Page 1

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
Firmware Version 9.0.7
59273-00 C
Page 2
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the preparation of
this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and recommendations in this
document do not constitute the warranty of any kind, express or implied.
This product is covered by one or more of the following patents: 6697359, 7,660,302, 7,542,676, 7,340,167,
7,573,909, 7,583,597, 7,580,354, 7,649,903, 7,61 3,816, 7,430,175, 7,525,983, 7,522,522, 7,447,224, 7,420,982,
7,512,067, 7,477,655, 7,630,384, 7,646,767, 7,55 8,281, 7,519,058, 7,525,968, 7,518,995, 7,548,560, 7,669,001,
7,684,398; other patents pending.
Document Revision History
Revision A, June, 2010
Revision B, September 2011
Revision C, July 2011
Changes Pages Affected
Updated for firmware version 9.0.7 Throughout
Added Security Consistency Checklist to menus 1-5, 1-6
Added RequireEnodeMACConfig 2-28, 2-14
Added IPV4 Gateway entry 2-15
Updated VLAN Manager Dialog 2-33
Updated FCF Configuration Manager Dialog 2-34
Updated Selective Restore Dialog 2-45
Updated Class 3 Toss entry 3-65
Updated Port Address entry 3-72
Replace Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window fig-
3-68
ure
Updated DCBX Enabled and PFC Priority entries 3-73
Removed references to E_Ports and E_Port status Table 3-17, Table 3-18
ii 59273-00 C
Page 3

Table of Contents
Preface
Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Related Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
JDOM License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
1 Using QuickTools
Workstation Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Opening QuickTools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
QuickTools User Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Graphic Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Data Windows and Tabs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Menu Bar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Popup Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Shortcut Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Selecting Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Setting QuickTools Preferences. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Using Online Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Viewing Software Version. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Exiting QuickTools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Displaying Interface Card Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Security Consistency Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Switch Data Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Managing User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Creating User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Removing a User Account. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Changing a User Account Password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Modifying a User Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Configuring Port Threshold Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Paging an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Setting the Date/Time and Enabling NTP Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Resetting an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
59273-00 C iii
Page 4

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
Switch Properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Syslog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Symbolic Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Administrative States . . . . . . 29
ENODE MAC Address Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Managing System Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Configuring FCoE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Configuring VLAN Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Configuring FCF Configuration Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Configuring Network Properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configuring SNMP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
SNMP Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
SNMPv3 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Archiving an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Restoring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Restoring the Factory Default Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Testing an Interface Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Using the Event Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Filtering the Event Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Sorting the Event Browser. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Saving the Event Browser to a File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Downloading a Support File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Installing Firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Using Call Home . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Using the Call Home Profile Manager. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Using the Call Home Profile Editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Applying All Profiles on a Switch to Other Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Using the Call Home Message Queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Testing Call Home Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Change Over. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3Managing Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
FC Port Statistics Data Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Port Information Data Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Viewing and Configuring Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Port Symbolic Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
iv 59273-00 C
Page 5

Glossary
Index
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
Port States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
External Port Operational States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Internal Port Operational States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Port Administrative States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Port Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Port Speeds. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Port Transceiver Media Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Device Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
DCBX. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
PFC Priority. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Resetting a Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Testing Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Mapping Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
59273-00 C v
Page 6

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
Figures
Figure Page
1-1 Login to Switch Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-2 Password Change Required Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1-3 QuickTools Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1-4 Preferences Dialog – QuickTools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2-5 Security Consistency Checklist Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2-6 Switch Data Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2-7 Switch Data Window Buttons. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2-8 User Account Administration Dialog – Add Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2-9 User Account Administration Dialog – Remove Account. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2-10 User Account Administration Dialog – Change Password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2-11 User Account Administration Dialog—Modify Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2-12 Port Threshold Alarm Configuration Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2-13 Port Threshold Alarm Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2-14 Switch Properties Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2-15 System Services Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2-16 FCF Virtual Links Data Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2-17 VLAN Manager Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2-18 Add New VLAN Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2-19 FCF Configuration Manager Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2-20 FCF Editor - Create New FCF Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2-21 Network Properties Dialog—DNS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2-22 SNMP Properties Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2-23 SNMP v3 Manager Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2-24 SNMP v3 User Editor Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
2-25 Restore Dialogs – Full and Selective. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
2-26 Switch Diagnostics Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
2-27 Events Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2-28 Filter Events Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
2-29 Load Firmware Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
2-30 Call Home Setup Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
2-31 Call Home Profile Manager Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
2-32 Call Home Profile Editor Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
2-33 Call Home Profile Multiple Switch Apply Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
2-34 Call Home Message Queue Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
2-35 Call Home Profile Manager Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3-36 FC Port Statistics Data Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3-37 Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
3-38 Port Information Data Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3-39 Port Information Data Window Buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3-40 Port Properties Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
3-41 Port Diagnostics Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
3-42 Map Ports Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
vi 59273-00 C
Page 7

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
Tables
Table Page
1-1 Workstation Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1-2 Menu Bar Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2-3 Switch Data Window Entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2-4 Factory User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2-5 H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2-6 H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Administrative States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2-7 FCF Editor dialog parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2-8 Network Properties—DNS Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2-9 SNMP Configuration Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2-10 SNMP Trap Configuration Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2-11 SNMP v3 User Editor Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
2-12 Factory Default Configuration Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
2-13 Severity Levels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2-14 Call Home Setup Dialog Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3-15 FC Port Statistics Data Window Entries. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3-16 Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window Entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
3-17 Port Information Data Window Entries. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
3-18 External Port Operational States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
3-19 Internal Port Operational States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
3-20 Port Administrative States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
3-21 Port Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
3-22 Port Speeds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
3-23 Port Transceiver Media View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
59273-00 C vii
Page 8

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
viii 59273-00 C
Page 9

Preface
This guide describes the QuickTools™ web applet for the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card (firmware version 9.0.7). QuickTools is the primary focus of this
guide which is organized as follows:
Section 1 describes how to use QuickTools, its menus, and its displays.
Section 2 describes H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card management tasks.
Section 3 describes port and device management tasks.
A glossary of terms and an index are also provided.
Intended Audience
This guide introduces the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card management product
and explains how to use it. This guide is intended for users responsible for
installing and using management tools.
Related Materials
Refer to the following guides for information about H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card hardware and installation.
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Command Line Interface Guide
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Installation Guide
59273-00 C ix
Page 10

JDOM License
This product includes software developed by the JDOM Project
(http://www.jdom.org/). Copyright (C) 2000-2002 Brett McLaughlin & Jason
Hunter. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification,
are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
list of conditions, and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
this list of conditions, and the disclaimer that follows these conditions in the
documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
3. The name "JDOM" must not be used to endorse or promote products
derived from this software without prior written permission. For written
permission, please contact license@jdom.org.
4. Products derived from this software may not be called "JDOM", nor may
"JDOM" appear in their name, without prior written permission from the
JDOM Project Management (pm@jdom.org).
In addition, we request (but do not require) that you include in the end-user
documentation provided with the redistribution and/or in the software itself an
acknowledgement equivalent to the following: "This product includes software
developed by the JDOM Project (http://www.jdom.org/)."
Alternatively, the acknowledgment may be graphical using the logos available at
http://www.jdom.org/images/logos.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE JDOM AUTHORS
OR THE PROJECT CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT,
INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS;
OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY
OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF
THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
SUCH DAMAGE.
This software consists of voluntary contributions made by many individuals on
behalf of the JDOM Project and was originally created by Brett McLaughlin
<brett@jdom.org> and Jason Hunter <jhunter@jdom.org>. For more information
on the JDOM Project, please see <http://www.jdom.org/>.
x 59273-00 C
Page 11

1 Using QuickTools
This section describes how to use QuickTools and its menus. The following topics
are covered:
Workstation Requirements
Opening QuickTools
QuickTools User Interfaces
Setting QuickTools Preferences
Using Online Help
Viewing Software Version
Exiting QuickTools
Workstation Requirements
The requirements for fabric management workstations running QuickTools are
listed in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1. Wo rkstation Requirements
Operating System
Memory 512 MB or more (1 GB or more recommended)
Disk Space 150 MB per installation
Processor 1 GHz or faster
Hardware
59273-00 C 1
Windows® 2003, XP SP1/SP2
Solaris™ 9, 10, and 10 x86
Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® 4, 5
SUSE™ Linux Enterprise Server 9, 10
CD-ROM drive,
RJ-45 Ethernet port, RS-232 serial port (optional)
Page 12
Using QuickTools
Opening QuickTools
Table 1-1. Wo rkstation Requirements
Internet Browser
(to view online help
Microsoft® Internet Explorer® 6.0 and later
Netscape® Navigator® 6.0 and later
Firefox® 1.5 and later
Safari® 1.0 on Windows OS
Java 2 Standard Edition Runtime Environment 1.4.2 to support
the web applet
Opening QuickTools
After the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is operational, open QuickTools by
entering the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card IP address in an Internet browser. If
your workstation does not have the Java 2 Run Time Environment program, you
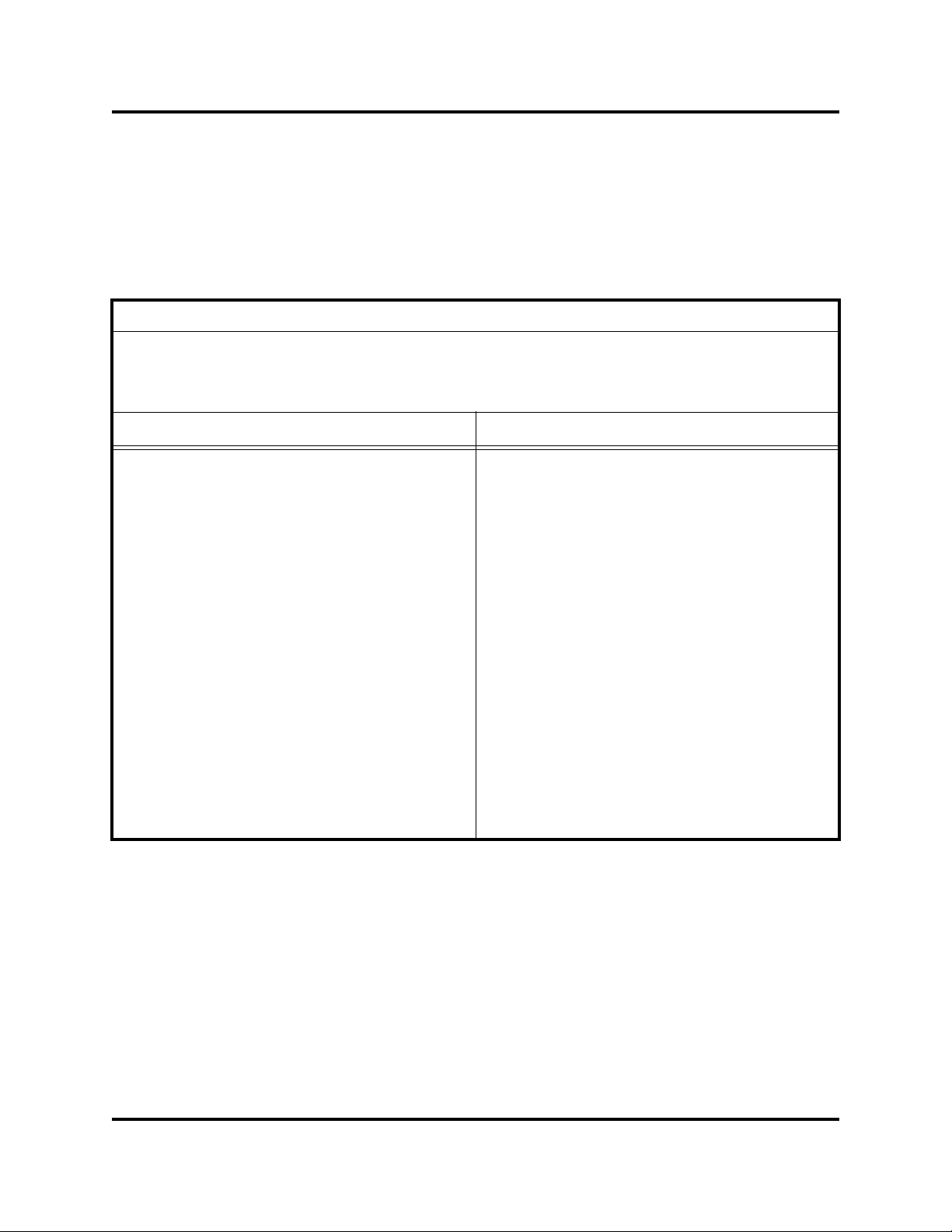
will be prompted to download it. The Login to Switch dialog (Figure 1-1) prompts
you for your username and password. Leave NAT mode unchecked unless there
is a router between the management workstation and the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card that is configured with network address translation (NAT). Click the
Add Fabric button to open the fabric.
Figure 1-1. Login to Switch Dialog
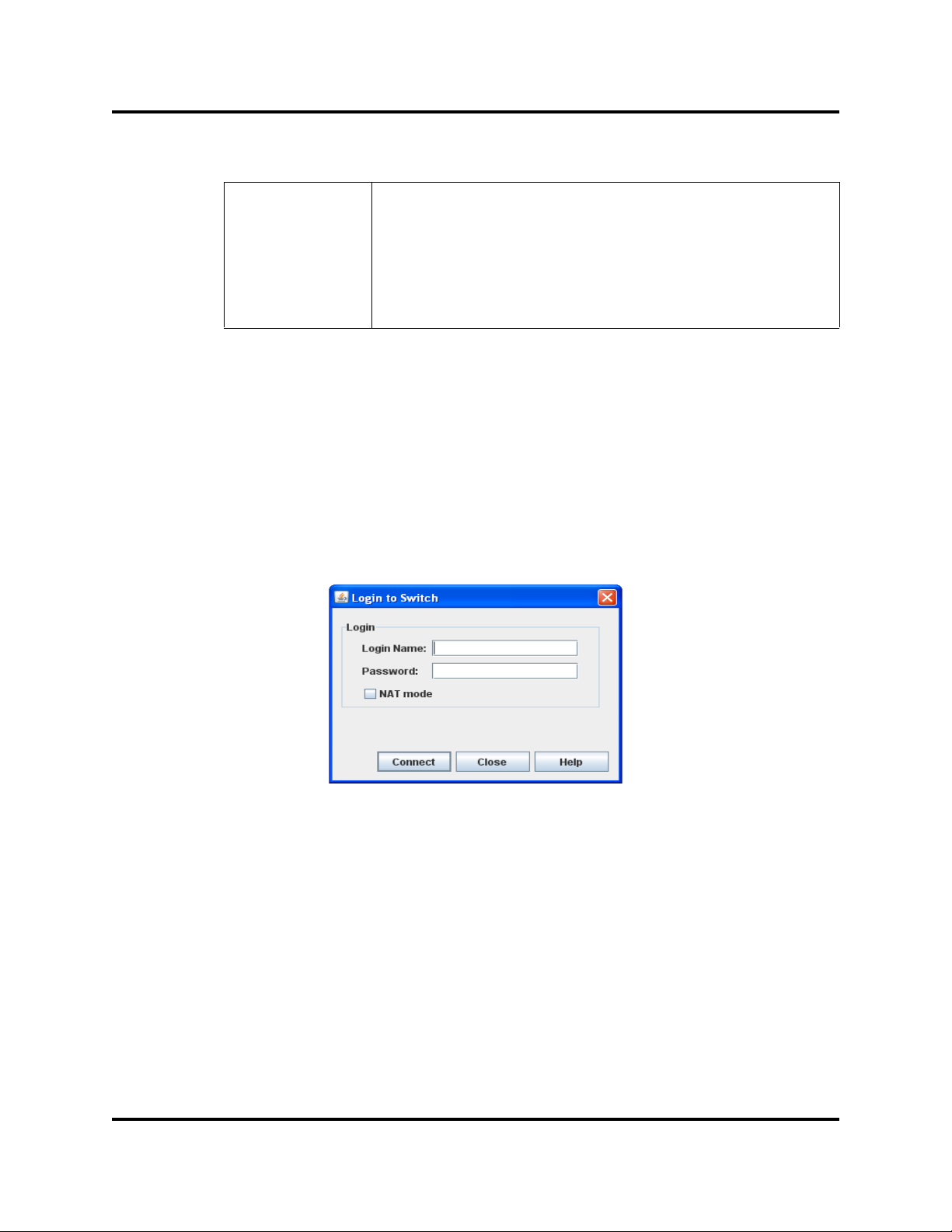
The opening window is displayed (Figure 1-3). For security reasons, you will be
prompted to change your user account password that was initially set up by the
administrator (Figure 1-2). You will be prompted to change the password each
time you attempt to open the fabric until you change the default password. Click
the OK button, and change the user account password. Refer to ”Managing User
Accounts” on page 2-18 for more information.
2 59273-00 C
Page 13
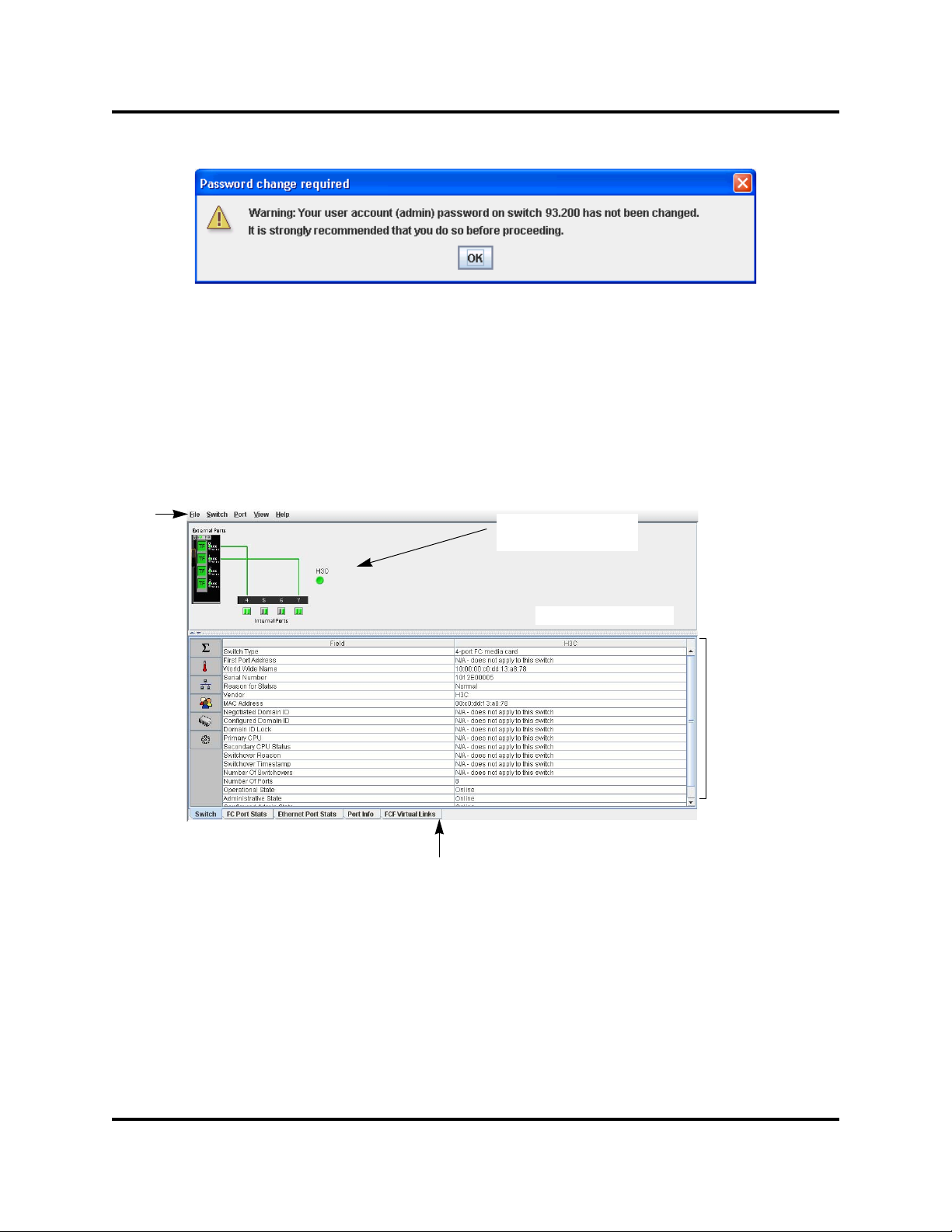
Figure 1-2. Password Change Required Dialog
Data Window Tabs
Data Window
Graphic Window
Menu
Bar
Switch Name and
Status
QuickTools User Interfaces
The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card faceplate is displayed in the graphic
window and shows the front of a single H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card and its
ports. The QuickTools interface (Figure 1-3) consists of a menu bar, graphic
window, data windows (some with buttons), and data window tabs.
Using QuickTools
QuickTools User Interfaces
Figure 1-3. QuickTools Interface
59273-00 C 3
Page 14

Using QuickTools
QuickTools User Interfaces
Graphic Window
The graphic window shows the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card faceplate
display (Figure 1-3). The card name has a small icon next to it that uses color to
indicate operational status:
A green icon indicates normal operation.
A yellow icon indicates that the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is
operational, but may require attention to maintain maximum performance.
A red icon indicates a potential failure or non-operational state as when the
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is offline.
A blue icon indicates that an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is unknown,
unreachable, or unmanageable.
The window height can be adjusted by clicking and dragging the window border
that it shares with the data window.
Data Windows and Tabs
The data window (Figure 1-3) presents a table of data and statistics associated
with the selected tab for the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card displayed in the
graphic window . Use the scroll bar to browse through t he data. The window leng th
can be adjusted by clicking and dragging the border that it shares with the graphic
window. Adjust the column width by moving the pointer over the column heading
border shared by two columns until a right/left arrow graphic is displayed. Click
and drag the arrow to the desired width. The data windows and t abs are described
below.
Switch
—displays current network and configuration data for the selected
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. Refer to ”Switch Data Window” on
page 2-12 for more information.
FC Port Statistics
—displays performance data for the selected Fibre
Channel (External) ports. Refer to ”FC Port Statistics Data Window” on
page 3-64 for more information.
Ethernet Port Statistics
—displays performance data for the selected
Ethernet (Internal) ports. Refer to ”Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window” on
page 3-68 for more information.
Port Information
— displays information for the selected ports. Refer to
”Port Information Data Window” on page 3-71 for more information.
FCF Virtual Links
— displays all configured Fibre Cha nnel Forwarder virtual
LAN links. Refer to Figure 2-16 for more information.
4 59273-00 C
Page 15
Menu Bar
Using QuickTools
QuickTools User Interfaces
QuickTools menu bar options are listed in Table 1-2.
Table 1-2. Menu Bar Options
Menu Options
File Preferences
Show Event Browser
Switch Archive
Restore
User Accounts
Set Date/Time
Switch Properties
Services
FCoE (VLAN Manager, FCF Manager)
Call Home (Setup, Profile Manager, Messenger Queue, Test Pro-
file, Change Over)
Security Consistency Checklist
Network Properties
SNMP (SNMP Properties, SNMP v3 Manager)
Switch Diagnostics (Offline Switch Diagnostics)
Toggle Beacon
Port Threshold Alarm Configuration
Load Firmware
Reset Switch (Hot Reset, Reset, Hard Reset)
Restore Factory Defaults
Features
Download Support File
Port Port Properties
Reset Port
Port Diagnostics (Online Port Diagnostics, Other Port Diagnostics)
Map Ports
59273-00 C 5
Page 16
Using QuickTools
QuickTools User Interfaces
Menu Options
View Refresh
Help Help Topics
Popup Menus
Popup menus are displayed when you right-click the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card faceplate image in the graphic window. Popup menu options give you quick
access to the common tasks and dialogs, such as:
Table 1-2. Menu Bar Options (Continued)
View Port Types
View Port States
View Port Speeds
View Port Media
Hide TH Map
About
Refreshing an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Selecting all ports
Security Consistency Checklist
Properties dialogs (Port, Switch, Network, and SNMP)
Services dialog
Port diagnostics dialogs
Shortcut Keys
Shortcut key combinations provide an alternative method of accessing menu
options in the web applet. For example, to open the Preferences dialog, press
Alt+F, then press R. The shortcut key combinations are not case-sensitive.
Shortcut keys are not supported on the Mac platform.
Selecting Ports
Ports are selectable and serve as access points for other displays and menus.
You select ports to display information about them in the data window or to modify
them. Context-sensitive popup menus are displayed when you right-click the
faceplate image or on a port icon. Refer to 3 Managing Ports for detailed port
information.
6 59273-00 C
Page 17

Using QuickTools
Setting QuickTools Preferences
Selected ports in the faceplate display are outlined in blue. You can select ports
the following ways.
To select a port, click the port.
To select all ports, right-click on the faceplate image and select Select All
Ports from the popup menu.
To select a range of consecutive ports, click a port, press the Shift key and
click another port. The web applet selects both end ports and all ports in
between the end ports.
NOTE:
When using the Shift key to select a range of ports, the first port you click in
the range is the anchor selection. Subsequent ranges are based on this
anchor selection. For example, after clicking port 4 and port 7 respectively,
port 4 becomes the anchor selection. The next range includes all ports
between port 4 and the next port you select.
To select several non-consecutive ports, press the Control key while
clicking each port.
To un-select ports in a group of selected ports, press the Control key while
clicking each port.
To cancel a selection, press the Control key and select it again.
Setting QuickTools Preferences
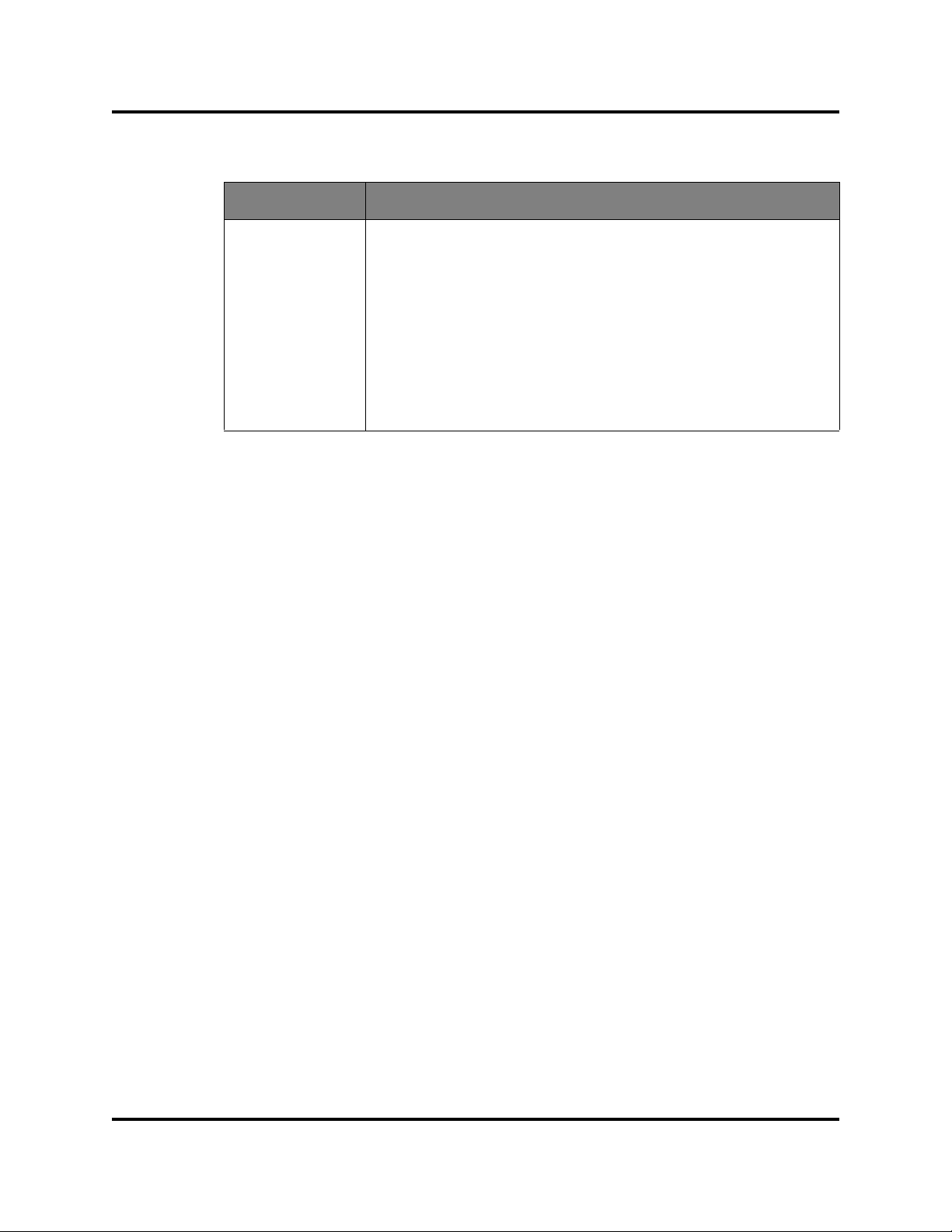
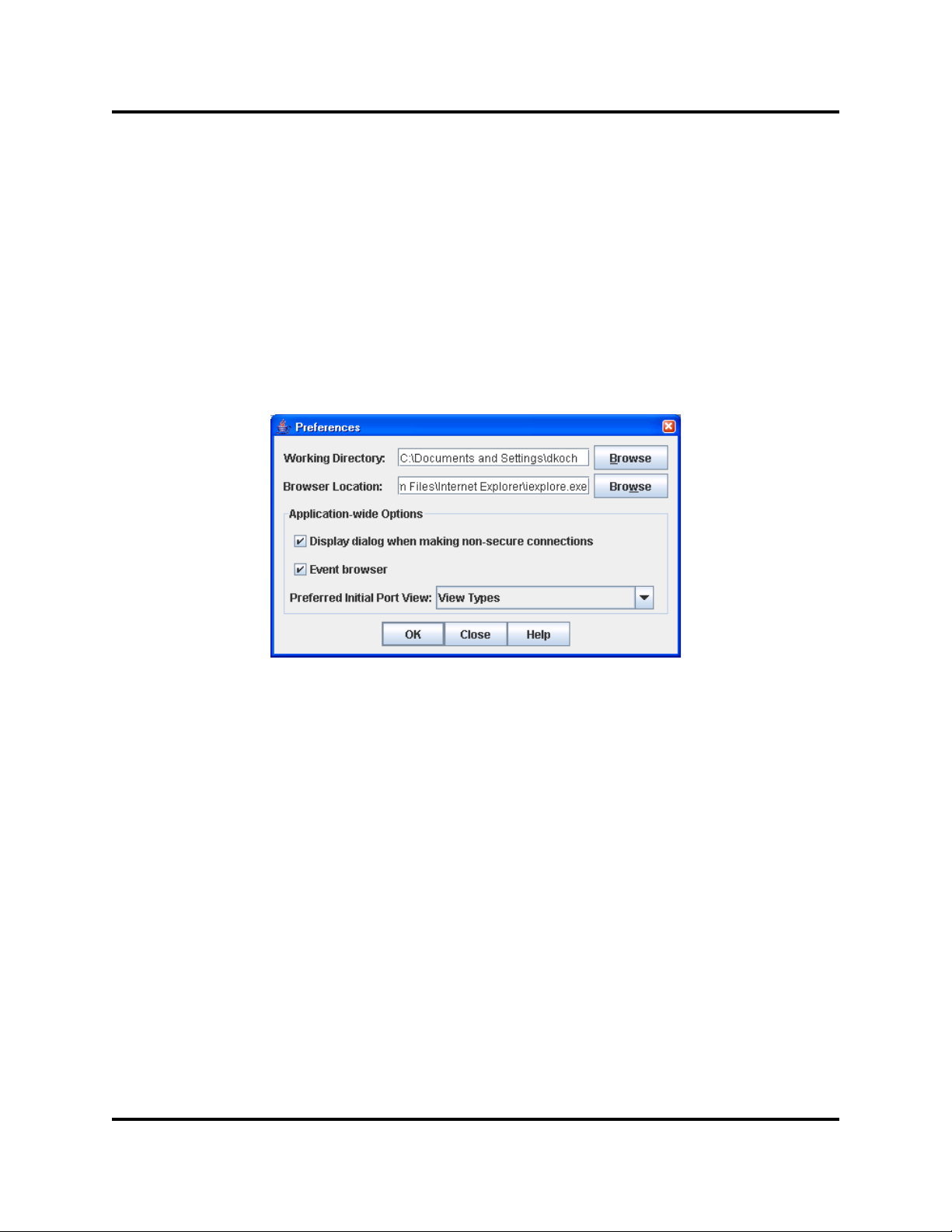
Using the preferences settings, you can:
Change the location of the working directory in which to save files.
Change the location of the browser used to view the online help. The
Browser Location field is not supported/displayed for Mac OS X.
Select a Display Dialog When Making Non-secure Connections option. If
enabled, the Non-secure Connections Check dialog is displayed when you
attempt to open a non-secure fabric. You then have the option of opening a
non-secure fabric. If disabled, you cannot open a fabric with a non-secure
connection).
Enable (default) or disable the Event Browser. Refer to ”Using the Event
Browser” on page 2-49. If the Event Browser is enabled using the
Preferences dialog (Figure 1-4) the next time QuickTools is started, all
events will be displayed. If the Event Browser is disabled when QuickTools is
started and later enabled, only those events from the time the Event
Browser was enabled and forward will be displayed.
59273-00 C 7
Page 18
Using QuickTools
Setting QuickTools Preferences
Choose the default port view when opening the faceplate display. You can
set the faceplate to reflect the current port type (default), port speed, port
operational state, or port transceiver media. Regardless of the default port
view you choose, you can change the port view in the faceplate display by
opening the View menu and selecting a different port view option. Refer to
the corresponding subsection for more information:
”Port Types” on page 3-79
”External Port Operational States” on page 3-76
”Port Speeds” on page 3-80
”Port Transceiver Media Status” on page 3-80
Figure 1-4. Preferences Dialog – QuickTools
To set preferences for your QuickTools sessions, do the following:
1. Open the File menu, and select Preferences to open the Preferences
dialog.
2. Enter, or browse, for paths to the working directory and browser.
3. In the Application-wide Options area, choose the preferences you want.
4. Click the OK button to save the changes.
8 59273-00 C
Page 19

Using Online Help
The browser-based online help system can be accessed from QuickTools several
ways. Online help is also context-sensitive, that is, the online help opens to the
topic that describes the dialog you have open.
To open the first topic in the help system, choose one of the following:
Open the Help menu and select Help Topics
With no dialog displayed, press the F1 function key
To open the help system to the topic that describes the dialog you have open,
choose one of the following:
Click the Help button in the dialog
Press the F1 function key
Viewing Software Version
Using QuickTools
Using Online Help
To view the QuickTools software version information, open the Help menu and
select About.
Exiting QuickTools
To exit a QuickTools session, close the browser.
59273-00 C 9
Page 20

Using QuickTools
Exiting QuickTools
10 59273-00 C
Page 21

2 Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card
This section describes the following tasks that manage an H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card in a fabric.
Displaying Interface Card Information
Managing User Accounts
Configuring Port Threshold Alarms
Paging an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Setting the Date/Time and Enabling NTP Client
Resetting an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Archiving an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Restoring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Restoring the Factory Default Configuration
Testing an Interface Card
Using the Event Browser
Downloading a Support File
Installing Firmware
Using Call Home
Displaying Interface Card Information
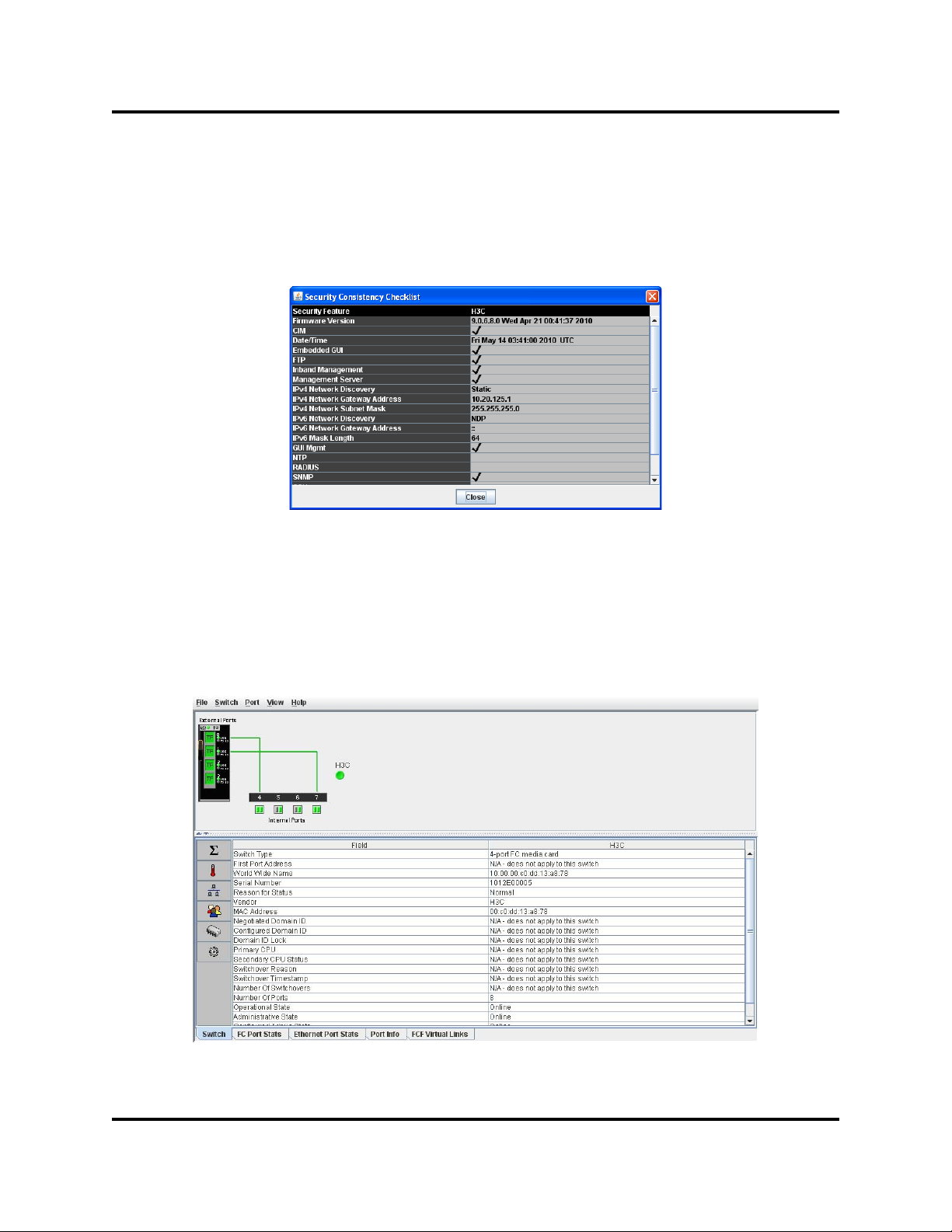
Y ou can display interface card information using the security consistency checklist
and the Switch data window.
59273-00 C 11
Page 22
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Displaying Interface Card Information
Security Consistency Checklist
To display configuration information for the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card,
open the Switch menu, and select Security Consistency Checklist. The
Security Consistency Checklist dialog displays current configuration information
as shown in Figure 2-5.
Figure 2-5. Security Consistency Checklist Dialog
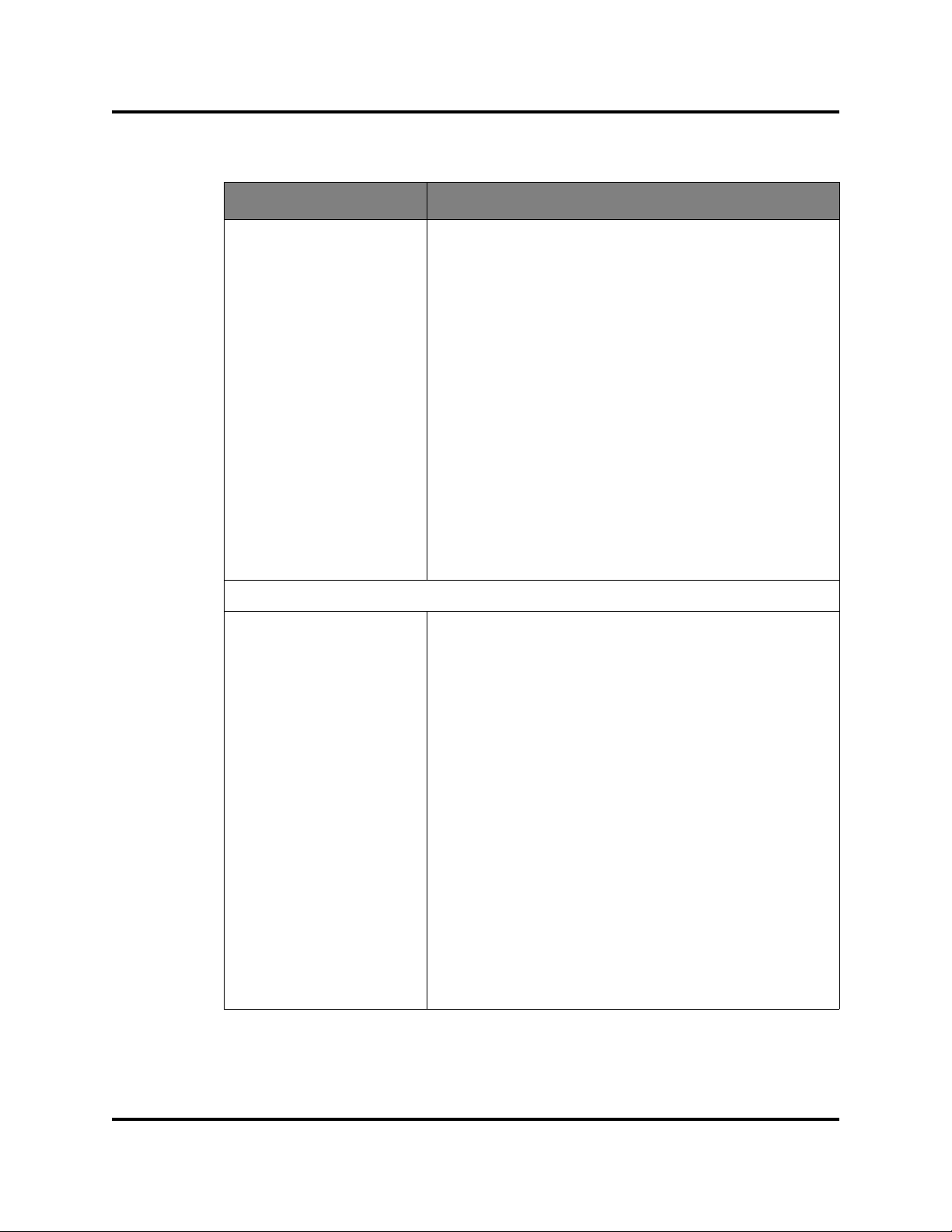
Switch Data Window
The Switch data window (Figure 2-6) displays the current network and H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card information for the selected H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card. To open the Switch data window, click the Switch tab below the
data window.
Figure 2-6. Switch Data Window
12 59273-00 C
Page 23

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Displaying Interface Card Information
Information in the Switch data window is grouped and accessed b y the Summary,
Status, Network, User Login, Firmware, Services, and Advanced buttons. Click a
button to display the grouped information in the data window on the right.
Figure 2-7 describes the Switch data window buttons.
Figure 2-7. Switch Data Window Buttons
The Switch data window entries are listed in Table 2-3.
Table 2-3. Switch Data Window Entries
Entry Description
Summary Group
Switch Type Switch model
First Port Address N/A - does not apply to this switch
World Wide Name Switch world wide name
Serial Number Number assigned to each chassis.
Reason for Status The reason for the operational state.
Vendor Switch manufacturer
MAC Address Media Access Control address
Negotiated Domain ID N/A - does not apply to this switch
Configured Domain ID N/A - does not apply to this switch
Domain ID Lock N/A - does not apply to this switch
Primary CPU N/A - does not apply to this switch
Secondary CPU Status N/A - does not apply to this switch
Switchover Reason N/A - does not apply to this switch
59273-00 C 13
Page 24
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Displaying Interface Card Information
Table 2-3. Switch Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
Switchover Timestamp N/A - does not apply to this switch
Number of Switchovers N/A - does not apply to this switch
Number of Ports Number of ports activated on the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Inter-
Operational State Switch operational state: Online, Offline, Diagnostic,
Administrative State Current H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card administrative
Configured Admin State Switch administrative state that is stored in the H3C
Beacon Status Switch LEDs are blinking (On) or not (off).
face Card
Down
state
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration
Require Enode Mac Config MAC-address checking status on the switch. When
enabled, MAC-address checking ensures that each FCF
responds to one and only one CNA.
Status Group
Operational State Switch operational state: Online, Offline, Diagnostic,
Down
Administrative State Current H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card administrative
state
Configured Admin State Switch administrative state that is stored in the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration
Beacon Status Switch LEDs are blinking (On) or not (off).
Reason for Status The reason for the operational state.
Secondary CPU Status N/A - does not apply to this switch
Fan 1 St atus N/A - does not apply to this switch
Fan 2 St atus N/A - does not apply to this switch
Fan 3 St atus N/A - does not apply to this switch
Power Supply 1 Statu s N/A - does not apply to this switch
Power Supply 2 Statu s N/A - does not apply to this switch
14 59273-00 C
Page 25
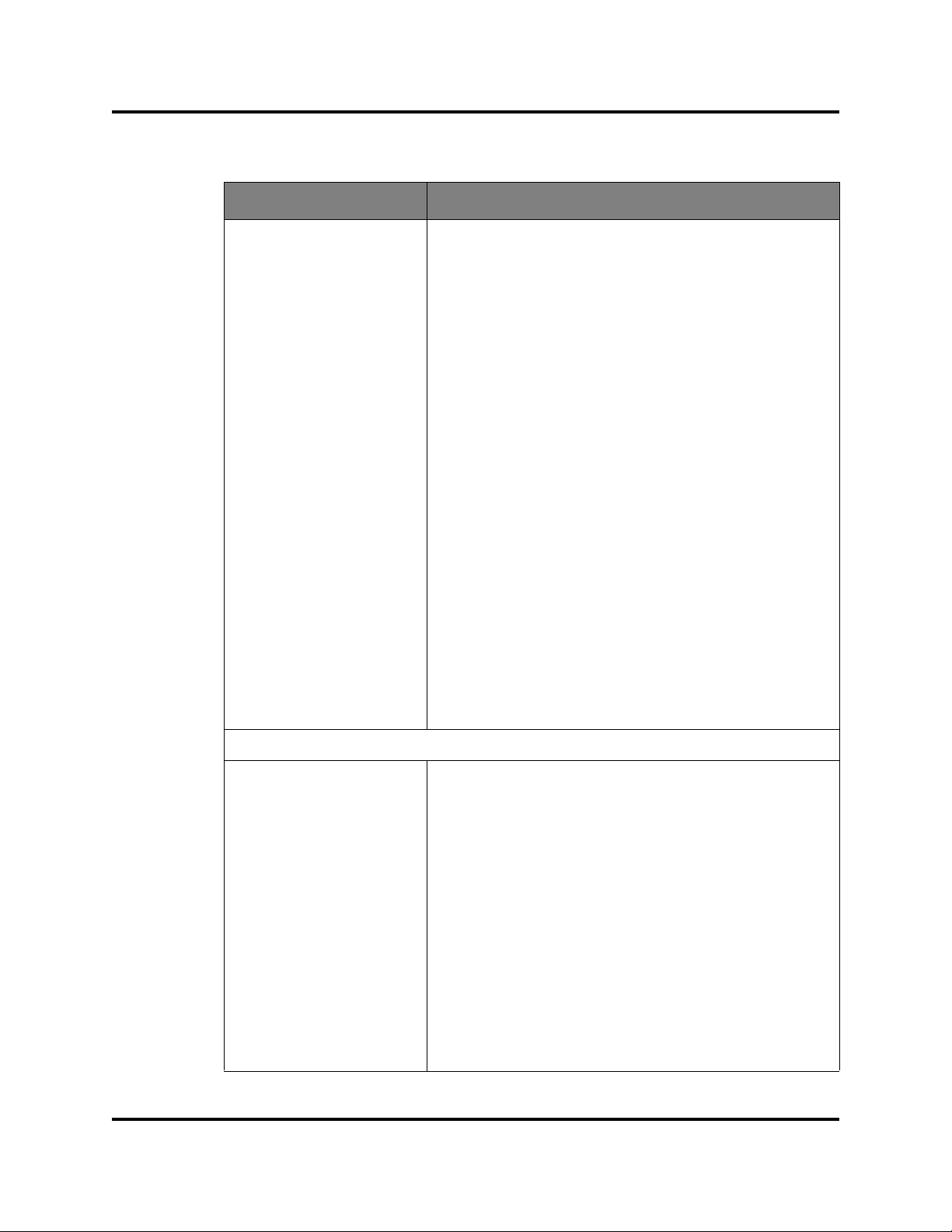
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Displaying Interface Card Information
Table 2-3. Switch Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
Temperature Failure Port
Shutdown
ASIC Temperature Temperature of the ASIC
ASIC Warning Tempera-
ture
ASIC Failure Temperature Non-configurable temperature threshold (105° Celsius)
Board Temperature Temperature of the Board
Board Warning Tempera-
ture
Board Failure Temperature Non-configurable temperature threshold (81° Celsius)
POST Sta tus Status from the most recent Power On Self Test
POST Fault Code Fault code from the most recent Power On Self Test
Test Status The current diagnostic test status of the H3C
Non-configurable (always enabled for this H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card). All ports are downed when
the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card temperature
exceeds the Failure Temperature.
Non-configurable temperature threshold (102° Celsius)
above which a warning condition alarm is generated.
above which a failure condition alarm is generated.
Non-configurable temperature threshold (75° Celsius)
above which a warning condition alarm is generated.
above which a failure condition alarm is generated.
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
Test Fault Code The code value for the last re corded diagnostic test st atus
recorded on the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
Network Group
IPv4 Enabled Internet Protocol version 4 Enabled status
IPv4 Address Mask that determines the IP address subnet
IPv4 Subnet Mask Mask that determines the IP address subnet
IPv4 Gateway IPV4 gateway address
IPv6 Enabled Internet Protocol version 6 Enabled status
IPv6 Address Mask that determines the IP address subnet
IPv6 Gateway IPV6 gateway address
CPU0 MAC Address N/A - does not apply to this switch
CPU1 MAC Address N/A - does not apply to this switch
SNMP Enabled SNMP enabled or disabled
59273-00 C 15
Page 26
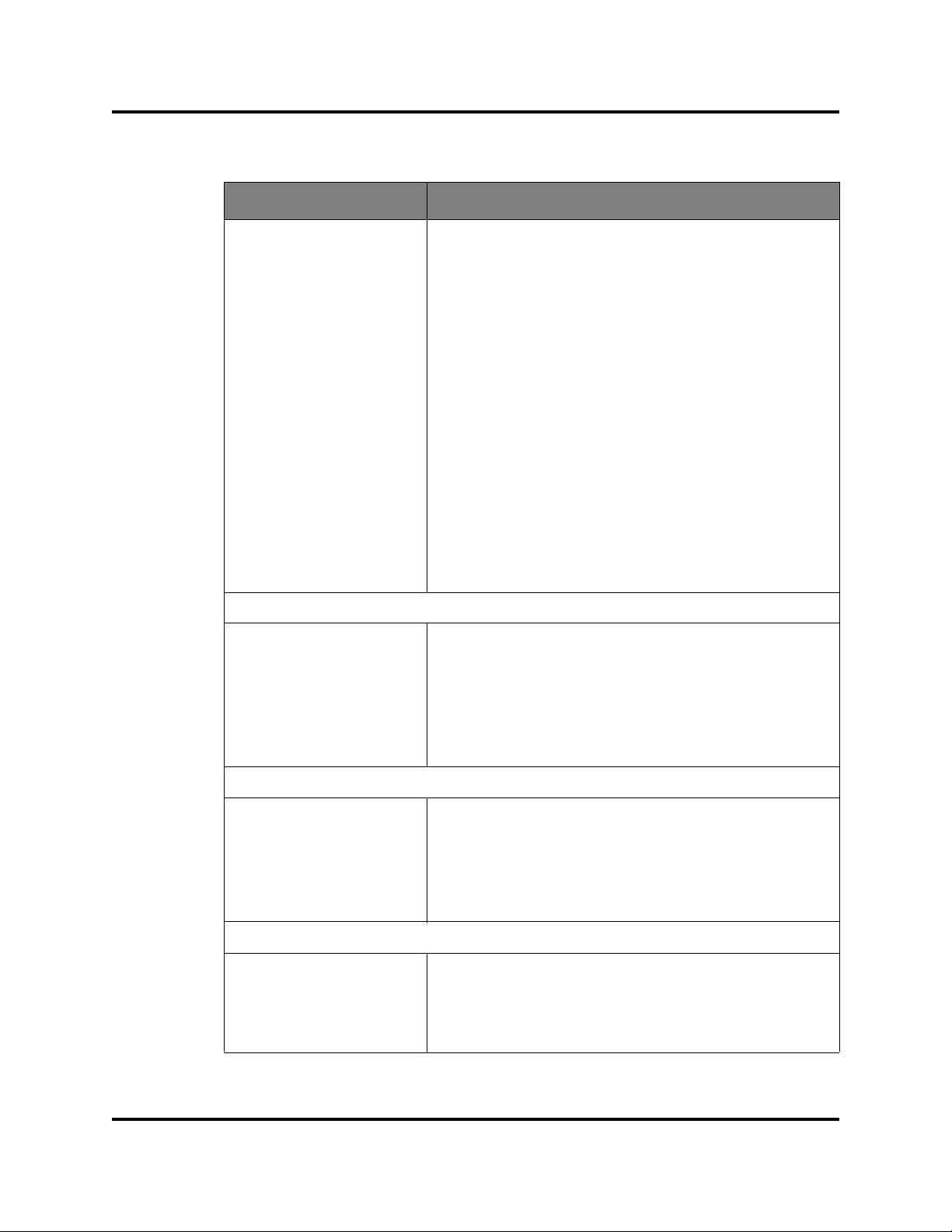
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Displaying Interface Card Information
Table 2-3. Switch Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
SNMP v3 Security Enabled SNMP v3 Security enabled or disabled
Broadcast Support N/A - does not apply to this switch
NTP Client Enabled Enabled or disabled. Allows for switches to synchronize
NTP Server Address The IP address of the centralized NTP server. Ethernet
Use Front Port N/A - does not apply to this switch
DNS Enabled DNS Enabled status
their time to a centralized server.
connection to NTP server is required.
Configured Local Hostname
Assigned Hostname Hostname assigned to the switch.
IPv6 Assigned Address
(1-20)
User Name Account name
Login Level Authority level
Super User Super user privileges enabled/disabled
UserAuthentication
Enabled
Firmware Version Active firmware version
Inactive Firmware Version N/A - does not apply to this switch
Pending Firmware Version Firmware version that will be activated at the next reset
PROM/Boot Version PROM firmware version
Hostname for the switch. If a fully qualified domain name
is given, the domain suffix is used as the first suffix in the
DNS search list for DNS lookups performed by the switch.
The set of IPv6 addresses assigned by DHCPv6, NDP, or
the switch administrator.
User Login Group
Enforcement of account names and authority (always
True)
Firmware Group
Services Group
NTP Client Enabled Enabled or disabled. Allows for the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card to synchronize time to a centralized server.
NTP Server Address The IP address of the centralized NTP server. Ethernet
connection to NTP server is required.
16 59273-00 C
Page 27
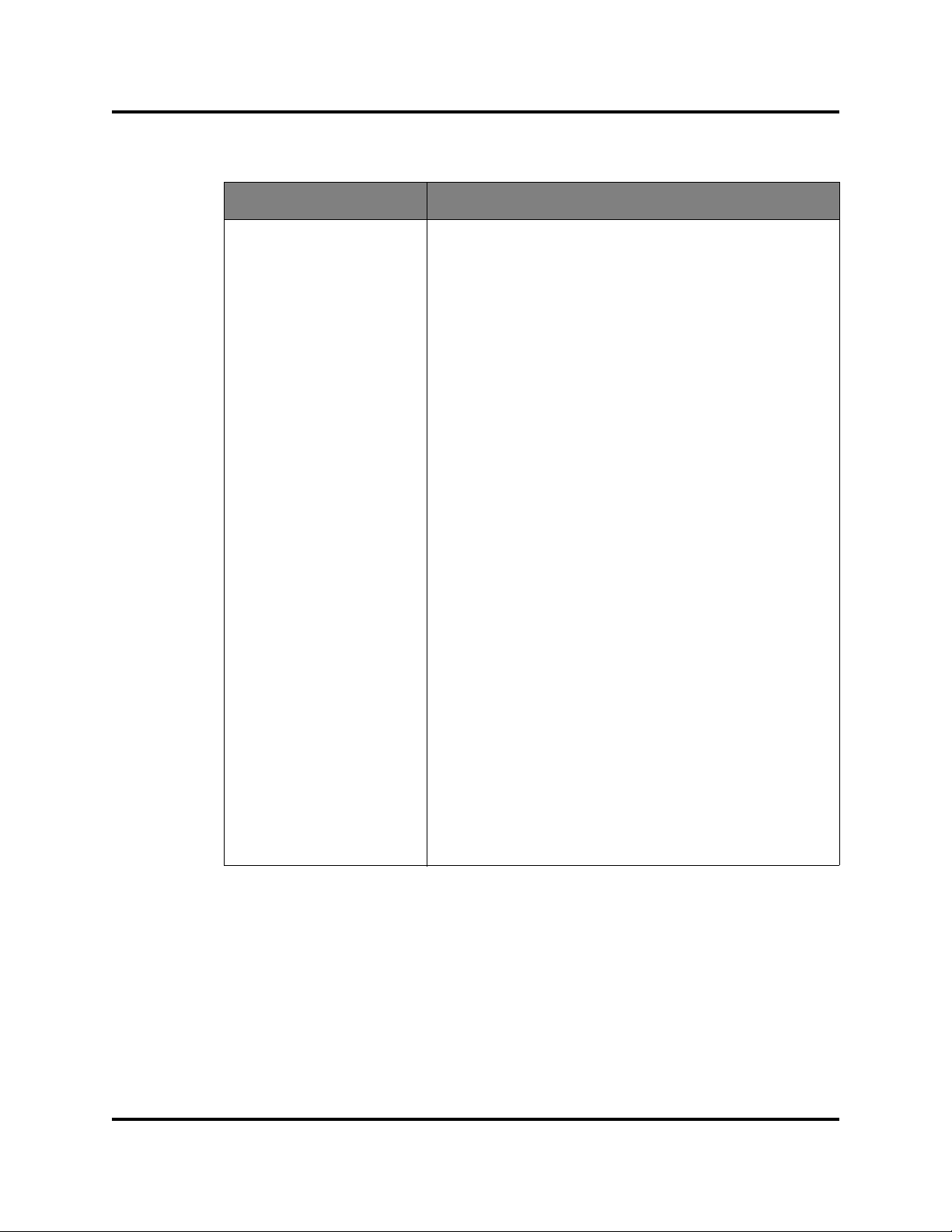
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Displaying Interface Card Information
Table 2-3. Switch Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
FDMI Enabled N/A - does not apply to this switch
FDMI HBA Entry Limit N/A - does not apply to this switch
Embedded GUI Enabled QuickTools web applet status. Enables or disables the
web applet on the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
Inactivity Timeout Number of minutes the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
waits before terminating an idle command line interface
session. Zero (0) disables the time out threshold.
GUI Mgmt Enabled Web applet status. If disabled, the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card cannot be managed using the web applet.
Telnet Enabled Telnet client status
SSH Enabled Secure Shell status. If enabled, an encrypted data path is
provided for command line interface sessions.
SSL Enabled Secure Sockets Layer status. If enabled, encryption for
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card management web
applet and CIM sessions is provided.
CIM Enabled Common Information Model status. The CIM agent is
based on the SNIA Storage Man agement Initiative Speci-
fication (SMI-S), which is the standard for SAN manage-
ment in a heterogeneous environment.
FTP Enabled FTP status
Management Server
N/A - does not apply to this switch
Enabled
SNMP Enabled SNMP enabled or disabled.
Call Home Enabled If enabled and configured, switches can send alerts and
events to pagers and Email. Users can configure the type
of events and where the alerts are sent.
59273-00 C 17
Page 28
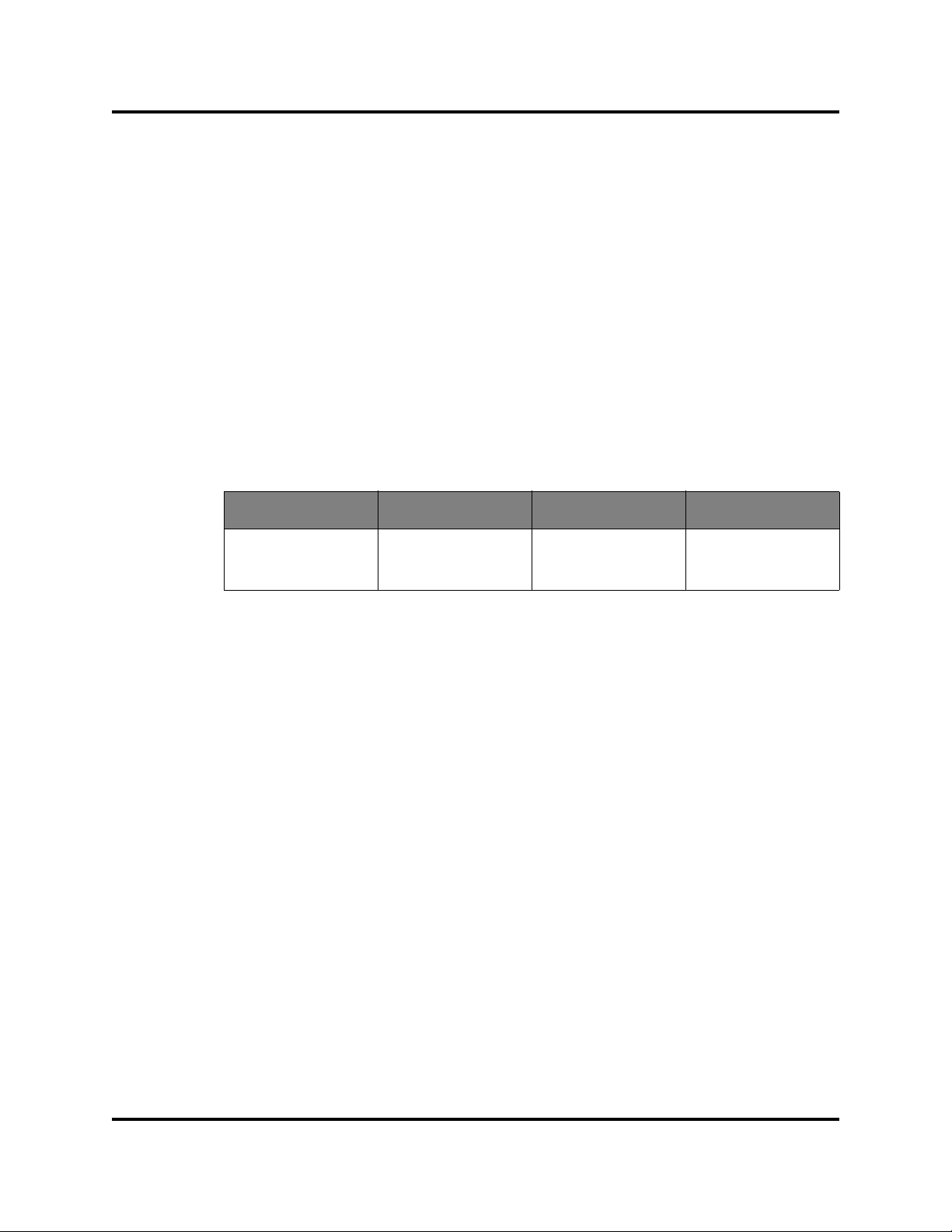
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Managing User Accounts
Managing User Accounts
Only the Admin account can manage user accounts with the User Account
Administration dialogs. However, any user can modify their own password. To
open the User Account Administration dialogs, open the Switch menu and select
User Accounts. A user account consists of the following:
Account name or login
Password
Authority level
Expiration date
The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card come from the factory with the following
user accounts:
Table 2-4. Factory User Accounts
Account Name Password Admin Authority Expiration
admin password true never expires
images images false never expires
Users with Admin authority can view and modify the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card and its configuration using QuickTools. Users without Admin authority are
limited to viewing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card status and configuration.
The Images account is used to exchange files with the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card using FTP. The Images account can not be removed.
NOTE:
If the same user account exists on an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card and
its RADIUS server , that user can login with either p assword, but the authority
and account expiration will always come from the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card database.
18 59273-00 C
Page 29
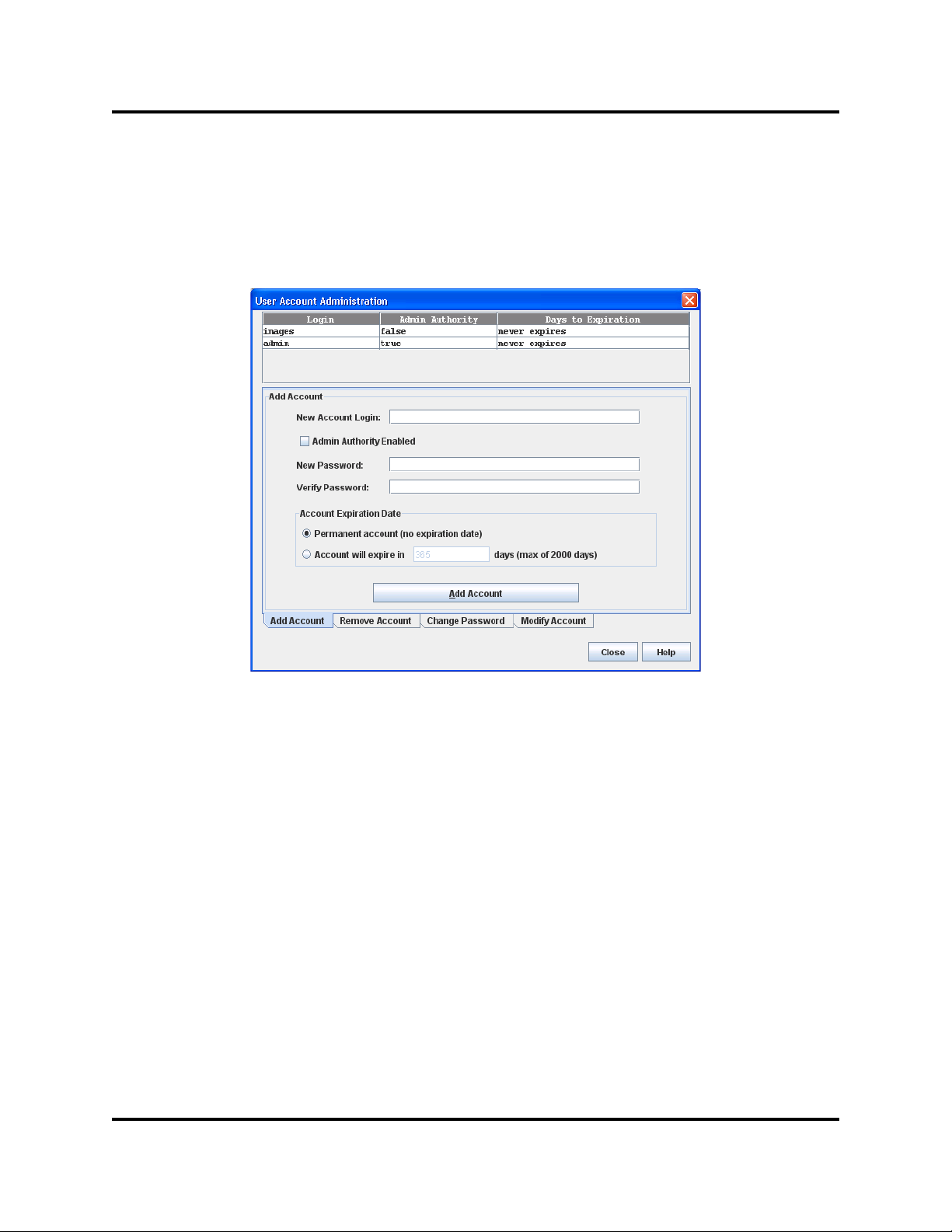
Creating User Accounts
To create a user account on an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, open the Switch
menu and select User Accounts to open the User Account Administration dialog
(Figure 2-8). An H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card can have a maximum of 15
user accounts.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Managing User Accounts
Figure 2-8. User Account Administration Dialog – Add Account
1. To open the User Account Administration dialogs, open the Switch menu
and select User Accounts.
2. Click the Add Account tab to open the Add Account tab page.
3. Enter an account name in the New Account Login field. Account names are
limited to 15 characters.
4. If the account is to have the ability to modify H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card configurations, select the Admin Authority Enabled option.
5. Enter a password in the New Password field and enter it again in the Verify
Password field. A password must have a minimum of 8 characters and no
more than 20.
6. If this account is to be permanent with no expiration date, select the
Permanent Account option. Otherwise, click the Account Will Expire
button and enter the number days in which the account will expire.
7. Click the Add Account button to add the newly defined account.
59273-00 C 19
Page 30
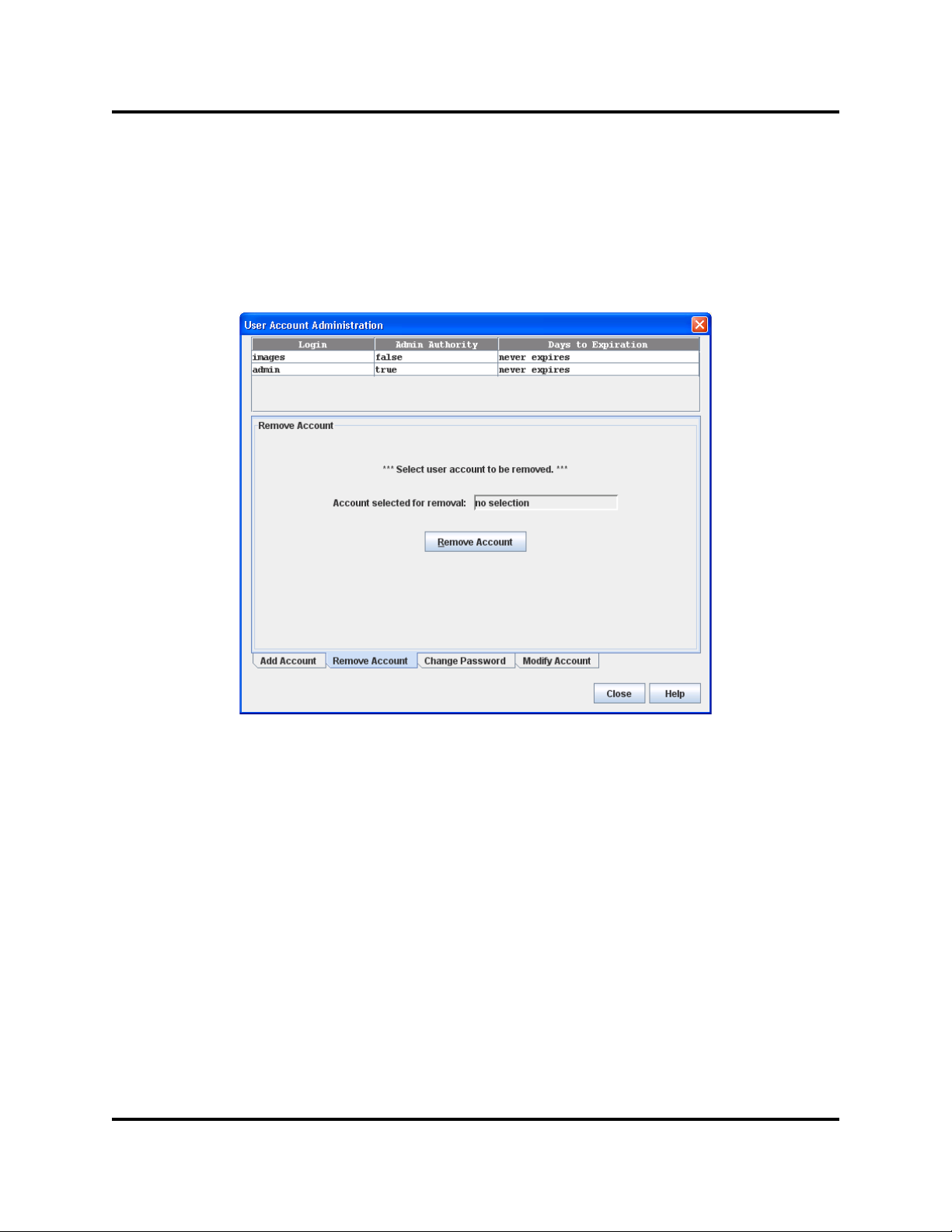
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Managing User Accounts
Removing a User Account
To remove a user account on an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, open the
Switch menu and select User Accounts. Click the Remove Account tab in the
User Account Administration dialog to present the display (Figure 2-9). Select the
account (login) name from the list of accounts at the top of the dialog and click the
Remove Account button.
Figure 2-9. User Account Administration Dialog – Remove Account
20 59273-00 C
Page 31

Changing a User Account Password
To change the password for an account on an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card,
open the Switch menu and select User Accounts. Click the Change Password
tab in the User Account Administration dialog to present the display (Figure 2-10).
Select the account (login) name from the list of accounts at the top of the dialog,
then enter the old password, the new password, and verify the new password in
the corresponding fields. Click the Change Password button. Any user can
change their password for their account, but only the Admin account name can
change the password for another user’s account. If the administrator does not
know the user’s original password, the administrator must remove the account
and add the account.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Managing User Accounts
Figure 2-10. User Account Administration Dialog – Change Password
59273-00 C 21
Page 32

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Managing User Accounts
Modifying a User Account
To modify a user account on an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, open the
Switch menu and select User Accounts. Click the Modify Account tab in the
User Account Administration dialog to present the display (Figure 2-11). Select
the account (login) name from the list of accounts at the top of the dialog. Select
the Admin Authority Enabled option to grant admin authority to th e account name.
Select an Account Expiration Date option. If the account is not to be permanent,
enter the number of days until the account expires. Click the Modify Account
button to save the changes. Click the Close button to close the User Account
Administration dialog.
Figure 2-11. User Account Administration Dialog—Modify Account
22 59273-00 C
Page 33

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring Port Threshold Alarms
Configuring Port Threshold Alarms
You can configure the interface card to generate alarms for selected events.
Configuring an alarm involves choosing an event type, rising and falling triggers, a
sample window, and finally enabling or disabling the alarm. To configure port
threshold alarms, do the following:
1. In the faceplate display, open the Switch menu and select Port Threshold
Alarm Configuration. The Port Threshold Alarm Configuration dialog
(Figure 2-12) prompts you to enable or disable all alarms, select an event,
set triggers, set a sample window and enable or disable an individual alarm.
Figure 2-12 Port Threshold Alarm Configuration Dialog
2. Select the Enable All Port Threshold Alarms option to enable monitoring
for all the individual alarm types that are enabled. The Enable All Port
Threshold Alarms option is the master control for the individual alarms. For
example, the switch will monitor CRC errors only if both the CRC Error
Enable and Enable All Port Threshold Alarms options are selected.
3. Select an event type from the Port Threshold Alarm drop-down list. Choose
from the following options:
CRC error monitoring
Decode error monitoring
ISL monitoring
Login monitoring
Logout monitoring
Loss of signal monitoring
4. Select the Enable option to make the alarm eligible for use.
59273-00 C 23
Page 34

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Rising
Trigger
Falling
Trigger
Event
Count
Sample Window
Generate falling
trigger alarm;
eligibility is reset
Generate rising
trigger alarm;
eligibility ends
Generate rising
trigger alarm;
eligibility ends
Paging an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
5. Enter a value for the rising trigger. A rising trigger alarm is generated when
the event count per interval exceeds the rising trigger . The interface ca rd will
not generate another rising trigger alarm for that event until the count
descends below the falling trigger and rises again above the rising trigger.
Consider the example in Figure 2-13.
6. Enter a value for the falling trigger. A fa lling trigger alarm is g enerate d when
the event count per interval descends below the falling trigger.
NOTE:
The interface card will down a port if a rising trigger alarm is not
cleared after three consecutive sample windows.
Figure 2-13 Port Threshold Alarm Example
7. Enter a sample window in seconds. The sample window defines the period
of time in which to count events.
8. Repeat steps 3 through 7 for each alarm you want to configure or enable.
Paging an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Use the toggle beacon feature to cause all Logged-In LEDs to flash, making the
9. Click the OK button to save all changes.
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card easier to visually recognize. To page an H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, open the Switch menu in the faceplate display and
select Toggle Beacon. To cancel the beacon, reselect Toggle Beacon.
24 59273-00 C
Page 35

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Setting the Date/Time and Enabling NTP Client
Setting the Date/Time and Enabling NTP Client
The Date/Time dialog allows you to manually set the date, time, and time zone on
a switch, or to enable NTP (Network Time Protocol) Client to synchronize the date
and time on the switch with an NTP server. Enabling the NTP client requires an
Ethernet connection to an NTP server, but ensures the consistency of date and
time stamps in alarms and log entries. When the date/time is set or displayed in
the firmware, it is always in Universal Time. However, when displayed in the
Date/Time dialog, the value is always in local time. If the NTP Client Enabled
option is selected (default is un-selected), the Date and Time areas becomes
inactive, thus preventing you from manually setting the date and time on the
switch. The NTP Server Discovery and NTP Server IP Address fields become
active, and allow you to select a discovery method (S tatic, DHCP, DHCPv6) and to
specify an IP address.
NOTE:
The difference between switch and workstation times must not exceed 24
hours, or the switch management application can not connect using SSL.
To manually set the date and time on a switch, do the following:
1. Open the Switch menu, and select Set Date/Time.
2. In the NTP area of the Date/Time dialog, clear (un-select) the NTP Client
Enabled option. The fields in the Date and Time areas become active.
3. Enter the day, year, hour, and minutes.
4. Select a month and time zone from the drop-down lists.
5. Click the OK button. The new date and time take effect immediately.
To synchronize the date and time on the switch with an NTP server, do the
following:
1. Open the Switch menu, and select Set Date/Time.
2. In the NTP area of the Date/Time dialog, select the NTP Client Enabled
option. The fields in the Date and Time areas become in-active.
3. Select a time zone from the Select Time Zone drop-down list.
4. Select an NTP Server Discovery option from the drop-down list.
5. Enter an NTP Server IP Address.
6. Click the OK button.
59273-00 C 25
Page 36

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Resetting an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Resetting an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Resetting an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card reboots the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card using configuration parameters in memory. Depending on the reset
type, an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card reset may or may not include a Power
On Self Test or it may or may not disrupt traffic. Table 2-5 describes the types of
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card resets.
During a hotreset operation, fabric services will be unavailable for a short period
(30-75 seconds depending on the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card model). V erify
all administrative changes to the fabric (if any) are complete before performing an
Nondisruptive Code Load and Activation (NDCLA). When upgrading firmware
across a fabric using non-disruptive activation, upgrade one H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card at a time and allow 75 seconds between each H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card.
CAUTION!
Changes to the fabric may disrupt the NDCLA process.
Common administrative operations that change the fabric include:
Adding, moving or removing devices attached to the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card fabric. This includes powering up or powering down at t ached
devices.
Adding, moving or removing ISLs or other connections.
After an NDCLA operation is complete, management connections must be
re-initiated:
QuickTools sessions will re-connect automatically
Telnet sessions must be restarted manually.
Applicable Code Versions:
Future H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card code releases will be upgraded
non-disruptively unless specifically indicated in its associated release notes
An NDCLA operation to previous H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card code
releases is not supported.
26 59273-00 C
Page 37

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Table 2-5. H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Resets
Type Description
Hot Reset Resets an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card without a Power On
Self Test. This reset activates the pending firmware, but does not
disrupt H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card traffic. If errors are
detected on a port during a hot reset, the port is reset automatically.
Reset Resets an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card without a Power On
Self Test. This reset activates the pending firmware and it is disruptive to H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card traffic.
Hard Reset Resets an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card with a Power On Self
Test. This reset activates the pending firmware and it is disruptive
to H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card traffic.
To reset an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card using QuickTools, open the Switch
menu and select the Reset Switch:
Select Hot Reset to perform a hot reset.
Select Reset to perform a standard reset.
Select Hard Reset to perform a hard reset.
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration is divided into three areas:
chassis, network, and SNMP. Chassis configuration specifies H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card-wide Fibre Channel settings. Network configuration specifies IP
settings, remote logging, and the NTP client. SNMP configuration specifies SNMP
settings and traps.
Switch Properties
To open the Switch Properties dialog, choose one of the following:
Open the faceplate display for the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card you are
configuring. Open the Switch menu and select Switch Properties.
Right-click an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card graphic in the faceplate
display, and select Switch Properties from the popup menu.
59273-00 C 27
Page 38

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Use the Switch Properties dialog to change the following H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card configuration parameters:
Syslog
Symbolic Name
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Administrative States
ENODE MAC Address Configuration
Figure 2-14. Switch Properties Dialog
Syslog
The Syslog (Remote Logging) feature enables saving of the log information to a
remote host that supports the syslog protocol. When enabled, the log entries are
sent to the syslog host at the IP address that you specify in the Logging Host IP
Address field. Log entries are saved in the internal H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card log whether this feature is enabled or not.
To save log information to a remote host, you must edit the syslog.conf file
(located on the remote host) and then restart the syslog daemon. Consult your
operating system documentation for information on how to configure Remote
Logging. The syslog.conf file on the remote host must contain an entry that
specifies the name of the log file in which to save error messages. Add the
following line to the syslog.conf file. A <tab> separates the selector field
(local0.info) and action field which contains the log file path name
(/var/adm/messages/messages.name).
Symbolic Name
The symbolic name is a user-defined name of up to 32 characters that identifies
the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. The symbolic name is used in the displays
and data windows to help identify an H3C L SW1FC4P0 Interface Card. The illegal
characters are the pound sign (#), semi-colon (;), and comma (,).
local0.info <tab> /var/adm/messages.name
28 59273-00 C
Page 39

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Administrative States
The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card administrative state determines the
operational state of the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. The H3C LSW1FC4 P0
Interface Card administrative state exists in two forms: the configured
administrative state and the current administrative state.
Configured administrative state — the state that is saved in the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration and is preserved across H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card resets. QuickTools always makes changes to
the configured administrative state. The configured administrative state is
displayed in the Switch Properties dialog.
Current administrative state — the state that is applied to the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for temporary purposes and is not retained
across H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card resets. The current administrative
state is set using the Set Switch command.
Table 2-6 describes the administrative state values.
Table 2-6. H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card Administrative States
Parameter Description
Online The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is available.
Offline The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is unavailable.
Diagnostics The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is in diagnostics mode, is
unavailable, and tests can then be run on all ports of the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
ENODE MAC Address Configuration
Enabling the RequireEnodeMACAddressConfig parameter performs MAC
address checking to ensure that each FCF responds to one and only one CNA
when connecting to more than one Fibre Channel fabric.
59273-00 C 29
Page 40

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Managing System Services
The System Services dialog (Figure 2-15) provides a central location for you to
enable or disable any of the external user services such as Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP), embedded web applet, command line interface,
Network Time Protocol (NTP), and Common Information Model (CIM). To display
the System Services dialog, open the Switch menu and select Services.
Figure 2-15. System Services Dialog
Use caution when disabling the Embedded GUI, GUI Mgmt, and Telnet, as it is
possible to disable all access to the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card except
through a serial connection.
Embedded GUI (Graphical User Interface) — allows users to point a
browser at the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card and use QuickTools.
GUI Mgmt — allows out-of-band management of the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card from the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card management
application (GUI). If disabled, the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card can not
be specified as the entry H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for a fabric in the
GUI, but can still be managed through an in-band connection.
Telnet (Command line interface) — allows users to manage the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card through a Telnet command line interface
session. Disabling Telnet access to the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is
not recommended.
30 59273-00 C
Page 41

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) — allows management of
the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card through third-party applications that
use SNMP.
NTP (Network Time Protocol) — allows the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card to obtain its time and date setting s from an NTP server. Configuring all
of your H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Cards and your workstations to utilize
NTP will keep their date/time settings in sync and will prevent difficulties with
SSL certificates and event logs.
CIM (Common Information Model) — allows management of the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card through third-party applications that use CIM.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) — allows file transfers to the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card using FTP. FTP is required for out-of-band firmware uploads
which will complete faster than in-band Firmware uploads.
Call Home — allows users to configure their switches to send alerts and
events to pagers and Email. Users can configure the type of events and
where the alerts are sent.
59273-00 C 31
Page 42

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring FCoE
The FCoE (Fibre Channel over Ethernet) feature enables you create a bridge
between the Fibre Channel fabric and an Ethernet VLAN (Virtual Local Area
Network). This bridge allows devices using an Ethernet connection to log in to a
Fibre Channel fabric through a FCF (Fibre Channel over Ethernet Forwarder).
Configuring FCoE includes:
VLAN configuration
FCF configuration
To display all configured Fibre Channel Forwarder virtual LAN links, click the FCF
Virtual Links tab below the data window to open the FCF Virtual Links data
window (Figure 2-16).
Figure 2-16. FCF Virtual Links Data Window
32 59273-00 C
Page 43

Configuring VLAN Manager
The VLAN Manager dialog enables you to add, remove, or reset VLAN port
assignments. To open the VLAN Manager dialog (Figure 2-17), open the Switch
menu, select FCoE, and select VLAN Manager. In the VLANs area, the list of
existing VLANs on this switch is displayed along with the maximum number of
VLANs allowed on the switch. The VLAN Assignments area shows the VLAN
each Ethernet port is in. Only Ethernet internal ports can be in VLANs, and any
given Ethernet port can only be assigned to a single VLAN at a time. There will
always be a default VLAN on the switch, and the default VLAN will always be
1002. By default, all the internal Ethernet ports are in the default VLAN. You are
not allowed to remove that default VLAN.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Figure 2-17. VLAN Manager Dialog
Adding a New VLAN The Add New VLAN dialog enables you to create a new
VLAN ID number . To open the Add New VLAN dialog (Figure 2-18), open the Add
menu and select Add, or click the Add VLAN button on the VLAN Manger dialog
toolbar. Enter a number between 1 and 4094 in the VLAN ID box and click OK.
Figure 2-18. Add New VLAN Dialog
59273-00 C 33
Page 44

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring FCF Configuration Manager
The FCF is a Fibre Channel Switching Element with one or more “lossless”
Ethernet MACs, each coupled with an FCoE Controller. An FCF forwards FCoE
frames addressed to it based on the D_ID of the encapsulated FC frames. The
FCF Configuration Manager dialog (Figure 2-19) enables you to add a new FCF
configuration, or remove/ edit an existing FCF configuration. To open the FCF
Configuration Manager dialog, open the Switch menu, select FCoE, and select
FCF Manager.
Figure 2-19. FCF Configuration Manager Dialog
34 59273-00 C
Page 45

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Creating a new FCF The FCF Editor dialog (Figure 2-20) enables you to
add/modify the following: FCMap, Enforce Keep Alive Timer, the Keep Alive T imer
Range, the FIP Priority, VLANs, and MAC Addresses. Click the OK button and if
the FCF passes validation, it will be added to the configured list in the FCF
Configuration Manager dialog. Click the Cancel button and all changes will be
lost, and the user is returned to the FCF Configuration Manager dialog.
Figure 2-20. FCF Editor - Create New FCF Dialog
59273-00 C 35
Page 46

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Table 2-7 defines the parameters in the FCF Editor dialog.
Table 2-7. FCF Editor dialog parameters
Parameter Description
FCmap Name A user-defined name consisting of 6 hexadecimal characters
Enforce Keep
Alive Timer
Keep Alive Timer
Determines if the Keep Alive Timer is enforced. The Keep Alive
Timer Range can still be modified, even if this box is not modified.
An integer value from 0 to 90 seconds
Range
Priority The FIP Priority is a value from 0 to 255 where 0 is the highest pri-
ority, and 255 is lowest.
VLAN The VLAN drop down comes populated with all the configured
VLAN IDs on the switch. The user may select from the list, or type
in a VLAN ID that is not yet configured.
NOTE: This does not create a VLAN with that ID.
Add Click the Add button to add the VLAN to the VLAN list for the FCF.
The maximum number of VLANs for the FCF is displayed above
the list.
MAC Address Allows you to add MAC addresses (hexidecimal characters only).
The maximum number allowed is indicated in the label above the
MAC list. The MAC addresses entered are displaye d in th e MAC
list and are automatically delimited with colons in the MAC list.
Add Click the Add button to add the MAC address entered in the MAC
Address field to MAC address list for the FCF. The maximum number of MAC addresses for the FCF is displayed above the list.
36 59273-00 C
Page 47

Configuring Network Properties
Use the Network Properties DNS (Domain Name Service) dialog (Figure 2-21) to
enable the DNS Client on the switch and the DNS server to map domain names to
IP addresses. To open the Network Properties dialog, select a switch in the
topology display or open the faceplate display, open the Switch menu, select
Network, and select Network Properties. After making changes, click the OK
button to put the new values into effect.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Figure 2-21. Network Properties Dialog—DNS Configuration
59273-00 C 37
Page 48

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Table 2-8 describes the Network Properties DNS values.
Table 2-8. Network Properties—DNS Configuration
Parameter Description
DNS Client Domain Name Service client
Local Hostname The name of local host
Server Discovery Choose one of the following methods by which to assign the IP address:
Static
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
Dhcpv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6)
— uses the IP configuration parameters entered in the Network
Properties dialog.
— acquires the IP configura-
tion from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is obtained, the DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured lease. If the previous lease
cannot be used, no IP address will be assigned to this switch in order to
avoid an IP address conflict.
— acquires the IP
configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is obtained, the
DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured lease. If the previou s
lease cannot be used, no IP address will be assigned to this switch in order
to avoid an IP address conflict.
DNS Server Addresses The IP address of the DNS server
Search List Discovery Choose one of the following methods by which to assign the IP address:
Search List Domain
Names
Static
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
Dhcpv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6)
The suffix that is appended to the user-specified hostname for the search.
— uses the IP configuration parameters entered in the Network
Properties dialog.
— acquires the IP configura-
tion from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is obtained, the DHCP cli-
ent attempts to use the previously configured lease. If the previous lease
cannot be used, no IP address will be assigned to this switch in order to
avoid an IP address conflict.
— acquires the IP
configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is obtained, the
DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured lease. If the previou s
lease cannot be used, no IP address will be assigned to this switch in order
to avoid an IP address conflict.
38 59273-00 C
Page 49

Configuring SNMP
Configuring the Simple Network Management Protocol includes:
SNMP Properties Configuration
SNMP Trap Configuration
SNMP v3 Manager and User Configuration
SNMP Properties
Use the SNMP Properties dialog (Figure 2-22) to change SNMP configuration
parameters. After making changes, click the OK button to p ut t he new values into
effect. To open the SNMP Properties dialog, choose one of the following:
Open the faceplate display for the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card that you
are configuring. Open the Switch menu, select SNMP, and select SNMP
Properties.
Right-click an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card graphic in the faceplate
display, and select SNMP Properties from the popup menu.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
NOTE:
Since Read Community , T rap Community, and Write Community settings are
like passwords and are write-only fields, the current settings are displayed as
asterisks.
Figure 2-22. SNMP Properties Dialog
59273-00 C 39
Page 50

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
SNMP Configuration The SNMP configuration defines how authentication
traps are managed. Table 2-9 describes the SNMP configuration parameters. The
illegal characters for the user-defined fields are the pound sign (#), semi-colon (;),
and comma (,).
Table 2-9. SNMP Configuration Parameters
Parameter Description
SNMP Enabled Enables or disables SNMP communication with other H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Cards in the fabric. If disabled, the user cannot use an SNMP application at a workstation to talk to the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card that has this setting disabled.
Contact Specifies the name (up to 64 characters) of the person who is to be
contacted to respond to trap events. The default is “undefined”.
Read Community
SNMP Proxy If enabled, you can use SNMP to monitor and configure any H3C
Location Specifies the name (up to 64 characters) for the H3C LSW1 FC4P0
Authentication
Trap
Write Community
Read community password (up to 32 characters) that authorizes an
SNMP agent to read information from the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. This is a write-only field. The value on the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card and the SNMP management server
must be the same. The default is “public”.
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card in the fabric.
Interface Card location. The default is “undefined”.
Enables or disables the reporting of SNMP authentication failures. If
enabled, a notification trap is sent when incorrect community string
values are used. The default value is "False".
Write community password (up to 32 characters) that authorizes an
SNMP client to write information to the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card. This is a write-only field. The value on the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card and the SNMP management server must be the
same. The default is “private”.
40 59273-00 C
Page 51

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
SNMP Trap Configuration The SNMP trap configuration defines how traps
are set. Choose from the tabs Trap1–Trap 5 to configure each trap. Table 2-10
describes the SNMP configuration parameters.
Table 2-10. SNMP Trap Configuration Parameters
Parameter Description
Trap Version Specifies the SNMP version (1 or 2) with which to format traps.
Trap 1 Enabled Enables or disables the trap. If disabled, traps are not sent to trap
monitoring stations and the trap settings are not configurable.
a
Trap Address
Trap Community Trap community password (up to 32 characters) that authorizes an
Trap Port
1
Specifies the IP address to which SNMP traps are sent. A maxim um
of 5 trap addresses are supported. The default address for trap 1 is
10.0.0.254. The default address for traps 2–5 is 0.0.0.0.
SNMP agent to receive traps. This is a write-only field. The value on
the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card and the SNMP management
server must be the same. The default is “public”.
The port number on which the trap is sent. The default is 162.
Trap Severity Specifies a severity level to assign to the trap. Open the drop-down
list and choose a level. The Trap 1 Enabled option on the SNMP
Properties dialog must be enabled to access this drop-down list.
Trap severity levels include Unknown, Emergency, Alert, Critical,
Error, Warning, Notify, Info, Debug, and Mark
a
Trap address (other than 0.0.0.0) and trap port combinations must be unique. For example, if trap
1 and trap 2 have the same address, then they must have different port values. Similarly, if trap 1
and 2 have the same port value, they must have different addresses.
59273-00 C 41
Page 52

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
SNMPv3 Security
Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3 (SNMPv3) is an interoperable
standards-based protocol for network management. SNMPv3 provides secure
access to devices by a combination of authenticating and encrypting packet s over
the network. SNMPv3 security is an additional layer of security offered with the
9.0.7 firmware. The SNMPv3 security is available to a switch that has a secure
connection, and can only be configured on the entry switch. The security features
provided in SNMPv3 are:
Message integrity—ensures that a packet has not been tampered with
during transit.
Authentication—determines the message is from a valid source.
Encryption—scrambles the contents of a packet to prevent it from being
seen by an unauthorized source.
The SNMP v3 Manager dialog allows you to add, remove, and edit an SNMPv3
user. To display the SNMP v3 Manager dialog (Figure 2-23) open the Switch
menu, select SNMP, and select SNMP v3 Manager. The SNMP v3 Security
option allows you to turn SNMPv3 security on or off.
Click the Add button to open the SNMPv3 User Editor dialog (Figure 2-24), and
add an SNMPv3 user. After SNMPv3 users are configured and saved, they are
displayed in the SNMPv3 Users list window in the SNMP v3 Manager dialog.
Select a user from the list, and that user’s settings are displayed on the right in the
Selected SNMPv3 User area. The Remove and Edit buttons become active when
you select a user from the SNMP v3 Users list. Click the Remove button to delete
the selected user. Click the Edit button to open the SNMP v3 User Editor dialog in
which to change the selected user's configuration.
Figure 2-23. SNMP v3 Manager Dialog
42 59273-00 C
Page 53

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Configuring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Figure 2-24. SNMP v3 User Editor Dialog
Table 2-11 describes the SNMP v3 User Editor dialog parameters. After
configuring the user , click the OK button to sa ve the settings and close the dialog.
Table 2-11. SNMP v3 User Editor Dialog
Parameter Description
User Name Name for this SNMPv3 user.
Group Read Only permits user to view only SNMPv3 user settings. Read
Write permits user to view and change SNMPv3 user settings.
Authentication
Type
Authentication
Phrase
Confirm Authentication Phrase
Privacy Type DES or None. If None, no privacy phrase is required.
Privacy Phrase A unique string or phrase to serve as an password-like privacy
None, MD5, SHA. If None, no authentication phrase is required. MD5
and SHA require authentication phrase.
A unique string or phrase to serve as an password-like authentication phrase.
Re-enter the same unique string or phrase to serve as an password-like authentication phrase.
phrase.
Confirm Privacy
Phrase
59273-00 C 43
Re-enter the unique string or phrase to serve as an password-like
privacy phrase.
Page 54

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Archiving an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Archiving an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
You can create an .XML archive file containing the configuration parameters.
Basically any data received by QuickTools is archived. This archive file can be
used to restore the configuration on the same H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card or
on a replacement H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. You can also use the archive
file as a template for configuring new H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Cards to add to
a fabric. Passwords are not archived. Security Group secrets are not included in
the archive and must be re-configured using the CLI after a restore.
Archived parameters include the following:
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card properties and statistics
IP configuration
SNMP configuration
Port properties and statistics
Alarm configuration
User account information (but not restored)
Configured security (only with SSL connection to the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card)
RADIUS Server information (only with SSL connection to the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card)
To archive an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, do the following:
1. Open the Switch menu and select Archive.
2. In the Save dialog, enter a file name.
3. Click the Save button.
Restoring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Restoring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card loads the archived H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration parameters to the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card. The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration must be
archived before it can be restored. The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card archive
must be compatible with the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card to be restored.
That is, you can only restore an 8-Port H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card with an
archive from an 8-Port H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. Refer to ”Archiving an
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card” on page 2-44 for more information.
44 59273-00 C
Page 55

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Restoring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
CAUTION!
The H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card being restored should be physically
disconnected from the fabric. Restoring an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
in a fabric can severely disrupt the fabric. After the restore process is
complete, the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card can be reconnected to the
fabric.
To restore an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, do the following:
1. Log in to the fabric through the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card you want
to restore. You cannot restore an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card over an
ISL.
2. Open the Switch menu and select Restore to display the Restore dialog
(Figure 2-25). The Restore dialog offers a Full Restore and a Selective
Restore tab.
Figure 2-25. Restore Dialogs – Full and Selective
3. Enter the archive file name or browse for the file. This archive file must be
one that was produced by the QuickTools archive function. Configuration
backup files created with the Config Backup command are not compatible
with the QuickTools restore function. The Config Ba ckup command does not
archive the primary or secondary secrets for any security groups.
59273-00 C 45
Page 56

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Restoring the Factory Default Configuration
4. T o restore all configuration setting s, click the Full Restore tab, then click the
Restore button. To restore selected configuration settings, click the
Selective Restore tab and select one or more of the following options, then
click the Restore button:
Network Properties—restores all settings presented in the Network
properties dialog except the IP address. Refer to ”SNMP Properties”
on page 2-39.
IP Address—restores H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card IP address in
addition to the other network properties
Port Properties—restores all settings presented in the Port properties
dialog. Refer to ”Port Symbolic Name” on page 3-75.
Call Home—restores all Call Home configuration and profiles settings
Switch Properties—restores all settings presented in the Switch
Properties dialog except the domain ID. Refer to ”Switch Properties”
on page 2-27.
Domain ID—restores the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card domain ID
in addition to the other switch properties.
Radius Server Info—restores all RADIUS server information defined in
the switch database
FCoE Settings—restores the last saved VLAN and FCF configurations
5. Click the OK button and view the results in the top pane of the Restore
dialog.
Restoring the Factory Default Configuration
You can restore the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card and port configuration
settings to the factory default values. To restore the factory configuration on an
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, open the Switch menu and select Restore
Factory Defaults. Table 2-12 lists the factory default H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card configuration settings.
Restoring the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card to the factory default configuration
does not restore the account name and password settings.To restore user
accounts, you must select the Reset User Accounts to Default option in the
maintenance menu. Refer to “Recovering a Switch” in the Installation Guide for
your H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for information about maintenance mode
and the maintenance menu.
46 59273-00 C
Page 57

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Restoring the Factory Default Configuration
Table 2-12. Factory Default Configuration Settings
Setting Value
Symbolic Name H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Administrative State Online
I/O Stream Guard Disabled
Device Scan Enabled True
SNMP Enabled True
SNMP Proxy True
IP Address 10.90.90.xx
Where xx changes based on slot
Subnet Mask Address 255.255.255.0
Gateway Address 0.0.0.0
Network Discovery Static
Remote Logging False
Remote Logging Host Ip Address 10.0.0.254
NTP Client Enabled False
NTP Server IP Address 10.0.0.254
Contact Undefined
Location Undefined
Trap Enabled False
Trap Port 162
Trap Address Trap 1: 10.0.0.254; Traps 2-5: 0.0.0.0
Trap Community Public
Read Community Public
Write Community Private
Port State Online
Port Speed Auto-detect
Port Type GL
59273-00 C 47
Page 58

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Testing an Interface Card
Testing an Interface Card
The Switch Diagnostics dialog (Figure 2-26) allows you to test and verify
operational status of switches. To open the Switch Diagnostic dialogs, open the
Switch menu, select Switch Diagnostics > Offline Switch Diagnostics. Two
types of disruptive tests are available:
Offline Test (internal)—a disruptive test that exercises all port connections
between the ASIC and the SerDes chip for an interface card in the
diagnostics state.
Connectivity Tests (internal)—a disruptive test that exercises all port
connections between the ASIC and the SerDes chip and all inter-port
connections for an interface card in the diagnostics state.
When you run an offline or connectivity test, the switch is put into the diagnostics
state for you. The switch does not return to its original state until the Switch
Diagnostics dialog closes, which initiates a disruptive reset.
Figure 2-26 Switch Diagnostics Dialog
To test an interface card, do the following:
1. Open the Switch menu and select Switch Diagnostics > Offline Switch
Diagnostics.
2. Select the test type in the drop-down list.
48 59273-00 C
Page 59

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using the Event Browser
3. Enter a frame size in the Frame Size field.
4. Enable or disable the Terminate Test Upon Error option.
5. Select a Loop Count option. The Loop Forever option runs the test until you
click the Stop Test button. The Loop Count option runs the test the number
of times you specify in the Loop Count field.
6. Select the default test pattern or enter a user-defined (hexadecimal) test
pattern.
7. Click the Start Test button to begin the next test. Observe the results in the
Test Results area.
NOTE:
If the Test Status field in the Test Results area indicates Failed, note the
POST Fault Code displayed in the Switch data window, and contact
technical support.
Using the Event Browser
The Event Browser displays a list of events generated by the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card in the fabric and QuickTools. Events that are generated by
QuickTools are not saved on the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, but can be
saved to a file during the QuickTools session.
Entries in the Event Browser (Figure 2-27) are formatted by severity, time stamp,
source, type, and description. The maximum number of entries allowed in the
Event Browser is 10,000. The maximum number of entries allowed on an H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is 1200. Once the maximum is reached, the event list
wraps and the oldest events are discarded and replaced with the new events.
Event entries from the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, use the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card time stamp, while event entries generated by the web
applet have a workstation time stamp. You can filter, sort, and export th e content s
of the Event Browser to a file. The Event Browser begins recording when enabled
and QuickTools is running.
If the Event Browser is enabled using the Preferences dialog, the next time
QuickTools is started all event s from the H3C LSW1 FC4P0 Interface Card log will
be displayed. If the Event Browser is disabled when QuickTools is started and
later enabled, only those events from the time the Event Browser was enabled
and forward will be displayed.
59273-00 C 49
Page 60

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Column Sorting
Buttons
Severity
Column
Using the Event Browser
To display the Event Browser, open the File menu and select Show Event
Browser. If the Show Event Browser selection is grayed-out, you must first
enable the Events Browser preference. Refer to ”Setting QuickTools
Preferences” on page 1-7.
Figure 2-27. Events Browser
Severity is indicated in the severity column using icons as described in Table 2-13.
Table 2-13. Severity Levels
Severity
Icon
Alarm—an alarm is a serviceable event. This means that attention by the
user or field service is required. Alarms are posted asynchronously to the
screen and cannot be turned off. If the alarm denotes that a system error
has occurred the customer and/or field representative will generally be
directed to provide the output file from the Show Support command.
Critical event—an event that indicates a potential failure. Critical log messages are events that warrant notice by the user. By default, these log messages will be posted to the screen. Critical log messages do not have alarm
status as they require no immediate attention from a user or service representative.
Warning event—an event that indicates errors or other conditions tha t may
require attention to maintain maximum performance. Warning messages
will not be posted to the screen unless the log is configured to do so. Warning messages are not disruptive and, therefore, do not meet the criteria of
Critical. The user need not be informed asynchronously
No icon Informative—an unclassified event that provides supporting information.
Description
50 59273-00 C
Page 61

NOTE:
Events (Alarms, Critical, Warning, and Informative) generated by the
web applet are not saved on the switch. They are permanently discarded
when you close a QuickTools session, but you can save these events to
a file on the workstation before you close QuickTools and read it later
with a text editor or browser.
Events generated by the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card are stored on
the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, and will be retrieved when the
web applet is restarted. Some alarms are configurable.
Filtering the Event Browser
Filtering the Event Browser enables you to display only those events that are of
interest based on the event severity, timestamp, source, type, and description. To
filter the Event Browser, open the Filter menu and select Filter Entries. This
opens the Filter Events dialog (Figure 2-28). The Event Browser displays those
events that meet all of the criteria in the Filter Events dialog. If the filtering criteria
is cleared or changed, then all the events that were previously hidden that satisfy
the new criteria will be shown.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using the Event Browser
You can filter the event browser in the following ways:
Severity—select one or more of the corresponding options to display alarm
events, critical events, warning events, or informative events.
Date/Time—select one or both of the From: and To: options. Enter the
bounding timestamps (MM/DD/YY HH:MM AA) to display only those events
that fall within those times. (AA indicates AM or PM.) The current year (YY)
can be entered as either 2 or 4 digits. For example, 12/12/07 will be
interpreted December 12, 2007.
Text—select one or more of the corresponding options and enter a text
string (case sensitive) for event source, type, and description. The Event
Browser displays only those events that satisfy all of the search
specifications for the Source, Type, and Description text.
59273-00 C 51
Page 62

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using the Event Browser
Figure 2-28. Filter Events Dialog
Sorting the Event Browser
Sorting the Event Browser enables you to display the events in alphanumeric
order based on the event severity , timest amp, source, type, or description. Initially,
the Event Browser is sorted in ascending order by timestamp. To sort the Event
Browser, click the Severity, Timestamp, Source, Type, or Description column
buttons. You can also open the Sort menu and select By Severity, By
Timestamp, By Source, By Type, or By Description. Successive sort
operations of the same type alternate between ascending and descending order.
Saving the Event Browser to a File
You can save the displayed Event Browser entries to a file. Filtering affects the
save operation, because only displayed events are saved. To save the Event
Browser to a file, do the following:
1. Filter and sort the Event Browser to obtain the desired display.
2. Open the File menu and select Save As.
3. Select a folder and enter a file name in which to save the event log and click
the Save button. The file can be saved in XML, CSV, or text format. XML
files can be opened with an internet browser or text editor. CSV files can be
opened with most spreadsheet applications.
52 59273-00 C
Page 63

Downloading a Support File
The Download Support File menu option assembles all log files and H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card memory data into a core dump file
(dump_support.tgz). This file can be sent to technical support personnel for
troubleshooting H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card problems. The menu option is
not accessible (displayed) for an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card that doesn't
support the download support file function.
To create a support file, do the following:
1. Open the Switch menu, and select Download Support File.
2. In the Download Support File dialog, click the Browse button to define a
location for the support file or type the path in the text field.
3. Click the Start button to begin the process of creating and downloading the
support file to your workstation. Observe the status in the Status area.
4. After the support file is saved to your workstation, click the Close button to
close the Download Support File dialog.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Downloading a Support File
Installing Firmware
Installing firmware involves loading, unpacking, and activating the firmware image
on the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card. QuickTools does this in one operation.
To provide consistent performance throughout the fabric, ensure that every H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card is running the same version of firmware.
During a hotreset operation, fabric services will be unavailable for a short period
(30-75 seconds depending on switch model). To ensure that an NDCLA operation
is successful, verify that all administrative changes to the fabric (if any) are
complete.
CAUTION!
Changes to the fabric may disrupt the NDCLA process.
Common administrative operations that change the fabric include:
Adding, moving or removing devices attached to the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card fabric. This includes powering up or powering down at t ached
devices.
Adding, moving or removing ISLs or other connections.
59273-00 C 53
Page 64

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Installing Firmware
After an NDCLA operation is complete, management connections must be
re-initiated:
QuickTools sessions will re-connect automatically
Telnet sessions must be restarted manually.
The applicable code versions are:
Future H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card code releases will be upgraded
non-disruptively unless specifically indicated in its associated release notes
An NDCLA operation to previous H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card code
releases is not supported.
The Load Firmware dialog (Figure 2-29) allows you to select and install a firmware
image file. To open the Load Firmware dialog for an individual switch, open the
Switch menu and select Load Firmware. When the Load Firmware dialog is
opened, the path displayed in the Firmware Image Folder field is automatically
searched for firmware image files that can be installed. The default path to sea rch
for firmware image files is the user's working directory. To change the path, click
the Browse button and select a new path. Click the Rescan button to search the
folder displayed in the Firmware Image Folder field. The firmware image files
found are listed in and can be selected from the Version drop-down list.
Figure 2-29. Load Firmware Dialog
NOTE:
Some NDCLA restrictions may apply when upgrading some versions of
firmware. Please contact the appropriate technical support for specific
details before upgrading firmware.
54 59273-00 C
Page 65

To install firmware, do the following:
1. In the faceplate display, open the Switch menu and select Load Firmware.
2. In the Load Firmware dialog, click the Browse button next to the Firmware
Image Folder field to browse for and select the folder containing firmware file
to be loaded.
3. Select the firmware file from the Firmware Image Folder.
4. Click the Start button to begin the firmware load process. You will be shown
a message indicating the type of reset required in order to activate the
firmware.
5. Click the OK button to continue firmware installation.
6. Click the Close button to close the Load Firmware dialog.
Using Call Home
The Call Home feature allows you to configure switches to send alerts regarding
events and faults to Email addresses. Examples of Email destinations are p agers,
cell phones, NOC (Network Operations Center) operators/applications, and
support organizations. You can configure the type of events and where the alerts
are sent. Use the Call Home Setup dialog (Figure 2-30) to configure call home
parameters. To display the Call Home Setup dialog, open the Switch menu, select
Call Home, and select Setup.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using Call Home
Figure 2-30. Call Home Setup Dialog
59273-00 C 55
Page 66

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using Call Home
Table 2-14 lists the fields in the Call Home Setup dialog.
Table 2-14. Call Home Setup Dialog Fields
Setting Value
Primary SMTP: (active) The "(active)" indicates the Primary SMTP (Simple
Primary SMTP Server Address: This is the IP address of the primary (first) SMTP
Primary SMTP Server Port: This is the service port number that the primary
Mail Transfer Protocol) is the SMTP server th at CallHome is going to try to use when transmitting Email
messages. CallHome operates as an SMTP client, or
more correctly, and SMTP sending agent.
After any system configuration, the Primary SMTP
server will always become the active SMTP, provided
it is enabled and has a non-default address defined
(0.0.0.0 is the default).
server.
SMTP server is listening on to accept connections
from SMTP sending agents.
Secondary SMTP: The Secondary SMTP is the second SMTP server. If
the primary SMTP is not enabled/defined, or if there
was a failure in communicating with the primary
SMTP server, the Secondary SMTP server will
become the (active) SMTP server — the one used by
Call Home for the next attempt to transmit Email.
Secondary SMTP Server
Address:
Secondary SMTP Server Port: The service port number that the secondary SMTP
Contact Email Address: The Email address of the point-of-contact for the
Phone Number: The phone number of the point-of-contact for the
Street Address: The address of the point-of-contact for the switch.
The IP address of the secondary (second) SMTP
server.
server is listening on to accept connection from
SMTP sending agents.
switch. This Email address will be included in the text
of Email messages using the FullText format under
the section for Contact Information.
switch. This value will be included in the text of Email
messages using the FullText format under the section
for Contact Information.
This value will be included in the text of Email messages using the FullText format under the section for
Contact Information.
56 59273-00 C
Page 67

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using Call Home
Table 2-14. Call Home Setup Dialog Fields (Continued)
Setting Value
From Email Address: The Email address that will be provided to the SMTP
server to indicate the sender of the Email being transmitted. In Emails sent by Call Home, this address will
appear in the message heading as the "From : "
address. This value is required to send Emails. If
there are any problems encountered in routing the
Email to any of the intended recipients, the notice of
the problem will be sent to this address. It is an important address for receiving Email notices concerning
problems.
This address is also the default address used when
replies are sent to an Email by a recipient. If the
"Reply-To: " Email address is supplied it will override
the sending of replies to the "From: " Email address
by recipients. However, any notifications of Email
problems sent by any SMTP server used to route the
message to the final recipient will always send those
notifications to the "From: " address.
ReplyTo Email Address: The Email address used by mail reading programs to
determine the address that an Email should be
addressed to for a reply to a received message. This
value will override the use of the "From: " address as
the recipient for a reply message.
Throttle Duplicates: This boolean setting indicates if duplicate messages
should be suppressed and accumulated. If "True",
then after an Email has been transmitted, Call Home
will not transmit Email for switch events that would
result in duplicate Emails during a specified time window (default is 15 seconds). The time window can be
only be configured using the command line interface.
During this time window, these duplicate switch
events will be accumulated to keep track of how
many have occurred. After the time window has
expired, an Email message for the event will be transmitted that also includes the count of how many duplicate events were accumulated and the time of the
last received event. If additional switch events are
received that would result in duplicate Email messages being sent.
59273-00 C 57
Page 68

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using Call Home
Using the Call Home Profile Manager
Use the Call Home Profile Manager dialog (Figure 2-31) to manage all profiles on
a switch. You can add new profiles, remove profiles, edit profiles, and make
copies of existing profiles. To display the Call Home Profile Manager dialog, open
the Switch menu, select Call Home, and select Profile Manager. The Profiles list
shows all profiles on the switch. The Email List shows all Email addresses
associated with the selected profile in the Profiles list. The Apply Changes to
Multiple Switches in Fabric option allows you to propagate all profiles on the
switch to one or more switches in the fabric. Refer to “Applying All Profiles on a
Switch to Other Switches” for more information.
Figure 2-31. Call Home Profile Manager Dialog
58 59273-00 C
Page 69

Using the Call Home Profile Editor
Use the Call Home Profile Editor dialog when creating a new profile, and
editing/copying an existing profile. The Call Home Profile Editor dialog is
displayed after clicking the Add, Edit, or Copy buttons on the Call Home Profile
Manager dialog. Alternatively, you can open the Edit menu, and select Add New
Profile, Edit Profile, or Copy Profile The name in the title bar changes to reflect
adding a new profile, making a copy of an existing profile, or editing an existing
profile. Enter a name for the profile, select an event level threshold, a format type
for the message text being sent (short/full), enter the size of the message being
sent, enter the subject of the Email, and enter the Email address(es) of the
recipients. Click the Add button to add the Email address(es) to the list. Click the
OK button to save the changes.
You can use the Call Home Profile Editor dialog (Figure 2-32) to make a copy of
an existing profile. In the Call Home Profile Manager dialog, select a profile in the
list of existing profiles. To open the Call Home Profile Editor dialog, click the Copy
button or open the Edit menu and select Copy Profile. The dialog is
pre-populated with all of the information from the selected profile, except the
name. Enter a unique name for the profile copy and click the OK button to save
the new profile.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using Call Home
Figure 2-32. Call Home Profile Editor Dialog
59273-00 C 59
Page 70

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using Call Home
Applying All Profiles on a Switch to Other Switches
You can apply all profiles on a switch to one or more switches in a fabric. The Call
Home Profile Multiple Switch Apply dialog (Figure 2-33) is displayed after
selecting the Apply Changes to Multiple Switches in Fabric option on the Call
Home Profile Manager dialog. The Available Switches list shows all switches in
the fabric. Switch names that are greyed-out do not have current Call Home
firmware, and can not receive any profiles. The Selected Switches list shows the
switch names that you selected to receive all profiles from the switch. In the
Available Switches list, select the switches in the fabric to receive all profiles, and
click the double-arrow button to move them to the Selected Switches list. Click the
OK button to start the process. The Results area indicates success or failure of
applying all the profiles on a switch to the switches you selected.
Figure 2-33. Call Home Profile Multiple Switch Apply Dialog
60 59273-00 C
Page 71

Using the Call Home Message Queue
Use the Call Home Message Queue dialog (Figure 2-34) to access the logged call
home statistics. Click the Update Stats button to refresh with the most recent
switch Call Home information. Click the Clear Queue button to clear the current
statistics.
Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using Call Home
Figure 2-34. Call Home Message Queue Dialog
Testing Call Home Profiles
Use the Call Home Test Profile dialog (Figure 2-35) to test the Call Home
parameters currently configured. Select a profile in the window , and click the Test
button. To display the Call Home Test Profile dialog, open the Switch menu, select
Call Home, and select Test Profile.
Figure 2-35. Call Home Profile Manager Dialog
Change Over
Changes the inactive SMTP server to become the active SMTP server. To make
the inactive SMTP become the active SMTP, open the Switch menu, select Call
Home, and select Change Over. Click the OK button to confirm the change over.
59273-00 C 61
Page 72

Managing H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card
Using Call Home
62 59273-00 C
Page 73

3 Managing Ports
The data windows provide port information and port statistics for selected ports.
This section describes the following tasks that manage ports and devices:
Port Statistics Data Windows
Port Information Data Window
Viewing and Configuring Ports
Resetting a Port
Testing Ports
Mapping Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows
Port statistics data windows display statistics about port performance. There are
two port statistics data windows: FC Port Stats and Ethernet Port Stats.
To open the Port S t atistics dat a window, select one or more ports and click the FC
Port Stats or Ethernet Port Stats data window tab.
The Statistics drop-down list is available on the Port Statistics data window, and
provides different ways to view detailed port information. Click the down arrow to
open the drop-down list. Open the drop-down list and select Absolute to view the
total count of statistics since the last H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card or port
reset. Select Rate to view the number of statistics counted per second over the
polling period. Select Baseline to view the total count of statistics since the last
time the baseline was set. When viewing baseline statistics, click the Clear
Baseline button to set the current baseline. The baseline will also be set when the
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card status changes from unreachable to r each able.
59273-00 C 63
Page 74

Managing Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows
FC Port Statistics Data Window
The FC Port Stats data window (Figure 3-36) displays performance statistics for
the Fibre Channel (External) ports.
Figure 3-36. FC Port Statistics Data Window
Table 3-15 describes the FC Port Statistics data window entries.
Table 3-15. FC Port Statistics Data Window Entries
Entry Description
Star t Time The beginning of the period over which the st atistics apply. The
start time for the Absolute view is not applicable. The start time
for the Rate view is the beginning of polling interval. The start
time for the Baseline view is the last time the baseline was set.
End Time The last time the statistics were updated on the display.
Total Time Total time period from start time to end time.
Al Init Number of times the port entered the initialization state.
AL Init Error Number of times the port entered initialization and the initial-
ization failed. Increments count when port has a sync loss.
64 59273-00 C
Page 75

Managing Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows
Table 3-15. FC Port Statistics Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
Bad Frames Number of frames that were truncated due to a loss of sync or
the frame didn't end with an EOF.
BB_CreditRecoveryFr
ameFailure
BB_CreditRecoveryR
RDYFailure
Class 2 Frames In Number of class 2 frames received by this port.
Class 2 Frames Out Number of class 2 frames transmitted by this port.
Class 2 Words In Number of class 2 words received by this port.
Class 2 Words Out Number of class 2 words transmitted by this port.
Class 3 Frames In Number of class 3 frames received by this port.
Class 3 Frames Out Number of class 3 frames transmitted by this port.
Class 3 Toss N/A - does not apply to this switch.
Class 3 Words In Number of class 3 words received by this port.
Class 3 Words Out Number of class 3 words transmitted by this port.
Decode Errors Number of invalid transmission words detected during decod-
Number of times more frames were lost during a credit
recovery period than the recovery process could resolve. This
causes a Link Reset to recover the credits.
Number of times more R_RDYs were lost during a credit
recovery period than the recovery process could resolve. This
causes a Link Reset to recover the credits.
ing. Decoding is from the 10-bit characters and special K char-
acters.
Ep Connects Number of E_Port logins.
FBusy Number of class 2 and class 3 fabric busy (F_BSY) frames
generated by this port in response to incoming frames. This
usually indicates a busy condition on the fabric or N_port that
is preventing delivery of this frame.
Flow Errors Number of times a frame is received and all the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card ports receive buffers are full. The
normal Fabric Login exchange of flow control credit should
prevent this from occurring. The frame will be discarded.
FReject Number of frames, from devices, that have been rejected.
Frames can be rejected for any of a large number of reasons.
Invalid CRC Number of invalid Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) frames
detected.
59273-00 C 65
Page 76

Managing Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows
Table 3-15. FC Port Statistics Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
Invalid Destination
Address
Link Failures Number of optical link failures detected by this port. A link fail-
LIP (AL_PD,AL_PS) Number of F7, AL_PS LIPs, or AL_PD (vendor specific) resets,
LIP(F7,AL_PS) This LIP is used to reinitialize the loop. An L_port, identified by
LIP(F7,F7) A loop initialization primitive frame used to acquire an AL_PA.
LIP(F8,AL_PS) This LIP denotes a loop failure detected by the L_port identi-
LIP(F8,F7) A loop initialization primitive frame used to indicate that a Loop
Login Count Number of device logins that have occurred on the H3C
Number of address identifier (S_ID, D_ID) errors. AL_PA
equals non-zero AL_PA found on F_Port.
ure is a loss of synchronization or by loss of signal while not in
the offline state. A loss of signal causes the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card to attempt to re-establish the link. If the link is
not re-established, a link failure is counted. A link reset is per-
formed after a link failure.
performed.
AL_PS, may have noticed a performance degradation and is
trying to restore the loop.
fied by AL_PS.
Failure has been detected at its receiver and does not have a
valid AL_PA.
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
Logout Count Number of device logouts that have occurred on the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
Loop Timeouts Number of loop timeouts.
Loss Of Sync Number of synchronization losses (>100 ms) detected by this
port. A loss of synchronization is detected by receipt of an
invalid transmission word.
Primitive Sequence
Errors
Rx Link Resets Number of link reset primitives received from an attached
Rx Offline Sequences Number of offline sequence primitives received by the port.
Total Errors Total number of primitive and non-primitive port link errors.
Total Link Resets Number of link-reset primitives transmitted and received by the
66 59273-00 C
Number of bad primitives received by the port.
device.
port.
Page 77

Managing Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows
Table 3-15. FC Port Statistics Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
Total LIPs Received Number of loop initialization primitive frames received.
Total LIPs Transmitted Number of loop initialization primitive frames transmitted.
Tx Offline Sequences Number of offline primitives transmitted by the port.
Total Rx Frames Total number of frames received by the port.
Total Rx Words Total number of words received by the port.
Total Tx Frames Total number of frames transmitted by the port.
Total Tx Words Total number of words transmitted by the port.
Tx Link Resets Number of link reset primitives sent from this port to an
attached port.
TotalTXErrors Total number of errors transmitted by the port.
TotalRXErrors Total number of errors received by the port.
Total Offline
Sequences
Total number of offline se quences transmitted a nd rece ived by
the port.
59273-00 C 67
Page 78

Managing Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows
Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window
The Ethernet Port S tat s data window (Figure 3-37) displays performance statistics
for the Ethernet (Internal) ports.
Figure 3-37. Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window
Table 3-16 describes the Ethernet Port Statistics data window entries.
Table 3-16. Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window Entries
Entry Description
Start Time The beginning of the period over which the statistics apply.
The start time for the Absolute view is not applicable. The
start time for the Rate view is the beginning of polling interval. The start time for the Baseline view is the last time the
baseline was set.
End Time The last time the statistics were updated on the display.
Total Time Total time period from start time to end time.
Bad Frames Number of frames that were truncated due to a loss of syn-
chronization or the frame didn't end with an EOF.
68 59273-00 C
Page 79

Managing Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows
Table 3-16. Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
Class 3 Toss Number of class 3 frames that were discarded by this port. A
frame can be discarded because of detection of a missing
frame (based on SEQ_CNT), detection of an E_D_T OV time-
out, receiving a reject frame, or receiving a frame on an
offline port.
Decode Errors Number of invalid transmission words detected during
decoding. Decoding is from the 10-bit characters and special
K characters.
FBusy Number of class 2 and class 3 fabric busy (F_BSY) frames
generated by this port in response to incoming frames. This
usually indicates a busy condition on the fabric or N_port that
is preventing delivery of this frame.
Flow Errors Number of times a frame is r eceived and all the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card ports receive buffers are full.
The normal Fabric Login exchange of flow control credit
should prevent this from occurring. The frame will be dis-
carded.
FReject Number of frames, from devices, that have been rejected.
Frames can be rejected for any of a large number of rea sons.
Invalid CRC Number of invalid Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) frames
detected.
Login Count Number of device logins that have occurred on the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
Logout Count Number of device logouts that have occurred on the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
Long Frames In Number of long frames received
Loss Of Sync Number of synchronization losses (>100 ms) detected by this
port. A loss of synchronization is detected by receipt of an
invalid transmission word.
Rx Control Pkts Number of control packets received
Rx FCoE Pkts Number of FCoE packets received
Rx FCS Pkts Number of FCS packets received
Rx FCS Error Pkts Number of FCS error packets received
Rx Internal MAC Error Number of internal MAC errors received
Rx Length Error Number of length errors received
59273-00 C 69
Page 80

Managing Ports
Port Statistics Data Windows
Table 3-16. Ethernet Port Statistics Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
Rx Mgmt Pkts Number of management packets received
Rx Octets OK Number of valid octets received
Rx Oversize Pkts Number of oversize packets received
Rx Pause Pkts Number of pause packets received
Rx Pkts Number of packets received
Rx Pkts OK Number of valid packets received
Rx Symbol Error Number of symbol errors received
Total Errors Total number of primitive and non-primitive port link errors.
Total Rx Errors Total number of errors received
Total Rx Octets Total number of octets received
Total Rx Pkts Total number of packets received
Total Tx Errors Total number of errors transmitted by the port
Total Tx Octets Total number of octetes transmitted by the port
Total Tx Pkts Total number of packets transmitted by the port
Tx Control Pkts Number of control packets transmitted by the port
Tx FCoE Pkts Number of FCoE packets transmitted by the port
Tx Mgmt Pkts Number of management packets transmitted by the port
Tx Octets Number of octets transmitted by the port
Tx Pause Pkts Number of pause packets transmitted by the port
Tx Pkts Number of packets transmitted by the port
Tx Unicast Pkts Number of unicast packets transmitted by the port
70 59273-00 C
Page 81

Port Information Data Window
The Port Information data window (Figure 3-38) displays detailed port information
for the selected ports. To open the Port Information data window, click the Port
Info data window tab.
Managing Ports
Port Information Data Window
Figure 3-38. Port Information Data Window
Information in the Port Information data window is grouped and viewed by the
Summary, Advanced, and Media buttons. Click a button to display the
corresponding information in the data window on the right.
Figure 3-39. Port Information Data Window Buttons
The Port Information data window entries are listed below in Table 3-17.
59273-00 C 71
Page 82

Managing Ports
Port Information Data Window
Port Address N/A - does not apply to this switch
Administrative Port Type The administrative port type (TF, TH, and
Operational Port Type The port type that is currently active. This
Administrative Port State The port state (Online, Offline, Diagnos-
Table 3-17. Port Information Data Window Entries
Entry Description
Summary Group
PT). This value is persistent; it will be
maintained during an H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card reset. During port auto-configuration, it will be used to determine
which operational port states are allowed.
will be set during port auto-configuration
based on the administrative port type.
tics, or Down) which has been set by the
user. This state may be different from the
configured administrative state if the user
has not saved it in the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card configuration. This state is
used at the time it is set to try to set the
port operational state. This value is not
persistent and will be lost on an H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card reset.
Operational Port State The port state that is currently active. This
value may be different from the administrative port state, for example due to an
error condition.
Configured Administrative Port State The port state (Online, Offline, Diagnos-
tics, or Down) which is saved in the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration,
either by the user or at the factory. This
value is persistent; it will be maintained
during an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card reset, and will be used after a reset
to set the port operational state.
Logged In Indicates whether logged in or not.
Port Connection Status Port connection status. Status can be
None, Connecting, Connected.
Reason for Status N/A - does not apply to this switch
Administrative Port Speed The speed requested by the user.
72 59273-00 C
Page 83

Managing Ports
Port Information Data Window
Table 3-17. Port Information Data Window Entries (Continued)
Entry Description
Operational Port Speed The speed actually being used by the port.
Port Speed Supported The TF port speeds supported are:2Gbps,
4Gbps, and 8Gbps. The speed supported
for TH and PT ports is 10Gbps.
Symbolic Name Port symbolic name
POST Status S t atus from the most recent Power On Self
Test
POST Fault Code Fault code from the most recent Power On
Self Test
Test Status Status from the most recent port test
Test Fault Code Fault code from the most recent port test
DCBX Enabled Data center bridging capability exchange
status (internal ports only)
PFC Priority Priority-based flow control priority (internal
ports only)
VLAN Virtual Local Area Network status
Advanced Group
MFS Mode Multiple Frame Sequence bundling status.
Configured I/O Stream Guard N/A - does not apply to this switch
Operational I/O Stream Guard N/A - does not apply to this switch
Device Scan Device scan status. Enabled means the
H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card queries
the connected device during login for FC-4
descriptor information.
Auto Performance Tuning N/A - does not apply to this switch
AL Fairness N/A - does not apply to this switch
Port Binding N/A - does not apply to this switch
Upstream ISL The ISL over which the switch sends
requests intended for the principal switch
Downstream ISL N/A - does not apply to this switch
Remote Switch WWN The world wide name of the remote switch
59273-00 C 73
Page 84

Managing Ports
Viewing and Configuring Ports
Table 3-17. Port Information Data Window Entries (Continued)
VLAN The VLAN for the selected port
MAC Address N/A - does not apply to this switch
Fabric WWN N/A - does not apply to this switch
Login Limit Exceeded Indicates if the maximum number of logins
Media Type The transceiver fibre type, such as single
Media Speed The maximum transceiver speed
Media The transceiver type.
Entry Description
is reached
Media Group
mode, multi-mode, copper.
Media Transmitter The transceiver transmitter type, such as
longwave, shortwave, electrical.
Media Distance The maximum transceiver transmission
distance
Media Vendo r The company that manufactured the SFP
Media Vendor ID The IEEE registered company ID
Media Part Number The part number assigned to the SFP
Media Revision Transceiver hardware version
Viewing and Configuring Ports
Port color and text provide information about the port and its operational state. To
display port number and status information for a port, position the cursor over a
port on the faceplate display. The status information changes depending on the
View menu option selected. Green indicates active; gray indicates inactive.
Context-sensitive popup menus are displayed when you right-click a port icon in
the faceplate display. Use the drop-down lists in the Port Properties dialog to
change the following parameters:
Port Symbolic Name
Port States
Port Types
Port Speeds
74 59273-00 C
Page 85

Managing Ports
Viewing and Configuring Ports
Port Transceiver Media Status
Device Scan
DCBX
PFC Priority
The port settings or characteristics are configured using the Port Properties dialog
(Figure 3-40). To open the Port Properties dialog, select one or more ports, open
the Port menu and select Port Properties.
Figure 3-40. Port Properties Dialog
NOTE:
Use the Select to Propagate Changes to Entire Column options to
propagate the same change to all selected ports, select the options before
making a change to a port.
Port Symbolic Name
To change the symbolic name of a port, do the following:
1. Open the faceplate display and select a port.
2. Open the Port menu and select Port Properties to open the Port Properties
dialog.
3. Click inside the Symbolic Name field, and enter a new name for the port in
the port symbolic name.
4. Click the OK button.
59273-00 C 75
Page 86

Managing Ports
Viewing and Configuring Ports
Port States
The port operational state refers to actual port state and not the administrative
state you may have assigned. Refer to ”External Port Operational States” on
page 3-76 and ”Internal Port Operational States” on p age 3-77 for port operational
state information. The port administrative state refers to the user-requested state.
Port administrative states have two forms: the configured administrative state and
the current administrative state. Refer to ”Port Administrative S t ates” on page 3-78
for more information.
External Port Operational States
To view the operational state on each external port in the faceplate display, select
an external port, open the View menu, and then select View Port States.
Table 3-18 lists the possible operational states and their meanings.
Table 3-18. External Port Operational States
State Description
Online—port is active and ready to send data.
None Inactive—port operational state is offline, but administrative state is
online.
Offline—port is active, can receive signal, but cannot accept a device
login.
Diagnostics—port is in diagnostics mode in preparation for testing
Downed—the port is disabled, power is removed from the lasers, and
can’t be logged in.
76 59273-00 C
Page 87

Internal Port Operational States
The operational states on the internal ports in the faceplate display are described
in Table 3-19.
Table 3-19. Internal Port Operational States
State Description
Logged In — DCBX enabled. The Port SyncS t atus has been acquired,
and Port Link State is "Active".
Logged In—DCBX not enabled
Down—Both sides always red if the Port's operational State is "Down"
Managing Ports
Viewing and Configuring Ports
Testing (Diagnostics)—Always displayed for internal ports if Operation State is "Diagnostic" or "Test"
Other—DCBX enabled. The Port SyncStatus has been acquired, and
Port Link State is "Active".
Other—DCBX enabled. The Port SyncStatus has been acquired, but
Port Link State is NOT Active.
Other—One of the following:
DCBX enabled. The Port SyncStatus is NOT Acquired
DCBX not enabled, or any other case not above.
59273-00 C 77
Page 88

Managing Ports
Viewing and Configuring Ports
Port Administrative States
The port administrative state determines the operational state of a port. The port
administrative state has two forms: the configured administrative state and the
current administrative state.
Configured administrative state — the state that is saved in the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration and is preserved across H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card resets. QuickTools always makes changes to
the configured administrative state.
Current administrative state — the state that is applied to the port for
temporary purposes and is not preserved across H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card resets. The current administrative state is set with the Set
Port command using the command line interface.
Table 3-20 describes the port administrative states. To change port administrative
state, do the following:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Open the Port menu and select Port Properties to open the Port Properties
dialog.
3. Select the Port State option from the drop-down list.
4. Click the OK button to write the new port state request to the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
Table 3-20. Port Administrative States
State Description
Online A ctiva te s an d pr epares por t to sen d data.
Offline Prevents port from receiving signal and accepting a device login.
Diagnostics Prepares port for testing and prevent s the port from accepting a
device login.
Downed Disables the port.
78 59273-00 C
Page 89

Port Types
The 4 external ports connect to fabrics and can be configured as Transparent
Fabric (TF) or Pass-thru (PT) ports. The 4 internal ports connect to servers and
can be configured as Transparent Host (TH) or Pass-thru (PT) ports. See
”Mapping Ports” on page 3-83 for more information.
To display port type status, open the View menu, and select View Port Types.
Table 3-21 lists the possible port types and their meanings. The ports can be
configured to self-discover the proper type to match the device or H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card to which it is connected.
To change the port type, do the following:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Open the Port menu and select Port Properties to open the Port Properties
3. Select the Port Type option from the drop-down list.
4. Click the OK button to write the new port type to the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Managing Ports
Viewing and Configuring Ports
dialog.
Interface Card.
Table 3-21. Port Types
State Description
External The 4 external ports connect to fabrics and can be configured as Trans-
parent Fabric (TF) ports or Pass-thru (PT) ports.
Internal The 4 internal ports connect to servers and can be configured as Trans-
parent Host (TH) or Pass-thru (PT) ports.
NOTE:
The Map Ports dialog enables you to configure data traffic routes from
server bay ports to one or more uplink port s. Server bay ports are referred to
as TH (Transparent Host) ports. When an uplink port is used to attach an
external server, it must be configured to a TH port. At least 1 uplink port
must connect to an H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card that supports NPIV
(N-Port ID Virtualization). When an uplink port is connected to an H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card, it is called a TF (Transparent Fabric) Port. By
default, the 4 uplink ports are TF ports. Refer to ”Mapping Ports” on
page 3-83 for more information.
59273-00 C 79
Page 90

Managing Ports
Viewing and Configuring Ports
Port Speeds
The external ports can support 1Gbps, 2Gbps, 4Gbps, or 8Gbps. Internal ports
are 10Gbps and can not be changed. Auto-detect is not an option on internal
ports. To display the speed of each port, open the View menu and select View
Port Speeds. Table 3-22 lists the possible port speeds.
To change the port transmission speed, do the following:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Open the Port menu and select Port Properties to open the Port Properties
dialog.
3. Select the Port Speed option from the drop-down list.
4. Click the OK button to write the new port speed to the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card.
Table 3-22. Port Speeds
State Description
Auto-Detect Matches the transmission speed of the connected device. This is the
default. Applies to external ports only.
2Gbps Sets the transmission speed to 2Gbps (on external po rts only.
4Gbps Sets the transmission speed to 4Gbps (on external po rts only.
8Gbps Sets the transmission speed to 8Gbps (on external po rts only.
10Gbps The transmission speed for (internal or external) ports configured as
PT ports, or internal ports configu red as a TH port.
Port Transceiver Media Status
To display transceiver media status, open the View menu and select View Port
Media. Table 3-23 lists the port media states and their meanings.
80 59273-00 C
Page 91

.
Table 3-23. Port Transceiver Media View
Media Icon Description
Optical SFP, online (green/black), logged-in, active, and ready to send
data.
Optical SFP, offline (gray/black), not logged-in, active, can receive signal, but cannot accept a device login
Optical SFP, unlicensed (dark gray/black)
Optical SFP, unknown, unlicensed (dark gray/blue)
Managing Ports
Resetting a Port
None Empty port; no transceiver installed (gray) or unlicensed (dark gray)
Device Scan
The Device Scan feature queries the connected device during login for FC-4
descriptor information. Disable this parameter only if the scan creates a conflict
with the connected device.
DCBX
The DCBX (data center bridging capability exchange) parameter on the Port
Properties dialog enables the peer-to-peer DCBX protocol capability on the
internal (only) ports. This parameter is not allowed on PT ports.
PFC Priority
The PFC Priority parameter on the Port Properties dialog enables you to set the
priority-based flow control parameter for internal (only) ports. This parameter is
not allowed on PT ports.
Resetting a Port
The Reset Port option reinitializes the port using the saved configuration. To reset
a port, do the following:
1. In the faceplate display, select the port(s) to be reset.
2. Open the Port menu and select Reset Port.
3. Click the OK button to reset the selected port(s).
59273-00 C 81
Page 92

Managing Ports
Testing Ports
Testing Ports
Offline port diagnostic tests are available for external port s (0–3) and internal ports
(4–7). Offline tests disrupt data traffic. Performing an offline test automatically
places the port in diagnostics mode, and then the port is reset after the test is
complete. There are two types of offline port tests: internal and external.
An internal test sends a test frame from the ASIC through the SerDes chip
and back to the ASIC for the selected port. The intern al port test is ava ilable
for all ports (0–7).
An external test sends a test frame from the ASIC through the SerDes chip,
through the SFP transceiver fitted with an external loopback plug, and back
to the ASIC for the selected port. External port tests are available only for
external ports (0–3).
To test a port, do the following:
1. Select a port in the faceplate display.
2. Open the Port menu, and then select Port Diagnostics > Other Port
Diagnostics to open the Port Diagnostics dialog (Figure 3-41).
Figure 3-41. Port Diagnostics Dialog
3. Keep the selected port or choose a new port from the Select Port:
drop-down list.
82 59273-00 C
Page 93

Managing Ports
Mapping Ports
4. Select the test type from the Select Test Type drop-down list.
Select Internal to test the internal port connections.
Select External to test the port and the SFP. You must install an SFP
transceiver and a loopback plug in the port for this test.
5. Enter a frame size (default is 256).
6. Enable or disable the Terminate Test Upon Error option.
7. Select a Loop Count option. The Loop Forever option runs the test until you
click the Stop Test button. The Loop Count option runs the test a specific
number of times.
8. Select a Test Pattern option. Accept the default test pattern, or select the
User Defined option and enter a value.
9. Click the Start Test button to begin the test. Observe the results in the Test
Results area.
NOTE:
If the Test S t atus field in the Test Results area indicates Failed, note the Test
Fault Code displayed in the Port Information data window and contact your
technical support representative.
Mapping Ports
The Map Ports dialog enables you to configure data traffic routes from server bay
ports to one or more uplink ports. Server bay ports are referred to as TH
(Transparent Host) ports. At least one uplink port must connect to a fabric switch
that supports NPIV (N-Port ID Virtualization). When an uplink port is connected to
a fabric switch, it is called a TF (Transparent Fabric) port.
NOTE:
The Map Ports dialog requires at least one internal port to be configured as
a TH port and at least one external port to be configured as a TF port. If all
internal ports or all external ports are configured as PT ports, the Map Ports
dialog becomes inactive in the Port menu and can not be selected.
59273-00 C 83
Page 94

Managing Ports
Mapping Ports
Using the Map Ports dialog, you can assign a TH port to multiple TF ports. For
redundancy purposes, a backup port mapping can also be specified. To open the
Map Ports dialog (Figure 3-42) open the Port menu, and select Map Ports.
Leaving a TH port unmapped has the same effect as unplugging a Fibre Channe l
cable. You can map multiple primary and backup ports for any TH port. A port
designated as primary will be the first path chosen. If there are multiple primary
ports, the TH ports are distributed (using an algorithm) across the TF ports. Ports
designated as backup ports only become active when all primary ports fail.
Figure 3-42. Map Ports Dialog
The four external ports (numbered 0-3) can be configured as Transparent Fabric
(TF) or Pass-thru (PT) ports. The four internal ports (numbered 4-7) can be
configured as Transparent Host (TH) ports or Pass-thru (PT) ports. By default, all
TH ports are mapped to all TF ports as primary.
NOTE:
How ports are mapped affects the operational state of TH ports. If a TH port
is not mapped to a TF port, the TH port will be listed as of fline. If a TH port is
mapped to a TF port but the TF port is offline or non-existent, the TH port will
also be listed as offline. If a TH port is mapped to a TF port and the TF port
is online, the TH port will be listed as online. Any TH port must be mapped to
a TF port to activate the connection and allow data to pass through. Without
a connection, the TH port is offline.
84 59273-00 C
Page 95

Glossary
Active Firmware
The firmware image on the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card that is in use.
Activity LED
A port LED that indicates when frames are
entering or leaving the port.
Administrative State
State that determines the operating state
of the port or H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card. The configured administrative state
is stored in the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card configuration. The configured
administrative state can be temporarily
overridden using the command line interface.
Alarm
A message generated by the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card that specifically requests attention. Alarms are generated by several H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card processes. Some alarms
can be configured.
ASIC
Application Specific Integrated Circuit
Class 3 Service
A service which multiplexes frames at
frame boundaries to or from one or more
N_Ports without acknowledgment.
Event Log
Log of messages describing events that
occur in the fabric.
Frame
Data unit consisting of a start-of-frame
(SOF) delimiter, header, data payload,
CRC, and an end-of-frame (EOF) delimiter.
Inactive Firmware
The firmware image on the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card that is not in
use.
Initiator
The device that initiates a data exchange
with a target device.
In-Order-Delivery
A feature that requires that frames be
received in the same order in which they
were sent.
BootP
A type of network server.
Class 2 Service
A service which multiplexes frames at
frame boundaries to or from one or more
N_Ports wit h acknowledgment provided.
59273-00 C Glossary-1
IP
Internet Protocol
Logged-in LED
A port LED that indicates device login or
loop initialization status.
Page 96

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
Maintenance Button
Momentary button on the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card used to reset
the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card or
place the H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card in maintenance mode.
Maintenance Mode
Maintenance mode sets the IP address to
10.0.0.1 and provides access to the H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for maintenance purposes.
Management Information Base
A set of guidelines and definitions for
SNMP functions.
Management Workstation
PC workstation that manages the fabric
through the fabric management H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
MIB
Management Information Base
NL_Port
Node Loop Port. A Fibre Channel device
port that supports arbitrated loop protocol.
N_Port
Node Port. A Fibre Channel device port in
a point-to-point or fabric connection.
Pending Firmware
The firmware image that will be activated
upon the next H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface
Card reset.
POST
Power On Self Test
Power On Self Test (POST)
Diagnostics that the H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card chassis performs at start
up.
PT_Port
Pass-thru port. A port that operates at
10Gbps only and passes Ethernet traffic
straight through the switch. PT_Ports are
matched one-to-one, from the internal to
the external, there is no mapping on these.
For example, internal PT_Port 4 is
matched to external port 0 only, port 5 is
matched to port 1, and so on, straight
though the switch.
QuickTools
The web applet used to manage H3C
LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card.
SFP
Small Form-Factor Pluggable.
Small Form-Factor Pluggable
A transceiver device, smaller than a
GigaBit Interface Converter , that plugs into
the Fibre Channel port.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
Target
A storage device that responds to an initiator device.
User Account
An object stored on an H3C LSW1FC4P0
Interface Card that consists of an account
name, password, authority level, and
expiration date.
VCCI
Voluntary Control Council for Interference
World Wide Name (WWN)
A unique 64-bit address assigned to a
device by the device manufacturer.
WWN
World Wide Name
Glossary-2 59273-00 C
Page 97

Index
A
administrative state
configured 29, 78
current 29, 78
port 78
switch 29
alarm configuration 23
archive configuration 44
authentication trap 40
B
browser
location 7
supported programs 2
C
Call 31
Call Home 31
Common Information Model service 31
configuration
archive 44
information 12
restore 44
configured administrative state 29
connectivity test 48
contact 40
CRC error 23
current administrative state 29
D
data window
description 4
port information 71
port statistics 63
switch 12
date 25
Decode error 23
default configuration 46
device scan 81
diagnostic test 82
disk space 1
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol 38
E
embedded GUI service 30
Enode MAC address 29
event browser
filter 51
preference 7
sort 52
event logging 50
external test 82
F
factory defaults 46
FC-4 descriptor 81
FCF Virtual Links data window 32
Fibre Channel over Ethernet 32
File Transfer Protocol service 31
59273-00 C Index-1
Page 98

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
G
graphic window 4
GUI management service 30
H
hard reset 27
help 9
hot reset 27
I
internal test 82
Internet browser 2
ISL monitoring 23
L
login monitoring 23
logout monitoring 23
loss of signal monitoring 23
M
MAC address 29
management workstation 1
media status 80
memory, workstation 1
O
offline test 48, 82
online
help 9
test 82
operating systems 1
P
password 21
port
administrative state 78
configuration 75
media 80
operational state 76, 77
reset 81
status 74
symbolic name 75
test 82
threshold alarms 23
transceiver 80
type 79
view 8, 74
Port Information data window 71
Port Statistics data window 63
processor 1
Q
QuickTools 9
N
R
NDCLA - See Non-disruptive code load and
activation
network properties 37
Network Time Protocol
description 25
service 31
node-to-node test 82
Non-disruptive code load and activation 26
NTP - See Network Time Protocol
Index-2 59273-00 C
read community 40
remote log 28
reset
with POST 27
without POST 27
restore configuration 44
Page 99

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
S
security consistency checklist 12
SerDes level test 82
services 30
severity levels 50
Simple Network Management Protocol
configuration 40
enable 40
properties 39
proxy 40
service 31
trap configuration 41
SNMPv3 security 42
static boot method 38
status icon color 4
support file 53
switch
administrative state 29
hard reset 27
hot reset 27
location 40
management service 30
properties 27
reset 26
reset without POST 27
restore factory defaults 46
Switch data window 12
symbolic name
port 75
switch 28
syslog 28
system services 30
trap
authentication 40
community 41
configuration 41
SNMP version 41
U
user account
create 19
modify 22
password 21
remove 20
V
version, QuickTools 9
W
web applet service 30
working directory 7
workstation requirements 1
write community 40
T
Telnet service 30
testing ports 48, 82
time 25
transceiver status 80
59273-00 C Index-3
Page 100

H3C LSW1FC4P0 Interface Card for S5820X-28C Ethernet Switches
QuickTools User Guide
Index-4 59273-00 C
 Loading...
Loading...