Page 1
Table of contents
PCI / PCI EXPRESS Error Recovery White Paper
Executive Summary ................................................................................................................................2
Problem Statement................................................................................................................................. 2
Historical Evolution of PCI/PCI-Express Error Recovery (ER).........................................................................2
Why PCI/PCI-Express Error Recovery .......................................................................................................2
Types of Error Recovery..........................................................................................................................5
How PCI / PCI-Express Error Recovery Works ...........................................................................................6
Support of PCI/PCI-Express Error Handling and Error Recovery on HP-UX.....................................................8
Summary ..............................................................................................................................................8
References ............................................................................................................................................8
Glossary...............................................................................................................................................8
For more information
.............................................................................................................................................................. 10
Page 2

2
Executive Summary
In the context of software applications, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability (RAS) mean failures in
the underlying processes and hardware components must not cause any interruptions in the overall system
operation. Service transactions are adversely impacted during system failure and performance is affected
because of the service down time in the failed system. Recovering from the failure early,
managing the remaining working components of the system, or both, with minimal impact to the
business services, is the key for an optimized system that meets the RAS criteria.
In computer systems, PCITMfailures constitute a significant percentage of errors. The PCI Error
Recovery (PCI ER) feature enables the detection of PCI bus parity errors, isolation of the failed I/O path,
and recovery of cards from errors. Enabling the PCI ER feature avoids system crash, decreases system
downtime, and supports single system high availability.
On HP-UX 11i v2 OS legacy systems, user intervention is required to attempt recovery from PCI errors. The
olrad (1 M) command and the Attention Button can be used to recover and restore the slot, card, and
driver to a usable state, without taking the system down. Whereas, HP-UX 11i v3 has the ability to
automatically recover from PCI errors and restore the slot/driver without user intervention.
Problem Statement
Without PCI/PCI EXPRESS®(PCIe®) error recovery, I/O paths operate in Hardfail mode. While
operating in this mode, a PCI I/O error/a rope error / PCIe errors, causes an MCA on a PIO read and
brings the system down. Using the PCI ER feature, PCI I/O paths can be set to SoftFail mode if the platform
and all the adapter drivers support this feature.
Historical Evolution of PCI/PCI-Express Error Recovery (ER)
On systems running HP-UX 11i v1, the PCI bus errors are handled and the cards are recovered
manually. This feature was shipped as a site specific patch.
On systems running HP-UX 11i v2, the PCI bus errors are handled and the cards are recovered
manually. The product was shipped as an optional product bundle (PCIErrorHandling) on the
SupportPack media starting with AR0806 release.
On systems running HP-UX 11i v3, the PCI bus errors are handled and the cards are recovered
automatically. This feature is part of the Base Operating Environment.
Why PCI/PCI-Express Error Recovery
Interruptions in online transaction processing system and enterprise resource planning service caused from
a failed application or system or hardware component, can be costly and disruptive. The impact of service
downtime continues to grow as companies move toward a real-time business model. Moreover, as
companies become more connected and response times shorten, the cost of service downtime continues to
increase. For these reasons, businesses invest large amounts of money in maintaining the RAS of
servers in the IT infrastructure. The PCI ER feature can enable a drastic reduction in downtime of the
system caused by PCI errors.
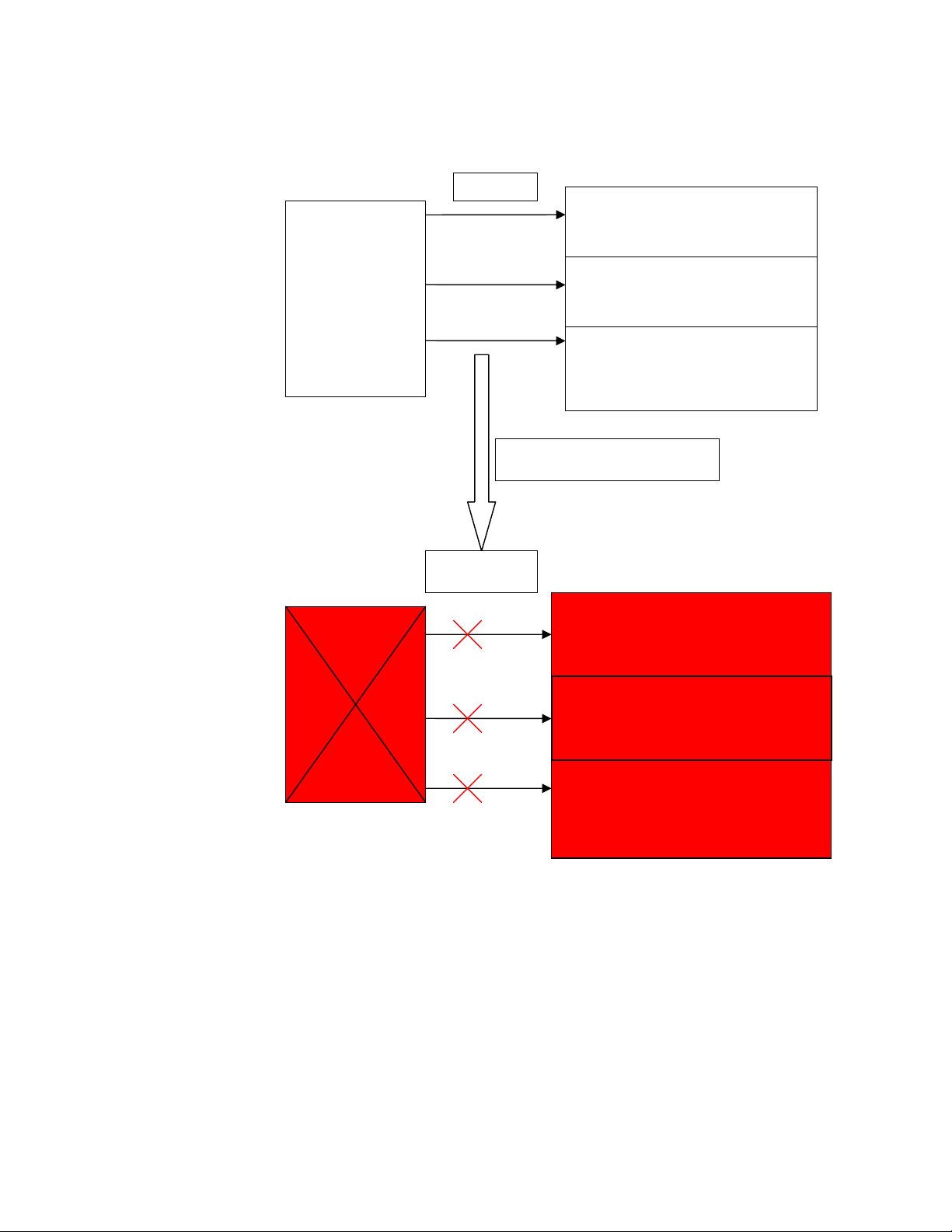
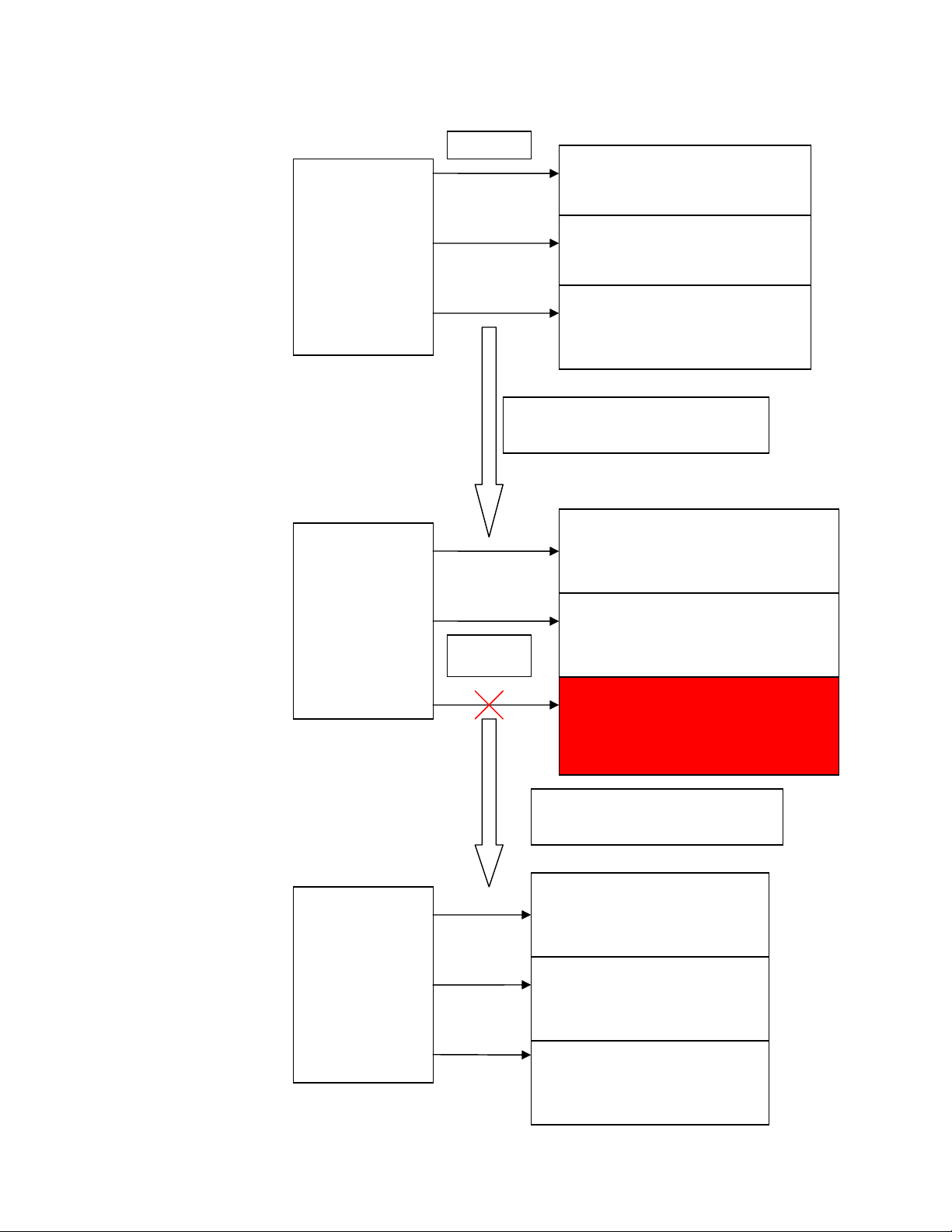
Figure 1 and Figure 2 compares the system behavior, when a PCI error occurs, with and without error
recovery feature.
Page 3
3
Figure 1: Without PCI Error
PCI b
us
disconnected
Recovery
HP-UX
(Up and
Running)
Server
I/O Card 1
Status: Available
I/O Card 2
Status: Available
I/O Card 3
Status: Available and has
encountered PCI error.
Causes an HPMC/MCA
HP-UX
Server
(Down)
PCI bus is
I/O Card 1
Status: Not available
I/O Card 2
Status: Not available
I/O Card 3
Status: Not available
Page 4
4
Figure 2: With PCI Error Recovery
PCI b
us
isolated
I/O Card 1
Status: Available
HP-UX
Server
(Up and
Running)
HP-UX
Server
(Up and
Running)
I/O Card 2
Status: Available
I/O Card 3
Status: Available and has
encountered PCI error.
Recovering I/O Card 3 using PCI Error
Recovery
I/O Card 1
Status: Available
I/O Card 2
Status: Available
PCI bus
HP-UX
Server
(Up and
Running)
I/O Card 3
Status: Driver suspended.
Card not available due to PCI error.
After Successful Card Recovery
I/O Card 1
Status: Available
I/O Card 2
Status: Available
I/O Card 3
Status: Driver resumed.
Card available
Page 5

5
PCI ER decreases the frequency of crashes, service calls, & repair rates for PCI errors by a factor of 20 to
Types of
OS Support
On HP
-
UX 11i v1 and HP
-
UX 11i v2
OS legacy platforms
,
users
25 times. Without PCI error recovery, the entry-level system I/O errors account for more than 20% of all
errors in the system.
Tables below list the time taken by the PCI/PCIe cards to recover from PCI errors with the error recovery
feature.
Table 1: PCI / PCIe Card Recovery with PCI Error Recovery Feature on Legacy Platform
Event Time Taken
PCI / PCIx slot card
recovery
PCIe card recovery ~ 6 secs
Table 2: PCIe Card Recovery with PCI Error Recovery Feature on HP Superdome 2
Platform
Event Time Taken
PCIe card recovery ~ 5 secs
Refer to concurrent dump whitepaper (link provided below) for details on time taken for the system to
recover from MCA due to PCI I/O errors, without error recovery functionality.
http://www.hp.com/go/hpux-core-docs under HP-UX 11i v3 category.
In the range:
10 secs – 2.5 mins
Types of Error Recovery
The PCI/PCIe cards can be recovered from the errors either manually or automatically.
Manual recovery, also known as Error Handling, is supported on HP-UX 11i v2 OS on legacy
platforms only. In this type of error recovery, the PCI / PCIe cards are isolated due to errors and must be
manually recovered. Users can use olrad (1 M) command or Attention Button to recover the cards
manually.
Automatic recovery, also known as Error Recovery, is supported on HP-UX 11i v3 OS. In this type of error
recovery, the PCI / PCIe cards that are isolated because of errors are automatically recovered by the
core PSM (Platform Support Module).
Table 3 provides the error recovery OS support details.
Table 3: Error Recovery OS Support Details
Error
Recovery
Manual error
recovery
are required to manually recover* cards from PCI errors.
Non hot-pluggable slots are not supported on HP-UX 11i v1
and HP-UX 11i v2 systems.
Page 6

6
Automatic error
recovery
Note: The PCI Error recovery feature is neither supported on shared/switched hot-pluggable slots on
HP-UX 11i v1, HP-UX 11i v2, and HP-UX 11i v3 Operating Environments, nor on Core IO on HP
Superdome 2 platform.
*Manual recovery may also fail if there is persistent error condition.
On an HP-UX 11i v3 system, PCI errors are recovered
automatically.
If automatic recovery fails, users can attempt to manually
recover* cards on hot-pluggable slots but cannot manually
recover cards on non hot-pluggable slots.
Page 7
7
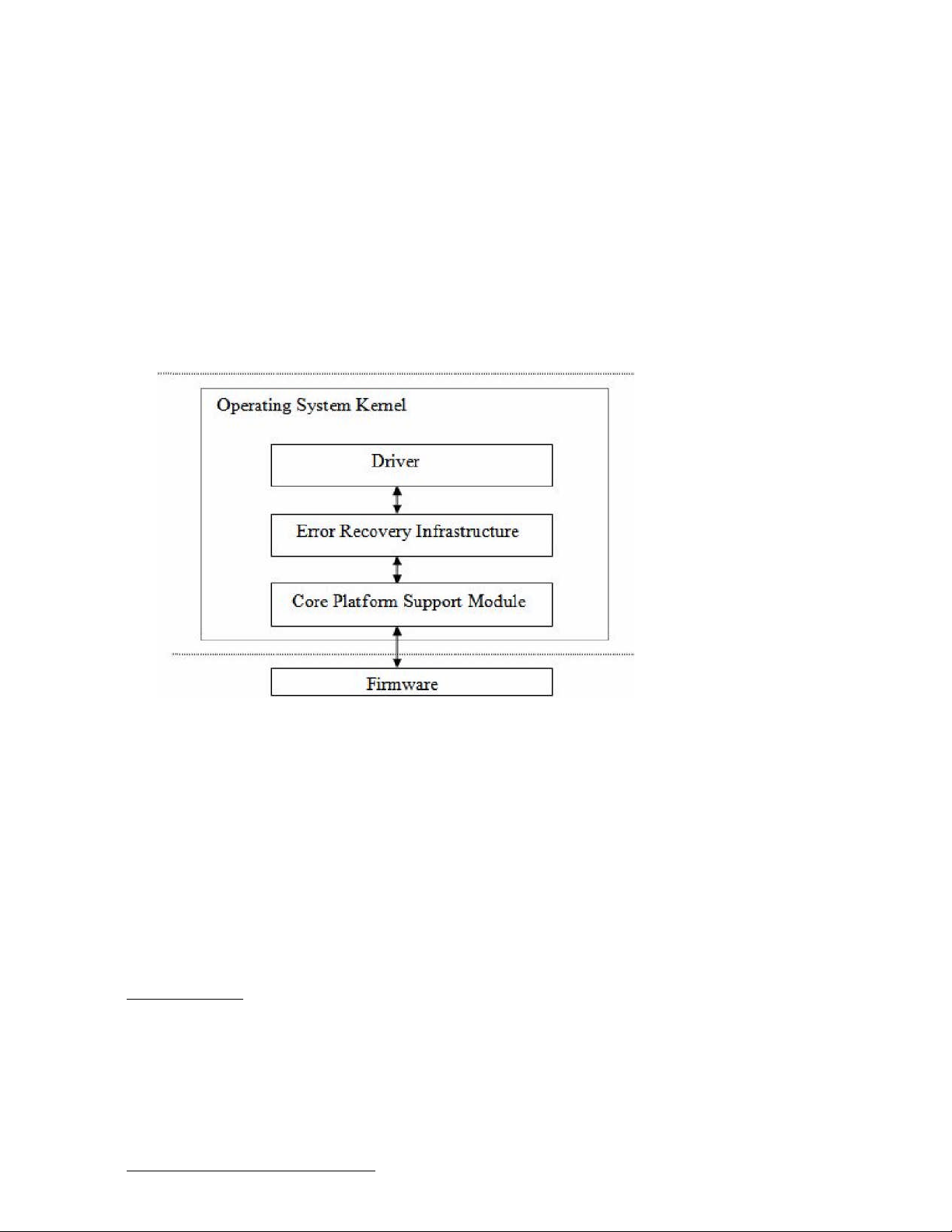
How PCI / PCI-Express Error Recovery Works
When an I/O driver detects PCI bus parity errors, it reports the errors to Error Recovery Infrastructure
and then to the core platform support module.
Core PSM implements error recovery functionality using interfaces that are independent of the
platform. This module verifies if the error is a device error or a bus error. If the error is a device error
then the PSM ignores the error. Otherwise, the PSM module handles the I/O error and notifies the
error recovery infrastructure about error handling. While handling the error, the core PSM invokes
firmware interface (like Health checker daemon as shown in the figure below) which logs and clears
the error.
Figure 3 depicts the PCI I/O error recovery control flow.
Figure 3: PCI Error Recovery Flow Diagram
The PCI I/O errors are handled as follows by the system that supports error recovery functionality:
Determine whether the platform and the drivers are error recovery capable. If that is the case,
set the I/O paths to SoftFail mode.
When a driver detects an error, it reports the error to error recovery Infrastructure. The report
is sent to the core PSM.
To handle and recover from PCI error, the core PSM completes the following three phases:
- Diagnose Phase
- Synchronization (suspension) Phase and
- Release (resumption) Phase
Diagnose Phase: During this phase, the I/O node information is passed from the driver to the core
PSM. This node forms the initial root of the error path. The primary goal of this state is to gather
additional information and determine the actual root of the error path. On PA-RISC platform system,
during this phase the errors are logged in the firmware in SAL format on legacy platforms and UEFI
format on HP Integrity Superdome platform.
No attempt is made during this state to recover the path from the error, and some hardware may be
inaccessible.
Synchronization (suspension) Phase: During this phase, the core PSM attempts to clear logged errors
Page 8

8
and suspend the I/O modules in the error path. When this phase is completed, it is assumed that
drivers have suspended all activities for the devices in the error path. On HP Superdome 2 platform
system, during this phase the Health Checker Daemon is invoked to log and clear the errors.
Release Phase: During this phase, the suspended I/O path is restored. It involves resuming the driver.
If any I/O cards were left in a suspended state, the card will be replaced via a PCI OLR action.
For more information about PCI OLR, see InterfaceCard OL* SupportGuide, postedat the following
location:
http://www.hp.com/go/hpux-networking-docs under
HP-UX 11i v3 Networking Software category.
The following diagram depicts various phases of core PSM.
Figure 4: PCI Error Recovery Phases
Diagnostics decodes the error logs and saves the error information in /var/opt/resmon/log/event.log
file.
Note: Only the PCI bus parity errors are handled by the error recovery feature. Device errors are not
handled by this feature.
To summarize, when an error occurs on a PCI bus containing an I/O card, events occur in the
following order:
The I/O drivers are suspended
The PCI bus is isolated from further I/O
The error is logged and cleared
The bus is reset
The I/O drivers are resumed
Page 9

9
Support of PCI/PCI-Express Error Handling and Error
Recovery on HP-UX
PCI error handling and error recovery are supported only with some HP-UX version, I/O products and
servers. For more information, see the support matrix available at the following location:
http://www.hp.com/go/hpux-networking-docs under HP-UX 11i v3 I/O Cards category.
There are several kernel tunables that can change the behavior of PCI error recovery operation. For
more information about the kernel tunables, see Tunable Kernel Parameters section in the PCI Error
Recovery Product Note, 4thEdition, March 2010 document, posted at the following location:
http://www.hp.com/go/hpux-networking-docs under HP-UX 11i v3 I/O Cards category.
The above link provides information about PCI Error Recovery functionality, which is supported on HPUX 11i v3 system.
For more information about the type of errors and corresponding events supported by the product on
all platforms, see PCI / PCIe Error Recovery Product Note available at
http://www.hp.com/go/hpux-networking-docs under HP-UX 11i v3 I/O Cards category.
Summary
The basic RAS features designed for HP Integrity and HP 9000 servers, when coupled with the PCI
error handling and recovery mechanisms, enables high-end servers to meet the needs of a
mission-critical environment. This is made possible by preventing customers from experiencing
down-time as a result of system hang or unusable state of a system.
References
For more information about Error Handling functionality supported on HP-UX 11i v2 system, see PCI
Error Handling Product Note 3rd Edition, at the following location:
http://www.hp.com/go/hpux-networking-docs under HP-UX 11i v2 I/O Cards
Glossary
Following is a list of terms used throughout this document:
Name Definition
LBA Local Bus Adapter
EBA Express Bus Adapter
Machine Check Highest Priority interruption on Itanium® based
Abort (MCA) / systems (MCA) and on PA-RISC based systems
HPMC (HPMC).
PIO Programmable IO
PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect
HardFail mode The mode of operation of LBA, during which PCI
errors cause an HPMC/MCA for fatal error
during PIO read.
Page 10

1
RC (Root Complex) An entity that includes a host bridge and one or more root ports.
RP (Root Port) A PCI Express port on a root complex that maps a portion of the tree
structured PCI Express I/O interconnect through an associated virtual PCI
bridge.
SoftFail mode The mode of operation of LBA, during which PCI errors does not cause an
HPMC/MCA for PCI I/O errors during PIO read. The LBA/EBA set in soft fail
mode will be able to detect the Error appropriately, handle them, and then finally
recover from the error.
Platform Support A module that implements routines to support
Module (PSM) some specific features for a functionality.
SPPA Super Parallel Precision Architecture
Ropes The PCI I/O protocol used to interconnect
components in SPPA architecture
Page 11

For more information
www.hp.com/go/hpux11i
© Copyright 2008-2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The
information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties
for HP products and services a re set forth i n the express warranty statem ents
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial
errors or omissions contained herein.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. Microsoft and Windows are
U.S. registe re d trademarks o f Mic rosoft Corporation. UNIX is a registered
trademark of The Open Group.
4AA1-xxxxENW, May 2008-2009
 Loading...
Loading...