defaultTempFileDir parameter in the
conguration le is also left blank, temporary
les generated during multipart download are
saved in the directory where to-bedownloaded
the sux of .obs.temp.
● Temporary les generated during multipart
download are stored in this directory.
Therefore, ensure that the user who executes
obsutil has the write permission on the path.
● The available space of the partition where the
path is located must be greater than the size
of the objects to be downloaded.
les are located and end with
dryRun Optional
Conducts a dry run.
(additional
parameter)
u Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates incremental download. If this
parameter is set, each object can be
downloaded only when it does not exist in
the local path, its size is dierent from the
namesake one in the local path, or it has
the latest
vlength Optional
(additional
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 72
Checks whether the sizes of the local les
are the same as those of the objects in the
bucket after the download is complete.
modication time.
Page 78
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
vmd5 Optional
(additional
parameter)
p Optional
(additional
parameter)
threshold Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Checks whether MD5 values of the local
les are the same as those of the objects in
the bucket after the download is complete.
NOTE
Objects in the bucket must contain metadata xobs-md5chksum. Otherwise, MD5 verication
will be skipped.
Indicates the maximum number of
concurrent multipart download tasks when
downloading an object. The default value is
the value of defaultParallels in the
conguration le.
Indicates the threshold for enabling
multipart download, in bytes. The default
value is the value of defaultBigleThres-
hold in the conguration le.
NOTE
● If the size of the object to be downloaded is
smaller than the threshold, download the
object directly. If not, a multipart download is
required.
● If you download an object directly, no part
record is generated, and resumable
transmission is not supported.
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For
example, 1 MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
versionId Optional for
downloading an
object (additional
parameter)
ps Optional
(additional
parameter)
Source object version ID that can be
specied when downloading an object
Indicates the size of each part in a multipart
download task, in bytes. The default value is
the value of defaultPartSize in the
conguration le.
NOTE
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For
example, 1 MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
● The parameter can be set to auto. In this
case, obsutil automatically sets the part size
for each multipart task based on the source
object size.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 73
Page 79

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
cpd Optional
(additional
parameter)
r Mandatory for
downloading
objects in batches
(additional
parameter)
f Optional for
downloading
objects in batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the folder where the part records
reside. The default value
is .obsutil_checkpoint, the subfolder in the
home directory of the user who executes
obsutil commands.
NOTE
A part record is generated during a multipart
download and saved to the down subfolder. After
the download succeeds, its part record is deleted
automatically. If the download fails or is
suspended, the system attempts to resume the
task according to its part record when you
perform the download the next time.
Copies objects in batches based on a
specied object name prex.
Runs in force mode.
j Optional for
downloading
objects in batches
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the maximum number of
concurrent tasks for downloading objects in
a batch. The default value is the value of
defaultJobs in the conguration le.
NOTE
The value is ensured to be greater than or equal
to 1.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 74
Page 80

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
exclude Optional for
downloading
objects in batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the matching patterns of source
objects that are excluded, for example: *.txt.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of
characters, and the question mark (?)
represents any single character. For instance,
abc*.txt indicates any
with abc and ends with .txt.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to
represent ?.
● If the name of the object to be downloaded
matches the value of this parameter, the
object is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for
the matching pattern to prevent special
characters from being escaped by the OS and
leading to unexpected results. Use single
quotation marks for Linux or macOS and
quotation marks for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute
path of an object, including the object name
prex and object name starting from the root
directory. For example, if the path of an object
in the bucket is obs://bucket/src1/src2/
test.txt, then the absolute path of the object
is src1/src2/test.txt.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects
whose names do not end with a slash (/).
● Multiple exclude parameters can be
for example, -exclude=*.xxx -exclude=*.xxx.
le whose name starts
specied,
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 75
Page 81

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
include Optional for
downloading
objects in batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the matching patterns of source
objects that are included, for example: *.jpg.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of
characters, and the question mark (?)
represents any single character.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to
represent ?.
● Only after identifying that the name of the
le to be downloaded does not match the
value of exclude, the system checks whether
le name matches the value of this
the
parameter. If yes, the le is downloaded. If
not, the le is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for
the matching pattern to prevent special
characters from being escaped by the OS and
leading to unexpected results. Use single
quotation marks for Linux or macOS and
quotation marks for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute
path of an object, including the object name
prex and object name starting from the root
directory. For example, if the path of an object
in the bucket is obs://bucket/src1/src2/
test.txt, then the absolute path of the object
is src1/src2/test.txt.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects
whose names do not end with a slash (/).
● Multiple include parameters can be
for example, -include=*.xxx -include=*.xxx.
specied,
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 76
Page 82

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
timeRange Optional for
downloading
objects in batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the time range matching pattern
when downloading objects. Only objects
whose latest modication time is within the
congured time range are downloaded.
This pattern has a lower priority than the
object matching patterns (exclude/include).
That is, the time range matching pattern is
executed after the
congured object
matching patterns.
NOTE
● The matching time range is represented in
time1-time2
than or the same as
yyyyMMddHHmmss
● Automatic formatting is supported. For
example, yyyyMMdd is equivalent to
yyyyMMdd000000, and yyyyMM is equivalent
to yyyyMM01000000.
● If this parameter is set to *-
whose latest modication time is earlier than
time2
les whose latest modication time is later
than
NOTICE
● Time in the matching pattern is the UTC time.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects
whose names do not end with a slash (/).
, where
are matched. If it is set to
time1
are matched.
time1
must be earlier
time2
. The time format is
.
time2
, all les
time1
-*, all
mf
Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates that the name matching pattern
(include or exclude) and the time matching
pattern (timeRange) also take eect on
objects whose names end with a slash (/).
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 77
Page 83

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
o Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the folder where operation result
lists reside. After the command is executed,
result lists (possibly including success,
failure, and warning les) are generated in
the folder. The default value
is .obsutil_output, the subfolder in the
home directory of the user who executes
obsutil commands.
NOTE
● The naming rule for result lists is as follows:
cp_{succeed | failed |
time
warning}_report_
● By default, the maximum size of a single
result list is 30 MB and the maximum number
of result lists that can be retained is 1024. You
can set the maximum size and number by
conguring recordMaxLogSize and
recordBackups in the conguration le.
● If there are multiple folders and les and you
need to conrm the detailed error
information about a failed task, refer to the
failure list cp_failed_report_
in the result list folder and the log les in the
log path.
_TaskId.txt
time
_TaskId.txt
cong
Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
User-dened conguration le for executing
a command. For details about parameters
that can be congured, see Parameter
Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 78
Page 84

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Response
Refer to Response for uploading an object.
5.9 Generating the Download Link of an Object
Function
You can use this command to generate the download link of a specied object in a
bucket or generate the download links of objects in a bucket in batches by object
name
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
prex.
– Generating the download link of a single object
obsutil sign obs://bucket/key [-e=300] [-cong=xxx] [-endpoint=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Generating the download links of objects in batches by object name
prex
obsutil sign obs://bucket[/key] -r [-e=300] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-include=*.xxx] [exclude=*.xxx] [-o=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-endpoint=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
– Generating the download link of a single object
./obsutil sign obs://bucket/key [-e=300] [-cong=xxx] [-endpoint=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Generating the download links of objects in batches by object name
prex
./obsutil sign obs://bucket[/key] -r [-e=300] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-include=*.xxx] [exclude=*.xxx] [-o=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-endpoint=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil sign obs://buckettest/test.txt command to generate the download link of a single object.
obsutil sign obs://bucket-test/test.txt
Download url of [obs://bucket-test/test.txt] is:
http://your-endpoint/bucket-test/test.txt?AccessKeyId=xxxx&Expires=1552548758&Signature=xxxx
Parameter Description
Parame
ter
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
key Optional Object name used for generating the download link of
Optional or
Mandatory
Description
a single object, or object name prex used for
generating download links of objects in batches
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 79
Validity period of the generated download links of
objects, in seconds. Minimum value: 60s. Default
value: 300s
Page 85

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parame
ter
Optional or
Mandatory
r Mandatory
when
generating
download
links of
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
exclude Optional
when
generating
download
links of
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Generates the download links of objects in batches by
a specied object name prex.
Indicates the matching patterns of objects that are
excluded, for example: *.txt.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of characters, and
the question mark (?) represents any single character. For
instance, abc*.txt indicates any le whose name starts
with abc and ends with .txt.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to represent ?.
● If the name of the object to be downloaded matches the
value of this parameter, the object is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the matching
pattern to prevent special characters from being escaped
by the OS and leading to unexpected results. Use single
quotation marks for Linux or macOS and quotation marks
for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute path of an
object, including the object name prex and object name
starting from the root directory. For example, if the path
of an object in the bucket is obs://bucket/src1/src2/
test.txt, then the absolute path of the object is src1/src2/
test.txt.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
● Multiple exclude parameters can be
example, -exclude=*.xxx -exclude=*.xxx.
specied, for
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 80
Page 86

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parame
ter
Optional or
Mandatory
include Optional
when
generating
download
links of
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the matching patterns of objects that are
included, for example: *.jpg.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of characters, and
the question mark (?) represents any single character.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to represent ?.
● Only after identifying that the name of the
downloaded does not match the value of exclude, the
system checks whether the le name matches the value
of this parameter. If yes, the
le is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the matching
pattern to prevent special characters from being escaped
by the OS and leading to unexpected results. Use single
quotation marks for Linux or macOS and quotation marks
for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute path of an
object, including the object name
starting from the root directory. For example, if the path
of an object in the bucket is obs://bucket/src1/src2/
test.txt, then the absolute path of the object is src1/src2/
test.txt.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
● Multiple include parameters can be
example, -include=*.xxx -include=*.xxx.
le is downloaded. If not, the
prex and object name
le to be
specied, for
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 81
Page 87
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parame
ter
Optional or
Mandatory
timeRangeOptional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the time range matching pattern when
generating download links of objects. Only the
download links of objects whose latest modication
time is within the congured time range are
generated.
This pattern has a lower priority than the object
matching patterns (exclude/include). That is, the time
range matching pattern is executed after the
congured object matching patterns.
NOTE
● Time in the matching pattern is the UTC time.
● This matching pattern applies only to objects whose
names do not end with a slash (/).
● The matching time range is represented in
where
time1
must be earlier than or the same as
The time format is
● Automatic formatting is supported. For example,
yyyyMMdd is equivalent to yyyyMMdd000000, and
yyyyMM is equivalent to yyyyMM01000000.
● If this parameter is set to *-
modication time is earlier than
is set to
later than
time1
time1
yyyyMMddHHmmss
time2
, all les whose latest
time2
-*, all les whose latest modication time is
are matched.
time1-time2
.
are matched. If it
time2
,
.
o
Optional
when
generating
download
links of
objects in
batches
(additional
parameter)
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
endpointOptional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the folder where operation result lists reside.
After the command is executed, result lists (possibly
including success and failure les) are generated in
the folder. The default value is .obsutil_output, the
subfolder in the home directory of the user who
executes obsutil commands.
NOTE
● The naming rule for result lists is as follows:
sign_{succeed | failed}_report_
By default, the maximum size of a single result list is 30
MB and the maximum number of result lists that can be
retained is 1024. You can set the maximum size and
number by conguring recordMaxLogSize and
recordBackups in the conguration le.
time
_TaskId.txt
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can be
congured, see Parameter Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 82
Page 88

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parame
ter
Optional or
Mandatory
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
5.10 Deleting an Object
Function
● You can use this command to delete a
● You can also use this command to delete objects in batches based on a
specied object name prex.
Description
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a bucket.
specied object.
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
– Deleting a single object
obsutil rm obs://bucket/key [-f] [-versionId=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Deleting objects in batches
obsutil rm obs://bucket/[key] -r [-j=1] [-f] [-v] [-o=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx]
[-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
– Deleting a single object
./obsutil rm obs://bucket/key [-f] [-versionId=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx]
[-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
– Deleting objects in batches
./obsutil rm obs://bucket/[key] -r [-j=1] [-f] [-v] [-o=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil rm obs://buckettest/key -f command to delete a single object named key in bucket buckettest.
obsutil rm obs://bucket-test/key -f
Delete object [key] in the bucket [bucket-test] successfully!
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil rm obs://bucket-test -
r -f command to delete all objects in bucket bucket-test.
obsutil rm obs://bucket-test -r -f
[===============================================] 100.00% 21s
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 83
Page 89

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Succeed count is: 1313 Failed count is: 0
Task id is: 95936984-f81a-441a-bba0-1fd8254d9241
Parameter Description
Parameter Optional or
Description
Mandatory
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
key Mandatory for
deleting a single
object.
Optional for
deleting objects in
batches.
fr Optional for
deleting a single
Indicates the name of the object to be
deleted, or the name prex of the objects to
be deleted in batches.
NOTE
If this parameter is left blank when deleting
objects in batches, all objects in the bucket are
deleted.
Generates an operation result list when
deleting an object.
object (additional
parameter)
f Optional
Runs in force mode.
(additional
parameter)
versionId Optional for
Version ID of the object to be deleted.
deleting a single
object (additional
parameter)
r Mandatory for
deleting objects in
batches (additional
parameter)
j Optional for
deleting objects in
batches (additional
parameter)
v Optional for
deleting objects in
batches (additional
parameter)
Deletes objects in batches based on a
specied object name prex.
Indicates the maximum number of
concurrent tasks for deleting objects in
batches. The default value is the value of
defaultJobs in the conguration le.
NOTE
The value is ensured to be greater than or equal to
1.
Deletes versions of an object and the delete
markers in batches based on a specied
object name prex.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 84
Page 90

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Parameter Optional or
Mandatory
o Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the folder where operation result
lists reside. After the command is executed,
result lists (possibly including success and
failure les) are generated in the folder. The
default value is .obsutil_output, the
subfolder in the home directory of the user
who executes obsutil commands.
NOTE
● The naming rule for result lists is as follows:
time
rm_{succeed | failed}_report_
● By default, the maximum size of a single result
list is 30 MB and the maximum number of
result lists that can be retained is 1024. You can
set the maximum size and number by
conguring recordMaxLogSize and
recordBackups in the conguration le.
● If there are multiple folders and les and you
need to
about a failed task, refer to the failure list
rm_failed_report_
list folder and the log les in the log path.
conrm the detailed error information
time
_TaskId.txt in the result
_TaskId.txt
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
payer Optional
(additional
parameter)
User-dened conguration le for executing
a command. For details about parameters
that can be congured, see Parameter
Description.
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
Species that requester-pays is enabled on a
bucket.
Response
Refer to Response for uploading an object.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 85
Page 91

NO TICE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
5.11 Synchronously Uploading Incremental Objects
Function
This function synchronizes all content in the local source path to the specied
target bucket on OBS, ensuring that the content is consistent between the local
path and the target bucket. Incremental synchronization has the following
meanings: 1) Increment: Compare the source le with the target object and
upload only the source
command is executed, ensure that the local source path is a subset of the target
bucket
specied by OBS. That is, any le in the local source path has its
corresponding object in the target bucket on OBS.
● Do not change the local le or folder during synchronization. Otherwise, the
synchronization may fail or data may be inconsistent.
● Each le can be synchronously uploaded only when it does not exist in the
bucket, its size is dierent from the namesake one in the bucket, or it has the
modication time.
latest
le that has changes. 2) Synchronization: After the
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
– Uploading a
obsutil sync le_url obs://bucket[/key] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-p=1]
[-threshold=5248800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-o=xxx] [cpd=xxx] [-fr]
– Uploading a folder synchronously
obsutil sync folder_url obs://bucket[/key] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-at] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
– Uploading a
./obsutil sync le_url obs://bucket[/key] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [p=1] [-threshold=5248800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-o=xxx] [cpd=xxx] [-fr]
– Uploading a folder synchronously
./obsutil sync folder_url obs://bucket[/key] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-at] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil sync d:\temp\test.txt
obs://bucket-test/key command to synchronously upload a
obsutil sync d:\temp\test.txt obs://bucket-test/key
le synchronously
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-
le synchronously
[-cong=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
[-
le.
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 86
Page 92

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
[====================================================] 100.00% 1.68 MB/s 5s
Upload successfully, 8.46MB, d:\temp\test.txt --> obs://bucket-test/key
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil sync d:\temp obs://
bucket-test/temp command to synchronously upload a folder.
obsutil sync d:\temp obs://bucket-test/temp
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
OutputDir: xxxx
[========================================================] 100.00% 2.02 KB/s 0s
Succeed count is: 5 Failed count is: 0
Metrics [max cost:90 ms, min cost:45 ms, average cost:63.80 ms, average tps:35.71]
Task id is: 104786c8-27c2-48fc-bc6a-5886596fb0ed
● For more examples, see Synchronous Upload.
Parameter Description
ParameterOptional or
Description
Mandatory
le_url Mandatory
Local le path
for uploading
a le
synchronousl
y
folder_url Mandatory
Local folder path
for uploading
a folder
synchronousl
y
bucket Mandatory Bucket name
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 87
Page 93

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
ParameterOptional or
Description
Mandatory
key Optional Indicates the object name or object name prex
specied when uploading a le synchronously, or
the object name prex specied when uploading a
folder synchronously.
The rules are as follows:
● If this parameter is left blank when
synchronously uploading a
le, the le is
uploaded to the root directory of the bucket and
the object name is the
le name. If the value
ends with a slash (/), the value is used as the
object name
prex when the le is uploaded,
and the object name is the value plus the le
name. Otherwise, the le is uploaded with the
value as the object name.
● If this parameter is left blank when
synchronously uploading a folder, all objects in
the root directory of the bucket are the same as
les in the local folder. If this parameter is
the
congured, objects whose name prex is the
congured value are the same as the les in the
local folder.
NOTE
● If the value of this parameter does not end with a
slash (/) when synchronously uploading a folder, the
obsutil tool automatically adds a slash (/) at the end
congured value as the object name prex.
of the
● For details about how to use this parameter, see
Synchronous Upload.
fr
Optional for
synchronousl
Generates an operation result list when
synchronously uploading a le.
y uploading a
le
(additional
parameter)
arcDir Optional
(additional
Path to which the synchronously uploaded les are
archived
parameter)
dryRun Optional
Conducts a dry run.
(additional
parameter)
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 88
Page 94

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
ParameterOptional or
Mandatory
link Optional
(additional
parameter)
vlength Optional
(additional
parameter)
vmd5 Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Uploads the actual path of the symbolic-link le/
folder
NOTICE
● If this parameter is not specied and the le to be
uploaded is a symbolic-link le whose target le does
not exist, the exception message "The system cannot
nd the le specied" will be displayed in Windows
OS, while the exception message "No such le or
directory" will be displayed in macOS or Linux OS.
● Avoid the symbolic link loop of a folder, otherwise, the
upload will exit due to panic. If you do not want the
system to panic, set panicForSymbolicLinkCircle to
false in the
conguration le.
After the synchronous upload is complete, check
whether the sizes of the objects in the bucket are
the same as those of the local les.
After the synchronous upload is complete, check
whether the MD5 values of the objects in the
bucket are the same as those of the local les.
NOTE
● If the size of the le or folder to be uploaded is too
large, using this parameter will degrade the overall
performance due to MD5 calculation.
● After the MD5 value
parameter value is set to the object metadata x-obs-
md5chksum, which is used for later MD5 verication
during download or copy.
verication is successful, the
p Optional
(additional
parameter)
threshold Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
multipart upload tasks when uploading a le. The
default value is the value of defaultParallels in the
conguration le.
Indicates the threshold for enabling multipart
upload, in bytes. The default value is the value of
defaultBigleThreshold in the conguration le.
NOTE
● If the size of the le or folder to be uploaded is
smaller than the threshold, upload it directly.
Otherwise, a multipart upload is required.
● If you upload a
generated, and resumable transmission is not
supported.
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For example, 1
MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
le or folder directly, no part record is
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 89
Page 95

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
ParameterOptional or
Mandatory
acl Optional
(additional
parameter)
sc Optional
(additional
parameter)
Description
Access control policies that can be specied when
synchronously uploading les. Possible values are:
● private
● public-read
● public-read-write
● bucket-owner-full-control
NOTE
The preceding four values indicate private read and write,
public read, public read and write, and bucket owner full
control.
Indicates the storage classes of objects that can be
specied when synchronously uploading les.
Possible values are:
● standard: OBS Standard, which features low
access latency and high throughput, and is
applicable to storing frequently accessed data
(multiple accesses per month) or data that is
smaller than 1 MB
● warm: OBS Infrequent Access. It is applicable to
storing infrequently accessed (less than 12 times
a year) data that requires quick response.
● cold: OBS Archive. It is secure, durable, and
inexpensive, and applicable to archiving rarelyaccessed (once a year) data.
meta Optional
(additional
parameter)
ps Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates the customized metadata that can be
specied when uploading les. The format is
key1:value1#key2:value2#key3:value3.
NOTE
The preceding value indicates that the object in the
bucket contains three groups of customized metadata
after the
key3:value3.
le is uploaded: key1:value1, key2:value2, and
Indicates the size of each part in a multipart
upload task, in bytes. The value ranges from 100
KB to 5 GB. The default value is the value of
defaultPartSize in the conguration le.
NOTE
● This value can contain a capacity unit. For example, 1
MB indicates 1048576 bytes.
● The parameter can be set to auto. In this case, obsutil
automatically sets the part size for each multipart
task based on the source
le size.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 90
Page 96

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
ParameterOptional or
Mandatory
cpd Optional
(additional
parameter)
j Optional for
synchronousl
y uploading a
folder
(additional
parameter)
exclude Optional for
synchronousl
y uploading a
folder
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the folder where the part records reside.
The default value is .obsutil_checkpoint, the
subfolder in the home directory of the user who
executes obsutil commands.
NOTE
A part record is generated during a multipart upload and
saved to the upload subfolder. After the upload succeeds,
its part record is deleted automatically. If the upload fails
or is suspended, the system attempts to resume the task
according to its part record when you perform the upload
the next time.
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent
tasks for uploading a folder synchronously. The
default value is the value of defaultJobs in the
conguration le.
NOTE
The value is ensured to be greater than or equal to 1.
Indicates the le matching patterns that are
excluded, for example: *.txt.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of characters,
and the question mark (?) represents any single
character. For instance, abc*.txt indicates any le
whose name starts with abc and ends with .txt.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to represent ?.
● If the name of the le to be uploaded matches the
value of this parameter, the
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the
matching pattern to prevent special characters from
being escaped by the OS and leading to unexpected
results. Use single quotation marks for Linux or
macOS and quotation marks for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute
(including the le name and le directory).
● The matching pattern takes eect only for les in the
folder.
● Multiple exclude parameters can be specied, for
example, -exclude=*.xxx -exclude=*.xxx.
le is skipped.
le path
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 91
Page 97

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
ParameterOptional or
Mandatory
include Optional for
synchronousl
y uploading a
folder
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the le matching patterns that are
included, for example: *.jpg.
NOTE
● The asterisk (*) represents any group of characters,
and the question mark (?) represents any single
character.
● You can use \* to represent * and \? to represent ?.
● Only after identifying that the name of the
uploaded does not match the value of exclude, the
system checks whether the
value of this parameter. If yes, the
not, the le is skipped.
NOTICE
● You are advised to use quotation marks for the
matching pattern to prevent special characters from
being escaped by the OS and leading to unexpected
results. Use single quotation marks for Linux or
macOS and quotation marks for Windows.
● The matching pattern applies to the absolute
(including the le name and le directory).
● The matching pattern takes eect only for les in the
folder.
● Multiple include parameters can be
example, -include=*.xxx -include=*.xxx.
le name matches the
le is uploaded. If
le to be
le path
specied, for
at
disableDir
Object
Optional for
synchronousl
y uploading a
folder
(additional
parameter)
Optional for
synchronousl
y uploading
folders
(additional
parameter)
Indicates that when synchronously uploading a
folder, only the les whose latest access time is
within the value of timeRange are uploaded.
NOTE
● This parameter must be used together with
timeRange.
Indicates the folders themselves are not uploaded
as an object. Conguring this parameter can avoid
uploading empty folders to a bucket. If a folder
contains les, the les will be uploaded and the
original path format is retained.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 92
Page 98

Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
ParameterOptional or
Mandatory
timeRangeOptional for
synchronousl
y uploading a
folder
(additional
parameter)
Description
Indicates the time range matching pattern when
synchronously uploading les. Only les whose
latest modication time is within the congured
time range are uploaded.
This pattern has a lower priority than the le
matching patterns (exclude/include). That is, the
time range matching pattern is executed after the
congured le matching patterns.
NOTE
time1
● The matching time range is represented in
time2
, where
as
time2
● Automatic formatting is supported. For example,
yyyyMMdd is equivalent to yyyyMMdd000000, and
yyyyMM is equivalent to yyyyMM01000000.
● If this parameter is set to *-
latest modication time is earlier than
matched. If it is set to
modication time is later than
NOTICE
Time in the matching pattern is the UTC time.
time1
must be earlier than or the same
. The time format is
time1
yyyyMMddHHmmss
time2
, all les whose
time2
-*, all les whose latest
time1
are matched.
-
.
are
mf Optional
(additional
parameter)
o Optional
(additional
parameter)
Indicates that the name matching pattern (include
or exclude) and the time matching pattern
(timeRange) also take eect on folders.
Indicates the folder where operation result lists
reside. After the command is executed, result lists
(possibly including success, failure, and warning
les) are generated in the folder. The default value
is .obsutil_output, the subfolder in the home
directory of the user who executes obsutil
commands.
NOTE
● The naming rule for result lists is as follows:
sync_{succeed | failed |
time
warning}_report_
● By default, the maximum size of a single result list is
30 MB and the maximum number of result lists that
can be retained is 1024. You can set the maximum
size and number by
and recordBackups in the conguration le.
● If there are multiple folders and les and you need to
conrm the detailed error information about a failed
task, refer to the failure list
sync_failed_report_
folder and the log les in the log path.
_TaskId.txt
conguring recordMaxLogSize
time
_TaskId.txt in the result list
cong Optional
(additional
parameter)
User-dened conguration le for executing a
command. For details about parameters that can
be congured, see Parameter Description.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 93
Page 99

NO TICE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Response
ParameterOptional or
Mandatory
e Optional
(additional
parameter)
i Optional
(additional
parameter)
k Optional
(additional
parameter)
t Optional
(additional
parameter)
Refer to Response for uploading an object.
Description
Species the endpoint.
Species the user's AK.
Species the user's SK.
Species the user's security token.
5.12 Synchronously Copying Incremental Objects
Function
This function synchronizes all objects in the
with objects in the specied path in the destination bucket to keep data
consistency. Incremental synchronization has the following meanings: 1)
Increment: Compare the source object with the target object and copy only the
source object that has changes. 2) Synchronization: After the command is
executed, ensure that the
target bucket. That is, any object in the
corresponding object in the target bucket.
● Do not change the source objects in the OBS bucket during synchronization.
Otherwise, the synchronization may fail or data may be inconsistent.
● If the storage class of the object to be copied is cold, you must restore the
object to be copied rst. Otherwise, the copy fails.
● To copy objects, you must have the read permission on the objects to be copied
and the write permission on the destination bucket.
● If the client-side cross-region replication function is not enabled, ensure that
the source bucket and destination bucket are in the same region.
● Each object can be synchronously copied only when it does not exist in the
destination bucket, its size is
destination bucket, or it has the latest modication time.
specied path of the source bucket is a subset of the
dierent from the namesake one in the
specied path in the source bucket
specied path of the source bucket has its
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 94
Page 100

NO TE
Object Storage Service
Tool Guide (obsutil) 5 Object Commands
Command Line Structure
● In Windows
obsutil sync obs://srcbucket[/key] obs://dstbucket[/dest] [-dryRun] [-crr] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx] [-cong=xxx] [e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
● In Linux or macOS
./obsutil sync obs://srcbucket[/key] obs://dstbucket[/dest] [-dryRun] [-crr] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx]
e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
The source path and destination path cannot be the same or nested when synchronously
copying objects.
[-cong=xxx] [-
Examples
● Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil sync obs://bucket-
test/temp/ obs://bucket-test2 /temp/ command to synchronously copy
objects.
obsutil sync obs://bucket-test/temp/ obs://bucket-test2/temp
Parallel: 3 Jobs: 3
Threshold: 524288000 PartSize: 5242880
Exclude: Include:
VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false
CheckpointDir: xxxx
OutputDir: xxxx
[=============================================================] 100.00% 10/s 0s
Succeed count is: 5 Failed count is: 0
Metrics [max cost:298 ms, min cost:192 ms, average cost:238.00 ms, average tps:9.71]
Task id is: 0476929d-9d23-4dc5-b2f8-0a0493f027c5
● For more examples, see Synchronous Copy.
Parameter Description
Parameter
srcbucket Mandatory Source bucket name
dstbucket Mandatory Destination bucket name
dest Optional Name prex of destination objects.
Optional or
Mandatory
Description
NOTE
If the value of this parameter does not end with a
slash (/), the obsutil tool automatically adds a
slash (/) at the end of the congured value as the
name prex of destination objects.
Issue 16 (2021-03-22) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 95
 Loading...
Loading...