Page 1

HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation
Technical Reference Manual
Page 2

Notice
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Hewlett-Packard makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this
material, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental
or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or
use of this material.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or reliability of its
software on equipment that is not furnished by Hewlett-Packard.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright.
All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied,
reproduced, or translated to another language without the prior written consent
of Hewlett-Packard Company.
®
Adaptec
Adobe and Acrobat are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
ELSA
and/or ELSA Inc., Santa Clara.
Matrox
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation.
Windows NT® is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Pentium® , and AGPset
SCSISelect
WOL
is a registered trademark of Adaptec, Inc.
®
and Synergy® are registered trademarks of ELSA AG, Aachen
®
is a registered trademark of Matrox Electronic Systems Ltd.
®
, Windows® and MS-DOS® are registered trademarks of the
TM
TM
TM
is a trademark of Adaptec, Incorporated.
(Wake on LAN) is a trademark of IBM.
are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
Hewlett-Packard France
Business Desktop Division (BDD)
Outbound Marketing Communications
38053 Grenoble Cedex 9
France
1999
Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 3

Contents
1 System Overview
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Front and Side Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Rear View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Internal Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Specifications and Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Physical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Power Consumption and Cooling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Environmental Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Power Saving and Ergonometry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Power Saving and Ergonometry for APM Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Power Saving Modes and Resume Events for ACPI Systems . . . . . . . . . 20
Power-On from Space-Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Soft Power Down. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Where to Find the Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3
Page 4

Contents
2 System Board
System Board Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Architectural View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Accessory Card Slots. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Universal AGP Pro Slot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
PCI Slots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
System Board Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Chipset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Memory Controller Hub (8240) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) Bus Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
AGP 4x Bus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Main Memory Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
PCI 64-bit Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
PCI 64-bit 66 MHz Bus Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Devices on the PCI 32-bit 33 MHz Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Dual Chip PCI Audio Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Devices on the SMBus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Devices on the Low Pin Count Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
The Super I/O Controller (NS 87364) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
FirmWare Hub (82802AB). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Host Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Intel Pentium III Processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Optional Second Processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Cache Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Assigned Device Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Input/Output Controller Hub Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
PCI 64-bit Hub Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Interrupt Controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
4
Page 5

Contents
3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Matrox Millennium G250 Graphics Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Matrox Millennium G400 Graphics Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
3Dlabs Oxygen GVX1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
ELSA Synergy II Graphics Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Network Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
HP 10/100 TX PCI LAN Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Supported LAN Cards. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
3COM NIC (Network Interconnect) LAN Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
INTEL NIC (Network Interconnect) LAN Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
4 Mass Storage Devices
Flexible Disk Drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Hard Disk Drives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
CD-ROM Drives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
5HP BIOS
HP/NBA BIOS Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Using the HP Setup Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Updating the System BIOS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Restoring BIOS Default Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Clearing the CMOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Clearing Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Recovering the BIOS (Crisis Mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Adaptec SCSISelect Configuration Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Default Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Starting the SCSISelect Configuration Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
BIOS Addresses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
System Memory Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
HP I/O Port Map (I/O Addresses Used by the System). . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
5
Page 6

Contents
DMA Channel Controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
IRQs Used by the PC Workstation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
6 Tests and Error Messages
MaxiLife Test Sequence and Error Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Basic Pre-boot Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Post Test Sequence and Post Error. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Operating System Boot Phase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Run-Time Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Order in Which POST Tests Are Performed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Error Message Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Beep Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
7 Connectors and Sockets
Rear Panel Socket Pin Layouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
6
Page 7

Preface
This manual is a technical reference and BIOS document for engineers
and technicians providing system level support. It is assumed that the
reader possesses a detailed understanding of AT-compatible
microprocessor functions and digital addressing techniques.
Technical information that is readily available from other sources, such
as manufacturers’ proprietary publications, has not been reproduced.
This manual contains summary information only. For additional
reference material, refer to the bibliography on the following page.
For all warning and safety instructions, refer to the user guide
delivered with the PC Workstation.
Conventions
The following conventions are used throughout this manual to identify
specific numeric elements:
Hexadecimal numbers are identified by a lower case h.
For example, 0FFFFFFFh or 32F5h
Binary numbers and bit patterns are identified by a lower case b.
For example, 1101b or 10011011b
7
Page 8

Bibliography
Online documentation can be obtained from the HP World Wide Web
www.hp.com/go/kayaksupport.
site:
1
2
— as
.
❒ HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation User’s Guide D8369-90001
well as English, this guide is also available in various languages.
❒ HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Troubleshooting Guide —
available in English, French, Italian, German, Spanish, Swedish and
Japanese.
❒ HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Technical Notes — English only.
❒ HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Service Handbook Chapter —
English only.
❒ Image Creation and Recovery CD-ROM — 5011-6692-xx
Extra Information Can
Be Obtained At:
❒ ELSA GLoria Synergy graphics card
http://www.elsa.com
❒ Matrox graphics cards
http://www.matrox.com
❒ 3D Labs Oxygen GVX1 graphics card
http://www.3dlabs.com
❒ Intel Chipsets. Intel I840 chipset
http://developer.intel.com
❒ Intel Pentium III Processor
http://developer.intel.com
1. Also includes information about the HP Kayak XM600 Minitower PC
Workstation.
2. xx = Language code.
8
Page 9

1
System Overview
This manual describes the HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation and provides
detailed system specifications.
This chapter introduces the external features, and lists the specifications
and characteristic data of the system. It also provides a summary of the
documentation available.
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Overview
The HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation is based on the Extended ATX
(E-ATX) form factor.
The following table provides an overview of the system.
Feature Description
System Board
Processor
Cache Memory
(integrated in processor
package)
Internal CPU Clock Rate
External Processor Bus
Chipset
Super I/O Chip
BIOS (Basic Input/Output
System)
E-ATX with a dimension of 12.8-inch x 11.4-inch.
All models have support for up to two Intel Pentium® III processors.
For Processor 1, a VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) is integrated on the
system board, while there is a VRM socket for a second processor.
• Level-One: 16 KB code, 16 KB data.
• Level-Two: i256 KB.
533 MHz, 600 MHz, 667 MHz, 733 MHz, 800 MHz and higher.
133 MHz Front Side Bus
Intel® Chipset (I840) including, Input/Output Controller Hub (ICH), PCI 64-bit
Hub (P64H), FirmWare Hub (FWH) and Memory Repeater Hub (MRH-S) for
SDRAM support.
NS 87364.
Based on the core of AMIBIOS, including:
• 4 M/bits of flash memory.
• Support for PCI 2.2 Specification.
• Support for RDRAM or SDRAM memory modules.
.
Firmware - BIOS
Flash EEprom: Intel’s Firmware hub concept.
9
Page 10

1 System Overview
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Overview
Feature Description
HP MaxiLife Utility
(available on all models)
Operating System
Main Memory
Maximum amount of
memory that can be
installed is:
2 GB (4 x 512 MB)
Mass Storage
Hardware monitoring utility that monitors system components via the I
2
C bus
and a LCD status panel.
All models are preloaded with Windows NT® 4.0 SP5.
Models include either:
• Four RIMM sockets supporting RDRAM ECC memory modules installed in
pairs. Any unused RIMM sockets must contain a continuity module.
Models are supplied with either 128 MB or 256 MB RDRAM ECC main
memory installed in pairs.
Memory upgrades are available in pairs of: 64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB or
512 MB RDRAM ECC modules.
• Four DIMM sockets supporting SDRAM 100 MHz ECC memory modules
installed in pairs. Models are supplied with 128 MB of SDRAM unbuffered
ECC main memory.
Memory upgrades are available in pairs of: 64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB or
512 MB unbuffered 100 MHz ECC SDRAM modules.
Seven shelves supporting:
• Two front-access, third-height 3½-inch (one for the floppy disk drive and
one free) (height 1”);
• Three front-access, half-height, 5¼-inch drives (height 1.0”);
Possibility of installing a 3½-inch hard disk drive in one of the
5¼-inch shelves.
• Two internal 3½-inch hard disk drives (height 1.0”).
SCSI Controller
IDE Controller
10
Ultra 160 SCSI controller:
Adaptec® AIC-7892 Ultra 160 16-bit integrated SCSI controller (160 MB/s).
The internal SCSI connectors allow for up to five internal devices to be
connected. Additional devices can be added outside the PC Workstation by
connecting directly to the rear panel SCSI connector. The external connector
allows up to ten external devices to be connected. This gives a maximum of 15
(internal + external) devices that can be connected.
All models include an integrated Ultra ATA-66 controller that supports up to
four IDE devices
.
Page 11

HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Overview
Feature Description
1 System Overview
Video Controllers
Accessory Card Slots
LAN Card
CD-ROM Drive
Audio
Models include either:
• ELSA GLoria Synergy® II AGP video controller with 32 MB of installed
SGRAM video memory (maximum configuration).
• Matrox® Millennium G250 AGP video controller with
8 MB SGRAM video memory which can be upgraded to 16 MB.
• Matrox Millennium G400-Dual monitor AGP video controller with
16 MB SGRAM video memory (maximum configuration).
• 3Dlabs Oxygen® GVX1, 32 MB SGRAM video memory (maximum configu-
ration).
All models have:
• One Universal AGP Pro 4X 50 W 32-bit slot. The AGP bus provides a high
performance graphics interface.
• Three 32-bit 33 MHz PCI
• Two 64-bit 66 MHz PCI slots: 3 and 4 (3.3 V).
1
slots: 1, 2 and 5 (5 V).
The majority of the configurations are delivered with PCI slots 1 to 4 vacant.
All models are supplied with an HP 10/100BT PCI Ethernet Adapter LAN card
installed in PCI slot 5, supporting Wake-On LAN (WOL) and PCI 2.2
Specification.
Models include either an IDE 48X CD-ROM, CD-RW drive or DVD drive.
Integrated on the system board CS4280 audio PCI chip and AC97 Codec
(CS4297) audio.
HP UltraFlow Cooling
System
1. All five PCI slots comply with the PCI Specification 2.2.
Cooling system with multiple temperature-regulated fans to optimize cooling.
Alert reporting to MaxiLife and TopTools.
11
Page 12

1 System Overview
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Overview
Feature Description
System Board
Connectors
Rear Panel Connectors
(color coded)
• One flexible disk drive connector
• Two ATA-66 IDE connectors (for up to four IDE devices)
• One 16-bit Ultra 160 SCSI connector and one SCSI terminator.
The SCSI cable is routed from the SCSI connector on the system board
(located near the system switches) to the SCSI devices inside the chassis,
onto an onboard SCSI terminator (behind the processor), and finally onto the
external SCSI connector on the rear panel. The onboard SCSI terminator is
automatically deactivated when an external device is attached.
• One CD-IN audio connector
• AUX connector
• Internal speaker connector
• One WOL connector
• One status panel connector
• Two power supply connectors that must be connected
• Two fan connectors (one for the PCI fan, and one for the rear fan)
• One battery socket
The system board layout with all connectors can be found on page 28
• 9-pin serial (two, buffered)
❒ Standard: Two UART 16550 buffered serial ports
(both RS-232-C).
❒ Serial Ports A and B: 2F8h (IRQ 3), 2E8h (IRQ 3),
3F8h (IRQ 4), 3E8h (IRQ 4), or Off—
(if one port uses 2xxh, the other port must use 3xxh).
• Dual USB connectors
• External 16-bit U160m SCSI connector
• Audio
❒ Joystick/Dual MIDI connector
❒ LINE IN jack (3.5 mm)
❒ LINE OUT jack (3.5 mm)
❒ MIC IN jack (3.5 mm)
• Keyboard/Mouse
❒ HP enhanced keyboard with mini-DIN connector
❒ HP enhanced scrolling mouse with mini-DIN connector
• 25-pin parallel connector
❒ Mode: Centronics or bidirectional modes (ECP/EPP)
❒ Parallel port: 1 (378h, IRQ 7), 2 (278h, IRQ 5), or Off.
.
12
Page 13

1 System Overview
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Package
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation Package
The following two diagrams show the front and rear views of the HP Kayak
XU800 PC Workstation.
Front and Side Views
Power Supply Unit
HP UltraFlow Airflow Guide
Front Access
Drives, for
- three 5.25-inch
drive shelves. Possibility of installing
a 3½-inch hard disk
drive in one of the
5¼-inch shelves.
- two 3.5-inch
Rear Fan
Spare mounting rails (not shown) for:
- 3.5-inch (short green) devices
(for example, zip drive),
- 5.25-inch (long green) devices,
- 3.5-inch (short blue) hard disk drives
shelves including a
1.44 MB floppy
disk drive
Primary Internal Hard
Disk Drive Shelf
Secondary Internal
Hard Disk Drive Shelf
Second 3.5-inch shelf
13
Page 14

1 System Overview
Internal Features
Rear View
External SCSI
connector
Keyboard connector
Dual USB (12 Mbps)
connectors
Serial port A
Serial port B
Line Out connector
Line In connector
Microphone connector
Display connector
Mouse connector
Parallel port
MIDI connector
Internal Features
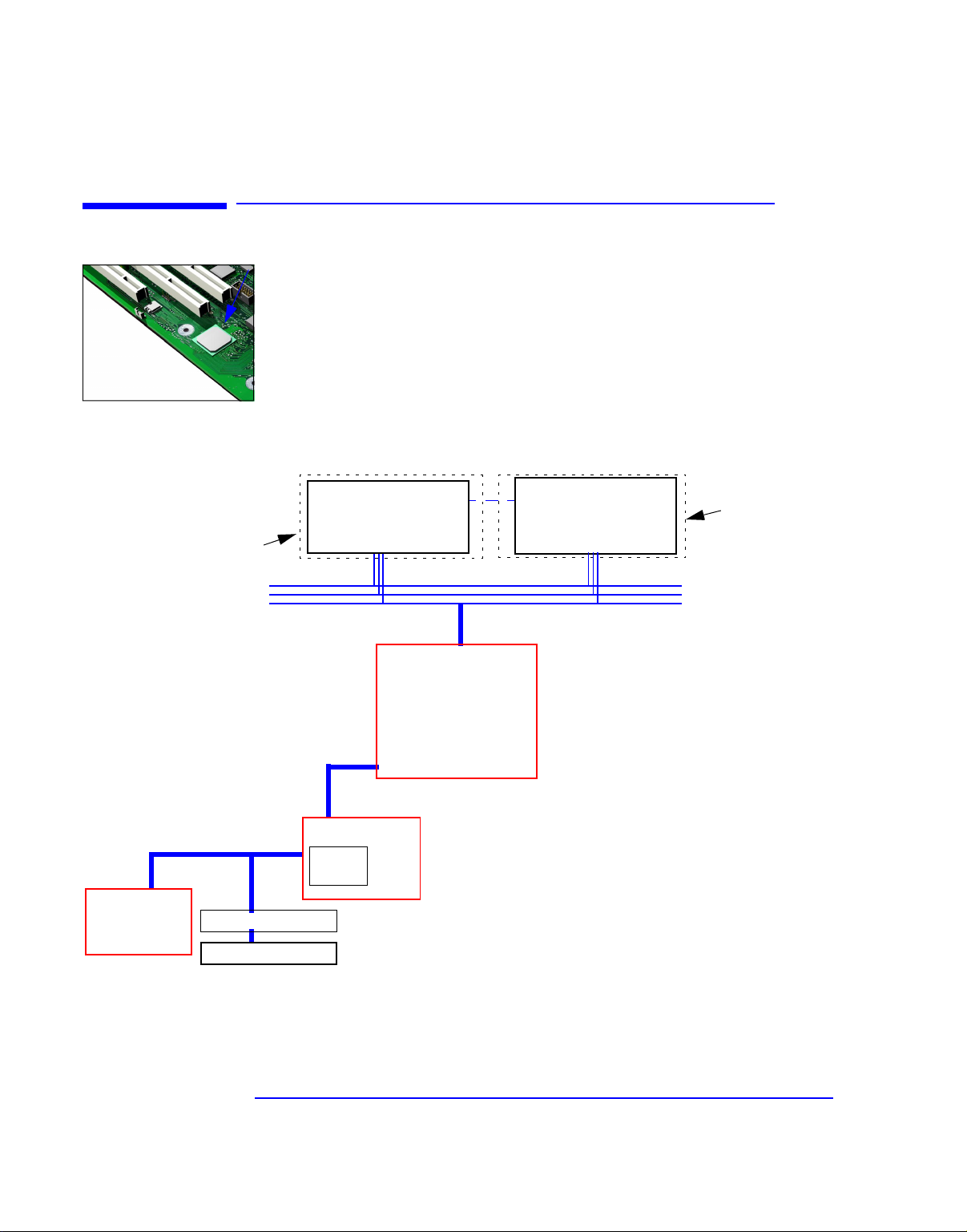
The core architecture of the HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation is
constructed around: Memory Controller Hub (MCH), Input/Output
Controller Hub (ICH), FirmWare Hub (FWH) and the Host bus.
The HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation can support up to two Pentium III
processors. This processor is described on page 65
.
The components of the system board are described in chapter 2
; the
characteristics of the PC Workstation’s video and storage devices are
described in chapter 3
HP BIOS routines are summarized in chapter 5
routines are described in chapter 6
14
; mass storage devices are described in chapter 4; the
; and the Power-On Self-Test
.
Page 15

1 System Overview
Front Panel
Front Panel
The front panel of HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation has the following
features:
LCD Control Buttons
Power On/Off
Button
Reset Button
Hard Disk
Activity Light
• Liquid Crystal Display (LCD). LCD error messages and available menus
are described on page 107
.
• On/Off LED. There are five states:
Blank. Indicates that the computer is turned off.
Green. Indicates that the computer is turned on and running correctly.
Red. Indicates that there is a Power-On Self-Test (POST) error.
Red flashing. Indicates that there is a MaxiLife (Diag/Alarm) error.
Amber. Displayed during system reset, system lock, Standby mode
(Windows 98) or Suspend mode (Windows 95).
• Hard disk drive activity LED. Activated during POST and when the
hard disk drive is being accessed.
15
Page 16

1 System Overview
Specifications and Characteristics
Specifications and Characteristics
Physical Characteristics
System Processing Unit
Weight (excl. keyboard and display): 14.4 kilograms (31.68 pounds)
Dimensions: 47.0 cm max. (D) by 21,0 cm (W) by 49.0 cm (H)
(18.50 inches by 8.26 inches by 19.29 inches)
2
Footprint: 0.09 m
Electrical Specifications
(1.06 sq ft)
Parameter Total Rating
Input voltage Switch select
100 - 127
VAC
200 -
250 V Vac
Peak
(15
secs.)
Maximum per
PCI Slots
(1,2 & 5)
32-bit 33 MHz
—— — —
1
Maximum per
PCI Slots
1
(3 & 4)
64-bit 66 MHz
Maximum for
Universal
AGP Pro Slot
Input current (max) 9 A 4.5 A — — — —
Input frequency 50 to 60 Hz — — — —
Available power 300 W 320 W 100 W for PCI slots and AGP Pro slot
Max current at +12 V 13.5 A 15 A 0.5 A 0.5 A 9.2 A
Max current at -12 V 0.8 A — 0.1 A 0.1 A —
Max current at +3.3 V 1.5 A — 7.6 A 7.6 A Imax(Vcc) = 7.6 A
Max current at Vddq
— — — — Imax(Vddq) = 2 A
(3.3 V or 1.5 V)
Max current at +5 V 32 A — 5 A 5 A 2 A
Max current at -5 V 0.5 A — — — —
Max current at +5Vstdby
2 A — 1.5 A total on 3.3 V stdby
3
combined with 3.3 V stdby
1.
The maximum power dissipation for a PCI card is 25 W (refer to PCI specifications 2.2 on page 31).
2.
An AGP Pro card uses the electrical and cooling resources of both the Universal AGP Pro slot and the adjacent PCI slot. Power
limitation is managed in the BIOS.
3.
Refer to System Board Switch 10 on page 33.
2
16
Page 17

1 System Overview
Specifications and Characteristics
Some examples of a supported configuration with combined power
consumption of 100 W (PCI slots + Universal AGP Pro slot):
Number of
PCI Accessory
Cards
Four One AGP Pro Card
Four
Five
AGP Pro Slot Accessory Card Power Consumption
(50 W)
One AGP Pro Card
(50 W)
One AGP Standard
Card (25 W)
1 x 5 W PCI accessory card + 3 x 15 W PCI accessory cards + 0 W empty PCI
slot (adjacent to Universal AGP Pro slot) + 1 x 50 W AGP Pro card
1 x 5 W PCI accessory card + 1 x 15 W PCI accessory card + 2 x 12.5 W PCI
accessory cards+ 0 W empty PCI slot (adjacent to Universal AGP Pro slot) + 1
x 50 W AGP Pro card
1 x 5 W PCI accessory card + 2 x 25 W PCI accessory cards + 2 x 10 W PCI
accessory cards + 1 x 25 W AGP standard card
Total Power
Supply
Used
100 W
100 W
100 W
An attempt to draw too much current (such as a short circuit across edgeconnector pins, or an accessory board that is not suitable for this PC
Workstation), will cause the overload protection in the power supply to be
triggered, and will shut down the PC Workstation.
NOTE When the PC Workstation is turned off with the power button on the front
panel, the power consumption falls below the low power consumption (refer
to the following table), but is not zero. The special on/off method used by this
PC Workstation extends the lifetime of the power supply. To reach zero
power consumption in “off” mode, either unplug the PC Workstation from the
power outlet or use a power block with a switch.
Power Consumption and Cooling
The power consumption and acoustics (shown in the Environmental
Specifications table) are valid for a standard configuration as shipped (one
processor, 256 MB of memory, 300 W power supply, one hard disk drive,
video card, LAN card).
All information in this section is based on primary power consumptions
Power consumption - Windows NT:
• Operating with input/output (disk access)
• Operating without input/output (idle)
• Off with LAN card
1.
1 W = 3.4121 Btu/h
230 V / 50 Hz
85.5 W - 291.7 Btu/h
75.8 W - 258.6 Btu/h
4.2 W - 14.3 Btu/h
115 V / 60 Hz
1
84.5 W - 288.3 Btu/h
77.2 W - 263.4 Btu/h
4 W - 13.6 Btu/h
.
17
Page 18

1 System Overview
Specifications and Characteristics
Component:
• Processor:
• SCSI HDD with access:
• SCSI HDD with no access:
• PCI card:
50 W
23 W
16 W
10 W - 36 W
-
170.6 Btu/h
-
78.4 Btu/h
-
54.5 Btu/h
-
34.1 Btu/h - 122.8 Btu/h
Environmental Specifications
Environmental Specifications (System Processing Unit, with Hard Disk)
Operating Temperature +10 °C to +35 °C (+50 °F to +95 °F)
Storage Temperature -40 °C to +70°C (-40 °F to +158 °F)
Operating Humidity 15% to 85% (relative)
Storage Humidity 8% to 85% (relative)
Acoustic noise emission (as defined ISO 7779):
• Operating
• Operating with hard disk access
• Operating with floppy disk access
Sound Power
LwA <= 43.9 dB
LwA <= 44.9 dB
LwA <= 46.7 dB
Operating Altitude 10000 ft (3100m) max
Storage Altitude 15000ft (4600m) max
1.
non condensing conditions.
1
1
Sound Pressure
LpA <= 30.8 dB
LpA <= 31.8 dB
LpA <= 33.6 dB
Operating temperature and humidity ranges may vary depending upon the mass
storage devices installed. High humidity levels can cause improper operation of
disk drives. Low humidity levels can aggravate static electricity problems and
cause excessive wear of the disk surface.
18
Page 19

1 System Overview
Power Saving and Ergonometry
Power Saving and Ergonometry
Depending on the operating system, the following power management types
are available:
• No sleeping state: Windows NT 4 (Full On and Off).
• APM: Windows 95 and Windows 98 SE APM (Full On, Standby, Suspend
and Off).
• ACPI: Windows 98 SE ACPI and Windows 2000 (Full On, S1, Suspend to
RAM, Suspend to disk, Off).
Windows 2000 Windows 98 SE Windows NT 4 Windows 95
Full On
A
Standby
P
Suspend
M
Off
S1 (processor stopped) Supported Supported
A
S31(suspend to RAM) Supported Supported
C
S4 (suspend to disk / hibernation) Supported Not Supported by
P
I
S5 (off) Supported Supported
1.
It is anticipated that the S3 feature will be supported by HP Windows 2000 models. More information about this feature will be
documented with the HP Windows 2000 release.
Not Supported by
Windows 2000
Supported Supported Supported
Supported
Not Supported by
Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported
Windows 98
Windows NT 4
APM only Operating System
Supported
19
Page 20

1 System Overview
Power Saving and Ergonometry
Power Saving and Ergonometry for APM Systems
Processor
Display
Hard disk drive
Power
consumption
Resume events
Resume delay
1.
Not supported by Windows NT 4.
Processor
Normal speed Halted Off Off Off
Full On Standby
1
Suspend
1
Normal speed Normal speed Halted Halted
On Blanked, <30 W, on
Blanked, <5 W (typ) Blanked, <5 W (typ)
models with integrated
graphics
Normal speed Stopped Halted Halted
supports up to 300 W <40 W (230V, 50 Hz)
<27 W (115V, 60 Hz)
Keyboard, mouse, alarms,
LAN, modem, USB
<40 W (230V, 50 Hz)
<21 W (115V, 60 Hz)
Keyboard, network (RWU),
modem, USB
(plugged in but turned off)
<5 W (average)
Space bar or power
button, RPO
Instantaneous a few seconds Boot delay
Power Saving Modes and Resume Events for ACPI Systems
Full On S1 Suspend to RAM Suspend to Disk Off
Off
Display
Hard Disk
Drive
Active Power
Planes
Power
Consumption
Resume Events
Resume Delay
On Blanked Off Off Off
Normal speed Halted Off Off Off
VCC
VCCAux
Supports up to
VCC
VCCAux
Memory
VCCAux
VCCAux VCCAux
<40 W <10 W <10 W <10 W
300 W
Power button,
LAN,
Modem,
USB,
Scheduler,
Power button,
LAN,
Modem,
Scheduler,
HP Start Key
Power button,
LAN,
Modem,
Scheduler,
HP Start Key
Power button,
HP Start Key
HP Start Key
Instantaneous Instantaneous BIOS boot delay Regular boot delay
20
Page 21

1 System Overview
Power Saving and Ergonometry
Power-On from Space-Bar
The power-on from the space-bar function is enabled provided that:
• The computer is connected to a Power-On keyboard (recognizable by the
Power-On icon on the space bar).
• The function has been enabled by setting SW-7 to
up (default setting) on
the system board switches.
• The function has been enabled in the “Power” menu of the Setup
program (default configuration).
Soft Power Down
When the user requests the operating system to shut down, the environment
is cleared, and the computer is powered off. Soft Power Down is available
with the Windows NT operating system.
21
Page 22

1 System Overview
Documentation
Documentation
The table below summarizes the availability of the documentation that is
appropriate to the HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation. Only selected
publications are available in paper-based form. Most are available as
printable files from the HP division support servers, or from the HP website.
Title Division Support Server
HP Kayak XU800 User’s Guide
HP Kayak XU800
Troubleshooting Guide
HP Kayak XU800 Training
Module
HP Kayak XU800 Technical
Reference Manual
HP Kayak XU800 Service
Handbook Chapter
HP Kayak XU800 Technical
Notes
1.
Refer to the Service Handbook Chapter for the availability of the localized monolingual and multilingual User’s Guides.
2.
Also available in French, Italian, German, Spanish, Swedish and Japanese.
PDF file PDF file Shipped with the PC
2
PDF file
CD-ROM No No
PDF file
(this document)
PDF file PDF file When available, it will be
PDF file PDF file No
Online at HP WWW Site
(see address below)
Workstation
PDF file No
PDF file No
included in the fourth edition
of the Service Handbook
Paper-based
1
Access HP World Wide
Web Site
Additional online support documentation, BIOS upgrades and drivers are
available from HP’s World Wide Web site, at the following address:
World-Wide Web URL: http://www.hp.com/go/kayaksupport
then select HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation.
22
Page 23

1 System Overview
Documentation
Where to Find the Information
The table below summarizes the availability of information within the
HP Kayak XU800 PC Worksta ti on documentation set.
Product features
Product model
numbers
Environmental
Safety Warnings
Finding on-line
information
Technical
information
Formal documents
User’s Guide
Standard
configuration.
Setting up the PC.
Working in comfort.
Electrical,
multimedia, safety,
unpacking, removing
& replacing cover.
Preloaded,
HP Web sites.
Basic details. Basic details. Advanced. Advanced.
Certificate of
Conformity.
Software License
agreement.
Troubleshooting
Safety.
HP Web sites. HP Web sites. HP Web sites. HP Web
1
Guide
Introducing the PC
Training
Module
New features. Exploded view.
Service
Handbook
Parts list.
Product range.
CPL dates.
Technical
Information
Configuration. Key features.
Technical
Reference
Manual
sites, others.
Connecting
devices and
turning on
BIOS
Fields and their
options within
Setup
Manageability
Rear panel connectors,
starting and stopping.
Basic details. Updating and
recovering.
Basic details.
Viewing Setup screen,
using, passwords
Power management,
Software and drivers.
Basic details. New fields. Complete
Using the PC
New features. Memory maps. Technical
details.
Memory
maps.
list.
23
Page 24

1 System Overview
Documentation
Opening the PC
Supported
accessories
Installing
accessories
Configuring
devices
System board
Troubleshooting
User’s Guide
Troubleshooting
1
Guide
Training
Module
Service
Handbook
Technical
Information
Upgrading the PC
Full description. New
procedures.
Full PN details Full PN details
Processor(s), memory,
accessory boards,
Error messages,
problem solving.
New
procedures.
mass storage devices.
Installing devices Installing devices. Network
connection.
Installing and
removing, connectors
and switch settings.
Switch settings. Jumpers,
switches,
connectors
Jumpers,
switches and
connectors.
Layout and
switch
settings.
and replacing.
Repairing the PC
Basic, MaxiLife,
hardware diagnoses.
MaxiLife, hardware
diagnoses and
Repair policy. Service notes. Advanced.
suggested
solutions.
Technical
Reference
Manual
Jumpers,
switches and
connectors.
Chip-set
details.
Power-On SelfTest routines
(POST)
Kayak diagnostic
utility
Audio Accessories
Basic details. Error Messages,
EMU and
suggestions for
corrective action.
HP DiagTools,
CD-ROM recovery.
HP DiagTools,
CD-ROM recovery
Peripheral Devices
Refer to Audio User’s
Guide for information
on setting up and
configuring audio
accessories.
Refer to online
version of Audio
User’s Guide for
information on
setting up and
configuring audio
accessories.
24
New features. Error codes
and
suggestions
for corrective
action.
Order of
tests.
New features Technical
details.
Page 25

1 System Overview
Documentation
Troubleshooting
Refer to online
version (preloaded
on hard disk) of
LAN
Administrator’s
Guide for
LAN Accessories
User’s Guide
Refer to LAN
Administrator’s Guide
for information on
setting up and
configuring LAN cards
and systems.
information on
setting up and
configuring LAN
cards and systems.
1.
For address, “Access HP World Wide Web Site” on page 22.
Guide
1
Module
Training
Service
Handbook
Technical
Information
Technical
Reference
Manual
25
Page 26

1 System Overview
Documentation
26
Page 27

2
System Board
This chapter describes the components of the system board, taking in turn
the components of the Memory Controller Hub (MCH), the Input/Output
Controller Hub (ICH), FirmWare Hub (FWH) and the Host Bus.
The following diagram shows in detail the HP Kayak XU800 PC
Workstation Extended ATX (E-ATX) system board.
1
1
.
4
-
i
nc
he
s
w
i
de
12.
h
g
i
h
s
e
h
c
n
i
8-
27
Page 28

2 System Board
System Board Overview
System Board Overview
The following diagram shows where the different chips and connectors are
located on the E-ATX system board.
Mouse (upper) &
Keyboard (lower) - J3
Two USB - J8
Serial Port A - J5
Serial Port B - J4
(Both ports are stacked with
the Parallel Port)
Midi & Audio - J2
Memory Expansion
Memory Expansion Card
Card Connectors- J22
Connectors - XU1, XU4
Universal AGP PRO Slot - J22
PCI Slot 1
(32-bit 33 MHz, 5V) - J15
PCI Slot 2
(32-bit 33 MHz, 5V) - J14
Super I/O NS 87364 Chip - U6
CS4280 Audio PCI chip- U7
PCI Slot 5
(32-bit 33 MHz, 5V)- J11
Fan CPU 1c - J17
Line Out
Line In
MIC
Anti-Intrusionb - J10
XU1 XU4
PCI Slot 4 -J14
(64-bit 66 MHz, 3.3V)
SCSI Termination
Connector - J23
Processor 1 Connector - XU3
Processor 2 Connector - XU2
Rear Fan- J18
Fan CPU2c
- J19
Wake-On Lanc
(WOL)- J26
PCI Slot 3 - J13
(64-bit 66 MHz, 3.3V)
Memory Controller Hub
(MCH) 8284O-QP - U24
Input/Output Controller
Hub (ICH) 82801AA- U34
MaxiLife -
U25
PCI 64-bit Hub
(P64H)- U32
Additional SCSI
LED Connector -
J25
AUX Power- J31
FirmWare Hub
Controller (FWH)
82802AB- U35
Power Supply - J47
FDD - J38
Secondary IDE - J44
Primary IDE - J37
VRM socket for
VRM for CPU 2 - J45
CPU2 - J45
Battery - XU6
HDD Temperature
Sensor - J56
Battery - XU6
PCI Fan - J50
CD-ROM Audio In - J52
AUX Audio In - J51
Internal Speaker- J48
Status Panel - J43
Internal SCSI U160
Connector to Internal
Devices - J43
Adaptec 7892 SCSI
U160 Controller - U44
Configuration
Switches - SW1
a
a. Refer to “Switch Boxes” on page 33 or the Switch Block Label located on the chassis of the system box for the different system board switch
settings.
b. Connector for the Anti-Intrusion switch.
c. Optional.
d. Connector for additional control of HDD LED on the status panel through the SCSI controller on a PCI add-on card.
28
Page 29

Architectural View
2 System Board
Architectural View
Keyboard,
Mouse and
Floppy
Parallel and
Serial Ports
SECC-2 cartridge
Address (36)
Control
Data (64)
PCI Bus (64-bit, 66 MHz)
533 MB/s data transfer rate
Onboard AIC7892
SCSI U160
Controller
Universal
AGP
PRO
Connector
Slot 3 - 64-bit/66 MHz
Slot 4 - 64-bit/66 MHz
2 IDE
Connectors
2 USB
Connectors
Super I/O
NS 87364
Intel Pentium III
Processor
with L2 cache memory
AGP 4x Bus (133
MHz (1 GB MB/s data
transfer rate)
LINK 16
(533 MB/s data
transfer rate)
PCI 64-Bit
Hub (P64H)
ATA 66, 2 Channels
USB
LPC / FWH Link
FirmWare
Hardware
(FWH) 82802
HUB
Controller Hub
82840-QP
I/O Controller Hub
I/O Controller Hub
(ICH) 82801AA
(ICH) 82801AA
Controller
2 x USB
Controller
LPC
Bridge
Serial
EEPROM
I840
Memory
(MCH)
HUB LINK 8
(266 MB/s data
transfer rate)
PCI BridgeIDE
AC’97a
Controller
SM Bus
Controller
SMBus
Intel Pentium III
(optional second processor)
with L2 cache memory
Dual Rambus Channel
(2.4 GB/s at 300 MHz or
3.2 GB/s at 400 MHzdata transfer rate)
133 MB/s data transfer rate
Audio
MaxiLife
Monitoring
Slot 1 - 32-bit/33 MHz
Slot 2- 32-bit/33 MHz
Slot 5 - 32-bit/33 MHz
Chip
Processor
Memory
Expansion Card
Connector
PCI Bus (32-bit, 33 MHz)
Fans
MIDI
LCD
Status
Panel
SECC-2 cartridge
Host (also called FSB)
Bus 100/133 MHz,
1 GB/sec data transfer
rate)
AC ‘97
Digital
Audio PCI
Chip
(CS4280)
Port
Link
Codec
Audio AC‘97
a. It should be noted that the AC’97 Audio Controller is not used. The PCI CS4280 and CS4297 audio is a full PCI solution that is independent of the ICH
core logic.
29
Page 30

2 System Board
Accessory Card Slots
Accessory Card Slots
The following block diagram shows the position of the accessory card slots
on the system board.
One Universal AGP Pro slot.
Used for a graphics controller.
Three 32-bit 33 MHz PCI slots:
PCI Slot 1,
PCI Slot 2,
PCI Slot 5
Two 64-bit 66 MHz PCI slots:
PCI Slot 3,
PCI Slot 4
System board edge
(Universal AGP Pro Slot) - J22
(PCI Slot 1) - J15
(PCI Slot 2) - J14
(PCI Slot 3) - J13
(PCI Slot 4) - J12
(PCI Slot 5) - J11
Universal AGP Pro Slot
The Universal AGP Pro (Accelerated Graphics Port) bus, provides
a high-performance graphics interface. It uses a 66.6 MHz base
clock, and provides a peak bandwidth of 1064 MB/second in AGP
4x mode.
The Universal AGP Pro slot is a Universal-type connector which
provides power through 3.3 V, 12 V or 5 V power rails with a
maximum allocated power consumption of 50 W.
The Universal AGP Pro slot supports AGP 1x and 2x modes (uses 3.3 V or
1.5 V signals), and AGP 4x mode (1.5 V signalling is required).
≤
50 W
1
≤
25 W
≤
50 W
Supported
operation in the
≤
Universal AGP Pro
Slot
2
AGP1x
2
AGP2x
2
AGP4x
PCI-type
1.
AGP Pro video cards are supported up to 50 W.
2.
With or without sideband addressing.
AGP Video Card
1.5 V Universal 3.3 V
25 W
50 W≤25 W
≤
yes yes yes yes yes yes
yes yes yes yes yes yes
yes yes yes yes no no
yes yes yes yes yes yes
30
Page 31

2 System Board
Accessory Card Slots
AGP 4x mode transfers data at twice the speed of AGP 2x mode, which is
itself twice the speed of the basic AGP 1x mode. This is achieved by
multiplying the 66 MHz AGP clock frequency, so that four packets of data
are transferred on each cycle (transfers on both rising and falling edges of
the clock speed). Each packet of data contains four bytes, giving a transfer
rate of 66.6 MHz x 4 (quad-clock mechanism) x 4 bytes, a maximum
bandwidth of 1064 MB/s.
The AGP interface and bus are explained on page 38
.
PCI Slots
There is a total of five Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) connectors
on the system board:
• Three 32-bit 33 MHz PCI slots: 1, 2 and 5.
• Two 64-bit 66 MHz PCI slots: 3 and 4.
The three 32-bit/33 MHz PCI slots accept 5 V PCI cards and
Universal PCI cards (support for 3.3 V or 5 V), while the two
64-bit/66 MHz PCI slots support 3.3 V PCI cards and Universal PCI
cards (support for 3.3 V or 5 V).
A universal compatible 32-bit 33 MHz accessory card can also be installed in
PCI slots 3 or 4. However in this case the PCI 64-bit bus will only perform at
33 MHz.
The maximum supported power consumption per slot is 25W, from the 5V
and/or the 3.3V supply, and must respect the electrical specifications of the
PCI 2.2 specification. The power consumption of each PCI board is
automatically reported to the system through the two Presence Detect pins
of each PCI slot. These pins code the following cases:
• No accessory board in the PCI slot.
• 7 W maximum PCI board in the PCI slot.
• 15 W maximum PCI board in the PCI slot.
• 25 W maximum PCI board in the PCI slot.
If a standard AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) card is installed in the AGP
Pro slot, the maximum power consumption for the PCI accessory and AGP
slot must not exceed 100 W.
31
Page 32

2 System Board
Accessory Card Slots
If an AGP Pro card (>25 W and ≤50 W) is installed, then the PCI slot 1 is
made inaccessible as defined in the AGP Pro specification (PCI slot must be
left unoccupied to provide its sources, in terms of cooling and electrical
power, to the AGP Pro card. The following table shows the various PCI
board installations for the different PCI slots:
PCI Card
5 V 3.3 V
PCI Slot
Slots 1, 2 & 5
5V,
32-bit/33 MHz
Slots 3 and 4
3.3 V,
64-bit/66 MHz
1.
A 64-bit card can be installed in a 32-bit slot. However, this card will only operate in 32-bit mode.
2.
A 66 Mhz card can be installed in a 33 MHz slot. However, this card will only operate in 33 MHz mode.
3.
A 33 MHz card can be installed in a 66 MHz slot, However, the card will operate in 33 MHz mode and will force all other PCI devices to operate
at 33 MHz as well.
4.
A 32-bit card can be installed in a 64-bit slot without preventing other 64-bit PCI devices to operate in 64-bit mode.
32-bit/
33 MHz
yes yes
not
supported
64-bit/
33 MHz
1
not
supported
32-bit/
33 MHz or 66 MHz
not supported not supported yes yes
33 MHz 66MHz 33 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz 66 MHz
yes
3,4
yes
4
64-bit/
33 MHz or 66 MHz
3
yes
yes yes
32-bit/
33 MHz or 66 MHz
3,4
Universal
(3.3 V or 5 V compatible)
33 MHz or 66 MHz
2
4
yes
The system board and BIOS support the PCI specification 2.2. This
specification supports PCI-to-PCI bridges and multi-function PCI devices,
and each of the five PCI slots have Master capabilities.
PCI slots 1, 2 and 5 are connected to the ICH PCI 32-bit 33 MHz bus, while
PCI slots 3 and 4 are connected to the PCI 64-bit 66 MHz bus via the P64H.
In addition to these PCI slots, the following devices are also connected to a
PCI Bus:
yes
yes
64-bit/
1
3
yes
1,2
yes
PCI 32-bit/33 MHz Bus PCI 64-bit/66 MHz Bus
ICH (Input/Output Controller Hub) chip, bridge between the MCH (Memory Controller
Hub), USB ports and IDE buses.
Digital audio CS4280 controller.
The PCI 64-bit 66 MHz bus is explained on page 45
bus is explained on page 53
32
.
Onboard AIC7892 SCSI U160 controller.
. The PCI 32-bit 33 MHz
Page 33

2 System Board
System Board Switches
System Board Switches
There are ten system board switches used for configuration, numbered from
1 to 10. Of these a certain number are reserved and should not be modified,
otherwise it could lead to a system failure.
Switch
Default
Position
1 UP UP enables normal mode.
DOWN enables the BIOS recovery mode at next boot.
2 UP
1
UP allows Processor(s) to automatically choose the FSB speed.
DOWN forces the FSB speed to 100 MHz.
3 UP UP enables User and System Administrator passwords.
DOWN clears the passwords at next boot.
4 UP UP retains CMOS memory.
DOWN clears CMOS memory at next boot.
5 UP
1
UP = Automatic FSB frequency setting.
DOWN = Sets operation to 133 FSB/300 Rambus.
6
DOWN
7
DOWN
8
DOWN
9
DOWN
10 UP
1
UP. AGP¨110 W cards appear as 50 W.
1
DOWN enables AGP 110 W detection.
UP disables keyboard power-on.
1
DOWN enables keyboard power-on.
UP forces the PCI 64 bus to 33 MHz if slots 3 and 4 are empty.
1
DOWN disables this option.
UP disables this option.
1
DOWN enables spread spectrum clocking.
UP Disables this option.
DOWN provides 3.3 V Stdby to AGP Pro connector.
1.
These are default settings and should not be changed.
Function:
Switch Boxes There are two types of system board switch boxes that may be used on the
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation.
Default Configuration
OPEN = UP CLOSED = DOWN
or
OFF = OPEN ON = CLOSED
UP = OPEN
DOWN = CLOSED
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
X
X X X X
X X X X X
33
Page 34

2 System Board
P64H FWH ICH MCH
Chipset
Chipset
The Intel® I840 chipset is a high-integration chipset designed for graphics/
multimedia PC platforms and is comprised of the following:
• The 82840 Memory Controller Hub (MCH) is a bridge between: the Host
bus, Dual Rambus bus (main memory), the PCI bus (64-bits/66 MHz),
AGP 4x (graphic) bus, Hub Link 8-bit and Hub Link 16-bit, and the
PCI 64-bit Hub (P64H). The MCH chip feature is described in detail on
page 35
• The PCI 64-bit Hub (P64H) performs PCI bridging between the MCH and
the PCI 64-bit 66 MHz bus. The P64H is described in detail on page 44
• The 82801AA Input/Output Controller Hub (ICH) is a bridge between the
following buses: the PCI bus (32-bits/33 MHz) and SMBus. In addition,
the ICH supports the integrated IDE controller (Ultra ATA/66), En-
hanced DMA controller, USB controller, Interrupt controller, Low Pin
Count (LPC) interface, FWH interface, ACPI Power Management
Logic, AC’97 2.1 Compliant Link, AOL (Alert-On-LAN) and Real
Time Clock (RTC) and CMOS. The ICH is described in detail on page 48
.
.
.
• The 82802AB Firmware Hub (FWH) stores system BIOS and SCSI BIOS,
nonvolatile memory component. In addition, the FWH contains an Intel®
Random Number Generator (RNG). The RNG provides random numbers
to enable fundamental security building blocks for stronger encryption,
digital signing and security protocols for the PC Workstation. The FWH is
described in detail on page 62
.
34
Page 35

2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
The MCH Host Bridge/Controller is contained in a 544-pin Ball Grid Array
(BGA) package and is the bridge between the Host bus, Dual Rambus bus
(main memory), AGP 4x (graphic) bus, Hub Link 8-bit and Hub Link
16-bit.
The following figure shows an example of the system block diagram using
the MCH.
SECC-2 cartridge
PCI Bus (64-bit, 66 MHz)
533 MB/s data transfer rate
Onboard AIC7892
SCSI U160
Controller
Address (36)
Control
Data (64)
Universal
AGP
PRO
Connector
(133 MHz (1 GB MB/s
Slot 3 - 64-bit/66 MHz
Slot 4 - 64-bit/66 MHz
Intel Pentium III
with L2 cache memory
AGP 4x Bus
data transfer rate)
HUB
LINK 16
(533 MB/s data
transfer rate)
PCI
Interface
Processor
P64H
I840 Memory
Controller Hub (MCH)
82840-QP
AGP
Interface
I/O Controller Hub
(ICH) 82801AA
(optional second processor)
Memory
Controller
HUB LINK 8
(266 MB/s data
transfer rate)
Intel Pentium III
Processor
with L2 cache memory
Dual Rambus Bus
(2.4 GB/s at 300 MHz or
3.2 GB/s at 400 MHzdata transfer rate)
SECC-2 cartridge
Host (also called FSB) Bus
100/133 MHz, 1 GB/sec
data transfer rate)
Memory
Expansion Card
Connector
35
Page 36

2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
The following table shows the features that are available in the MCH Host
Bridge/Controller.
Feature Feature
• Processor/Host Bus:
❒ Supports up to two Pentium III processors at: 100 MHz/133
MHz Host Bus frequency.
❒ Supports full Symmetric Multiprocessor (SMP) Protocol for
up to two processors.
❒ Provides an 8-deep In-Order Queue supporting up to eight
outstanding transaction requests on the host bus.
❒ Desktop optimized GTL+ bus driver technology (gated GTL+
receivers for reduced power).
❒ Support for 36-bit host bus address.
❒ IERR and BERR signals generate SCi/SERR.
❒ Parity protection on address and resource signals:
Parity errors generate SERR.
• Memory Controller.
Direct Rambus:
❒ Dual Direct Rambus Channels operating in lock-step (both
channels must be populated with a memory module).
Supporting 300 MHz or 400 MHz.
❒ RDRAM 64 Mb, 128 Mb, 256 Mb devices.
❒ Minimum upgrade increment of 16 MB using 64 Mb DRAM
technology.
❒ Up to 64 Direct Rambus devices (without using MRH-R).
Dual channel maximum memory array size is:
— 512 MB using 64 Mb DRAM technology.
— 1 GB using 128 Mb DRAM technology.
— 2 GB using 256 Mb DRAM technology.
❒ Up to 8 simultaneous open pages:
— 1 KByte page size support for 64 Mbit, 128 Mbit and 256
Mbit RDRAM devices.
— KByte page size support for 256 Mbit RDRAM devices.
• Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) Interface:
❒ Single Universal AGP PRO connector.
❒ AGP Rev 2.0 compliant, including AGP 4x data transfers and
2x/4x Fast Write protocol.
❒ AGP Universal Connector support via dual mode buffers to al-
low AGP 2.0 3.3 V or 1.5 V signalling.
❒ AGP PIPE# or SBA initiated accesses to DRAM is not
snooped
❒ AGP FRAME initiated accesses to DRAM are snooped
(snooper identifies that data is coherent in cache memory).
❒ Hierarchical PCI configuration mechanism.
❒ Delayed transaction support for AGP-to-DRAM reads that
cannot be serviced immediately.
SDRAM:
❒ Up to 8 GB of SDRAM using four external Memory Repeater
Hubs for SDRAM (MRH-S).
Currently, two MRH-S devices are supported.
❒ Interleaved 100 MHz support using 4 MRH-S for a maximum
bandwidth.
❒ Non-Interleaved 100 MHz support using 2 MRH-s for lower
cost and upgrade path.
❒ Unbuffered DIMMs are supported.
❒ Up to 4 rows or 2 DS DIMMs per MRH-S.
❒ Up to 8 simultaneous open pages:
— 2 KByte page size support for 64 Mbit SDRAM devices.
— 4 KByte - 16 KByte page sizes supporting 64 MBit to
256 Mbit SDRAM devices.
❒ Configurable optional ECC operation:
— ECC with single bit Error Correction and multiple bit Error
Detection.
— Single bit errors corrected and written back to memory
(scrubbing).
• Hub Link 8-bit Interface to ICH:
❒ High-speed interconnect between the MCH and ICH
(266 MB/sec).
36
• Hub Link 16-bit Interface to P64H:
❒ High-speed interconnect between the MCH and P64H
(533 MB/sec).
Page 37

Feature Feature
2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
• Power management:
❒ SMRAM space re-mapping to A0000h - BFFFFh (128 KB).
❒ Extended SMRAM space above 256 MB, additional 128 K,
256 K, 512 K, 1 MB TSEG from Top of Memory, cacheable
(cacheability controlled by processor).
❒ Suspend to RAM.
❒ ACPI Rev. 1.0 compliant power management.
❒ APM Rev. 1.2 compliant power management.
❒ Power-managed states are supported for up to two
processors.
• 544 mBGA MCH package. • Input/Output Device Support:
• Arbitration:
❒ Distributed Arbitration Model for Optimum Concurrency
Support.
❒ Concurrent operations of host, hub interface, AGP and
memory buses supported via a dedicated arbitration and
data buffering logic.
❒ Input/Output Controller Hub (ICH).
❒ PCI 64 Hub (P64H).
MCH Interface
The MCH interface provides bus control signals and address paths via the
Hub Link 8-bit access to the ICH and via the Hub Link 16-bit access to the
P64H for transfers between the processor(s) on the Host bus (FSB), Dual
Rambus bus and AGP 4x bus.
The MCH supports 36-bit host addresses, allowing the processor to address
a space of 64 GB. It also provides an 8-deep In-Order Queue supporting up
to eight outstanding transaction requests on the host bus.
Host-initiated input/output signals are positively decoded to AGP, Hub Link
16-bit interface, or MCH configuration space and subtractively decoded to
Hub Link 8-bit interface. Host-initiated memory cycles are positively
decoded to AGP, Hub Link 16-bit interface, or DRAM, and are again
subtractively decoded to Hub Link 8-bit interface.
AGP semantic memory accesses initiated from AGP to DRAM do not require
a snoop cycle (not snooped) on the Host bus, since the coherency of data
for that particular memory range will be maintained by the software.
However, memory accesses initiated from AGP using PCI Semantics and
accesses from either Hub Link interface (8-bit or 16-bit) to DRAM do
require a snoop cycle on the Host bus.
Memory access whose addresses are within the AGP aperture are translated
using the AGP address translation table, regardless of the originating
interface.
37
Page 38

2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
Write accesses from Hub Link interface (8-bit or 16-bit) to the AGP are
supported.
The MCH can support one or two Pentium III processors, at FSB frequencies
of 100/133 MHz using GTL+ signalling. Refer to page 64
for a description of
the Host bus.
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) Bus Interface
A controller for the Universal AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) Pro slot is
integrated in the MCH. The AGP Bus interface is compatible with the
Accelerated Graphics Port Specification, Rev 2.0, operating at 133 MHz, and
supporting up to 1 GB/sec data transfer rates. The MCH supports only a
synchronous AGP interface, coupling to the Host bus frequency.
AGP 4x Bus
The AGP bus is a dedicated bus for the graphics subsystem, which meets the
needs of high quality 3D graphics applications. It has a direct link to the
MCH
The AGP bus is based upon a 66 MHz, 32-bit PCI bus architecture, to which
several signal groups have been added to provide AGP-specific control and
transfer mechanisms.
AGP specific transactions always use pipelining. This control mechanism
increases the bus efficiency for data transfer. Sideband Addressing (SBA)
may also be used by AGP transaction requests which further increases the
bus efficiency for data transfer. The supported modes are detailed below:
• FRAME based AGP. Only the PCI semantics are: 66 MHz, 32-bit, 3.3 V,
266 MB/s peak transfer rate.
• AGP 1X with pipelining, sideband addressing can be added: uses 66 MHz,
32-bit, 3.3 V, increased bus efficiency, 266 MB/s peak transfer rate.
• AGP 2X with pipelining, sideband addressing can be added: 66 MHz
double clocked, 32-bit, 3.3 V, 533 MB/s peak transfer rate.
• AGP 4X with pipelining, sideband addressing can be added: 133 MHz
double clocked, 32-bit, 1.5 V, increased bus efficiency, 1066 MB/s peak
transfer rate
38
Page 39

AGP PCI Bus
Implementation
2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
Pentium III Processor
Universal
AGP
PRO
Connector
AGP 4x Bus
(133 MHz)
Two PCI
64-bit 66
MHz slots
GX-Device 1
AGP Port
Interface
PCI-to-PCI
PCI-to-PCI
Hub Link 16-bit
PCI 64-bit 66 MHz
Hub (P64H)
PCI-to-PCI
Device 0
I840
Memory
Controller Hub
(MCH)
Hub Link 8-bit
I/O Controller
Hub (ICH)
Main Memory Controller
The main memory controller is integrated in the MCH supporting two
primary rambus channels (A and B).
DRAM Interface
The MCH provides optional Host bus error checking for data, address,
request and response signals. Only 300 MHz and 400 MHz Direct Rambus
devices are supported in any of 64, 128 or 256 Mb technology. 64 and 128
MBit RDRAMs use page sizes of 1 kbytes, while 256 Mb devices target
1 kbyte or 2 kbyte pages.
A maximum number of 64 Rambus devices (32 devices maximum per
channel) is supported. Both channels must be populated with paired
memory modules.
39
Page 40

2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
The following table shows the number of Rambus devices and memory
technology available on a memory module.
Memory Technology (number of Megabits)
Number of devices
per RIMM
4
8
16
64 Mbits 128 Mbits 256 Mbits
N/A 64 MB module 128 MB module
N/A 128 MB module 256 MB module
128 MB module 256 MB module 512 MB module
MCH also provides optional data integrity features including ECC in the
memory array. During DRAM writes, ECC is generated on a QWord (64 bit)
basis. During DRAM reads, the MCH supports multiple-bit error detection
and single-bit error correction when the ECC mode is enabled.
MCH will scrub single bit errors by writing the corrected value back into
DRAM for all reads when hardware scrubbing is enabled. This, however does
not include reads launched in order to satisfy an AGP transaction.
Dual Rambus Bus
The Dual Rambus bus is comprised of 16 x 2 bits of data information, and
8 bits of Error Correcting Code (ECC). The bus is connected to the Memory
Expansion Card Connector and to the MCH chip supporting two Dual
Rambus channels (A and B).
Both channels run at 300 or 400 MHz supporting up to 32 rambus devices
per channel (individual chips) or one MRH-S (Memory Repeater Hub) per
channel for DIMM sockets. The maximum available data bandwidth is
3.2 GB/s at 400 MHz.
The configuration of both primary rambus channels must be symmetrical.
That is to say, whatever the configuration on channel A, the same must be
on channel B.
40
Page 41

2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
Memory Expansion Card Connector
The actual memory array is on a Memory Expansion Card installed in a
Memory Expansion Card Connector (MECC) located on the system board.
On the HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation there are two types of Memory
Expansion Cards supporting the following configurations:
Four-RIMM Memory
Expansion Card
Four RIMM sockets support RDRAM ECC and memory modules installed in
pairs. Any unused RIMM sockets must contain a continuity module.
RIMM SOCKET A0
RIMM SOCKET A1
RIMM SOCKET B0
RIMM SOCKETB1
Models are supplied with either 128 MB or 256 MB RDRAM ECC main
memory. Memory upgrades are available in pairs of RIMMs, with an
individual RIMM size of 64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB or 512 MB. The following
diagram shows installed memory. There are always two RIMMs working in
parallel.
Memory modules must be
installed in pairs (A0-B0).
A0 A1
I840
Memory
Controller Hub
(MCH)
82840-QP
Rambus Channel A
Rambus Channel B
B0 B1
Upgrades are then
installed as pairs in
sockets (A1-B1).
Otherwise, continuity
modules are installed
in sockets (A1-B1).
Each RIMM socket is connected to the SMBus and is described on page 57
.
41
Page 42

2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
Four-DIMM Memory
Expansion Card
Four DIMM sockets support SDRAM 100 MHz unbuffered ECC memory
modules installed in pairs. Unused DIMM sockets can be left free.
DIMM SOCKET A0
DIMM SOCKET B0
DIMM SOCKET A1
DIMM SOCKET B1
The MCH supports one Rambus Memory Hub for SDRAM (MRH-S) per
connected channel. Each MRH-S allows bridging of a single SDRAM channel
on to the main Rambus channel. The MRH-S also translates RDRAM and
SDRAM protocols, thus enabling the DIMM Memory Expansion Card to be
used on the Rambus channels.
As only one MRH-S is connected to each channel, the MCH operates the
MRH-S pair in non-interleaved mode.
Memory modules must be
installed in pairs (A0-B0).
A0 A1
Rambus Channel A
I840
Memory
Controller Hub (MCH)
82840-QP
Rambus Channel B
MRH-S
MRH-S
Upgrades are then
installed in pairs
(A1-B1).
B0 B1
Models are supplied with 128 MB of SDRAM unbuffered ECC main memory.
Memory upgrades are available in 64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB or 512 MB
unbuffered 100 MHz ECC SDRAM modules.
MRH-S (Memory Repeater Hub-SDRAM) provides support for two doublesided 100 MHz SDRAM DIMM sockets.
Each DIMM socket is connected to the SMBus and is described on page 57
42
.
Page 43

2 System Board
Memory Controller Hub (8240)
Read/Write Buffers The MCH defines a data buffering scheme to support the required level of
concurrent operations and provide adequate sustained bandwidth between
the DRAM subsystem and all other system interfaces (CPU, AGP and PCI).
System Clocking The MCH operates the host interface at 100 MHz or 133 MHz, PCI at 33 MHz
and AGP at 66/133 MHz. Coupling between all interfaces and internal logic is
done in a synchronous manner. The clocking scheme uses an external clock
synthesizer (which produces reference clocks for the host, AGP and PCI
interfaces).
I/O APIC I/O APIC is used to support dual processors as well as enhanced interrupt
processing in the single processor environment. The I/O APIC controller of
the ICH is used in conjunction with a second I/O APIC controller in the
P64H.
43
Page 44
2 System Board
PCI 64-bit Hub
PCI 64-bit Hub
The P64H is a peripheral chip that performs PCI bridging functions
between the MCH and the PCI 64-bit 66 MHz bus. The P64H has a 16-bit
primary hub interface to the MCH and a secondary 64-bit PCI bus
interface. This controller inter-operates transparently with either 64-bit or
32-bit devices.
The following figure shows how the P64H chip is connected to the MCH via
the Hub Link 16 and to the supported devices such as those in the two PCI
64-bit 66 MHz PCI slots and AIC-7892 Ultra 160 SCSI controller via the PCI
64-bit 66 MHz bus.
SECC-2 cartridge
PCI Bus (64-bit, 66 MHz)
533 MB/s data transfer rate
Onboard AIC7892
SCSI U160
Controller
Address (36)
Control
Data (64)
Slot 3 - 64-bit/66 MHz
Slot 4 - 64-bit/66 MHz
Intel Pentium III
Processor
with L2 cache memory
Controller Hub (MCH)
HUB
LINK 16
(533 MB/s data
transfer rate)
P64H
PCI
Interface
I840 Memory
82840-QP
Intel Pentium III
Processor
(optional second processor)
with L2 cache memory
SECC-2 cartridge
Host (also called FSB)
two-way Bus 100/
133 MHz, 1 GB/sec
data transfer rate)
44
Page 45

The following table shows the available P64H features.
Feature Feature
2 System Board
PCI 64-bit Hub
• PCI Interface:
❒ Both 64-bit and 32-bit 33 MHz or 66 MHz devices.
❒ Provides Synchronous operation to the P64H using
1:1(66 MHz) or 2:1 (33 MHz) hub interface/PCI bus gearing
ratio.
❒ Allows input/output operations to occur with processor
transactions to isolate traffic.
❒ Parity and System Error (PERR
# /
PERR
#).
❒ Allows peer-to-peer communication within a single PCI bus
segment.
❒ Provides PCI transaction forwarding for all I/O and memory
(Type 1-to-Type 1, Type 1-to-Type 0, Type 1 to a special
cycle).
❒ Provides address decoding for:
16-bit I/O addressing.
32-bit memory mapped I/O addressing.
44-bit prefetchable memory addressing (upstream only).
VGA addressing.
❒ Includes downstream LOCK
capabilities.
#
❒ Fast Back-to-Back cycles (upstream only).
❒ Bus parking.
❒ Implements Delayed Transaction for;
PCI configuration read/written I/O read, and memory read
commands (downstream).
Memory read, I/O read and I/O write commands (upstream).
• Scalability / Flexibility:
❒ Provides arbitration support for all PCI devices.
❒ Supports 2 x 66 MHz PCI slots.
❒ Processes dual address cycle (DAC) for upstream access
>4 GB.
❒ Handles 3.3 V operation with 5.0 V tolerant on all input pins.
• Upstream Hub Link 16 Interface:
❒ Connects to the MCH via a 16-bit hub interface.
❒ Provides 64-bit and 32-bit addressing.
❒ Utilizes 66 MHz base clock.
❒ Utilizes 133 MHz double-clocked strobes.
• Integrated Functions:
❒ I/O APIC to provide 24 interrupts.
❒ Six copies of PCLKOUT signals to its PCI devices.
PCI 64-bit 66 MHz Bus Interface
The P64H provides the interface to a PCI 64-bit 66 MHz bus interface
supporting both 64-bit and 32-bit 33 MHz or 66 MHz devices.
This interface implementation is compliant with PCI Rev 2.2 Specification,
and it can support up to 533 MB/sec data transfer rates.
It also supports PCI master capabilities and the Adaptec AIC 7892
16-bit Ultra 160 SCSI controller.
A table on page 68
shows the P64H interrupts.
45
Page 46

2 System Board
Internal U-160
SCSI Connector
PCI 64-bit Hub
Devices Supported on the PCI 64-bit 66 MHz Bus
The following devices are supported on the PCI 64-bit 66 MHz bus.
PCI 64-bit 66 MHz Slots There are two PCI 64-bit 66 MHz PCI slots (slots 4 and 5) connected to the
PCI 64-bit 66 MHz bus. These two 64-bit/66 MHz PCI slots support 3.3 V
PCI cards and Universal PCI cards (support for 3.3 V or 5 V).
A universal compatible 32-bit 33 MHz accessory card can also be installed in
PCI slots 3 or 4. However in this case the PCI 64-bit bus will only perform at
33 MHz.
.
Ultra-Wide 160 SCSI
Controller
PCI slots are explained in detail on page 31
The Adaptec AIC-7892 Ultra 160 SCSI PCI controller is integrated on the
system board. Data is transferred at 160 MB/s on 16-bit wide, Low Voltage
Differential (LVD) bus.
NOTE If an Ultra-wide, or older SCSI device is connected on the SCSI bus, all
Ultra 160 and Ultra 2 SCSI devices will automatically be switched to Ultrawide SCSI. In this case, the LVD bus works as a single-ended bus, and data
will only be transferred at 40 MB/s.
The controller is fitted with a 16-bit SCSI flat cable with five connectors,
plus a SCSI termination device on the system board; so a maximum of five
internal SCSI internal devices are supported. Additional devices can be
added outside the PC Workstation by connecting directly to the rear panel
SCSI connector. The external connector allows up to ten external devices to
be connected. This gives a maximum of 15 (internal + external) devices that
can be connected.
The last connector on the SCSI cable is connected to the external SCSI
connector on the rear chassis. The connector before this is connected to the
onboard SCSI terminator (located behind the processor).
46
Page 47

2 System Board
PCI 64-bit Hub
In the following diagram, the T1 (SCSI terminator located near the
AIC-7892 SCSI controller) and T2 boxes are SCSI terminators. If an external
cable is connected, then the T2 termination is automatically deactivated.
16-bit SCSI
Terminator
T1
Onboard
AIC-7892
SCSI controller
Internal U-160
68-pin SCSI
Connector on the
System Board
* The External SCSI cable must not exceed 1 metre in length
Connector on the
System Board
Internal 68-pin SCSI
Connectors on the SCSI Flat
Cable
T2
Inside Chassis Edge
of the PC
Workstation
Rear Panel External
68-pin SCSI
Connector
Connected
External Device
External Cable*
Outside Chassis
Edge of the PC
Workstation
By default, the internal SCSI bus is configured to run in Ultra 160 SCSI mode
(providing a maximum band-width of 160 MB/s). The user may configure
the SCSI system using the SCSISelect utility, included in the system BIOS.
Refer to page 99
for details about the SCSISelect utility. This utility is also
described in more detail in the SCSI User’s Guide.
The Adaptec AIC-7892 Ultra 160 SCSI PCI controller is BBS compliant, but
does not support Hot Swap.
47
Page 48

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
The ICH, is encapsulated in a 241-pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) package and
is located on the system board just underneath the Memory Expansion
Card Connector. It provides the interface between the PCI bridge (PCI
Rev. 2.2 compliant with support for 32-bit 33 MHz PCI operations),
PCI-to-LPC (Low Pin Count) bridge, IDE controller, USB controller,
SMBus controller and AC’97 controller.
The ICH functions and capabilities are discussed in detail later on in this
section. The following figure shows an example of the system block
diagram using the ICH.
Intel Pentium III
Processor
Address (36)
Control
Data (64)
with L2 cache memory
Host (also called FSB) twoway Bus 100/133 MHz,
Keyboard,
Mouse and
Floppy
Parallel and
Serial Ports
2 IDE
Connectors
2 USB
Connectors
Super I/O
NS 87364
ATA 66, 2 Channels
USB
LPC / FWH Link
FirmWare
Hardware
(FWH) 82802
I840 Memory
Controller Hub
82840-QP
I/O Controller Hub
I/O Controller Hub
(ICH) 82801AA
(ICH) 82801AA
IDE
Controller
2 x USB
Controller
DMA
Controller
Serial
EEPROM
(MCH)
HUB LINK 8
(233 MB/s data
transfer rate)
PCI Bridge
SM Bus
Controller
SMBus
MaxiLife
Monitoring
Chip
PCI Bus (32-bit, 33 MHz)
133 MB/s data transfer rate
Slot 1 - 32-bit/33 MHz
Slot 2- 32-bit/33 MHz
Slot 5 - 32-bit/33 MHz
Fans
LCD
Status
Panel
Audio PCI
Chip
(CS4280)
MIDI
Port
AC ‘97
Digital
Link
Codec
Audio AC‘97
48
Page 49

The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
The following table shows the available ICH features.
Feature Feature
2 System Board
• Multi-function PCI Bus Interface:
❒ PCI at 32-bit 33 MHz.
❒ PCI Rev 2.2 Specification.
❒ 133 Mbyte/sec data transfer rate.
❒ Master PCI Device Support for up to six devices.
• USB, supporting:
❒ USB revision 1.1 compliant.
❒ UHCI Implementation with Two USB Ports for serial
transfers at12 or 1.5 Mbit/sec.
❒ Wake-up from sleeping states (refer to table on page 19
❒ Legacy keyboard/mouse software.
• Power Management Logic:
❒ ACPI 1.0 compliant.
❒ Support for APM-based legacy power management for non-
ACPI implementations.
❒ ACPI defined power states (S1, S3, S4, S5).
❒ ACPI power management timer.
❒ SMI generation.
❒ All registers readable/restorable for proper resume from 0 V
suspend states.
❒ PCI PME#.
• Enhanced DMA Controller:
❒ Two 82C37 DMA controllers.
❒ PCI DMA with 2 PC/PCI Channels in pairs.
❒ LPC DMA.
❒ DMA Collection Buffer to provide Type-F DMA performance
for all DMA channels.
• Interrupt Controller:
❒ Two cascaded 82C59 controllers.
❒ Integrated I/O APIC capability.
❒ 15 Interrupt support in 8259 Mode, 24 supported in I/O APIC
).
mode.
❒ Serial Interrupt Protocol.
• Integrated IDE Controller:
❒ Independent Timing of up to four drives.
❒ Ultra ATA/66 Mode (66 Mbytes/sec).
❒ Ultra ATA/33 Mode (33 Mbytes/sec).
❒ PIO Mode 4 transfers up to 14 Mbytes/sec.
❒ Separate IDE connections for Primary and Secondary cables.
❒ Integrated 16 x 32-bit buffer for IDE PCI Burst transfers.
❒ Write Ping-Pong Buffer for faster write performances.
• Real-Time Clock, supporting:
❒ 256-byte battery-backed CMOS RAM.
❒ Hardware implementation to indicate Century Rollover.
• System TCO Reduction Circuits:
❒ Timers to Generate SMI# and Reset Upon.
❒ Timers to Detect Improper Processor Reset.
❒ Integrated Processor Frequency Strap Logic.
• Timers Based on 82C54:
❒ System Timer, Refresh Request, Speaker Tone Output.
•SMBus
❒ Host Interface allows processor to communicate via SMBus.
2
❒ Compatible with 2-wire I
C bus.
• System Timer, Refresh Request, Speaker Tone Output. • GPIO:
❒ TTL, Open-Drain, Inversion.
• Firmware Hub (FWH) interface. • 3.3 V operation with 5 V Tolerant Buffers for IDE and PCI signals.
• 241 BGA Package. • Alert-On-LAN (AOL) support.
49
Page 50

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
ICH Architecture The ICH interface architecture ensures that the I/O subsystems, both PCI
and the integrated input/output features (for example: IDE, AC’97 and USB)
receive the adequate bandwidths.
To achieve this, by placing the I/O bridge directly on the ICH interface, and
no longer on the PCI bus, the ICH architecture ensures that both the input/
output functions integrated into the ICH and the PCI peripherals obtain the
bandwidth necessary for peak performance.
ICH PCI Bus Interface The ICH PCI provides the interface to a PCI bus interface operating at
33 MHz. This interface implementation is compliant with PCI Rev 2.2
Specification, supporting up to six external PCI masters in addition to the
ICH requests and AC’97 controller. The PCI bus can reach a data transfer
rate of 133 MBytes/sec. The maximum PCI burst transfer can be between
256 bytes and 4 KB. It also supports advanced snooping for PCI master
bursting, and provides a pre-fetch mechanism dedicated for IDE read.
Refer to the table page 68
for ICH interrupts.
SMBus Controller The System Management (SM) bus is a two-wire serial bus which runs at a
maximum of (100 kHz). The SMBus Host interface allows the processor to
communicate with SMBus slaves and an SMBus Slave interface that allows
external masters to activate power management events. The bus connects
to sensor devices that monitor some of the hardware functions of the system
board, both during system boot and run-time.
Refer to page 55
for information on the MaxiLife ASIC.
for a description of the devices on the SMBus, or to page 58
Low Pin Count Interface The ICH implements the LPC interface 1.0 specification.
Enhanced USB Controller The USB (Universal Serial Bus) controller provides enhanced support for
the Universal Host Controller Interface (UHCI). This includes support that
allows legacy software to use a USB-based keyboard and mouse. The USB
supports two stacked connectors on the back panel. These ports are built
into the ICH, as standard USB ports.
The ICH is USB revision 1.1 compliant.
USB works only if the USB interface has been enabled within the HP Setup
program. Currently, only the Microsoft Windows 95 and Windows 98
operating systems provide support for the USB.
50
Page 51

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
AC’97 Controller This controller, even though available in the ICH, is not used. The HP Kayak
PC Workstation uses the dedicated dual chip PCI solution of the CS4280
audio controller and the CS4297 Codec Audio Codec ‘97 (AC’97).
Refer to page 54
solution.
for information about the CS4280 and CS4297 audio
IDE Controller The IDE controller is implemented as part of the ICH chip and has PCI-
Master capability. Two independent ATA/66 IDE channels are provided with
two connectors per channel. Two IDE devices (one master and one slave)
can be connected per channel. In order to guarantee data transfer integrity,
Ultra-ATA cables must be used for Ultra-ATA modes (Ultra-ATA/33 and
Ultra-ATA/66).
The PIO IDE transfers of up to 14 Mbytes/sec and Bus Master IDE transfer
rates of up to 66 Mbytes/sec are supported. The IDE controller integrates
16 x 32-bit buffers for optimal transfers.
It is possible to mix a fast and a slow device, such as a hard disk drive and a
CD-ROM, on the same channel without affecting the performance of the fast
device. The BIOS automatically determines the fastest configuration that
each device supports.
DMA Controller The seven-channel DMA controller incorporates the functionality of two
82C37 DMA controllers. Channels 0 to 3 are for 8-bit count-by-byte
transfers, while channels 5 to 7 are for 16-bit count-by-word transfers (refer
to table on page 104
seven DMA channels can be programmed to support fast Type-F transfers.
for allocated DMA channel allocations). Any two of the
The ICH DMA controller supports the LPC (Low Pin Count) DMA. Single,
Demand, Verify and Incremental modes are supported on the LPC interface.
Channels 0-3 are 8-bit, while channels 5-7 are 16-bit. Channel 4 is reserved
as a generic bus master request.
Interrupt Controller The Interrupt controller is equivalent in function to the two 82C59 interrupt
controllers. The two interrupt controllers are cascaded so that 14 external
and two internal interrupts are possible. In addition, the ICH supports a
serial interrupt scheme and also implements the I/O APIC controller. A table
on page 68
shows how the master and slave controllers are connected.
51
Page 52

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
Timer/Counter Block The timer/counter block contains three counters that are equivalent in
function to those found in one 82C54 programmable interval counter/timer.
These three counters are combined to provide the system timer function,
and speaker tone. The 14.318 MHz oscillator input provides the clock source
for these three counters.
Advanced Programmable
Interrupt Controller
Incorporated in the ICH, the APIC can be used in either single-processor or
multi-processor systems, while the standard interrupt controller supports
only single-processor systems.
Real Time Clock The RTC is 146818A-compatible, with 256 bytes of CMOS. The RTC
performs two key functions: keeping track of the time of day and storing
system data.
The RTC operates on a 32.768 kHz crystal and a separate 3V lithium battery
that provides up to 7 years of protection for an unplugged system. It also
supports two lockable memory ranges. By setting bits in the configuration
space, two 8-byte ranges can be locked to read and write accesses. This
prevents unauthorized reading of passwords or other security information.
Another feature is a date alarm allowing for a schedule wake-up event up to
30 days in advance.
Enhanced Power
Management
The ICH’s power management functions include enhanced clock control,
local and global monitoring support for 14 individual devices, and various
low-power (suspend) states. A hardware-based thermal management circuit
permits software-independent entry points for low-power states.
The ICH includes full support for the Advanced Configuration and Power
Interface (ACPI) specifications.
52
Page 53

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
Devices on the PCI 32-bit 33 MHz Bus
The following devices are connected to the PCI 32-bit 33 MHz bus.
Intel Pentium III
Processor
Host (also called FSB)
Bus 100/133 MHz
I840 Memory
Controller Hub
(MCH)
HUB LINK 8 (233
MB/s data transfer
rate)
I/O Controller Hub
I/O Controller Hub
(ICH) 82801AA
(ICH) 82801AA
IDE
Controller
2 x USB
Controller
DMA
Controller
PCI Bridge
SM Bus
Controller
PCI Bus (32-bit, 33 MHz)
133 MB/s data transfer rate
Slot 1 - 32-bit/33 MHz
Slot 2- 32-bit/33 MHz
Slot 5 - 32-bit/33 MHz
Audio PCI
Chip
(CS4280)
AC ‘97
Digital
Link
MIDI
Port
Audio AC‘97
PCI 32-bit/33 MHz Slots There are three 32-bit/33 MHz PCI slots accepting 5 V PCI cards and
Universal PCI cards (support for 3.3 V or 5 V). The LAN card should be
installed in PCI Slot 5. PCI slots are explained in detail on page 31
.
Codec
53
Page 54

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
Dual Chip PCI Audio Solution
CS4280 PCI Audio
Interface Features
CS4297 Audio Codec‘97
Features
The integrated PCI audio solution in the PC Workstation is a dual-chip
™
solution made up of the CrystalClear
CS4280 PCI audio controller and the
CrystalClear CS4297 Audio Codec ‘97 (AC’97).
The CS4280 PCI audio controller interfaces with the PCI bus and performs
all digital operations such as sample rate conversions and synthesis. The
CS4297 AC’97 chip mixes and processes all the analog signals.
The interface between audio PCI chip and the audio codec is known as the
AC’97 Digital Link.
• PCI Version 2.1 Bus Master.
• Windows ® 95, Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0, Windows NT 2000 Drivers.
• Compliant with PC’99.
• MPU-401 interface, FM synthesizer, and Game Port.
• Full duplex operation.
• Advanced Power Management (PPMI).
• AC’97 1.03 compatibility.
• Sophisticated mixed signal technology.
• 18-bit stereo full-duplex Codec with fixed 48kHz sampling rate.
• High quality differential CD input.
• Mono microphone input.
• Two analog line-level stereo inputs for LINE IN and CD (or VIDEO)
connection.
• Single stereo line level output.
• Extensive power management support.
• Meets Microsoft’s PC’99 audio performance requirements.
54
Page 55

Audio Chip
Specifications
2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
Feature Description
Digitized Sounds
Music Synthesizer
Mixer
Line Input
Line Output
Microphone Input
• 16-bit and 8-bit stereo sampling from 4 kHz to 48 kHz.
• Hardware Full Duplex Conversion.
• 16-bit software-based real-time audio compression/
decompression system.
• Integrated OPL3 compatible music synthesizer.
• MPC-3 audio mixer.
• Input mixing sources: microphone, LINE In,
CD Audio, AUX Audio, and digitized sounds.
• Output mixing of all audio sources to the LINE Out or
integrated PC Workstation speaker.
• Multiple source recording and Left/Right channels balance.
• Input impedance: 17k
• Input range: 0 to 2.83 Vpp
• Stereo output of 100 mW per channel with headphone
speakers (impedance 32
• Output impedance: 570
• Output range: 0 to 2.83 Vpp.
• 20 dB gain preamplifier. The boost can be muted with
(ohms).
Ω
Ω).
Ω.
software.
• 32-level programmable volume control.
• Input impedance: 600
• Sensitivity: 30 mVpp to 283 mVpp.
Ω.
Stereo Out Jack
• Impedance: 32
Ω.
Devices on the SMBus
The SMBus is a subset of the I2C bus. It is a two-wired serial bus which runs
at a maximum speed of 100 kHz. It is used to monitor some of the hardware
functions of the system board (such as voltage levels, temperature, fan
speed, memory presence and type), both at system boot and during normal
run-time. It is controlled by the SMBus controller located in the ICH.
55
Page 56

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
The following devices are connected to the SMBus:
• LCD status panel.
• One Serial EEPROM MaxiLife (also includes backup values of CMOS
settings).
• PCI slot 5, thus being ready for Alert-On LAN (AOL) from a hardware
level.
• ICH SMBus Master Controller 100 kHz maximum.
• MaxiLife for hardware management, bus master controller.
• One LM75 thermal sensor on the system board.
• One ADM1024 hardware monitoring sensor.
• RIMM or DIMM serial EEPROM.
Intel Pentium III
Processor
Host (also called FSB)
Bus 100/133 MHz,
I840 Memory
Controller Hub
I/O Controller Hub
I/O Controller Hub
(ICH) 82801AA
(ICH) 82801AA
Controller
2 x USB
Controller
DMA
Controller
Serial
EEPROM
(MCH)
HUB LINK 8
(233 MB/s data
transfer rate)
PCI BridgeIDE
SM Bus
Controller
Monitoring
SMBus
MaxiLife
Chip
Fans
LCD
Status
Panel
56
Page 57

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
ICH SMBus Master
Controller
The ICH provides a processor-to-SMBus controller. All access performed to
the SMBus is done through the ICH SMBus interface. Typically, the
processor has access to all the devices connected to the SMBus.
DIMM Sockets Each DIMM socket is connected to the SMBus. The 168-pin DIMM modules
2
include a 256 byte I
information, including the DRAM chips’ manufacturer name, DIMM speed
rating, DIMM type, etc. The second 128 bytes of the Serial EEPROM can be
used to store data online.
C Serial EEPROM. The first 128 bytes contain general
RIMM Sockets Each RIMM socket is connected to the SMBus. The 168-pin RIMM modules
2
include a 256 byte I
information, including the DRAM chips’ manufacturer name, RIMM speed
rating, RIMM type, etc. The second 128 bytes of the Serial EEPROM can be
used to store data online.
C Serial EEPROM. The first 128 bytes contain general
ADM1024 The ADM1024 chip is a hardware monitoring sensor dedicated to the
processor temperature. This chip uses the thermal diodes integrated into
each processor cartridge and makes the temperature information available
through the SMBus. It also monitors processor power supply voltages.
Serial EEPROM This is the non-volatile memory which holds the default values for the CMOS
memory (in the event of battery failure).When installing a new system
board, the Serial EEPROM will have a blank serial number field. This will be
detected automatically by the BIOS, which will then prompt the user for the
serial number which is printed on the identification label on the back of the
PC Workstation. The computer uses 16KBytes of Serial EEPROM
implemented within two chips. Serial EEPROM is ROM in which one byte at
a time can be returned to its unprogrammed state by the application of
appropriate electrical signals. In effect, it can be made to behave like very
slow, non-volatile RAM. It is used for storing the tatoo string, the serial
number, and the parameter settings for the Setup program as well as
MaxiLife firmware.
LM75 Temperature
Sensor
The LM75 temperature sensor and alarm are located on the system board.
The sensor is used to measure the temperature in various areas of the
system board. This information is used to regulate fans.
57
Page 58

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
HP MaxiLife Hardware
Monitoring Chip
MaxiLife is a hardware monitoring chip which is resident on the system
board. Its responsibility includes On/Off and reset control, status panel
management (Lock button, LEDs), hardware monitoring (temperature and
voltage), early diagnostics (CPU, memory, PLLs, boot start), run-time
diagnostics (CPU errors), fan speed regulation, and other miscellaneous
functions (such as special OK/FAIL symbols based on a smiling face).
The integrated microprocessor includes a Synopsys cell based on Dallas
2
“8052” equivalent, a 2 KB boot ROM, 256 bytes of data RAM, an I
C cell, an
Analog-to-Digital (ADC) with 5 entries, and an additional glue logic for
interrupt control, fan regulation, and a status panel control.
2
MaxiLife downloads its code in 96 milliseconds from an I
C serial EEPROM.
The total firmware (MaxiLife 8051-code, running in RAM) size is 14 KB. As
it exceeds the 2 KB program RAM space, a paging mechanism will swap
code as it is required, based on a 512 byte buffer. The first 2 KB pages of
firmware code is critical because it controls the initial power on/reset to
boot the system. This initial page is checked with a null-checksum test and
the presence of MaxiLife markers (located just below the 2 KB limit).
MaxiLife is not accessible in I/O space or memory space of the system
2
platform, but only through the SMBUS (which is a sub-set of the I
2
via the ICH. Its I
C cell may operate either in Slave or Master mode,
C bus),
switched by firmware, or automatically in the event of ‘Arbitration’ loss.
Test Sequence and
Error Messages
As a monitoring chip, MaxiLife reports critical errors at start-up, and is
therefore powered by Vstandby (3.3V) power. For MaxiLife to work, the PC
Workstation must be connected to a grounded outlet. This enables the PC
Workstation’s hardware monitoring chip to be active, even if the system has
been powered off.
Refer to “MaxiLife Test Sequence and Error Messages” on page 107 for
detailed information about the different test sequences and error messages
58
Page 59

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
MaxiLife Architecture The MaxiLife chip continuously monitors temperature and voltage sensors
located in critical regions on the system board. This chip receives data about
the various system components via a dedicated I
communications bus to control the integrated circuit boards.
LCD Status Panel
Serial EEPROM
2
C bus, which is a reliable
System Fans
Voltage
Sensors
I2C bus
ADM024
PCI Slot 5 for
Alert On Lan
support
Memory
Memory
Memory
Memory
Speed up/slow down
HP MaxiLife
Temperature
Sensors
NOTE MaxiLife is powered by VSTBY. This means that it is functional as soon as the
power cord is plugged in.
59
Page 60
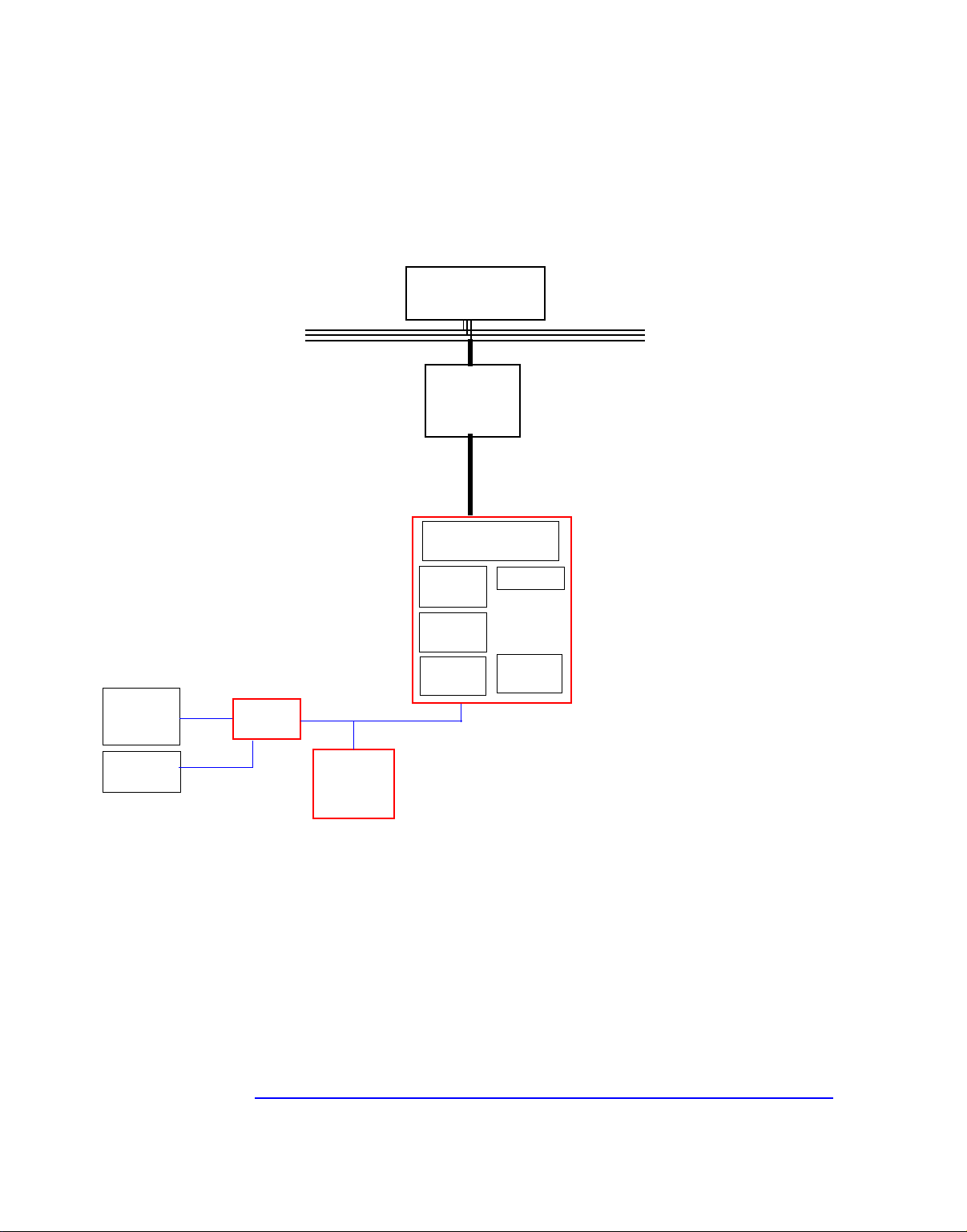
2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
Devices on the Low Pin Count Bus
The following devices are connected to the LPC bus.
Intel Pentium III
Processor
with L2 cache memory
I840 Memory
Controller Hub
(MCH)
HUB LINK 8 (233
MB/s data trans-
fer rate)
I/O Controller Hub
I/O Controller Hub
(ICH) 82801AA
(ICH) 82801AA
Host (also called FSB)
Bus 100/133 MHz,
Keyboard,
Mouse and
Floppy
Parallel and
Serial Ports
Super I/O
NS 87364
LPC / FWH Link
FirmWare
Hardware
(FWH) 82802
Controller
2 x USB
Controller
DMA
Controller
PCI BridgeIDE
SM Bus
Controller
60
Page 61

2 System Board
The Input/Output Controller Hub (82801AA)
The Super I/O Controller (NS 87364)
The Super I/O chip (NS 87364) provides the control for two FDD devices,
two serial ports, one bidirectional multi-mode parallel port and a keyboard
and mouse controller.
Device Index Data
Serial / Parallel
Communications Ports
Super I/O
The 9-pin serial ports (whose pin layouts are depicted on page 138) support
RS-232-C and are buffered by 16550A UARTs, with 16-Byte FIFOs. They can
be programmed as COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, or disabled.
The 25-pin parallel port (also depicted on page 139
compatible, supporting IEEE 1284. It can be programmed as LPT1, LPT2, or
disabled. It can operate in the four following modes:
❒ Standard mode (PC/XT, PC/AT, and PS/2 compatible).
❒ Bidirectional mode (PC/XT, PC/AT, and PS/2 compatible).
❒ Enhanced mode (enhanced parallel port, EPP, compatible).
❒ High speed mode (MS/HP extended capabilities port, ECP, compatible).
2Eh 2Fh
) is Centronics
FDC The integrated floppy disk controller (FDC) supports any combination of
two of the following: tape drives, 3.5-inch flexible disk drives, 5.25-inch
flexible disk drives. It is software and register-compatible with the 82077AA,
and 100% IBM-compatible. It has an A and B drive-swapping capability and
a non-burst DMA option.
Keyboard and Mouse
Controller
The computer has an 8042-based keyboard and mouse controller. The
connector pin layouts are shown on page 137
.
61
Page 62

2 System Board
FirmWare Hub (82802AB)
FirmWare Hub (82802AB)
The FWH (also known as flash memory) is connected to the LPC bus. It
contains 4 Mbit (512 kB) of flash memory.
The hardware features of the FWH include: a Random Number Generator
(RNG), five General Purpose Inputs (GPI), register-based block locking and
hardware-based locking. An integrated combination of logic features and
non-volatile memory enables better protection for the storage and update of
system code and data, adds flexibility through additional GPIs, and allows
for quicker introduction of security/manageability features.
The following table shows the available FWH features
Feature Feature
• Platform Compatibility:
❒ Enables security-enhanced platform infrastructure.
❒ Part of the Intel I840 chipset.
• FirmWare Hub Interface Mode:
❒ Five signal communication interface supporting x8 reads and
writes.
❒ Register-based read and write protection for each code/data
storage blocks.
❒ Five additional GPIs for system design and flexibility.
❒ A hardware RNG (Random Number Generator).
❒ Integrated CUI (Command User Interface) for requesting
access to locking, programming and erasing options. It also
handles requests for data residing in status, ID and block lock
registers.
❒ Operates with 33 MHz PCI clock and 3.3 V input/output.
• A/A Mux Interface/Mode, supporting:
❒ 11-pin multiplexed address and 8-pin data I/O interface.
❒ Fast on-board or out-of-system programming.
.
• Two Configurable Interfaces:
❒ FirmWare Hub interface for system operation.
❒ Address/Address Multiplexed (A/A Mux) interface.
• 4 Mbits of Flash Memory for system code/data non-volatile
storage:
❒ Symmetrically blocked, 64 Kbyte memory sections.
❒ Automated byte program and block erase through an
integrated WSM (Write State Machine).
• Power Supply Specifications:
❒ Vcc: 3.3 V +/- 0.3 V.
❒ Vpp: 3.3 V and 12 V for fast programming, 80 ns.
• Industry Standard Packages:
❒ 40L TSOP or 32L PLCC.
• Case Temperature Operating Range.
62
Page 63

2 System Board
FirmWare Hub (82802AB)
The FWH includes two hardware interfaces:
• FirmWare Hub interface.
• Address/Address Multiplexed (A/A Mux) interface.
The IC (Interface Configuration) pin on the FWH provides the control
between these interfaces. The interface mode needs to be selected prior to
power-up or before return from reset (RST# or INIT# low to high
transition).
The FWH interface works with the ICH during system operation, while the
A/A Mux interface is designed as a programming interface for component
pre-programming.
An internal CUI (Command User Interface) serves as the control center
between the FWH and A/A Mux interfaces, and internal operation of the
non-volatile memory. A valid command sequence written to the CUI initiates
device automation. An internal WSM (Write State Machine) automatically
executes the algorithms and timings necessary for block erase and program
operations.
63
Page 64

2 System Board
Host Bus
Host Bus
The Host bus of the Pentium III processors, also referred to as the FSB
(Front Side Bus), is implemented in the GTL (Gunning Transceiver Logic)+
technology. This technology features open-drain signal drivers that are
pulled-up to 1.5 V through resistors at bus extremities; these resistors also
act as bus terminators, and are integrated in the processor.
If only one processor is installed, a terminating board must be installed in
the second processor slot.
SECC-2 cartridge
Address (36)
Control
Data (64)
The supported operating frequencies of the GTL+ bus are 100 MHz or
133 MHz. The width of the data bus is 64 bits, while the width of the address
is 36 bits. Along with the operating frequencies, the processor voltage is set
automatically.
Intel Pentium III
Processor
with L2 cache memory
AGP 4x Bus
HUB
LINK 16
I840
Memory
Controller Hub
(MCH)
82840-QP
HUB LINK 8
I/O Controller
Hub
(ICH) 82801AA
Intel Pentium III
Processor
(optional second processor)
with L2 cache memory
Dual Rambus Bus
SECC-2 cartridge
Host (also called FSB)
Bus 100/133 MHz,
1 GB/sec data transfer rate)
Memory
Expansion Card
Connector
The control signals of the Host bus allow the implementation of a “split transaction” bus protocol. This allows the Pentium III processor to send its
request (for example, for the contents of a given memory address) and then
to release the bus, rather than waiting for the result, thereby allowing it to
64
Page 65

2 System Board
Host Bus
accept another request. The MCH, as target device, then requests the bus
again when it is ready to respond, and sends the requested data packet. Up
to eight transactions are allowed to be outstanding at any given time.
Intel Pentium III Processor
The Pentium III processor has several features that enhance performance:
• Dual Independent Bus architecture, (supporting level cache sizes of
i256 KB) plus a 64-bit system bus that enables multiple simultaneous
transactions (refer to “split -transaction” above).
• MMX2 technology, which gives higher performance for media,
communications and 3D applications.
• Dynamic execution to speed up software performance.
• Internet Streaming SIMD Extensions for enhanced floating point and 3D
application performance.
• Processor Serial Number is an electronic number incorporated in the
processor. If enabled, the Processor Serial Number can serve as a means
of identifying the system. By default, this option is set to Disabled in the
Setup program.
• Uses multiple low-power states, such as AutoHALT, Stop-Grant, Sleep and
Deep Sleep to conserve power during idle times.
The Pentium III processor is packaged in a self-contained Single Edge
Contact Cartridge (SECC-2) installed in a Slot 1 processor slot. The SECC-2
cartridge requires a 242-contact Slot 1 connector on the system board. It
includes a processor core chip and GTL+ termination resistors.
There are two Slot 1 processor slots, along with one VRM (Voltage
Regulation Module) socket. A single Pentium III processor for Slot 1 is
powered through an onboard voltage regulator.
Optional Second Processor
Single processor models can be upgraded to a dual processor system by
installing a second processor in the vacant slot. The second processor must
be a Pentium III processor for Slot 1 of the same speed as the first. The VRM
supplied with the processor accessory kit is installed in the vacant VRM slot.
The second processor is powered through the VRM.
65
Page 66

2 System Board
Host Bus
NOTE When upgrading a processor or installing a second processor, the processor
type and speed is automatically recognized by the BIOS. This means that no
particular switch settings are required.
Upgrading a single processor to a dual processor system on Windows NT
and Windows 2000 platforms is made easier with the HP DualExpress!
application which is included in the HP processor application kit.
Installing a second processor is only advantageous when the software can
make use of parallel activity. In particular, you need to be running a multithreaded operating system that supports multiprocessing (one that is SMP-
ready), such as Windows NT. The Windows NT operating system makes the
best use of the Pentium III 32-bit architecture (though other operating
systems will also show some benefit if 32-bit application programs are run).
The two processors must have the same speed.
Configuring for
Multi-Processing
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstations support Symmetric Multi-Processing
(SMP). When a second processor is added, it is automatically detected so
there is no specific configuration required.
The “mono-processing” mode has been implemented in order to support
operating systems that rely on the “legacy” interrupt controller 82C59 and
are not aware of I/O APIC controller operation. Refer to page 68
details.
for further
Processor Clock The 100/133 MHz Host Bus clock is provided by a PLL. The processor core
clock is derived from the Host Bus by applying a “fix ratio”.
Bus Frequencies There is a 14.318 MHz crystal oscillator on the system board. This frequency
is multiplied to 133 MHz by a phase-locked loop. This is further scaled by an
internal clock multiplier within the processor.
The bus frequency and the processor voltage are set automatically.
66
Page 67

2 System Board
Host Bus
Cache Memory
The cache memory is sealed within a single Pentium III package that
contains the processor L1 and L2 cache.
The L1 cache memory has a total capacity of 32KB (16 KB data, 16 KB
instructions). The L2 cache memory has a capacity of i256 KB, and is
composed of four-way set-associative static RAM. Data is stored in lines of
32 bytes (256 bits). Thus two consecutive 128-bit transfers with the main
memory are involved in each transaction.
TagRam and Burst-pipelined Synchronous Static RAM (BSRAM) memories
and are implemented on die. Transfer rates between the processor’s core
and L2 cache are at full processor core clock frequency and scale with the
processor core frequency. Both the TagRam and BSRAM receive clocked
data directly from the processor’s core.
The amount of cache memory is set by Intel at the time of manufacture, and
cannot be changed.
67
Page 68

2 System Board
Assigned Device Interrupts
Assigned Device Interrupts
Input/Output Controller Hub Interrupts
Device
AC’97 Audio Controller
USB Controller
AGP slot
PCI 32-bit slot #1
PCI 32-bit slot #2
PCI 32-bit slot #5 (LAN card)
PCI 64-bit Hub Interrupts
Device
Ultra-wide SCSI U160 Controller
PCI 64-bit slot #3
PCI 64-bit slot #4
Reference
Name
CS4280 4 (ICH) 5 21 — A — —
— — — — A — — —
J34 — 0 16 A B — —
J37 1 (ICH) 6 22 C D A B
J38 0 (ICH) 8 24 A B C D
J42 5 (ICH) 11 27 B C D A
Reference
Name
AIC-7892 2 (P64H) 9 25 — — — — — — — — A
J39 1 (P64H) 4 20 — — — — A B C D —
J40 0 (P64H) 7 23 A B C D — — — — —
REQ/
GNT
REQ/
GNT
IDSEL
ID
AD[xx]
IDSEL
ID
AD[xx]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Chip-set Interrupt Connection
INTA INTB INTC INTD
Interrupt Requests (IRQ)
Interrupt Controllers
The system has an Interrupt controller which is equivalent in function to
that of two 82C59 interrupt controllers. The following table shows how the
interrupts are connected to the APIC controller. The Interrupt Requests
(IRQ) are numbered sequentially, starting with the master controller, and
followed by the slave (both of 82C59 type).
68
Page 69

2 System Board
Assigned Device Interrupts
Although the Setup program can be used to change some of the settings, the
following address map is not completely BIOS dependent, but is determined
partly by the operating system. Note that some of the interrupts are
allocated dynamically.
APIC Controller Interrupt Signalling on
Interrupt Source
INTA - PCI slot 3 (64/66) P64H IRQ0 BT_INT APIC bus
INTB - PCI slot 3 (64/66) P64H IRQ1 BT_INT APIC bus
INTC - PCI slot 3 (64/66) P64H IRQ2 BT_INT APIC bus
INTD - PCI slot 3 (64/66) P64H IRQ3 BT_INT APIC bus
INTA - PCI slot 4 (64/66) P64H IRQ4 BT_INT APIC bus
INTB - PCI slot 4 (64/66) P64H IRQ5 BT_INT APIC bus
INTC - PCI slot 4 (64/66) P64H IRQ6 BT_INT APIC bus
INTD - PCI slot 4 (64/66) P64H IRQ7 BT_INT APIC bus
INTA - onboard SCSI controller P64H IRQ8 BT_INT APIC bus
AGP - INTA, PCI Slot 1 - INTC, PCI
Slot 2 - INTA, PCI Slot 5 - INTB
PCI Audio - INTA, AGP - INTB, PCI
Slot 1 - INTD, PCI Slot 2 - INTB,
PCI Slot 5 - INTC
BT_INT, PCI Slot 1 - INTA, PCI
Slot 2 - INTC, PCI Slot 5 - INTD
USB - INTA, PCI Slot 1 - INTB, PCI
Slot 2 - INTD, PCI Slot 5 - INTA
Device on Primary IDE Channel ICH IRQ14 INT APIC bus
Device on Secondary IDE Channel ICH IRQ15 INT APIC bus
Serial Interrupt from Super I/O ICH SERIRQ INT APIC bus
1.
In PIC mode, the Interrupts signaled to the P64H are chained as INTC to the ICH.
of
device
ICH INTA INT APIC bus
ICH INTB INT APIC bus
ICH INTC INT APIC bus
ICH INTD INT APIC bus
Input (PIC mode)
1
(APIC
modes)
There are three major interrupt modes available:
PIC mode: This mode uses only the “Legacy” interrupt controllers, so that
only one processor can be supported. Because this system has dual
processor capability, this mode is not chosen by default by Windows NT.
However, during Windows NT installation, you have the possibility of
selecting this mode.
69
Page 70

2 System Board
Assigned Device Interrupts
Virtual wire mode: This mode is implemented with APIC controllers in the
ICH and P64H and used during boot time. The virtual wire mode allows the
transition to the “symmetric I/O mode”. In the virtual wire mode, only one
processor executes instructions.
Symmetric I/O mode: This mode is implemented with APIC controllers in
the ICH and P64H, and allows for multiple processor operations.
NOTE In “PIC mode” and “virtual wire mode”, the PCI interrupts are routed to the
INT line. In the “symmetric I/O mode”, the PCI interrupts are routed to the
I/O APIC controllers and forwarded over an APIC bus to the processors.
PCI Interrupt Request Lines
PCI devices generate interrupt requests using up to four PCI interrupt
request lines (INTA#, INTB#, INTC#, and INTD#).
PCI interrupts can be shared; several devices can use the same interrupt.
However, optimal system performance is reached when minimizing the
sharing of interrupts. Refer to page 68
interrupts.
for a table of the PCI device
70
Page 71

3
Interface Cards
This chapter describes the graphics and network devices that are supplied
with the PC Workstation.
Graphics Cards
HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation models are supplied with a graphics
card. This graphics card is one of the following, depending on the PC
Workstation model:
• Matrox Millennium G250.
• Matrox Millennium G400.
• 3Dlabs Oxygen GVX1.
• ELSA Synergy™ II.
Matrox Millennium G250 Graphics Card
The Matrox Millennium G250 graphics card has a total of 8 MB of installed
video memory, which can be upgraded to a maximum of 16 MB.
The Matrox Millennium G250 on-board MGA G-250 processor
communicates directly with the Pentium II processor along the AGP 2X bus.
The controller can be characterized as follows:
• Supports full AGP 2X mode
• Graphics controller in 272-pin BGA (Ball Grid Array) package
• Integrated 64-bit, 250 MHz RAMDAC
• New, high-performance triangle setup engine to off-load system CPU
• Improved 3D drawing engine supports:
• Bilinear texture filtering
• Fogging.
• Alpha blending
• Anti-aliasing
• Specular highlighting
71
Page 72

3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
• High-performance VGA
• Integrated front-end and back-end scalers
• Fully Direct Draw, Direct 3D, Mini Client Drivers (MCD), and OpenGL
®
compliant
• 143 MHz SGRAM (LVTTL) memory configurations
(up to 16 MB maximum)
• Support for memory upgrade via 144-pin SO_DIMM memory modules
(SGRAM)
• Serial EEPROM video BIOS interface (32 KB)
• ITU-656 and VMI-like host port provides interface to low-cost decoders/
CODECs
• 12-bit digital RGB port (MAFC) provides support for video encoders and
panel link interfaces
The diagram below shows the Matrox Millennium G250 graphics card .
Available Video Resolutions
The number of colors supported is limited by the graphics device and the
video memory. The resolution/color/refresh-rate combination is limited by a
combination of the display driver, the graphics device, and the video
memory. If the resolution/refresh-rate combination is set higher than the
display can support, you risk damaging the display.
72
Page 73

3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
The tables below summarize the video resolutions and refresh rates that are
supported.
Resolution
2D/3D
8-bit
256 colors
16-bit
64k colors
24-bit
16.7 million
colors
16.7 million
640x480 200 Hz 200 Hz 200 Hz 200 Hz
800x600 180 Hz 180 Hz 180 Hz 180 Hz
1024x768 140 Hz 140 Hz 140 Hz 140 Hz
1152x864 120 Hz 120 Hz 120 Hz 120 Hz
1280x1024 100 Hz 100 Hz 100 Hz 90 Hz
1600x1200 90 Hz 90 Hz 85 Hz 65 Hz
1800x1440 80 Hz 80 Hz 75 Hz 650 Hz
1920x1440 76 Hz 76 Hz 70 Hz -
2048x1536 70 Hz 70 Hz 65 Hz -
Maximum Refresh Rates
1
Resolution 8 bpp / 16 bpp 24 bpp 32 bpp
640x480 200 Hz 200 Hz 200 Hz
32-bit
colors
800x600 180 Hz 180 Hz 180 Hz
1024x768 140 Hz 140 Hz 140 Hz
1152x864 120Hz 120Hz 120Hz
1280x1024 100 Hz 100 Hz 90 Hz
1600x1200 90 Hz 85 Hz 65 Hz
1920x1080 80Hz 80Hz 60Hz
1920x1200 76 Hz 70 Hz -
1800x1440 70 Hz
1.
Your display may not support the maximum refresh rates shown here. Refer to the User’s Guide
2
65 Hz -
supplied with your display for details of the refresh rates supported by your display.
2.
Limitation due to 250 MHz RAMDAC.
73
Page 74

3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
Matrox Millennium G400 Graphics Card
The Matrox Millennium G400 Dual AGP 2X/4X graphics card has 16MB of
installed video memory (non-upgradeable), and can be characterized as
follows:
• Powered by the Matrox MGA-G400 chip
• Full AGP 2X/AGP 4X support (up to 1GB/s bandwidth)
• Integrated 300MHz RAMDAC with Ultra Sharp technology for highly
saturated and separated colors
• Matrox DualHead Display technology with PowerDesk desktop manager:
• Easy multiple resolutions support
• Simple dialog box
• Effortless multiple-window management
• DDC2B support for Plug & Play detection of monitor
• 256-bit dual bus architecture; true 128-bit external bus to video memory
• Vibrant color quality - true 32-bit ARGB
• Supports 32-bit Z buffering for exceptional rendering precision
• 32-bit internal precision specially enhanced for multi-texturing using
32-bit text sources
• 16/10 monitor support
• Support for true 32-bit color (16.7 million colors) at resolutions of up to
2048 x 1536
• Bilinear, trilinear, and anisotropic filtering
• Floating-point 3D setup engine
• DirectX 6 and OpenGL
®
compliant
74
Page 75

The diagram below shows the Matrox Millennium G400 graphics card .
Port 1
Port 2
NOTE If only one monitor is used, then Port 1 must be used.
In the case where a second monitor is installed, it is detected by the driver
during the operating system boot (not after).
3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
If only one monitor is detected, then only the mono head settings will be
available in the Driver Configuration screens.
Available Video Resolutions
The number of colors supported is limited by the graphics device and the
video memory. The resolution/color/refresh-rate combination is limited by a
combination of the display driver, the graphics device, and the video
memory. If the resolution/refresh-rate combination is set higher than the
display can support, you risk damaging the display.
The tables below summarize the 2D and 3D video resolutions that are
supported, and the refresh rates.
Color palette
8-bit 2048 x 1536
15- or 16-bit 2048 x 1536 2048 x 1536 1880 x 1440 1600 x 1200
124-bit 2048 x 1536 - - -
32-bit 2048 x 1536 1600 x 1200 1280 x 1024 1280 x 1024
Max. 2D display
area
Max. 3D display
area
Double-
buffered + 16-
bit Z
Double-
buffered + 16-
bit Z
75
Page 76

3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
Maximum Refresh Rates
Resolution (4:3 aspect ratio)
640x480 200 Hz 200 Hz
800x600 200Hz 180 Hz
1024x768 160 Hz 115 Hz
1152x864 140 Hz 95 Hz
1280x1024 120 Hz 75 Hz
1600x1200 100 Hz 43 Hz
1600x1280 90 Hz 43 Hz
1800x1440 80Hz -
1920x1440 75 Hz -
2048x1536 70Hz -
Resolution (16:9 aspect ratio)
1600x1024 120 Hz 43
Main Display
(8-/16-/24-/32-bit)
Main Display
(8-/16-/24-/32-bit)
Second Display
Second Display
(16-/32-bit)
(16-/32-bit)
76
1920x1035 100 Hz -
1920x1080 100 Hz -
1920x1200 90 Hz -
Page 77

3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
3Dlabs Oxygen GVX1
There is a total of 32 MB of video Synchronous Graphics RAM (SGRAM)
memory installed on the graphics card .
Features
• OpenGL-based geometry and lighting acceleration entirely in the
hardware, freeing the processor for other applications
• OpenGL specific extensions that double the performance under AutoCad
• Innovative virtual textures technology, using on-board graphics memory
to cache large textures
• Multi-screen support (with additional PCI cards)
• Supports 16: 10 wide-format monitors
• PowerThreads™ SSE OpenGL drivers fully tested with all leading
professional graphics applications
Specifications
• Full AGP 1X support
• Professional 3D rendering features that include:
• Perspectively correct bilinear and trilinear filtering
• Perspectively correct per-pixel MIP mapping
• Single pass dual bilinear mip-mapped textures
• Flat and Gouraud shading
• Source and destination Alpha blending for transparency
• High-quality anti-aliasing
• Fog and depth-cueing
• Overlay and stencil buffers
• 32-bit Z-buffering
• GID clipping
• GLINT R3 Rasterization processor for:
• Virtual texture memory management unit
• Up to 256 MB virtual texture address space
• Integrated 300MHz RAMDAC
• High-speed 128-bit memory interface
• 2D/3D raster engine
• Integrated SVGA controller
77
Page 78

3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
The diagram below shows the 3Dlabs Oxygen GVX1 graphics card .
Video Memory
The video memory, also known as SGRAM, is a local block of RAM for
holding major data structures: Frame Buffer (double buffer), Z-Buffer and
T-Buffer (Texture Buffer). The Frame Buffer holds one frame steady on the
screen while the next one is being processed, while the Z-buffer stores
depth information for each pixel.
Available Video Resolutions
The number of colors supported is limited by the graphics device and the
video memory. The resolution/color/refresh-rate combination is limited by a
combination of the display driver, the graphics device, and the video
memory. If the resolution/refresh-rate combination is set higher than the
display can support, you risk damaging the display. The table below
summarizes the 3D video resolutions and refresh rates that are supported.
Display resolution Color depth Refresh rates
640 x 480 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
800 x 600 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1024 x 768 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1152 x 864 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1280 x 960 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1280 x 1024 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1600 x 1200 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1920 x 1080 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1920 x 1200 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 76 Hz
2048 x 1536 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 60 Hz
78
Page 79

3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
ELSA Synergy II Graphics Card
The ELSA Synergy™ II graphics card has 32 MB of Synchronous Graphics
RAM (SGRAM) installed video memory.
Features
• Fastest 128-bit 2D performance
• 3D hardware texture acceleration
• Resolution support up to 1920 x 1200 at 96 Hz
• Multi-screen support (up to 4 with additional PCI cards)
• Supports 16: 10 wide-format monitors
• Software tools: ELSA POWERdraft, ELSA MAXtreme, ELSA Views3D
• OpenGL
®
extensions for AutoCAD 2000 that doubles performance
• PowerThreads™ SSE OpenGL drivers fully tested with all leading
professional graphics applications
Specifications
• Full AGP 2X/AGP 4X support
• RIVA TNT2 (NVIDIA) graphics processors
• VESA 3 (flash ROM)
• Integrated 300 MHz RAMDAC
• 3D standards: Hardware accelerated OpenGL
• Standards: VESA DPMS, DDC2B, Plug & Play
The diagram below shows the ELSA Synergy
®
, DirectX3, DirectX5/6
II graphics card .
79
Page 80

3 Interface Cards
Graphics Cards
Video Memory
The video memory, also known as SGRAM, is a local block of RAM for
holding major data structures: Frame Buffer (double buffer), Z-Buffer and
T-Buffer (Texture Buffer). The Frame Buffer holds one frame steady on the
screen while the next one is being processed, while the Z-buffer stores
depth information for each pixel.
Available Video Resolutions
The number of colors supported is limited by the graphics device and the
video memory. The resolution/color/refresh-rate combination is limited by a
combination of the display driver, the graphics device, and the video
memory. If the resolution/refresh-rate combination is set higher than the
display can support, you risk damaging the display.
The table below summarizes the 3D video resolutions and refresh rates that
are supported.
Display resolution Color depth Refresh rates
640 x 480 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 200, 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
800 x 600 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 200, 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1024 x 768 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 200, 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1152 x 864 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 200, 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1280 x 960 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1280 x 1024 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1600 x 1200 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1920 x 1080 8-bit, 16-bit, True color 100, 85, 75, 60 Hz
1920 x 1200 8-bit, 16-bit, True color up to 96 Hz
NOTE 200 Hz accepted if supported by the monitor.
80
Page 81

3 Interface Cards
Network Cards
Network Cards
Most HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation models are supplied with an
HP 10/100 TX LAN card.
A description and features of other supported LAN cards are also mentioned
in this section.
HP 10/100 TX PCI LAN Interface
The 10/100 TX LAN Interface is a 32-bit PCI 2.2 card that supports 10 Mbits
per second (10 BaseT) and 100 Mbits per second (100 TX) transfer speeds,
and both half and full duplex operation.
81
Page 82

3 Interface Cards
Network Cards
HP 10/100 TX PCI LAN Interface Features
Feature: Description:
RJ45 Connector
BootROM
Remote Power On (RPO)
Remote Wake Up (RWU)
Power Management
Manageability
Diagnostic
Connection to Ethernet 10/100 TX autonegotiation
Protocols:
• PxE 2.0,
• On-board socket support up to 128 Kb.
Full remote power on using Magic Packet for Microsoft Windows 95,
Windows 98, Windows NT4 in APM mode.
Enable and Wake Up from Suspend state using Magic Packet and Pattern
Matching for Microsoft Win98SE and Win2000 in ACPI mode.
This feature enables a host computer to remotely (over the network) power
on computers and wake computers up from energy-saving Sleep mode. For
these features to work, use the Setup program to configure the BIOS.
• OnNow 1.0,
• Advanced Power Management 1.2,
• PCI Power Management 1.1,
• WfM 2.0 compliant, ACPI.
• Desktop Management Interface (DMI) 2.0 Dynamic driver,
• DMI 2.0 SNMP mapper,
• PXE 2.0 Flashable BootROM (optional on socket).
• Mac address DOS report tool,
• User Diag for DOS.
HP 10/100 TX PCI LAN Interface LED Descriptions
LED Description Flashing Steady Off
Link integrity Reversed polarity Good 10 Base-T
10 LNK
100 LNK
ACT
82
Link integrity Reversed polarity Good 100 TX
Yellow:
Port traffic for
Network traffic
present
either speed
connection between
NIC and hub.
connection between
NIC and hub.
Heavy network
traffic
No connection
between NIC and
hub
No connection
between NIC and
hub
No traffic
Page 83

3 Interface Cards
Network Cards
Supported LAN Cards
The following LAN cards are supported on the HP Kayak XU800 PC
Workstation.
3COM NIC (Network Interconnect) LAN Card
3COM NIC LAN Card Features
Feature Description
Interface
LED
Labels
Power Management
Manageability
Diagnostic
Drivers
Boot ROM
32-bit 10/100 BT full duplex RJ LAN Port.
Three LEDs:
• activity,
• 10 MB/s speed,
• 100 MB/s speed.
PCI 2.2 Specification, PC 99, Intel WfM 2.0.
1
• RPO and RWU for APM Windows 95 and Windows 98,
• RWU for ACPI Windows 98 and Windows 2000,
• RPO for Windows NT 4,
• OnNow 1.0, APM 1.2,
• PCI power management. 1.1,
• WOL, PCI VccAux 3.3 V.
DMI 2.0 Component Code.
• Mac address DOS report tool,
• User Diag for DOS, Windows NT 4, Windows 95 and Windows 98.
Major OSes, Minor OSes.
Multiboot BootROM (BIOS or socket).
Remote Wake Up
(RWU)
This feature enables a host computer to remotely (over the network) power
on computers and wake computers up from energy-saving Sleep mode. For
these features to work, use the Setup program to configure the BIOS.
83
Page 84

3 Interface Cards
Network Cards
3COM LAN Card LED Descriptions
LED Description Flashing Steady Off
10 LNK
100 LNK
ACT
GREEN:
Link integrity
GREEN:
Link integrity
Yellow:
Port traffic for
either speed
Reversed polarity Good 10 Base-T
connection between
NIC and hub.
Reversed polarity Good 100 TX
connection between
NIC and hub.
Network traffic
present
Heavy network
traffic
No connection
between NIC and
hub
No connection
between NIC and
hub
No traffic
84
Page 85
INTEL NIC (Network Interconnect) LAN Card
INTEL NIC LAN Card Features
Feature Description
IEEE802.3 100 Base-TX,
Interface
LED
Labels
IEEE802.3 10 Base-T,
32-bit 10/100 BT full duplex RJ LAN Port.
Two LEDs:
• one for act/lnk (activity and link),
• one for 10 MB operation (on = 100 MB, off = 10MB).
PCI 2.2 Specification, PC 99.
3 Interface Cards
Network Cards
Power Management
Manageability
Diagnostic
Drivers
Boot ROM
Remote Wake Up
(RWU)
• Wfm 2.0 compliant,
• RPO and RWU for APM Windows 95 and Windows 98,
• OnNow 1.0, APM 1.2,
• PCI power management 1.1,
• VccAux s3.3 V support via PCI bus 2.2,
• VccAux 5 Vsupport via 3-pin WOL.
DMI 2.0 and DMI 2.0 SNMP mapper.
• Windows and DOS based,
• Mac address DOS report tool,
• User Diag for DOS, Windows NT 4, Windows 95 and Windows 98.
Major OSes, Minor OSes.
Onboard flash ROM.
This feature enables a host computer to remotely (over the network) power
on computers and wake computers up from energy-saving Sleep mode. For
these features to work, use the Setup program to configure the BIOS.
INTEL NIC LAN Card LED Descriptions
LED On Flashing Off
ACT/LNK
Adapter and hub are
receiving power. Cable
connection is good.
Receiving or sending
packets
Adapter and hub are not
receiving power. Cable
connection could be faulty
or there is a driver
configuration problem.
100 TX
Operating at 100 Mbps N/A Operating at 10 Mbps
85
Page 86

3 Interface Cards
Network Cards
86
Page 87

4
Mass Storage Devices
This chapter describes the mass storage devices that are supplied with the
PC Workstation. Refer to the diagram on page 13
different mass storage devices in the PC Workstation. This chapter also
summarizes the pin connections on internal and external connectors.
HP product numbers and replacement part numbers for mass storage
devices are listed in the Service Handbook Chapter, which can be accessed
from the HP World Wide Web site at the following address:
http://www.hp.com/go/kayaksupport.
Flexible Disk Drives
A 3.5-inch, 1.44 MB flexible disk drive is supplied in the front-access shelf.
for the position of the
Hard Disk Drives
The following table lists the 3.5-inch (1-inch high) hard disk drives (which
are subject to change) that may be supplied (type and quantity depends on
model) on internal shelves, connected to the SCSI or IDE controller.
Cheetah 18LP
SCSI Seagate
(10 krpm)
Capacity 9.1 GB and 18 GB 9.1 GB and 18 GB 15 GB
Interface Ultra2 Wide SCSI Ultra160 UltraIDE ATA/66
External peak transfer rate 80 MB/s 160 MB/s 66 MB/s
Average seek time (read) 5.4 ms 5.4 ms 7.6 ms
Internal formatted transfer rate (MB/s) 29.5 max. 20 to 29 43
Number of discs/heads 9.1 GB: 3/6
18 GB: 6/12
Buffer size 1 MByte 2 MBytes 512 KBytes
Atlas (Tornado)
SCSI Quantum
(10 krpm)
9.1 GB: 3/6
18 GB: 6/12
Barracuda IDE
Seagate
(7.2 krpm)
15 GB: 2/4
87
Page 88

4 Mass Storage Devices
CD-ROM Drives
IDE 48X CD-ROM Drive Some models
front-access shelf ATAPI, supporting ATAPI commands and with audio
playback capability. It can play any standard CD-Audio disks, in addition to
CD-ROM disks, conforming to optical and mechanical standards as specified
in the Red, Yellow, Green and Orange Book.
Some of the 48X IDE CD-ROM features include:
• Application Disk type (confirmed by Red, Yellow, Green, Orange Book)
• CD-ROM data disk (Mode 1 and Mode 2)
• Photo-CD Multisession
• CD Audio disk
• Mixed mode CD-ROM disk (data and audio)
• CD-ROM XA, CD-I, CD-Extra, CD-R, CD-RW
Data capacity 650 MB
Data transfer rate Sustained transfer rate (1X=150 KB/s); Outerside: 7,200 KB/s
Buffer memory size 128 kbytes
Access time Average Stroke (1 / 3) 110 ms
Rotational speed 2,048 bytes (Mode-1)
Interface ATAPI
Power requirements 5V, 1.2A
1
have a 48X IDE CD-ROM drive supplied in a 5.25-inch
Description
Burst transfer rate:
PIO mode 4 - 16.6 Mbytes/s maximum
Single Word DMA Mode 2 - 8.3 Mbytes/s maximum
Multi Word DMA Mode 2 - 16.6 Mbytes/s maximum
Full Stroke 180 ms
2,336 bytes (Mode-2)
12V, 0.8A
1. Refer to the HP Kayak PC Workstations Service Handbook to find out which
models are installed with the
48X IDE CD-ROM.
88
Page 89

4 Mass Storage Devices
8X Video IDE DVD-ROM
Drive
Some models1 have a DVD-ROM (Read Only) drive. It can play any standard
CD-Audio disks, in addition to CD-ROM disks, conforming to optical and
mechanical standards as specified in the Red, Yellow, Orange and Green
Books.
Description
Data capacity 650 MB
Data transfer rate Sustained transfer rate (1X=150 KB/s); Outerside: 7,200 KB/s
Burst transfer rate:
PIO mode 4 - 16.6 Mbytes/s maximum
Single Word DMA Mode 2 - 8.3 Mbytes/s maximum
Multi Word DMA Mode 2 - 16.6 Mbytes/s maximum
Buffer memory size 128 kbytes
Access time Average Stroke (1 / 3) 110 ms
Full Stroke 180 ms
Rotational speed 2,048 bytes (Mode-1)
2,336 bytes (Mode-2)
Interface ATAPI
Power requirements 5V, 1.2A
12V, 0.8A
1. Refer to the HP Kayak PC Workstations Service Handbook to find out which
models are installed with the
DVD-ROM drive.
89
Page 90

4 Mass Storage Devices
4X IDE CD-Writer Plus
Drive
Some models1 have a CD-RW (ReWritable) drive supplied in a 5.25-inch
front-access shelf ATAPI, supporting ATAPI commands and with audio
playback capability. It can play any standard CD-Audio disks, in addition to
CD-ROM disks, and can record both write-once (CD-R) and CD-RW optical
media. It conforms to optical and mechanical standards as specified in the
Red, Yellow, Orange and Green Books.
Description
Data capacity 650 MB or up to 74 minutes of audio per disc
547MB in CD-UDF data format
Performance Seek time (1/3 stroke: <150 ms (CD-ROM))
Data transfer rate:
Read: Up to 24X (1X=150 KB/s)
Write: 4X (CD-R); 2X (CD-RW)
Minimum burst transfer rate 2.5Mbytes/sec.
Spin-up time (2X) 2 seconds max. (from spin down state until disc ready)
Initialization time (2X) 5 seconds max. (from new disc inserted until disc ready)
HP fast format time (CD-RW) 5 minutes max.
Disc finalization time (2X 2 minutes typical
Corrected error rate Audio, Mode 2, Mode 2 Form 2: < 1 frame in 109 bits read
12
Mode 1, Mode 2 Form 1: < 1 frame in 10
Buffering 1MByte (>6 sec at 1X speed). If buffered data drops to less than one
sector, the recording stops.
Write methods - Track at once
- Disc at once
- Incremental (packet)
- Multisession
Write verification Automatic Power Control to dynamically adjust laser writer power
Format and EEC standard Red, Yellow, Orange, Green books
MTBF 150,000 hours
Interface ATAPI
bits read
1. Refer to the HP Kayak PC Workstations Service Handbook to find out which
models are installed with the
90
HP CD-RW drive.
Page 91

5
HP BIOS
The Setup program and BIOS are summarized in the two sections of this
chapter. The POST routines are described in the next chapter.
®
The BIOS is based on an AMIBIOS
4 M/bits flash parts, PCI 2.2 Specification, and RIMM or DIMM memory
modules. Added to this, a New BIOS Architecture (NBA) has been
implemented. The main principle of the NBA is that HP features are
independent modules and run at defined moments in the boot process. They
are installed as hooks, either in:
• Source code form, for small tasks, or before memory is available.
• Binary. As .COM files, for larger tasks once memory is available.
They both communicate with the BIOS through CMOS and memory tables
providing information to the operating system through SMBIOS tables.
So, what are hooks? Hooks are architected points in the BIOS where specific
code can be run. HP code is integrated, as mentioned above, in either
source/object files, or as separate binaries.
core, which includes support for
HP/NBA BIOS Summary
The System ROM contains the POST (Power-On-Self-Test) routines and the
BIOS: the System BIOS, video BIOS, and low option ROM. This chapter,
together with the following one, give an overview of the following aspects:
• Menu-driven Setup with context-sensitive help, described next in this
chapter.
• The address space, with details of the interrupts used, described at the
end of this chapter.
• The Power-On-Self-Test or POST, which is the sequence of tests the
computer performs to ensure that the system is functioning correctly,
described in the next chapter.
The system BIOS is identified by the version number qXX.YM.mm, where:
• q is an optional letter indicating non-production status (removed at
release).
• XX is a two-letter code indicating the system (IA).
• Y is a one-digit code indicating the HP entity.
• M is the major BIOS version.
• mm is the minor BIOS version.
91
Page 92

5 HP BIOS
HP/NBA BIOS Summary
An example of a released version would look similar to the following
example: IA.11.02.
The procedure for updating the System ROM firmware is described on
page 95
.
Using the HP Setup Program
To run the Setup program, press while the initial “Kayak” logo is
displayed immediately after restarting the PC.
Alternatively, press to view the summary configuration screen. The
summary screen will remain visible until a key is pressed.
The band along the top of the Setup screen offers the following menus:
Main, Advanced, Security, Boot, Power and Exit. These are selected using
the left and right arrow keys.
Main Menu
The Main Menu presents a list of fields, for example, “PnP Operating
System” (selects whether the BIOS or Plug and Play operating system
configures Plug and Play devices); “Reset Configuration Data”, “System
Time”, “System Date”, “Key Click”, “Key auto-repeat speed” “Delay before
auto-repeat” and Numlock at Power-on”. By default the “Reset
Configuration Data” item is set to “No”. Selecting “Yes”, will clear the system
configuration data.
Advanced Menu
The Advanced Menu does not have the same structure as the Main Menu
and Power Menu. Instead of presenting a list of fields, it offers a list of
sub-menus. The Advanced Menu contains the following sub-menus:
• Processors, Memory and Cache. Configures processor, CPU speed,
Processor Serial Number, memory controller and cache operations (error
correction, shadowing and caching).
• Floppy Disk Drives. Enables or disables the on-board floppy disk
controller.
• IDE Devices. Configures IDE devices. Setting of IDE Primary and Master
slave devices, and IDE Secondary Master slave devices. To use both these
channels, the Integrated BUS IDE adapter is set to
Both Enabled.
92
Page 93

5 HP BIOS
HP/NBA BIOS Summary
• Integrated USB Interface. Enable or disable the integrated USB
(Universal Serial Bus) interface. Setting this option to
Auto lets the BIOS
or PnP operating system configure the device. However, disabling this option leaves the devices disabled by the BIOS, but a PnP operating system
can still configure it.
• Integrated Audio Interface. Enables or disables the audio interface. Set-
ting this option to
Auto lets the BIOS or PnP operating system configure
the device. Disabling this option frees resources used by the device.
• Integrated I/O Ports. Enables or disables the on-board parallel and
serial ports at the specified address.
• Integrated SCSI. Enables or disables the Option ROM scan, Bus Master
and Bus Latency Timer.
Security
Sub-menus are presented for changing the characteristics and values of the
System Administrator Password, User Password, Power-on Password, boot
device security and Hardware Protection. The Security Menu contains the
following sub-menus:
• Administrator Password. This password prevents unauthorized access
to the computer’s configuration. It can also be used to start the computer
when power-on password is set to
• User Password. This password can only be set when an administrator
Auto.
password has been set. The User Password prevents unauthorized use of
the computer and is used to start the computer when power-on password
is set to
• Power-on Password. If enabled, a password will be requested on boot.
• Start from Floppy, Start from CD-ROM and Start from HDD. These de-
Auto.
vices can be disabled to prevent unauthorized use to start the computer.
• Hardware Protection. The following devices can have their accesses
unlocked/locked: floppy disk drives and hard disk boot sector.
93
Page 94

5 HP BIOS
HP/NBA BIOS Summary
Boot Menu
The QuickBoot Mode option allows the system to skip certain tests while
booting. This decreases the time needed to boot the system
menu, you can also display the option ROM messages. Enabling this option
is recommended when installing an accessory card. It can be disabled when
accessory card installation has been completed.
If both AGP and PCI video cards are installed, use the setting to select which
will be used as a boot display device. If only one video card is installed, the
setting is not used.
Select the order of the devices from which you want the BIOS to attempt to
boot the operating system. During POST, if the BIOS is unsuccessful at
booting from one device, it will then try the next one on the Boot Device
Priority list until an operating system is found.
. From this
Power Menu
This menu allows you to set the standby delay and suspend delay. Standby
mode slows down the processor, while the suspend mode saves a maximum
of energy. Both these options are only available with Windows 95. For other
operating systems, Windows 98 and Windows 2000, use the control panel for
similar options
Modem ring enables or disables the system to return to full speed when an
IRQ is generated. Network interface enables or disables the system to return
to full speed when a specific command is received by the network interface.
94
Page 95

5 HP BIOS
Updating the System BIOS
Updating the System BIOS
The System BIOS can be updated with the latest BIOS firmware. This can be
downloaded from HP’s World Wide Web site:
http://www.hp.com/go/kayaksupport
then select HP Kayak XU800 PC Workstation.
Instructions on updating the BIOS are supplied with the downloaded BIOS
files and a BIOS flash utility (flash.txt).
The BIOS update not only flashes the BIOS, but also updates MaxiLife. How
the System BIOS flash is carried out is shown below.
Boot from
floppy disk
Flash
BIOS
PC Workstation
powers off
automatically
PC Workstation
reboots
automatically
Flash
MaxiLife
PC Workstation
powers off
automatically
PC Workstation
reboots
Do not switch off the computer until the system BIOS update procedure has
completed, successfully or not, otherwise irrecoverable damage to the ROM
may be caused. While updating the flash ROM, the power supply switch and
the reset button are disabled to prevent accidental interruption of the flash
programming process.
Restoring BIOS Default Settings
Suspected hardware errors may be caused by BIOS and configuration
issues. If the BIOS settings are suspected to be wrong, perform the following
steps to restore the BIOS to its default setting:
1 Press while the initial “Kayak” logo is displayed immediately after re-
starting the PC Workstation to access the Setup program.
2 Press to load the default settings from the Setup program.
3 Set the “Reset Configuration Data” to Yes in the Main menu.
It is recommended that before you make any modifications to the BIOS
you take note of the system setup.
95
Page 96

5 HP BIOS
Clearing the CMOS
Clearing the CMOS
1 Turn off the PC Workstation, disconnect the power cord and data cables,
then remove the cover.
2 Set the system board switch 4 to the DOWN position to clear the CMOS
memory.
3 Replace the cover, and only reconnect the power cord.
4 Reboot the PC Workstation. A message similar to the following will be dis-
played:
“Configuration has been cleared.
You can now:
Switch off the PC Workstation and remove the cover.
Reset the “Clear Configuration” switch to OFF (Up).
Replace the cover.
Switch on the PC Workstation and allow it to startup.
To modify the default configuration information:
press [F2] when prompted during self-test (POST), to enter
Setup.”
5 Turn off the PC Workstation, disconnect the power cord, and remove the
cover.
6 Set the system board switch 4 to the UP position to retain the
configuration.
7 Replace the cover, and reconnect the power cord and data cables.
8 Switch on the PC Workstation. Run the Setup program by pressing .
Then press . The CMOS default values will be automatically downloaded and saved.
9 Press to save the configuration and exit from the Setup program.
96
Page 97

5 HP BIOS
Clearing Passwords
Clearing Passwords
To clear the Administrator and User password (for example, Administrator
password has been forgotten), perform the following steps:
1 Turn off the PC Workstation, disconnect the power cord and data cables,
then remove the cover.
2 Set the system board switch 3 to the UP position to clear passwords.
3 Replace the cover, and only reconnect the power cord.
4 Reboot the PC Workstation. A message similar to the following will be
displayed:
“Passwords have been cleared.
You can now:
Switch off the PC Workstation and remove the cover.
Reset the “Clear Password” switch to ON (Down).
Replace the cover.
Switch on the PC Workstation and allow it to startup.
To modify the password setting:
press [F2] when prompted during self-test (POST),
to enter Setup.”
5 Turn off the PC Workstation, disconnect the power cord, and remove the
cover.
6 Set the system board switch 3 to the DOWN position to retain the
configuration.
7 Replace the cover, and reconnect the power cord and data cables.
8 Switch on the PC Workstation. Run the Setup program by pressing .
Then select the Security menu from the band along the top of the Setup
screen.
9 Press to save the configuration and exit from the Setup program.
97
Page 98

5 HP BIOS
Recovering the BIOS (Crisis Mode)
Recovering the BIOS (Crisis Mode)
If for some reason the BIOS is corrupted and the standard flash cannot be
used, use the BIOS Recovery Mode (exceptional BIOS recovery operation)
to restore the BIOS.
The following recovery operation is also documented in the flash.txt file
which is supplied with the downloaded BIOS files.
To restore the BIOS:
1 Copy the BIOS files on to the floppy disk.
2 Rename the file AI11xx.rom to
3 Shut down the PC Workstation.
4 Power off the PC Workstation and remove the power cord and cables.
5 Remove the cover.
6 Set switch 1
to the DOWN position.
7 Insert the floppy disk into the floppy disk drive.
8 Reconnect the power cord and switch on the PC Workstation.
9 The PC Workstation boots from the floppy disk, then flashes the BIOS.
However, it should be noted that during the flash process, the screen
remains blank. MaxiLife will display a message on the LCD panel
“RECOVERY MODE”.
10 The recovery process is finished when there are four beeps.
11 Power off the PC Workstation. Remove the floppy disk from the drive.
Remove the power cord.
12 Set switch 1
back to the UP position.
13 Replace the cover, reconnect the power cord, then reboot the PC
Workstation.
amiboot.rom.
98
Page 99

5 HP BIOS
Adaptec SCSISelect Configuration Utility
Adaptec SCSISelect Configuration Utility
The AIC-7892 BIOS includes the SCSISelect configuration utility, which
allows you to view and change host adapter settings. SCSISelect also lists
the SCSI IDs of devices on the host adapter, formats SCSI disk drives, and
checks drives for defects.
Default Settings
The following tables show the default configuration settings that can be
changed. The first table shows the global settings which impact the host
adapter; the second table shows the boot device options which allow you to
specify the boot device; the third table shows the different advance
configuration options; and the fourth table shows the device settings which
apply to individual devices.
SCSI BUS Interface Options
Host Adapter and SCSI Parity
Checking Settings
Host Adapter SCSI ID 7 Each device on the SCSI bus, including the adapter,
SCSI Parity Checking Enabled Each adapter verifies the accuracy of data transfer on
Boot Target ID and Boot LUN
Number Settings
Boot Target ID 0 To specify a different boot device, choose a SCSI ID
Boot LUN Number 0
Options Default
Reset SCSI Bus at IC Initialization Enabled BIOS resets the SCSI at POST time (scans the bus for
Default
Settings
Boot Device Options
Default
Settings
Advanced Configuration Options
Settings
Comments
must have a unique SCSI ID. Allowable IDs are 0 - 15.
the SCSI bus.
Comments
0 - 15. If the boot device has multiple logical units, you
must specify the boot LUN, which can be 0 - 7.
Comments
SCSI devices).
99
Page 100

5 HP BIOS
Adaptec SCSISelect Configuration Utility
Advanced Configuration Options
Options Default
Comments
Settings
Extended BIOS Translation for DOS
drives > 1 GByte
Enabled Includes an extended translation scheme that supports
disk drives of more than 1 GByte.
Verbose/Silent Mode Verbose Displays messages on the screen at POST.
Host Adapter BIOS Enabled Controls the state of the BIOS at POST.
Support for Removable Disks Under
BIOS as Fixed Disks
Disabled No removable media drives running under DOS are
treated as hard disk drives. Driver software is required
because the drives are not controlled by the BIOS.
Display <F6> message during
BIOS Initialization
Enabled Displays
Press F6 for SCSISelect(TM)
Utility!
BIOS Support for Bootable CD-ROM Enabled Enables booting from a CD-ROM.
BIOS Support for Int 13h Extensions Enabled Host adapter BIOS supports Int 13h extensions.
Domain Validation Disabled Downgrades the performance while maintaining the
integrity of data transmission
SCSI Device Configuration Options
SCSI Device Options Default
Comments
Settings
SyncTransfer Rate 160 Determines the synchronous data transfer rate that
the host adapter will negotiate with the device.
Enable Disconnection Yes Determines whether the host adapter allows a SCSI
device to disconnect from the SCSI bus (also referred
to as Disconnect/Reconnect).
Initiate Wide Negotiation
(16-bit adapters only)
Yes Allows the adapter to initiate wide negotiation with a
16-bit SCSI device.
Send Start unit Command Yes Determines whether the host adapter sends the Start
Unit command to the SCSI bus.
Enable Write Back Cache N/C Allows the BIOS to program the state of the write
back cache in the hard disk drive.
BIOS Multiple Lun Support No Allows the BIOS to support multiple logical units.
Include in BIOS Scan Yes Determines whether the host adapter BIOS supports
devices attached to the SCSI bus without the need for
device driver software.
100
 Loading...
Loading...