Page 1

HP StorageWorks
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide
Part number: 5697-0177
Third edition: September 2009
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2008-2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211
and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items
are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Page 3

Contents
1 Overview of HP EVA Virtualization Adapter ........................................... 7
Discovery of disk arrays and LUNs ................................................................................................ 7
Disk array discovery sequence ............................................................................................... 8
LUN discovery sequence ....................................................................................................... 8
Failover testing ........................................................................................................................... 9
Failover recovery ........................................................................................................................ 9
Communication path ................................................................................................................. 10
Replication options ................................................................................................................... 11
Command View EVA Configuration Options .......................................................................... 11
2 Configuring SRM and the HP EVA disk array ....................................... 13
Setting up the HP EVA SAN environment ...................................................................................... 13
Adding an ESX server ......................................................................................................... 13
Installing licenses ............................................................................................................... 13
Creating vdisks for datastores .............................................................................................. 14
Presenting LUNs ................................................................................................................. 14
Creating and configuring datastores ..................................................................................... 14
Installing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter ...................................................................................... 14
Pairing SRM sites ...................................................................................................................... 15
Configuring SRM to communicate with HP Command View EVA ..................................................... 15
Create protection groups .......................................................................................................... 18
Create recovery plans ............................................................................................................... 19
3 Installing and removing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter ......................... 21
Installation directory .................................................................................................................. 21
Installation prerequisites ............................................................................................................. 21
Installing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter ...................................................................................... 21
Checking the installation ............................................................................................................ 23
Removing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter ..................................................................................... 24
4 Failover and failback with SRM .......................................................... 25
Failover ................................................................................................................................... 25
Failback .................................................................................................................................. 25
Failback scenario with SRM ................................................................................................. 25
Snapconfig utility ...................................................................................................................... 26
5 Troubleshooting HP EVA Virtualization Adapter .................................... 29
HP StorageWorks EVA disk arrays do not appear in Site Recovery Manager .................................... 29
HP StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter does not install ......................................................... 29
Virtual machines do not start at recovery site after failover. ............................................................. 29
Site Recovery Manager timeout failure in large array configurations ................................................ 29
Virtual machines do not start at recovery site during the test failover test. .......................................... 30
Error messages ......................................................................................................................... 30
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 3
Page 4

SRM log .................................................................................................................................. 30
EVA log ................................................................................................................................... 30
HP EVA Virtualizaton Error Messages .......................................................................................... 31
6 Reference ........................................................................................ 33
Intended audience .................................................................................................................... 33
Related documentation .............................................................................................................. 33
Document conventions and symbols ............................................................................................. 34
HP technical support ................................................................................................................. 34
Subscription service .................................................................................................................. 35
HP websites ............................................................................................................................. 35
Documentation feedback ........................................................................................................... 35
Glossary ............................................................................................ 37
Index ................................................................................................. 39
4
Page 5

Figures
Discovered Information .............................................................................................. 81
Using snapshots for failover test ................................................................................. 92
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter architecture ................................................................. 103
Snapconfig.xml file ................................................................................................. 274
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 5
Page 6

Tables
EVA Virtualization Adapter log messages ................................................................... 311
6
Page 7

1 Overview of HP EVA Virtualization
Adapter
HP StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter (HP EVA Virtualization Adapter) is installed on VMware
Site Recovery Manager (SRM) servers and enables communications between SRM and HP
StorageWorks Command View EVA (and HP StorageWorks Continuous Access EVA for remote
replication).
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter performs the following functions:
• Discovers disk arrays
• Discovers replicated LUNs
• Fails over storage for testing (test a recovery plan)
• Fails over storage for recovery (execute a recovery plan)
For detailed operational information on HP StorageWorks Command View EVA, HP StorageWorks
Continuous Access EVA, HP StorageWorks Business Copy EVA, or VMware Site Recovery Manager
see the sources cited in Related documentation.
Discovery of disk arrays and LUNs
During SRM configuration, HP EVA Virtualization Adapter is called to discover available arrays and
replicated LUNs.
The following information is discovered:
• Storage array IDs (WWN)
• Controller Port WWNs
• Physical host HBAs
• LUNs assigned to local (protected) physical and virtual hosts
• Remote recovery storage array ID
• Remote vdisk name
Remote vdisks are members of HP EVA data replication groups, and are replicated between protected
and recovery HP EVAs using HP Continuous Access EVA.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 7
Page 8
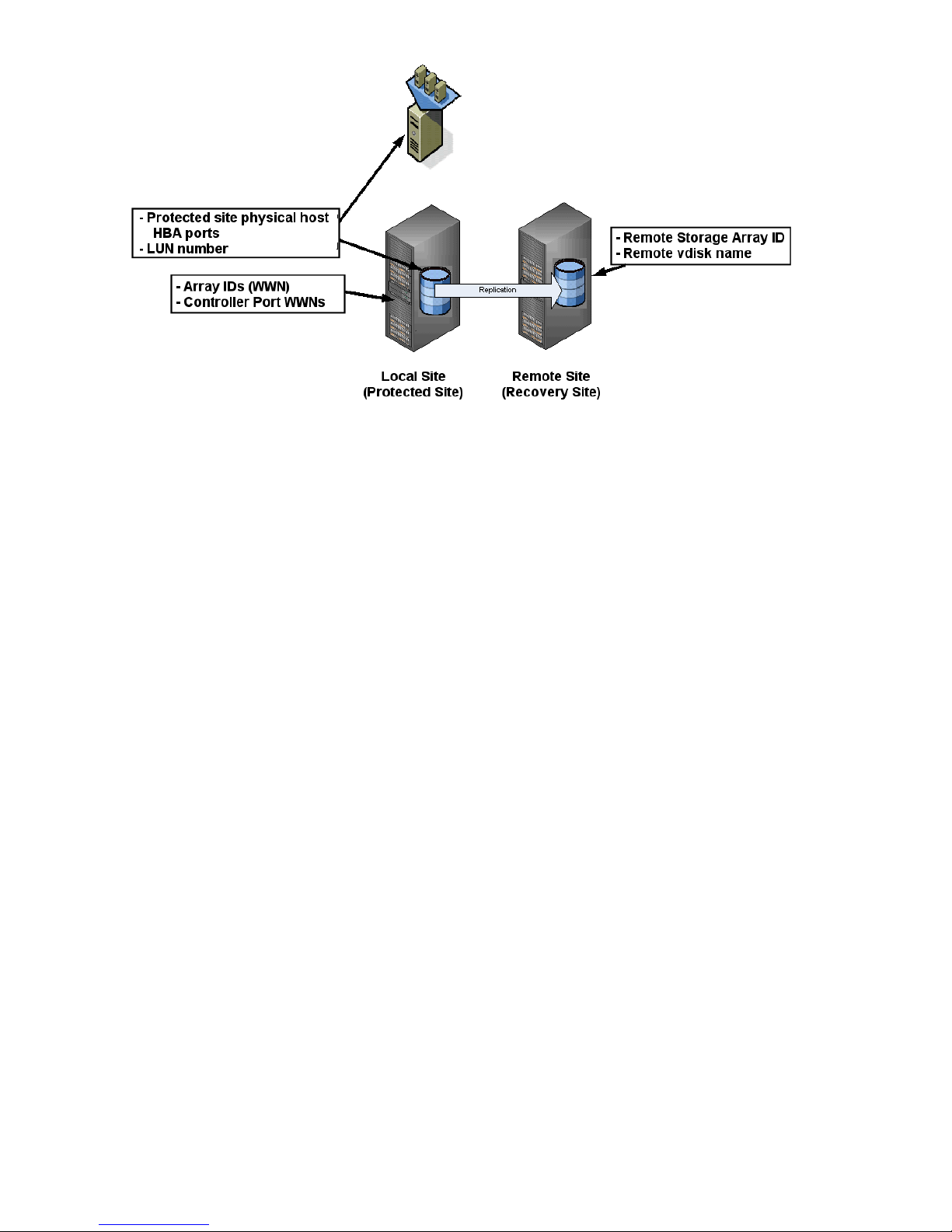
Figure 1 Discovered Information
.
Disk array discovery sequence
The array discovery sequence is:
1. SRM makes a request to HP EVA Virtualization Adapter for available arrays.
2. HP EVA Virtualization Adapter connects to HP Command View EVA servers and requests array
controller port information (WWN).
3. HP EVA Virtualization Adapter returns the results to SRM.
LUN discovery sequence
The LUN discovery sequence is:
1. SRM makes a request to HP EVA Virtualization Adapter for replicated LUNs on a local (protected)
array.
2. HP EVA Virtualization Adapter connects to HP Command View EVA servers and requests replicated
vdisks on the protected array.
3. HP Command View EVA looks for vdisks that are members of data replication groups.
4. For each replicated vdisk found on the protected array, HP EVA Virtualization Adapter gathers
the following information:
• Remote array ID
• Remote vdisk name
• Local presentation information
• Host the LUN is presented to
• ID assigned to host
5. HP EVA Virtualization Adapter returns this information to SRM.
6. SRM correlates LUNs with datastores.
Overview of HP EVA Virtualization Adapter8
Page 9
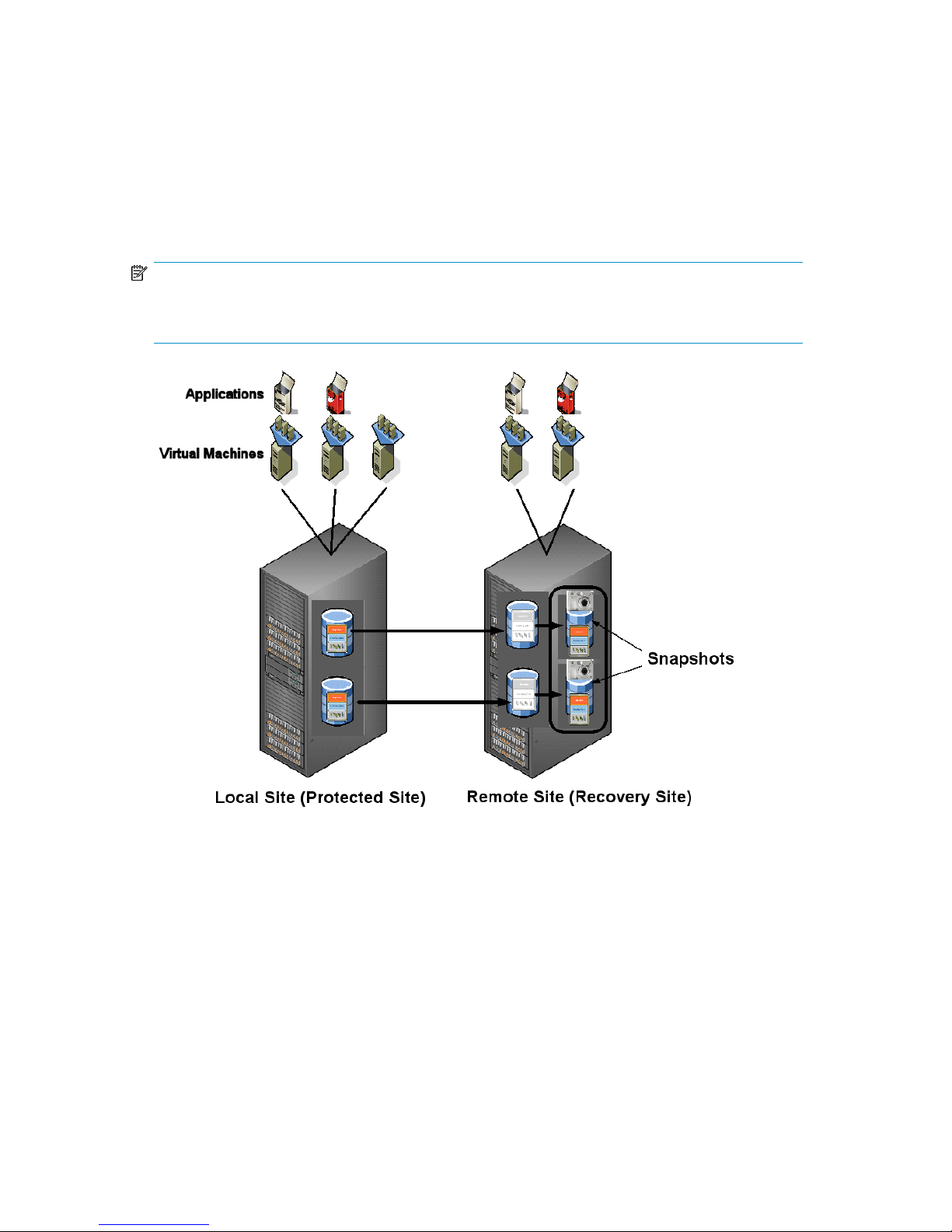
Failover testing
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter provides information and performs EVA operations for nondisruptive
testing of SRM failover recovery plans. SRM uses the information gathered during the discovery process
to create snapshots of remote vdisks (see Figure 2). After testing verifies the vdisks snapshots can be
recovered after failure of the local array (via a recovery plan), SRM uses HP StorageWorks EVA
Virtualization Adapter to unpresent and delete the snapshots. HP Business Copy EVA is used to create
snapshots during recovery plan testing.
NOTE:
For Failover, the ESX LVM settings must be set to default for Snapshot (default is disallow) and
resignature (default is allow).
Figure 2 Using snapshots for failover test
.
Failover recovery
During recovery, SRM executes a recovery plan. When SRM reaches the Prepare Storage step in the
recovery plan, it provides the LUN information needed for failover to HP EVA Virtualization Adapter.
The information includes:
• Recovery site storage array ID
• Vdisk name
• Recovery ESX server HBA ports (WWNs) for post-failover LUN presentation
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 9
Page 10
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter then communicates with HP Command View EVA and correlates the
requested vdisks with data replication groups. The adapter fails over each data replication group
associated with the LUN information provided by SRM. HP EVA Virtualization Adapter then obtains
LUN presentation information for each vdisk that has failed over and returns the information to SRM.
The information includes:
• vdisk name
• LUN number assignment to recovery HBA ports
NOTE:
During initial setup, replicated vdisks need to be presented to both the protected and recovery ESX
hosts.
NOTE:
For failover testing, LUN number assignment is the LUN number used by the
parent vdisk.
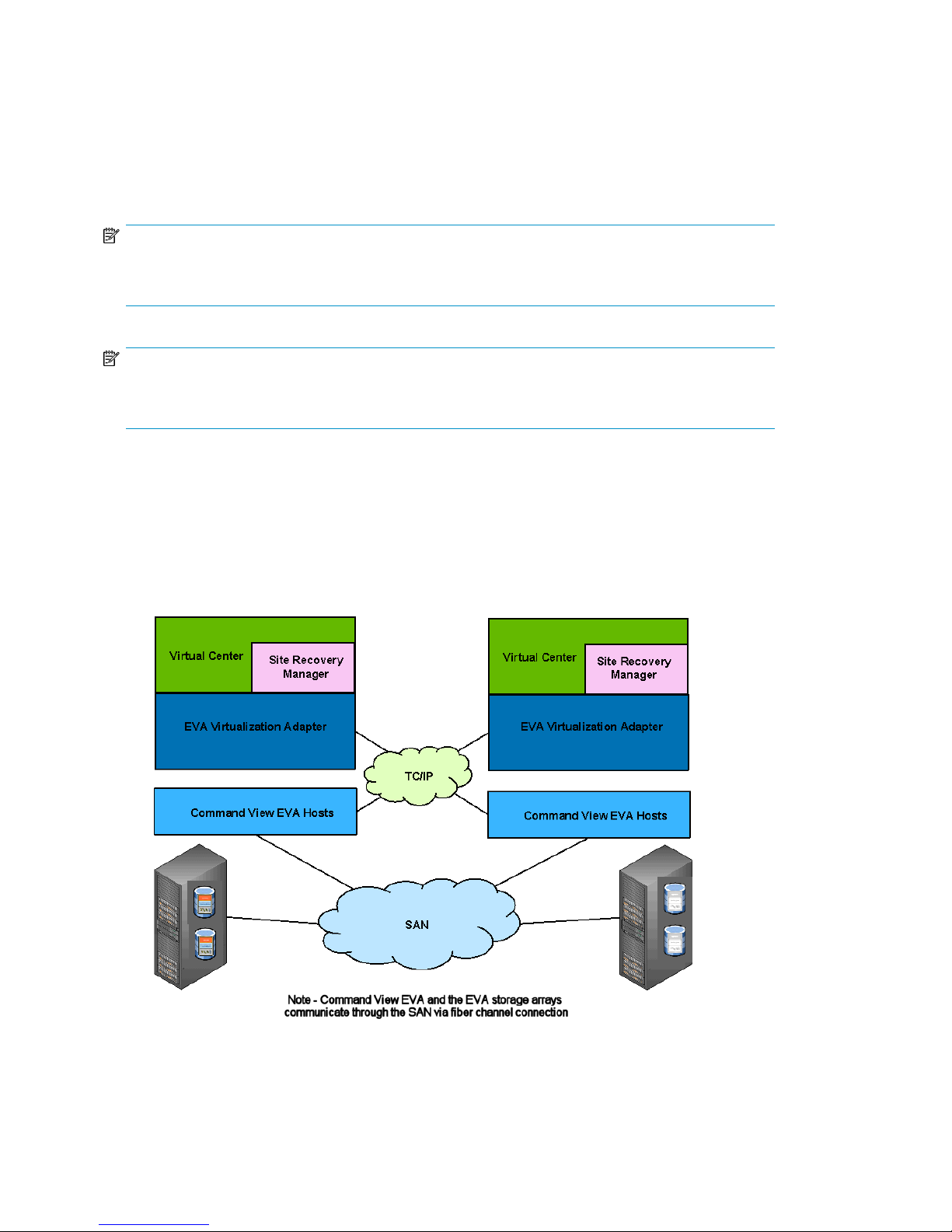
Communication path
snapshot
and not the
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter provides communications between HP StorageWorks Command View
EVA and SRM. A detailed view of the architecture is shown in Figure 3.
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter processes SRM requests through HP Command View EVA. Once the
information is received by HP EVA Virtualization Adapter, it is passed on to SRM.
Figure 3 HP EVA Virtualization Adapter architecture
.
Overview of HP EVA Virtualization Adapter10
Page 11
Replication options
SRM with HP EVA Virtualization Adapter supports HP Continuous Access EVA synchronous and
asynchronous replication operations.
Command View EVA Configuration Options
There are two configuration options for the disaster recovery environment with SRM and HP EVA
Virtualization Adapter:
• Single active Command View EVA server In this configuration, the Command View EVA manage-
ment server manages the protected and recovery arrays actively. A second Command View EVA
management server manages the protected and recovery arrays passively.
NOTE:
In this configuration (during failover or test failover) if the primary Command View EVA site is
down, the recovery Command View EVA site will be forced to actively manage the recovery array.
• Split active Command View EVA server In this configuration, each Command View EVA manage-
ment server actively manages a single array (the local array). Each Command View EVA management server manages the remote array passively.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 11
Page 12

Overview of HP EVA Virtualization Adapter12
Page 13

2 Configuring SRM and the HP EVA disk
array
This chapter summarizes the steps to set up SRM and the HP EVA disk array for use with HP EVA
Virtualization Adapter. For detailed information on these steps, see the documents listed in Related
documentation.
The following steps need to be completed:
1. Set up EVA SAN environment.
2. Install HP EVA Virtualization Adapter.
3. Pair SRM sites (Protected/Recovery).
4. Configure SRM to communicate with Command View EVA.
5. Create Protection Group(s).
6. Create Recovery Plan(s).
Setting up the HP EVA SAN environment
Setting up the EVA SAN environment involves the following steps:
• Set up zones
• Install licenses for HP StorageWorks Continuous Access EVA and HP StorageWorks Business Copy
EVA
• Create vdisks for datastores
• Add vdisks to data replication groups
• Create datastores
Adding an ESX server
After zoning, use HP Command View EVA to add an ESX server to the hosts that are available to the
local HP EVA disk array. You can assign an alias (host name) to HBA ports (initiator IDs) that can be
seen by the HP EVA disk array and will be used for LUN presentation.
For more information on these tasks, see the HP StorageWorks Command View EVA user guide.
Installing licenses
HP StorageWorks Continuous Access EVA (needed to create replication pairs and perform failover
between data centers) and HP StorageWorks Business Copy EVA (needed to create snapshots during
recovery plan testing) need to be on the HP EVA disk arrays at the protected site and recovery site.
For more information on HP StorageWorks Continuous Access EVA and HP StorageWorks Business
Copy EVA, see the documents in Related documentation.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 13
Page 14

NOTE:
Snapclones, mirrorclones, and the ability to choose different disk group for clones are not currently
supported with SRM or HP EVA Virtualization Adapter.
Creating vdisks for datastores
Vdisks (vdisks) need to be created for virtual machine datastores. Create the vdisks on the protected
HP EVA disk array, using HP StorageWorks Command View EVA or HP StorageWorks Storage System
Scripting Utility (SSSU) Command Line Interface.
Once vdisks have been created on the local EVA, create data replication groups containing the vdisks.
Data replication groups are created on the local HP EVA disk array and provide vdisk failover between
two HP EVA disk arrays. You can create data replication groups using HP StorageWorks Command
View EVA or SSSU.
For more information on these tasks, see the HP StorageWorks Command View EVA user guide and
the HP StorageWorks Storage Software Scripting Utility Reference.
Presenting LUNs
Once vdisks have been created and put into a data replication group local LUNs should be presented
to local ESX server. When you put a vdisk into a data replication group, it will be replicated to the
remote EVA. At the remote data center, you then need to present the replica vdisk to the ESX servers
that are hosts to the remote EVA.
After you present the vdisks to both local and remote ESX servers, log into the local ESX servers and
do a rescan. There is no need to rescan for LUNs on the remote ESX servers, since SRM does this
during failover. You can present LUNs using HP StorageWorks Command View EVA or SSSU.
For more information on these tasks, see the HP StorageWorks Command View EVA user guide and
the HP StorageWorks Storage Software Scripting Utility Reference.
Creating and configuring datastores
The following tasks need to be done on protected and recovery ESX servers after LUN presentation:
On protected ESX servers
• Create datastores on ESX server
• Install virtual machines onto the datastores
• Create resource pools and folders as needed
On recovery ESX servers
• Rescan to make sure LUNs can be seen from protected site
For more information on these tasks, see the VMware Site Recovery Manager Administration Guide.
Installing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter
To install HP EVA Virtualization Adapter, see Chapter 3
Configuring SRM and the HP EVA disk array14
Page 15

Pairing SRM sites
You should now pair the protected and recovery sites in SRM. For more information, see the VMware
Site Recovery Manager Administration Guide.
Configuring SRM to communicate with HP Command View
EVA
When the protected and recovery SRM servers have been paired, configure SRM to use HP EVA
Virtualization Adapter by configuring array managers. To configure SRM to communicate with HP
Command View EVA disk arrays, complete the following steps:
1. Click Configure on the summary tab.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 15
Page 16

2. From the Configure Array Managers window, click Add to add connection information for the
Command View EVA servers managing your EVA disk arrays.
3. In the Add Array Manager window, enter the storage manager addresses, usernames, and
passwords in the entry fields without spaces and separating each entry with a semicolon (;).
For example:
Storage Manager Address - address1;address2
Username - username1;username2
Password - password1;password2
NOTE:
With this release, HP EVA Virtualization Adapter limits the number of Command View EVA
management servers that can be configured to two (one in each data center).
From the Manager Type menu, select HP StorageWorks Enterprise Virtual Array. Then enter the
address and login credentials used for HP Command View EVA and click Connect.
After the connection completes, all HP EVA disk arrays managed by the HP Command View EVA
server are displayed.
Configuring SRM and the HP EVA disk array16
Page 17

4. Select the HP EVA disk array name that is connected to protected ESX servers.
NOTE:
You will also need to configure the recovery site array manager using this procedure.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 17
Page 18

5. Verify that the array managers are configured by looking for the following information in the
Configure Array Managers window:
• Array Manager Info
• Local and remote array information
• LUN count (equals the number of replicated LUNs on each EVA)
6. Verify the array mangers have been configured for both protected and recovery sites, and rep-
licated datastores in the Review Replicated Datastores window.
Create protection groups
You are ready to create protection groups in the protected site using SRM. Protection groups (containing
virtual machines) fail over together to the recovery site during test and recovery. For more information
on creating protection groups, see the VMware Site Recovery Manager Administration Guide.
Configuring SRM and the HP EVA disk array18
Page 19

Create recovery plans
Create recovery plans on the recovery site. A recovery plan is a list of steps the SRM follows on a
protected site to switch operation from the protected site to the recovery site during a disaster (or test).
For more information on creating recovery plans, see the VMware Site Recovery Manager
Administration Guide.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 19
Page 20

Configuring SRM and the HP EVA disk array20
Page 21

3 Installing and removing HP EVA
Virtualization Adapter
This chapter explains how to install and configure HP EVA Virtualization Adapter.
NOTE:
You do not need to remove the previous HP EVA Virtualization Adapter when upgrading to a newer
version.
IMPORTANT:
A successful installation depends on using compatible versions of the OS and all installed software.
See
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter release notes
Installation directory
for version requirements.
Depending on the version of SRM, HP EVA Virtualization Adapter is installed in the following (default)
directoy:
• For SRM 1.0
C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Site Recovery Manager\scripts\SAN\HP
StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter
• For SRM 4.0
C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware vCenter Site Recovery Manager\scripts\
SAN\SAN\HP StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter
Installation prerequisites
To install HP EVA Virtualization Adapter, you need administrator privileges, and VMware Site Recovery
Manager must already be installed on the server.
Installing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter is installed using an executable (setup.exe).
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 21
Page 22

NOTE:
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter must be installed on both the local site SRM server (protected site)
and the remote site SRM server (recovery site).
1. Download HP EVA Virtualization Adapter installation file from the HP web page (http://
www.hp.com/go/storage/vmware) and save it in a temporary folder.
2. Browse to the temporary folder and extract HP EVA Virtualization Adapter installation files.
3. After the files are extracted, click Setup.exe to start the installation. The InstallShield Wizard
window appears.
4. Click Next. The License Agreement window opens.
5. Click I accept the terms of the license agreement and then click Next. The Ready to Install the
Program window opens.
6. Click Install.
7. At the prompt indicating the Site Recovery Manager Service needs to be restarted, click OK.
The InstallShield Wizard Complete window opens.
Installing and removing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter22
Page 23

8. Click Finish to complete the installation. You will need to restart Site Recover Manager (see
Restarting Site Recovery Manager.
NOTE:
After this step, a readme file is displayed.
Restarting Site Recovery Manager
1. Restart Site Recovery Manager by clicking Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Administrative Tools. then double-click Services.
NOTE:
Restarting the SRM service halts any operations SRM may have been performing and requires
you to configure the connection between SRM sites. (see Configuring SRM to communicate with
HP Command View EVA and Pairing SRM sites).
3. Select the VMware Site Recovery Manager Service in the list and click Restart.
Checking the installation
After HP EVA Virtualization Adapter is installed, it appears in the Windows Add or Remove Programs
window.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 23
Page 24

Removing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter
To remove HP EVA Virtualization Adapter:
1. In Windows, select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Add or Remove Programs.
3. Select HP StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter.
4. Click Change/Remove. Windows removes the program.
NOTE:
After removing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter, restart SRM service so it can be reflect that EVA
Virtualization Adapter is no longer available.
Installing and removing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter24
Page 25

4 Failover and failback with SRM
This section discusses failover and failback with SRM. It also provides a scenario as a guide for the
manual process of failback.
Failover
Failover occurs when an SRM recovery plan is executed, and the SRM recovery plan is configured
to fail over SRM protection groups that use replicated EVA vdisks as a datastore.
During normal operation, the replication path is from a protected site (local site) to a recovery site
(remote site). When a failure occurs at the local site (due to hardware failure or the entire site loss) a
failover occurs and the replication path is reversed from the recovery site to the protected site. With
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter and SRM, the failover process is an automated feature and the process
is executed using a recovery plan located at the recovery site.
NOTE:
HP recommends that the user sets the DR group write mode to
failover. This will ensure:
• the data is current
• the failover does not result in full-copy (reverse copy) from secondary site to primary site vdisks
Sync
before performing a planned
Failback
Failback is the process of setting the replication environment back to its original state at the protected
site (local site) prior to failover. Failback can be managed as a normal server migration process.
However, managing the failback process with SRM is a manual process and the steps vary with
respect to the degree of failure at the protected site (local site). For example, the failover could have
been due to a hardware error or the loss of the entire data center.
Failback scenario with SRM
In the following failback scenario, SRM is used as a failback tool to return a protected site (Site A) to
its original state after executing a recovery plan (R1) at a recovery site (Site B).
To execute a failback manually:
1. Delete recovery plan at the recovery site (Site B).
2. If the protected site (Site A) still has HP Continuous Access EVA or data replication groups con-
figured for the protection groups (P1) in recovery plan (R1), delete protection groups (P1) at the
protected site. This could be the case if some of the hardware at the protected site was not replaced
after a disaster and you will be employing the existing hardware. If new hardware has been installed, it is not necessary to delete existing protection groups.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 25
Page 26

3. If you have not already, install SRM and HP EVA Virtualization Adapter on the updated hardware
at the protected site (Site A).
4. Using the VI Client at the recovery site (Site B), establish the protected site (Site A) as the remote
site for the recovery site (Site B).
5. Configure array replication from the recovery site (Site B) to the protected site (Site A) for datastores
containing recovered virtual machines. For more information, see the HP StorageWorks Continuous
Access EVA administrator guide.
6. Create any protection group(s) (P2) at the recovery site (Site B) to protect the recovered virtual
machines at the protected site (Site A).
7. On the protected machine (Site A) create a recovery plan (R2) for the protection group(s) (P2)
8. After the virtual machines have been fully replicated to the protected site (Site A), execute recovery
plan R2 at the protected site (Site A) in test mode.
9. If the test is successful, execute the recovery plan (R2) in recovery mode.
If desired, you can now protect the recovered virtual machines on the protected site (Site A) back to
the recovery site (Site B). To do this, perform the following steps:
1. Delete the recovery plan R2 from the protected site (Site A).
2. Delete the protection group(s) P2 at the recovery site (Site B).
3. Configure array replication from the recovery site (Site B) to the protected site (Site A) for datastores
containing recovered virtual machines. For more information, see the HP StorageWorks Continuous
Access EVA administrator guide.
4. Create protection group(s) P3 at the protected site (Site A) to protect recovered virtual machines
from the protected site (Site A) to the recovery site (Site B).
5. Create a recovery plan R3 at the recovery site (Site B) for the protection group(s).
Snapconfig utility
The Snapconfig utility file is an xml file that is installed with HP EVA Virtualization Adapter, and is
used during failover test operations. Typically, this file is not modified; however, it can be used to
customize the way test snapshots are created. After installation, Snapconfig.xml can be edited in the
Windows Notepad and accessed from Start->All Programs->Hewlett-Packard->StorageWorks EVA
Virtualization->SRM SnapConfig Utility
The parameters that can be modified using Snapconfig are RAID type and allocation policy.
The possible settings for RAID type are:
• vraid5 (default)
• vraid0
The possible settings for allocation type are:
• demand (default)
• full
A listing of the default file is show in Figure 4.
NOTE:
Any changes made to SnapConfig.xml will be global to all vdisks created during a test failover.
Failover and failback with SRM26
Page 27

Figure 4 Snapconfig.xml file
.
NOTE:
With the current release, <SnapType> and <Continue> are deprecated.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 27
Page 28

Failover and failback with SRM28
Page 29

5 Troubleshooting HP EVA Virtualization
Adapter
NOTE:
Error messages are logged to the SRM log files.
The following problems and solutions are typical.
HP StorageWorks EVA disk arrays do not appear in Site
Recovery Manager
Solutions:
• If HP EVA disk arrays are not appearing in Site Recovery Manager, make sure that Site Recovery
Manager has been restarted (see Restarting Site Recovery Manager, page 23).
• Also make sure that the array manager that SRM is connected to is actively managing arrays.
HP StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter does not install
Solution:
• Make sure that SRM is installed. HP EVA Virtualization Adapter will not install if SRM is not on
the disk array.
Virtual machines do not start at recovery site after failover.
Causes:
• The ESX recovery hosts are not configured with the correct HBA port WWN on the recovery EVA.
• The replicated vdisks used in failover were not presented to the recovery ESX servers.
Site Recovery Manager timeout failure in large array
configurations
Solution:
• Increase the SRM timeout value (CommandTimeout) by editing the vmware-dr.xml file located in
the <SRM Install Path>\config directory as shown in the following example:
</SanProvider>
.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 29
Page 30

.
.
<!..
Timeout in seconds for execution of a single command using array vendor adapter. Default: 5
minutes —>
<CommandTimeout> 300 </CommandTimeout>
</SanProvider>
NOTE:
After increasing the SRM timeout value, you will need to restart the VMware Site Recovery Manager
service.
Virtual machines do not start at recovery site during the test
failover test.
Causes:
• The ESX recovery hosts are not configured with the correct HBA port WWN on the recovery EVA.
Error messages
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter error messages are logged to SRM and HP EVA Virtualization Adapter
log files. Table 1 lists error messages and their meanings.
SRM log
SRM Logs (vmware-dr-X.log (X=0 to 9) is located in:
%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\VMware\VMware Site Recovery Manager\Logs
ALLUSERSPROFILE=C:\Documents and Settings\All Users
NOTE:
• Logs rollover after reaching 5 MB by default
• vmware-dr-index contains the most recent Log File number
EVA log
HP EVA Virtualization Adapter log (hpsrmeva.log) is located in:
<SRM Install Path>\scripts\SAN\HP StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter\
logs
For the <SRM Install Path>, see Installation directory, page 21.
Troubleshooting HP EVA Virtualization Adapter30
Page 31

HP EVA Virtualizaton Error Messages
Table 1 EVA Virtualization Adapter log messages
DescriptionLog Message
Array <EVA ID>s being actively managed by
a different SMA
Could not create snapshot
Could not determine DR Group membership
of one or more virtual disk
Could not find the specified VDisk: <LUN ID>
Could not populated array information
Could not populated list of managed arrays
Data Replication Group for <DR Group>
already in source mode
Failover of DR Group <DR Group name> was
unsuccessful
Initialization of CV Client failed using IP address <management host address>
The array being requested by SRM is actively managed by a
different Command View EVA host.
During a test failover operation, the action to create a snapshot failed due to an internal error on the EVA.
A LUN ID was input from SRM to the adapter, but it could not
be found in any existing DR Group.
A LUN ID was input from SRM to the adapter, but it could not
be found on the EVA.
A connection was made to Command View EVA, but the EVA
information could not be obtained.
A connection was made to Command View EVA, but the EVA
information could not be obtained.
A snapshot of the replicated LUN is currently being created.Creating snapshot of <LUN ID>
A LUN ID input from SRM has already been failed over at the
DR Group level.
During a failover of a DR Group associated with a replicated
LUN, an error occurred.
The address or login credentials to the management host may
be incorrect, preventing the adapter from connecting.
Initialization of the Element Manager object
failed
No test snapshots found
Presentation of the vdisk <LUN ID> to the host
<host name> has failed
previously created SRM snapshot found
Storage Array <EVA ID> not found on current
management host
Successfully deleted <SRM test snapshot name>
There are no Data Replication Groups to failover
VDisk <LUN ID> is not a member of a known
Data Replication Group
Connection to the Command View EVA host could not be
initialized.
A test failover stop operation was called, but no test snapshots
from the test failover stop operation exists.
During a test failover operation, the presentation of a snapshot
to a ESX host failed due to an internal error on the EVA.
During test failover start or stop, a test SRM snapshot has been
detected on the array.
The array being requested by SRM is actively managed by a
different Command View EVA host.
During test failover stop, a test SRM snapshot has been deleted.
All replicated LUNs specified by SRM are already in a failed
over state, or do not belong to a DR Group.
A LUN ID input from SRM does not belong to any known DR
Group.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 31
Page 32

Troubleshooting HP EVA Virtualization Adapter32
Page 33

6 Reference
This guide provides information about:
• HP StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter (HP EVA Virtualization Adapter) for HP StorageWorks
EVA disk arrays
• Requirements and procedures for installing HP EVA Virtualization Adapter
• Configuring HP EVA Virtualization Adapter
For supported disk array models and operating system versions, see the release notes for HP EVA
Virtualization Adapter.
For information on VMware and VMware Site Recovery Manager, see the VMware website.
This guide does not describe the operation of related products, including HP StorageWorks Command
View EVA, HP StorageWorks Continuous Access EVA, HP StorageWorks Business Copy EVA, HP
StorageWorks Storage Software Scripting Utility, or VMware Site Recovery Manager. For information
about these products, see the respective user guides.
Intended audience
This guide is intended for system administrators with knowledge of:
• Host hardware
• HP StorageWorks EVA disk arrays
• VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM)
Related documentation
The following documents provide related information:
• HP StorageWorks Continuous Access EVA administrator guide
• HP StorageWorks Business Copy EVA administrator guide
• HP StorageWorks Command View EVA user guide
• HP StorageWorks Storage System Scripting Utility reference
You can find these documents from the Manuals page of the HP Business Support Center website:
http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
Below Storage, click Storage Software.
The following book is available on the VMware website:
• VMware Site Recovery Manager Administration Guide
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 33
Page 34

Document conventions and symbols
ElementConvention
Cross-reference links and e-mail addressesBlue text: Document conventions and symbols
Website addressesBlue, underlined text: http://www.hp.com
• Keys that are pressed
Bold text
CAUTION:
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT:
Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
• Text typed into a GUI element, such as a box
• GUI elements that are clicked or selected, such as menu
and list items, buttons, tabs, and check boxes
Text emphasisItalic text
NOTE:
Provides additional information.
TIP:
Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
HP technical support
For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website:
http://www.hp.com/support
Before contacting HP, collect the following information:
• Product model names and numbers
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
Reference34
Page 35

Subscription service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber's Choice for Business website:
http://www.hp.com/go/e-updates
After registering, you will receive e-mail notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
HP websites
For additional information, see the following HP websites:
• http://www.hp.com
• http://www.hp.com/go/storage
• http://www.hp.com/service_locator
• http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
• http://www.hp.com/support/downloads
Documentation feedback
HP welcomes your feedback.
To make comments and suggestions about product documentation, please send a message to
storagedocsFeedback@hp.com. All submissions become the property of HP.
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 35
Page 36

Reference36
Page 37

Glossary
This glossary defines acronyms and terms used in this guide or related to this product and is not a
comprehensive glossary of computer terms.
Command View
EVA
disk array A RAID. A collection of disk drives within a cabinet or multiple cabinets and
DR Group Data replication group. A logical group of vdisks in a remote replication
EVA HP StorageWorks Enterprise Virtual Array.
failback Restoring a system back to its original state after a system failure.
failover When the recovery site takes over operation in place of the protected site after
HBA Host Bus Adapter
LUN Logical Unit Number. A physically addressable storage unit as surfaced by a
Protected Site The datacenter containing the protected virtual machines from which data is
HP StorageWorks Command View, a browser-based interface that allows
management of an HP disk array.
including a controller and software allowing drives to be ganged together in
various configurations to create virtual drives (LUNs).
relationship with a corresponding group on another array.
hardware or the entire protected site fails.
hardware RAID subsystem. A vdisk, consisting of multiple portions of physical
disks addressed as a single unit.
being replicated to the recovery site.
RAID Redundant array of independent disks.
Recovery Site The datacenter containing the virtual machines that will be recovered and perform
work while the protected site is unavailable.
snapshot A generic term meaning a static point-in-time copy of a volume, typically used
for backup.
SRM VMware Site Recovery Manager
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 37
Page 38

Glossary38
Page 39

Index
A
audience, 33
C
communications path
overview, 10
conventions
document, 34
D
document
conventions, 34
documentation
providing feedback, 35
related, 33
documentation, HP website, 33
E
error messages, 29, 30
F
Failback
overview, 25
scenario, 25
Failover
overview, 25
Failover testing
overview, 9
HP StorageWorks EVA Virtualization Adapter
checking installation, 23
installation, 21
installation directory, 21
installation prerequisites, 21
installation process, 21
overview, 7
R
related documentation, 33
S
Site Recovery Manager (SRM)
discovery process, 7
Snapconfig utility
overview, 26
Subscriber's Choice, HP, 35
T
technical support
HP, 34
service locator website, 35
troubleshooting, 29
W
websites, 33
HP ,
HP Subscriber's Choice for Business, 35
G
glossary, 37
H
help
obtaining, 34
HP
technical support, 34
EVA Virtualization Adapter administrator guide 39
Page 40

40
 Loading...
Loading...