Page 1

HP ProLiant Essentials Intelligent Networking
J
Pack Linux Edition
User Guide
Part Number 396352-00B
une 2007 (Second Edition)
Page 2

© Copyright 2005, 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212,
Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S.
Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
Audience assumptions
This document is for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers and storage systems.
HP assumes you are qualified in the servicing of computer equipment and trained in recognizing hazards
in products with hazardous energy levels.
Page 3

Contents
Overview..................................................................................................................................... 4
HP ProLiant Essentials Intelligent Networking Pack -Linux Introduction ...............................................................4
Intelligent Networking Pack licenses............................................................................................................. 4
Linux operating system requirements ..................................................................................................5
Downloading files ........................................................................................................................... 5
Installing the INP rpm packages .................................................................................................................. 5
Installing an INP license ............................................................................................................................. 5
Using Virus Throttle ....................................................................................................................... 7
How Virus Throttle works............................................................................................................................ 7
Starting Virus Throttle................................................................................................................................. 7
Configuring Virus Throttle parameters ..........................................................................................................8
Monitoring Virus Throttle status.................................................................................................................... 8
Stopping Virus Throttle ............................................................................................................................... 9
Restarting Virus Throttle.............................................................................................................................. 9
Log and Event File ................................................................................................................................... 10
Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................................... 11
Potential solutions for INP configuration problems........................................................................................ 11
Installing an Intelligent Networking Pack license ................................................................................ 11
Using Virus Throttle........................................................................................................................ 11
Technical support........................................................................................................................ 13
Before you contact HP.............................................................................................................................. 13
HP contact information............................................................................................................................. 13
Free automated customer support services ..................................................................................................13
Acronyms and abbreviations........................................................................................................ 15
Index......................................................................................................................................... 16
Contents 3
Page 4

Overview
In this section
HP ProLiant Essentials Intelligent Networking Pack -Linux Introduction ............................................................. 4
Intelligent Networking Pack licenses ........................................................................................................... 4
Installing the INP rpm packages................................................................................................................. 5
Installing an INP license ............................................................................................................................ 5
HP ProLiant Essentials Intelligent Networking Pack Linux Introduction
The HP ProLiant Essentials Intelligent Networking Pack-Linux Edition is part of the ProLiant Essentials
software family and is integrated with HP Systems Insight Manager (SIM), SmartStart, and HP
Management agents.
The Intelligent Networking Pack (INP) includes Virus Throttle, a network packet-filtering feature that helps
slow down the spread of viruses on your system. Virus Throttle monitors all outbound connection requests
and counts the number of unique connections. It detects abnormal ("virus-like") behavior in the requests,
and slows down excessive connection requests to new hosts until you can determine if they are viral in
nature and take action.
The INP features are included with the networking software (release 8.10 and higher). To enable the INP
features, an INP license must be installed on the system. This user guide describes how to install these
licenses on your system and how to configure the features.
For the latest driver, firmware, and documentation updates, go to HP Networking website
(http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/networking/index.html
Intelligent Networking Pack licenses
Each server requires a separate INP license. When installed on the system, the license is "attached" to the
server and cannot be revoked. The license will stay with that server for the life of the server. The license is
associated with the server's serial number, so a change in the server's name or IP address will not
invalidate the license. One INP license enables all INP features on the server.
Four categories of INP licenses are available. Each license offers full, unlimited functionality.
• Single license pack—Authorizes one licensed seat.
• Flexible Quantity license pack—Authorizes the set number of licensed seats ordered.
).
• Activation Key Agreement license pack—Allows you to authorize additional licensed seats under the
terms of a signed and implemented Activation Key Agreement (AKA) only.
• Demo—Allows you to evaluate the features for a set number of seats and a set number of days
Overview 4
Page 5

Linux operating system requirements
To install and enable Virus Throttle on your server, you need the following:
• Two INP rpm packages (release 8.10 or higher) located on the HP website (http://www.hp.com)
o hp-pel. Contains the HP ProLiant Essentials INP licensing utility (nalicense)
o hp-vt. Contains the HP Virus Throttle for Linux application
• An INP license activation key, located on the back of the HP ProLiant Essentials Intelligent
Networking Pack Kit
Downloading files
1. Go to the HP website (http://www.hp.com).
2. Click Software & Driver Downloads from the left menu bar.
3. Type the product name in the For product box and press Enter. For example, type NC370T.
4. Select an operating system.
5. Click HP ProLiant Networking Software.
6. Click download and save the HP SoftPaq (sp#####.exe) file to a directory on your hard drive. The
SoftPaq file is a self-extracting executable with a file name based on the SoftPaq number.
Installing the INP rpm packages
The INP licensing (hp-pel) package must be installed on your system before the Virus Throttle (vt pel)
package can be installed.
To install the rpm packages:
1. Download the SoftPaq as described above.
2. Navigate to the Linux Virus Throttle directory.
Example:
# cd linux/hp-vt
3. Install the licensing rpm package (hp-pel).
# rpm -Uvh hp-pel-<version>.<operating system>.linux.rpm
4. Install the Virus Throttle rpm package (hp-vt).
# rpm -Uvh hp-vt-<version>.<operating system>.linux.rpm
The INP licensing utility and Virus Throttle packages are now installed. The next step is to install your INP
license.
Installing an INP license
Use the following command to add the license key to your system:
/opt/hp/hp-pel/nalicense -a <license_string> [-l <log-file>]
Overview 5
Page 6
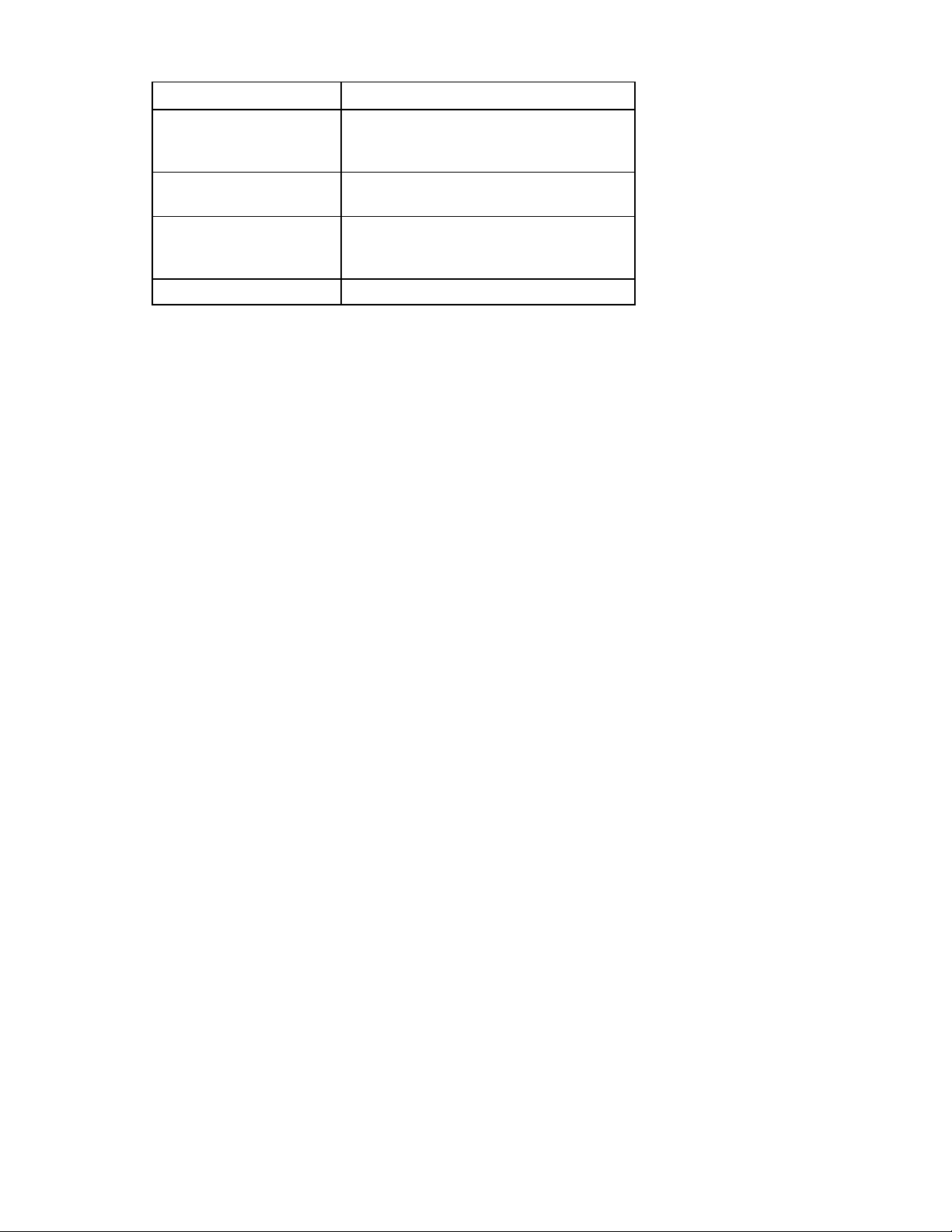
Argument Description
-a <license_string> Valid INP license activation key. The string
must be entered in dash separated form, such
as DE9DF-VHDL9-7SLR8-73LOS-OSM3K
[-l <log-file>] Optional parameter specifying a location to
write successful or error messages.
-d Displays information about an INP license
installed on your system. For example,
/opt/hp/hp-pel/nalicense –d
-h or --help Displays usage information.
For example, the following command adds the license to the system:
nalicense -a DE9DF-VHDL9-7SLR8-73LOS-OSM3K
Upon successful operation writes the following message to STDOUT:
“Mon Sep 15 15:42:14 2003: Adding License “DE9DF-VHDL9-7SLR8-73LOS-OSM3K”.
Success”
HP recommends that you retain the license key for future use. The key is needed for technical support and
future upgrades.
Overview 6
Page 7

Using Virus Throttle
In this section
How Virus Throttle works........................................................................................................................... 7
Starting Virus Throttle................................................................................................................................ 7
Configuring Virus Throttle parameters......................................................................................................... 8
Monitoring Virus Throttle status .................................................................................................................. 8
Stopping Virus Throttle.............................................................................................................................. 9
Restarting Virus Throttle............................................................................................................................. 9
Log and Event File .................................................................................................................................. 10
How Virus Throttle works
Viruses typically spread by connecting to as many different machines as possible. Virus Throttle, a
network packet-filtering feature, monitors all outbound connection requests and helps to stop the spread of
viruses on your system by detecting abnormal ("virus like") behavior in the requests. It slows down
excessive connection requests to new hosts until you can determine if they are viral in nature and take
action.
When you install Virus Throttle on your system, the Virus Throttle iptable_filter and ip_queue modules are
loaded and a QUEUE target is created so all connection requests pass through it. The driver maintains a
delay queue of connection requests and a list of known hosts that have established connections.
The driver examines all outbound connection requests and determines if the request is for a known host. If
known, the request is passed down the protocol stack as a normal request. If the request is unknown, it is
added to the delay queue. Periodically, the delay queue is examined, and the oldest request and all other
connection requests to that same host are removed and passed down the protocol stack.
A high water mark and low water mark are maintained for the delay queue and are used to determine
when "virus-like" behavior is occurring or has stopped.
• When the rate of connection requests exceeds the rate of the driver removing them from the delay
queue, a high water mark in the queue is exceeded, and the driver indicates "virus-like" activity.
• When the rate of connection requests slows so that the number of queue entries falls below a low
water mark, the driver indicates that the "virus-like" activity has stopped.
When "virus-like" activity is detected or has stopped, Virus Throttle logs an event. If HP Management
agents are installed and configured correctly, a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap will
be sent.
Starting Virus Throttle
By default, Virus Throttle is configured to start on system boot-up. To start Virus Throttle immediately after
installation, run the following command:
# /etc/init.d/hp-vt start
Using Virus Throttle 7
Page 8

Virus Throttle requires both the iptable_filter and ip_queue modules. If both modules are not installed on
the system when Virus Throttle is started, an error message is displayed. Currently, only one application
may register for the iptables QUEUE target. If another application has already registered for the QUEUE
target, an error message is displayed.
Configuring Virus Throttle parameters
When you first install Virus Throttle the configuration parameters for the filter driver are set to the defaults.
Changes to the configuration file can be made with any text editor. However, Virus Throttle must be
restarted before any changes can take affect. See Restarting Virus Throttle.
The Virus Throttle configuration file is located at
# /etc/opt/hp/hp-vt/hp-vt.conf
The following default parameters can be edited:
• delay_queue_size=200
Controls the maximum number of delayed connection requests in the delay queue. When the queue
is full, connection requests are dropped. The default is 200 delayed connection requests. The valid
range is 10–1000.
• delay_queue_high_watermark=160
Controls the number of connection requests in the delay queue at which "virus-like" activity is
considered to be occurring. The default is 160 connection requests. The valid range is 8–the value of
delay_queue_size.
• delay_queue_low_watermark=100
Controls the number of connection requests in the delay queue below which "virus-like" activity is
considered to be stopped. The default is 100 connection requests. The valid range is 4–the value of
delay_queue_high_watermark minus 4.
• delay_queue_delay_seconds=1
Controls the rate at which the oldest connection request and all other connection requests to that
same host are passed down the protocol stack. The default is 1 second. The valid range is 1–10
seconds.
• host_working_set_size=5
Controls the number of known hosts to which connections are established without delay. When a
new connection is made, the oldest member of the working set is replaced with the new host. The
default is 5 hosts. The valid range is 1–100.
• shared_memory_key=0x48505654
Used in shmget calls, and should not normally be changed. An example of when this key may need
to be changed is if there is a conflict with another application using the key. If the key is changed,
the hp-vt status will not work until hp-vt has been restarted. The format of the key is four bytes in hex
that start with “0x,” in other words 0x48505654. To show the shared memory segments currently in
use, run ipcs –m. The default value is hex representing ascii “HPVT”.
Monitoring Virus Throttle status
When Virus Throttle is running, use the following command to display the status:
# /etc/init.d/hp-vt status
Using Virus Throttle 8
Page 9

The overall status, statistics, and delay queue information since the Virus Throttle filter driver was
initialized is displayed.
Status information
• Virus-like activity is currently occurring. "Virus-like" activity is currently detected.
• Virus-like activity has not occurred. No "virus-like" activity is currently detected and none has been
detected since the filter driver was initialized.
• Virus-like activity has occurred in the past. No "virus-like" activity is currently detected, but "virus-
like" activity has been detected since the filter driver was initialized.
Statistics
• Connection establishing packets. Number of connection packets seen.
• Packets passed without delay. Number of connection packets that were passed without a delay
because the target was a known host.
• Packets placed on queue. Number of connection packets queued.
• Packets removed from queue. Number of connection packets removed from the delay queue.
• Currently queued packets. Number of connection packets currently on the delay queue.
• Maximum packets on queue. Maximum number of packets on the queue at any point since Virus
Throttle was last started.
• Times virus-like activity seen. Number of times "virus-like" activity was detected.
• Packets dropped due to queue overflow. Number of packets that were dropped due to the delay
queue being full.
Configuration information
• Delay queue size. The maximum number of connection requests in the delay queue.
• Delay queue seconds. The rate at which the oldest connection request and all other connection
requests to that same host are removed and passed down the protocol stack.
• Known host working set size. The number of known hosts.
• Delay queue high water mark. The number of connection requests in the delay queue at which point
"virus-like" activity is indicated.
• Delay queue low water mark. The number of connection requests in the delay queue below which
"virus-like" activity is no longer indicated.
Stopping Virus Throttle
To manually stop Virus Throttle, run the following command.
# /etc/init.d/hp-vt stop
Restarting Virus Throttle
Run the following command to restart Virus Throttle.
# /etc/init.d/hp-vt restart
Using Virus Throttle 9
Page 10

Log and Event File
All messages are logged to /var/opt/hp/hp-vt/hp-vt.log.
To display the log file, run the following command in a separate window:
# more /var/opt/hp/hp-vt/hp-vt.log
Message format
Log messages are displayed in the following format [TAG] SP [DATE] SP TEXT, where:
• [TAG] is one of the following. Lines that do not begin with a tag are a continuation of the previous
line.
o ALERT_VLA_DETECTED. Indicates virus-like activity detected.
o ALERT_VLA_STOPPED. Indicates virus-like activity has stopped.
o DROPPING_CONNECTIONS. Indicates connections are being dropped. After this event is logged,
it will not be logged again until the low water mark is reached.
o ERROR. Indicates errors, such as out of range configuration parameters in hp-vt.conf.
o WARNING. Indicates warnings, such as not being able to load the ip6_queue module.
o INFO. Indicates informative events, such as HP LVT starting and stopping
• SP is one or more spaces
• [DATE] is the current date stamp in the following format:
Thu Feb 10 12:54:35 CST 2005
• TEXT is free-form text that may or may not exist for every message
Message example
The following is an example message.
[INFO] [Thu Feb 10 10:34:15 CST 2005]…hp-vt started
[ALERT_VLA_DETECTED] [Thu Feb 10 12:54:35 CST 2005]
[INFO] [Thu Feb 10 12:54:36 CST 2005]
first text line of second info message
second text line of second info message
[ALERT_VLA_STOPPED] [Thu Feb 10 12:54:58 CST 2005]
Using Virus Throttle 10
Page 11
Troubleshooting
In this section
Potential solutions for INP configuration problems ...................................................................................... 11
Potential solutions for INP configuration problems
This section provides possible solutions to problems that may occur during the configuration of INP
features. The following tables provide steps to take before calling your service representative.
• Installing an Intelligent Networking Pack License—contains troubleshooting information about
installing an Intelligent Networking Pack license.
• Using Virus Throttle—contains troubleshooting information about using Virus Throttle.
Installing an Intelligent Networking Pack license
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
The Intelligent Networking
Pack license is installed but I
cannot uninstall it.
This is correct behavior of
ProLiant Essentials licensing.
After installed on the system,
the license is "attached" to the
server and cannot be revoked.
The license stays with that
server for the life of the server.
The license is attached to the
server serial number, so a
change in server's name or IP
address will not jeopardize
the license.
N/A
Using Virus Throttle
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
The Virus Throttle Status and
Configuration utility Status
tab indicates that "virus-like"
activity is occurring.
A virus has infected your
server.
OR
A non-virus program is
exhibiting "virus-like" behavior
by making more connections
to more unknown hosts than
the Virus Throttle
Configuration parameter
settings.
In a time-sensitive manner, identify the
program or programs responsible for the
"virus-like" behavior.
If the program or programs is/are unknown,
treat as a virus.
If the program or programs is/are known,
then reconfigure the Virus Throttle
Configuration parameters to not trigger on
such normal or expected activity
Troubleshooting 11
Page 12

Problem Possible cause Possible solution
All connection request
packets are not being
processed by Virus Throttle.
A firewall rule may be
intercepting the connection
request and not allowing them
to reach the Virus Throttle
iptable rule (hp_vt iptable
chain).
Start Virus Throttle prior to loading any
firewall rules. Use the following command to
list all rules:
iptables -L
Troubleshooting 12
Page 13

Technical support
In this section
Before you contact HP............................................................................................................................. 13
HP contact information............................................................................................................................ 13
Free automated customer support services................................................................................................. 13
Before you contact HP
Be sure to have the following information available before you call HP:
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial number
• Product model name and number
• Applicable error messages
• Add-on boards or hardware
• Third-party hardware or software
• Operating system type and revision level
HP contact information
For the name of the nearest HP authorized reseller:
• In the United States, see the HP US service locator webpage (http://www.hp.com/service_locator).
• In other locations, see the Contact HP worldwide (in English) webpage
(http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/wwcontact.html
For HP technical support:
• In the United States, for contact options see the Contact HP United States webpage
(http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/contact_us.html
o Call 1-800-HP-INVENT (1-800-474-6836). This service is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a
week. For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
o If you have purchased a Care Pack (service upgrade), call 1-800-633-3600. For more
information about Care Packs, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com
• In other locations, see the Contact HP worldwide (in English) webpage
(http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/wwcontact.html
).
). To contact HP by phone:
).
).
Free automated customer support services
The following sites offer troubleshooting information, compatibility notes, and software upgrades
(including Softpaqs and drivers).
Technical support 13
Page 14

HP Worldwide Web Server
• Navigate to a specific product, and then look for support information from the list of support
resources at the HP support website (http://h18007.www1.hp.com/support/files/server
).
• For downloadable support software for HP Digital Networking Products, Hubs, Integrated Access
Devices, Modems and ISDN, Adapters, Remote Access Concentrators/Servers, Software, and
Switches, go to the HP software and drivers website
(http://h18007.www1.hp.com/support/files/server
).
• All SoftPaqs sorted by SoftPaq number can be found at the HP ftp support website
(ftp://ftp.compaq.com/pub/softpaq/
An ASCII version of a SoftPaq can be found by selecting a SoftPaq at the HP ftp support website.
(ftp://ftp.compaq.com/pub/softpaq/
).
)
• An index of available software sorted by product can be found at the HP software and drivers
website (http://h18007.www1.hp.com/support/files/server
HP FTP Server
Navigate to a specific product, and then look for support information from the list of support resources at
the HP ftp support website (ftp://ftp.compaq.com/pub/softpaq/
).
).
Technical support 14
Page 15

Acronyms and abbreviations
IP
Internet Protocol
LLDP
Link Layer Discovery Protocol
NDIS
network driver interface specification
SIM
Systems Insight Manager
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
Acronyms and abbreviations 15
Page 16

Index
C
configuration 8
I
installing virus throttle 5
L
license key, installing 5
log file 10
P
ProLiant Essentials Intelligent Networking Pack 4
S
support 13
T
troubleshooting 11
V
Virus Throttle, defined 7
Index 16
 Loading...
Loading...