Page 1

HP V1910 Switch Series
User Guide
*5998-2238*
Part number: 5998-2238
Document version: 2
1
Page 2

The HP V1910 Switch Series User Guide describes the software features for the HP 1910 switches and
guides you through the software configuration procedures. It also provides configuration examples to help
you apply software features to different network scenarios.
This documentation set is intended for:
Network planners
Field technical support and servicing engineers
Network administrators working with the HP V1910 switches
Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
No part of this documentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS
MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or
for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this
material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Warranty
The Hewlett-Packard Limited Warranty Statement for this product and the HP Software License Terms which
apply to any software accompanying this product are available on the HP networking Web site at
http://www.hp.com/networking/warranty. The customer warranty support and services information are
available on the HP networking Web site at http://www.hp.com/networking/support. Additionally, your
HP-authorized network reseller can provide you with assistance, both with services that they offer and with
services offered by HP.
2
Page 3

Contents
Overview ······································································································································································ 1
Configuration through the web interface ··················································································································· 2
Web-based network management operating environment ····························································································· 2
Logging in to the web interface ·········································································································································· 2
Default login information ·············································································································································· 2
Example ·········································································································································································· 3
Logging out of the web interface ······································································································································· 4
Introduction to the web interface ········································································································································ 4
Web user level ····································································································································································· 5
Introduction to the web-based NM functions ···················································································································· 5
Introduction to the common items on the web pages ··································································································· 13
Configuration guidelines ·················································································································································· 15
Configuration at the CLI ············································································································································· 16
Getting started with the CLI ············································································································································· 16
Setting up the configuration environment ················································································································· 16
Setting terminal parameters ······································································································································· 17
Logging in to the CLI ··················································································································································· 20
CLI commands ··································································································································································· 21
initialize ······································································································································································· 21
ipsetup ·········································································································································································· 21
password ····································································································································································· 22
ping ·············································································································································································· 23
quit ················································································································································································ 23
reboot ··········································································································································································· 24
summary ······································································································································································· 24
upgrade ······································································································································································· 25
Configuration example for upgrading the system software image at the CLI ···························································· 26
Configuration wizard ················································································································································· 28
Overview ··········································································································································································· 28
Basic service setup ···························································································································································· 28
Entering the configuration wizard homepage ········································································································· 28
Configuring system parameters ································································································································· 28
Configuring management IP address ······················································································································· 29
Finishing configuration wizard ·································································································································· 31
IRF stack management ··············································································································································· 32
Configuring stack management ······································································································································ 32
Stack management configuration task list ················································································································ 32
Configuring global parameters of a stack ··············································································································· 33
Configuring stack ports ·············································································································································· 35
Displaying topology summary of a stack ················································································································· 35
Displaying device summary of a stack ····················································································································· 36
Logging into a member switch from the master switch ··························································································· 36
Stack configuration example ··········································································································································· 36
Configuration guidelines ·················································································································································· 42
3
Page 4

Summary ····································································································································································· 43
Displaying device summary ············································································································································· 43
Displaying system information ··································································································································· 43
Displaying device information ··································································································································· 44
Device basic information configuration ···················································································································· 46
Configuring device basic information ···························································································································· 46
Configuring system name ·········································································································································· 46
Configuring idle timeout period ································································································································ 46
System time configuration ·········································································································································· 48
Configuring system time ··················································································································································· 48
System time configuration example ································································································································ 49
Configuration guidelines ·················································································································································· 51
Log management configuration ································································································································ 52
Configuring log management ········································································································································· 52
Configuration task list ················································································································································· 52
Setting syslog related parameters ····························································································································· 52
Displaying syslog ························································································································································ 53
Setting loghost ····························································································································································· 55
Configuration management ······································································································································· 56
Back up configuration ······················································································································································ 56
Restore configuration ························································································································································ 56
Save configuration ···························································································································································· 57
Initialize ············································································································································································· 58
Device maintenance ··················································································································································· 59
Software upgrade ····························································································································································· 59
Device reboot ···································································································································································· 60
Electronic label ·································································································································································· 61
Diagnostic information ····················································································································································· 61
File management ························································································································································ 63
File management configuration ······································································································································· 63
Displaying file list ························································································································································ 63
Downloading a file ····················································································································································· 64
Uploading a file ·························································································································································· 64
Removing a file ··························································································································································· 64
Port management configuration ································································································································ 65
Configuring a port ···························································································································································· 65
Setting operation parameters for a port ··················································································································· 65
Viewing the operation parameters of a port ··········································································································· 69
Port management configuration example ······················································································································ 70
Port mirroring configuration ······································································································································ 74
Introduction to port mirroring··········································································································································· 74
Implementing port mirroring ······································································································································ 74
Configuring local port mirroring ····································································································································· 75
Configuration task list ················································································································································· 75
Creating a mirroring group ······································································································································· 75
Configuring ports for a mirroring group ·················································································································· 76
Configuration examples ··················································································································································· 78
Local port mirroring configuration example ············································································································· 78
Configuration guidelines ·················································································································································· 81
4
Page 5

User management ······················································································································································ 82
Overview ··········································································································································································· 82
Managing users ································································································································································ 82
Adding a local user ···················································································································································· 82
Setting the super password ········································································································································ 83
Switching to the management level ·························································································································· 84
Loopback test configuration ······································································································································ 85
Overview ··········································································································································································· 85
Loopback operation ·························································································································································· 85
Configuration guidelines ·················································································································································· 86
VCT·············································································································································································· 87
Overview ··········································································································································································· 87
Testing cable status ··························································································································································· 87
Flow interval configuration ········································································································································ 89
Overview ··········································································································································································· 89
Monitoring port traffic statistics ······································································································································· 89
Setting the traffic statistics generating interval ········································································································· 89
Viewing port traffic statistics ······································································································································ 89
Storm constrain configuration ··································································································································· 91
Overview ··········································································································································································· 91
Configuring storm constrain ············································································································································ 91
Setting the traffic statistics generating interval ········································································································· 91
Configuring storm constrain ······································································································································ 92
RMON configuration ················································································································································· 95
Working mechanism ·················································································································································· 95
RMON groups ···························································································································································· 96
Configuring RMON ·························································································································································· 97
Configuration task list ················································································································································· 97
Configuring a statistics entry ····································································································································· 99
Configuring a history entry ······································································································································ 100
Configuring an event entry ······································································································································ 101
Configuring an alarm entry ····································································································································· 102
Displaying RMON statistics information ················································································································ 104
Displaying RMON history sampling information ·································································································· 106
Displaying RMON event logs ·································································································································· 108
RMON configuration example ······································································································································ 108
Energy saving configuration ··································································································································· 113
Overview ········································································································································································· 113
Configuring energy saving on a port ··························································································································· 113
SNMP configuration ··············································································································································· 115
SNMP mechanism ···················································································································································· 115
SNMP protocol version ············································································································································ 116
SNMP configuration ······················································································································································· 116
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 116
Enabling SNMP ························································································································································ 117
Configuring an SNMP view ···································································································································· 119
Configuring an SNMP community ·························································································································· 121
Configuring an SNMP group ·································································································································· 122
Configuring an SNMP user ····································································································································· 123
5
Page 6

Configuring SNMP trap function ····························································································································· 125
SNMP configuration example ······································································································································· 127
Interface statistics ···················································································································································· 133
Overview ········································································································································································· 133
Displaying interface statistics ········································································································································· 133
VLAN configuration ················································································································································ 135
Introduction to VLAN ················································································································································ 135
VLAN fundamentals ·················································································································································· 135
VLAN types ································································································································································ 136
Introduction to port-based VLAN ····························································································································· 137
Configuring a VLAN ······················································································································································· 138
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 138
Creating VLANs ························································································································································ 138
Selecting VLANs ························································································································································ 139
Modifying a VLAN ···················································································································································· 140
Modifying ports ························································································································································· 142
VLAN configuration example ········································································································································ 143
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 148
VLAN interface configuration ································································································································· 149
Configuring VLAN interfaces ········································································································································· 149
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 149
Creating a VLAN interface ······································································································································ 149
Modifying a VLAN interface ···································································································································· 150
Voice VLAN configuration ······································································································································ 153
OUI addresses ··························································································································································· 153
Voice VLAN assignment modes ······························································································································ 153
Security mode and normal mode of voice VLANs ································································································ 155
Configuring the voice VLAN ·········································································································································· 155
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 155
Configuring voice VLAN globally ··························································································································· 157
Configuring voice VLAN on a port ························································································································· 157
Adding OUI addresses to the OUI list ···················································································································· 159
Voice VLAN configuration examples ···························································································································· 160
Configuring voice VLAN on a port in automatic voice VLAN assignment mode ·············································· 160
Configuring a voice VLAN on a port in manual voice VLAN assignment mode ··············································· 165
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 171
MAC address configuration ··································································································································· 172
Configuring MAC addresses ········································································································································· 173
Configuring a MAC address entry ························································································································· 173
Setting the aging time of MAC address entries ····································································································· 175
MAC address configuration example ··························································································································· 176
MSTP configuration ················································································································································· 177
STP 177
STP protocol packets ················································································································································ 177
Basic concepts in STP ··············································································································································· 177
How STP works ························································································································································· 178
RSTP ·················································································································································································· 184
MSTP ················································································································································································ 185
STP and RSTP limitations ·········································································································································· 185
MSTP features ···························································································································································· 185
6
Page 7

MSTP basic concepts ················································································································································ 185
How MSTP works ······················································································································································ 189
Implementation of MSTP on devices ······················································································································· 189
Protocols and standards ··········································································································································· 190
Configuring MSTP ··························································································································································· 190
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 190
Configuring an MST region ····································································································································· 190
Configuring MSTP globally ······································································································································ 192
Configuring MSTP on a port ···································································································································· 194
Displaying MSTP information of a port ·················································································································· 196
MSTP configuration example ········································································································································· 199
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 203
Link aggregation and LACP configuration ············································································································ 205
Basic concepts ··························································································································································· 205
Link aggregation modes ··········································································································································· 206
Load sharing mode of an aggregation group ······································································································· 208
Configuring link aggregation and LACP ······················································································································ 208
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 208
Creating a link aggregation group ························································································································· 209
Displaying information of an aggregate interface ································································································ 211
Setting LACP priority ················································································································································· 211
Displaying information of LACP-enabled ports ······································································································ 212
Link aggregation and LACP configuration example ··································································································· 214
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 217
LLDP configuration ··················································································································································· 218
Background ······························································································································································· 218
Basic concepts ··························································································································································· 218
How LLDP works ························································································································································ 222
Compatibility of LLDP with CDP ······························································································································· 222
Protocols and standards ··········································································································································· 223
Configuring LLDP ····························································································································································· 223
LLDP configuration task list ······································································································································· 223
Enabling LLDP on ports ············································································································································· 224
Configuring LLDP settings on ports ·························································································································· 225
Configuring global LLDP setup ································································································································ 229
Displaying LLDP information for a port ··················································································································· 231
Displaying global LLDP information ························································································································ 236
Displaying LLDP information received from LLDP neighbors················································································· 238
LLDP configuration examples ········································································································································· 238
Basic LLDP configuration example ·························································································································· 238
CDP-compatible LLDP configuration example ········································································································ 244
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 250
IGMP snooping configuration ································································································································ 251
Overview ········································································································································································· 251
Principle of IGMP snooping ····································································································································· 251
IGMP snooping related ports ·································································································································· 251
Work mechanism of IGMP snooping ····················································································································· 252
IGMP snooping querier ············································································································································ 254
Protocols and standards ··········································································································································· 254
Configuring IGMP snooping ·········································································································································· 254
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 254
7
Page 8

Enabling IGMP snooping globally ·························································································································· 255
Configuring IGMP snooping in a VLAN ················································································································ 256
Configuring IGMP snooping port functions ··········································································································· 257
Display IGMP snooping multicast entry information ····························································································· 258
IGMP snooping configuration example························································································································ 259
Routing configuration ·············································································································································· 266
Routing table ····························································································································································· 266
Static route ································································································································································· 266
Default route ······························································································································································ 267
Configuring IPv4 routing ················································································································································ 267
Displaying the IPv4 active route table ···················································································································· 267
Creating an IPv4 static route ··································································································································· 268
Static route configuration example ······························································································································· 269
Precautions ······································································································································································ 273
DHCP overview ······················································································································································· 274
Introduction to DHCP ······················································································································································ 274
DHCP address allocation ··············································································································································· 274
Allocation mechanisms ············································································································································· 274
Dynamic IP address allocation process ·················································································································· 275
IP address lease extension ······································································································································· 275
DHCP message format ··················································································································································· 276
DHCP options ·································································································································································· 277
DHCP options overview ··········································································································································· 277
Introduction to DHCP options ·································································································································· 277
Introduction to Option 82 ········································································································································ 277
Protocols and standards ················································································································································· 278
DHCP relay agent configuration ···························································································································· 279
Introduction to DHCP relay agent ································································································································· 279
Application environment ·········································································································································· 279
Fundamentals ···························································································································································· 279
DHCP relay agent configuration task list ······················································································································ 280
Enabling DHCP and configuring advanced parameters for the DHCP relay agent ················································ 281
Creating a DHCP server group ····································································································································· 282
Enabling the DHCP relay agent on an interface ········································································································· 283
Configuring and displaying clients' IP-to-MAC bindings ···························································································· 284
DHCP relay agent configuration example ··················································································································· 285
DHCP snooping configuration ······························································································································· 288
DHCP snooping overview ·············································································································································· 288
Functions of DHCP snooping ··································································································································· 288
Application environment of trusted ports ················································································································ 289
DHCP snooping support for Option 82 ················································································································· 290
DHCP snooping configuration task list ························································································································· 290
Enabling DHCP snooping ·············································································································································· 291
Configuring DHCP snooping functions on an interface ······························································································ 29 3
Displaying clients' IP-to-MAC bindings ························································································································· 293
DHCP snooping configuration example ······················································································································· 294
Service management configuration ······················································································································· 299
Configuring service management ································································································································· 300
Diagnostic tools ······················································································································································· 302
Ping ············································································································································································ 302
8
Page 9

Trace route ································································································································································· 302
Diagnostic tool operations ············································································································································· 303
Ping operation ··························································································································································· 303
Trace route operation ··············································································································································· 304
ARP management ···················································································································································· 306
ARP overview ·································································································································································· 306
ARP function ······························································································································································ 306
ARP message format ················································································································································· 306
ARP operation ··························································································································································· 307
ARP table ··································································································································································· 307
Managing ARP entries···················································································································································· 308
Displaying ARP entries ············································································································································· 308
Creating a static ARP entry ······································································································································ 309
Static ARP configuration example ··························································································································· 309
Gratuitous ARP ································································································································································ 313
Introduction to gratuitous ARP ································································································································· 313
Configuring gratuitous ARP ····································································································································· 313
ARP attack defense configuration ·························································································································· 315
ARP detection ·································································································································································· 315
Introduction to ARP detection ··································································································································· 315
Configuring ARP detection ······································································································································· 317
Creating a static binding entry ································································································································ 319
802.1X fundamentals ············································································································································· 320
Architecture of 802.1X ··················································································································································· 320
Controlled/uncontrolled port and port authorization status ······················································································· 320
802.1X-related protocols ··············································································································································· 321
Packet formats ··························································································································································· 321
EAP over RADIUS ······················································································································································ 323
Initiating 802.1X authentication ···································································································································· 323
802.1X client as the initiator ··································································································································· 323
Access device as the initiator ·································································································································· 323
802.1X authentication procedures ······························································································································· 324
A comparison of EAP relay and EAP termination ································································································· 324
EAP relay ··································································································································································· 325
EAP termination ························································································································································· 327
802.1X configuration ············································································································································· 328
HP implementation of 802.1X ······································································································································· 328
Access control methods ············································································································································ 328
Using 802.1X authentication with other features ·································································································· 328
Configuring 802.1X ······················································································································································· 329
Configuration prerequisites······································································································································ 329
802.1X configuration task list ································································································································· 330
Configuring 802.1X globally ·································································································································· 330
Configuring 802.1X on a port ································································································································ 332
Configuration examples ················································································································································· 334
802.1X configuration example ······························································································································· 334
ACL assignment configuration example ················································································································· 341
AAA configuration ·················································································································································· 351
Overview ········································································································································································· 351
Introduction to AAA ·················································································································································· 351
9
Page 10

Domain-based user management ···························································································································· 352
Configuring AAA ···························································································································································· 352
Configuration prerequisites······································································································································ 352
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 352
Configuring an ISP domain ····································································································································· 353
Configuring authentication methods for the ISP domain ······················································································ 354
Configuring authorization methods for the ISP domain ························································································ 355
Configuring accounting methods for the ISP domain ··························································································· 356
AAA configuration example ·········································································································································· 358
RADIUS configuration ············································································································································· 363
Introduction to RADIUS ············································································································································· 363
Client/server model ·················································································································································· 363
Security and authentication mechanisms ··············································································································· 363
Basic message exchange process of RADIUS ······································································································· 364
RADIUS packet format ·············································································································································· 365
Extended RADIUS attributes ····································································································································· 367
Protocols and standards ··········································································································································· 368
Configuring RADIUS ······················································································································································· 368
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 368
Configuring RADIUS servers ···································································································································· 369
Configuring RADIUS parameters ···························································································································· 370
RADIUS configuration example ····································································································································· 373
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 378
Users ········································································································································································ 379
Configuring users ···························································································································································· 379
Configuring a local user ·········································································································································· 379
Configuring a user group ········································································································································ 381
PKI configuration ····················································································································································· 383
PKI overview ···································································································································································· 383
PKI terms ···································································································································································· 383
Architecture of PKI ···················································································································································· 383
Applications of PKI ··················································································································································· 384
Operation of PKI ······················································································································································· 385
Configuring PKI ······························································································································································· 385
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 385
Creating a PKI entity ················································································································································· 388
Creating a PKI domain ············································································································································· 389
Generating an RSA key pair ··································································································································· 392
Destroying the RSA key pair ···································································································································· 392
Retrieving a certificate ·············································································································································· 393
Requesting a local certificate ··································································································································· 395
Retrieving and displaying a CRL ····························································································································· 396
PKI configuration example ············································································································································· 397
Configuring a PKI entity to request a certificate from a CA ················································································· 397
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 402
Port isolation group configuration ·························································································································· 403
Overview ········································································································································································· 403
Configuring a port isolation group ······························································································································· 403
Port isolation group configuration example ················································································································· 404
10
Page 11

Authorized IP configuration ···································································································································· 406
Overview ········································································································································································· 406
Configuring authorized IP ·············································································································································· 406
Authorized IP configuration example ··························································································································· 407
Authorized IP configuration example ····················································································································· 407
ACL configuration ··················································································································································· 410
ACL overview ·································································································································································· 410
Introduction to IPv4 ACL ··········································································································································· 410
Effective period of an ACL ······································································································································· 411
ACL step ····································································································································································· 412
Configuring an ACL ························································································································································ 412
Configuration task list ··············································································································································· 412
Configuring a time range ········································································································································ 413
Creating an IPv4 ACL ··············································································································································· 414
Configuring a rule for a basic IPv4 ACL ················································································································ 414
Configuring a rule for an advanced IPv4 ACL ······································································································ 416
Configuring a rule for an Ethernet frame header ACL ·························································································· 419
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 421
QoS configuration ··················································································································································· 422
Introduction to QoS ························································································································································ 422
Networks without QoS guarantee ·························································································································· 422
QoS requirements of new applications ·················································································································· 422
Congestion: causes, impacts, and countermeasures ···························································································· 422
End-to-end QoS ························································································································································· 424
Traffic classification ·················································································································································· 424
Packet precedences ·················································································································································· 425
Queue scheduling ····················································································································································· 427
Line rate ····································································································································································· 429
Priority mapping ······················································································································································· 430
Introduction to priority mapping tables ·················································································································· 431
QoS configuration ·························································································································································· 432
Configuration task lists ············································································································································· 432
Creating a class ························································································································································ 434
Configuring match criteria ······································································································································· 435
Creating a traffic behavior ······································································································································ 437
Configuring traffic mirroring and traffic redirecting for a traffic behavior ························································· 438
Configuring other actions for a traffic behavior ···································································································· 439
Creating a policy ······················································································································································ 440
Configuring classifier-behavior associations for the poli cy ·················································································· 440
Applying a policy to a port ····································································································································· 441
Configuring queue scheduling on a port ··············································································································· 442
Configuring line rate on a port ······························································································································· 443
Configuring priority mapping tables ······················································································································ 444
Configuring priority trust mode on a port ·············································································································· 445
Configuration guidelines ················································································································································ 447
ACL/QoS configuration examples ························································································································ 448
ACL/QoS configuration example ································································································································· 448
PoE configuration ···················································································································································· 458
PoE overview ··································································································································································· 458
Advantages ······························································································································································· 458
Composition ······························································································································································ 458
11
Page 12

Protocol specification ··············································································································································· 459
Configuring PoE ······························································································································································ 459
Configuring PoE ports ·············································································································································· 459
Configuring non-standard PD detection ················································································································· 461
Displaying information about PSE and PoE ports·································································································· 462
PoE configuration example ············································································································································ 462
Support and other resources ·································································································································· 465
Contacting HP ································································································································································· 465
Related information ························································································································································· 465
Conventions ····································································································································································· 465
Subscription service ························································································································································ 466
Index ········································································································································································ 467
12
Page 13

Overview
The HP V1910 Switch Series can be configured through the command line interface (CLI), web interface,
and SNMP/MIB. These configuration methods are suitable for different application scenarios.
The web interface supports all V1910 Switch Series configurations.
The CLI provides some configuration commands to facilitate your operation. To perform other
configurations not supported by the CLI, use the web interface.
1
Page 14

2
Configuration through the web interface
Web-based network management operating
environment
HP provides the web-based network management function to facilitate the operations and maintenance on
HP’s network devices. Through this function, the administrator can visually manage and maintain network
devices through the web-based configuration interfaces.
a. Web-based network management operating environment
Logging in to the web interface
Default login information
The device is provided with the default Web login information. You can use the default information to log
in to the web interface.
1. The default web login information
Information needed at lo
g
in Default value
Username admin
Password None
IP address of the device (VLAN-interface 1)
Default IP address of the device, depending on the status
of the network where the device resides.
Table 1 The device is not connected to the network, or no DHCP server exists in the subnet where the device
resides
If the device is not connected to the network, or no DHCP server exists in the subnet where the device resides,
you can get the default IP address of the device on the label on the device, as shown in b. The default subnet
mask is 255.255.0.0.
b. Default IP address of the device
Page 15

Table 2 A DHCP server exists in the subnet where the device resides
If a DHCP server exists in the subnet where the device resides, the device will dynamically obtain its default
IP address through the DHCP server. You can log in to the device through the console port, and execute the
summary command to view the information of its default IP address.
<Sysname> summary
Select menu option: Summary
IP Method: DHCP
IP address: 10.153.96.86
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Default gateway: 0.0.0.0
<Omitted>
Example
Assuming that the default IP address of the device is 169.254.52.86, follow these steps to log in to the
device through the web interface.
Connect the device to a PC
Connect the GigabitEthernet interface of the device to a PC by using a crossover Ethernet cable (by default,
all interfaces belong to VLAN 1).
Configure an IP address for the PC and ensure that the PC and device can communicate with each
other properly.
Select an IP address for the PC from network segment 169.254.0.0/16 (except for the default IP address
of the device), for example, 169.254.52.86.
Open the browser, and input the login information.
On the PC, open the browser (IE 5.0 or later), type the IP address http://169.254.52.86 in the address bar,
and press Enter to enter the login page of the web interface, as shown in a. Input the username admin and
verification code, leave the password blank, and click Login.
a. Login page of the web interface
3
Page 16

g
CAUTION:
The PC where you configure the device is not necessarily a web-based network mana
A web-based network management terminal is a PC used to log in to the web interface and is required
to be reachable to the device.
After logging in to the web interface, you can select Device Users from the navigation tree, create
a new user, and select Wizard or Network VLAN interface to configure the IP address of the VLAN
interface acting as the management interface. For more information, see the corresponding
configuration guides of these modules.
If you click the verification code displayed on the web login page, you can get a new verification code.
Up to five users can concurrently log in to the device through the web interface.
Logging out of the web interface
Click Logout in the upper-right corner of the web interface, as shown in a to quit the web console.
The system does not save the current configuration automatically. Therefore, it is recommended to save the
current configuration before logout.
ement terminal.
Introduction to the web interface
The Web interface is composed of three parts: navigation tree, title area, and body area, as shown in a.
a. Web-based configuration interface
(1) Navigation tree (2) Body area (3) Title area
Navigation tree—Organizes the web-based NM functions as a navigation tree, where you can select
and configure functions as needed. The result is displayed in the body area.
Body area—Allows you to configure and display features.
Title area—Displays the path of the current configuration interface in the navigation tree; provides the
Help button to display the web related help information, and the Logout button to log out of the web
interface.
4
Page 17

g
p
CAUTION:
The web network management functions not supported by the device are not displayed in the navi
tree.
Web user level
Web user levels, from low to high, are visitor, monitor, configure, and management. A user with a higher
level has all the operating rights of a user with a lower level.
Visitor—Users of this level can only use the network diagnostic tools ping and Trace Route. They can
neither access the device data nor configure the device.
Monitor—Users of this level can only access the device data but cannot configure the device.
Configure—Users of this level can access device data and configure the device, but they cannot
upgrade the host software, add/delete/modify users, or back up/restore configuration files.
Management—Users of this level can perform any operations to the device.
Introduction to the web-based NM functions
ation
NOTE:
User level in 1 indicates that users of this level or users of a higher level can perform the corresponding
operations.
1. Description of Web-based NM functions
Function menu Descri
Wizard IP Setup
Setup
IRF
Topology
Summary
Device
Summary
System
Information
Summary
Device
Information
Allows you to perform quick configuration of the
device.
Displays global settings and port settings of a
stack.
Allows you to configure global parameters and
stack ports.
Displays the topology summary of a stack. Configure
Displays the control panels of stack members. Configure
Displays the basic system information, system
resource state, and recent system operation logs.
Displays the port information of the device. Monitor
tion
User level
Management
Configure
Management
Monitor
Displays and allows you to configure the system
name.
Displays and allows you to configure the idle
timeout period for logged-in users.
Configure
Configure
Devi
ce
System Name
Basic
Web Idle
Timeout
5
Page 18

p
Function menu Descri
Device
Maintenan
ce
System
Time
Syslog
Configurati
on
Software
Upgrade
Reboot Allows you to configure to reboot the device. Management
Electronic Label Displays the electronic label of the device. Monitor
Diagnostic
Information
System Time
Loglist
Loghost Displays and allows you to configure the loghost. Configure
Log Setup
Backup
Restore
Allows you to configure to upload upgrade file
from local host, and upgrade the system software.
Generates diagnostic information file, and allows
you to view or save the file to local host.
Displays and allows you to configure the system
date and time.
Displays and refreshes system logs. Monitor
Allows you to clear system logs. Configure
Displays and allows you to configure the buffer
capacity, and interval for refreshing system logs.
Allows you to back up the configuration file to be
used at the next startup from the device to the host
of the current user.
Allows you to upload the configuration file to be
used at the next startup from the host of the current
user to the device.
tion
User level
Management
Management
Configure
Configure
Management
Management
File
Managem
ent
Port
Managem
ent
Port
Mirroring
Users
Save
Initialize Allows you to restore the factory default settings. Configure
File
Management
Summary Displays port information by features. Monitor
Detail Displays feature information by ports. Monitor
Setup
Summary
Create Allows you to create a port mirroring group. Configure
Remove Allows you to remove a port mirroring group. Configure
Modify Port
Summary
Super Password
Allows you to save the current configuration to the
configuration file to be used at the next startup.
Allows you to manage files on the device, such as
displaying the file list, downloading a file,
uploading a file, and removing a file.
Allows you to create, modify, delete, and
enable/disable a port, and clear port statistics.
Displays the configuration information of a port
mirroring group.
Allows you to configure ports for a mirroring
group.
Displays the brief information of FTP and Telnet
users.
Allows you to configure a password for a
lower-level user to switch from the current access
level to the management level.
Configure
Management
Configure
Monitor
Configure
Monitor
Management
Create Allows you to create an FTP or Telnet user. Management
6
Page 19

p
Function menu Descri
Modify
Remove Allows you to remove an FTP or a Telnet user. Management
Switch To
Management
Loopback Loopback
VCT VCT
Port Traffic
Flow
Interval
Storm
Constrain
Statistics
Interval
Configuration
Storm Constrain
Statistics
Allows you to modify FTP or Telnet user
information.
Allows you to switch the current user level to the
management level.
Allows you to perform loopback tests on Ethernet
interfaces.
Allows you to check the status of the cables
connected to Ethernet ports.
Displays the average rate at which the interface
receives and sends packets within a specified time
interval.
Allows you to set an interval for collecting traffic
statistics on interfaces.
Displays and allows you to set the interval for
collecting storm constrain statistics.
Displays, and allows you to create, modify, and
remove the port traffic threshold.
Displays, and allows you to create, modify, and
clear RMON statistics.
tion
User level
Management
Visitor
Configure
Configure
Monitor
Configure
Configure
Configure
RMON
Energy
Saving
SNMP
History
Alarm
Event
Log Displays log information about RMON events. Configure
Energy Saving
Setup
Community
Group
User
Displays, and allows you to create, modify, and
clear RMON history sampling information.
Allows you to view, create, modify, and clear
alarm entries.
Allows you to view, create, modify, and clear event
entries.
Displays and allows you to configure the energy
saving settings of an interface.
Displays and refreshes SNMP configuration and
statistics information.
Allows you to configure SNMP. Configure
Displays SNMP community information. Monitor
Allows you to create, modify and delete an SNMP
community.
Displays SNMP group information. Monitor
Allows you to create, modify and delete an SNMP
group.
Displays SNMP user information. Monitor
Allows you to create, modify and delete an SNMP
user.
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Monitor
Configure
Configure
Configure
7
Page 20

p
Function menu Descri
Displays the status of the SNMP trap function and
information about target hosts.
Allows you to enable or disable the SNMP trap
function, or create, modify and delete a target host.
Displays SNMP view information. Monitor
Allows you to create, modify and delete an SNMP
view.
Displays and allows you to clear the statistics
information of an interface.
Allows you to modify the description and member
ports of a VLAN.
Allows you to change the VLAN to which a port
belongs.
Interface
Statistics
VLAN
Trap
View
Interface
Statistics
Select VLAN Allows you to select a VLAN range. Monitor
Create Allows you to create VLANs. Configure
Port Detail Displays the VLAN-related details of a port. Monitor
Detail Displays the member port information of a VLAN. Monitor
Modify VLAN
Modify Port
Remove Allows you to remove VLANs. Configure
tion
User level
Monitor
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Net
work
VLAN
Interface
Voice
VLAN
MAC
Summary
Create
Modify
Remove Allows you to remove VLAN interfaces. Configure
Summary
Setup Allows you to configure the global voice VLAN. Configure
Port Setup Allows you to configure a voice VLAN on a port. Configure
OUI Summary
OUI Add
OUI Remove
MAC
Setup
Displays information about VLAN interfaces by
address type.
Allows you to create VLAN interfaces and
configure IP addresses for them.
Allows you to modify the IP addresses and status of
VLAN interfaces.
Displays voice VLAN information globally or on a
port.
Displays the addresses of the OUIs that can be
identified by voice VLAN.
Allows you to add the address of an OUI that can
be identified by voice VLAN.
Allows you to remove the address of an OUI that
can be identified by voice VLAN.
Displays MAC address information. Monitor
Allows you to create and remove MAC addresses. Configure
Displays and allows you to configure MAC address
aging time.
Monitor
Configure
Configure
Monitor
Monitor
Configure
Configure
Configure
MSTP Region Displays information about MST regions. Monitor
8
Page 21

p
Function menu Descri
Allows you to modify MST regions. Configure
Global Allows you to set global MSTP parameters. Configure
Port Summary Displays the MSTP information of ports. Monitor
Port Setup Allows you to set MSTP parameters on ports. Configure
Displays information about link aggregation
groups.
Displays information about LACP-enabled ports
and their partner ports.
Displays the LLDP configuration information, local
information, neighbor information, statistics
information, and status information of a port.
Allows you to modify LLDP configuration on a port. Configure
Displays global LLDP configuration information. Monitor
Allows you to configure global LLDP parameters. Configure
Link
Aggregati
on
LACP
LLDP
Summary
Create Allows you to create link aggregation groups. Configure
Modify Allows you to modify link aggregation groups. Configure
Remove Allows you to remove link aggregation groups. Configure
Summary
Setup Allows you to set LACP priorities. Configure
Port Setup
Global Setup
tion
User level
Monitor
Monitor
Monitor
Global
Summary
Neighbor
Summary
Basic
IGMP
Snooping
Advanced
Summary Displays the IPv4 active route table. Monitor
IPv4
Routing
DHCP DHCP Relay
Create Allows you to create an IPv4 static route. Configure
Remove Allows you to delete the selected IPv4 static routes. Configure
Displays global LLDP local information and
statistics.
Displays global LLDP neighbor information. Monitor
Displays global IGMP snooping configuration
information or the IGMP snooping configuration
information in a VLAN, and allows you to view the
IGMP snooping multicast entry information.
Allows you to configure IGMP snooping globally or
in a VLAN.
Displays the IGMP snooping configuration
information on a port.
Allows you to configure IGMP snooping on a port. Configure
Displays information about the DHCP status,
advanced configuration information of the DHCP
relay agent, DHCP server group configuration,
DHCP relay agent interface configuration, and the
DHCP client information.
Monitor
Monitor
Configure
Monitor
Monitor
9
Page 22

p
Function menu Descri
Allows you to enable/disable DHCP, configure
advanced DHCP relay agent settings, configure a
DHCP server group, and enable/disable the DHCP
relay agent on an interface.
Displays the status, trusted and untrusted ports and
DHCP
Snooping
Service Service
Diagnostic
Tools
ARP
Managem
ent
Ping Allows you to ping an IPv4 address. Visitor
Trace Route Allows you to perform trace route operations. Visitor
ARP Table
Gratuitous ARP
DHCP client information of DHCP snooping.
Allows you to enable/disable DHCP snooping,
and configure DHCP snooping trusted and
untrusted ports.
Displays the states of services: enabled or
disabled.
Allows you to enable/disable services, and set
related parameters.
Displays ARP table information. Monitor
Allows you to add, modify, and remove ARP
entries.
Displays the configuration information of gratuitous
ARP.
Allows you to configure gratuitous ARP. Configure
tion
User level
Configure
Monitor
Configure
Configure
Management
Configure
Monitor
Auth
entic
ation
ARP
Anti-Attack
802.1X 802.1X
AAA
ARP Detection
Domain Setup
Authentication
Authorization
Accounting
Displays ARP detection configuration information. Monitor
Allows you to configure ARP detection. Configure
Displays 802.1X configuration information
globally or on a port.
Allows you to configure 802.1X globally or on a
port.
Displays ISP domain configuration information. Monitor
Allows you to add and remove ISP domains. Management
Displays the authentication configuration
information of an ISP domain.
Allows you to specify authentication methods for an
ISP domain.
Displays the authorization method configuration
information of an ISP domain.
Allows you to specify authorization methods for an
ISP domain.
Displays the accounting method configuration
information of an ISP domain.
Monitor
Configure
Monitor
Management
Monitor
Management
Monitor
10
Page 23

p
Function menu Descri
Allows you to specify accounting methods for an
ISP domain.
RADIUS Server
RADIUS
RADIUS Setup
Local User
Users
User Group
Entity
Domain
Displays and allows you to configure RADIUS
server information.
Displays and allows you to configure RADIUS
parameters.
Displays configuration information about local
users.
Allows you to create, modify and remove a local
user.
Displays configuration information about user
groups.
Allows you to create, modify and remove a user
group.
Displays information about PKI entities. Monitor
Allows you to add, modify, and delete a PKI entity. Configure
Displays information about PKI domains. Monitor
Allows you to add, modify, and delete a PKI
domain.
tion
User level
Management
Management
Management
Monitor
Management
Monitor
Management
Configure
Secu
rity
QoS
PKI
Port Isolate
Group
Authorized
IP
Time
Range
ACL IPv4
Displays the certificate information of PKI domains
and allows you to view the contents of a certificate.
Certificate
CRL
Summary Displays port isolation group information. Monitor
Modify Allows you to configure a port isolation group. Configure
Summary
Setup Allows you to configure authorized IP. Management
Summary Displays time range configuration information. Monitor
Create Allows you to create a time range. Configure
Remove Allows you to delete a time range. Configure
Summary Displays IPv4 ACL configuration information. Monitor
Create Allows you to create an IPv4 ACL. Configure
Basic Setup Allows you to configure a rule for a basic IPv4 ACL. Configure
Allows you to generate a key pair, destroy a key
pair, retrieve a certificate, request a certificate, and
delete a certificate.
Displays the contents of the CRL. Monitor
Allows you to receive the CRL of a domain. Configure
Displays the configurations of authorized IP, the
associated IPv4 ACL list, and the associated IPv6
ACL list.
Monitor
Configure
Management
Advanced
Setup
Allows you to configure a rule for an advanced
IPv4 ACL.
Configure
11
Page 24

p
Function menu Descri
Link Setup Allows you to create a rule for a link layer ACL. Configure
Remove Allows you to delete an IPv4 ACL or its rules. Configure
Queue
Line Rate
Classifier
Behavior
Summary Displays the queue information of a port. Monitor
Setup Allows you to configure a queue on a port. Configure
Summary Displays line rate configuration information. Monitor
Setup Allows you to configure the line rate. Configure
Summary Displays classifier configuration information. Monitor
Create Allows you to create a class. Configure
Setup
Remove
Summary Displays traffic behavior configuration information. Monitor
Create Allows you to create a traffic behavior. Configure
Setup
Allows you to configure the classification rules for a
class.
Allows you to delete a class or its classification
rules.
Allows you to configure actions for a traffic
behavior.
tion
User level
Configure
Configure
Configure
QoS Policy
Port Policy
Priority
Mapping
Port Priority Port Priority
PoE PoE
Port Setup
Remove Allows you to delete a traffic behavior. Configure
Summary Displays QoS policy configuration information. Monitor
Create Allows you to create a QoS policy. Configure
Setup
Remove
Summary Displays the QoS policy applied to a port. Monitor
Setup Allows you to apply a QoS policy to a port. Configure
Remove Allows you to remove the QoS policy from the port. Configure
Priority
Mapping
Summary
Setup Allows you to configure a PoE interface. Configure
Allows you to configure traffic mirroring and traffic
redirecting for a traffic behavior
Allows you to configure the classifier-behavior
associations for a QoS policy.
Allows you to delete a QoS policy or its
classifier-behavior associations.
Displays priority mapping table information. Monitor
Allows you to modify the priority mapping entries. Configure
Displays port priority and trust mode information. Monitor
Allows you to modify port priority and trust mode. Configure
Displays PSE information and PoE interface
information.
Configure
Configure
Configure
Monitor
12
Page 25

13
Introduction to the common items on the web pages
Buttons and icons
1. Commonly used buttons and icons
Button and icon Function
Used to apply the configuration on the current page.
Used to cancel the configuration on the current page, and return to the
corresponding list page or the Device Info page.
Used to refresh the information on the current page.
Used to clear all the information on a list or all statistics.
Used to enter a page for adding an item.
,
Used to remove the selected items.
Used to select all the entries on a list, or all the ports on the device panel.
Used to deselect all the entries on a list, or all the ports on the device panel.
Generally present on the configuration wizard; used to buffer but not apply
the configuration of the current step and enter the next configuration step.
Generally present on the configuration wizard; used to buffer but not apply
the configuration of the current step and return to the previous configuration
step.
Generally present on the configuration wizard; used to apply the
configurations of all configuration steps.
Generally present on the “Operation” column on a list; used to enter the
modification page of an item so that you can modify the configurations of
the item.
Generally present on the “Operation” column on a list; used to delete the
item corresponding to this icon.
Click the plus sign before a corresponding item. You can see the collapsed
contents.
Page display
The web interface can display a long list by pages, as shown in a. You can set the number of entries
displayed per page, and use the First, Prev, Next, and Last links to view the contents on the first, previous,
next, and last pages, or go to any page that you want to view.
Page 26

14
a. Content display by pages
Search function
On some list pages, the web interface provides basic and advanced search functions. You can use the
search function to display those entries matching certain search criteria.
Basic search function—Select a search item from the drop-down list as shown in a, input the keyword,
and click the Query button to display the entries that match the criteria.
Advanced search function—Click
before Search Item, as shown in a. You can select Match case
and whole word, that is, the item to be searched must completely match the keyword, or you can select
Search in previous results. If you do not select exact search, a fuzzy search is performed.
a. Advanced search
Sorting function
On some list pages, the web interface provides the sorting function to display the entries in a certain order.
As shown in a, you can click the blue heading item of each column to sort the entries based on the heading
item you selected. Then, the heading item is displayed with an arrow beside it. The upward arrow indicates
the ascending order, and the downward arrow indicates the descending order.
Page 27

a. Sort display (based on MAC address in the ascending order)
Configuration guidelines
The web console supports Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 SP2 and higher.
The web console does not support the Back, Next, Refresh buttons provided by the browser. Using
these buttons may result in abnormal display of web pages.
When the device is performing the spanning tree calculation, you cannot log in to or use the web
interface.
The Windows firewall limits the number of TCP connections, so when you use IE to log in to the web
interface, sometimes you may be unable to open the web interface. To avoid this problem, turn off the
Windows firewall before login.
If the software version of the device changes, when you log in to the device through the web interface,
delete the temporary Internet files of IE; otherwise, the web page content may not be displayed
correctly.
15
Page 28

16
Configuration at the CLI
NOTE:
The HP V1910 Switch Series can be configured through the CLI, web interface, and SNMP/MIB,
among which the web interface supports all V1910 Switch Series configurations. These configuration
methods are suitable for different application scenarios. As a supplementary to the web interface, the
CLI provides some configuration commands to facilitate your operation, which are described in this
chapter. To perform other configurations not supported by the CLI, use the web interface.
You will enter user view directly after you log in to the device. Commands in the document are all
performed in user view.
Getting started with the CLI
As a supplementary to the web interface, the CLI provides some configuration commands to facilitate your
operation. For example, if you forget the IP address of VLAN-interface 1 and cannot log in to the device
through the web interface, you can connect the console port of the device to a PC, and reconfigure the IP
address of VLAN-interface 1 at the CLI.
This section describes using the CLI to manage the device.
Setting up the configuration environment
To set up the configuration environment, connect a terminal (a PC in this example) to the console port on the
switch with a console cable.
A console cable is an 8-core shielded cable, with a crimped RJ-45 connector at one end for connecting to
the console port of the switch, and a DB-9 female connector at the other end for connecting to the serial port
on the console terminal.
a. Console cable
Use a console cable to connect a terminal device to the switch, as follows:
Table 3 Plug the DB-9 female connector to the serial port of the console terminal or PC.
Table 4 Connect the RJ-45 connector to the console port of the switch.
Page 29

V
b. Network diagram for configuration environment setup
CAUTION:
erify the mark on the console port to ensure that you are connecting to the correct port.
NOTE:
The serial port on a PC does not support hot swapping. When you connect a PC to a powered-on
switch, connect the DB-9 connector of the console cable to the PC before connecting the RJ-45
connector to the switch.
When you disconnect a PC from a powered-on switch, disconnect the DB-9 connector of the console
cable from the PC after disconnecting the RJ-45 connector from the switch.
Setting terminal parameters
To configure and manage the switch, you must run a terminal emulator program on the console terminal, for
example, a PC. This section uses Windows XP HyperTerminal as an example.
The following are the required terminal settings:
Bits per second—38400
Data bits—8
Parity—None
Stop bits—1
Flow control—None
Emulation—VT100
Follow these steps to set terminal parameters, for example, on a Windows XP HyperTerminal:
Table 5 Select Start All Programs Accessories Communications HyperTerminal, and in the
Connection Description dialog box that appears, type the name of the new connection in the Name text
box and click OK.
17
Page 30

b. Connection description of the HyperTerminal
Table 6 Select the serial port to be used from the Connect using drop-down list, and click OK.
c. Set the serial port used by the HyperTerminal connection
Table 7 Set Bits per second to 38400, Data bits to 8, Parity to None, Stop bits to 1, and Flow control to
None, and click OK.
18
Page 31
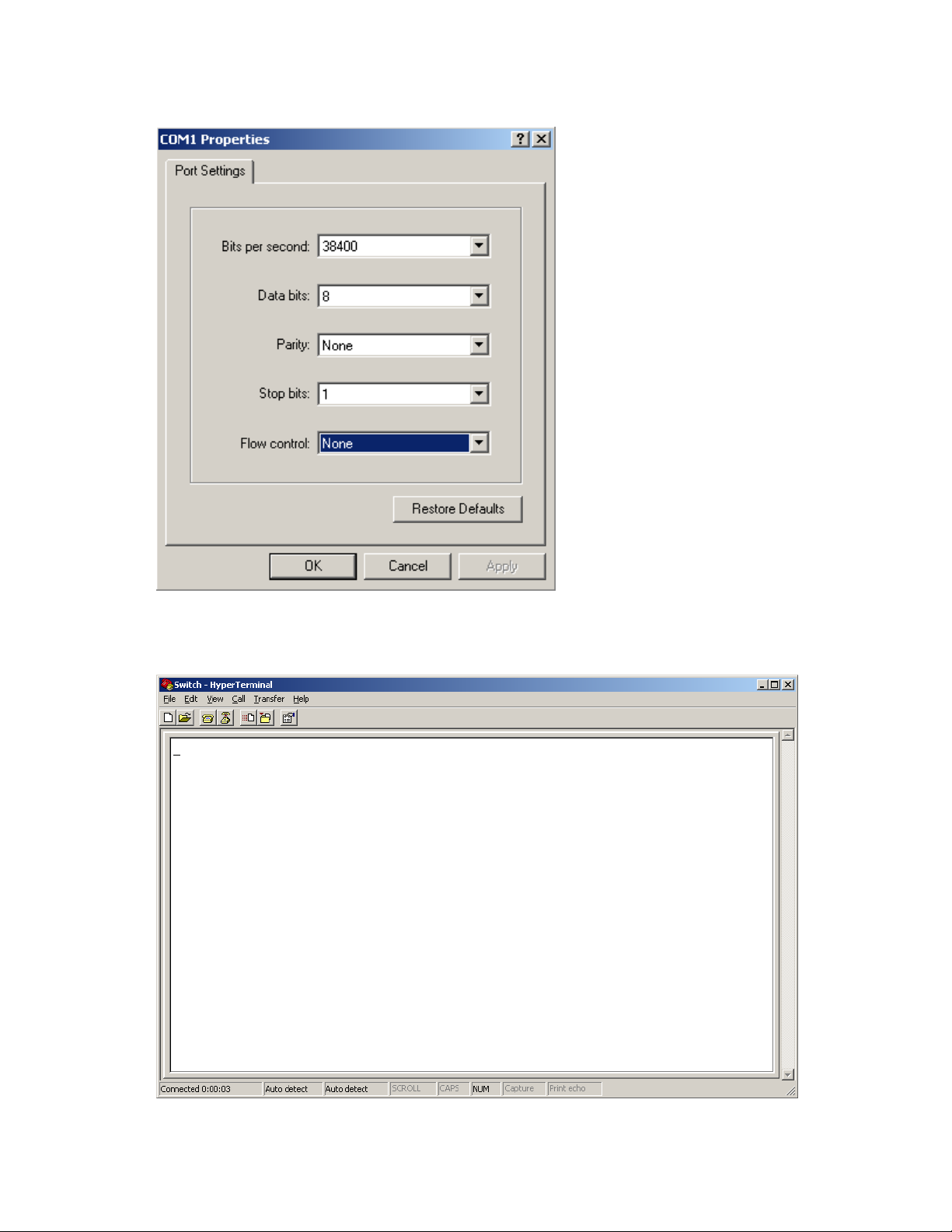
d. Set the serial port parameters
Table 8 Select File Properties in the HyperTerminal window.
e. HyperTerminal window
19
Page 32

Table 9 Click the Settings tab, set the emulation to VT100, and click OK in the Switch Properties dialog box.
f. Set terminal emulation in Switch Properties dialog box
Logging in to the CLI
The login process requires a username and password. The default username for first time configuration is
admin, no password is required. Usernames and passwords are case sensitive.
To log in to the CLI:
Table 10 Press Enter. The Username prompt displays:
Login authentication
Username:
Table 11 Enter your username at the Username prompt.
Username:admin
Table 12 Press Enter. The Password prompt display
Password:
The login information is verified, and displays the following CLI menu:
<HP V1910 Switch>
If the password is invalid, the following message appears and process restarts.
% Login failed!
20
Page 33

CLI commands
This Command section contains the following commands:
To do… Use the command…
Display a list of CLI commands on the device ?
Reboot the device and run the default configuration initialize
Specify VLAN-interface 1 to obtain an IP address through
DHCP or manual configuration
Modify the login password of a user password
Download the Boot ROM image or system software image file
from the TFTP server and specify as the startup configuration
file
Reboot the device and run the main configuration file reboot
View the summary information of the device summary
Ping a specified destination ping host
initialize
Syntax
initialize
Parameters
None
Description
ipsetup { dhcp | ip address ip-address { mask
| mask-length } [ default-gateway
ip-address ] }
upgrade server-address source-filename
{ bootrom | runtime }
Use the initialize command to delete the current configuration file and reboot the device with the default
configuration file.
Use the command with caution because it deletes the configuration file to be used at the next startup and
restores the factory default settings.
Examples
# Delete the configuration file to be used at the next startup and reboot the device with the default
configuration being used during reboot.
<Sysname> initialize
The startup configuration file will be deleted and the system will be rebooted.Continue?
[Y/N]:y
Please wait...
ipsetup
Syntax
ipsetup { dhcp | ip address ip-address { mask | mask-length } [ default-gateway ip-address ] }
21
Page 34

Parameters
dhcp: Specifies the interface to obtain an IP address through DHCP.
ip-address ip-address: Specifies an IP address for VLAN-interface 1 in dotted decimal notation.
mask: Subnet mask in dotted decimal notation.
mask-length: Subnet mask length, the number of consecutive ones in the mask, in the range of 0 to 32.
default-gateway ip-address: Specifies the IP address of the default gateway or the IP address of the
outbound interface. With this argument and keyword combination configured, the command not only
assigns an IP address to the interface, but also specifies a default route for the device.
Description
Use the ipsetup dhcp command to specify VLAN-interface 1 to obtain an IP address through DHCP.
Use the ipsetup ip address ip-address { mask | mask-length } command to assign an IP address to
VLAN-interface 1.
By default, the device automatically obtains its IP address through DHCP; if fails, it uses the assigned default
IP address. For more information, see b.
If there is no VLAN-interface 1, either command creates VLAN-interface 1 first, and then specifies its IP
address.
Examples
# Create VLAN-interface 1 and specify the interface to obtain an IP address through DHCP.
<Sysname> ipsetup dhcp
# Create VLAN-interface 1 and assign 192.168.1.2 to the interface, and specify 192.168.1.1 as the
default gateway.
<Sysname> ipsetup ip-address 192.168.1.2 24 default-gateway 192.168.1.1
password
Syntax
password
Parameters
None
Description
Use the password command to modify the login password of a user.
Examples
# Modify the login password of user admin.
<Sysname> password
Change password for user: admin
Old password: ***
Enter new password: **
Retype password: **
The password has been successfully changed.
22
Page 35

ping
Syntax
ping host
Parameters
host: Destination IP address (in dotted decimal notation), URL, or host name (a string of 1 to 20 characters).
Description
Use the ping command to ping a specified destination.
You can enter Ctrl+C to terminate a ping operation.
Examples
# Ping IP address 1.1.2.2.
<Sysname> ping 1.1.2.2
PING 1.1.2.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 1.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=205 ms
Reply from 1.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=1 ms
Reply from 1.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=1 ms
Reply from 1.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=1 ms
Reply from 1.1.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=1 ms
--- 1.1.2.2 ping statistics -- 5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 1/41/205 ms
The output shows that IP address 1.1.2.2 is reachable and the echo replies are all returned from the
destination. The minimum, average, and maximum roundtrip intervals are 1 millisecond, 41 milliseconds,
and 205 milliseconds respectively.
quit
Syntax
quit
Parameters
None
Description
Use the quit command to log out of the system.
Examples
# Log out of the system.
<Sysname> quit
******************************************************************************
* Copyright (c) 2004-2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. *
* Without the owner's prior written consent, *
23
Page 36

* no decompiling or reverse-engineering shall be allowed. *
******************************************************************************
User interface aux0 is available.
Please press ENTER.
reboot
Syntax
reboot
Parameters
None
Description
Use the reboot command to reboot the device and run the main configuration file.
Use this command with caution because reboot results in service interruption.
If the main configuration file is corrupted or does not exist, the device cannot be rebooted with the reboot
command. In this case, you can specify a new main configuration file to reboot the device, or you can
power off the device, and then power it on, and the system will automatically use the backup configuration
file at the next startup.
If you reboot the device when file operations are being performed, the system does not execute the
command to ensure security.
Examples
# If the configuration does not change, reboot the device.
<Sysname> reboot
Start to check configuration with next startup configuration file, please wait.........DONE!
This command will reboot the device. Continue? [Y/N]:y
Now rebooting, please wait...
# If the configuration changes, reboot the device.
<Sysname> reboot
Start to check configuration with next startup configuration file, please wait.........DONE!
This command will reboot the device. Current configuration will be lost in next startup if
you continue. Continue? [Y/N]:y
Now rebooting, please wait...
summary
Syntax
summary
Parameters
None
24
Page 37

Description
Use the summary command to view the summary information of the device, including the IP address of
VLAN-interface 1, and software version information.
Examples
# Display summary information of the device.
<Sysname> summary
Select menu option: Summary
IP Method: DHCP
IP address: 10.153.96.86
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Default gateway: 0.0.0.0
Current boot app is: flash:/v1910-cmw520-a1108.bin
Next main boot app is: flash:/v1910-cmw520-a1108.bin
Next backup boot app is: NULL
HP Comware Platform Software
Comware Software, Version 5.20 Alpha 1108,
Copyright (c) 2004-2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
HP V1910-24G-PoE (365W) Switch uptime is 0 week, 0 day, 6 hours, 28 minutes
HP V1910-24G-PoE (365W) Switch
128M bytes DRAM
128M bytes Nand Flash Memory
Config Register points to Nand Flash
Hardware Version is REV.B
CPLD Version is 002
Bootrom Version is 138
[SubSlot 0] 24GE+4SFP+POE Hardware Version is REV.B
upgrade
Syntax
upgrade server-address source-filename { bootrom | runtime }
Parameters
server-address: IP address or host name (a string of 1 to 20 characters) of a TFTP server.
source-filename: Software package name on the TFTP server.
bootrom: Specifies the Boot ROM image in the software package file as the startup configuration file.
runtime: Specifies the system software image file in the software package file as the startup configuration
file.
25
Page 38

26
Description
Use the upgrade server-address source-filename bootrom command to upgrade the Boot ROM image. If the
Boot ROM image in the downloaded software package file is not applicable, the original Boot ROM image
is still used as the startup configuration file.
Use the upgrade server-address source-filename runtime command to upgrade the system software image
file. If the system software image file in the downloaded software package file is not applicable, the original
system software image file is still used as the startup configuration file.
To make the downloaded software package file take effect, reboot the device.
NOTE:
The HP V1910 Switch Series does not provide an independent Boot ROM image; instead, it integrates the
Boot ROM image with the system software image file together in a software package file with the
extension name of .bin.
Examples
# Download software package file main.bin from the TFTP server and use the Boot ROM image in the
package as the startup configuration file.
<Sysname> upgrade 192.168.20.41 main.bin bootrom
# Download software package file main.bin from the TFTP server and use the system software image file in
the package as the startup configuration file.
<Sysname> upgrade 192.168.20.41 main.bin runtime
Configuration example for upgrading the system
software image at the CLI
Network requirements
As shown in a, a V1910 switch is connected to the PC through the console cable, and connected to the
gateway through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. The IP address of the gateway is 192.168.1.1/24, and the TFTP
server where the system software image (SwitchV1910.bin) is located is 192.168.10.1/24. The gateway
and the switch can reach each other.
The administrator upgrades the Boot ROM image and the system software image file of the V1910 switch
through the PC and sets the IP address of the switch to 192.168.1.2/24.
a. Network diagram for upgrading the system software image of the V1910 switch at the CLI
Configuration procedure
Table 13 Run the TFTP server program on the TFTP server, and specify the path of the file to be loaded.
(Omitted)
Table 14 Perform the following configurations on the switch.
Page 39

# Configure the IP address of VLAN-interface 1 of the switch as 192.168.1.2/24, and specify the default
gateway as 192.168.1.1.
<Switch> ipsetup ip-address 192.168.1.2 24 default-gateway 192.168.1.1
# Download the software package file SwitchV1910.bin from the TFTP server to the switch, and upgrade the
system software image in the package.
<Switch> upgrade 192.168.10.1 SwitchV1910.bin runtime
File will be transferred in binary mode
Downloading file from remote TFTP server, please wait.../
TFTP: 10262144 bytes received in 71 second(s)
File downloaded successfully.
# Download the software package file SwitchV1910.bin from the TFTP server to the switch, and upgrade the
Boot ROM image.
<Switch> upgrade 192.168.10.1 SwitchV1910.bin bootrom
The file flash:/SwitchV1910.bin exists. Overwrite it? [Y/N]:y
Verifying server file...
Deleting the old file, please wait...
File will be transferred in binary mode
Downloading file from remote TFTP server, please wait.../
TFTP: 10262144 bytes received in 61 second(s)
File downloaded successfully.
BootRom file updating finished!
# Reboot the switch.
<Switch> reboot
After getting the new image file, reboot the switch to have the upgraded image take effect.
27
Page 40

Configuration wizard
Overview
The configuration wizard guides you through the basic service setup, including the system name, system
location, contact information, and management IP address (IP address of the VLAN interface).
Basic service setup
Entering the configuration wizard homepage
From the navigation tree, select Wizard to enter the configuration wizard homepage, as shown in a.
a. Configuration wizard homepage
Configuring system parameters
In the wizard homepage, click Next to enter the system parameter configuration page, as shown in a.
28
Page 41

p
a. System parameter configuration page
2. System parameter configuration items
Item Descri
Specify the system name.
The system name appears at the top of the navigation tree.
Sysname
Syslocation
Syscontact
You can also set the system name in the System Name page you enter by selecting
Device Basic. For more information, see the chapter “Device basic information
configuration”.
Specify the physical location of the system.
You can also set the physical location in the setup page you enter by selecting Device
Set the contact information for users to get in touch with the device vendor for help.
You can also set the contact information in the setup page you enter by selecting Device
tion
SNMP. For more information, see the chapter “SNMP configuration”.
SNMP. For more information, see the chapter “SNMP configuration”.
Configuring management IP address
NOTE:
Modifying the management IP address used for the current login will tear down the connection to the
device. Use the new management IP address to re-log in to the system.
29
Page 42

p
A management IP address is the IP address of a VLAN interface, which can be used to access the device.
You can also set configure a VLAN interface and its IP address in the page you enter by selecting Network
VLAN Interface. For more information, see the chapter “VLAN interface configuration”.
After finishing the configuration, click Next to enter the management IP address configuration page, as
shown in a.
a. Management IP address configuration page
2. Management IP address configuration items
Item Descri
Select a VLAN interface.
Select VLAN Interface
Admin Status
Configure IPv4
address
Available VLAN interfaces are those configured in the page you enter by selecting
Network VLAN Interface and selecting the Create tab.
Enable or disable the VLAN interface.
When errors occurred on the VLAN interface, disable the interface and then enable
the port to bring the port to work properly.
By default, the VLAN interface is in the down state if all Ethernet ports in the VLAN are
down. The VLAN is in the up state if one or more ports in the VLAN are up.
Disabling or enabling the VLAN interface does not affect the status of the Ethernet ports
in the VLAN. That is, the port status does not change with the VLAN interface status.
DHCP
tion
IMPORTANT:
Configure how the VLAN interface obtains an IPv4 address.
DHCP: Specifies the VLAN interface to obtain an IPv4 address by
30
Page 43

Item Description
DHCP.
BOOTP
BOOTP: Specifies the VLAN interface to obtain an IPv4 address
through BOOTP.
Manual: Allows you to specify an IPv4 address and a mask length.
Manual
IPv4
address
MaskLen
IMPORTANT:
Support for IPv4 obtaining methods depends on the device model.
Specify an IPv4 address and the mask length for the VLAN interface.
These two text boxes are configurable if Manual is selected.
Finishing configuration wizard
After finishing the management IP address configuration, click Next, as shown in a.
a. Configuration finishes
The page displays your configurations. Review the configurations and if you want to modify the settings
click Back to go back to the page. Click Finish to confirm your settings and the system then performs the
configurations.
31
Page 44

32
IRF stack management
The HP V1910 IRF stack management feature enables you to configure and monitor a stack of connected HP
V1910 switches by logging in to one switch in the stack, as shown in a.
IMPORTANT:
The HP V1910 IRF stack management feature does not provide the functions of HP Intelligent Resilient
Framework (IRF) technology. To avoid confusion, IRF stack management is simply called stack
management in this document.
a. Network diagram for stack management
To set up a stack, you must log in to one switch to create the stack, and this switch becomes the master for
the stack. You then configure and monitor all other member switches on the master switch. The ports that
connect the stack member switches are called stack ports.
Configuring stack management
Stack management configuration task list
Perform the tasks in 1 to configure stack management.
1. Stack management configuration task list
Task Remarks
Configuring
the master
switch of a
stack
Configuring global
parameters of a
stack
Required
Configure a private IP address pool for a stack and establish the stack,
with the switch becoming the master switch of the stack.
By default, no IP address pool is configured for a stack and no stack is
established.
Page 45

Task Remarks
Required
Configuring stack
ports
Configure the ports of the master switch that connect to member
switches as stack ports.
By default, a port is not a stack port.
Configuring
member
switches of a
stack
Displaying topology summary of a
stack
Displaying device summary of a stack
Logging into a member switch from
the master switch
Configuring stack
ports
Required
Configure a port of a member switch that connects to the master switch
or another member switch as a stack port.
By default, a port is not a stack port.
Optional
Display the information of stack members.
Optional
Display the control panels of stack members.
IMPORTANT:
Before viewing the control panel of a member switch, you must ensure
that the username, password, and access right you used to log on to the
master switch are the same with those configured on the member switch;
otherwise, the control panel of the member switch cannot be displayed.
Optional
Log in to the web interface of a member switch from the master switch.
IMPORTANT:
Before logging into a member switch, you must ensure that the
username, password, and access right you used to log on to the master
switch are the same with those configured on the member switch;
otherwise, you cannot log into the member switch. You can configure
them by selecting Device and then clicking Users from the navigation
tree.
Configuring global parameters of a stack
Select IRF from the navigation tree to enter the page shown in a. You can configure global parameters of a
stack in the Global Settings area.
33
Page 46

p
a. Setup
2. Configuration items of global parameters
Item Descri
Configure a private IP address pool for the stack.
Private Net IP
Mask
The master switch of a stack must be configured with a private IP address pool to
ensure that it can automatically allocate an available IP address to a member switch
when the device joints the stack.
When you configure a private IP address pool for a stack, the number of IP addresses
in the address pool needs to be equal to or greater than the number of switches to be
added to the stack. Otherwise, some switches may not be able to join the stack
automatically for lack of private IP addresses.
tion
IMPORTANT:
34
Page 47
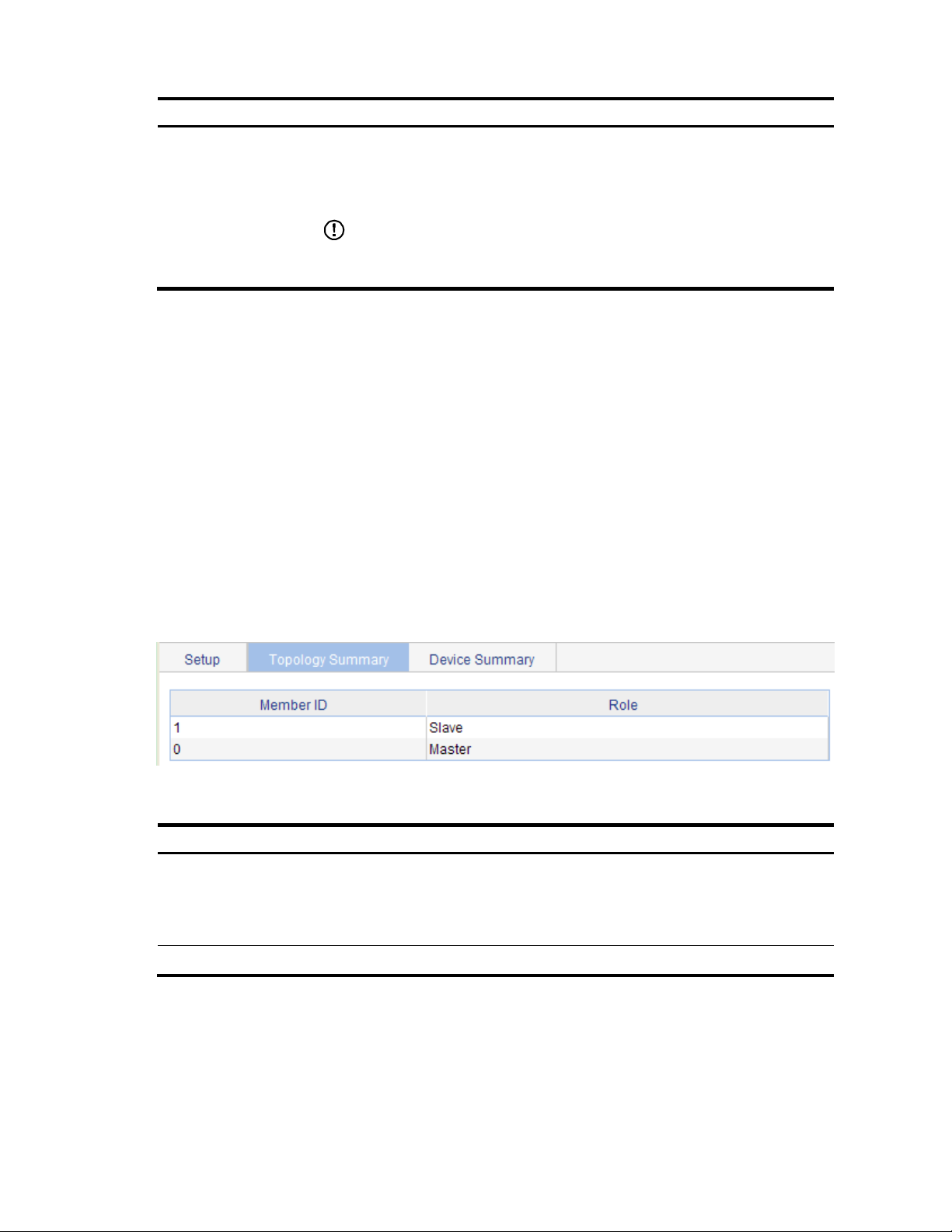
p
Item Description
Enable the switch to establish a stack.
After you enable the switch to establish a stack, the switch becomes the master switch
of the stack and automatically adds the switches connected to its stack ports to the
Build Stack
stack.
IMPORTANT:
You can delete a stack only on the master switch of the stack. The Global Settings area
on a member switch is grayed out.
Return to Stack management configuration task list.
Configuring stack ports
Select IRF from the navigation tree to enter the page shown in a. You can configure stack ports in the Port
Settings area.
Select the check box before a port name, and click Enable to configure the port as a stack port.
Select the check box before a port name, and click Disable to configure the port as a non-stack port.
Return to Stack management configuration task list.
Displaying topology summary of a stack
Select IRF from the navigation tree and click the Topology Summary tab to enter the page shown in a.
a. Topology summary
2. Fields of topology summary
Fields Descri
Member ID of the device in the stack:
Member ID
Value 0 indicates that the switch is the master switch of the stack.
A value other than 0 indicates that the switch is a member switch and the value
Role Role of the switch in the stack: master or member.
Return to Stack management configuration task list.
tion
is the member ID of the switch in the stack.
35
Page 48

Displaying device summary of a stack
Select IRF from the navigation tree and click the Device Summary tab to enter the page shown in a. On this
page, you can view interfaces and power socket layout on the panel of each stack member by clicking the
tab of the corresponding member switch.
a. Device summary (the master switch)
Return to Stack management configuration task list.
Logging into a member switch from the master switch
Select IRF from the navigation tree, click the Device Summary tab, and click the tab of a member switch to
enter the page shown in a.
Click the Configuring the Device hyperlink, you can log on to the web interface of the member switch to
manage and maintain the member switch directly.
a. Device summary (a member switch)
Return to Stack management configuration task list.
Stack configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in a, Switch A, Switch B, Switch C, and Switch D are connected with one another.
36
Page 49

37
Create a stack, where Switch A is the master switch, Switch B, Switch C, and Switch D are stack
members. An administrator can log in to Switch B, Switch C and Switch D through Switch A to perform
remote configurations.
a. Network diagram for stack management
Eth1/0/1
Eth1/0/3
Switch B
Eth1/0/1Eth1/0/1
Switch C Switch D
Stack
Eth1/0/1
Eth1/0/2
Switch A
(Master switch)
Configuration procedure
Table 15 Configure the master switch
# Configure global parameters for the stack on Switch A.
Select IRF from the navigation tree of Switch A to enter the page of the Setup tab.
Page 50

b. Configure global parameters for the stack on Switch A
Type 192.168.1.1 in the text box of Private Net IP.
Type 255.255.255.0 in the text box of Mask.
Select Enable from the Build Stack drop-down list.
Click Apply.
Now, switch A becomes the master switch.
38
Page 51

# Configure a stack port on Switch A.
On the page of the Setup tab, perform the following configurations, as shown in c.
c. Configure a stack port on Switch A
In the Port Settings area, select the check box before GigabitEthernet1/0/1.
Click Enable.
Table 16 Configure the member switches
39
Page 52

# On Switch B, configure local ports GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 connecting with switch A, GigabitEthernet
1/0/1 connecting with Switch C, and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 connecting with Switch D as stack ports.
Select IRF from the navigation tree of Switch B to enter the page of the Setup tab.
d. Configure stack ports on Switch B
In the Port Settings area, select the check boxes before GigabitEthernet1/0/1, GigabitEthernet1/0/2,
and GigabitEthernet1/0/3.
Click Enable.
40
Page 53

Now, switch B becomes a member switch.
# On Switch C, configure local port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 connecting with Switch B as a stack port.
Select IRF from the navigation tree of Switch C to enter the page of the Setup tabe.
e. Configure a stack port on Switch C
In the Port Settings area, select the check box before GigabitEthernet1/0/1.
Click Enable.
41
Page 54

Now, Switch C becomes a member switch.
# On Switch D, configure local port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 connecting with Switch B as a stack port.
Select IRF from the navigation tree of Switch D to enter the page of the Setup tab.
In the Port Settings area, select the check box before GigabitEthernet1/0/1.
Click Enable.
Now, Switch D becomes a member switch.
Table 17 Verify the configuration
# Display the stack topology on Switch A.
Select IRF from the navigation tree of Switch A and click the Topology Summary tab.
You can view the information as shown in f.
f. Verify the configuration
Configuration guidelines
When configuring a stack, note the following issues:
Table 18 If a switch is already configured as the stack master, you are not allowed to modify the private IP
address pool on the switch.
Table 19 If a switch is already configured as a stack member, the Global Settings area on the member
switch is grayed out.
42
Page 55

Summary
The device summary module helps you understand the system information, port information, power
information, and fan information on the device. The system information includes the basic system
information, system resources state, and recent system operation logs.
Displaying device summary
Displaying system information
After you log in to the web interface, the System Information tab appears by default, as shown in a.
a. System information
If you select a certain time period, the system refreshes the system information at the specified interval.
If you select Manual from the Refresh Period drop-down list, the system refreshes the information only
when you click the Refresh button.
The system information tab is divided into three sections, which display the following information:
Basic system information
System resource state
Recent system operation logs
43
Page 56

p
g
g
Basic system information
The INFO area on the right of the page displays the basic system information such as device name, product
information, device location, contact information, serial number, software version, hardware version, Boot
ROM version, and running time. The running time displays how long the device is up since the last boot.
You can configure the device location and contact information on the Setup page you enter by selecting
Device SNMP.
System resource state
The System Resource State displays the latest CPU usage and memory usage.
Recent system operation logs
1. Description about the recent system operation logs
Field Descri
Time Displays the time when the system operation logs are generated.
Level Displays the severity of the system operation logs.
Description Displays the description of the system operation logs.
NOTE:
The Summary page displays up to five latest system operation lo
For more system operation logs, click More to enter the Log List pa
selecting Device Syslog. For more information, see the chapter “Log management configuration”.
tion
Displaying device information
After logging in to the web interface, you can click the Device Information tab to enter the page displaying
the device ports. Hover the cursor over a port and the port details appears, including the port name, type,
speed, utilization, and status, as shown in a. For the description about the port number and its color, see a.
Similarly, you can view the power type and working status and the fan working status.
s about the login and logout events.
e. You can also enter this page by
44
Page 57

a. Device information
If you select a certain time period from the Refresh Period drop-down list, the system refreshes the
information at the specified interval.
If you select Manual from the Refresh Period drop-down list, the system refreshes the information only
when you click the Refresh button.
45
Page 58

p
Device basic information configuration
The device basic information feature provides the following functions:
Set the system name of the device. The configured system name is displayed on the top of the
navigation bar.
Set the idle timeout period for logged-in users. The system logs an idle user off the web for security
purpose after the configured period.
Configuring device basic information
Configuring system name
Select Device Basic from the navigation tree to enter the system name configuration page, as shown in a.
a. Configure system name
2. System name configuration item
Item Descri
Sysname Set the system name.
tion
Configuring idle timeout period
Select Device Basic from the navigation tree, and then click the Web Idle Timeout tab to enter the page
for configuring idle timeout period, as shown in a.
46
Page 59

p
a. Configure idle timeout period
2. Idle timeout period configuration item
Item Descri
Idle timeout Set the idle timeout period for logged-in users.
tion
47
Page 60

System time configuration
The system time module allows you to display and set the device system time on the web interface. The
device supports setting system time through manual configuration and automatic synchronization of NTP
server time.
An administrator can keep time synchronized among all the devices within a network by changing the
system clock on each device, however, this is a huge amount of workload and cannot guarantee the clock
precision.
Defined in RFC 1305, the Network Time Protocol (NTP) synchronizes timekeeping among distributed time
servers and clients. NTP allows quick clock synchronization within the entire network and ensures a high
clock precision so that the devices can provide diverse applications based on the consistent time.
Configuring system time
Select Device System Time from the navigation tree. The system time configuration page appears by
default, as shown in a. The current system time and clock status are displayed.
a. System time configuration page
48
Page 61

49
2. System time configuration items
Item Descri
p
tion
Manual
Select to manually configure the system time, including the setting
of Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, and Second.
NTP
Source Interface
Set the source interface for an NTP message.
If you do not want the IP address of a certain interface on the local
device to become the destination address of response messages,
you can specify the source interface for NTP messages, so that the
source IP address in the NTP messages is the primary IP address of
this interface.
Key 1 Set an NTP authentication key.
The NTP authentication feature should be enabled for a system
running NTP in a network where there is a high security demand.
This feature enhances the network security by means of
client-server key authentication, which prohibits a client from
synchronizing with a device that has failed authentication.
You can set two authentication keys, each of which is composed of
a key ID and key string.
ID is the ID of a key.
Key string is a character string for MD5 authentication key.
Key 2
External
Reference
Source
NTP Server
1/Reference
Key ID
Specify the IP address of an NTP server, and configure the
authentication key ID used for the association with the NTP server.
Only if the key provided by the server is the same with the
specified key will the device synchronize its time to the NTP server.
You can configure two NTP servers. The clients will choose the
optimal reference source.
IMPORTANT:
The IP address of an NTP server is a unicast address, and cannot be
a broadcast or a multicast address, or the IP address of the local
clock source.
NTP Server
2/Reference
Key ID
TimeZone Set the time zone for the system.
System time configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in a, the local clock of Device A is set as the reference clock.
Switch B works in the client mode, and uses Device A as the NTP server.
Configure NTP authentication on Device A and Switch B.
a. Network diagram for configuring system time
Page 62

Configuration procedure
Table 20 Configure Device A
# Configure the local clock as the reference clock, with the stratum of 2. Enable NTP authentication, set the
key ID to 24, and specify the created authentication key aNiceKey as a trusted key. (Configuration omitted.)
Table 21 Configure Switch B
# Configure Device A as the NTP server of Switch B.
Select Device System Time from the navigation tree, and then select the Net Time tab to perform the
configurations as shown in b.
b. Configure Device A as the NTP server of Switch B
Select NTP.
Type 24 in the ID box, and type aNiceKey in the Key String text box for key 1.
Type 1.0.1.11 in the NTP Server 1 text box and type 24 in the Reference Key ID text box.
Click Apply.
Table 22 Verify the configuration
After the above configuration, you can see that the current system time on Device A is the same as Switch
B.
50
Page 63

Configuration guidelines
When configuring system time, note the following guidelines:
A device can act as a server to synchronize the clock of other devices only after its clock has been
synchronized. If the clock of a server has a stratum level higher than or equal to that of a client’s clock,
the client does not synchronize its clock to the server’s.
The synchronization process takes a period of time. Therefore, the clock status may be unsynchronized
after your configuration. In this case, you can refresh the page to view the clock status and system time
later on.
51
Page 64

p
Log management configuration
System logs contain a large amount of network and device information, including running status and
configuration changes. System logs are an important way for administrators to know network and device
status. With system log information, administrators can take corresponding actions against network
problems and security problems.
System logs can be stored in the log buffer, or sent to the loghost.
Configuring log management
Configuration task list
Perform the tasks in 1 to configure log management.
1. Log management configuration task list
Task Descri
Optional
Setting syslog related parameters
Displaying syslog Display detailed information of system logs.
Setting loghost
Set the number of logs that can be stored in the log buffer.
Set the refresh period of the log information displayed on the
Optional
Set the loghost that can receive system logs.
tion
web interface.
Setting syslog related parameters
Select Device Syslog from the navigation tree, and click the Log Setup tab to enter the syslog
configuration page, as shown in a.
52
Page 65

p
a. Set system logs related parameters
2. Syslog configuration items
Item Descri
Buffer Capacity
Refresh Interval
Return to Log management configuration task list.
Displaying syslog
Select Device Syslog from the navigation tree to enter the syslog display page, as shown in a.
tion
Set the number of logs that can be stored in the log buffer.
Set the refresh period on the log information displayed on the web interface.
You can select manual refresh or automatic refresh:
Manual—Click Refresh to refresh the Web interface when displaying log
information.
Automatic—Select a time period to refresh the Web interface every 1 minute, 5
minutes, or 10 minutes.
53
Page 66

p
a. Display syslog
2. Syslog display items
Item Descri
Time/Date
Source
Level
Digest Displays the brief description of system logs.
Description
3. System logs severity level
Displays the time/date when system logs are generated.
Displays the module that generates system logs.
Displays the severity level of system logs. For more information about severity levels,
see 3.
Displays the contents of system logs.
tion
Severity level Description Value
Emergency
Alert Information that demands prompt reaction
Critical Critical information
Error Error information
The system is unavailable.
0
1
2
3
Warning Warnings
Notification Normal information that needs to be noticed
Informational Informational information to be recorded
Debugging Information generated during debugging
Note: A smaller value represents a higher severity level.
4
5
6
7
Return to Log management configuration task list.
54
Page 67

p
Setting loghost
Select Device Syslog from the navigation tree, and click the Loghost tab to enter the loghost configuration
page, as shown in a.
a. Set loghost
2. Loghost configuration item
Item Descri
IP address of the loghost.
Loghost IP
You can specify up to four loghosts.
tion
You must input a valid IP address.
Return to Log management configuration task list.
55
Page 68

Configuration management
Back up configuration
Configuration backup provides the following functions:
Open and view the configuration file (.cfg file or .xml file) for the next startup
Back up the configuration file (.cfg file or .xml file) for the next startup to the host of the current user
Select Device Configuration from the navigation tree to enter the backup configuration page, as shown
in a.
a. Backup configuration page
When you click the upper Backup button in this figure, a file download dialog box appears. You can
select to view the .cfg file or to save the file locally.
When you click the lower Backup button in this figure, a file download dialog box appears. You can
select to view the .xml file or to save the file locally.
Restore configuration
Configuration restore provides the following functions:
Upload the .cfg file on the host of the current user to the device for the next startup
Upload the .xml file on the host of the current user to the device for the next startup, and delete the
previous .xml configuration file that was used for the next startup
Select Device Configuration from the navigation tree, and then click the Restore tab to enter the
configuration restore page, as shown in a.
56
Page 69

g
a. Configuration restore page
When you click the upper Browse button in this figure, the file upload dialog box appears. Select the
.cfg file to be uploaded, and then click OK.
When you click the lower Browse button in this figure, the file upload dialog box appears. Select the
.xml file to be uploaded, and then click OK.
Save configuration
The save configuration module provides the function to save the current configuration to the configuration
file (.cfg file or .xml file) for the next startup.
CAUTION:
Saving the configuration takes some time.
The system does not support the operation of savin
such a case occurs, the system prompts the latter users to try later.
You can save the configuration in one of the following ways:
Fast—Click the Save button at the upper right of the auxiliary area.
Common—Select Device or Configuration from the navigation tree, and then click the Save tab to enter
the save configuration confirmation page, as shown in a. Click Save Current Settings.
a. Save configuration confirmation
configuration of two or more consecutive users. If
57
Page 70

Initialize
This operation restores the system to factory defaults, deletes the current configuration file, and reboots the
device.
Select Device Configuration from the navigation tree, and then click the Initialize tab to enter the initialize
confirmation page as shown in a.
a. Initialize confirmation dialog box
Click the Restore Factory-Default Settings button to restore the system to factory defaults.
58
Page 71

p
Device maintenance
Software upgrade
A system software image file is used to boot the device. Software upgrade allows you to obtain a target
system software image file from the local host and set the file as the startup configuration file. In addition,
you can select whether to reboot the device to bring the upgraded system software image file into effect.
CAUTION:
Software upgrade takes some time. Avoid performing any operation on the web interface during the
upgrading procedure. Otherwise, the upgrade operation may be interrupted.
Select Device Device Maintenance from the navigation tree to enter the software upgrade configuration
page, as shown in a.
a. Software upgrade configuration page
2. Software upgrade configuration items
Item Descri
File
Filename
Specifies the filename of the local system software image file, which must be with an
extension .bin.
Specifies a filename for the file to be saved on the device. The filename must have
an extension, which must be the same as that of the source file.
tion
59
Page 72

g
Item Description
Specifies the type of the startup configuration file:
File Type
Main
Backup
If a file with same name
already exists, overwrite
it without prompt.
Reboot after the
upgrading finished.
Device reboot
CAUTION:
Before rebootin
after device reboot.
When the device reboots, you need to re-log in to the web interface.
Select Device Device Maintenance from the navigation tree, click the Reboot tab to enter the device
reboot configuration page, as shown in a.
a. Device reboot page
the device, save the configuration; otherwise, all unsaved configuration will be lost
Specifies whether to overwrite the file with the same name.
If you do not select the option, when a file with the same name exists, a dialog box
appears, telling you that the file already exists and you cannot continue the
upgrade.
Specifies whether to reboot the device to make the upgraded system software
image file take effect after the system software image file is uploaded.
Click Apply to reboot the device. You can check whether the current configuration has been saved to the
startup configuration file.
If you select Check configuration with next startup configuration file, the system checks the
configuration before rebooting the device. If the check succeeds, the system reboots the device; if the
check fails, a dialog box appears, telling you that the current configuration and the saved
configuration are inconsistent, and the device will not be rebooted. In this case, you need to save the
current configuration manually before you can reboot the device.
If you do not select the check box, the system reboots the device directly.
60
Page 73

Electronic label
Electronic label allows you to view information about the device electronic label, which is also known as the
permanent configuration data or archive information. The information is written into the storage medium of
a device or a card during the debugging and testing processes, and includes the card name, product bar
code, MAC address, debugging and testing date(s), manufacture name, and so on.
Select Device Device Maintenance from the navigation tree, and click the Electronic Label tab to enter the
page as shown in a.
a. Electronic label
Diagnostic information
Each functional module has its own running information, and generally, you view the output information for
each module one by one. To receive as much information as possible in one operation during daily
maintenance or when system failure occurs, the diagnostic information module allows you to save the
running statistics of multiple functional modules to a file named default.diag. This allows you to locate
problems faster by checking this file.
Select Device Device Maintenance from the navigation tree, and click the Diagnostic Information tab to
enter the page as shown in a.
a. Diagnostic information
When you click Create Diagnostic Information File, the system begins to generate a diagnostic information
file, and after the file is generated, the page is as shown in b.
61
Page 74

b. The diagnostic information file is created
Click Click to Download, and the File Download dialog box appears. You can select to open this file or save
this file to the local host.
NOTE:
The generation of the diagnostic file takes some time. During this process, do not perform any
operation on the web page.
After the diagnostic file is generated successfully, you can view this file by selecting Device File
Management, or downloading this file to the local host. For more information, see the chapter “File
management configuration”.
62
Page 75

File management
The device saves files such as host software and configuration file into the storage device, and provides the
file management function for users to manage those files conveniently and effectively. File management
function provides the following operations:
Displaying file list
Downloading a file
Uploading a file
Removing a file
File management configuration
Displaying file list
Select Device File Management from the navigation tree to enter the file management page, as shown in
a. Select a disk from the Please select disk drop-down list on the top of the page, and the page then displays
used space, free space and capacity of the disk at the right of the drop-down list, and all files saved in this
disk (in the format of path + filename) and file sizes.
a. File management
63
Page 76

Downloading a file
Select Device File Management from the navigation tree to enter the file management page, as shown in
a. Select a file from the list, click the Download File button, and then a File Download dialog box appears.
You can select to open the file or to save the file locally, and you can download only one file at a time.
Uploading a file
Select Device File Management from the navigation tree to enter the file management page, as shown in
a. In the Upload File area, select a disk from the Please select disk drop-down list to save the file, and then
select the file path and filename by clicking Browse. Click Apply to upload the file to the specified storage
device.
CAUTION:
Uploading a file takes some time. HP recommends you not to perform any operation on the web interface
during the upgrading procedure.
Removing a file
Select Device File Management from the navigation tree to enter the file management page, as shown in
a. You can remove a file by using one of the following ways:
Click the
Select one or multiple files from the file list, and then click Remove File.
icon to remove a file.
64
Page 77

Port management configuration
You can use the port management feature to set and view the operation parameters of a Layer 2 Ethernet
port, including but not limited to its state, rate, duplex mode, link type, PVID, MDI mode, flow control settings,
MAC learning limit, and storm suppression ratios.
Configuring a port
Setting operation parameters for a port
Select Device Port Management from the navigation tree, and then select the Setup tab on the page that
appears to enter the page as shown in a.
a. The Setup tab
65
Page 78

p
2. Port configuration items
Item Descri
Enable or disable the port. Sometimes, after you modify the operation
Port State
parameters of a port, you need to disable and then enable the port to have the
modifications take effect.
Set the transmission rate of the port.
Available options include:
10: 10 Mbps
100: 100 Mbps
1000: 1000 Mbps
Auto: auto-negotiation
Auto 10: auto-negotiated to 10 Mbps
Speed
Auto 100: auto-negotiated to 100 Mbps
Auto 1000: auto-negotiated to 1000 Mbps
Auto 10 100: auto-negotiated to 10 or 100 Mbps
Auto 10 1000: auto-negotiated to 10 or 1000 Mbps
Auto 100 1000: auto-negotiated to 100 or 1000 Mbps
Auto 10 100 1000: auto-negotiated to 10, 100, or 1000 Mbps
IMPORTANT:
SFP optical ports do not support the 10 or 100 option.
Set the duplex mode of the port.
Auto: auto-negotiation
Full: full duplex
Duplex
Half: half duplex
tion
Link Type
PVID
IMPORTANT:
Ethernet electrical ports whose transmission rate is configured as 1000 Mbps
and SFP optical ports do not support the half option.
Set the link type of the current port, which can be access, hybrid, or trunk. For
more information, see the chapter “VLAN configuration.”
IMPORTANT:
To change the link type of a port from trunk to hybrid or vice versa, you must first
set its link type to access.
Set the default VLAN ID of the interface. For more information about setting the
PVID, see the chapter “VLAN configuration.”
IMPORTANT:
To enable a link to properly transmit packets, be sure the trunk or hybrid ports at
the two ends of the link have the same PVID.
66
Page 79

Item Description
Set the Medium Dependent Interface (MDI) mode of the port. Two types of
Ethernet cables can be used to connect Ethernet devices: crossover cable and
straight-through cable. To accommodate these two types of cables, an Ethernet
port can operate in one of the following three MDI modes: across, normal, and
auto.
An Ethernet port is composed of eight pins. By default, each pin has its
particular role. For example, pin 1 and pin 2 are used for transmitting signals;
pin 3 and pin 6 are used for receiving signals. You can change the pin roles
by setting the MDI mode.
For an Ethernet port in across mode, pin 1 and pin 2 are used for
transmitting signals; pin 3 and pin 6 are used for receiving signals. The pin
roles are cannot be changed.
For an Ethernet port in auto mode, the pin roles are decided through auto
negotiation.
MDI
For an Ethernet port in normal mode, the pin roles are changed. Pin 1 and
pin 2 are used for receiving signals; pin 3 and pin 6 are used for
transmitting signals.
To enable normal communication, you must connect the local transmit pins to
the remote receive pins. Therefore, you should configure the MDI mode
depending on the cable types.
HP does not recommend you to use the auto mode. The other two modes
are used only when the device cannot determine the cable type.
When straight-through cables are used, the local MDI mode must be
different from the remote MDI mode.
When crossover cables are used, the local MDI mode must be the same as
the remote MDI mode, or the MDI mode of at least one end must be set to
auto.
Flow Control
Power Save
Max MAC Count
IMPORTANT:
SFP optical ports do not support this feature.
Enable or disable flow control on the port.
With flow control enabled at both sides, when traffic congestion occurs on the
ingress port, the ingress port will send a Pause frame notifying the egress port
to temporarily suspend the sending of packets. The egress port is expected to
stop sending any new packet when it receives the Pause frame. In this way,
flow control helps to avoid dropping of packets.
IMPORTANT:
Flow control works only after it is enabled on both the ingress and egress ports.
Enable or disable auto power down on the port.
With auto power down enabled, when an Ethernet port does not receive any
packet for a certain period of time, it automatically enters the power save
mode and resumes its normal state upon the arrival of a packet.
By default, auto power down is disabled.
Set the MAC learning limit on the port. Available options include:
User Defined: Select this option to set the limit manually.
No Limited: Select this option to set no limit.
67
Page 80

Item Description
Set broadcast suppression on the port. You can suppress broadcast traffic by
percentage or by PPS as follows:
ratio: Sets the maximum percentage of broadcast traffic to the total
bandwidth of an Ethernet port. When this option is selected, you need to
input a percentage in the box below.
pps: Sets the maximum number of broadcast packets that can be
forwarded on an Ethernet port per second. When this option is selected,
Broadcast Suppression
you need to input a number in the box below.
kbps: Sets the maximum number of broadcast kilobits that can be
forwarded on an Ethernet port per second. When this option is selected,
you need to input a number in the box below.
IMPORTANT:
Do not configure this item if the storm constrain function for broadcast traffic is
enabled on the port. Otherwise, the suppression result will be unpredictable. To
set storm constrain for broadcast traffic on a port, select Device Storm
Constrain.
Set multicast suppression on the port. You can suppress multicast traffic by
percentage or by PPS as follows:
ratio: Sets the maximum percentage of multicast traffic to the total
bandwidth of an Ethernet port. When this option is selected, you need to
input a percentage in the box below.
pps: Sets the maximum number of multicast packets that can be forwarded
on an Ethernet port per second. When this option is selected, you need to
Multicast Suppression
input a number in the box below.
kbps: Sets the maximum number of multicast kilobits that can be forwarded
on an Ethernet port per second. When this option is selected, you need to
input a number in the box below.
Unicast Suppression
IMPORTANT:
Do not configure this item if the storm constrain function for multicast traffic is
enabled on the port. Otherwise, the suppression result will be unpredictable. To
set storm constrain for multicast traffic on a port, select Device Storm
Constrain.
Set unicast suppression on the port. You can suppress unicast traffic by
percentage or by PPS as follows:
ratio: Sets the maximum percentage of unicast traffic to the total bandwidth
of an Ethernet port. When this option is selected, you need to input a
percentage in the box below.
pps: Sets the maximum number of unicast packets that can be forwarded
on an Ethernet port per second. When this option is selected, you need to
input a number in the box below.
kbps: Sets the maximum number of unicast kilobits that can be forwarded
on an Ethernet port per second. When this option is selected, you need to
input a number in the box below.
IMPORTANT:
Do not configure this item if the storm constrain function for unicast traffic is
enabled on the port. Otherwise, the suppression result will be unpredictable. To
set storm constrain for unicast traffic on a port, select Device Storm Constrain.
68
Page 81

Item Description
Port or ports that you have selected from the chassis front panel and the
aggregate interface list below, for which you have set operation parameters.
IMPORTANT:
Selected Ports
Only in the presence of link aggregations groups, Aggregation ports will
be displayed under the chassis front panel.
You can set only the state and MAC learning limit for an aggregate
interface.
Viewing the operation parameters of a port
Select Device Port Management from the navigation tree. The Summary tab is displayed by default.
Select the parameter you want to view by clicking the radio button before it to display the setting of this
parameter for all the ports in the lower part of the page, as shown in a.
a. The Summary tab
Select Device Port Management from the navigation tree, select the Details tab on the page that appears,
and then click the port whose operation parameters you want to view in the chassis front panel, as shown
in b. The operation parameter settings of the selected port are displayed on the lower part of the page (in
the square brackets).
69
Page 82

70
b. The Details tab
Port management configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in a:
Server A, Server B, and Server C are connected to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2,
and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 or the switch respectively. The rates of the network adapters of these
servers are all 1000 Mbps.
The switch connects to the external network through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 whose rate is 1000
Mbps.
To avoid congestion at the egress port, GigabitEthernet 1/0/4, configure the auto-negotiation rate
range on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as 100 Mbps.
a. Network diagram for port rate configuration
Page 83

Configuration procedure
# Set the rate of GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to 1000 Mbps.
Select Device Port Management from the navigation tree, click the Setup tab to enter the page
shown in a, and make the following configurations:
a. Configure the rate of GigabitEthernet 1/0/4
Select 1000 in the Speed dropdown list.
Select GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 on the chassis front panel.
Click Apply.
# Batch configure the auto-negotiation rate range on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and
GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as 100 Mbps.
Select Auto 100 in the Speed dropdown list on the page shown in b.
Select GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 on the chassis
front panel.
Click Apply.
71
Page 84

b. Batch configure port rate
# Display the rate settings of ports.
Click the Summary tab.
Select the Speed option to display the rate information of all ports on the lower part of the page, as
shown in c.
72
Page 85

c. Display the rate settings of ports
73
Page 86
Port mirroring configuration
Introduction to port mirroring
Port mirroring is the process of copying the packets passing through a port (called a mirroring port) to
another port (called the monitor port) connected with a monitoring device for packet analysis.
You can mirror inbound, outbound, or bidirectional traffic on a port as needed.
Implementing port mirroring
Port mirroring is implemented through local port mirroring groups. The following subsections describe how
local port mirroring is implemented.
Local port mirroring
In local port mirroring, all packets (including protocol and data packets) passing through a port can be
mirrored. Local port mirroring is implemented through a local mirroring group.
As shown in a, packets on the mirroring port are mirrored to the monitor port for the data monitoring device
to analyze.
a. Local port mirroring implementation
How the device processes packets
Traffic
mirrored to
Mirroring port
Mirroring port
PC
Monitor port
Monitor port
Data monitoring device
74
Page 87

Configuring local port mirroring
Configuration task list
Configuring local port mirroring
To configure local port mirroring, you must create a local mirroring group and then specify the mirroring
ports and monitor port for the group.
1. Local port mirroring configuration task list
Task Remarks
Create a local mirroring group
Configure the mirroring ports
Configure the monitor port
Required
For more information, see “Creating a mirroring group”.
Required
For more information, see “Configuring ports for a mirroring group”.
During configuration, you need to select the port type Mirror Port. You
can configure multiple mirroring ports for a mirroring group.
Required
For more information, see “Configuring ports for a mirroring group”.
During configuration, you need to select the port type Monitor Port. You
can configure one only monitor port for a mirroring group.
Creating a mirroring group
Select Device Port Mirroring from the navigation tree and click Create to enter the page for creating a
mirroring group, as shown in a.
75
Page 88

p
a. Create a mirroring group
2. Configuration items of creating a mirroring group
Item Descri
Mirroring Group ID
Type
ID of the mirroring group to be created
Specify the type of the mirroring group to be created:
Local: Creates a local mirroring group.
tion
Return to Local port mirroring configuration task list.
Configuring ports for a mirroring group
Select Device Port Mirroring from the navigation tree and click Modify Port to enter the page for
configuring ports for a mirroring group, as shown in a.
76
Page 89

p
a. The Modify Port tab
2. Configuration items of configuring ports for a mirroring group
Item Descri
Mirroring
Group ID
Port Type
ID of the mirroring group to be configured
The available groups were created previously.
Set the type of
the port to be
configured
tion
Configure ports for a local mirroring group:
Monitor Port: Configures the monitor ports for the local mirroring
group.
Mirror Port: Configures mirroring ports for the local mirroring group.
Set the direction of the traffic monitored by the monitor port of the mirroring group
This configuration item is available when Mirror Port is selected is the Port Type drop-down
Stream
Orientation
list.
both: Mirrors both received and sent packets on mirroring ports.
inbound: Mirrors only packets received by mirroring port.
outbound: Mirrors only packets sent by mirroring ports.
Click the ports to be configured on the chassis front panel. If aggregate interfaces are
Select port(s)
configured on the device, the page displays a list of aggregate interfaces below the chassis
front panel. You can select aggregate interfaces from this list and configure them as
mirroring ports of a port mirroring group.
Return to Local port mirroring configuration task list.
77
Page 90

Configuration examples
Local port mirroring configuration example
Network requirements
Department 1 accesses Switch C through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
Department 2 accesses Switch C through GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
Server is connected to GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 of Switch C.
Configure port mirroring to monitor the bidirectional traffic of Department 1 and Department 2 on the
server.
To satisfy the requirement through local port mirroring, perform the following configuration on Switch C:
Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as mirroring ports.
Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as the monitor port.
a. Network diagram for local port mirroring configuration
Configuration procedure
# Create a local mirroring group.
Select Device Port Mirroring from the navigation tree and click Create to enter the page to create a local
mirroring group, as shown in a.
78
Page 91

a. Create a local mirroring group
Type in mirroring group ID 1.
Select Local in the Type drop-down list.
Click Apply.
# Configure the mirroring ports.
Click Modify Port to enter the page for configuring the mirroring group ports, as shown in b.
79
Page 92

b. Configure the mirroring ports
Select 1 – Local in the Mirroring Group ID drop-down list.
Select Mirror Port in the Port Type drop-down list.
Select both in the Stream Orientation drop-down list.
Select GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on the chassis front panel.
Click Apply. A configuration progress dialog box appears, as shown in c.
c. Configuration progress dialog box
After the configuration process is complete, click Close.
# Configure the monitor port.
80
Page 93

Click Modify Port to enter the page for configuring the mirroring group ports, as shown in d.
d. Configure the monitor port
Select 1 – Local in the Mirroring Group ID drop-down list.
Select Monitor Port in the Port Type drop-down list.
Select GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 on the chassis front panel.
Click Apply. A configuration progress dialog box appears.
After the configuration process is complete, click Close in the dialog box.
Configuration guidelines
Consider the following points during local port mirroring configuration:
To ensure operation of your device, do not enable STP, MSTP, or RSTP on the monitor port.
You can configure multiple mirroring ports but only one monitor port for a local mirroring group.
81
Page 94

p
User management
Overview
The switch provides the following user management functions:
Add local user accounts for FTP and Telnet users, and specify the password, access level, and service
types for each user.
Set the super password for non-management level users to switch to the management level.
Switch to the management level from a lower level.
Managing users
Adding a local user
Select Device Users from the navigation tree, and click the Create tab to add a local user, as shown in a.
a. Add a user
2. Local user configuration items
Item Descri
tion
Username Set a username for the user
82
Page 95

Item Description
Select an access level for the user.
Users of different levels can perform different operations. User levels, in order from low
to high, are visitor, monitor, configure, and management.
Visitor: Users of this level can only perform ping and traceroute operations. They can
neither access data on the switch nor configure the switch.
Access Level
Monitor: Users of this level can perform ping and traceroute operations and access
data on the switch but cannot configure the switch.
Configure: Users of this level can perform ping and traceroute operations, access
data on the switch, and configure the switch, but they cannot upgrade the host
software, add/delete/modify users, or back up/restore the configuration file.
Management: Users of this level can perform any operations on the switch.
Password
Confirm Password
Password Display
Mode
Set the password for the user.
Input the same password again. Otherwise, the system will prompt that the two
passwords are not consistent when you apply the configuration.
Set the password displaying mode.
Options include:
Simple: Saves the password in the configuration file in plain text so that the
password is displayed in plain text.
Cipher: Saves the password in the configuration file in cipher text so that the
password is displayed in cipher text.
A plaintext password is not safe. It is good practice to use the cipher mode.
Service Type Set the service type, including FTP and Telnet services. You must select either of them.
Setting the super password
A management level user can set the password for non-management level users to switch to the
management level. If the super password is not configured, no switchover can occur.
Select Device Users from the navigation tree, and click the Super Password tab to set the super password.
a. Super password
83
Page 96

p
2. Super password configuration items
Item Descri
Select the operation type.
Create/Remove
Options include:
Create: Configure or modify the super password.
tion
Remove: Remove the current super password.
Password
Confirm Password
Password Display
Mode
Set the password for non-management level users to switch to the management level.
Input the same password again. Otherwise, the system will warn that the two passwords
input are not consistent when you apply the configuration.
Set the password displaying mode.
Options include:
Simple: Saves the password in the configuration file in plain text so that the
password is displayed in plain text.
Cipher: Saves the password in the configuration file in cipher text so that the
password is displayed in cipher text.
A plaintext password is not safe. It is good practice to use the cipher mode.
Switching to the management level
This function allows a user to switch from the current user level to the management level. To switch to the
management level, a user must provide the correct super password.
The access level switchover of a user is valid for the current login only; it does not change the access level
configured for the user. When the user re-logs in to the Web interface, the access level of the user is still the
original level.
To switch to the management level, select Device Users from the navigation tree, click the Switch To
Management tab, input the correct super password, and click Login.
a. Switch to the management level.
84
Page 97

p
Loopback test configuration
Overview
You can check whether an Ethernet port works normally by performing the Ethernet port loopback test,
during which the port cannot forward data packets normally.
Ethernet port loopback test can be an internal loopback test or an external loopback test.
In an internal loopback test, self loop is established in the switching chip to check whether there is a
chip failure related to the functions of the port.
In an external loopback test, a loopback plug is used on the port. Packets forwarded by the port will
be received by itself through the loopback plug. The external loopback test can be used to check
whether there is a hardware failure on the port.
Loopback operation
Select Device Loopback from the navigation tree to enter the loopback test configuration page, as shown
in a.
a. Loopback test configuration page
2. Loopback test configuration items
Item Descri
Testing
type
External
Set the loopback test type, which can be External or Internal.
Internal
tion
85
Page 98

After selecting a testing type, you need to select a port on which you want to perform the loopback test from
the chassis front panel.
After that, click Test to start the loopback test, and you can see the test result in the Result box, as shown in
a.
a. Loopback test result
Configuration guidelines
Note the following when performing a loopback test:
You can perform an internal loopback test but not an external loopback test on a port that is physically
down, but you can perform neither test on a port that is manually shut down.
The system does not allow Rate, Duplex, Cable Type and Port Status configuration on a port under a
loopback test.
An Ethernet port works in full duplex mode when the loopback test is performed, and restores its
original duplex mode after the loopback test.
86
Page 99

VCT
Overview
NOTE:
The fiber interface of a SFP port does not support this feature.
A link in the up state goes down and then up automatically if you perform this operation on one of the
Ethernet interfaces forming the link.
You can use the Virtual Cable Test (VCT) function to check the status of the cable connected to an Ethernet
port on the device. The check result is returned in less than 5 seconds. The test covers whether short circuit
or open circuit occurs on the cable and the length of the faulty cable.
Testing cable status
Select Device VCT from the navigation tree to enter the page for testing cable status. Select the port you
want to test in the chassis front panel and then click Test. The test result is returned in less than 5 seconds and
displayed in the Result text box, as shown in a.
a. Test the status of the cable connected to an Ethernet port
87
Page 100

2. Description on the cable test result
Item Description
Status and length of the cable.
The status of a cable can be normal, abnormal, abnormal(open), abnormal(short), or
failure.
When a cable is normal, the cable length displayed is the total length of the cable.
Cable status
When a cable is not normal, the cable length displayed is the length of the cable
between the current port and the location where fault occurs.
IMPORTANT:
The error of the length detected is within 5 meters.
88
 Loading...
Loading...