Page 1

Getting Started
Page 2

The only warranties for Hewlett-Packard products and services are set forth in the express
statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or
omissions contained herein.
HP assumes no responsibility for the use or reliability of its software on equipment that is not
furnished by HP.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. No part of this
document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another language without the prior
written consent of HP.
Hewlett-Packard Company
P.O. Box 4010
Cupertino, CA 95015-4010
USA
Copyright © 2000–2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
This product incorporates copyright protection technology that is protected by U.S. patents and
other intellectual property rights. Use of this copyright protection technology must be authorized by
Macrovision, and is intended for home and other limited pay-per-view viewing uses only unless
otherwise authorized by Macrovision. Reverse engineering or disassembly is prohibited.
Microsoft and Windows Vista are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
The Windows logo and Windows Vista are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the United States and/or other countries/regions.
HP supports lawful use of technology and does not endorse or encourage the use of our products
for purposes other than those permitted by copyright law.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Getting Help ............................................................................................1
Finding Onscreen Guides........................................................................................1
Finding Guides on the Web.....................................................................................1
Using the Onscreen Help and Support Center............................................................2
Using the PC Help & Tools Folder.............................................................................2
Using the hardware diagnostic tools ....................................................................2
Using HP Total Care Advisor Software ......................................................................3
Turning On the Computer for the First Time ..............................................5
Turning Off the Computer ........................................................................................6
Using Shut Down...............................................................................................6
Using Lock........................................................................................................7
Using Sleep mode .............................................................................................7
Using Hibernate mode .......................................................................................8
Automatic Sleep, Hibernate, or Away mode .........................................................9
Restarting the Computer ..........................................................................................9
Connecting to the Internet......................................................................................10
Using the Computer with Safety and Comfort...........................................................11
Setting Up User Accounts ......................................................................................11
Protecting the Computer ........................................................................................12
Using passwords .............................................................................................13
Using antivirus software....................................................................................14
Using firewall software.....................................................................................14
Configuring the computer for automatic Microsoft software updates.......................15
Installing critical security updates.......................................................................16
Guidelines for Installing Software and Hardware Devices..........................................16
Transferring Files and Settings from an Old Computer to a New Computer.................. 17
Table of Contents iii
Page 4

Using the Keyboard...............................................................................19
Identifying Keyboard Features................................................................................19
Alphanumeric keys ..........................................................................................19
Function keys ..................................................................................................20
Edit keys.........................................................................................................20
Arrow keys .....................................................................................................21
Numeric keys..................................................................................................21
Keyboard indicators ........................................................................................22
Special keyboard buttons .................................................................................22
Identifying Special Keyboard Buttons ......................................................................23
Customizing the keyboard buttons .....................................................................25
Keyboard Shortcuts...............................................................................................26
Wireless Mouse and Keyboard Troubleshooting.......................................................26
Synchronizing a wireless mouse and keyboard ...................................................26
Using the Mouse ....................................................................................29
Using the Mouse Buttons .......................................................................................30
Scrolling.........................................................................................................30
Autoscrolling...................................................................................................30
Panning..........................................................................................................31
Changing Mouse Settings......................................................................................31
Switching mouse button functions.......................................................................31
Changing mouse pointer speed.........................................................................31
Changing the double-click speed.......................................................................32
Turning on the ClickLock option.........................................................................32
Changing the scroll wheel speed.......................................................................32
Wireless Mouse and Keyboard Troubleshooting.......................................................33
iv Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 5

Configuring Speaker and Sound Options ...............................................35
Adjusting speaker volume.................................................................................36
Selecting a microphone....................................................................................37
Configuring audio output..................................................................................37
Using the Creative Sound Blaster X-Fi or X-Fi Fatality audio card............................38
Configuring the FlexiJack connector ...................................................................39
Sound Blaster X-Fi configuration modes ..............................................................39
Configuring speakers with Realtek HD Audio Manager ........................................40
The Realtek HD Audio Manager control screens ..................................................41
Configuring sound for recording with the Realtek HD Audio Manager....................43
Retasking front panel audio connectors ..............................................................44
Configuring multistreaming audio ...................................................................... 45
When to use multistreaming audio.....................................................................46
Setting up multistreaming audio......................................................................... 46
Configuring audio for Windows Media Center ...................................................47
Selecting recording devices ..............................................................................48
Resolving sound issues .....................................................................................48
Using the Windows Media Center Remote Control ..................................49
Remote Control Buttons Overview...........................................................................50
About the Remote Control......................................................................................52
Troubleshooting the Remote Control........................................................................53
Remote sensor is not receiving a signal from the remote control.............................53
Introducing Your Computer Software .....................................................55
Learning More About Software...............................................................................55
Using the Desktop.................................................................................................55
Removing desktop icons ...................................................................................56
Retrieving desktop icons ...................................................................................56
Removing files permanently...............................................................................56
Using the Windows Start Button Menu ....................................................................56
Using the All Programs menu ............................................................................56
Organizing the All Programs list........................................................................57
Using the Control Panel.........................................................................................57
Resizing Windows................................................................................................58
Working with Digital Images .................................................................................58
About the Internet ................................................................................................. 59
Using a Browser...................................................................................................60
Searching the Internet ......................................................................................60
Restricting Internet content.................................................................................61
Table of Contents v
Page 6

Using the Norton Internet Security Antivirus Software ................................................ 62
Configuring and registering Norton Internet Security software ...............................62
Manually running a scan ..................................................................................62
Setting a Full System Scan time .........................................................................63
Setting up a Custom Scan time..........................................................................63
Sending and Receiving E-Mail................................................................................64
Using Windows Mail ....................................................................................... 64
Using the e-mail program provided by your ISP...................................................64
Software Quick Reference Table.............................................................................65
Managing Files ......................................................................................69
Organizing Files with Folders.................................................................................69
Creating Folders...................................................................................................70
Moving Files ........................................................................................................ 70
Finding Files ........................................................................................................71
Renaming Files.....................................................................................................72
Deleting Files .......................................................................................................72
Retrieving Files from the Recycle Bin .......................................................................72
Copying Files....................................................................................................... 73
Using a Printer .....................................................................................................73
Using CD and DVD Media Drives ............................................................75
Using the CD and DVD Drives................................................................................ 75
Handling CDs and DVDs ..................................................................................76
Inserting and removing CDs and DVDs............................................................... 76
Compatibility Information ......................................................................................78
Disc Features and Compatibility Table ....................................................................79
Optical Drive Quick Reference Table ......................................................................80
Using Blu-ray and HD Disc Drives...........................................................................81
Using the Memory Card Reader .............................................................83
Media Insertion Guide ..........................................................................................84
Understanding the Activity Light .............................................................................87
Formatting a Memory Card ...................................................................................87
Troubleshooting the Memory Card Reader............................................................... 88
Using the HP Personal Media Drive and HP Pocket Media Drive .............89
Connecting the Drive ............................................................................................90
Inserting the Drive into an HP Drive Bay ..................................................................90
Connecting the Drive to a Computer Without a Drive Bay .........................................91
Locating the Drive and Assigning a Drive Letter ........................................................92
Using the Drive ....................................................................................................93
Transferring files to another computer manually...................................................93
Disconnecting the Drive.........................................................................................94
Troubleshooting the HP Media Drive.......................................................................95
vi Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 7

Using Windows Media Center ................................................................97
Setting Up Windows Media Center ........................................................................98
Completing the setup wizard.............................................................................98
Windows Media Center Start Menu......................................................................100
Windows Media Center Start menu items .........................................................100
Windows Media Center Features .........................................................................101
Watch and record live TV............................................................................... 102
The right music for the moment........................................................................103
Playing FM or Internet radio............................................................................103
Sharing your digital memories.........................................................................103
Transforming your living space into a theater ....................................................104
Online media................................................................................................104
Navigating Windows Media Center.....................................................................104
Opening Windows Media Center with a mouse................................................104
Opening Windows Media Center with the Windows Media Center remote control105
Using the Windows Media Center menu bars ...................................................105
Selecting items in Windows Media Center........................................................106
Windows Media Center control menu..............................................................107
Changing Windows Media Center Settings ........................................................... 108
Windows Media Center Settings categories...................................................... 108
Using Windows Media Center power settings...................................................109
Playing CDs, DVDs, or VCDs .................................................................111
Using Music.......................................................................................................111
Using Music with Windows Media Center.............................................................112
Using the music library........................................................................................113
Adding music to the music library ....................................................................113
Adding music files from the hard disk drive....................................................... 113
Adding music files from a CD..........................................................................114
Deleting music files from the music library.........................................................115
Using supported music file types......................................................................115
Playing Music Files in Windows Media Center.......................................................116
Changing the visualization settings .................................................................. 117
Playing an album in Windows Media Center....................................................117
Playing a song in Windows Media Center .......................................................118
Creating a Queue in Windows Media Center........................................................ 118
Finding and Playing an Album in Windows Media Center ......................................119
Using album details .......................................................................................119
Using Search in Windows Media Center...............................................................120
Searching for music tracks and files .................................................................120
Creating a Playlist in Windows Media Center........................................................ 120
Copying Music Files to CD in Windows Media Center............................................ 122
Table of Contents vii
Page 8

Listening to Online Radio Stations......................................................................... 123
Listening to FM Radio Stations.............................................................................. 124
Setting Up the TV Signal...................................................................................... 125
Playing FM Radio Stations ...................................................................................126
Organizing and Using Preset Radio Stations..........................................................128
Using preset radio stations.............................................................................. 129
Using the FM Radio and the TV Signal at the Same Time.........................................129
Playing Music CDs .............................................................................................129
Playing CDs with Windows Media Player..............................................................130
Playing DVDs.....................................................................................................130
Using Windows Media Center to play DVDs.....................................................131
Troubleshooting poor playback when playing DVDs ..........................................131
Using country/region codes............................................................................ 132
Playing DVD Movies in Windows Media Center ....................................................132
Changing the DVD Settings..................................................................................133
Changing the DVD movie language.................................................................133
Changing DVD remote control options .............................................................134
Changing DVD closed captioning....................................................................135
Changing DVD Audio Settings .............................................................................136
Playing DVDs with Windows Media Player............................................................ 136
Using DVD Play to Play DVDs, Videos, High-Definition DVDs, and Blu-ray DVDs......... 137
Playing Video CDs (VCDs)...................................................................................139
Playing video CDs (VCDs) with Windows Media Player .....................................139
Creating Audio and Data Discs.............................................................141
Erasing Rewritable Discs Before Recording ............................................................142
Working with Audio CDs ....................................................................................142
Audio CD tips ...............................................................................................143
Before you begin creating discs.......................................................................143
Creating audio CDs.......................................................................................144
Creating video discs ......................................................................................144
Copying a disc .............................................................................................145
Creating data discs........................................................................................146
Making a disc label using LightScribe Technology .............................................147
Making a paper disc label..............................................................................149
viii Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 9

Working with Pictures and Videos .......................................................151
Working with Digital Images ...............................................................................151
Viewing Pictures in Windows Media Center ..........................................................152
Adding Pictures in Windows Media Center ...........................................................152
Adding picture files from the hard disk drive ..................................................... 152
Viewing Pictures in Windows Media Center ..........................................................153
Viewing pictures as a slide show .....................................................................154
Viewing a slide show with music .....................................................................154
Using supported picture file types in Windows Media Center..............................155
Editing Pictures in Windows Media Center ............................................................ 156
Fixing red eye or contrast ............................................................................... 156
Cropping pictures in Windows Media Center ...................................................156
Rotating pictures............................................................................................157
Printing Pictures in Windows Media Center ...........................................................158
Copying Pictures to CDs and DVDs in Windows Media Center ................................ 158
Playing Videos in Windows Media Center ............................................................159
Playing digital videos.....................................................................................159
Using supported video file types......................................................................160
Transferring and Recording Video Files .................................................................160
Recording analog and digital video files ..........................................................160
Creating a DVD from Video Files in Windows Media Center ................................... 161
Creating Movies by Using muvee autoProducer....................................163
Basic steps for making a movie .......................................................................163
Using muvee autoProducer ..................................................................................165
Getting started ..............................................................................................165
Capturing video from a digital video camera....................................................167
Adding videos...............................................................................................168
Adding pictures.............................................................................................170
Adding music................................................................................................ 171
Selecting the style ..........................................................................................171
Changing the settings.....................................................................................171
Making the movie.......................................................................................... 173
Previewing the movie .....................................................................................173
Modifying the movie ...................................................................................... 174
Saving the movie project ................................................................................175
Recording the movie project to disc .................................................................176
Upgrading muvee autoProducer ......................................................................177
Supported muvee autoProducer output file types ................................................177
Table of Contents ix
Page 10

Watching and Recording TV Programs .................................................179
Navigating TV + Movies .....................................................................................179
Watching TV .....................................................................................................181
Watching live TV...........................................................................................181
Controlling TV playback ................................................................................. 182
Using the remote control in TV + Movies...........................................................183
Using the Television Program Guide .....................................................................184
Using Windows Media Center without the guide...............................................184
Television Program Guide errors...................................................................... 185
Viewing the Television Program Guide ............................................................. 186
Setting up how Windows Media Center downloads the guide ............................187
Adding a postal code to receive the correct guide ............................................. 188
Adding missing channels to the guide ..............................................................188
Editing and removing channels in the guide......................................................189
Searching for TV Programs ..................................................................................189
Searching for TV programs by using categories................................................. 190
Recording TV Programs.......................................................................................191
Recording TV by using the guide .....................................................................192
Recording programs manually without using the guide .......................................192
Recording quality and hard disk drive storage space .........................................193
Watching TV programs stored on the HP Media Drive .......................................194
About recording TV to the HP Media Drive .......................................................195
Recording TV programs to the HP Media Drive..................................................195
Changing the TV recording path to the HP Media Drive .....................................196
Changing the TV recording path to the local hard disk drive...............................196
Add TV recording folder for Windows Media Center to find ............................... 197
Changing disk space for recording TV programs...............................................197
Updating recorded TV list after removing the HP Media Drive ............................. 197
System requirements to view recorded TV programs on other computers...............198
Copying recorded TV programs to DVD or CD..................................................198
Media copy protection ...................................................................................199
Playing Recorded TV Programs.............................................................................200
Playing DVDs in Windows Media Center ..............................................................200
Index...................................................................................................201
x Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 11

Finding Onscreen Guides
Onscreen guides are available in the User’s Guides folder (select models only).
1 Click the Windows Start Button
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click User Guides.
4 Click an item to view it or use it.
NOTE: If there are no guide titles listed in the folder, your computer has no onscreen
guides.
Finding Guides on the Web
You can find guides and information for your computer by using the Internet to access the
Support Web site.
®
on the taskbar.
Getting Help
1 Go to http://www.hp.com/support in your Web browser.
2 Select your country/region and language.
3 Click Support and Drivers.
4 Enter the model number of your computer, and then click Search .
5 Click Manuals.
6 Locate the manual you want, and then do one of the following:
Click the title to display the file in Adobe Acrobat Reader (which you can
download from the Manuals page if it is not currently installed on your computer).
Right-click the title, click Save Target As, specify a location on the computer
where you want to save the file, rename the file (retaining the .pdf extension), and
then click Save.
Getting Help 1
Page 12

Using the Onscreen Help and Support Center
Information about your computer is in the onscreen Help and Support Center (select
models only). Here, you can find links to driver updates, access to technical support
options, and information about commonly asked questions.
To open the Help and Support Center:
Press the Help button (select models only) on your keyboard.
Or
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Help
and Support.
Using the PC Help & Tools Folder
The PC Help & Tools folder contains special utilities for computer owners, such as
support information and programs.
To see the items in the PC Help & Tools folder:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click PC Help & Tools.
4 Click Hardware Diagnostic Tools to view or use these tools.
Using the hardware diagnostic tools
The hardware diagnostic tools help you to do the following:
View the computer system information, such as memory usage, drive capacity
and CPU usage.
Find alerts about your computer.
Show information, and run diagnostic tests on computer hardware and some
computer peripheral hardware, such as printers, monitors, speakers, and
network adapters.
Run a computer system test.
2 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 13

Using HP Total Care Advisor Software
HP Total Care Advisor is a desktop tool you use to monitor and access system health
information about key areas of your computer. HP Total Care Advisor has four major
areas:
PC Health & Security provides a dashboard view of the status of key areas of
your computer.
PC Action Center receives messages and alerts that inform you of changes in
the status of your computer health.
PC Help provides simple access to help and support information for your
computer.
Products Showcase provides a listing of products and services available for
your computer, and presents comparison shopping information about those
items.
To ope n HP Tota l Care A dviso r:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click HP Total Care Advisor.
Getting Help 3
Page 14

4 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 15

Turning On the Computer for the First Time
After you have completed the steps on the setup poster, you are ready to turn on the
computer.
1 Press the Power button on the monitor.
2 Press the On button on the front of the computer.
3 Turn on the speakers, if they are present.
4 Set up the computer by following the onscreen instructions. If prompted, select the
country/region in which you are physically located, and wait while the computer
makes preparations. (When you select an alternate language, it may take up to
30 minutes for this one-time language setup on the computer.)
5 Set up Microsoft
6 Follow the onscreen instructions to register with HP or Compaq, sign up for updates,
and get online. If you do not want to set up an Internet connection at this time, you can
do so later by manually starting Easy Internet Services. See “Connecting to the
Internet.”
7 Norton Internet Security automatically opens. Follow the onscreen instructions to set up
this tool, which protects the computer and your privacy.
®
Windows Vista® by following the onscreen instructions.
NOTE: If you stop the setup procedure, when you are ready to finish, double-click the
Easy Setup icon on the desktop to run the first-time wizard.
Turning On the Computer for the First Time 5
Page 16

Turning Off the Computer
For best results, when using Microsoft Windows Vista, do not shut down the computer,
except when you must turn off the power for safety reasons, such as to make repairs, install
new hardware or cards in the computer chassis, or change a battery.
As an alternative to shutting down the computer, you can lock it or put it into either Sleep
or Hibernate mode, if it is available. You can set the power management timers to put the
computer automatically into Sleep or Hibernate mode.
Sleep and Hibernate modes are power states. Sleep mode saves your work to memory, so
you can resume quickly; saves your work to the hard disk; and then goes to a
reduced-power state. During Sleep mode, the computer hardware light remains on, and
the computer is ready to wake quickly and resume your work where you left off. Hibernate
mode saves the system memory to a temporary file on the hard disk and then turns off the
hardware.
Some computers also have a reduced-power state called Away mode. Away mode turns
off the display and mutes the audio, but otherwise keeps the computer operational. During
Away mode, the computer can perform tasks such as recording a scheduled TV program
or streaming video and music files to a remote location.
Using Shut Down
For best results, when using Windows Vista, turn off the computer without pressing any
buttons on the computer chassis.
NOTE: For information on the Windows Start Button , see “Using the Windows Start
Button Menu.”
1 Close any open software programs by clicking the X at the upper-right corner of each
program window.
2 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
3 Click the Arrow button next to the Lock button.
4 Click Shut Down.
5 Turn off the monitor.
To turn on the computer after a shut down:
1 Press the power button on the monitor.
2 Press the On button on the front of the computer.
6 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 17

Using Lock
If you lock the computer, only you or the administrator can log on to it.
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click the Lock button.
3 To unlock this computer, you must enter your password.
Using Sleep mode
When the computer is in Sleep mode, it goes into a reduced-power state. The monitor is
blank, as if it were turned off. By using Sleep mode:
You save time, because you do no have to wait for the computer to go through the
normal startup routine when you wake it again. The next time that you use the
computer, any programs, folders, and documents that were open before you put the
computer into Sleep mode are available.
The computer can receive faxes, if you set it to do so.
The computer can retrieve e-mail messages and download information from the
Internet automatically, if you set it to do so.
To put the computer into Sleep mode manually:
Press the Sleep button on the keyboard, if it is present.
Or
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click the Power button.
Or
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click the Arrow button next to the Lock button.
3 Click Sleep.
To wake the computer from Sleep mode:
Press the Sleep button on the keyboard.
Or
Quickly press the On button on the front of the computer.
Turning On the Computer for the First Time 7
Page 18

If the computer does not work properly when you wake it from Sleep mode, restart the
computer.
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click the Arrow button next to the Lock button.
3 Click Restart.
Or
Quickly press the On button on the front of the computer.
Using Hibernate mode
Hibernate mode is available as an advanced power setting. When the computer is in
Hibernate mode, it saves to the hard disk drive everything that is in computer memory,
turns off the monitor and the hard disk drive, and then turns itself off. When you turn on the
computer again, your programs, folders, and documents are restored to the screen.
To put the computer into Hibernate mode manually:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click the Arrow button next to the Lock button.
3 Click Hibernate, if it is present.
NOTE: If Hibernate is not present, you can set up the computer to go into Hibernate
mode automatically; see “Automatic Sleep, Hibernate, or Away mode.”
To wake the computer from Hibernate mode, press the On button on the front of the
computer.
If the computer does not work properly when you wake it from Hibernate mode, restart the
computer.
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click the Arrow button next to the Lock button.
3 Click Restart.
8 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 19

Automatic Sleep, Hibernate, or Away mode
You can set the computer to go into Sleep, Hibernate, or Away modes automatically when
it is idle for a specified number of minutes. To put the computer into a mode automatically,
modify the power management settings.
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click System and Maintenance.
4 Click Power Options.
5 Click Change when the computer sleeps.
6 For Sleep or Away mode, select an option from the Put the computer to sleep
drop-down menu, and click Save changes.
Or
For Hibernate or Away mode:
a Click Change advanced power settings.
b Click the plus sign (+) next to Sleep.
c Click an item and make selections, and then click Apply.
d Click OK.
Restarting the Computer
When you restart the computer, the computer clears some settings and starts over using the
operating system and software in its memory. Restarting is the easiest and most effective
way to solve many software issues for the computer.
Also, you may want to install additional software programs or hardware devices onto the
computer, and doing so may require that you restart the computer after installation.
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click the Arrow button next to the Lock button.
3 Click Restart.
Or
Quickly press the On button on the front of the computer.
Turning On the Computer for the First Time 9
Page 20

Connecting to the Internet
The computer can connect to the Internet through the telephone modem. There are other
ways to connect to the Internet that do not use the telephone modem, such as a LAN (local
area network) or DSL (digital subscriber line). Check with your Internet Service Provider
(ISP) for specific information on the connection. See “About the Internet” for more
information about using the Internet.
Refer to “Setting Up the Computer” in the other setup information that came with your
computer to make the hardware connections: for a modem, see “Connecting a Modem”
and for a network see “Setting Up a Local Area Network.”
To connect to the Internet, you must have:
A computer.
A dial-up modem, a cable modem, or a DSL modem for high-speed broadband
connections. Contact your ISP for any specific software and hardware that you
may need.
Internet service with an ISP.
A Web browser.
To connect to the Internet:
1 Sign up with an ISP. If you already have an account with an ISP, skip this step and
follow the instructions provided by the ISP.
2 If you did not set up for Internet service during the initial setup of the computer, set it
up now by using Easy Internet Services.
a Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
b Click All Programs.
c Click Online Services and then click Easy Internet Services.
d Follow the onscreen instructions to select an ISP and set up Internet service.
NOTE: Easy Internet Services provides a list of ISPs; however, you may choose
another ISP or transfer an existing account to this computer. To transfer existing
accounts, follow the instructions provided by the ISP.
3 Connect to the Internet. You must connect through your ISP.
Double-click the ISP-provided icon on the desktop, and log in.
4 Open your Web browser and browse the Internet.
You can use any Web browser; most computers have Microsoft Internet Explorer. To
open Internet Explorer:
a Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
b Click Internet Explorer.
NOTE: If you have questions, contact your ISP directly.
10 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 21

Using the Computer with Safety and Comfort
WARNING: To reduce the risk of serious injury, read the Safety & Comfort
Guide. It describes proper workstation setup, posture, and health and work
habits for computer users. It also provides important electrical and mechanical
safety information.
Before you begin using the computer, arrange the computer and your work area to
maintain your comfort and productivity. Refer to the Safety & Comfort Guide for important
ergonomic information:
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, click All Programs, click
User Guides, and then click Safety & Comfort Guide.
Or
Type
http://www.hp.com/ergo
into the Web browser address box, and then press Enter on the keyboard.
Setting Up User Accounts
User accounts enable you to set the privileges for each user of the computer. For example,
you can set the software programs that each user is allowed to access.
Windows Vista provides three types of user accounts:
Administrator:
Is allowed to change account types for other users, change passwords, change
system-wide settings, access all files on the computer, and install software and drivers
that are compatible with Windows Vista.
Limited - Standard User:
Is not allowed to change other user settings or passwords. A Limited account may
not be able to install or run some software.
Is allowed to change the limited account picture, and to create, edit, or delete the
account password.
Guest:
Is allowed to use most software and change system settings that do not affect other
users or the security of the computer.
Is not allowed to change other user settings or passwords, or install software.
Does not have access to password-protected files, folders, and settings.
Turning On the Computer for the First Time 11
Page 22

Creating multiple user accounts on the same computer has certain advantages, as well as
some drawbacks.
Advantages to multiple user accounts:
Ability to create individual user settings
Ability to limit access to software for certain users
Drawbacks to multiple user accounts:
More memory (RAM) usage
Multiple Temporary Internet Files folders to remove during Disk Cleanup
More data to back up
Longer time to complete virus scan
Protecting the Computer
Protect the computer, personal settings, and data from a variety of risks by using:
Passwords.
Antivirus software.
Firewall software.
Critical security updates.
NOTE: Security solutions are designed to act as deterrents, but they may not be able to
prevent software attacks or to prevent the computer from being mishandled or stolen.
Computer risk Security feature
Unauthorized use of the computer
User password
or user account
Computer viruses Norton Internet Security software (antivirus
program)
Unauthorized access to data Norton Internet Security software (firewall program)
updates
Unauthorized access to Setup
Windows Vista
Administrator password
Utility, BIOS settings, and other
system identification information
Ongoing or future threats to the
Critical security updates from Microsoft
computer
12 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 23

Using passwords
A password is a group of characters that you choose to secure the computer information.
Several types of passwords can be set, depending on how you want to control access to
your information. Passwords can be set in the Microsoft Windows
on the computer.
CAUTION: To avoid being locked out of the computer, record each password
you set. Because passwords are not displayed as they are set, changed, or
deleted, it is essential to record each password immediately and store it in a
secure place.
Use the following list as a basic guide when choosing a password:
Choose a password that is easy for you to remember but difficult for others to guess.
Choose a long password (minimum of six characters).
Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
Don’t use personal information that others can easily figure out, such as your birthday,
child’s name, or phone number.
Don’t write down passwords unless you store them in a secure place away from the
computer. Do not store passwords in a file on the computer.
You can use the same password for more than one Windows Vista security feature.
A password can have any combination of up to eight letters and numbers, and it is not
case sensitive.
Vista operating system
A password must be set and entered with the same keys. For example, if you set the
password with number keys on the keyboard, the password is not recognized if you
subsequently try to enter it with the embedded numeric keypad.
NOTE: Select models include a separate numeric keypad, which functions exactly like
the keyboard number keys, except in the case of passwords.
A password set in Windows Vista must be entered at a Windows Vista prompt.
The following table lists the Windows Vista passwords and describes their functions. For
information on how to set passwords, see “Using passwords.” For additional information
on Windows Vista passwords, such as screen saver passwords, type passwords into the
Search Help box in the Help and Support Center.
Password Function
Windows Vista Administrator
password
Protects administrator-level access to
computer contents.
Windows Vista User password Protects access to a Windows Vista user account and
the computer contents. It must be entered when you
resume from Sleep or Away mode.
CAUTION: If you forget the Administrator password, you cannot access
Setup Utility.
Turning On the Computer for the First Time 13
Page 24

Using antivirus software
When you use the computer for e-mail, network, or Internet access, you expose it to
computer viruses. Computer viruses can disable the operating system, software programs,
or utilities, or cause them to function abnormally.
Antivirus software can detect most viruses, destroy them, and in most cases repair any
damage that viruses may have caused. To provide ongoing protection against newly
discovered viruses, antivirus software must be kept up to date.
The Norton Internet Security program, which is preinstalled on the computer, includes
antivirus and firewall components. The software includes a free update period. It is
strongly recommended that you protect the computer against new viruses beyond the free
period by purchasing extended update service. Instructions for using and updating Norton
Internet Security software, and for purchasing extended update service, are provided
within the program.
To open and access Norton Internet Security:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click Norton Internet Security, and then click Norton Internet Security in
the list.
See “Using the Norton Internet Security Antivirus Software” for more information about
using the Norton antivirus software.
For more information about computer viruses, type viruses into the Search Help box in the
Help and Support Center.
Using firewall software
When you use the computer for e-mail, network, or Internet access, unauthorized persons
may be able to gain access to information about you, the computer, and your data. To
protect your privacy, use firewall software. Microsoft Windows Vista includes firewall
software preinstalled on the computer. Also, Norton Internet Security, which is preinstalled
on the computer, includes a firewall program.
Firewall features include logging, reporting, and automatic alarms to monitor all incoming
and outgoing communications.
To open and access Norton Internet Security:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click Norton Internet Security, and then click Norton Internet Security in
the list.
Under some circumstances, a firewall can block access to Internet games, interfere with
printer or file sharing on a network, or block authorized e-mail attachments. To solve the
problem temporarily, disable the firewall, perform the task that you want to perform, and
then enable the firewall again. To resolve the problem permanently, reconfigure the
firewall.
14 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 25

Configuring the computer for automatic Microsoft software updates
Microsoft continually updates the Windows Vista operating system. HP recommends that
you run Windows Vista Update monthly to install these updates. One way to keep the
operating system up to date is to use the Automatic Updates feature.
When you are connected to the Internet, Windows Vista Update automatically notifies you
through a pop-up message or icon in the notification area when critical updates are
available. When you see the Windows Vista Update message, allow the updates to
download to your system. If you update the system weekly, or even monthly, the time
required for download is minimal.
To configure Automatic Updates:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Security.
4 Click Windows Update.
5 Click Change settings.
6 Select the desired configuration:
Install updates automatically (recommended) — This is the default
setting, and it enables you to specify a day and time to automatically download
and install recommended updates.
Download updates but let me choose whether to install them
Check for updates but let me choose whether to download and
install them
Never check for updates (not recommended) — This option makes the
computer more vulnerable to security threats and performance problems and is not
recommended.
7 Click OK.
Turning On the Computer for the First Time 15
Page 26

Installing critical security updates
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of information damage or loss from security
breaches and computer viruses, install all critical updates from Microsoft as
soon as you receive an alert.
Additional updates to the operating system and other software may have become
available after the computer was shipped. Download all available updates and install
them onto the computer.
To get the latest updates for the computer:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Help and Support, and then click Software, drivers, and BIOS
updates.
3 Follow any onscreen instructions to complete downloading and installing the
latest updates.
Guidelines for Installing Software and Hardware Devices
After you set up the computer, you may want to install additional software programs or
hardware devices. Keep in mind the following important guidelines:
Before installation, make a restore point by using the Microsoft System Restore
program.
a Make sure you are logged in as an Administrator.
b Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
c Click Control Panel.
d Click System and Maintenance.
e Click Backup and Restore Center.
f Click Create a restore point or change settings.
g In the System Properties window, on the System Protection tab, click Create.
Follow the onscreen instructions.
The restore point is a snapshot of the computer settings. By using System Restore, you
ensure that you have a stable set of settings to use. For information on System Restore,
go to the Microsoft Web site at: http://www.microsoft.com/worldwide
Choose software that is compatible with the computer; check the operating system,
memory, and other requirements listed for the new software.
Install the new software according to the directions provided by the software
manufacturer. If you need help, check the manufacturer’s documentation or customer
service information.
16 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 27

If you need to restore factory settings after you install a program that is incompatible:
a Make sure you are logged in as an Administrator.
b Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
c Click Help and Support.
d Click Recover factory settings.
e Choose an option, and then follow the onscreen instructions.
For antivirus software, uninstall the existing software program before reinstalling it or
installing a new antivirus program.
NOTE: Use only licensed original software. Installing copied software may be illegal, or it
may result in an unstable installation or infect the computer with a virus.
Transferring Files and Settings from an Old Computer to a New Computer
You can copy files from the old computer to a new computer by using media such as CDs
or DVDs, memory sticks, or personal media drives. You can also copy certain settings such
as Web browser Favorites and address books by using Windows Easy Transfer software,
which is included with Microsoft Windows Vista.
To transfer your files and settings:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Help and Support.
3 Type transfer files into the Search Help box.
4 Click the overview article Transfer files and settings from another computer.
This article describes a Microsoft solution for moving your files to your new computer.
5 Click Windows Easy Transfer.
6 Follow the onscreen instructions in the Windows Easy Transfer wizard to transfer your
files from an old computer to a new one.
Turning On the Computer for the First Time 17
Page 28

18 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 29

Using the Keyboard
IMPORTANT: Please see the documentation that came with the keyboard for additional
information about using the keyboard, customizing keyboard buttons, and using any
special keyboard keys. You may need to install keyboard software and drivers to access
all the special features and functions of the keyboard.
Your computer may include either a standard keyboard or a wireless keyboard. Using the
keyboard is the primary way that you enter text and commands for the computer.
A standard keyboard connects to the keyboard connector in the back of the computer.
A wireless keyboard (select models only) uses a receiver/transmitter, instead of a
connector cable, to communicate with the computer. A light on the receiver indicates
receiver activity.
Identifying Keyboard Features
The keyboard contains an arrangement of standard keys, indicator lights, and special
buttons (select models only). Your keyboard may vary from the illustrations that follow.
Alphanumeric keys
The alphanumeric keys are the main keys found on a standard typewriter.
Using the Keyboard 19
Page 30
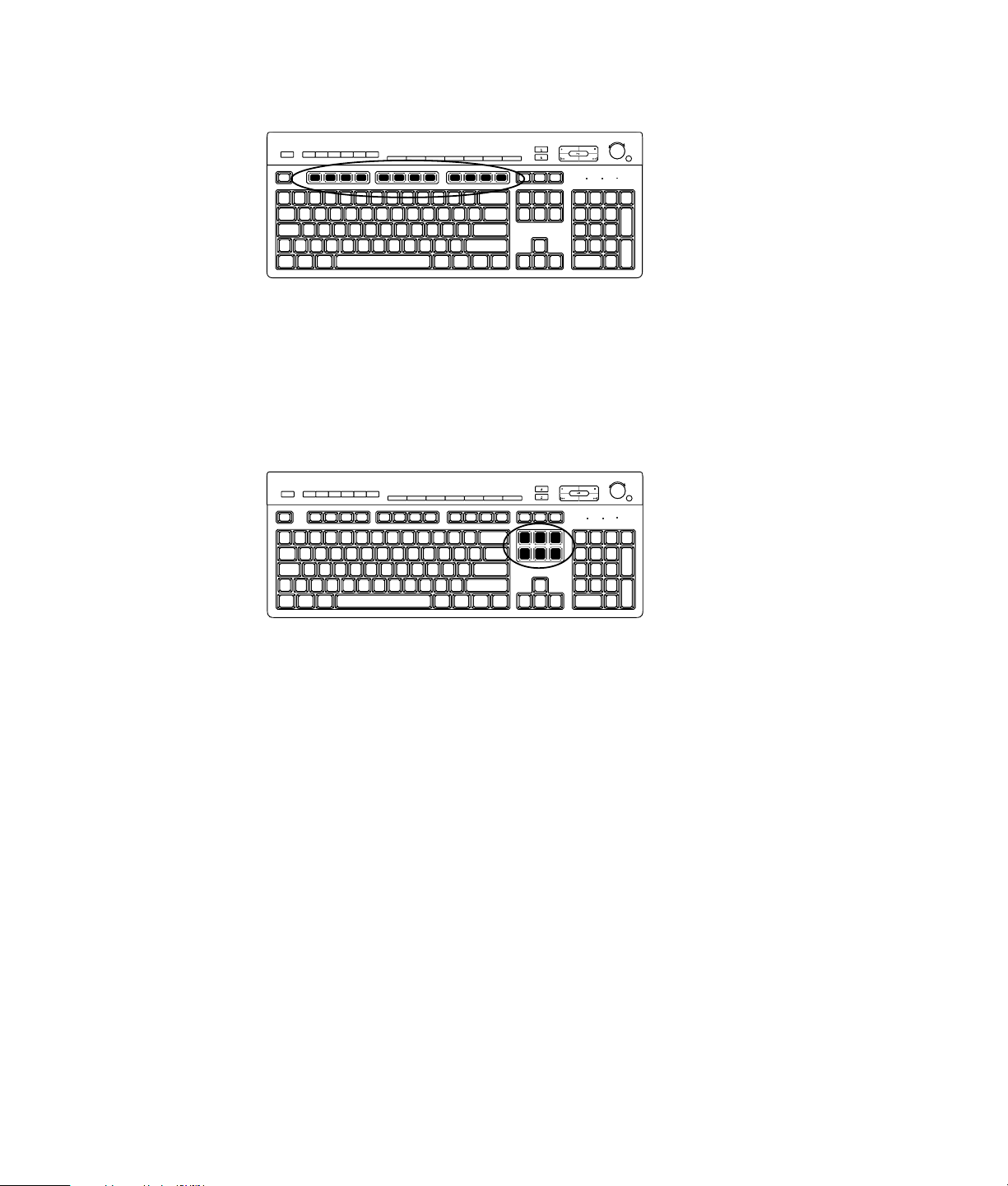
Function keys
The function keys, located above the main keys, are labeled F1 through F12. Most function
key operations vary by software program. F1 and F3 are available at all times:
Pressing F1 opens a Help window for the software program being used.
Pressing F3 opens a search window.
Edit keys
The edit keys are Insert, Home, Page Up, Delete, End, and Page Down. Use these keys to
insert and delete text, and to quickly move the cursor on the screen. The edit keys function
differently with some software programs.
20 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 31

Arrow keys
The arrow keys are controls for moving up, down, right, and left. You can use these keys
instead of the mouse to move the cursor for navigation on a Web page, in a document, or
in a game.
Numeric keys
Press the Num Lock key to lock and unlock the numeric key functions:
When the Num Lock light on the keyboard is on, the numeric keys work in the same
way as the number keys and arithmetic functions found on a basic calculator.
When the Num Lock light on the keyboard is off, the numeric keys are directional keys
used to move the cursor or play games.
Using the Keyboard 21
Page 32

Keyboard indicators
Each keyboard indicator is a light labeled with a name or with an icon for its status:
Icon Name Description
Num Lock When lit, numeric keys are locked as number keys and
arithmetic functions.
Caps Lock When lit, alphanumeric keys are locked to uppercase.
Scroll Lock When lit, scroll function is locked.
Special keyboard buttons
There are special buttons (select models only) at the top of the keyboard. These buttons
operate a CD or DVD player, control speaker volume, connect you to the Internet, or
provide quick access to specific functions. (Some keyboard models have some of these
special buttons to the left side of the main keys, some do not have the Internet buttons, and
some use a different layout on the top right.)
22 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 33

Identifying Special Keyboard Buttons
Your keyboard may not include some of the buttons listed.
NOTE: The number, location, and labeling of buttons vary by keyboard model.
Access buttons
Icon Feature Description
Sleep Puts computer into or out of power-saving
mode. It may take 10–30 seconds before
screen reappears.
User Switches between computer users.
Information Opens Help and Support Center.
? Or
Or
Or
Or
hp Or
Compaq Or
Pictures
(Photos)
Music Opens music software program. Can be
Video Opens video software program. Can be
Internet Opens an Internet browser. Can be
Search Opens page designed to search the Internet.
E-mail Opens e-mail program. Can be reconfigured
HP Club Links to HP Web site.
Compaq
My Presario
Opens imaging software program. Can be
reconfigured.
reconfigured.
reconfigured.
reconfigured to open any Web site or
software program.
Can be reconfigured to open any Web site
or software program.
to open any Web site or software program.
Links to Compaq Web site.
Using the Keyboard 23
Page 34

Icon Feature Description (continued)
Shopping Goes to a shopping Web site. Can be
Or
reconfigured to open a site or software
program.
Sports Goes to a sports Web site. Can be
Or
reconfigured to open a site or software
program.
Finance Goes to a finance Web site. Can be
Or
reconfigured to open a site or software
program.
Connect to
Or
Internet
Search Goes to a search engine. Can be
Or
Chat Goes to chat Web site. Can be reconfigured
Or
Entertainment Goes to a entertainment Web site. Can be
Offers Goes to popular Web site. Can be
Calculator Opens calculator. Can be reconfigured.
Media control or playback buttons
Icon Label Description
Goes to an Internet browser page. Can be
reconfigured to open a site or software
program.
reconfigured to open a site or software
program.
to open a site or software program.
reconfigured to open a site or software
program.
reconfigured to open a site or software
program.
Eject 1 and
Eject 2
Rec Starts recording to selected media.
Stop Stops media.
Play/Pause Plays or pauses media.
Prev Rewinds media.
Next Fast-forwards media.
24 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Opens or closes upper and lower optical drive trays.
Page 35

Icon Label Description (continued)
Volume Volume knob controls speaker volume: Turn clockwise to
increase speaker volume and counterclockwise to decrease
volume.
NOTE: The Volume knob can continue to be turned, even
after maximum volume has been reached.
Volume Up and Down buttons control speaker volume:
Or
– +
Press the Volume Up button to increase volume and the
Volume Down button to decrease volume.
Mute Turns speaker sound on and off.
Or
Customizing the keyboard buttons
You can customize some of the special buttons on the keyboard (select models only) to
open different programs or files or go to favorite Web sites.
If you cannot customize the keyboard buttons using the following procedure, see the
documentation that came with the keyboard.
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, if it is present.
4 Click Keyboard.
5 Click the Buttons tab, and then double-click the button that you want to change.
NOTE: You can click the Speed tab to adjust the character repeat delay speed or the
cursor blink rate. You can also click the Hardware tab, and then click the
Properties button to view keyboard information.
6 For the button configuration, click the Down arrow to the right of the list and choose
the button capability, such as Complex remote page with label or Simple
local file with label.
7 Enter a display label and the address information. For a Web page, enter the URL.
8 Click OK.
9 On the Buttons tab, click Apply.
10 Repeat steps 5 through 9 for each button that you want to customize.
11 Click OK to finish.
NOTE: Click the Restore Defaults button on the Buttons tab to restore all of the buttons
to the factory settings.
Using the Keyboard 25
Page 36

Keyboard Shortcuts
Keyboard shortcuts are combinations of keys that you press simultaneously to perform
specific actions. For example, from the Windows Vista desktop, press the Alt (alternate)
key, the Ctrl (control) key, and the S key (the letter S) to display support information for the
computer (including the model number, serial number, and service ID). You see this
combination of keys represented as Alt+Ctrl+S. In Windows Vista, press Ctrl+C to copy an
item that you’ve highlighted or selected, Ctrl+V to paste a copied item, or Ctrl+Z to undo
the previous action. These shortcuts perform the same actions that you can perform
through menus, but they save you time and mouse clicks.
Wireless Mouse and Keyboard Troubleshooting
Synchronizing a wireless mouse and keyboard
If the wireless mouse and keyboard do not respond, use this procedure to resynchronize
the devices.
1 Plug the receiver into a USB port on the computer. If you have a choice, a USB port on
the front of the computer is best if it will be closer to the mouse and keyboard.
2 Push the Connect button (A) on the receiver, and hold it for 5 to 10 seconds until the
blue light starts to flash.
26 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 37

3 Push and hold the Connect button (B) on the underside of the mouse until the blue LED
on the receiver stops flashing.
NOTE: The receiver connection session times out after 60 seconds. To ensure the
connection was established instead of the receiver timing out, move the mouse and check
for response.
After the mouse connection is established, repeat the procedure with the keyboard:
1 Push the Connect button on the receiver, and hold it for 5 to 10 seconds until the blue
light starts to flash.
2 Push and hold the Connect button (C) on the underside of the keyboard until the blue
LED on the receiver stops flashing.
For additional mouse and keyboard troubleshooting tips, refer to the Troubleshooting and
Maintenance Guide.
Using the Keyboard 27
Page 38

28 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 39

Using the Mouse
IMPORTANT: Please see any documentation that came with the mouse for additional
information about using the mouse, customizing mouse buttons, and using special buttons
or features that are included with the mouse. You may need to install mouse software and
drivers to access all the special features and functions of the mouse.
Your computer includes a mouse for directing the cursor (pointer) on the Windows Vista
desktop. The mouse uses a roller ball or optics (a light and sensor) to sense movement and
cause the cursor on the screen to move. Use the mouse on a flat surface.
NOTE: The optical mouse cannot work on a glass, translucent, or reflective surface.
A wireless mouse (select models only) is an optical mouse that uses a receiver/transmitter,
instead of a connector cable, to communicate with your computer. A light on the receiver
indicates receiver activity.
NOTE: The wireless mouse goes into a sleep or suspend mode after 20 minutes of
inactivity. Click a button on the mouse to wake it. (Moving the wireless mouse does not
wake it.)
Using the Mouse 29
Page 40

Using the Mouse Buttons
The mouse has two or three buttons on the top:
Click the left mouse button (A) to position the cursor or select
an item.
Click the right mouse button (C) to display a menu of
commands for the item you clicked.
On select models, use the scroll wheel button (B) in the center
for scrolling and panning.
NOTE: Your mouse may look different from the one
shown here.
You see these terms for using the mouse:
Click means to press and release the left mouse button once.
Double-click means to click the left mouse button and then
quickly click it again.
Right-click means to press and release the right button once.
To select an item, click it.
To select sequential items in a list or group, click the first item in the list, and then press and
hold the Shift key on the keyboard while you click the last item.
To select non-sequential items, click the first item, and then press and hold the Ctrl key on
the keyboard while you click the additional items.
You can switch the function of the left and right buttons for left-handed use. See “Changing
Mouse Settings.”
Scrolling
Click the left mouse button to place the cursor in a document, and then:
To scroll toward the beginning of the document, roll the scroll wheel button up
(away from you).
To scroll toward the end of the document, roll the scroll wheel button down
(toward you).
Autoscrolling
1 Place the cursor anywhere in the document, and then press the scroll wheel
button once. An autoscroll icon appears.
2 Move the mouse in the direction you want to scroll. The farther you move the
mouse from the starting point, the faster the document scrolls.
3 To stop autoscrolling, press the scroll wheel button again.
NOTE: Autoscrolling does not work with some software programs.
30 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 41

Panning
1 Place the cursor anywhere in the document, and then press and hold down the scroll
wheel button.
2 Slowly move the mouse in the direction you want to pan. The farther that you move the
mouse from the starting point, the faster the document pans.
3 To stop panning, release the scroll wheel button.
NOTE: Panning works only if the horizontal scroll bar in the window is active. Panning
does not work with some software programs.
Changing Mouse Settings
Switching mouse button functions
To switch the functions of the right and left mouse buttons for left-handed use:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, if it is present.
4 Click Mouse.
5 Click the Buttons tab, and check Switch primary and secondary buttons.
6 Click Apply (using the new primary button), and then click OK.
Changing mouse pointer speed
To change the speed of the cursor on the screen relative to the motion of the mouse:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, if it is present.
4 Click Mouse.
5 Click the Pointer Options tab.
6 In the Motion area, use the slider to adjust the pointer speed. You can select other
pointer options by placing a check in the check box next to the setting that you want.
7 Click Apply, and then click OK.
Using the Mouse 31
Page 42

Changing the double-click speed
To change the double-click speed of the right mouse button:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, if it is present.
4 Click Mouse.
5 Click the Buttons tab.
6 In the Double-click speed area, use the slider to adjust the double-click speed.
7 Click Apply, and then click OK.
Turning on the ClickLock option
ClickLock enables you to highlight or drag an object without holding down the
mouse button.
To turn on the ClickLock option:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, if it is present.
4 Click Mouse.
5 Click the Buttons tab.
6 In the ClickLock area, place a check in the Turn on ClickLock check box.
7 Click Apply, and then click OK.
Changing the scroll wheel speed
To change the scroll wheel speed:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, if it is present.
4 Click Mouse.
5 Click the Wheel tab.
6 In the Vertical Scrolling area, adjust the number of lines per scroll by clicking the
arrow buttons.
Or
In the Horizontal Scrolling area, adjust the number of lines per scroll by clicking the
arrow buttons.
7 Click Apply, and then click OK.
32 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 43

Wireless Mouse and Keyboard Troubleshooting
If the wireless mouse and keyboard do not respond, see “Synchronizing a wireless mouse
and keyboard” in the “Using the Keyboard” chapter to resynchronize the devices.
Using the Mouse 33
Page 44

34 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 45

Configuring Speaker and Sound Options
Speakers are included with the monitor (select models only), or they are sold separately.
For details about connecting stereo speakers to the computer, see the setup poster. For
details about connecting multichannel speakers, see “Connecting Speakers or
Microphone” in the Advanced Setup Guide.
NOTE: Speakers may be passive (no power button or power cord) or active (power button
or power cord). Your computer supports only active (powered) speaker systems; the
speaker system must have its own power cord.
A stereo speaker set is a left-right, two-channel speaker system. A multichannel audio
speaker system is a system with more than two channels, and it may include a subwoofer.
For example, a 5.1 channel speaker system, referred to as six-speaker mode, uses two
front speakers (left-right), two rear speakers (left-right), a center speaker, and a subwoofer.
If your computer has multichannel audio speaker capacity (select models only), you can
connect four channels for four-speaker output, or six channels for 5.1 speaker output.
Your model may include one of three analog sound connector types on the back of
the computer:
Three connectors (Realtek Audio)
Six connectors (Realtek Audio)
Audio sound card (Creative Sound Blaster X-Fi and X-Fi Fatality, or Analog Devices,
Inc (ADI))
Your system may also have a separate Digital Out connector (select models only).
See “Connecting Speakers or Microphone” in the Advanced Setup Guide for more
information about connecting your speaker system, and then configure the audio software
for sound output as described in this section.
Configuring Speaker and Sound Options 35
Page 46

Adjusting speaker volume
Use the Volume icon on the taskbar to set speaker volume. Then, you can adjust the volume
by using:
The Volume knob or buttons on the keyboard (select models only).
The Volume knob on the speakers (select models only).
There are two ways to use the Volume icon:
1 Click the orange Realtek HD Audio Manager Volume icon on the
taskbar.
2 Select a tab, such as Digital Output, and then adjust the volume by clicking
the slider and moving it.
3 When you are satisfied with the sound level, click outside the Volume window to
close it.
Or
1 Right-click the white Microsoft Volume icon on the taskbar, and then click
Open Volume Mixer. The Volume Mixer settings window opens.
2 Adjust the volume by clicking the slider and moving it.
3 When you are satisfied with the sound level, click the Close box (the X in the
upper-right corner) to close this window.
36 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 47

Selecting a microphone
Your computer comes with one microphone connector on the back of the computer. Some
models have a second microphone connector on the front of the computer. Only one
microphone connector works at a time, and the back connector is ready to use unless you
have the multichannel audio speakers option. For computers with the multichannel audio
speakers option, the microphone connector on the front of the computer, if it is present, is
ready to use.
To use a microphone connected to the front of your computer (select models only), select
the working microphone:
NOTE: If you connect your microphone to the back of your computer, you do not need to
perform this procedure.
1 Right-click the white Microsoft Volume icon on the taskbar, and then click
Recording Devices. The Sound window opens.
2 Select the Recording tab.
3 Double-click Microphone, and select the General tab.
4 Click the microphone connector that you want to use, and then click Apply.
5 Click OK.
Adjusting microphone volume
To adjust the volume of the microphone:
1 Right-click the orange Realtek HD Audio Manager Volume icon on the
taskbar, and then click Audio Devices.
2 Click the Recording tab.
3 Double-click Microphone, and then click the General tab.
4 Click the microphone connector that you want to use.
5 Click the Levels tab.
6 Adjust the volume for the microphone by clicking the slider and moving it.
7 Click OK, and then click OK again.
Configuring audio output
You can configure your speaker audio output by using the following software. Use the
software that applies to your computer model:
Creative Sound Blaster X-Fi or X-Fi Fatality Speaker Settings Configuration
(audio card)
Realtek HD Audio Manager (multistreaming audio)
Windows Media Center (all systems)
Configuring Speaker and Sound Options 37
Page 48

Using the Creative Sound Blaster X-Fi or X-Fi Fatality audio card
This section provides an overview of configuring and recording with the Creative Sound
Blaster X-Fi or X-Fi Fatality audio card (select models).
Configuring the audio card software
After you have installed and connected the speakers, follow these steps to configure
multichannel audio output for computers:
NOTE: Three modes are available; Entertainment Mode is selected here. For information
about the other modes, see “Sound Blaster X-Fi configuration modes.”
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Point to All Programs.
3 Click Creative, Sound Blaster X-Fi, and then click Creative Console
Launcher.
4 The Entertainment Mode window opens. If a different mode displays, click the Mode
button, and then select Entertainment Mode.
5 Click the Windows Start Button , All Programs, Creative, and then
Creative Console Launcher.
6 Click the Speakers button.
7 Click Auto Detect. Creative automatically detects the type of speakers that
are connected to your system.
8 Click X to close the window.
Now that you have configured the audio card software, you must configure audio output
for your media software program. The procedure is different for each program. Refer to
the instructions that came with the media software program.
38 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 49

Configuring the FlexiJack connector
Your audio device may have a FlexiJack connector that supports both microphone and Line
input. If so, you can change the FlexiJack mode, if necessary. To do this, you must select
the function in the Creative Console Launcher after you connect the audio cable to the
FlexiJack connector on the audio card.
NOTE: If you are using the FlexiJack as your Digital In connection, and you want to
connect digital speakers as your output device, you need a special connector from
Creative.
1 Connect your audio cable to the FlexiJack connector on the audio card.
2 Click the Windows Start Button , All Programs, Creative, and then
Creative Console Launcher.
3 Click the Jacks button.
4 Under FlexiJack Mode, select either Digital I/O or Mic-In/Line-In.
5 Close the window.
Sound Blaster X-Fi configuration modes
The Sound Blaster X-Fi audio card includes three modes: Audio Creation Mode,
Entertainment Mode, and Game Mode.
The main functions, such as speaker configuration, equalizer, and volume control, are
available in all three modes. However, each mode optimizes the audio card resources to
provide the best audio performance for different activities.
Using Audio Creation Mode
The Audio Creation Mode enables advanced recording functions.
Available features:
Recording from several audio sources
Applying studio-quality effects
Mixer settings
Equalizer settings
Using Entertainment Mode
The Entertainment Mode optimizes the audio card for playing movies and music.
Available features:
Configuring speakers and headphones
Configuring surround sound, DTS, and THX
Volume, bass, and treble controls
Mixer settings
Configuring Speaker and Sound Options 39
Page 50

Using Game Mode
The Game Mode optimizes the audio card for playing games.
Available features:
Volume, bass, and treble controls
Mixer settings
Configuring speakers and headphones
Configuring surround sound
More information
For more information about configuring and using the audio card, go to the Creative
Sound Blaster X-Fi documentation:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Point to All Programs.
3 Click Creative, Sound Blaster X-Fi, and then click Documentation.
4 Click Online Manual.
Configuring speakers with Realtek HD Audio Manager
After you have installed and connected your speakers, complete the following steps if your
computer model has type 6 connectors and is capable of multistreaming audio:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound.
4 Click Realtek HD Audio Manager. The window opens.
NOTE: You must have your speakers connected for Realtek to display the
Speakers tab.
5 Click the Speakers tab to open that control screen.
6 Click the Speaker Configuration tab.
7 Select your type of speakers from the drop-down menu.
8 Click OK.
40 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 51

The Realtek HD Audio Manager control screens
Digital Output: Enables you to select the Environment and Equalizer settings. You
can select an environment, such as Stone Room or Auditorium. Under Equalizer,
you can either click a preset button, such as Pop or Live, or manually adjust the
settings and then save them for easy selection later.
Speakers: Enables you to select the number of speakers, view whether the
connectors are analog or digital, and select the digital audio output and digital audio
input devices. Only speakers that are currently being used are displayed.
Configuring Speaker and Sound Options 41
Page 52

Microphone: Enables fine control over the recording volume and playback volume
of the microphone. Includes buttons for noise suppression and acoustic echo
cancellation.
Line In (Digital Input): Enables control over volume, playback, mute, recording,
and multistreaming audio.
42 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 53
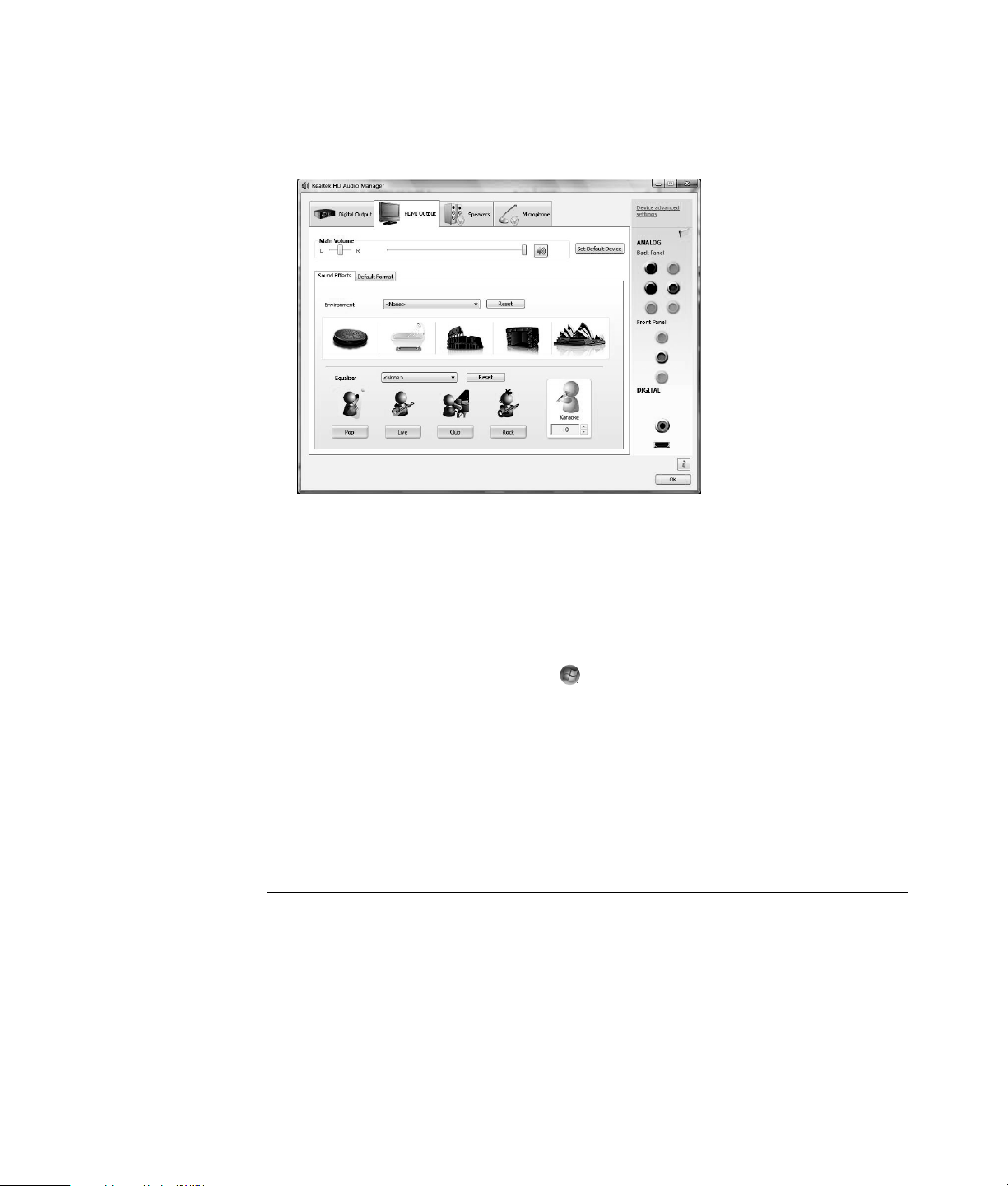
HDMI Output: Enables you to select the Environment and Equalizer settings. You
can select an environment, such as Stone Room or Auditorium. Under Equalizer,
you can either click a preset button, such as Pop or Live, or manually adjust the
settings and then save them for easy selection later.
Configuring sound for recording with the Realtek HD Audio Manager
The microphone connector is ready to use for recording sound. If you want to use another
connector for recording, such as the Digital Audio In connector, complete the following
steps to select it:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, and then Realtek HD Audio Manager.
4 Click the Line In tab.
5 Click Digital In tab, and then select Set Default Device.
6 Click OK to close the window.
NOTE: You can retask the front pink, blue, and green connectors to perform other audio
functions; see “Retasking front panel audio connectors.”
Configuring Speaker and Sound Options 43
Page 54

Retasking front panel audio connectors
You can retask the Line In, Mic In, Headphone, and Front Speaker Out connectors on the
front of the computer, as necessary.
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, and then click Realtek HD Audio Manager.
4 Click a front connector icon that you want to retask.
NOTE: Only the connectors that are not dimmed are able to be retasked.
5 Place a check in the device check box that you want to select, and then click OK.
You can now use the front connectors as either input or output devices.
44 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 55

Configuring multistreaming audio
The Realtek HD Audio Manager software enables you to listen to two different audio
sources on two different speaker sets.
For example, you can hear one audio source through a rear-panel speaker connection,
and a second source through a front-panel headphone or speaker connection. You must
configure multistreaming audio for the system if you want to hear two audio sources on
separate speakers.
Audio output overview
The front-panel audio output is the green stereo headphone connector only.
The rear-panel outputs are the speaker connectors that can be set up as multichannel out
from stereo 2.0 to 7.1 (select models only) configurations. Refer to your user
documentation for information about setting up powered speakers or your AV receiver.
Audio input overview
You can select two of the following audio sources to play through front-panel headphone
and rear-panel speaker connectors:
1 From an externally connected device source, such as:
A microphone with cable connected to Mic In (pink).
An MP3 player with cable connected to Line In (blue).
2 From an internal source inside, or directly connected to, the computer, audio files may
reside on: hard disk drives, DVDs, CDs, USB drives, HP Personal Media Drives, or
any connected device. Play internal media files through programs such as:
Microsoft Windows Media Player.
Other installed media player software.
NOTE: Digital Audio In cannot be multistreamed.
Configuring Speaker and Sound Options 45
Page 56

When to use multistreaming audio
You may multistream two audio sources as described in the following typical examples:
1 For online gaming:
You hear 5.1 game sound on AV receiver or powered speakers.
You also hear gaming conversation on a headset.
See “Example 1: For online gaming.”
2 For digital home entertainment:
You hear DVD sound on a living room TV/display or AV receiver from the
rear-speaker connections.
You also hear sound on the computer or powered speakers that are connected to
the front-panel green headphone jack, from one of the following external
computer audio sources:
a Front-panel Line In
b Internal source residing on a hard disk drive, DVD, CD, USB drive, or other
external device
See “Example 2: For digital home entertainment.”
Setting up multistreaming audio
Example 1: For online gaming
To configure multistreaming audio output for online gaming with Realtek HD Audio
Manager, you must enable Voice-over-IP software (software used to converse over the
Internet). Other players hear your voice from the microphone via the Internet, and you hear
the game audio from the rear speakers.
1 Connect the audio input and output connectors as follows:
A headphone set to the front Headphone Out (green) connector
A microphone to the front Mic In (pink) connector for online conversation
A set of powered stereo 5.1 or 7.1 speakers to the rear Speaker Out connectors
for gaming sound output
2 Click the Realtek HD Audio Manager icon on the taskbar to open the
Realtek HD Audio Manager window.
3 Click the Device Advanced Settings button.
4 Select Make front and rear output devices playback two different audio
streams simultaneously.
5 Place a check in the Output Mic In/Line In to front panel check box, and
click OK.
Or
Place a check in the Output Mic In/Line In to rear panel check box, and
click OK.
46 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 57

Example 2: For digital home entertainment
To configure multistreaming audio output for digital home entertainment with Realtek HD
Audio Manager:
1 Connect the audio output connectors as follows:
A headphone set or powered speakers to the front Headphone Out (green)
connector for stereo music playback
A set of powered stereo 5.1 or 7.1 speakers to the rear Speaker Out connectors
for DVD playback sound output
2 Click the Realtek HD Audio Manager icon on the taskbar to open the
Realtek HD Audio Manager window.
3 Click the Device Advanced Settings button.
4 Select Make front and rear output devices playback two different audio
streams simultaneously.
5 Place a check in the Output Mic In/Line In to front panel check box, and then
click OK.
Or
Place a check in the Output Mic In/Line In to rear panel check box, and then
click OK.
Configuring audio for Windows Media Center
After you have installed, connected, and configured the speakers, follow these steps to
configure multichannel audio output for Windows Media Center:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Windows Media Center.
3 Under Tasks, click settings, General, and then click Windows Media
Center Setup.
4 Click Set Up Your Speakers. The Welcome to Speaker Setup window opens.
5 Click Next.
6 Choose the speaker connection type, and then click Next.
7 Select the number of speakers, and then click Next.
8 Click Test to test the speakers.
9 Click Finish.
Configuring Speaker and Sound Options 47
Page 58

Selecting recording devices
(Type 6 connectors only)
To select a sound recording device:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
3 Click Sounds and Audio Devices (or Sounds, Speech and Audio Devices).
The Sounds and Audio Devices window opens.
4 Click the Audio tab.
5 Under Sound Recording, select a recording device, such as Realtek HD Front
Pink Jack.
6 Click OK.
7 Close the window.
Resolving sound issues
If you do not have sound from the speakers, try the following:
Check the volume and mute settings.
Use active (powered) speakers, or speakers with an amplifier.
Check the sound cable connections.
Ensure that the software program and sound software are properly configured.
Some software programs may result in low volume, even when the Volume is turned to
the maximum value. If this is the case, click the Volume icon on the taskbar, and
increase the system volume.
Reconfigure the sound software for surround sound.
Reinstall the audio card drivers by using application reinstallation program; refer to
the Troubleshooting and Maintenance Guide that came with the computer.
48 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 59
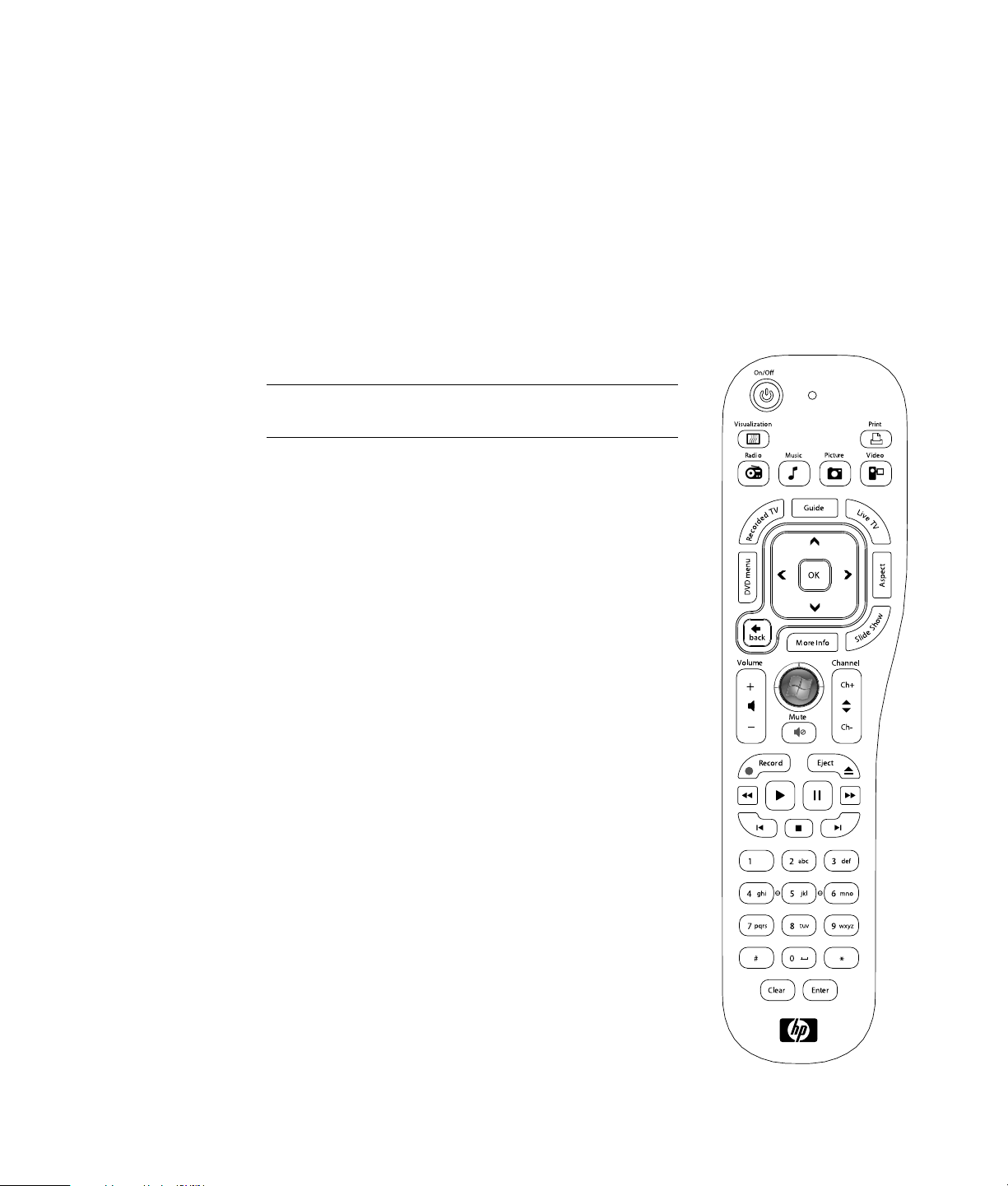
Using the Windows Media Center
Remote Control
(Select models only)
NOTE: The remote control is included with select models
only. Features and location may vary.
The remote control is designed to work with Windows Media
Center. You can use the remote control with Windows Media
Center to play CDs and DVDs, view pictures, and much more.
This remote control helps you navigate the Windows Media
Center windows on the computer just as a TV remote control
helps you navigate cable TV options or control the playback of
a movie in a VCR or DVD player.
The remote control can:
Navigate and control all Windows Media Center
windows.
Control the video display.
Place the computer in and out of sleep mode.
Shut down or restart the computer.
Log off from Windows Media Center or switch users.
The remote control cannot:
Navigate the Windows desktop or control other computer
programs outside of Windows Media Center.
Be used as a VCR, DVD player, or stereo remote control.
Turn on or off a TV that is connected to the computer (select
models only).
Turn on the computer.
Using the Windows Media Center Remote Control 49
Page 60

Remote Control Buttons Overview
1 On/Off (Sleep) — Puts the computer into and out of
a power-reduced Sleep mode. It does not turn the
computer off.
2 Visualization — Displays visual imagery that is
synchronized to the sound of the music tracks.
3Music — Opens the Music Library window in
Windows Media Center.
4Radio — Opens the FM Radio window in Windows
Media Center.
5Guide — Opens the Television Program Guide.
6 Recorded TV — Opens the recorded tv window
where recorded TV programs are listed.
7Arrows — Moves the cursor to navigate and select
actions within all Windows Media Center windows.
8DVD Menu — Opens the Play DVD window in
Windows Media Center or opens the main menu of a
DVD movie, if available.
9Back — Returns to the previous window within
Windows Media Center.
10 More Info — Displays available information about a
selected media file and displays other menus.
11 Start — Opens the Windows Media Center
main menu.
12 Volume — Increases (+) and decreases (–) volume.
13 Mute — Turns computer sound off. The word Mute is
displayed when Mute is turned on.
14 Record — Records a selected television program and
stores it on the hard disk drive.
15 Play — Plays the selected media.
16 Rewind — Moves the media backward at
three speeds.
17 Skip Backward — Moves media backward
7 seconds, or to the beginning of a music track or a
DVD chapter.
50 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 61

18 0 to 9, #, * — Enters text and numbers into a Windows Media Center search or text box. Each time
you press a number button, a different character appears. Press the Enter button to select a character.
19 Clear — Deletes the last character entered.
20 LED — Activity indicator light. The LED tells you that the remote control is emitting a signal when you
press a button.
21 Print — Prints an item in Windows Media Center.
22 Picture — Opens the Pictures Library window in Windows Media Center.
23 Video — Opens the Videos Library window in Windows Media Center.
24 Live TV — Displays the full-screen view of live TV. Moves a TV program forward to the end of the pause
buffer and resumes playing live TV.
25 OK — Selects the desired action or window option and acts as the Enter key.
26 Aspect — Changes the aspect ratio of the display. Zooms in on the picture three times then returns to
the full-screen aspect ratio.
27 Slide Show — Plays a slide show of all the pictures on the hard disk drive.
28 CH/PG up (+) and down (–) — Changes the TV channels or moves pages up and down, depending
on available options. Moves to the next DVD chapter.
29 Eject — Ejects CD or DVD drive.
30 Pause — Pauses audio and video tracks and live or recorded TV programs.
31 Fast Forward — Moves media forward at three speeds.
32 Skip Forward — Moves media forward 30 seconds in videos and live TV, one music track, or one
DVD chapter.
33 Stop — Stops the media currently playing.
34 Enter — Selects the desired action, menu, or window option.
NOTE: The remote control requires two AA batteries. The remote control operates up to 8 meters (26 feet) away
from the remote sensor. Make sure there is nothing blocking the pathway between the remote control and the
remote sensor.
NOTE: Make sure you turn off the monitor and turn down or mute the volume, for example, if you have a
scheduled recording in the middle of the night and do not want to be disturbed. The computer does not
automatically go into Sleep mode if Windows Media Center is open. It is recommended that you close Windows
Media Center before you manually place the computer in sleep mode.
NOTE: If the computer model does not include a TV tuner, some remote control buttons are inactive.
Using the Windows Media Center Remote Control 51
Page 62

About the Remote Control
Use the remote control to open the Windows Media Center program, and use it to view
TV, record TV programs, play previously recorded TV programs, and play music, movies,
or video.
To open Windows Media Center using the remote control, simply point it at the remote
sensor, and press the Windows Media Center Start button .
Use the remote control at a maximum distance of 8 meters (26 feet) from the remote sensor
and at a maximum of 22.5 degrees (45 degrees total) from the center of the remote
sensor.
NOTE: Use alkaline batteries in the remote control.
52 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 63

Troubleshooting the Remote Control
If the remote doesn’t work:
Make sure that the batteries for the remote control are charged and installed correctly.
Make sure the front of the remote sensor (IR receiver) is not blocked.
Point the remote control within a 45-degree angle range and less than 8 meters
(26 feet) away.
If a pressed key repeats itself or sticks, unplug the remote sensor from the USB
connector, wait 1 minute, and plug the remote sensor back in. Try altering the lighting
conditions in the room or moving the location of the remote sensor if this continues.
Press the Enter button on the remote control after changing a channel.
Point the remote control toward the remote sensor, and press a button. A faint red light
should appear on the remote sensor. If the light appears, then the problem is probably
in the Windows Media Center software. Close Windows Media Center, restart the
computer, and then open Windows Media Center again.
If the remote control works in Windows Media Center but not when changing
channels, you need to reconfigure the Windows Media Center software settings for
the cable set-top box or satellite receiver.
Remote sensor is not receiving a signal from the remote control
If a faint red light doesn’t appear when you point the remote control at the remote sensor
and press the OK button, try the following:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, right-click Computer, and
then select Properties.
2 Click Device Manager.
3 Click the plus (+) sign next to Universal Serial Bus Controllers.
4 If the eHome Infrared Receiver is listed under Universal Serial Bus Controllers,
Windows is properly detecting the IR Receiver. If it is not listed, go to the next step.
5 Unplug the end of the USB cable on the remote sensor from the computer, and plug it
into the same USB port.
6 Disconnect all other USB devices, leave the remote sensor plugged in, and then restart
the computer. Plug in other USB devices after the remote sensor appears in the Device
Manager window.
Using the Windows Media Center Remote Control 53
Page 64

54 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 65

Introducing Your Computer Software
The operation of your computer is controlled by two kinds of software:
The Microsoft Windows Vista operating system, which displays the desktop on the
monitor and controls your computer’s hardware, peripherals, and software programs.
Software programs that perform specific functions, such as word processing.
The software programs included with the computer may vary by model and by
country/region.
Learning More About Software
You can find information on using software and on the Microsoft Windows Vista operating
system in this guide and the onscreen Help. For Microsoft Windows Vista, you can also
open the built-in Help and Support Center.
Press the Help button (labeled with a question-mark icon) on your keyboard (select
models only).
Or
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Help and
Support.
For help with specific software, refer to the onscreen Help within the program.
Using the Desktop
The desktop is the work area that appears on the monitor screen. It includes the taskbar
along one edge, and shortcut icons that make it easy to find the things you need.
The taskbar shows the Windows Start Button ; a button for each open window, so that
you can switch between programs; and the notification area that includes the time.
A shortcut icon is a small picture that you click to open a folder or start a program. One
icon on the desktop that performs a special function is for the Recycle Bin, which collects
files or shortcuts that you delete. When you empty the Recycle Bin, the files or shortcuts are
permanently deleted. You can retrieve items from the Recycle Bin until you empty it.
Introducing Your Computer Software 55
Page 66

Removing desktop icons
You can remove most desktop icons by deleting them.
To delete a desktop icon:
1 Right-click the desktop icon.
2 Click Delete. The icon is placed in the Recycle Bin.
Retrieving desktop icons
1 Double-click the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop.
2 Drag the icon onto the desktop.
Removing files permanently
1 Right-click a file, and then click Delete.
2 Right-click the Recycle Bin icon on the desktop, and then click Empty Recycle Bin.
Using the Windows Start Button Menu
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar to open the Start menu. From the
Start menu, you can:
Open programs or documents.
Open the Help and Support Center.
Start a search.
Open the Control Panel to view or change settings.
Using the All Programs menu
To find the software programs on your computer:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click All Programs.
The All Programs menu displays a list of folders organized according to task
(select models only).
A folder contains a list of items. Each item is actually a shortcut, or link, to a program, a
document, or another folder. The Music folder, for example, contains shortcuts to the
programs that you use to play music CDs.
56 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 67

Organizing the All Programs list
To change the name of an item:
1 Right-click the item.
2 Click Rename.
3 Type the new name, and then press Enter on the keyboard.
4 Click Yes in the message that appears.
To copy an item:
1 Right-click the item.
2 Click Copy.
3 Go to the desktop or folder, right-click an empty area, and then click Paste.
If you use Add or Remove Programs in the Control Panel to delete a software program, the
shortcut in All Programs may not be removed. To remove a shortcut:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click the folder.
4 Right-click the shortcut, and then click Delete.
Using the Control Panel
The Control Panel is where you can set up or change properties and settings for the
monitor, the keyboard, the mouse, the modem, a network connection, and other
components and features of the computer. The Control Panel also provides tools for
changing system performance, adding hardware, adding or removing programs, and
other tasks.
To open the Control Panel:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Control Panel.
Introducing Your Computer Software 57
Page 68

Resizing Windows
All windows have three buttons in the upper-right corner. The middle
button is either the Maximize button or the Restore Down button,
depending on the state of the window.
Feature Name Description
Minimize Collapses the window to the taskbar (but does not close it).
Maximize Expands the window to the full-screen size.
To bring the window back up, click the taskbar button with
the name of the window.
Restore
Down
Close Closes the window, and stops the program or task.
Resize Resizes a window (not available when window is
Scroll bar Appears in a window when the information does not fit on
Reduces the window from full-screen size, so that it covers
only a portion of the screen.
maximized). Move your mouse cursor over any window
border until the cursor becomes a double-headed arrow.
Click and hold down the left mouse button. Drag the border
to the left or right to change the width. Drag the border up or
down to change the height.
one screen. Clicking and dragging a vertical scroll bar
moves the screen up and down. Clicking and dragging a
horizontal scroll bar moves the screen left and right.
Working with Digital Images
You can connect a digital image source, such as a digital camera or a digital video
camera, to the computer either directly or through a docking station. Digital picture files
that you copy or download from the device appear in the Pictures folder.
Digital cameras and other digital imaging devices use memory cards, or media, to store
digital picture files. You can copy digital picture files from the memory cards used by
digital cameras and other digital imaging devices by using the memory card reader (select
models only).
58 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 69

About the Internet
This section describes connecting to and using the Internet, including how to use a Web
browser and electronic mail (e-mail).
Use the Internet to search for information or services on the Web, or to retrieve, read, or
send e-mail messages.
The Internet is a group of computers that communicate with each other through telephone
lines, digital services, or cable lines. Each Internet computer is independent, and its
operators choose which files to make available to users of the Internet. To connect your
computer to the Internet and use the information and services available there, you need an
Internet Service Provider (ISP).
ISPs are businesses that give you access to the Internet, and most of them provide e-mail
service. ISPs usually charge a monthly fee for their services. When your computer connects
to the Internet, it is actually communicating with the Internet computer belonging to the ISP.
The ISP verifies your account, and then provides you access to the Internet. You use a Web
browser program to search for and display Web site information. Some ISPs allow you to
choose a browser program, while others provide their own browser.
Your connection to an ISP may be through a traditional telephone dial-up modem, local
area network (LAN), cable modem, digital subscriber line (DSL), or asymmetric digital
subscriber line (ADSL). (DSL, ADSL, and cable ISPs are not available in all countries/
regions.)
The World Wide Web (WWW), also called the Web, is a public part of the Internet used
by individuals, companies, governments, and organizations. These individuals and groups
have created millions of Web sites in support of their activities. A Web site consists of one
or more Web pages. A Web page is a file or group of files that a user can access by
entering the file location, or Uniform Resource Locator (URL).
The URL identifies a Web site location, typically in the form http://www.name.extension
(for example, http://www.hp.com). The URL may include the path to a specific file
within that site. Each period, or dot, in the URL separates elements within the address. For
example, you will see the URL extension .com used by companies. When you enter the URL
into your browser address box and press the Enter key on your keyboard, the browser
contacts that location and opens the Web page for you.
Imagine that you are reading a newspaper. On page 1, you may read something like “For
more details, see page 3, column 2.” You turn the page for more information. A hyperlink
on a Web page works the same way, except that you move to the new page by clicking
the hyperlink. The way that a hyperlink links files together is what gives the Web its name,
because the Web weaves together and connects ideas from all over the world.
Your e-mail address identifies the electronic post office box where people can send you
electronic mail. E-mail addresses have the form name@domain.extension. The domain is
usually the name of the ISP or organization. The extension usually identifies the type of
organization. For example, if your name is Jane Jones, and XYZ is your ISP, your e-mail
address might be JaneJones@xyz.com, with the extension .com indicating that XYZ is a
company. For information on using e-mail, see “Sending and Receiving E-Mail.”
Introducing Your Computer Software 59
Page 70

Using a Browser
A Web browser program searches for and displays Web site information. How you
explore the Internet depends on whether your ISP provides the browser or allows you to
choose your own.
Once you are connected to the Internet, your browser opens the home Web page. You can
go to a different Web site by entering its address (such as http://www.hp.com) into
the address box in the browser, and then pressing Enter on your keyboard. Or you can
use the browser search feature to search for references to a specific word or phrase on
the Web.
Searching the Internet
Most Web browser programs include a search feature. You may need to click a button or
select a menu option to display the search feature, depending on the type of browser
program. Type a question, or a word that describes the information that you want to find,
into the Search box, and then press Enter.
The Windows search feature includes direct use of Internet Explorer Search.
NOTE: If your ISP provides the browser, you may not be able to use Internet Explorer to
search the Internet.
To begin a search:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Type a word or question; what you type automatically appears in the Start Search
box. As you type, the search results appear in the left pane.
3 Do one of the following:
Click a result to open it.
Click the X in the search window to clear the results of the search and return to the
main list of programs.
Click See all results to display a list of all found search items on the computer
and for advanced options.
Click Search the Internet to search the Internet by opening your browser.
60 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 71

Restricting Internet content
The Internet provides you with a wide variety of information, but some information may
not be suitable for every viewer. With Content Advisor (a feature of Internet Explorer),
you can:
Set up a password.
Control Internet access.
Set up a list of Web sites that people who use your computer cannot view.
Adjust the type of content people can view with and without your permission.
Once you set up restricted rating levels in Content Advisor, users can view Web sites and
other pages that you have specified under the rating setup. However, to view unrated Web
sites or pages, users must enter the Content Advisor password that you have set. This
means that any unrated page, even Help and Support or Internet Explorer, is not viewable
if the user does not know the password.
To enable Content Advisor:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click Internet Explorer.
3 Click Tools, and then click Internet Options.
4 Click the Content tab.
5 In the Content Advisor area, click Enable.
6 Click the General tab, click Create password, and type a password.
7 Click OK, and then click OK again.
To allow access to an unrated site or page you approve of:
1 Open the Web site.
2 When the password window appears, select the Always allow viewing or
Allow viewing only this time option.
Introducing Your Computer Software 61
Page 72

Using the Norton Internet Security Antivirus Software
When you use the computer for e-mail, network, or Internet access, you expose it to
computer viruses. Computer viruses can disable or damage your operating system,
software programs, or computer utilities.
Antivirus software can detect most viruses, remove them, and, in most cases, repair any
damage that they have caused. To provide ongoing protection against newly discovered
viruses, you must keep antivirus software up to date.
Norton Internet Security, an antivirus software program, is preinstalled on your computer
and includes a free trial subscription of protection updates. You can enable Symantec’s
LiveUpdate™ to obtain updates automatically whenever you are online. Hewlett-Packard
strongly recommends that you protect the computer against new viruses beyond the trial
period by purchasing an extended update service.
Configuring and registering Norton Internet Security software
When you first set up the computer, Norton Internet Security helps you to configure and
register your copy of Norton Internet Security.
Ensure that you set up Norton Internet Security before you start using the Internet.
1 Double-click the Norton Internet Security icon on the desktop.
Or
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, All Programs, Norton
Internet Security, and then click Norton Internet Security.
2 Click a task under Tasks & Scans, and then follow any onscreen instructions.
For information about using and updating the Norton Internet Security software, open
Norton Internet Security, and then click Help under Quick Links.
Manually running a scan
To select and run a scan:
1 Double-click the Norton Internet Security icon on the desktop.
2 Click the Norton Internet Security tab.
3 Click the Tasks & Scans bar.
4 Click Run a Scan.
5 Select Run Full System Scan to scan your entire hard disk drives for viruses and
security risks. Depending on the number of files on your computer, this may take
several minutes.
6 When the scan is complete, click Finish.
62 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 73

Setting a Full System Scan time
To schedule a time for a Norton Internet Security Full System Scan:
1 Double-click the Norton Internet Security icon on the desktop.
2 Click the Norton Internet Security tab.
3 Click the Tasks & Scans bar.
4 Click Configure a Scan.
5 Click Schedule Full System Scan.
6 Click New.
7 Set the frequency and time that you want the scan to run.
8 When you are done, click OK.
NOTE: If the computer is in Sleep mode, the Norton Internet Security program does not
perform a scheduled antivirus scan.
NOTE: Performing an antivirus scan during a scheduled Windows Media Center
recording can result in a failed TV recording. Recording a TV program requires a TV tuner,
which is included with select models only.
Setting up a Custom Scan time
To create a Custom Scan for specific files, folders, and drives:
1 Double-click the Norton Internet Security icon on the desktop.
2 Click the Norton Internet Security tab.
3 Click the Tasks & Scans bar.
4 Click Configure a Scan.
5 Click Manage Custom Scans.
6 Click Create Custom Scan, and then click Next.
7 Click Add Folders or Add Files. Place a check mark next to the files and folders
that you want to scan, click Add, and then click Next.
8 Type a name for your customized scan, and then click Finish.
9 Click Schedule next to the customized scan that you just created.
10 Click New.
11 Set the frequency and time that you want the scan to run.
12 When you are done, click OK.
NOTE: If the computer is in Sleep mode, the Norton Internet Security program does not
perform a scheduled antivirus scan.
NOTE: Performing an antivirus scan during a scheduled Windows Media Center
recording can result in a failed TV recording. Recording a TV program requires a TV tuner,
which is included with select models only.
Introducing Your Computer Software 63
Page 74

Sending and Receiving E-Mail
E-mail enables you to send and receive letters, pictures, postcards, and even music and
video clips.
NOTE: E-mail may contain a virus in the message itself or as an attachment. To protect
your computer, do not open any message that originates from an unfamiliar source or that
appears suspect to you. Instead, delete such messages.
Your computer comes with an e-mail program from Microsoft called Windows Mail (select
models only). You may also use e-mail programs from other vendors. Some ISPs provide
their own e-mail programs. You use an e-mail program to send, receive, and organize your
messages. You can organize, read, and create new messages even when you are offline
(not connected to the Internet).
Using Windows Mail
To set up Windows Mail, you first need some information from your ISP: your e-mail
address, user name, password, the names of your incoming and outgoing e-mail servers,
and perhaps some other details.
The first time you start Windows Mail, make sure the computer is connected to the Internet,
and follow the wizard to set up your account.
To add an account in Windows Mail:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click Windows Mail.
4 Click Tools, and then click Accounts.
5 Click Add, E-mail Account, and then click Next.
6 Follow the onscreen instructions to add your account.
Using the e-mail program provided by your ISP
Follow the instructions provided by your ISP to install its Web browser and e-mail program,
and to set up and use your e-mail account. You can then send and receive e-mail when
your computer is connected to your ISP.
64 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 75

Software Quick Reference Table
(Select models only)
Your computer includes a number of software programs that:
Record and play CDs.
Record data CDs.
Import and edit video files.
Record video CDs and DVDs.
Organize digital media files.
The following table describes the functionality that is specific to each of these programs. Use the table to determine
which program to use to perform a task.
Note that some of the programs that are listed may not be included with your model, and that this is not a
complete list of all included software.
To open any of these programs, click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, click All Programs,
select the program folder (for example, DVD Play), and then click the program name to open the software.
With this program: You can:
DVD Play
(select models only)
HP Photosmart
Essential
(select models only)
Rhapsody
(select models only)
Play DVD movies and video CDs (VCDs).
Play Blu-ray and High-Definition DVDs if the computer has a Blu-ray and
HD DVD disc drive.
Use the Zoom and Pan features.
Create viewing bookmarks.
View, organize, and print your photos.
Share your photos with friends and family.
Create electronic photo albums.
Edit your photos: crop, resize, flip, rotate, make black and white, change the
contrast, and more.
To open this program, click the Windows Start Button , All Programs,
HP, and then click HP Photosmart Essential.
Play music CDs, .mp3s, and other audio files.
Record music files.
Record a copy of an existing music or data CD to use on the computer.
Organize digital files into a library for recording or listening.
Introducing Your Computer Software 65
Page 76

With this program: You can: (continued)
muvee autoProducer
(select models only)
CyberLink Power2Go
(select models only)
CyberLink
PowerDirector
(select models only)
Add your own style to your movies with music, pictures, titles, scene transitions,
and captions.
Edit your home movies.
Save and burn multiple movie files to DVD.
Use the magicSpot feature to control the motion effects applied to your pictures.
Record data and music files.
Record a copy of an existing music or data CD to use on the computer.
Create customized music CDs from CDs in your collection, or from .wav, .mp3,
or .wma files. These CDs can be played in your home or car stereo.
Copy and share data files.
Create archive CDs or DVDs from files on your computer.
Copy video files.
Verify that the disc has been created without errors.
Record movie files to create VCDs and DVDs that you can play on some DVD
players.
Copy and share video files.
Capture video files.
Edit video files.
CyberLink LabelPrint
(select models only)
HP Total Care Advisor
(select models only)
Burn a label directly onto LightScribe-enabled CDs, DVDs, and mini-discs by
using LightScribe technology.
Burn a label directly onto the disc’s label side by using Labelflash technology.
Print labels to attach directly onto a disc.
Quickly organize the Web links you want to keep available to you on your
desktop.
Comparison-shop using the convenient shopping search engine.
Get HP software and driver updates.
Get important messages from HP.
Access PC Health and Security and PC Help tools.
66 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 77

With this program: You can: (continued)
Backup My PC
(select models only)
Create computer backup files to protect your data and other important files on
your computer.
NOTE: This software is included with the Personal Media Drive only.
Microsoft Windows
Movie Maker
(select models only)
Import audio, video, and other media files from videotape, audiotape, Web
cameras, or television broadcasts.
Record audio and video files to create a video project that becomes a
Microsoft Windows Media source file with a .wmv extension.
Edit and preview files.
Send a movie in an e-mail or upload it to a Web server.
Add music files (.mp3).
Import audio files such as .mp3, .asf, or .wma; video files such
as .wmv, .asf, .avi, or .mpg; or image files such as .jpg or .gif.
Create .avi and .wmv (Windows Media Video) files.
NOTE: You may have a software update CD included with your computer. You may need to install this CD before
using the DVD Writer/CD Writer drive. To do this, follow the installation instructions that came with the CD.
Introducing Your Computer Software 67
Page 78

68 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 79

A file is any unit of information that is named and stored on the computer hard disk drive
or other electronic storage media, such as a CD, diskette, or even in a digital camera. A
file can be a document, picture, music, video, or other data. Almost everything that you do
on the computer involves working with files.
The computer can copy files to other storage media within component drives, such as
diskettes, memory cards, CDs or DVDs, or it can send them to output devices, such as a
printer.
Organizing Files with Folders
In Windows Vista, folders enable you to organize the files on the computer. Like paper
folders within a filing cabinet, folders on the computer provide a way to group related files
together.
A folder can contain any type of file, and it can even contain other folders. Each file within
a folder must have a unique name, but two different folders can have files with the
same name.
Managing Files
There are two methods for working with files and folders on the computer:
The Computer view enables you to quickly see all the files and folders within a specific
folder on the computer. It also contains links to common tasks for managing files, such
as copying, moving, deleting, and renaming.
To open the Computer view, click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar,
and then click Computer.
Windows Explorer enables you to quickly see all the folders and files on the computer.
It also makes it easy to move or copy files from one folder to another.
To open Windows Explorer, click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar,
and then click Windows Explorer.
To navigate the Computer and Windows Explorer views, double-click folders to open and
display their contents. Click the Back arrow button to retrace the path through the opened
folders.
Managing Files 69
Page 80

Creating Folders
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Computer.
Or
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Windows
Explorer.
2 Navigate to the location where you want to place the new folder.
3 Click Organize, and then click New Folder.
4 Type a name for the folder, and then press Enter on the keyboard.
Moving Files
CAUTION: Do not move any file that is part of an installed program. Doing so
can cause the program to become unusable.
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Computer.
Or
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Windows
Explorer.
2 Find the file that you want to move, and then click it to select it.
3 Click Organize, and then Cut.
4 Find and open the folder in which you want to put the file.
5 Click Organize, and then Paste.
NOTE: You can also move files by dragging them into a new location. (You can have two
or more Windows Explorer windows open at one time.) Select an item in Computer or in
Windows Explorer, and then press and hold the right mouse button while moving the item
into another folder. Release the mouse button and click Move Here to place the item in
the new location.
70 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 81

Finding Files
To find a file, you can use the Search box at the top of every folder, or the search box on
the Windows Start Button menu, which searches the whole computer.
To search from a folder Search box:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Computer.
2 Find the folder that you want to search. Search looks in the current folder and all
3 Click in the search box at the top of the window, and begin to type.
To search from the Windows Start Button menu:
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar.
2 Type a word or question; what you type automatically appears in the Start Search
Or
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Windows
Explorer.
subfolders.
The Search box filters according to what you type. It displays files if your term matches
the file name, tags, or other file properties. It displays text documents if the term occurs
in any of the text inside the document file.
box. As you type, the search results appear in the left pane.
3 Do one of the following:
Click a result to open it.
Click the X to clear the results of the search and return to the main list of
programs.
Click See all results to show the results in a folder for advanced options.
Click Search the Internet to search the Internet by opening the browser.
Managing Files 71
Page 82

Renaming Files
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Computer.
Or
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Windows
Explorer.
2 Find the file or folder you want to rename, and then click it to select it.
3 Click Organize, and then Rename.
4 Type the new name, and then press Enter on the keyboard.
NOTE: Another way to rename a file is to right-click the file, and then click Rename.
Deleting Files
CAUTION: Do not change the file name extension (the last three characters of a
file name, after the period). Doing so could make the file unrecognizable to
the computer.
CAUTION: Do not delete any file that is part of an installed program. Doing so
can cause the program to become unusable.
1 Find the file that you want to delete, and then click it to select it.
2 Click Organize, and then Delete.
3 Click Yes to confirm the delete and send the file to the Recycle Bin.
If you make a mistake and need to retrieve the deleted file, see “Retrieving Files from the
Recycle Bin.”
NOTE: Another way to delete a file is to right-click the file, and then click Delete.
Retrieving Files from the Recycle Bin
If you discover that you need a file that you have deleted, you can usually retrieve it from
the Recycle Bin. When a file is deleted, it goes to the Recycle Bin and stays there until the
Recycle Bin is emptied manually or it is cleared to make room for more recently
deleted files.
1 Double-click the Recycle Bin icon on the desktop.
2 Right-click the file that you want to retrieve, and then click Restore this item.
The file is removed from the Recycle Bin and goes back to its previous location.
72 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 83

Copying Files
1 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Computer.
Or
Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Windows
Explorer.
2 Find the file that you want to copy, and then click it to select it.
3 Click Organize, and then Copy.
4 Find and open the folder in which you want to put the file.
5 Click Organize, and then Paste.
NOTE: You can also copy files by dragging them into a new location. Select an item in
Computer or in Windows Explorer, and then press and hold the right mouse button while
moving the item into another folder. Release the mouse button, and then select Copy
Here to copy the item to the new location.
Using a Printer
For instructions on connecting and using a printer, refer to the user manual that came with
the printer.
Printers receive instructions from the computer by means of software programs called
printer drivers. In many cases, the computer automatically finds the necessary printer
driver for your particular printer to work with the computer. If it does not, follow the
instructions that came with the printer to install the specific printer driver manually.
You can print text and graphics from most software programs and Web sites if you have
a printer connected to the computer, and if the computer has the necessary software
installed for the printer.
To prin t:
1 Click File on the program menu bar, and then click Print.
2 Select your printing options:
Select the printer.
Choose the page range (for example: all pages, current page, or range of
pages).
Determine the number of copies.
3 Click OK or Print.
Managing Files 73
Page 84

74 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 85

Using CD and DVD Media Drives
Using the CD and DVD Drives
Your computer can come with several types of CD or DVD drives that allow you to perform different tasks. What
you can do depends on what kind of drive you have.
Blu-ray
Allows you to: CD-ROM CD-RW DVD-ROM DVD+RW/+R
Read data
from CDs.
Play music CDs. • • • • • •
Read DVDs. • • • •
Record (burn) data
or music to discs.
Play DVD movies. • • • •
Record (burn) DVD
movies.
Read Blu-ray discs. •
Record data to
Blu-ray discs.
Read HD discs. •
••• • • •
••••
•••
DVD+RW/+R
•
HD
DVD+RW/+R
Using CD and DVD Media Drives 75
Page 86

The combination (combo) drive is available on select models only. It combines the functions
of two drives into one: either a DVD+RW/+R drive (DVD writer) and a CD-RW drive
(CD writer), or a DVD-ROM drive and a CD-RW drive.
Handling CDs and DVDs
To avoid damaging a disc, follow these guidelines:
Return the disc to the case when you are finished using it.
Handle the disc by its outside edges or center hole only.
Do not touch the unlabeled side of a disc or place the unlabeled side down on a desk.
Doing so could scratch the surface of the disc.
Store discs at room temperature.
Inserting and removing CDs and DVDs
CAUTION: Use only standard-shaped (circular) discs in the drives. Using
non-standard discs, such as heart-shaped discs or business-card discs, may
damage the drive.
To insert a CD or DVD:
1 With the computer turned on, press the Eject button near the front of the drive to open
the disc tray.
NOTE: On some computers, the drive is located behind a door on the front of the
computer.
2 Remove the CD or DVD from its case, holding the disc edges or center hole only.
3 Gently place the disc in the tray with the label facing up or facing right if the CD drive
is vertically positioned in the computer.
NOTE: On a double-sided DVD, read the text around the center hole to determine
which side (A versus B or Standard versus Widescreen) to play. Place the disc in the
tray with the label facing up for the side that you want to play. If the CD drive is
vertically positioned in the computer, place the disc with the label facing right for the
side that you want to play.
76 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 87

4 Close the disc tray by:
Gently pushing the tray into the computer.
Or
Clicking the open/close button on the control panel for the program that controls
the drive.
Or
Pressing the media control open/close button or Eject button on the keyboard
(select models only).
Or
Pressing the Eject button on the drive, if it is accessible.
To remove a CD or DVD:
1 With the computer turned on, open the disc tray by pressing the Eject button.
2 Holding on to the disc edges or center hole only, lift the CD or DVD out of the tray.
3 Place the disc in its case.
4 Close the disc tray by gently pushing the tray into the computer.
Using CD and DVD Media Drives 77
Page 88

Compatibility Information
An important feature of a DVD Writer/CD Writer drive is its high level of compatibility
with other optical drives and CD and DVD players:
The CDs that you create play in most home and car stereos as well as most computer
DVD-ROM and CD-ROM drives.
The DVDs that you create are compatible with some DVD video players and with most
computer DVD-ROM drives.
CD-R discs are more compatible with home and car stereos than CD-RW discs are.
Blu-ray disc drives are required to play Blu-ray discs.
Blu-ray disc drives can read Blu-ray discs and record to Blu-ray discs.
HD disc drives are capable of playing HD discs but not recording HD data to disc.
The DVD Writer/CD Writer drive is able to read from and record to almost every type of
optical disc. Writing speed rates for the DVD Writer/CD Writer drive are fast, allowing
quick recording times.
78 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 89

Disc Features and Compatibility Table
Can be
recorded
Disc File type
CD-ROM Data No Yes No No
Music No Yes Yes Varies by model
CD-R Data Yes Yes No No
Music Yes Yes Varies by model Varies by model
CD-RW Data Yes Yes No No
Music Yes Yes Varies by model Varies by model
DVD-ROM Data No Yes No No
DVD movie No Yes No Yes
DVD-RAM Data Yes Varies by model No No
DVD movie Yes Varies by model No Varies by model
DVD+R and
DVD-R
Double-layer
DVD+R/DVD-R
Data Yes Yes No No
DVD movie Yes Yes No Varies by model
Data Yes Varies by model No Varies by model
DVD movie Yes Varies by model No Varies by model
onto
Plays in
computer
Plays in
home or car
stereo
Plays in
home DVD
player
DVD+RW and
DVD-RW
Blu-ray DVD Data Yes Yes No Varies by model
HD DVD Data No Yes No Varies by model
VCD DVD movie No Yes No Varies by model
NOTE: Some computers come with the double-layer DVD Writer. It supports single-layer and double-layer DVD media. Double-layer
technology gives you greater capacity and allows you to store up to 8 GB* of data on double-layer DVD+R or DVD-R media.
Double-layer is a new technology. Double-layer media compatibility varies widely with some home DVD players and DVD-ROM drives.
*1 GB is defined as 1 billion bytes. 1 GB = 1 billion bytes when referring to hard disk drive capacity. Actual formatted capacity
is less.
For the latest disc compatibility information for your computer, go to the HP Support Web site at: http://www.hp.com/support
NOTE: Double-layer DVD technology is supported by select models only.
Data Yes Yes No No
DVD movie Yes Yes No Varies by model
Movie Yes Yes No Varies by model
Movie No Yes No Varies by model
Using CD and DVD Media Drives 79
Page 90

Optical Drive Quick Reference Table
DoubleOptical
drive can:
Read CDs,
CD-Rs, and
CD-RWs.
Read DVDs. No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Read data on
a CD.
Play music. Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Record data
or music to
disc for
storage or
backup.
View DVD
movies.
Record DVD
movies.
Pla y ga m es. Yes Yes Yes N o Ye s Yes Yes Yes Ye s
Create
LightScribe
label.
CD-ROM CD-RW
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
No No Yes Yes Ye s Ye s Yes Yes Ye s
No No No Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
No No No No No No No Yes Yes
DVDROM
DVDRAM
DVD+RW/+R
DVD-RW/-R
layer
DVD
Combo
CD-RW/
DVD
LightScribe
DVD+RW/+R
BD HD
DVD+RW/+R
Play
Blu-ray DVD.
Play
HD DVD.
Record
data to
Blu-ray disc.
Record HD
data to DVD.
No No No No No No No No Yes
No No No No No No No No Yes
No No No No No No No No Yes
No No No No No No No No No
80 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 91

Using Blu-ray and HD Disc Drives
If the computer came with a Blu-ray (BR) and high-definition (HD) disc drive, there are three
programs that are designed specifically for use with this drive:
DVD Play plays Blu-ray, high-definition (HD), and regular commercial DVD discs.
PowerDirector is a video editing program for creating Blu-ray or DVD discs.
PowerToGo is a Blu-ray disc recording (burning) program for different types of data
storage, such as video, music, pictures, and other data. This program enables you to
record data to Blu-ray, HD DVD, and other recordable DVD discs.
NOTE: The BD HD DVD+RW/+R drive does not support recording high-definition data
to disc.
For more information about using these programs, see “Playing DVDs” and “Creating
Audio and Data Discs.”
Using CD and DVD Media Drives 81
Page 92

82 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 93

Using the Memory Card Reader
Digital cameras and other digital imaging devices use memory cards, or media, to store
digital picture files. The optional memory card reader (select models only) can read from
and write to a variety of types of memory cards and the IBM Microdrive disk drive.
The card reader is accessible directly on the front of the computer. It has four or two
horizontal card slots, which accept the memory cards and the Microdrive disk drive.
You can place media in one or more of the card slots and use each media independently.
Place only one piece of media in a slot at one time.
Each card slot has its own drive letter and icon. When you insert media, the display label
may change to the title of the media, if a title is present.
When you insert media, the Safely Remove Hardware window may appear. If it opens, or
if you open the Safely Remove Hardware window by mistake, click Close.
CAUTION: Do not click Stop in the Safely Remove Hardware window with the
USB Mass Storage Device selected. Doing so removes the operating system
recognition of the memory card reader from your computer, and you must
restart the computer to see your memory card reader again.
To use the memory card reader:
1 Insert the media into the card slot until it stops.
The activity light (A) on the memory card reader lights, and the computer
automatically detects the media.
NOTE: You must insert media correctly. Note the direction of the notched corner on
the media. For more information, see “Media Insertion Guide.” CompactFlash and
Microdrive are keyed and cannot be inserted incorrectly. Insert the receptacle edge
(holes) of this media into the slot.
Using the Memory Card Reader 83
Page 94
2 Select a program to access your files. The computer opens a program, so that you can
access the media contents. You can copy files from or to the media.
Or
If the AutoPlay window does not open, click the Windows Start Button on the
taskbar, click Computer, and then double-click the Memory Card icon to display
the files on the memory card.
3 When you are finished, right-click the drive icon, click Eject, check that the activity
light is on but not blinking, and then remove the media. A steady activity light
indicates that the computer is not reading or writing the media card.
CAUTION: Do not try to remove media when the activity light is blinking. Doing
so may cause loss of data.
Media Insertion Guide
4-slot memory card reader (select models only)
A Activity light
B Upper-left slot
C Lower-left slot
D Upper-right slot
E Lower-right slot
Card Insert the media
SmartMedia (SM) memory card Facing up B (upper-left) SM
xD media Facing up B (upper-left) xD
CompactFlash Type I media Receptacle edge (holes) C (lower-left) CF/l
CompactFlash Type II media Receptacle edge (holes) C (lower-left) CF/II
Microdrive disk drive Receptacle edge (holes) C (lower-left) MD
84 Getting Started (features vary by model)
4-slot reader
location
Page 95

4-slot reader
Card (continued) Insert the media
location
Secure Digital (SD) memory card Facing up D (upper-right) SD
Mini Secure Digital (MiniSD)
Memory Card
*
Facing up D (upper-right)
MiniSD
MultiMediaCard (MMC) Facing up D (upper-right) MMC
Reduced size MultiMediaCard
(RSMMC)
*
MultiMediaCard Plus (MMC +)
Facing up D (upper-right)
RSMMC
*
Facing up D (upper-right)
MMC Plus
MultiMediaCard Mobile
(MMC Mobile)
*
Facing up D (upper-right)
MMC Mobile
Memory Stick (MS) memory card Facing up E (lower-right) MS
Memory Stick (MS-Pro)
Facing up E (lower-right) PRO
memory card
Memory Stick (MS-Pro Duo)
memory card
*
Memory Stick (MS-Duo)
memory card
*
Facing up E (lower-right)
PRO Duo
Facing up E (lower-right)
MS Duo
*Select models only. Not available in all countries/regions.
NOTE: Some memory cards, such as CF Ultra/III, are not compatible with the memory
card reader that came with the computer.
Using the Memory Card Reader 85
Page 96

2-slot memory card reader (select models only)
A Activity light
F Upper slot
G Lower slot
2-slot reader
Card Insert the media
location
Secure Digital (SD)
Memory Card
MultiMediaCard (MMC) Facing up
Memory Stick (MS)
Memory Card
Memory Stick (MS-Pro)
Memory Card
SmartMedia (SM)
Memory Card
xD media Facing up
IBM Microdrive disk drive Receptacle edge (holes) G (lower)
CompactFlash Type I media Receptacle edge (holes) G (lower)
CompactFlash Type II media Receptacle edge (holes) G (lower)
Facing up
(gold connector fingers down)
(gold connector fingers down)
Facing up
(gold connector fingers down)
Facing up
(gold connector fingers down)
Facing down
(gold connector fingers up)
(gold connector fingers down)
F (upper)
F (upper)
F (upper)
F (upper)
F (upper)
F (upper)
NOTE: Do not use SM and xD media in the memory card reader at the same time. Only
the first one that is inserted is recognized by the memory card reader.
86 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 97

Understanding the Activity Light
The memory card reader activity light is off when there are no media cards plugged into
the slots.
The light turns on when a media card is inserted into a slot.
The light blinks when data is being transferred between the card and the computer.
Formatting a Memory Card
If you have not used the memory card before, or if the card has become corrupted, you
may need to format the card before using it.
NOTE: Some memory cards have a lock position. To view or edit your picture files, make
sure that the memory card is in the unlocked position.
1 Format the memory card in your digital camera. Follow the instructions that came with
your digital camera.
Or
Insert the media into the correct card slot on the reader until it stops and locks into
place. The activity light on the memory card reader lights, and the computer
automatically detects the media.
2 Click the Windows Start Button on the taskbar, and then click Computer.
3 In the Devices with Removable Storage area, right-click the correct memory card icon.
4 Select Format, and then type a label name into the label box.
5 For best compatibility, select FAT as the file system settings.
6 Click Start.
7 Click OK in the Format Complete window, and then click Close.
Using the Memory Card Reader 87
Page 98

Troubleshooting the Memory Card Reader
If you are having problems reading from or writing to a memory card, try the following:
Some cards have a read/write or security switch on the card. Make sure that the
read/write switch is set to Write Enabled before attempting to write data to the card.
Make sure that the amount of data that you want to store is not larger than the storage
limit of the memory card.
Make sure that the memory card is one of the supported types: CompactFlash
Type I and II, Microdrive, Memory Stick, Memory Stick Pro, MultiMediaCard, Secure
Digital, SmartMedia, or xD media.
Make sure that the memory card is fully inserted into the correct slot.
Remove the memory card when the activity light is not blinking, and shine a flashlight
into the empty slot. If any of the pins are bent, replace the memory card reader, or
have the computer serviced if a pin is touching another pin. To straighten slightly bent
pins, use the tip of a fine-point retracted ballpoint pen with the computer off.
Inspect the ends of the memory cards for anything that could be blocking a proper
connection. Clean the contacts with a lint-free cloth and small amounts of alcohol.
Replace the memory card, if necessary.
The memory card reader is a device that uses the Safely Remove Hardware task. This
appears as a taskbar icon next to the time. Do not click Stop in the Safely Remove
Hardware window. Doing so disconnects the drive. If this happens, restart
the computer.
Do not insert or remove memory cards when the activity light is blinking. Doing so
may cause data loss, or it may permanently damage the card reader.
Format a memory card before you use it. See “Formatting a Memory Card.”
88 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 99

Using the HP Personal Media Drive and
HP Pocket Media Drive
The HP Personal Media Drive and the HP Pocket Media Drive (HP Media Drives) can be
used as internal or external USB hard disk drives designed to quickly and easily increase
the storage capacity and to transfer media files such as digital photos, music, videos, and
other important files. You can also use the HP Media Drives to back up other drives on the
computer.
NOTE: The HP Personal Media Drive and the HP Pocket Media Drive are included with
select models only. Both drives are sold separately.
The HP Media Drives are designed to:
Work with computers that have a USB port.
Store large media files and personal files from digital cameras, digital video
camcorders, and MP3 players.
Quickly transfer files between PCs.
Play media files.
Back up your files. Perform system backups for added data security.
For more information about using HP Media Drives with Windows Media Center, refer to
the documentation on the HP Support Web site at: http://www.hp.com/support
Using the HP Personal Media Drive and HP Pocket Media Drive 89
Page 100

Connecting the Drive
The HP Media Drive is designed to work with most computers as an external drive that is
connected by using a USB cable, but it also can be inserted into specifically designed
HP computers. These computers have a special horizontal or vertical drive bay that
connects to the drive by using an internal USB connector. The drive can be easily inserted
and removed from the hard disk drive bay without turning off the computer. This is
sometimes referred to as warm-swappable.
The drive turns on when it is plugged into an active USB port. If the computer is turned on
with the drive connected, the drive automatically turns on. When the USB cable for the
drive is not plugged in or when the USB power from the computer is turned off, the drive
automatically turns off. When the computer is in sleep mode (a reduced-power state), the
drive remains turned on.
WARNING: Do not move the computer with the HP Media Drive inserted in the
bay or connected to a USB port on the computer. This can cause both damage
to the drive and data loss.
Inserting the Drive into an HP Drive Bay
1 Turn on the computer.
2 In the horizontal position, insert the drive with the HP logo facing up and the HP
product name right-reading. In the vertical position, the drive’s flat side is down, and
the rounded side is up. Do not force the drive into the bay; it should slide easily into
the bay.
3 Slide the drive all the way into the drive bay until the drive is firmly connected to the
internal connections. With the computer turned on and the drive inserted correctly, the
power LED (B, D) on the front of the drive is lit.
90 Getting Started (features vary by model)
 Loading...
Loading...