Huawei OceanStor 2000 V3, OceanStor 5500 V3, OceanStor 6000 V3, OceanStor 5600 V3, OceanStor 6800 V3 Features Manual
...Page 1

OceanStor V3 Series
V300R006
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Issue 05
Date 2018-01-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2018. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://e.huawei.com
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Page 3
DANGER
WARNING
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Purpose
This document describes the working principle and application scenarios of the HyperMetro
feature. It also explains how to configure and manage the feature.
The following table lists the product models applicable to this document.
About This Document
About This Document
Product Series
OceanStor 2000 V3 series OceanStor 2600 V3
OceanStor 5000 V3 series OceanStor 5300 V3, 5500 V3, 5600 V3, and
OceanStor 6000 V3 series OceanStor 6800 V3
OceanStor 18000 V3 series OceanStor 18500 V3 and 18800 V3
Intended Audience
This document is intended for:
l Technical support engineers
l Maintenance engineers
Symbol Conventions
Product Model
5800 V3
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Symbol
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Description
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
ii
Page 4

NOTE
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Symbol Description
About This Document
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, could result in equipment damage, data loss,
performance deterioration, or unanticipated results.
NOTICE is used to address practices not related to
personal injury.
Calls attention to important information, best practices and
tips.
NOTE is used to address information not related to
personal injury, equipment damage, and environment
deterioration.
Change History
Changes between document issues are cumulative. The latest document issue contains all the
changes in earlier issues.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30)
This is the fifth official release.
Optimized descriptions about section Impact and Restrictions.
Added the following FAQ: How Can I Use OVA Templates to Quickly Deploy Virtual
Quorum Servers?
Issue 04 (2017-11-30)
This is the fourth official release.
Added the description about arbitration mechanism or configuration operations when
configuring two quorum servers.
Issue 03 (2017-08-30)
This is the third official release.
Synchronizes some software interface changes.
Issue 02 (2017-06-01)
This is the second official release.
Optimized descriptions about section Impact and Restrictions.
Synchronizes some software interface changes.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
Page 5

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Issue 01 (2017-11-30)
This issue is the first official release.
About This Document
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv
Page 6

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block Contents
Contents
About This Document.....................................................................................................................ii
1 Feature Description....................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Overview........................................................................................................................................................................ 1
1.2 License Requirements and Compatible Products........................................................................................................... 2
1.3 Working Principle........................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.3.1 Basic Concepts............................................................................................................................................................ 3
1.3.2 HyperMetro Solution Overview.................................................................................................................................. 5
1.3.3 Arbitration Mechanism................................................................................................................................................9
1.3.4 HyperMetro I/O Processing Mechanism................................................................................................................... 17
1.3.5 Functions of a HyperMetro Consistency Group........................................................................................................19
1.4 Impact and Restrictions................................................................................................................................................ 22
1.5 Application Scenarios...................................................................................................................................................24
2 Planning........................................................................................................................................ 27
3 Installation.................................................................................................................................... 28
3.1 Installation Process....................................................................................................................................................... 29
3.2 Preparations for Installation..........................................................................................................................................29
3.2.1 Preparing Tools, Meters, and Documentation........................................................................................................... 30
3.2.2 Quick checklist for the installation environment.......................................................................................................32
3.3 Device Installation........................................................................................................................................................38
3.4 Cable Connection......................................................................................................................................................... 41
3.5 Power-on.......................................................................................................................................................................46
3.6 Storage Array Initialization.......................................................................................................................................... 49
3.7 Multipathing Software Installation...............................................................................................................................49
3.7.1 UltraPath Software Installation................................................................................................................................. 49
3.7.2 Third-party Multipathing Software Installation........................................................................................................ 49
3.8 Arbitration Software Installation.................................................................................................................................. 50
4 Configuration............................................................................................................................... 53
4.1 Configuration Process...................................................................................................................................................54
4.2 Configuration Preparations...........................................................................................................................................56
4.3 Configuring Switch.......................................................................................................................................................57
4.4 Configure Quorum Server Software.............................................................................................................................57
4.4.1 Configuring the Arbitration Software (SUSE).......................................................................................................... 57
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
v
Page 7

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block Contents
4.4.2 Configuring the Arbitration Software (Red Hat/Red Flag/NeoKylin/CentOS)........................................................ 62
4.4.3 Configuring the Arbitration Software (Ubuntu)........................................................................................................68
4.5 Configuring Basic Storage Services............................................................................................................................. 73
4.6 Creating SAN HyperMetro...........................................................................................................................................74
4.6.1 Checking the License File......................................................................................................................................... 75
4.6.2 Adding a Remote Device...........................................................................................................................................76
4.6.3 Creating a Quorum Server.........................................................................................................................................79
4.6.4 Creating a HyperMetro Domain................................................................................................................................ 81
4.6.5 Creating a HyperMetro Pair...................................................................................................................................... 82
4.6.6 Creating a HyperMetro Consistency Group.............................................................................................................. 88
4.7 Configure a Multipathing Policy for Host....................................................................................................................91
4.7.1 Configuring a UltraPath Policy for Host................................................................................................................... 92
4.7.2 (Optional) Configuring a Third-party Multipathing Policy for Host........................................................................ 97
4.8 Verifying the Configuration........................................................................................................................................100
5 Management............................................................................................................................... 101
5.1 Managing a HyperMetro Pair..................................................................................................................................... 101
5.1.1 Viewing HyperMetro Pair Information................................................................................................................... 102
5.1.2 Modifying HyperMetro Pair Properties...................................................................................................................107
5.1.3 Synchronizing a HyperMetro Pair...........................................................................................................................109
5.1.4 Suspending a HyperMetro Pair................................................................................................................................110
5.1.5 Switching the Preferred Site for a HyperMetro.......................................................................................................110
5.1.6 Forcibly Enabling a HyperMetro Pair......................................................................................................................111
5.1.7 Deleting a HyperMetro Pair.....................................................................................................................................112
5.1.8 Expanding the Capacity of a HyperMetro LUN......................................................................................................113
5.2 Managing HyperMetro Domains................................................................................................................................114
5.2.1 Viewing HyperMetro Domain Information.............................................................................................................115
5.2.2 Modifying a HyperMetro Domain...........................................................................................................................115
5.2.3 Deleting a HyperMetro Domain.............................................................................................................................. 116
5.3 Managing Quorum Servers.........................................................................................................................................117
5.3.1 Viewing Quorum Server Information......................................................................................................................117
5.3.2 Modifying Quorum Server Information.................................................................................................................. 118
5.3.3 Adding a Link.......................................................................................................................................................... 118
5.3.4 Removing a Link..................................................................................................................................................... 119
5.3.5 Removing a Quorum Server.................................................................................................................................... 119
5.3.6 Uninstalling the Arbitration Software..................................................................................................................... 120
5.4 Managing a HyperMetro Consistency Group.............................................................................................................121
5.4.1 Viewing the HyperMetro Consistency Group Information.....................................................................................121
5.4.2 Modifying the Properties of a HyperMetro Consistency Group............................................................................. 124
5.4.3 Synchronizing a HyperMetro Consistency Group...................................................................................................127
5.4.4 Pausing a HyperMetro Consistency Group............................................................................................................. 128
5.4.5 Switching the Prior/Non-prior for a HyperMetro Consistency Group.................................................................... 128
5.4.6 Starting a HyperMetro Consistency Group Forcibly...............................................................................................129
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vi
Page 8

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block Contents
5.4.7 Adding a HyperMetro Pair...................................................................................................................................... 130
5.4.8 Remove HyperMetro Pair........................................................................................................................................130
5.4.9 Deleting a HyperMetro Consistency Group............................................................................................................ 131
5.5 Importing Certificates.................................................................................................................................................132
6 FAQs.............................................................................................................................................135
6.1 What Can I Do If a Quorum Link Fails to Be Added Because the HyperMetro Arbitration Certificate Becomes
Invalid or the System Time Becomes Abnormal?............................................................................................................136
6.2 Active and Standby IP Ports Are Configured on the Quorum Server. After the Port in Use Is Down, the Quorum
Server Goes Offline. Why?...............................................................................................................................................137
6.3 How Do I Power Off Active-Active Storage Systems and Resume the HyperMetro Service?................................. 138
6.4 When Both the HyperMetro and Remote Backup Services Are Created, the Excessively Low Link Bandwidth
Between Storage Systems Causes the Remote Backup Service to Fail............................................................................139
6.5 How Can I Query HyperMetro LUN Identifiers?.......................................................................................................140
6.6 What Can I Do If the Remote Connection Fails to Be Created with the TOE Interface Module.............................. 140
6.7 In the SQL Server database scenario, how can I adjust parameters to reduce the I/O latency and achieve the optimal
performance?.................................................................................................................................................................... 141
6.8 How Can I Use OVA Templates to Quickly Deploy Virtual Quorum Servers?......................................................... 141
7 Troubleshooting........................................................................................................................ 146
7.1 A Quorum Link Fails to Be Added After the Quorum Server Is Replaced................................................................146
A How to Obtain Help.................................................................................................................148
A.1 Preparations for Contacting Huawei..........................................................................................................................148
A.1.1 Collecting Troubleshooting Information................................................................................................................ 148
A.1.2 Making Debugging Preparations............................................................................................................................ 149
A.2 How to Use the Document.........................................................................................................................................149
A.3 How to Obtain Help from Website............................................................................................................................ 149
A.4 Ways to Contact Huawei............................................................................................................................................149
B Glossary...................................................................................................................................... 150
C Acronyms and Abbreviations................................................................................................ 151
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vii
Page 9

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
About This Chapter
HyperMetro provides you with disaster recovery functions and enables you to synchronize
and replicate data between storage arrays, monitor service operating status, and perform
failovers. You can switch over services and implement service load sharing while your storage
array is running.
1 Feature Description
1 Feature Description
1.1 Overview
This section describes the background, definition, and benefits of HyperMetro.
1.2 License Requirements and Compatible Products
This section describes the availability of HyperMetro in terms of the license requirement and
applicable version.
1.3 Working Principle
This section introduces the basic concepts, I/O processing mechanism, and arbitration
mechanism of HyperMetro and describes how to use HyperMetro for service switchover and
recovery.
1.4 Impact and Restrictions
This section describes the impact and restrictions of HyperMetro feature.
1.5 Application Scenarios
This section introduces the application scenarios of HyperMetro.
1.1 Overview
This section describes the background, definition, and benefits of HyperMetro.
Background
With the rapid development of the information technology (IT), storage systems are becoming
ever important for critical services in a variety of industries. Service interruptions in storage
systems may lead to severe economic loss, damaged brand images, or critical data loss,
especially in the fields of communications, finance, medical care, e-commerce, logistics, and
governments. Therefore, service continuity is critical to the construction of storage systems.
Traditionally, one production center and one disaster recovery center are constructed, and the
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1
Page 10
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
disaster recovery center is active only when the production center is down. This disaster
recovery system is facing the following challenges:
l If the production center encounters power supply failures, fires, floods, or earthquakes,
you must switch services from the production center to the disaster recovery center.
Services are interrupted for a long time and service continuity cannot be ensured.
l The disaster recovery center remains idle for most of the time, lowering resource
utilization.
Definition
HyperMetro enables storage systems in two different data centers to process services
simultaneously, establishing a mutual backup relationship. If the storage system in one data
center malfunctions, the storage system in the other data center automatically takes over
services without data loss or service interruption.
Benefits
Table 1-1 lists the benefits of HyperMetro.
1 Feature Description
Table 1-1 Benefits of HyperMetro
Benefit
Robust reliability If the storage system in one data center
High compatibility By integrating SmartVirtualization, HyperMetro
Description
malfunctions, the storage system in the other data
center automatically takes over services without
data loss or service interruption.
enables full utilization of storage resources,
minimizes upgrade costs, and is fully compatible
with storage systems from most vendors,
including EMC, IBM, HDS, HP, and SUN.
1.2 License Requirements and Compatible Products
This section describes the availability of HyperMetro in terms of the license requirement and
applicable version.
License Requirement
HyperMetro is a value-added feature that requires a software license for use on both local and
remote storage systems.
Applicable products
Product Series
OceanStor 2000 V3 series OceanStor 2600 V3 V300R006
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Product Model Version
2
Page 11
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Product Series Product Model Version
1 Feature Description
OceanStor 5000 V3 series OceanStor 5300 V3, 5500
OceanStor 6000 V3 series OceanStor 6800 V3 V300R006
OceanStor 18000 V3 series OceanStor 18500 V3 and
Applicable Software Versions
Software
OceanStor
UltraPath
OceanStor
QuorumServer
NOTE
Log in to http://support.huawei.com/enterprise/ and you can register for an account on the website. After
you log in with the applied user name and password. Choose Support > Enterprise Storage and click the
corresponding product model to access the product document page.
l Input Version Mapping in the search box and press Enter to obtain the product document.
l Enter the software name to obtain the software.
V300R006
V3, 5600 V3, and 5800 V3
V300R006
18800 V3
Version
When configuring HyperMetro services, use OceanStor UltraPath
V100R008C50SPC500 or later.
When configuring HyperMetro services, use OceanStor
QuorumServer V300R006 or later.
1.3 Working Principle
This section introduces the basic concepts, I/O processing mechanism, and arbitration
mechanism of HyperMetro and describes how to use HyperMetro for service switchover and
recovery.
1.3.1 Basic Concepts
This section describes basic concepts of HyperMetro, including local logical unit number
(LUN), remote LUN, dual-write, data change log (DCL), HyperMetro pair, HyperMetro
consistency group, synchronization, paused, force start, priority switchover and so on.
Local LUN and Remote LUN
Local LUNs are LUNs that belong to the local storage system. Remote LUNs are LUNs that
belong to the remote storage system.
Dual-Write
Dual-write enables the synchronization of application host I/O requests with both local and
remote LUNs.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3
Page 12

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
DCL
DCLs record changes in the data of storage systems.
HyperMetro Domain
A HyperMetro domain consists of the local and remote storage systems, and the quorum
server. Application servers can access data across data centers using a HyperMetro domain.
HyperMetro Pair
A HyperMetro pair indicates an active-active relationship between a local and remote LUN.
With HyperMetro configured, a local and remote LUN form a HyperMetro pair. You must
create HyperMetro pairs in a HyperMetro domain. By viewing the state of a HyperMetro pair,
you can determine whether you need to perform operation such as synchronization,
suspension, and priority switchover. After performing an operation, you can view the state of
the HyperMetro pair to determine whether the operation succeeded. Configure a HyperMetro
domain before configuring HyperMetro pairs.
1 Feature Description
HyperMetro Consistency Group
A HyperMetro consistency group is a collection of HyperMetro pairs that have a service
relationship with each other. For example, the local storage system has three local LUNs that
respectively store service data, logs, and change tracking information of a database. If data on
any of the three LUNs becomes invalid, all data on the three LUNs becomes unusable. Upon
configuration, create a consistency group and add the three HyperMetro pairs to the
consistency group.
Synchronization
Synchronization refers to the synchronization of differential data between a local LUN and a
remote LUN. Data synchronization takes place between two LUNs in a HyperMetro pair. You
can synchronize data in multiple HyperMetro pairs in a consistency group.
Pause
Pause is a state indicating the suspension of a HyperMetro pair.
Force Start
To ensure data consistency when the local and remote storage systems malfunction
simultaneously, HyperMetro stops hosts from accessing both. To quickly restore services, you
can forcibly start the local or remote storage system.
Priority Switchover
Priority switchover indicates that the preferred site takes precedence during arbitration. If the
HyperMetro replication network is down, the storage system that wins arbitration continues
providing services to hosts. After the creation of a HyperMetro pair, the local data center is by
default the preferred site and the remote data center is the non-preferred site.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4
Page 13
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Locking Mechanism
To prevent different host I/Os from being written to the same location in the storage system at
the same time, the storage system uses the locking mechanism to prevent access conflicts. The
host I/O can only be written to the storage system that obtains the locking mechanism.
1.3.2 HyperMetro Solution Overview
This section describes the HyperMetro solution network and provides a logical HyperMetro
network topology to show the mapping relationship and data flows between host applications
and storage arrays.
HyperMetro enables active-active block storage services. LUN data is synchronized between
two data centers in real time and can be accessed by hosts.
If the storage array in one data center malfunctions, host services are switched to the storage
array in the other data center. If the link between two storage arrays in two data centers is
down, only one storage array can be accessed by hosts. The quorum server determines which
storage array continues providing services.
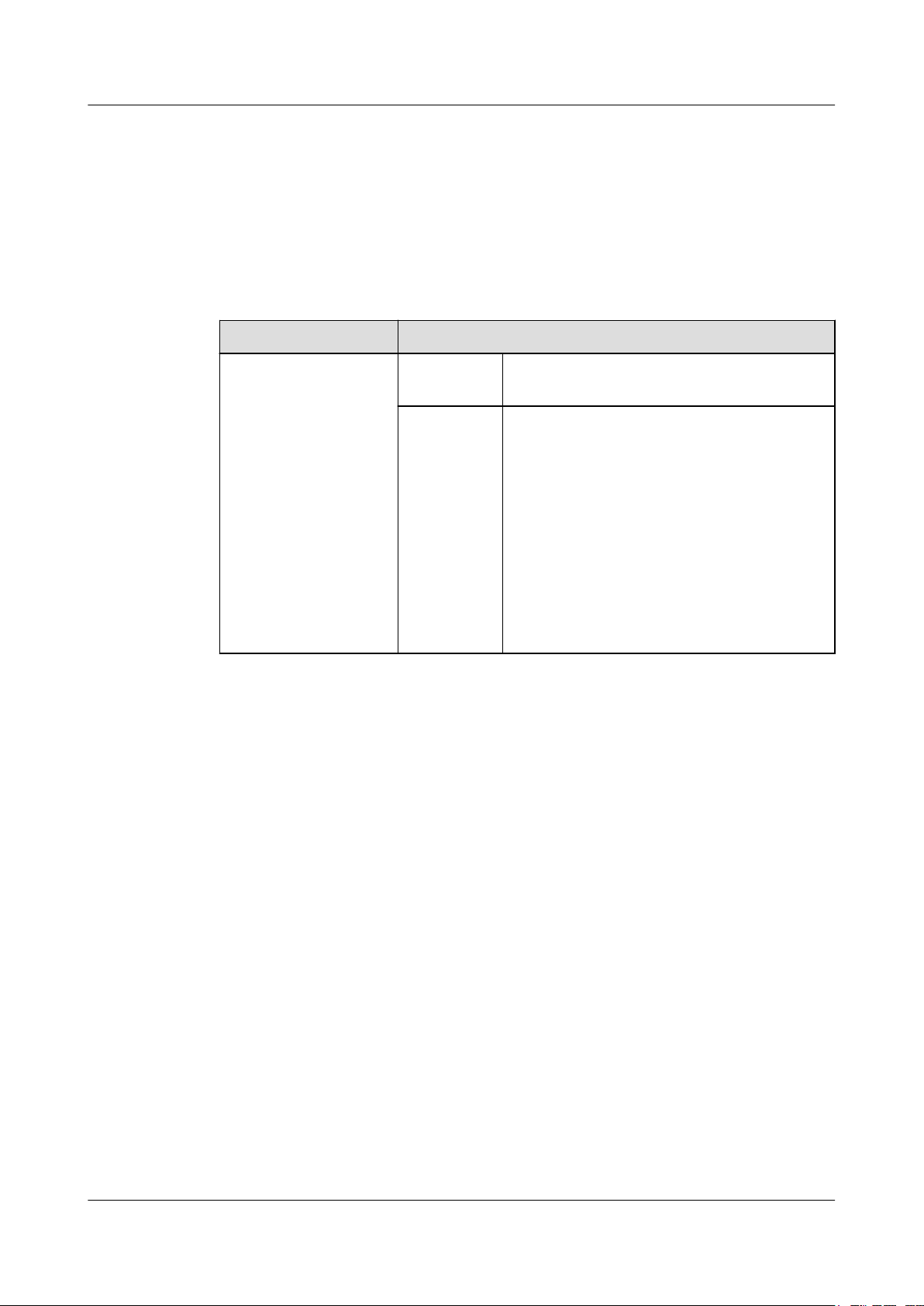
Figure 1-1 shows the HyperMetro solution network topology.
1 Feature Description
Figure 1-1 HyperMetro solution network topology
Data center A Data center B
Host cluster
Switch
FC/IP
Switch
Storage array A
Switch
Switch
Switch
Switch
Storage array B
Switch Switch
LAN/WAN
Quorum server
Quorum site
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Network of hosts and
storage arrays
Same-city network
between data centers
HyperMetro
replication network
Quorum network
5
Page 14
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Network Overview
To ensure reliability of storage arrays, establish redundant links among the network between
hosts and storage arrays, HyperMetro replication network, same-city network between data
centers, and quorum network.
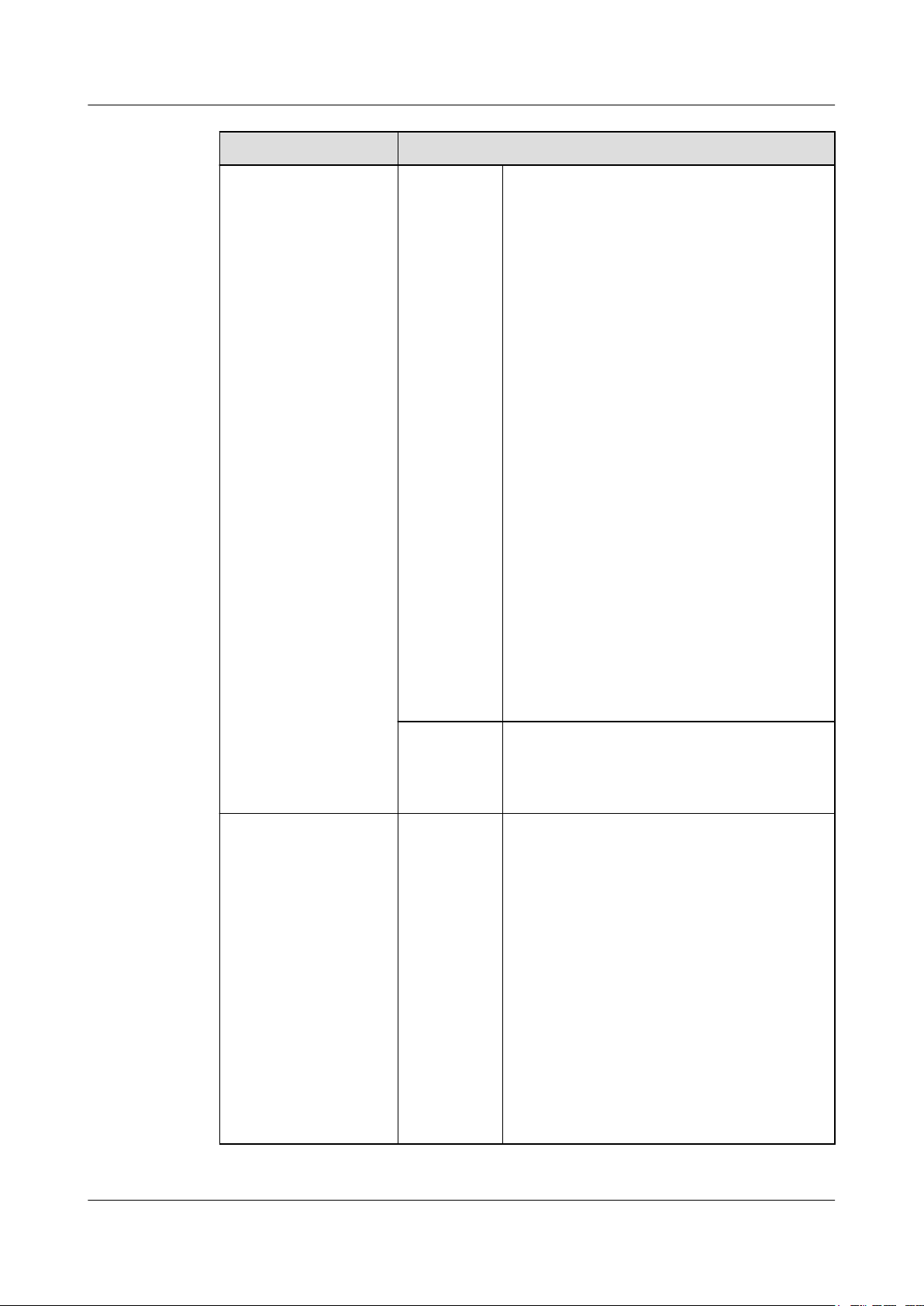
Table 1-2 Network Overview
1 Feature Description
Network
Network of hosts and
storage systems
All hosts in the two data
centers can form a
cluster and host
networks can
interconnect across data
centers.
Description
Network
type
Networking
mode
Supports 8 Gbit/s Fibre Channel, 16 Gbit/s
Fibre Channel, 10GE, and GE networks.
l A fully interconnected network in which
each host is physically and logically
connected to the storage arrays in both data
centers.
l A host must connect to both storage arrays
using the same type of network.
l Dual-switch networking must be used.
l The HyperMetro replication network,
storage-to-host network, and quorum
network need to be physically isolated and
common ports are not recommended.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
6
Page 15
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
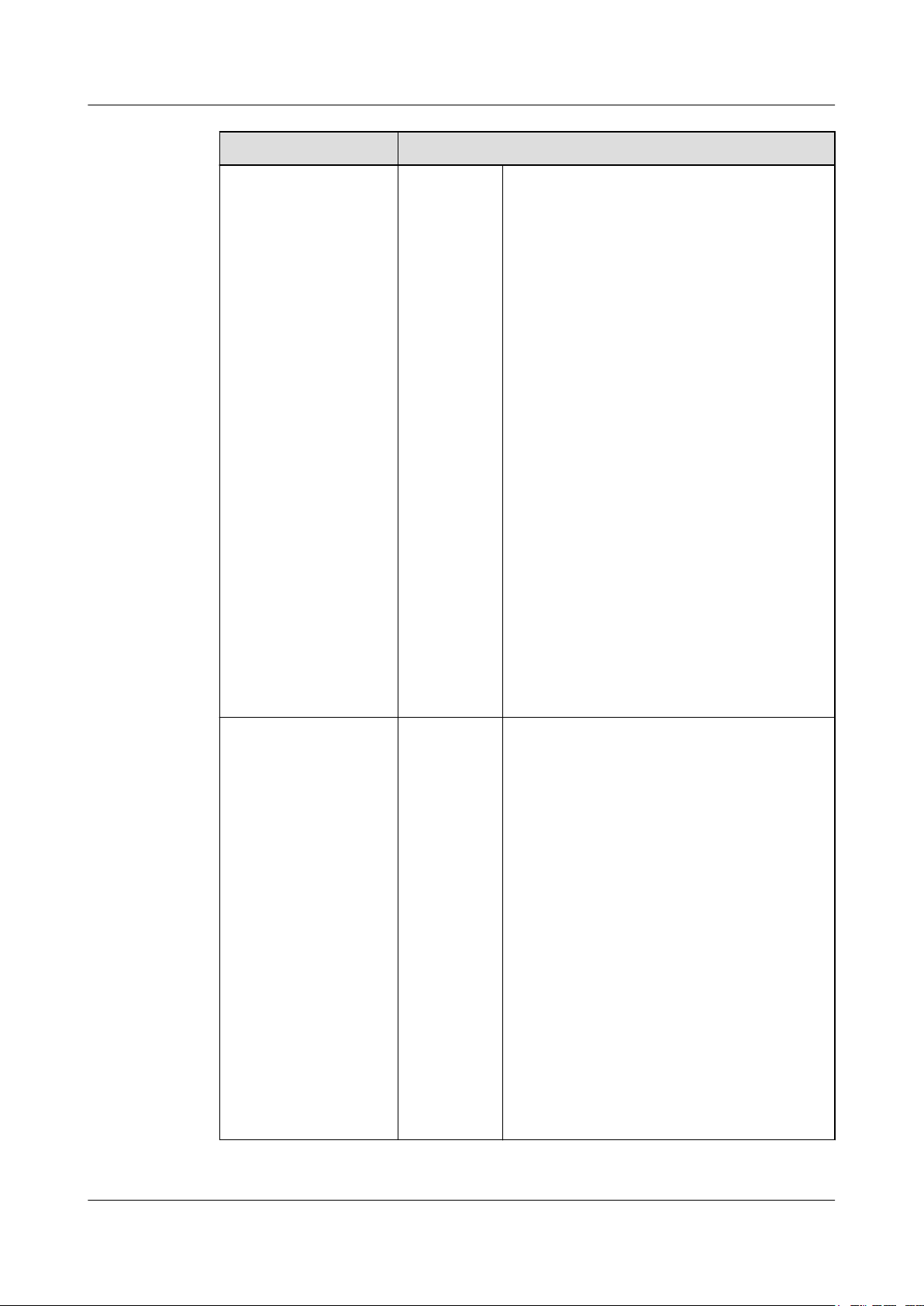
Network Description
1 Feature Description
HyperMetro replication
network
This is the heartbeat
network between the
storage systems in the
two data centers. It
enables the storage
systems to provide
services for hosts
concurrently and
ensures data
synchronization
between them.
NOTE
The storage system sets
link priorities for different
types of information for
transferring data. The link
priority of heartbeat
information is higher than
that of data
synchronization
information.
Network
type
l Supports 10GE, 8 Gbit/s Fibre Channel, and
16 Gbit/s Fibre Channel networks.
NOTE
When using the 10GE network, you are advised
to use the L2 network.
l Network quality and bandwidth
requirements for deploying the network:
– Bandwidth: ≥ peak service bandwidth
(total bandwidth of the two ends)
– Latency: The maximum supported RTT
is 10 ms (distance < 300 km)
NOTE
In practice, the latency is determined by the
requirements of the application layer. The
active/active solution must meet the
minimum latency requirement. The round-trip
time (RTT) of the Oracle RAC, SQL Server,
and DB2 applications is less than 1 ms (with
a distance of less than 100 km). The RTT of
the VMware vSphere applications is less than
10 ms (with a distance of less than 300 km).
– No jitter and packet loss
– BER: ≤ 10
-12
l The HyperMetro replication network,
storage-to-host network, and quorum
network need to be physically isolated and
common ports are not recommended.
Same-city network
between data centers
The storage systems in
data centers A and B
provide the same
services for hosts. There
is a mutual backup
relationship between the
two storage systems. If
the storage system in
one data center
malfunctions, the
storage system in the
other data center
automatically takes over
services without data
Networking
mode
Network
type
Each controller on every storage array in both
data centers has at least two redundant links. It
is recommended that you use four redundant
links.
The network uses bare fibers.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
7
Page 16
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Network Description
1 Feature Description
loss or service
interruption.
Networking
mode
l For Fibre Channel networks:
– The two data centers can be directly
connected using bare fibers if their
distance is within 25 km. Ensure that the
storage and application layers each have
at least two pairs (four wires) of bare
fibers for heartbeat interconnection in the
cluster.
– If the data centers are greater than or
equal to 25 km apart, use dense
wavelength division multiplexing
(DWDM) devices to build the
interconnection network between DCs.
l For IP networks:
– The two data centers can be directly
connected using bare fibers if their
distance is within 80 km. If core switches
are deployed, ensure that at least two
pairs (four wires) of bare fibers are
connected to the core switches for
HyperMetro mirroring at the storage
layer and heartbeat interconnection at the
application layer.
– If the data centers are greater than or
equal to 80 km apart, use DWDM
devices to interconnect them.
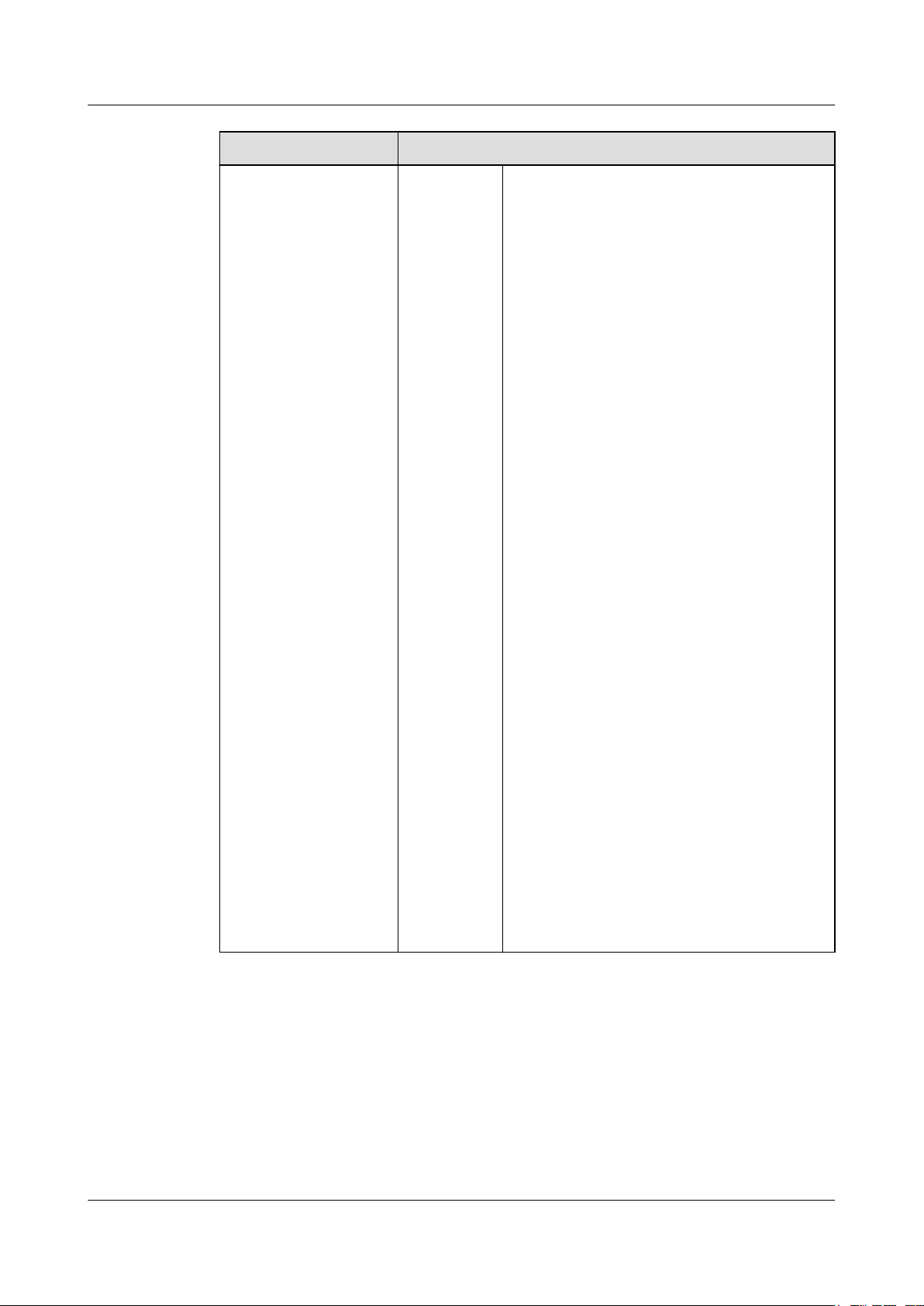
Quorum network
If communication
between the storage
systems in data centers
A and B is interrupted
or a storage system
malfunctions, the
quorum server
determines which
storage system is
accessible.
Network
type
l Quorum links support GE and 10GE
networks, but not a Fibre Channel network.
l Quorum links support IPv4 and IPv6
addresses.
l For versions earlier than V300R006C10, the
arbitration link port cannot use a storage
device's management or maintenance
network port. For V300R006C10 and later
versions, the arbitration link port can use a
storage device's management network port,
but cannot use its maintenance network port.
l Network quality and bandwidth
requirements for deploying the network:
– Latency: RTT ≤ 50 ms
– Bandwidth: ≥ 10 Mbit/s
l The HyperMetro replication network,
storage-to-host network, and quorum
network need to be physically isolated and
common ports are not recommended.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
8
Page 17
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Network Description
1 Feature Description
NOTE
A quorum server is
deployed on the quorum
network. If storage arrays
in the two data centers
encounter a device fault
or a link between the
storage arrays is down,
the quorum server
determines the access
status of data center A
and data center B
according to the
arbitration result.
Networking
mode
l Quorum servers are supported but quorum
disks are not.
l You are advised to deploy the quorum server
at a third-place site. If there is no third-place
site, you are advised to deploy the quorum
server at the preferred site. In this case, the
quorum server and related devices should
have uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
protection.
l A dual-switch network is recommended. A
GE/10GE port on each controller of a
storage array is connected to the third-place
quorum server and the service network ports
on the quorum server are connected to two
storage arrays, ensuring that the quorum
server is connected to all controllers of each
storage array.
l If each controller has two quorum ports,
connect the first quorum port on each
controller to switch 1 and configure IP
network segment 1. In addition, connect the
second quorum port on each controller to
switch 2 and configure IP network segment
2.
l The quorum server can be a physical or a
virtual server. If a virtual server is used, you
are advised to deploy VMware vSphere/
FusionSphere FT or HA to achieve high
availability.
l Huawei Enterprise Cloud (HEC) can be used
as a quorum server.
When the HEC is used as the quorum server,
apply for a VM (including the CPU,
memory, disk, and OS). The VM
specifications are the same as those of the
quorum server. Apply for 2 Mbit/s exclusive
bandwidth and one elastic IP address for
each disk array.
1.3.3 Arbitration Mechanism
If the link between the two data centers breaks down, they can no longer be synchronized and
only one will continue providing services. HyperMetro supports two arbitration modes to
determine which data center continues providing services and ensure data consistency:
l Static priority mode is used when there is no quorum server available.
l Quorum server mode is used when quorum servers have been deployed.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
9
Page 18
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
NOTE
The quorum server mode is recommended. After a quorum server is deployed, the non-preferred site of
HyperMetro will automatically take over services once the preferred site becomes faulty, without
causing HyperMetro service interruption.
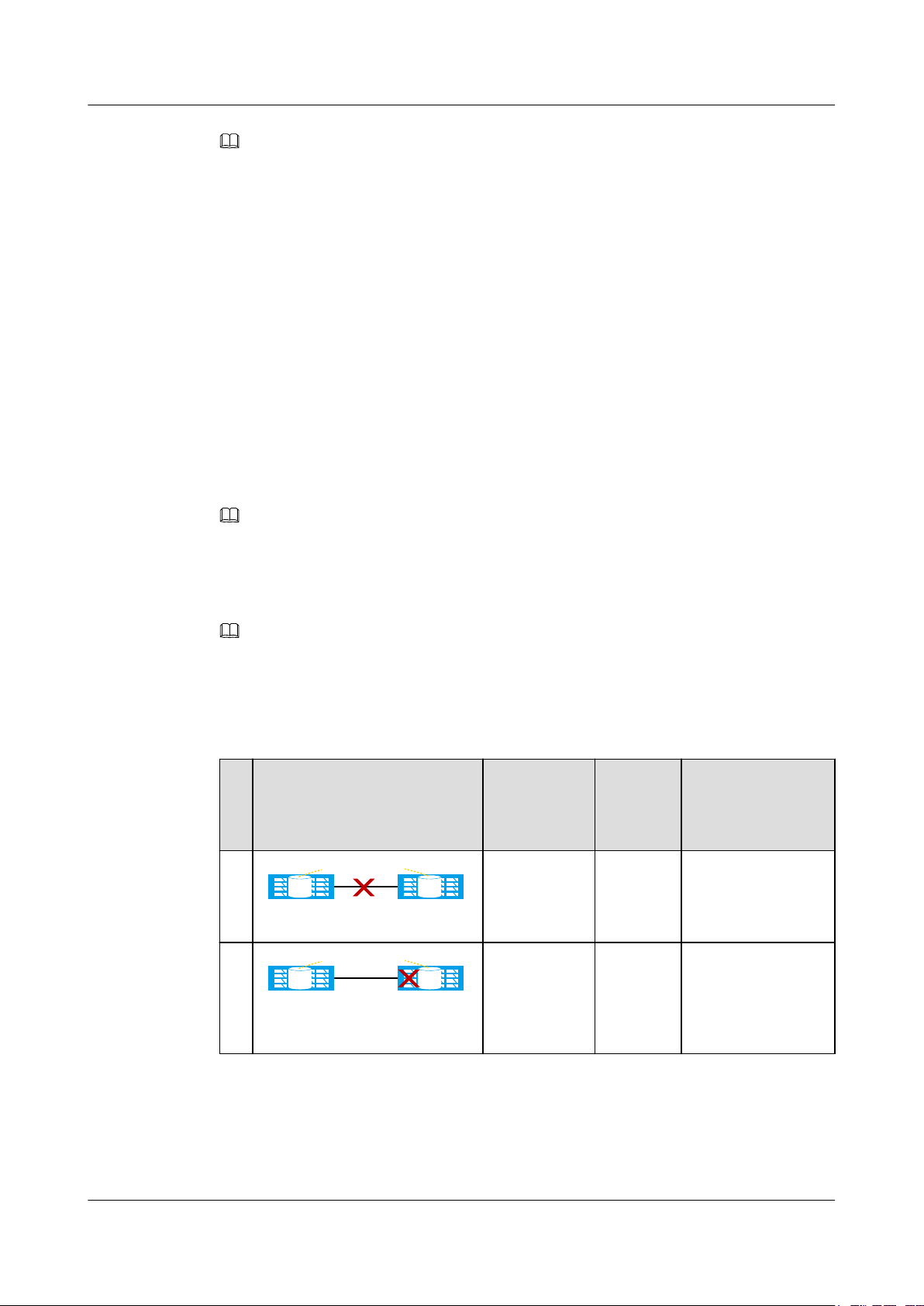
Static Priority Mode
The static priority mode applies to scenarios where no third-place quorum server is deployed.
In a HyperMetro pair, you can set one data center as the preferred site and the other as the
non-preferred site.
l If the link between the two storage arrays in the two data centers is disconnected or the
storage array at the non-preferred site breaks down, the storage array at the preferred site
continues providing services for hosts and the storage array at the non-preferred site
stops.
l If the storage array at the preferred site breaks down, the storage array at the non-
preferred site cannot automatically take over HyperMetro services from the storage array
at the preferred site. As a result, HyperMetro services stop. In this case, you must
forcibly start the storage array at the non-preferred site to provide services for hosts.
NOTE
When you use OceanStor DeviceManager or CLI to power off a storage device, it will notify its peer
storage device of taking over its services. This event is not a device fault.
1 Feature Description
In the following example, data center A is used as a preferred site. Table 1-3 describes the
arbitration mechanism in static priority mode.
NOTE
You can set the Recovery Policy for HyperMetro pair failures by Modifying HyperMetro Pair Properties.
l Automatic: The system automatically synchronizes data for data recovery.
l Manual: You must manually synchronize data for data recovery.
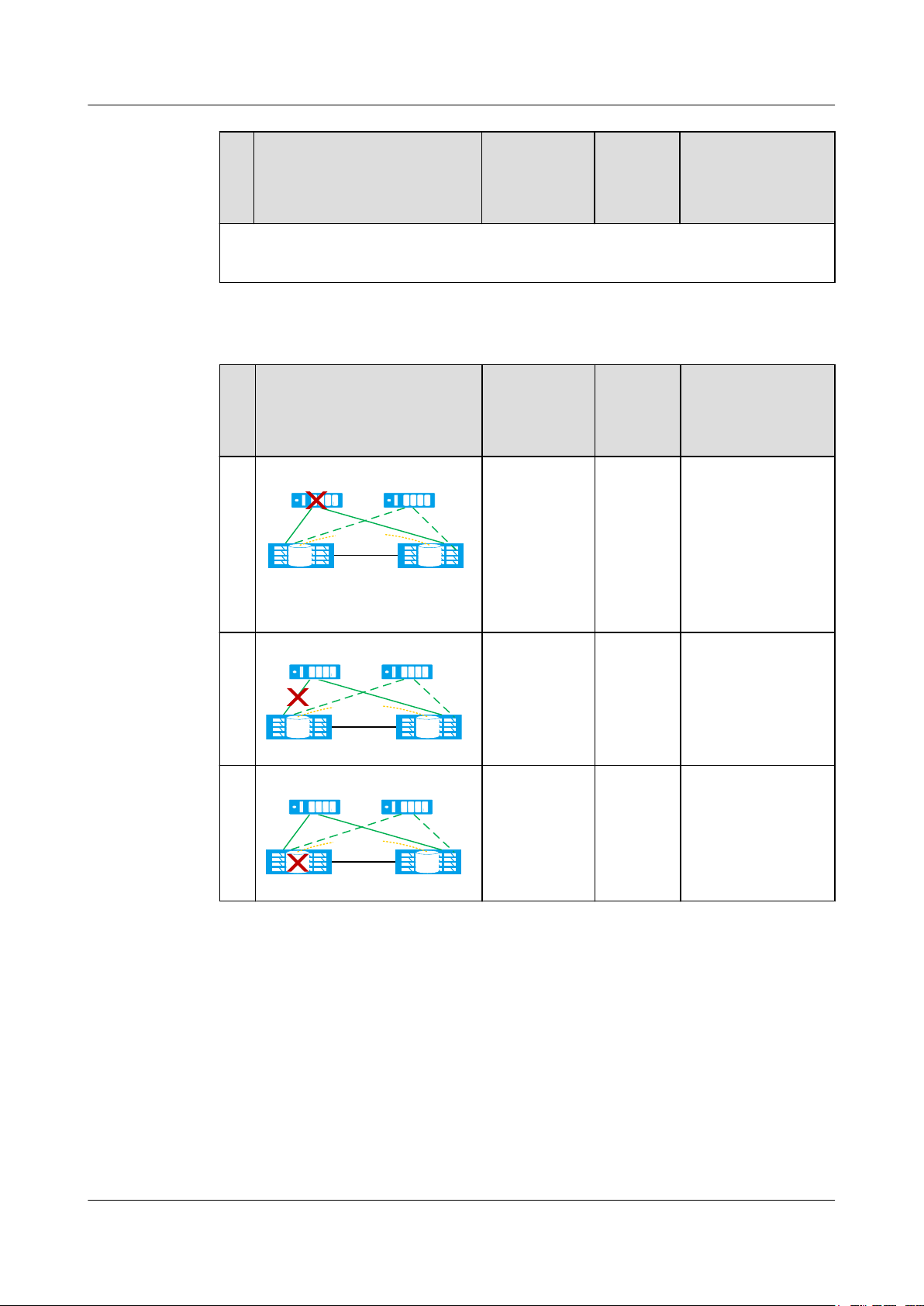
Table 1-3 Arbitration mechanism in static priority mode
N
Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
o.
etro Pair
Arbitration Result
Running
Status
1
Data center A Data center B
HyperMetro Pair
LUN LUN
The link
between two
storage arrays
To be
synchroni
zed
A continues
providing services
while B stops.
breaks down.
2
Data center A Data center B
HyperMetro Pair
LUN LUN
The storage
array in data
center B (non-
To be
synchroni
zed
A continues
providing services
while B stops.
preferred site)
malfunctions.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10
Page 19
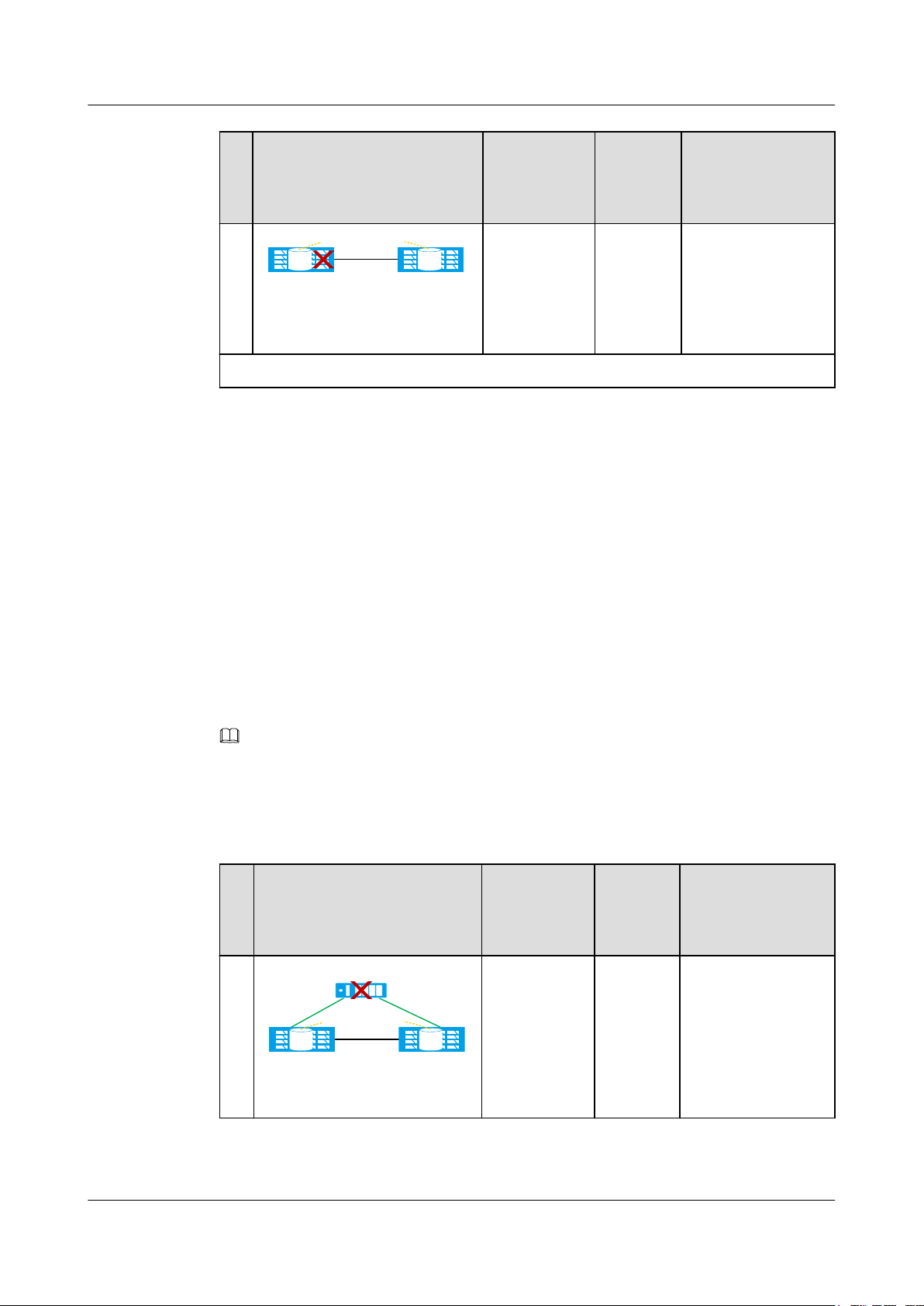
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
1 Feature Description
No.Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
3
Data center A Data center B
Black cable: HyperMetro replication network
Quorum Server Mode
In quorum server mode, the heartbeat network determines whether the storage arrays are
working properly. If a malfunction occurs, each data center sends an arbitration request to the
quorum server, and only the winner continues providing services.
The quorum site supports two quorum servers for V300R006C10 and later versions. The two
quorum servers work in active/standby mode. Once the active quorum server is faulty, the
system automatically switches to the standby quorum server to execute the arbitration
function.
HyperMetro Pair
LUN LUN
The storage
array in data
center A
(preferred
site)
malfunctions.
etro Pair
Running
Status
To be
synchroni
zed
Arbitration Result
Both A and B stop.
You must forcibly
start B to resume
providing services
for hosts.
In a HyperMetro pair, you can set one data center as the preferred site, which takes
precedence in arbitration, and the other as the non-preferred site. In the following example,
data center A is used as a preferred site. Table 1-4 and Table 1-5 describe the arbitration
mechanisms when one and two quorum servers are deployed, respectively.
NOTE
You can set the Recovery Policy for HyperMetro pair failures by Modifying HyperMetro Pair Properties.
l Automatic: The system automatically synchronizes data for data recovery.
l Manual: You must manually synchronize data for data recovery.
Table 1-4 Arbitration mechanism in single-quorum-server mode
N
Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
o.
etro Pair
Arbitration Result
Running
Status
1
Data center A Data center B
Quorum server
HyperMetro Pair
LUNLUN
The quorum
server breaks
down.
Normal Both A and B
continue providing
services.
NOTE
HyperMetro
automatically
switches to static
priority arbitration.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11
Page 20
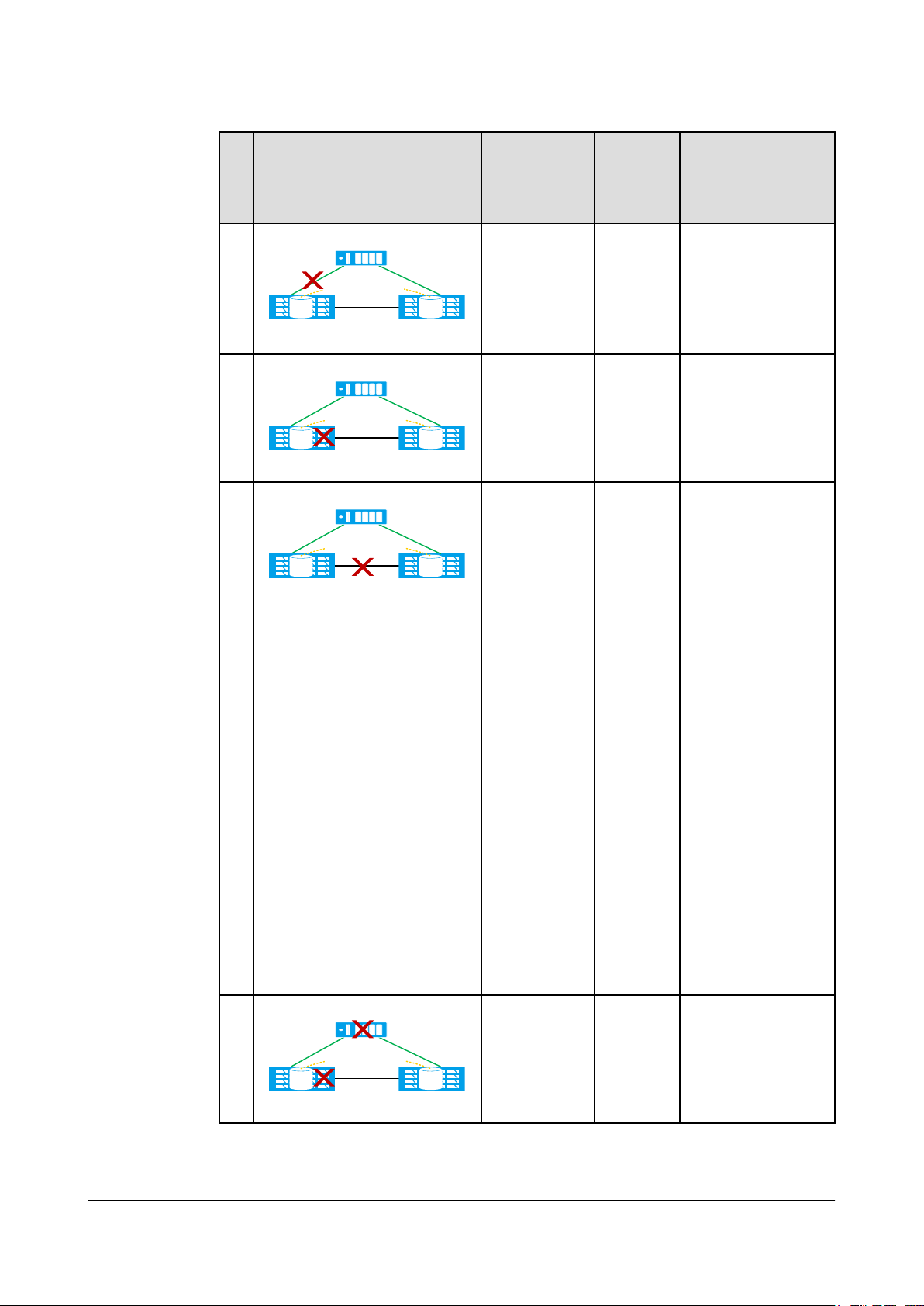
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
1 Feature Description
No.Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
etro Pair
Running
Status
2
Quorum server
The link
Normal Both A and B
between one
HyperMetro Pair
Data center A Data center B
3
Data center A Data center B
4
Data center A Data center B
Quorum server
HyperMetro Pair
Quorum server
HyperMetro Pair
LUNLUN
LUNLUN
LUNLUN
storage array
and the
quorum server
breaks down.
One storage
array
malfunctions.
The link
between two
storage arrays
breaks down.
To be
synchroni
zed
To be
synchroni
zed
Arbitration Result
continue providing
services.
B continues
providing services
while A stops.
Result 1: A
continues providing
services while B
stops.
Result 2: B
continues providing
services while A
stops.
NOTE
l A has arbitration
priority, so the
normal result is
Result 1.
l (For
V300R006C10
and later
versions) If the
link between data
center A and the
application server
has become faulty
before the link
between the two
storage arrays
breaks down, data
center B will win
the arbitration.
5
Quorum server
One storage
array and the
HyperMetro Pair
LUNLUN
Data center A Data center B
quorum server
both
malfunction.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
To be
synchroni
zed
Both A and B stop.
NOTE
You must forcibly
start B to resume
providing services for
hosts.
12
Page 21
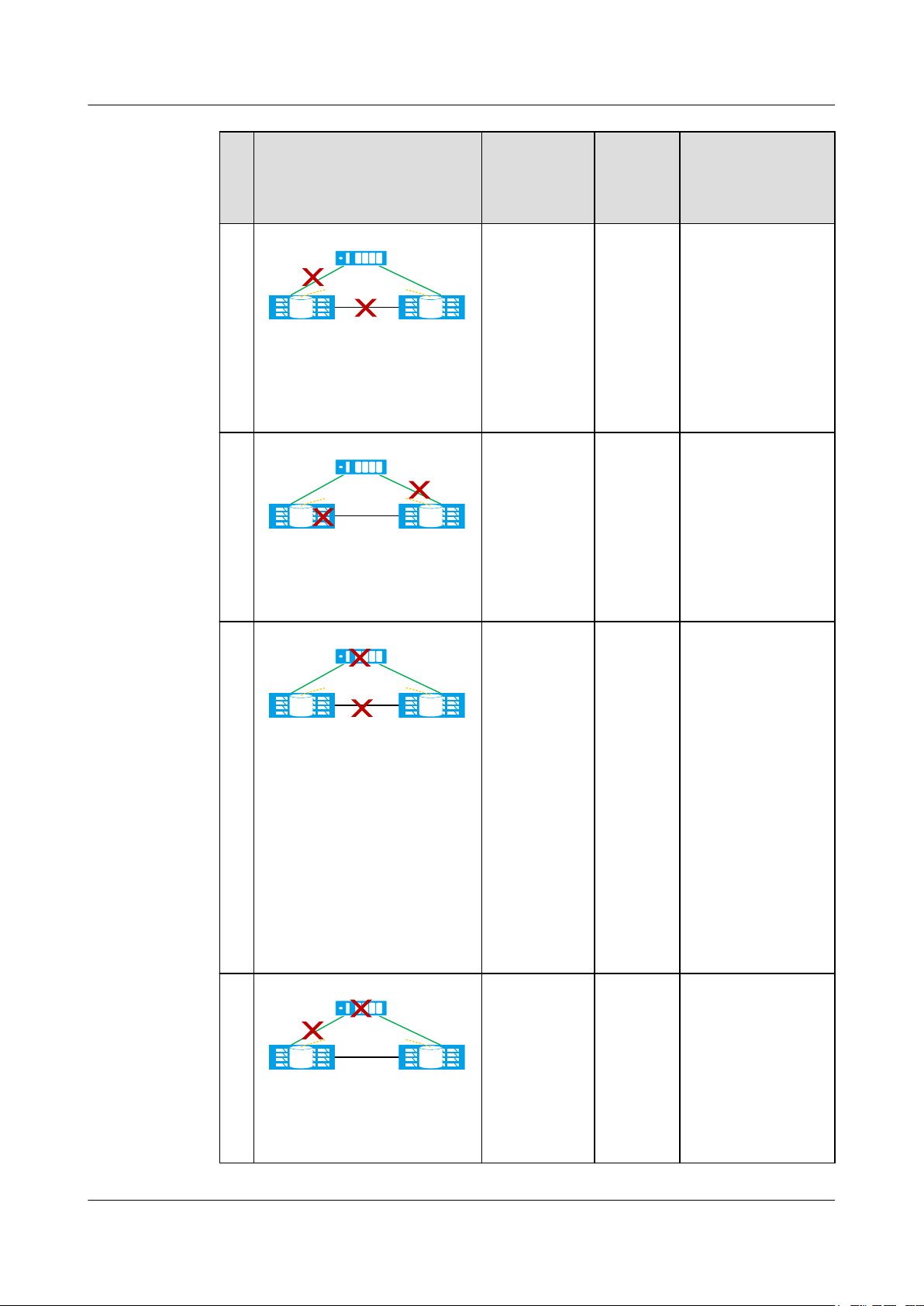
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
1 Feature Description
No.Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
etro Pair
Running
Status
6
Data center A Data center B
Quorum server
HyperMetro Pair
LUNLUN
The link
between the
two storage
arrays and the
link between
one storage
To be
synchroni
zed
array and the
quorum server
both break
down.
7
Data center A Data center B
Quorum server
HyperMetro Pair
LUNLUN
One storage
array
malfunctions
and the link
between the
other storage
To be
synchroni
zed
array and the
quorum server
is down.
Arbitration Result
B continues
providing services
while A stops.
Both A and B stop.
NOTE
You must forcibly
start B to resume
providing services for
hosts.
8
Data center A Data center B
9
Data center A Data center B
Quorum server
HyperMetro Pair
Quorum server
HyperMetro Pair
The quorum
server
malfunctions
LUNLUN
and then the
link between
two storage
arrays is
down.
To be
synchroni
zed
Result 1: If the link
is interrupted more
than 60 seconds after
the quorum server
fails, A continues
providing services
while B stops.
Result 2: If the link
is interrupted within
60 seconds of the
quorum server
failure, both A and B
stop. You must
forcibly start either
A or B to resume
providing services
for hosts.
The quorum
server
malfunctions
LUNLUN
and the link
between the
quorum server
and one
storage array
Normal Both A and B
continue providing
services.
NOTE
HyperMetro
automatically
switches to static
priority arbitration.
is down.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
Page 22
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
1 Feature Description
No.Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
etro Pair
Running
Status
Black cable: HyperMetro replication network
Green cable: quorum network
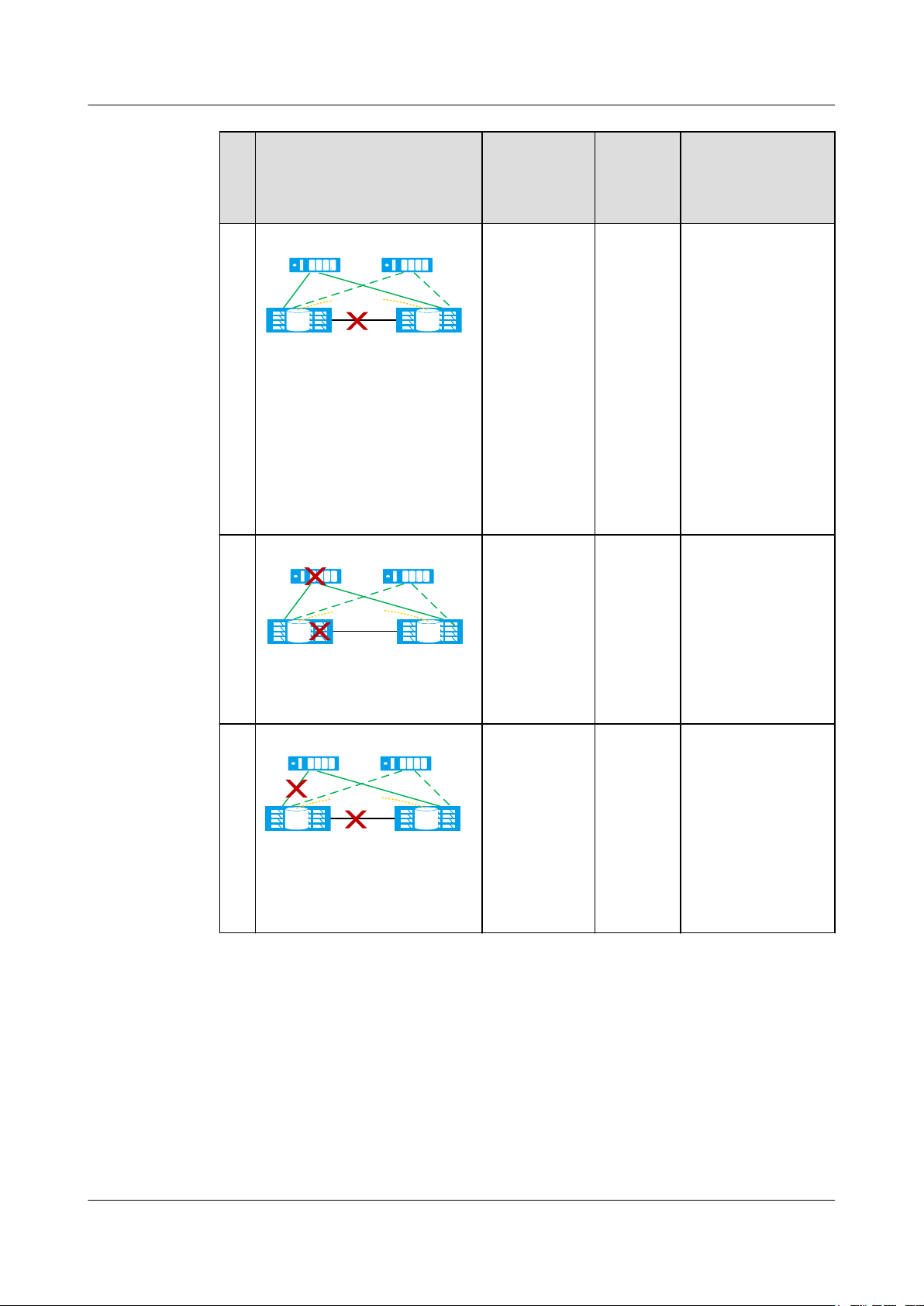
Table 1-5 Arbitration mechanism in dual-quorum-server mode
Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
N
o.
etro Pair
Running
Status
1
Quorum server
(active)
Quorum server
(standby)
The active
quorum server
Normal The standby quorum
breaks down.
HyperMetro
Pair
LUNLUN
Data center A Data center B
Arbitration Result
Arbitration Result
server takes over the
arbitration services
from the active
quorum server.
Both A and B
continue providing
services.
2
3
Quorum server
(active)
HyperMetro
Pair
Data center A Data cente B
Quorum server
(active)
HyperMetro
Pair
Data center A
Quorum server
(standby)
LUNLUN
Quorum server
(standby)
LUNLUN
Data cente B
The link
between one
storage array
and the active
quorum server
breaks down.
One storage
array
malfunctions.
Normal The active quorum
server runs properly.
Both A and B
continue providing
services.
To be
synchroni
zed
The active quorum
server runs properly.
B continues
providing services
while A stops.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14
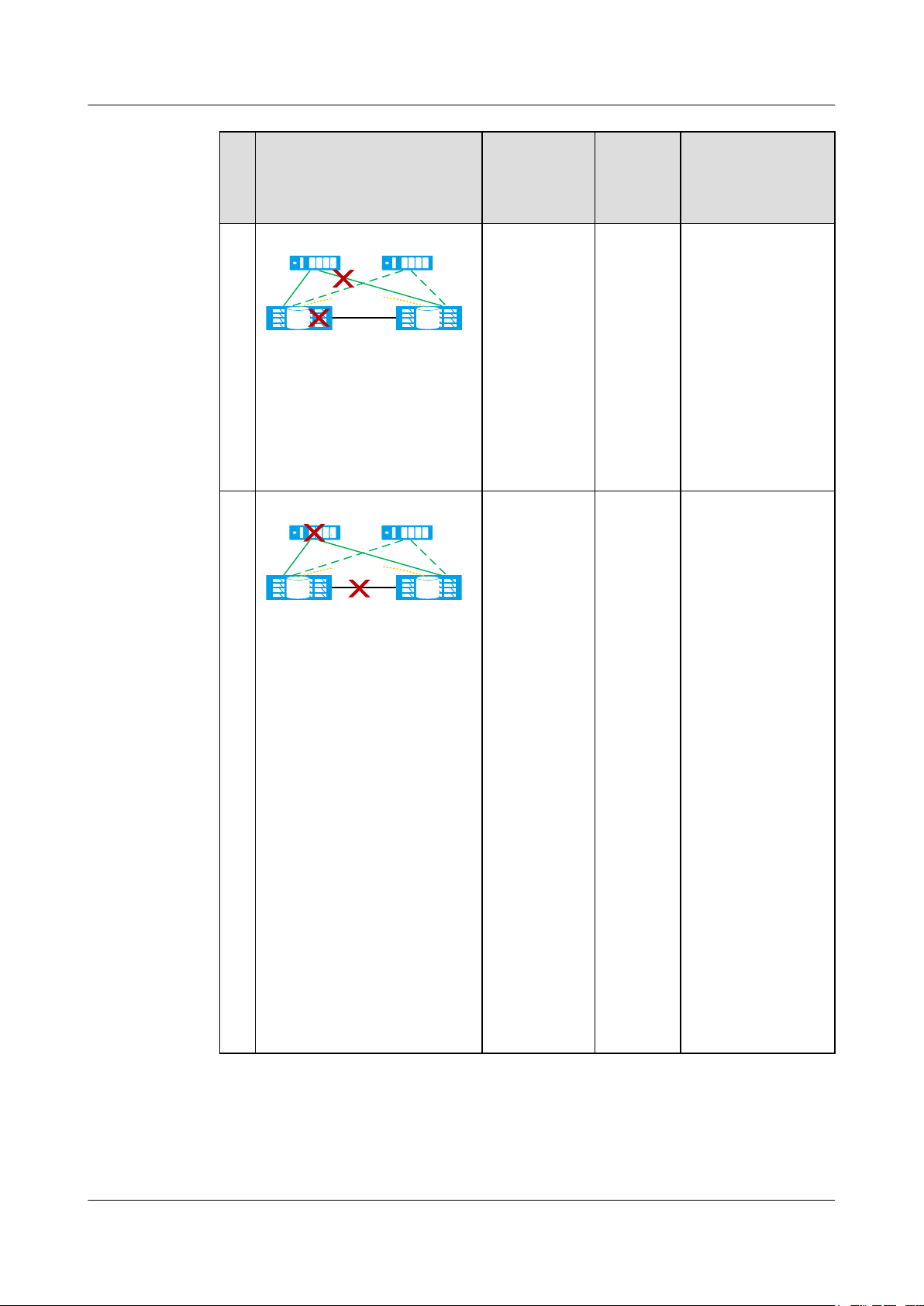
Page 23
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
1 Feature Description
No.Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
etro Pair
Running
Status
4
5
Quorum server
(active)
Data center A Data cente B
Quorum server
(active)
Data center A Data cente B
HyperMetro
Pair
HyperMetro
Pair
Quorum server
(standby)
LUNLUN
Quorum server
(standby)
LUNLUN
The link
between two
storage arrays
breaks down.
The active
quorum server
fails and then
the storage
array at the
preferred site
To be
synchroni
zed
To be
synchroni
zed
fails after
more than 60
seconds.
Arbitration Result
The active quorum
server runs properly.
Result 1: A
continues providing
services while B
stops.
Result 2: B
continues providing
services while A
stops.
NOTE
A has arbitration
priority, so the
normal result is
Result 1.
The standby quorum
server takes over the
arbitration services
from the active
quorum server.
B continues
providing services
while A stops.
6
Quorum server
(active)
HyperMetro
Data center A Data cente B
Quorum server
Pair
(standby)
The link
between the
two storage
arrays and the
LUNLUN
link between
To be
synchroni
zed
The active quorum
server runs properly.
B continues
providing services
while A stops.
one storage
array and the
active quorum
server both
break down.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
15
Page 24
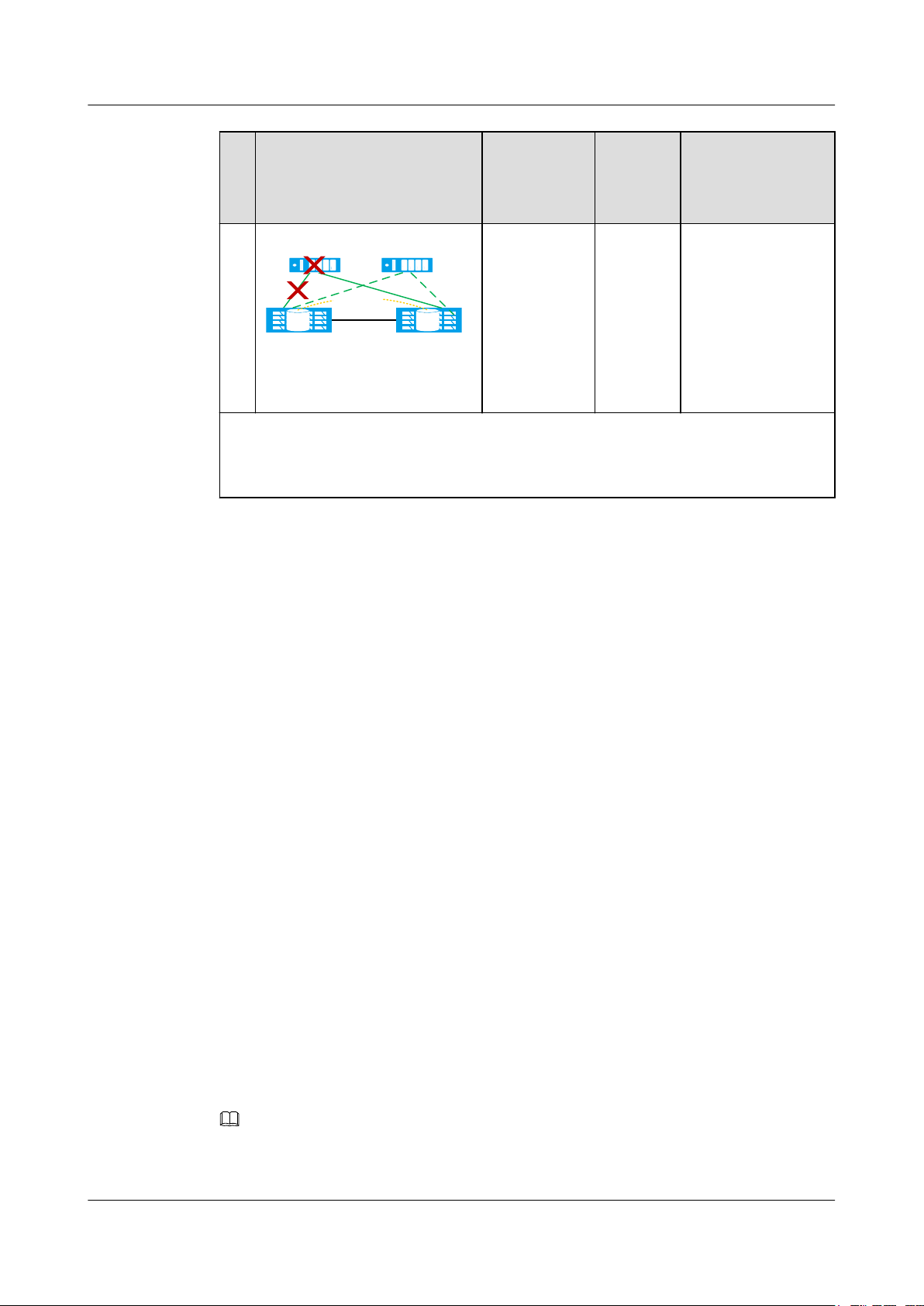
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
1 Feature Description
No.Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
etro Pair
Running
Status
7
Quorum server
(active)
Data center A Data cente B
HyperMetro
Pair
Quorum server
(standby)
LUNLUN
The link
between the
active quorum
server and
non-preferred
site breaks
To be
synchroni
zed
down and then
the storage
array at the
preferred site
fails after
more than 60
seconds.
8
Quorum server
(active)
Data center A
HyperMetro
Pair
Quorum server
(standby)
LUNLUN
Data cente B
The active
quorum server
malfunctions
and then the
link between
two storage
To be
synchroni
zed
arrays is
down.
Arbitration Result
The standby quorum
server takes over the
arbitration services
from the active
quorum server.
B continues
providing services
while A stops.
The standby quorum
server takes over the
arbitration services
from the active
quorum server.
Result 1: If the link
is interrupted more
than 60 seconds
after the active
quorum server fails,
A continues
providing services
while B stops.
If the link is
interrupted within 60
seconds of the
quorum server
failure, both A and
B may win the
arbitration and
continue providing
services.
NOTE
A has arbitration
priority, so generally
A continues
providing services
while B stops.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16
Page 25
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
1 Feature Description
No.Fault Example Fault Type HyperM
9
Quorum server
(active)
Quorum server
(standby)
The active
quorum server
malfunctions
HyperMetro
Pair
LUNLUN
Data center A Data cente B
and the link
between the
active quorum
server and one
storage array
is down.
Black cable: HyperMetro replication network
Green solid cable: quorum network between the active quorum server and data centers
Green dotted cable: quorum network between the standby quorum server and data centers
1.3.4 HyperMetro I/O Processing Mechanism
HyperMetro uses the dual-write and DCL technologies to synchronize data changes between
two data centers, ensuring data consistency. In addition, HyperMetro enables the storage
arrays in the two data centers to concurrently provide services for hosts.
Arbitration Result
etro Pair
Running
Status
Normal The standby quorum
server takes over the
arbitration services
from the active
quorum server.
Both A and B
continue providing
services.
Basic Concepts
You are advised to read about the key concepts of HyperMetro before reading about the I/O
processing mechanism. For details, see 1.3.1 Basic Concepts.
Write I/O Process
l Dual-write and DCL technologies have two ways of synchronizing data while services
l Two storage systems with HyperMetro installed can process I/O requests concurrently.
Figure 1-2 shows the write I/O process of an application host delivering an I/O request and
causing data changes.
are running. Dual-write enables the delivery of I/O requests from application servers to
both local and remote caches, ensuring data consistency between caches. If the storage
system in one data center malfunctions, the DCL records data changes in a data center.
After the storage system recovers, the data changes are synchronized to the storage
system, ensuring data consistency across data centers.
The locking mechanism prevents access conflicts that occur when different hosts access
the same storage system at the same time. Data can be written to a storage system only
after the locking mechanism grants permission to the storage system. If the locking
mechanism does not grant priority, the storage system must wait until the previous I/O is
complete. It must then obtain write permission after the locking mechanism releases the
previous storage system.
NOTE
In the following figure, the write I/O accesses the local storage system, and the local storage system
writes data to the remote storage system for dual-write purposes.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17
Page 26
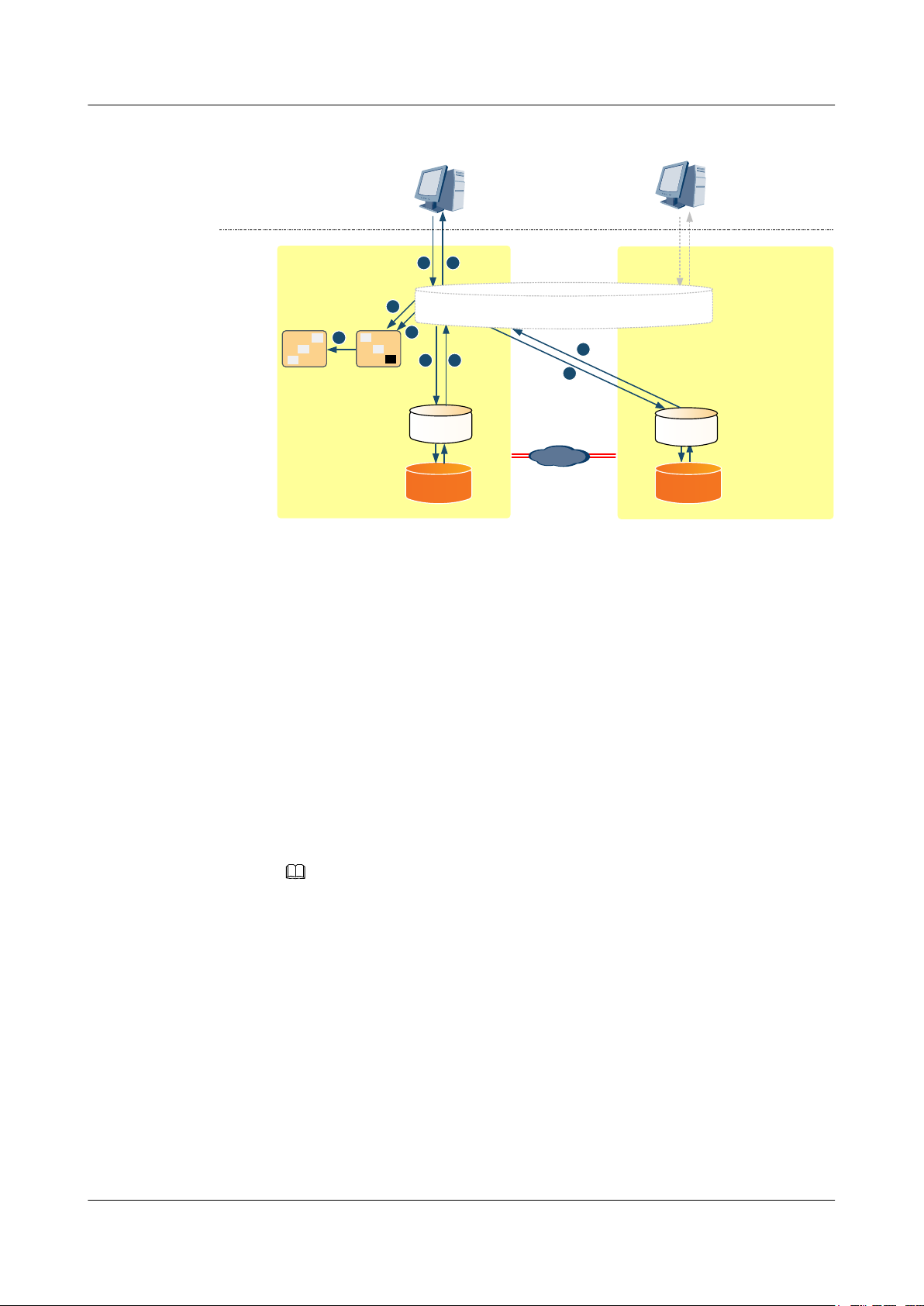
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 1-2 Write I/O process
Host
1 Feature Description
Storage
DCL
2
LOG
6
Local storage array
51
HyperMetro management module
6
3
4
Local
cache
Local
LUN
4
4
3
DWDM
Same-city network
between data centers
Remote
cache
Remote
LUN
Remote storage array
1. An application host delivers a write I/O to the HyperMetro management module.
2. A log is recorded.
3. HyperMetro writes the write I/O to both the local and remote caches concurrently.
4. The local and remote caches return the write I/O result to HyperMetro.
5. A storage system returns the write I/O result to the application host after receiving
6. The storage system determines whether dual-write is successful.
Read I/O Process
Data on the LUNs of both storage systems is synchronized in real time and both are accessible
to hosts. If the storage system in one data center malfunctions, the storage system in the other
data center continues providing host services alone.
feedback from the local and remote caches.
– If the write I/O request is processed successfully, the log is deleted.
– If the write I/O fails to be written to the local or remote cache, the log is converted
into a DCL. The DCL records the differential data between the local and remote
LUNs.
NOTE
If the write I/O fails to be written to the local or remote cache, HyperMetro services are
suspended and the storage system in each data center sends an arbitration request to the
quorum server. The storage system that wins the arbitration continues providing services and
the one that fails stops. In the background, the storage system uses the DCL to synchronize
data. Once the data on the local LUN is identical to the data on the remote LUN,
HyperMetro services are restored.
The DCL is stored on all the disks in the disk domain and four-disk RAID 1 is used for data
protection while storage system logs are stored on coffer disks.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18
Page 27
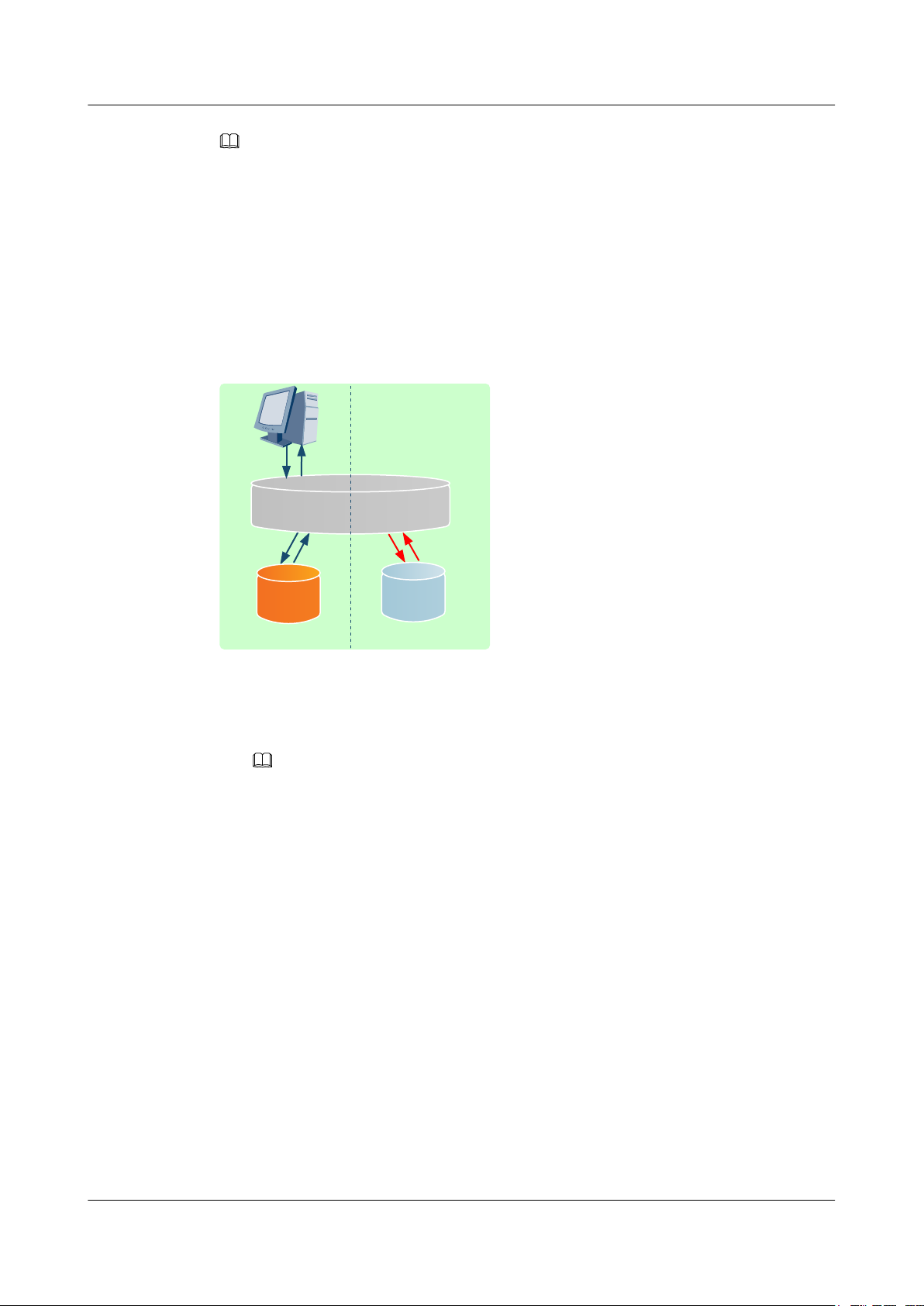
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
NOTE
l UltraPath is recommended for HyperMetro. Huawei UltraPath to meet HyperMetro requirements.
After the optimization, UltraPath can identify host locations so that hosts can access the nearest
storage array, reducing cross-site accesses and latency while improving access efficiency and storage
performance.
l If the customer needs to use non-Huawei multipathing software on the application server, the
function of Uses third-party multipath software for initiators must be enabled on Huawei storage.
After this function is enabled, third-party multipathing software can identify and aggregate LUNs for
servers to access to ensure normal operation of server services.
Figure 1-3 shows the read I/O process.
Figure 1-3 Read I/O process
1
HyperMetro management
2
3
Application
host
5
module
1 Feature Description
4
4
Local
LUN
Data center A
Remote
LUN
Data center B
1. An application host applies for read permission from the HyperMetro management
module.
NOTE
If the link between the storage arrays in the two data centers is down, the quorum server
determines which storage array continues providing services for hosts.
2. The HyperMetro management module enables the local storage system to respond to the
read I/O request made by the host.
3. If the local storage system is operating properly, it returns data to the HyperMetro
management module. If not, the HyperMetro management module enables the host to
read data from the remote storage system.
4. If the local storage array is working improperly, the HyperMetro management module
enables the host to read data from the remote storage array. The remote storage array
returns data to the HyperMetro management module.
5. The read I/O request made by the host is processed successfully.
1.3.5 Functions of a HyperMetro Consistency Group
A consistency group is a collection of multiple HyperMetro pairs. It ensures that the read/
write control policies of the multiple LUNs on a storage array are synchronized.
In medium- and large-sized database applications, data, logs, and modification information
are stored on different LUNs. If data on one of the LUNs becomes unavailable, data on the
other LUNs also becomes invalid. A consistency group is a collection of multiple HyperMetro
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
19
Page 28

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
pairs. It ensures that the read/write control policies of the multiple LUNs on a storage array
are synchronized. The operation and control policies of all members that have been added to a
consistency group must be consistent with those of the consistency group.
HyperMetro applications can use a consistency group to manage multiple HyperMetro pairs
in a unified manner.
The following compares synchronization in a consistency group with synchronization without
using a consistency group to prove that a consistency group is effective in preventing data
loss.
Without a HyperMetro Consistency Group
If LUNs are not added to a HyperMetro consistency group, the possibility of data loss is quite
high for these LUNs, as shown in Figure 1-4.
1 Feature Description
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
20
Page 29

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 1-4 Without a HyperMetro consistency group
1 Feature Description
Local storage array
Local
LUN01
Local
LUN02
Local
LUN03
Local
LUN01
Local
LUN02
Local
LUN03
Before data changes
HyperMetro pair 01
HyperMetro pair 02
HyperMetro pair 03
After data changes
HyperMetro pair 01
HyperMetro pair 02
HyperMetro pair 03
Remote storage array
Remote
LUN01
Remote
LUN02
Remote
LUN03
Remote
LUN01
Remote
LUN02
Remote
LUN03
1. No consistency group is
created.
· Data, logs, and
modification information of
a database application are
stored on local LUN01,
LUN02, and LUN03
respectively.
· No consistency group is
created on the local
storage array.
2. Synchronization fails, resulting
in data inconsistency.
Data synchronization fails
between two LUNs in
HyperMetro pair 02 due to a
fault of the HyperMetro pair.
Data synchronization
succeeds between LUNs in
HyperMetro pairs 01 and 03.
Phases in a process of data becoming invalid
Data recovery
Local
HyperMetro pair 01
LUN01
Local
HyperMetro pair 02
LUN02
Local
HyperMetro pair 03
LUN03
With a HyperMetro Consistency Group
If LUNs are added to a HyperMetro consistency group, no data is lost, as shown in Figure
1-5.
Remote
LUN01
Remote
LUN02
Remote
LUN03
3. Data becomes invalid.
After the local storage array
malfunctions due to a disaster,
data on the remote storage
array is used for data
recovery. Data in the database
of the local storage array is still
invalid because data on the
three local LUNs are not
stored at the same point in
time.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
21
Page 30
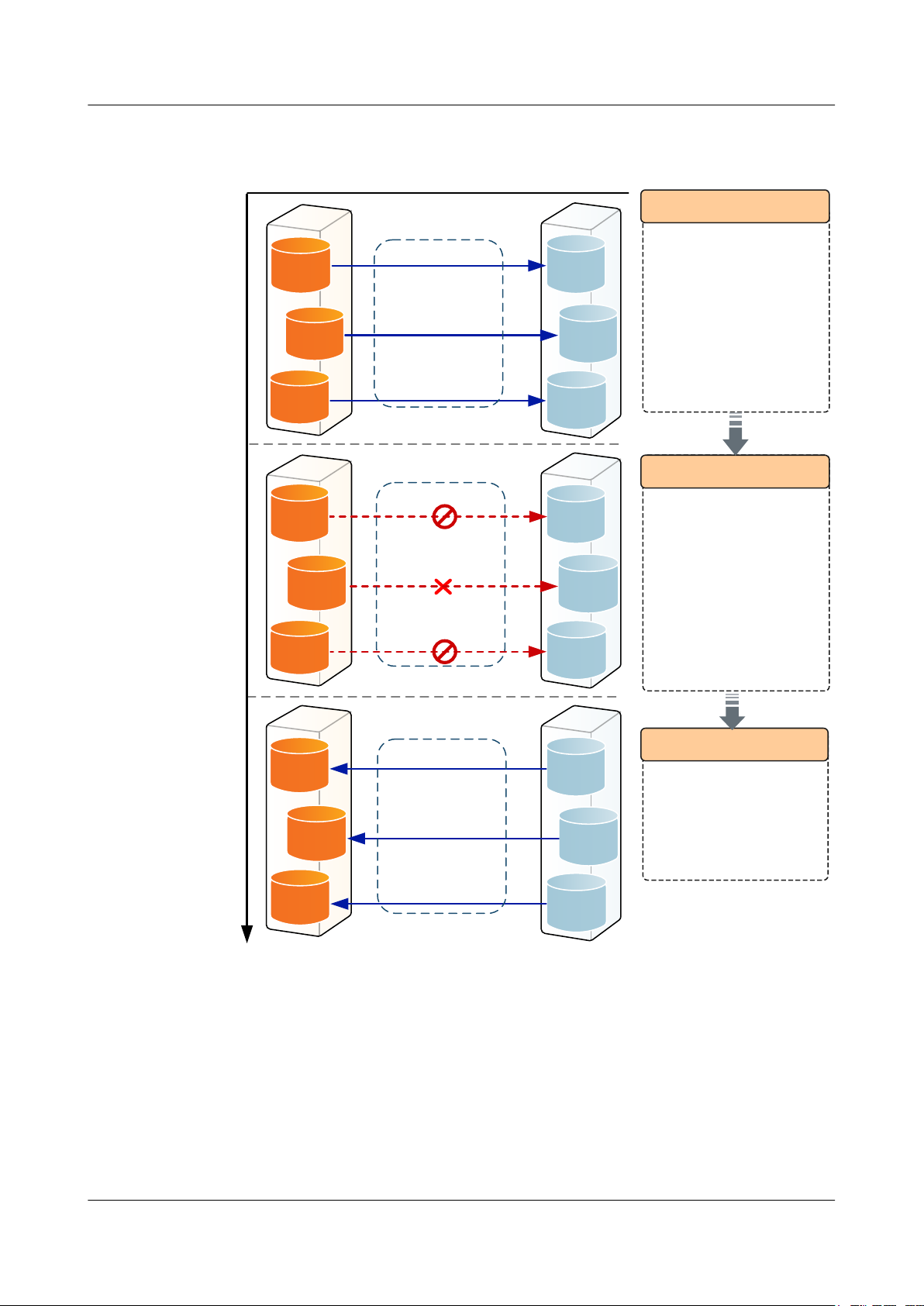
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 1-5 With a HyperMetro consistency group
1 Feature Description
Local storage array
Local
LUN01
Local
LUN02
Local
LUN03
Local
LUN01
Local
LUN02
Local
LUN03
Before data changes
HyperMetro pair 01
HyperMetro pair 02
HyperMetro pair 03
Consistency group 01
After data changes
HyperMetro pair 01
HyperMetro pair 02
HyperMetro pair 03
Consistency group 01
Remote storage array
Remote
LUN01
Remote
LUN02
Remote
LUN03
Remote
LUN01
Remote
LUN02
Remote
LUN03
1. A consistency group is
created.
· Data, logs, and
modification information
of a database application
are stored on local
LUN01, LUN02, and
LUN03 respectively.
· Consistency group 01 is
created on the local
storage array and three
HyperMetro pairs are
added to the consistency
group.
2. The consistency group stops
the replication task.
· HyperMetro pair 02
encounters a fault during
data synchronization.
· The consistency group
stops HyperMetro pairs
01 and 03 immediately.
· After the fault is rectified,
data is replicated.
Data recovery
Phases in a process of ensuring data validity by a consistency group
Local
HyperMetro pair 01
LUN01
Local
HyperMetro pair 02
LUN02
Local
HyperMetro pair 03
LUN03
Consistency group 01
1.4 Impact and Restrictions
This section describes the impact and restrictions of HyperMetro feature.
Network Restrictions
For details about network restrictions, see HyperMetro Solution Overview.
Remote
LUN01
Remote
LUN02
Remote
LUN03
3. The consistency group
ensures data validity.
After a disaster occurs, the
data on the remote storage
array is used for data
recovery. The data in the
database is valid.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
22
Page 31

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Device Restrictions
Table 1-6 Device configuration requirements
Device Configuration Requirement
1 Feature Description
Quorum server
l The arbitration software can be deployed on either a physical
machine or a virtual machine (VM). The configuration
requirements are as follows:
– CPU: X86-64 architecture; 2-core 1.6 GHz CPU (minimum
configuration)
– Memory: 4 GB DDR memory (minimum configuration)
– Operating system: Asianux Server 4 SP4 for x86_64, CentOS
6.5 for x86_64, NeoKylin 6.5 for x86_64, Red Hat Enterprise
Linux 6 for x86_64, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.1 for
x86_64, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.2 for x86_64, Red Hat
Enterprise Linux 6.3 for x86_64, Red Hat Enterprise Linux
6.5 for x86_64, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.6 for x86_64,
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.7 for x86_64, Red Hat Enterprise
Linux 7.2 for x86_64, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2 for
x86_64, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1 for x86_64,
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP2 for x86_64, SUSE
Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP3 for x86_64, SUSE Linux
Enterprise Server 11 SP4 for x86_64, SUSE Linux Enterprise
Server 12 SP2 for x86_64, Ubuntu 14.04 LTS for x86_64,
CentOS 6.8 for x86_64
NOTE
V300R006C00SPC100 and later versions support CentOS 6.8.
The arbitration software does not support operating systems that use
CPU architectures such as MIPS, ARM, and PPC.
– Storage capacity for installing the arbitration software: ≥ 10
GB
– Number of network ports: ≥ 3
NOTE
One network port is used for operating system management and the
other two are used as arbitration ports that connect to the storage
arrays.
l In the event of virtual machine deployment, virtual machines can
only use servers' local disks or LUNs that are provided by other
storage systems instead of the active-active storage systems as
system disks and data disks.
l Arbitration granularity can be a HyperMetro pair or a consistency
group.
Storage array
l The versions of the local and remote storage systems in a
HyperMetro relationship are the same. In addition, the hardware
configurations of the two storage systems are the same.
l The HyperMetro license must be available for the storage arrays
in two data centers.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
23
Page 32

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Compatibility
When using HyperMetro, ensure that the host operating system, multipathing software, and
arbitration software are compatible with each other. You can query the compatibility using the
OceanStor Interoperability Navigator.
1.5 Application Scenarios
This section introduces the application scenarios of HyperMetro.
Industry Application
HyperMetro is widely used in the following industries:
l Health Care
As hospital services develop, the number of beds increases, and new clinic buildings are
constructed, hospitals have higher requirements for service continuity. Once critical
services such as out-patient, in-patient, and electronic medical record (EMR) services are
interrupted, medical treatment will be delayed and hospitals will suffer from great
economic loss and inestimable damage to their reputation. Hospitals require zero
recovery point objective (RPO) and the recovery time objective (RTO) must be within
five minutes. In addition, the out-patient building and in-patient network information
center in a hospital and two hospitals in the same city are physically close to each other.
HyperMetro can meet hospitals' requirements.
1 Feature Description
l Finance
In the finance industry, banking services, 24-hour ATM services, POS services, and ebank services are developing quickly. These services require that banking systems
process services around the clock. Banks need a solution to meet their service
construction requirements (RPO = 0, RTO ≈ 0) and ensure business continuity. Service
interruptions damage banks' reputation, posing huge pressure on technical departments.
HyperMetro meets requirements of hospitals' class-A+ and class-A services (Class-A+
services include core system services, payment system services, counter services, and
encryption platform services and class-A services include ESB services, ECIF services,
trade system services, e-channel services, centralized operation services, and e-bank
services).
l Social Insurance
The social insurance industry also has high requirements for service continuity. Monthly
accounting and year-end settlement require 24/7 services. If social insurance systems
malfunction, livelihood issues will appear. For example, people cannot obtain their
pensions on time and health insurance problems cannot be resolved. HyperMetro is
applicable to social insurance application scenarios including the basic information
management, social insurance card system, labor relationship management, public
services, public resource management, employment, and social insurance management.
Application of HyperMetro Paired with Other Features
For the HyperMetro feature, due to distance restrictions, two data centers must be constructed
in the same city. Because the Disaster Recovery Data Center Solution (Active-Active Mode)
cannot be used to cope with regional disasters, a remote DR center is constructed to expand
the existing solution to the Disaster Recovery Data Center Solution (Geo-Redundant Mode).
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
24
Page 33

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
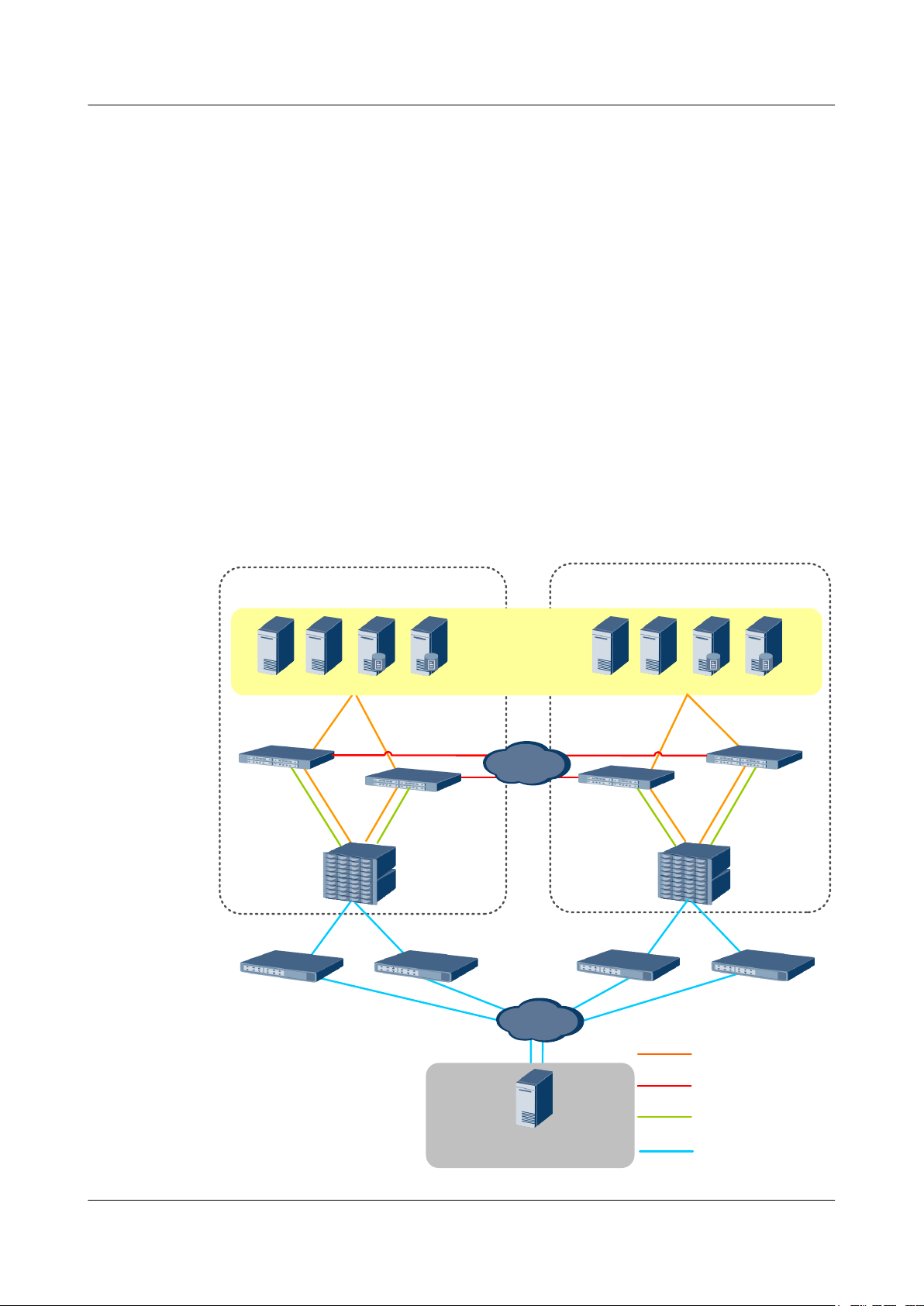
Figure 1-6 shows the network of the 3DC with HyperMetro and asynchronous remote
replication.
Figure 1-6 Network of the 3DC with HyperMetro and asynchronous remote replication
1 Feature Description
Site A
Storage system
LUN
Production center
Optical fiber
Network cable
Site B
LUN
HyperMetro
Storage system
Same-city
production center
Asynchronous
remote
replication
Site C
LUN
Storage system
Remote DR center
NOTE
A remote replication relationship can be established between the remote DR center and either production
center.
Besides, HyperMetro + synchronous remote replication network can be achieved. However,
due to distance restrictions, synchronous remote replication is used to implement shortdistance DR. Figure 1-7 shows the network.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
25
Page 34

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 1-7 Network of the 3DC with HyperMetro and synchronous remote replication
1 Feature Description
Site A
Storage system
LUN
Production center
Optical fiber
Site B
LUN
HyperMetro
Storage system
Same-city
production center
Synchronous
remote replication
Site C
LUN
Storage system
Same-city DR
center
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
26
Page 35

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
This chapter describes the networks and data you must plan before HyperMetro configuration.
This document describes how HyperMetro works and related operations on storage devices.
For details about data planning and service configuration process, see BC&DR Solution
Product Documentation V200R001 (Active-Active Data Center).
2 Planning
2 Planning
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
27
Page 36

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
About This Chapter
This chapter describes how to install the HyperMetro feature and devices related to the
feature, connect cables, and power on devices, helping you avoid unnecessary rework during
and after installation.
3 Installation
3 Installation
3.1 Installation Process
Before the installing a storage array, view the installation process. The installation process
guides you through a smooth and complete installation.
3.2 Preparations for Installation
Preparations before installing devices include preparing tools and meters, checking the
installation environment, and unpacking and checking goods. Sufficient preparation ensures a
safe and proper installation.
3.3 Device Installation
Install devices as instructed in the following description to avoid unnecessary rework at your
site.
3.4 Cable Connection
HyperMetro cable connection involves: network between hosts and storage arrays,
HyperMetro replication network, same-city data center network, and quorum network.
3.5 Power-on
After installing all devices, power on them and check their operating status. Ensure that all
devices and their hardware are properly installed. Otherwise, do not power on them.
3.6 Storage Array Initialization
After powering on a storage array, you must initialize it.
3.7 Multipathing Software Installation
This section describes installation environment requirements, pre-installation preparations,
and the installation procedure of multipathing software.
3.8 Arbitration Software Installation
This section describes how to install the arbitration software. Quorum server software needs
to be installed only when a quorum server is used for HyperMetro.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
28
Page 37

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
3.1 Installation Process
Before the installing a storage array, view the installation process. The installation process
guides you through a smooth and complete installation.
Figure 3-1 shows the installation process.
Figure 3-1 Installation process
Start
Preparations for Installation
Device Installation
3 Installation
Cable Connection
Power-on
Storage Array Initialization
Multipathing Software
Installation
Arbitration Software
Installation
End
3.2 Preparations for Installation
Preparations before installing devices include preparing tools and meters, checking the
installation environment, and unpacking and checking goods. Sufficient preparation ensures a
safe and proper installation.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
29
Page 38

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
3.2.1 Preparing Tools, Meters, and Documentation
Before installing devices, ensure that necessary installation support materials including tools,
meters, and documentation are available. A good preparation helps ensure a correct and
smooth installation.
Table 3-1 lists the tools required in the installation process.
Table 3-1 Tools required in the installation process
3 Installation
Name
Marker Marks a location and
Phillips screwdriver
(M3 to M6)
Flat-head screwdriver
(M3 to M6)
Diagonal pliers Cuts insulation tubes
Crimping tool Crimps the metal jacket
Segmented blade
utility knife
Pictogram Function
scale.
Fastens small screws or
bolts, and has a crossshaped head.
Fastens small screws or
bolts, and has a flat
head.
and cable ties.
at the end of a coaxial
cable assembly.
Cuts the adhesive tapes
on a carton.
Floating nut mounting
bar
Antistatic clothing Prevents operators
ESD glove Prevents operators
ESD wrist strap Prevents operators
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Installs or removes a
floating nut.
against electrostatic
charges.
against electrostatic
charges.
against electrostatic
charges.
30
Page 39

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Table 3-2 lists the meters required in the installation process.
Table 3-2 Meters required in the installation process
Name Pictogram Function
Multimeter Measures the insulation
Network cable tester Tests whether a network
3 Installation
of a cabinet, connection
of a cable, and electric
performance
specifications of a
device, such as the
voltage, current, and
resistance.
cable works properly.
Prepare the following materials before installing devices: contract/agreement, device
configuration table, equipment room design and construction drawing paper (provided by the
customer), and product documentation.
Obtaining Documentation
Before configuration, get the documentation in Table 3-3 ready.
Table 3-3 Documentation list
Document Name
Installation Guide For example, if you want to
CloudEngine 6800&5800 V100R002CXX Product
Documentation
OceanStor SNS2124&SNS2224&SNS2248 Fibre Channel
Switch V100R002CXX User Guide
How to Obtain
obtain OceanStor UltraPath
for Linux V100R008C50
User Guide, log in to http://
support.huawei.com/
enterprise/, enter UltraPath
in the search bar, and press
Enter to view or download
the document of the relevant
version.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
31
Page 40

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Document Name How to Obtain
3 Installation
l OceanStor UltraPath for Linux V100R008CXX User
Guide
l OceanStor UltraPath for AIX V100R008CXX User
Guide
l OceanStor UltraPath for Solaris V100R008CXX User
Guide
l OceanStor UltraPath for vSphere V100R008CXX User
Guide
l OceanStor UltraPath for Windows V100R008CXX User
Guide
NOTE
This document uses product
versions in Table 3-3 as
examples. If the onsite product
versions are different from
those in the document, Log in
to http://
support.huawei.com/
enterprise/, and obtain the
Version Mapping specific to
the product versions at your
site and complete the
configuration.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Solution
V200R001CXX User Guide (Active-Active Mode)
HUAWEI Rack Server Product Documentation
3.2.2 Quick checklist for the installation environment
To implement a correct and smooth device installation, ensure that the installation
environment meets requirements before installing storage devices.
Table 3-4 lists the check items and requirements on the installation environment.
Table 3-4 Quick checklist for the installation environment
No.
Item Requirement
1 Site selection The site of the equipment room must be free of: high or low
temperature, heavy dust, harmful gas, inflammable or
explosive materials, electromagnetic interference (nearby
large-sized radar station, broadcast transmitting station, or
transformer station), unstable electric voltage, and large
vibration or strong noise. Therefore, during the engineering
design, you need to consider hydrology, geography,
earthquake, electric power, and transportation conditions
according to the technical requirements for communication
network planning and communication devices.
2 Civil construction The size of the equipment room must be sufficient for product
installation and capacity expansion. The floor can meet the
requirements for the bearing weight. The cable slot, cable
ladder, and cable holes are complete or ready. The decoration
is complete.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
32
Page 41

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
No. Item Requirement
3 Installation
3 Operating
ambient
temperature
4 Altitude
5 Particle
Contaminants
l When the altitude is lower than 1800 m (5904 feet), the
room temperature of controller enclosures and disk
enclosures must be kept within 5°C to 40°C (41°F to
104°F), and that of high-density disk enclosures must be
kept within 5°C to 35°C (41°F to 95°F).
l When the altitude ranges between 1800 m (5904 feet) and
3000 m (9840 feet), the room temperature must be kept
within 5°C to 30°C (41°F to 86°F).
l Operating altitude of disks
– HDDs: –304.8 m to +3048 m (–999.99 ft. to
+9999.99 ft.)
– SSDs: –305 m to +3048 m (–1000.64 ft. to +9999.99
ft.)
l Non-operating altitude of disks
– HDDs: –305 m to +12192 m (–1000.64 ft. to
+39999.51 ft.)
– SSDs: –305 m to +12192 m (–1000.64 ft. to
+39999.51 ft.)
l ISOa 14664-1 Class8.
l You are advised to ask a professional organization to
monitor the particle contaminants in the equipment room.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
33
Page 42

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
No. Item Requirement
3 Installation
6 Corrosive
Airborne
Contaminants
l Copper corrosion rate: less than 300 Åb/month per ANSIc/
ISAd-71.04 severity level G1.
l Silver corrosion rate: less than 200 Åb/month per ANSIc/
ISAd-71.04 severity level G1.
l You are advised to ask a professional organization to
monitor the corrosive airborne contaminants in the
equipment room.
l The following is an example of initial evaluation for
environmental corrosion risks.
– Whether the equipment room is near any sulfurous gas
emission sources, for example, porcelain factories,
rubber plants, tire factories, chemical factories, sewage
plants, power stations, paper mills, smelters,
automobile factories, coal mines, electroplating
factories, food factories, and tanneries? If yes,
environmental corrosion risks may exist.
– Whether the equipment room is near the sea, saline,
sewer outlets, sewage treatment tanks, and industrial/
heating boilers? If yes, environmental corrosion risks
may exist.
– Whether the equipment room was decorated in the
latest six months? If yes, environmental corrosion risks
may exist.
– Whether batteries are stocked in the equipment room?
Whether the storage battery leaks? If yes,
environmental corrosion risks may exist.
– Whether the equipment room is closed tightly?
Whether the room windows and doors are always
closed? If no, environmental corrosion risks may exist.
7
Vibration and
shock
l Operating vibration
5 Hz to 300 Hz: 1.5 m/s2, 0.5 oct/min 3 axes, 1 sweep
cycles per axis; 5 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.27 Grms, 3 axes, 10 min
per axis
l Non-operating vibration
5 Hz to 20 Hz, PSD: 1.0 m2/s3; 20 Hz to 200 Hz, –3 dB/
oct; 3 axes, 30 min per axis
l Non-operating shock
Half sine, 6 ms, 300 m/s2, 6 directions, 3 times per
direction
8 Air conditioner If the temperature in the room exceeds 35°C, you are
recommended to install air conditioners (which can be
restarted after power-off). Do not let the air conditioner blow
directly toward the devices.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
34
Page 43

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
No. Item Requirement
3 Installation
9 Moisture-proof
measures
If the relative humidity is greater than 70%, install the
dehumidifying device, such as the air conditioner with the
dehumidification function or special dehumidifier. Ensure that
the equipment room is protected from water seepage and dew.
10 Heating For an environment where the average daily temperature is
lower than 5°C for at least 90 days each year, heating devices
are required. For an environment where the average
temperature is lower than 5°C for 60 to 90 days each year,
heating devices are recommended.
11 Ventilation and
heat dissipation
To ensure smooth ventilation, the cabinet should be at least
100 cm (39.4 inches) away from the walls and you should
leave a clearance of at least 120 cm (47.28 inches) between
the cabinets. To keep a convective air transfer between the
cabinet and the equipment room, no enclosed space is allowed
in the cabinet. 1 U space should be left above and below each
device.
12 Dust-proof
measures
For the equipment room near dust sources (such as coal
mines, country roads, or farmland), use double-layer
aluminum alloy windows for proper sealing and an anti-theft
and fireproof door. Separate the devices from the door with a
partition board to avoid dust.
13 Ground resistance Less than 10 Ω. The distance between the top of the ground
terminal and the ground should be at least 0.7 m (27.58
inches). In the cold regions, the ground terminal should be
buried under the layer of frozen earth. Periodically monitor
ground resistance to ensure ground effectiveness.
14 Ground lead-in The ground bar in the equipment room should be connected to
the network of ground cables. The ground lead-in should not
be longer than 30 m (98.4 feet) and should use the zinc-coated
flat steel whose cross-sectional area is equal to or more than
40 mm (1.57 inches) x 4 mm (0.157 inches). The contact point
should be handled for insulation and anticorrosive purposes.
The above-ground steel should be provided with measures to
avoid mechanical damage and should be intact without
soldering points for the break.
15 Lightning
protection
The equipment room must be provided with lightning
conductors such as the lightning rod or lightning belt. The
lightning conductors share the ground bars with the protection
ground cables of the equipment room.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
35
Page 44

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
No. Item Requirement
16 AC The AC distribution switches and AC power cables are
3 Installation
properly installed.
The 2 U controller enclosure
l 100 V to 240 V, ±10%, 10 A to 12 A, single-phase, 50/60
Hz
l Supports dual-live-line input (2W+PE), 200 V to 240 V,
±10%
The 3 U and 6 U controller enclosure
l 200 V to 240 V, ±10%, 10 A, single-phase, 50/60 Hz
l Supports dual-live-line input (2W+PE), 200 V to 240 V,
±10%
Disk enclosure
l 100 V to 240 V, ±10%, 10 A, single-phase, 50/60 Hz
High-density disk enclosure
l 100 V to 127 V, ±10%, 10 A, single-phase, 50/60 Hz
l 200 V to 240 V, ±10%, 5 A, single-phase, 50/60 Hz
17 High voltage DC The high voltage DC distribution switches and high voltage
DC power cables are properly installed.
l The high voltage DC power module of the 2 U controller
enclosure (N/A for North America and Canada): 240 V,
±20%, 6.5 A
l The high voltage DC power module of the 3 U and 6 U
controller enclosure (N/A for North America and Canada):
240 V, ±20%, 10 A
l The high voltage DC power module of the disk enclosure
(N/A for North America and Canada) : 240 V, ±20%, 10 A
18 DC The DC distribution switches and DC power cables are
properly installed.
l The DC power module of the 2 U controller enclosure: -48
V to -60 V, ±20%, 30 A
l The DC power module of the disk enclosure: -48 V to -60
V, ±20%, 18.5 A
19 Circuit breaker To prevent other devices connected to the circuit breakers
from being incorrectly powered off due to a power supply
failure of the storage device, you are advised to ensure that the
electric current of the circuit breakers of the external power
supplies to which the storage device is connected complies
with the following specifications:
l AC power supplies: greater than 16 A
l DC power supplies: greater than 32 A
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
36
Page 45

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
No. Item Requirement
20 AC power ground Do not connect the neutral line of a power cable to the
3 Installation
protection ground bar of any communication devices in the
equipment room. It is recommended that you set leading-out
terminals for AC safety ground in the equipment room for the
connection to devices.
21 AC surge
protection
The AC power system of the equipment room must be
equipped with a lightning arrestor with the rated discharging
current no less than 20 kA. The arrestor must be properly
grounded.
22 DC power ground The storage device is a type of DC-I device on which the
"RTN" terminals and the ground terminal of the system
chassis are separated. The DC power module of the storage
device does not provide any ground terminals. Therefore, the
storage device is grounded through the ground terminal of the
system chassis.
23 Transmission
device
The debugging of the transmission device is complete, and the
capacity of the transmission device meets the engineering
requirements. The protection ground of the transmission
system must be connected to the ground bar in the equipment
room.
24 Cabinet The cabinet for installing the devices must be a standard 19-
inch cabinet. The depth of the cabinet must be at least 1000
mm (39.37 inches). The depth of a cabinet for installing highdensity disk enclosures must be at least 1100 mm (43.31
inches).
a: ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
b: Å is the international symbol for the non-SI unit ångström, a physical unit of length. One
Å is equal to ten-billionth of one meter.
c: ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
d: ISA (Instrument Society of America)
In addition, make sure that the following special requirements on the site are met:
l Ensure that doors, passageways, and elevators are of adequate dimensions to allow
passage of the cabinets.
l Before installation, check whether to submit the qualification certificate of the
installation company to the property management entity in charge of the installation site.
l Confirm the delivery time and installation time in advance, for example, from 8:00 a.m.
to 6:00 p.m.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
37
Page 46

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
NOTICE
l Take particular care to avoid bumping into doors, walls, or shelves during transportation,
relocation, or installation of storage devices.
l Do not touch the components or uncoated metal surface of any unit with dirty gloves.
3.3 Device Installation
Install devices as instructed in the following description to avoid unnecessary rework at your
site.
Install devices in data center A, data center B, and a third-place quorum site. The following
components are used as an example. Install devices based on onsite requirements. The
installation process is as follows:
3 Installation
Instal
lation
Sequ
ence
1 Data centerA1. Install the storage devices. For details about how to install it, see
Site Procedure
the Installation Guide of the corresponding product model.
2. Install CloudEngine 5800 series switches. For details about how
to install a CloudEngine 5800 switch, see:
l CloudEngine 7800&6800&5800 Hardware Installation and
Maintenance Guide
l CloudEngine 7800&6800&5800 V100R005C00
Configuration Guide
NOTE
If you use other switches, see the installation guide specific to the
switches at your site to install them.
3. Install SNS2248 series switches. For details about how to install
an SNS2248 switch, see the OceanStor
SNS2124&SNS2224&SNS2248 Fibre Channel Switch
V100R002C00 User Guide.
NOTE
If you use other switches, see the installation guide specific to the
switches at your site to install them.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
38
Page 47

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
3 Installation
Instal
Site Procedure
lation
Sequ
ence
2 Data centerB1. Install the storage devices. For details about how to install it, see
the Installation Guide of the corresponding product model.
2. Install CloudEngine 5800 series switches. For details about how
to install a CloudEngine 5800 switch, see:
l CloudEngine 7800&6800&5800 Hardware Installation and
Maintenance Guide
l CloudEngine 7800&6800&5800 V100R005C00
Configuration Guide
NOTE
If you use other switches, see the installation guide specific to the
switches at your site to install them.
3. Install SNS2248 series switches. For details about how to install
an SNS2248 switch, see the OceanStor
SNS2124&SNS2224&SNS2248 Fibre Channel Switch
V100R002C00 User Guide.
NOTE
If you use other switches, see the installation guide specific to the
switches at your site to install them.
3 Third-
place
quorum
site
1. Install the quorum server.
NOTE
For details about how to install a quorum server, see the installation
guide specific to the quorum server at your site.
2. Install CloudEngine 5800 series switches. For details about how
to install a CloudEngine 5800 switch, see:
l CloudEngine 7800&6800&5800 Hardware Installation and
Maintenance Guide
l CloudEngine 7800&6800&5800 V100R005C00
Configuration Guide
NOTE
If you use other switches, see the installation guide specific to the
switches at your site to install them.
For details about the device layout, see Figure 3-2 or Figure 3-3. The device models and
number of devices depend on the onsite requirements.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
39
Page 48

39 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
38 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
37 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
36 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
35 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
34 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
33 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
32 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
31 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
30 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
29 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
28 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
27 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
26 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
25 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
24 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
23 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
22 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
21 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
20 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
19 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
18 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
17 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
16 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
15 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
14 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
13 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
12 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
11 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
10 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
9 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
8 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
7 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
6 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
5 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
4 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
3 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
2 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
1 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
Data ce nter 1
Cabine t: H05
SNS2248
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
RH2288(s evice host)
Data ce nter 2
Cabine t: H05
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Disk enc losure
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
SNS2248
Filler panel
CE5800
Filler panel
CE5800
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
SNS2248
Filler panel
RH2288(s evice host)
Filler panel
Third-place quorum site
Cabine t: H01
SNS2248 Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
CE5800 CE5800
Filler panel Filler panel
CE5800 CE5800
Filler panel
Filler panel RH1288 V3 ( quorum server)
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Disk enc losure
Filler panel
Filler panel
Disk enc losure Disk enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel Filler panel
Controller enc los ure Controller enc los ure
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Disk enc losure Disk enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel
Disk enc losure Disk enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
42 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
41 1U 0U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
40 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
39 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
38 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
37 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
36 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
35 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
34 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
33 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
32 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
31 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
30 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
29 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
28 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
27 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
26 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
25 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
24 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
23 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
22 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
21 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
20 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
19 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
18 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
17 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
16 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
15 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
14 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
13 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
12 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
11 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
10 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
9 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
8 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
7 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
6 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U 1U
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Sevice host Sevice host
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel Fill er panel Fil ler panel
Filler panel Fill er panel Fil ler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel Fi ller panel
Filler panel Filler panel Fi ller panel Fil ler panel Filler panel
CE5800 Filler panel CE5800 Filler panel Fi ller panel
CE5800 Filler panel CE5800
Engine
Filler panel
Filler panel Fill er panel Fil ler panel
SNS2248 SNS2248 Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Engine
SNS2248
KVM
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel SVP Filler panel SVP Fil ler panel
KVM
Filler panel
CE5800
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel CE5800
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
RH 1288V3
Filler panel
Data center 2 Third-place q uorum site
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel Fill er panel Fil ler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
SNS2248
Data center 1 Data center 1 Data center 2
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Disk
enclosure
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
Filler panel
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 3-2 Device layout (3 U storage device)
3 Installation
Figure 3-3 Device layout (6 U storage device)
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
40
Page 49

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
l Storage device layout
– To conveniently maintain and operate a controller enclosure, install it in the middle
of the cabinet (15 U to 25 U).
– Reserve 2 U space above and below the controller enclosure to install the cable tray
(also to facilitate the operation of removing and inserting the modules in the
controller enclosure).
– Symmetrically install disk enclosures above and below the controller enclosure.
– Do not stack disk enclosures. Enable five disk enclosures to form a group. In a
cabinet, reserve at least 1 U space between disk enclosure groups for easier
management and minimum vibration transfer.
– Reserve 2 U space at the bottom of the cabinet to facilitate cabling, ventilation and
heat dissipation, and maintenance of the devices in the lower part of the cabinet.
l Switch layout
– Install two SNS2248 switches into two cabinets respectively or the same cabinet in
a data center. Use different power supplies to provide power for them.
– Reserve 1 U space below each switch for cabling.
3 Installation
3.4 Cable Connection
HyperMetro cable connection involves: network between hosts and storage arrays,
HyperMetro replication network, same-city data center network, and quorum network.
Figure 3-4, Figure 3-5 and Figure 3-6 show how switches, controller enclosures, and service
hosts are connected using cables in and across data centers.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
41
Page 50

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 3-4 Cable connections in and across data centers (2 U storage device)
3 Installation
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
42
Page 51

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 3-5 Cable connections in and across data centers (3 U storage device)
3 Installation
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
43
Page 52
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 3-6 Cable connections in and across data centers (6 U storage device)
3 Installation
NOTE
l The ports that are numbered in digits are connected using cables in data centers and the ports that are
numbered in upper-case letters are connected using cables across data centers.
l For details about cable connections between disk enclosures and controller enclosures, see
Cascading Disk Enclosures in the Installation Guide of the corresponding product model.
l The quorum site supports two quorum servers in active/standby mode for V300R006C10 and later
versions.
Fibre Channel networking is used as an example to explain cable connection principles. For
details, see Table 3-5.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
44
Page 53
OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Table 3-5 Cable connection principles
3 Installation
Network
Type
Network
between hosts
and storage
arrays
HyperMetro
replication
network
Cable Connection Principle
l Hosts and storage devices are connected through Fibre Channel
switches. Each data center has two Fibre Channel switches.
l Each Fibre Channel switch has at least N ports to connect hosts and
storage devices. N = 1 x Number of Servers + 2 x Number of
Storage Devices.
l Host-Fibre Channel switch connection: Each host has at least two
Fibre Channel ports to connect two Fibre Channel switches of the
data center. It is recommended that the two ports be separated on two
HBAs.
l Storage device-Fibre Channel switch connection: Each controller has
at least two ports to connect two Fibre Channel switches of the data
center. It is recommended that the two ports be separated on two
Fibre Channel interface cards.
l The HyperMetro replication network between storage devices uses
Fibre Channel switches for connection. Each data center has two
Fibre Channel switches.
l Storage device-Fibre Channel switch connection: Each controller has
two Fibre Channel ports to connect two Fibre Channel switches of the
data center. It is recommended that the two ports be separated on two
Fibre Channel interface cards.
Same-city
network
between data
centers
Arbitration
network
Management
network
l Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) devices are
recommended for data center interconnection.
l If the HyperMetro replication network is a Fibre Channel network,
Fibre Channel switches are cascaded in one-to-one mode. If the
HyperMetro replication network is an IP network, Ethernet switches
are cascaded in one-to-one mode.
l The quorum server is connected to storage devices through Ethernet
switches. Each data center has two Ethernet switches.
l Each controller of a storage device has one IP port to connect to one
Ethernet switch of the data center.
l The quorum server is connected to Ethernet switches. It is
recommended that two IP ports be separated on two network adapters
to connect two Ethernet switches at the quorum site.
l An Ethernet switch is used for management. The management
network ports of the host and controller are connected to one Ethernet
switch of the data center.
l You can use BCManager eReplication to manage networks. For
details, see Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Solution
V200R001CXX User Guide (Active-Active Mode). For details about
how to obtain the documentation, see 3.2.1 Preparing Tools, Meters,
and Documentation.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
45
Page 54

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
3.5 Power-on
After installing all devices, power on them and check their operating status. Ensure that all
devices and their hardware are properly installed. Otherwise, do not power on them.
Power-on Principles
l Both parties (Huawei and the customer) must be at the power-on site. Devices can be
powered on only after both parties confirm the power-on operation.
l Operations on power sourcing equipment (PSE), power distribution equipment (PDE),
and powered devices (PDs) must comply with standards and regulations.
l You must submit a power-on application to the customer's administrative unit. After an
approval, power on and operate devices under the assistance and supervision of power
engineers and supervision personnel assigned by the customer at the site.
l PDs must be connected to the positions specified by PSE and PDE to ensure that PSE
and PDE can provide power for PDs.
l You must use measuring instrument to check whether power supplies meet the following
requirements before powering on a device: The power supply of the device is not shortcircuited; the power cable plug is firmly connected; the output switch of the PSE is
turned off and the output voltage is within the normal range; all power switches of the
PDs are turned off; the PDs are not short-circuited.
3 Installation
Check Before Power-on
l Checking the device installation
Table 3-6 lists the check items.
Table 3-6 Device installation checklist
Check
Item
Controller
enclosure
Disk
enclosure
Switch
Host
Filler
panel
Entirety
Normal Abnormal
l Stably installed on the guide
rails without displacement.
l Tightly screwed.
The vacant slots in the cabinet are
covered by filler panels.
l All devices are stably installed
without displacement.
l All screws are tightly screwed.
l Tilted.
l Screws are loose or dropped
off.
The vacant slots in the cabinet are
exposed.
l One ore more devices are
displaced.
l One or more devices are tilted.
l Screws are loose or dropped
off.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
46
Page 55

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
l Checking the cable layout
Table 3-7 lists the check items.
Table 3-7 Cable layout checklist
No. Check Item
1 Labels are correctly attached to cables.
2 Cables are laid out in an untangled and orderly fashion.
3 When cables pass through the cable ladder, cables are secured to the beam of
4 Troughs are used to route cables outside the cabinet and cables do not
5 The bending radius of optical fibers is equal to or larger than 50 mm.
6 The power cable and the protection ground (PGND) cable are bent smoothly.
7 The power and PGND cables are connected correctly and firmly.
3 Installation
the cable ladder.
overflow the troughs.
8 Ground cables of a cabinet are connected correctly and firmly.
9 The diameters of the power and PGND cables meet the power distribution
requirements.
10 The power cables, grounding cables, and signal cables outside the cabinet are
laid separately with a distance of larger than 30 mm.
11 Cables are bound in a rectangular shape. (Single-core cables can be bound in
a round shape.)
12 Cables are bent with a bend radius of greater than 60 mm at turning points
and are not bundled at bend points.
13 Optical fibers are laid out without using force or having unnatural bends and
squeezes.
14 OT terminals of the power cables and grounding cables are welded or
crimped firmly.
15 Protection tubes or insulating adhesive plasters are used to wrap power
cables, naked cables, and OT terminal stems of ground cables. There should
be no bare copper wires in OT terminals.
16 All cabinets and enclosures with metal or partially metal shells are correctly
grounded and connected.
17 Cables are correctly bundled at an even spacing. After cables are bundled
with cable ties, the excess parts of the cable ties are cut off without burrs. All
the cable ties face the same direction for a neat appearance.
18 The DC power cables shipped with the storage device are black and blue,
and the PGND cable is olive or yellow.
19 Power cables and grounding cables use the entire copper core without a joint.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
47
Page 56

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
No. Check Item
20 Labels are attached to the power cables and grounding cables in the same
Power-on Procedure
l Step 1 Connect grounding cables.
a. Huawei is responsible for connecting grounding cables of storage devices and
cabinets and checking whether ground resistance connectors are connected firmly.
b. Huawei is responsible for testing the ground resistance between storage cabinets
and the equipment room and checking whether ground resistance connectors are
connected firmly.
l Step 2 Power on power distribution frames (PDFs) and array cabinets.
a. Huawei is responsible for turning on/off miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) and
switches of PDFs and array cabinets.
3 Installation
direction for users' convenient check.
b. The customer is responsible for using a multimeter to check the output voltage of
l Step 3 Power on devices.
a. Huawei is responsible for turning on/off switches of power distribution units
b. The customer is responsible for checking the operating status of input power to
Check After Power-on
After powering on devices, check the following items:
array cabinets and PDFs and ensure that the output voltage is in a normal range and
PSEs have sufficient redundant power supplies to meet power requirements of
storage devices and cabinets.
(PDUs) and powering on devices in sequence under the supervision of the customer.
The power-on sequence is: storage devices > Fibre Channel switches > core
switches > application hosts.
NOTE
Power on the next device only after the previous device is running properly. For details
about how to power on storage devices, see Powering On Devices in the Installation Guide
of the corresponding product model.
ensure that input power is stable during the power-on process of cabinets and
storage devices.
l Check whether fans of the devices are working properly and air is discharged from the
air vent.
l Check whether device indicators are normal.
NOTE
For details about device indicator status, see Powering On Devices in the Installation Guide of
the corresponding product model.
l Log in to devices and check their operating status.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
48
Page 57

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
3.6 Storage Array Initialization
After powering on a storage array, you must initialize it.
Storage array initialization includes configuring an initial IP address for the management
network port as well as applying for and importing a license. For details about how to
initialize a storage array, see Initializing the Storage System in the Installation Guide of the
corresponding product model.
3.7 Multipathing Software Installation
This section describes installation environment requirements, pre-installation preparations,
and the installation procedure of multipathing software.
Context
Multipathing software must be installed for the HyperMetro solution. You can use either
Huawei UltraPath or third-party multipathing software.
l In terms of multipathing, UltraPath is recommended for HyperMetro. UltraPath can
identify host locations so that hosts can access the nearest storage array, reducing crosssite accesses and latency while improving access efficiency and storage performance.
3 Installation
NOTE
For details on how to install UltraPath, see UltraPath Software Installation.
l If the customer needs to use third-party multipathing software on the application server,
the function of Uses third-party multipath software for initiators must be enabled on
Huawei storage.
NOTE
For details on how to install third-party multipathing software, see Third-party Multipathing
Software Installation.
3.7.1 UltraPath Software Installation
Selecting and managing paths between an application server and the storage system can be
realized after the UltraPath software is installed.
Context
To ensure that link aggregation can be implemented in the scenario that a HyperMetro LUN is
mapped to a host, install UltraPath on the host before configuring HyperMetro pairs.
Install UltraPath software following instructions in the relevant documentation. For details
about applicable software versions, see 1.2 License Requirements and Compatible
Products. For details about how to obtain the documentation, see 3.2.1 Preparing Tools,
Meters, and Documentation.
3.7.2 Third-party Multipathing Software Installation
This section describes installation environment requirements, pre-installation preparations,
and the installation procedure of third-party multipathing software.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
49
Page 58

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Context
The operating systems type of third-party multipathing software supported by the
HyperMetro, refer to the HyperMetro Configuration Guide for Huawei SAN Storage
Using OS Native Multipathing Software.
NOTE
Log in to http://support.huawei.com/enterprise/. In the search bar, enter the document name. Search,
browse, and download the Host Connectivity Guide for corresponding operating systems to install the thirdparty multipathing software.
For example, if you want to obtain HUAWEI SAN Storage Host Connectivity Guide for Oracle, log in to
http://support.huawei.com/enterprise/, enter Host Connectivity Guide Oracle in the search bar, and press
Enter to view or download the document of the relevant version.
3.8 Arbitration Software Installation
This section describes how to install the arbitration software. Quorum server software needs
to be installed only when a quorum server is used for HyperMetro.
3 Installation
Prerequisites
Context
l For details about how to obtain this software, see the Availability section.
l The quorum server has been deployed and its hardware meets the requirements.
NOTE
l For the hardware requirements on the quorum server, see section Impact and Restrictions.
l If you deploy the quorum server on a VM, you can export an OVA template of this VM for
quick deployment once the VM fails. For details, see 6.8 How Can I Use OVA Templates to
Quickly Deploy Virtual Quorum Servers?.
l The validity period of the default arbitration certificate is 10 years (start from September
2015). Ensure the system time of the quorum server is correct so that the default
arbitration certificate is valid.
l Use a Secure Shell (SSH) tool such as Xshell, PuTTY to log in to the quorum server.
NOTE
To ensure security of the operating system, you are advised to harden its security. For details about
how to harden security of an operating system, see the official security operation guide of the
operating system.
By default, the Ubuntu system uses dash upon the installation. However, the arbitration
software must be installed in bash mode. Therefore, you must disable dash when installing the
arbitration software in the Ubuntu system.
NOTE
In any directory of the Ubuntu system's operating system, run the sudo dpkg-reconfigure dashcommand.
Press the → key, select No, and press Enter to disable dash.
The system shell is the default command interpreter for shell scripts.
xUsing dash as the system shell will improve the system's overall performance. It
does not alter the shell presented to interactive users.
Use dash as the default system shell (/bin/sh)?
<Yes> <No>
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
50
Page 59

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the quorum server.
Select a user account according to your quorum server:
l When using a third-party quorum server, log in to the server using the root user.
l When using a Huawei quorum server, perform the following operations:
a. Use the quorumAdmin user to log in to the quorum server.
NOTE
b. Run the su root command to switch to user root.
NOTE
Step 2 Decompress the installation package.
1. In the operating system of the quorum server, run the unzip command to decompress the
installation package.
XXX@Linux:~# unzip OceanStor/QuorumServer/
OceanStor_QuorumServer_VXXXRXXXCXX.zip
Archive: OceanStor_QuorumServer_VXXXRXXXCXX.zip
package/
package/quorum_server.sh
package/packages/
package/packages/QuorumServer-VXXXRXXXCXX-linux.x86_64.rpm
package/qs_version.ini
package/tools/
2. After decompressing the installation package, run the cd package command to go to the
directory that is decompressed.
XXX@Linux:~# cd package
3. (Optional) Run the ll command to list files in the directory.
3 Installation
The default password of the quorumAdmin user is Huawei@SYS3. You are advised to
periodically change your password for your account's security.
Enter the password of user root as instructed. The default password of the root user is
Huawei@SYS3. You are advised to periodically change your password for your account's
security.
Step 3 Install the arbitration software.
1. Log in to the quorum server as user root and run the ./quorum_server.sh -install
command to install the arbitration software.
NOTE
Perform software-related operations and management as the non-root user.
XXX@Linux:~# ./quorum_server.sh -install
Verify the QuorumServer existence.
The QuorumServer is not installed.
The current user is the root user. A quorum server administrator account
needs to be provided. Continue to install?
<Y|N>:Y #Enter "Y" to install the
arbitration software.
Enter an administrator account for the quorum server:[default:
quorumsvr]: #Press "Enter". The system installs the arbitration software
under the default user account quorumsvr.
Created new account: quorumsvr.
Changing password for quorumsvr.
New Password: #Set the password
of user quorumsvr.
Reenter New Password: #Repeat the
password.
Password changed.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
51
Page 60

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Installing the quorum server.
Preparing... ########################################### [100%]
1:QuorumServer ########################################### [100%]
[Notice] No old configuration need to resume.
QuorumServer install success completed.
NOTE
quorumsvr is the default user account for the arbitration software installation. If you want to install the
arbitration software under another user account, enter the user name after Enter an administrator
account for the quorum server:[default: quorumsvr], for example, Enter an administrator
account for the quorum server:[default: quorumsvr]:User_test.
For security purpose, restrict the permissions of the non-root user. In this condition, to ensure that the
arbitration software is successfully installed, create a non-root user before installing the arbitration
software and ensure that the non-root user can obtain the permissions of the following commands by
running the sudo command: cat, ps, sh, useradd, groupadd, userdel, groupdel, usermod, passwd,
sed, rm, rpm, ls, chmod, chown, find, xargs, killall, mv, ln, and unzip. For example, run the sudo cat
xxx command. In the command, xxx indicates the name of a file in the system.
Step 4 (Optional) Check whether the arbitration software is installed successfully.
1. After the arbitration software is installed, it automatically restarts. Enter the CLI of the
quorum server, go to any directory, run the qsadmin command in any directory to open
the arbitration software. If the arbitration software page is displayed, the arbitration
software restarts successfully.
XXX@Linux:~# qsadmin
start main!
Waiting for connecting to server...
admin:/>
2. Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run the ps -elf |grep quo*
command to check whether the arbitration software is installed successfully. If ./bin/
quorum_serverd is displayed in the command output, the arbitration software is
installed successfully.
XXX@Linux:~# ps -elf |grep quo*
3 Installation
0 S testUser 7013 1 0 80 0 - 3700 wait 22:56 ?
0 S testUser 7021 7013 0 80 0 - 22958 - 22:56 ?
0 S testUser 7232 6394 0 80 0 - 2452 pipe_w 22:57 pts/0
00:00:00 /bin/sh /opt/quorum_server/bin/quorum_server_monitor.sh
00:00:00 ./bin/quorum_serverd
00:00:00 grep quo*
Step 5 Optional: When two quorum servers are configured at the quorum site in V300R006C10,
perform Step 2 to Step 4 to install the arbitration software.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
After the installation is successful, you can directly close the quorum server's CLI window.
If you want to uninstall the arbitration software, see 5.3.6 Uninstalling the Arbitration
Software.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
52
Page 61

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
About This Chapter
This chapter describes how to configure HyperMetro, including configuration preparations,
process, and procedures.
4 Configuration
4 Configuration
4.1 Configuration Process
Before configuring HyperMetro, you must know the configuration process to ensure smooth
operations.
4.2 Configuration Preparations
This section describes prerequisites and documents that you must prepare before you
configure HyperMetro.
4.3 Configuring Switch
This section describes the configuration requirements of core switches and access switches at
the network layer and configuration procedure of the Fibre Channel switches at the storage
layer.
4.4 Configure Quorum Server Software
This section describes how to configure the quorum server software. Quorum server software
needs to be configured only when a quorum server is used for HyperMetro.
4.5 Configuring Basic Storage Services
This section describes how to configure basic storage services for the HyperMetro.
4.6 Creating SAN HyperMetro
This chapter describes how to create a SAN HyperMetro.
4.7 Configure a Multipathing Policy for Host
This section describes how to configure the Multipathing software.
4.8 Verifying the Configuration
After configured, you can view the status of the data on the local and remote storage systems
to check whether HyperMetro between the local and remote storage systems is successful.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
53
Page 62

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
4.1 Configuration Process
Before configuring HyperMetro, you must know the configuration process to ensure smooth
operations.
Figure 4-1 shows the configuration process of HyperMetro.
Figure 4-1 Configuration process of HyperMetro
Start
Configuration
Preparations.
Configuring Switch.
4 Configuration
Configuring Quorum
Server Software.
Configure Basic Storage
Services.
Configure HyperMetro.
Configure a Multipathing
Policy for Host.
Verifying the
Configuration
End
Checking the License File.
Adding a Remote Device.
Creating a Quorum
Server.
Creating a HyperMetro
Domain.
Creating a HyperMetro
Pair.
Creating a HyperMetro
Consistency Group.
Mandatory
item
Optional
This operation is performed on
both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
This operation is only performed on
the local storage system.
This operation is performed on
both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
This operation is only performed on
the local storage system.
This operation is only performed on
the local storage system.
This operation is only performed on
the local storage system.
item
Mandatory
sub-item
Optional
sub-item
Table 4-1 describes the configuration procedure of HyperMetro.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
54
Page 63

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Table 4-1 Configuration procedure of HyperMetro
4 Configuration
Configuration
Description Operation Location
Procedure
Configuration
Preparations.
Describes prerequisites and
documents that you must prepare
before you configure HyperMetro.
Configuring Switch. Describes the configuration
requirements of core switches and
access switches at the network layer
and the configuration procedure of
Fibre Channel switches at the storage
layer.
Ethernet switches serve as the core
switches and access switches at the
network layer and Fibre Channel
switches are used at the storage layer.
Configuring
Quorum Server
Software.
Configuring Basic
Storage Services
This section describes how to
configure, and manage the quorum
server software.
Configure the storage system to
divide the storage space into LUNs
and map them to application servers
so that the application server can read
and write the storage space provided
by the storage system.
Local storage systems,
remote storage systems and
third-place quorum servers.
Switches.
Quorum servers.
This operation is
performed on both the
local and the peer remote
storage systems.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
55
Page 64

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
4 Configuration
Configuration
Procedure
Configure
HyperMetro:
1. Check the
license file.
2. Add a remote
device.
3. Add the quorum
server.
4. Create a
HyperMetro
domain.
5. Create a
HyperMetro pair.
6. Create a
HyperMetro
consistency
group.
Description Operation Location
Describes how to check the
HyperMetro license, add a remote
device and quorum server, and create
a HyperMetro domain and
HyperMetro pair.
1. Check the license file.
(This operation is
performed on both the
local and the peer
remote storage
systems.)
2. Add a remote device.
(This operation is only
performed on the local
storage system.)
3. Add the quorum server.
(This operation is
performed on both the
local and the peer
remote storage
systems.)
4. Create a HyperMetro
domain. (This operation
is only performed on
the local storage
system.)
5. Create a HyperMetro
pair. (This operation is
only performed on the
local storage system.)
6. Create a HyperMetro
consistency group.
(This operation is only
performed on the local
storage system.)
Configure a
Multipathing Policy
for Host.
This section describes how to
configure an UltraPath policy for
HyperMetro. For HyperMetro, the
UltraPath software is configured to
improve the I/O processing efficiency
and reduce the access latency.
4.2 Configuration Preparations
This section describes prerequisites and documents that you must prepare before you
configure HyperMetro.
Prerequisites for configuring HyperMetro are as follows:
l All devices have been installed.
l The IP/Fibre Channel network is working properly between the two data centers.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Host.
56
Page 65

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
l Storage units have been deployed at a third-place quorum site.
l If other features besides HyperMetro need to be configured for the storage system, see
the Impact and Restrictions section about the interaction among features.
l The required licenses have been applied and imported based on the license operation
guide.
4.3 Configuring Switch
This section describes the configuration requirements of core switches and access switches at
the network layer and configuration procedure of the Fibre Channel switches at the storage
layer.
Context
For the detailed configurations on switches (includes setting domain IDs, configuring the
long-distance mode for links, and creating a zone), see BC&DR Solution Product
Documentation V200R001 (Active-Active Data Center).
4 Configuration
4.4 Configure Quorum Server Software
This section describes how to configure the quorum server software. Quorum server software
needs to be configured only when a quorum server is used for HyperMetro.
4.4.1 Configuring the Arbitration Software (SUSE)
This section describes how to configure the arbitration software in SUSE.
Prerequisites
The arbitration software must be configured in user mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Prepare for the configuration.
Before the configuration, make sure that the quorum server has been configured with service
IP address and firewall.
1. Configure a service IP address for the quorum server.
NOTE
If two ports of the quorum server are not bonded, IP addresses of the two ports must be from different
network segments. If the two ports of the quorum server are bonded, you only need to configure a
virtual IP address for arbitration.
– When deploying the arbitration software using VMs, you need to create network
adapters and switches for VMs. In this example, arbitration software is deployed on
VMs, and two ports of the quorum server are not bonded. Figure 4-2 and Table 4-2
show configuration requirements.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
57
Page 66

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Figure 4-2 Configuration requirements of virtual network adapters
Table 4-2 Configuration requirements of virtual network adapters
4 Configuration
Name
Configuration
Example
Requirement
Networ
k
adapter
2
Networ
k
adapter
3
vmnic0 connects to
controller A of the local
and remote storage
systems in the HyperMetro
pair.
vmnic1 connects to
controller B of the local
and remote storage
systems in the HyperMetro
pair.
n Switch name: vSwitch 1
n Physical adapters name: vmnic0
n Physical adapters IP addresses and
mask: 192.168.6.31/255.255.255.0
n Switch name: vSwitch 2
n Physical adapters name: vmnic1
n Physical adapters IP addresses and
mask: 192.168.7.31/255.255.255.0
– When deploying the arbitration software using physical machines, the two ports of
the quorum server are not bonded and you are advised to configure service IP
addresses at two different network segments for arbitration ports. In this example,
arbitration software is deployed on physical machines, and two ports of the quorum
server are not bonded. Table 4-3 lists configuration examples.
Table 4-3 Examples for configuring IP addresses of arbitration services
Arbitration
Service IP Address Mask
Port
Arbitration
192.168.6.31 255.255.255.0
port 1
Arbitration
192.168.7.31 255.255.255.0
port 2
Run the vi command to open the configuration file of the network adapter used by the
quorum server for arbitration. The following uses network adapters eth1 and eth2 for
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
58
Page 67

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
arbitration ports as an example to describe how to modify the file. Modify the IPADDR
in this file and then save the file.
Parameter STARTMODE must be set to auto.
XXX@Linux:~# vi /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth1
BOOTPROTO='static'
BROADCAST=''
ETHTOOL_OPTIONS=''
IPADDR='192.168.6.31/24'
MTU=''
NAME='82540EM Gigabit Ethernet Controller'
NETWORK=''
REMOTE_IPADDR=''
STARTMODE='auto'
USERCONTROL='no'
XXX@Linux:~# vi /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth2
BOOTPROTO='static'
BROADCAST=''
ETHTOOL_OPTIONS=''
IPADDR='192.168.7.31/24'
MTU=''
NAME='82540EM Gigabit Ethernet Controller'
NETWORK=''
REMOTE_IPADDR=''
STARTMODE='auto'
USERCONTROL='no'
4 Configuration
NOTICE
2. Check whether the service IP address configuration of the quorum server takes effect.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run the service network restart
command in any directory to enable the IP address configuration to take effect. Then run
the ifconfig command to check whether the configuration for eth1 and eth2 takes effect.
If the IP address that you configure is displayed in the command output, the
configuration takes effect.
XXX@Linux:~#ifconfig
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:45:7A:E2
inet addr: 192.168.6.31 Bcast:192.168.6.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe2e:fba6/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:43285954 errors:0 dropped:5051127 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:5819 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:2916916679 (2781.7 Mb) TX bytes:720809 (703.9 Kb)
eth2 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:45:7A:EB
inet addr: 192.168.7.31 Bcast:192.168.7.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe2e:fba7/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:43285954 errors:0 dropped:5051127 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:5819 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:2916916679 (2781.7 Mb) TX bytes:720809 (703.9 Kb)
3. Configure a port ID for the firewall of the quorum server.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run the vi /etc/sysconfig/
SuSEfirewall2 command in any directory to open the firewall configuration file and add
the port ID of FW_SERVICES_EXT_TCP to 30002.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
59
Page 68

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
NOTE
– If you want to enable other ports for the firewall, add the port IDs to the
FW_SERVICES_EXT_TCP configuration item. For example, if you want to enable port 22,
type FW_SERVICES_EXT_TCP="30002 22".
– If a virtual machine (VM) is used to deploy the arbitration software, enable the firewall port of
the physical machine where the VM is deployed.
XXX@Linux:~# ## Type: string
#
# 9.)
# Which TCP services _on the firewall_ should be accessible from
# untrusted networks?
#
# Format: space separated list of ports, port ranges or well known
# service names (see /etc/services)
#
# Examples: "ssh", "123 514", "3200:3299", "ftp 22 telnet 512:514"
#
# Note: this setting has precedence over FW_SERVICES_ACCEPT_*
#
FW_SERVICES_EXT_TCP="30002"
4. Check whether the firewall configuration of the quorum server takes effect.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run the rcSuSEfirewall2 restart
command in any directory to restart the firewall. Then run the iptables -L command to
check whether the firewall configuration takes effect. If the ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere
anywhere tcp dpt:pago-services2 information is displayed in the command output, the
firewall configuration takes effect.
4 Configuration
XXX@Linux:~# iptables -L
.
.
.
.
.
.
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:pago-services2
.
.
.
.
.
.
Step 2 Go to the command-line interface (CLI) of the arbitration software.
In any directory of the quorum server's operating system, run the qsadmin command to open
the arbitration software. The arbitration software page is displayed.
XXX@Linux:~# qsadmin
start main!
Waiting for connecting to server...
admin:/>
NOTE
After the arbitration software is started, run the help command to check help information and understand
the commands that are required during the configuration process.
Step 3 Add the service IP address and port ID of the quorum server to the arbitration software.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the add server_ip command to add the service IP
address and port ID of the quorum server to the arbitration software for management.
admin:/>add server_ip ip=192.168.6.31 port=30002
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
60
Page 69

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Command executed succesfully.
admin:/>add server_ip ip=192.168.7.31 port=30002
Command executed succesfully.
NOTE
l Service IP addresses of the quorum server are used for interworking with the storage array when an
arbitration server is added to the storage array. If two ports of the quorum server are not bonded, IP
addresses of the two ports must be from different network segments. If two ports of the quorum
server are bonded, IP addresses of the two ports must be the same.
l The ID of the arbitration software's listening port must be the same as that of the port enabled on the
firewall.
After configuration is complete, run the show server_ip command. If the command output
shows the IP address and port ID that are added, the configuration succeeds.
admin:/>show server_ip
Index Server IP Server Port
----- ------------ -----------------1 192.168.6.31 30002
2 192.168.7.31 30002
Index Local IP Local Port Remote IP Remote Port State
----- ------------ --------- -------- --------- -----
4 Configuration
Step 4 (Optional) Replace the original certificates of the quorum server with new ones.
NOTE
To further improve storage system security, you are advised to replace the default security certificate and
private key of the storage systems and those of the quorum server with your own security certificate and
private key.
1. Export the certificate request file of the quorum server.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the export tls_cert command to export the
device information. The qs_certreq.csr file is generated in the /opt/quorum_server/
export_import directory of the quorum server.
admin:/>export tls_cert
Command executed successfully.
NOTE
– The certificates must be replaced in user mode.
– The certificate request file of the quorum server can be used to generate certificates in a third-
party Certificate Authority (CA) organization. Copy the certificates to the /opt/
quorum_server/export_import directory of the quorum server. The certificates ensure
security of the quorum server.
– After installing the arbitration software, you are advised to grant the Secure File Transfer
Protocol (SFTP) permission only to the /opt/quorum_server/export_import/ directory to
ensure that the security certificates can be imported and exported.
2. Use the certificate request file to generate certificates.
Send the qs_certreq.csr file to a third party for the third-party CA organization to
generate certificates.
3. Copy the certificates to the quorum server.
After the certificates are generated, copy the certificate (such as qs_cert.crt) of the
quorum server and the CA certificate (such as qs_cacert.crt) to the /opt/quorum_server/
export_import directory of the quorum server.
4. Import the certificates to the arbitration software.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the import tls_cert ca=qs_cacert.crt
cert=qs_cert.crt command to import the certificates to the arbitration software.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
61
Page 70

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
admin:/>import tls_cert ca=qs_cacert.crt cert=qs_cert.crt
Command executed successfully.
5. After replacing certificates on the quorum server, replace the certificates on the local and
remote storage arrays. For details, see Managing Certificates section.
Step 5 (Optional) Configure a whitelist.
After you replace a certificate, you must configure a whitelist.
NOTICE
The arbitration software allows a storage system to connect to the quorum server only after
you configure a whitelist and add the SN of storage system to the arbitration software. If you
replace another certificate, you do not need to configure a whitelist anymore.
1. In the CLI of the storage system, run the show system general command to query the
storage system SN.
admin:/>show system general
4 Configuration
System Name : XXXXXX
Health Status : Normal
Running Status : Normal
Total Capacity : X.XXXTB
SN : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Location :
Product Model : XXXXX
Product Version : VX00R00XC00
High Water Level(%) : XX
Low Water Level(%) : XX
WWN : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Time : XXXX-XX-XX/15:11:15 UTC+08:00
2. In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the add white_list sn=? command to add the
storage system SN to the arbitration software for management.
admin:/>add white_list sn=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Command executed successfully.
3. (Optional) Run the change white_list enable_switch=no command to close the whitelist
if you do not need to configure it.
----End
4.4.2 Configuring the Arbitration Software (Red Hat/Red Flag/ NeoKylin/CentOS)
This section describes how to configure the arbitration software in Red Hat, Red Flag,
NeoKylin, or CentOS.
Prerequisites
The arbitration software must be configured in user mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Prepare for the configuration.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
62
Page 71

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Before the configuration, make sure that the quorum server has been configured with service
IP address and firewall.
1. Configure a service IP address for the quorum server.
NOTE
If two ports of the quorum server are not bonded, IP addresses of the two ports must be from different
network segments. If the two ports of the quorum server are bonded, you only need to configure a
virtual IP address for arbitration.
– When deploying the arbitration software using VMs, you need to create virtual
network adapters and switches for VMs. In this example, arbitration software is
deployed on VMs, and two ports of the quorum server are not bonded. Figure 4-3
and Table 4-4 show configuration requirements.
Figure 4-3 Configuration requirements of virtual network adapters
4 Configuration
Table 4-4 Configuration requirements of virtual network adapters
Name
Configuration
Example
Requirement
Networ
k
adapter
2
Networ
k
adapter
3
vmnic0 connects to
controller A of the local
and remote storage
systems in the HyperMetro
pair.
vmnic1 connects to
controller B of the local
and remote storage
systems in the HyperMetro
pair.
n Switch name: vSwitch 1
n Physical adapters name: vmnic0
n Physical adapters IP addresses and
mask: 192.168.6.31/255.255.255.0
n Switch name: vSwitch 2
n Physical adapters name: vmnic1
n Physical adapters IP addresses and
mask: 192.168.7.31/255.255.255.0
– When deploying the arbitration software using physical machines, the two ports of
the quorum server are not bonded and you are advised to configure service IP
addresses at two different network segments for arbitration ports. In this example,
arbitration software is deployed on physical machines, and two ports of the quorum
server are not bonded. Table 4-5 lists configuration examples.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
63
Page 72

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Table 4-5 Examples for configuring IP addresses of arbitration services
4 Configuration
Arbitration
Service IP Address Mask
Port
Arbitration
192.168.6.31 255.255.255.0
port 1
Arbitration
192.168.7.31 255.255.255.0
port 2
Run the vi command to open the configuration file of the network adapter used by the
quorum server for arbitration. The following uses network adapters eth1 and eth2 for
arbitration ports as an example to describe how to modify the file. Modify the IPADDR
and NETMASK in this file and then save the file.
NOTICE
Parameter ONBOOT must be set to yes.
XXX@Linux:~# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
DEVICE=eth1
HWADDR=08:00:27:45:7A:E2
TYPE=Ethernet
#UUID=e9f75670-fde9-4bf0-941e-c9a251341405
ONBOOT=yes
NM_CONTROLLED=no
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR=192.168.6.31 #IP address of network
adapter
NETMASK=255.255.255.0 #Subnet mask
XXX@Linux:~# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth2
DEVICE=eth2
HWADDR=08:00:27:45:7A:EB
TYPE=Ethernet
#UUID=e9f75670-fde9-4bf0-941e-c9a251341406
ONBOOT=yes
NM_CONTROLLED=no
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR=192.168.7.31 #IP address of network
adapter
NETMASK=255.255.255.0 #Subnet mask
2. Check whether the service IP address configuration of the quorum server takes effect.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run the service network restart
command in any directory to enable the IP address configuration to take effect. Then run
the ifconfig command to check whether the configuration for eth1 and eth2 takes effect.
If the IP address that you configure is displayed in the command output, the
configuration takes effect.
XXX@Linux:~#ifconfig
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:45:7A:E2
inet addr: 192.168.6.31 Bcast:192.168.255.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe2e:fba6/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:43285954 errors:0 dropped:5051127 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:5819 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
64
Page 73

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
RX bytes:2916916679 (2781.7 Mb) TX bytes:720809 (703.9 Kb)
eth2 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:45:7A:EB
inet addr: 192.168.7.31 Bcast:192.168.255.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe2e:fba7/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:43285954 errors:0 dropped:5051127 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:5819 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:2916916679 (2781.7 Mb) TX bytes:720809 (703.9 Kb)
3. Configure a port ID for the firewall of the quorum server.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run the vi /etc/sysconfig/
iptables command in any directory to open the firewall configuration file and add the
port ID to 30002.
NOTE
If you want to enable other ports for the firewall, add the port IDs to the -I INPUT –p XXX –dport=XXX –j ACCEPT configuration item. For example, -I INPUT -p tcp --dport=22 -j
ACCEPT.
XXX@Linux:~# vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
*filter
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
4 Configuration
-I INPUT -p tcp --dport=30002 -j ACCEPT
COMMIT
NOTE
– If /etc/sysconfig/iptables does not exist or is empty, write all the preceding content into the
configuration file.
– If /etc/sysconfig/iptables has content, add -I INPUT –p tcp –-dport=30002 –j ACCEPT at the
beginning of COMMIT.
– If you want to enable other ports for the firewall, add the port IDs to the -I INPUT –p XXX –-
dport=XXX –j ACCEPT configuration item. For example, if you want to enable port 22, type -I
INPUT –p tcp –-dport=22 –j ACCEPT.
– If a virtual machine (VM) is used to deploy the arbitration software, enable the firewall port of the
physical machine where the VM is deployed.
4. Check whether the firewall configuration of the quorum server takes effect.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run the service iptables restart
command in any directory to restart the firewall. Then run the iptables -L command to
check whether the firewall configuration takes effect. If the ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere
anywhere tcp dpt:pago-services2 information is displayed in the command output, the
firewall configuration takes effect.
XXX@Linux:~# iptables -L
.
.
.
.
.
.
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:pago-services2
.
.
.
.
.
.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
65
Page 74

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Step 2 Go to the command-line interface (CLI) of the arbitration software.
In any directory of the quorum server's operating system, run the qsadmin command to open
the arbitration software. The arbitration software page is displayed.
XXX@Linux:~# qsadmin
start main!
Waiting for connecting to server...
admin:/>
NOTE
After the arbitration software is started, run the help command to check help information and understand
the commands that are required during the configuration process.
Step 3 Add the service IP address and port ID of the quorum server to the arbitration software.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the add server_ip command to add the service IP
address and port ID of the quorum server to the arbitration software for management.
admin:/>add server_ip ip=192.168.6.31 port=30002
Command executed successfully.
admin:/>add server_ip ip=192.168.7.31 port=30002
4 Configuration
Command executed successfully.
NOTE
l Service IP addresses of the quorum server are used for interworking with the storage array when an
arbitration server is added to the storage array. If two ports of the quorum server are not bonded, IP
addresses of the two ports must be from different network segments. If two ports of the quorum
server are bonded, IP addresses of the two ports must be the same.
l The ID of the arbitration software's listening port must be the same as that of the port enabled on the
firewall.
After configuration is complete, run the show server_ip command. If the command output
shows the IP address and port ID that are added, the configuration succeeds.
admin:/>show server_ip
Index Server IP Server Port
----- ------------ ------------------
1 192.168.6.31 30002
2 192.168.7.31 30002
Index Local IP Local Port Remote IP Remote Port State
----- ------------ --------- -------- --------- -----
Step 4 (Optional) Replace the original certificates of the quorum server with new ones.
NOTE
To further improve storage system security, you are advised to replace the default security certificate and
private key of the storage systems and those of the quorum server with your own security certificate and
private key.
1. Export the certificate request file of the quorum server.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the export tls_cert command to export the
device information. The qs_certreq.csr file is generated in the /opt/quorum_server/
export_import directory of the quorum server.
admin:/>export tls_cert
Command executed successfully.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
66
Page 75

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
NOTE
– The certificates must be replaced in user mode.
– The certificate request file of the quorum server can be used to generate certificates in a third-
party Certificate Authority (CA) organization. Copy the certificates to the /opt/
quorum_server/export_import directory of the quorum server. The certificates ensure
security of the quorum server.
– After installing the arbitration software, you are advised to grant the Secure File Transfer
Protocol (SFTP) permission only to the /opt/quorum_server/export_import/ directory to
ensure that the security certificates can be imported and exported.
2. Use the certificate request file to generate certificates.
Send the qs_certreq.csr file to a third party for the third-party CA organization to
generate certificates.
3. Copy the certificates to the quorum server.
After the certificates are generated, copy the certificate (such as qs_cert.crt) of the
quorum server and the CA certificate (such as qs_cacert.crt) to the /opt/quorum_server/
export_import directory of the quorum server.
4. Import the certificates to the arbitration software.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the import tls_cert ca=qs_cacert.crt
cert=qs_cert.crt command to import the certificates to the arbitration software.
admin:/>import tls_cert ca=qs_cacert.crt cert=qs_cert.crt
Command executed successfully.
4 Configuration
5. After replacing certificates on the quorum server, replace the certificates on the local and
remote storage arrays. For details, see Managing Certificates section.
Step 5 (Optional) Configure a whitelist.
After you replace a certificate, you must configure a whitelist.
NOTICE
The arbitration software allows a storage system to connect to the quorum server only after
you configure a whitelist and add the SN of storage system to the arbitration software. If you
replace another certificate, you do not need to configure a whitelist anymore.
1. In the CLI of the storage system, run the show system general command to query the
storage system SN.
admin:/>show system general
System Name : XXXXXX
Health Status : Normal
Running Status : Normal
Total Capacity : X.XXXTB
SN : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Location :
Product Model : XXXXX
Product Version : VX00R00XC00
High Water Level(%) : XX
Low Water Level(%) : XX
WWN : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Time : XXXX-XX-XX/15:11:15 UTC+08:00
2. In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the add white_list sn=? command to add the
storage system SN to the arbitration software for management.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
67
Page 76

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
admin:/>add white_list sn=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Command executed successfully.
3. (Optional) Run the change white_list enable_switch=no command to close the whitelist
if you do not need to configure it.
----End
4.4.3 Configuring the Arbitration Software (Ubuntu)
This section describes how to configure the arbitration software in Ubuntu.
Prerequisites
The arbitration software must be configured in user mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Prepare for the configuration.
Before the configuration, make sure that the quorum server has been configured with service
IP address and firewall.
4 Configuration
1. Configure a service IP address for the quorum server.
NOTE
If two ports of the quorum server are not bonded, IP addresses of the two ports must be from different
network segments. If the two ports of the quorum server are bonded, you only need to configure a
virtual IP address for arbitration.
– When deploying the arbitration software using VMs, you need to create virtual
network adapters and switches for VMs. In this example, arbitration software is
deployed on VMs, and two ports of the quorum server are not bonded. Figure 4-4
and Table 4-6 show configuration requirements.
Figure 4-4 Configuration requirements of virtual network adapters
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
68
Page 77

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Table 4-6 Configuration requirements of virtual network adapters
4 Configuration
Name Configuration
Example
Requirement
Networ
k
adapter
2
Networ
k
adapter
3
vmnic0 connects to
controller A of the local
and remote storage
systems in the HyperMetro
pair.
vmnic1 connects to
controller B of the local
and remote storage
systems in the HyperMetro
pair.
n Switch name: vSwitch 1
n Physical adapters name: vmnic0
n Physical adapters IP addresses and
mask: 192.168.6.31/255.255.255.0
n Switch name: vSwitch 2
n Physical adapters name: vmnic1
n Physical adapters IP addresses and
mask: 192.168.7.31/255.255.255.0
– When deploying the arbitration software using physical machines, the two ports of
the quorum server are not bonded and you are advised to configure service IP
addresses at two different network segments for arbitration ports. In this example,
arbitration software is deployed on physical machines, and two ports of the quorum
server are not bonded. Table 4-7 lists configuration examples.
Table 4-7 Examples for configuring IP addresses of arbitration services
Arbitration
Service IP Address Mask
Port
Arbitration
192.168.6.31 255.255.255.0
port 1
Arbitration
192.168.7.31 255.255.255.0
port 2
Run the sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces command to open the configuration file of the
network adapter used by the quorum server for arbitration. The following uses network
adapters eth1 and eth2 for arbitration ports as an example to describe how to modify the
file. Modify the address and netmask in this file and then save the file.
NOTICE
The start mode must be set to auto.
XXX@ubuntu:~$sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces
auto eth1 //The parameter must be set to auto.
iface eth1 inet static
address 192.168.6.31
gateway 192.168.6.1
netmask 255.255.255.0
auto eth2 //The parameter must be set to auto.
iface eth2 inet static
address 192.168.7.31
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
69
Page 78

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
gateway 192.168.7.1
netmask 255.255.255.0
2. Check whether the service IP address configuration of the quorum server takes effect.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run sudo ifdown eth1 and sudo
ifup eth1 command in any directory to restart the network adapter. Then run the ifconfig
eth1 command to check whether the configuration takes effect. If the IP address that you
configure is displayed in the command output, the configuration takes effect.
XXX@ubuntu:~$ifconfig eth1
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:45:7A:E2
inet addr: 192.168.6.31 Bcast:192.168.6.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe2e:fba6/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:43285954 errors:0 dropped:5051127 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:5819 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:2916916679 (2781.7 Mb) TX bytes:720809 (703.9 Kb)
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run sudo ifdown eth2 and sudo
ifup eth2 command in any directory to restart the network adapter. Then run the ifconfig
eth2 command to check whether the configuration takes effect. If the IP address that you
configure is displayed in the command output, the configuration takes effect.
4 Configuration
XXX@ubuntu:~$ifconfig eth2
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:45:7A:EB
inet addr: 192.168.7.31 Bcast:192.168.7.255 Mask:255.255.0.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe2e:fba7/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:43285954 errors:0 dropped:5051127 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:5819 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:2916916679 (2781.7 Mb) TX bytes:720809 (703.9 Kb)
3. Configure a port ID for the firewall of the quorum server.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, (take ufw as example), run the
sudo ufw allow 30002/tcp command in any directory to add the port to 30002.
NOTE
– If you want to enable other ports for the firewall, run the sudo ufw allow XXX/XXX
command to add the port IDs to the firewall. For example, if you want to enable port 22, run
the sudo ufw allow 22/tcp command.
– If a virtual machine (VM) is used to deploy the arbitration software, enable the firewall port of
the physical machine where the VM is deployed.
XXX@ubuntu:~$sudo ufw allow 30002/tcp
Rule added
Rule added (v6)
4. Check whether the firewall configuration of the quorum server takes effect.
Enter the CLI of the quorum server, go to any directory, run the sudo ufw status
command to check whether the firewall configuration takes effect. If the 30002/tcp
ALLOW Anywhere and 30002/tcp(v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) information is
displayed in the command output, the firewall configuration takes effect.
XXX@ubuntu:~$sudo ufw status
To Action From
-- ------ --- .
.
.
.
30002/tcp ALLOW Anywhere
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
70
Page 79

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
.
.
.
30002/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Step 2 Go to the command-line interface (CLI) of the arbitration software.
In any directory of the quorum server's operating system, run the qsadmin command to open
the arbitration software. The arbitration software page is displayed.
XXX@Linux:~# qsadmin
start main!
Waiting for connecting to server...
admin:/>
NOTE
After the arbitration software is started, run the help command to check help information and understand
the commands that are required during the configuration process.
Step 3 Add the service IP address and port ID of the quorum server to the arbitration software.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the add server_ip command to add the service IP
address and port ID of the quorum server to the arbitration software for management.
admin:/>add server_ip ip=192.168.6.31 port=30002
4 Configuration
Command executed succesfully.
admin:/>add server_ip ip=192.168.7.31 port=30002
Command executed succesfully.
NOTE
l Service IP addresses of the quorum server are used for interworking with the storage array when an
arbitration server is added to the storage array. If two ports of the quorum server are not bonded, IP
addresses of the two ports must be from different network segments. If two ports of the quorum
server are bonded, IP addresses of the two ports must be the same.
l The ID of the arbitration software's listening port must be the same as that of the port enabled on the
firewall.
After configuration is complete, run the show server_ip command. If the command output
shows the IP address and port ID that are added, the configuration succeeds.
admin:/>show server_ip
Index Server IP Server Port
----- ------------ ------------------
1 192.168.6.31 30002
2 192.168.7.31 30002
Index Local IP Local Port Remote IP Remote Port State
----- ------------ --------- -------- --------- -----
Step 4 (Optional) Replace the original certificates of the quorum server with new ones.
NOTE
To further improve storage system security, you are advised to replace the default security certificate and
private key of the storage systems and those of the quorum server with your own security certificate and
private key.
1. Export the certificate request file of the quorum server.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the export tls_cert command to export the
device information. The qs_certreq.csr file is generated in the /opt/quorum_server/
export_import directory of the quorum server.
admin:/>export tls_cert
Command executed successfully.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
71
Page 80

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
NOTE
– The certificates must be replaced in user mode.
– The certificate request file of the quorum server can be used to generate certificates in a third-
party Certificate Authority (CA) organization. Copy the certificates to the /opt/
quorum_server/export_import directory of the quorum server. The certificates ensure
security of the quorum server.
– After installing the arbitration software, you are advised to grant the Secure File Transfer
Protocol (SFTP) permission only to the /opt/quorum_server/export_import/ directory to
ensure that the security certificates can be imported and exported.
2. Use the certificate request file to generate certificates.
Send the qs_certreq.csr file to a third party for the third-party CA organization to
generate certificates.
3. Copy the certificates to the quorum server.
After the certificates are generated, copy the certificate (such as qs_cert.crt) of the
quorum server and the CA certificate (such as qs_cacert.crt) to the /opt/quorum_server/
export_import directory of the quorum server.
4. Import the certificates to the arbitration software.
In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the import tls_cert ca=qs_cacert.crt
cert=qs_cert.crt command to import the certificates to the arbitration software.
admin:/>import tls_cert ca=qs_cacert.crt cert=qs_cert.crt
Command executed successfully.
4 Configuration
5. After replacing certificates on the quorum server, replace the certificates on the local and
remote storage arrays. For details, see Managing Certificates section.
Step 5 (Optional) Configure a whitelist.
After you replace a certificate, you must configure a whitelist.
NOTICE
The arbitration software allows a storage system to connect to the quorum server only after
you configure a whitelist and add the SN of storage system to the arbitration software. If you
replace another certificate, you do not need to configure a whitelist anymore.
1. In the CLI of the storage system, run the show system general command to query the
storage system SN.
admin:/>show system general
System Name : reppub_10.103.20.176
Health Status : Normal
Running Status : Normal
Total Capacity : 2.025TB
SN : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Location :
Product Model : S5800T
Product Version : V200R003C00
High Water Level(%) : 80
Low Water Level(%) : 20
WWN : 21000022a1072506
Time : 2015-06-27/15:11:15 UTC+08:00
2. In the CLI of the arbitration software, run the add white_list sn=? command to add the
storage system SN to the arbitration software for management.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
72
Page 81

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
admin:/>add white_list sn=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Command executed successfully.
3. (Optional) Run the change white_list enable_switch=no command to close the whitelist
if you do not need to configure it.
----End
4.5 Configuring Basic Storage Services
This section describes how to configure basic storage services for the HyperMetro.
Context
This document describes how to configure basic storage services for the HyperMetro. For
details about configuration process, see OceanStor V3 Series V300R006 Basic Storage
Service Guide for Block.
Table 4-8 describes each step of the configuration process.
4 Configuration
NOTE
You are advised to use the same configuration when configuring basic storage services on the local storage
array and remote storage array.
Table 4-8 Storage space configuration procedures
Configuration
Operation Location
Procedure
Create a disk
domain.
Create a storage
pool.
This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
NOTE
You are advised to use the same configuration when creating disk domains on
the local storage array and remote storage array.
This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
NOTE
You are advised to use the same configuration when creating storage pools on
the local storage array and remote storage array.
Create a LUN. This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
NOTICE
l It is recommended that the local LUN and remote LUN have the same
attributes such as the owning controller, capacity, and block size.
l In the VMware ESXi 6.5 GA version, the host LUN ID of the two LUNs
in a HyperMetro pair must be the same when the LUNs map to the same
host. You can run the show host lun host_id=xx command on the storage
array to query information about LUNs mapping to a host. (xx indicates
the host ID).
Create a LUN
group.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
73
Page 82

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
4 Configuration
Configuration
Operation Location
Procedure
Configure host
connectivity.
This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
Create a host. This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
Create a host group. This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
(Optional)
Configure
This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
Challenge
Handshake
Authentication
Protocol (CHAP)
authentication
(iSCSI connection).
(Optional) Create a
port group.
Create a mapping
view.
This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote
storage systems.
NOTICE
Both the local and remote LUNs in a HyperMetro pair must be mapped to a
host. However, before creating a HyperMetro pair, ensure that the remote
LUN to be added to the HyperMetro pair is not mapped to a host. Otherwise,
the HyperMetro pair may fail to be created. After the HyperMetro pair is
created and the Pair Running Status becomes Normal, map the remote
LUN to the host.
NOTE
When a large number of HyperMetro LUNs are created, to ensure that all
HyperMetro LUNs are mapped to the host, you can run the show lun
hyper_metro_pair lun_mapped=no command on the storage devices to
view the HyperMetro LUNs that are not mapped to the host.
Enable an
application server
to use storage
space.
This operation is performed on the host. After creating the
HyperMetro pair, enable an application server to use storage space.
NOTE
When LUNs provide storage space for SQL Server databases, you can adjust
relevant parameters to reduce the I/O latency and achieve the optimal
performance. For details, see 6.7 In the SQL Server database scenario,
how can I adjust parameters to reduce the I/O latency and achieve the
optimal performance?.
4.6 Creating SAN HyperMetro
This chapter describes how to create a SAN HyperMetro.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
74
Page 83

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
4.6.1 Checking the License File
Before configuring HyperMetro, ensure that the license file in use grants the permission to use
HyperMetro.
Prerequisites
A license file that contains the HyperMetro license information has been imported into the
storage system and activated.
Context
This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote storage systems.
On the DeviceManager interface, HyperMetro is displayed in Feature of HyperMetro (for
LUN).
In a scenario where both SAN HyperMetro and NAS HyperMetro are required, you can
purchase the license for both file system and LUN. In the license file, HyperMetro License
(for FS&LUN) is displayed.
4 Configuration
Precautions
The capacity of the HyperMetro license for 18500 V3&18800 V3 storage systems must be
equal to or larger than the total capacity of LUNs equipped with this feature. However, if the
total capacity of the LUNs in a storage pool equipped with this feature is larger than that of
the storage pool, use the capacity of the storage pool to calculate the capacity required for the
HyperMetro license. The following is a capacity calculation example.
Storage
Pool Name
StoragePool
001
StoragePool
002
StoragePool
003
LUN Capacity
(Total
Capacity of
Thin and
Thick LUNs)
5 GB 10 GB 5 GB ≥25 GB
10 GB 10 GB 10 GB
20 GB 10 GB 10 GB
Capacity of the
Storage Pool To
Which LUNs
Belong
License Capacity
You Must Apply
for the Storage
Pool
Total
License
Capacity
You
Must
Apply
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to DeviceManager.
Step 2 Choose Settings > License Management.
Step 3 Check the active license files.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
75
Page 84

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
1. In the navigation tree on the left, choose Active License.
2. In the middle information pane, verify the information about active license files.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
If a suitable HyperMetro license is unavailable, apply for and import a license file as
instructed in the Installation Guide of the corresponding product model.
4.6.2 Adding a Remote Device
This operation enables you to establish a logical connection between a local storage device
and a remote storage device for data transfer between the two devices.
Prerequisites
l A local storage device is normally connected to a remote storage device.
l To add remote devices when firewalls are configured, enable ports 36061 and 3260.
4 Configuration
Context
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to DeviceManager.
Step 2 Choose Data Protection > HyperMetro.
Step 3 Click Add Remote Device.
This operation is only performed on the local storage system.
The link between a local storage device and a remote storage device can be a Fibre Channel
link or an iSCSI link.
NOTE
l On a Fibre Channel network, clear zone configurations of ports connecting to the storage system
from the switch before adding the remote device. You are advised to allocate two ports in one zone
to prevent excessive remote links because too many ports exist in one zone.
l A maximum of eight available links can be identified between a controller and the remote device,
and at most eight of these links can be used for replication when you add a remote device.
The Add Remote Device Wizard dialog box is displayed.
NOTE
When a large number of remote storage devices exist, you can select desired remote devices through
their WWNs. Click Home on DeviceManager. In the Basic Information area, you can view WWN.
Step 4 Set up the connection to the remote device.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
76
Page 85

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
NOTICE
l If Running Status of an added link is Invalid, delete and add the link again.
l To ensure data transfer security among storage systems, you are advised to use a device
such as a security gateway to encrypt links to prevent information leakage.
l If the version of the local device is different from that of the remote device, you need to
add a remote device on the newer version device. Otherwise the operation may fail.
l In HyperMetro scenarios, the two storage arrays need redundant links. Therefore, add
two Fibre Channel links or iSCSI links.
l Add an iSCSI Link
a. Set Link Type to iSCSI.
b. Set parameters for the iSCSI link. Table 4-9 lists related parameters.
Table 4-9 iSCSI link parameters
4 Configuration
Parameter
Description Setting
Immediate Data The immediate data
function can speed up
data transfer in the
scenario where iSCSI
replication links transfer
service data between
storage arrays.
Controller Name of the local
storage device's
controller connected to
the remote storage
device.
Local Port Local storage device's
Ethernet port connected
to the remote storage
device.
NOTE
This host port cannot be
used for Ethernet port
bonding. Otherwise, the
HyperMetro service fails.
[Example]
Enable
[Example]
XXX0.A
[Example]
XXX0.A0.P0
IP Address IP address of the
Ethernet port on the
remote storage device.
NOTE
This host port cannot be
used for Ethernet port
bonding. Otherwise, the
HyperMetro service fails.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
[Example]
192.168.26.12
77
Page 86

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Parameter Description Setting
4 Configuration
Username The user name of the
machine-machine user.
Password The password of the
machine-machine user.
TCP/IP Port Ethernet port number on
the remote storage
[Value]
mm_user
[Value]
mm_user@storage
[Example]
3260
device.
l Add an FC Link
a. Set Link Type to FC.
b. In the Fibre Channel link list, select one or multiple Fibre Channel links.
c. Set parameters for the FC link. Table 4-10 lists related parameters.
Table 4-10 FC link parameters
Parameter
Username The user name of the
Description Setting
[Value]
machine-machine user.
mm_user
Step 5 Click Next.
The information summary is displayed.
Step 6 Click Finish.
The Execution Result dialog box is displayed indicating that the operation succeeded.
Step 7 Click Close.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
In the HyperMetro, if the distance between the local and remote storage devices exceeds 25
km, you can run the following command to enable the fast write function to ensure link
transfer efficiency.
l FC link: By default, this function is disabled. This function is only enabled for 4-port 8
Gbit/s Fibre Channel links. You can run the change port fc fc_port_id=XXX
fast_write_enable=yes command to enable the fast write function. To obtain the value
of fc_port_id, run show port general. The function needs to be enabled on both the
local and remote storage system. Run the show port general port_id=XXX command.
When the status of Fast Write Enable in the output is Yes, this function is successfully
enabled.
Password The password of the
machine-machine user.
[Value]
mm_user@storage
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
78
Page 87

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
l iSCSI link: By default, this function is enabled. You are advised to enable this function.
You can run the change remote_device link link_type=iSCSI link_id=XXX
fast_write_enable=no command to disable the fast write function. To obtain the value of
link_id, run show remote_device link. The function needs to be enabled only on the
local storage system. You can run the show remote_device link link_type=iSCSI
link_id=XXX command to query the status of this function. When the status of Fast
Write Enable in the output is Yes, this function is successfully enabled.
For details, see the Command Reference of the corresponding product model.
4.6.3 Creating a Quorum Server
Through this operation, you can create a third-party quorum server for HyperMetro domains.
When the communication between storage devices in a HyperMetro pair becomes abnormal,
the quorum server decides which site continues to provide services, thereby greatly improving
service continuity.
Prerequisites
To enable quorum links to be added to storage arrays successfully, ensure the following items
before creating a quorum server.
l The system time of the storage arrays and quorum server is correct. The validity period
of the default arbitration certificate is 10 years (start from September 2015). Ensure the
system time of the quorum server is correct so that the default arbitration certificate is
valid.
l The service IP addresses of the quorum server are correctly configured and correct
firewall ports (30002) are enabled.
l The white list of the quorum server is configured correctly. (You do not need to check
this item if the default security policy is used.)
l Service IP addresses have been configured for the service ports that are used to connect
storage arrays and the quorum server. In addition, the service IP address of the storage
arrays and quorum server can ping through with each other. For details about how to
configure service IP addresses for storage arrays, see OceanStor V3 Series V300R006
Basic Storage Service Guide for Block. After configuring the service IP addresses, query
and record the IP addresses' ports. Then perform the operation in step 7 to select a port.
Perform the following operation to query the ports: On DeviceManager management
4 Configuration
page, choose
Provisioning > Port > Ethernet Ports.
Context
l To ensure the reliability between quorum servers and storage devices, you are advised to
add at least one link between each controller of storage devices and a quorum server.
l This operation is performed on both the local and the peer remote storage systems.
l The quorum site supports two quorum servers for V300R006C10 and later versions. In
following operations, the first added quorum server becomes the active quorum server
and the other becomes the standby quorum server.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to DeviceManager.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
79
Page 88

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Step 2 Choose Data Protection > HyperMetro > Quorum Server.
Step 3 Click Create.
The Create Quorum Server dialog box is displayed.
Step 4 Set Name and Description of the quorum server and click Next.
NOTE
l The name contains 1 to 31 characters.
l The name can contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), periods (.), and hyphens (-).
Step 5 Set the properties of the quorum server and click Next.
Table 4-11 lists related configuration parameters.
Table 4-11 Quorum server parameters
4 Configuration
Parameter
Active IP Address Primary IP address of a
Active Port Primary port ID of a quorum
Description Example Value
[Example]
quorum server.
192.168.0.8
[Value Range]
server. The default port ID is
30002.
The value ranges from 1 to
65535.
[Example]
30002
Standby IP Address Standby IP address of a
quorum server.
Standby Port Standby port ID of a
quorum server. The default
port ID is 30002.
[Example]
192.168.1.8
[Value Range]
The value ranges from 1 to
65535.
[Example]
30002
Step 6 Optional: If you select Configure Later, you can configure the links between the quorum
server and controllers of storage devices later.
NOTE
If no quorum server link is configured, the quorum server cannot communicate with either of storage devices.
When the communication is abnormal between the two storage devices, services are provided by the preferred
site.
If you want to add the quorum server subsequently, modify the HyperMetro domain to add it.
Step 7 Select Controller and Port of storage devices to be connected and click Add. Select Port
Type of storage devices to be connected, configure corresponding settings, and click Add.
l If the port type is Host port, select Controller and Port.
l If the port type is Management port, select Port. (To use a management network port as
an arbitration port, the storage system version must be V300R006C10 or later.)
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
80
Page 89

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
NOTE
To ensure the reliability between quorum servers and storage devices, you are advised to add at least one link
between each controller of storage devices and a quorum server.
Step 8 Click Next.
NOTE
The Summary page is displayed. Confirm the newly added link information and click Finish.
Step 9 Optional: If two quorum servers are configured, perform Step 3 to Step 8 to add another
quorum server.
Step 10 Log in to the remote storage device, execute the steps above to configure quorum server for
the remote storage device.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
By default, a quorum server does not have policy routes. It can only receive and send data via
one IP port although it has two IP ports on the same network segment. As a result, after the
port in use goes down, the other port cannot take over services. Log in to the quorum server
and configure routing policies for it. For details, see Active and Standby IP Ports Are
Configured on the Quorum Server. After the Port in Use Is Down, the Quorum Server
Goes Offline. Why?
4 Configuration
4.6.4 Creating a HyperMetro Domain
After configuring a remote device and a quorum server, you need to create a HyperMetro
domain for the remote and local devices, and the quorum server. When creating a HyperMetro
domain, you determine the relationships among the local device, remote device, and quorum
server in the domain.
Prerequisites
l In V300R006C00, a HyperMetro domain can have only one quorum server. In
V300R006C10 and later versions, a HyperMetro domain can have two quorum servers.
l If you need to configure a quorum server for the HyperMetro domain, you must add
quorum server for both local and remote storage devices.
NOTE
Log in to the quorum server. In the CLI of the quorum server, run command qsadmin to open the
arbitration software. Then, run command show server_ip to view the status of the local and
remote storage devices. If they are both in the Established state, the quorum server has been
added successfully.
Context
l A HyperMetro Domain supports one quorum server at most.
l This operation is only performed on the local storage system.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to DeviceManager.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
81
Page 90

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Step 2 Choose Data Protection > HyperMetro > HyperMetro Domain.
Step 3 Click Create.
The Create HyperMetro Domain wizard is displayed.
Step 4 Set Name and Description of the HyperMetro domain and click Next.
NOTE
l The name contains 1 to 31 characters.
l The name can contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), periods (.), and hyphens (-) and it must start
with a letter or digit.
Step 5 In the Remote Device area, select a remote device that you want to add to the HyperMetro
domain and click Next.
NOTE
Click Add Remote Device to add a remote device in the dialog box that is displayed.
Step 6 In the Quorum server area, select a quorum server that you want to add to the HyperMetro
domain and click Next.
4 Configuration
NOTE
If you select Configure Later, you can add the quorum server to the HyperMetro domain later. If a fault
occurs, the local and remote devices in the HyperMetro domain cannot use the arbitration mechanism
provided by the quorum server to determine which site can continue to provide services. By default, the
device in Prior Service Site provides services.
Step 7 Click Next.
The information summary is displayed.
Step 8 Click Finish.
The Execution Result dialog box is displayed indicating that the operation succeeded.
Step 9 Click Close.
----End
4.6.5 Creating a HyperMetro Pair
After specifying a HyperMetro domain (including local and remote devices and a quorum
server), device resources at two storage arrays, and data synchronization properties, you can
create HyperMetro relationships for devices at the two storage arrays. After the HyperMetro
relationships are established, the quorum server and preferred site mechanism determine
which site continues to provide services if a disaster occurs.
Prerequisites
l The local and remote devices work normally and correctly communicate with each other.
l These devices must support the HyperMetro feature.
l The remote LUN of HyperMetro pair is not mapped to host.
Context
l After HyperMetro pair is created, the WWN of the remote LUN is changed to the WWN
of the local LUN.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
82
Page 91

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
l This operation is only performed on the local storage system.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to DeviceManager.
4 Configuration
Step 2 Choose
Data Protection > HyperMetro > HyperMetro Pair.
Step 3 Select the HyperMetro Pair tab.
The HyperMetro Pair management page is displayed.
Step 4 Click Create.
The Create HyperMetro Pair Wizard dialog box is displayed.
Step 5 Select HyperMetro Domain, Resource Type and Host Multipathing Software for the
HyperMetro and click Next.
Step 6 In Available Local Resources and Available Remote Resources, select local and remote
LUNs for which you want to configure the HyperMetro feature and click Add to Pairs.
NOTE
Local and remote LUNs must have the same number of sectors.
Step 7 Click Next.
Step 8 Set the data synchronization properties for the HyperMetro. Table 4-12 describes related
parameters.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
83
Page 92

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Table 4-12 HyperMetro parameters
Parameter Description Example Value
4 Configuration
Speed Data replication speed of a
HyperMetro.
l Low: When the speed is
set to low, remote
replication will take a
long time. This value is
applicable to scenarios
where the service load is
heavy. The speed is
normally from 0 to 5
MB/s.
l Medium: When the
speed is set to medium,
remote replication will
take relatively short
period. This value is
applicable to scenarios
where the service load is
heavy. The speed is
normally from 10 to 20
MB/s.
l High: When the speed is
set to high, remote
replication will take a
short period. This value
is applicable to scenarios
where the service load is
relatively light. The
speed is normally from
50 to 70 MB/s.
l Highest: When the speed
is set to highest, remote
replication will be
complete in the shortest
period. This value is
applicable to scenarios
where the service load is
light. The speed is
normally above 100
MB/s.
[Value range]
Possible values are Low,
Medium, High, and
Highest.
NOTE
If the LUN for which you want
to implement HyperMetro is
carrying host services and it is
difficult to determine when the
system is busy or idle, you are
advised to set the parameter to
Medium to minimize the
impact on host services.
[Default value]
Medium
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
84
Page 93

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Parameter Description Example Value
4 Configuration
Recovery Policy A recovery policy
determines whether the
system automatically
synchronizes data after a
HyperMetro fault is
rectified.
l Automatic: The system
automatically
synchronizes data.
l Manual: The
synchronization
operation must be
performed manually.
Initial Synchronization Initial synchronization
method for data at local and
remote ends.
[Value range]
Possible values are
Automatic and Manual.
[Default value]
Automatic
[Value range]
l Local and remote data is
inconsistent. After the
creation is complete,
manually synchronize
data.
l Data at the local and
remote ends is
consistent.
Synchronization is not
required after the
creation is complete.
l Local and remote data is
inconsistent. After the
creation is complete, data
is automatically
synchronized.
[Example]
Local and remote data is
inconsistent. After the
creation is complete, data is
automatically synchronized.
Step 9 Click Next.
Step 10 Optional: Add the HyperMetro pair into consistency group.
NOTE
The Running Status of the consistency group you want to pause must be Paused.
1. Choose Select a consistency group and add HyperMetro pairs to it.
2. Choose the consistency group you want to add the HyperMetro pair, or click Create
HyperMetro Consistency Group. Table 4-13 describes related parameters.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
85
Page 94

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Table 4-13 Consistency group parameters
Parameter Description Example Value
4 Configuration
Name The name of the
HyperMetro consistency
group.
Description The description of the
HyperMetro consistency
group.
HyperMetroGroup_001
—
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
86
Page 95

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Parameter Description Example Value
4 Configuration
Speed Data replication speed of a
HyperMetro.
– Low: When the speed
is set to low, remote
replication will take a
long time. This value is
applicable to scenarios
where the service load
is heavy. The speed is
normally from 0 to 5
MB/s.
– Medium: When the
speed is set to medium,
remote replication will
take relatively short
period. This value is
applicable to scenarios
where the service load
is heavy. The speed is
normally from 10 to 20
MB/s.
– High: When the speed
is set to high, remote
replication will take a
short period. This value
is applicable to
scenarios where the
service load is
relatively light. The
speed is normally from
50 to 70 MB/s.
– Highest: When the
speed is set to highest,
remote replication will
be complete in the
shortest period. This
value is applicable to
scenarios where the
service load is light.
The speed is normally
above 100 MB/s.
[Value range]
Possible values are Low,
Medium, High, and
Highest.
NOTE
If the LUN for which you
want to implement
HyperMetro is carrying host
services and it is difficult to
determine when the system
is busy or idle, you are
advised to set the parameter
to Medium to minimize the
impact on host services.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
87
Page 96

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Parameter Description Example Value
4 Configuration
Recovery Policy A recovery policy
determines whether the
system automatically
synchronizes data after a
HyperMetro fault is
rectified.
– Automatic: The
system automatically
synchronizes data.
– Manual: The
synchronization
operation must be
performed manually.
3. Click OK.
4. Click Close.
Step 11 Click Next.
The Information Summary page is displayed.
Step 12 Confirm the newly created HyperMetro information and click Finish.
The security alert dialog box is displayed.
[Value range]
Possible values are
Automatic and Manual.
[Default value]
Automatic
Step 13 Select I have read and understand the consequences associated with performing this
operation. and click OK.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
Both the local and remote LUNs in a HyperMetro pair must be mapped to a host. However,
before creating a HyperMetro pair, ensure that the remote LUN to be added to the
HyperMetro pair is not mapped to a host. Otherwise, the HyperMetro pair may fail to be
created. After the HyperMetro pair is created and the Pair Running Status becomes Normal,
map the remote LUN to the host. For details about how to scan for LUNs, see the UltraPath
User Guide specific to your host operating system.
4.6.6 Creating a HyperMetro Consistency Group
If an application or one type of services requires multiple HyperMetro LUNs and a preferable
service site needs to be determined by the system or quorum server upon faults, you need to
add owning HyperMetro LUNs of the application and services to a same HyperMetro
consistency group for unified maintenance.
Prerequisites
l The HyperMetro pairs in a HyperMetro consistency group must belong to the same
HyperMetro domain.
l HyperMetro pairs in a HyperMetro consistency group must have the same Data
Synchronization Direction and Pair Running Status as the HyperMetro consistency
group.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
88
Page 97

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
l Before creating a HyperMetro consistency group, stop the HyperMetro pair to be added
to the consistency group.
Context
This operation is only performed on the local storage system.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to DeviceManager.
4 Configuration
Step 2 Choose
Data Protection > HyperMetro > HyperMetro Pair > HyperMetro
Consistency Group.
Step 3 Click Create.
The Create HyperMetro Consistency Group Wizard page is displayed.
Step 4 Set the name, description and HyperMetro domain of the HyperMetro consistency group.
Table 4-14 describes related parameters.
Table 4-14 HyperMetro consistency group parameters
Parameter
Name The name of the HyperMetro
Description Example Value
HyperMetroGroup_001
consistency group.
Description The description of the
—
HyperMetro consistency
group.
HyperMetro Domain HyperMetro domain to which
HyperMetroDomain_001
the HyperMetro consistency
group belongs. The
HyperMetro pair in
HyperMetro consistency group
must belong to the same
HyperMetro domain.
NOTE
Click Create to create a
HyperMetro domain in the dialog
box that is displayed.
Step 5 Click Next.
Step 6 Set the properties for the HyperMetro consistency group. Table 4-15 describes related
parameters.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
89
Page 98

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Table 4-15 HyperMetro consistency group properties
Parameter Description Example Value
4 Configuration
Speed Data replication speed of a
HyperMetro.
l Low: When the speed is set
to low, remote replication
will take a long time. This
value is applicable to
scenarios where the service
load is heavy. The speed is
normally from 0 to 5 MB/s.
l Medium: When the speed
is set to medium, remote
replication will take
relatively short period. This
value is applicable to
scenarios where the service
load is heavy. The speed is
normally from 10 to 20
MB/s.
l High: When the speed is
set to high, remote
replication will take a short
period. This value is
applicable to scenarios
where the service load is
relatively light. The speed
is normally from 50 to 70
MB/s.
l Highest: When the speed is
set to highest, remote
replication will be complete
in the shortest period. This
value is applicable to
scenarios where the service
load is light. The speed is
normally above 100 MB/s.
[Value range]
Possible values are Low,
Medium, High, and Highest.
NOTE
If the LUN for which you want to
implement HyperMetro is
carrying host services and it is
difficult to determine when the
system is busy or idle, you are
advised to set the parameter to
Medium to minimize the impact
on host services.
[Default value]
Medium
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
90
Page 99

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
Parameter Description Example Value
4 Configuration
Recovery Policy A recovery policy determines
whether the system
automatically synchronizes
[Value range]
Possible values are Automatic
and Manual.
data after a HyperMetro fault
is rectified.
l Automatic: The system
[Default value]
Automatic
automatically synchronizes
data.
l Manual: The
synchronization operation
must be performed
manually.
Step 7 Click Next.
Step 8 In Available HyperMetro Pairs select the HyperMetro pair, and click to add the
selected HyperMetro pair into Selected HyperMetro Pairs area, and click Next.
Step 9 In Summary page, confirm the information and click Finish.
Step 10 Click Close.
----End
4.7 Configure a Multipathing Policy for Host
This section describes how to configure the Multipathing software.
Context
Multipathing software must be installed for the HyperMetro solution. You can use either
Huawei UltraPath or third-party multipathing software.
l In terms of multipathing, UltraPath is recommended for HyperMetro. UltraPath can
identify host locations so that hosts can access the nearest storage array, reducing crosssite accesses and latency while improving access efficiency and storage performance.
NOTE
For details on how to configure UltraPath, see Configuring an UltraPath Policy for Host.
l If the customer needs to use third-party multipathing software on the application server,
the function of Uses third-party multipath software for initiators must be enabled on
Huawei storage.
NOTE
For details on how to configure third-party multipathing software, see Configuring a Third-party
Multipathing Policy for Host.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
91
Page 100

OceanStor V3 Series
HyperMetro Feature Guide for Block
4.7.1 Configuring a UltraPath Policy for Host
This section describes how to configure the UltraPath software. For HyperMetro, the
UltraPath software is configured to improve the I/O processing efficiency and reduce the
access latency.
Context
In UltraPath, the local storage array is granted with the prior read and write permission. The
local storage array is preferentially used to process host services. If the local storage array
malfunctions, the remote storage array will be used. In this way, service response efficiency is
improved and access latency is reduced.
UltraPath must be configured on all application servers.
When configuring UltraPath, ensure that Uses third-party multipath software is disabled as
it is not needed.
NOTE
For details about how to disable Uses third-party multipath software, see section Configuring a Thirdparty Multipathing Policy for Host.
4 Configuration
Procedure
Step 1 Set the HyperMetro working mode.
The commands for setting the HyperMetro working mode vary with OSs on application
servers.
l For Linux, Windows, AIX, and Solaris OSs,
a. Log in to the application server.
b. Log in to the CLI of OceanStor UltraPath.
n In Linux OSs, run upadmin to log in to the CLI of OceanStor UltraPath.
n In Windows, AIX, and Solaris OSs, run upadm to log in to the CLI of
OceanStor UltraPath.
c. Run set hypermetro workingmode={ priority | balance } primary_array_id=ID
[vlun_id={ ID | ID1,ID2... | ID1-ID2 } ]. Table 4-16 describes the key parameters
in the command.
Table 4-16 Parameter description
Keyword and
Description Default Value
Parameter
workingmode={ priorit
y | balance }
Used to specify the
HyperMetro working
mode.
n priority: preferred
storage array mode
n balance: load
balancing mode
priority
priority is
recommended. balance
is applicable to scenarios
where the two activeactive data centers are in
the same building.
Issue 05 (2018-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
92
 Loading...
Loading...