Page 1

Technical white paper
HP FutureSmart Firmware Device Hard Disk,
SSD and eMMC Security
Table of contents
Overview .................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Hard Disk Drive Security Overview ......................................................................................................................... 2
Hard Disk Architecture ............................................................................................................................................. 2
Secure Erase Commands ........................................................................................................................................ 2
Disk Initialization Commands .................................................................................................................................. 5
SSD and eMMC Security Overview .......................................................................................................................... 6
Secure Erase Data Overwrite Functionality Not Supported on SSD/eMMC ....................................................... 6
Secure Volatile Storage Feature with SSD and eMMC ......................................................................................... 6
SSD and eMMC Impact to Disk Management Features ........................................................................................ 7
Accessory Hard Disk Drive Option .......................................................................................................................... 9
Disk Erase confirmation ........................................................................................................................................ 10
Government Erase Standards .............................................................................................................................. 11
Appendix A: Secure Erase Data Overwrite and Specifications ......................................................................... 11
Appendix B: Device Hard Drive Support .............................................................................................................. 13
Appendix C: Device SSD and eMMC Support ...................................................................................................... 16
Appendix D: ATA secure erase not supported ................................................................................................... 19
Appendix E: Optional HDD Accessory capable devices ...................................................................................... 19
Page 2
Overview
This document discusses secure erase options and hard disk, SSD and eMMC security on HP FutureSmart
Firmware printing devices. It replaces previous security documents HP FutureSmart Firmware Device Hard Disk
Security, Solid State Drive Security for HP Printing Devices and eMMC Security for HP Enterprise Printing Device.
Hard Disk Drive Security Overview
To protect customer data on devices using hard disk drives, all data written to the data disk areas are
encrypted using AES-128 or AES-256 encryption (on products manufactured after November 2012). The
section of the hard disk containing job data can be securely erased on demand, instead of performing an entire
disk wipe (See Erase Job Data). Industry standard ATA Secure Erase is an available option which securely wipes
all data including spared and reallocated sectors for decommissioning devices (See Secure Disk Erase).
Hard Disk Architecture
The printing device Hard Disk is divided into different sections for different classes of data
Job Data: Contains all job data, including temporary files for print and scan jobs, and Stored Jobs.
Configuration Data: Contains printing device dependent configuration settings and system
information. Information stored here includes printing defaults, authentication configuration, and
some customer specific configuration settings.
System Data: Contains the HP FutureSmart Firmware operating system code. This code must be
present on the hard disk for the printing device to boot. Previous HP printing device operating systems
booted from a compressed image stored in non-volatile memory.
Repository: This area contains a compressed copy of the device operating system installation code,
providing a way to restore a corrupted operating system image or recover from a failed firmware
upgrade.
Secure Erase Commands
HP FutureSmart Firmware printing devices support four different data erase features to securely erase
ongoing job data, and for device decommissioning or redeployment.
1. Managing Temporary Job Files
The feature controls how temporary job files are erased at the completion of print, copy, fax, or digital
send jobs.
Temporary job files include:
o Temporary data for print jobs
o Temporary data for copy, fax, e-mail, and send to network folder jobs
The File Erase Modes available are:
o Non-secure Fast Erase (No overwrite)
o Secure Fast Erase (Overwrite 1 time)
o Secure Sanitizing Erase (Overwrite 3 times)
Note: For File Erase mode specifications see Appendix A
PUBLIC 2
Page 3
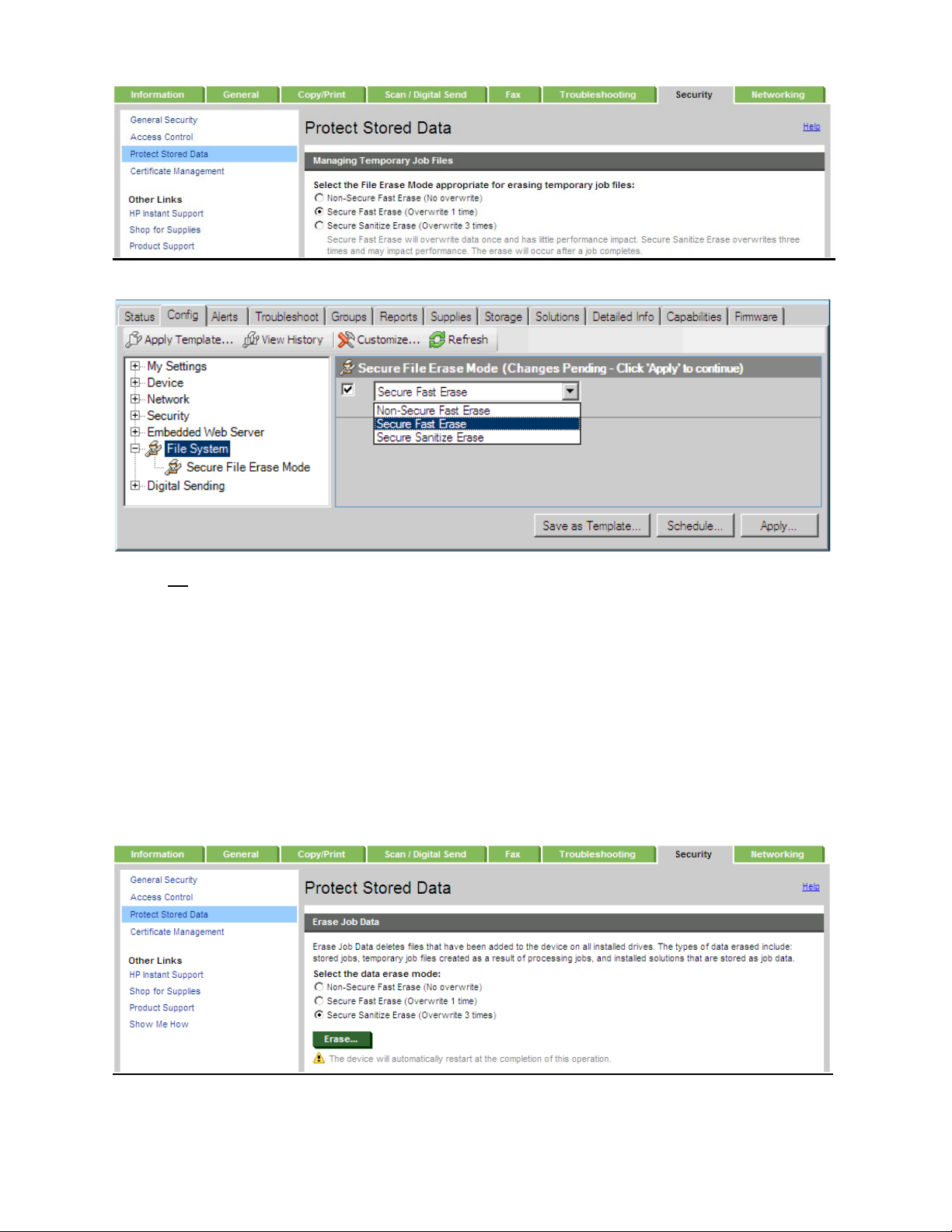
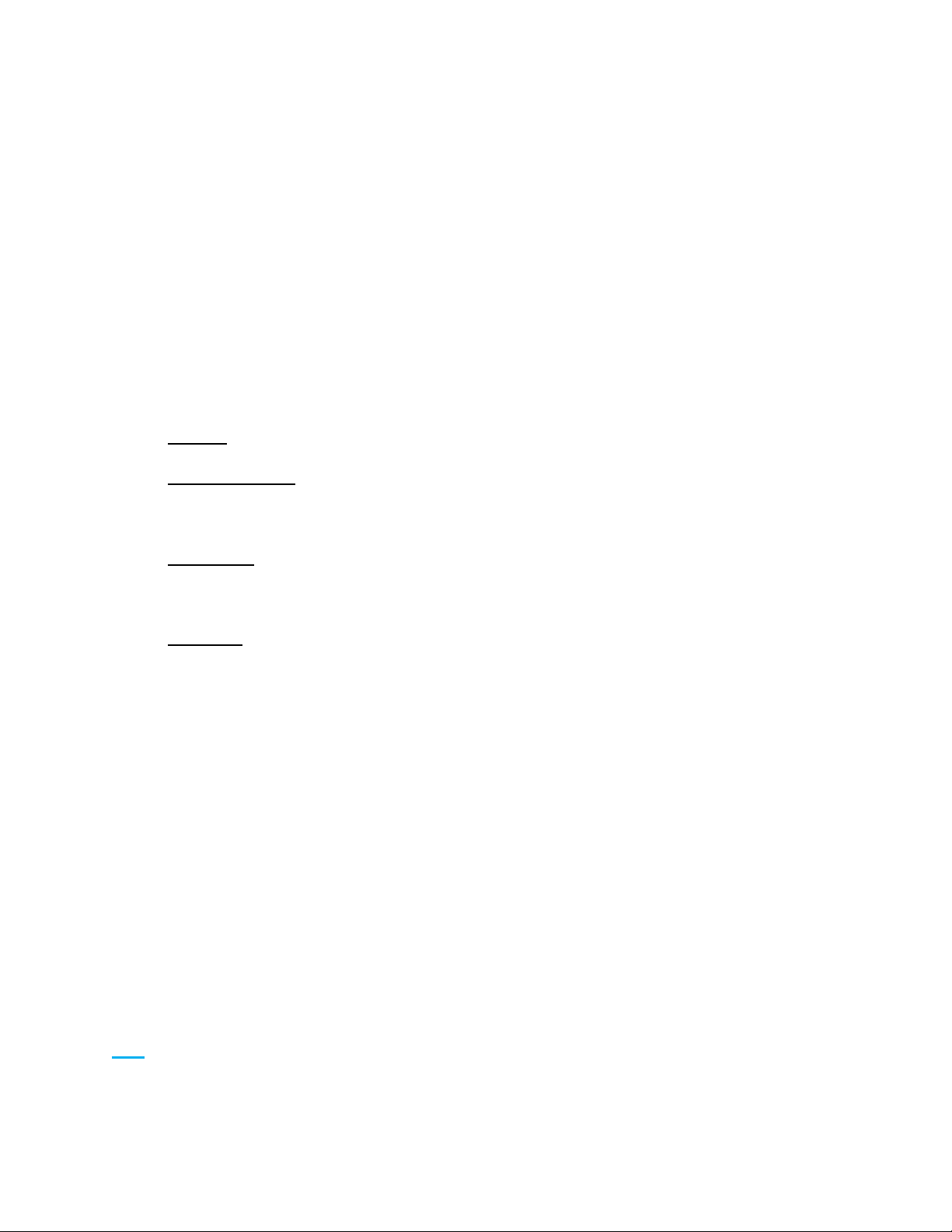
Figure 1: Managing Temporary Job Files settings in the Embedded Web Server (EWS)
Figure 2: Secure File Erase Mode settings in Web Jetadmin
Note: This setting corresponds to Managing Temporary Job Files setting in EWS
2. Erase Job Data
This feature will erase and overwrite all job data files stored on the disk including:
o Temporary data for print jobs
o Temporary data for copy, fax, e-mail, and send to network folder jobs
o Stored Jobs, Stored Fax jobs
The File Erase Modes available are:
o Non-secure Fast Erase (No overwrite)
o Secure Fast Erase (Overwrite 1 time)
o Secure Sanitizing Erase (Overwrite 3 times)
Figure 3: Erase Job Data settings in the Embedded Web Server
Page 4
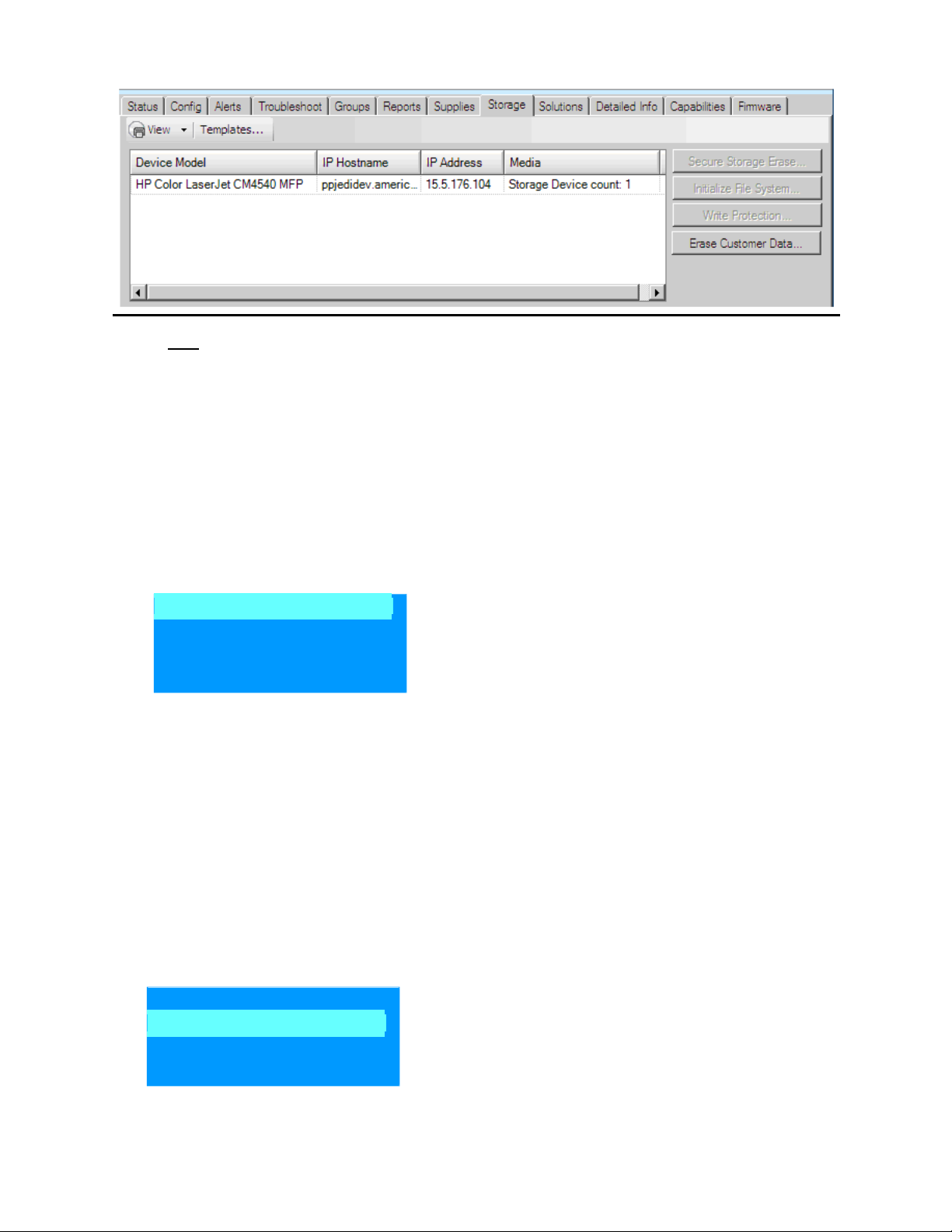
Figure 4: Erase Customer Data settings in Web Jetadmin
NOTE: This setting corresponds to Erase Job Data setting in EWS
3. Secure Disk Erase
This feature securely erases all data on the hard disk, including disk sectors spared and relocated sectors.
This erase operation, also known as ATA Erase, is executed directly by the hard disk controller.
Secure Disk Erase meets the “Purge” erase standard defined in NIST Special Publication 800-88, Guidelines
for Media Sanitation. (See the Government Erase Specifications.)
This erase mode is only accessible from the pre - boot menus for the main system disk. It is available for
accessory disks in EWS and Web Jetadmin. If the erased disk contained the system firmware, performing
an Erase/Unlock will render the device inoperable, and a new firmware image must be installed to the disk
before the device can be used again.
1 Secure Erase
1 Secure Erase
2 Erase / Unlock
3 Get Statuses
Figure 5: Secure Disk Erase in device Pre - boot Menu
4. Erase / Unlock Encrypted Disk
The HP High Performance Secure Hard Disk supports a special erase referred to as a “Crypto Erase”.
Selecting the Erase/Unlock option for one of these disks forces its encryption keys to be destroyed and
new keys generated. This instantly renders all the encrypted data on the disk unreadable. There is no
method to recover the encryption keys and no method to recover the encrypted data once the keys have
been changed.
This erase mode is only accessible from the pre - boot menus for the main system disk. It is available for
accessory disks in EWS and Web Jetadmin. If the erased disk contained the system firmware, performing
an Erase/Unlock will render the device inoperable, and a new firmware image must be installed to the disk
before the device can be used again.
1 Secure Erase
2 Erase / Unlock
2 Erase / Unlock
3 Get Status
Figure 6: Erase / Unlock in device Pre - boot Menu
PUBLIC 4
Page 5

Disk Initialization Commands
These commands reinitialize the hard disk or sections of the disk to provide troubleshooting and diagnostic
capabilities. The commands are similar to disk formatting commands and do not provide sector level data
overwrite. These erase commands are not recommended for securely removing customer data.
These commands are only accessible from the device pre - boot menus.
Clean Disk removes all data from the disk. This command will render the device inoperable. The device
firmware must be re-installed to the disk before the device can be used again.
+1 Download
2 Clean Disk
2 Clean Disk
3 Partial Clean
4 Change Password
Figure 7: Clean Disk in device Pre - boot Menu
Partial Clean removes all data from the disk except for the compressed operating system installation
code in the repository and initiates a reload of the device operation system.
+1 Download
2 Clean Disk
3 Partial Clean
3 Partial Clean
4 Change Password
Figure 8: Partial Clean in device Pre - boot Menu
Page 6
SSD and eMMC Security Overview
Some models of HP printing devices use Solid State Drive (SSD) or embedded MultiMediaCard (eMMC) mass
storage devices as the system disk (See Appendix C for these models). SSD and eMMC are mass storage devices
that use NAND-based flash memory instead of spinning disks used in traditional hard disk drives (HDD). These
memory-based drives appear to the printing device operating system as a traditional Hard Disk Drive.
SSDs and eMMCs have operational characteristics that affect some security features available in traditional HDD
enabled devices. For high security environments and security sensitive applications, HP recommends
Selecting models that include a HDD (See Appendix B Device List)
Adding an optional HDD when supported (See Accessory Drive Option for Job Data)
Secure Erase Data Overwrite Functionality Not Supported on SSD/eMMC
Due to the nature of Flash memory operation, SSDs and eMMCs are not able to securely delete files by directly
overwriting their data as can be done with a hard disk drive. The following SSD and eMMC read / write
characteristics prevent the implementation of HP’s Secure Erase Data Overwrite feature using Secure Fast
Erase (1- pass) or Secure Sanitize Erase (3-pass) algorithms to securely delete files on an ongoing basis.
SSD and eMMC controllers use a technique called “wear leveling” to evenly distribute data across all
flash blocks in the SSD. This causes data previously written to be moved dynamically to different
locations when writing new data. The previous data locations cannot be tracked for overwriting.
SSD and eMMC “write amplification” behavior also causes the memory controller to dynamically
relocate previously written data. Data is written to flash locations using 4 to 8 KB pages but must be
erased in blocks of typically 256KB. Existing data is relocated to free entire blocks for erasure, as
flash needs to be erased before it can be written again.
Secure Volatile Storage Feature with SSD and eMMC
To protect customer data on devices using SSD and eMMC, HP uses firmware encryption to specific areas of
the storage device containing customer job data. All files written to the customer job data disk areas are
encrypted using AES-128 encryption. This can be configured to AES-256 encryption, if desired (Figure 9).
Data stored on the encrypted partition includes: Stored print jobs, temporary print job files, PJL and PostScript
filesystem files including downloaded fonts, and extensibility customer data (if stored there by the extensibility
solution).
Figure 9: Managing Job Data Encryption on an SSD or eMMC system disk in the Embedded Web Server (EWS)
PUBLIC 6
Page 7

NOTE: Because SSD and eMMC product memory does not have onboard encryption it will list as “Status: Disk
Cannot be encrypted” (Figures 10); however, any data written to the memory is encrypted by the device
firmware as configured as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 10: EWS Protect Data displaying Status Disk cannot be encrypted
For devices without a hard disk drive, the customer data partition is rebuilt, and the encrypted data is
cryptographically erased after a system power cycle as the encryption keys are not preserved. This provides a
secure erase of all customer data from the encrypted sections of the SSD or eMMC.
SSD and eMMC Impact to Disk Management Features
The following security features are impacted when using SSD as the device system disk.
1.
Managing Temporary Job Files
This feature controls how temporary job files are erased at the completion of print, copy, fax, or digital
send jobs.
SSD and eMMC devices do not support the following erase modes:
o Secure Fast Erase (Overwrite 1 time)
o Secure Sanitizing Erase (Overwrite 3 times)
Figure 11: Managing Temporary Job Files option using an SSD or eMMC system disk in the Embedded Web Server (EWS)
2.
Erase Job Data
This feature erases all job data files stored on the system disk including temporary data for print, copy,
fax, e-mail, and send to network folder jobs, Stored Jobs and Stored Fax jobs
SSD and eMMC devices do not support the following erase modes:
o Secure Fast Erase (Overwrite 1 time)
o Secure Sanitizing Erase (Overwrite 3 times)
Page 8

Figure 12: Erase Job Date option using an SSD system disk in the Embedded Web Server (EWS)
Figure 13: Erase Job Date option using an eMMC system disk in the Embedded Web Server (EWS)
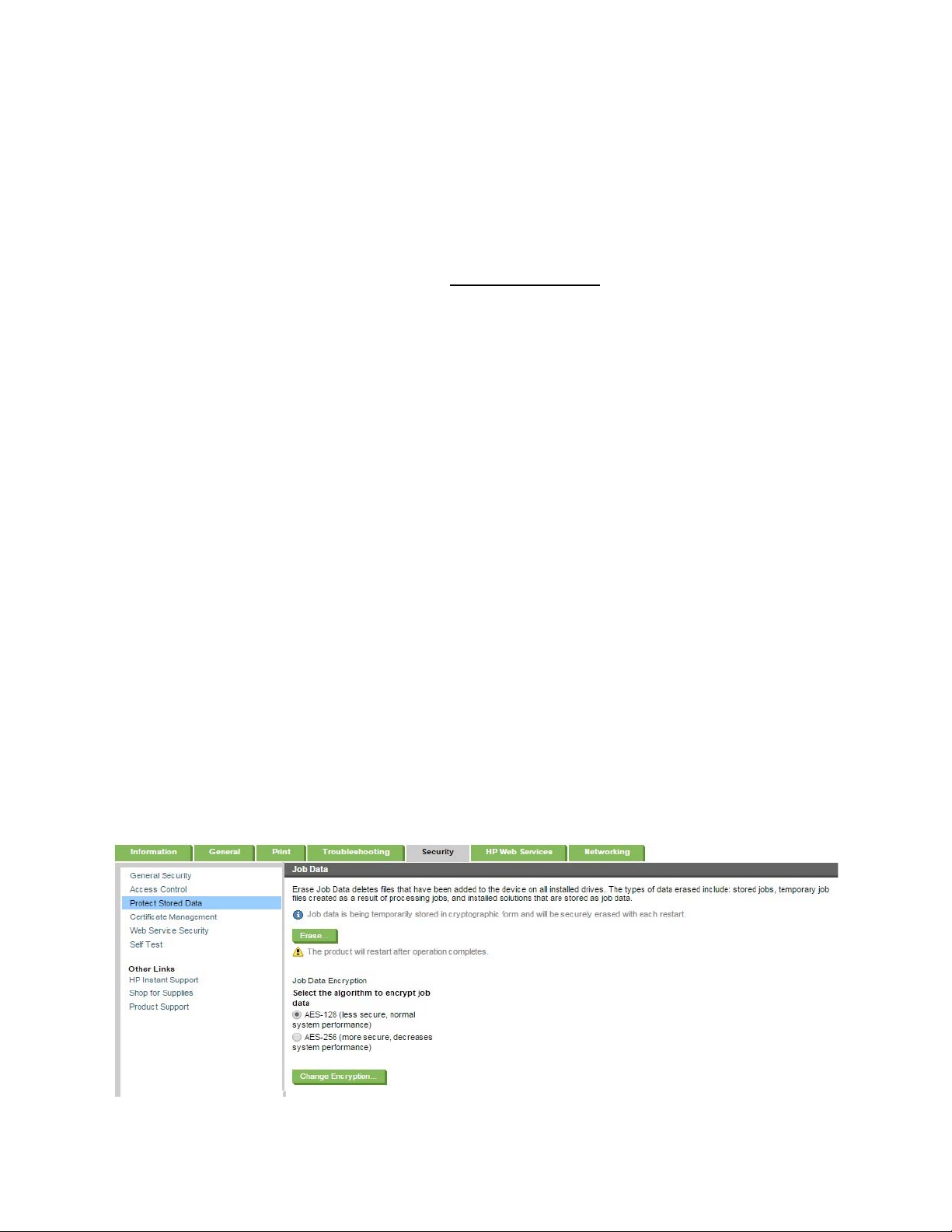
3. Job Data Encryption
Job data is temporarily stored in cryptographic form and will be securely erased with each restart. The
default setting is AES-128 which provides the best system performance. AES-256 provides more
security however will impact system performance.
Figure 14: Job Data Encryption using an eMMC system disk in the Embedded Web Server (EWS)
4. Secure Erase
HP printing devices with SSD used in HP printing devices supports ATA Secure Erase, which clears all
addressable and spared storage. This erase meets the NIST 800-88r1 standard for Purge. (See
Government Erase Standards)
PUBLIC 8
Page 9

NOTE: The early generation of SSD used in HP printing devices did not support ATA Secure Erase; however,
executing the Secure Erase command will manually clear all addressable memory locations
cells as empty. (See Appendix
D: for devices which did not support ATA erase.)
marking all
HP printing devices with eMMC support Secure Erase. The eMMC used in HP printing devices does not
support ATA Secure Erase, but instead uses the equivalent Trim with Sanitize, which clears all addressable
and spared storage. This erase meets the NIST 800-88r1 definition for Purge. (See Government Erase
Standards)
The Secure Erase mode is only accessible from the pre - boot menus. Because the SSD or eMMC acts as
the system drive containing the operating system firmware, performing a Secure Erase will render the
device inoperable, and a new firmware image must be installed before the device can be used again.
This erase mode is recommended when decommissioning a device.
1 Secure Erase
1 Secure Erase
2 Erase / Unlock
3 Get Statuses
Figure 15: Secure Erase in device Pre - boot Menu
Accessory Hard Disk Drive Option
An accessory hard drive can be added to some devices to store all customer job data. Once the drive is
installed, it is enabled on default or by selecting the drive and clicking the Use option (See Figure 15). All
existing customer job data is then transferred to the external drive automatically. From that point forward all
job data including temporary files for print and scan jobs use the accessory drive instead of the main system
drive. The accessory drive will be listed as “Internal Disk” and SSD or eMMC will be listed as “Accessory Drive 1”.
NOTE: SSD and eMMC product memory will list as “Status: Disk Cannot be encrypted” as it does not have
onboard encryption; however, any data written to the memory is encrypted by the device firmware.
Figure 16: Accessory Drive settings in the Embedded Web Server (EWS)
The accessory HDD can be securely erased independently of the system drive. Two erase operations are
available.
If the drive is an HP Secure Disk encrypted hard drive, a cryptographic erase can be performed.
(See the Erase / Unlock section in the Secure Erase section)
Page 10

Secure Disk Erase selects the most secure method to remove the drive’s data, other than a
cryptographic erase. The method will either be a Secure Erase using data overwrite or an ATA Secure
Disk Erase.
o
NOTE: This erase mode is recommended when decommissioning a device.
(See the Secure Disk Erase topic in the Secure Erase Command section)
Figure 17: Accessory Drive Erase command in Hard Disk Status of EWS
Figure 18: Erase options for accessory drive in the Embedded Web Server (EWS)
Disk Erase confirmation
When a secure fast erase or secure sanitize erase is performed an entry will appear in the event log confirming
successful completion of disk clean. (Figure 18) Confirmation is not available for Secure Erase or Erase/Unlock
the pre-boot menu. As these actions remove the printer firmware, including all logs, the BIOS is unable to
record completion of the action.
Figure 19: Event log entry for Secure Fast erase or Secure Sanitize erase.
PUBLIC 10
Page 11

Government Erase Standards
These devices comply with current US Government requirements for Clear and Purge when clearing
confidential data from a hard disk as specified in Updated DSS Clearing and Sanitization Matrix AS OF June 28,
2007 and NIST Special Publication 800-88, Guidelines for Media Sanitation (R1 December 2014).
NIST 800-88 defines three levels of sanitization, from weakest to strongest:
Clear Overwrite all storage space one or more times
Purge Degauss the disk or execute the ATA Secure Erase command if the drive supports it (all hard
disks used by HP support this command)
Destroy Incinerate, crush, or chemically destroy the disk
Secure Erase Feature NIST Sanitization Level
Managing Temporary
Clear when using Secure Fast Erase or Secure Sanitize Erase modes
Job Files
Erase Job Data Clear
Secure Disk Erase Clear and Purge
Erase/Unlock
encrypted disk
Purge
Appendix A: Secure Erase Data Overwrite and Specifications
Normally when a file is deleted from a HDD, the filename entry is erased from the disk’s file allocation table,
removing the file’s presence. The file’s data still exists in the disk’s individual sectors and is overwritten only
when that sector is allocated for a different file.
HP Secure Erase technology overwrites a deleted file’s data from the individual sectors with random data
using either a one pass or three-pass overwrite, which conform to current US Government specifications.
Note: See the Government Erase Specifications section for further information
To enable Secure Erase using data overwrite, select the following options for “File Erase Mode” when
available:
Non-secure Fast Erase mode: Performs standard file system delete only (does not overwrite file data)
Secure Fast Erase mode: Performs a one pass overwrite of all data
Secure Sanitizing Erase mode: Performs a three pass overwrite of all data
Note: The system default is Non-Secure Fast Erase mode. Secure Fast Erase mode is recommended for best
overwrite system performance.
Overwrite Specifications
Secure Fast Erase mode follows the National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 80088, Guidelines for Media Sanitization.
For Secure Fast Erase, each deleted file’s data is overwritten once with:
the hexadecimal character 0x48.
Page 12

Secure Sanitizing Erase mode follows the U.S. Department of Defense 5220-22.M specification using a
succession of multiple data overwrites.
For Secure Sanitizing Erase, each deleted file is overwritten with:
the fixed character pattern (binary 01001000).
the complement of the fixed character pattern (binary 10110111).
a random character:
o A 32k byte buffer of random characters is generated for each file delete operation using the
device’s unique uptime as the seed.
o Each byte of file data uses a unique random character from the buffer.
o The random character buffer is reused up to 32 times, and then regenerated using new random
data.
To ensure successful completion of each overwrite operation, each overwritten byte is verified.
Note: NIST SP-800-88 “Guidelines for Media Sanitization” (R1 December 2014) supersedes the US DOD 5220-
2.M (1997 edition) specification.
PUBLIC 12
Page 13

Appendix B: Device Hard Drive Support
The following printing devices support HP FutureSmart Firmware functionality and HP High Performance Secure
Hard Disk.
NOTE: A * indicates the device requires an optional HP High Performance Secure Hard Disk Accessory or EIO
Accessory. See product datasheet for details.
HP Color LaserJet CM4540 MFP
HP Color LaserJet CP5525xh
HP LaserJet Enterprise M4555 MFP
HP LaserJet Enterprise M506 Series*
HP LaserJet Enterprise M507 Series*
HP LaserJet Enterprise 500 MFP M525f
HP LaserJet Managed MFP M525fm
HP LaserJet Managed Flow MFP M525cm
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M527dn*, M527f, M527c, M527z
HP LaserJet Managed Flow MFP M527cm
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M528dn*, M528f
HP LaserJet Enterprise Flow MFP M528c, M528z
HP LaserJet Enterprise 500 Color M551xh
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M553n*, M553dn*, M553x*, M553dh
HP Color LaserJet Managed M553 series*
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M555 series*
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP M575dnm*
HP LaserJet Enterprise 500 color MFP M575dn, M575f
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP M575 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed Flow MFP M575cm
HP LaserJet Enterprise color Flow MFP M575c series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise MFP M577 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP M577
HP Color LaserJet Managed Flow MFP M577
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise MFP M578 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise Flow MFP M578 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise 600 M603xh
HP LaserJet Enterprise M604 series*
HP LaserJet Enterprise M605n*, M605dn*, M605x*, M605dh
HP LaserJet Managed M605 series*
Page 14

HP LaserJet Enterprise M606 series*
HP LaserJet Enterprise M607, M608 series*
HP LaserJet Enterprise M609dn*, M609x* M609dh
HP LaserJet Enterprise M610, M611, M612 series *
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M630 series HP LaserJet Managed MFP M630
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP Flow M630 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise Managed Flow MFP M630 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M631 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M632, M633 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP Flow M632, M633 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M634, M635, M636 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP Flow M634, M635, M636 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M651xh
HP Color LaserJet Managed M651xhm
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M652, M653 series*
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M680 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP M680 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP Flow M680z
HP Color LaserJet Managed Flow MFP M680zm
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise MFP M681 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise Flow MFP M681, M682 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise 700 M712xh
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M725 series
HP LaserJet Managed MFP M725 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M750 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M751 series*
HP LaserJet Enterprise 700 color M775 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP M775 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise MFP M776 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise Flow MFP M776 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M806
HP LaserJet Enterprise Flow MFP M830 series
HP LaserJet Managed Flow MFP M830 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M855
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M856 Printer series*
HP LaserJet Enterprise Flow MFP M880 series
HP LaserJet Managed Flow MFP M880 series
HP LaserJet Managed E50045dw*
PUBLIC 14
Page 15

HP LaserJet Managed E50145dn*
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E52545dn*
HP LaserJet Managed Flow MFP E52545c
HP Color LaserJet Managed E55040dw*
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP E57540 series
HP LaserJet Managed E60055,65,75 series*
HP LaserJet Managed E60155,65,75 series*
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62555dn*
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62565h
HP LaserJet Managed Flow MFP E62565, 75 series
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62655dn*
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62665hs
HP LaserJet Managed Flow MFP E62665 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP E67550dh
HP Color LaserJet Managed E65050, 60 series*
HP Color LaserJet Managed E65150, 60 series*
HP Color LaserJet Managed Flow MFP E67560z
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP E67650dh
HP Color LaserJet Managed Flow MFP E67660z
HP Color LaserJet Managed E75245dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed E85055 series*
HP Officejet Enterprise X585 series
HP OfficeJet Managed Color MFP X585dnm
HP OfficeJet Managed Color Flow MFP X585zm
HP PageWide Enterprise Color 765 series*
HP PageWide Enterprise Color MFP 780 series
HP PageWide Enterprise Color Flow MFP 785 series
HP PageWide Managed Color MFP E58650dn
HP PageWide Managed Color Flow MFP E58650z
HP PageWide Managed Color E75160dn*
HP PageWide Managed Color MFP E77650/60 series
HP PageWide Managed Color Flow MFP E77660
HP PageWide Managed Color MFP P77960 series
HP Digital Sender Flow 8500 fn2
HP ScanJet Enterprise Flow N9120 fn2 Document Scanner
Page 16

Appendix C: Device SSD and eMMC Support
The following HP printing devices include SSD storage:
HP Color LaserJet CP5525n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise M4555 MFP base (EMEA only)
HP LaserJet Enterprise 600 M601n, dn, x; M602n, dn, x; M603n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M630dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise M651n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise 500 M525 dn, f
HP LaserJet Enterprise 500 color M551n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise 600 M601n, dn, x; M602n, dn, x; M603n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M630dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise M651n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise 700 M712n
HP OfficeJet Enterprise X555
The following HP printing devices include eMMC storage:
HP LaserJet Enterprise M406, M407 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M430, M431 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M455 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise MFP M480 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M604, M605, M606 series
HP LaserJet Managed M605 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M607, M608 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M609dn, M609x
HP LaserJet Enterprise M610, M611, M612 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M652, M653 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M506 series
HP LaserJet Managed M506 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M507 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M527 dn
HP LaserJet Managed MFP M527dnm
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M528dn
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M552, M553 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed M553 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M554 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M555 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M652 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed M651dnm
PUBLIC 16
Page 17

HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M751 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M856 Printer series
HP LaserJet Managed E40040 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed E45028 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP E47528 series
HP LaserJet Managed E50045dw
HP LaserJet Managed E50145dn
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E52545dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed E55040dw
HP LaserJet Managed E60055,65,75 series
HP LaserJet Managed E60155,65,75 series
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62555dn
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62655dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed E65050, 60 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed E65150, 60 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed E75245dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP E78223, 28 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed E85055 series
HP PageWide Enterprise Color 556 series
HP PageWide Color 755dn
HP PageWide Enterprise Color 765dn
HP PageWide Color MFP 774 series
HP PageWide Color MFP 779 series
HP PageWide Managed Color E55650
HP PageWide Managed Color E75160dn
HP PageWide Managed Color P75250dn
HP PageWide Managed Color MFP P77440dn
HP PageWide Managed Color MFP P77940, 50 series
The following HP printing devices include Secure Volatile Storage encryption:
HP Color LaserJet CP5525n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise M506 series
HP LaserJet Managed M506 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M507 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise 500 M525 dn, f
HP LaserJet Enterprise M527dn
HP LaserJet Managed MFP M527dnm
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M528dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise 500 color M551n, dn
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M552, M553 series
Page 18

HP Color LaserJet Managed M553 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M577 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise 600 M601n, dn, x; M602n, dn; M603n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise M604, M605, M606 series
HP LaserJet Managed M605 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M607, M608 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M609dn, M609x
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M630dn
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M651n, dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed M651dnm
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M652, M653 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise 700 M712n
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M751 series*
HP LaserJet Managed E50045dw
HP LaserJet Managed E50145dn
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E52545dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed E55040dw
HP LaserJet Managed E60055,65,75 series
HP LaserJet Managed E60155,65,75 series
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62555dn
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62655dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed E65050, 60 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed E65150, 60 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed E75245dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP E78223, 28 series
HP OfficeJet Enterprise X555
HP OfficeJet Enterprise X585
HP PageWide Enterprise Color 556 series
HP PageWide Enterprise Color MFP 586 series
HP PageWide Color 755dn
HP PageWide Enterprise Color 765dn
HP PageWide Color MFP 774 series
HP PageWide Color MFP 779 series
HP PageWide Managed Color E75160dn
HP PageWide Managed Color P75250dn
HP PageWide Managed Color MFP P77440dn
HP PageWide Managed Color MFP P77940, 50 series
PUBLIC 18
Page 19

Appendix D: ATA secure erase not supported
The following HP printing devices do not support ATA secure erase
HP Color LaserJet CP5525n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise M4555 MFP base (EMEA only)
Appendix E: Optional HDD Accessory capable devices
The following HP printing devices accept the optional HDD Accessory
HP LaserJet Enterprise M506 Series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M507 Series
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M527dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise MFP M528dn
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M553n, M553dn, M553x
HP Color LaserJet Managed M553 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP M575dnm
HP LaserJet Enterprise M604 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M605n, M605dn, M605x
HP LaserJet Managed M605 series
:
HP LaserJet Enterprise M606 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M607, M608 series
HP LaserJet Enterprise M609dn, M609x
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M652, M653 series
HP Color LaserJet Enterprise M751 series
HP LaserJet Managed E50045dw
HP LaserJet Managed E50145dn
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E52545dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed E55040dw
HP LaserJet Managed E60055,65,75 series
HP LaserJet Managed E60155,65,75 series
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62555dn
HP LaserJet Managed MFP E62655dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed E65050, 60 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed E65150, 60 series
HP Color LaserJet Managed E75245dn
HP Color LaserJet Managed MFP E78223, 28 series
Page 20

HP PageWide Enterprise Color 765 series HP PageWide Managed Color E75160dn
HP PageWide Managed Color MFP E77650/60 series
The following HP printing devices accept the optional EIO HDD Accessory
HP Color LaserJet CP5525n, dn
HP LaserJet Enterprise M4555 MFP
hp.com/go/support
Current HP driver, support, and security alerts
delivered directly to your desktop
© Copyright 2021HP Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP
products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed
as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Created February 2021
Version 2.9
PUBLIC
c06102462
PUBLIC 20
 Loading...
Loading...