HP Vectra XM5 4, Vectra XM 5, Vectra XM 4 Technical Reference Manual

Technical Reference
Manual
Hardware and BIOS
HP Vectra XM 5/xx
Series 4 PC

NOTICE
Information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Hewlett-Packard makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including,
but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose.
Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential
damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or reliability of its software on equipment
that is not furnished by Hewlett-Packard.
This document contains proprietary information which is protected by copyright. All rights are
reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another
language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Centronics® is a U.S. registered trademark of Centronics Data Computer Corporation.
Microsoft®, Windows® and MS-DOS® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
NextStep™ is a trademark of Next Incorported.
Novell® and Netware® are registered trademarks of Novell Inc.
O/S2™ is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
PENTIUM™ is a trademark of Intel Cor[oration.
SCO UNIX® is a registered trademark of the Santa Cruz Operation.
Part Number: 5964-1466
©1996 Hewlett-Packard Company

PREFACE
This manual is a technical reference and BIOS document for engineers and technicians
providing system level support. It is assumed that the reader possesses a detailed
understanding of AT-compatible microprocessor functions and digital addressing techniques.
Technical information that is readily available from other sources, such as manufacturer’s
proprietary publications, has not been reproduced.
This manual contains summary information only. For additional reference material, refer to the
bibliography.
CONVENTIONS
The following conventions are used throughout this manual to identify specific elements:
• Hexadecimal numbers are identified by a lower case h.
For example, 0FFFFFFFh or 32F5h
• Binary numbers and bit patterns are identified by a lower case b.
For example, 1101b or 10011011b

BIBLIOGRAPHY
• HP Vectra XM 5/xx series 4 PC
• HP Vectra XM 5/xx series 4 PC
• HP
•
•
• HP
The following Intel® publication provides more detailed information:
•
Network Administrator's Guide
HP Vectra Accessories Service Handbook - 5th edition
HP Vectra PC Service Handbook (Volume 1) - 9th edition
Support Assistant
CD-ROM
Pentium Microprocessor Data Sheet
User’s Guide
manual kit (D3960A).
Familiarization Guide
(5964-1467).
(241595-002)
(D3960-90901)
(5963-8034)
(5963-8033)

Table of Contents
NOTICE......................................................................................................................................................2
PREFACE...................................................................................................................................................3
CONVENTIONS.........................................................................................................................................3
BIBLIOGRAPHY.......................................................................................................................................4
1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW............................................................................................. 7
EXTERNAL FEATURES...........................................................................................................................7
INTERNAL FEATURES............................................................................................................................7
SPECIFICATIONS AND CHARACTERISTIC DATA ............................................................................8
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATION ...................................................................................................9
CONTROL PANEL ..................................................................................................................................9
DOCUMENTATION................................................................................................................................10
WHERE TO FIND THE INFORMATION.............................................................................................. 10
2 SYSTEM BOARD................................................................................................. 12
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS AND FEATURES ................................................................................... 12
THE BACKPLANE ................................................................................................................................14
ARCHITECTURAL VIEW.....................................................................................................................15
DEVICES ON THE PROCESSOR-LOCAL BUS...................................................................................15
THE INTEL PENTIUM MICROPROCESSOR....................................................................................... 16
CACHE MEMORY ................................................................................................................................ 17
MAIN MEMORY................................................................................................................................... 17
DEVICES ON THE PCI BUS ..................................................................................................................18
VIDEO CONTROLLER..........................................................................................................................18
INTEGRATED DRIVE ELECTRONICS (IDE)......................................................................................19
OTHER PCI ACCESSORY DEVICES ................................................................................................... 20
DEVICES ON THE ISA BUS...................................................................................................................20
SUPER I/O CONTROLLER....................................................................................................................21
SYSTEM ROM....................................................................................................................................... 22
OTHER ISA ACCESSORY DEVICES ...................................................................................................23

3 INTERFACE BOARDS AND MASS-STORAGE DRIVES .................................... 24
THE INTEGRATED ULTRA VGA VIDEO CONTROLLER............................................................... 24
AVAILABLE BIOS VIDEO RESOLUTIONS.........................................................................................28
CONNECTORS......................................................................................................................................29
ENHANCED ETHERNET NETWORK BOARD...................................................................................29
MASS-STORAGE DRIVES .....................................................................................................................30
HARD DISK DRIVES ............................................................................................................................30
FLEXIBLE DISK DRIVES.....................................................................................................................31
CD-ROM DRIVES..................................................................................................................................31
TAPE DRIVES.......................................................................................................................................31
INTERNAL CONNECTORS...................................................................................................................32
4 SUMMARY OF THE HP/PHOENIX BIOS.............................................................34
SETUP PROGRAM.................................................................................................................................. 34
MAIN MENU.........................................................................................................................................34
CONFIGURATION MENU.................................................................................................................... 34
SECURITY MENU................................................................................................................................. 35
POWER MENU......................................................................................................................................36
HP/PHOENIX BIOS DESCRIPTION ..................................................................................................... 36
I/O ADDRESSES USED BY THE SYSTEM*.........................................................................................38
BIOS I/O PORT MAP.............................................................................................................................39
ADDRESSING SYSTEM BOARD COMPONENTS...............................................................................40
5 FACILITIES OF THE BIOS................................................................................... 42
REMOTE POWER-ON (RPO)................................................................................................................42
DESKTOP MANAGEMENT INTERFACE (DMI) ................................................................................ 46
6 POWER-ON SELF-TESTS AND ERROR MESSAGES ....................................... 51
OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................................51
BEEP CODES...........................................................................................................................................54
ERROR MESSAGES................................................................................................................................55
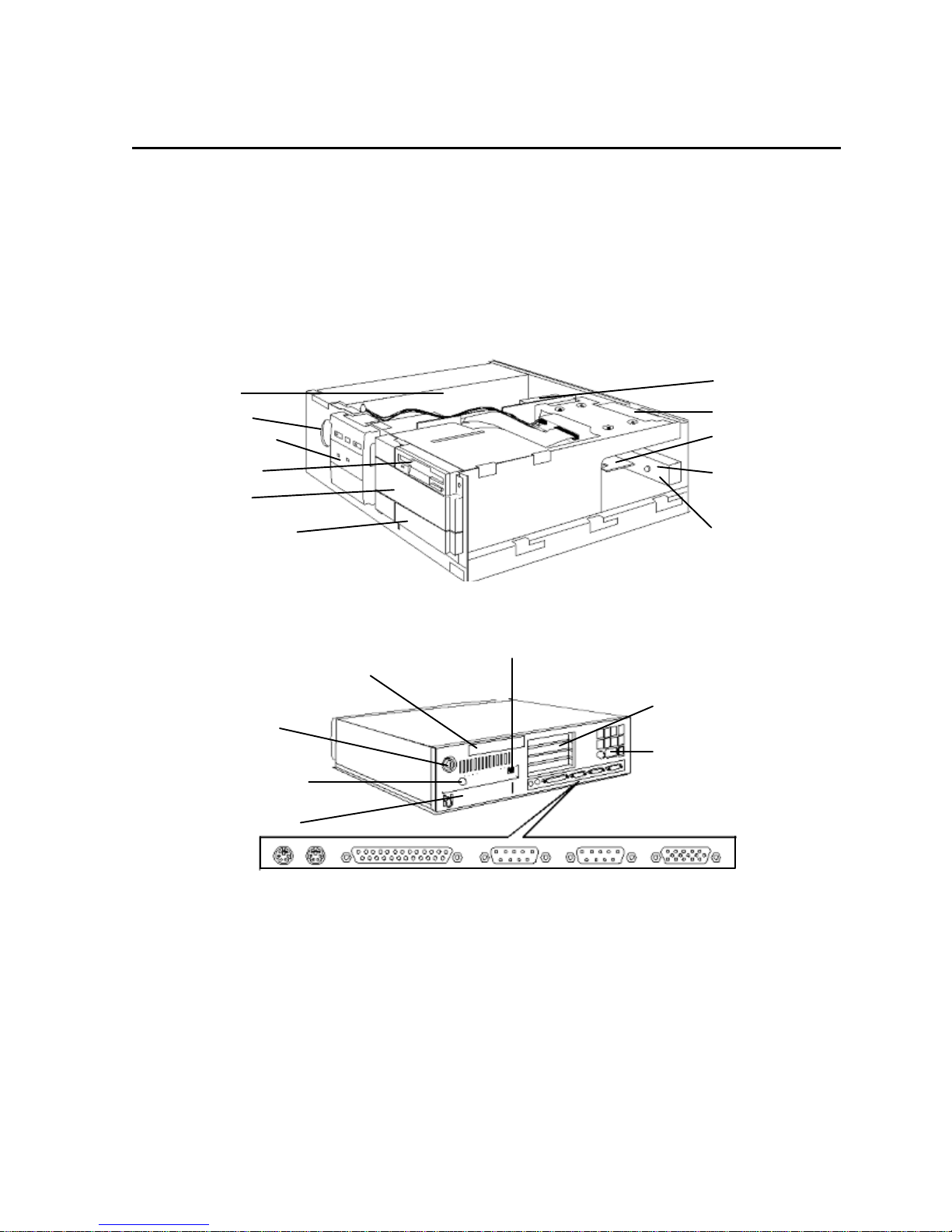
1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
4 accessory slot
panel blanks
Power connector
This manual describes the
HP Vectra XM 5/xx series 4 PC
, and provides detailed system
specifications. The PC is constructed around the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus
and Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bus. Its central feature is the Enhanced Ethernet
Network board fitted as standard in a new PCI slot on the backplane, and the ability to be
turned on remotely from another PC on the network.
EXTERNAL FEATURES
The following diagrams show the front and rear views of the
Power supply
Speaker position
Status (control) panel
Flexible disk drive in
top 3.5-inch shelf
5.25-inch shelf
(for CD-ROM drive)
Vacant 3.5/5.25-inch shelf
HP Vectra XM 5/xx series 4 PC
Double-sided backplane
with 5 accessory slots
(4 standard)
Hard disk drive
Enhanced Ethernet
10 Base T LAN boa rd
BNC coax hole
metal plug
Network I/O panel
.
RJ-45 network
IIdentification label
Cover lock
BNC coax hole
metal plug
New I/O panel
Mouse Keyboard Parallel port Serial Port A Serial Port B Display
connector
INTERNAL FEATURES
Diagrams of the double-sided back-plane and the system board can be found at the beginning
of the next chapter. These show the locations of the PC’s main field-serviceable components.
The components of the system board are described in the same chapter. The characteristics of
the PC’s video, disk and networking devices are described in Chapter 3. The HP BIOS routines
are described in Chapter 4; the Remote Power-On (RPO) facility and Desktop Management
Interface (DMI) are described in Chapter 5; and the Power-On Self-Test routines are
summarized in Chapter 6.

SPECIFICATIONS AND CHARACTERISTIC DATA
Limit per ISA
Accessory Slot
—
—
—
—
—
15 W (max)
1.5 A
0.3 A
4.5 A
0.1 A
Physical Characteristics
Desktop Unit
Weight: 20 lbs (9 kg)
Dimensions: 15.3 inches (D) by 16.5 inches (W) by 4.9 inches (H)
(39 cm by 42 cm by 12.5 cm)
Footprint: 1.8 sq ft (0.17 m
Keyboard: 18 inches (W) by 7 inches (D) by 1.3 inches (H), when flat, or
18 inches (W) by 7 inches (D) by 2 inches (H), when standing
(464mm by 178mm by 33mm when flat, or
464mm by 178mm by 51mm, when standing)
Electrical Specification
Parameter Limit for the Power Supply
Input voltage 100-240 Vac (wide-ranging) —
Input current (max) 3 A —
Input power (max) 150 W —
Input frequency 47 Hz to 63 Hz —
Heat dissipation 150 W —
Available power 100 W (continuous) 15 W (max)
Max current at +12 V 4 A 0.5 A
Max current at -12 V 0.3 A 0.1 A
Max current at +5V 13.5 A 4.5 A
Max current at -5V 0.1 A
Input power (when
turned Off)
Available power
(when Off)
Available current
(when Off)
Less than 5 W
0.1 W
0.05 A
2)
Limit per PCI
Accessory Slot
When the PC is Off, but still
plugged in, an independent mini
power supply keeps the network
board active enough to watch out
for the “Remote Power-On” (RPO)
signal
An attempt to draw too much current (such as a short circuit across edge-connector pins, or an
accessory board that is not suitable for the PC), will cause the overload protection in the power
supply to be triggered, and the PC could fail to boot.

ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATION
Environmental Specifications (System Processing Unit, with Hard Disk)
Operating Temperature + 40°F to 104° F (+5°C to +40°C)
Recommended Operating
Temperature
Storage Temperature -40°F to +158°F (-40°C to +70°C)
Over Temperature Shutdown +122°F (+50°C)
Operating Humidity 15% to 80% (relative)
Storage Humidity 8% to 80% (relative)
Acoustic noise emission <40 dB in the workplace under normal conditions
Operating Altitude 10000 ft (3100m) max
Storage Altitude 15000ft (4600m) max
Operating temperature and humidity ranges may vary depending upon the mass storage
devices installed. High humidity levels can cause improper operation of disk drives. Low
humidity levels can aggravate static electricity problems and cause excessive wear of the disk
surface.
+59°F to +158°F (+15°C to +30°C)
as defined by DIN 45635 T.19 and ISO 7779
CONTROL PANEL
The control (status) panel of the
• a power on/off button with integrated on/error status light (which flickers in power-saving
mode)
press-and-hold
• a
• a hard disk activity light (for IDE drives)
• a keyboard lock button with integral status light
• a LAN activity light (for the network board).
RESET button
HP Vectra XM 5/xx series 4 PC
has the following features:
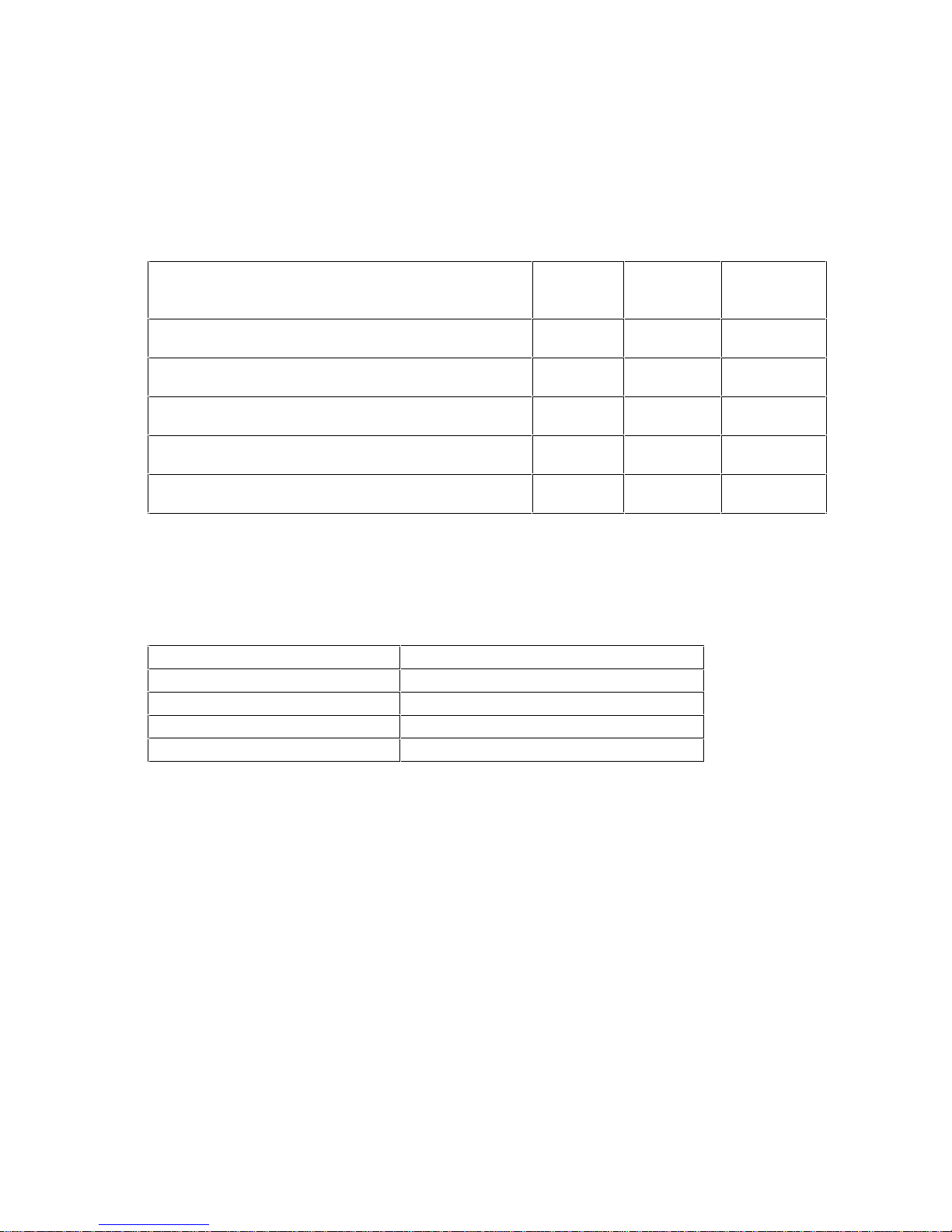
DOCUMENTATION
The table below summarizes the documentation that is available for the
series 4 PC
.
HP Vectra XM 5/xx
Only selected publications are available in paper-based form. Most are available as printable
files from the HP regional support servers, or from the
Title
HP Vectra XM 5/xx series 4 PC User’s Guide printable
HP Vectra XM 5/xx series 4 PC Technical Reference
Manual: Hardware and BIOS
HPVectra PC Service Handbook Volume 1 (9th Edition) printable
HPVectra Accessory Service Handbook (5th Edition) printable
Network Administrators Guide WinHelp
HP Support Assistant
Regional
Support
Servers
PCL file
printable
PCL file
PCL file
PCL file
format
Support
Assistant
CD-ROM
yes D3960A
yes no
yes 5963-8033
yes 5963-8034
yes 5964-1467
CD-ROM.
Paperbased
WHERE TO FIND THE INFORMATION
The following table summarizes the availability of information within the
series 4 PC
documentation set. In addition, documentation is available for each HP peripheral
device. Notably, this includes the following:
HP Vectra XM 5/xx
Display User’s Guide
Disk drive User’s Guide
Audio User’s Guide
Network Administrator’s Guide
User’s Guide or Installation Guide
Information on setting up and configuring
Information on setting up and configuring
Information on setting up and configuring
Information on setting up and configuring
User’s Guide
Product features Key features Exploring New features
Product model
numbers
Connecting
cables and
turning on
Finding on-line
information
Preloaded
software
Environmental Setting up the PC Working in
Formal
documents
Opening the PC Full details
Supported
accessories
Installing
accessories
Configuring
devices
Fields and their
options within
Keyboard, mouse,
display, network, printer,
power
Finding READ.MEs and
on-line documentation
Finding, initializing,
starting
License agreement
Warranty information
Part number details Full PN details Full PN
How to install New procedures
Installing drivers Configuring
Complete list New fields Key fields
User
Online
Introducing the PC
Using the PC
Using
comfort
License
agreement
Upgrading the PC
peripherals
Familiarization
Guide
Vectra PC
comparison
Product range Product range
Service
Handbook
Exploded view
Parts list
CPL dates
details
Technical
Reference
Manual
Key features
Setup
Repairing the PC
Troubleshooting Basic Repair policy Service notes Advanced
Technical
information
System board Switches and connectors Switches and
BIOS Basic details New features Technical
Power-On SelfTest routines
(POST)
Basic Basic Advanced
Key error codes and
suggestions for
corrective action
connectors
How to replace
New features Error codes
Switches and
connectors
Switches and
connectors
Chip-set
details
details
Memory maps
and
suggestions
for corrective
action
Order of tests
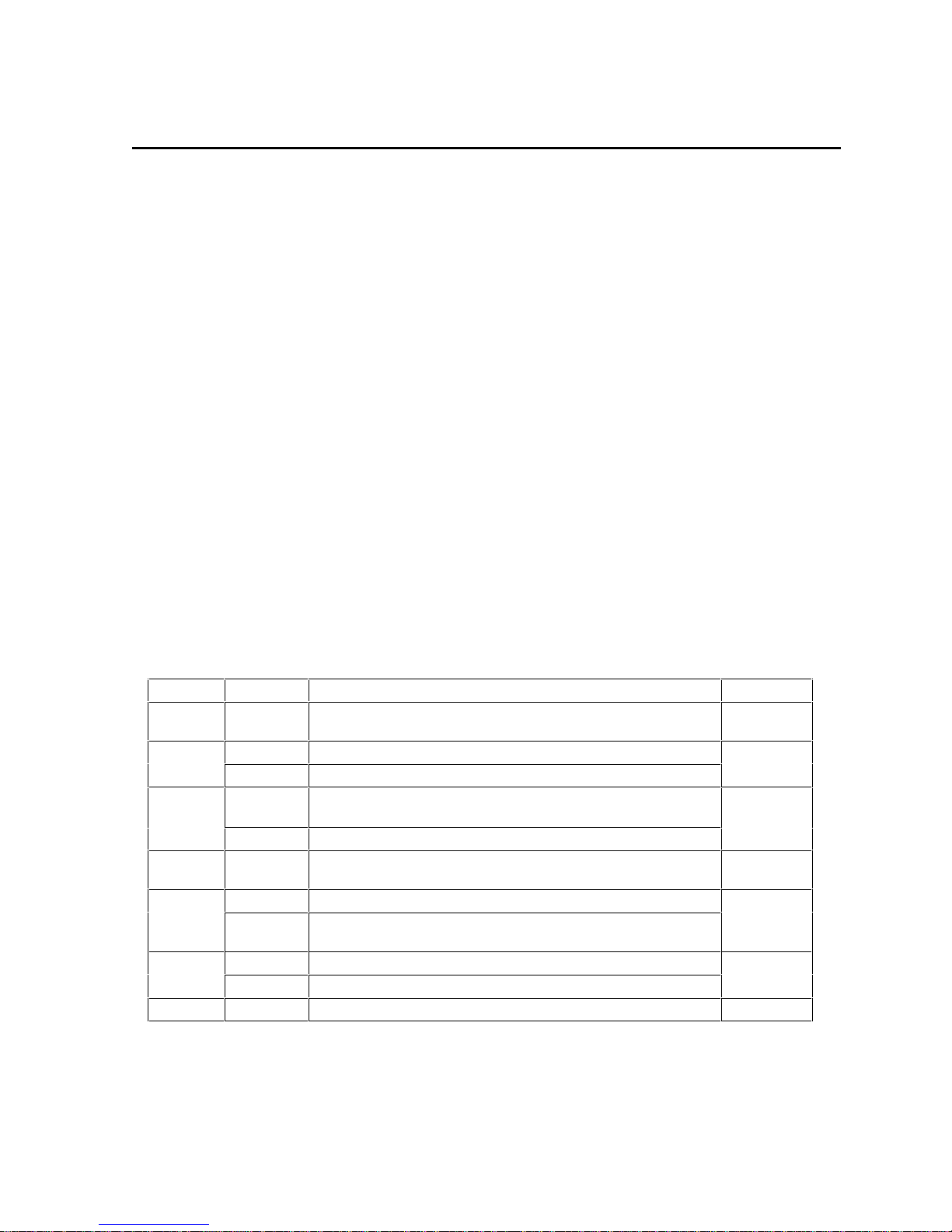
2 SYSTEM BOARD
The next chapter describes the video, disk and network devices which are supplied with the
PC.
This chapter describes the components of the system board.
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS AND FEATURES
The system board, as depicted on the next page, contains the following components:
Processor Socket
The microprocessor is packaged in a
zero-insertion-force
in a
(ZIF)
socket
pin-grid-array
.
(PGA), which is seated on the system board
VRM Socket
P54C (75, 90 and 100 MHz) Pentium processors, and P54CS (133 and 150 MHz) Pentium
processors require a 3.3 V supply. Since the power supply of the PC has a regulated 3.3 V
output, a shorting block is used to connect this directly to the Pentium processor.
P54C (120 and 166 MHz) Pentium processors require slightly more than 3.3 V, and therefore
need an active VRE
voltage regulator module
(VRM), in which the voltage is derived both from
the 3.3 V and 5 V outlets of the power supply.
System Board Switches
The functions of the
system board switches
, used for configuring the PC, are summarized in
the following table:
Switch Function Default
1-4
5 Open Enables User and Administrator passwords Open
6 Open CMOS memory acts as non-volatile store for the
7
8 Open Disables secure mode Open
9 Open Disables keyboard power-on Closed
10 Open Not used Open
- Processor frequency, see the table under "Bus Frequencies"
later in this chapter
Closed Clears User and Administrator passwords
Setup
data
Closed
- Processor frequency, see the table under "Bus Frequencies"
Closed
Closed Enables keyboard power-on
Clears the
later in this chapter
Enables secure mode - prevents modification of the
data and flashing of the BIOS
Setup
configuration data in the CMOS memory
Setup
-
Open
-
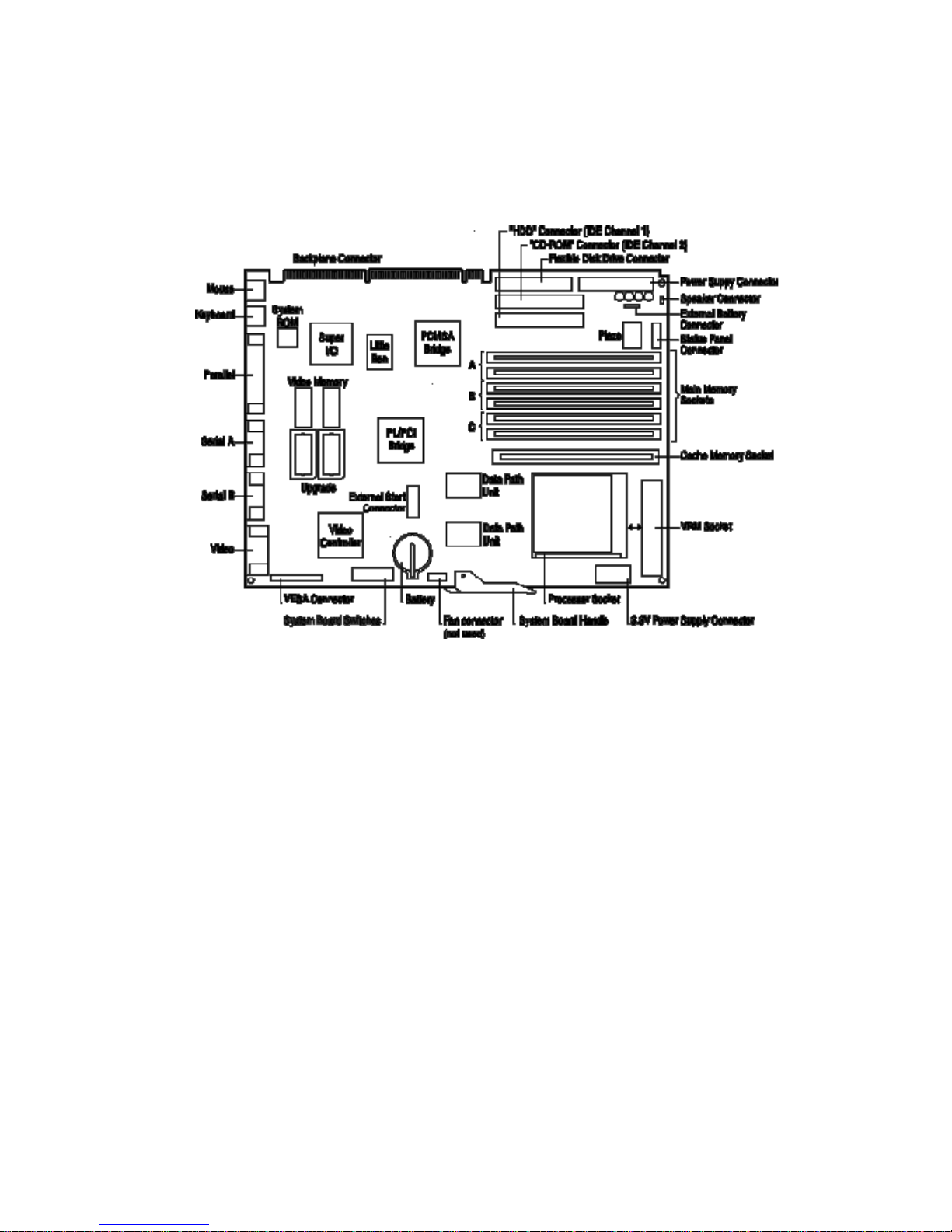
Main Memory Sockets
There are six
main memory module sockets
installation up to 128 MB DRAM. One bank is already occupied by the pair of
, arranged in three banks (A to C), allowing
memory modules
that contain the 8 or 16 MB of memory that is fitted as standard (depending on the model of the
PC).
Video Controller and VESA Connector
There is an integrated 64-bit Ultra VGA controller (S3 Trio 64 PnP) on the PCI bus, with a
VESA connector.
External Start Connector
This connector includes the VStandby power supply line that supplies the network board with its
power whilst the rest of the PC is turned off. It also includes the control lines which the network
board uses to turn on the main power supply, and to send or receive other control and status
information.
Super I/O Chip
The
Super I/O
chip, driven from the ISA bus, provides the control for two slow mass-storage
devices (any suitable combination of flexible disk and tape drives), one parallel and two serial
communications ports.
Chip-Set
Intel Triton 82437/8 PCI chip-set
The
consists of four chips that interface between the three
main buses (the Processor-Local bus, the PCI bus and the ISA bus).
• The PL/PCI Bridge chip (82437FX) also provides the control for the PCI bus, L2 cache
memory, and main memory.
• Two Data Path Unit chips (82438FX).
82371FB
PCI/IS A Bridge
PCI
Master
APIC
BIOS
1/3 Length Slot
• The PCI/ISA Bridge chip (82371FB) also provides the control for the IDE.
Pentium
Processor
Host Bus
82438FX
Data Path Unit
Level-Two
Cache
82437FX PCI, Ca che and
Memory Controller
Cache
Controller
Write
Buffer
82438FX
Data Path Unit
Main
Memory
Main
Memory
Controller
PCI Bus
PCI
Slave
ISA Bus
Controller
IDE
Controller
ISA Bus
PCI
Master
PCI
Slave
THE BACKPLANE
The left-hand side of the double-sided back-plane, as viewed from the front of the PC, is shown
in the diagram below. It shows two
accessory slots
one that lies on either bus. Thus there are three PCI accessory sockets, and three ISA bus
accessory sockets. The lowest ISA socket can only accommodate an HP proprietary ISA
accessory board.
on the PCI bus, two on the ISA bus, and
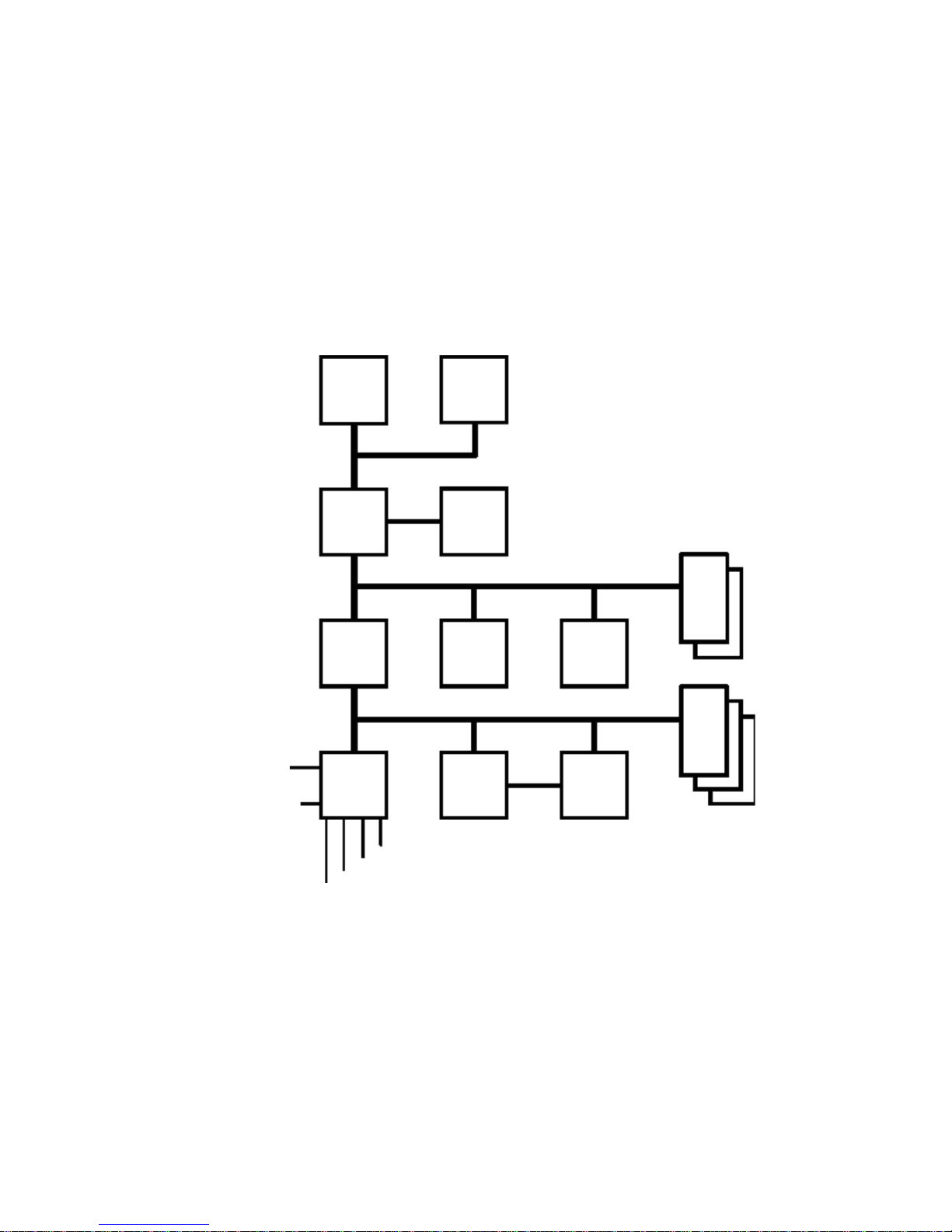
The other side of the back-plane bears a single PCI slot. This accommodates the Enhanced
ISA Accessory
Board Slots
Ethernet 10 BaseT Network board.
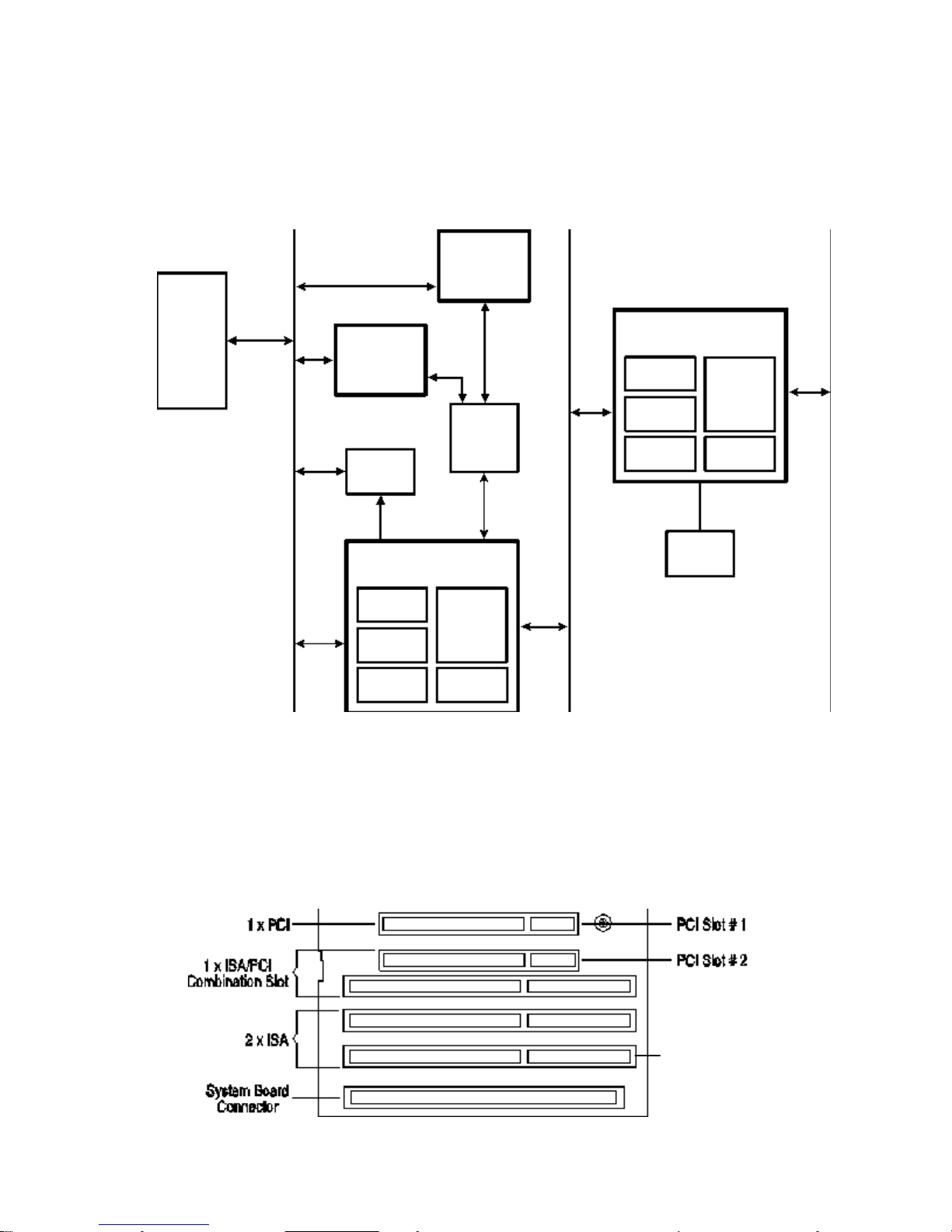
ARCHITECTURAL VIEW
The block diagram on the next page gives an architectural view of the
series 4 PC
. The next section in this chapter describes the devices on the system board which
HP Vectra XM 5/xx
are associated with the Processor-Local (PL) bus. The section after describes the devices on
the system board that are associated with the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus.
The final section describes the devices on the system board that are associated with the
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bus.
Pentium
Processor
Processor-Local
Intel Triton
82437/8FX
Chipset
Intel
82371FB
PCI/ISA
Bridge
Bus
PCI
Bus
IDE
Controller:
Channel 1
Channel 2
256 KB
Level-Two
Cache
Memory
(8 MB -
128 MB)
S3 Trio
Video
Controller
PCI Accessory
Board Slots
Enhanced
Ethernet
Controller
I ISA Bus
Flash
Support
Keyboard
Mouse
Serial 2
SMC932
Super I/O
Controller
FDD
Parallel
Serial 1
I/O
Decode
Logic
BIOS
Flash
ROM
DEVICES ON THE PROCESSOR-LOCAL BUS
The following subsystems are associated with the Processor-Local bus:
• The Intel Pentium microprocessor
• cache memory
• main memory.

THE INTEL PENTIUM MICROPROCESSOR
Frequency
Ratio
Processor :
Local Bus
1.5 : 1
1.5 : 1
1.5 : 1
2 : 1
2 : 1
2.5 : 1
2.5 : 1
The Pentium is a 32-bit architecture processor on a 64-bit bus, and is 100% software
compatible with Intel’s family of x86 processors. All application software that has been written
for Intel 80386 and Intel 80486 processors can run on the Pentium without modification. The
Pentium processor contains all the features of the Intel 80486 processor, with the following
added features which enhance performance:
Superscalar Architecture
The Pentium processor’s
static superscalar architecture
has two instruction pipelines and a
floating-point unit, each capable of independent operation. The two pipelines allow the Pentium
to execute two integer instructions in parallel, in a single clock cycle. This is called instruction
pairing. Each instruction must be simple. One pipeline will always receive the next sequential
instruction of the one issued to the other pipeline. Using the pipelines in this way halves the
instruction execution time and almost doubles the performance of the processor, compared
with an Intel 80486 microprocessor of the same frequency.
FPU
floating point unit
The
(FPU) incorporates optimized algorithms and dedicated hardware for
multiply, divide, and add functions. This increases the processing speed of common
operations.
Dynamic Branch Prediction
To implement the Pentium’s 4-state
dynamic branch prediction
, the processor uses two
prefetch buffers. One buffer is used to prefetch instruction code in a linear way, and one to
prefetch instruction code depending on the contents of the
branch target buffer
(BTB). The BTB
is a small cache which keeps a record of the way that the instruction branched the last time it
was used. When this information leads to a correct prediction on the subsequent branch, the
branch is executed without delay, thereby enhancing performance.
Bus Frequencies
Like the 80486 DX2 processor, the Pentium uses internal clock multiplication. For example,
the Pentium 150 MHz processor multiplies the 60 MHz system clock by 2.5. Switches 1 and 2,
on the system board switch bank, set the frequency of the Processor-Local bus. Switches 3, 4
and 7 set the clock multiplier ratio. The relationship of the switch settings to Processor-Local
bus and processor frequencies is summarized in the following table:
Processor-
Switch
12 347
Closed Closed 50 MHz Open Open Open
Closed Open 60 MHz Open Open Closed
Open Closed 66 MHz Open Open Closed
Closed Open 60 MHz Closed Open Closed
Open Closed 66 MHz Closed Open Closed
Closed Open 60 MHz Closed Closed Closed
Open Closed 66 MHz Closed Closed Closed
*The 90 MHz model is not available for the HP Vectra XM 5/xx series 4 PCs at the time of printing.
This information is provided for completeness only.
Local Bus
Frequency Switch
Processor
Frequency
75 MHz
90 MHz*
100 MHz
120 MHz
133 MHz
150 MHz
166 MHz

The computer will execute erratically, if at all, if the configuration switches are set to operate at
a higher processor speed than the processor is capable of supporting. This can cause damage
to the PC.
Setting the switches to operate at a slower speed, than the processor is capable of supporting,
would not cause any failure of operation, but would not execute instructions as fast as might
otherwise have been possible.
CACHE MEMORY
The PC allows for the provision of two levels of cache memory: Level-1 (L1), cache memory
which is fabricated by Intel within the Pentium processor chip; Level-2 (L2), cache memory is
optionally installed as a memory module on the system board. Each acts as temporary storage
for data and instructions from the main memory; since the system is likely to use the same data
several times, it is faster to get it from the on-chip cache than from the main memory.
The L1 cache memory is divided into two separate banks: an L1 I-cache for instruction words,
and an L1 D-cache for data words. Each has a capacity of 8 KB, organized on a 32-byte (256bit) line width. The I-cache is two-way set-associative. The D-cache four-way set-associative,
and is configured for Write-Back on a line-by-line basis.
The cache memory line width is four times that of the Pentium’s Processor-Local data bus.
Since reads and writes involve a full cache line, they require four back-to-back cycles on the
bus. The first cycle in each burst of four always requires more time to complete than the three
subsequent cycles. This is because the first cycle includes the addressing phase and precharge timing (for memory). The read and write access timing has the pattern 3-1-1-1.
The L2 cache memory, when fitted, also has a 32-byte line size. It is controlled by the PL/PCI
bridge chip (see page 10) in the system board chip-set. A single HP cache memory module
consists of 256 KB of direct mapped, synchronous or asynchronous, static random access
memory (SRAM). The synchronous cache memory module produces 10% better performance
than the asynchronous module.
MAIN MEMORY
Fast memory access, with the timing pattern 7-2-2-2, is achieved by installing EDO DRAM. The
can use 60 ns
PC
access memory
The PL/PCI bridge chip provides the dedicated DRAM memory address and data buses. It
implements a page mode of operation, allowing one or two pages to be open simultaneously. It
supports pipelined accesses, and full RAS/CAS programmability. It allows for RAS only refresh.
The two data path unit chips, controlled by the PL/PCI bridge chip, implement a 64-bit data
path (not interleaved) between the Processor-Local bus and main memory modules. They also
provide a buffer, four 64-bit words in depth, which is used for: writes from processor to main
memory; L2 cache write back cycles; and transfers from PCI to main memory. It also provides
a one-level posted write buffer for all processor writes to the PCI bus memory.
There is no parity detecting logic for the main memory on this PC.
extended data-out
(DRAM).
(EDO) or 70 ns
fast page-mode
(FPM)
dynamic random-
 Loading...
Loading...