Page 1

HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch
QuickTools Switch Management User Guide
This user guide describes the QuickTools web applet (version 8.00.4) for the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch (firmware
version 8.0.4). The QuickTools web applet is a graphical user interface that provides tools for fabric, switch, and port
management tasks. This user guide is intended for users responsible for installing and using switch management tools.
Part Number: 5697-0417
Published June 2010
Edition: 2
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
© 2000–2010 This product includes software developed by the JDOM Project
reserved.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial
Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under
vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
QuickTools is a trademark of eMarkmonitor Inc.
Java and Solaris are registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Gnome is a trademark of the GNOME Foundation Corporation.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Mac OS and Safari are registered trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc.
Microsoft, Windows, and Internet Explorer are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Netscape Navigator and Mozilla are registered trademarks of Netscape Communications Corporation.
Red Hat is a registered trademark of Red Hat Software Inc.
SUSE is a trademark of Novell, Inc.
(http://www.jdom.org/), Brett McLaughlin and Jason Hunter. All rights
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide
Page 3

Contents
1 Using QuickTools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Workstation requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Opening QuickTools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
QuickTools user interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Fabric tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Graphic window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Data windows and tabs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Alerts panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Menu bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Popup menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Shortcut keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Selecting switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Selecting ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Setting QuickTools preferences. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Using online Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Viewing the software version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Exiting QuickTools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2 Managing Fabrics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Fabric services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Enabling SNMP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Enabling in-band management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Rediscovering a fabric. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Adding a new switch to a fabric. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Replacing a failed switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Transparent Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
TR Mapping Manager dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Removing an inter-fabric route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Add TR Mapping dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Mapping a new inter-fabric zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Remote Fabric Zoning dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Transparent Routes data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Event Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Filtering the Event Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Sorting the Event Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Saving the Event Browser to a file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Device information and nicknames . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Devices data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Displaying detailed device information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Managing device port nicknames . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Creating a nickname . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Editing a nickname . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Deleting a nickname . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Exporting nicknames to a file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Importing a nicknames file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Active Zoneset data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Configured Zonesets data window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Zoning concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Aliases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
zone sets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Viewing zoning limits and properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 3
Page 4

Managing the zoning database. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Editing the zoning database. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Options for resolving zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Configuring the zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Merge Auto Save. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Default Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Discard Inactive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Saving and restoring the zoning database to a file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Saving the zoning database to a file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Restoring the zoning database from a file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Restoring the default zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Removing all zone and zone set definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Managing zone sets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Creating a zone set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Activating and deactivating a zone set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Renaming a zone set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Removing a zone set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Managing zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Creating a zone in a zone set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Copying a zone to a zone set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Adding zone members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Renaming a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Removing a zone member . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Removing a zone from a zone set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Removing a zone from all zone sets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Managing aliases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Creating an alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Adding a member to an alias. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Removing an alias from all zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Merging fabrics and zoning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Zone merge failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Zone merge failure recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3 Managing Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Switch data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Switch data window buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Stack Links data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Managing Switch Stacks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Security Consistency Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Managing user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Creating user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Removing a user account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Changing a user account password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Modifying a user account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Paging a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Setting the date/time and enabling NTP client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Resetting a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Configuring a switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Using the configuration wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Switch properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Domain ID and Domain ID Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Syslog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Symbolic name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Switch administrative states . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Broadcast support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
In-band management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Fabric device management interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Advanced switch properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Timeout values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4
Page 5

Managing system services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Network properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Network IP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Network DNS configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
SNMP configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
SNMP properties and trap configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
SNMP v3 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Adding an SNMP v3 user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Modifying an SNMP v3 user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Removing an SNMP v3 user. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Testing a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Archiving a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Restoring a switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Restoring the factory default configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Installing feature license keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Downloading a support file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Installing firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Using Call Home . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Using the Call Home Profile Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Using the Call Home Profile Editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Using the Call Home Profile Editor—Tech Support Center Profile dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Applying all profiles on a switch to other switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Using the Call Home Message Queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Testing Call Home Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Change Over . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
4 Managing Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Port Information data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Port Statistics data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Viewing and configuring ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Port symbolic name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Port states . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Port operational states . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Port administrative states . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Port types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Port speeds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Port transceiver media status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
I/O Stream Guard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Device Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Auto Performance Tuning and AL Fairness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Resetting a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Testing ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
5 Support and Other Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Document conventions and symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
JDOM license. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Contacting HP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
HP contact information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Subscription service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Documentation feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
New and changed information in this edition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Related information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Other HP websites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 5
Page 6

Figures
1 Add a New Fabric dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2 Password Change Required dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3 QuickTools faceplate display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4 QuickTools backplate display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5 Alerts panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6 Preferences dialog box–QuickTools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
7 TR Mapping Manager dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
8 Add TR Mapping dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
9 Remote Fabric Zoning dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
10 Transparent Routes data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
11 Transparent Route dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
12 Event Browser dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
13 Filter Events dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
14 Devices data window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
15 Detailed Devices Display dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
16 Active Zoneset data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
17 Configured Zoneset data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
18 Edit Zoning dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
19 Zoning Config dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
20 Switch data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
21 Switch data window buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
22 Stack Links data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
23 Security Consistency Checklist dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
24 User Account Administration–Add Account dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
25 User Account Administration–Remove Account dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
26 User Account Administration–Change Password dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
27 User Account Administration–Modify Account dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
28 Date/Time dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
29 Switch Properties dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
30 Advanced Switch Properties dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
31 System Services dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
32 Network Properties dialog boxes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
33 SNMP Properties dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
34 SNMP v3 Manager dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
35 SNMP v3 User Editor dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
36 Switch Diagnostics dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
37 Restore dialog boxes—full and selective . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
38 Feature Licenses dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
39 Add License Key dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
40 Download Support File dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
41 Load Firmware dialog box for a single switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
42 Load Firmware dialog box for a stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
43 Call Home Setup dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
44 Call Home Profile Manager dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
45 Call Home Profile Editor dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
46 Call Home Profile Editor—Tech Support Center Profile dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
47 Call Home Profile Multiple Switch Apply dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
48 Call Home Message Queue dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
49 Call Home Test Profile dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
50 Call Home Change Over dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
51 Port Information data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
52 Port Information data window buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
53 Port Statistics data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
54 Port Properties dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
55 Advanced Port Properties dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
56 Port Diagnostics dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
6
Page 7

Tables
1 Workstation requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Menu bar options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3 Transparent Routes data window fields. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4 Port operational states . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
5 Devices data window fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
6 Edit Zoning dialog box tool bar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
7 Port/Device icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8 Switch data window fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
9 Stack Links data window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
10 Switch resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
11 Network Properties dialog box—IP fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
12 Network Properties dialog box—DNS fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
13 SNMP Properties dialog box fields. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
14 SNMP v3 User Editor dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
15 Factory default configuration settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
16 Call Home Setup fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
17 Call Home Editor—Tech Support Center Profile dialog box fields. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
18 Port Information data window fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
19 Port Statistics data window fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
20 Port Properties dialog box fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
21 Port operational states . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
22 Port administrative states. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
23 Port types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
24 Port speeds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
25 Port transceiver media view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
26 Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 7
Page 8

8
Page 9
1Using QuickTools
This section describes how to use the QuickTools web applet and its menus.
Workstation requirements
The requirements for fabric management workstations running the QuickTools web applet are described in
Table 1.
Table 1 Workstation requirements
Component Options/Requirements
Operating systems Windows XP SP1/SP2/SP3
Windows 2003 SP2
Windows 2008 SP2 and R2
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4, 5
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9, 10 and 11
Memory 512 MB or more (1GB recommended)
Processor 2 GHz or faster
Internet Browser Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or later
Netscape Navigator 6.0 and later
Hardware RJ-45 Ethernet port
1. You must disable caching of temporary files and applets in Java to prevent conflicts with past or future versions
of QuickTools. Furthermore, you may need to disable caching again after upgrading Java.
IMPORTANT: Java must be configured to disable caching of temporary files and applets to prevent
conflicts with past or future versions of QuickTools. Also, caching may become enabled if the Java version
is upgraded, so you may need to disable caching again after a Java upgrade.
Opening QuickTools
Once the switch is operational, open the QuickTools web applet.
To open the QuickTools web applet:
1. In an Internet browser, enter the switch IP address (the default switch IP address is 10.0.0.1). (If your
workstation does not have the Java 2 Run Time Environment program, you will be prompted to
download it.)
Firefox 1.5 and later
Java Runtime Environment 1.4.2 or later
RS-232 serial port (optional)
1
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 9
Page 10
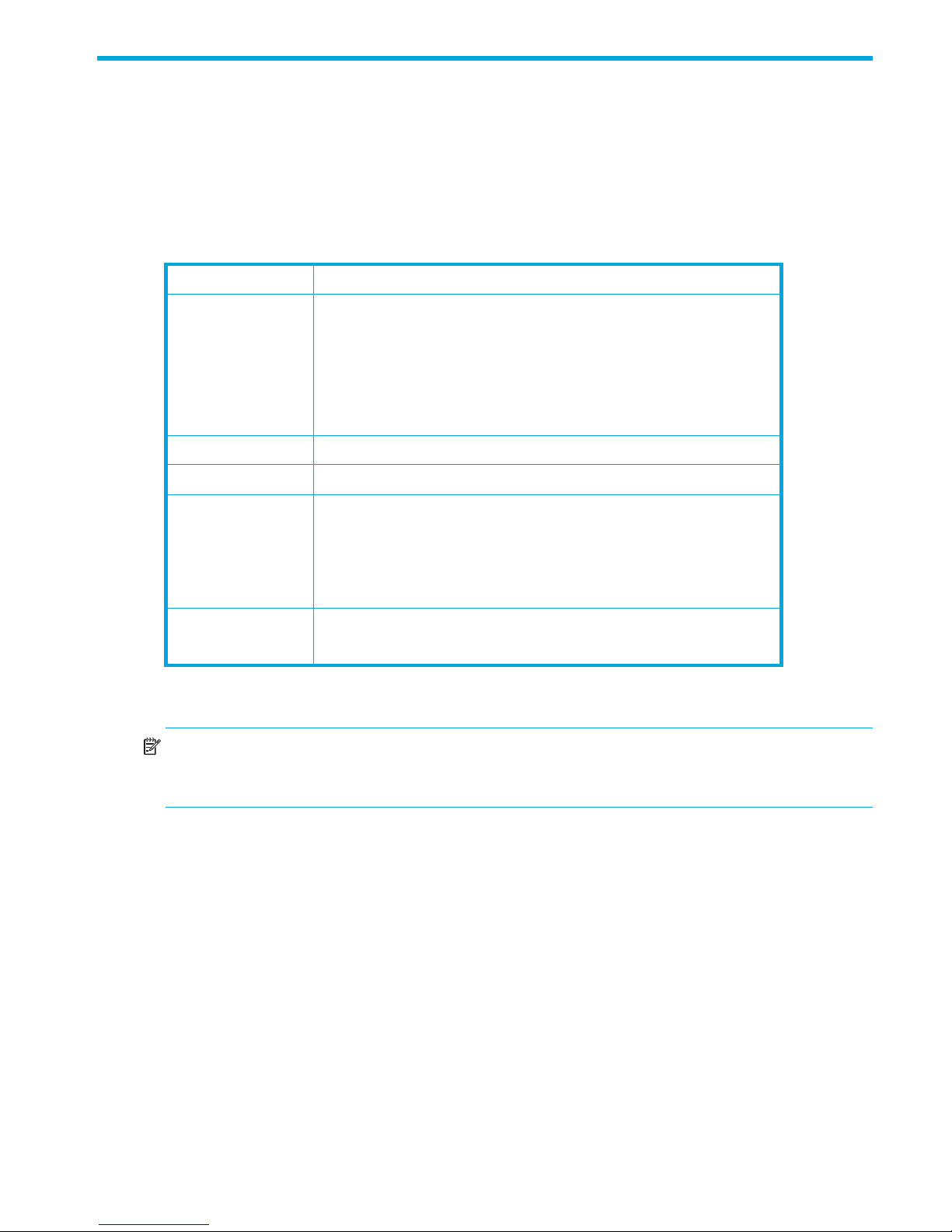
2. The Add a New Fabric dialog box (Figure 1) prompts you for your username (the default is admin) and
password (the default is password).
Figure 1 Add a New Fabric dialog box
3. Click Add Fabric to open the fabric. (If you do not have a secure Ethernet connection, the Non Secure
Connection Check dialog box will prompt you to establish a non-secure connection.)
4. The opening window is displayed (Figure 3). For security reasons, you will be prompted to change your
user account password that was initially set up by the administrator (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Password Change Required dialog box
NOTE: Until you change the default password, you will be prompted to change the password each time
you attempt to open the fabric.
5. Click OK, and change the user account password. See ”Managing user accounts” (page 55) for more
information.
10
Page 11
QuickTools user interface
Data window tabs
Graphic window
Fabric
tree
Menu
bar
Data window
Fabric/Switch name
and status
The QuickTools web applet uses faceplate and backplate displays to manage the switches in a fabric. The
interface (Figure 3) consists of a menu bar, fabric tree, graphic window, data windows (some with
buttons), and data window tabs. The switch faceplate is displayed in the graphic window and shows the
front of a single switch and its ports. While there is no topology display, the fabric name is displayed for
reference in the fabric tree above the switch names. Click a switch name or icon to display a different
switch faceplate in the graphic window. Information displayed in the data windows corresponds to the
data window tab selected.
The faceplate display (Figure 3) shows the front of a single SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch.
Figure 3 QuickTools faceplate display
The backplate display (Figure 4) shows the back of a dual-power supply SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch.
Figure 4 QuickTools backplate display
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 11
Page 12

Fabric tree
The QuickTools web applet enables you to manage the switches in one fabric. The fabric tree (Figure 3)
provides access to each switch faceplate display in the fabric. Click a switch name or icon to display that
switch faceplate in the graphic window. The width of the fabric tree window can be adjusted by clicking
and dragging the moveable window border.
Next to each fabric tree entry is a small icon that uses color to indicate operational status:
• A green icon indicates normal operation.
• A yellow icon indicates that a switch is operational, but may require attention to maintain maximum
performance.
• A red icon indicates a potential failure or non-operational state, as when the switch is offline.
• A blue icon indicates that a switch is unknown, unreachable, or unmanageable.
If the status of the fabric is not normal, the fabric icon in the fabric tree indicates the reason for the
abnormal status. The same message is provided when you rest the mouse on the fabric icon in the fabric
tree.
Graphic window
The graphic window shows either the front of a switch (the faceplate, as shown in Figure 3) or the back of
the switch (the backplate). The height of the window can be adjusted by clicking and dragging the border
that it shares with the data window. To view the faceplate display, select View > View Faceplate. To view
the backplate display, select View > View Backplate.
Data windows and tabs
The data window (Figure 3) displays a table of data and statistics associated with the selected tab for the
switch displayed in the graphic window. Use the scroll bar to browse through the data. To adjust the length
of the window, click and drag the border that it shares with the graphic window.To adjust the column
width, move the pointer over the column heading border shared by two columns until a right/left arrow
graphic is displayed. Click and drag the arrow to the desired width.
The data windows and tabs are described below:
• Devices—Displays information about devices (hosts and storage targets) connected to the switch. See
”Devices data window” (page 30) for more information.
• Transparent Routes—Displays the currently configured inter-fabric zones/routes using a TR_Port. See
”Transparent Router” (page 20) for more information.
• Switch—Displays current network and switch configuration data for the selected switch. See ”Switch
data window” (page 47) for more information.
• Port Statistics—Displays performance data for the selected ports. See ”Port Statistics data window”
(page 94) for more information.
• Port Information—Displays information for the selected ports. See ”Port Information data window”
(page 91) for more information.
• Configured Zonesets—Displays all zone sets, zones, and zone membership in the zoning database. A
zone is a named group of ports or devices. See ”Configured Zonesets data window” (page 34) for
more information.
• Active Zoneset—Displays the active zone set for the fabric including zones and their member ports. See
”Active Zoneset data window” (page 33) for more information about this data window. See ”Zoning”
(page 33) for information about zone sets and zones.
12
Page 13
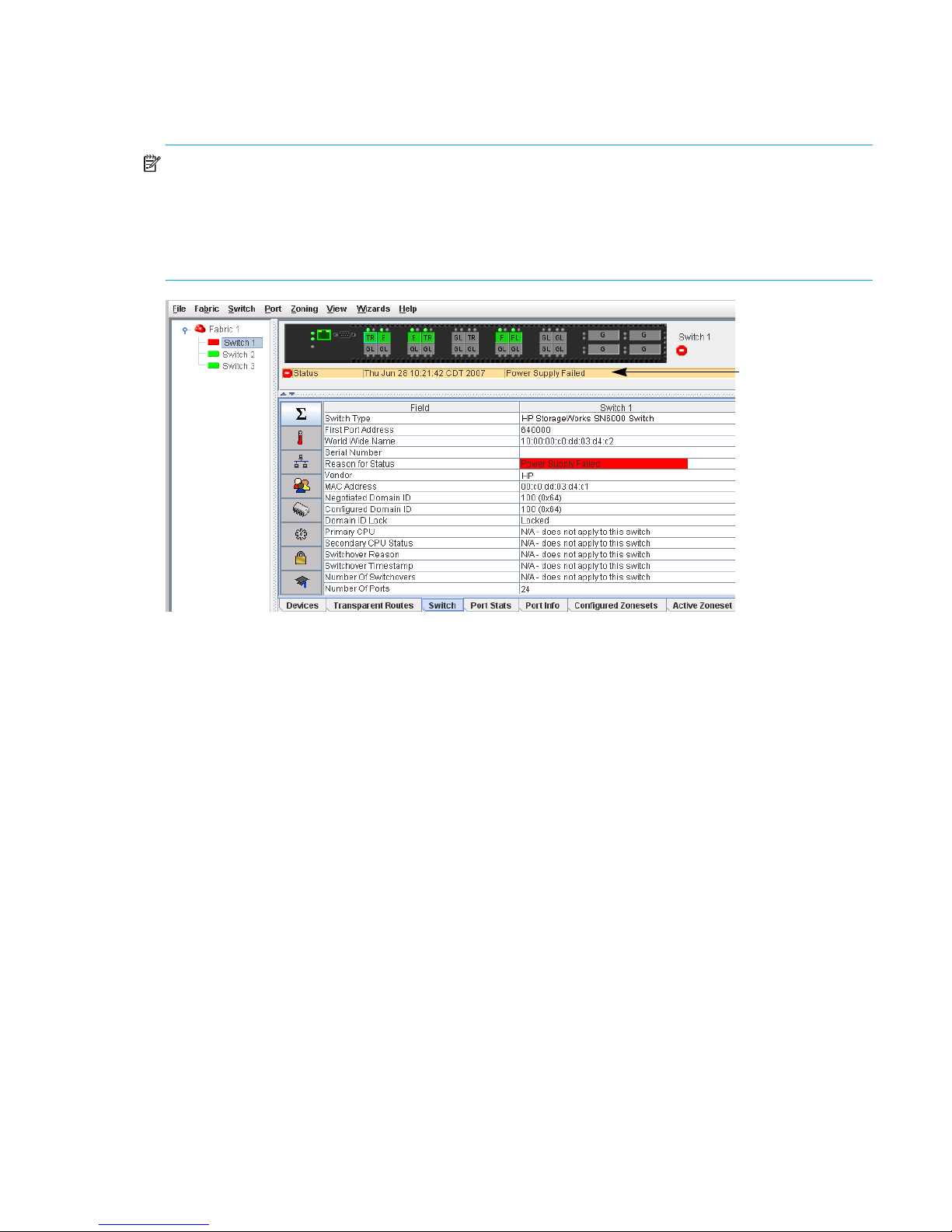
Alerts panel
Status section
The Alerts panel shows all reasons for status, including faults. The Alerts panel entries are the highlighted
rows between the faceplate image and the data window entries.
NOTE: The up/down arrows on the divider bar between the Alerts panel entries and data windows
enable you to move the divider bar up or down incrementally. With the faceplate image in the graphic
window and the data window displayed, click the up arrow (on left) to move the divider up to the top of
the window, completely hiding the faceplate image. Click the down arrow (on right) to move the divider
back to the middle; click the down arrow again to completely hide the data window. You can also
click-and-drag the divider bar to manually move it up or down.
Figure 5 Alerts panel
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 13
Page 14
Menu bar
The QuickTools web applet menu bar options are described in Table 2.
Table 2 Menu bar options
Option Sub-options
File Preferences
Fabric Nicknames
Switch Archive
Rediscover Fabric
TR Mapping Manager
Show Event Browser
Restore (available on entry switch only)
User Accounts
Set Date/Time
Switch Properties
Advanced Switch Properties (available on entry switch only)
Services
Call Home (Setup, Profile Manager, Message Queue, Test Profile, Change
Over)
Network Properties (IP, DNS)
SNMP (SNMP Properties, SNMP v3 Manager (SSL is required and only
enabled on entry switch))
Switch Diagnostics (Online Switch Diagnostics, Offline Switch Diagnostics
(available on entry switch only))
Toggle Beacon
Load Firmware
Reset Switch (Hot Reset, Reset, Hard Reset)
Restore Factory Defaults
Features
Download Support File
14
Page 15

Table 2 Menu bar options (Continued)
Option Sub-options
Stack
These options are available
only if the stack icon or
name is selected in the
fabric tree.
Refresh Stack
Select All Ports
Syslog
SNMP Properties
Set Date/Time
User Accounts
Security Consistency Checklist
Reset (Hot Reset, Reset, Hard Reset)
Load Firmware
Move Switch Up (available when a switch (except top switch) in stack is
selected)
Move Switch Down (available when a switch (except bottom switch) in
stack is selected)
Remove Switch (available when a switch in stack is selected)
Remove Links (available when an active port with ISL connected is
selected)
Port Port Properties
Advanced Port Properties
Reset Port
Port Diagnostics (Online Port Diagnostics, Offline Por t Diagnostics)
Zoning Edit Zoning
Resolve Zoning (Capture Active Zoning, Restore Configured Zoning,
Capture Merged Zoning, View Merged/Configured Differences)
Edit Zoning Config
Activate Zoneset
Deactivate Zoneset
Restore Default Zoning
View Refresh
View Port Types
View Port States
View Port Speeds
View Port Media
View Faceplate
View Backplate
Wizards Configuration Wizard
Help Help Topics
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 15
About
Page 16
Popup menus
Popup menus appear when you right-click the switch faceplate or backplate images in the graphic window.
Popup menu options give you quick access to the common tasks and dialog boxes, such as:
• Refreshing a switch
• Selecting all ports
• Properties dialog boxes (Switch, Network, and SNMP)
• Services dialog box
• Port diagnostics dialog boxes
Shortcut keys
Shortcut key combinations provide an alternative method of accessing menu options in the web applet. For
example, to open the Preferences dialog box, press Alt+F, and then press R.
NOTE: The shortcut key combinations are not case-sensitive. Shortcut keys are not supported on the Mac
platform.
Selecting switches
To select a switch, you can either select the switch name or switch icon from the fabric tree to display its
faceplate display in the graphic window. See ”Managing Switches” (page 47) for detailed switch
information.
Selecting ports
Ports are selectable and serve as access points for other displays and menus. You select ports to display
information about them in the data window or to modify them. Context-sensitive popup menus appear
when you right-click the faceplate image or on a port icon. See ”Managing Ports” (page 91) for detailed
port information.
Selected ports in the faceplate display are outlined in white. You can select ports in the following ways:
• To select a port, click the port.
• To select all ports, right-click on the faceplate image, and select Select All Ports from the popup menu.
• To select a range of consecutive ports, click a port, press and hold down the Shift key, and then click
the last port in the desired range. The web applet selects both end ports and all ports in between the
end ports.
NOTE: When using the Shift key to select a range of ports, the first port you click in the range is the
anchor selection. Subsequent ranges are based on this anchor selection. For example, when you click port
4 and port 9 respectively, port 4 becomes the anchor selection. The next range will include all ports
between port 4 and the next port you select.
• To select several non-consecutive ports, press and hold down the Control key while clicking each port.
• To deselect ports in a group of selected ports, press and hold down the Control key while clicking each
port.
• To cancel a selection, press and hold down the Control key and select it again.
16
Page 17
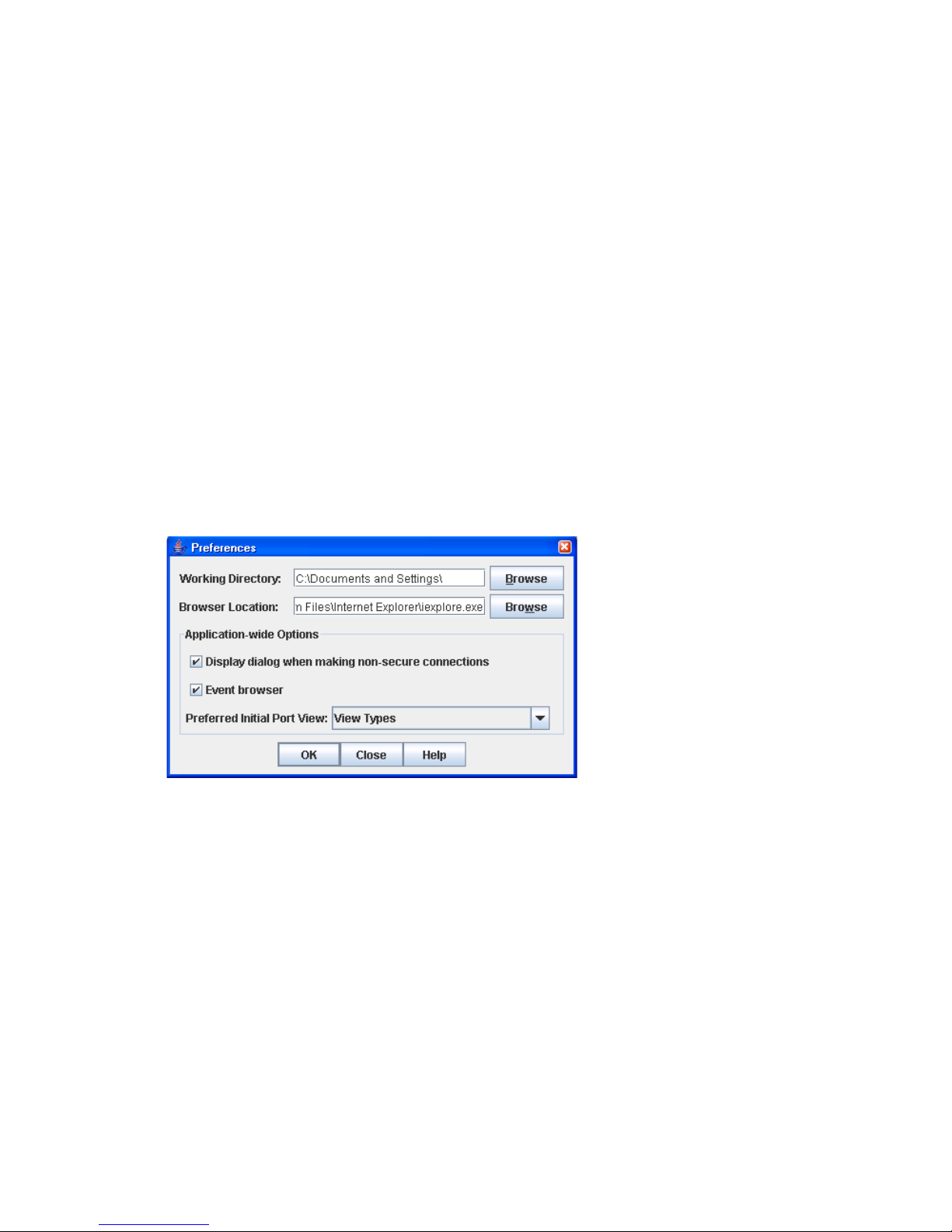
Setting QuickTools preferences
Using the preferences settings, you can:
• Change the location of the working directory in which to save files.
• Change the location of the browser used to view the online Help.
• Select the Display Dialog When Making Non-secure Connections option. If this option is enabled, the
Non-secure Connections Check dialog box appears when you attempt to open a non-secure fabric and
you have the option of opening the non-secure fabric. If this option is disabled, you cannot open a
fabric that has a non-secure connection.
• Enable (default) or disable the Event Browser. See ”Event Browser” (page 27) for more information. If
the Event Browser is enabled using the Preferences dialog box (Figure 6), the next time QuickTools is
started all events appear. If the Event Browser is disabled when QuickTools is started and enabled later,
only those events from the time the Event Browser was enabled and forward appear.
• Choose the default port view when opening the faceplate display. You can set the faceplate to reflect
the current port type (default), speed, port operational state, or port transceiver media. Regardless of
the default port view you choose, you can change the port view in the faceplate display by opening the
View menu and selecting a different port view option. See the corresponding subsection for more
information:
• Port types, page 100
• Port operational states, page 98
• Port speeds, page 100
• Port transceiver media status, page 101
Figure 6 Preferences dialog box–QuickTools
To set preferences for your QuickTools sessions:
1. Select File > Preferences to open the Preferences dialog box.
2. Enter or browse for paths to the working directory and browser.
3. Choose the preferences you want in the Application-wide Options area.
4. Click OK to save the changes.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 17
Page 18

Using online Help
The browser-based online Help system can be accessed from the QuickTools web applet several ways.
Online Help is also context-sensitive; that is, the online Help opens to the topic that describes the dialog
box you have opened.
To open the first topic in the Help system, choose one of the following options:
• Select Help > Help Topics from the Menu bar.
• Click Help on the tool bar.
• If no dialog box appears, press the F1 function key.
To open the Help system to the topic that describes the dialog box you have open, choose one of the
following options:
• Click Help in dialog box.
• Press the F1 function key.
Viewing the software version
Select Help > About to view the version of the software.
Exiting QuickTools
To exit a QuickTools web applet session, close the browser.
18
Page 19

2 Managing Fabrics
This section describes the following options for managing fabrics.
Fabric services
Fabric services security includes SNMP and In-band management. SNMP is the protocol governing
network management and monitoring of network devices. SNMP security consists of a read community
string and a write community string, that are basically the passwords that control read and write access to
the switch. The read community string (public) and write community string (private) are set at the
factory to these well-known defaults and should be changed when SNMP is enabled using the System
Services or SNMP Properties dialog boxes. If SNMP is enabled (default) and the read and write
community strings have not been changed from their defaults, you risk unwanted access to the switch. See
”Enabling SNMP configuration” (page 19) for more information. SNMP is enabled by default.
In-band management is the ability to manage switches across inter-switch links using QuickTools, SNMP,
management server, or the application programming interface. The switch comes from the factory with
in-band management enabled. If you disable in-band management on a particular switch, you can no
longer communicate with that switch by means other than a direct Ethernet or serial connection. See
”Enabling in-band management” (page 19) for more information.
Enabling SNMP configuration
To enable the SNMP configuration:
1. Select Switch > SNMP > SNMP Properties to open the SNMP Properties dialog box.
2. Select the SNMP Enabled option in the SNMP Configuration area.
3. Click OK to save the change to the database.
Enabling in-band management
To enable in-band management:
1. Select Switch > Switch Properties to open the Switch Properties dialog box.
2. Select the In-band Management Enable option.
3. Click OK to save the change to the database.
Rediscovering a fabric
After making changes to or deleting switches from a fabric view, it may be helpful to again view the actual
fabric configuration. The Rediscover Fabric option clears out the current fabric information being displayed,
and rediscovers all switch information.
To rediscover a fabric, select Fabric > Rediscover Fabric. The Rediscover function is more comprehensive
than the Refresh function.
Adding a new switch to a fabric
If there are no special conditions to be configured for a new switch, plug in the switch; the switch becomes
functional with the default fabric configuration. The default fabric configuration settings are:
• Fabric zoning is sent to the switch from the fabric.
• All 8 Gb/s ports will be GL_Ports.
• The default IP address 10.0.0.1 is assigned to the switch without configuring a gateway or boot
protocol (RARP, BOOTP, and DHCP).
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 19
Page 20
If you are adding a new switch to a fabric and do not want to accept the default fabric configuration:
1. If the switch is not new from the factory, reset the switch to the factory configuration before adding the
switch to the fabric by selecting Restore Factory Defaults from the Switch menu.
2. If you want to manage the switch through the Ethernet port, configure the IP address using the Network
Properties dialog box or the Configuration Wizard.
3. Configure any special switch settings. To open the Zoning Config dialog box, select Zoning > Edit
Zoning Config.
4. Plug in the ISLs, but do not connect the devices.
5. Configure the port types for the new switch using the Port Properties dialog box.
6. Connect the devices to the switch.
7. To make any necessary zoning changes, select Zoning > Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog
box.
Replacing a failed switch
The Restore menu option is not available for the switches being managed in-band through the fabric
management switch. You can only restore a switch out-of-band via Ethernet connection to the fabric
management switch. Certain parameters are not archived, and these are not restored by QuickTools. For
more information, see ”Archiving a switch” (page 74) and ”Restoring a switch” (page 74).
Use the following procedure to replace a failed switch for which an archive is available.
1. Turn off the power to the failed switch and disconnect the AC cords. Note port locations and remove
the interconnection cables and small form-factor pluggable (SFPs).
2. Remove the failed switch.
3. Mount the replacement switch in the location where the failed switch was removed.
4. Install the SFPs using the same ports as were used on the failed switch. Do not reconnect inter-switch
links, target devices, and initiator devices at this time. Doing so could invalidate the fabric zoning
configuration.
5. Attach the AC cords and power up the switch.
6. Restore the configuration from the failed switch to the replacement switch:
a. Open a new fabric through the replacement switch.
b. Open the faceplate display for the replacement switch. Select Switch > Restore.
c. In the Restore dialog box, enter the archive file from the failed switch or browse for the file.
d. Click Restore.
7. Select Switch > Reset Switch to reset the replacement switch to activate the configuration formerly
possessed by the failed switch including the domain ID and the zoning database.
8. Reconnect the inter-switch links, target devices, and initiator devices to the replacement switch using the
same ports as were used on the failed switch.
Transparent Router
IMPORTANT: The SSCM application can manage HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switches with active
TR_Ports; however, SSCM cannot manage or discover remote switches or devices in the remote fabric. Use
QuickTools and the storage management interface to present LUNs to remote devices. SSCM displays the
remote fabric as a grayed-out switch, and no management can be performed. SSCM version 3.0 or later is
required for the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch. SSCM version 2.0 and earlier versions do not support
the management of fabrics that include switches with active TR_Ports and may disrupt communication
between an HP SN6000 or 8/20q Fibre Channel Switch and the remote fabric.
The Transparent Router feature on the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch provides inter-fabric routing to
enable controlled and limited access between devices on an HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch (local)
fabric and devices on a remote fabric of B-series or C-series switches.
20
Page 21

The local fabric may consist of one or multiple HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switches connected by their
ISLs. A specific device attached to an HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch can be mapped with one or more
devices in one remote fabric over only one TR_Port on that HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch. If a device
attached to an HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch is mapped with multiple devices in the same remote
fabric, the same TR_Port must be used.
A device attached to a remote fabric can be mapped with multiple devices in multiple local fabrics. If a
device in a remote fabric is mapped with multiple devices in the local fabric attached to a given HP
SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch, the same TR_Port on the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch must be used
for all mappings involving that remote device. However, the same remote device can be mapped with
other local devices attached to a different HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch in the same local fabric over
a TR port from that switch. A remote device can be mapped through more than one TR port, as long as
each of those TR ports is on a different HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch.
Furthermore, you cannot map a local device to a remote device over an E_Port to another local switch and
then over a TR_Port to the remote switch. The transparent route cannot include an E_Port on the local fabric.
Local devices will not discover remote devices until the corresponding inter-fabric zones are activated on
both the local and remote fabrics. To remove a mapping, in addition to removing the local inter-fabric
zone, you must also remove the corresponding remote inter-fabric zone.
NOTE: When a local device is mapped over a TR_Port to a remote device, the local device and its
TR_Port appear as an NPIV connected device in the remote fabric. It is possible, though not recommended,
to map such a local device over a second TR_Port to a local device in a second local fabric. In this case, if
you merge the two local fabrics, the transparent route becomes inactive for the devices that now have a
path over an ISL, and an alarm is generated.
For details of switches supported in a remote fabric, see release notes for the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel
Switch, and the HP StorageWorks SAN Design Reference Guide on the HP website
http://www.hp.com/go/sandesignguide. A user (admin rights required) can configure TR mappings to
connect devices on the local HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch fabric with devices on remote fabrics.
The transparent route between these devices is accomplished by connecting a remote switch to a TR_port
on the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch, mapping the devices together, and then creating and activating
the IFZ (inter-fabric zones) in both fabrics. Each fabric will contain a matching IFZ. Each IFZ must contain
exactly three WWN members: the local device, the remote device, and the TR_Port attached to the remote
fabric.
NOTE: Be sure to configure the TR_Port before connecting the remote fabric to the HP SN6000 Fibre
Channel Switch. If the remote fabric is connected to a port on the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch that is
not a TR_Port, the two fabrics may establish an E_Port connection and the local and remote fabrics may
merge. This mixed fabric is not a supported configuration. If the port type is changed to TR_Port after
connecting the remote fabric, a port reset may be required to completely establish the TR connection.
A TR_Port is used as a bridge between the transparent router’s local fabric and a remote fabric. A TR_Port
uses standard NPIV login methods to attach to the remote fabric. For remote B-series or C-series fabrics, the
switch to which the TR_Port connects must support N-Port ID Virtualization (NPIV) and for B-series fabrics the
interoperability mode must be configured to InteropMode=0. The TR_Port logs into the remote fabric using
the WWN of the TR_Port. The TR_Port accesses fabric services of the remote fabric, such as Name Server
and Management Server, and may receive registered state change notifications (RSCNs). The TR_Port uses
FDISCs to login proxies for devices attached to an N_Port on the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch. Any of
the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch 8Gb ports may be configured as a TR_Port.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 21
Page 22
IMPORTANT: Since C-series switches do not support the Unzoned Name Server, C-series fabrics
must be “pre-zoned” before you can set up TR mappings to a remote C-series fabric using the TR
Mapping Manager dialog box. The C-series fabric zone set must be changed to add zones so that
the WWNs of the remote devices to be mapped and the WWNs of the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel
Switch TR ports are zoned together. For more information, see the C-series documentation for
specific information to configure zoning. Retain these zones in the zone set after completion of the
TR mapping as a best practice, until you no longer need to map the device to the local fabric.
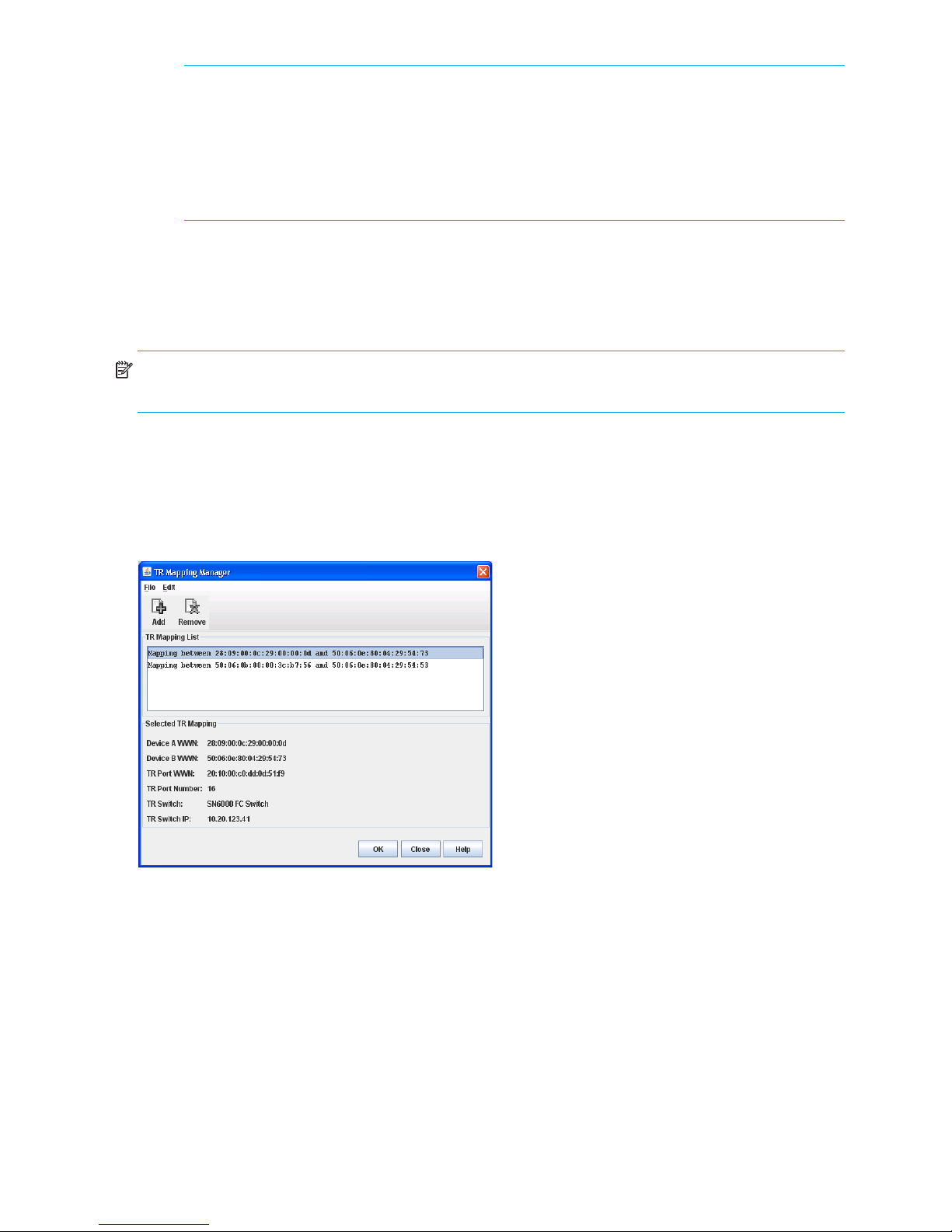
TR Mapping Manager dialog
The TR Mapping Manager dialog (Figure 7) displays the currently mapped inter-fabric routes. You can
create new inter-fabric routes, view detail information on existing inter-fabric routes, and remove existing
inter-fabric routes. To open the TR Mapping Manager dialog, select Fabric > TR Mapping Manager.
NOTE: The Merge Auto Save option in the Config Zoning dialog must be selected before you can open
the TR Mapping Manager dialog. See ”Merge Auto Save” (page 39) for more information.
To create a new TR mapping, click Add or select Edit > Add to open the Add TR Mapping dialog. See
”Add TR Mapping dialog” (page 23) for more information.
Select a TR mapping member in the TR Mapping List window to:
• Delete that TR mapping member
• View detailed information for that TR mapping member in the Selected TR Mapping area
Figure 7 TR Mapping Manager dialog
After you click OK in the TR Mapping Manager dialog, the IFZs are created and saved to the switch. If
there is an active zone set with TR mappings, the old IFZs are deleted and replaced with the new IFZs, and
then the active zone set is re-activated. If there is no active zone set, a zone set named TR_MAPPING_SET”
(default name) is created, the new IFZs are added to the zone set, and then the zone set is activated. If
there are no TR mappings, the old IFZs are deleted from the active zone set, and then the active zone set is
re-activated. If there are no zones and no IFZs in the active set, the active zone set is deactivated.
22
Page 23
Removing an inter-fabric route
To remove an inter-fabric route:
1. Open the faceplate display, and select Fabric > TR Mapping Manager.
2. In the TR Mapping Manager dialog (Figure 7), select a TR mapping member from the TR Mapping list,
and then click Remove or select Edit > Remove.
A warning dialog prompts you to confirm the removal of the selected mapping members.
3. Click OK to confirm the removal of the selected TR mapping member.
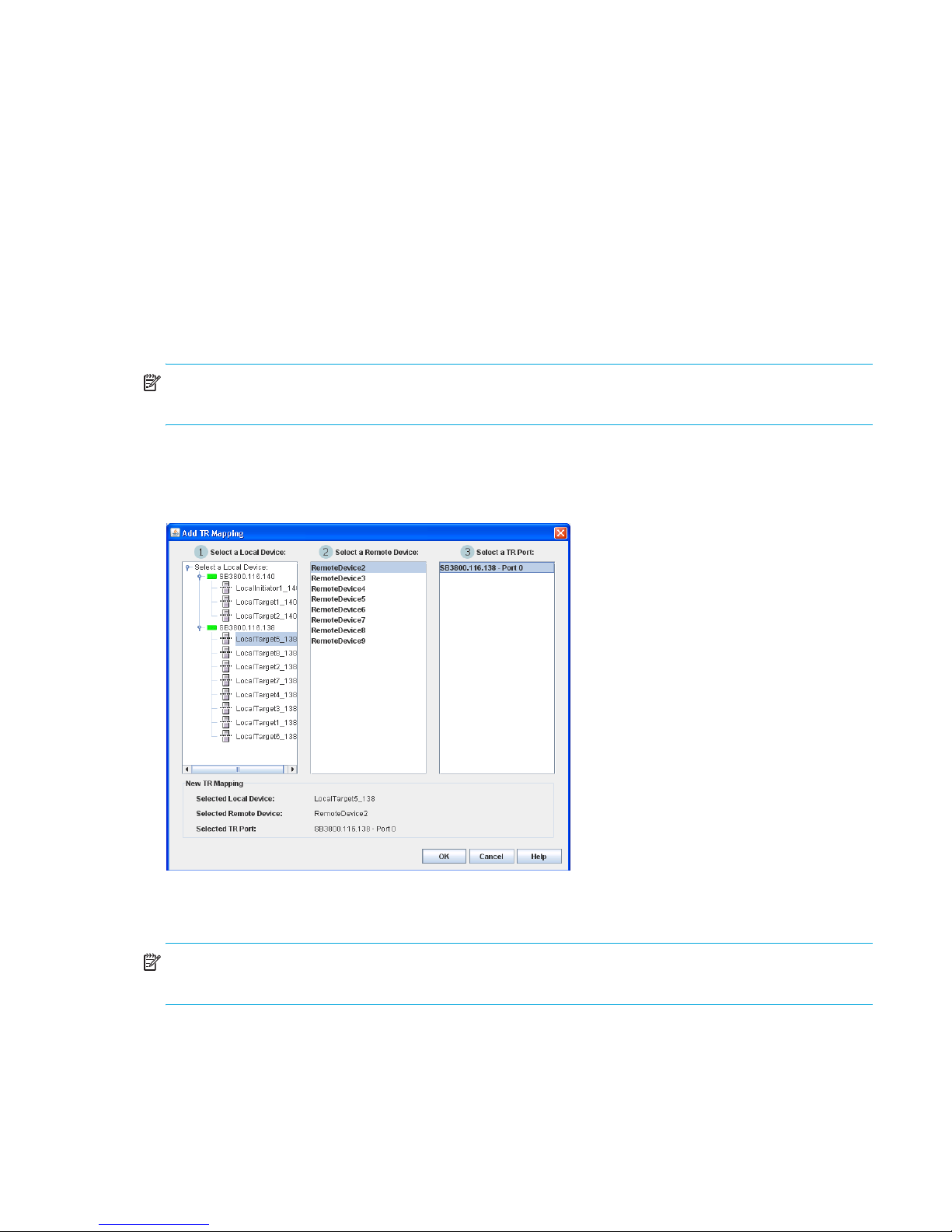
Add TR Mapping dialog
The Add TR Mapping dialog (Figure 8) enables you to map a new inter-fabric zone. The Add TR Mapping
dialog displays the selectable local devices, remote devices, and TR-configured ports that can be mapped
to the inter-fabric zone. The Add TR Mapping dialog appears after you click Add or select Edit > Add in the
TR Mapping Manager dialog.
NOTE: You can map a remote device through multiple TR ports, as long as each of those TR ports are on
different HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switches.
Select a local device from the 1 Select a Local Device column to display the selectable remote devices in the
2 Select a Remote Device column. After selecting a remote device, the selectable TR ports appear in the 3
Select a TR Port column.
Figure 8 Add TR Mapping dialog
Mapping a new inter-fabric zone
NOTE: The local fabric port to be used in the inter-fabric zone must be configured as a TR_Port before the
devices are mapped. See ”Por t types” (page 100) for information on changing port types.
To map a new inter-fabric zone:
1. Open the faceplate display, and select Fabric > TR Mapping Manager.
2. In the TR Mapping Manager dialog (Figure 7), click Add or select Edit > Add.
3. In the Add TR Mapping dialog (Figure 8), select a local device from the 1 Select a Local Device column.
4. Select a remote device from the 2 Select a Remote Device column.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 23
Page 24
5. Select a TR port from the 3 Select a TR Port column.
After selecting an option from the 3 Select a TR Port column, the OK button becomes active.
6. Click OK to save the changes and close the Add TR Mapping dialog.
7. Verify that the new TR mapping members appear in the TR Mapping list of the TR Mapping Manager
dialog, and click OK.
NOTE: After you click OK in the TR Mapping Manager dialog, the IFZs are created and saved to the
switch. If there is an active zone set with TR mappings, the old IFZs are deleted and replaced with the new
IFZs, and then the active zone set is re-activated. If there is no active zone set, a zone set named
TR_MAPPING_SET” (default name) is created, the new IFZs are added to the zone set, and then the zone
set is activated. If there are no TR mappings, the old IFZs are deleted from the active zone set, and then the
active zone set is re-activated. If there are no zones and no IFZs in the active set, the active zone set is
deactivated.
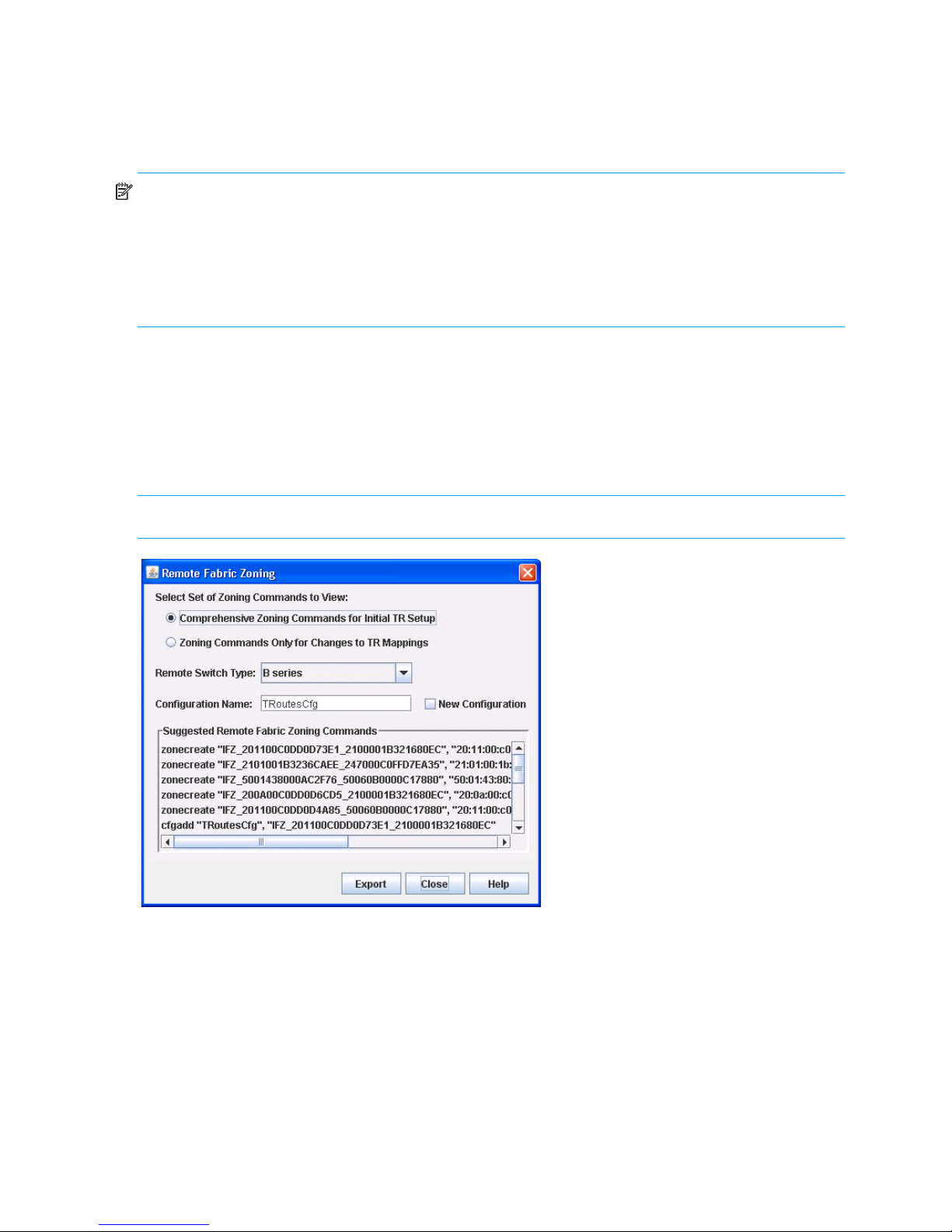
Remote Fabric Zoning dialog
The Remote Fabric Zoning dialog (Figure 9) enables you to generate and save a text file containing the
zoning commands required to be executed on the remote fabric so that the inter-fabric connection using a
TR port is established. The user can choose the kind of remote fabric/switches to connect with the TR port
so that QuickTools knows which zoning commands to generate for the user. Fabrics with B-series and
C-series switches are supported.
NOTE: Before modifying zoning, HP recommends that you back up the configuration.
Figure 9 Remote Fabric Zoning dialog
To create a zoning commands text file for the remote fabric:
1. Open the faceplate display, and select Fabric > TR Mapping Manager.
2. Create a new TR mapping for a inter-fabric zone, if one does not exist. See ”Mapping a new
inter-fabric zone” (page 23) for more information.
3. In the TR Mapping Manager dialog (Figure 8), select an entry from the TR Mapping List window.
4. Select File > Generate Remote Zoning.
24
Page 25

5. In the Remote Fabric Zoning dialog (Figure 9), if you made and saved changes in the TR Mapping
Manager dialog, you can choose the type of zoning commands to view in the Suggested Remote
Fabric Zoning Commands window of the Remote Fabric Zoning dialog.
Choose one of the following options from Select Set of Zoning Commands to View:
• The Comprehensive Zoning Commands for Initial TR Setup option to show the list of zoning
commands to set up all the IFZs.
• The Zoning Commands Only for Changes to TR Mappings option to show the list of zoning
commands only for changes you just made during this session (after opening the TR Mapping
Manager dialog).
NOTE: The Remote Fabric Zoning dialog displays the Select Set of Zoning Commands to View option
only if you made and saved changes in the TR Mapping Manager dialog. If you opened the Remote
Fabric Zoning dialog after selecting File > Generate Remote Zoning, the Select Set of Zoning Commands
to View option is not displayed, and the Suggested Remote Fabric Zoning Commands window displays the
list of zoning commands to set up all the IFZs.
6. Choose one of the following options from the Remote Switch Type drop-down list to generate the
corresponding zoning commands:
• B-series—to connect remotely with B-series switches
• C-series—to connect remotely with C-series switches
7. Enter the Configuration Name, which is used as the zone set name in the commands. This must be the
same zone set name as the zone set on the remote fabric to which this zoning will be applied, or else
the commands generated can be saved and edited to change the zone set name as needed. The
default Configuration Name displayed is TRoutesCfg.
8. Select one of the following:
•Clear the New Configuration option if the remote fabric has an active zone set. Executing the
updated zoning commands on the remote fabric automatically adds the changes to the already
active zone set, provided that the Configuration Name entered is the same as the name of that
active zone set.
NOTE: If the commands are run and the Configuration Name is not the name of the active zone
set in the remote fabric, the commands attempt to replace the active zone set with a new zone set
with the new name, containing only the Inter Fabric Zones. This will not succeed unless you respond
to CLI queries to accept activation of this new zone set.
• Select the New Configuration option if the remote fabric does not have an active zone set.
Executing the commands on the remote fabric automatically adds the commands (inter-fabric zones)
to create and activate the zone set. The Configuration Name entered is the name of the active zone
set that is created.
9. Click Export and select a path name (TXT file extension only) in the Save dialog.
Selecting the same path name will overwrite the first path name.
10.Click Save to save the zoning commands text file on your workstation.
NOTE: The commands generated for C-series switches assume that zoning will be applied to
VSAN 1. If this is not the correct VSAN, you must edit the commands accordingly before executing
the commands.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 25
Page 26
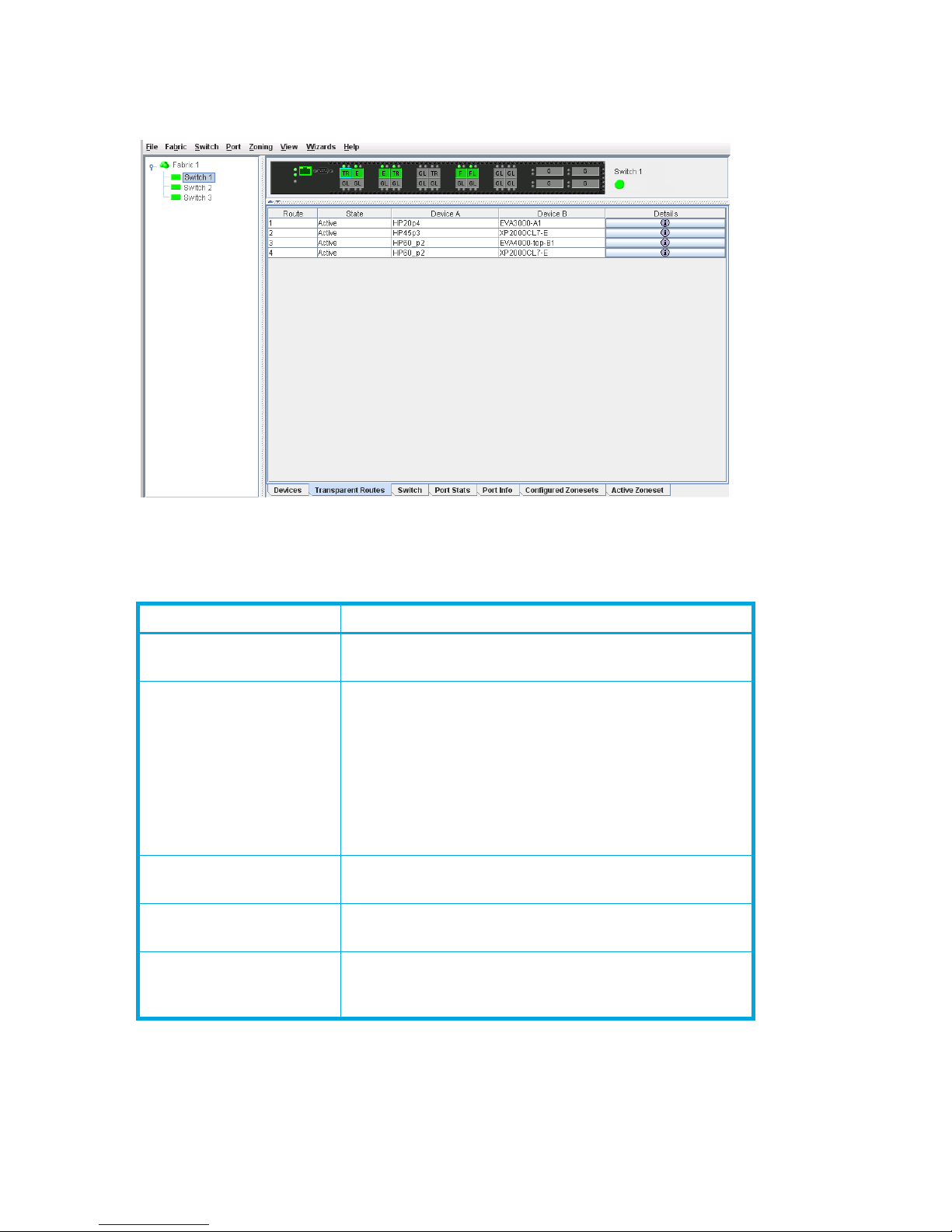
Transparent Routes data window
The Transparent Routes data window displays the currently configured inter-fabric zones/routes using a
TR_Port.
Figure 10 Transparent Routes data window
The Transparent Routes data window fields are described in Table 3.
Table 3 Transparent Routes data window fields
Field Description
Route Route number reference for each listing in the Transparent
Routes data window table
State The current TR mapping state (Active or Inactive)
• Active—Indicates that the mapping's TR port is on
this switch, and both devices have logged in.
• Inactive—Indicates that the mapping's TR port is on
this switch, and the mapping is not active. The
reasons are shown in the details display as the three
Status column entries (one for the overall mapping
and one for each device in the mapping).
Device A The WWN of one of the two devices linked by the TR
mapping. Assigned nicknames are also displayed.
Device B The WWN of the other device linked by the TR mapping.
Assigned nicknames are also displayed.
Details Click (i) in the Details column to open the Transparent Route
dialog, which displays detailed information on the
transparent route.
26
Page 27
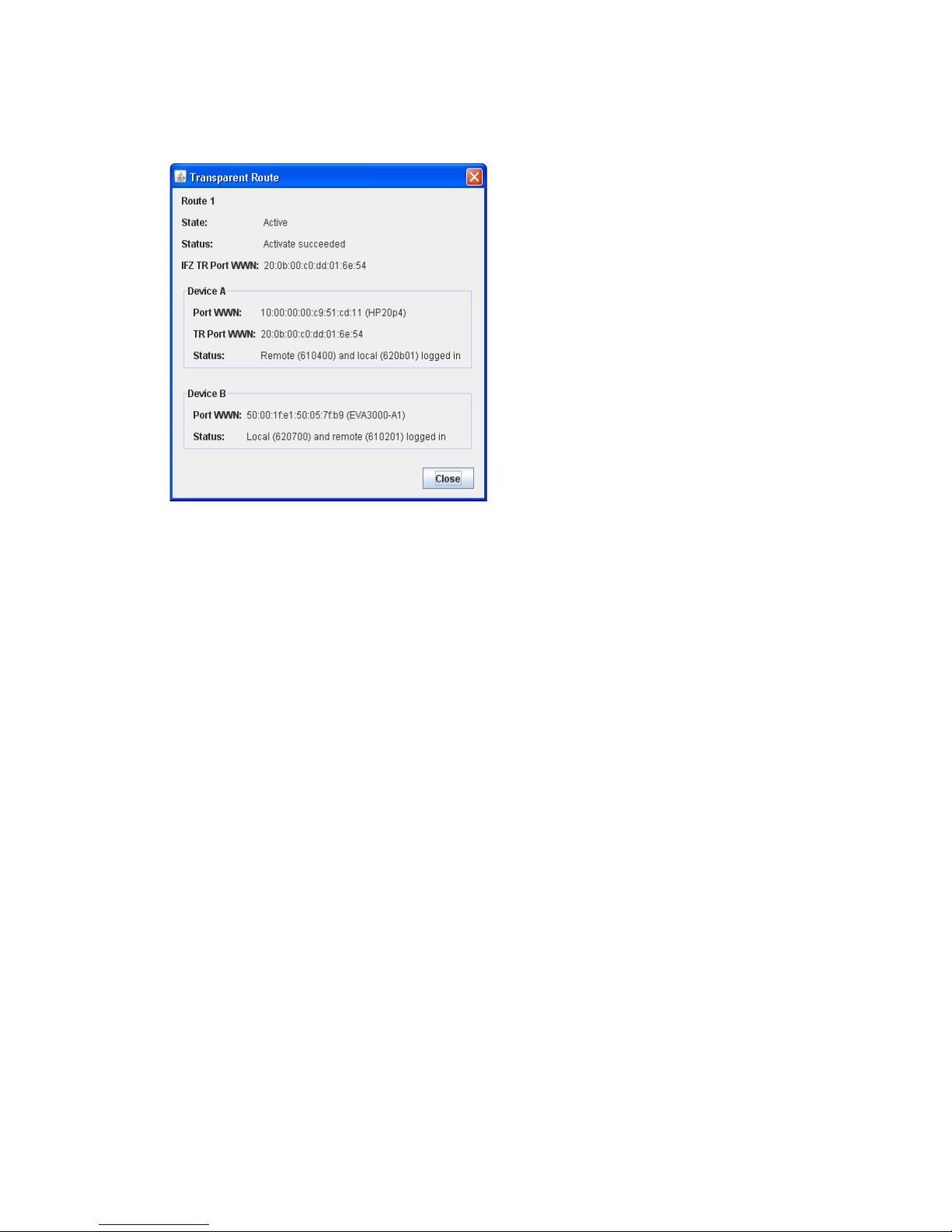
The Transparent Route dialog (Figure 11) displays detailed information about the transparent route you
selected from the Transparent Routes data window. The state of the route (Active or Inactive) is shown, and
Port WWN, TR Port WWN, and Status fields are displayed for both sides of the route. Device A will not
necessarily correspond to the HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch side of the route, as the end points of the
route could be in any order.
Figure 11 Transparent Route dialog
Event Browser
The Event Browser displays a list of events generated by the switches in the fabric and the QuickTools web
applet. Events that are generated by the QuickTools web applet are not saved on the switch, but can be
saved to a file during a QuickTools session.
The Event Browser (Figure 12) lists events that have occurred, displaying the severity, time, source, type,
and description of the events. The maximum number of entries allowed in the Event Browser is 10,000. The
maximum number of entries allowed on a switch is 1,200. Once the maximum is reached, the oldest
events in the event list are deleted when new events occur. Event entries from the switch, use the switch time
stamp, while event entries generated by the web applet have a workstation time stamp. You can filter, sort,
and export the contents of the Event Browser to a file. The Event Browser begins recording when it is
enabled and QuickTools is running.
If the Event Browser is enabled using the Preferences dialog box, the next time QuickTools is started all
events from the switch log appear. If the Event Browser is disabled when QuickTools is started and later
enabled, only those events that occur after the time the Event Browser was enabled will appear.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 27
Page 28
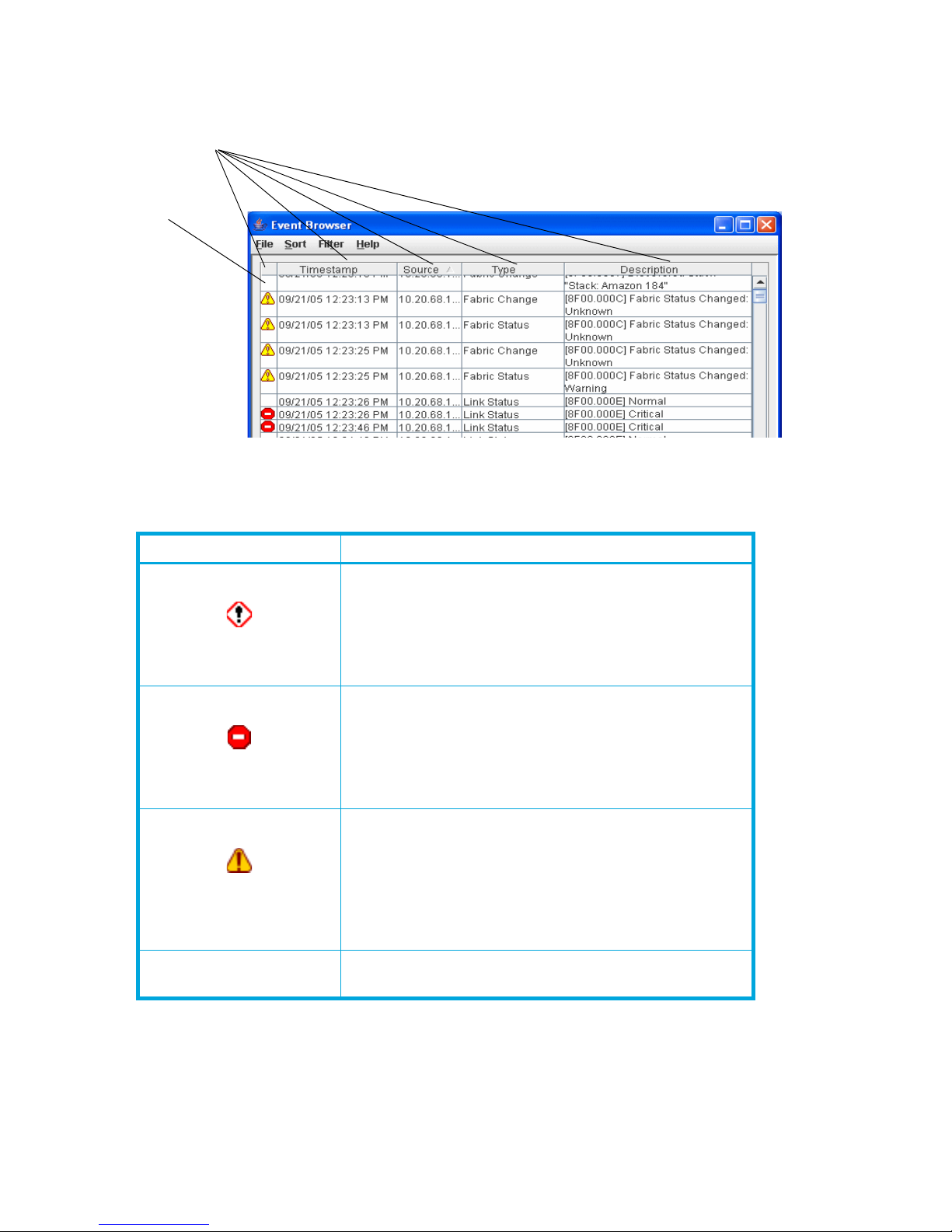
To display the Event Browser, open the Fabric menu and select Show Event Browser. If the Show Event
Column sorting
buttons
Severity
column
Browser selection is grayed-out, you must first enable the Events Browser preference. See ”Setting
QuickTools preferences” (page 17).
Figure 12 Event Browser dialog box
The icons in the Severity column identify the operational state of the port, as described in Table 4.
Table 4 Port operational states
State Description
Alarm—An alarm is a "serviceable event." This means that
attention by the user or field service is required. Alarms are
posted asynchronously to the screen and cannot be turned
off. If the alarm denotes that a system error has occurred,
the customer and/or field representative will generally be
directed to provide the support file from the switch.
Critical event—An event that indicates a potential failure.
Critical log messages are events that warrant notice by the
user. By default, these log messages will be posted to the
screen. Critical log messages do not have alarm status as
they require no immediate attention from a user or service
representative.
Warning event—An event that indicates errors or other
conditions that may require attention in order to maintain
maximum performance. Warning messages will not be
posted to the screen unless the log is configured to do so.
Warning messages are not disruptive and therefore, do not
meet the criteria of Critical. The user need not be informed
asynchronously
No icon Informative—An unclassified event that provides only
supporting information.
28
Page 29
NOTE: Events (Alarms, Critical, Warning, and Informative) generated by the web applet are not saved on
the switch. They are permanently discarded when you close a QuickTools session; however, you can save
these events to a file on the workstation before you close QuickTools and read it later with a text editor or
browser.
Events generated by the switch are stored on the switch, and will be retrieved when the web applet is
restarted. Some alarms are configurable.
Filtering the Event Browser
Filtering the Event Browser enables you to display only those events that are of interest based on the event
severity, timestamp, source, type, and description. To filter the Event Browser, open the Filter menu and
select Filter Entries. This opens the Filter Events dialog box (Figure 13). The Event Browser displays those
events that meet all of the criteria in the Filter Events dialog box. If the filtering criteria are cleared or
changed, then all the events that were previously hidden that satisfy the new criteria will be shown.
You can filter the Event Browser in the following ways:
• Severity—Select one or more of the corresponding options to display alarm events, critical events,
warning events, or informative events.
• Date/Time—Select one or both of the From: and To: options, and enter the bounding timestamps
(MM/DD/YY HH:MM:SS AA, where "AA" indicates AM or PM) to display only those events that fall
within the selected times. The current year (YY) can be entered as either 2 or 4 digits.
• Text—Select one or more of the corresponding options and enter a text string (case sensitive)
identifying the source, type, and/or description of the events to be monitored. The Event Browser
displays only those events that satisfy all of the search specifications for the criteria defined.
Figure 13 Filter Events dialog box
Sorting the Event Browser
Sorting the Event Browser enables you to display the events in alphanumeric order based on the event
severity, timestamp, source, type, or description. By default, the Event Browser is sorted in ascending order
by timestamp. To sort on another column of the Event Browser, click the Severity, Timestamp, Source, Type,
or Description column button. Alternatively, select Sort > By Severity, By Timestamp, By Source, By Type, or
By Description. Successive sort operations of the same type alternate between ascending and descending
order.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 29
Page 30
Saving the Event Browser to a file
You can save the displayed Event Browser entries to a file. Filtering affects the save operation, because only
displayed events are saved. To save the Event Browser to a file:
1. Filter and sort the Event Browser to obtain the desired display.
2. Select File > Save As.
3. Select a folder and enter a file name in which to save the event log, and then click Save. The file can be
saved in XML, CSV, or text format. XML files can be opened with an internet browser or text editor. CSV
files can be opened with most spreadsheet applications.
Device information and nicknames
Devices are hosts and storage targets connected to the switch. A nickname is a user-definable, meaningful
name that can be used in place of the World Wide Name (WWN). This sub-section describes how to view
and manage device information and nicknames.
• Devices data window, page 30
• Displaying detailed device information, page 31
• Managing device port nicknames, page 32
Devices data window
The Devices data window (Figure 14) displays information about name server devices and proxied devices
(from configuration of TR ports) connected to the switch. To display the Devices data window, click the
Devices tab below the data window.
Figure 14 Devices data window
Remote devices are proxied, so there are limitations in available information:
• The Details button is disabled.
• The Target/Initiator field will always read "Unknown".
• The Vendor field text will be decoded from the OUI in the Port WWN, rather than potentially being
read from the FC4Descriptors, as is the case with local devices.
• The proxied devices are indicated in the Device data window by italic text and the notation "(TR)" after
the port number.
• Proxied devices are also grayed-out in the Active Zoneset data window. See ”Active Zoneset data
window” (page 33) for more information.
30
Page 31
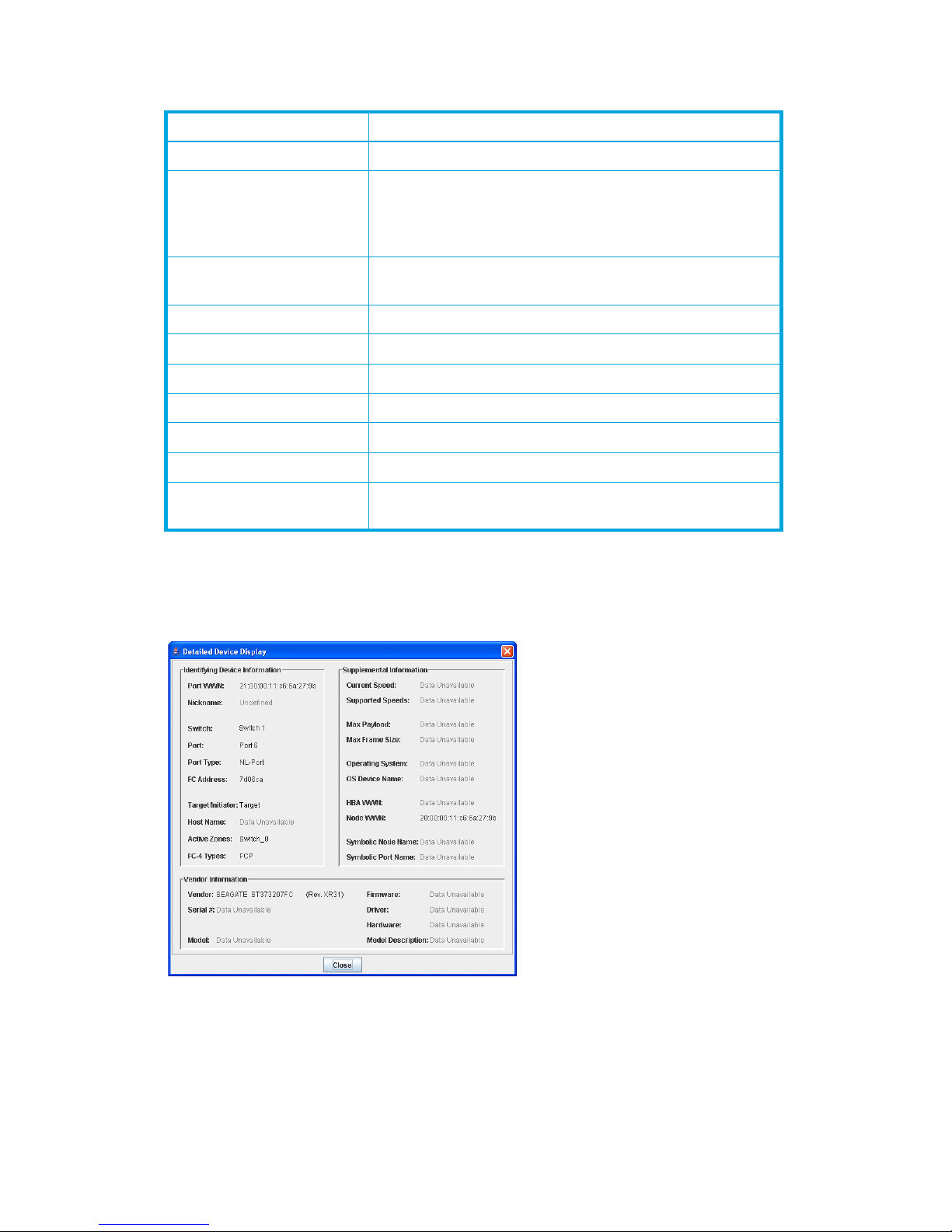
The Devices data window fields are described in Table 5.
Table 5 Devices data window fields
Field Description
Port WWN Port World Wide Name
Nickname Device port nickname. To create a new nickname or edit an
existing nickname, double-click the cell and enter a
nickname in the Edit Nickname dialog box. See ”Managing
device port nicknames” (page 32) for more information.
Details Click (i) to display additional information about the device.
See ”Displaying detailed device information” (page 31).
FC Address Fibre Channel address
Switch Switch name
Port Switch port number
Target/Initiator Device type: Target, Initiator, or Both
Vendor Host Bus Adapter/Device Vendor
Active Zones The active zone to which the device belongs
Row # Row number reference for each listing in the Devices data
window table
Displaying detailed device information
To display detailed information for a device listed in the Devices data window, click (i) in the Details
column for that device to open the Detailed Devices Display window (Figure 15).
Figure 15 Detailed Devices Display dialog box
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 31
Page 32

Managing device port nicknames
You can assign a nickname to a device port World Wide Name. A nickname is a user-definable,
meaningful name that can be used in place of the World Wide Name. Assigning a nickname makes it
easier to recognize device ports when zoning your fabric or when viewing the Devices data window.
In addition to creating, editing, and deleting nicknames, you can also export the nicknames to a file, which
can be imported into the Nicknames.xml file on other workstations. The maximum number of nicknames
allowed is 5,000.
Nicknames are saved to an XML file stored on the switch. If different nickname files exist on other switches
in the fabric, you are prompted to resolve differences before the Nicknames dialog box is displayed.
When a conflict exists, a series of dialog boxes is presented to resolve differences between the nicknames
stored on that switch with nicknames stored on other switches. The most recent nickname takes precedence
during nickname resolution. Changes made in the Nickname dialog box are propagated to all switches in
the fabric only after you click Apply.
Creating a nickname
To create a device port nickname:
1. Select Fabric > Nicknames to open the Nicknames dialog box. The device entries are listed in table
format.
2. Choose one of the following options to enter a nickname. A nickname must start with a letter and can
have up to 64 characters. Valid characters include alphanumeric characters [aA–zZ][0–9] and special
symbols [$ _ - ^ ].
• Double-click a cell in the Nicknames column, and enter a new nickname in the text field. Click Save
to save the changes and exit the Nicknames dialog box.
• Click on a device in the table. Select Edit > Create Nickname to open the Add Nickname dialog
box. In the Add Nickname dialog box, enter a nickname and WWN, and then click OK.
Editing a nickname
To edit a nickname:
1. Select Fabric > Nicknames to open the Nicknames dialog box. The device entries are listed in table
format.
2. Choose one of the following options to edit a nickname:
• Double-click a cell in the Nicknames column and edit the nickname in the text field. In the
Nicknames dialog box, click Apply to save the changes.
• Click on a device entry in the table and then select Edit > Edit Nickname to open the Edit
Nicknames dialog box. Edit the nickname in the text field, and then click OK. In the Nicknames
dialog box, click Apply to save the changes.
Deleting a nickname
To delete a device port nickname:
1. Select Fabric > Nicknames to open the Nicknames dialog box.
2. Choose one of the following options to delete a nickname:
• Click a device in the table and then select Edit > Delete Nickname.
• Double-click a cell in the Nicknames column, and then delete the nickname text.
3. Click Apply to save the changes.
32
Page 33
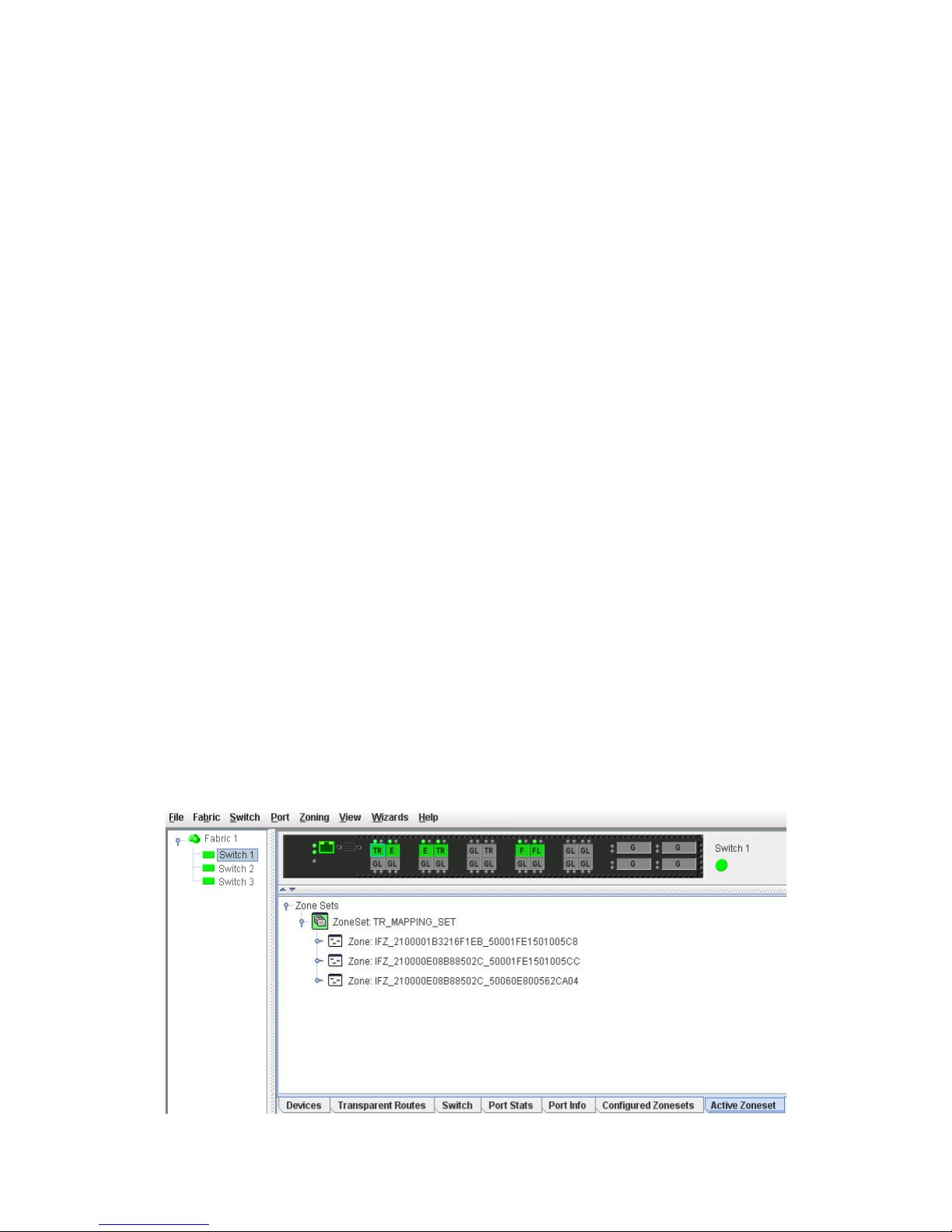
Exporting nicknames to a file
You can save nicknames to a file. This is useful for distributing nicknames to other management
workstations.
To save nicknames to an XML file:
1. Select Fabric > Nicknames to open the Nicknames dialog box.
2. Select File > Export.
3. Enter a name for the XML nickname file in the Save dialog box.
4. Click Save.
Importing a nicknames file
Importing a nicknames file copies its contents into and replaces the contents of the Nicknames.xml file
which is used by QuickTools. To import a nickname file:
1. Select Fabric > Nicknames to open the Nicknames dialog box.
2. Select File > Import.
3. Click an XML nickname file in the Open dialog box.
4. Click Open.
5. When prompted to overwrite existing nicknames, click Yes.
Zoning
Zoning a fabric enables you to divide the ports and devices of the fabric into zones for more efficient and
secure communication among functionally grouped nodes.
Active Zoneset data window
The Active Zoneset data window (Figure 16) displays the zone membership for the active zone set that
resides on the fabric management switch. The active zone set is the same on all switches in the fabric. To
open the Active Zoneset data window, click the Active Zoneset tab below the data window. The Active
Zoneset data window uses display conventions for expanding and contracting entries that are similar to the
fabric tree. An entry handle located to the left of an entry in the tree indicates that the entry can be
expanded. Click this handle or double-click the following entries:
• A zone set expands to show its member zones.
• A zone expands to show its member ports/devices.
• Ports/devices that are zoned by WWN or FC address, but no longer part of the fabric, are grayed-out.
Proxied devices are also grayed-out.
Figure 16 Active Zoneset data window
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 33
Page 34
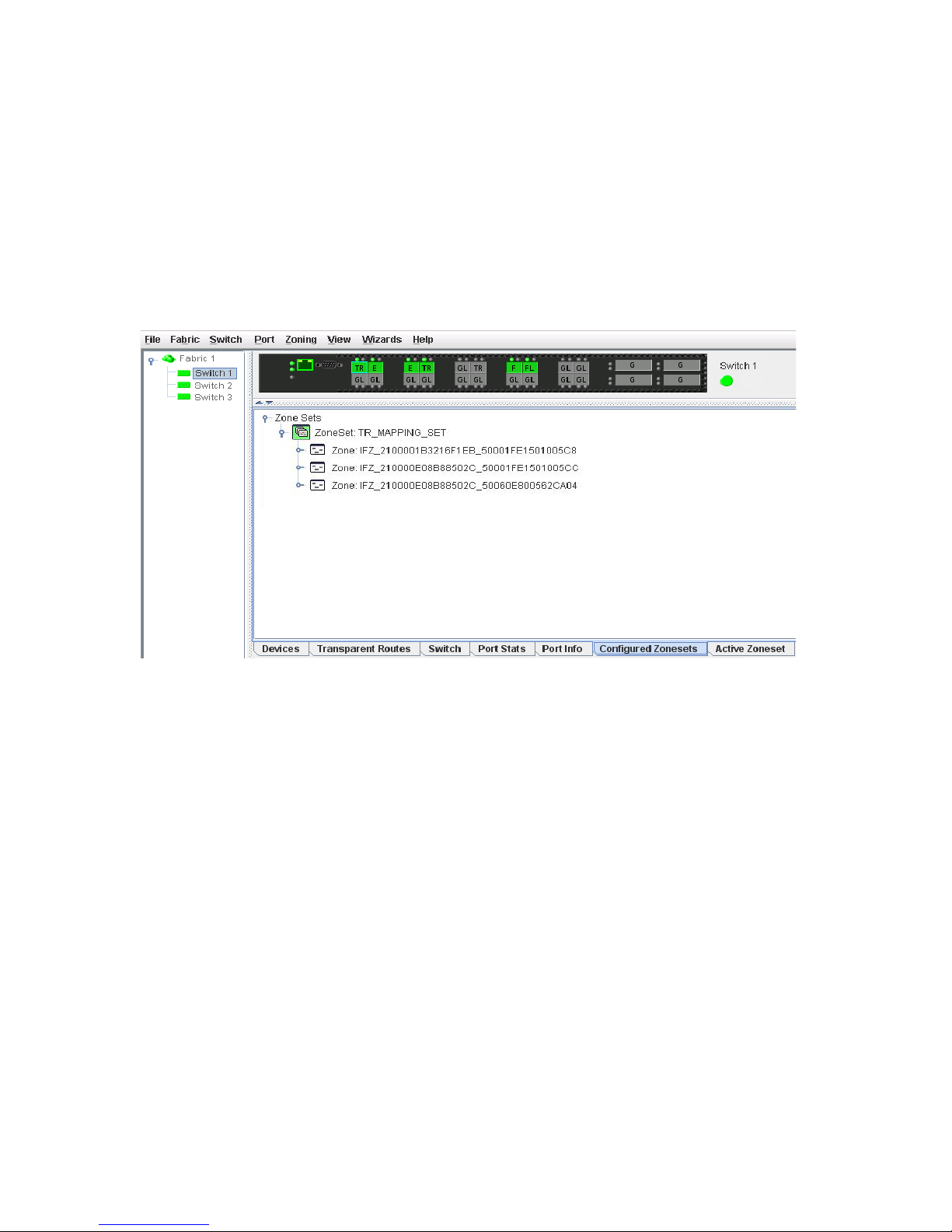
Configured Zonesets data window
The Configured Zonesets data window (Figure 17) displays all zone sets, zones, aliases, and zone
membership in the zoning database. To open the Configured Zonesets data window, click the Configured
Zonesets tab below the data window.
The Configured Zonesets data window uses display conventions for expanding and contracting entries that
are similar to those used by the fabric tree. An entry handle located to the left of an entry in the tree
indicates that the entry can be expanded. Click this handle or double-click the following entries to expand
or collapse them:
• A zone set expands to show its member zones.
• A zone expands to show its members by device port World Wide Name or device port Fibre Channel
address.
• The alias expands to show its entries.
Figure 17 Configured Zoneset data window
Zoning concepts
The following zoning concepts provide some context for the zoning tasks described in this section:
• Zones, page 34
• Aliases, page 35
• zone sets, page 35
• Zoning database, page 35
• Configuring the zoning database, page 39
Zones
Zoning divides the fabric for the purpose of controlling discovery and inbound traffic. A zone is a named
group of ports or devices. Members of the same zone can communicate with each other and transmit
outside the zone, but cannot receive inbound traffic from outside the zone. Zoning is hardware-enforced
only when a port/device is a member of no more than eight zones whose combined membership does not
exceed 64. If this condition is not satisfied, that port behaves as a soft zone member.
Zoning is hardware enforced on a switch port if the sum of the logged-in devices plus the devices zoned
with devices on that port is 64 or less. If a port exceeds this sum, that port behaves as a soft zone member,
which means the zone can automatically discover and communicate freely with all other member of the
same zone. The port continues to behave as a soft zone member until the sum of logged-in and zoned
devices falls back to 64, and the port is reset.
34
Page 35

Aliases
A zone can be a component of more than one zone set. Several zone sets can be defined for a fabric, but
only one zone set can be active at one time. The active zone set determines the zoning of the fabric.
Membership in a zone can be defined by switch domain ID and port number, device FCID, or device
WWN.
• WWN entries define zone membership by the World Wide Name of the attached device. With this
membership method, you can move WWN member devices to different switch ports in different zones
without having to edit the member entry as you would with a domain ID/port number member.
Furthermore, unlike FCID members, WWN zone members are not affected by changes in the fabric
that could change the Fibre Channel address of an attached device.
• FCID entries define zone membership by the Fibre Channel address of the attached device. With this
membership method you can replace a device on the same port without having to edit the member
entry as you would with a WWN member.
• Domain ID/Port number entries define zone membership by switch domain ID and port number. All
devices attached to the specified port become members of the zone. The specified port must be an
F_Port or an FL_Port.
To make it easier to add a group of ports or devices to one or more zones, you can create an alias. An
alias is a named set of ports or devices that are grouped together for convenience. Unlike a zone, an alias
imposes no communication restrictions between its members. You can add an alias to one or more zones.
However, you cannot add a zone to an alias, nor can an alias be a member of another alias.
zone sets
A zone set is a named group of zones. A zone can be a member of more than one zone set. Each switch
in the fabric maintains its own zoning database containing one or more zone sets. This zoning database
resides in non-volatile or permanent memory and is therefore retained after a reset. See ”Configured
Zonesets data window” (page 34) for information about displaying the zoning database.
Zones that are currently not in a zone set are considered to be part of the orphan zone set. The orphan
zone set is not an actual zone set, but rather a way of displaying the zones that are not currently in a zone
set.
To apply zoning to a fabric, choose a zone set and activate it. When you activate a zone set, the switch
distributes that zone set and its zones, excluding aliases, to every switch in the fabric. This zone set is
known as the active zone set. See ”Active Zoneset data window” (page 33) for information about
displaying the active zone set.
Zoning database
Each switch has its own zoning database. The zoning database is made up of all aliases, zones, and zone
sets that have been created on the switch or received from other switches. The switch maintains two copies
of the inactive zoning database: one copy is maintained in temporary memory for editing purposes; the
second copy is maintained in permanent memory. Zoning database edits are made on an individual
switch basis and are not propagated to other switches in the fabric when saved.
The Merge Auto Save parameter determines whether changes to the active zone set that a switch receives
from another switch in the fabric will be saved to permanent memory on that switch. See ”Configuring the
zoning database” (page 39) for information about zoning configuration.
Viewing zoning limits and properties
Zoning limits vary depending on the firmware installed on the switch:
• MaxZoneSets—The maximum number of zone sets that can be configured on the switch.
• MaxZones—The maximum number of zones that can be configured on the switch, including orphan
zones.
• MaxAliases—The maximum number of aliases that can be configured on the switch.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 35
Page 36

• MaxTotalMembers—The maximum number of zone and alias members that can be stored in the
switch’s zoning database. Each instance of a zone member or alias member counts toward this
maximum.
• MaxZonesInZoneSets—The maximum number of zone linkages to zone sets that can be configured on
the switch. A linkage is configured every time a zone is added to a zone set.
• MaxMembersPerZone—The maximum number of zone members that can be added to any zone on the
switch. When added to a zone, an alias is considered to be a zone member.
• MaxMembersPerAlias—The maximum number of zone members that can be added to any alias on the
switch.
To view zoning properties and limits on a switch:
1. On the faceplate display, select Zoning > Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog box.
2. Choose one of the following options:
• View the zoning properties/limits located directly below the zoning tool bar (Figure 18).
• In the zone sets tree (left pane), right-click the Zone Sets entry at the top of the tree, and then select
Properties.
• In the zone sets tree (left windowpane), select the zone sets entry at the top of the tree, and then
select Edit > Properties from the menu bar.
3. When you have finished viewing the zoning properties information, click OK to close the Properties
dialog box.
Managing the zoning database
The zoning database is managed using the following options:
• Editing the zoning database, page 36
• Options for resolving zoning, page 39
• Configuring the zoning database, page 39
• Saving and restoring the zoning database to a file, page 40
• Restoring the zoning database from a file, page 40
• Restoring the default zoning database, page 40
• Removing all zone and zone set definitions, page 41
Editing the zoning database
Use the Edit Zoning dialog box (Figure 18) to edit the zoning database of a particular switch or stack. To
open the Edit Zoning dialog box:
1. Select a switch or a stack in the fabric tree.
2. Select Zoning > Edit Zoning.
3. If you selected a stack and the zoning database is not identical on all switches in the stack, choose a
switch from the Select Source Switch list. Changes that you make to this switch are distributed to the
other switches in the stack.
4. Click OK.
36
Page 37

Figure 18 Edit Zoning dialog box
To apply zoning to a fabric, choose a zone set and activate it. When you activate a zone set, the switch
distributes that zone set and its zones, excluding aliases, to every switch in the fabric. This zone set is then
known as the active zone set.
Changes can only be made to inactive zone sets. These are stored in flash (non-volatile) memory and
retained after any switch reset. You must configure an inactive zone set to your needs and then activate that
updated zone set to apply the changes to the fabric. When you activate a zone set, the switch distributes
that zone set to the temporary zoning database on every switch in the fabric. However, in addition to the
merged active zone set, each switch maintains its own original zone set in its zoning database. However,
only one zone set can be active at one time.
NOTE: If the Merge Auto Save parameter is enabled on the Zoning Configuration dialog box, then every
time the active zone set changes, the switch will copy it into an inactive zone set stored on the switch. To
conveniently apply the changes to the active zone set, you can edit the copy of the active zone set, and
then activate the updated copy. The edited copy then becomes the active zone set.
The Edit Zoning dialog box has a Zone Sets tree on the left and a Port/Device (or members) tree on the
right. Both trees use display conventions similar to those used by the fabric tree for expanding and
contracting zone sets, zones, and ports. An expanded port shows the port Fibre Channel address; an
expanded address shows the port World Wide Name. You can select zone sets, zones, and ports in any
one of the following ways:
• Click a zone, zone set, or port icon.
• Right-click to select a zone set or zone, and then open the corresponding popup menu.
• Press and hold down the Shift key while clicking several consecutive icons.
• Press and hold down the Control key while clicking several non-consecutive icons.
Using tool bar buttons, popup menus, or the drag-and-drop method, you can create and manage zone sets
and zones in the zoning database. Table 6 describes the zoning tool bar operations.
To create and manage zone sets:
1. Use the Edit Zoning dialog box to define zoning changes, and then click Apply to open the Error Check
dialog box.
2. Click Error Check to have QuickTools check for zoning conflicts, such as empty zones, aliases, or zone
sets, and zones with non-domain ID/port number membership.
3. Click Save Zoning to implement the changes.
4. Click Close to close the Error Check dialog box.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 37
Page 38
5. On the Edit Zoning dialog box, click Close to close the Edit Zoning dialog box.
Table 6 Edit Zoning dialog box tool bar
Button Description
Create Zone Set button—Creates a new zone set
Create Zone button—Creates a new zone
Create Alias button—Creates another name for a set of
objects
Add Member button—Adds selected port/device to a zone
Remove Member button—Deletes the selected zone from a
zone set, or deletes the selected port/device from a zone
Copy button—Copies selected zoning items to the clipboard
Paste button—Pastes clipboard items in selected zoning
item, where applicable
Table 7 Port/Device icons
Icon Description
Switch port icon—When not logged in
Switch port icon—When logged in
NL_Port (loop) device icon—When logged in to fabric
NL_Port (loop) device icon—When not logged in to fabric
38
Page 39
Table 7 Port/Device icons
Icon Description
Options for resolving zoning
The Resolving Zoning options enable you to manage the active, configured, and merged zone sets in the
zoning database. To access the Resolving Zoning dialog box options, open the faceplate display, and then
select Zoning > Resolve Zoning.
• Capture Active Zoning—The Capture Active Zoning option copies the active zone set to the configured
zone set.
• Restore Configured Zoning—The Restore Configured Zoning option reverts back to the previously saved
configured zone set.
• Capture Merged Zoning—The Capture Merged Zoning option saves the merged zone set into the
configured zone set.
• View Merged/Configured Differences—The View Merged/Configured Differences option opens a
dialog box to display the Merged and Configured zone sets in split panes. The items in the Merged
pane but not in the Configured pane are shown in red and are not persistent after a switch reset. The
items in the Configured pane but not in the Merged pane are shown in green and are persistent after a
switch reset. The bottom pane shows a summary description of the differences between the Merged
and Configured zone sets.
N_Port device icon—When logged in to fabric
N_Port device icon—When not logged in to fabric
Configuring the zoning database
Use the Zoning Config dialog box (Figure 19) to change the Merge Auto Save, Default Zone, and Discard
Inactive configuration parameters. To open the Zoning Config dialog box, open the Zoning menu and
select Edit Zoning Config. After making the changes, click OK to put the new values into effect.
Figure 19 Zoning Config dialog box
Merge Auto Save
The Merge Auto Save parameter determines whether changes to the active zone set that a switch receives
from other switches in the fabric will be saved to the zoning database on that switch. Changes are saved
when an updated zone set is activated. Zoning changes are always saved to temporary memory.
• If Merge Auto Save is enabled, the switch firmware saves changes to the active zone set in temporary
memory and to the zoning database.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 39
Page 40
• If Merge Auto Save is disabled, changes to the active zone set are stored only in temporary memory,
which is cleared when the switch is reset.
NOTE: Disabling the Merge Auto Save parameter can be useful to prevent the propagation of zoning
information when experimenting with different zoning schemes. However, leaving the Merge Auto Save
parameter disabled can disrupt device configurations should a switch have to be reset. For this reason, the
Merge Auto Save parameter should be enabled in a production environment.
Default Zone
The Default Zone parameter enables (Allow) or disables (Deny) communication among ports/devices that
are not defined in the active zone set or when there is no active zone set. This parameter must have the
same value throughout the fabric. However, the Default Zone parameter is not automatically distributed
throughout the fabric and must be configured to the same state in every switch in the fabric.
Discard Inactive
The Discard Inactive parameter automatically removes inactive zones and zone sets when a zone set is
activated or deactivated from a remote switch.
Saving and restoring the zoning database to a file
You can save the zoning database to an XML file, restore the saved database or the default zoning (which
clears the switch of all definitions). You can also remove all zones and zone set definitions.
Saving the zoning database to a file
To save a zoning database to an XML file:
1. Select Zoning > Edit Zoning.
2. In the Edit Zoning dialog box, select File > Save As.
3. In the Save dialog box, enter a file name for the database file.
4. Click Save to save the zoning file.
Restoring the zoning database from a file
To restore the zoning database from an XML file:
CAUTION: Restoring the zoning database from a file will replace the current zoning database on the
switch.
1. Select Zoning > Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning window.
2. Select File > Open File.
A popup window prompts you to select an XML zoning database file.
3. Select a file and then click Open.
Restoring the default zoning database
Restoring the default zoning clears the switch of all zoning definitions.
NOTE: This command will deactivate the active zone set.
To restore the default zoning database:
1. Select Zoning > Restore Default Zoning.
2. Click OK to confirm that you want to restore default zoning and save changes to the zoning database.
40
Page 41
Removing all zone and zone set definitions
To remove all zone and zone set definitions, choose one of the following options:
• Select Edit > Clear Zoning. In the Removes All dialog box, and then click Yes to confirm that you want
to delete all zones and zone sets.
• Right-click the Zone Sets heading at the top of the Zone Sets tree, and then select Clear Zoning from the
popup menu. Click Yes to confirm that you want to delete all zone sets and zones.
Managing zone sets
Zoning a fabric involves creating a zone set, creating zones as zone set members, then adding devices as
zone members. The zoning database supports multiple zone sets to serve the different security and access
needs of your storage area network, but only one zone set can be active at one time.
NOTE: Changes that you make to the zoning database are limited to the managed switch and do not
propagate to the rest of the fabric. To distribute changes to configured zone sets fabric wide, you must edit
the zoning databases on the individual switches.
Creating a zone set
To create a zone set:
1. Open the Zoning menu and select Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog box.
2. Open the Edit menu and select Create Zoneset to open the Create Zoneset dialog box.
3. Enter a name for the zone set, and then click OK. The new zone set name is displayed in the Zonesets
dialog box.
A zone set name must begin with a letter and be no longer than 64 characters. Valid characters are
0–9, A–Z, a–z, _, -, ^, and $.
4. Choose one of the following options to create new zones in a zone set:
• Right-click a zone set and select Create A Zone from the popup menu. In the Create a Zone dialog
box, enter a name for the new zone, and then click OK. The new zone name is displayed in the
Zonesets dialog box.
• Copy an existing zone by dragging a zone into the new zone set. See ”Copying a zone to a zone
set” (page 43).
5. Click Apply to save changes to the zoning database.
Activating and deactivating a zone set
You must activate a zone set to apply its zoning definitions to the fabric. When you activate a zone set, the
switch distributes that zone set to the temporary zoning database on every switch in the fabric. Only one
zone set can be active at one time.
The purpose of the deactivate function is to suspend all fabric zoning which results in free communication
fabric-wide (when Default Zone is set to Allow) or no communication (when Default Zone is set to Deny). It
is not necessary to deactivate the active zone set before activating a new one.
To activate a zone set, open the Zoning menu and select Activate Zoneset to open the Activate Zoneset
dialog box. Select a zone set from the Select Zoneset drop-down list, and click Activate.
To deactivate the active zone set, open the Zoning menu, select Deactivate Zoneset. Acknowledge the
warning about traffic disruption, and click Yes to confirm that you want to deactivate the active zone set.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 41
Page 42

Renaming a zone set
To rename a zone set:
1. In the Zone Sets tree of the Edit Zoning dialog box, click the zone set to be renamed.
2. Open the Edit menu and select Rename.
3. In the Rename Zoneset dialog box, enter a new name for the zone set.
4. Click OK.
Removing a zone set
Removing a zone set from the database affects the member zones in the following ways.
• Member zones that are members of other zone sets are not affected.
• Zones that are currently not in a zone set are considered to be part of the orphan zone set. The orphan
zone set is not an actual zone set, but rather a way of displaying the zones that are not currently in a
zone set.
To remove a zone set:
1. Select Zoning > Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog box.
2. In the Zone Sets tree, select the zone set to be removed.
3. Select Edit > Remove to remove the zone set.
4. Click Apply to save changes to the zoning database.
Alternatively, you may right-click and use shortcut menus to remove a zone set from the database.
Managing zones
Changes that you make to the zoning database are limited to the managed switch and do not propagate
to the rest of the fabric. To distribute changes to configured zone sets fabric wide, you must edit the zoning
databases on the individual switches.
Creating a zone in a zone set
To create a zone in a zone set:
1. Select Zoning > Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog box.
2. Select a zone set.
3. Select Edit > Create a Zone.
4. In the Create a Zone dialog box, enter a name for the new zone, and then click OK. A zone name must
begin with a letter and be no longer than 64 characters. Valid characters are 0–9, A–Z, a–z, _, ^, $,
and -.
The new zone name is displayed in the Zonesets dialog box.
5. Click OK.
NOTE: If you enter the name of a zone that already exists in the database, the QuickTools web applet
asks if you would like to add that zone and its membership to the zone set.
6. To add switch ports or attached devices to the zone, choose one of the following options:
• In the Zone Sets tree, select the zone set. In the graphic window, select the port to add to the zone.
Select Edit > Add Members.
• Select a port by switch port number, Fibre Channel address, or WWN in the Port/Device tree, and
drag it into the zone.
• Select a port by switch port number, Fibre Channel address, or WWN in the Port/Device tree.
Right-click the zone and select Add Zone Members from the popup menu.
7. Click Apply to save the changes to the zoning database.
42
Page 43

Copying a zone to a zone set
To copy an existing zone and its membership from one zone set to another:
1. In the faceplate display, select Zoning > Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog box.
2. In the Zone Sets tree, select the zone to copy, and drag it to the chosen zone set.
3. Click OK to display the Error Check dialog box.
4. Click Error Check to have the application check for zoning conflicts, such as empty zones, aliases, or
zone sets.
5. Click Save Zoning to implement the changes.
6. Click Close to close the Error Check dialog box.
Adding zone members
You can zone a port/device by switch domain ID and port number, device port Fibre Channel address, or
the device port WWN. Adding a port/device to a zone affects every zone set in which that zone is a
member. To add ports/devices to a zone:
1. Select Zoning > Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog box.
2. Choose one of the following options to add the port/device:
• Select a port/device in the Port/Device tree, and drag it into the zone. To select multiple
ports/devices, press and hold down the Control key while selecting and dragging.
• Select a port/device in the Port/Device tree. To select multiple ports/devices, press and hold down
the Control key while selecting. Select a zone set in the left pane. Select Edit > Add Members.
• Select a port/device in the Port/Device tree. To select multiple ports/devices, press and hold down
the Control key while selecting. Select a zone set in the left pane, and then click Insert.
If the port/device you want to add is not in the Port/Device tree, you can add it by doing the following:
a. Right-click the selected zone.
b. Select Edit > Create Members.
c. Select the WWN, Domain/Port, or First Port Address option.
d. Enter the hexadecimal value for the port/device according to the option selected: 16 digits for a
WWN member, 4 digits for a Domain/ Port member (in format: DDPP), or a 6-digit Fibre Channel
Address for a First Port Address member (in format: DDPPAA), where DD=domain ID, PP=port
number, and AA=AL_PA.
3. Click OK to display the Error Check dialog box.
4. Click Error Check to have the application check for zoning conflicts, such as empty zones, aliases, or
zone sets.
5. Click Save Zoning to implement the changes.
6. Click Close to close the Error Check dialog box.
7. Click Close to close the Edit Zoning dialog box.
NOTE: Domain ID conflicts can result in automatic reassignment of switch domain IDs. These
reassignments are not reflected in zones that use a domain ID/port number pair to define their
membership. Be sure to reconfigure zones that are affected by a domain ID change.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 43
Page 44

Renaming a zone
To rename a zone:
1. In the Zone Sets tree of the Edit Zoning dialog box, click the zone to be renamed.
2. Select Edit > Rename.
3. In the Rename Zone dialog box, enter a new name for the zone.
4. Click OK.
5. Click Apply in the Edit Zoning dialog box to save the change.
6. Click Close to close the Edit Zoning dialog box.
Removing a zone member
Removing a zone member will affect every zone and zone set in which that zone is a member. To remove
a member from a zone:
1. In the Edit Zoning dialog box, select the zone member to be removed.
2. Select Edit > Remove.
3. Click Yes in the Remove dialog box to save the change.
4. Click Apply in the Edit Zoning dialog box to save the change.
5. Click Close to close the Edit Zoning dialog box.
Removing a zone from a zone set
To remove a zone from a zone set:
1. In the Edit Zoning dialog box, select the zone to be removed.
The selected zone will be removed from that zone set only.
2. Select Edit > Remove.
3. Click Yes in the Remove dialog box to save the change.
4. Click Apply in the Edit Zoning dialog box to save the change.
5. Click Close to close the Edit Zoning dialog box.
Removing a zone from all zone sets
To remove a zone from all zone sets:
1. In the Edit Zoning dialog box, select the zone to be removed.
2. Select Edit > Delete Zone.
3. Click Yes in the Remove dialog box to save the change.
4. Click Apply in the Edit Zoning dialog box to save the change.
5. Click Close to close the Edit Zoning dialog box.
Managing aliases
An alias is a collection of objects that can be zoned together. An alias is not a zone, and cannot have a
zone or another alias as a member.
NOTE: Changes that you make to the zoning database are limited to the managed switch and do not
propagate to the rest of the fabric. To distribute changes to configured zone sets fabric wide, you must edit
the zoning databases on the individual switches. You will not see aliases in the active zone set.
44
Page 45

Creating an alias
To create an alias:
1. Open the Zoning menu, and select Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog box.
2. Select Edit > Create Alias to open the Create Alias dialog box.
3. Enter a name for the alias, and click OK. The alias name is displayed in the Zonesets dialog box. An
alias name must begin with a letter and be no longer than 64 characters. Valid characters are 0–9,
A–Z, a–z, _, $, ^, and -.
4. Click Apply to save the alias name to the zoning database.
Adding a member to an alias
You can add a port/device to an alias by domain ID and port number, device port Fibre Channel address,
or the device port WWN. To add ports/devices to an alias:
1. Select Zoning > Edit Zoning to open the Edit Zoning dialog box.
2. Choose one of the following options to add the port/device:
• Select a port/device in the Port/Device tree, and drag it into the alias. To select multiple
ports/devices, press and hold the Control key while selecting.
• Select a port/device in the Port/Device tree. Click an alias to select multiple ports/devices, press
and hold the Control key while selecting. Select an alias. Open the Edit menu and then select Add
Members.
• Select a port/device in the Port/Device tree. To select multiple ports/devices, press and hold the
Control key while selecting. Select an alias, and then click Insert.
3. If the port/device you want to add is not in the Port/Device tree, you can add it by doing the following:
• Right-click the selected alias.
• Select Edit > Create Members.
• Select the WWN, Domain/Port, or First Port Address option.
• Enter the hexadecimal value for the port/device according to the option selected: 16 digits for a
WWN member, 4 digits for a Domain/ Port member (DDPP), or a 6-digit Fibre Channel Address
for a First Port Address member (DDPPAA), where DD=domain ID, PP=port number, and
AA=AL_PA.
4. Click OK to add the member and save the change.
Removing an alias from all zones
To remove an alias from all zones:
1. In the Zone Sets tree in the Edit Zoning dialog box, select the alias to be removed.
2. Select Edit >Delete Alias.
3. Click Yes in the Remove dialog box.
4. Click Apply in the Edit Zoning dialog box to save the change.
5. Click Close to close the Edit Zoning dialog box.
Merging fabrics and zoning
If you join two fabrics with an inter-switch link, the active zone sets from the two fabrics attempt to merge
automatically. The fabrics may consist of a single switch or many switches already connected together. The
switches in the two fabrics attempt to create a new active zone set containing the union of each fabric's
active zone set. The propagation of zoning information affects only the active zone set, not the configured
zone sets, unless Merge Auto Save is turned on.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 45
Page 46

Zone merge failure
If a zone merge is unsuccessful, the inter-switch links between the fabrics will be isolated due to the zone
merge failure, which will generate an alarm. The reason for the E_Port isolation can also be determined by
viewing the port information. See Table 18 for more information.
A zone merge will fail if the two active zone sets have member zones with identical names but differ in
membership or type. For example, consider Fabric A and Fabric B each with a zone named ZN1 in its
active zone set. Fabric A ZN1 contains a member specified by Domain ID 1 and Port 1; Fabric B ZN1
contains a member specified by Domain ID 1 and Port 2. In this case, the merge will fail because the two
zones have the same name, but different membership.
A zone merge may also fail if the merged zones/members exceed the maximum zoning limits. See
”Viewing zoning limits and properties” (page 35) for more information on zoning limits.
Zone merge failure recovery
When a zone merge failure occurs, the conflict that caused the failure must be resolved. You can correct a
failure due to a zone conflict by deactivating one of the active zone sets or by editing the conflicting zones
so that their membership is the same. You can deactivate the active zone set on one fabric if the active
zone set on the other fabric accurately defines your zoning needs. If not, you must edit the zone
memberships, and reactivate the zone sets. After correcting the zone membership, reset the isolated ports
to allow the fabrics to join.
NOTE: If you deactivate the active zone set in one fabric and the Merge Auto Save parameter is enabled,
the active zone set from the second fabric will propagate to the first fabric and replace all zones with
matching names in the configured zone sets.
For more information about adding and removing zone members, see ”Managing zones” (page 42). For
more information about resetting a port, see ”Resetting a port” (page 102).
46
Page 47

3 Managing Switches
This section describes the tasks that manage switches in the fabric.
Switch data window
The Switch data window (Figure 20) displays the current network and switch information for the selected
switch. To open the Switch data window, click the Switch tab below the data window.
Figure 20 Switch data window
Switch data window buttons
Information in the Switch data window is grouped and accessed by the Summary, Status, Network, User
Login, Firmware, Services, Zones/Security, and Advanced buttons. Click a button to display the switch
information for the selected data category (Figure 20). The Switch data window buttons are identified in
Figure 21.
Figure 21 Switch data window buttons
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 47
Page 48
The Switch data window fields are described in Table 8.
Table 8 Switch data window fields
Field Description
Summary Group
Switch Type Switch model
First Port Address Switch Fibre Channel address
World Wide Name Switch world wide name
Serial Number Number assigned to each chassis.
Reason for Status The reason for the operational state.
Vendor Switch manufacturer
MAC Address Media Access Control address
Negotiated Domain ID The domain ID currently being used by the fabric
Configured Domain ID The domain ID, defined by network administrator
Domain ID Lock Domain ID lock status. Prevents (True) or permits (False)
dynamic domain ID reassignment.
Number of Ports Number of physical ports on the switch
Operational State Switch operational state: Online, Offline, Diagnostic, Down
Administrative State Current switch administrative state
Configured Admin State Administrative state that is stored in the switch configuration
Beacon Status Beacon status. Switch LEDs are blinking (On) or not blinking
(Off).
Status Group
Operational State Switch operational state: Online, Offline, Diagnostic, Down
Administrative State Current switch administrative state
Configured Admin State Administrative state that is stored in the switch configuration
Beacon Status Beacon status. Switch LEDs are blinking (On) or not blinking
(Off).
Reason for Status The reason for the operational state.
Temperature Internal switch temperature °C
Fan 1 Status Fan 1 status (dual-power supply model only)
Fan 2 Status Fan 2 status (dual-power supply model only)
Power Supply 1 Status Power supply 1 status
Power Supply 2 Status Power supply 2 status (dual-power supply model only)
Temperature Failure Port
Shutdown
Warning Temperature Non-configurable temperature threshold, above which a
Failure Temperature Non-configurable temperature threshold, above which a
48
Non-configurable (always enabled for this switch). All ports
are shut down when the switch temperature exceeds the
Failure Temperature.
warning condition alarm is generated.
failure condition alarm is generated.
Page 49
Table 8 Switch data window fields (Continued)
Field Description
POST Status The current diagnostic state of the switch.
POST Fault Code The code value for the last recorded diagnostic test result
recorded on the switch.
Test Status The current diagnostic test status of switch.
Test Fault Code The code value for the last recorded diagnostic test status
recorded on the switch.
Network Group
IPv4 Enabled Internet Protocol version 4 Enabled or Disabled
IPv4 Address Internet Protocol version 4 address
IPv4 Subnet Mask Mask that determines the IP address subnet
IPv4 Gateway Gateway address
IPv6 Enabled Internet Protocol version 6 Enabled or Disabled
IPv6 Address Mask that determines the IP address subnet
IPv6 Gateway Gateway address
SNMP Enabled SNMP Enabled or Disabled
SNMP v3 Security Enabled SNMP v3 Security Enabled or Disabled
Broadcast Support Broadcast support status. Broadcast support is enabled
(default) or disabled.
NTP Client Enabled NTP Client Enabled or Disabled. If Enabled, this parameter
enables switches to synchronize their time to a centralized
server.
NTP Server Address The IP address of the centralized NTP server. Ethernet
connection to NTP server is required.
DNS Enabled Domain Name Service Enabled or Disabled
Configured Local Hostname The requested hostname for the switch. If a fully qualified
domain name is given, the domain suffix is used as the first
suffix in the DNS search list for DNS lookups performed by
the switch.
Assigned Hostname The actual hostname for the switch. If a fully qualified
domain name is given, the domain suffix is used as the first
suffix in the DNS search list for DNS lookups performed by
the switch.
IPv6 Assigned Address
(1–20)
The set of IPv6 addresses assigned by DHCP v6, NDP, or
the switch administrator.
User Login Group
User Name Account name
Login Level Authority level of the user name
Super User Super user privileges Enabled or Disabled.
UserAuthentication Enabled Enforcement of account names and authority (always True)
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 49
Page 50
Table 8 Switch data window fields (Continued)
Field Description
Firmware Group
Firmware Version Active firmware version
Inactive Firmware Version This field does not apply to this switch
Pending Firmware Version Firmware version that will be activated at the next reset
PROM/Flasher Version Installed version of PROM firmware
Services Group
NTP Client Enabled Enables switches to synchronize their time to a centralized
server. Enabled or Disabled.
NTP Server Address The IP address of the centralized NTP server. Ethernet
connection to NTP server is required.
FDMI Enable Fabric Device Management Interface status. If enabled,
device information can be obtained, managed, and saved
through the fabric using Name Service Management Server
functions. If FDMI is Enabled on the entry switch, QuickTools
reports all FDMI information reported by the entry switch.
FDMI HBA Entry Limit Maximum number of HBAs that can be registered with a
switch.
Embedded GUI Enabled QuickTools web applet status. Indicates whether the web
applet on the switch is Enabled or Disabled.
Inactivity Timeout Number of minutes the switch waits before terminating an
idle command line interface (CLI) session. Zero (0) disables
the timeout threshold.
GUI Mgmt Enabled Web applet status. If Disabled, the switch cannot be
managed using the web applet.
Telnet Enabled Telnet client status Enabled or Disabled.
SSH Enabled Secure Shell status. If Enabled, an encrypted data path is
provided for command line interface sessions.
SSL Enabled Secure Sockets Layer status. If enabled, encryption for
QuickTools web applet, Enterprise Fabric Management
Suite, and CIM sessions is provided.
CIM Enabled Common Interface Model status. The CIM agent is based on
the Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) Storage
Management Initiative Specification (SMI-S), which is the
standard for SAN management in a heterogeneous
environment.
FTP Enabled FTP status Enabled or Disabled.
Management Server
Management server status Enabled or Disabled.
Enabled
SNMP Enabled SNMP status, Enabled or Disabled.
Call Home Enabled Call Home status. If enabled and configured, switches can
50
send alerts to pagers and email. Users can configure the
type of events and where the alerts are sent.
Page 51
Table 8 Switch data window fields (Continued)
Field Description
Zones/Security Group
Interop Mode Standard
Legacy Address Format None
Merge Auto Save If Enabled, any zoning updates from the fabric will be saved
in permanent (non-volatile) memory as well as temporary
memory. If Disabled, any zoning updates from the fabric will
be saved only in temporary memory and will be lost after a
switch reset.
Default Zone Enables or disables communication between ports and
devices not defined in the active zone set, or when there is
no active zone set.
Discard Inactive Automatically removes the previously active zone set when a
zone set is activated on a switch.
Implicit Hard Zoning Introduces hardware enforcement of zoning regardless of
type. All zones and all supported zone member types will
have hardware enforcement.
Security Auto Save Enable to automatically save security settings to permanent
memory on the switch.
Security Fabric Binding
Enabled
If Enabled, the expected domain ID of a switch is required
before the switch can be attached to the fabric.
Advanced Group
R_A_TOV Resource allocation timeout value (in milliseconds)
E_D_TOV Error detect timeout value (in milliseconds)
Number of Donor Groups Total number of donor port groups. A donor group is a set
of ports on a switch that can donate buffer credits to one
another.
Inactivity Timeout Number of minutes the switch waits before terminating an
idle command line interface session. Zero (0) disables the
time out threshold.
Interop Mode Standard
Legacy Address Format None
In-band Enabled In-band management status. Permits (True) or prevents
(False) a switch from being managed over an ISL.
Principal Switch If there is a domain ID conflict in the fabric, the switch with
the highest principal priority, or the principal switch, will
reassign any domain ID conflicts and establish the fabric.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 51
Page 52
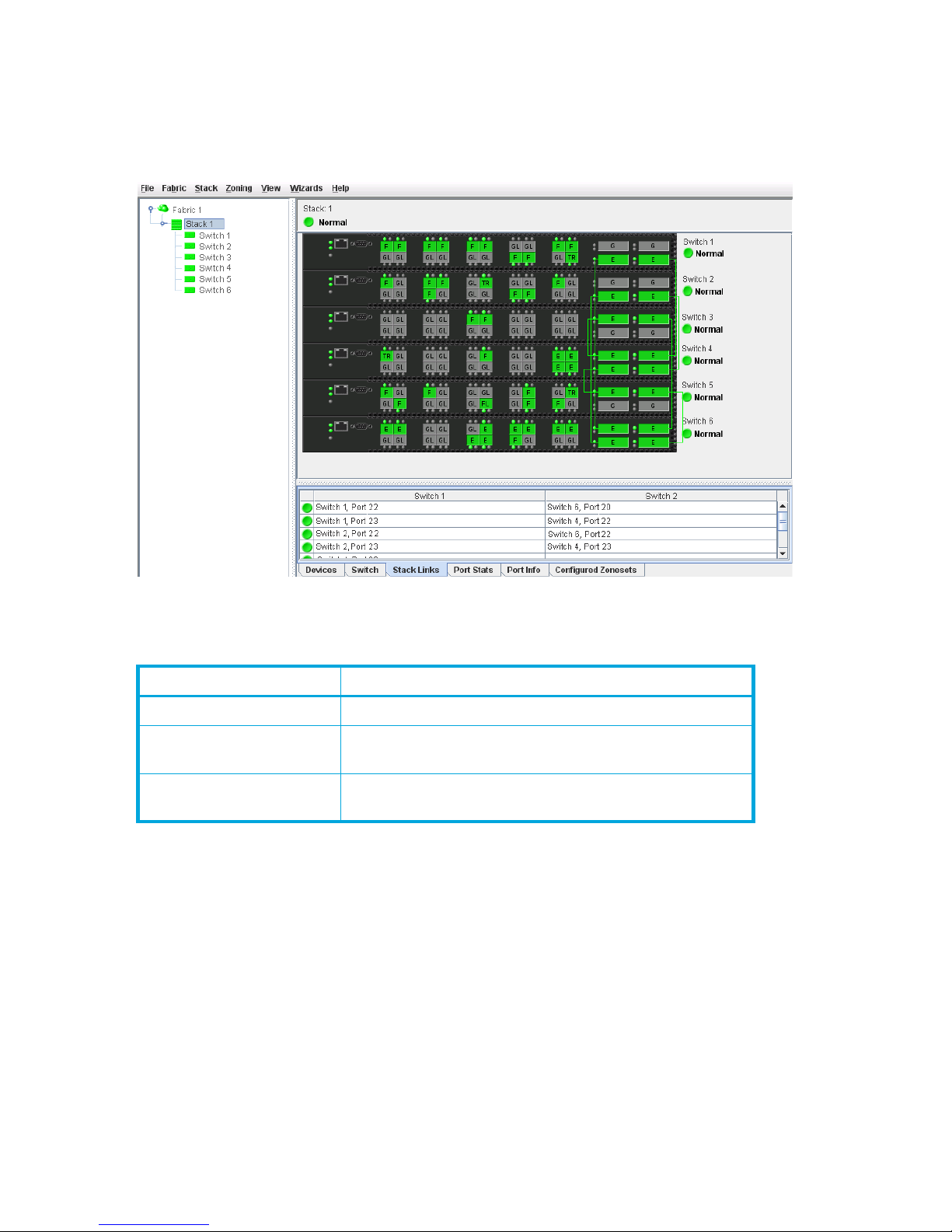
Stack Links data window
The Stack Links data window displays information about all switch links for a stack of switches in the
faceplate display. This information includes the switch names, the port number at the end of each link, and
the link status icon. To open the Stack Links data window, click a stack icon in the fabric tree, and click the
Stack Links tab below the data window in the stack faceplate display.
Figure 22 Stack Links data window
The Stack Links data window fields are described in Table 9.
Table 9 Stack Links data window
Field Description
Status Icon depicting current link status
Switch 1 The first switch discovered in the fabric. Displays the port
Switch 2 The second switch discovered in the fabric. Displays the port
Managing Switch Stacks
The QuickTools web applet recognizes switches as a stack if they are connected by their high speed
stacking ports. QuickTools will auto-detect switches connected by these 10 Gb/s or 20 Gb/s ports and
display these stacked switches as a single stack entity in the faceplate display (Figure 22).
The graphic window (upper right pane of the faceplate display) displays one faceplate image for each
switch in the stack.
In the fabric tree (left window pane), the switches in each stack are nested under the stack icon, which is
nested under the fabric icon. Expanding the fabric and stack icons in the fabric tree displays all switches in
a stack. The lock image on the fabric icon indicates that the application is communicating with the fabric
through a secure (Secure Sockets Layer) connection.
number that the ISL is currently connected to on the switch.
number that the ISL is currently connected to on the switch.
The stack dialogs are essentially the same as their corresponding switch dialogs, except that the Select
Switch for Initial Configuration pull-down menu is added to each dialog. The stack dialogs display the
information for the switch selected in the Select Switch for Initial Configuration pull-down menu. Choose
another switch in the pull-down menu to display information for that switch. After you click OK, the switch
52
Page 53

configuration that was displayed is the configuration that is applied to all other switches in the stack. The
following operations are available to configure the stack as a single entity.
Under Stack menu:
• Date/time and NTP settings. For more information, see ”Setting the date/time and enabling NTP
client” (page 58).
• Firmware load and activation. For more information, see ”Installing firmware” (page 79).
• Switch reset. For more information, see ”Resetting a switch” (page 59).
• Editing user accounts. For more information, see “”Managing user accounts” (page 55).
• SNMP configuration. For more information, see ”SNMP configuration” (page 69).
• Security Consistency Checklist. For more information, see ”Security Consistency Checklist” (page 53).
• Syslog configuration. For more information, see ”Syslog” (page 61).
Additional stack operations include the following:
• Move the selected switch up or down one position in the stack within the graphic window. To move a
switch image up, select a switch, open the Stack menu, and select Move Switch Up. To move a switch
image down, select a switch, open the Stack menu, and select Move Switch Down.
• Remove a switch from being associated with the stack if the switch is not connected to any other switch
in the fabric with an ISL connection. To remove a switch from a stack, select a switch, open the Stack
menu, and select Remove Switch.
• Remove a dead ISL connection in the stack display between two switches that is either offline or has
been physically disconnected. To remove a dead link (red), select one of the linked XPAK ports, open
the Stack menu, and select Remove Links.
• Refresh the stack to update the faceplate display with current information for all switches in the stack
• Select all ports on all switches in the stack.
Under Zoning menu:
• Edit Zoning. For more information see ”Editing the zoning database” (page 36).
• Edit Zoning Config. For more information see ”Configuring the zoning database” (page 39).
• Activate Zoning. For more information see ”Activating and deactivating a zone set” (page 41).
• Deactivate Zoning. For more information see ”Activating and deactivating a zone set” (page 41).
Security Consistency Checklist
The Security Consistency Checklist dialog box (Figure 23) enables you to view current security-related
settings, such as, firmware versions, embedded GUI, in-band management, date/time on switches. Any
changes must be made through the appropriate dialog, such as Network Properties dialog, Switch
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 53
Page 54

Properties dialog, or SNMP Properties dialog. To open the Security Consistency Checklist dialog, open the
Stack menu and select Security Consistency Checklist.
Figure 23 Security Consistency Checklist dialog box
54
Page 55
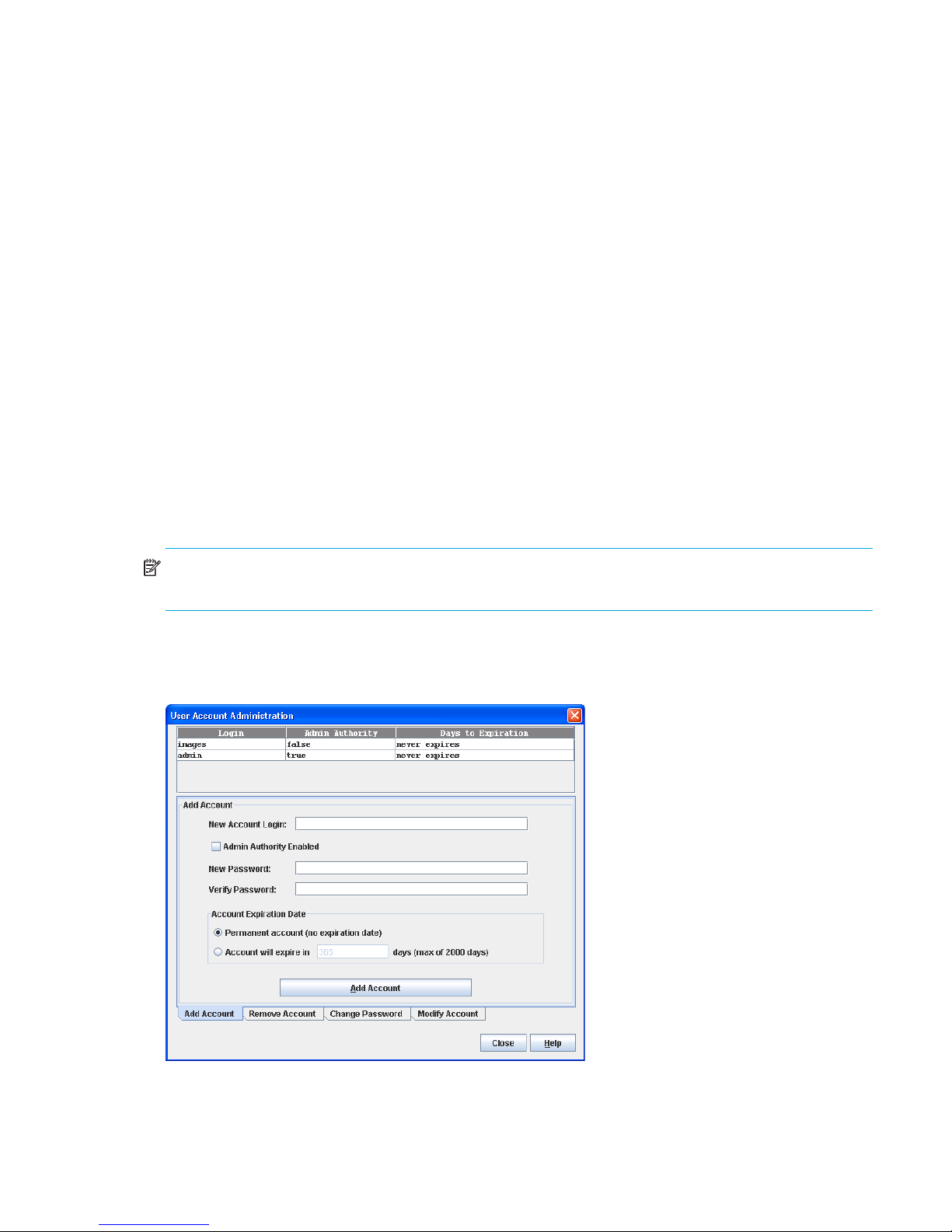
Managing user accounts
Only the Admin account can manage user accounts with the User Account Administration dialog boxes.
However, any user can modify their own password. To open a User Account Administration dialog box,
open the Switch menu and select User Accounts.
A user account consists of the following data:
• Account name or login
• Password
• Authority level
• Expiration date
Switches come from the factory with the following user accounts:
• admin—Admin authority, never expires, password is password
• images—No Admin authority, never expires, password is images,
The Admin account is the only user that can manage all user accounts with the User Account
Administration dialog boxes. The Admin account can create, remove, or modify user accounts, and
change account passwords. The Admin account can also view and modify the switch and its configuration
with QuickTools. The Admin account can not be removed.
Users with Admin authority can use QuickTools to view and modify the switch and its configuration. Users
without Admin authority are limited to viewing only the switch status and configuration.
The Images account is used to exchange files with the switch using FTP. The Images account can not be
removed.
NOTE: If the same user account exists on a switch and its RADIUS server, that user can log in with either
password, but the authority and account expiration will always come from the switch database.
Creating user accounts
A switch can have a maximum of 15 user accounts.
Figure 24 User Account Administration–Add Account dialog box
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 55
Page 56

To create a user account on a switch:
1. Select Switch > User Accounts.
2. Click the Add Account tab to open the Add Account tab page (Figure 24).
3. Enter an account name in the New Account Login field. Account names are limited to 15 characters.
The first character must be alphanumeric.
4. If the account is to have the ability to modify switch configurations, select the Admin Authority Enabled
option.
5. Enter a password in the New Password field and enter it again in the Verify Password field. A password
must have a minimum of 8 characters and no more than 20.
6. If this account is to be permanent with no expiration date, select the Permanent Account option.
Otherwise, click Account Will Expire and enter the number days in which the account will expire.
7. Click Add Account to add the newly defined account.
8. Click Close to close the User Account Administration dialog box.
Removing a user account
To remove a user account on a switch:
1. Select Switch > User Accounts.
2. Click the Remove Account tab to open the Remove Account tab page (Figure 25).
3. Select the account (Login) name from the list of accounts at the top of the dialog box.
4. Click Remove Account.
5. Click Close to close the User Account Administration dialog box.
Figure 25 User Account Administration–Remove Account dialog box
56
Page 57
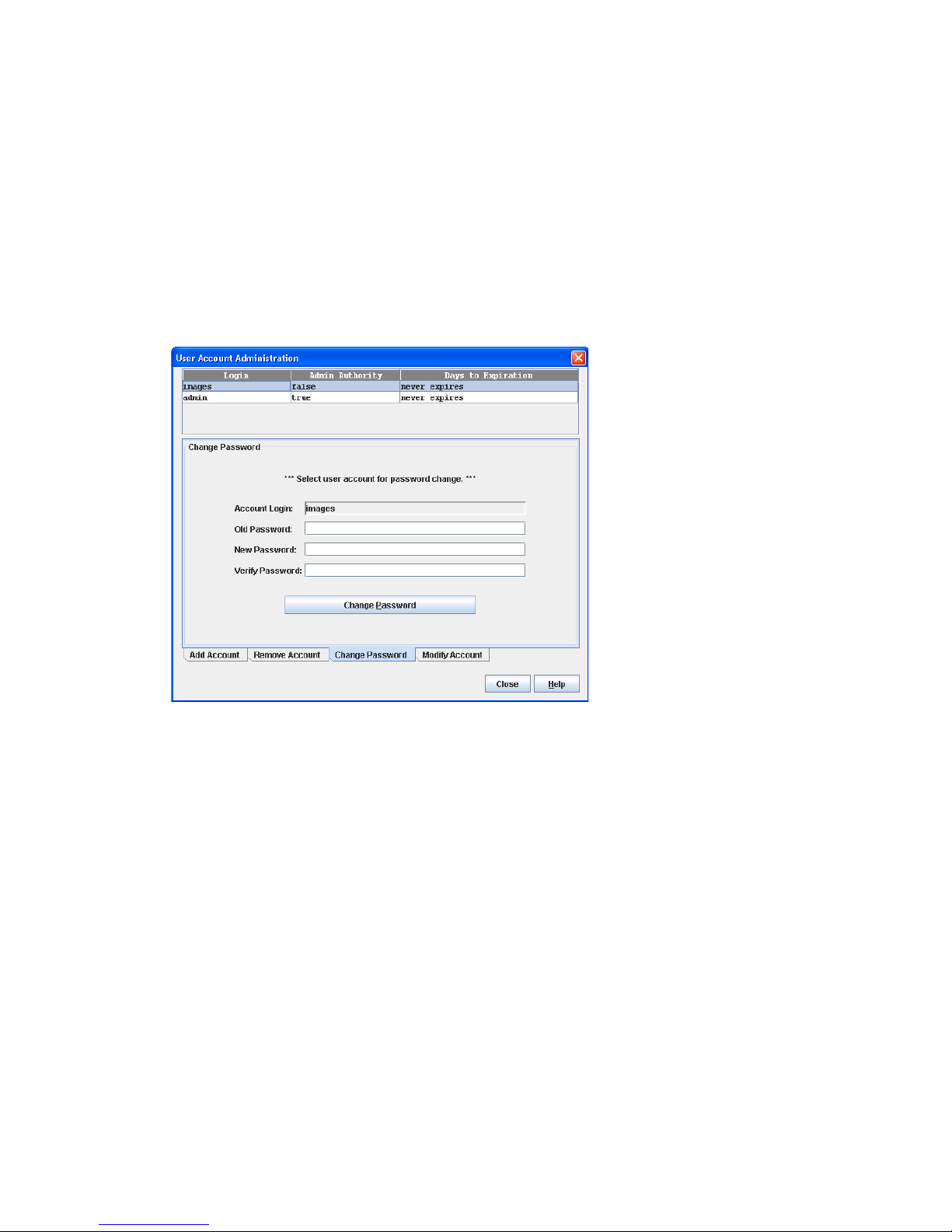
Changing a user account password
A user can change the password for their account, but only the Admin account user can change the
password for another user’s account. If the user’s original password is not known, the Admin account user
must remove the account and then add the account with the new password.
To change the password for an account on a switch:
1. Select Switch > User Accounts.
2. Click the Change Password tab to open the Change Password tab page (Figure 26).
3. Select the account (Login) name from the list of accounts at the top of the dialog box.
4. Enter the old password and the new password, and then verify the new password in the corresponding
fields.
5. Click Change Password.
6. Click Close to close the User Account Administration dialog box
Figure 26 User Account Administration–Change Password dialog box
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 57
Page 58
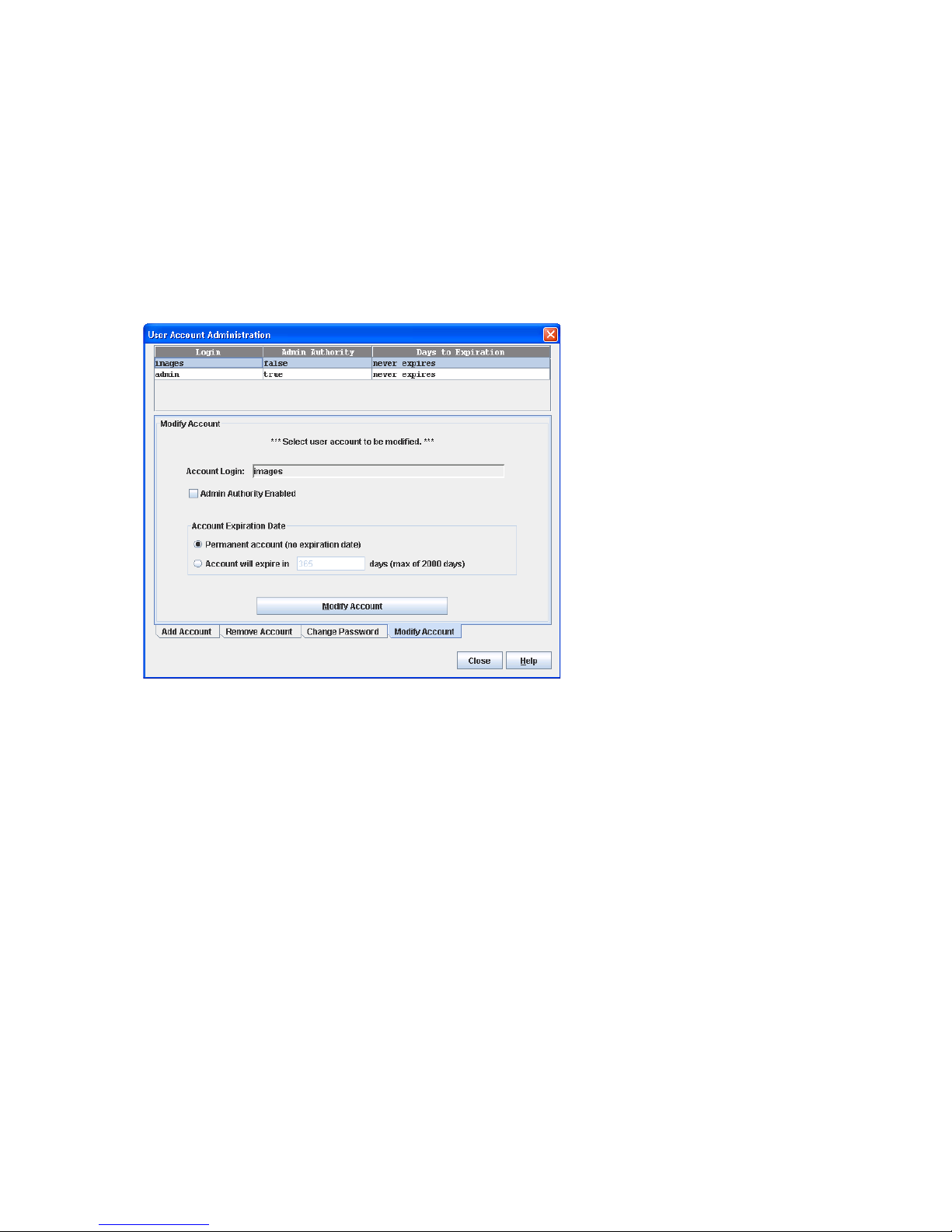
Modifying a user account
To modify a user account on a switch:
1. Select Switch > User Accounts.
2. Click the Modify Account tab in the User Account Administration dialog box to display the Modify
Account dialog box (Figure 27).
3. Select the account (login) name from the list of accounts at the top of the dialog box.
4. Select the Admin Authority Enabled option to grant admin authority to the account name.
5. Select an Account Expiration Date option (Permanent account or Account will expire in). If the account
is not to be permanent, enter the number of days until the account expires.
6. Click Modify Account to save the changes.
7. Click Close to close the User Account Administration dialog box.
Figure 27 User Account Administration–Modify Account dialog box
Paging a switch
You can use the Beacon feature to page a switch. The Beacon feature causes all Logged-In LEDs to flash,
making them easier to recognize. To page a switch, open the faceplate display and select Switch > Toggle
Beacon. To cancel the beacon, reselect Toggle Beacon.
Setting the date/time and enabling NTP client
The Date/Time dialog box enables you to manually set the date, time, and time zone on a switch, or to
enable NTP (Network Time Protocol) Client to synchronize the date and time on the switch with an NTP
server. Enabling the NTP Client, which requires an Ethernet connection to an NTP server, ensures the
consistency of date and time stamps in alarms and log entries. Although the date/time is set or displayed
in the firmware in Universal Time, when displayed in the Date/Time dialog box, the value is always in
local time.
If you select the NTP Client Enabled option (the default is deselected):
• The Date and Time areas become active and you are prevented from manually setting the date and
time on the switch
• The NTP Server Discovery and NTP Server IP Address fields become active and allow you to select a
discovery method
58
Page 59

The NTP Server Discovery and NTP Server IP Address fields become active, and allow you to select a
discovery method (Static, DHCP, DHCPv6) and to specify an IP address (IPv4 or IPv6).
Figure 28 Date/Time dialog box
To manually set the date and time on a switch:
1. Select Switch > Set Date/Time to open the Date/Time dialog box.
2. In the NTP area of the Date/Time dialog box, clear (deselect) the NTP Client Enabled option.
The fields in the Date and Time areas become active.
3. Select the month, day, year, hour, minutes, and time zone from the drop-down lists.
4. Click OK.
The new date and time take effect immediately.
To synchronize the date and time on the switch with an NTP server:
1. Select Switch > Set Date/Time.
2. In the NTP area of the Date/Time dialog box, select the NTP Client Enabled option.
The fields in the Date and Time areas become inactive.
3. Select a time zone from the Select Time Zone drop-down list.
4. Select an NTP Server Discovery option from the drop-down list.
5. Enter an NTP Server IP Address (IPv4 or IPv6).
6. Click OK.
Resetting a switch
Resetting a switch reboots the switch using the configuration parameters in memory. Depending on the
reset type, a switch reset may or may not include a Power On Self Test (POST) and/or may or may not
disrupt traffic. Table 10 describes the types of switch resets. During a Hot Reset operation, fabric services
will be unavailable for a short period (30—75 seconds, depending on switch model).
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 59
Page 60
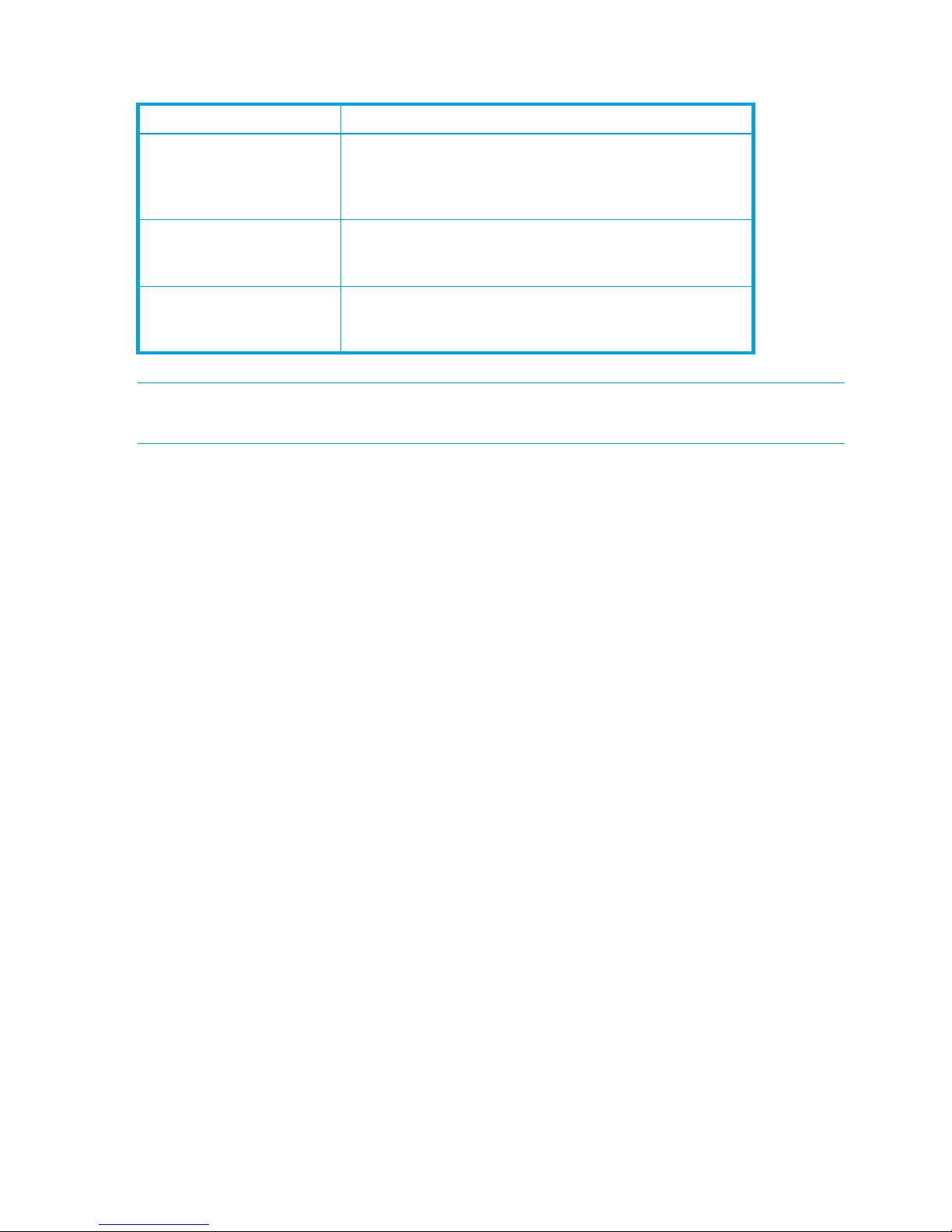
Table 10 Switch resets
Reset Type Description
Hot Reset Resets a switch without a Power On Self Test. This reset
activates the pending firmware, but does not disrupt switch
traffic. If errors are detected on a port during a hot reset, the
port is reset automatically.
Reset Resets a switch without a Power On Self Test. This reset
activates the pending firmware and it is disruptive to switch
traffic.
Hard Reset Resets a switch with a Power On Self Test. This reset
activates the pending firmware and it is disruptive to switch
traffic.
IMPORTANT: If performing a Reset or a Hard Reset, the support files, the firmware image files that have
not been unpacked, and the configuration backup files that were created on the switch will be deleted.
To reset a switch using QuickTools:
1. Select the switch to be reset from the fabric tree.
2. Select Switch > Reset Switch, and then choose one of the following options:
• Select Hot Reset to perform a hot reset.
• Select Reset to perform a standard reset.
• Select Hard Reset to perform a hard reset.
Configuring a switch
Switch configuration is divided into three areas: chassis configuration, network configuration, and SNMP
configuration.
• Chassis configuration specifies switch-wide Fibre Channel settings.
• Network configuration specifies IP and DNS settings.
• SNMP configuration specifies SNMP settings, SNMP traps, and SNMP security.
Using the configuration wizard
Use the configuration wizard to configure the IP address and password for new or replacement switches.
To start the configuration wizard, select Wizards > Configuration Wizard.
Switch properties
Use the Switch Properties dialog box to change the following switch configuration parameters:
• Domain ID and Domain ID Lock
• Syslog
• Symbolic name
• Switch administrative state
• Broadcast support
• In-band management
• Fabric Device Management Interface (FDMI)
To open the Switch Properties dialog box, choose one of the following options:
• Open the faceplate display for the switch you are configuring, and then select Switch > Switch
Properties.
60
Page 61
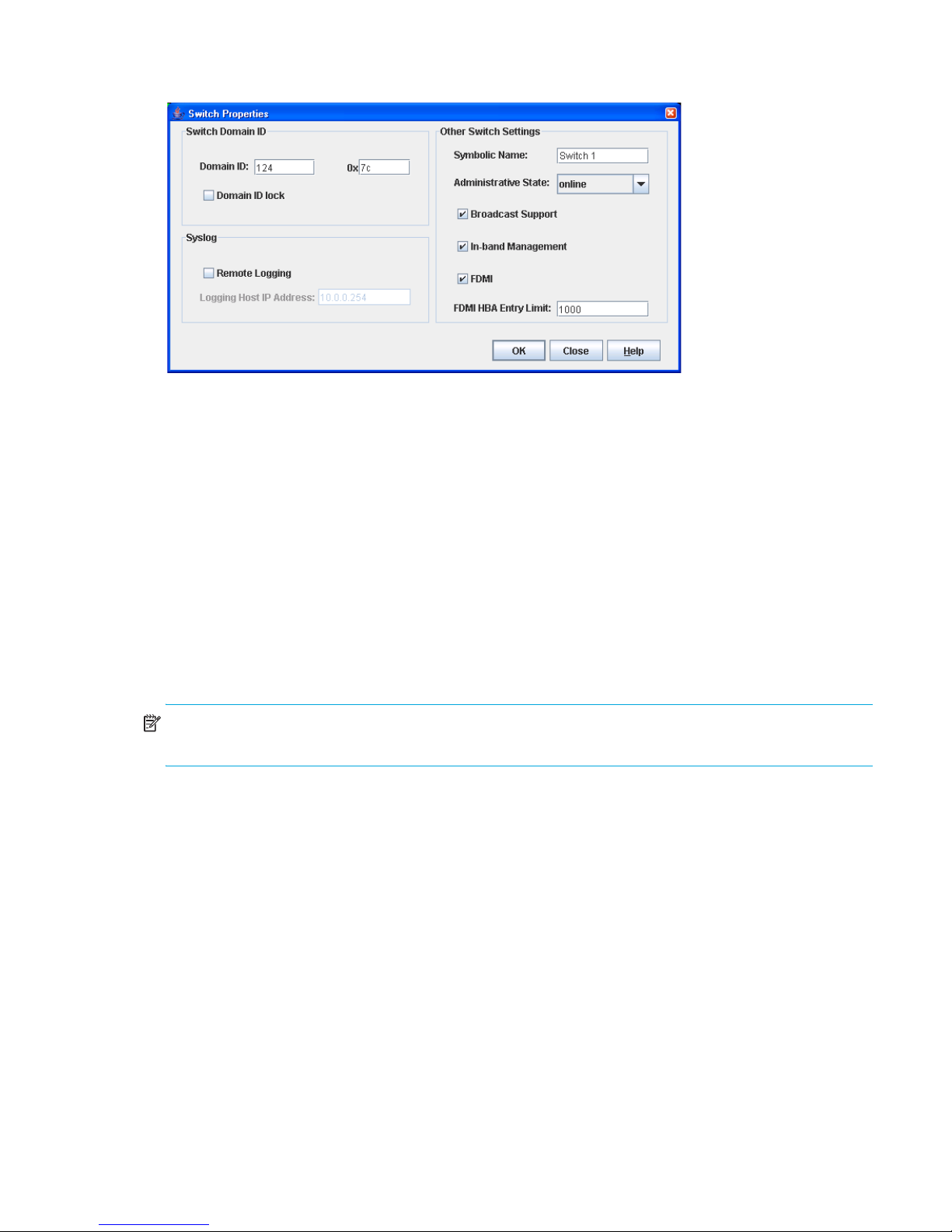
• Right-click a switch graphic in the faceplate display, and then select Switch Properties from the popup
menu.
Figure 29 Switch Properties dialog box
Domain ID and Domain ID Lock
The domain ID is a unique Fibre Channel identifier for the switch. The Fibre Channel address consists of the
domain ID, port ID, and the Arbitrated Loop Physical Address (AL_PA).
Switches come from the factory with the domain IDs unlocked. This means that if there is a domain ID
conflict in the fabric, the switch with the highest principal priority, or the principal switch, reassigns any
domain ID conflicts and establishes the fabric. If you lock the domain ID on a switch and a domain ID
conflict occurs, one of the switches is isolated as a separate fabric and the Logged-In LEDs on both switches
will flash to show the affected ports. See the HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch Command
Line Interface Guide for information about the Domain ID Lock and Principal Priority parameters.
If you connect a new switch to an existing fabric with its domain ID unlocked, and a domain conflict
occurs, the new switch is isolated as a separate fabric. However, you can remedy this by resetting the new
switch or taking it offline then back online. The principal switch reassigns the domain ID and the switch
joins the fabric.
NOTE: Domain ID reassignment is not reflected in zoning that is defined by domain ID and port number
pair. You must reconfigure zones that are affected by domain ID reassignment.
Syslog
The Syslog (Remote Logging) feature enables saving the log information to a remote host that supports the
syslog protocol. When enabled, the log entries are sent to the syslog host at the IP address that you specify
in the Logging Host IP Address field. Log entries are saved in the internal switch log, whether this feature is
enabled or not.
To save log information to a remote host, you must edit the syslog.conf file (located on the remote host) and
then restart the syslog daemon. Consult your operating system documentation for information on how to
configure Remote Logging. The syslog.conf file on the remote host must contain an entry that specifies
the name of the log file in which to save error messages. Add the following line to the syslog.conf file. A
<tab> separates the selector field (local0.info) and action field which contains the log file path name in the
format /var/adm/messages/messages.name:
local0.info <tab> /var/adm/messages.name
Symbolic name
The symbolic name is a user-defined name of up to 32 characters that identifies the switch. The symbolic
name is used in the displays and data windows to help identify switches. The following characters may not
be used in the symbolic name: pound sign (#), semi-colon (;), and comma (,).
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 61
Page 62

Switch administrative states
The switch administrative state determines the operational state of the switch. The switch administrative
state exists in two forms: the configured administrative state and the current administrative state.
The configured administrative state is the state that is saved in the switch configuration and is preserved
across switch resets. QuickTools always makes changes to the configured administrative state. The
configured administrative state is displayed in the Switch Properties dialog box.
The current administrative state is the state that is applied to the switch for temporary purposes and is not
retained across switch resets. The current administrative state is set using the Set Switch command. See
the HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch Command Line Interface Guide for information about
the command line interface.
The switch administrative state values are:
• Online—The switch is available.
• Offline—The switch is unavailable.
• Diagnostics—The switch is in diagnostics mode, is unavailable, and tests can be run on all ports of the
switch.
Broadcast support
Broadcast is supported on the switch and enables TCP/IP support. Broadcast is implemented using the
proposed standard specified in Multi-Switch Broadcast for FC-SW-3, T11 Presentation Number
T11/02-031v0. Fabric Shortest Path First (FSPF) is used to set up a fabric spanning tree used in
transmission of broadcast frames. Broadcast frames are retransmitted on all ISLs indicated in the spanning
tree and all online N_Ports and NL_Ports. Broadcast zoning is supported with zones. The default setting is
Enabled.
In-band management
In-band management is the ability to manage switches across inter-switch links. QuickTools, SNMP,
management server, and the application programming interface use the in-band management capability.
The switch comes from the factory with in-band management enabled. If you disable in-band management
on a particular switch, you can no longer communicate with that switch by means other than a direct
Ethernet or serial connection.
62
Page 63
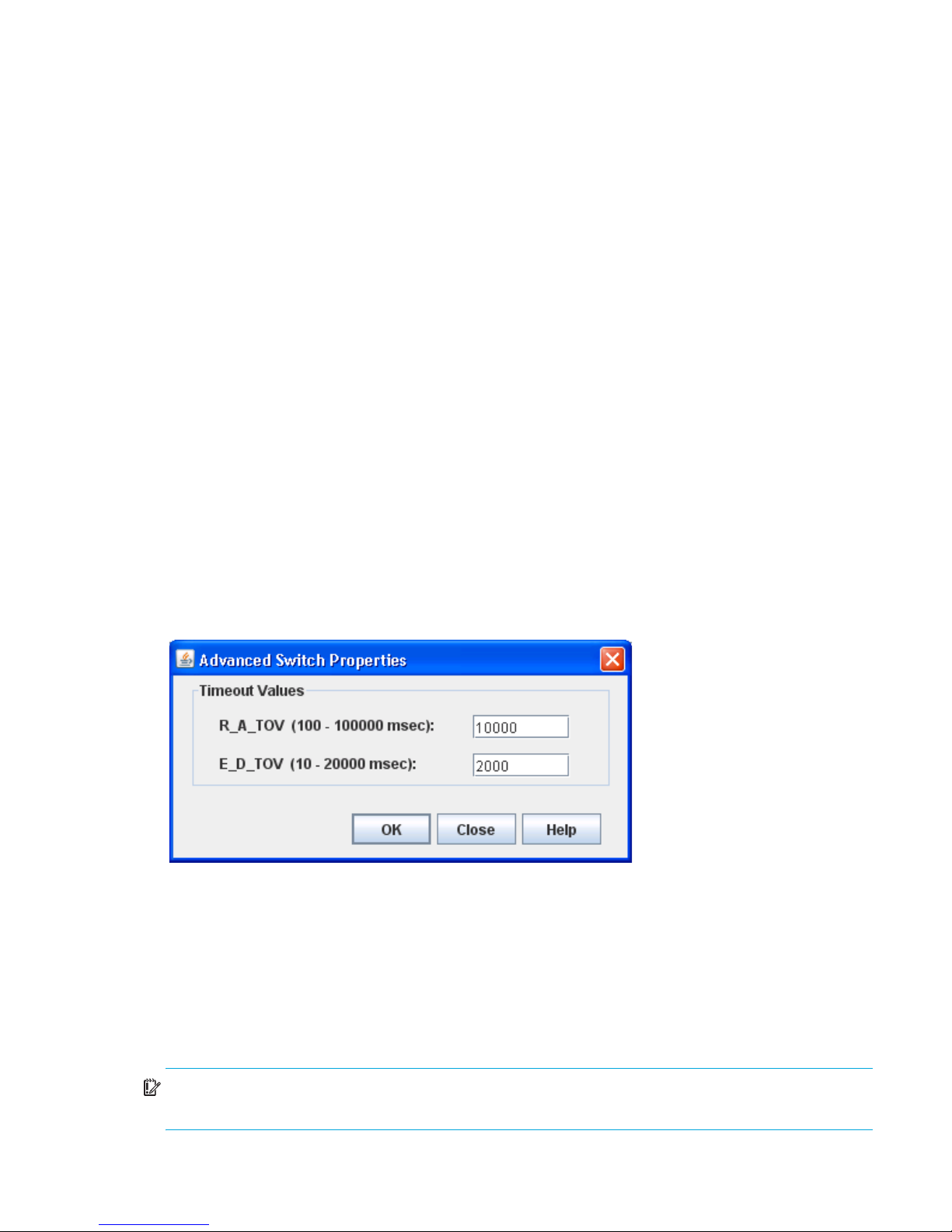
Fabric device management interface
Fabric Device Management Interface (FDMI) provides a means to gather and display device information
from the fabric and enables FDMI-capable devices to register certain information with the fabric, when
FDMI is Enabled. QuickTools will report any and all FDMI information reported by the entry switch, if FDMI
is enabled on the entry switch. To view FDMI data, FDMI must be enabled on the entry switch and on all
other switches in the fabric which are to report FDMI data.
FDMI is comprised of the fabric-to-device interface and the application-to-fabric interface. The
fabric-to-device interface enables a device’s management information to be registered. The
application-to-fabric interface provides the framework by which an application obtains device information
from the fabric. Use the FDMI HBA Entry Limit field on the Switch Properties dialog box to configure the
maximum number of HBAs that can be registered with a switch. If the number of HBAs exceeds the
maximum number, the FDMI information for those HBAs can not be registered.
Select the FDMI Enabled option on the Switch Properties dialog box to Enable or Disable FDMI. If FDMI is
Enabled on an HBA, the HBA forwards information about itself to the switch when the HBA logs into the
switch. If FDMI is Enabled on a switch, the switch stores the HBA information in its FDMI database.
Disabling FDMI on a switch clears the FDMI database. If you Disable FDMI on a switch and then re-enable
it, you must reset the ports to cause the HBAs to log in again, and thus forward HBA information to the
switch.
To view detailed FDMI information for a device, click the Devices tab, and click (i) in the Details column of
the Devices data window. The Detailed Devices Display dialog box displays the specific information for
that device. See ”Devices data window” (page 30) for more information.
Advanced switch properties
The Advanced Switch Properties dialog box (Figure 30) enables you to set the timeout values. The dialog
box is available for only the entry switch. The switch is automatically taken offline temporarily while the
timeout values are set and the switch is restored to its original state after the changes are completed. To
open the Advanced Switch Properties dialog box, open the Switch menu and select Advanced Switch
Properties. After making changes, click OK to put the new values into effect.
Figure 30 Advanced Switch Properties dialog box
Timeout values
The switch timeout values determine the timeout values for all ports on the switch. The timeout values must
be the same for all switches in the fabric.
• R_A_TOV (Resource Allocation Timeout)—The maximum time a frame could be delayed and still be
delivered. The default is 10000 milliseconds.
• E_D_TOV (Error Detect Timeout)—The maximum round trip time that an operation between two N_Ports
could require. The default is 2000 milliseconds.
IMPORTANT: Mismatched timeout values will disrupt the fabric. These should not be changed unless
absolutely necessary. The switch is temporarily placed offline to change these values.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 63
Page 64
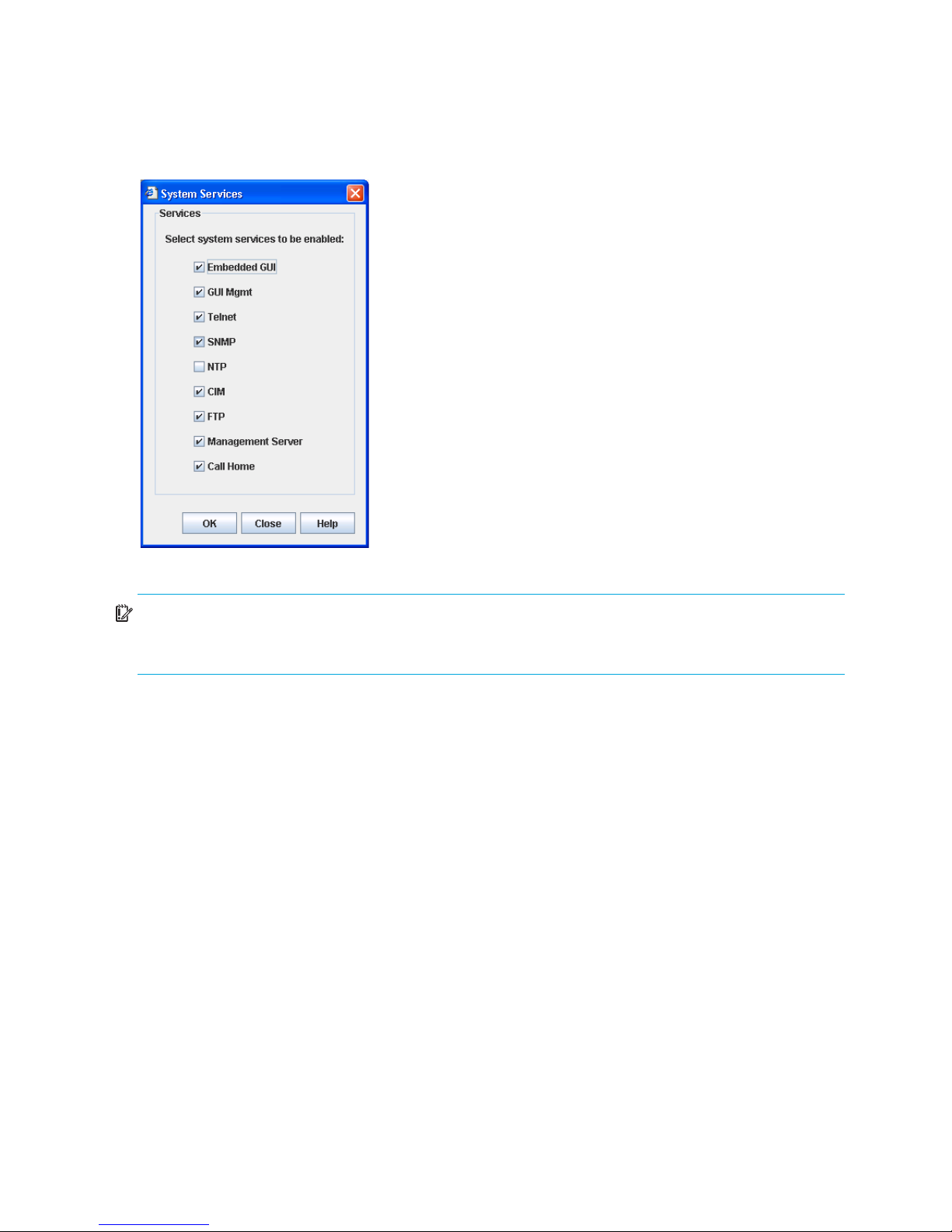
Managing system services
The System Services dialog box (Figure 31) provides a central location for you to enable or disable any of
the external user services such as Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), embedded web applet,
command line interface, Network Time Protocol (NTP), Common Information Model (CIM), and Call
Home. To display the System Services dialog box, select Switch > Services.
Figure 31 System Services dialog box
IMPORTANT: Use caution when disabling the Embedded GUI, GUI Mgmt, and Telnet, as it is possible to
disable all access to the switch except through a serial connection. Both SSH and SSL can be configured
using the CLI.
The following system services are available:
• Embedded GUI (Graphical User Interface)—Enables users to point a browser at the switch and use the
QuickTools web applet.
• GUI Mgmt—Enables out-of-band management of the switch from the switch management application
(GUI). If disabled, the switch can not be specified as the entry switch for a fabric in QuickTools or
Enterprise Fabric Management Suite, but can still be managed through an in-band connection.
• Telnet (Command line interface)—Enables users to manage the switch through a Telnet command line
interface session. Disabling Telnet access to the switch is not recommended.
• SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)—Enables management of the switch through
third-party applications that use SNMP.
• NTP (Network Time Protocol)—Enables the switch to obtain its time and date settings from an NTP
server. Configuring all of your switches and your workstations to utilize NTP will keep the date/time
settings in sync and will prevent difficulties with SSL certificates and event logs.
• CIM (Common Information Model)—Enables management of the switch through third-party
applications that use CIM.
• FTP (File Transfer Protocol)—Enables file transfers to the switch using FTP. FTP is required for out-of-band
firmware uploads which will complete faster than in-band Firmware uploads.
• Management Server—Enables management of the switch through third-party applications that use the
GS-3 Management Server.
• Call Home—Enables you to configure switches and send alerts and events to email addresses or
pagers. This email-based Call Home cannot be used to contact HP Services. Call Home to HP Services
64
Page 65

can be accomplished using HP Service Essentials Remote Support Pack as described in the HP
StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch Installation and Reference Guide.
Network properties
Use the Network Properties dialog boxes (Figure 32) to configure IP and DNS parameters.
1. Open the Network Properties dialog box, using one of the following methods:
• Open the faceplate display for the switch you are configuring, and then select Switch > Network
Properties, or
• Right-click a switch graphic in the faceplate display, and then select Network Properties from the
popup menu.
2. Click the IP tab to open the Network Properties IP dialog box or the DNS tab to open the Network
Properties DNS dialog box, as appropriate for your network setup.
3. Make the desired changes to the network properties.
4. After making changes, click OK to put the new values into effect.
Figure 32 Network Properties dialog boxes
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 65
Page 66

Network IP configuration
The IP configuration identifies the switch on the Ethernet network, determines which network discovery
method to use, and enables/disables the IPv4 and IPv6 network addressing.
An IPv4 address is 32 bits and consists of four blocks of decimal numbers, with each block separated by a
period. Each block can have up to three numbers. A single zero character displayed in a block indicates
that the block consists of all zeroes. An example of an IPv4 address is 10.20.30.40. All four blocks
contain numbers. Table 11 describes the IPv4 and IPv6 configuration parameters.
An IPv6 address provides a much wider range of IP addresses than an IPv4 address. An IPv6 address is
128 bits, and consists of eight blocks of hexadecimal numbers, with each block separated by a colon. The
maximum number of numerals in each block is four. One or more blocks with all zeroes are represented by
two colon characters. The total number of blocks always adds up to eight. To determine how many
contiguous blocks contain only zeroes, subtract the number of populated blocks from eight. For example,
the IPv6 address 2eee::49:24:7a:54:3434 is equivalent to 2eee:0000:0000:49:24:7a:54:3434. The
number of blocks containing zeroes in this example is two (8-6=2).
NOTE: Switches without IPv6 addressing enabled can not communicate over Ethernet with hosts or
switches using the IPv6 addressing.
Table 11 describes the network IP configuration parameters.
66
Page 67
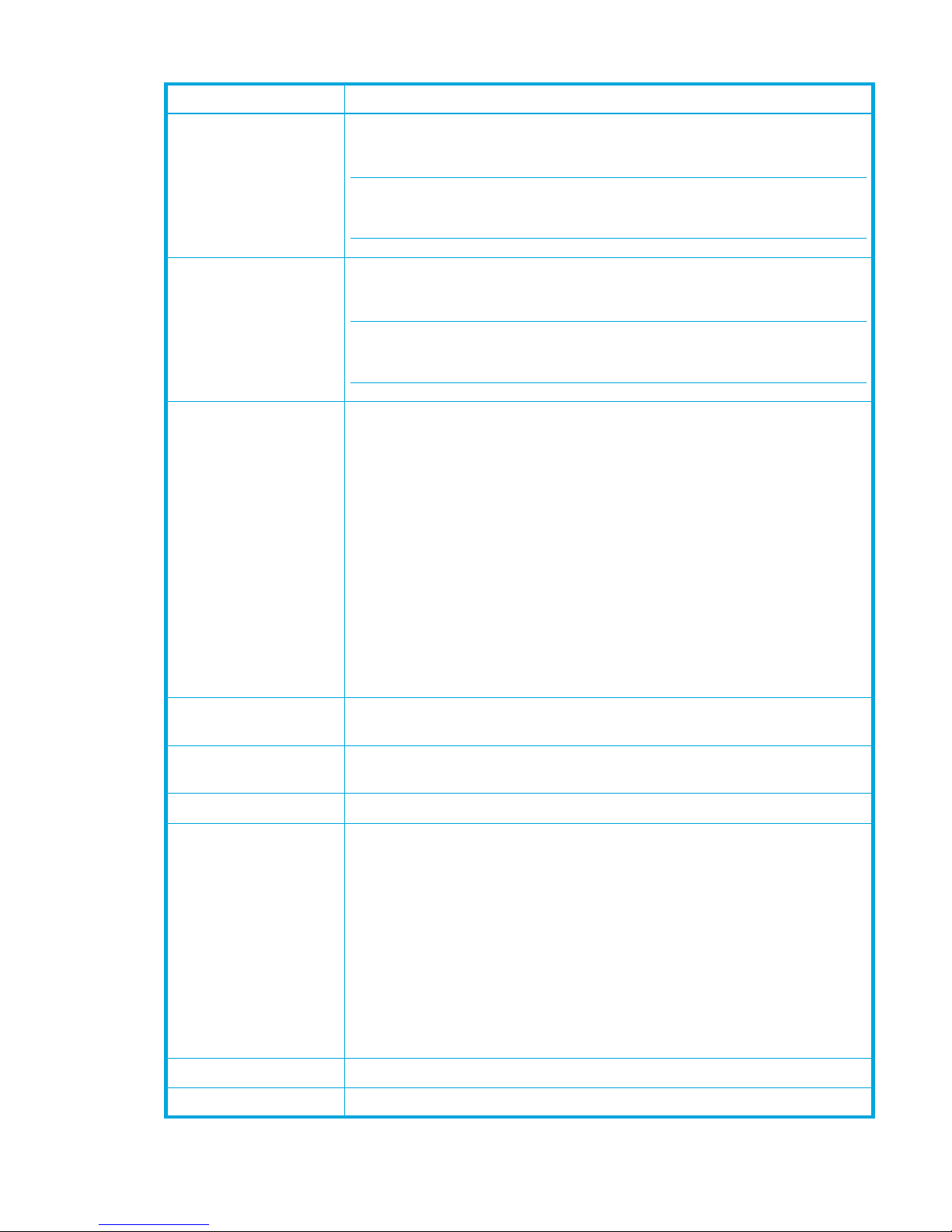
Table 11 Network Properties dialog box—IP fields
Field Description
IPv4 Network Enable this option to permit the IPv4 addressing format to be used anytime
you are required to enter an IP address.
CAUTION: Disabling this option will prevent you from using an IPv4 IP
address for system services.
IPv6 Network Enable this option to permit the IPv6 addressing format to be used anytime
you are required to enter an IP address.
CAUTION: Disabling this option will prevent you from using an IPv6 IP
address for system services.
Network Discovery Choose one of the following methods for assigning the IP address:
• Static—Uses the IP configuration parameters entered in the Network
Properties dialog box.
• BootP—Acquires the IP configuration from a BootP server. If no IP address
is obtained, the switch reverts to the previously configured IP address.
• RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol)—Acquires the IP address from
a RARP server. A RARP request is broadcast with up to three retries, each
at 5 second intervals. If no IP address is obtained, the switch reverts to the
previously configured IP address.
• DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)—Acquires the IP
configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is obtained, the
DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured lease. If the previous
lease cannot be used, no IP address will be assigned to this switch in
order to avoid an IP address conflict.
IP Address Enter the Internet Protocol address for the Ethernet port. The default value is
10.0.0.1.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask address for the Ethernet port. The default value is
255.0.0.0.
Gateway Enter the IPv4 gateway address
Discovery Choose one of the following methods for assigning the IP address:
• Static—Uses the IP configuration parameters entered in the Network
Properties dialog box
• DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6)—Acquires the
IP configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is obtained,
the DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured lease. If the
previous lease cannot be used, no IP address will be assigned to this
switch in order to avoid an IP address conflict.
• NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol)—Part of the Stateless Address Auto
configuration protocol. It replaces the Address Resolution Protocol used
with IPv4.
Config IPv6 Address Enter the IPv6 address for the Ethernet port
Gateway Enter the IPv6 gateway address
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 67
Page 68

Network DNS configuration
The Network Properties dialog box has two tabs: IP and DNS. Click the DNS tab to open the Network
Properties DNS dialog box (Figure 32). Use the Network Properties DNS dialog box to enable the DNS
Client on the switch and the DNS server to map domain names to IP addresses. Table 12 describes the
network DNS configuration parameters.
Table 12 Network Properties dialog box—DNS fields
Field Description
DNS Client Select this option to enable the Domain Name Service client.
Local Hostname Enter the name of the local host
Server Discovery Choose one of the following methods by which to assign the IP address:
• Static—Uses the IP configuration parameters entered in the Network
Properties dialog box.
• DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)—Acquires the IP
configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is obtained,
the DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured lease. If the
previous lease cannot be used, no IP address will be assigned to this
switch in order to avoid an IP address conflict.
• DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6)—Acquires
the IP configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is
obtained, the DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured
lease. If the previous lease cannot be used, no IP address will be
assigned to this switch in order to avoid an IP address conflict.
DNS Server Addresses Enter the IP address of the DNS server.
Search List Discovery Choose one of the following methods by which to assign the IP address:
• Static—Uses the IP configuration parameters entered in the Network
Properties dialog box.
• DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)—Acquires the IP
configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is obtained,
the DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured lease. If the
previous lease cannot be used, no IP address will be assigned to this
switch in order to avoid an IP address conflict.
• DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6)—Acquires
the IP configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is
obtained, the DHCP client attempts to use the previously configured
lease. If the previous lease cannot be used, no IP address will be
assigned to this switch in order to avoid an IP address conflict.
Search List Domain Names The suffix that is appended to the user-specified hostname for the search.
68
Page 69
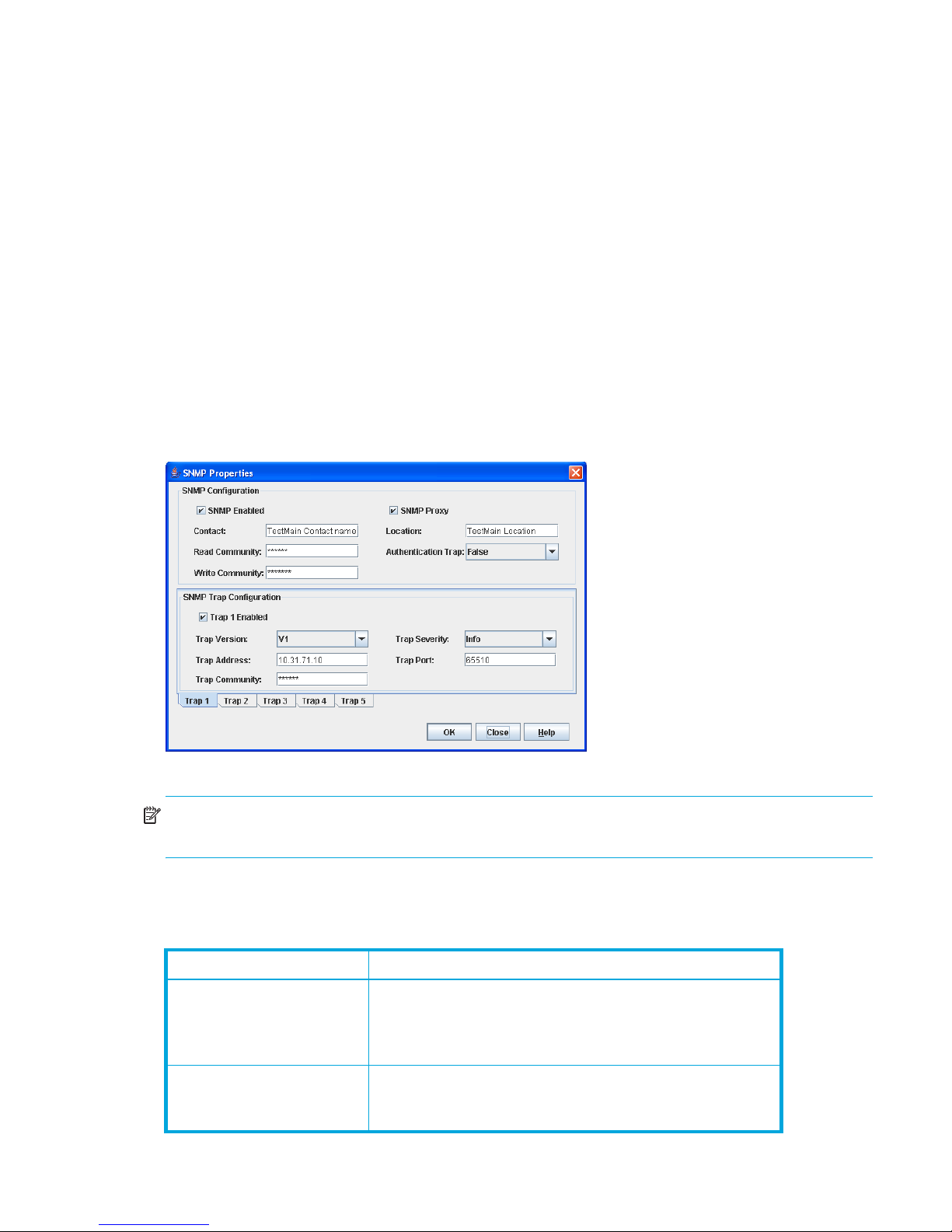
SNMP configuration
The Simple Network Management Protocol configuration includes properties and trap parameters plus
SNMP v3 manager and user parameters.
SNMP properties and trap configuration parameters
Use the SNMP Properties dialog box (Figure 33) to change the SNMP properties and trap configuration
parameters.
• The SNMP configuration defines how authentication traps are managed. The following characters may
not be used in the user-defined fields: pound sign (#), semi-colon (;), and comma (,).
• The SNMP trap configuration defines how traps are set. Choose from the tabs Trap1–Trap 5 to
configure each trap.
To set the SNMP properties:
1. Select a switch or stack in the fabric tree to open the faceplate/backplate display.
2. If you selected a switch, open the Switch menu, and select SNMP > SNMP Properties. If you selected a
stack, open the Stack menu, select SNMP Properties, and then select switch for initial configuration.
3. Select the desired SNMP parameters, referring to the descriptions of the SNMP parameters in
Table 13.
4. When you have finished setting the parameters, click OK to put the new values into effect.
Figure 33 SNMP Properties dialog box
NOTE: Since Read Community, Trap Community, and Write Community settings are like passwords and
are write-only fields, the current settings are displayed as asterisks.
Table 13 describes the SNMP Properties dialog box fields.
Table 13 SNMP Properties dialog box fields
Field Description
SNMP Enabled Enables or disables SNMP communication with other
switches in the fabric. The user cannot use an SNMP
application at a workstation to talk to a switch that has this
setting disabled.
Contact Specifies the name (up to 64 characters) of the person who
is to be contacted to respond to trap events. The default is
<sysContact undefined>.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 69
Page 70
Table 13 SNMP Properties dialog box fields (Continued)
Field Description
Read Community Read community password (up to 32 characters) that
authorizes an SNMP agent to read information from the
switch. This is a write-only field. The Read Community value
on the switch and the SNMP management server must be
the same. The default is public.
SNMP Proxy Enables or disables the use of SNMP to monitor and
configure switches in the fabric.
Location Specifies the name (up to 64 characters) for the switch
location. The default is <sysLocation undefined>.
Authentication Trap Enables or disables the reporting of SNMP authentication
failures. If enabled, a notification trap is sent when incorrect
community string values are used. The default value is
False.
Write Community Write community password (up to 32 characters) that
authorizes an SNMP client to write information to the switch.
This is a write-only field. The value on the switch and the
SNMP management server must be the same. The default
value is private.
Trap Version Specifies the SNMP version (1 or 2) with which to format
traps.
Trap 1 Enabled Enables or disables the trap. If disabled, traps are not sent
to trap monitoring stations and the trap settings are not
configurable.
Trap Address Specifies the IP address to which SNMP traps are sent. A
maximum of 5 trap addresses are supported. The default
address for trap 1 is 10.0.0.254. The default address for
traps 2–5 is 0.0.0.0.
Trap Community Trap community password (up to 32 characters) that
authorizes an SNMP agent to receive traps. This is a
write-only field. The value on the switch and the SNMP
management server must be the same. The default is
public.
Trap Severity Specifies a severity level to assign to the trap. Open the
drop-down list and choose a level. The Trap 1 Enabled
option on the SNMP Properties dialog box must be enabled
to access this drop-down list. Trap severity levels include
Unknown, Emergency, Alert, Critical, Error, Warning,
Notify, Info, Debug, and Mark
Trap Port Specifies the port number (between 1—65535) on which a
trap is set. The default is 162.
SNMP v3 Security
Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3 (SNMPv3) is an interoperable standards-based protocol
for network management. SNMPv3 provides secure access to devices using a combination of
authenticating and encrypting packets over the network. SNMP v3 security is an additional layer of
security. The SNMP v3 security is available on a secure (SSL) entry switch. The security features provided in
SNMPv3 are:
• Message integrity—Ensuring that a packet has not been tampered with during transit.
70
Page 71

• Authentication—Determining that the message is from a valid source.
• Encryption—Scrambling the contents of a packet to prevent it from being seen by an unauthorized
source.
You configure SNMP v3 security in the SNMP v3 Manager dialog box (Figure 34).
Figure 34 SNMP v3 Manager dialog box
Adding an SNMP v3 user
To enable SNMP v3 security and add an SNMP v3 user:
1. Select the entry switch in the fabric tree.
2. Select Switch > SNMP > SNMP v3 Manager to open the SNMP v3 Manager dialog box (Figure 34).
3. Check the SNMP v3 Security checkbox to enable SNMP v3 security for the specified SNMP v3 users.
4. Select Edit > Add New User to open the SNMP v3 User Editor dialog box (Figure 35) and enter
information in the fields described in Table 14.
Figure 35 SNMP v3 User Editor dialog box
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 71
Page 72

Table 14 SNMP v3 User Editor dialog box fields
Field Description
User Name Name assigned to this SNMP v3 user.
Group Sets user's Read privileges: Read Only permits user to view
only SNMP v3 user settings, Read Write permits user to view
and change SNMP v3 user settings.
Authentication Type None, MD5, SHA. If None, no authentication phrase is
required. MD5 and SHA require an authentication phrase.
Authentication Phrase A unique string or phrase that functions as a password that
verifies the authenticity of the user.
Confirm Authentication
Phrase
Privacy Type DES or None. If None, no privacy phrase is required.
Privacy Phrase A unique string or phrase that functions as a password that
Confirm Privacy Phrase Re-enter the Privacy Phrase to confirm it.
5. Click OK to save the settings and close the SNMP v3 User Editor dialog box.
6. In the SNMP v3 Manager dialog box, click OK to save and activate the SNMP v3 security
configuration.
Modifying an SNMP v3 user
To modify an SNMP v3 user:
1. Select the entry switch in the fabric tree.
2. Select Switch > SNMP > SNMP v3 Manager to open the SNMP v3 Manager dialog box (Figure 34).
3. Select a user in the user list, and select Edit > Edit User to open the SNMP v3 User dialog box.
4. Modify the entries as needed, and click OK. For information about the entry fields, see Table 14.
5. Click OK to save the settings and close the SNMP v3 User Editor dialog box.
6. In the SNMP v3 Manager dialog box, click OK to save and activate the SNMP v3 security
configuration.
Re-enter the Authentication Phrase to confirm it.
verifies the privacy of the user.
Removing an SNMP v3 user
To remove an SNMP v3 user:
1. Select the entry switch in the fabric tree.
2. Select Switch > SNMP > SNMP v3 Manager to open the SNMP v3 Manager dialog box (Figure 34).
3. Select a user in the user list, and select Edit > Remove User.
4. Click Yes to remove the user; click Cancel to cancel the removal.
5. Click OK to save the settings and close the SNMP v3 User Editor dialog box.
6. In the SNMP v3 Manager dialog box, click OK to save and activate the SNMP v3 security
configuration.
Testing a switch
The Switch Diagnostics dialog box (Figure 36) enables you to test and verify the operational status of
switches (online and offline). To open the Switch Diagnostic dialog box, open the Switch menu, select
Switch Diagnostics, and then select Online Switch Diagnostics or Offline Switch Diagnostics. For each type
of test, only one switch at a time can be tested. Offline Diagnostics can only be selected for the entry
switch.
The diagnostic tests are:
72
Page 73
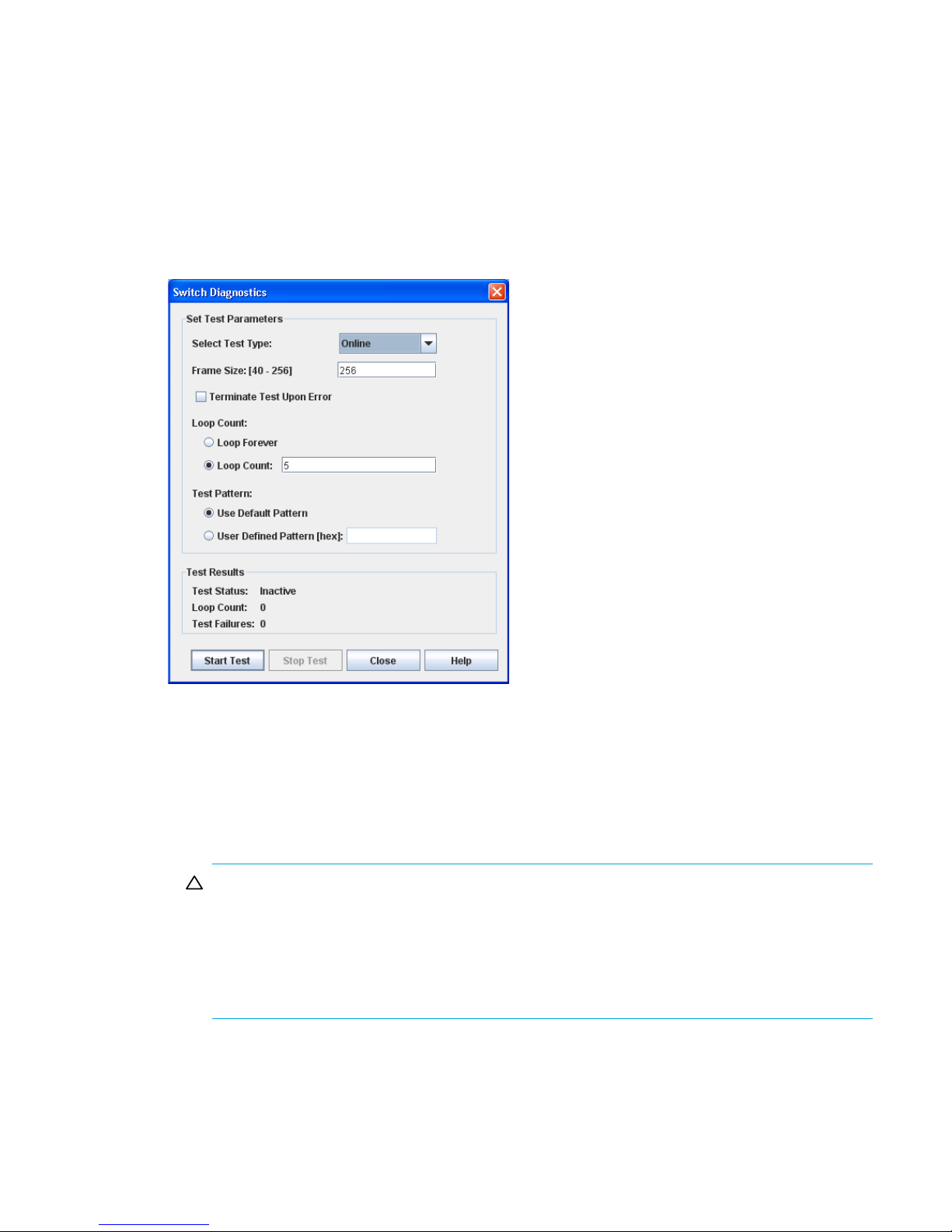
• Online—A non-disruptive test that exercises port-to-device connections for all ports on a switch that are
currently online except for TR ports, which are not included in Online Switch Diagnostics.
• Offline—A disruptive test that exercises all port connections for a switch in the diagnostics state. When
you run an offline test, the switch will automatically be put into diagnostics state, and the switch will not
be returned to its original state until the Switch Diagnostics dialog box is closed. A disruptive switch
reset must be done at that time to return the switch to its original state.
• Connectivity—A disruptive test that exercises all port and inter-port connections for a switch in the
diagnostics state. When you run a connectivity test, the switch will automatically be put into diagnostics
state, and the switch will not be returned to its original state until the Switch Diagnostics dialog box is
closed. A disruptive switch reset must be done at that time to return the switch to its original state. The
two types of connectivity tests are internal loopback and external loopback.
Figure 36 Switch Diagnostics dialog box
To test a switch:
1. Open the faceplate display of the switch to be tested.
2. Open the Switch menu and select Switch Diagnostics, and then select Online Switch Diagnostics or
Offline Switch Diagnostics to open the Switch Diagnostics dialog box.
3. Select the test type from the drop-down list.
CAUTION: If you selected the Offline Switch Diagnostics option, your test type options, Offline and
Connectivity, will disrupt traffic. When you run an Offline or Connectivity test, the switch will be put
into diagnostics state for you, and the switch will not be returned to its original state until you close
the Switch Diagnostics dialog box. A disruptive switch reset must be done at that time to return the
switch to its original state. If you selected the Online Switch Diagnostics option to run the online
switch test and there are no ports with an active login at that time, the test will return immediately
with a Passed status.
4. Enter a frame size in the Frame Size field.
5. Enable or disable the Terminate Test Upon Error option.
6. Select a Loop Count option. The Loop Forever option runs the test until you click Stop Test. The Loop
Count option runs the test the number of times you entered in the Loop Count field.
7. Select the default test pattern or enter a user-defined (hexadecimal) test pattern.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 73
Page 74
8. Click Start Test to begin the next test, or click Close to close the Switch Diagnostics dialog box.
Observe the results in the Test Results area. If the Test Status field in the Test Results area indicates
Failed, note the Test Fault Code displayed in the Switch Information data window and contact Tech
Support.
Archiving a switch
You can create an .XML archive file containing the configuration parameters. This archive file can be used
to restore the configuration on the same switch or on a replacement switch. You can also use the archive
file as a template for configuring new switches to add to a fabric.
Basically any data received by QuickTools is archived. Passwords are not archived. Security Group secrets
are not included in the archive and must be re-configured using the CLI after a restore.
Archived parameters include:
• Switch properties and statistics
• IP configuration
• SNMP configuration
• Port properties and statistics
• Name server
• Date/Time and NTP settings
• Alarm configuration
• Zoning configuration
• Nicknames configuration
• Call Home parameters
• User account information (but not restored)
• Configured security (available only with SSL connection to the switch).
• RADIUS Server information (available only with SSL connection to the switch)
NOTE: Security features must be configured using the CLI or Enterprise Fabric Management Suite. See the
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch Command Line Interface Guide for information about the
command line interface, and HP StorageWorks 8/20q and SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch Enterprise
Fabric Management Suite User Guide for information about Enterprise Fabric Management Suite..
To archive a switch:
1. Select Switch > Archive.
2. In the Save dialog box, enter a file name.
3. Click Save.
Restoring a switch
Restoring a switch loads the archived switch configuration parameters to the switch. The administrative
state of the switch must be set to Offline using the Switch Properties dialog box before an archive can be
used in the restore process. The switch type archive must be compatible with the switch to be restored. See
”Archiving a switch” (page 74) for more information.
74
Page 75

Figure 37 Restore dialog boxes—full and selective
CAUTION: The switch being restored should be physically disconnected from the fabric. Restoring a
switch in a fabric can severely disrupt the fabric. After the restore process is complete, the switch can be
reconnected to the fabric.
To restore a switch:
1. Log in to the fabric through the switch you want to restore. You cannot restore a switch over an ISL.
2. Open the Switch menu and select Restore to display the Restore dialog box (Figure 37). The Restore
dialog box offers a Full Restore tab and a Selective Restore tab.
3. Enter a name for the file to be archived or click Browse and search for a file name.
This archive file must be one that was produced by the QuickTools Archive function. Configuration
backup files created with the Config Backup command are not compatible with the QuickTools Restore
function. The Config Backup command does not archive the primary or secondary secrets for any
security groups.
4. To restore all configuration settings, click the Full Restore tab, then click Restore. To restore selected
configuration settings, click the Selective Restore tab, select one or more of the following options, and
then click Restore.
• Network Properties—Restores all settings presented in the Network properties dialog box except the
IP address. See ”Network properties” (page 65).
• IP Address—Restores switch IP address in addition to the other network properties.
• Port Properties—Restores all settings presented in the Port Properties dialog box. See ”Port symbolic
name” (page 98).
• Switch Properties—Restores all settings presented in the Switch properties dialog box except the
domain ID. See ”Switch properties” (page 60).
• Domain ID—Restores switch domain ID in addition to the other switch properties.
• Configured Zoning—Restores all configured zone sets, zones, and aliases in the switch’s zoning
database, excluding the active zone set.
• Nicknames—Restores the last saved nickname configuration.
• Call Home—Restores all Call Home configuration and profile settings.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 75
Page 76
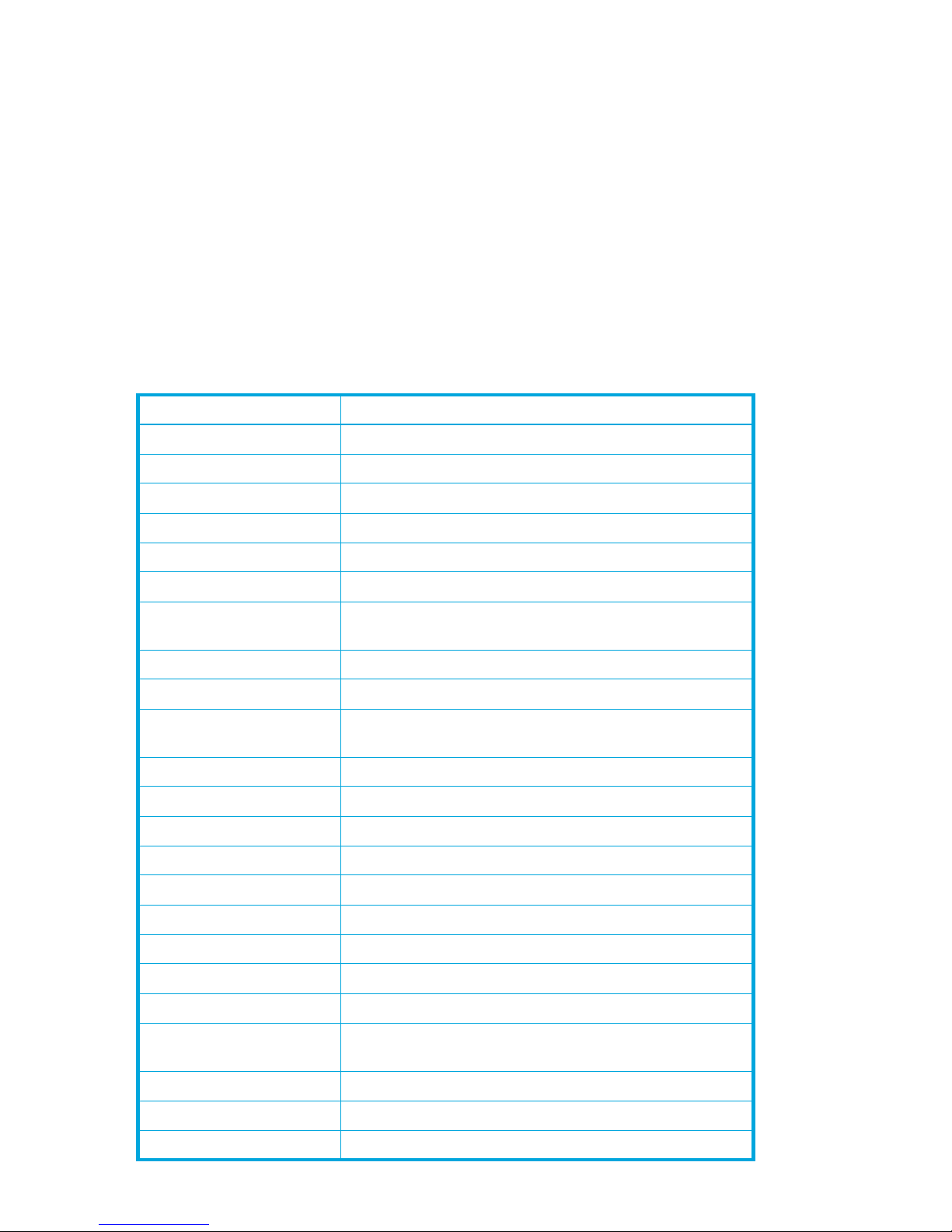
5. If you select the Configured Zoning or Full Restore option and the file contains zone sets, a dialog box
prompts you to activate one of those zone sets. Click Yes, and then select a zone set from the
drop-down list in the Select Zoneset to be Activated dialog box.
6. Click OK and view the results in the top pane of the Restore dialog box.
Restoring the factory default configuration
You can restore the switch and port configuration settings to the factory default values. To restore the
factory configuration on a switch, select Switch > Restore Factory Defaults. The factory default switch
configuration settings are listed in Table 15.
Restoring the switch to the factory default configuration does not restore the account name and password
settings. The most current port license will remain in effect. To restore user accounts, you must select the
Reset User Accounts to Default option in the maintenance menu. See “Recovering a Switch” in the HP
StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch Installation and Reference Guide for your switch for
information about maintenance mode and the maintenance menu.
Table 15 Factory default configuration settings
Setting Value
Symbolic Name SN6000 FC Switch
Administrative State Online
Domain ID 1
Domain ID Lock False
In-band Management True
Broadcast Support Enable
Resource Allocation Timeout
(R_A_TOV)
I/O Stream Guard Auto
Device Scan Enabled True
Error Detect Timeout
(E_D_TOV)
SNMP Enabled True
SNMP Proxy True
IP Address 10.0.0.1
FDMI Enabled True
FDMI HBA Entry Level 1000
Subnet Mask Address 255.0.0.0
Gateway Address 10.0.0.254
10000 milliseconds
2000 milliseconds
Network Discovery Static
Remote Logging False
Remote Logging Host IP
Address
NTP Client Enabled False
NTP Server IP Address 10.0.0.254
Contact Undefined
76
10.0.0.254
Page 77
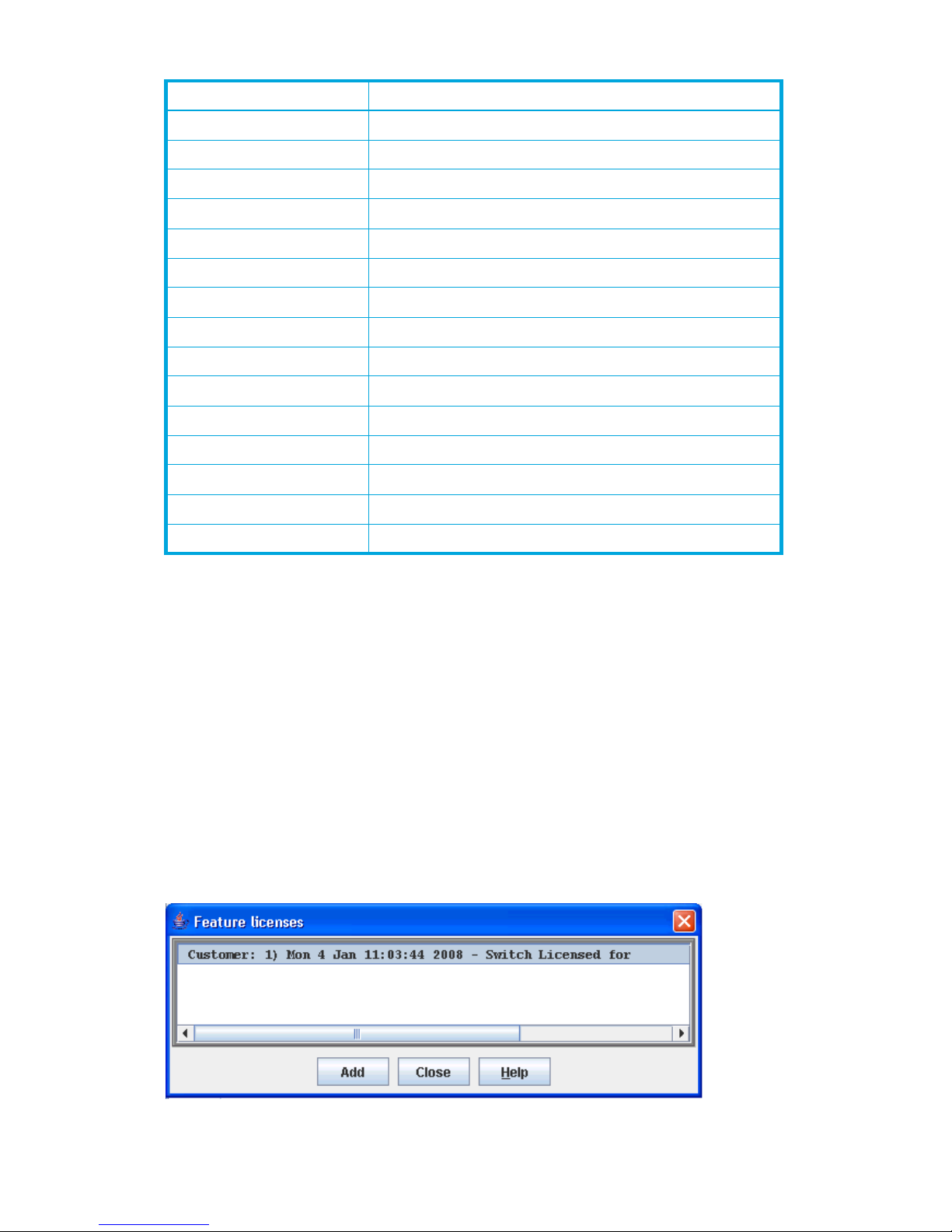
Table 15 Factory default configuration settings
Setting Value
Location Undefined
Trap Enabled False
Trap Port 162
Trap Address Trap 1: 10.0.0.254; Traps 2–5: 0.0.0.0
Trap Community Public
Read Community Public
Write Community Private
Port State Online
Port Speed Auto -detect
Port Type GL
Call Home Setup <undefined>
Call Home Profile <undefined>
Default Zone Allow
Merge Auto Save True
Discard Inactive False
Installing feature license keys
A feature license key is a password that enables you to upgrade your switch. To obtain a feature license
key, contact a switch distributor or authorized reseller. License keys vary according to the features you
purchase. The following license key features are available:
• The HP StorageWorks SN6000 Stackable 20Gb ISL Upgrade LTU enables the XPAK ports to transmit at
20 Gb/s instead of the default 10 Gb/s.
• The HP StorageWorks SN6000 Port Activation Upgrade LTU enables additional SFP ports in increments
of four on the HP StorageWorks SN6000 Stackable 8Gb 12-port Single Power Fibre Channel Switch
for totals of 16, 20, or 24 ports.
To install a license key and upgrade the switch:
1. Open the faceplate display for the switch you want to upgrade.
2. Select Switch > Features.
3. In the Feature Licenses dialog box (Figure 38), click Add.
The Add License Key dialog box is displayed.
Figure 38 Feature Licenses dialog box
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 77
Page 78
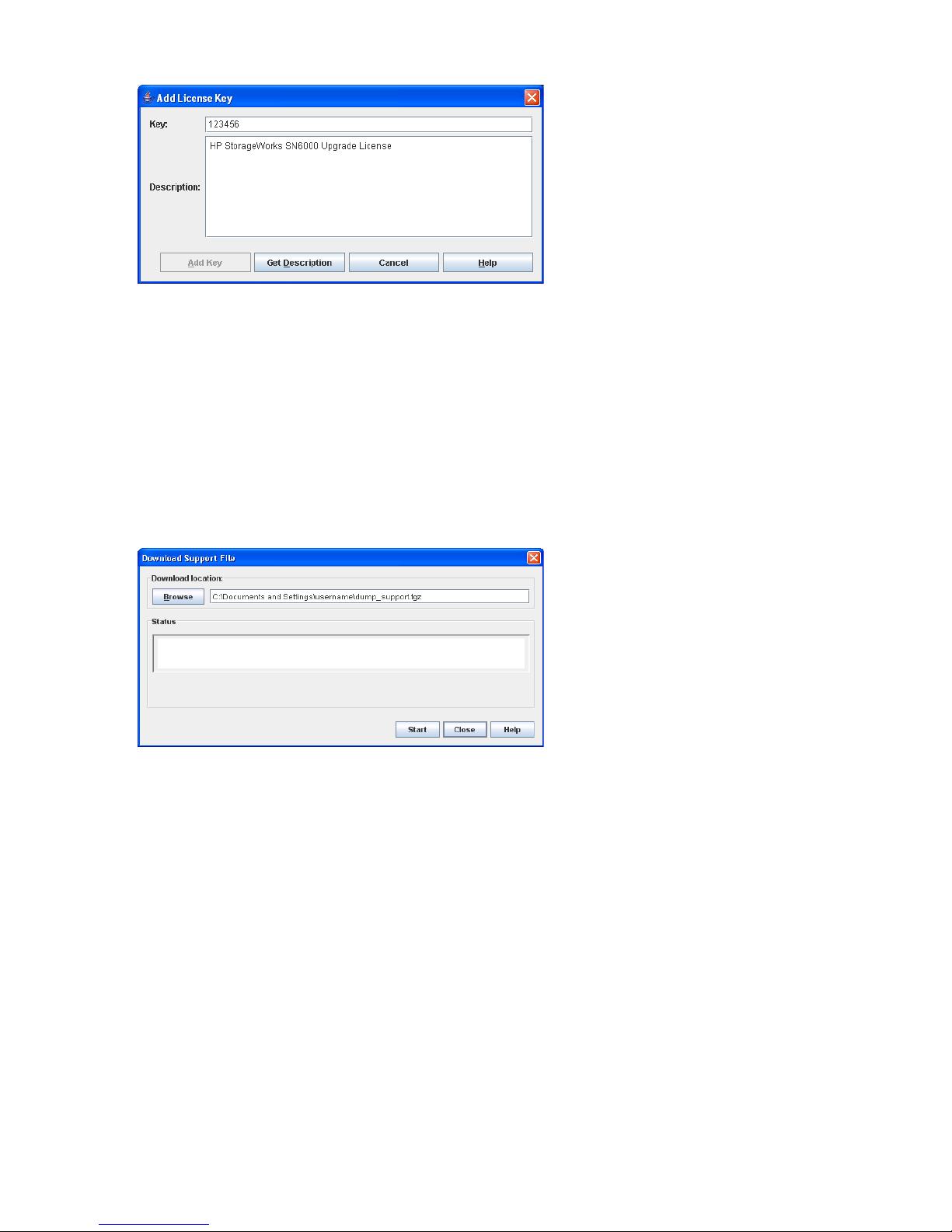
4. In the Add License Key dialog box (Figure 39), enter the license key in the Key box.
Figure 39 Add License Key dialog box
5. Click Get Description. The license key description is retrieved and displayed in the Description area for
you to verify that this is the license key you ordered. If it is not the correct key, repeat steps 4 and 5.
6. Click Add Key to upgrade the switch. Allow a minute or two for the upgrade to complete.
Downloading a support file
The Download Support File menu option assembles all log files and switch memory data into a core dump
file (the default file name is dump_support.tgz). This file can be sent to technical support personnel for
troubleshooting switch problems.
To create a support file:
1. Select Switch > Download Support File.
Figure 40 Download Support File dialog box
2. In the Download Support File dialog box (Figure 40), click Browse to define a location for the support
file, or type the path in the text field. You can rename the support file at this time if desired.
3. Click Start to begin the process of creating and downloading the support file to your workstation.
Observe the status in the Status area.
4. After the support file is saved to your workstation, click Close to close the Download Support File dialog
box.
78
Page 79

Installing firmware
Installing firmware involves loading, unpacking, and activating the firmware image on the switch.
QuickTools does this in one operation. To provide consistent performance throughout the fabric, ensure
that all switches are running the same version firmware.
An NDCLA of firmware can be achieved on an operating switch without disrupting data traffic or having to
re-initialize attached devices. As part of an NDCLA operation, a switch Hot Reset is executed. During a
Hot Reset operation, fabric services will be unavailable for a short period (30—75 seconds depending on
switch model). To ensure that an NDCLA operation is successful, verify that all administrative changes to
the fabric (if any) are complete. If you are installing firmware on more than one switch in the fabric, wait
until the activation is complete on the first switch before installing firmware on a second switch. If you
attempt to activate firmware on a second switch before activation is complete on the first, you will receive a
message advising you to wait and perform a hot reset later on the second switch to complete the
installation.
CAUTION: Changes to the fabric may disrupt the NDCLA process.
Common administrative operations that change the fabric include:
• Zoning modifications
• Adding, moving or removing devices attached to the switch fabric. This includes powering up or
powering down attached devices.
• Adding, moving or removing ISLs or other connections.
After an NDCLA operation is complete, management connections must be re-initiated:
• QuickTools sessions will re-connect automatically
• Telnet sessions must be restarted manually.
Future switch firmware releases will support non-disruptive upgrades unless specifically indicated in its
associated release notes.
An NDCLA operation to earlier switch firmware releases is not supported.
The Load Firmware dialog box for a single switch (Figure 41) or for a stack (Figure 42) enables you to
select and install a firmware image file. To open the Load Firmware dialog box for an individual switch,
select Switch > Load Firmware, or for a stack, select Stack > Load Firmware. When the Load Firmware
dialog box is opened, the path displayed in the Firmware Image Folder field is automatically searched for
firmware image files that can be installed. The default path to search for firmware image files is the user's
working directory.
To change the search path:
1. Click Browse and select a new path.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 79
Page 80

2. Click Rescan to search the folder displayed in the Firmware Image Folder field. The firmware image files
found are listed in and can be selected from the Version drop-down list.
Figure 41 Load Firmware dialog box for a single switch
Figure 42 Load Firmware dialog box for a stack
To install firmware:
1. Choose one of the following:
• To install firmware on a switch, open the switch faceplate display, and select Switch > Load
Firmware.
• To install firmware on a statck, open the stack faceplate display, and select Stack > Load Firmware.
NOTE: The Load Firmware dialog for a stack shows all switches in the stack, and allows you to
load firmware on all switches in the stack. When loading firmware on all switches in the stack, each
phase of the load firmware process is performed on all switches in the stack before the next phase
of the process is started.
2. In the Load Firmware dialog box, choose one of the following:
• Select a firmware image file from the Version drop-down list.
• To change the folder (path), click Browse to search for a different firmware image file, select the
desired folder, and then click Rescan to search the selected folder.
3. Click Start to begin the firmware load process.
You will be shown a message indicating the type of reset required in order to activate the firmware.
4. Click OK to continue the firmware installation.
5. Click Close to close the Load Firmware dialog box.
80
Page 81
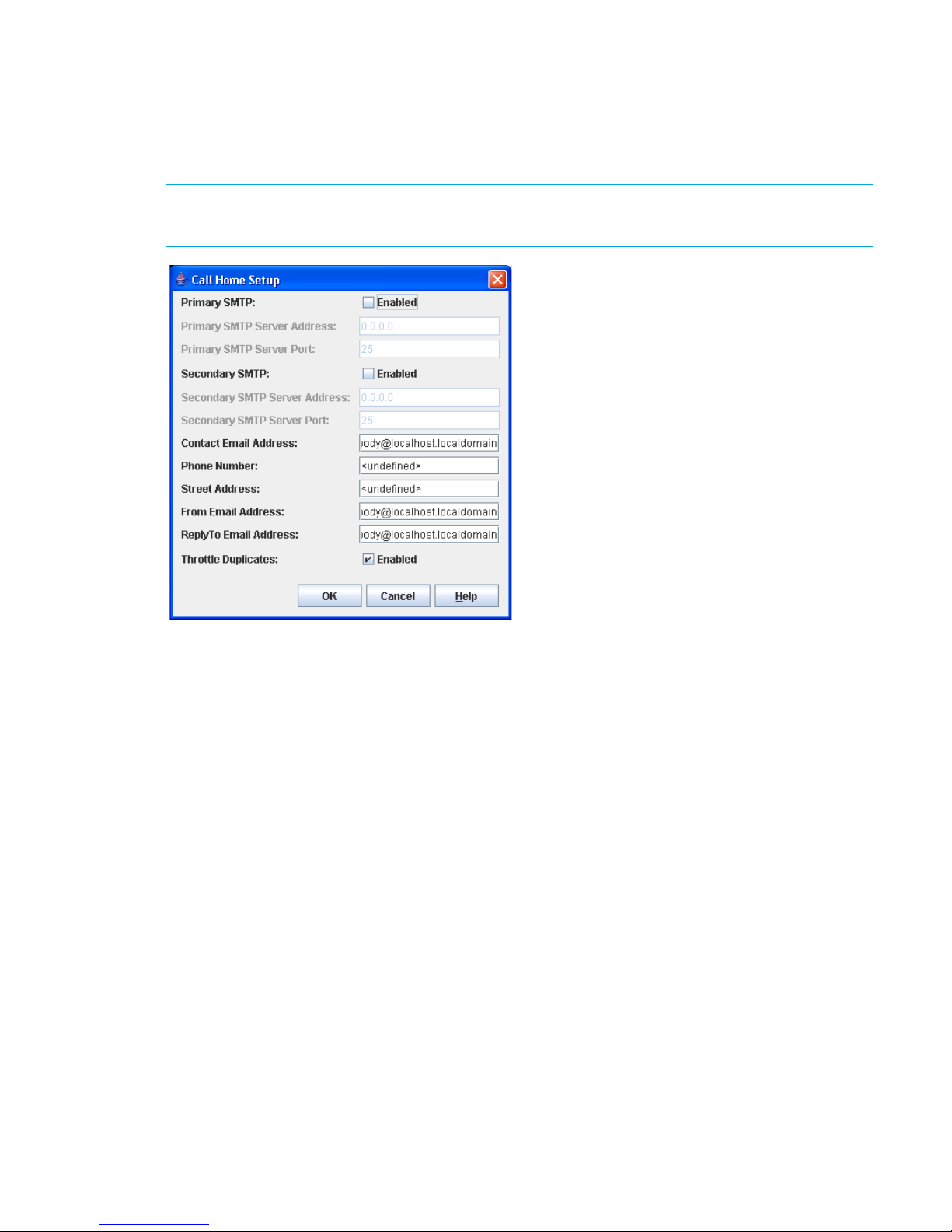
Using Call Home
The Call Home feature enables you to configure switches to send alerts and events to pagers and email.
You can configure the types of events to cover and where to send the alerts. Use the Call Home Setup
dialog box (Figure 43) to configure call home parameters. To display the Call Home Setup dialog box,
open the Switch menu, select Call Home > Setup.
IMPORTANT: The Call Home feature provides an email notification capability for the switch. This service
has no relationship with the HP Call Home feature, which notifies HP services.
Figure 43 Call Home Setup dialog box
Table 16 describes the fields of the Call Home Setup dialog box.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 81
Page 82

Table 16 Call Home Setup fields
Field Description
Primary SMTP: (active) (active) indicates that the Primary SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer
Protocol) is the SMTP server that Call Home will try to use when
transmitting email messages. Call Home operates as an SMTP sending
agent.
After any system configuration, the Primary SMTP server will always
becomes the active SMTP, provided it is enabled and has a non-default
address defined (0.0.0.0 is the default).
Primary SMTP Server
The IP address of the primary (first) SMTP server.
Address:
Primary SMTP Server Port: The service port number that the primary SMTP server is listening on to
accept connections from SMTP sending agents.
Secondary SMTP: The second SMTP server. If the primary SMTP is not enabled/defined, or if
there is a failure in communicating with the primary SMTP server, the
Secondary SMTP server will become the (active) SMTP server—the one
used by Call Home for the next attempt to transmit email.
Secondary SMTP Server
The IP address of the secondary SMTP server.
Address:
Secondary SMTP Server
Port:
The service port number that the secondary SMTP server is listening on to
accept connection from SMTP sending agents.
Contact Email Address: The email address of the point-of-contact for the switch. This email address
is included in the text of email messages using the FullText format under
the section for Contact Information.
Phone Number: The phone number of the point-of-contact for the switch. This value is
included in the text of email messages using the FullText format under the
section for Contact Information.
Street Address: The address of the point-of-contact for the switch. This value is included in
the text of email messages using the FullText format under the section for
Contact Information.
82
From Email Address: The email address that is provided to the SMTP server indicating the
sender of the email being transmitted. In emails sent by Call Home, this
address appears in the message heading as the From: address. This value
is required to send emails. If there are any problems encountered in
routing the email to any of the intended recipients, the notice of the
problem is sent to this address. It is an important address for receiving
email notices concerning problems.
This address is also the default address used when replies are sent to an
email by a recipient. If the Reply-To: Email address is supplied it overrides
the sending of replies to the From: Email address by recipients. However,
any notifications of email problems sent by any SMTP server used to route
the message to the final recipient always sends those notifications to the
From: address.
Page 83
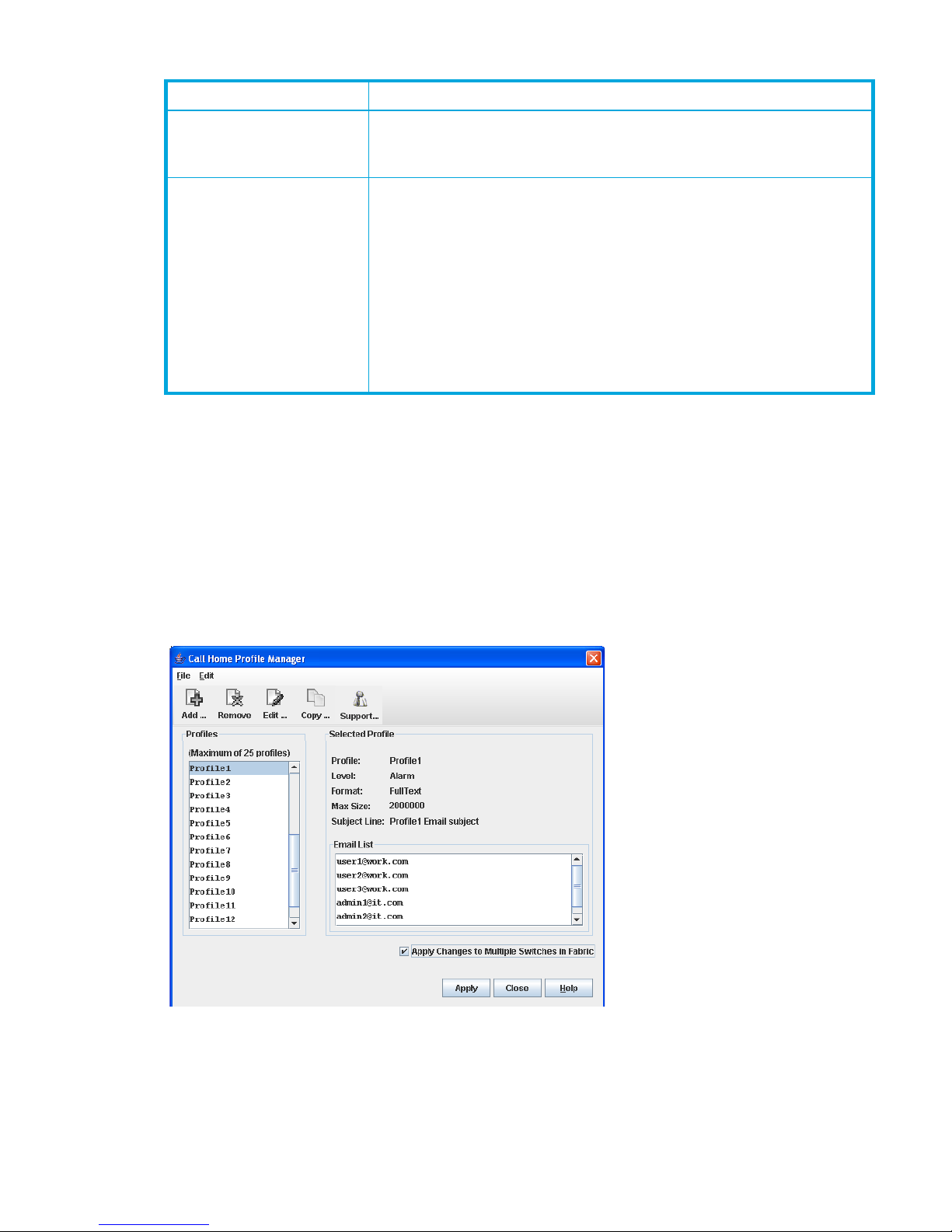
Table 16 Call Home Setup fields (Continued)
Field Description
ReplyTo Email Address: The email address used by mail reading programs to determine the
address to send the reply to the message received. This value will override
the use of the From: address as the recipient for a reply message.
Throttle Duplicates: This Boolean setting indicates if duplicate messages should be suppressed
and accumulated. If True, after an email has been transmitted, Call Home
will not transmit email for switch events that would result in duplicate
emails during a specified time window (default is 15 seconds). The time
window can only be configured using the CLI. During this time window,
these duplicate switch events are accumulated to keep track of how many
duplicate switch events have occurred. After the time window has expired,
an email message for the event is transmitted reporting the number of
duplicate events accumulated and the time of the last received event.
Receiving additional switch events results in duplicate email messages
being sent.
Using the Call Home Profile Manager
The Call Home Profile Manager is used to configure the type of events for which an email alert is sent, and
where the alerts are sent. Use the Call Home Profile Manager dialog box (Figure 44) to manage all
profiles on a switch. You can add new profiles, remove profiles, edit profiles, and make copies of existing
profiles.
To display the Call Home Profile Manager dialog box, select Switch > Call Home > Profile Manager. The
Profiles list shows all profiles on the switch. The Email List shows all email addresses associated with the
selected profile in the Profiles list. The Apply Changes to Multiple Switches in Fabric option enables you to
propagate all profiles on the switch to one or more switches in the fabric. See ”Applying all profiles on a
switch to other switches” (page 87) for more information.
Figure 44 Call Home Profile Manager dialog box
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 83
Page 84

Using the Call Home Profile Editor
Use the Call Home Profile Editor dialog box (Figure 45) when creating a new profile, or when editing or
copying an existing profile. The Call Home Profile Editor dialog box is displayed by clicking Add, Edit, or
Copy on the Call Home Profile Manager dialog box. Alternatively, you can open the Edit menu, and select
Add New Profile, Edit Profile, or Copy Profile. The name in the title bar changes to reflect the option
selected—adding a new profile, adding a new profile, making a copy of an existing profile, or editing an
existing profile.
To create a profile:
1. Click Add (Figure 44) in the Call Home Profile Manager dialog box.
The Call Home Profile Editor dialog box appears (Figure 45).
2. Enter a name for the profile.
3. Select an event level threshold.
4. Select a format type for the message text being sent (FullText, ShortText, or Tsc1).
5. Enter the maximum size of the message being sent.
6. Enter the subject of the email.
7. Enter the email address(es) of the recipients.
8. Click Add to add the email address(es) to the list.
9. Click OK to save the changes.
To edit a profile:
1. Select a profile from the list of profiles (Figure 44) in the Call Home Profile Manager dialog box.
The Call Home Profile Editor dialog box is displayed (Figure 45) pre-populated with all of the
information for the selected profile.
2. Enter any changes to the name for the profile.
3. Select any changes to the event level threshold.
4. Select any change to the format type for the message text being sent (FullText, ShortText, or Tsc1).
5. Enter any changes to the maximum size of the message being sent.
6. Enter any changes to the subject of the email.
7. Add any new email address(es) of the recipients.
8. Click Add to add the email address(es) to the list.
9. Select any email address(es) of the recipients to be removed.
10.Click Remove to remove the selected email address(es) from the list.
11.Click OK to save the changes.
You can use the Call Home Profile Editor dialog box to make a copy of and rename an existing profile.
To copy a profile:
1. Select a profile from the list of profiles (Figure 44) in the Call Home Profile Manager dialog box.
2. To open the Call Home Profile Editor dialog box, click Copy or open the Edit menu and then select
Copy Profile.
The dialog box is pre-populated with all of the information from the selected profile, except the name.
3. Enter a unique name for the profile copy.
84
Page 85
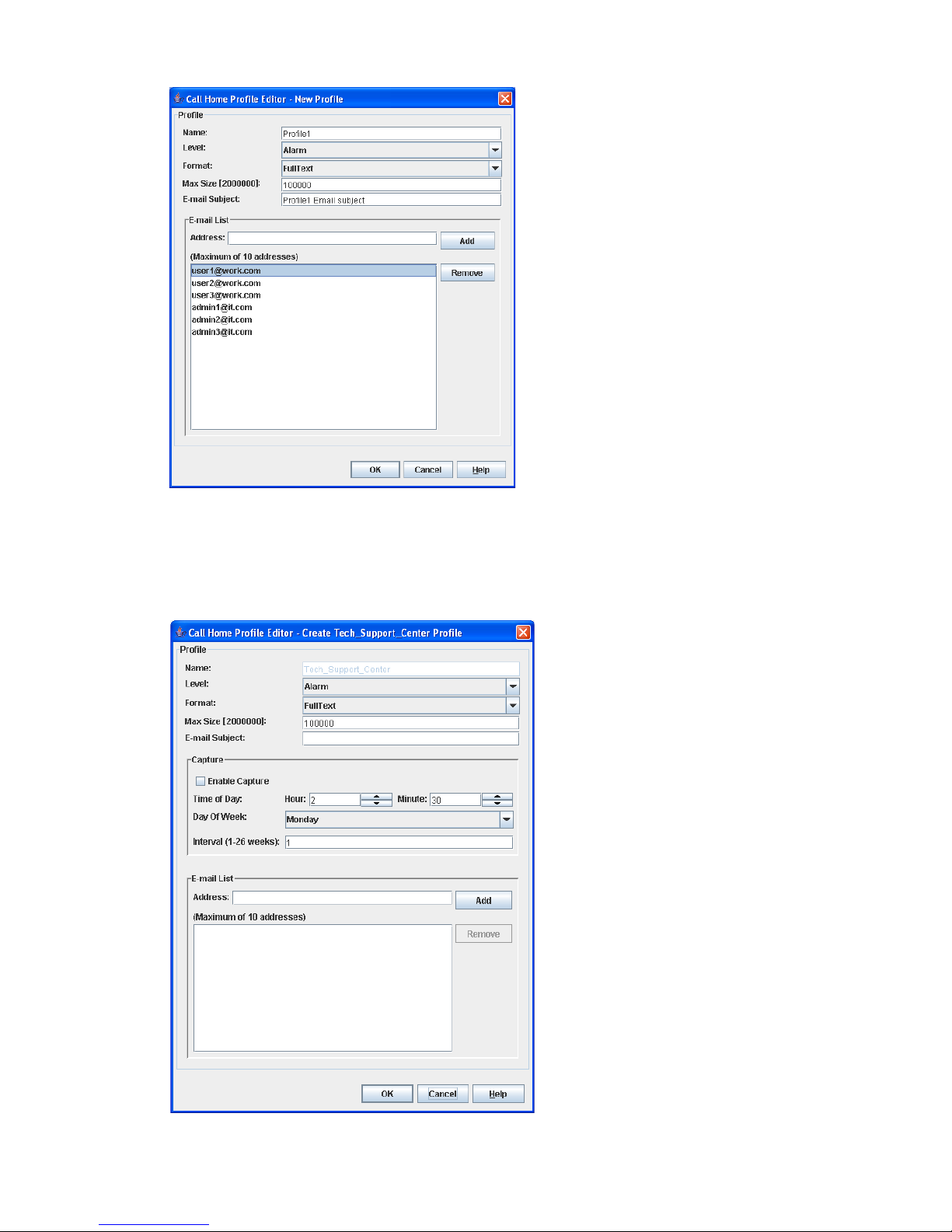
4. Click OK to save the new profile.
Figure 45 Call Home Profile Editor dialog box
Using the Call Home Profile Editor—Tech Support Center Profile dialog box
You can use the Call Home Profile Editor—Tech Support Center Profile dialog box (Figure 46) to create,
edit, or remove a Tech Support Center profile.
Figure 46 Call Home Profile Editor—Tech Support Center Profile dialog box
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 85
Page 86

Table 17 describes the fields in the Call Home Editor—Tech Support Center Profile dialog box.
Table 17 Call Home Editor—Tech Support Center Profile dialog box fields
Field Description
Name The name automatically assigned to the profile. This profile can not be
changed or deleted, but the settings can be modified.
Level The severity level of the event (Alarm, Critical, Warning, None). The level
of events processed by the profile to produce emails that will be sent to the
email addresses listed in the profile.
Format The format used to compile and email a message in response to an
incoming event that is processed by the profile. Formats allowed include:
• ShortText includes the minimum amount of detail required to describe
the event and identify the switch sending the message; it is the
intended format for reading on mobile electronic devices.
• FullText includes the same information as ShortText and provides
additional information to identify switch location and contact
information for switch administrators; it is the intended format for
reading via standard email clients.
• The Tsc1 format is similar to the ShortText format but is compiled to
simplify machine processing of email messages.
Max Size
(650—2,000,000)
The maximum number of bytes allowed for an email message compiled
for the profile. Most email messages are relatively small, under 2KB.
However, emails that are produced by a capture operation can be as
large as 1MB due to the inclusion of file attachments.
Email Subject The subject line in the email to be sent. It is the string that is appended to
the string generated by CallHome for the email message subject line.
Enable Capture Enables or disables the capture operations for the profile. Only the Tech
Support Center profile is allowed to define and execute capture
operations on the switch.
Time of Day The time of day, in HH:MM format, when the capture operation will be
executed on the switch. Only the Tech Support Center profile is allowed to
define and execute capture operations on the switch. The default is 02:30.
Day of Week The day of the week–specified as Sunday, Monday, Tuesday,
Wednesday, Thursday, Friday or Saturday–when the capture operation
will be executed on the switch. The default is Monday.
Interval (1—26 weeks) The number of weeks that must pass between executions of the capture
operation. The default is 1.
Address The email address of the recipient added to the Tech Support Center
profile. A maximum of 10 addresses is allowed and displayed in the
Addresses window.
To create a Call Home Tech Support Center profile:
1. Open the Switch menu, select Call Home, and then select Profile Manager.
2. The Call Home Profile Manager dialog box is displayed.
3. Choose one of the following options to open the Call Home Profile Editor—Create Tech Support Center
Profile dialog box:
•Click Support on the tool bar.
• Select Edit > Create Tech Support Center Profile.
• Select an event level threshold option (Alarm, Critical, Warn, None) from the Level drop-down list.
86
Page 87

4. Select a format type for the message text being sent (FullText, ShortText, or Tsc1) from the Format
drop-down list.
5. Enter any changes to the maximum size of the message being sent.
6. Enter any changes to the subject of the email.
7. In the Capture area, select the Enable Capture option to enable the capture feature, and specify the
time of day, day of week, and number of weeks between captures.
8. Enter the email addresses of the recipient, and then click Add to add that person to the list of recipients.
9. Click OK to save the changes and close the dialog box.
Applying all profiles on a switch to other switches
You can apply all profiles on a switch to one or more switches in a fabric. The Call Home Profile Multiple
Switch Apply dialog box (Figure 47) appears if you select the Apply Changes to Multiple Switches in
Fabric option on the Call Home Profile Manager dialog box (Figure 44). The Available Switches list shows
all the switches in the fabric. Switch names that are disabled do not have current Call Home firmware and
cannot receive any profiles. The Selected Switches list shows the switch names that you selected to receive
all profiles from the switch.
To apply a profile to other switches:
1. Select the switches to receive the profile from the Available Switches list.
2. Click the double-arrow button to move your selections to the Selected Switches list.
3. Click OK to start the process.
The Results area indicates success or failure of applying the profile to the switches you selected.
Figure 47 Call Home Profile Multiple Switch Apply dialog box
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 87
Page 88

Using the Call Home Message Queue
Use the Call Home Message Queue dialog box (Figure 48) to access the logged call home statistics. Click
Update Stats to refresh with the most recent switch Call Home information. Click Clear Queue to clear the
current statistics.
Figure 48 Call Home Message Queue dialog box
Testing Call Home Profiles
Use the Call Home Test Profile dialog box (Figure 49) to test the Call Home parameters currently
configured. Select one or more profiles in the window, and then click Test. To display the Call Home Test
Profile dialog box, open the Switch menu, select Call Home, and then select Test Profile.
Figure 49 Call Home Test Profile dialog box
88
Page 89
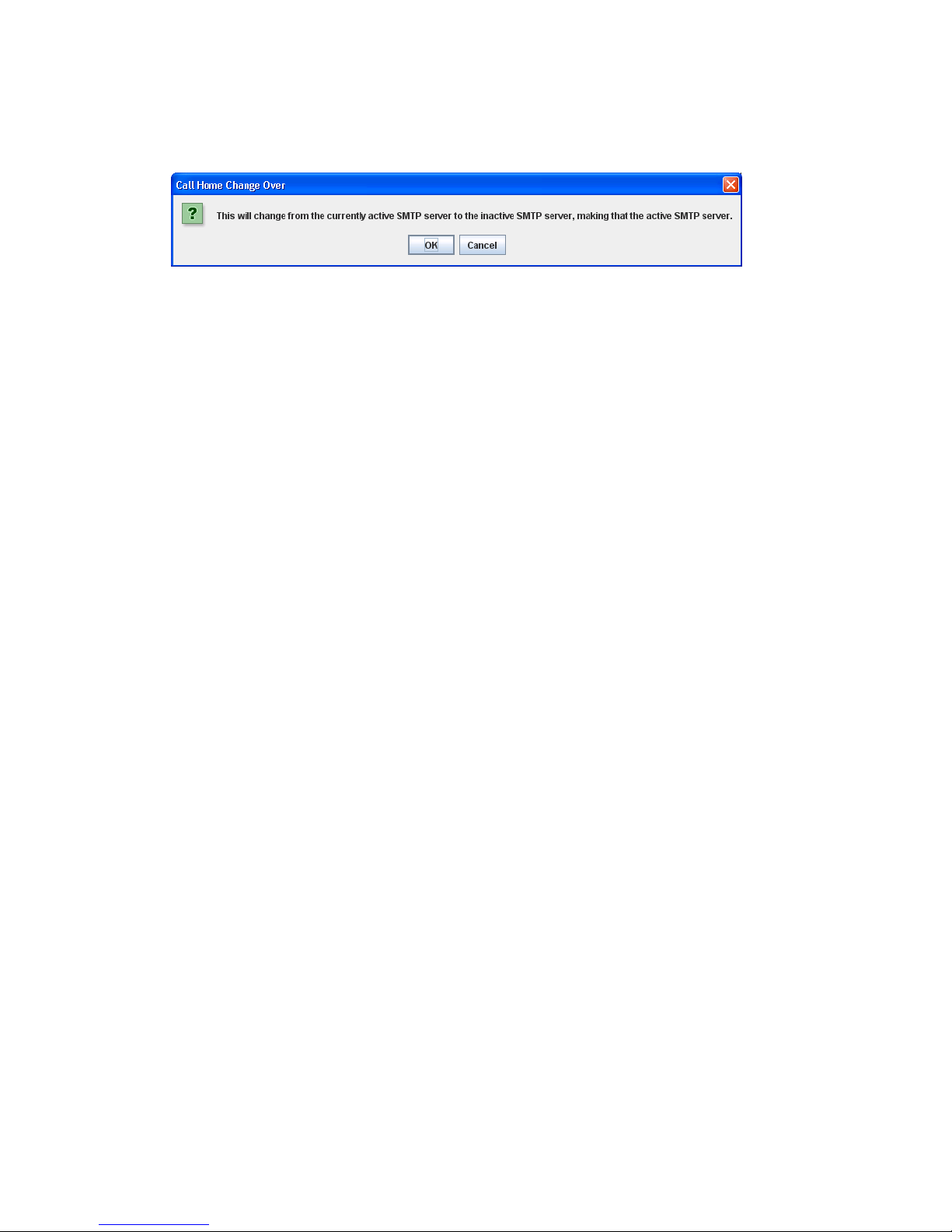
Change Over
The Change Over option changes the inactive SMTP server to the active SMTP server.
To make the inactive SMTP become the active SMTP:
1. Select Switch > Call Home > Change Over.
Figure 50 Call Home Change Over dialog box
2. Click OK to confirm the change over.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 89
Page 90

90
Page 91
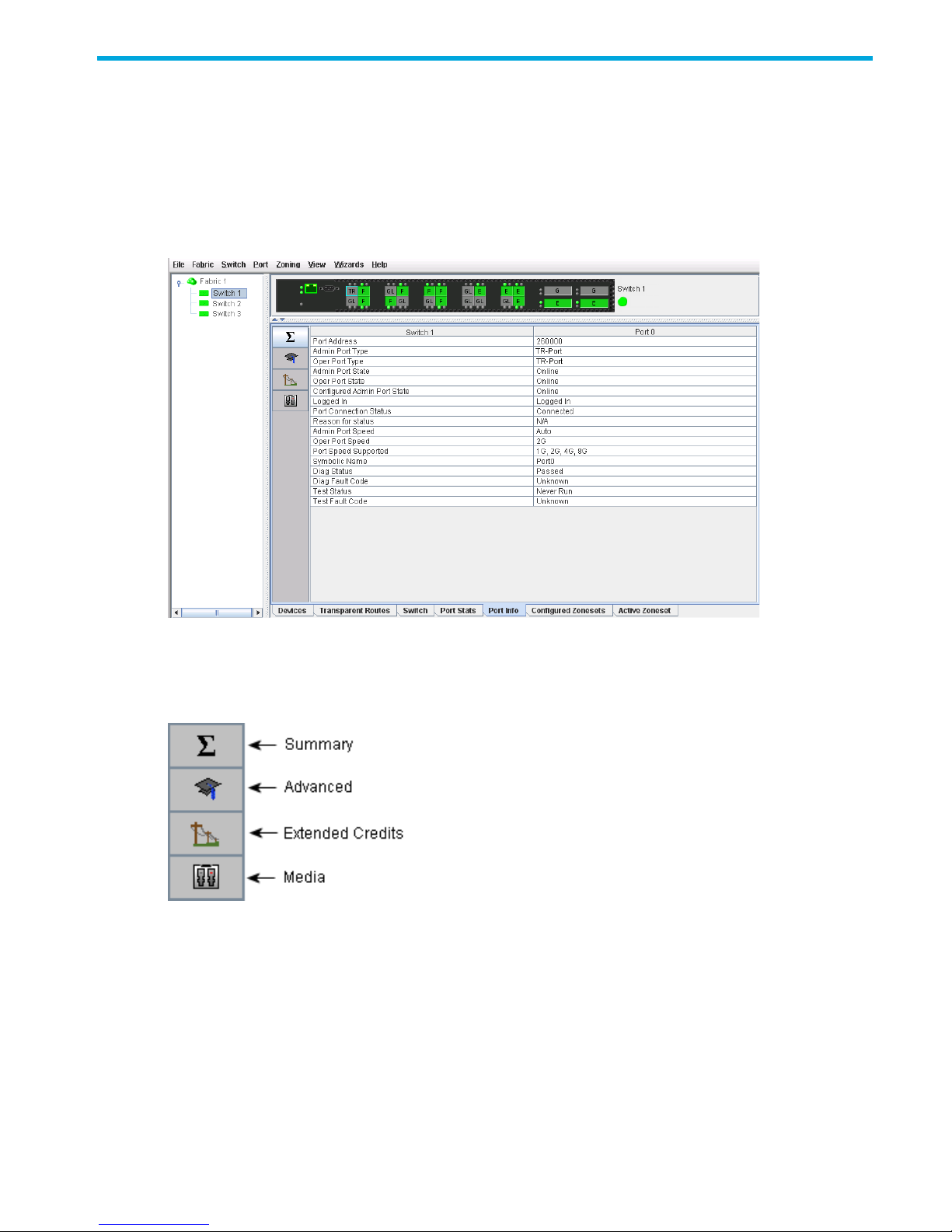
4 Managing Ports
The data windows provide port information and port statistics for selected ports. This section describes the
tasks that manage the ports and devices.
Port Information data window
The Port Information data window (Figure 51) displays detailed port information for the selected ports. To
open the Port Information data window, click the Port Info data window tab.
Figure 51 Port Information data window
Information in the Port Information data window is grouped and viewed by the Summary, Advanced,
Extended Credits, and Media buttons (Figure 18). Click a button to display the corresponding information
in the data window on the right.
Figure 52 Port Information data window buttons
The Port Information data window fields are described in Table 18.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 91
Page 92
Table 18 Port Information data window fields
Field Description
Summary Group
Port Address Port Fibre Channel address.
Administrative Port Type The administrative port type (G, GL, F, FL, TR, or Donor). This value is
persistent; it will be maintained during a switch reset. During port
auto-configuration, it will be used to determine which operational port
states are allowed.
Operational Port Type The port type that is currently active. This will be set during port
auto-configuration based on the administrative port type.
Administrative Port State The port state (Online, Offline, Diagnostics, or Down) that has been set by
the user. This state may be different from the configured administrative
state if the user has not saved it in the switch configuration. This state is
used at the time it is set to try to set the port operational state. This value is
not persistent and will be lost on a switch reset.
Operational Port State The port state that is currently active. This value may be different from the
administrative port state; for example, due to the presence of an error
condition.
Configured Administrative
Port State
The port state (Online, Offline, Diagnostics, or Down) which is saved in
the switch configuration, either by the user or at the factory. This value is
persistent; it will be maintained during a switch reset, and will be used
after a reset to set the port operational state.
Logged In Indicates whether the device connected to the port is logged in or not.
Port Connection Status E_Port connection status. Status can be None, Connecting, Connected or
Isolated.
Reason for Status Reason why E_Port is isolated.
Administrative Port Speed The port speed requested by the user.
Operational Port Speed The speed actually being used by the port.
Port Speed Supported The speeds supported by the port (1Gb/s, 2 Gb/s, 4 Gb/s, 8 Gb/s, 10
Gb/s and 20 Gb/s).
Symbolic Name User-defined name for a port.
Port WWN Port world wide name
POST Status Status from the most recent Power On Self Test
POST Fault Code Fault code from the most recent Power On Self Test
Test Status Status from the most recent port test
Test Fault Code Fault code from the most recent port test
Advanced Group
MFS Mode Multiple Frame Sequence bundling status.
Configured I/O Stream
Guard
Operational I/O Stream
Guard
Device Scan Device scan status. Enabled means the switch queries the connected
92
Configured RSCN message suppression status. If supported, status can be
enabled, disabled, or automatically determined by the switch.
The actual RSCN message suppression status. If supported, status can be
enabled, disabled, or automatically determined by the switch.
device during login for FC-4 descriptor information.
Page 93

Table 18 Port Information data window fields (Continued)
Field Description
Auto Performance Tuning Enables the switch to dynamically control the MFS_Enable, VI_Enable and
LCF_Enable features based on the operational state of the port.
AL Fairness Controls how frequently the switch can arbitrate for access. Affects only
ports running in loop (FL) mode.
Port Binding Ties a specific device WWN to a physical port number.
Upstream ISL The ISL over which the switch sends requests intended for the principal
switch
Downstream ISL The ISL over which the switch receives requests intended for the principal
switch.
Remote Switch WWN Displays WWN, if known, of the isolated switch attempting a connection
on that port.
Extended Credits Group
Extended Credits Requested Number of credits requested by other ports
Max Credits Available The maximum number of credits granted to a port that can be used when
extending port credits.
Credits to Donate The number of credits available to be donated by the selected port.
Donor Group The donor group of the selected port.
Valid Donor Groups The number of separate groups within which extended credits may be
donated and assigned.
Media Group
Media Type The transceiver fibre type, such as single mode, multi-mode, or copper.
Media Speed The maximum transceiver speed
Media The transceiver type.
Media Transmitter The transceiver transmitter type, such as longwave, shortwave, or
electrical.
Media Distance The maximum transceiver transmission distance
Media Vendor The company that manufactured the SFP
Media Vendor ID The IEEE registered company identification number
Media Part Number The part number assigned to the SFP
Media Revision Transceiver hardware version
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 93
Page 94

Port Statistics data window
The Port Statistics data window (Figure 53) displays statistics for port performance. To open the Port
Statistics data window, select one or more ports and click the Port Stats data window tab.
Figure 53 Port Statistics data window
The Statistics drop-down list is available on the Port Statistics data window, and provides different ways to
view detailed port information. Click the down arrow to open the drop-down list and select one of the
following:
• Select Absolute to view the total count of statistics since the last switch or port reset.
• Select Rate to view the number of statistics counted per second over the polling period.
• Select Baseline to view the total count of statistics since the last time the baseline was set. When
viewing baseline statistics, click Clear Baseline to set the current baseline. The baseline will also be set
when the switch status changes from unreachable to reachable.
The Port Statistics data window fields are described in Table 19.
Table 19 Port Statistics data window fields
Field Description
Start Time Beginning of the period over which the statistics apply.
• The start time for the Absolute view is not applicable.
• The start time for the Rate view is the beginning of polling interval.
• The start time for the Baseline view is the last time the baseline was
set.
End Time Last time the statistics were updated on the display.
Total Time Total time period from start time to end time.
Al Init Number of times the port entered the initialization state.
AL Init Error Number of times the port entered initialization and the initialization failed.
Bad Frames Number of frames that were truncated due to a loss of sync or the frame
94
Increments count when port has a sync loss.
didn't end with an EOF.
Page 95
Table 19 Port Statistics data window fields (Continued)
Field Description
BB_CreditRecoveryFrameFail
ure
Number of times more frames were lost during a credit recovery period
than the recovery process could resolve. This generates a Link Reset to
recover the credits.
BB_CreditRecoveryRRDYFail
ure
Number of times more R_RDYs were lost during a credit recovery period
than the recovery process could resolve. This generates a Link Reset to
recover the credits.
Class 2 Frames In Number of class 2 frames received by this port.
Class 2 Frames Out Number of class 2 frames transmitted by this port.
Class 2 Words In Number of class 2 words received by this port.
Class 2 Words Out Number of class 2 words transmitted by this port.
Class 3 Frames In Number of class 3 frames received by this port.
Class 3 Frames Out Number of class 3 frames transmitted by this port.
Class 3 Toss Number of class 3 frames that were discarded by this port. A frame may
be discarded because a missing frame or an E_D_TOV timeout is
detected, a reject frame is received, or a frame is received on an offline
port.
Class 3 Words In Number of class 3 words received by this port.
Class 3 Words Out Number of class 3 words transmitted by this port.
Decode Errors Number of invalid words transmitted detected during decoding. Decoding
is from the 10-bit characters and special K characters.
Ep Connects Number of E_Port logins.
FBusy Number of class 2 and class 3 fabric busy (F_BSY) frames generated by
this port in response to incoming frames. This usually indicates a busy
condition on the fabric or the N_port that is preventing delivery of this
frame.
Flow Errors Number of times a frame is received when all the switch ports receive
buffers are full. The normal Fabric Login exchange of flow control credit
should prevent this from occurring. The frame will be discarded.
FReject Number of frames, from devices, that have been rejected. Frames can be
rejected for any of a large number of reasons.
Invalid CRC Number of invalid Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) frames detected.
Invalid Destination Address Number of address identifier (S_ID, D_ID) errors. AL_PA equals non-zero
AL_PA found on F_Port.
Link Failures Number of optical link failures detected by this port. A link failure is a loss
of synchronization or by loss of signal while not in the offline state. A loss
of signal causes the switch to attempt to re-establish the link. If the link is
not re-established, a link failure is counted. A link reset is performed after
a link failure.
LIP(AL_PD,AL_PS) Number of F7, AL_PS LIPs, or AL_PD (vendor specific) resets performed.
LIP(F7,AL_PS) Used to reinitialize the loop. An L_port, identified by AL_PS, may have
LIP(F7,F7) A loop initialization primitive frame used to acquire an AL_PA.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 95
noticed a performance degradation and is trying to restore the loop.
Page 96

Table 19 Port Statistics data window fields (Continued)
Field Description
LIP(F8,AL_PS) Denotes a loop failure detected by the L_port identified by AL_PS.
LIP(F8,F7) A loop initialization primitive frame used to indicate that a Loop Failure
has been detected at its receiver and does not have a valid AL_PA.
Login Count Number of device logins that have occurred on the switch.
Logout Count Number of device logouts that have occurred on the switch.
Long Frame Count Number of incidents in which one or more frames greater than the
maximum size (2,136 bytes) are received.
Loop Timeouts Number of loop timeouts. The Loop timeout value (LP_TOV) is 22 seconds.
LP_TOV is used to keep a Loop from deteriorating due to protocol errors or
lost Ordered Sets.
Loss Of Sync Number of synchronization losses (>100 ms) detected by this port. A loss
of synchronization is detected by receipt of an invalid transmission word.
Primitive Sequence Errors Number of invalid transitions made in the Link State Machine. Primitives
are recognized words that are not data words.
Rx Link Resets Number of link resets received from a device.
Rx Offline Sequences Number of offline sequence primitives received by the port.
Short Frame Count Number of incidents in which one or more frames smaller than the
minimum size (24 bytes) are received.
Total Errors Total number of primitive and non-primitive port link errors.
Total Link Resets Number of link-reset primitives transmitted and received by the port.
Total LIPs Received Number of loop initialization primitive frames received.
Total LIPs Transmitted Number of loop initialization primitive frames transmitted.
Tx Offline Sequences Number of offline primitives transmitted by the port.
Total Rx Frames Total number of frames received by the port.
Total Rx Words Total number of words received by the port.
Total Tx Frames Total number of frames transmitted by the port.
Total Tx Words Total number of words transmitted by the port.
TotalRXErrors Total number of errors received by the port.
TotalTXErrors Total number of errors transmitted by the port.
Tx Link Resets Number of link reset primitives sent from this port to an attached port.
Total Offline Sequences Total number of offline sequences transmitted and received by the port.
96
Page 97
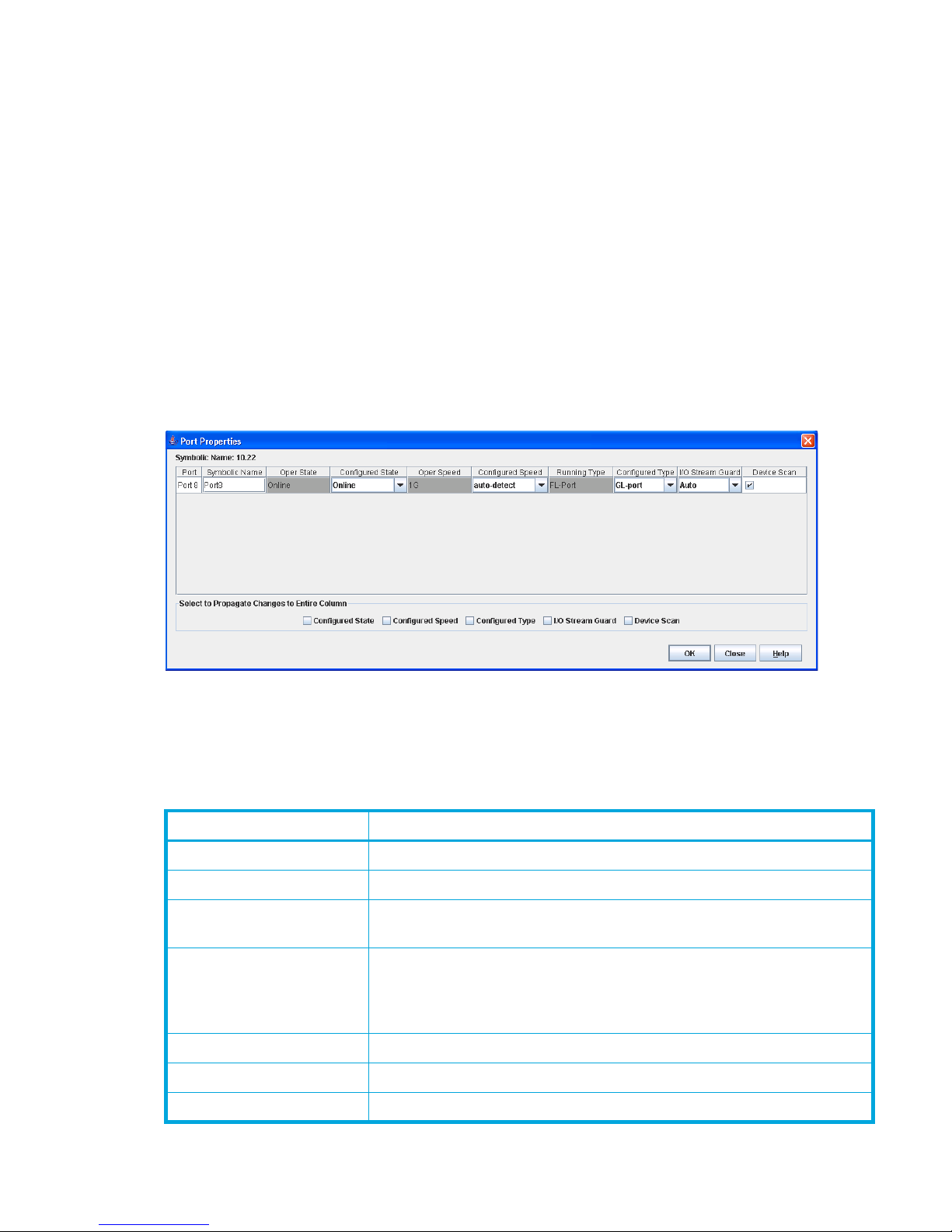
Viewing and configuring ports
Port color and text provide information about the port and its operational state. To display number and
status information for a port, position the cursor over a port on the faceplate display. The status information
changes depending on the View menu option selected. Green ports indicate active; gray ports indicate
inactive. Context-sensitive popup menus are displayed when you right-click a port icon in the faceplate
display. Use the drop-down lists in the Port Properties dialog box to change the following parameters:
• Port Symbolic Name
• Port States
• Port Types
• Port Speeds
• Port Transceiver Media Status
• I/O Stream Guard
• Device Scan
The port settings or characteristics are configured using the Port Properties dialog box (Figure 54). To open
the Port Properties dialog box, select one or more ports, open the Port menu, and then select Port
Properties.
Figure 54 Port Properties dialog box
Use the Select to Propagate Changes to Entire Column options to propagate the same change to all
selected ports. Select these options before making a change to a port.
The Port Properties dialog box fields are described in Table 20.
Table 20 Port Properties dialog box fields
State Description
Port The current port name
Symbolic Name User-defined name for a port.
Operational State The port state that is currently active. This value may be different from the
administrative port state, for example, due to an error condition.
Configured State The port state (Online, Offline, Diagnostics, or Down) saved in the switch
configuration, either by the user or at the factory. This value is persistent; it
will be maintained during a switch reset, and will be used after a reset to
set the port operational state.
Operational Speed The port speed that is currently active.
Configured Speed The port speed saved in the switch configuration.
Running Type The port type that is currently active.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 97
Page 98
Table 20 Port Properties dialog box fields (Continued)
State Description
Configured Type The port type saved in the switch configuration. To change, click in the
I/O Stream Guard The I/O Stream Guard option suppresses the Registered State Change
Device Scan The Device Scan feature queries the connected device during login for
Port symbolic name
To change the symbolic name of a port:
1. Open the faceplate display and select a port.
2. Select Port > Port Properties to open the Port Properties dialog box.
3. Click inside the Symbolic Name field and enter a new name for the port.
4. Click OK.
field and select an option from the drop-down list.
Notification (RSCN) messages on a port basis. I/O Stream Guard should
be enabled only on ports connected to initiator devices. To change, click
in the field and select an option from the drop-down list. The options are:
• Enable–Suppresses the reception of RSCN messages from ports for
which I/O Stream Guard is enabled.
• Disable–Enables free transmission and reception of RSCN messages.
• Auto–Suppresses the reception of RSCN messages when the port is
connected to an initiator device with an HBA. The default is Auto.
FC-4 descriptor information. Disable this option only if the scan creates a
conflict with the connected device.
Port states
The port operational state refers to the actual port state and not to the administrative state you may have
assigned. The port administrative state refers to the user-requested state. For more information, see ”Port
operational states” (page 98). Port administrative states have two forms: the configured administrative state
and the current administrative state. For more information, see ”Port administrative states” (page 99).
Port operational states
To view the operational state of each port in the faceplate display, open the View menu and select View
Port States. Table 21 lists the possible operational states and descriptions.
98
Page 99

Table 21 Port operational states
State Description
None Inactive—Port operational state is offline, but administrative state is online.
Port administrative states
The port administrative state determines the operational state of a port. The port administrative state has
two forms: the configured administrative state and the current administrative state.
Online—Port is active and ready to send data.
Isolated—E_Port has lost its connection. See Table 18 for information
about why the E_Port is isolated.
Offline—Port is active, can receive signal, but cannot accept a device
login.
Diagnostics—Port is in diagnostics mode in preparation for testing.
Downed—The port is disabled, power is removed from the lasers, and the
port cannot be logged in.
• Configured administrative state—The state that is saved in the switch configuration and is preserved
across switch resets. QuickTools always makes changes to the configured administrative state.
• Current administrative state—The state that is applied to the port for temporary purposes and is not
preserved across switch resets. The current administrative state is set with the Set Port command using
the CLI.
Table 22 describes the port administrative states.
To change the port administrative state:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Open the Port menu and select Port Properties to open the Port Properties dialog box.
3. Select the Port State option from the drop-down list.
4. Click OK to write the new port state request to the switch.
Table 22 Port administrative states
State Description
Online Activates and prepares port to send data.
Offline Prevents port from receiving signal and accepting a device login.
Diagnostics Prepares port for testing and prevents the port from accepting a device
login.
Downed Disables the port.
HP StorageWorks SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch QuickTools Switch Management User Guide 99
Page 100
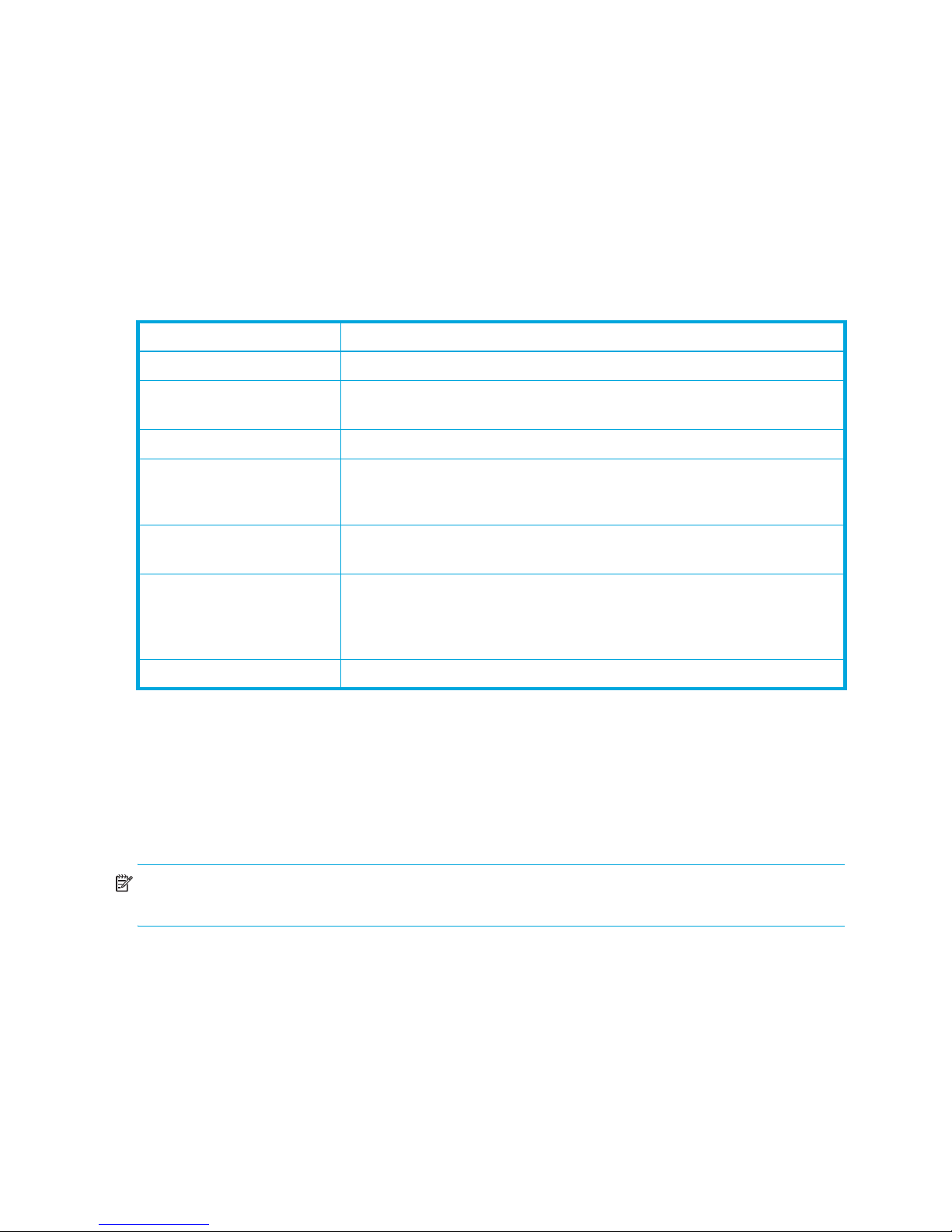
Port types
To display the port type status, open the View menu and select View Port Types. Table 23 lists the possible
port types and their descriptions. Each port can be configured to self-discover the proper port type to
match the device or switch to which it is connected. The Running Type field on the Port Properties dialog
box indicates the port type that is currently active.
To change the port type:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Select Port > Port Properties to open the Port Properties dialog box.
3. Select the Port Type option from the drop-down list.
4. Click OK to write the new port type to the switch.
Table 23 Port types
State Description
F_Port Fabric port—Supports a single public device (N_Port).
FL_Port Fabric loop port—Self-discovers a single device (N_Port) or a loop of up
to 126 public devices (NL_Port).
G_Port Generic port—Self-discovers as an F_Port or an E_Port.
GL_Port Generic loop port—Self-discovers as an F_Port, FL_Port, or an E_Port.
GL_Port is the default port type. A single device on a public loop will
attempt to configure as an F_Port first, then if that fails, as an FL_Port.
E_Port Expansion port—The mode that a G_Port or GL_Port is in when attached
TR_Port Transparent Router port—Enables devices on a remote fabric to be
Donor Donor port—Enables buffer credits to be used by another port.
Port speeds
SFP ports with 8Gb SFPs installed can transmit and receive at 2 Gb/s, 4 Gb/s, or 8 Gb/s. XPAK ports
can transmit and receive at 10 Gb/s or 20 Gb/s. All ports can be configured for either a fixed
transmission speed or to sense (auto-detect) the transmission speed of the device to which it is connected.
To display the speed of each port, open the View menu and select View Port Speeds. See Table 24 for the
possible port speeds.
NOTE: 8 Gb/s SFPs do not support 1 Gb/s speed. You should not set the port speed to 1 Gb/s if an 8
Gb/s SFP is inserted, as the port will be downed if you do.
To change the port transmission speed:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Open the Port menu and select Port Properties to open the Port Properties dialog box.
3. Select the Port Speed option from the drop-down list.
4. Click OK to write the new port speed to the switch.
by an ISL (inter-switch link) to another fibre channel switch.
mapped to devices on the local HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch fabric.
TR_Ports do not support online port diagnostics. See ”Testing ports”
(page 103).
100
 Loading...
Loading...