Page 1

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide
Issue 01
Date 2020-12-02
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2021. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specied in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every eort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
Page 3

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide Contents
Contents
1 Service Overview..................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 What is DMS for Kafka?........................................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Product Advantages................................................................................................................................................................1
1.3 Application Scenarios............................................................................................................................................................. 2
1.4 Specications............................................................................................................................................................................ 4
1.5 Comparing Kafka Instances and DMS Advanced Queues.........................................................................................6
1.6 Comparing DMS for Kafka and Open-Source Kafka...................................................................................................8
1.7 Notes and Constraints......................................................................................................................................................... 10
1.8 Related Services..................................................................................................................................................................... 11
1.9 Basic Concepts....................................................................................................................................................................... 11
2 Preparing Required Resources............................................................................................14
3 Creating an Instance.............................................................................................................16
4 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance............................................................................... 20
4.1 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance Without SASL................................................................................................ 20
4.2 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance with SASL....................................................................................................... 22
5 Managing Instances..............................................................................................................26
5.1 Viewing an Instance............................................................................................................................................................. 26
5.2 Restarting an Instance........................................................................................................................................................ 27
5.3 Deleting an Instance............................................................................................................................................................ 28
5.4 Modifying the Information About an Instance...........................................................................................................30
5.5 Conguring Public Access.................................................................................................................................................. 31
5.6 Resetting Kafka Password..................................................................................................................................................32
5.7 Viewing Background Tasks................................................................................................................................................ 33
6 Managing Topics.................................................................................................................... 35
6.1 Creating a Topic..................................................................................................................................................................... 35
6.2 Deleting a Topic.....................................................................................................................................................................37
7 Auditing................................................................................................................................... 38
7.1 Operations That Can Be Recorded by CTS................................................................................................................... 38
7.2 Viewing Traces on the CTS Console................................................................................................................................41
8 FAQs..........................................................................................................................................42
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
Page 4

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide Contents
8.1 Instances.................................................................................................................................................................................. 42
8.1.1 Why Can't I Select Two AZs?......................................................................................................................................... 42
8.1.2 Why Can't I View the Subnet and Security Group Information When Creating a DMS Instance?.......42
8.1.3 How Do I Select Storage Space for a Kafka Instance?.........................................................................................42
8.1.4 How Do I Choose Between High I/O and Ultra-high I/O?..................................................................................43
8.1.5 Which Capacity Threshold Policy Should I Use?..................................................................................................... 43
8.1.6 Which Kafka Version Is Supported?............................................................................................................................ 43
8.1.7 What Is the ZooKeeper Version of a Kafka Instance?.......................................................................................... 43
8.1.8 Are Kafka Instances in Cluster Mode?....................................................................................................................... 43
8.1.9 Can I Modify the Connection Address for Accessing a Kafka Instance?........................................................ 43
8.1.10 How Long Are Kafka SSL Certicates Valid for?..................................................................................................44
8.1.11 How to Synchronize Data from One Kafka Instance to Another?.................................................................44
8.1.12 How Do I Change the SASL_SSL Setting of a Kafka Instance?....................................................................... 44
8.1.13 Are Kafka Brokers and ZooKeeper Deployed on the Same VM or on
8.1.14 What Cipher Suites Are Supported by Kafka?.......................................................................................................44
8.1.15 Can I Change an Instance from Single-AZ Deployment to Multi-AZ Deployment?................................44
8.1.16 Does DMS for Kafka Support Cross-AZ Disaster Recovery? Where Can I View the AZs
for a Purchased Instance?......................................................................................................................................................... 44
8.1.17 Can I Change the VPC and Subnet After a Kafka Instance Is Created?....................................................... 45
8.1.18 Where Can I Find Kafka Streams Use Cases?........................................................................................................45
8.2 Connections............................................................................................................................................................................ 45
8.2.1 Troubleshooting Kafka Connection Exceptions....................................................................................................... 45
8.2.2 How Do I Select and
8.2.3 Can I Access a Kafka Premium Instance Over a Public Network?................................................................... 48
8.2.4 How Many Connection Addresses Does a Kafka Instance Have by Default?.............................................. 49
8.2.5 Do Kafka Instances Support Cross-Region Access?............................................................................................... 49
8.2.6 Can I Access a Kafka Instance Using DNAT?........................................................................................................... 49
8.2.7 Do Kafka Premium Instances Support Cross-Subnet Access?............................................................................49
8.2.8 Why Do I Fail to Access Kafka Using SSL from a Go Client?............................................................................. 49
8.2.9 What If
8.2.10 Does DMS for Kafka Support Password-Free Access?........................................................................................49
8.2.11 Obtaining Kafka Clients................................................................................................................................................ 50
8.2.12 Does DMS for Kafka Support Authentication on Clients by the Server?.....................................................50
8.2.13 Can I Use PEM SSL Truststore When Connecting to a Kafka Instance with SASL_SSL Enabled?........50
8.2.14 What Are the
8.2.15 Which TLS Version Does DMS for Kafka Support, 1.0, 1.1, or 1.2?............................................................... 50
8.2.16 Is There a Limit on the Number of Connections to a Kafka Instance?........................................................ 50
8.2.17 How Many Connections from Each IP Address Are Allowed?.........................................................................50
8.3 Topics and Partitions............................................................................................................................................................50
8.3.1 Is There a Limit on the Number of Topics in a Kafka Instance?....................................................................... 51
8.3.2 Why Is Partition Quantity Limited?............................................................................................................................. 51
8.3.3 Can I Reduce the Partition Quantity?.........................................................................................................................51
8.3.4 Why Do I Fail to Create Topics?................................................................................................................................... 51
Certicates Fail to Be Loaded for SASL Connection?............................................................................49
Congure a Security Group?................................................................................................47
Dierences Between JKS and CRT Certicates?....................................................................... 50
Dierent VMs?........................... 44
Congured
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii
Page 5

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide Contents
8.3.5 Do Kafka Instances Support Batch Importing Topics or Automatic Topic Creation?.................................51
8.3.6 Why Do Deleted Topics Still Exist?.............................................................................................................................. 51
8.3.7 How Do I Create a Topic?............................................................................................................................................... 51
8.3.8 Are Periods (.) Allowed in Topic Names?.................................................................................................................. 52
8.3.9 What Should I Do If Kafka Storage Space Is Used Up Because Retrieved Messages Are Not Deleted?
............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 52
8.3.10 What Can I Do If Disk Usage Is as High as 96%?............................................................................................... 52
8.3.11 Will a Kafka Instance Be Restarted After Its Automatic Topic Creation Setting Is Modied?............. 52
8.3.12 How Do I Disable Automatic Topic Creation?.......................................................................................................52
8.3.13 Can I Delete Unnecessary Topics in a Consumer Group?................................................................................. 52
8.4 Consumer Groups................................................................................................................................................................. 52
8.4.1 Do I Need to Create Consumer Groups, Producers, and Consumers for Kafka Instances?..................... 52
8.4.2 How Do I Delete Consumer Groups?..........................................................................................................................53
8.4.3 Do I Need to Unsubscribe from a Topic Before Deleting a Consumer Group?............................................53
8.5 Messages..................................................................................................................................................................................53
8.5.1 What Is the Maximum Size of a Message that Can be Created?.....................................................................54
8.5.2 Why Do I Frequently Fail to Poll Due to Rebalancing?........................................................................................54
8.5.3 Why Do Messages Still Exist After the Retention Period Elapses?...................................................................54
8.5.4 Do Kafka Instances Support Delayed Message Delivery?................................................................................... 54
8.5.5 Does the Message Query Function on the Console Show the Replica Message Quantity?....................54
A Change History...................................................................................................................... 55
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iv
Page 6

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
1 Service Overview
1.1 What is DMS for Kafka?
Apache Kafka is distributed message middleware that features high throughput,
data persistence, horizontal scalability, and stream data processing. It adopts the
publish-subscribe pattern and is widely used for log collection, data streaming,
online/oine system analytics, and real-time monitoring.
Distributed Message Service (DMS) for Kafka is a message queuing service that
uses the open-source Apache Kafka. It provides Kafka premium instances with
isolated computing, storage, and bandwidth resources. DMS for Kafka allows you
to apply resources,
requirements. It can be used out of the box and frees you from deployment and
O&M so that you can focus on the agile development of your applications.
congure topics, partitions, and replicas based on service
Readers' Guide
This documentation introduces DMS for Kafka and its
Kafka. You will learn about the detailed information about the specications,
console operations, API calling, and client access to instances of DMS for Kafka.
For more information about the basic knowledge of Kafka or technical details
about creating and retrieving messages, please go to the ocial Apache Kafka
website.
1.2 Product Advantages
DMS for Kafka provides easy-to-use message queuing based on Apache Kafka.
Services can be quickly migrated to the cloud without any change, reducing
maintenance and usage costs.
dierences from Apache
● Rapid deployment
Simply set instance information on the DMS for Kafka console, submit your
order, and a complete Kafka premium instance will be automatically created
and deployed.
● Service migration without
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
modications
Page 7

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
DMS for Kafka is compatible with open-source Kafka APIs and supports all
message processing functions of open-source Kafka.
If your application services are developed based on open-source Kafka, you
can easily migrate them to DMS for Kafka after specifying a few
authentication
Kafka premium instances are compatible with Apache Kafka 2.3.0.
● Security
Operations on Kafka premium instances are recorded and can be audited.
Messages can be encrypted before storage.
In addition to SASL, Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and security groups also
provide security controls on network access.
● Data reliability
Kafka premium instances support data persistence and replication. Messages
can be replicated synchronously or asynchronously between replicas.
● High availability
Kafka runs in clusters, enabling failover and fault tolerance so that services
can run smoothly.
Kafka premium instances can be deployed across AZs to further enhance
service availability.
● Simple O&M
The public cloud provides a whole set of monitoring and alarm services,
eliminating the need for 24/7 attendance. A set of Kafka premium instance
metrics are monitored and reported, including the number of partitions,
topics, and accumulated messages. You can
SMS or email
● Flexible specications
You can customize the bandwidth and storage space for the instance and the
number of partitions and replicas for topics in the instance.
congurations.
congure alarm rules and receive
notications on how your services are running in real time.
1.3 Application Scenarios
Kafka is popular message-oriented middleware that features highly reliable,
asynchronous message delivery. It is widely used for transmitting data between
dierent systems in the enterprise application, payment, telecommunications, ecommerce, social networking, instant messaging, video, Internet of Things, and
Internet of Vehicle industries.
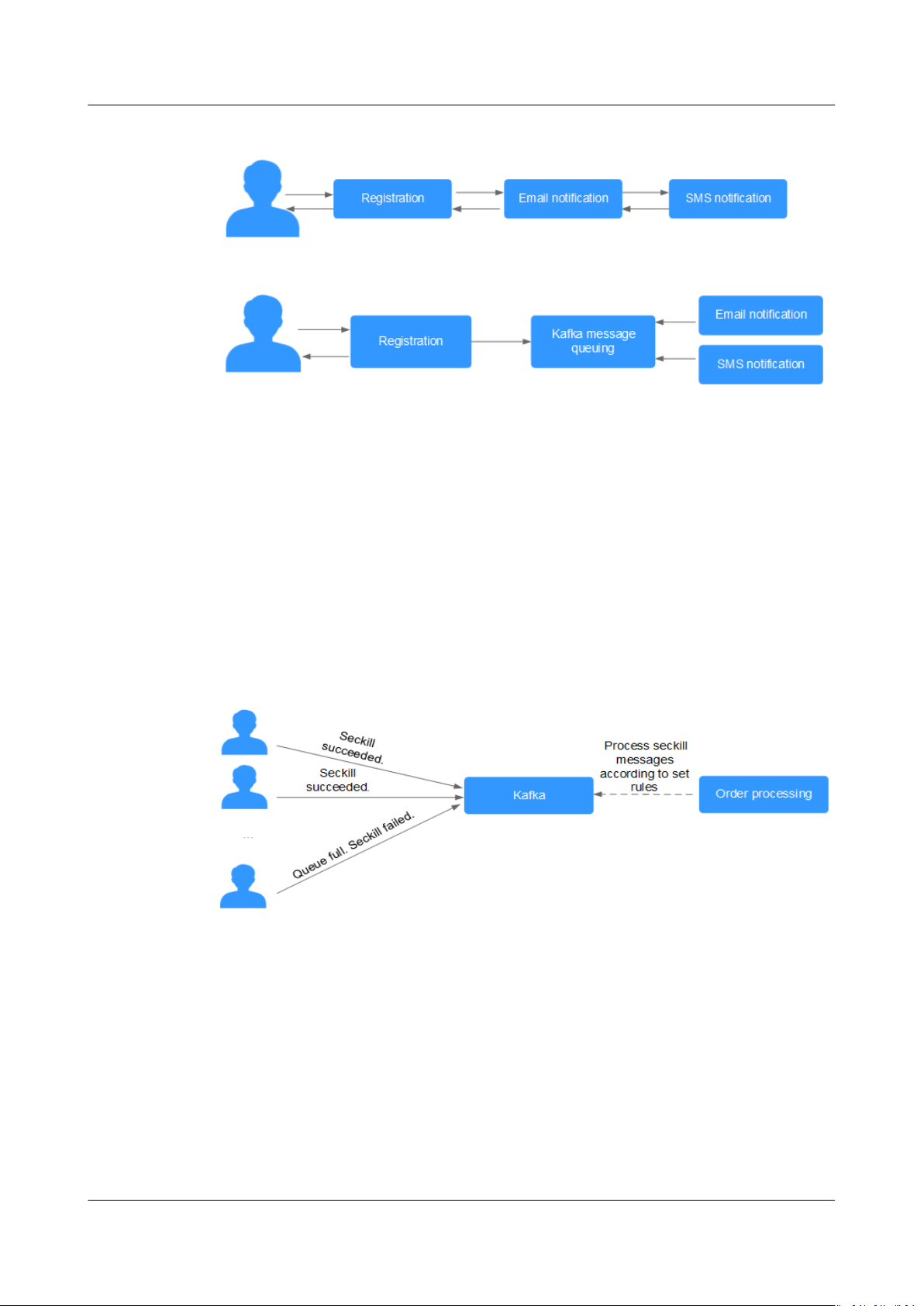
Asynchronous Communication
Non-core or less important messages are sent asynchronously to receiving
systems, so that the main service process is not kept waiting for the results of
other systems, allowing for faster responses.
For example, Kafka can be used to send a
after a user has registered with a website, providing fast responses throughout the
registration process.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
notication email and SMS message
Page 8
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
Figure 1-1 Serial registration and notication
Figure 1-2 Asynchronous registration and notication using message queues
Trac Control
In e-commerce systems or large-scale websites, there is a processing capability
gap between upstream and downstream systems. Trac bursts from upstream
systems with high processing capabilities may have a large impact on downstream
systems with lower processing capabilities. For example, online sales promotions
involve a huge amount of
provides a three-day
as orders and other information. In this way, message consumption systems can
process the messages during
trac ooding into e-commerce systems. Kafka
buer by default for hundreds of millions of messages, such
o-peak periods.
In addition, ash sale trac bursts originating from frontend systems can be
handled with Kafka, keeping the backend systems from crashing.
Figure 1-3
Log Synchronization
In large-scale service systems, logs of dierent applications are collected for quick
troubleshooting, full-link tracing, and real-time monitoring.
Kafka is originally designed for this scenario. Applications asynchronously send log
messages to message queues over reliable transmission channels. Other
components can read the log messages from message queues for further analysis,
either in real time or
monitor applications.
Trac burst handling using Kafka
oine. In addition, Kafka can collect key log information to
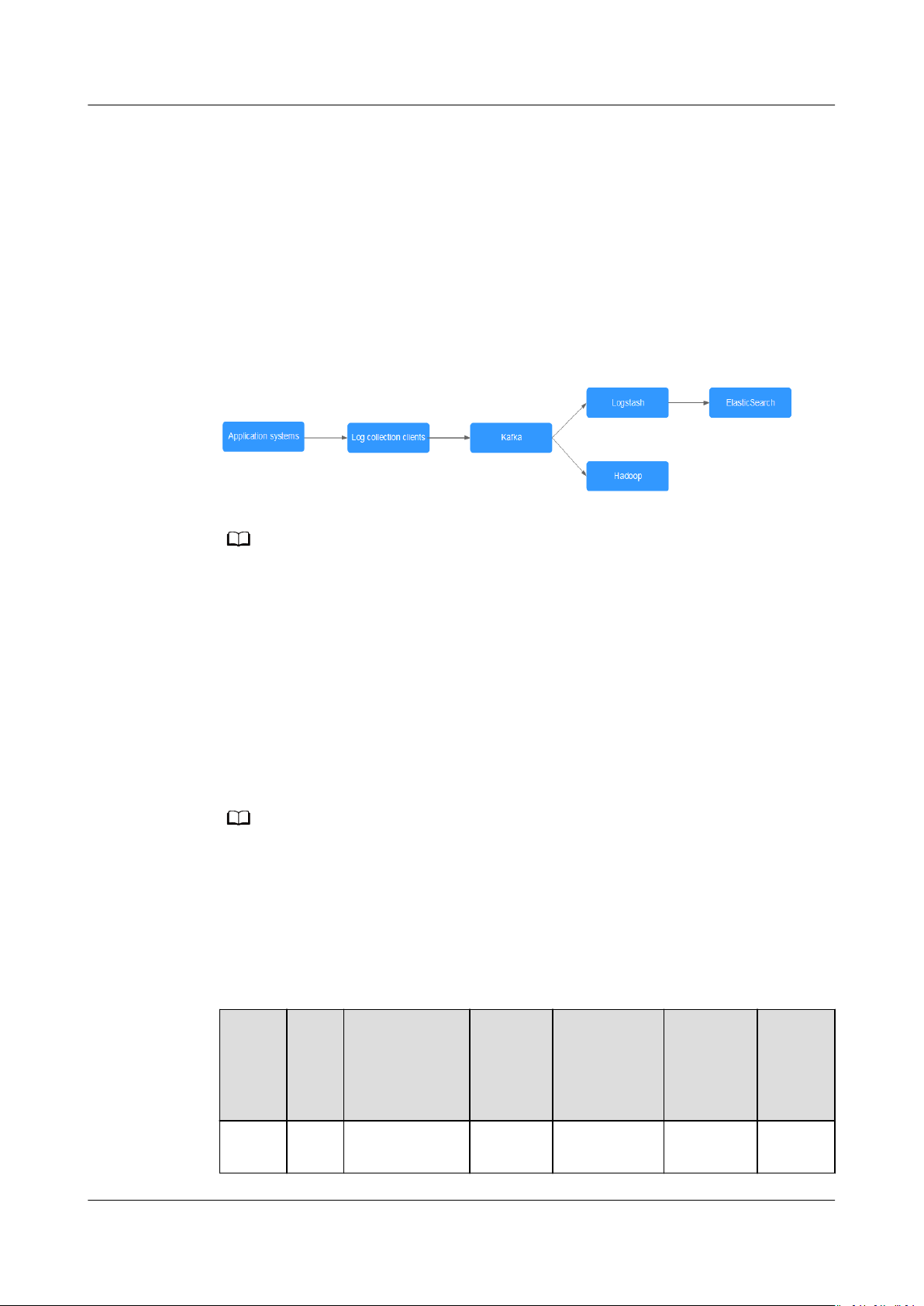
Log synchronization involves three major components: log collection clients, Kafka,
and backend log processing applications.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
Page 9
NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
1. The log collection clients collect log data from a user application service and
asynchronously send the log data in batches to Kafka clients.
Kafka clients receive and compress messages in batches. This only has a
minor impact on the service performance.
2. Kafka persists logs.
3. Log processing applications, such as Logstash, subscribe to messages in Kafka
and retrieve log messages from Kafka. Then, the messages are searched for
by le search services or delivered to big data applications such as Hadoop for
storage and analysis.
Figure 1-4 Log synchronization process
Logstash is for log analytics, ElasticSearch is for log search, and Hadoop is for big data
analytics. They are all open-source tools.
1.4 Specications
Kafka Premium Instance Specications
Kafka premium instances are compatible with open-source Kafka 2.3.0. The
instance
MB/s, 600 MB/s, and 1200 MB/s.
Table 1-1 TPS and maximum number of partitions supported by dierent instance
specications
specications are classied based on bandwidth, namely, 100 MB/s, 300
● The number of brokers varies according to the underlying resources, and the
underlying resources vary from region to region. The following table lists the
specications.
● In the following table, transactions per second (TPS) are calculated assuming that the
size of a message is 1 KB.
Band
width
Brok
ers
Underlying
Resource
Type
I/O
Type
TPS (HighThroughput
)
TPS
(Synchro
nous
Replicati
Maxim
um
Partitio
ns
on)
100
3 c6_2 vCPUs | 4GBHigh I/O 100,000 60,000 300
MB/s
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
Page 10
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
Band
width
300
MB/s
600
MB/s
1200
MB/s
Bandwidth Selection
Brok
ers
3 c6_4 vCPUs | 8GBHigh I/O 300,000 150,000 900
4 c6_8 vCPUs |
8 c6_8 vCPUs |
Underlying
Resource
Type
c6_2 vCPUs | 4GBUltra-
c6_4 vCPUs | 8GBUltra-
16 GB
16 GB
I/O
Type
high I/O
high I/O
Ultrahigh I/O
Ultrahigh I/O
TPS (HighThroughput
)
100,000 80,000 300
300,000 200,000 900
600,000 300,000 1800
1.2 million 400,000 1800
TPS
(Synchro
nous
Replicati
on)
Maxim
um
Partitio
ns
The bandwidth of a Kafka instance refers to the maximum read or write
bandwidth. You are advised to select a bandwidth 30% higher than what is
required.
● 100 MB/s
Recommended for up to 3000 client connections, 60 consumer groups, and 70
MB/s of service
● 300 MB/s
Recommended for up to 10,000 client connections, 300 consumer groups, and
210 MB/s of service
● 600 MB/s
Recommended for up to 20,000 client connections, 600 consumer groups, and
420 MB/s of service
● 1200 MB/s
Recommended for up to 20,000 client connections, 600 consumer groups, and
840 MB/s of service
Storage Space Selection
Kafka premium instances support storage with 1 to 3 replicas. The storage space is
space consumed by all replicas. When creating an instance, specify its storage
space based on the expected service message size and the number of replicas.
trac.
trac.
trac.
trac.
For example, if the estimated message size is 100 GB, the disk capacity must be at
least: 100 GB x Number of replicas + 100 GB (reserved).
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
Page 11
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
Topic Quantity
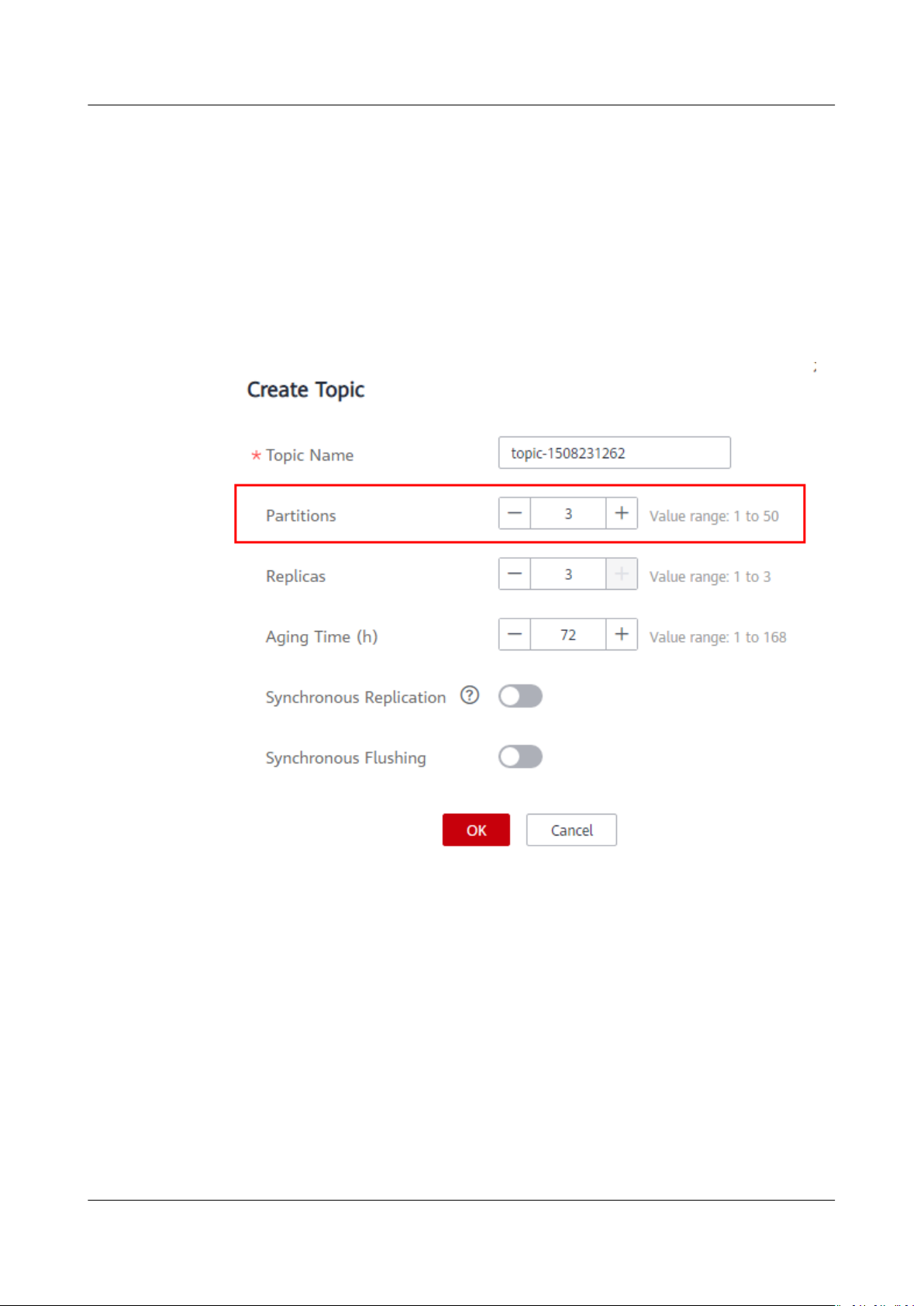
There is no limit on the topic quantity, but there is an upper limit on the
aggregate number of partitions in the topics. When the partition quantity limit is
reached, you can no longer create topics.
The number of topics is related to the maximum number of partitions allowed
(see Table 1-1) and the specied number of partitions in each topic (see Figure
1-5).
Figure 1-5 Setting the number of partitions
For example, the maximum number of partitions for a 100 MB/s instance is 300.
If the number of partitions of each topic in the instance is 3, the number of topics
is 300/3 = 100.
If the number of partitions of each topic in the instance is 1, the number of topics
is 300/1 = 300.
1.5 Comparing Kafka Instances and DMS Advanced Queues
Both Kafka premium instances and DMS advanced queues are compatible with
Apache Kafka. However, they
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
dier in the following aspects.
Page 12

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
Open-Source Compatibility
● DMS advanced queues:
Kafka 0.10.2.1
● Kafka premium instances:
Kafka 2.3.0
With each version upgrade, Apache Kafka introduces new features, improves
APIs, and updates producer and consumer
whether your application features and APIs are compatible with your Kafka
clients, see the upgrade notes on the
conguration les. To check
ocial Apache Kafka website.
Creation
● DMS advanced queues:
An advanced queue (equivalent to a topic) is created on the DMS console.
You do not need to
these resources are allocated by the system.
● Kafka premium instances:
A Kafka premium instance is created on the DMS for Kafka console. Before
creating a Kafka premium instance, determine the required bandwidth and
storage space based on your service expectations for the next one or two
years. You also need to prepare a VPC and security group for the instance.
After the instance has been created, you must create topics in the instance
congure the number of partitions and replicas for the topics.
and
congure the storage space or the bandwidth because
Usage
Performance
● DMS advanced queues:
Advanced queues are compatible with Kafka APIs. DMS provides SDKs in Java,
Python, Lua, C, and Go languages..
To use open-source Kafka clients, see "Using the Enhanced Java SDK" in
Developer Guide
Kafka to the directory of the open-source client package and then pass the
security authentication.
● Kafka premium instances:
DMS for Kafka is fully compatible with open-source Kafka. You can access
Kafka premium instances and topics using open-source Kafka clients. If SASL
access is enabled, you must use the SSL
● DMS advanced queues:
There are two queue modes: high-throughput and high-reliability. In the highthroughput mode, messages are
concurrency.
● Kafka premium instances:
Compute, bandwidth, and storage resources are physically isolated for each
instance. Determine the required bandwidth and storage space when creating
an instance. For storage space, you can choose Ultra-high I/O, which
indicates that messages are stored on SSDs.
. Add the enhanced Kafka Java SDK provided by DMS for
certicate provided by DMS for Kafka.
ushed to disk asynchronously, ensuring high
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
Page 13

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
Other Dimensions
You can customize the number of partitions and replicas for a Kafka premium
instance. Each topic can have 1 to 50 partitions and 1 to 3 replicas.
By default, an advanced queue has three partitions and three replicas.
Divide a topic into a certain number of partitions so that messages can be evenly
distributed to partitions, enabling load balancing and horizontal scalability. Dierent
consumers can retrieve messages from one or more partitions, improving message
processing performance.
With more replicas come higher reliability. However, synchronizing messages between
replicas consumes bandwidth and osets compute performance.
1.6 Comparing DMS for Kafka and Open-Source Kafka
DMS for Kafka is compatible with open-source Kafka and has customized and
enhanced Kafka features. In addition to the advantages of open-source Kafka,
DMS for Kafka provides more reliable and useful features.
Table 1-2
Dierences between DMS for Kafka and open-source Kafka
Catego
ry
Ease of
use
Costs On-
Item DMS for Kafka Open-source Kafka
Readily
availab
le
Instances can be created
intuitively within minutes
and used right out of the
box with visualized
Preparing server resources and
installing and conguring the
software is time-consuming
and prone to mistakes.
operations and real-time
monitoring.
APIs Instances can be managed
N/A
easily by calling RESTful
APIs.
deman
d use
Multiple specications are
available to suit dierent
needs.
Expenses are incurred for
setting up a message service
and occupying underlying
resources.
Fully
manag
ed
Services are readily
available without requiring
additional hardware
resources or expenses.
Users must prepare hardware
resources and set up the
service by themselves, and bear
high usage and maintenance
costs.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
Page 14
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
CategoryItem DMS for Kafka Open-source Kafka
Proven
success
Mature DMS has been proven
successful in large ecommerce events such as
the Vmall 11.11 Shopping
Festival. It is also used in
the clouds of carrier-grade
customers across the
world, and meets strict
carrier-grade reliability
standards. DMS closely
follows up with
community updates to
continuously
x known
open-source vulnerabilities
and add support for new
features.
Feature
-rich
While maintaining 100%
open-source compatibility,
DMS further optimizes
open-source code to
improve performance and
reliability, and provides
message querying,
dumping, tracing
(available soon), and
many other features.
Using open-source software
requires lengthy selfdevelopment and verication
and has had few successful
cases.
Functionality is limited and
requires self-development.
Reliabil
ity
Highly
availab
le
DMS supports cross-AZ
deployment to improve
reliability. In addition,
automatic fault detection
and alarms ensure reliable
operations of key services.
Simple
O&M
O&M is entirely
transparent to tenants
with a full set of
monitoring and alarm
functions. O&M personnel
will be informed of any
exceptions, eliminating the
need for 24/7 attending.
Secure DMS uses VPC isolation
and SSL channel
encryption.
High availability requires selfdevelopment or open-source
code implementation, which
are costly and cannot
guarantee reliability.
Users need to develop and
optimize O&M functions,
especially alarm notication
functions. Otherwise, manual
attendance is required.
Security must be hardened by
users themselves.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
Page 15
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
1.7 Notes and Constraints
DMS for Kafka has the following constraints, as listed in Table 1-3.
Table 1-3 Kafka usage restrictions
Item Constraint Description
Kafka Zookeeper Not exposed externally DMS ZooKeeper does
not provide services
externally. It is only used
to serve Kafka instances.
Version 2.3.0 Clients later than version
0.10 are supported. Use
a version that is
consistent with the
service version.
Message size 10 MB The message size cannot
exceed 10 MB.
Otherwise, the message
creation will fail.
Logging in to the VM
where the Kafka brokers
reside
Partition quantity Limited Kafka manages
Automatic topic creation Supported Congurable during
No supported N/A
messages by partition. If
there are too many
partitions, message
creation, storage, and
retrieval will be
fragmented,
the performance and
stability. If the total
number of partitions of
topics reaches the upper
limit, you cannot create
more topics.
instance creation.
If it is enabled, a topic
will be automatically
created with 3 partitions
and 3 replicas when a
message is created in or
retrieved from a topic
that does not exist.
aecting
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
Page 16
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
Item Constraint Description
Creating consumer
groups, consumers, and
producers
Decreasing partition
quantity
1.8 Related Services
● CTS
Cloud Trace Service (CTS) generates traces to provide you with a history of
operations performed on cloud service resources. The traces include operation
requests sent using the management console or open APIs, as well as the
operation results. You can view all generated traces to query, audit, and
backtrack performed operations.
For details about the operations recorded by CTS, see section "Operations
That Can Be Recorded by CTS".
Not required Consumer groups,
consumers, and
producers are generated
automatically when you
use the instance.
Not supported The partition quantity
cannot be decreased due
to the limitations of
Apache Kafka.
● VPC
Kafka premium instances run in VPCs and use the IP addresses and bandwidth
of VPC. Security groups of VPCs enhance the security of network access to the
Kafka premium instances.
1.9 Basic Concepts
DMS for Kafka of the public cloud uses Kafka as the message engine. This chapter
presents explanations of basic concepts of Kafka.
Topic
A topic is a category for messages. Messages are created, retrieved, and managed
in the form of topics.
Topics adopt the publish-subscribe pattern. Producers publish messages into
topics. One or more consumers subscribe to the messages in the topics. The
producers and consumers are not directly linked to each other.
Producer
A producer publishes messages into topics. The messages are then delivered to
other systems or modules for processing as agreed.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
Page 17

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
Consumer
A consumer subscribes to messages in topics and processes the messages. For
example, a monitoring and alarm platform (a consumer) subscribing to log
messages in certain topics can identify alarm logs and then send SMS or email
alarm notications.
Broker
A broker is a Kafka process in a Kafka cluster. Each process runs on a server, so a
broker includes the storage, bandwidth, and other server resources.
Partition
Messages in a topic are distributed to multiple partitions to achieve scalability and
fault tolerance.
Replica
A replica is a redundant copy of a partition in a topic. Each partition can have one
or more replicas, enabling message reliability.
Messages in each partition are fully replicated and synchronized, preventing data
loss if one replica fails.
Each partition has one replica as the leader which handles the creation and
retrievals of all messages. The rest replicas are followers which replicate the
leader.
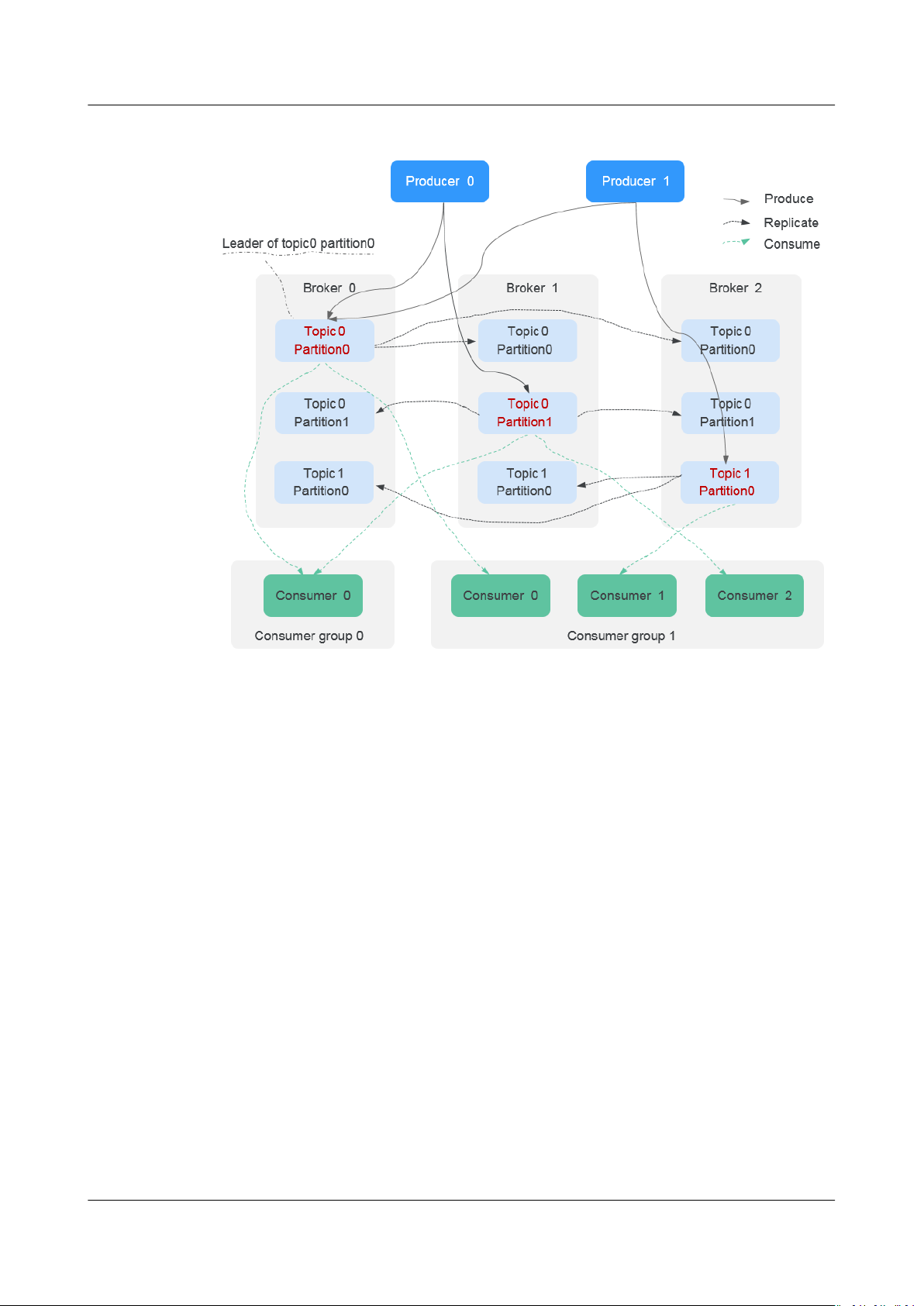
Topics and partitions are logical concepts, while replicas and brokers are physical
concepts. The following diagram shows the relationships between partitions,
brokers, and topics in messages streaming.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
Page 18
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 1 Service Overview
Figure 1-6 Kafka message streaming
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
Page 19

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 2 Preparing Required Resources
2 Preparing Required Resources
Overview
Before creating a Kafka instance, ensure the availability of resources, including a
virtual private cloud (VPC), subnet, security group, and security group rules. Each
Kafka instance is deployed in a VPC and bound to
groups. In this way, Kafka provides an isolated virtual network environment and
security protection policies that you can easily
specic subnets and security
congure and manage.
Required Resources
The following table lists the resources required by a Kafka instance.
Table 2-1 Kafka resources
Resource
VPC and
subnet
Requirement Operations
Dierent Kafka instances can use
the same or dierent VPCs and
subnets based on site
requirements. Note the following
when creating a VPC and subnet:
● The created VPC and the
Kafka instance must be in the
same region.
● Retain the default settings
unless otherwise
specied.
For details about how to
create a VPC and subnet, see
the
Virtual Private Cloud User
Guide
.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
Page 20

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 2 Preparing Required Resources
Resource Requirement Operations
Security
group
Dierent Kafka instances can use
the same or dierent security
groups. Note the following when
creating a security group:
● Set Template to Custom.
For details about how to
create a security group and
congure security group rules,
see the
User Guide
Virtual Private Cloud
.
● After a security group is
created, retain the default
inbound and outbound
trac
rules.
● To use Kafka, add the security
group rules described in Table
2-2. Other rules can be added
based on site requirements.
Table 2-2 Security group rules
DirectionProtocol Port Source Description
Inbound TCP 9094 0.0.0.0/0 Access Kafka through the
public network (without SSL
encryption).
Inbound TCP 9092 0.0.0.0/0 Access Kafka within a VPC
(without SSL encryption).
Inbound TCP 9095 0.0.0.0/0 Access Kafka through the
public network (with SSL
encryption).
Inbound TCP 9093 0.0.0.0/0 Access Kafka within a VPC
(with SSL encryption).
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
Page 21

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 3 Creating an Instance
3 Creating an Instance
Scenario
DMS for Kafka provides Kafka premium instances, which are physically isolated
and exclusively occupied by each tenant. You can customize the computing
capabilities and storage space of an instance based on service requirements.
Before You Start
● Before creating an instance, ensure that a VPC
● The broker quantity varies according to the underlying resources, and the
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
Step 4 Click Create Kafka Instance in the upper right corner of the page.
By default, you can create a maximum of 100 Kafka premium instances for each
project. To create more instances, contact the administrator to increase your
quota.
congured with security
groups and subnets is available.
underlying resources vary from region to region. Therefore,
have dierent broker quantities.
in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
dierent instances
Step 5 Specify Region, Project, and AZ.
Step 6 Enter an instance name.
Step 7
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
Congure the following instance parameters:
1. Version: Kafka version. Currently, only 2.3.0 is supported.
Page 22

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 3 Creating an Instance
2. CPU Architecture: Currently, only x86 architecture is supported.
3. Bandwidth:
You can view the ECS quantity and avor, the maximum number of partitions
allowed, and number of consumer groups recommended for each bandwidth
option.
The Maximum Partitions parameter indicates the maximum number of
partitions that can be created for a Kafka instance. If the total number of
partitions of all topics exceeds this threshold, topic creation will fail.
4. Storage Space: Total disk space for storing the instance data.
Disks are formatted when an instance is created. As a result, the actual
available disk space is 93% to 95% of the total disk space.
– 100 MB/s bandwidth: The value range of Storage Space is 600–90,000
GB.
– 300 MB/s bandwidth: The value range of Storage Space is 1200–90,000
GB.
– 600 MB/s bandwidth: The value range of Storage Space is 2400–90,000
GB.
– 1200 MB/s bandwidth: The value range of Storage Space is 4800–90,000
GB.
– High I/O + 100 MB/s bandwidth: If the average message size is 1 KB, the
transactions per second (TPS) can reach 100,000 in high throughput scenarios and
60,000 in synchronous replication scenarios.
– High I/O + 300 MB/s bandwidth: If the average message size is 1 KB, the TPS can
reach 300,000 in high throughput scenarios and 150,000 in synchronous replication
scenarios.
– Ultra-high I/O + 100 MB/s bandwidth: If the average message size is 1 KB, the TPS
can reach 100,000 in high throughput scenarios and 80,000 in synchronous
replication scenarios.
– Ultra-high I/O + 300 MB/s bandwidth: If the average message size is 1 KB, the TPS
can reach 300,000 in high throughput scenarios and 200,000 in synchronous
replication scenarios.
– Ultra-high I/O + 600 MB/s bandwidth: If the average message size is 1 KB, the TPS
can reach 600,000 in high throughput scenarios and 300,000 in synchronous
replication scenarios.
– Ultra-high I/O + 1200 MB/s bandwidth: If the average message size is 1 KB, the
TPS can reach 1,200,000 in high throughput scenarios and 400,000 in synchronous
replication scenarios.
5. Capacity Threshold Policy: policy used when the disk usage reaches the
threshold. The default capacity threshold is 95%.
– Stop production: New messages cannot be created, but existing
messages can still be retrieved.
– Automatically delete: Messages can be created and retrieved, but the
earliest 10% of messages will be deleted to ensure
sucient disk space.
6. Select a VPC and a subnet.
A VPC provides an isolated virtual network for your Kafka premium instances.
You can
congure and manage the network as required.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
Page 23

NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 3 Creating an Instance
After the Kafka instance is created, its VPC and subnet cannot be changed.
7. Select a security group.
A security group is a set of rules that control access to ECSs. It provides access
policies for mutually trusted ECSs with the same security protection
requirements in the same VPC.
Click Manage Security Group. On the displayed console, view or create
security groups.
Step 8 Click More Settings to
Congure public access.
1.
Public access is disabled by default. You can enable or disable it as required.
You can create three Kafka instances with public access enabled. To create
more instances with public access, contact the administrator to increase your
quota.
After public access is enabled, congure the bandwidth.
Kafka instances with 100 MB/s bandwidth do not support public access.
2. Congure Kafka SASL_SSL.
This parameter indicates whether to enable SSL authentication when a client
connects to the instance. If you enable Kafka SASL_SSL, data will be
encrypted before transmission to enhance security.
This setting cannot be changed after the instance is created. If you want
to use a
dierent SASL_SSL setting after the instance is created, you must
create a new instance.
If you enable Kafka SASL_SSL, you must also set the username and password
for accessing the instance.
Congure Automatic Topic Creation.
3.
congure more parameters.
If it is enabled, a topic will be automatically created with 3 partitions and 3
replicas when a message is created in or retrieved from a topic that does not
exist.
4. Enter a description of the instance.
Step 9 Click Create Now.
Step 10
Conrm the instance information and click Submit.
Step 11 When the new Kafka premium instance has been created, return to the Kafka
Premium page to view and manage your Kafka premium instances.
1. It takes 3 to 15 minutes to create a Kafka premium instance.
2. When a Kafka premium instance is successfully created, its default status is
Running.
3. If the new Kafka premium instance fails to be created, delete the unsuccessful
instance creation task by following the procedure in Deleting an Instance
and then create another Kafka premium instance. If the Kafka premium
instance creation fails again, contact the administrator.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
Page 24

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 3 Creating an Instance
Instances that fail to be created do not occupy other resources.
----End
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
Page 25

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 4 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance
4 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance
4.1 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance Without SASL
DMS for Kafka of the public cloud provides Kafka premium instances, which are
physically isolated and exclusively occupied by each tenant. After creating a Kafka
premium instance, you can use an open-source Kafka client to create and retrieve
messages in the instance.
Prerequisites
This section describes how to use an open-source Kafka client to access a Kafka
premium instance if SASL access is not enabled for the instance.
For details on how to use Kafka clients in
cwiki.apache.org/conuence/display/KAFKA/Clients
● The following describes the procedure for accessing a Kafka instance using CLI. To
access an instance in your service code, see the
● The Kafka server allows a maximum of 200 clients to be connected using a single IP
address. If the number of clients exceeds 200, the connection fails.
● Security group rules have been correctly
A Kafka premium instance with SASL disabled can be accessed within a VPC
or over public networks. Ensure that security group rules have been correctly
congured for the instance. For details about the security group conguration
requirements, see Table 2-2.
● The instance connection address has been obtained.
– For intra-VPC access, use port 9092. Obtain the instance connection
address on the instance details page.
dierent languages, visit https://
.
Developer Guide
congured.
.
Figure 4-1 Obtaining Kafka instance connection addresses for intra-VPC
access without SASL
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
Page 26

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 4 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance
– For public access, use port 9094. Obtain the instance access address on
the instance details page.
Figure 4-2 Obtaining Kafka instance connection addresses for public
access without SASL
● A topic has been created for the Kafka premium instance. Otherwise, create a
topic as instructed by Creating a Topic.
● Kafka CLI is available. Ensure that the Kafka instance and the CLI use the
same version.
● Java JDK has been installed in the environment where the Kafka CLI is used,
and related environment variables have been
congured.
Accessing the Instance in CLI Mode
The following uses Linux as an example.
Step 1 Decompress the Kafka CLI package.
Access the directory where the CLI package is stored and run the following
command to decompress the package:
tar -zxf
In the preceding command,
[kafka_tar]
[kafka_tar]
indicates the name of the CLI package.
For example:
tar -zxf kafka_2.11-2.3.0.tgz
Step 2 Access the /bin directory of the Kafka CLI.
In Windows, you need to access the /bin/windows directory.
Step 3 Run the following command to create messages:
./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list
${connection address}
Parameter description:
●
{connection-address}
is the address obtained in Prerequisites. For public
access, use Instance Access Address in the Public Access section. For intraVPC access, use Connection Address.
●
{topic-name}
is the name of the topic created for the Kafka instance.
--topic
${topic name}
The following example uses connection addresses
10.3.196.45:9094,10.78.42.127:9094,10.4.49.103:9094. After running the
preceding command, you can send a message to the Kafka instance by writing it
and pressing Enter. Each line of content is sent as a message.
[root@ecs-kafka bin]# ./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list
10.3.196.45:9094,10.78.42.127:9094,10.4.49.103:9094 --topic topic-demo
>Hello
>DMS
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
Page 27

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 4 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance
>Kafka!
>^C[root@ecs-kafka bin]#
To stop creating messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
Step 4 Run the following command to retrieve messages:
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server
beginning
${connection-address}
--topic
${topic name}
--from-
Parameter description:
{connection-address}
●
is the address obtained in Prerequisites. For public
access, use Instance Access Address in the Public Access section. For intraVPC access, use Connection Address.
●
{topic-name}
is the name of the topic created for the Kafka instance.
Example:
[root@ecs-kafka bin]# ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server
10.3.196.45:9094,10.78.42.127:9094,10.4.49.103:9094 --topic topic-demo --from-beginning
Kafka!
DMS
Hello
^CProcessed a total of 3 messages
[root@ecs-kafka bin]#
To stop retrieving messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
----End
4.2 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance with SASL
If you enable SASL_SSL when creating an instance, data will be encrypted before
transmission for enhanced security.
This section describes how to use an open-source Kafka client to access a Kafka
premium instance if SASL has been enabled for the instance.
● The Kafka server allows a maximum of 200 connections from each IP address. Excess
connections will be rejected.
● When accessing a Kafka instance with SASL, map host names to IP addresses in
the /etc/hosts le of the host where the client is deployed to facilitate instance broker
domain name resolution. Otherwise, latency may occur.
Set the IP address to the connection address of the instance. Set hosts to the names of
instance hosts. Specify a unique name for each host.
Examples:
10.154.48.120 server01
10.154.48.121 server02
10.154.48.122 server03
Prerequisites
● Security group rules have been correctly
A Kafka premium instance with SASL enabled can be accessed within a VPC
or over public networks. Ensure that security group rules have been correctly
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 22
congured.
Page 28

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 4 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance
congured for the instance. For details about the security group conguration
requirements, see Table 2-2.
● The instance connection address has been obtained.
– For intra-VPC access, use port 9093. Obtain the instance connection
address on the instance details page.
Figure 4-3 Obtaining Kafka instance connection addresses for intra-VPC
access with SASL enabled
– For public access, use port 9095. Obtain the instance access address on
the instance details page.
Figure 4-4 Obtaining Kafka instance connection addresses for public
access with SASL enabled
● A topic has been created for the Kafka premium instance. Otherwise, create a
topic as instructed by Creating a Topic.
● The client.truststore.jks certicate has been installed. The certicate can be
obtained by performing the following procedure:
Click the instance in the instance list. On the instance details page, click
next to Kafka SASL_SSL. Download and decompress the package to obtain
the client certicate le client.truststore.jks.
● Kafka CLI is available. Ensure that the Kafka instance and the CLI use the
same version.
● Java JDK has been installed in the environment where the Kafka CLI is used,
and related environment variables have been
Accessing the Instance in CLI Mode
The following uses Linux as an example.
Step 1 Decompress the Kafka CLI package.
Access the directory where the CLI package is stored and run the following
command to decompress the package:
tar -zxf
[kafka_tar]
congured.
In the preceding command,
For example:
tar -zxf kafka_2.11-2.3.0.tgz
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 23
[kafka_tar]
indicates the name of the CLI package.
Page 29

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 4 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance
Step 2 Modify the conguration le of the Kafka CLI.
Find the consumer.properties and producer.properties les in the /cong
directory of the Kafka CLI and add the following content to the les:
sasl.jaas.cong=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required \
username="**********" \
password="**********";
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
ssl.truststore.location=/opt/kafka_2.11-2.3.0/cong/client.truststore.jks
ssl.truststore.password=dms@kafka
ssl.endpoint.identication.algorithm=
Parameter description:
●
username
and
password
are set when you enable Kafka SASL_SSL during
instance creation.
● ssl.trustore.location: path for storing the client.truststore.jks
in Windows, you need to use slashes (/) for the certicate path. Do not use
backslashes (\), which used by default for paths in Windows. Otherwise, the
client will fail to obtain the
certicate.
● ssl.truststore.password: server certicate password, which must be set to
dms@kafka and cannot be changed
● ssl.endpoint.identication.algorithm: whether to verify the certicate
domain name. This parameter must be left blank, which indicates
disabling domain name
verication.
Step 3 Access the /bin directory of the Kafka CLI.
In Windows, you need to access the /bin/windows directory.
Step 4 Run the following command to create messages:
./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list ${connection-address} --topic ${topic-name} --producer.cong ../
cong/producer.properties
Parameter description:
●
{connection-address}
is the address obtained in Prerequisites. For public
access, use Instance Access Address in the Public Access section. For intraVPC access, use Connection Address.
{topic-name}
●
is the name of the topic created for the Kafka instance.
certicate Even
The following example uses connection addresses 10.xxx.xxx.202:9095,10.xxx.xxx.
197:9095,10.xxx.xxx.68:9095.
After running the preceding command, you can send a message to the Kafka
instance by writing it and pressing Enter. Each line of content is sent as a
message.
[root@ecs-kafka bin]#./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list 10.xxx.xxx.202:9095,10.xxx.xxx.
197:9095,10.xxx.xxx.68:9095 --topic topic-demo --producer.cong ../cong/producer.properties
>hello
>DMS
>Kafka!
>^C[root@ecs-kafka bin]#
To stop creating messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 24
Page 30

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 4 Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance
Step 5 Run the following command to retrieve messages:
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server
beginning --consumer.cong ../cong/consumer.properties
$[connection-address]
--topic
$[topic-name]
--from-
Parameter description:
●
{connection-address}
is the address obtained in Prerequisites. For public
access, use Instance Access Address in the Public Access section. For intraVPC access, use Connection Address.
{topic-name}
●
is the name of the topic created for the Kafka instance.
Example:
[root@ecs-kafka bin]# ./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server 10.xxx.xxx.202:9095,10.xxx.xxx.
197:9095,10.xxx.xxx.68:9095 --topic topic-demo --from-beginning --consumer.cong ../cong/
consumer.properties
hello
Kafka!
DMS
hello
^CProcessed a total of 4 messages
[root@ecs-kafka bin]#
To stop retrieving messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
----End
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 25
Page 31

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
5 Managing Instances
5.1 Viewing an Instance
Scenario
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click in the upper left corner to select a region.
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
Step 4 Search for a Kafka premium instance by status, name, ID, or connection address.
View detailed information about a Kafka premium instance on the Kafka console,
for example, the IP address and port number for accessing the instance.
Select the same region as your application service.
console.
Table 5-1 describes the various possible statuses of a Kafka premium instance.
Table 5-1 Kafka premium instance status description
Status
Description
Creating The instance is being created.
Running The instance is running properly.
Only Kafka premium instances whose status is Running can
provide the DMS for Kafka service.
Faulty The instance is not running properly.
Starting The status between Frozen and Running.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 26
Page 32

NO TICE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
Status Description
Restarting The instance is being restarted.
Changing Public access is being modied for the instance, or advanced
settings are being changed.
Change
failed
Creation
failed
Step 5 Click the name of the chosen Kafka premium instance and view detailed
information about the instance on the displayed page.
Table 5-2 Parameters for connecting to a Kafka instance
Section Parameter Description
Public
Access
Public access failed to be modied for the instance, or advanced
settings failed to be changed.
The instance failed to be created.
Public
Access
Public
Network
Bandwidth
Instance
Access
Address
Indicates whether public access has been enabled
for the instance. Click to change the public
network setting.
Indicates the public network bandwidth of the
instance. This parameter is displayed only when
public access is enabled.
Indicates the public network connection address of
the instance. This parameter is displayed only when
public access is enabled.
Connectio
n Address
----End
IPv4 Indicates the address for accessing the instance in a
VPC.
5.2 Restarting an Instance
Scenario
Restart one or more Kafka premium instances at a time on the Kafka console.
When a Kafka premium instance is being restarted, message retrieval and creation
requests of the client will be rejected.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 27
Page 33

NO TE
NO TE
NO TICE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
Prerequisites
The status of the Kafka premium instance you want to restart is either Running or
Faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
Step 4 Select one or more Kafka premium instances in the instance list.
Step 5 Click Restart on the top of the instance list.
Step 6 Click Yes.
It takes 3 to 15 minutes to restart a Kafka premium instance. After it is
successfully restarted, the Kafka premium instance status should be Running.
Restarting a Kafka premium instance only restarts the instance process and does not restart
the VM where the instance is located.
To restart a Kafka premium instance, you can also choose Operation > Restart in the same
row as the chosen Kafka premium instance on the Kafka Premium page.
----End
5.3 Deleting an Instance
Scenario
With a few clicks on the Kafka console, you can delete one or more Kafka
premium instances that have been created or failed to be created.
Deleting a Kafka premium instance will delete the data in the instance without
any backup. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
Prerequisites
The status of the Kafka premium instance you want to delete is in the Running or
Faulty state.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 28
Page 34

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
Deleting a Kafka Premium Instance
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
Step 4 Select one or more Kafka premium instances in the instance list.
Kafka premium instances in the Creating, Starting, Changing, Change failed, or
Restarting state cannot be deleted.
Step 5 Click Delete on the top of the instance list.
Step 6 Click Yes.
It takes 1 to 60 seconds to delete a Kafka premium instance.
To delete a Kafka premium instance, you can also choose Operation > Delete in the same
row as the chosen Kafka premium instance on the Kafka Premium page.
----End
Deleting a Kafka Premium Instance That Failed to Be Created
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
If there are Kafka premium instances that failed to be created, Instance Creation
Failures and quantity information will be displayed.
Instances that fail to be created do not occupy other resources.
Step 4 Click the icon or quantity next to Instance Creation Failures.
The Instance Creation Failures dialog box is displayed
Step 5 Delete Kafka premium instances that failed to be created in either of the following
ways:
● To delete all Kafka premium instances that failed to be created at once, click
Clear Failed Instance.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 29
Page 35

NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
● To delete a single Kafka premium instance that failed to be created, click
Delete in the same row as the chosen Kafka premium instance.
----End
5.4 Modifying the Information About an Instance
After creating a Kafka premium instance, you can modify some parameters of the
instance based on service requirements, including the instance name, description,
maintenance time window, security group, and capacity threshold policy.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
Step 4 Click the name of a Kafka premium instance for which you want to modify
information.
Step 5 Click behind a parameter to modify it.
You can modify the following parameters:
● Instance Name
● Time Window
● Description
● Security Group
● Public Access
● Capacity Threshold Policy
● Automatic Topic Creation
in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
For details about how to change the public access conguration, see Conguring Public
Access.
Step 6 Click to save the modication.
If Capacity Threshold Policy, Public Access, or Automatic Topic Creation has
been modied, you will be redirected to the Background Tasks page, which
displays the
If Instance Name, Description, Time Window, or Security Group has been
modied, the modication result will be displayed on the upper right corner of the
page.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 30
modication progress and result.
Page 36

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
Click to undo modication.
----End
5.5 Conguring Public Access
To access a Kafka instance over a public network, you can enable public access
congure public network bandwidth for the instance. After the instance has
and
been created with public access enabled, you can modify the public network
bandwidth. Currently, you can increase but cannot decrease the bandwidth.
If you no longer need public access to the instance, you can disable it as required.
Kafka instances with 100 MB/s bandwidth do not support public access.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
Step 4 In the navigation pane, choose Kafka Premium.
Step 5 Click the name of an instance.
Step 6 In the Public Access section, click
.
The Change Public Network Bandwidth page is displayed.
You can change the public access setting only when the instance is in the Running state.
Step 7 Perform the following operations as required:
● Enabling public access
Click
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 31
to enable public access and set the bandwidth.
Page 37

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
– You can enable public access for a maximum of three instances. If you want to
enable public access for more instances, contact the administrator to increase your
quota.
– If you have enabled and disabled public access before, the public access address
will be
dierent when you enable public access again.
– The following lists the value range of the public network bandwidth of instances
that use C6 ECSs:
▪ When the instance
must be a multiple of the number of brokers and fall in the range from 3 to
900.
When the instance specication is 600 MB/s, the public network bandwidth
▪
must be a multiple of the number of brokers and fall in the range from 4 to
1200.
When the instance
▪
must be a multiple of the number of brokers and fall in the range from 8 to
2400.
specication is 300 MB/s, the public network bandwidth
specication is 1200 MB/s, the public network bandwidth
● Disabling public access
Click
to disable public access.
● Modifying public network bandwidth
Next to Bandwidth (Mbit/s), slide the bar or enter a number in the text box
to set the bandwidth.
– The public network bandwidth can only be changed to a higher value.
– During public network bandwidth expansion, some services may fail. You are
advised to perform this operation during
o-peak hours.
Step 8 Click Submit to save the changes.
A message is displayed indicating that the task is successfully submitted. You can
view the operation progress on the Background Tasks page. If the task status is
Successful, the
modication has succeeded.
----End
5.6 Resetting Kafka Password
Scenario
You can reset the password of a Kafka premium instance if you forget it.
● You can reset the password of a Kafka premium instance only if Kafka SASL_SSL has
been enabled for the instance.
● You can reset the password of a Kafka instance only when it is in the Running state.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 32
Page 38

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
Step 4 Choose More > Reset Kafka Password in the same row as the Kafka premium
instance for which you want to reset the password.
Step 5 In the displayed Reset Kafka Password dialogue box, enter and
password.
Step 6 Click OK.
● If the password is successfully reset, a success message is displayed.
● If the password fails to be reset, a failure message is displayed. Reset the
password again. If you still fail to reset the password after multiple attempts,
contact the administrator.
The system will display a success message only after the password is successfully reset on
all nodes.
----End
5.7 Viewing Background Tasks
After you initiate certain instance operations such as
modifying the capacity threshold capacity, a background task will start for each
operation. On the console, you can view the background task status and clear task
information by deleting task records.
conrm the new
conguring public access and
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
Step 4 Click the name of the Kafka premium instance. The Basic Information page is
displayed.
Step 5 Click the Background Tasks tab.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 33
in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
Page 39

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 5 Managing Instances
A list of background tasks is displayed.
Step 6 Click , specify Start Date and End Date, and click OK to view tasks started in
the corresponding time segment.
● Click
to refresh the task status.
● To clear the record of a background task, choose Operation > Delete.
You can only delete the records of tasks in the Successful or Failed state.
----End
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 34
Page 40

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 6 Managing Topics
6 Managing Topics
6.1 Creating a Topic
A topic is a stream of messages. If automatic topic creation is not enabled during
instance creation, you need to manually create topics for creating and retrieving
messages. If you have enabled automatic topic creation during instance creation,
you do not need to create topics manually. When a message is created, a topic will
be automatically created with 3 partitions and 3 replicas.
The following describes three methods to manually create a topic.
● Method 1: Creating a Topic on the Console
● Method 2: Create a Topic by Using Kafka CLI
Method 1: Creating a Topic on the Console
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
Step 4 Click the name of a Kafka premium instance for which you want to create a topic.
The instance details page is displayed.
Step 5 Click the Topics tab, and click Create Topic.
The Create Topic dialog box is displayed.
Step 6 Specify the topic parameters listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 35
Page 41

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 6 Managing Topics
Table 6-1 Topic parameters
Parameter Description
Topic Name When creating a topic, you can modify the automatically
generated topic name.
Once the topic is created, you cannot modify its name.
Partitions A larger number of partitions for a topic indicates more
messages retrieved concurrently.
If this parameter is set to 1, messages will be retrieved in the
FIFO order.
Value range: 1 to 50
Default value: 3
Replicas A higher number of replicas delivers higher reliability. Data is
automatically backed up on each replica. When one Kafka
broker becomes faulty, data is still available on other brokers.
If this parameter is set to 1, only one set of data is available.
Value range: 1 to 3
Default value: 3
Aging Time (h) The number of hours for which messages will be preserved in
a topic. Messages older than this period will be deleted.
Deleted messages are not retrievable to consumer groups.
Value range: 1 to 168
Default value: 72
Synchronous
Replication
Synchronous
Flushing
A message is returned to the client only after the message
creation request has been received and the message has
been acknowledged by all replicas.
After enabling synchronous replication, congure acks = -1
on the client. Otherwise, this function will not take eect.
If there is only one replica, synchronous replication cannot be
enabled.
An indicator of whether a message is immediately ushed to
disk once created.
Enabled: A message is immediately ushed to disk once it is
created, resulting in higher reliability.
Disabled: A message is stored in the memory instead of
being immediately
ushed to disk once created.
Step 7 Click OK.
----End
Method 2: Create a Topic by Using Kafka CLI
You can use kafka-topics.sh to create topics and manage topic parameters.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 36
Page 42

NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 6 Managing Topics
kafka-topics.sh --create --topic {topic_name} --bootstrap-server {broker_ip}:
{port} --partitions {partition_num} --replication-factor {replication_num}
6.2 Deleting a Topic
Prerequisites
● A Kafka premium instance has been created, and a topic has been created in
this instance.
● The Kafka premium instance is in the Running state.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click
Step 3 Choose Application > Distributed Message Service for Kafka to open the Kafka
console.
Step 4 Click the name of a Kafka premium instance for which you want to delete a topic.
The instance details page is displayed.
Step 5 Click the Topics tab.
Step 6 Select one or more topics in the topic list.
Step 7 Click Delete Topic on the top of the topic list.
Step 8 Click Yes.
----End
in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
To delete a topic, you can also choose Operation > Delete in the same row as the chosen
topic on the Topics tab page.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 37
Page 43

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 7 Auditing
7 Auditing
7.1 Operations That Can Be Recorded by CTS
With CTS, you can record operations associated with DMS for later query, audit,
and backtrack operations.
Table 7-1 DMS operations that can be recorded by CTS
Operation
Successfully deleting a
background task
Failing to delete a
background task
Successfully creating
an order for creating
an instance
Failing to create an
order for creating an
instance
Successfully
submitting a request
to modify an instance
order
Failing to submit a
request to modify an
instance order
Resource Type Trace Name
kafka deleteDMSBackendJobSuccess
kafka deleteDMSBackendJobFailure
kafka createDMSInstanceOrderSuccess
kafka createDMSInstanceOrderFailure
kafka modifyDMSInstanceOrderSuc-
cess
kafka modifyDMSInstanceOrderFailure
Successfully
submitting a request
to reset instance
password
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 38
kafka resetDMSInstancePasswordSuc-
cess
Page 44

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 7 Auditing
Operation Resource Type Trace Name
Failing to submit a
request to reset
instance password
Successfully creating a
topic for a Kafka
premium instance
Failing to create a
topic for a Kafka
premium instance
Successfully deleting a
topic from a Kafka
premium instance
Failing to delete a
topic for a Kafka
premium instance
Successfully deleting
an instance failed to
be created
Failing to delete an
instance failed to be
created
kafka resetDMSInstancePasswordFai-
lure
kafka Kafka_platinum_create_topicSuc
cess
kafka Kafka_platinum_create_topicFail
ure
kafka Kafka_platinum_delete_topicsSu
ccess
kafka Kafka_platinum_delete_topicsFai
lure
kafka deleteDMSCreateFailureInstan-
cesSuccess
kafka deleteDMSCreateFailureInstan-
cesFailure
Successfully
submitting a request
to restart an instance
Failing to submit a
request to restart an
instance
Successfully
submitting a request
to delete multiple
instances at a time
Failing to submit a
request to delete
multiple instances at
a time
Successfully
submitting a request
to restart multiple
instances at a time
kafka restartDMSInstanceSuccess
kafka restartDMSInstanceFailure
kafka batchDeleteDMSInstanceSuccess
kafka batchDeleteDMSInstanceFailure
kafka batchRestartDMSInstanceSuc-
cess
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 39
Page 45

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 7 Auditing
Operation Resource Type Trace Name
Failing to submit a
request to restart
multiple instances at
a time
Successfully
submitting a request
to modify instance
information
Failing to submit a
request to modify
instance information
Deleting multiple
instance tasks at a
time
Successfully deleting
an instance
Failing to delete an
instance
Successfully creating
an instance
kafka batchRestartDMSInstanceFailure
kafka modifyDMSInstanceInfoSuccess
kafka modifyDMSInstanceInfoFailure
kafka batchDeleteDMSInstanceTask
kafka deleteDMSInstanceTaskSuccess
kafka deleteDMSInstanceTaskFailure
kafka createDMSInstanceTaskSuccess
Failing to create an
instance
Successfully restarting
an instance
Failing to restart an
instance
Successfully restarting
multiple instances at
a time
Failing to restart
multiple instances at
a time
Successfully modifying
instance information
Failing to modify
instance information
kafka createDMSInstanceTaskFailure
kafka restartDMSInstanceTaskSuccess
kafka restartDMSInstanceTaskFailure
kafka batchRestartDMSInstanceTask-
Success
kafka batchRestartDMSInstanceTask-
Failure
kafka modifyDMSInstanceInfoTaskSuc-
cess
kafka modifyDMSInstanceInfoTaskFai-
lure
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 40
Page 46

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 7 Auditing
7.2 Viewing Traces on the CTS Console
Scenario
View traces of the last seven days on the CTS console.
This section describes how to view operation records of the last 7 days on the CTS
console.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click
Step 3 Choose Management & Deployment > Cloud Trace Service.
Step 4 In the navigation pane, choose Trace List.
Step 5 On the Trace List page, query traces based on a combination of the following
querying dimensions:
● Trace Source: Select DMS.
● Resource Type: Select group, queue, or kafka.
● Search By: Select an option from the drop-down list.
● Operator: Select a
● Trace Status: Select All trace statuses, Normal, Warning, or Incident.
● Start time and end time: You can specify the time period to query traces.
in the upper left corner to select a region.
Select the same region as your application service.
When you select Trace name, you also need to select a
When you select Resource ID, you also need to select a
When you select Resource name, you also need to select a specic resource
name.
specic operator (a user other than tenant).
specic trace name.
specic resource ID.
Step 6 Click
Step 7 Click View Trace in the Operation column. In the displayed dialog box, the trace
structure details are displayed
----End
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 41
on the left of a trace to expand its details.
Page 47

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
8 FAQs
8.1 Instances
8.1.1 Why Can't I Select Two AZs?
A Kafka cluster uses 3 ZooKeeper nodes regardless of instance specications.
Kafka uses the ZooKeeper cluster to manage congurations. If the ZooKeeper
cluster is faulty, Kafka will not work properly.
At least two ZooKeepers are required for the cluster to run properly.
Assume that you select only two AZs. AZ1 has one ZooKeeper node, and AZ2 has
two. If AZ1 is faulty, the instance can be used properly. If AZ2 is faulty, the cluster
cannot be used. In this case, the availability rate is just 50%. Therefore, do not
select 2 AZs.
8.1.2 Why Can't I View the Subnet and Security Group Information When Creating a DMS Instance?
This may be because you do not have the Server Administrator and VPC
Administrator permissions.
8.1.3 How Do I Select Storage Space for a Kafka Instance?
The storage space is the space for storing messages. Storage space
for a Kafka instance include the disk type and disk size. Currently supported disk
types are ultra-high I/O and high I/O.
congurations
For example, if the required disk size to store data for the retention period is 100
GB, the disk capacity must be at least: 100 GB x Number of replicas + 100 GB
(reserved). In a Kafka cluster, each node uses a 33 GB disk to store logs and
ZooKeeper data. Therefore, the actual available storage space is less than the
purchased storage space.
The number of replicas (3 by default) can be
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 42
congured when you create a topic.
Page 48

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
8.1.4 How Do I Choose Between High I/O and Ultra-high I/O?
● High I/O: The average latency is 1 to 3 ms, and the maximum bandwidth is
150 MB/s (read + write).
● Ultra-high I/O: The average latency is 1 ms, and the maximum bandwidth is
350 MB/s (read + write).
You are advised to select ultra-high I/O, because ultra-high I/O disks deliver much
higher bandwidth than high I/O.
8.1.5 Which Capacity Threshold Policy Should I Use?
Currently, the following policies are supported:
● Stop production
When the memory usage reaches 95% of the disk capacity threshold, new
messages will no longer be created, but existing messages can still be
retrieved until they are discarded. The default retention time is three days.
This policy is suitable for scenarios where no data losses can be tolerated.
● Automatically delete
When the memory usage reaches the disk capacity threshold, the earliest data
will be deleted from the disk to ensure uninterrupted services. However, data
may be lost.
Select a proper policy based on requirements for data and service reliability. Both
policies are only used for handling extreme scenarios. To avoid extreme
scenarios, buy
sucient disk space in the rst place.
8.1.6 Which Kafka Version Is Supported?
Kafka 2.3.0.
8.1.7 What Is the ZooKeeper Version of a Kafka Instance?
DMS ZooKeeper does not provide services externally. It is only used to serve Kafka
instances.
You can use open-source Kafka clients to connect to Kafka instances and call the
native APIs to create and retrieve messages.
8.1.8 Are Kafka Instances in Cluster Mode?
Yes. A Kafka instance is a cluster.
8.1.9 Can I Modify the Connection Address for Accessing a Kafka Instance?
No. You must access a Kafka instance through one of the following ports:
● Accessing a Kafka premium instance without SASL:
Use port 9092 for intra-VPC access and port 9094 for public access.
● Accessing a Kafka premium instance with SASL:
Use port 9093 for intra-VPC access and port 9095 for public access.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 43
Page 49

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
Ensure that correct rules have been congured for the security group of the
instance. For details, see How Do I Select and Congure a Security Group?
8.1.10 How Long Are Kafka SSL Certicates Valid for?
The
certicates are valid for more than 15 years. You do not need to worry about
certicate expiration. The certicates are used for one-way authentication when
enabling SASL for Kafka instances.
8.1.11 How to Synchronize Data from One Kafka Instance to Another?
Unfortunately, you cannot synchronize two Kafka instances in real time. To
migrate services from one instance to another, create messages to both instances.
After the retrieval or aging of all messages in the original instance, you can
migrate services to the new instance.
8.1.12 How Do I Change the SASL_SSL Setting of a Kafka Instance?
The SASL_SSL setting cannot be changed once the instance has been created. Be
careful when
change the setting, you must create another instance.
conguring this setting during instance creation. If you need to
8.1.13 Are Kafka Brokers and ZooKeeper Deployed on the
Same VM or on Dierent VMs?
Kafka brokers and ZooKeeper are deployed on the same VM.
8.1.14 What Cipher Suites Are Supported by Kafka?
For security purposes, only TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 is
supported.
8.1.15 Can I Change an Instance from Single-AZ Deployment to Multi-AZ Deployment?
No. The AZ
multiple AZs, buy another instance.
conguration cannot be changed once the instance is created. To use
8.1.16 Does DMS for Kafka Support Cross-AZ Disaster
Recovery? Where Can I View the AZs
Congured for a
Purchased Instance?
DMS for Kafka supports cross-AZ disaster recovery. If you select multiple AZs for
an instance, cross-AZ disaster recovery will be available.
You can view the AZs congured for an instance on the Basic Information tab
page of the instance. If there are multiple AZs, cross-AZ disaster recovery is
available.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 44
Page 50

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
Figure 8-1 Instance basic information
8.1.17 Can I Change the VPC and Subnet After a Kafka Instance Is Created?
No. Once an instance is created, its VPC and subnet cannot be changed.
8.1.18 Where Can I Find Kafka Streams Use Cases?
You can
nd Kafka Streams use cases on the ocial Kafka website.
8.2 Connections
8.2.1 Troubleshooting Kafka Connection Exceptions
Overview
This section describes how to troubleshoot Kafka connection problems.
Problem Classication
If the connection to a Kafka instance is abnormal, perform the following
operations to troubleshoot the fault:
● Checking the Network
● Checking Consumer and Producer
● Common Errors on Java Clients
● Common Errors on the Go Client
Congurations
Checking the Network
Before connecting to a Kafka instance, ensure that the client and the instance are
interconnected. If they cannot be connected, check the network connection.
For example, if you have enabled SASL to access the Kafka instance, run the
following command:
curl -kv {ip}:{port}
● If the network is normal, information similar to the following is shown:
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 45
Page 51

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
● If the network is abnormal or disconnected, information similar to the
following is shown:
Solution:
1. Check whether the client and the Kafka instance are in the same VPC.
2. Check whether the security group rules are correctly congured. For details,
see How Do I Select and
Checking Consumer and Producer
View logs to check whether the parameters printed during the initialization of the
consumer and producer are the same as those set in the conguration les.
If they are dierent, check the parameters in the conguration le.
Common Errors on Java Clients
● Domain name
The following error is displayed:
verication enabled
Congure a Security Group?
Congurations
Solution: Check the consumer.properties and producer.properties les, in
which the
empty, indicating that domain name verication is disabled.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 46
ssl.endpoint.identication.algorithm parameter must be left
Page 52

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
ssl.endpoint.identication.algorithm=
● SSL certicate failing to be loaded
The following error is displayed:
Solution:
a. Check whether the client.truststore.jks
address.
b. Check the permissions on the processes and les.
c. Check whether the ssl.truststore.password parameter in the
consumer.properties and producer.properties
ssl.truststore.password is the server certicate password, which must be
set to dms@kafka and cannot be changed.
ssl.truststore.password=dms@kafka
● Incorrect topic name
The following error is displayed:
Solution: Create another topic or enable the automatic topic creation
function.
Common Errors on the Go Client
The Go client fails to connect to Kafka over SSL and the error "rst record does
not look like a TLS handshake" is returned.
le exists in the corresponding
les is correctly set.
Solution: Enable the TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 cipher suite
(which is disabled by default).
8.2.2 How Do I Select and
To access a Kafka premium instance within a VPC or over public networks,
congure the security group rules as follows:
● Intra-VPC access
To access a Kafka premium instance, you must deploy your client on an ECS in
the same VPC and subnet as the instance.
In addition, before you can access the instance through your client, you must
congure correct rules for the security groups of both the ECS and the Kafka
premium instance.
a. You are advised to
Kafka premium instance. After a security group is created, network access
in the group is not restricted by default.
b. If
dierent security groups are congured, you may need to refer to the
following congurations:
Congure a Security Group?
congure the same security group for the ECS and
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 47
Page 53

NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
● Assume that security groups sg-53d4 and Default_All are congured
respectively for your ECS and Kafka premium instance.
● You can specify a security group or IP address as the remote end in the
following rules.
To ensure that your client can access the instance, add the following rule
to the security group congured for the ECS:
Table 8-1 Security group rule
Direction Protocol Port Destination
Outbound All All Default_All
To ensure that your client can access the Kafka premium instance, add
the following rule to the security group
congured for the instance.
Table 8-2 Security group rule
Direction
Inbound All All sg-53d4
● Public access
Congure security group rules according to Table 8-3.
Table 8-3 Security group rules
Directi
on
InboundTCP 9094 0.0.0.0/0 Access Kafka through the
InboundTCP 9095 0.0.0.0/0 Access Kafka through the
Protocol Port Source Description
Protocol Port Source
public network (without
SSL encryption).
public network (with SSL
encryption).
8.2.3 Can I Access a Kafka Premium Instance Over a Public Network?
Yes.
You can create a maximum of three Kafka instances with public access enabled. If
you want to create more instances with public access, increase your quota.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 48
Page 54

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
8.2.4 How Many Connection Addresses Does a Kafka Instance Have by Default?
The number of connection addresses of a Kafka instance is the same as the
number of brokers of the instance.
8.2.5 Do Kafka Instances Support Cross-Region Access?
Yes. You can access a Kafka instance across regions over a public network or by
using direct connections.
8.2.6 Can I Access a Kafka Instance Using DNAT?
Yes.
8.2.7 Do Kafka Premium Instances Support Cross-Subnet Access?
Yes.
If the client and the instance are in the same VPC, cross-subnet access is
supported.
If the client and the instance are in
VPC a peering connection. For details about VPC peering connection, see .
You can also access an instance through the public access address bound to the
instance.
dierent VPCs, connect the two VPCs using
8.2.8 Why Do I Fail to Access Kafka Using SSL from a Go Client?
Symptom: A Go client fails to connect to Kafka over SSL and the error
does not look like a TLS handshake" is returned.
Solution: Enable the TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 cipher suite
(which is disabled by default).
8.2.9 What If
Certicates Fail to Be Loaded for SASL
"rst record
Connection?
If the certicate fails to be loaded during SASL connections, add the following
parameters to the conguration le:
# Disable certicate domain name verication.
ssl.endpoint.identication.algorithm=
8.2.10 Does DMS for Kafka Support Password-Free Access?
Yes. You can access a Kafka instance.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 49
Page 55

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
8.2.11 Obtaining Kafka Clients
Kafka premium instances are fully compatible with open-source clients. You can
obtain clients in other programming languages and access your instance as
instructed by the ocial Kafka website.
8.2.12 Does DMS for Kafka Support Authentication on Clients by the Server?
No.
8.2.13 Can I Use PEM SSL Truststore When Connecting to a Kafka Instance with SASL_SSL Enabled?
No. You can only use JKS
8.2.14 What Are the
Dierences Between JKS and CRT
certicates for connecting to instances in Java.
Certicates?
JKS certicates are used for connecting to instances in Java and CRT certicates
are used for connecting to instances in Python.
8.2.15 Which TLS Version Does DMS for Kafka Support, 1.0,
1.1, or 1.2?
TLS 1.2.
8.2.16 Is There a Limit on the Number of Connections to a Kafka Instance?
Yes. The maximum allowed number of connections varies by instance
specications.
● If the bandwidth is 100 MB/s, a maximum of 3000 connections are allowed.
● If the bandwidth is 300 MB/s, a maximum of 10,000 connections are allowed.
● If the bandwidth is 600 MB/s, a maximum of 20,000 connections are allowed.
● If the bandwidth is 1200 MB/s, a maximum of 20,000 connections are
allowed.
8.2.17 How Many Connections from Each IP Address Are Allowed?
The Kafka server allows a maximum of 200 connections from each IP address.
Excess connections will be rejected.
8.3 Topics and Partitions
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 50
Page 56

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
8.3.1 Is There a Limit on the Number of Topics in a Kafka Instance?
No, there is no limit on the topic quantity. However, there is an upper limit on the
aggregate number of partitions of topics. After the partition limit is reached, you
can no longer create topics.
8.3.2 Why Is Partition Quantity Limited?
Kafka manages messages by partition. If there are too many partitions, message
creation, storage, and retrieval will be fragmented, aecting the performance and
stability. If the total number of partitions of topics reaches the upper limit, you
cannot create more topics.
8.3.3 Can I Reduce the Partition Quantity?
No. If you want to use fewer partitions, delete the corresponding topic, create
another one, and specify the desired number of partitions.
8.3.4 Why Do I Fail to Create Topics?
Possible cause: The aggregate number of partitions of created topics has reached
the upper limit.
Solution: Delete unnecessary topics.
8.3.5 Do Kafka Instances Support Batch Importing Topics or Automatic Topic Creation?
Automatic topic creation is supported, but batch topic import is not supported.
Currently, you can only export topics in batches.
8.3.6 Why Do Deleted Topics Still Exist?
This may be because automatic topic creation has been enabled and a consumer
is connecting to the topic. If no existing topics are available for message creation,
new topics will be automatically created.
To solve this problem, disable automatic topic creation.
8.3.7 How Do I Create a Topic?
You can create a topic by using one the following three methods:
● By using the DMS for Kafka console
● By using Kafka CLI
You can use kafka-topics.sh to create topics and manage topic parameters.
kafka-topics.sh --create --topic {topic_name} --bootstrap-server
{broker_ip}:{port} --partitions {partition_num} --replication-factor
{replication_num}
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 51
Page 57

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
8.3.8 Are Periods (.) Allowed in Topic Names?
No. When you create a topic on the console, the topic name cannot contain
periods (.). For example, topic.test is an invalid topic name.
8.3.9 What Should I Do If Kafka Storage Space Is Used Up Because Retrieved Messages Are Not Deleted?
Messages are not deleted immediately after being retrieved. They are deleted only
when the aging time expires.
To solve this problem, you can shorten the aging time.
8.3.10 What Can I Do If Disk Usage Is as High as 96%?
You can shorten the aging time.
8.3.11 Will a Kafka Instance Be Restarted After Its Automatic
Topic Creation Setting Is
Yes. A Kafka instance will be restarted if you enable or disable automatic topic
creation for it.
Modied?
8.3.12 How Do I Disable Automatic Topic Creation?
1. On the Kafka console, click the name of your instance.
2. In the Advanced Settings area on the Basic Information tab page, click
next to Automatic Topic Creation and disable the option.
You can view the execution status of the task on the Background Tasks tab
page.
8.3.13 Can I Delete Unnecessary Topics in a Consumer Group?
Yes. To delete a topic, simply unsubscribe from it on the Kafka client.
8.4 Consumer Groups
8.4.1 Do I Need to Create Consumer Groups, Producers, and Consumers for Kafka Instances?
No. They are generated automatically when you use the instance.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 52
Page 58

NO TE
NO TE
Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
8.4.2 How Do I Delete Consumer Groups?
You can delete consumer groups from Kafka instances by using the Kafka
command line tool of your Kafka client.
Ensure that the client uses the same version as the Kafka instance.
● Querying consumer groups:
kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server {Kafka instance connection
address} --list
[root@zk-server-1 bin]# ./kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server
172.31.1.245:9091,172.31.1.86:9091,172.31.1.128:9091 --list
Note: This will not show information about old Zookeeper-based consumers.
KMOsetCache-zk-server-1
bbbb
KMOsetCache-zk-server-0
● Querying consumer group details:
kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server {Kafka instance connection
address} --describe --group {consumer group name}
[root@zk-server-1 bin]# ./kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server
172.31.1.245:9091,172.31.1.86:9091,172.31.1.128:9091 --describe --group bbbb
Note: This will not show information about old Zookeeper-based consumers.
Consumer group 'bbbb' has no active members.
TOPIC PARTITION CURRENT-OFFSET LOG-END-OFFSET LAG CONSUMER-ID
HOST CLIENT-ID
test 1 336 336 0 - - test 0 334 334 0 - - test 2 334 334 0 - - -
● Deleting a consumer group:
kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server {Kafka instance connection
address} --delete --group {consumer group name}
[root@zk-server-1 bin]# ./kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server
172.31.1.245:9091,172.31.1.86:9091,172.31.1.128:9091 --delete --group bbbb
Note: This will not show information about old Zookeeper-based consumers.
Deletion of requested consumer groups ('bbbb') was successful.
● If SASL authentication is enabled for the Kafka instance, the --command-cong
authentication
the preceding commands. For details about the conguration le consumer.properties,
see the CLI access instructions provided in Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance with
SASL.
● For details on how to congure the Kafka client environment, see the CLI access
instructions provided in Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance Without SASL and
Accessing a Kafka Premium Instance with SASL.
conguration le consumer.properties}
parameter must be added to
{SASL
8.4.3 Do I Need to Unsubscribe from a Topic Before Deleting a Consumer Group?
No. You can directly delete the consumer group.
8.5 Messages
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 53
Page 59

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide 8 FAQs
8.5.1 What Is the Maximum Size of a Message that Can be Created?
10 MB.
8.5.2 Why Do I Frequently Fail to Poll Due to Rebalancing?
Possible cause 1: The poll operation is not performed continuously. After a certain
period of time, the server considers the client unavailable.
Possible cause 2: The interval between two polls is too long, which exceeds the
heartbeat interval (max.poll.interval.ms). As a result, the server considers the
client unavailable.
8.5.3 Why Do Messages Still Exist After the Retention Period Elapses?
Symptom: Messages still exist after reaching the retention period (for example,
after 72 hours).
Possible cause 1: The segment
Solution: Wait until the segment is no longer in use or delete the topic where
messages have reached their retention period.
Possible cause 2: In a topic, there is a message whose CreateTime is a future
time. For example, assume that it is January 1, and the CreateTime is February 1.
The message will not be aged after 72 hours from now. As a result, messages
created subsequently will also not be aged.
Solution: Delete the topic where the CreateTime of a message is a future time.
les are in use.
8.5.4 Do Kafka Instances Support Delayed Message Delivery?
No.
8.5.5 Does the Message Query Function on the Console Show the Replica Message Quantity?
No.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 54
Page 60

Distributed Message Service for Kafka
User Guide A Change History
A Change History
Date Description
2020-12-02 This issue is the rst ocial release.
Issue 01 (2020-12-02) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 55
 Loading...
Loading...