HP StorageWorks P4000 User Manual

HP StorageWorks
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide
Part number: AW588-10501
First edition: March 2010

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2010, 2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211
and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items
are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Acknowledgements
Microsoft, Windows, Windows XP, and Windows NT are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Warranty
WARRANTY STATEMENT: To obtain a copy of the warranty for this product, see the warranty information website:
http://www.hp.com/go/storagewarranty

Contents
1 Component identification .................................................................. 11
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway hardware components .................................................................... 11
2 Installing and configuring the server ................................................... 15
Setup overview ......................................................................................................................... 15
Determine an access method ............................................................................................... 15
Check kit contents ..................................................................................................................... 15
Locate and record the serial number ............................................................................................ 16
Install the storage system hardware ............................................................................................. 16
Access the storage system .......................................................................................................... 16
Power on the server and log on .................................................................................................. 17
Configure the storage system using the HP StorageWorks Rapid Startup Wizard ............................... 18
Complete system configuration ................................................................................................... 19
Additional access methods ......................................................................................................... 20
Using the remote browser method ......................................................................................... 20
Using the Remote Desktop method ........................................................................................ 21
Using the Telnet method ...................................................................................................... 21
Enabling Telnet ............................................................................................................ 21
Default storage settings .............................................................................................................. 21
Physical configuration ......................................................................................................... 21
Default boot sequence ........................................................................................................ 22
3 Cluster configuration ........................................................................ 23
Creating and configuring the cluster ............................................................................................ 24
Set IP addresses for the network connections .......................................................................... 24
Join both storage servers to the domain ................................................................................. 27
Initialize and format the storage disks .......................................................................................... 29
Validate the configuration .......................................................................................................... 30
Create the cluster ...................................................................................................................... 32
Add services or applications to the cluster .................................................................................... 33
Verify that the cluster is operational ............................................................................................. 35
4 Cluster administration ....................................................................... 37
Cluster overview ....................................................................................................................... 37
Cluster terms and components .................................................................................................... 37
Nodes .............................................................................................................................. 37
Resources .......................................................................................................................... 37
Cluster groups ................................................................................................................... 38
Virtual servers .................................................................................................................... 38
Failover and failback .......................................................................................................... 38
Quorum disk ..................................................................................................................... 38
Cluster planning ....................................................................................................................... 39
Storage planning ............................................................................................................... 39
Network planning .............................................................................................................. 39
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 3

Protocol planning ............................................................................................................... 40
Cluster groups and resources, including file shares ........................................................................ 41
Cluster group overview ....................................................................................................... 41
Node-based cluster groups ........................................................................................... 41
Load balancing ........................................................................................................... 42
File share resource planning issues ....................................................................................... 42
Resource planning ....................................................................................................... 42
Permissions and access rights on share resources ............................................................. 42
NFS cluster-specific issues ............................................................................................. 43
Non-cluster aware file sharing protocols ................................................................................ 43
Adding new storage to a cluster ........................................................................................... 43
Creating physical disk resources .................................................................................... 44
Creating file share resources ......................................................................................... 44
Creating NFS share resources ....................................................................................... 44
Shadow copies in a cluster .................................................................................................. 44
Extend a LUN in a cluster .................................................................................................... 45
MSNFS administration on a server cluster .............................................................................. 45
Best practices for running Server for NFS in a server cluster ............................................... 45
Print services in a cluster ............................................................................................................ 45
Creating a cluster printer spooler .......................................................................................... 46
Advanced cluster administration procedures ................................................................................. 46
Failing over and failing back ............................................................................................... 46
Restarting one cluster node .................................................................................................. 47
Shutting down one cluster node ............................................................................................ 47
Powering down the cluster ................................................................................................... 47
Powering up the cluster ....................................................................................................... 48
5 System administration tools ................................................................ 49
Microsoft Windows Storage Server 2008 administration tools ........................................................ 49
Remote Desktop for Administration ....................................................................................... 49
Share and Storage Management .......................................................................................... 49
Microsoft Services for Network File System ............................................................................. 50
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (ADLDS) ........................................................... 50
Configuring ADLDS ...................................................................................................... 51
Single Instance Storage ....................................................................................................... 52
Print Management .............................................................................................................. 53
6 File server management .................................................................... 55
File services features in Windows Storage Server 2008 ................................................................. 55
Single Instance Storage ....................................................................................................... 55
File Server Resource Manager .............................................................................................. 55
Windows SharePoint Services .............................................................................................. 55
File services management .......................................................................................................... 55
Configuring data storage .................................................................................................... 56
Storage management utilities ............................................................................................... 56
Array management utilities ............................................................................................ 56
Array Configuration Utility ............................................................................................ 57
Disk Management utility ............................................................................................... 58
Guidelines for managing disks and volumes .......................................................................... 58
Disk quotas ....................................................................................................................... 58
Adding storage .................................................................................................................. 59
Expanding storage ...................................................................................................... 60
Extending storage using Windows Storage Utilities .......................................................... 60
Volume shadow copies .............................................................................................................. 61
4

Shadow copy planning ....................................................................................................... 61
Identifying the volume .................................................................................................. 62
Allocating disk space ................................................................................................... 62
Identifying the storage area .......................................................................................... 63
Determining creation frequency ..................................................................................... 63
Shadow copies and drive defragmentation ............................................................................ 63
Mounted drives .................................................................................................................. 64
Managing shadow copies ................................................................................................... 64
The shadow copy cache file .......................................................................................... 65
Enabling and creating shadow copies ............................................................................ 66
Viewing a list of shadow copies ..................................................................................... 67
Set schedules .............................................................................................................. 67
Viewing shadow copy properties ................................................................................... 67
Redirecting shadow copies to an alternate volume ........................................................... 68
Disabling shadow copies .............................................................................................. 68
Managing shadow copies from the storage system desktop ..................................................... 69
Shadow Copies for Shared Folders ....................................................................................... 69
SMB shadow copies .................................................................................................... 70
NFS shadow copies ..................................................................................................... 71
Recovery of files or folders ............................................................................................ 72
Recovering a deleted file or folder .................................................................................. 72
Recovering an overwritten or corrupted file ...................................................................... 73
Recovering a folder ...................................................................................................... 73
Backup and shadow copies .......................................................................................... 74
Shadow Copy Transport ...................................................................................................... 74
Folder and share management ................................................................................................... 74
Folder management ............................................................................................................ 75
Share management ............................................................................................................ 81
Share considerations .................................................................................................... 81
Defining Access Control Lists ......................................................................................... 82
Integrating local file system security into Windows domain environments ............................. 82
Comparing administrative (hidden) and standard shares ................................................... 82
Managing shares ........................................................................................................ 83
File Server Resource Manager .................................................................................................... 83
Quota management ........................................................................................................... 83
File screening management ................................................................................................. 84
Storage reports .................................................................................................................. 84
Other Windows disk and data management tools ......................................................................... 84
Additional information and references for file services .................................................................... 84
Backup ............................................................................................................................. 84
HP StorageWorks Library and Tape Tools .............................................................................. 84
Antivirus ............................................................................................................................ 85
7 Troubleshooting, servicing, and maintenance ....................................... 87
Troubleshooting the storage system .............................................................................................. 87
WEBES (Web Based Enterprise Services) ..................................................................................... 87
Maintenance and service ........................................................................................................... 88
Maintenance updates ......................................................................................................... 88
System updates ............................................................................................................ 88
Firmware updates ............................................................................................................... 88
Certificate of Authenticity ........................................................................................................... 88
8 Support and other resources .............................................................. 89
Contacting HP .......................................................................................................................... 89
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 5

Subscription service ............................................................................................................ 89
Related information ................................................................................................................... 89
HP websites ....................................................................................................................... 89
Typographic conventions ........................................................................................................... 90
Rack stability ............................................................................................................................ 91
Customer self repair .................................................................................................................. 91
HP product documentation survey ............................................................................................... 91
9 System recovery ............................................................................... 93
The System Recovery DVD .......................................................................................................... 93
To restore a factory image ......................................................................................................... 93
Managing disks after a restoration .............................................................................................. 93
A Regulatory compliance notices .......................................................... 95
Regulatory compliance identification numbers .............................................................................. 95
Federal Communications Commission notice ................................................................................ 95
FCC rating label ................................................................................................................ 95
Class A equipment ....................................................................................................... 95
Class B equipment ....................................................................................................... 96
Declaration of Conformity for products marked with the FCC logo, United States only ................. 96
Modification ...................................................................................................................... 96
Cables .............................................................................................................................. 96
Canadian notice (Avis Canadien) ............................................................................................... 96
Class A equipment ............................................................................................................. 96
Class B equipment .............................................................................................................. 97
European Union notice .............................................................................................................. 97
Japanese notices ...................................................................................................................... 97
Japanese VCCI-A notice ...................................................................................................... 97
Japanese VCCI-B notice ...................................................................................................... 97
Japanese power cord statement ............................................................................................ 97
Korean notices ......................................................................................................................... 98
Class A equipment ............................................................................................................. 98
Class B equipment .............................................................................................................. 98
Taiwanese notices ..................................................................................................................... 98
BSMI Class A notice ........................................................................................................... 98
Taiwan battery recycle statement .......................................................................................... 98
Laser compliance notices ........................................................................................................... 99
English laser notice ............................................................................................................. 99
Dutch laser notice ............................................................................................................... 99
French laser notice ........................................................................................................... 100
German laser notice ......................................................................................................... 100
Italian laser notice ............................................................................................................ 100
Japanese laser notice ........................................................................................................ 101
Spanish laser notice ......................................................................................................... 101
Recycling notices .................................................................................................................... 101
English notice .................................................................................................................. 101
Bulgarian notice ............................................................................................................... 102
Czech notice ................................................................................................................... 102
Danish notice .................................................................................................................. 102
Dutch notice .................................................................................................................... 102
Estonian notice ................................................................................................................ 103
Finnish notice ................................................................................................................... 103
French notice ................................................................................................................... 103
German notice ................................................................................................................. 103
6

Greek notice .................................................................................................................... 104
Hungarian notice ............................................................................................................. 104
Italian notice .................................................................................................................... 104
Latvian notice .................................................................................................................. 104
Lithuanian notice .............................................................................................................. 105
Polish notice .................................................................................................................... 105
Portuguese notice ............................................................................................................. 105
Romanian notice .............................................................................................................. 105
Slovak notice ................................................................................................................... 106
Spanish notice ................................................................................................................. 106
Swedish notice ................................................................................................................. 106
Turkish notice ................................................................................................................... 106
Battery replacement notices ...................................................................................................... 107
Dutch battery notice .......................................................................................................... 107
French battery notice ........................................................................................................ 108
German battery notice ...................................................................................................... 108
Italian battery notice ......................................................................................................... 109
Japanese battery notice .................................................................................................... 109
Spanish battery notice ...................................................................................................... 110
Index ............................................................................................... 111
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 7

Figures
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway front panel components ................................................ 111
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway front panel LEDs ........................................................... 122
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway rear panel components ................................................. 123
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway rear panel LEDs ........................................................... 134
HP StorageWorks Rapid Startup Wizard Welcome screen ............................................ 195
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway network infrastructure .................................................... 236
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway connections ................................................................. 257
Private connection status .......................................................................................... 268
Public connection status ........................................................................................... 269
Computer Name tab of System Properties .................................................................. 2810
Computer Name Changes dialog box ....................................................................... 2811
Initialize Disk 1 (the witness disk) .............................................................................. 2912
Create new simple volume ....................................................................................... 2913
Failover Cluster Management user interface ................................................................ 3014
Select servers to be validated for the cluster ................................................................ 3115
Validating the cluster configuration ............................................................................ 3216
Entering cluster name .............................................................................................. 3317
Select Service or Application .................................................................................... 3418
System administrator view of Shadow Copies for Shared Folders ................................... 6519
Shadow copies stored on a source volume ................................................................. 6520
Shadow copies stored on a separate volume .............................................................. 6621
Accessing shadow copies from My Computer ............................................................. 6922
Client GUI ............................................................................................................. 7123
Recovering a deleted file or folder ............................................................................. 7324
Properties dialog box, Security tab ............................................................................ 7625
Advanced Security settings dialog box, Permissions tab ............................................... 7726
User or group Permission Entry dialog box ................................................................. 7827
Advanced Security Settings dialog box, Auditing tab ................................................... 7928
Select User or Group dialog box ............................................................................... 7929
Auditing Entry dialog box for folder name NTFS Test ................................................... 8030
Advanced Security Settings dialog box, Owner tab ..................................................... 8131
8

Tables
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway front panel LED descriptions ........................................... 121
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway rear panel LED descriptions ........................................... 132
HP Rapid Startup Wizard configuration options .......................................................... 183
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway RAID configuration ....................................................... 224
Sharing protocol cluster support ................................................................................ 405
Tasks and utilities needed for storage system configuration ........................................... 566
Document conventions ............................................................................................. 907
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 9

10
1 Component identification
This chapter provides illustrations of the storage system hardware components.
NOTE:
The keyboard, mouse, and monitor are used only for the direct attached method of accessing the
server. They are not provided with your storage system.
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway hardware components
The following figures show components and LEDs located on the front and rear panels of the P4000
Unified NAS Gateway.
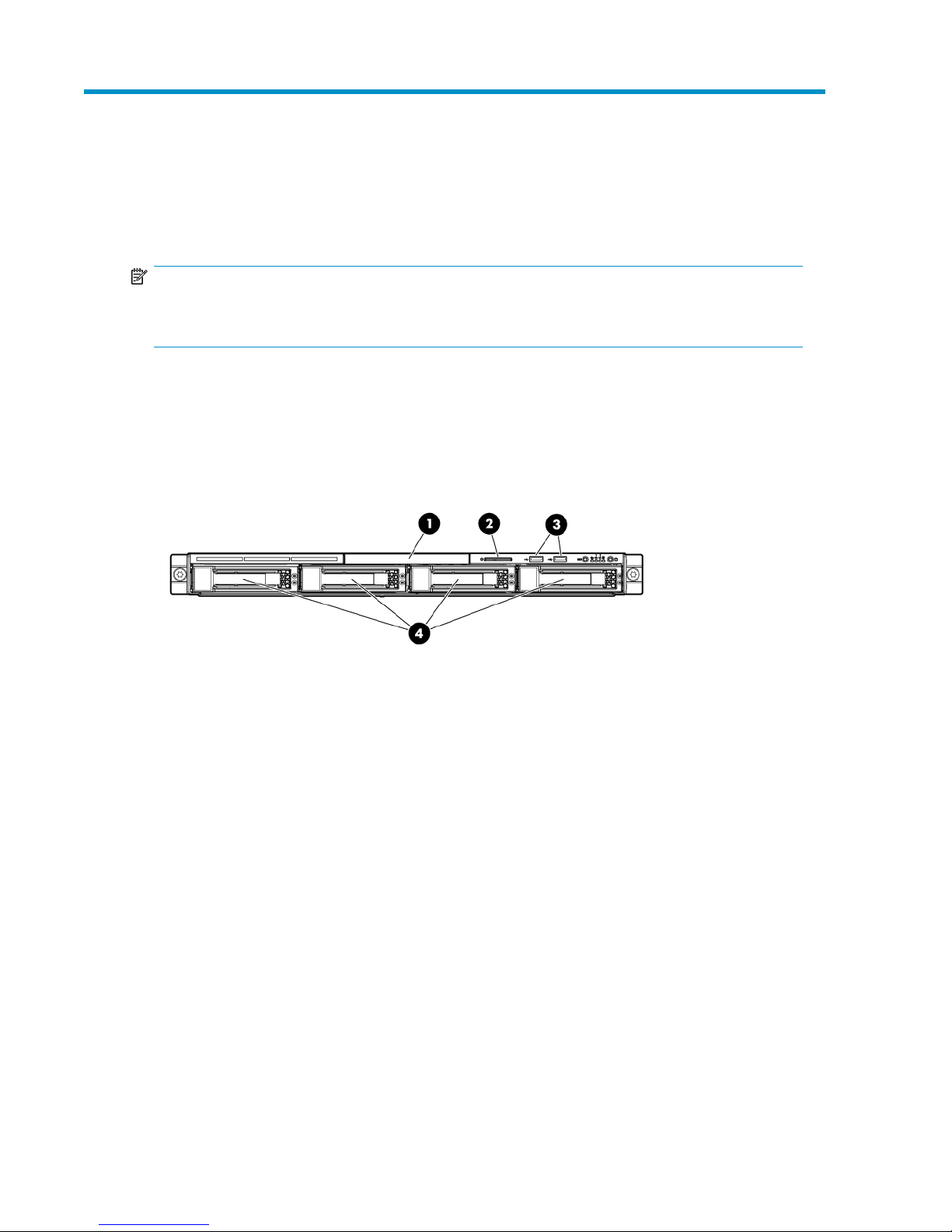
Figure 1 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway front panel components
.
1. DVD-RW drive
2. Serial label pull tab
3. Two (2) USB ports
4. Four (4) 3.5” hot-plug SAS/SATA hard drive bays
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 11
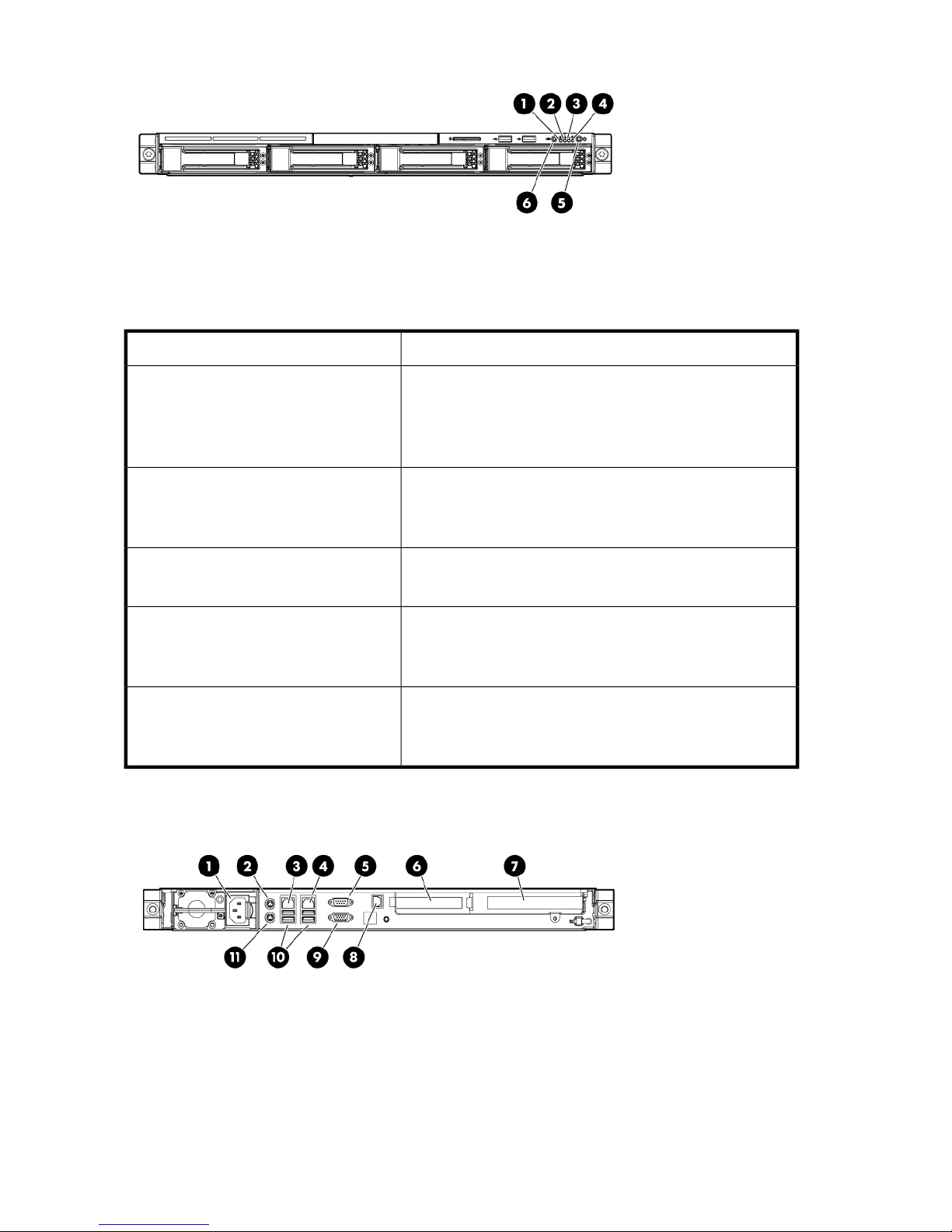
Figure 2 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway front panel LEDs
.
Table 1 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway front panel LED descriptions
StatusItem / Description
Green = System health is normal.
1. Internal health LED
Amber = System health is degraded.
Red = System health is critical.
Off = System health is normal (when in standby mode).
2. NIC 1 link/activity LED
3. NIC 2 link/activity LED
4. Drive activity LED
5. Power On/Standby button and system
power LED
6. UID button/LED
Green = Network link exists.
Flashing green = Network link and activity exist.
Off = No network link exists.
Green = Drive activity is normal.
Off = No drive activity exists.
Green = Normal (system on)
Amber = System is in standby, but power is still applied.
Off = Power cord is not attached or the power supply has failed.
Blue = Identification is activated.
Flashing blue = System is being managed remotely.
Off = Identification is deactivated.
Figure 3 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway rear panel components
.
Component identification12
1. Power cord connector
2. Mouse connector
3. 10/100/1000 NIC 1 connector/shared iLO 2 management port
4. 10/100/1000 NIC 2 connector
5. Serial connector
6. Low profile PCIe slot (occupied by Smart Array P212 controller)
7. Full-sized PCIe slot (occupied by NC364T 4-port NIC)
8. Dedicated iLO 2 management port (this port is optional and must be purchased separately)
9. Video connector
10. USB connectors (2)
11. Keyboard connector
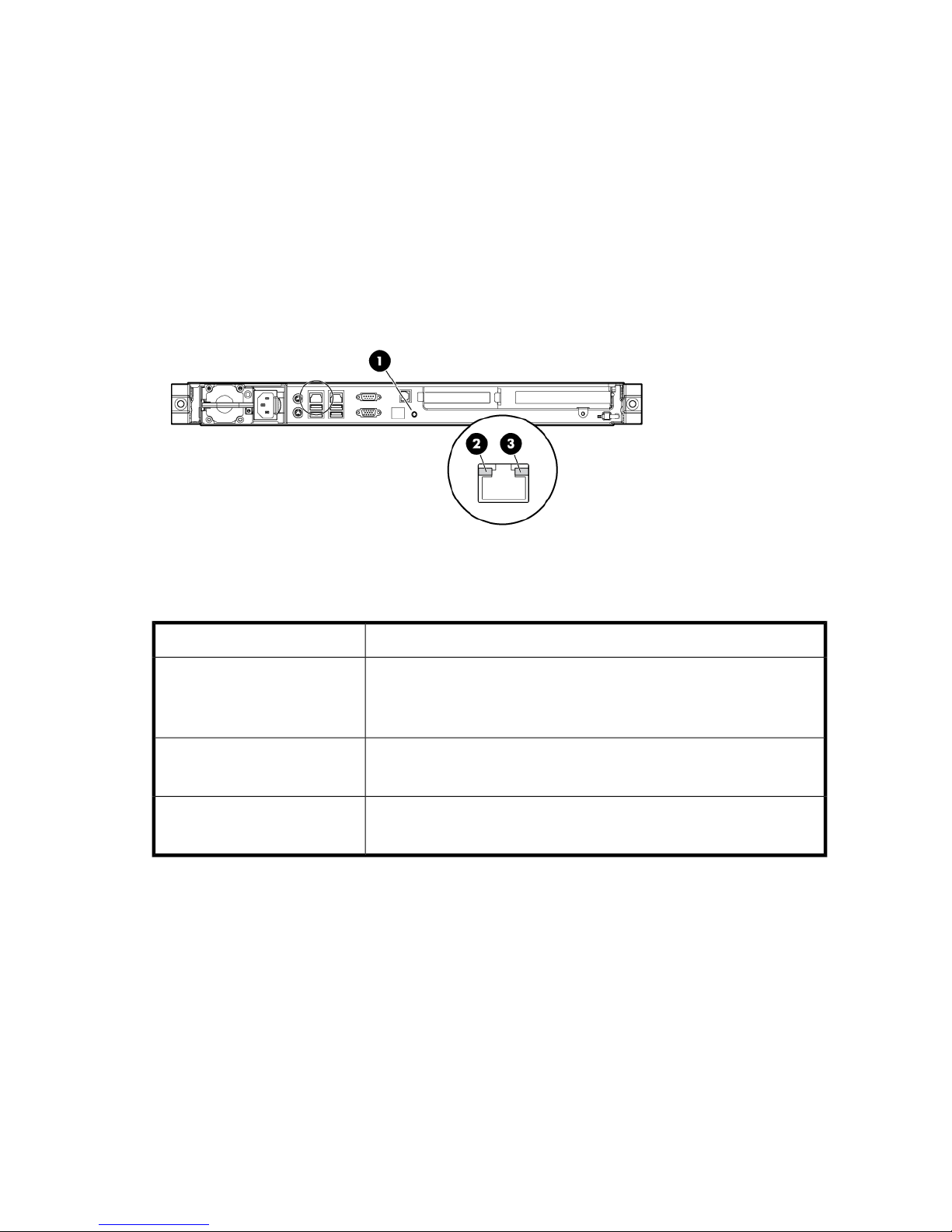
Figure 4 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway rear panel LEDs
.
Table 2 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway rear panel LED descriptions
StatusItem / Description
Blue = Activated
1. UID button/LED
2. NIC/iLO 2 link
3. NIC/iLO 2 activity
Flashing = System is being managed remotely.
Off = Deactivated
Green or flashing green = Activity exists.
Off = No activity exists.
Green = Link exists.
Off = No link exists.
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 13

Component identification14
2 Installing and configuring the server
Setup overview
The HP StorageWorks P4000 Unified NAS Gateway comes preinstalled with the Microsoft Windows®
Storage Server™ 2008 Enterprise x64 Edition operating system with Microsoft iSCSI Software Target
and a Microsoft Cluster Service (MSCS) license included.
IMPORTANT:
• Windows Storage Server 2008 x64 operating systems are designed to support 32–bit applications
without modification; however, any 32–bit applications that are run on these operating systems
should be thoroughly tested before releasing the storage system to a production environment.
• Windows Storage Server x64 editions support only x64-based versions of Microsoft Management
Console (MMC) snap-ins, not 32-bit versions.
Determine an access method
Before you install the storage system, you need to decide on an access method.
The type of access you select is determined by whether or not the network has a Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. If the network has a DHCP server, you can install the storage
system through the direct attachment or remote management methods. If your network does not have
a DHCP server, you must access the storage system through the direct attachment method.
The direct attachment method requires a display, keyboard, and mouse. These components are not
provided with the storage system.
IMPORTANT:
Only the direct attach and remote management access methods can be used to install the storage
system. After the storage system installation process is complete and the system's IP address has been
assigned, you can then additionally use the remote browser and remote desktop methods to access
the storage system.
Check kit contents
Remove the contents, making sure you have all the components listed below. If components are missing,
contact HP technical support.
• HP StorageWorks P4000 Unified NAS Gateway (with operating system preloaded)
• Power cord(s)
• Product Documentation and Safety and Disposal Documentation CD
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 15

• HP StorageWorks Storage System Recovery DVD
• End User License Agreement
• Certificate of Authenticity Card
• Slide rail assembly
• HP ProLiant Essentials Integrated Lights-Out 2 Advanced Pack
Locate and record the serial number
Before completing the installation portion of this guide, locate and write down the storage system's
serial number.
The storage system's serial number is located in three places:
• Top of the storage system
• Back of the storage system
• Inside the storage system shipping box
Install the storage system hardware
1. Install the rail kit by following the HP Rack Rail Kit installation instructions.
2. If connecting to the storage system using the direct attach method, connect the following cables
to the back panel of the storage system in the following sequence: keyboard, mouse, network
cable, monitor cable, and power cable.
NOTE:
• The keyboard, mouse, and monitor are not provided with the storage system.
3. If connecting to the storage system using the remote management method, connect a network
cable to a data port, a network cable to the iLO 2 port, and power cable.
Access the storage system
Use either the direct connect or remote management method to connect to the storage system.
IMPORTANT:
Only the direct attach and remote management access methods can be used to install the storage
system. After the storage system installation process is complete and the system's IP address has been
assigned, you can then additionally use the remote browser and remote desktop methods to access
the storage system.
• Direct attach — Connect a monitor, keyboard, and mouse directly to the storage system. This access
method is mandatory if your network does not have a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
server.
NOTE:
• The keyboard, mouse, and monitor are not provided with the storage system.
Installing and configuring the server16

• Remote management — Access the storage system using the Integrated Lights-Out 2 remote man-
agement method:
1. Ensure that a network cable is connected to the iLO 2 port located on the back of the storage
system.
2. Locate the iLO 2 Network Settings tag attached to the storage system and record the default
user name, password, and DNS name.
3. From a remote computer, open a standard Web browser and enter the iLO 2 management
hostname of the storage system.
NOTE:
By default, iLO 2 obtains the management IP address and subnet mask from your
network’s DHCP server. The hostname found on the iLO 2 tag is automatically registered
with your network’s DNS server.
4. Using the default user information provided on the iLO 2 Network Settings tag, log on to the
storage system.
For detailed instructions on using iLO 2, see the HP Integrated Lights–Out 2 user guide.
Power on the server and log on
Power on the server after installing the hardware and connecting the cables. Powering on the server
for the first time initiates the storage system installation process.
1. Power on the system by pushing the power button on the front panel. If using iLO 2, click
Momentary Press on the Power Management page to power on the server, then click Launch on
the Status Summary page to open the iLO 2 Integrated Remote Console and complete the
installation process.
The storage system starts and displays an HP Network Storage System installation screen. The
storage system installation process takes approximately 10–15 minutes.
NOTE:
Your storage system comes pre-installed with the Microsoft Windows Storage Server 2008
operating system. There is no operating system installation required.
When the storage system installation process nears completion, the Windows Storage Server
2008 desktop displays the following message: The user's password must be changed before
logging on the first time. Log on to the storage system by establishing an Administrator password:
2. Click OK.
3. Type an Administrator password in the New password box.
4. Re-type the Administrator password in the Confirm password box.
5. Click the blue arrow next to the Confirm password box.
6. Click OK.
After the Administrator password has been set, the storage system completes the installation
process and restarts.
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 17
7. When prompted, press CTRL+ALT+DELETE to log on to the system. If using iLO 2, on the iLO
2 Integrated Remote Console tab, click the button labeled CAD and then click the Ctrl-Alt-Del
menu item.
IMPORTANT:
After establishing the new Administrator password, be sure to remember it and record it in a safe
place if needed. HP has no way of accessing the system if the new password is lost.
After logging in for the first time, the Welcome screen of the HP StorageWorks Rapid Startup Wizard
opens. Use the HP StorageWorks Rapid Startup Wizard to set up your system with basic configuration
information.
Configure the storage system using the HP StorageWorks Rapid
Startup Wizard
The HP StorageWorks Rapid Startup Wizard is displayed after logging in for the first time. This wizard
guides you through configuring system settings. The HP StorageWorks Rapid Startup Wizard provides
the following options for configuring the storage system:
Table 3 HP Rapid Startup Wizard configuration options
Provide Computer Information
Customize This Server
Configure HP Recommended Settings
Configuration settingsRapid Startup Wizard Section
Set time zone, Configure networking, Provide computer name and domain
Enable automatic updating and feedback, Download and install updatesUpdate This Server
Add roles, Add features, Enable Remote Desktop, Configure Windows
Firewall
Alert E-mail Notification, SNMP Settings, HP Lights-Out Configuration
Utility
Installing and configuring the server18
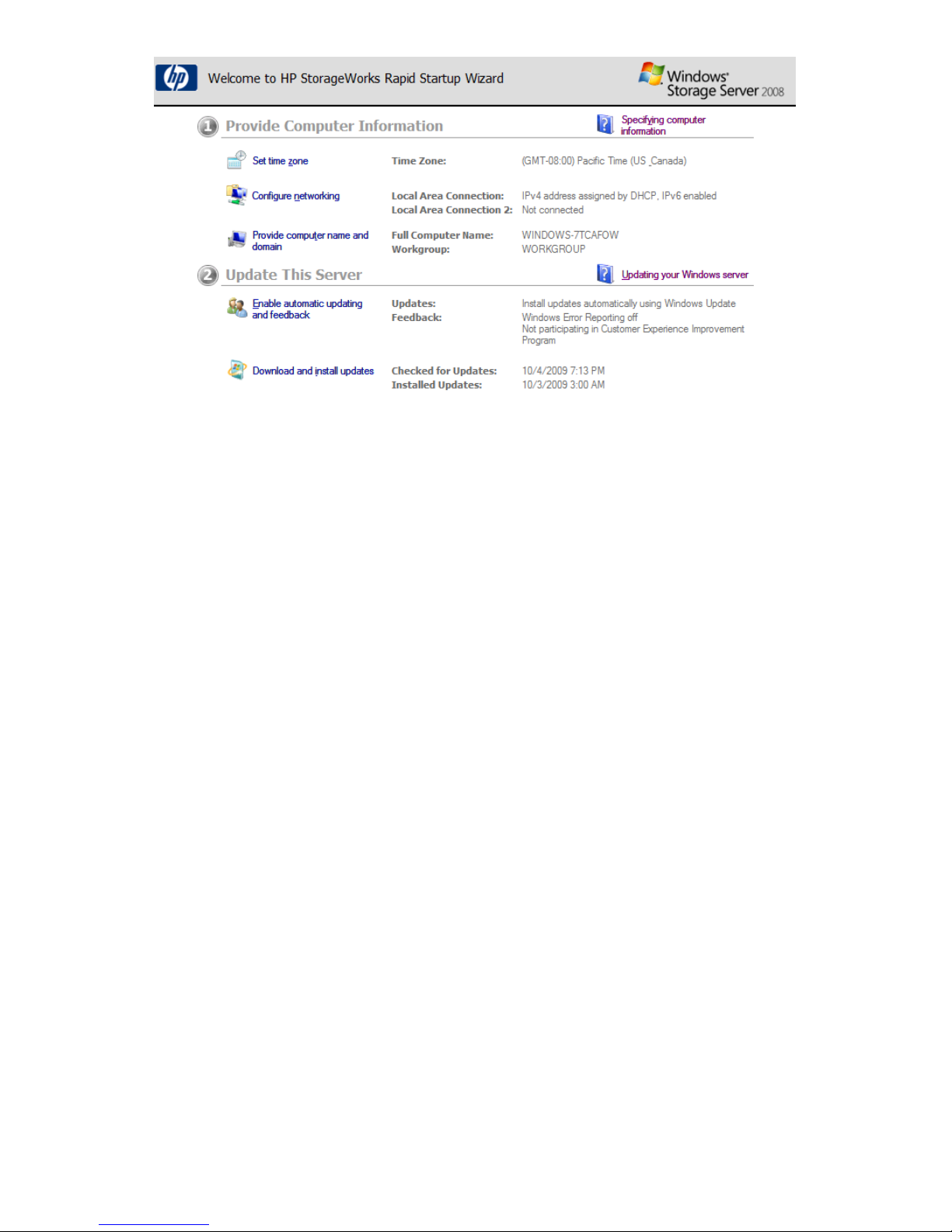
Figure 5 HP StorageWorks Rapid Startup Wizard Welcome screen
.
For detailed information about each of these configuration options, click the corresponding online
help link to the right of each section.
Complete system configuration
After the storage system is physically set up and the basic configuration is established, you must
complete additional setup tasks. Depending on the deployment scenario, these steps can vary.
Additional steps may include:
• Running Microsoft Windows Update — HP highly recommends running Microsoft Windows updates
to identify, review, and install the latest, applicable, critical security updates.
• Creating and managing users and groups—User and group information and permissions determine
whether a user can access files. If the storage system is deployed into a workgroup environment,
this user and group information is stored locally on the device. By contrast, if the storage system
is deployed into a domain environment, user and group information is stored on the domain.
• Joining workgroups and domains—These are the two system environments for users and groups.
Because users and groups in a domain environment are managed through standard Windows or
Active Directory domain administration methods, this document discusses only local users and
groups, which are stored and managed on the storage system. For information on managing users
and groups on a domain, see the domain documentation available on the Microsoft web site.
If the storage system is deployed in a domain environment, the domain controller will store new
accounts on the domain; however, remote systems will store new accounts locally unless they are
granted permissions to create accounts on the domain.
• Using Ethernet NIC teaming (optional)—Select models are equipped with an HP or Broadcom
NIC Teaming utility. The utility allows administrators to configure and monitor Ethernet network
interface controller (NIC) teams in a Windows-based operating system. These teams provide options
for increasing fault tolerance and throughput.
• Activating iLO 2 Advanced features using a license key—The Remote Console feature of iLO 2
requires a license key. The key is included with the storage system inside the Country Kit. See the
iLO 2 Advanced License Pack for activation instructions.
• Adjusting logging settings for system, application, and security events.
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 19

• Installing third-party software applications such as an antivirus application.
• Registering the server — To register the server, refer to the HP Registration website (http://re-
gister.hp.com).
Additional access methods
After the storage system installation process is complete and the system's IP address has been assigned,
you can then additionally use the remote browser, Remote Desktop, and Telnet Server methods to
access the storage system.
Using the remote browser method
The storage system ships with DHCP enabled on the network port. If the server is placed on a
DHCP-enabled network and the IP address or server name is known, the server can be accessed
through a client running Internet Explorer 5.5 (or later) on that network, using the TCP/IP 3202 port.
IMPORTANT:
Ensure that you have the following:
• Windows-based PC loaded with Internet Explorer 5.5 (or later) on the same local network as the
storage system
• DHCP-enabled network
• Server name or IP address of the storage system
To connect the server to a network using the remote browser method, ensure that the client is configured
to download signed ActiveX controls.
To connect the storage system to a network using the remote browser method
1. On the remote client machine open Internet Explorer and enter https:// and the server name
of the storage system followed by a hyphen (-), and then:3202. For example, https://
labserver-:3202.
NOTE:
If known, you can substitute the IP address for the server name. For example:
192.100.0.1:3202.
2. Click OK on the Security Alert prompt.
3. When prompted, log on to the storage system with the administrator user name and password.
IMPORTANT:
When using the remote browser method to access the storage system, always close the remote session
before closing your Internet browser. Closing the Internet browser does not close the remote session.
Failure to close your remote session impacts the limited number of remote sessions allowed on the
storage system at any given time.
Installing and configuring the server20
Using the Remote Desktop method
Remote Desktop provides the ability for you to log onto and remotely administer your server, giving
you a method of managing it from any client. Installed for remote administration, Remote Desktop
allows only two concurrent sessions.
To connect the storage system to a network using the Remote Desktop method
1. On the PC client, select Start > Run. At Open, type mstsc, then click OK.
2. Enter the IP address of the storage system in the Computer box and click Connect.
3. When prompted, log on to the storage system with the administrator user name and password.
Using the Telnet method
Telnet is a utility that lets you connect to servers, log on, and obtain a command prompt remotely.
Telnet is included with the OS but must be activated before use.
CAUTION:
For security reasons, Telnet is disabled by default. The service needs to be modified to enable access
to the storage system with Telnet.
Enabling Telnet
1. In Server Manager, expand the Configuration node in the left panel.
2. Click System and Network Settings.
3. Under System Settings Configuration, click Telnet.
4. Select Enable Telnet access to this server and then click OK.
Default storage settings
HP StorageWorks P4000 Unified NAS Gateway is preconfigured with default storage settings. This
section provides additional details about the preconfigured storage.
Physical configuration
The logical disks reside on physical drives as shown in the table below.
IMPORTANT:
The first two logical drives are configured for the storage system operating system.
The Operating System volume default factory settings can be customized after the operating system
is up and running. The following settings can be changed:
• RAID level can be changed to any RAID level except RAID 0
• OS logical drive size can be changed to 40 GB or higher
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 21

If the Operating System volume is customized and the System Recovery DVD is run at a later time,
the System Recovery process will maintain the custom settings as long as the above criteria are met
(RAID level other than RAID 0 and OS logical drive size of 40 GB or higher) and the OS volume is
labeled System. If the storage system arrays are deleted and the System Recovery DVD is run, the
System Recovery process will configure the storage system using the factory default settings listed in
the table below.
HP StorageWorks P4000 Unified NAS Gateways do not include preconfigured data volumes. The
administrator must configure data storage for the storage system. See
“Configuring data storage” on page 56 for more information.
Table 4 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway RAID configuration
Logical Disk 1Model
HP StorageWorks P4000 Unified NAS
Gateway
NOTE:
In the HP Array Configuration Utility (ACU), logical disks are labeled 1 and 2. In Microsoft Disk
Manager, logical disks are displayed as 0 and 1. For HP Smart Array configuration information, see
http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/proliantstorage/arraycontrollers/.
If the operating system has a failure that might result from corrupt system files, a corrupt registry, or
the system hangs during boot, see “System recovery” on page 93.
Default boot sequence
The BIOS supports the following default boot sequence:
1. DVD-ROM
2. HDD
3. Bootable USB flash drive
4. PXE (network boot)
• Operating System Volume
• RAID 1+0
• Physical Drives 0–1
Under normal circumstances, the storage systems boot up from the OS logical drive.
• If the system experiences a drive failure, the drive displays an amber disk failure LED.
• If a single drive failure occurs, it is transparent to the OS.
Installing and configuring the server22
3 Cluster configuration
HP StorageWorks P4000 Unified NAS Gateway hardware components are configured in a clustered
environment to a P4000 SAN Solution. The P4000 SAN Solution provides iSCSI block services while
the P4000 Unified NAS Gateway provides data services using CIFS/NFS protocols. The P4000
Unified NAS Gateway also supports optional data protection services with tools such as HP Data
Protector, Data Protection Manager (DPM), VMWare, and VMware Consolidated Backup (VCB).
The P4000 Unified NAS Gateways are clustered and connected to the HP P4000 SAN network
segment using standard Ethernet IP switches. Up to eight (8) P4000 Unified NAS Gateway nodes
can be clustered together.
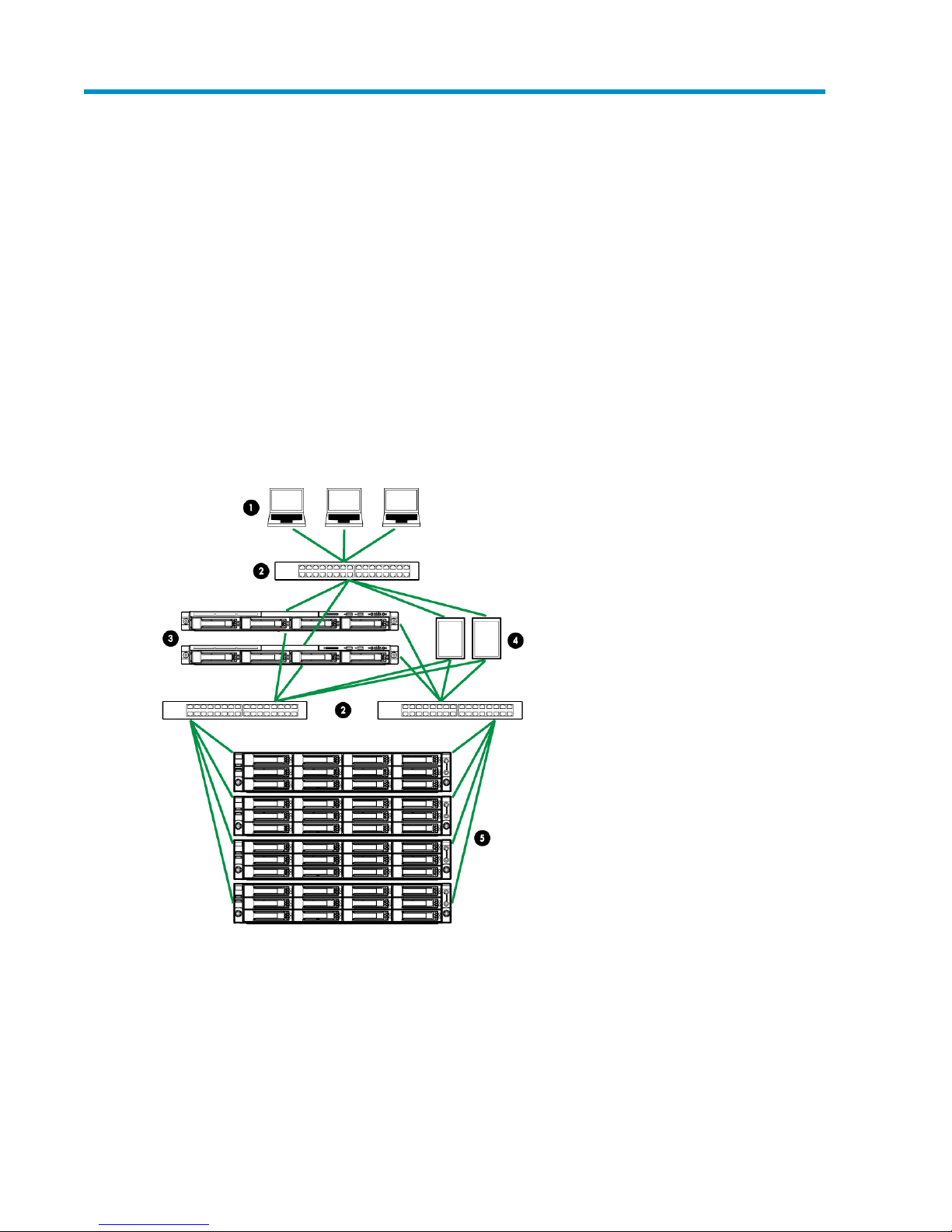
The following figure shows a complete network infrastructure comprised of two P4000 Unified NAS
Gateways connected to a P4000 SAN segment using standard IP switches while also connected to
the client network using a standard IP switch. Application servers are also connected the P4000 SAN
segment and client network using standard IP switches.
Figure 6 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway network infrastructure
.
1. Client network
2. Standard IP switch
3. P4000 Unified NAS Gateway nodes
4. Application servers
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 23

5. P4000 SAN segment
IMPORTANT:
Instructions and illustrations in this document describe the installation and configuration of a 2–node
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway. If you purchased the 1–node P4000 Unified NAS Gateway, all
instructions related to installing and configuring the second node of the solution do not apply. The
1–node solution does not support full High Availability (HA) capability, but is HA ready and can be
upgraded to a full HA solution by purchasing and installing an additional 1–node P4000 Unified
NAS Gateway.
After installing the P4000 Unified NAS Gateway nodes as detailed in the HP StorageWorks P4000
Unified NAS Gateway Installation Instructions, the system components should be racked, cabled,
powered on, and you should be logged in to the systems with Administrative privileges. In addition,
P4000 SAN storage should be created and mapped to the P4000 Unified NAS Gateway nodes
using P4000 Centralized Management Console (CMC) software, Microsoft iSCSI Initiator, and
Windows Disk Manager.
For complete information about creating and managing HP StorageWorks P4000 SAN Solutions,
see the user documentation at http://www.hp.com/go/p4000. Click HP Support and Drivers, select
your HP StorageWorks P4000 SAN Solution model, and then click Manuals.
Creating and configuring the cluster
The following section describes the process of creating the P4000 Unified NAS Gateway cluster.
Set IP addresses for the network connections
In order to accurately describe the physical connections between the clustered components, the P4000
Unified NAS Gateways are designated as Server 1 and Server 2 in this section.
Each P4000 Unified NAS Gateway includes six NIC connectors, each reserved for a specific network
connection purpose as shown in the figure below:
• One NIC connector is reserved for heartbeat connectivity between the two P4000 Unified NAS
Gateway storage systems (shown in red).
• Two NIC connectors are reserved for multi-path connectivity to P4000 SAN storage nodes (shown
in green and blue).
• Three NIC connectors are reserved for front file serving into a client network (shown in black).
Cluster configuration24
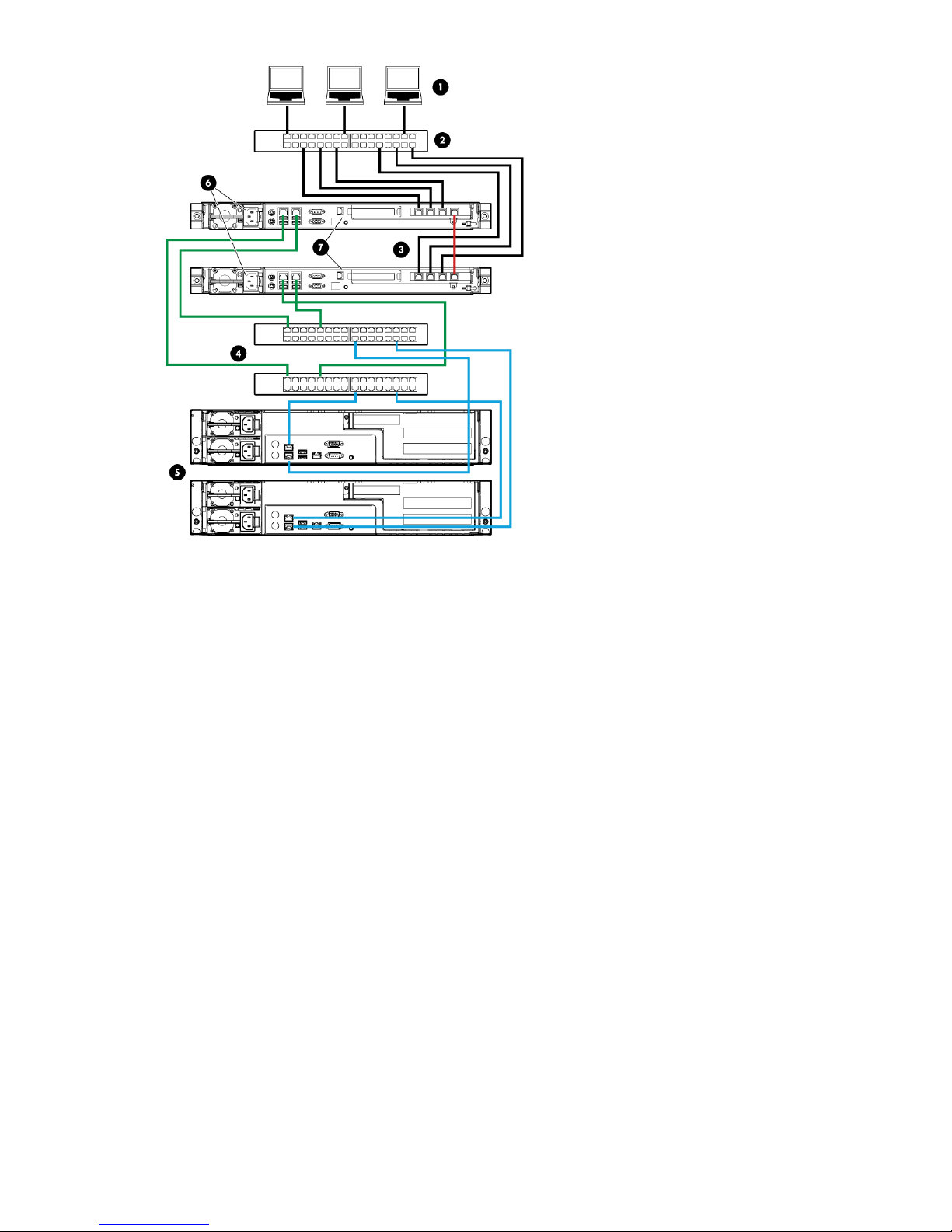
Figure 7 P4000 Unified NAS Gateway connections
.
1. Client network
2. Standard IP switch
3. P4000 Unified NAS Gateway nodes
4. Standard IP switches
5. P4000 SAN segment
For proper operation of the cluster, each storage server requires the following: a private heartbeat
network connection between the two servers, at least one private network connection to a P4000
SAN, and at least one connection for file serving purposes, which can be configured as a public or
private network connection based on your network infrastructure needs. The private connection NIC
adapters must be set with static IP addresses; the public NIC adapters can be set with a static IP
address, or may be automatically configured using DHCP. If a DHCP server is available on your
network, HP recommends allowing DHCP to automatically configure the public-facing network
connections; this is the default setting.
1. Log in to the Server 1 desktop as a user with Administrative privileges.
2. Click Close to dismiss the HP StorageWorks Rapid Startup Wizard.
3. In Server Manager, click View Network Connections.
If Server Manager is not already open, click Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager.
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 25
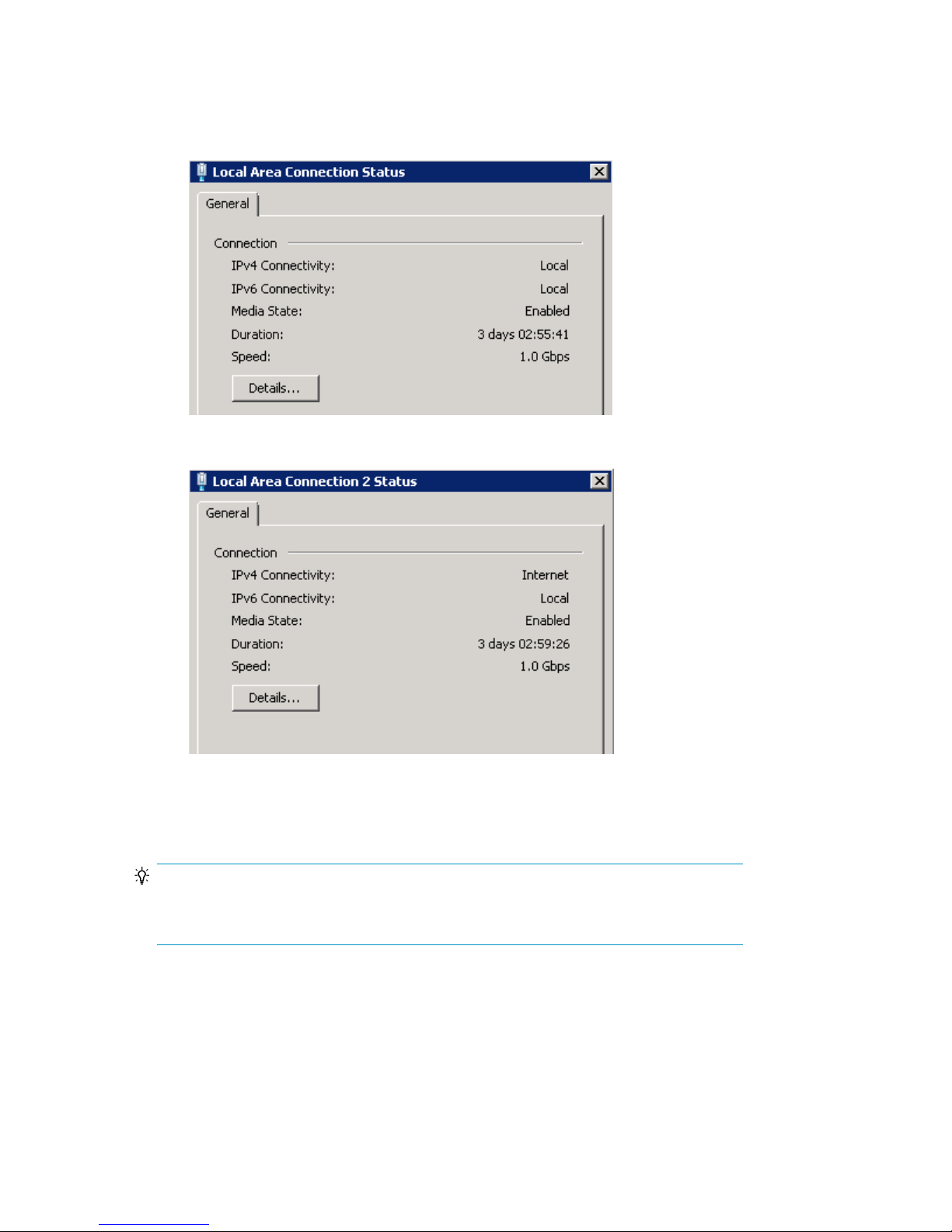
4. Identify the public and private connections:
a. Right-click one of the connections and select Status.
The connection status of the private connections will indicate Local in the IPv4 Connectivity
field; the connection status of the public-facing connections will indicate Internet in this field.
Figure 8 Private connection status
.
Figure 9 Public connection status
.
b. After identifying the private and public connections, click Close.
TIP:
To more easily identify public and private network connections, rename them (for example,
Cluster Heartbeat, Public File Serve 1, and P4000 SAN 1).
Cluster configuration26
5. To assign static IP addresses to a private connection:
a. Right-click the private connection and select Properties.
b. Clear all items on the General tab except for HP Network Configuration Utility, Internet
Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), and Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv).
c. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties.
NOTE:
For the purposes of this document, the IPv4 Internet Protocol is the documented IP
version. If you are familiar with IPv6 and prefer to use it in your network environment,
it is also supported.
d. Select Use the following IP address and enter a static IP address and subnet mask using
configuration information assigned by your network administrator.
e. Click Advanced, select the DNS tab, and clear the Register this connection's addresses in
DNS box.
f. Click OK twice and then click OK to dismiss the Local Area Connection Properties dialog
box.
The Server 1 private static IP addresses are now set.
6. To set the Server 1 public IP addresses, do one of the following:
• If a DHCP server is available on your network, allow DHCP to automatically configure your
public-facing network connections.
• If a DHCP server is not available on your network, configure a static IP address for the public-
facing network connections as documented above using configuration information assigned
by your network administrator. For the public-facing static IP address, do not clear any items
on the General tab of the connection's Properties page.
7. Repeat the preceding steps on Server 2, setting the private and public IP addresses as needed.
Join both storage servers to the domain
1. From Server 1, open Server Manager, and click Change System Properties.
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 27
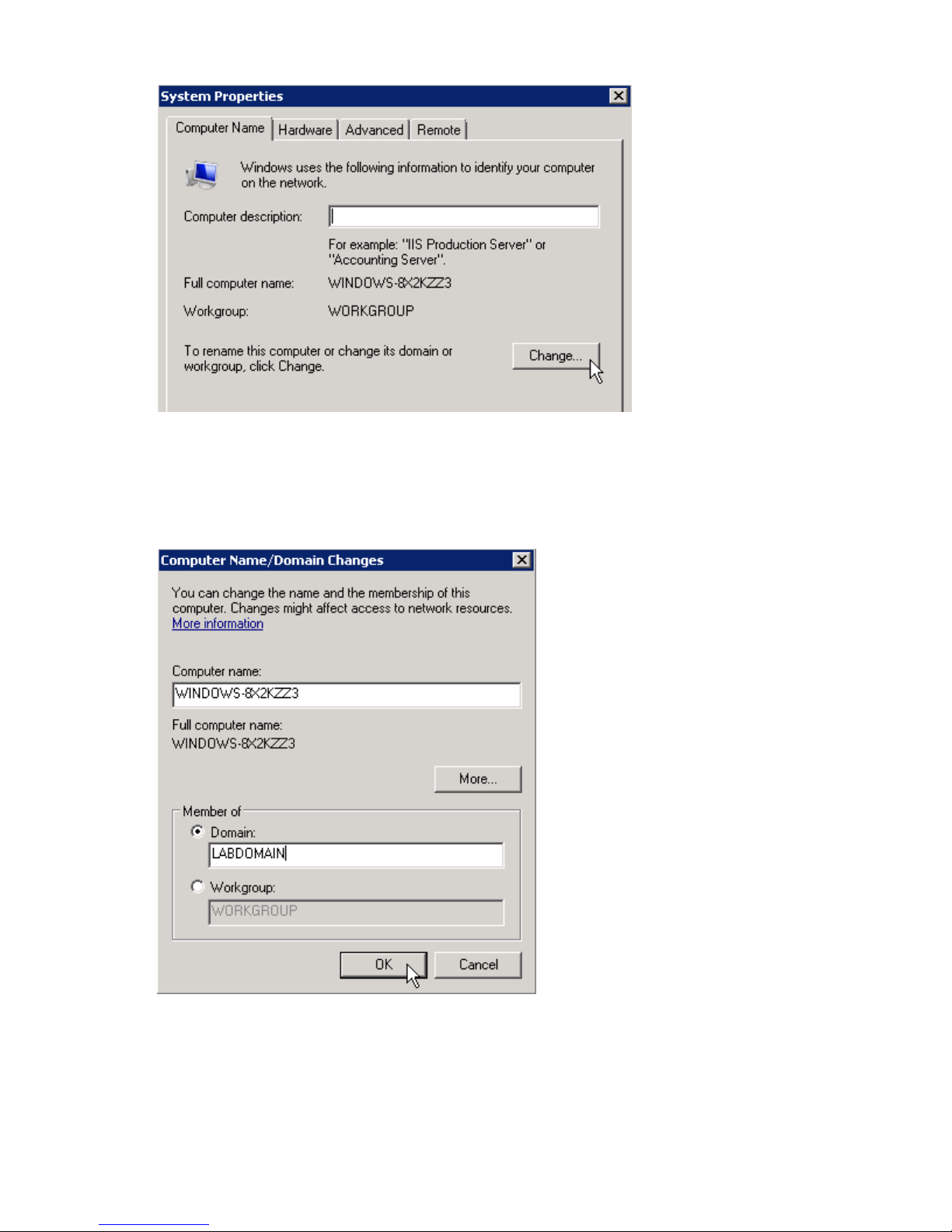
2. On the Computer Name tab, click Change.
Figure 10 Computer Name tab of System Properties
.
3. On the Computer Name/Domain Changes dialog box, in the Computer name field, enter a unique
name for the server.
4. Select the Domain radio button and type the name of the domain on which the cluster will reside
and then click OK.
Figure 11 Computer Name Changes dialog box
.
5. When prompted for credentials, enter valid domain account credentials and then click OK.
6. Click OK to accept the domain changes.
Cluster configuration28
7. When prompted, click Yes to restart the server.
8. Repeat these steps for Server 2.
Initialize and format the storage disks
The storage referenced in this section must be created and configured on the P4000 SAN. See the
HP StorageWorks P4000 Configuration Guide for more information about connecting the SAN
volumes to the Windows Storage Server instance.
1. From Server 1, open Server Manager, and under Storage, click Disk Management.
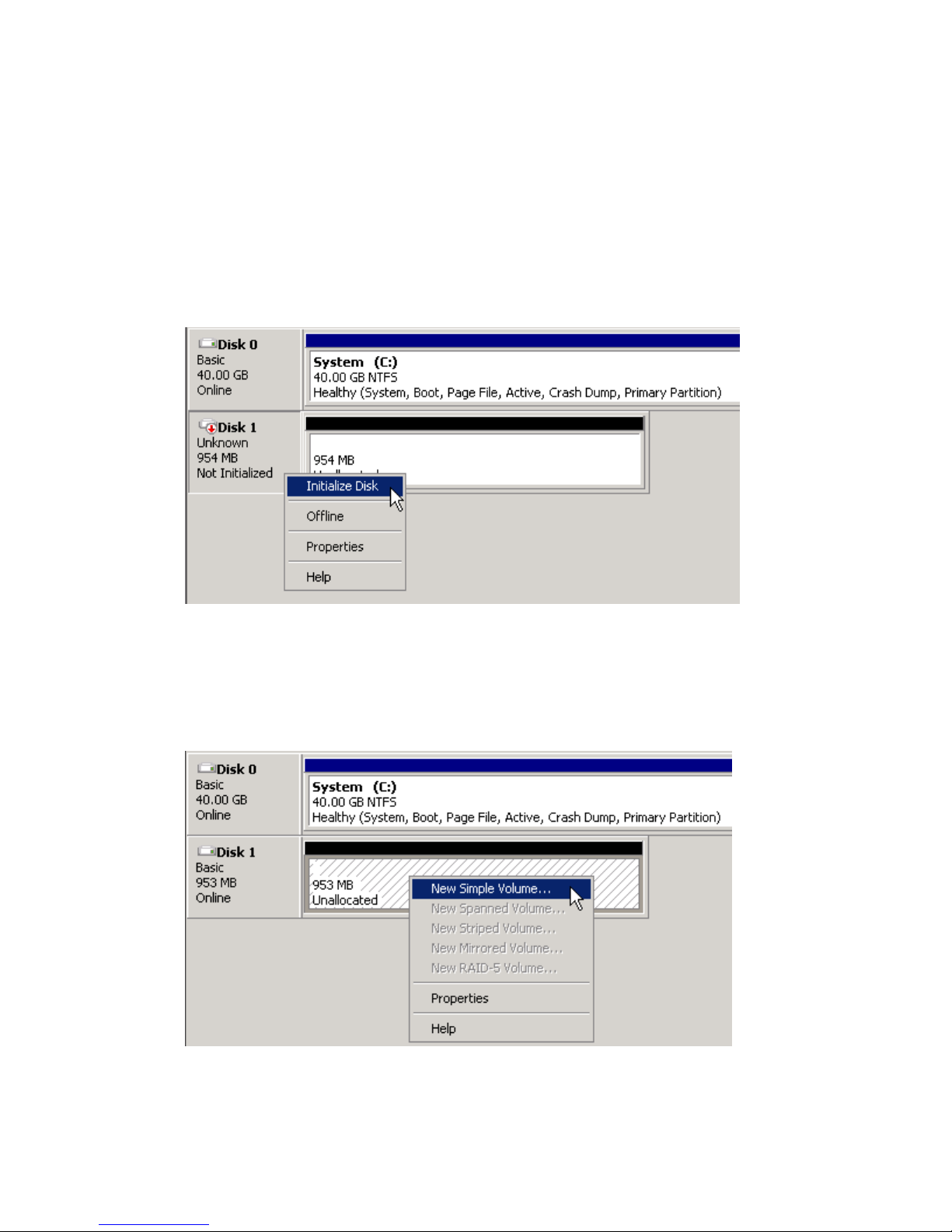
2. Right-click the Disk 1 label and select Online to bring the disk online.
3. Right-click the disk, and then click Initialize Disk.
Figure 12 Initialize Disk 1 (the witness disk)
.
4. In the Initialize Disk dialog box, select the disk to initialize, select a partition style, and then click
OK.
The disk is initialized as a basic disk.
5. In the storage allocation area, right-click and select New Simple Volume.
Figure 13 Create new simple volume
.
P4000 Unified NAS Gateway User Guide 29
6. Complete the New Simple Volume Wizard with the following settings:
• Accept the default assigned partition size
• Assign drive letter Q
• Formatted as NTFS
• Label the volume Witness
• Check Perform a quick format
7. Repeat the preceding steps to initialize and format the remaining data disks, assigning properties
such as volume size and labels as appropriate for the intended use of the storage.
NOTE:
Before proceeding to additional configuration tasks, ensure that all disks have been completely
initialized and formatted. After the disks have been completely initialized and formatted, the storage
allocation area will indicate the volume name, size, and state (Healthy, for example).
Validate the configuration
The process of validating your configuration may take a few minutes. If additional storage is configured
to be used by the cluster, the validation process takes additional time to complete.
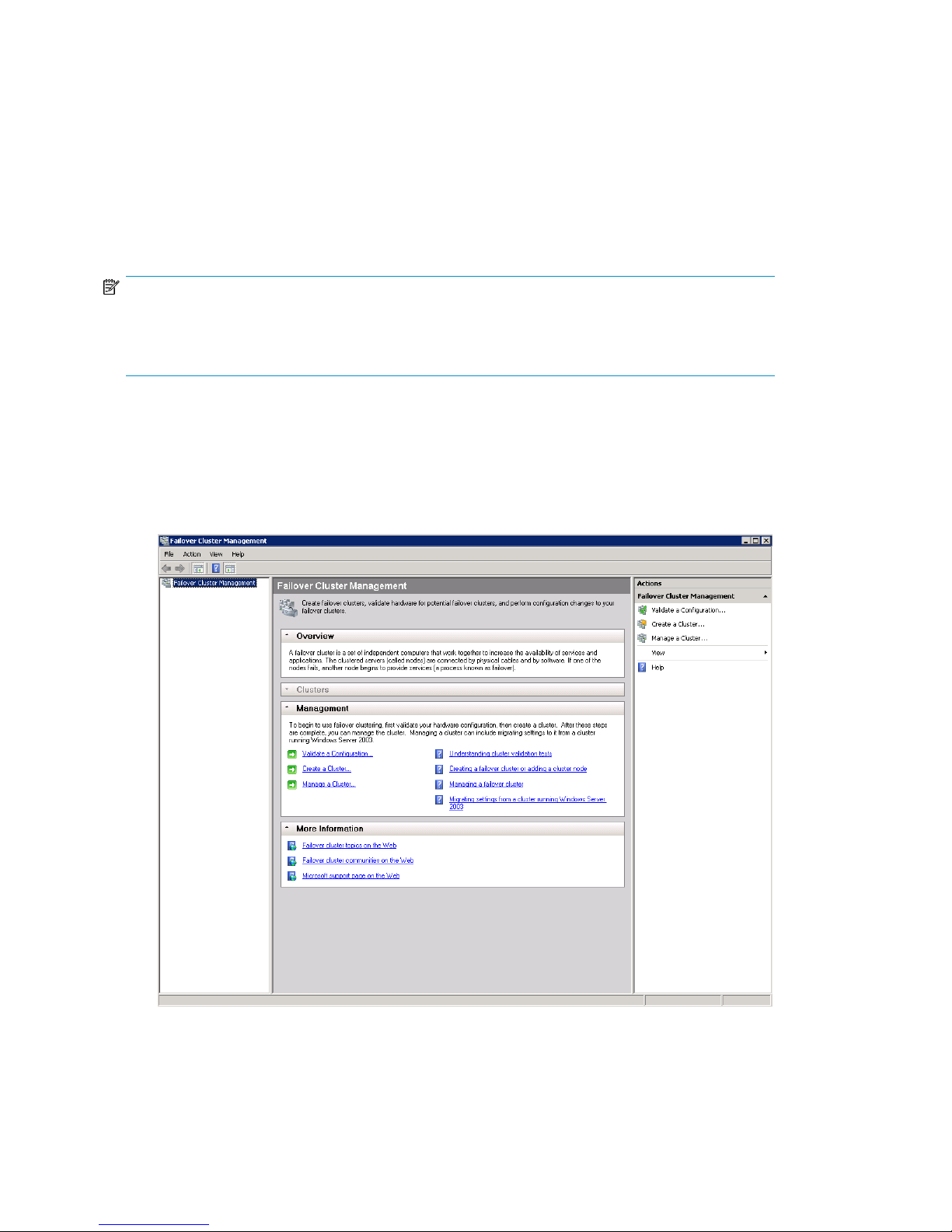
1. From Server 1, click Start > Administrative Tools > Failover Cluster Management.
Figure 14 Failover Cluster Management user interface
.
2. In the Management section, click Validate a Configuration.
Cluster configuration30
 Loading...
Loading...