
CANN
V100R020C20
AI CPU Custom Operator
Development Guide (Inference)
Issue 01
Date 2021-03-11
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2021. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specied in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every eort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i

NO TICE
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) About This Document
About This Document
Overview
An AI CPU operator is an operation of complete compute logic that runs on AI
CPU, one of the compute engines in the Ascend AI Processor. You might need to
develop a custom AI CPU operator in the following cases:
● During neural network (NN) training or inference, if you
operator when converting a third-party open-source network to adapt to the
Ascend AI Processor, a custom AI CPU operator can help you streamline the
model execution process and improve the functionality commissioning
eciency. After the functionality commissioning is passed, convert the custom
AI CPU operator into a TBE operator for performance commissioning.
● In certain scenarios, it is impossible to implement custom operators that run
on AI Core. For example, some operators require int64 data, which is
incompatible with AI Core instructions. When such an operator is not the
performance bottleneck of your network, you can develop a custom AI CPU
operator instead for Ascend AI Processor support.
In the moment, AI CPU custom operators can run only in EP standard form.
Intended Audience
This document is intended for developers who develop custom AI CPU operators.
After reading this document, you will be able to:
nd an unsupported
● Describe the principles and
● Develop custom AI CPU operators based on the samples provided in this
document.
To better understand this document, you need to have:
Prociency in C++ programming.
●
● Knowledge of mathematical expressions
● Knowledge of machine learning and deep learning
● Knowledge of the
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
workow and principles of the Ascend platform.
workow of AI CPU operator implementation.

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) About This Document
● Knowledge of the TBE custom operator development workow on the Ascend
platform.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) Contents
Contents
About This Document................................................................................................................ ii
1 Quick Start................................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Neural Network Introduction..............................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Operator Basics........................................................................................................................................................................ 1
2 AI CPU Introduction................................................................................................................ 7
2.1 Overview.................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Building and Running an Operator...................................................................................................................................9
3 Operator Development Workow.................................................................................... 13
4 Operator Development Preparations............................................................................... 16
4.1 Environment Setup...............................................................................................................................................................16
4.2 Operator Analysis................................................................................................................................................................. 16
4.3 Project Creation..................................................................................................................................................................... 18
5 Operator Development
5.1 Operator Code Implementation...................................................................................................................................... 20
5.2 Operator Prototype Denition......................................................................................................................................... 23
5.2.1 Principle................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
5.2.2 Implementation..................................................................................................................................................................24
5.3 Operator Information Library Denition...................................................................................................................... 29
5.4 Operator Adaptation........................................................................................................................................................... 32
5.4.1 Adaptation Plug-in Development (TensorFlow).....................................................................................................33
5.4.2 Adaptation Plug-in Development (Cae).................................................................................................................36
5.5 Operator Project Building and Deployment................................................................................................................ 40
5.5.1 Operator Project Building...............................................................................................................................................40
5.5.2 OPP Deployment............................................................................................................................................................... 41
Workow.................................................................................... 20
6 Operator ST.............................................................................................................................42
6.1 Introduction............................................................................................................................................................................ 42
6.2 Implementation..................................................................................................................................................................... 43
7 Operator Verication on Network....................................................................................53
8 Sample Reference..................................................................................................................54
8.1 Custom Operator Development.......................................................................................................................................54
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iv

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) Contents
8.2 Operator Verication on Network.................................................................................................................................. 54
9 API Reference......................................................................................................................... 56
9.1 Overview.................................................................................................................................................................................. 56
9.2 AI CPU APIs............................................................................................................................................................................. 57
9.2.1 Introduction......................................................................................................................................................................... 57
9.2.2 Class CpuKernelContext.................................................................................................................................................. 58
9.2.2.1 CpuKernelContext Constructor and Destructor................................................................................................... 58
9.2.2.2 GetOpType........................................................................................................................................................................59
9.2.2.3 Input................................................................................................................................................................................... 59
9.2.2.4 Output................................................................................................................................................................................60
9.2.2.5 GetAttr............................................................................................................................................................................... 61
9.2.2.6 GetInputsSize...................................................................................................................................................................61
9.2.2.7 GetOutputsSize............................................................................................................................................................... 62
9.2.2.8 Init....................................................................................................................................................................................... 62
9.2.3 Class TensorShape............................................................................................................................................................. 63
9.2.3.1 SetFormat......................................................................................................................................................................... 63
9.2.3.2 GetFormat........................................................................................................................................................................ 64
9.2.3.3 GetUnknownRank..........................................................................................................................................................64
9.2.3.4 SetUnknownRank...........................................................................................................................................................65
9.2.3.5 GetDimSizes..................................................................................................................................................................... 66
9.2.3.6 SetDimSizes......................................................................................................................................................................66
9.2.3.7 GetDimSize.......................................................................................................................................................................67
9.2.3.8 GetDims.............................................................................................................................................................................67
9.2.3.9 NumElements.................................................................................................................................................................. 68
9.2.4 Class Tensor......................................................................................................................................................................... 68
9.2.4.1 GetTensorShape..............................................................................................................................................................69
9.2.4.2 SetTensorShape...............................................................................................................................................................69
9.2.4.3 SetDataType.....................................................................................................................................................................70
9.2.4.4 GetDataType....................................................................................................................................................................70
9.2.4.5 SetData.............................................................................................................................................................................. 71
9.2.4.6 GetData............................................................................................................................................................................. 72
9.2.4.7 SetDataSize...................................................................................................................................................................... 72
9.2.4.8 GetDataSize..................................................................................................................................................................... 73
9.2.4.9 CalcDataSizeByShape................................................................................................................................................... 73
9.2.4.10 NumElements............................................................................................................................................................... 74
9.2.5 Class AttrValue................................................................................................................................................................... 74
9.2.5.1 GetString........................................................................................................................................................................... 74
9.2.5.2 GetListString.................................................................................................................................................................... 75
9.2.5.3 AddListString................................................................................................................................................................... 75
9.2.5.4 ListStringSize....................................................................................................................................................................76
9.2.5.5 SetString............................................................................................................................................................................77
9.2.5.6 SetListString..................................................................................................................................................................... 77
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. v

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) Contents
9.2.5.7 GetInt................................................................................................................................................................................. 78
9.2.5.8 GetListInt...........................................................................................................................................................................79
9.2.5.9 AddListInt..........................................................................................................................................................................79
9.2.5.10 ListIntSize....................................................................................................................................................................... 80
9.2.5.11 SetInt................................................................................................................................................................................80
9.2.5.12 SetListInt......................................................................................................................................................................... 81
9.2.5.13 GetFloat.......................................................................................................................................................................... 82
9.2.5.14 GetListFloat....................................................................................................................................................................82
9.2.5.15 AddListFloat...................................................................................................................................................................83
9.2.5.16 ListFloatSize...................................................................................................................................................................83
9.2.5.17 SetFloat........................................................................................................................................................................... 84
9.2.5.18 SetListFloat.................................................................................................................................................................... 85
9.2.5.19 GetBool........................................................................................................................................................................... 85
9.2.5.20 GetListBool.....................................................................................................................................................................86
9.2.5.21 AddListBool.................................................................................................................................................................... 86
9.2.5.22 ListBoolSize.................................................................................................................................................................... 87
9.2.5.23 SetBool............................................................................................................................................................................ 88
9.2.5.24 SetListBool......................................................................................................................................................................88
9.2.5.25 GetDataType..................................................................................................................................................................89
9.2.5.26 GetListDataType...........................................................................................................................................................90
9.2.5.27 AddListDataType..........................................................................................................................................................90
9.2.5.28 ListDataTypeSize.......................................................................................................................................................... 91
9.2.5.29 SetDataType.................................................................................................................................................................. 91
9.2.5.30 SetListDataType............................................................................................................................................................92
9.2.5.31 SetTensorShape............................................................................................................................................................ 93
9.2.5.32 SetListTensorShape..................................................................................................................................................... 93
9.2.5.33 AddListTensorShape....................................................................................................................................................94
9.2.5.34 GetTensorShape........................................................................................................................................................... 95
9.2.5.35 GetListTensorShape.....................................................................................................................................................95
9.2.5.36 ListTensorShapeSize....................................................................................................................................................96
9.2.5.37 SetTensor........................................................................................................................................................................ 96
9.2.5.38 SetListTensor................................................................................................................................................................. 97
9.2.5.39 AddListTensor................................................................................................................................................................97
9.2.5.40 GetTensor....................................................................................................................................................................... 98
9.2.5.41 GetListTensor.................................................................................................................................................................98
9.2.5.42 ListTensorSize................................................................................................................................................................ 99
9.2.6 GetSizeByDataType...........................................................................................................................................................99
9.2.7 Data Types.........................................................................................................................................................................100
9.2.7.1 DataType.........................................................................................................................................................................100
9.2.7.2 Format............................................................................................................................................................................. 101
9.2.7.3 DeviceType..................................................................................................................................................................... 102
9.2.8 Macro Denitions............................................................................................................................................................103
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. vi

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) Contents
9.2.8.1 REGISTER_CPU_KERNEL............................................................................................................................................ 103
9.3 Operator Prototype Denition APIs............................................................................................................................. 103
9.3.1 Introduction.......................................................................................................................................................................103
9.3.2 Operator Prototype Denition APIs..........................................................................................................................105
9.3.2.1 Prototype Denition (REG_OP)...............................................................................................................................105
9.3.2.2 Derivative APIs..............................................................................................................................................................111
9.3.3 Operator Prototype InferShape APIs........................................................................................................................115
9.3.3.1 IMPLEMT_INFERFUNC............................................................................................................................................... 115
9.3.3.2 IMPLEMT_COMMON_INFERFUNC........................................................................................................................ 116
9.3.3.3 INFER_FUNC_REG........................................................................................................................................................117
9.3.3.4 COMMON_INFER_FUNC_REG................................................................................................................................. 117
9.3.3.5 ELMTWISE_INFER_SHAPEANDTYPE......................................................................................................................118
9.3.3.6 BROADCAST_INFER.....................................................................................................................................................119
9.3.4 Operator Prototype Verify APIs..................................................................................................................................120
9.3.4.1 IMPLEMT_VERIFIER..................................................................................................................................................... 120
9.3.4.2 VERIFY_FUNC_REG...................................................................................................................................................... 121
9.3.5 Operator InferFormat APIs.......................................................................................................................................... 121
9.3.5.1 IMPLEMT_INFERFORMAT_FUNC............................................................................................................................121
9.3.5.2 INFER_FORMAT_FUNC_REG.................................................................................................................................... 122
9.3.6 Internal Associated APIs............................................................................................................................................... 123
9.3.6.1 Class OperatorFactory................................................................................................................................................123
9.3.6.1.1 CreateOperator......................................................................................................................................................... 123
9.3.6.1.2 GetOpsTypeList......................................................................................................................................................... 124
9.3.6.1.3 IsExistOp......................................................................................................................................................................125
9.3.6.2 Class OperatorCreatorRegister................................................................................................................................125
9.3.6.2.1 Constructor and Destructor.................................................................................................................................. 125
9.3.6.3 Class InferShapeFuncRegister..................................................................................................................................126
9.3.6.3.1 Constructor and Destructor.................................................................................................................................. 126
9.3.6.4 Class InferFormatFuncRegister............................................................................................................................... 127
9.3.6.4.1 Constructor and Destructor.................................................................................................................................. 127
9.3.6.5 Class VerifyFuncRegister........................................................................................................................................... 128
9.3.6.5.1 Constructor and Destructor.................................................................................................................................. 128
9.3.6.6 Class InferenceContext...............................................................................................................................................129
9.3.6.6.1 InferenceContext Constructor and Destructor............................................................................................... 129
9.3.6.6.2 SetInputHandleShapesAndTypes........................................................................................................................ 130
9.3.6.6.3 SetOutputHandleShapesAndTypes.....................................................................................................................130
9.3.6.6.4 GetInputHandleShapesAndTypes........................................................................................................................131
9.3.6.6.5 GetOutputHandleShapesAndTypes....................................................................................................................131
9.3.6.6.6 SetMarks..................................................................................................................................................................... 132
9.3.6.6.7 GetMarks.....................................................................................................................................................................133
9.3.6.6.8 Create........................................................................................................................................................................... 134
9.3.6.7 Class ShapeAndType...................................................................................................................................................134
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. vii

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) Contents
9.3.6.7.1 Constructor and Destructor.................................................................................................................................. 134
9.3.6.7.2 SetShape......................................................................................................................................................................135
9.3.6.7.3 GetShape.....................................................................................................................................................................136
9.3.6.7.4 SetType.........................................................................................................................................................................136
9.3.6.7.5 GetDataType.............................................................................................................................................................. 137
9.4 operator API......................................................................................................................................................................... 137
9.4.1 Overview............................................................................................................................................................................ 137
9.4.2 Class Operator..................................................................................................................................................................138
9.4.2.1 Constructor and Destructor..................................................................................................................................... 138
9.4.2.2 AddControlInput...........................................................................................................................................................139
9.4.2.3 BreakConnect................................................................................................................................................................ 139
9.4.2.4 IsEmpty............................................................................................................................................................................140
9.4.2.5 InferShapeAndType..................................................................................................................................................... 140
9.4.2.6 GetAttr.............................................................................................................................................................................141
9.4.2.7 GetAllAttrNamesAndTypes....................................................................................................................................... 144
9.4.2.8 GetDynamicInputNum...............................................................................................................................................144
9.4.2.9 GetDynamicInputDesc............................................................................................................................................... 145
9.4.2.10 GetDynamicOutputNum.........................................................................................................................................146
9.4.2.11 GetDynamicOutputDesc......................................................................................................................................... 146
9.4.2.12 GetDynamicSubgraph..............................................................................................................................................147
9.4.2.13 GetDynamicSubgraphBuilder................................................................................................................................148
9.4.2.14 GetInferenceContext.................................................................................................................................................149
9.4.2.15 GetInputConstData...................................................................................................................................................149
9.4.2.16 GetInputsSize.............................................................................................................................................................. 150
9.4.2.17 GetInputDesc.............................................................................................................................................................. 151
9.4.2.18 GetName...................................................................................................................................................................... 152
9.4.2.19 GetSubgraph............................................................................................................................................................... 152
9.4.2.20 GetSubgraphBuilder................................................................................................................................................. 153
9.4.2.21 GetSubgraphNamesCount......................................................................................................................................154
9.4.2.22 GetSubgraphNames................................................................................................................................................. 154
9.4.2.23 GetOpType...................................................................................................................................................................155
9.4.2.24 GetOutputDesc.......................................................................................................................................................... 155
9.4.2.25 GetOutputsSize.......................................................................................................................................................... 156
9.4.2.26 SetAttr........................................................................................................................................................................... 157
9.4.2.27 SetInput........................................................................................................................................................................ 160
9.4.2.28 SetInferenceContext................................................................................................................................................. 161
9.4.2.29 TryGetInputDesc........................................................................................................................................................ 162
9.4.2.30 UpdateInputDesc.......................................................................................................................................................163
9.4.2.31 UpdateOutputDesc................................................................................................................................................... 164
9.4.2.32 UpdateDynamicInputDesc..................................................................................................................................... 164
9.4.2.33 UpdateDynamicOutputDesc..................................................................................................................................165
9.4.2.34 VerifyAllAttr.................................................................................................................................................................166
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. viii

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) Contents
9.4.3 Class Tensor.......................................................................................................................................................................167
9.4.3.1 Constructor and Destructor..................................................................................................................................... 167
9.4.3.2 Clone................................................................................................................................................................................ 168
9.4.3.3 IsValid.............................................................................................................................................................................. 168
9.4.3.4 GetData...........................................................................................................................................................................169
9.4.3.5 GetTensorDesc.............................................................................................................................................................. 170
9.4.3.6 GetSize.............................................................................................................................................................................170
9.4.3.7 SetData............................................................................................................................................................................171
9.4.3.8 SetTensorDesc............................................................................................................................................................... 172
9.4.4 Class TensorDesc............................................................................................................................................................. 172
9.4.4.1 Constructor and Destructor..................................................................................................................................... 172
9.4.4.2 GetDataType..................................................................................................................................................................173
9.4.4.3 GetFormat...................................................................................................................................................................... 174
9.4.4.4 GetName........................................................................................................................................................................ 175
9.4.4.5 GetOriginFormat..........................................................................................................................................................175
9.4.4.6 GetOriginShape............................................................................................................................................................ 176
9.4.4.7 GetRealDimCnt.............................................................................................................................................................177
9.4.4.8 GetShape........................................................................................................................................................................ 177
9.4.4.9 GetShapeRange............................................................................................................................................................ 178
9.4.4.10 GetSize.......................................................................................................................................................................... 178
9.4.4.11 SetDataType................................................................................................................................................................179
9.4.4.12 SetFormat.................................................................................................................................................................... 180
9.4.4.13 SetName.......................................................................................................................................................................180
9.4.4.14 SetOriginFormat........................................................................................................................................................ 181
9.4.4.15 SetOriginShape.......................................................................................................................................................... 182
9.4.4.16 SetSize........................................................................................................................................................................... 182
9.4.4.17 SetRealDimCnt........................................................................................................................................................... 183
9.4.4.18 SetShape.......................................................................................................................................................................184
9.4.4.19 SetShapeRange.......................................................................................................................................................... 184
9.4.4.20 SetUnknownDimNumShape..................................................................................................................................185
9.4.4.21 Update.......................................................................................................................................................................... 186
9.4.5 Class Shape....................................................................................................................................................................... 187
9.4.5.1 Constructor and Destructor..................................................................................................................................... 187
9.4.5.2 GetDim............................................................................................................................................................................ 187
9.4.5.3 GetDims.......................................................................................................................................................................... 188
9.4.5.4 GetDimNum.................................................................................................................................................................. 189
9.4.5.5 GetShapeSize.................................................................................................................................................................189
9.4.5.6 SetDim............................................................................................................................................................................. 190
9.4.6 Class AttrValue.................................................................................................................................................................191
9.4.6.1 Constructor and Destructor..................................................................................................................................... 191
9.4.6.2 CreateFrom.................................................................................................................................................................... 191
9.4.6.3 GetValue......................................................................................................................................................................... 192
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ix

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) Contents
9.4.7 Data Type and Enumerated Value............................................................................................................................ 193
9.4.7.1 Format............................................................................................................................................................................. 193
9.4.7.2 DataType.........................................................................................................................................................................194
9.4.7.3 Struct UsrQuantizeFactor..........................................................................................................................................194
9.4.7.4 Struct TensorDescInfo................................................................................................................................................ 195
9.4.7.5 GetSizeByDataType..................................................................................................................................................... 195
9.5 Operator Plug-in APIs....................................................................................................................................................... 195
9.5.1 Overview............................................................................................................................................................................ 195
9.5.2 Class OpRegistrationData............................................................................................................................................ 196
9.5.2.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................................................... 196
9.5.2.2 Constructor and Destructor..................................................................................................................................... 196
9.5.2.3 REGISTER_CUSTOM_OP.............................................................................................................................................197
9.5.2.4 FrameworkType............................................................................................................................................................ 197
9.5.2.5 OriginOpType................................................................................................................................................................198
9.5.2.6 ParseParamsFn............................................................................................................................................................. 199
9.5.2.7 ParseParamsByOperatorFn.......................................................................................................................................200
9.5.2.8 FusionParseParamsFn.................................................................................................................................................201
9.5.2.9 FusionParseParamsFn (Overload) ........................................................................................................................ 202
9.5.2.10 ParseSubgraphPostFn.............................................................................................................................................. 203
9.5.2.11 ParseOpToGraphFn...................................................................................................................................................204
9.5.2.12 ImplyType.....................................................................................................................................................................206
9.5.2.13 DelInputWithCond.................................................................................................................................................... 207
9.5.2.14 DelInputWithOriginalType..................................................................................................................................... 208
9.5.2.15 GetImplyType..............................................................................................................................................................208
9.5.2.16 GetOmOptype............................................................................................................................................................ 209
9.5.2.17 GetOriginOpTypeSet................................................................................................................................................ 209
9.5.2.18 GetFrameworkType...................................................................................................................................................210
9.5.2.19 GetParseParamFn......................................................................................................................................................210
9.5.2.20 GetParseParamByOperatorFn............................................................................................................................... 210
9.5.2.21 GetFusionParseParamFn.........................................................................................................................................211
9.5.2.22 GetFusionParseParamByOpFn.............................................................................................................................. 211
9.5.2.23 GetParseSubgraphPostFn....................................................................................................................................... 212
9.5.2.24 GetParseOpToGraphFn............................................................................................................................................212
9.5.2.25 AutoMappingFn......................................................................................................................................................... 213
9.5.2.26 AutoMappingByOpFn.............................................................................................................................................. 213
9.5.2.27 AutoMappingFnDynamic........................................................................................................................................215
9.5.2.28 AutoMappingByOpFnDynamic............................................................................................................................. 216
9.5.2.29 AutoMappingSubgraphIndex................................................................................................................................ 218
9.5.2.30 InputReorderVector...................................................................................................................................................218
9.5.3 Class OpReceiver............................................................................................................................................................. 219
9.5.3.1 Constructor and Destructor..................................................................................................................................... 219
9.5.4 DECLARE_ERRORNO...................................................................................................................................................... 220
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. x

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 1 Quick Start
1 Quick Start
1.1 Neural Network Introduction
1.2 Operator Basics
1.1 Neural Network Introduction
To enable computers to master knowledge like human beings, a multi-layer
connection network needs to be constructed to
iterative computing and training of the network, it can extract object features.
Generally, this method is called deep learning (DL). With uninterrupted
development, deep learning has displayed its tremendous application value and is
receiving increasing attentions from the industry and academia. Deep learning has
achieved remarkable progresses in image, voice, natural language processing, big
data feature extraction, and ad click-through rate estimation. As a result, multiple
infrastructures, such as
promote deep learning across
Deep neural network research fuels rapid development of neural network models,
enabling them to complete more and more complex processing tasks in a wider
range of
technologies for decades, ever fast and
been provided for neural network models and data, such as CPUs, GPUs, TPUs,
and the latest Ascend AI Processor launched by Huawei.
Articial neural network (ANN) may also be referred to as neural network (NN)
for short, which is an important branch of machine learning (ML). Scientists
perform mathematical modeling on the most basic neurons and build
neural networks based on the certain hierarchical relationship of neurons,
enabling
structures through learning and training, and thereby achieve various complex
computations.
elds. With the rapid development of semiconductor chips and computer
articial neural networks to learn knowledge, adjust their internal
Cae, MXNet, and TensorFlow, have been developed to
elds.
energy-ecient computing resources have
dene a complex object. After
articial
1.2 Operator Basics
A deep learning algorithm consists of multiple compute units referred to as
operators (Ops). In network models, an operator describes the compute logic of
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 1 Quick Start
the layer, for example, the convolution layer that performs convolution and the
fully-connected (FC) layer that multiplies the input by a weight matrix.
The following introduces some basic terms about operators.
Operator Name
The name of an operator identies the operator on a network, and therefore must
be unique on a network. The example network has operators Conv1, Pool1, and
Conv2. Conv1 and Conv2 are of the same type convolution. Conv1 and Conv2 each
indicates a convolution operation.
Figure 1-1 Example network topology
Operator Type
Each operator is of a specic type. For example, the convolution operator is of the
convolution type. A network can have
dierent operators of the same type.
Tensor
Tensors are used to represent the input data and output data in operator
computations. TensorDesc (the tensor descriptor) describes the input data and
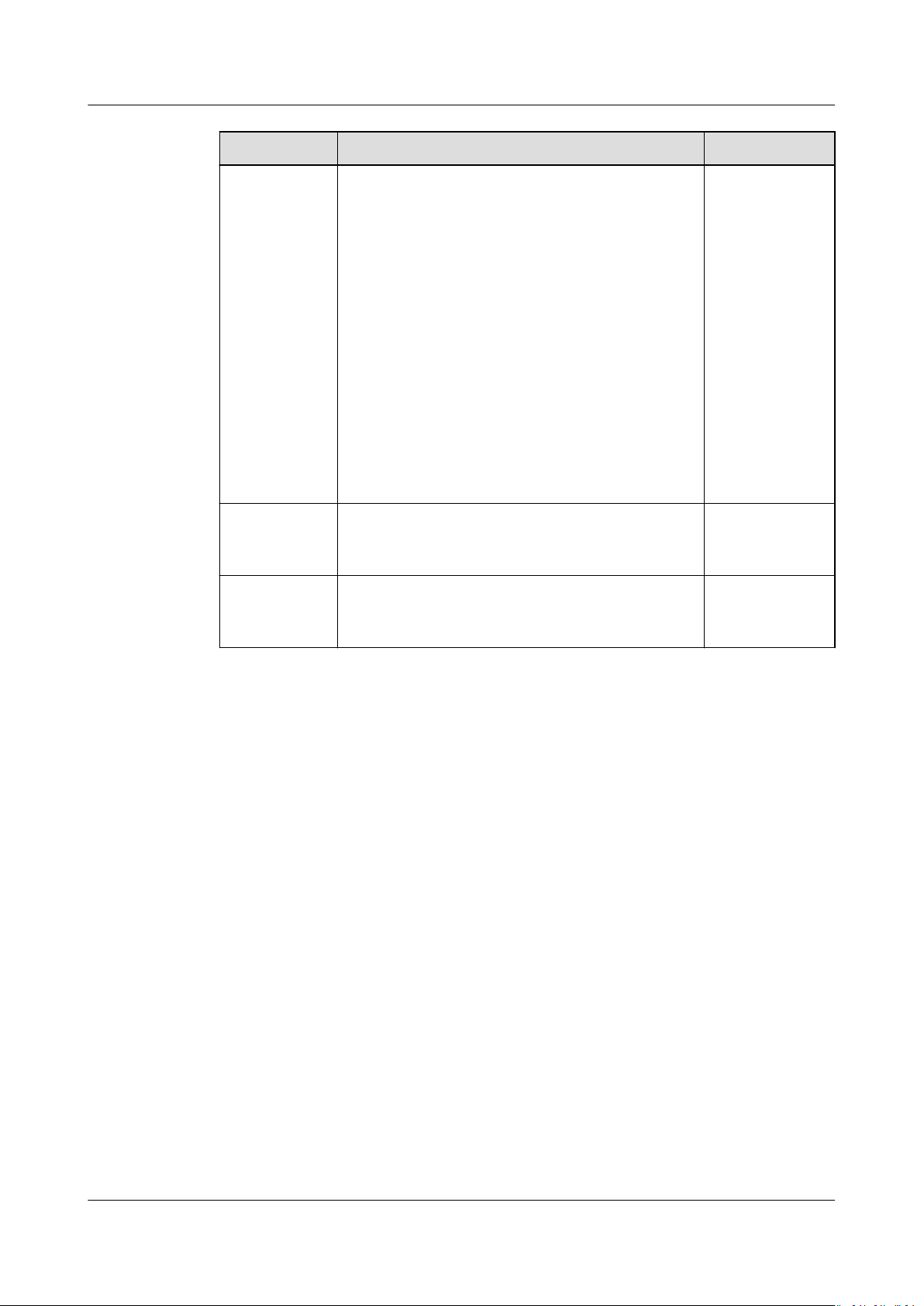
output data. Table 1-1 describes the attributes of the TensorDesc struct.
Table 1-1 Description of the TensorDesc attributes
Attribute
name Indexes a tensor and must be unique.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
Denition
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 1 Quick Start
Attribute Denition
shape Species the shape of a tensor, for example, (10,),
(1024,1024), or (2,3,4). For details, see Shape.
Default: none
Format: (i1, i2, ..., in), where, i1 to in are positive
integers.
dtype Species the data types of a tensor object.
Default: none
Value range: oat16, oat32, int8, int16, int32, uint8,
uint16, bool
Format Species the data layout format. For details, see Format.
Format
Shape
In the deep learning framework, n-dimensional data is stored in an n-dimensional
array. For example, a feature graph of a convolutional neural network is stored in
a four-dimensional array. The four dimensions are batch size (N), height (H),
width (W), and channels (C), respectively.
Data can be stored only in linear mode because the dimensions have a
Dierent deep learning frameworks store feature maps in dierent layouts. For
example,
while TensorFlow uses the layout [Batch, Height, Width, Channels], that is, NHWC.
As shown in Figure 1-2, for an RGB image, the pixel values of each channel are
clustered in sequence as RRRGGGBBB with the NCHW layout. However, with the
NHWC layout, the pixel values are interleaved as RGBRGBRGB.
Figure 1-2 NCHW and NHWC
Cae uses the layout [Batch, Channels, Height, Width], that is, NCHW,
xed order.
The shape of a tensor is described in the format of (D0, D1, ..., Dn – 1), where, D0
n
are positive integers.
to D
For example, the shape (3, 4) indicates a 3 x 4 matrix, where the rst dimension
has three elements, and the second dimension has four elements.
The number count in the round bracket equals to the dimension count of the
tensor. The
brackets, and the second element depends on the element count in the second left
square bracket, and so on. See the following examples.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
rst element depends on the element count in the outer square

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 1 Quick Start
Table 1-2 Tensor shape examples
Tensor Shape
1 (0,)
[1, 2, 3] (3,)
[[1, 2],[3, 4]] (2, 2)
[[[1, 2],[3, 4]], [[5, 6],[7, 8]]] (2,2,2)
The tensor shape has its physical meanings:
For a tensor with shape (4, 20, 20, 3), it indicates four 20 x 20 (corresponding to
the two 20s in the shape) pictures (corresponding to 4 in the shape), each of
whose pixel contains the red, green, and blue color components (corresponding to
3 in the shape).
Figure 1-3 Physical meanings of tensor shape
In programming, the shape can be simply understood as a loop of each layer of a
tensor. For example, for operating tensor A with shape (4, 20, 20, 3), the loop
statement is as follows.
produce A {
for (i, 0, 4) {
for (j, 0, 20) {
for (p, 0, 20) {
for (q, 0, 3) {
A[((((((i*20) + j)*20) + p)*3) + q)] = a_tensor[((((((i*20) + j)*20) + p)*3) + q)]
}
}
}
}
}
Axis
An axis is denoted by the index of a dimension of a tensor. For a 2D tensor with
ve rows and six columns, that is, with shape (5, 6), axis 0 represents the rst
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 1 Quick Start
dimension in the tensor, that is, the rows; axis 1 represents the second dimension
of tensor, that is, the columns.
For example, for tensor [[[1, 2],[3, 4]], [[5, 6],[7, 8]]] with shape (2, 2, 2), axis 0
represents data in the rst dimension, that is, matrices [[1, 2],[3, 4]] and [[5, 6],
[7, 8]], axis 1 represents data in the second dimension, that is, arrays [1, 2], [3, 4],
[5, 6], and [7, 8], and axis 2 indicates the data in the third dimension, that is,
numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8.
A negative axis is interpreted as indexing from the end.
n
The axes of an
Figure 1-4 Axis diagram
-dimensional tensor include 0, 1, 2, ..., and n – 1.
Weight
The input data is multiplied by a weight value in the compute unit. For example,
for a two-input operator, an associated weight value is allocated to each of the
inputs. Generally, data of more importance is assigned with a greater weight
value. Therefore, the feature indicated by data with zero weight can be ignored.
As shown in Figure 1-5, in the compute unit, input X1 is multiplied by its
associated weight W1, that is, X1 * W1.
Figure 1-5 Weight computation example
Bias
A bias is another linear component to be applied to the input data, in addition to
a weight. The bias is added to the product of the input and its weight.
As shown in Figure 1-6, in the compute unit, input X1 is multiplied by its
associated weight W1 and then added with its associated bias B1, that is, X1 * W1
+ B1.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 1 Quick Start
Figure 1-6 Bias computation example
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 2 AI CPU Introduction
2 AI CPU Introduction
2.1 Overview
2.2 Building and Running an Operator
2.1 Overview
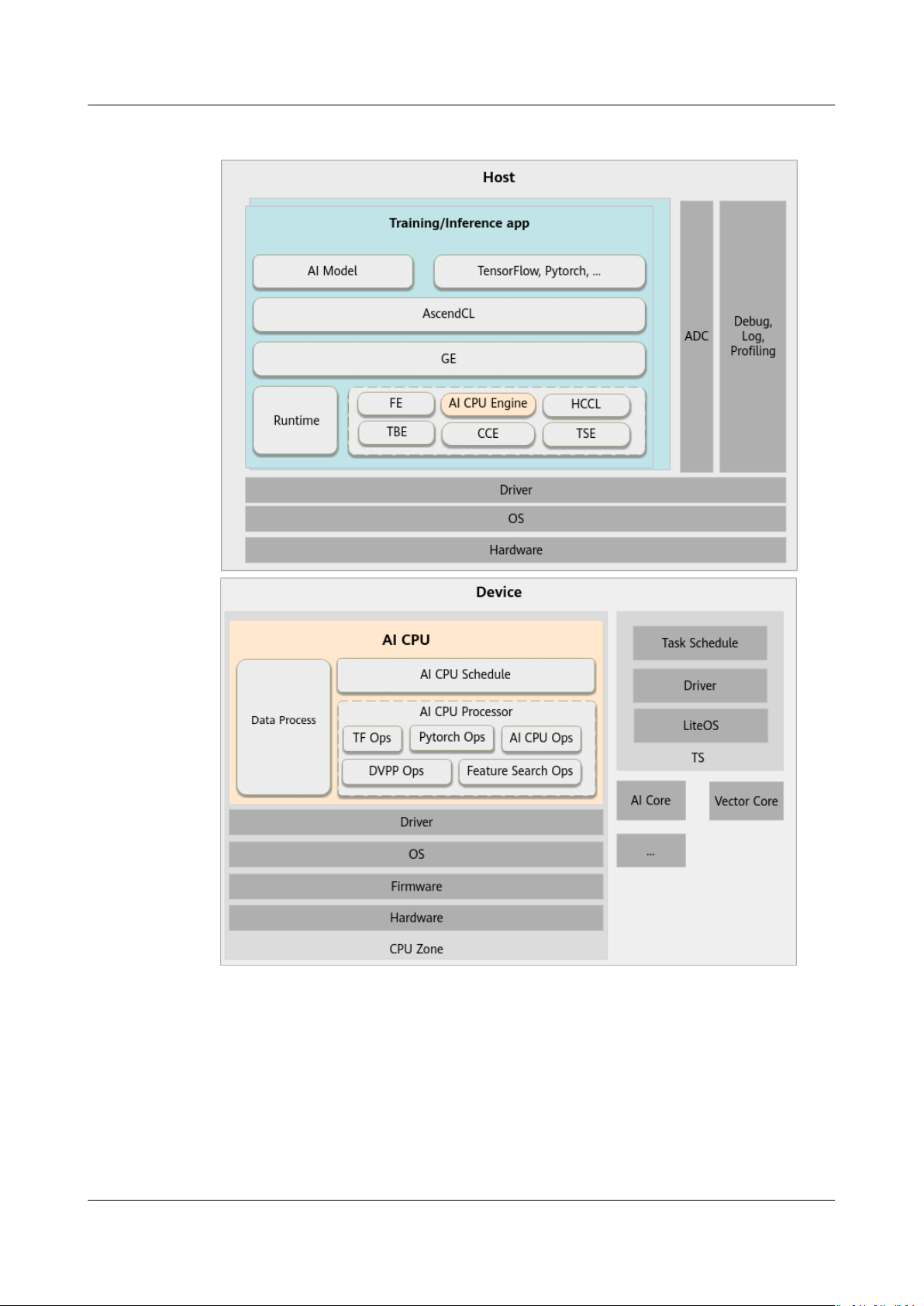
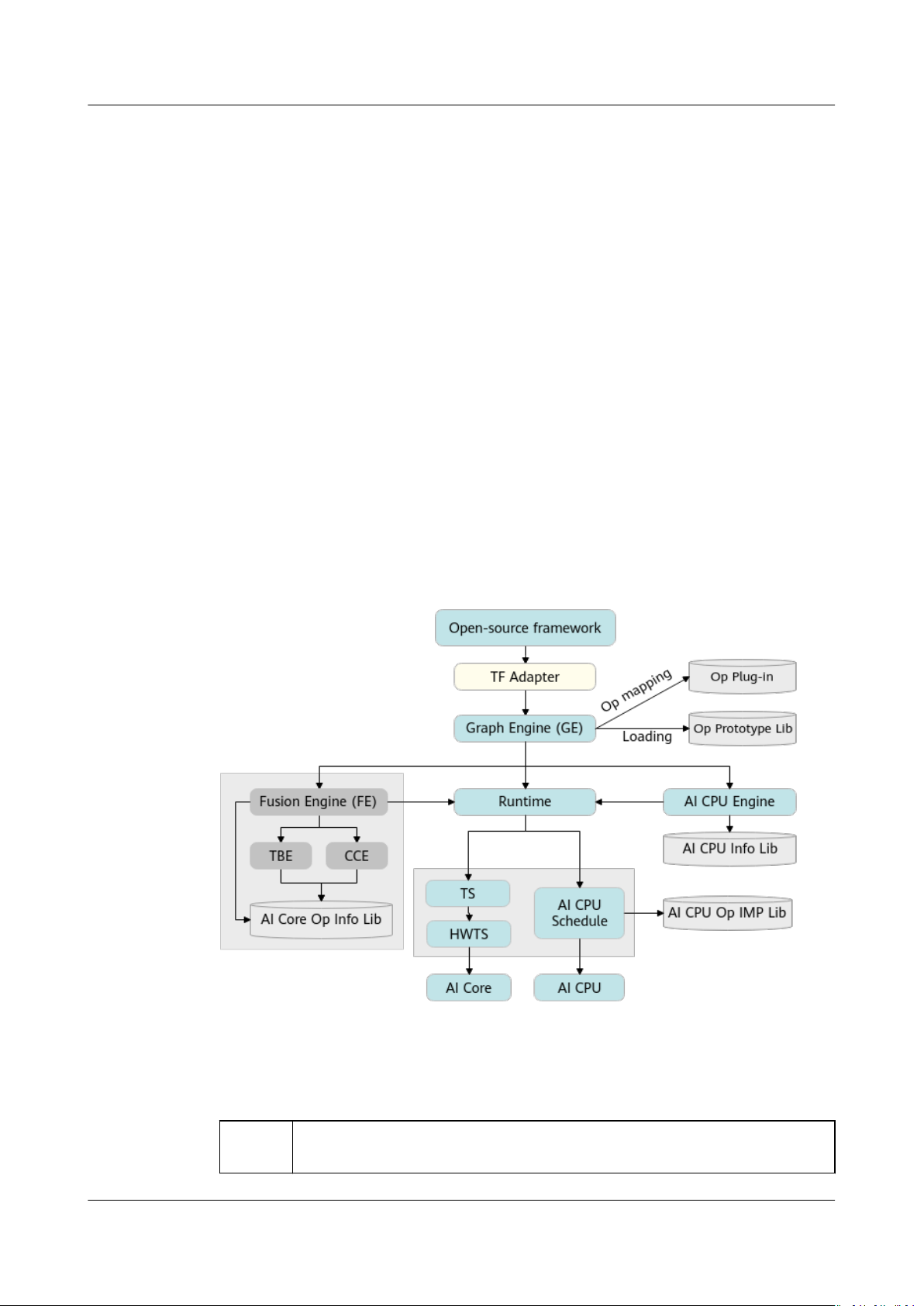
AI CPU executes CPU operators (including control, scalar, and vector operators) on
Ascend AI Processor. The following
architecture.
gure shows its context in the Ascend solution
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 2 AI CPU Introduction
Figure 2-1 System architecture
The following components are involved in building and executing AI CPU
operators:
● Graph Engine (GE): a
unied IR interface provided by Huawei based on the
Ascend AI Software Stack for interfacing with dierent machine learning
frameworks, such as TensorFlow and PyTorch. GE implements the preparation,
partition, optimization, compilation, loading, execution, and management of
the network topology, or the graph.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 2 AI CPU Introduction
● AI CPU Engine: interfaces with GE, provides the AI CPU operator information
library, and implements operator registration, operator memory allocation
calculation, subgraph optimization, and task generation.
● AI CPU Schedule: works with the Task Schedule to schedule and execute NN
models.
● AI CPU Processor: completes operator computations and provides the operator
implementation library for implementing the execution of AI CPU operators.
● Data Processor: preprocesses data of training samples in training scenarios.
2.2 Building and Running an Operator
Logical Architecture for Building and Running an Operator
A complete AI CPU operator consists of four parts: operator prototype denition,
operator adaption plug-in of the corresponding open-source framework, operator
information library denition, and operator implementation.
Figure 2-2 shows the logical architecture of building and running a developed
operator on the Ascend AI Processor hardware platform.
Figure 2-2 Logical architecture for building and running an operator
TFAdapter is used only for training based on the TensorFlow framework.
The columns in the preceding
during custom operator development.
Deliver
able
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
Description
gure are the deliverables to be implemented

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 2 AI CPU Introduction
Operat
or
implem
entatio
n
Operat
or
plug-in
Operat
or
prototy
pe
library
The operator class implementation includes the operator denition
and operator computation implementation.
In the custom operator development scenario based on a third-party
framework (such as TensorFlow and Cae), after developing
implementation code of the custom operator, you need to develop an
adaptation plug-in to map the third-party operator to an operator
supported by the Ascend AI Processor and register the operator
information with GE. To run a network trained on a third-party
framework, the operator plug-in information in GE is loaded and
called to parse and map the operators on the network to operators
supported by the Ascend AI Processor.
The operator prototype denition species the constraints on an
operator that runs on the Ascend AI Processor, mainly reecting the
mathematical meanings of the operator. The constraints include
dening the operator inputs, outputs, and other attributes, verifying
arguments, and inferring the shape. During network execution, GE
calls the
operator arguments. If the verication passes, GE infers the output
shape and dtype of each node by calling the inference function of the
operator prototype library and allocates static memory for the result
tensor.
verication API of the operator prototype library to verify
Operat
or
inform
ation
library
Building an Operator
Figure 2-3 shows the workow of building an AI CPU operator.
The operator information library mainly reects the restrictions on the
physical implementation of operators on the Ascend AI Processor,
including the input and output names and data types. During network
execution, AI CPU Engine performs basic verication and operator
matching based on the operator information in the operator
information library.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 2 AI CPU Introduction
Figure 2-3 Building an AI CPU operator
1. Deliver a third-party network model to GE.
For TensorFlow-based online training, TF Adapter is called to generate the
source TensorFlow model, which is then delivered to GE. For AscendCL-based
model inference, the source model is directly delivered to GE.
The topology of a network model is referred to as a graph.
2. GE calls the operator plug-in to map operators in the source network model
to operators supported by the Ascend AI Processor, so that the original
TensorFlow/Cae graph can be parsed into a graph supported by the Ascend
AI Processor.
3. GE calls the
verication API of the operator prototype library to verify
operator arguments. If the verication passes, GE infers the output shape and
dtype of each node by calling the inference function of the operator
prototype library and allocates memory for the result tensor.
4. GE delivers the entire graph to AI CPU Engine. AI CPU Engine reads the
operator information library, looks up an appropriate format for the operator,
and returns the format to GE.
5. GE partitions the graph into subgraphs and delivers the subgraphs to AI CPU
Engine. AI CPU Engine optimizes the subgraphs and returns the optimized
subgraphs to GE.
6. GE builds the graph (including memory and stream allocation) and sends a
genTask request to AI CPU Engine. Then, AI CPU Engine returns the taskinfo
of the operator to GE. After the graph build process is complete, a model
le
that adapts to the Ascend AI Processor is generated.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 2 AI CPU Introduction
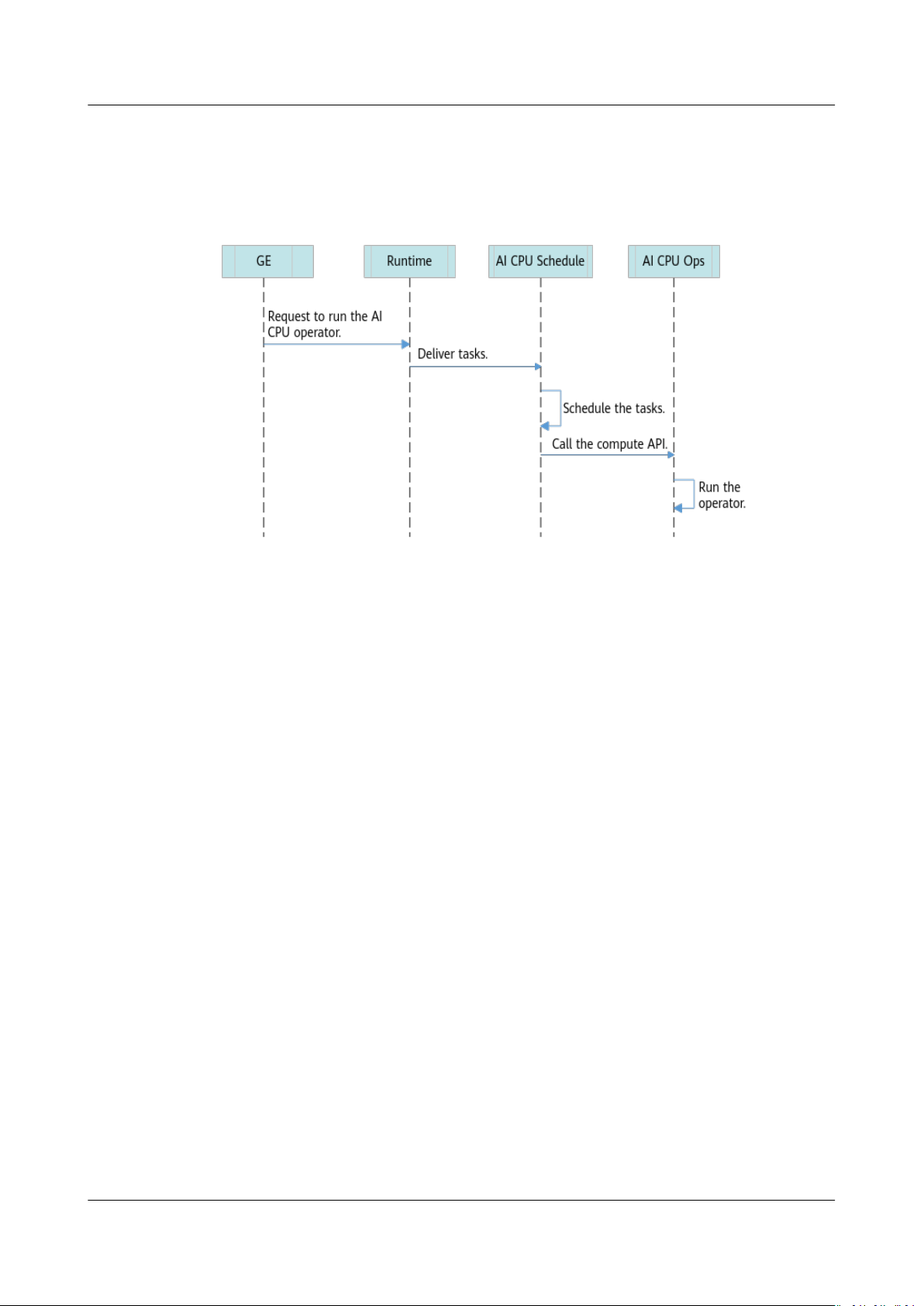
Running an Operator
Figure 2-4 shows the workow of running an AI CPU operator.
Figure 2-4 Running an AI CPU operator
1. GE delivers an operator execution request.
2. Runtime delivers the corresponding tasks to AI CPU Schedule.
3. AI CPU Schedule schedules tasks and calls the operator compute API.
4. The AI CPU Operator Package (OPP) parses and instantiates the operator
implementation, and executes the Compute function to run the operator.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 3 Operator Development Workow
3 Operator Development Workow
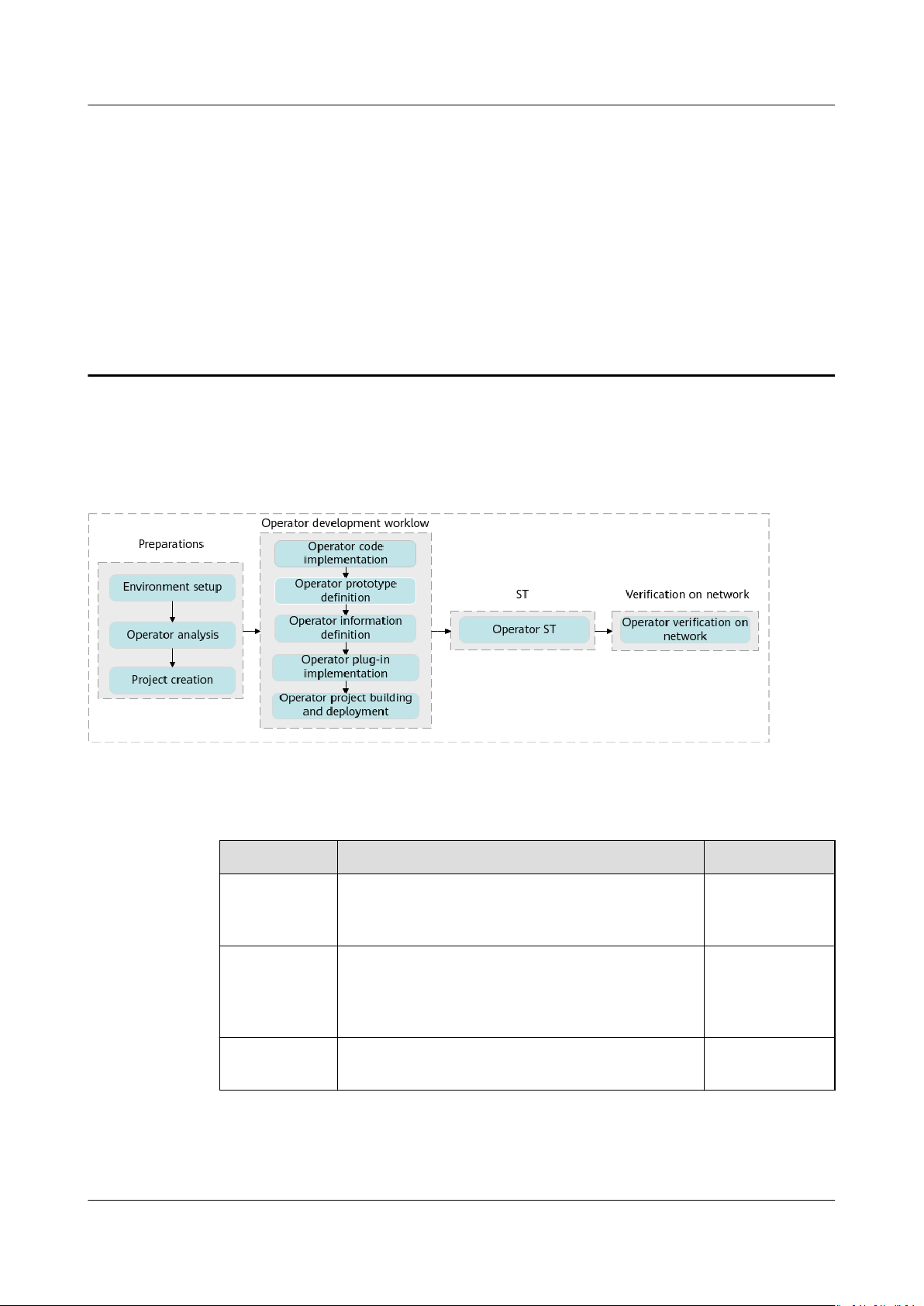
The following gure shows the AI CPU custom operator development workow.
Figure 3-1 Operator development workow
Table 3-1 describes the development workow.
Table 3-1 AI CPU operator command-line development workow
Action
Environment
setup
Operator
analysis
Project
creation
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
Description See Also
Set up the development and operating
environment required for operator
development, execution, and verication.
Analyze the operator, specify its functionality,
input, and output, and determine the operator
type and the name of the OPP le generated
after the operator is built.
Create a custom operator project. 4.3 Project
4 Operator
Development
Preparations
4.2 Operator
Analysis
Creation
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 3 Operator Development Workow
Action Description See Also
Operator
code
implementati
on
Operator
prototype
denition
Implement the compute logic of the operator. 5.1 Operator
Code
Implementati
on
Implement the operator prototype denition
le, which species the constraints on an
operator that runs on the Ascend AI Processor,
5.2 Operator
Prototype
Denition
mainly reecting the mathematical meanings
of the operator. The constraints include
dening the operator inputs, outputs,
attributes, and value ranges, verifying
arguments, and inferring the shape. The
information
dened by the prototype is
registered with the operator prototype library
of GE. During
oine model conversion, GE
calls the verication API of the operator
prototype library to verify operator arguments.
verication passes, GE infers the output
If the
shape and dtype of each node by calling the
inference function of the operator prototype
library and allocates static memory for the
result tensor.
Operator
information
denition
Operator
plug-in
implementati
on
The operator information conguration le is
used to register the operator information with
the operator information library, including the
OpType and input/output dtype and name.
During network execution, AI CPU Engine
performs basic
verication and operator
matching based on the operator information
in the operator information library.
If your custom operator is developed based on
a third-party framework (such as TensorFlow
or Cae), you need to develop a plug-in to
map the operator to one that adapts to the
Ascend AI Processor.
5.3 Operator
Information
Library
Denition
5.4 Operator
Adaptation
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 3 Operator Development Workow
Action Description See Also
Operator
project
building and
deployment
● Operator build: builds the operator plug-in
implementation le, prototype denition
le, and information denition le into the
operator plug-in library, operator prototype
library, and operator information library,
respectively.
● Operator deployment: deploys the operator
implementation
le, plug-in library,
prototype library, and information library to
the system OPP, that is, a corresponding
directory in the opp directory.
In the command line, you can use the build
script of the sample project for one-click
compilation. A custom OPP will be generated.
Specify the opp directory and execute the OPP
to deploy your custom operator.
Operator ST System Testing (ST) veries the operator
correctness in an actual hardware
environment.
Operator
verication
Load the custom operator to a model for
verication.
on network
5.5.1 Operator
Project
Building
6 Operator ST
7 Operator
Verication
on Network
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 4 Operator Development Preparations
4 Operator Development Preparations
4.1 Environment Setup
4.2 Operator Analysis
4.3 Project Creation
4.1 Environment Setup
● Before custom operator development, you need to set up the development
environment and operating environment.
Set the development environment and operating environment by referring to
CANN Software Installation Guide
a. Select an installation scheme and install the required hardware to run on
the development environment and operating devices.
b. Deploy and install Toolkit and congure environment variables in the
development environment.
c. Install the inference software and
operating environment.
Once the development environment is set up, you can obtain the API header
les and the library les required for building and running operators.
Once the operating environment is set up, you can run the executable le
generated after build.
AI CPU operator development depends on the AI CPU OPP. During
environment setup, make sure to install the AI CPU OPP.
.
congure environment variables in the
● If you tend to develop custom operators in MindStudio, install MindStudio by
referring to
MindStudio User Guide
.
4.2 Operator Analysis
Before developing an AI CPU operator, you need to determine the operator
function, input, output, development mode, operator type (
implementation function name, and more.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
OpType
),

CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 4 Operator Development Preparations
Step 1 Specify the operator function and mathematical expression.
Take the Add operator as an example. The mathematical expression of the Add
operator is as follows:
z=x+y
The Add operator adds two inputs and returns a result.
Step 2 Specify the inputs and output.
● The Add operator has two inputs, x and y, and outputs the result z.
● The supported input data types include
has the same data type as the inputs.
● The operator inputs support all shapes. The output has the same shape as the
inputs.
● The operator input supports the following formats: NCHW, NC1HWC0,
NHWC, and ND.
Step 3 Specify the operator implementation
● Name
OpType
in upper camel case and indicate the separation of words with
a single capitalized letter.
● Name the operator le in either of the following ways:
Name the operator
le after
OpType
– Convert the rst uppercase letter to a lowercase letter.
Example: Abc -> abc
– Replace each uppercase letter following lowercase letters with an
underscore (_) and a lowercase letter.
Example: AbcDef -> abc_def
– Uppercase letters following a digit or an uppercase letter are regarded as
a semantic string. If there is a lowercase letter after this string, replace
the last uppercase letter in this string with an underscore (_) and a
lowercase letter, and convert the other uppercase letters into lowercase
letters. If there is no lowercase letter after the string, directly convert the
string into lowercase letters.
oat16, oat32, and int32. The output
le name and operator type (
as follows:
OpType
).
Examples: ABCDef -> abc_def; Abc2DEf -> abc2d_ef; Abc2DEF -> abc2def;
ABC2dEF -> abc2d_ef
In this example,
OpType
of the operator is dened as Add. You are advised to
name the deliverables as follows:
● Code implementation (or kernel implementation)
les of the operator:
add_kernel.h and add_kernel.cc
● Plug-in implementation
le: add_kernel_plugin.cpp
● Prototype denition les: add.h and add.cpp
● Information
denition le: add.ini
Based on the preceding analysis, the design specications of the Add operator are
as follows.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
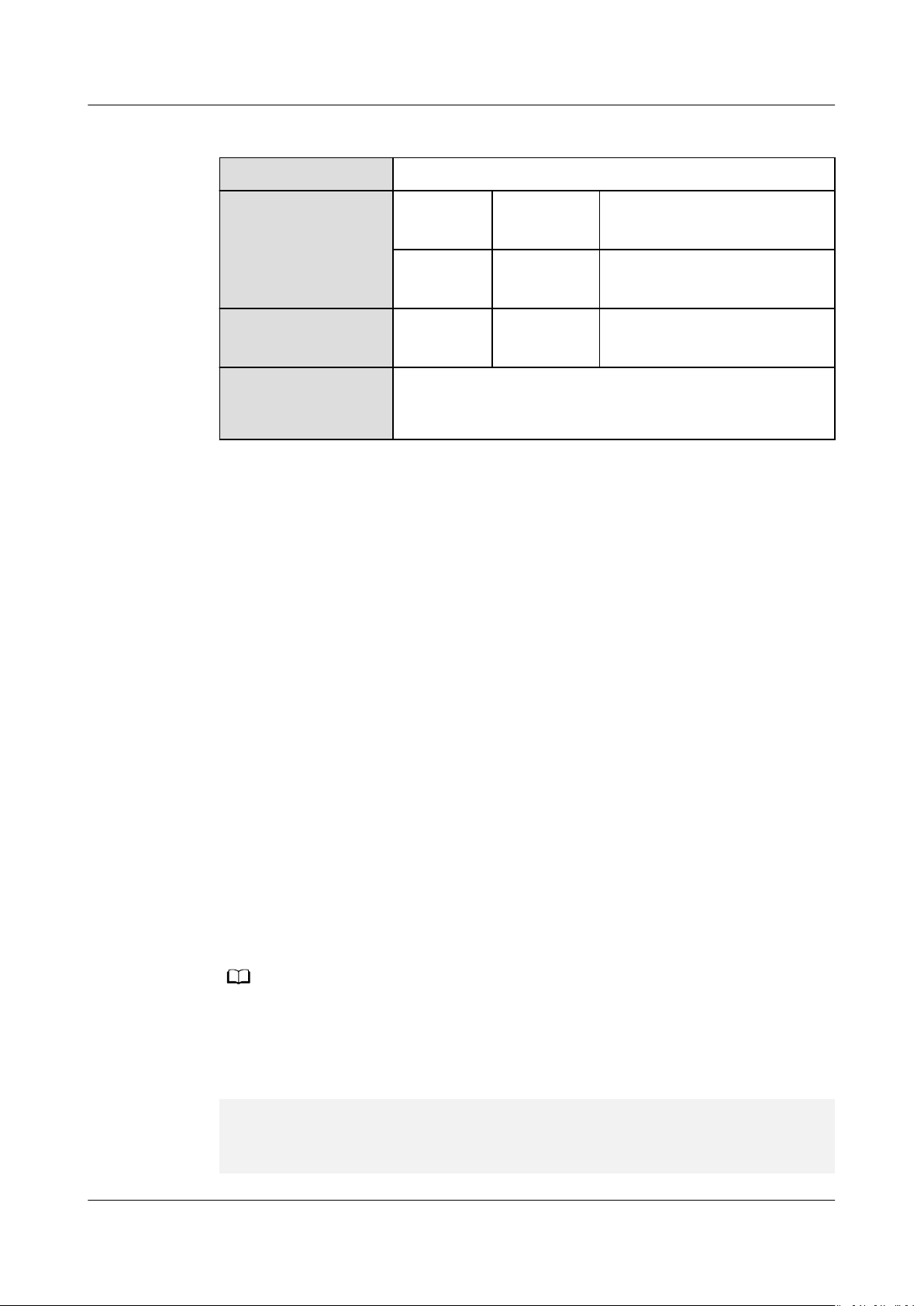
NO TE
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 4 Operator Development Preparations
Table 4-1 Add operator design specications
OpType Add
Operator Input Name: x Shape: all Data type:
oat16, oat32, int32
Name: y Shape: all Data type:
oat16, oat32, int32
Operator Output Name: z Shape: all Data type:
oat16, oat32, int32
Operator
Implementation
File Name
----End
4.3 Project Creation
Overview
Before developing an operator, you need to create an operator project.
MindStudio Mode
For details about how to create an operator project in MindStudio, see "Custom
Operator Development > Project Creation" in
Command Line Mode
Click here to download the sample package that matches your CANN version in
use. Find the sample in the samples/cplusplus/level1_single_api/4_op_dev/
1_custom_op directory.
add
MindStudio User Guide
.
Append your own custom operator to the sample project. The sample project
provides some AI CPU and TBE custom operator samples developed from their
Cae and TensorFlow counterparts.
Note: If you do not have enough permission to obtain the code, contact Huawei technical
support to apply for joining the Ascend community.
The directory structure of the operator project is as follows. Develop the operator
deliverables in the corresponding directory accordingly.
├── cpukernel
│ ├── impl // Directory of the operator implementation
│ ├── op_info_cfg
│ ├── aicpu_kernel
│ ├── xx.ini // Operator information library
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
le (.ini)
les (.h and .cc)
NO TICE
CANN
AI CPU Custom Operator Development Guide
(Inference) 4 Operator Development Preparations
├── framework
│ ├── xx_plugin // Directory of the operator adaptation plug-in les (.cpp)
├── op_proto // Directory of operator prototype denition les (.h and .cpp)
● If you need to develop multiple custom AI CPU operators, implement them in
the same operator project. Store the implementation les according to the
preceding directory structure.
● If you need to develop custom AI CPU operators and custom TBE operators at
the same time, you also need to implement them in the same operator project.
For details about TBE operator development, see
Development Guide
.
TBE Custom Operator
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
 Loading...
Loading...