HP ProLiant DL985 Troubleshooting Manual

HP ProLiant Servers
s document is intended
Troubleshooting Guide
Abstract
This document describes common procedures and solutions for the many levels of troubleshooting for an HP ProLiant server. Thi
for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers or server blades. HP assumes you are qualified in the servicing of computer
equipment and trained in recognizing hazards in products with hazardous energy levels.
Part Number: 375445-402
April 2011
Edition: 11

© Copyright 2004, 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows Server are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Intel and Pentium are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.

Contents
Introduction .................................................................................................................................. 8
What's new ................................................................................................................................................. 8
Revision history ............................................................................................................................................ 8
375445-401 (January 2011) .............................................................................................................. 8
375445-xx9 (June 2010) .................................................................................................................... 8
375445-xx8 (July 2009) ..................................................................................................................... 9
375445-xx7 (November 2008) ......................................................................................................... 10
375445-xx6 (September 2007)......................................................................................................... 10
375445-xx5 (June 2006) .................................................................................................................. 11
375445-xx4 (May 2006) ................................................................................................................. 11
375445-xx3 (September 2005)......................................................................................................... 11
Getting started ............................................................................................................................ 12
HP ProLiant 100 Series Server troubleshooting information ............................................................................. 12
How to use this guide ................................................................................................................................. 12
Pre-diagnostic steps .................................................................................................................................... 13
Important safety information .............................................................................................................. 13
Symptom information ........................................................................................................................ 16
Prepare the server for diagnosis ......................................................................................................... 16
Common problem resolution ........................................................................................................ 19
Loose connections ...................................................................................................................................... 19
Service notifications .................................................................................................................................... 19
Firmware updates ...................................................................................................................................... 19
DIMM handling guidelines .......................................................................................................................... 20
Hard drive guidelines ................................................................................................................................. 20
SAS and SATA hard drive guidelines ................................................................................................. 20
SCSI hard drive guidelines ................................................................................................................ 20
Hard drive LED combinations ...................................................................................................................... 21
Hot-plug SCSI hard drive LED combinations ........................................................................................ 21
SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations ...................................................................................... 21
Server updates with an HP Trusted Platform Module and BitLocker™ enabled ................................................... 22
Diagnostic flowcharts .................................................................................................................. 23
Troubleshooting flowcharts .......................................................................................................................... 23
Troubleshooting flowchart reference websites ...................................................................................... 23
Start diagnosis flowchart ................................................................................................................... 25
General diagnosis flowchart .............................................................................................................. 25
Power-on problems flowchart ............................................................................................................. 27
POST problems flowchart .................................................................................................................. 31
Operating system boot problems flowchart ......................................................................................... 33
Server fault indications flowchart ....................................................................................................... 35
Hardware problems .................................................................................................................... 38
Procedures for all ProLiant servers ................................................................................................................ 38
Power problems ......................................................................................................................................... 38
Power source problems ..................................................................................................................... 38
Power supply problems ..................................................................................................................... 38
Contents 3

UPS problems .................................................................................................................................. 39
General hardware problems ....................................................................................................................... 40
Problems with new hardware ............................................................................................................ 40
Unknown problem ............................................................................................................................ 41
Third-party device problems .............................................................................................................. 41
Internal system problems ............................................................................................................................. 42
Battery pack problems ...................................................................................................................... 42
CD-ROM and DVD drive problems ..................................................................................................... 42
Diskette drive problems ..................................................................................................................... 43
Drive problems (hard drives and solid state drives) .............................................................................. 44
SD card problems ............................................................................................................................ 46
USB drive key problems .................................................................................................................... 47
Fan problems ................................................................................................................................... 47
HP Trusted Platform Module problems ................................................................................................ 48
Memory problems ............................................................................................................................ 49
PPM problems .................................................................................................................................. 51
Processor problems .......................................................................................................................... 51
Tape drive problems ......................................................................................................................... 52
Graphics and video adapter problems ............................................................................................... 53
System open circuits and short circuits .......................................................................................................... 54
External device problems ............................................................................................................................ 54
Video problems................................................................................................................................ 54
Mouse and keyboard problems ......................................................................................................... 55
Audio problems ............................................................................................................................... 56
Printer problems ............................................................................................................................... 56
Cable problems ............................................................................................................................... 56
Local I/O cable problems ................................................................................................................. 56
Modem problems ............................................................................................................................. 57
Network controller problems ............................................................................................................. 59
Expansion board problems................................................................................................................ 60
Software problems ...................................................................................................................... 61
Operating system problems and resolutions .................................................................................................. 61
Operating system problems ............................................................................................................... 61
Operating system updates ................................................................................................................. 62
Restoring to a backed-up version ....................................................................................................... 63
When to Reconfigure or Reload Software ........................................................................................... 63
Linux operating systems .................................................................................................................... 64
Application software problems .................................................................................................................... 64
Software locks up ............................................................................................................................. 64
Errors occur after a software setting is changed ................................................................................... 64
Errors occur after the system software is changed ................................................................................ 64
Errors occur after an application is installed ........................................................................................ 64
ROM problems .......................................................................................................................................... 65
Remote ROM flash problems ............................................................................................................. 65
Boot problems .................................................................................................................................. 66
Software tools and solutions ......................................................................................................... 68
Configuration tools ..................................................................................................................................... 68
SmartStart software .......................................................................................................................... 68
HP ROM-Based Setup Utility .............................................................................................................. 68
Array Configuration Utility ................................................................................................................ 71
Option ROM Configuration for Arrays................................................................................................ 72
Re-entering the serial number and product ID ...................................................................................... 72
Contents 4

Management tools...................................................................................................................................... 73
Automatic Server Recovery ................................................................................................................ 73
ROMPaq utility ................................................................................................................................. 73
Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition II ..................................................................................................... 74
iLO and iLO 2 technology ................................................................................................................. 74
Integrated Lights-Out 3 technology ..................................................................................................... 74
Erase Utility ..................................................................................................................................... 75
Redundant ROM support ................................................................................................................... 75
USB support .................................................................................................................................... 75
Diagnostic tools ......................................................................................................................................... 76
HP Insight Diagnostics ...................................................................................................................... 76
HP Insight Diagnostics survey functionality .......................................................................................... 76
Integrated Management Log .............................................................................................................. 77
Array diagnostic software ................................................................................................................. 77
Remote support and analysis tools ............................................................................................................... 77
HP Insight Remote Support software ................................................................................................... 77
Keeping the system current .......................................................................................................................... 78
Drivers ............................................................................................................................................ 78
Version control ................................................................................................................................. 78
ProLiant Support Packs ...................................................................................................................... 79
Operating system version support ...................................................................................................... 79
Firmware ......................................................................................................................................... 79
HP Smart Update Manager ............................................................................................................... 79
System Online ROM flash component utility ........................................................................................ 80
Subscriber's choice .......................................................................................................................... 80
Care Pack ....................................................................................................................................... 81
Firmware maintenance ............................................................................................................................... 81
Types of ROM.................................................................................................................................. 81
Verifying firmware versions ............................................................................................................... 82
Updating firmware ........................................................................................................................... 83
Unsupported processor stepping with Intel® processors ....................................................................... 85
Unsupported processor stepping with AMD processors ........................................................................ 86
HP resources for troubleshooting ................................................................................................... 87
Online resources ........................................................................................................................................ 87
HP Technical Support website ............................................................................................................ 87
HP Guided Troubleshooting website ................................................................................................... 87
Server documentation ....................................................................................................................... 87
White papers .................................................................................................................................. 87
Service notifications, advisories, and notices ....................................................................................... 87
Subscription services ........................................................................................................................ 87
HP Care Pack Services...................................................................................................................... 88
Product information resources ...................................................................................................................... 88
Additional product information .......................................................................................................... 88
Registering the server........................................................................................................................ 88
Overview of server features and installation instructions ....................................................................... 88
Key features, option part numbers ...................................................................................................... 88
Server and option specifications, symbols, installation warnings, and notices ......................................... 88
Teardown procedures, part numbers, specifications ............................................................................. 89
Technical topics ............................................................................................................................... 89
Product installation resources ....................................................................................................................... 89
Switch settings, LED functions, drive, memory, expansion board and processor installation instructions, and
board layouts .................................................................................................................................. 89
External cabling information .............................................................................................................. 89
Contents 5

Power capacity ................................................................................................................................ 89
Product configuration resources ................................................................................................................... 89
Device driver information .................................................................................................................. 89
DDR3 memory configuration.............................................................................................................. 90
Operating System Version Support ..................................................................................................... 90
Operating system installation and configuration information (for factory-installed operating systems) ......... 90
Server configuration information ........................................................................................................ 90
Installation and configuration information for the server setup software .................................................. 90
Software installation and configuration of the server ............................................................................ 90
iLO information ................................................................................................................................ 90
Management of the server ................................................................................................................. 90
Installation and configuration information for the server management system .......................................... 91
Fault tolerance, security, care and maintenance, configuration and setup .............................................. 91
Error messages ........................................................................................................................... 92
ADU error messages ................................................................................................................................... 92
Introduction to ADU error messages ................................................................................................... 92
ADU version 8.0 through 8.28 error messages ................................................................................. 112
POST error messages and beep codes ....................................................................................................... 116
Introduction to POST error messages ................................................................................................ 116
Non-numeric messages or beeps only............................................................................................... 117
100 Series .................................................................................................................................... 127
200 Series .................................................................................................................................... 129
300 Series .................................................................................................................................... 133
400 Series .................................................................................................................................... 134
600 Series .................................................................................................................................... 135
1100 Series .................................................................................................................................. 136
1600 Series .................................................................................................................................. 136
1700 Series .................................................................................................................................. 140
Event list error messages ........................................................................................................................... 159
Introduction to event list error messages ............................................................................................ 159
A CPU Power Module (System Board, Socket X)... ............................................................................. 159
ASR Lockup Detected: Cause ........................................................................................................... 159
Automatic operating system shutdown initiated due to fan failure ........................................................ 160
Automatic Operating System Shutdown Initiated Due to Overheat Condition... ..................................... 160
Blue Screen Trap: Cause [NT]... ...................................................................................................... 160
Corrected Memory Error Threshold Passed (Slot X, Memory Module Y)... ............................................. 160
EISA Expansion Bus Master Timeout (Slot X)... ................................................................................... 160
PCI Bus Error (Slot X, Bus Y, Device Z, Function X) ............................................................................. 160
Processor Correctable Error Threshold Passed (Slot X, Socket Y) .......................................................... 161
Processor Uncorrectable Internal Error (Slot X, Socket Y) ..................................................................... 161
Real-Time Clock Battery Failing ........................................................................................................ 161
System AC Power Overload (Power Supply X) ................................................................................... 161
System AC Power Problem (Power Supply X) ..................................................................................... 161
System Fan Failure (Fan X, Location) ................................................................................................ 161
System Fans Not Redundant ............................................................................................................ 162
System Overheating (Zone X, Location) ............................................................................................ 162
System Power Supplies Not Redundant ............................................................................................. 162
System Power Supply Failure (Power Supply X) .................................................................................. 162
Unrecoverable Host Bus Data Parity Error... ...................................................................................... 162
Uncorrectable Memory Error (Slot X, Memory Module Y).................................................................... 162
HP BladeSystem p-Class infrastructure error codes ....................................................................................... 162
Server blade management module error codes .................................................................................. 163
Power management module error codes ........................................................................................... 166
Contents 6

Port 85 codes and iLO messages ............................................................................................................... 167
Troubleshooting the system using port 85 codes ................................................................................ 167
Processor-related port 85 codes ....................................................................................................... 167
Memory-related port 85 codes......................................................................................................... 168
Expansion board-related port 85 codes ............................................................................................ 169
Miscellaneous port 85 codes ........................................................................................................... 170
Windows® Event Log processor error codes ............................................................................................... 171
Message ID: 4137 ......................................................................................................................... 171
Message ID: 4140 ......................................................................................................................... 171
Message ID: 4141 ......................................................................................................................... 171
Message ID: 4169 ......................................................................................................................... 171
Message ID: 4190 ......................................................................................................................... 171
Insight Diagnostics processor error codes ................................................................................................... 172
MSG_CPU_RR_1 ............................................................................................................................ 172
MSG_CPU_RR_2 ............................................................................................................................ 172
MSG_CPU_RR_3 ............................................................................................................................ 172
MSG_CPU_RR_5 ............................................................................................................................ 173
MSG_CPU_RR_6 ............................................................................................................................ 173
MSG_CPU_RR_7 ............................................................................................................................ 173
MSG_CPU_RR_8 ............................................................................................................................ 173
MSG_CPU_RR_9 ............................................................................................................................ 174
MSG_CPU_RR_10 .......................................................................................................................... 174
MSG_CPU_RR_11 .......................................................................................................................... 174
MSG_CPU_RR_12 .......................................................................................................................... 174
MSG_CPU_RR_13 .......................................................................................................................... 175
MSG_CPU_RR_14 .......................................................................................................................... 175
MSG_CPU_RR_15 .......................................................................................................................... 175
MSG_CPU_RR_16 .......................................................................................................................... 175
MSG_CPU_RR_17 .......................................................................................................................... 176
Contacting HP .......................................................................................................................... 177
Contacting HP technical support or an authorized reseller ............................................................................ 177
Customer self repair ................................................................................................................................. 177
Server information you need ...................................................................................................................... 177
Operating system information you need ..................................................................................................... 178
Microsoft® operating systems .......................................................................................................... 178
Linux operating systems .................................................................................................................. 179
Novell NetWare operating systems .................................................................................................. 180
SCO operating systems................................................................................................................... 180
IBM OS/2 operating systems .......................................................................................................... 181
Sun Solaris operating systems .......................................................................................................... 182
Acronyms and abbreviations ...................................................................................................... 183
Index ....................................................................................................................................... 188
Contents 7

Introduction
What's new
The eleventh edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-402, includes
the following additions and updates:
• Updated the HP ProLiant 100 Series Server troubleshooting information (on page 12) section to provide
troubleshooting information for the HP ProLiant ML110 G7 Server and HP ProLiant DL120 G7 Server.
• Updated the following sections to include the HP Smart Update Firmware DVD:
o Firmware updates (on page 19)
o HP Smart Update Manager deployment (on page 84)
o ROM Update Utility (on page 85)
Revision history
375445-401 (January 2011)
The tenth edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-401, included the
following additions and updates:
• Added a new section to Getting started (on page 12):
Performing processor procedures in the troubleshooting process (on page 17)
• Updated Breaking the server down to the minimum hardware configuration (on page 17).
• Updated the introduction and sections in Hardware problems (on page 38):
o Unknown problem (on page 41)
o Processor problems (on page 51)
• Updated multiple messages in Error messages (on page 92):
o POST error messages and beep codes (on page 116)
o Event List Error Messages (on page 159)
o Port 85 codes and iLO messages (on page 167)
o Windows® Event Log processor error codes (on page 171)
o Insight Diagnostics processor error codes (on page 172)
375445-xx9 (June 2010)
The ninth edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx9, included the
following additions and updates:
• Added new section to Getting started (on page 12):
Introduction 8

Breaking the server down to the minimum hardware configuration (on page 17)
• Updated Diagnostic flowcharts (on page 23):
o General diagnosis flowchart (on page 25)
o Server power-on problems flowchart (on page 27)
o Server and p-Class server blade POST problems flowchart (on page 32)
o c-Class server blade POST problems flowchart (on page 33)
o Server and p-Class server blade fault indications flowchart (on page 35)
• Added and updated sections in Software tools and solutions (on page 68):
o Integrated Lights-Out 3 technology (on page 74)
o Firmware (on page 79)
o HP Smart Update Manager (on page 79)
• Added new sections to Hardware problems (on page 38):
o Battery pack problems (on page 42)
o Cable problems (on page 56)
• Added a new section to Software problems (on page 61):
ROM problems (on page 65)
• Updated a section in Online resources (on page 87):
Server documentation (on page 87)
• Updated Firmware maintenance (on page 81)
• Added new error messages:
o ADU error messages (on page 92)
o POST error messages and beep codes (on page 116)
375445-xx8 (July 2009)
The eighth edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx8, included the
following additions and updates:
• Added information to the introduction for the server power-on problems flowchart (on page 27).
• Added new steps to Power problems (on page 38).
• Added a new section to Fan problems (on page 47):
All fans in an HP ProLiant G6 server are not spinning or are not spinning at the same speed (on page
48)
• Added a new section to Memory problems (on page 49):
Server fails to boot, all DIMM LEDs illuminate amber, .... (on page 50)
• Updated the content for Tape drive problems (on page 52).
• Added new sections to Software tools and solutions (on page 68) :
o Diagnostics tasks (on page 71)
o HP Insight Server Migration software for ProLiant
o Array diagnostic software (on page 77)
Introduction 9

o
HP Insight Remote Support software (on page 77)
• Added new content to HP Resources for Troubleshooting (on page 87):
o HP Guided Troubleshooting website (on page 87)
o DDR3 memory configuration (on page 90)
o Power capacity (on page 89)
• Added new error messages:
o ADU Error Messages (on page 92)
o POST error messages and beep codes (on page 116)
375445-xx7 (November 2008)
The seventh edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx7, included
the following additions and updates:
• Added new information about Server updates with an HP Trusted Platform Module and BitLocker™
enabled (on page 22) to Common problem resolution (on page 19)
• Added TPM information to Drive problems (hard drives and solid state drives) (on page 44)
• Added information about HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure fan problems to Fan problems (on page
47)
• Added HP Trusted Platform Module problems (on page 48) to Hardware problems (on page 38)
• Added SD card problems (on page 46) to Hardware problems (on page 38)
• Added USB drive key problems (on page 47) to Hardware problems (on page 38)
• Added TPM information to Remote ROM flash problems (on page 65)
• Added Service Essentials Remote Support Pack to Software tools and solutions (on page 68)
• Added TPM information to Firmware maintenance (on page 81)
• Updated the ADU error messages (on page 92) section to reflect the supported versions for the
messages in this document
• Updated and added new POST error messages and beep codes (on page 116)
375445-xx6 (September 2007)
The sixth edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx6, included the
following additions and updates:
• Added new information about preventing electrostatic discharge (on page 15).
• Added new DIMM handling guidelines (on page 20).
• Added new procedures for troubleshooting drive problems (hard drives and solid state drives) (on page
44).
• Added information on new software tools and solutions:
o HP Insight Control Environment Suites
o HP Smart Update Manager (on page 79)
• Improved firmware maintenance (on page 81):
Introduction 10

o
Added new technology
o Expanded existing information
o Added new firmware update procedures for unsupported processor stepping
375445-xx5 (June 2006)
The fifth edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx5, included the
following additions:
• Added three new c-Class server blade flowcharts:
o c-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart (on page 29)
o c-Class server blade POST problems flowchart (on page 33)
o c-Class server blade fault indications flowchart (on page 37)
• Added new processor error codes:
o Windows® Event Log processor error codes (on page 171)
o Insight Diagnostics processor error codes (on page 172)
375445-xx4 (May 2006)
The fourth edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx4, included the
following additions:
• Hot-plug SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations (on page 21)
• Operating system issues with Intel® dual-core processors (Hyper-Threading enabled) (on page 62)
• Tape drive problems (on page 52)
• New error messages in ADU error messages (on page 92) and POST error messages and beep codes
(on page 116)
375445-xx3 (September 2005)
The third edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx3, included the
following changes:
• Updated SCSI hard drive guidelines
• Added hot-plug SCSI hard drive LED combinations (on page 21)
• Updated diagnostic flowcharts (on page 23)
• Added operating system problems (on page 61)
• Added Port 85 codes and iLO messages (on page 167)
• Added new error messages to ADU error messages and POST error messages and beep codes
• Updated contacting HP:
o Contacting HP technical support or an authorized reseller
o Server information you need
Introduction 11

Getting started
HP ProLiant 100 Series Server troubleshooting
information
Use this guide for troubleshooting information on the HP ProLiant ML110 G7 Server and the HP ProLiant
DL120 G7 Server.
For troubleshooting information on HP ProLiant 100 Series Servers other than the HP ProLiant ML110 G7
Server and HP ProLiant DL120 G7 Server, see the respective server user guides.
How to use this guide
NOTE: For common troubleshooting procedures, the term "server" is used to mean servers and
This guide provides common procedures and solutions for the many levels of troubleshooting a ProLiant
server—from the most basic connector issues to complex software configuration problems.
To understand the sections of this guide and to identify the best starting point for a problem, use the following
descriptions:
• Common problem resolution (on page 19)
• Diagnostic flowcharts (on page 23)
• Hardware problems (on page 38)
server blades.
Many server problems are caused by loose connections, outdated firmware, and other issues. Use this
section to perform basic troubleshooting for common problems.
When a server exhibits symptoms that do not immediately pinpoint the problem, use this section to
begin troubleshooting. The section contains a series of flowcharts that provide a common
troubleshooting process for ProLiant servers. The flowcharts identify a diagnostic tool or a process to
help solve the problem.
When the symptoms point to a specific component, use this section to find solutions for problems with
power, general components, system boards, system open circuits and short circuits, and external
devices.
• Software problems (on page 61)
When you have a known, specific software problem, use this section to identify a solution to the
problem.
• Software tools and solutions (on page 68)
Use this section as a reference for software tools and utilities.
• HP resources for troubleshooting (on page 87)
Getting started 12
When additional information becomes necessary, use this section to identify websites and
supplemental documents that contain troubleshooting information.
• Error messages (on page 92)
Use this section for a complete list of the following messages:
o ADU error messages (on page 92)
o POST error messages and beep codes (on page 116)
o Event list error messages (on page 159)
o HP BladeSystem infrastructure error codes ("HP BladeSystem p-Class infrastructure error codes" on
page 162)
o Port 85 codes and iLO messages (on page 167)
Pre-diagnostic steps
WARNING: To avoid potential problems, ALWAYS read the warnings and cautionary
information in the server documentation before removing, replacing, reseating, or modifying
1. Review the important safety information (on page 13).
2. Gather symptom information (on page 16).
3. Prepare the server for diagnosis (on page 16).
4. Use the Start diagnosis flowchart (on page 25) to begin the diagnostic process.
Important safety information
Familiarize yourself with the safety information in the following sections before troubleshooting the server.
system components.
IMPORTANT: This guide provides information for multiple servers. Some information may not
apply to the server you are troubleshooting. Refer to the server documentation for information on
procedures, hardware options, software tools, and operating systems supported by the server.
Important safety information
Before servicing this product, read the Important Safety Information document provided with the server.
Symbols on equipment
The following symbols may be placed on equipment to indicate the presence of potentially hazardous
conditions.
This symbol indicates the presence of hazardous energy circuits or electric shock
hazards. Refer all servicing to qualified personnel.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury from electric shock hazards, do not open this
enclosure. Refer all maintenance, upgrades, and servicing to qualified personnel.
Getting started 13

This symbol indicates the presence of electric shock hazards. The area contains no user
or field serviceable parts. Do not open for any reason.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury from electric shock hazards, do not open this
enclosure.
This symbol on an RJ-45 receptacle indicates a network interface connection.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electric shock, fire, or damage to the equipment, do
not plug telephone or telecommunications connectors into this receptacle.
This symbol indicates the presence of a hot surface or hot component. If this surface is
contacted, the potential for injury exists.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury from a hot component, allow the surface to
cool before touching.
This symbol indicates that the component exceeds the recommended weight for one
individual to handle safely.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury or damage to the equipment,
observe local occupational health and safety requirements and guidelines for manual
material handling.
weight in kg
weight in lb
These symbols, on power supplies or systems, indicate that the equipment is supplied
by multiple sources of power.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury from electric shock, remove all power cords
to completely disconnect power from the system.
Warnings and cautions
WARNING: Only authorized technicians trained by HP should attempt to repair this equipment.
All troubleshooting and repair procedures are detailed to allow only subassembly/module-level
repair. Because of the complexity of the individual boards and subassemblies, no one should
attempt to make repairs at the component level or to make modifications to any printed wiring
board. Improper repairs can create a safety hazard.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury or damage to the equipment, be sure that:
• The leveling feet are extended to the floor.
• The full weight of the rack rests on the leveling feet.
• The stabilizing feet are attached to the rack if it is a single-rack installation.
• The racks are coupled together in multiple-rack installations.
• Only one component is extended at a time. A rack may become unstable if more than one
component is extended for any reason.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to the equipment:
• Do not disable the power cord grounding plug. The grounding plug is an important safety
feature.
• Plug the power cord into a grounded (earthed) electrical outlet that is easily accessible at all
times.
• Unplug the power cord from the power supply to disconnect power to the equipment.
• Do not route the power cord where it can be walked on or pinched by items placed against it.
Pay particular attention to the plug, electrical outlet, and the point where the cord extends from
the server.
Getting started 14

WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury or damage to the equipment:
• Observe local occupation health and safety requirements and guidelines for manual
weight in kg
weight in lb
• Obtain adequate assistance to lift and stabilize the chassis during installation or
• The server is unstable when not fastened to the rails.
• When mounting the server in a rack, remove the power supplies and any other
CAUTION: To properly ventilate the system, you must provide at least 7.6 cm (3.0 in) of
clearance at the front and back of the server.
CAUTION: The server is designed to be electrically grounded (earthed). To ensure proper
operation, plug the AC power cord into a properly grounded AC outlet only.
Electrostatic discharge
Preventing electrostatic discharge
handling.
removal.
removable module to reduce the overall weight of the product.
To prevent damaging the system, be aware of the precautions you need to follow when setting up the system
or handling parts. A discharge of static electricity from a finger or other conductor may damage system
boards or other static-sensitive devices. This type of damage may reduce the life expectancy of the device.
To prevent electrostatic damage:
• Avoid hand contact by transporting and storing products in static-safe containers.
• Keep electrostatic-sensitive parts in their containers until they arrive at static-free workstations.
• Place parts on a grounded surface before removing them from their containers.
• Avoid touching pins, leads, or circuitry.
• Always be properly grounded when touching a static-sensitive component or assembly.
Grounding methods to prevent electrostatic discharge
Several methods are used for grounding. Use one or more of the following methods when handling or
installing electrostatic-sensitive parts:
• Use a wrist strap connected by a ground cord to a grounded workstation or computer chassis. Wrist
straps are flexible straps with a minimum of 1 megohm ±10 percent resistance in the ground cords. To
provide proper ground, wear the strap snug against the skin.
• Use heel straps, toe straps, or boot straps at standing workstations. Wear the straps on both feet when
standing on conductive floors or dissipating floor mats.
• Use conductive field service tools.
• Use a portable field service kit with a folding static-dissipating work mat.
If you do not have any of the suggested equipment for proper grounding, have an authorized reseller install
the part.
For more information on static electricity or assistance with product installation, contact an authorized
reseller.
Getting started 15

Symptom information
Before troubleshooting a server problem, collect the following information:
• What events preceded the failure? After which steps does the problem occur?
• What has been changed since the time the server was working?
• Did you recently add or remove hardware or software? If so, did you remember to change the
appropriate settings in the server setup utility, if necessary?
• How long has the server exhibited problem symptoms?
• If the problem occurs randomly, what is the duration or frequency?
To answer these questions, the following information may be useful:
• Run HP Insight Diagnostics (on page 76) and use the survey page to view the current configuration or
to compare it to previous configurations.
• Refer to your hardware and software records for information.
• Refer to server LEDs and their statuses.
Prepare the server for diagnosis
1. Be sure the server is in the proper operating environment with adequate power, air conditioning, and
humidity control. For required environmental conditions, see the server documentation (on page 87).
2. Record any error messages displayed by the system.
3. Remove all diskettes, CD-ROMs, DVD-ROMs, and USB drive keys.
4. Power down the server and peripheral devices if you will be diagnosing the server offline. If possible,
always perform an orderly shutdown:
a. Exit any applications.
b. Exit the operating system.
c. Power down the server.
5. Disconnect any peripheral devices not required for testing (any devices not necessary to power up the
server). Do not disconnect the printer if you want to use it to print error messages.
6. Collect all tools and utilities, such as a Torx screwdriver, loopback adapters, ESD wrist strap, and
software utilities, necessary to troubleshoot the problem.
o You must have the appropriate Health Drivers and Management Agents installed on the server.
To verify the server configuration, connect to the System Management homepage and select Version
Control Agent. The VCA gives you a list of names and versions of all installed HP drivers,
Management Agents, and utilities, and whether they are up-to-date.
o HP recommends you have access to the server documentation (on page 87) for server-specific
information.
o HP recommends you have access to the SmartStart CD for value-added software and drivers
required during the troubleshooting process. Download the current version of SmartStart from the
HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart).
Getting started 16

Performing processor procedures in the troubleshooting process
Because this document supports multiple generations of HP ProLiant server models, it also covers processes
that include troubleshooting of various models and types of processors.
Before performing any troubleshooting steps that involve processors, review the following guidelines:
• Be sure that only authorized personnel perform the troubleshooting steps that involve installation,
removal, or replacement of a processor.
• Always locate the documentation for your processor model before performing any steps that require
installing, removing, or replacing a processor. If you cannot locate the hard copy of the instructions,
locate your server user guide or maintenance and service guide on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/support/manuals).
• Some processor models require the use of a processor installation tool, and specific steps are
documented to ensure that you do not damage the processor or processor socket on the system board.
For server models that have pins inside the processor socket, remember that THE PINS ON THE SYSTEM
BOARD ARE VERY FRAGILE AND EASILY DAMAGED. If you damage the socket, you must replace the
system board.
• Depending on the server model, the contacts may be on the processor or they may be inside the
processor socket. Never touch the contacts. THE PINS ON THE SYSTEM BOARD ARE VERY FRAGILE AND
EASILY DAMAGED. If the contacts inside the processor socket are damaged, you must replace the
system board.
• Always complete all other troubleshooting procedures before removing or replacing a processor.
Breaking the server down to the minimum hardware configuration
During the troubleshooting process, you may be asked to break the server down to the minimum hardware
configuration. A minimum configuration consists of only the components needed to boot the server and
successfully pass POST.
When requested to break the server down to the minimum configuration, uninstall the following components,
if installed:
• All additional DIMMs
Leave only the minimum required to boot the server—either one DIMM or a pair of DIMMs. For more
information, see the memory guidelines in the server user guide.
• All additional cooling fans, if applicable
For the minimum fan configuration, see the server user guide.
• All additional power supplies, if applicable (leave one installed)
• All hard drives
• All optical drives (DVD-ROM, CD-ROM, and so forth)
• All optional mezzanine cards
• All expansion boards
Before removing the components, be sure to determine the minimum configuration for each component and
follow all guidelines in the server user guide.
Getting started 17
Always use the recommended minimum configuration above before removing any processors. If you are
unable to isolate the issue with the configuration above, you will then remove all but one of the additional
processors.
CAUTION: Before removing or replacing any processors, be sure to follow the guidelines
provided in "Performing processor procedures in the troubleshooting process (on page 17)."
Failure to follow the recommended guidelines can cause damage to the system board, requiring
replacement of the system board.
Getting started 18

Common problem resolution
Loose connections
Action:
• Be sure all power cords are securely connected.
• Be sure all cables are properly aligned and securely connected for all external and internal
components.
• Remove and check all data and power cables for damage. Be sure no cables have bent pins or
damaged connectors.
• If a fixed cable tray is available for the server, be sure the cords and cables connected to the server are
routed correctly through the tray.
• Be sure each device is properly seated. Avoid bending or flexing circuit boards when reseating
components.
• If a device has latches, be sure they are completely closed and locked.
• Check any interlock or interconnect LEDs that may indicate a component is not connected properly.
• If problems continue to occur, remove and reinstall each device, checking the connectors and sockets
for bent pins or other damage.
Service notifications
To view the latest service notifications, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport). Select
the appropriate server model, and then click the Troubleshoot a Problem link on the product page.
Firmware updates
Download firmware updates from the following locations:
• The HP Smart Components available on:
o The HP ProLiant Firmware Maintenance CD or DVD
o The HP Smart Update Firmware DVD
o The HP website (http://www.hp.com/support)
• The most recent version of a particular server or option firmware from the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/support)
• Components for option firmware updates available from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support)
HP offers a subscription service that can provide notification of firmware updates. For more information, see
"Subscriber's Choice (on page 80)."
For more information on updating firmware, see "Firmware maintenance (on page 81)."
Common problem resolution 19

DIMM handling guidelines
CAUTION: Failure to properly handle DIMMs can cause damage to DIMM components and the
When handling a DIMM, observe the following guidelines:
• Avoid electrostatic discharge (on page 15).
• Always hold DIMMs by the side edges only.
• Avoid touching the connectors on the bottom of the DIMM.
• Never wrap your fingers around a DIMM.
• Avoid touching the components on the sides of the DIMM.
• Never bend or flex the DIMM.
When installing a DIMM, observe the following guidelines:
• Before seating the DIMM, align the DIMM with the slot.
• To align and seat the DIMM, use two fingers to hold the DIMM along the side edges.
• To seat the DIMM, use two fingers to apply gentle pressure along the top of the DIMM.
For more information, see the HP website
(http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bizsupport/TechSupport/Document.jsp?lang=en&cc=us&objectID=c008
68283&jumpid=reg_R1002_USEN).
system board connector.
Hard drive guidelines
SAS and SATA hard drive guidelines
When adding hard drives to the server, observe the following general guidelines:
• The system automatically sets all drive numbers.
• If only one hard drive is used, install it in the bay with the lowest drive number.
• Drives must be the same capacity to provide the greatest storage space efficiency when drives are
grouped together into the same drive array.
• Drives in the same logical volume must be of the same type:
o ACU does not support mixing SAS and SATA drives in the same logical volume.
o ACU does not support mixing traditional drives and solid state drives (SSD) in the same logical
SCSI hard drive guidelines
• Each SCSI drive must have a unique ID.
• The system automatically sets all SCSI IDs.
• If only one SCSI hard drive is used, install it in the bay with the lowest number.
volume.
Common problem resolution 20
• Drives must be the same capacity to provide the greatest storage space efficiency when drives are
Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may terminate the current
•
•
•
•
•
•
grouped together into the same drive array.
Hard drive LED combinations
Hot-plug SCSI hard drive LED combinations
Activity
LED (1)
On, off, or
flashing
On, off, or
flashing
On or
flashing
On
Flashing
Off
Off
Online
LED (2)
On or off Flashing A predictive failure alert has been received for this drive.
On Off The drive is online and is configured as part of an array.
Flashing Off
Off Off Do not remove the drive.
Flashing Flashing Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may cause data loss in
Off On The drive has been placed offline due to hard disk drive failure or
Off Off One or more of the following conditions may exist:
Fault LED
(3)
Interpretation
Replace the drive as soon as possible.
If the array is configured for fault tolerance and all other drives in the
array are online, and a predictive failure alert is received or a drive
capacity upgrade is in progress, you may replace the drive online.
operation and cause data loss.
The drive is rebuilding or undergoing capacity expansion.
The drive is being accessed, but (1) it is not configured as part of an
array; (2) it is a replacement drive and rebuild has not yet started; or
(3) it is spinning up during the POST sequence.
non-fault-tolerant configurations.
One or more of the following conditions may exist:
The drive is part of an array being selected by an array
configuration utility
Drive Identification has been selected in HP SIM
The drive firmware is being updated
subsystem communication failure.
You may need to replace the drive.
The drive is not configured as part of an array
The drive is configured as part of an array, but it is a replacement
drive that is not being accessed or being rebuilt yet
The drive is configured as an online spare
If the drive is connected to an array controller, you may replace the
drive online.
SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations
NOTE: Predictive failure alerts can occur only when the server is connected to a Smart Array
controller.
Common problem resolution 21
The drive has failed, or a predictive failure alert has been received
On
Flashing irregularly
A predictive failure alert has been received for this drive. Replace
Online/activity
LED (green)
On, off, or flashing
On, off, or flashing
On
Flashing regularly
(1 Hz)
Flashing regularly
(1 Hz)
Flashing irregularly
Off
Off
Off
Fault/UID LED
(amber/blue)
Alternating amber
and blue
Steadily blue The drive is operating normally, and it has been selected by a
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off The drive is online, but it is not active currently.
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may terminate the
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off The drive is active, and it is operating normally.
Steadily amber A critical fault condition has been identified for this drive, and the
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off The drive is offline, a spare, or not configured as part of an array.
Interpretation
for this drive; it also has been selected by a management
application.
management application.
A predictive failure alert has been received for this drive.
Replace the drive as soon as possible.
Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may terminate the
current operation and cause data loss.
The drive is part of an array that is undergoing capacity expansion
or stripe migration, but a predictive failure alert has been received
for this drive. To minimize the risk of data loss, do not replace the
drive until the expansion or migration is complete.
current operation and cause data loss.
The drive is rebuilding, erasing, or it is part of an array that is
undergoing capacity expansion or stripe migration.
The drive is active, but a predictive failure alert has been received
for this drive. Replace the drive as soon as possible.
controller has placed it offline. Replace the drive as soon as
possible.
the drive as soon as possible.
Server updates with an HP Trusted Platform Module
and BitLocker™ enabled
When a TPM is installed and enabled in RBSU, and when the Microsoft® Windows® BitLocker™ Drive
Encryption feature is enabled, always disable BitLocker™ before performing any of the following
procedures:
• Restarting the computer for maintenance without a PIN or startup key
• Updating firmware (on page 83)
• Upgrading critical early boot components
• Upgrading the system board to replace or remove the TPM
• Disabling or clearing the TPM
• Moving a BitLocker™-protected drive to another server
• Adding an optional PCI device, such as a storage controller or network adapter
Common problem resolution 22

Diagnostic flowcharts
Troubleshooting flowcharts
To effectively troubleshoot a problem, HP recommends that you start with the first flowchart in this section,
"Start diagnosis flowchart (on page 25)," and follow the appropriate diagnostic path. If the other flowcharts
do not provide a troubleshooting solution, follow the diagnostic steps in "General diagnosis flowchart (on
page 25)." The General diagnosis flowchart is a generic troubleshooting process to be used when the
problem is not server-specific or is not easily categorized into the other flowcharts.
The available flowcharts include:
• Start diagnosis flowchart (on page 25)
• General diagnosis flowchart (on page 25)
• Power-on problems
o Server power-on problems flowchart (on page 27)
o p-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart (on page 29)
o c-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart (on page 29)
• POST problems flowchart (on page 31)
o Server and p-Class server blade POST problems flowchart (on page 32)
o c-Class server blade POST problems flowchart (on page 33)
• Operating system boot problems flowchart (on page 33)
• Server fault indications flowchart (on page 35)
o Server and p-Class server blade fault indications flowchart (on page 35)
o c-Class server blade fault indications flowchart (on page 37)
Troubleshooting flowchart reference websites
Each flowchart contains references to external websites. The following websites correspond to the numbered
websites in each flowchart:
1. HP Technical Support (http://www.hp.com/support)
Select your country and then follow the instructions to locate software, firmware, and drivers.
2. HP ProLiant maintenance and service guides:
o Business Support Center (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport)
Select Manuals. Under Servers, select ProLiant and tc series servers. Select the product, and then
locate the link for the maintenance and service guide.
o HP BladeSystem p-Class Support and Documents
(http://www.hp.com/products/servers/proliant-bl/p-class/info)
Under Product support, select the product. Select Manuals (guides, supplements, addendums, etc).
Under Service and maintenance information, locate the link for the maintenance and service guide.
Diagnostic flowcharts 23

o
HP BladeSystem c-Class Technical Documentation
(http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/documentation)
Select Support, Drivers and Manuals, and then select the product. Select Manuals, and then locate
the link for the maintenance and service guide.
3. HP BladeSystem p-Class Support and Documents
(http://www.hp.com/products/servers/proliant-bl/p-class/info)
To locate the HP BladeSystem p-Class System Maintenance and Service Guide, select the product.
Select Manuals (guides, supplements, addendums, etc). Under Service and maintenance information,
locate the link for the document.
4. HP BladeSystem Power Sizer (http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/powercalculator)
Use the Power Sizer to plan your power infrastructure and meet the needs of an HP BladeSystem
solution.
5. Remote management (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out)
To locate the Integrated Lights-Out User Guide, select the product, and then select Support &
Documents. Select Manuals and locate the link to the document.
6. SmartStart Support and Documents (http://www.hp.com/support/smartstart/documentation)
In the User guides section, locate the link for the HP ROM-Based Setup Utility User Guide.
7. System Management homepage (https://localhost:2381)
Access consolidated system management information.
Diagnostic flowcharts 24
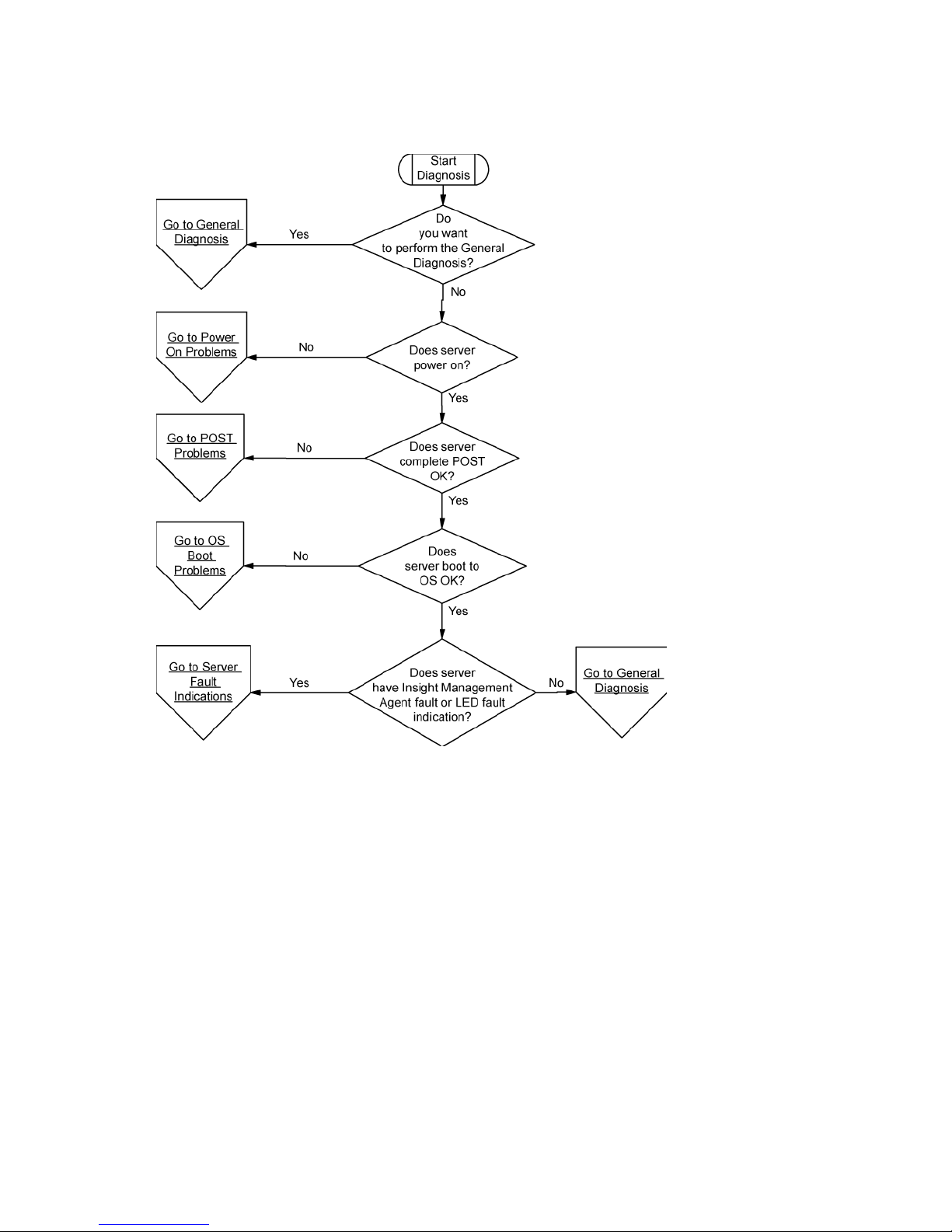
Start diagnosis flowchart
Use the following flowchart to start the diagnostic process.
General diagnosis flowchart
Diagnostic flowcharts 25

The General diagnosis flowchart provides a generic approach to troubleshooting. If you are unsure of the
problem, or if the other flowcharts do not fix the problem, use the following flowchart.
Diagnostic flowcharts 26

Power-on problems flowchart
Server power-on problems flowchart
Some servers have an internal health LED and an external health LED, while other servers have a single
system health LED. The system health LED provides the same functionality as the two separate internal and
external health LEDs. Depending on the model, the internal health LED and external health LED may either
appear solid or they may flash. Both conditions represent the same symptom.
For the location of server LEDs and information on their statuses, see the server documentation on the HP
website (http://www.hp.com/support).
Symptoms:
• The server does not power on.
• The system power LED is off or amber.
• The external health LED is red, flashing red, amber, or flashing amber.
• The internal health LED is red, flashing red, amber, or flashing amber.
• The system health LED is red, flashing red, amber, or flashing amber.
Possible causes:
• Improperly seated or faulty power supply
• Loose or faulty power cord
• Power source problem
• Improperly seated component or interlock problem
Diagnostic flowcharts 27
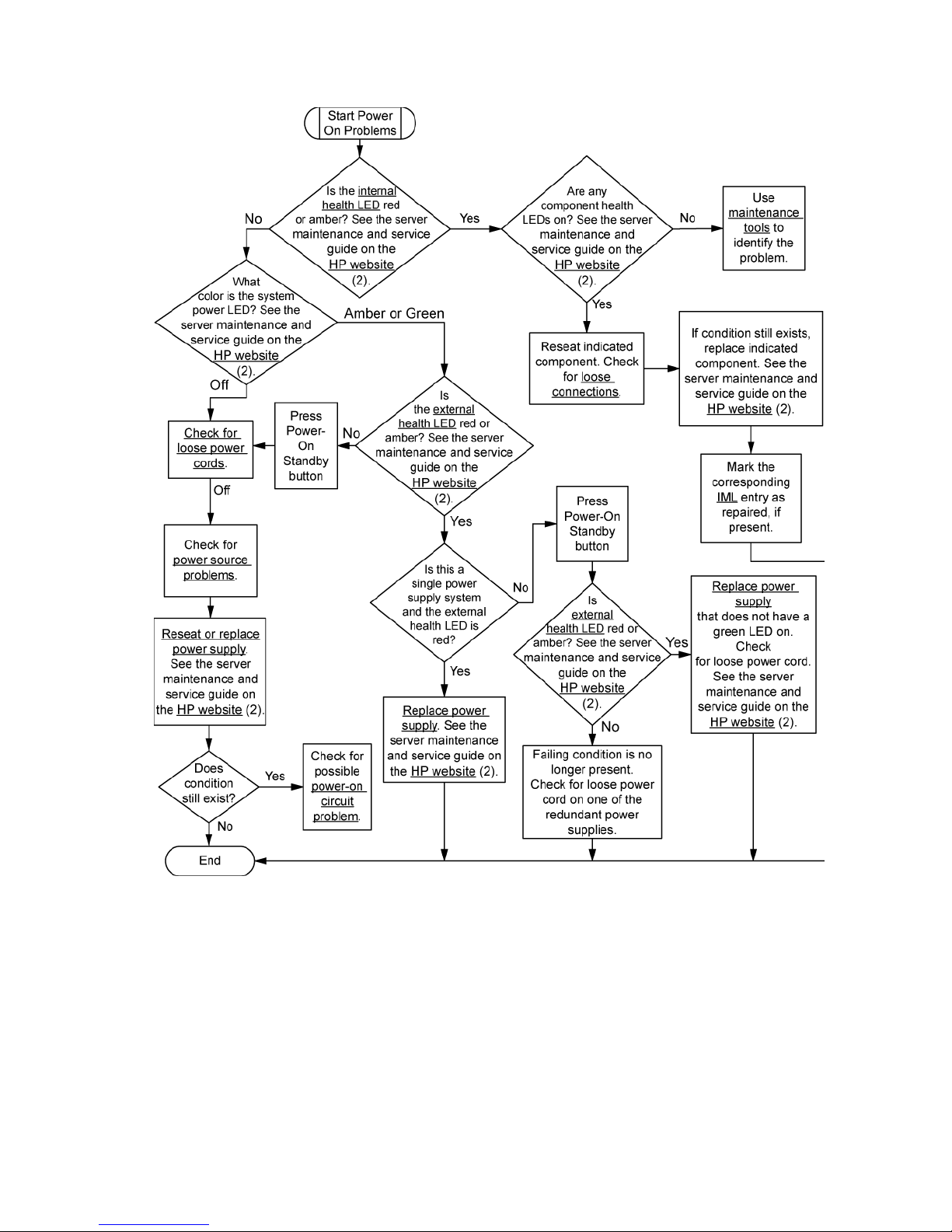
Diagnostic flowcharts 28
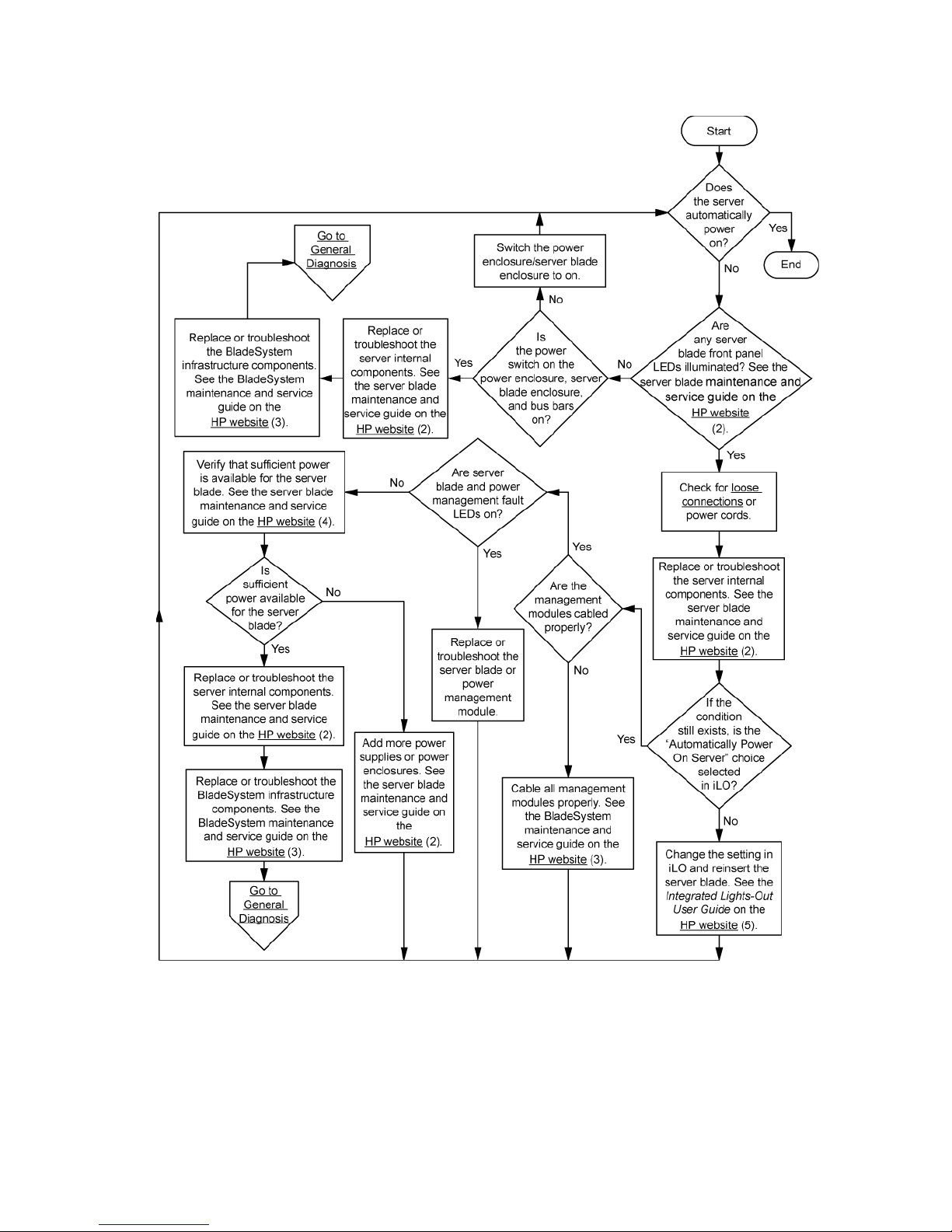
p-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart
c-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart
For the location of server LEDs and information on their statuses, see the server documentation on the HP
website (http://www.hp.com/support).
Diagnostic flowcharts 29
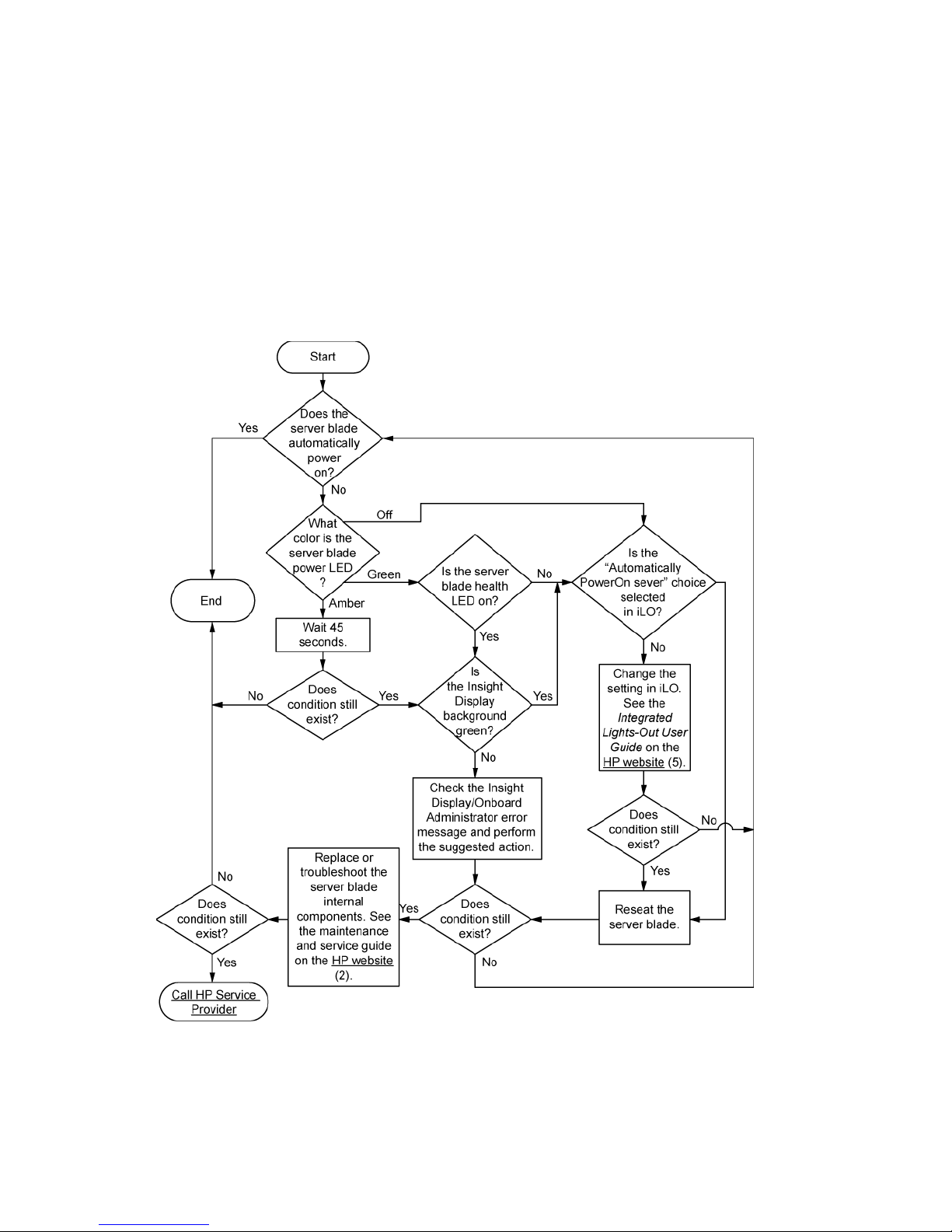
Symptoms:
• The server does not power on.
• The system power LED is off or amber.
• The health LED is red or amber.
Possible causes:
• Improperly seated or faulty power supply
• Loose or faulty power cord
• Power source problem
• Improperly seated component or interlock problem
Diagnostic flowcharts 30
 Loading...
Loading...